Patents
Literature
220 results about "Liquid copper" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing graphene
InactiveCN102491315ASimple and fast operationImprove product qualityGrapheneHydrogenConcentration ratio
The invention discloses a method for preparing graphene. The method comprises the following steps of: after heating a substrate loaded with a copper metal layer to a bulk phase melting point and above the bulk phase melting point of copper in the flowing anaerobic and anhydrous atmosphere, introducing a carbon-containing compound into a system to perform chemical vapor deposition to obtain the graphene on the surface of the copper metal layer after the deposition. According to the method, the graphene with various shapes is prepared by introducing inert gases under a liquid state copper catalyst. The method is easy and convenient to operate and high in quality of products, and can be used for large-scale production. The shapes of the graphene can be regulated and controlled by regulating a concentration ratio of the inert gases to carbon-containing substances and hydrogen.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
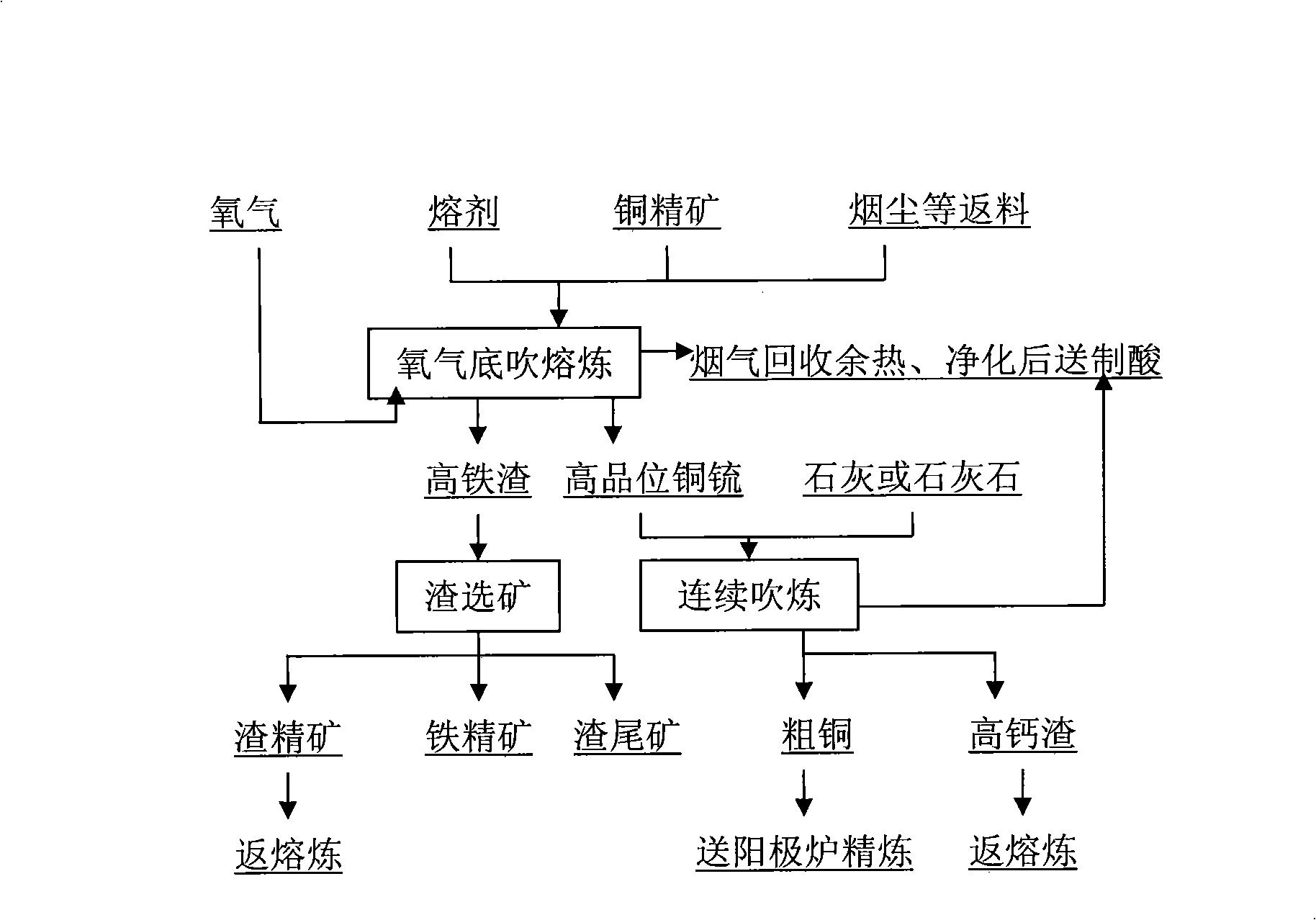
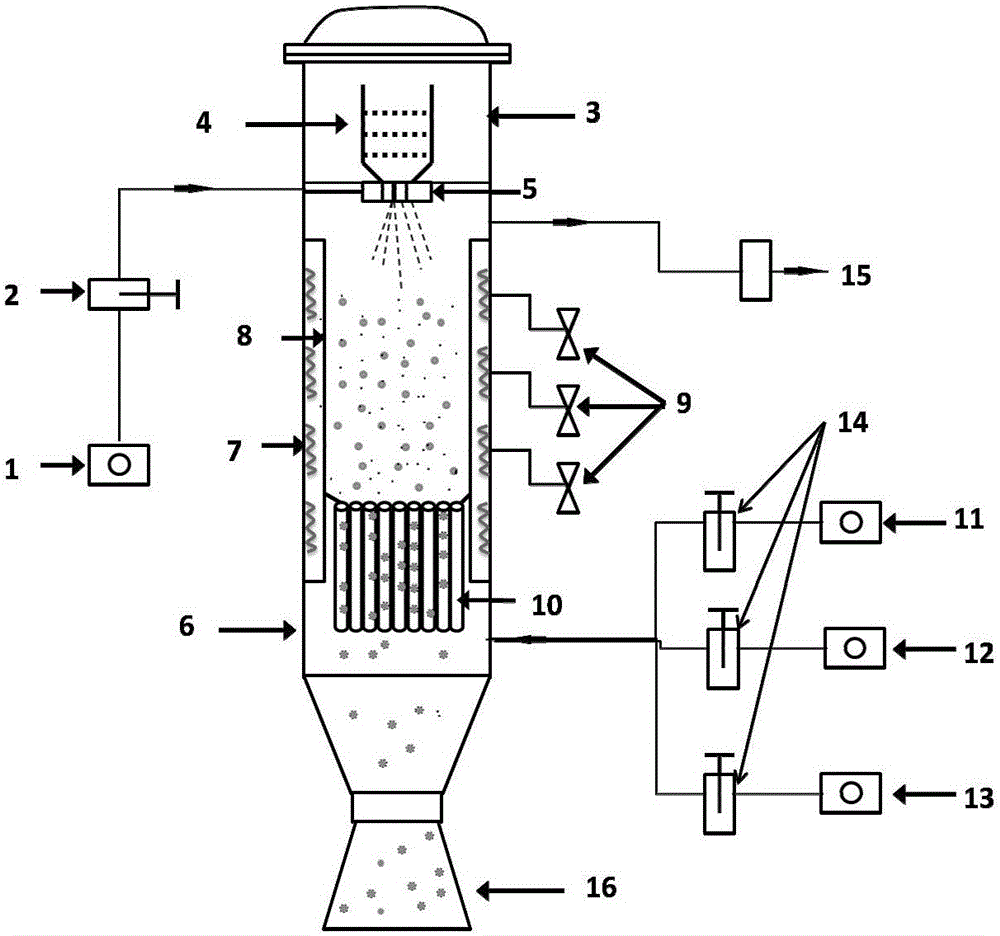
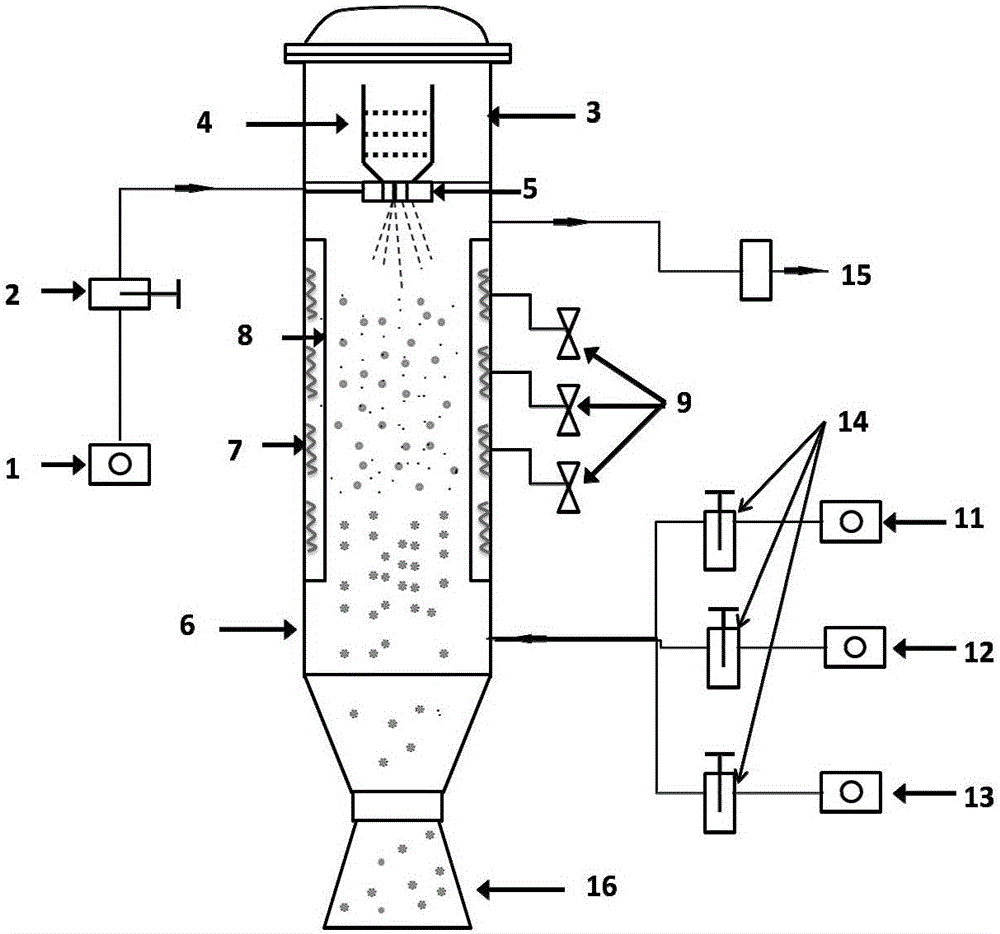
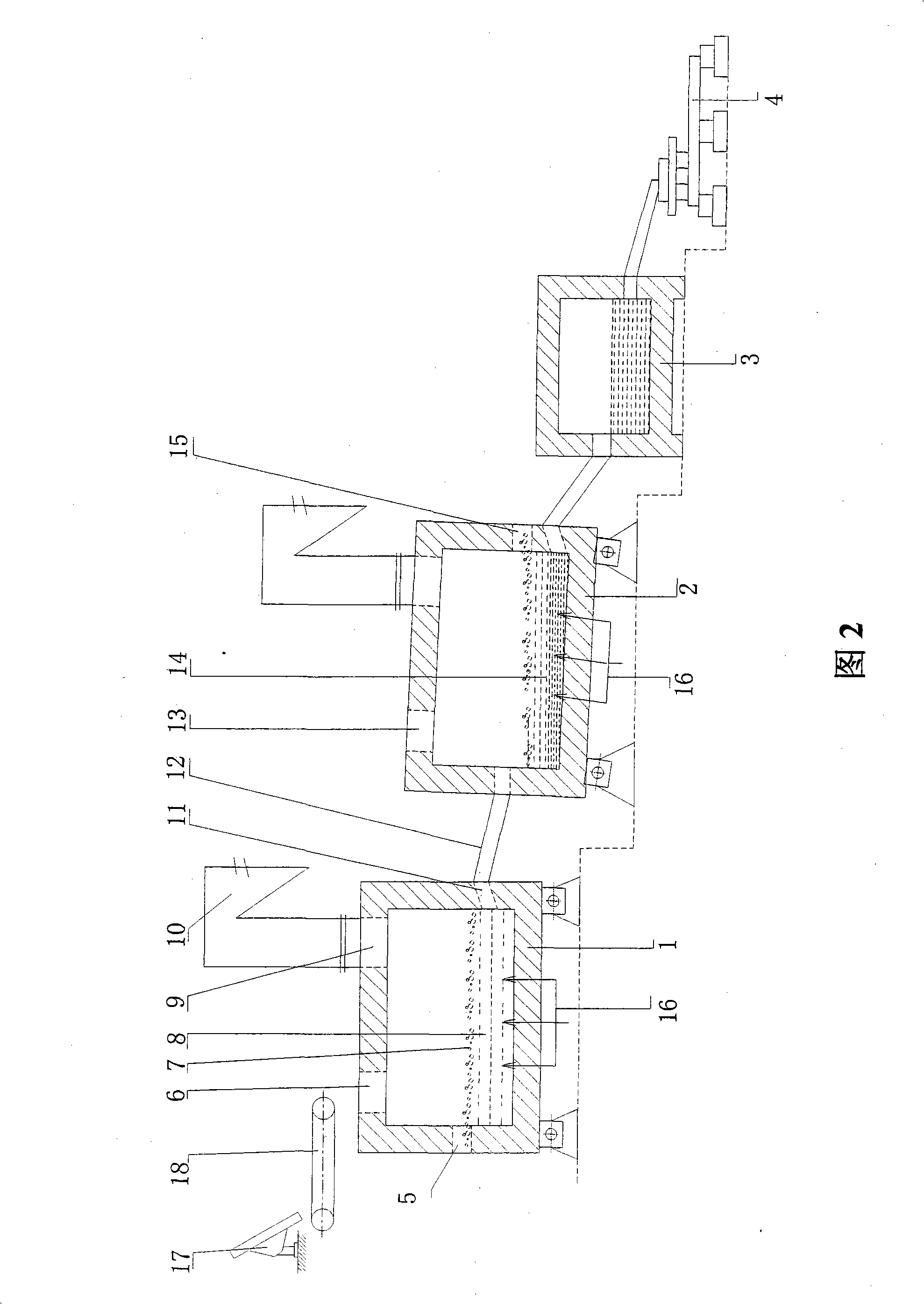
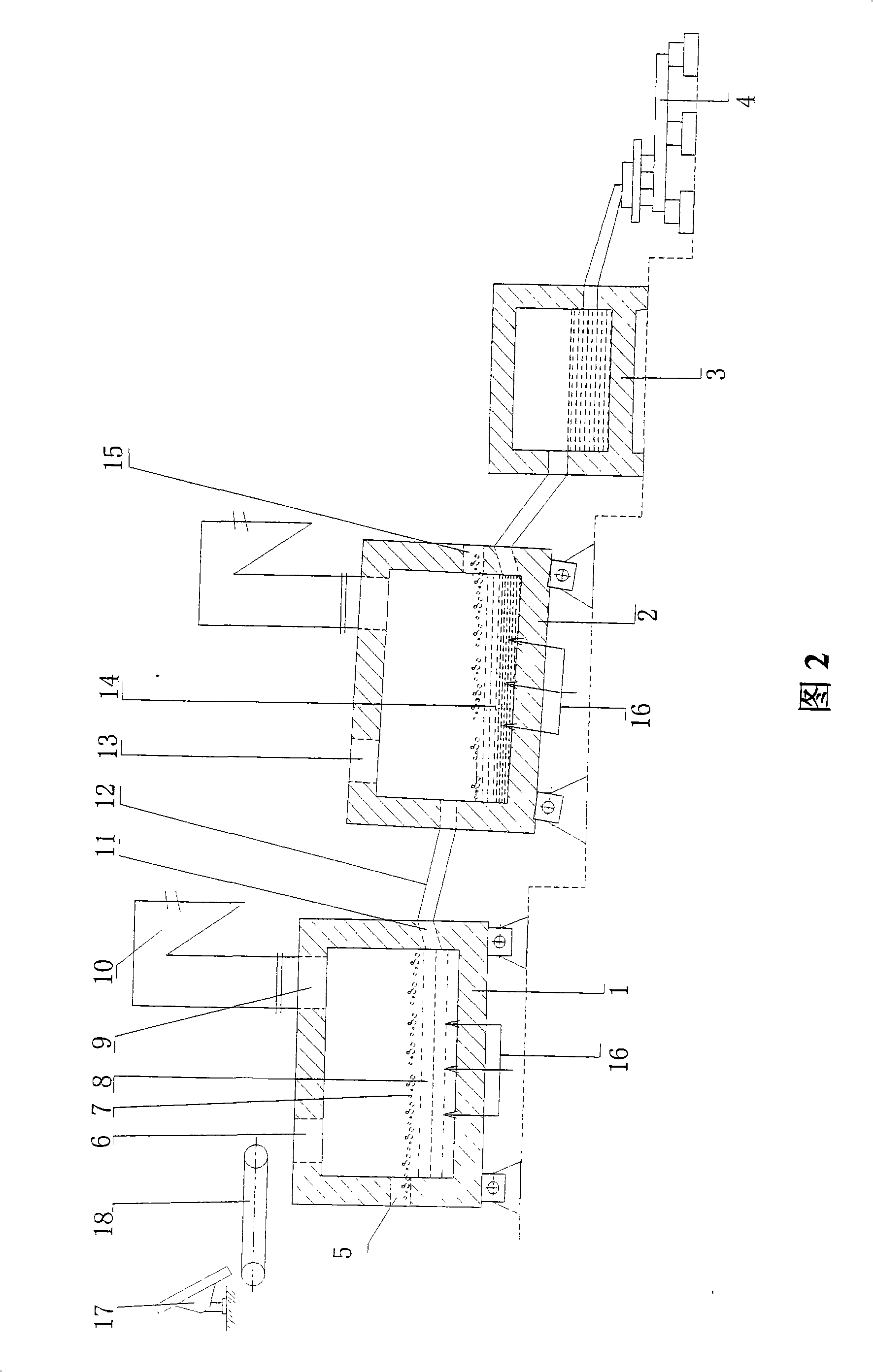
Oxygen bottom blowing continuous copper smelting apparatus
InactiveCN101328543ALess slagHigh yieldRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesSmelting processLiquid copper
The invention provides an oxygen bottom blowing continual copper smelting device used in the continual copper smelting process. The device is characterized in that the device comprises an oxygen bottom blowing smelting furnace, an oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace, an anode furnace and an anode plate casting machine, wherein the oxygen bottom blowing smelting furnace and the oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace are connected by a first chute, so that liquid copper matte smelted by the oxygen bottom blowing smelting furnace can be continuously injected into the oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace through the first chute to obtain coarse copper by the continuous converting of the oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace; the oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace and the anode furnace are connected by a second chute, so that the coarse copper can flow in the anode furnace through the second chute and is subjected to refining by the anode furnace to obtain anode copper; and the anode furnace and the anode plate casting machine are connected by a third chute, so that the anode copper can flow into the anode plate casting machine through the third chute and is subjected to casting by the anode plate casting machine to obtain the copper anode plate.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Treatment method of scrap copper
The invention discloses a treatment method of scrap copper. The treatment method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) carrying out detection and analysis on the scrap copper to be melted, and determining the application and smelting production process of the scrap copper according to the alloy components of the scrap copper; (2) according to the analytic result, removing impurity metal elements in the scrap copper on the basis of processes such as loading, melting, oxidizing, degassing, slagging, deslagging, reducing and refining for red impure copper and high-copper alloy;and (3) carrying out degassing, deslagging and deoxidization reduction on liquid copper obtained in the step (2) again. In the invention, a high-quality copper material is produced by directly utilizing the scrap copper, thus the treatment method has the advantages of low investment, low energy consumption, simple production process, low production cost and little environment pollution, valuable metals in the scrap copper can be reasonably utilized, and the competitiveness of a product in market competition can be greatly improved.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for recovering valuable metals by cooperatively disposing copper-nickel-cobalt smelting slag and gypsum slag
InactiveCN104404259AEfficient enrichment and recoveryAvoid pollutionCement productionProcess efficiency improvementSlagLiquid copper
The invention provides a method for recovering valuable metals by cooperatively disposing copper-nickel-cobalt smelting slag and gypsum slag. The method comprises: firstly adding solid or liquid copper-nickel-cobalt smelting slag into a slag-cleaning electric furnace, powering on for heating and constantly keeping a certain temperature scope, taking nitrogen as a carrier and spraying a reducing agent, the gypsum slag and a flux into the slag-cleaning electric furnace, so as to product a metal sulfonium phase and cleaned furnace slag through a reduction sulfuration reaction; and keeping warm, standing, sending the metal sulfonium phase to a fire-process blowing system through a siphon port for further recovering valuable metals, discharging the cleaned furnace slag from a slag discharge port and directly performing water quenching, so as to obtain the water-quenched slag which is applicable as a raw material for producing cement. By cooperatively disposing the copper-nickel-cobalt smelting slag and the industrial byproduct gypsum slag, efficient enriching recovery of copper, nickel, cobalt, gold, silver and other valuable metals in the smelting slag is realized, also an effective comprehensive utilization approach is provided for gypsum slag, and environmental pollution is avoided.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method and device for producing high-strength and high-conductivity graphene copper-based powder material
ActiveCN105965025ARealize dynamic in situ growthImprove performanceTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusTemperature controlAdditional values
The invention provides a preparation method and device for producing a high-strength and high-conductivity graphene copper-based powder composite. The preparation method is characterized in that a melt copper gas atomizing type powder preparation technology is adopted, a multi-gas-channel controllable gas feeding system and a controllable gas scrubbing device are additionally arranged at the outer part of an atomizing chamber of a traditional powder preparation device, and a gradual temperature control device and a material speed reduction device are additionally arranged in the atomizing chamber, and on that basis, high-temperature melt copper can be atomized into fine high-temperature melt copper droplets under the impacting effect of high-speed gas flow, and then the high-temperature melt copper droplets enter an atomizing chamber atmosphere containing carbon source gas components with a certain ratio, thus a graphene material can realize in-situ wrapping growth on the surfaces of copper powder particles when the atomized melt copper droplets are subjected to temperature-controlled solidification and / or under the speed reduction effect of the material speed reduction device, and as a result, the high-strength and high-conductivity graphene copper-based powder composite can be obtained. The preparation method and the preparation device can be directly applied to an existing copper-based material atomizing type powder preparation industry; the prepared product is high in performance and additional value; the preparation method and the preparation device are applicable to technology improvement and product upgrading of a copper powder production industry.
Owner:SPECIAL EQUIP SAFETY SUPERVISION INSPECTION INST OF JIANGSU PROVINCE
Copper bus bar with high strength, high conductivity and high toughness and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102034563AImprove conductivityImprove equipment technologySingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsManufacturing extensible conductors/cablesLiquid cathodeLiquid copper
The invention relates to a copper bus bar with high strength, high conductivity and high toughness and a preparation method thereof. The copper bus bar is characterized in that the material comprises 99.96-99.998% of copper and silver, 0.002-0.02% of yttrium rare earth and 0-0.038% of impurities, wherein silver accounts for 0.0005-0.01% of copper and silver; and the copper master alloy containing the yttrium rare earth is used as a modifier. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) melting a copper material: heating the cathode copper in a mains frequency core induction furnace to melt the cathode copper into liquid cathode copper; (2) modifying liquid copper: melting the modifier in the liquid cathode copper and fully mixing the modifier with the liquid cathode copper; (3) drawing a continuously cast copper bar upwards: causing a crystallizer of a continuous casting machine to stretch into the liquid cathode copper, condensing the liquid cathode copper into the copper bar in the crystallizer and drawing the copper bar upwards by means of two pairs of drawing roll mechanisms in the continuous casting machine to lead the copper bar to a take-up machine via a wheel frame; (4) continuously extruding the copper bar at medium temperature and carrying out anti-oxidation cooling; and (5) carrying out draw forming: putting copper bus bar blanks on a drawing machine, carrying out draw forming on the copper bus bar blanks.
Owner:福州市广福有色金属制品有限公司
Method for quickly preparing large-size single-crystal graphene
ActiveCN104389016ASpread flatEasy to manufacturePolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesLiquid copperWater vapor
The invention relates to a method for quickly preparing large-size single-crystal graphene on a liquid copper substrate by a chemical vapor deposition process. The method comprises the following steps: in a hydrogen and inert gas atmosphere, introducing vapor and a carbon source, growing large-size single-crystal graphene by using catalytic cracking of the carbon source on the liquid copper substrate surface, and cooling to room temperature in an inert gas atmosphere to obtain the large-size single-crystal graphene. Compared with the traditional solid metal substrate, the liquid copper substrate used in the method has the advantages of high growth speed, uniform nucleation and the like and can be recycled in the aspect of graphene preparation. The carbon source and water content are regulated to implement the controllable graphene size, thereby obtaining the centimeter-sized single-crystal graphene. The prepared graphene is applicable to preparing field-effect transistor devices.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
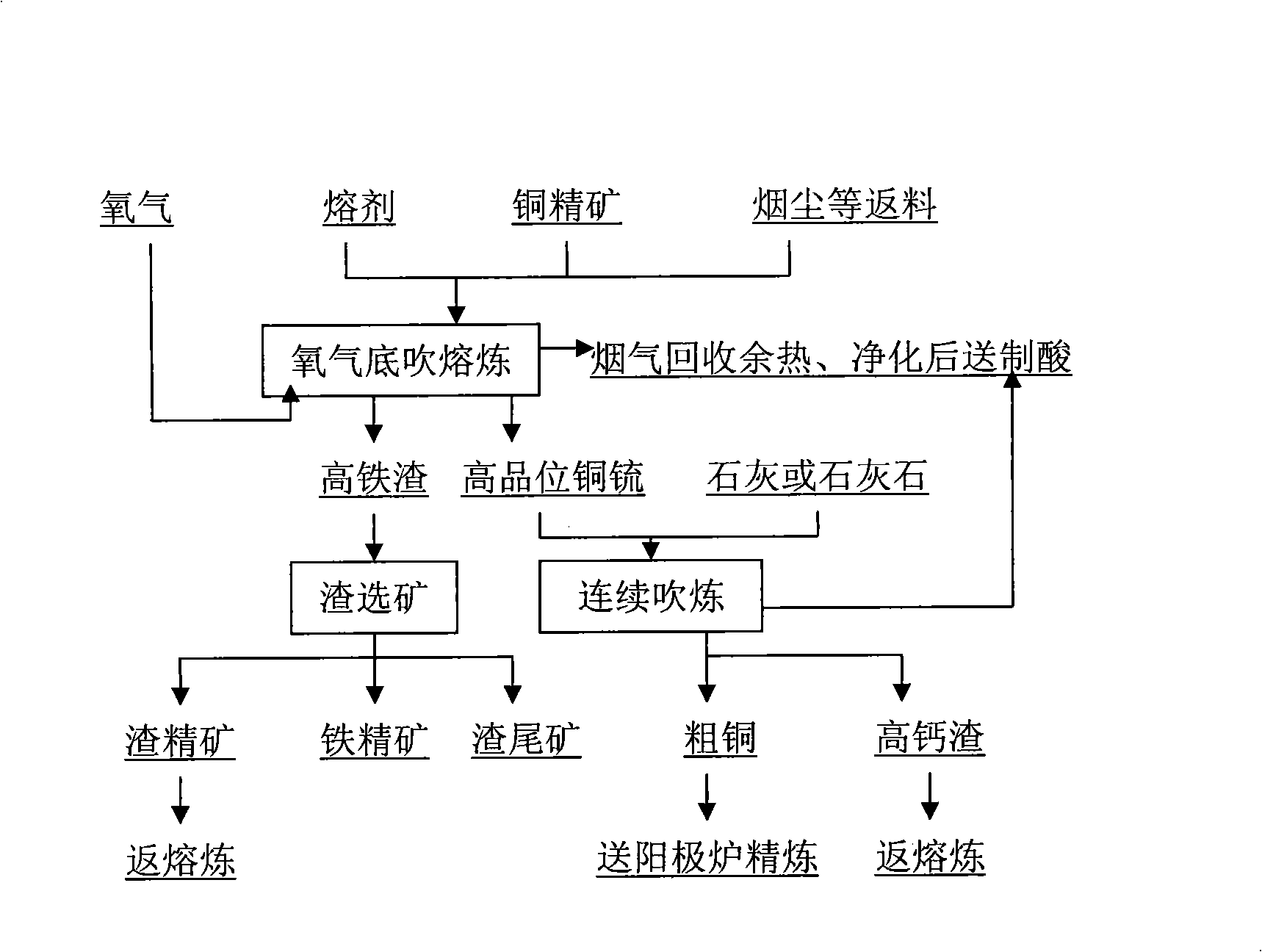
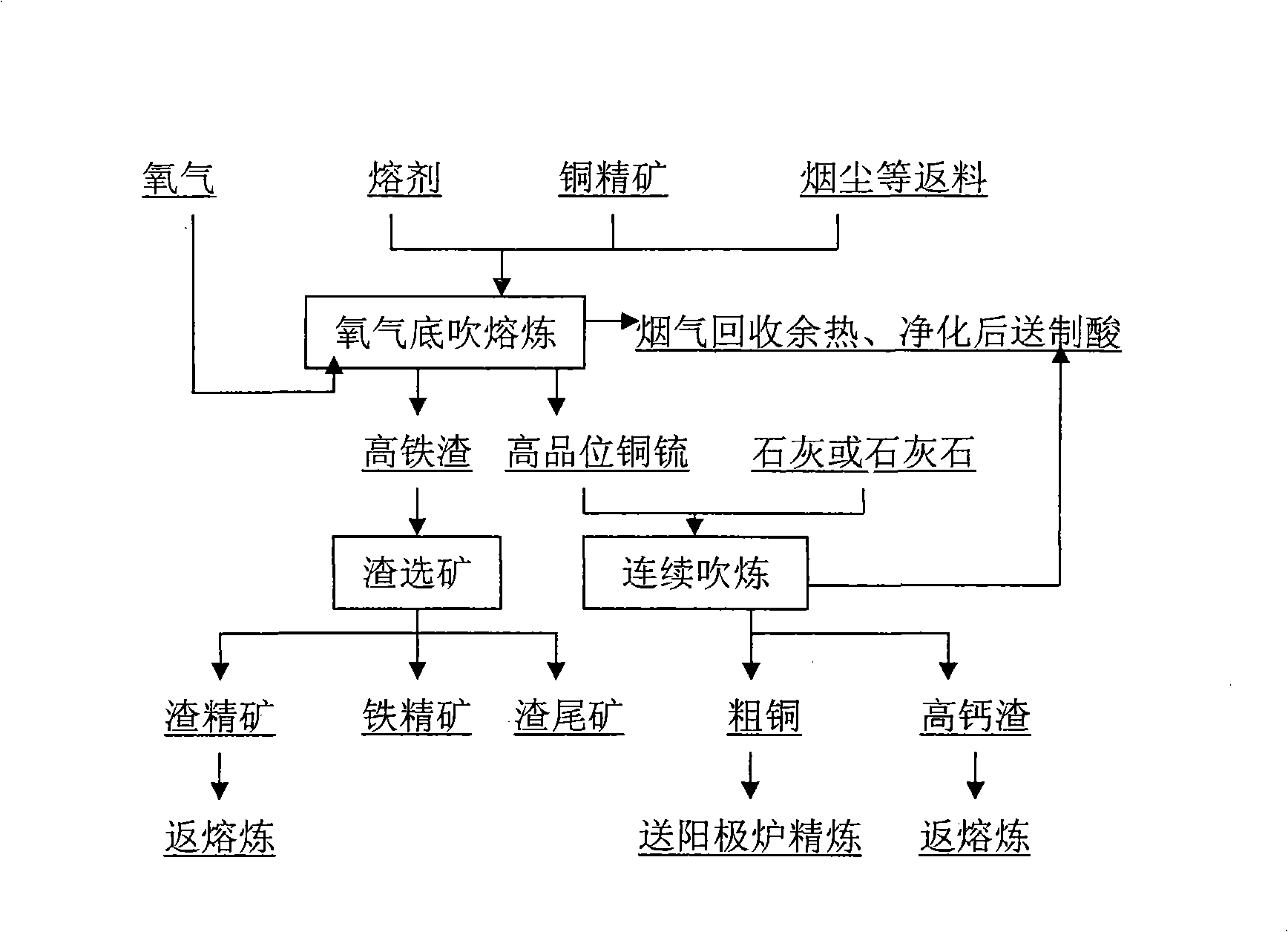
Converting process of bottom blowing converting furnace continuous copper smelting
The invention provides a converting process for continuous copper smelting by a bottom blowing converting furnace. The process is characterized in that liquid copper matte generated from a bottom blowing smelting furnace passes through a chute to be continuously injected into the oxygen bottom blowing smelting furnace, and oxygenized air is continuously blown in from the bottom part of the converting furnace to continuously convert the copper matte; simultaneously, lime flux or limestone is continuously added from an opening at the top of the converting furnace for slag making by a material bin and a measuring belt feeder according to the required quantity measured, or the top part of the converting furnace is not provided with the opening, the lime flux or the limestone is crushed into powder and fed together with oxygen gas in the furnace for slag making through an oxygen lance by the material bin and the measuring belt feeder; one end of the furnace has an upper part provided with an opening used for discharging smelting slag and a lower part provided with an opening used to be provided with a siphoning installation for discharging coarse copper, thereby realizing continuous addition of the copper matte, continuous converting, continuous addition of the flux, continuous slag making, continuous slag discharge and continuous coarse copper discharge and furthering realizing the continuous converting process.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Process of oxygen bottom blowing continuous copper smelting
The invention provides a process adopting the oxygen bottom blowing continual copper smelting. The process is characterized in that an oxygen bottom blowing smelting furnace is utilized to smelt copper-containing materials into liquid copper matte, and the oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace is utilized to continuously convert the liquid copper matte into coarse copper.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
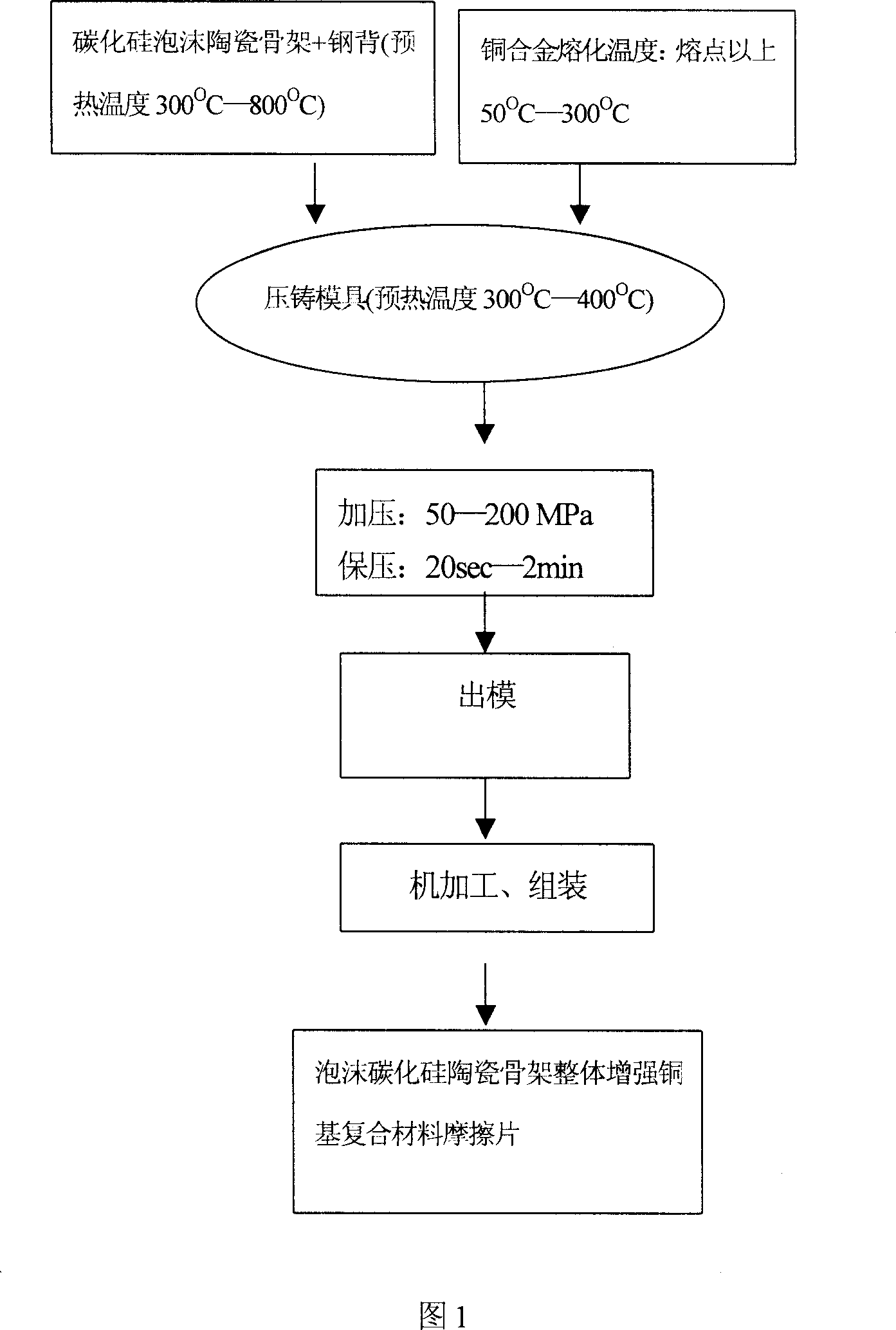
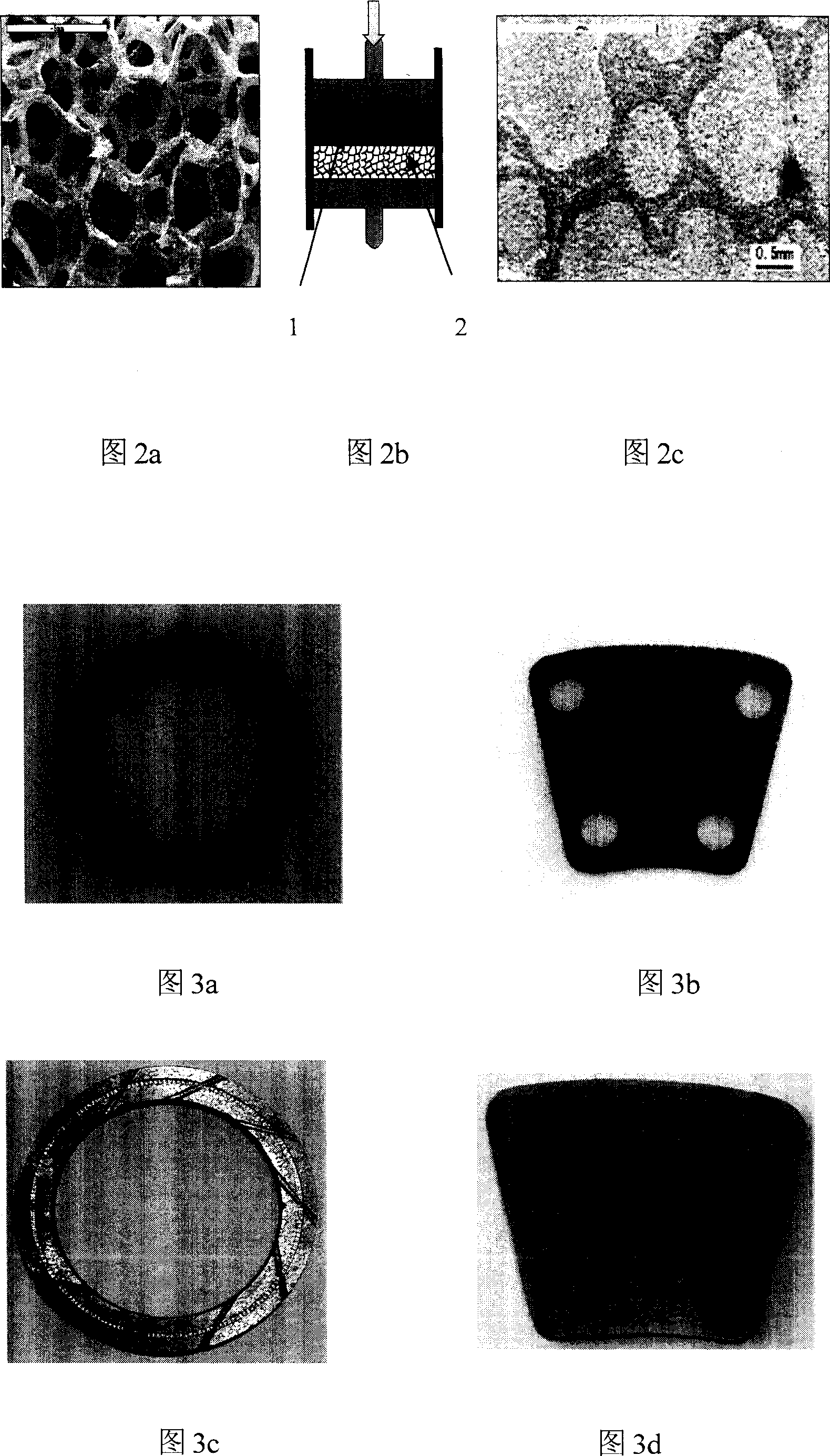
Foaming silican carbide ceramic strengthening copper base composite abrasive sheet and preparation process thereof
The invention relates to the friction material preparing technique, concretely a foam SiC ceramic-copper alloy two phase-combined, foam SiC ceramic frame whole reinforced copper-base composite friction plate and the preparing method thereof, and by volume fraction, the friction plate is composed of foam SiC ceramic 15%-50% and copper alloy 85%-50%; and the preparing method comprises the two key process steps of preparing high intensity, compact foam SiC ceramic and combining foam SiC ceramic with copper alloy: firstly preparing high intensity compact foam SiC ceramic, then making liquid copper alloy enter 3D connecting hole spacing of foam SiC ceramic by extrusion casting and solidify to make it. And it has characters of good heat resistance, excellent friction performance, high mechanical intensity and good process performance, able to act as novel high performance frictional brake and transmission material.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multivariate interalloy and smelting method thereof
The invention relates to a multivariate interalloy and a smelting method thereof. AI is taken as a base, other metals comprising Mn, Si, Fe, Ni, Co, Nb and Ti are added in certain ratio, and the AI and the added two or more metals form a ternary interalloy, a quaternary interalloy and a quinary interalloy. The interalloy and the method have the advantages that: 1, a stokehold material has stable chemical composition, the first time quality can reach 98 percent; 2, the cost is reduced, flash melt is realized, the time for liquid copper in a smelting furnace is shortened, metal oxide is reduced and the casting yield is improved; 3, the production period is quickened and the interalloy can be continuously produced; 4, the interalloy has short melting time, and the quinary interalloy AI-Fe-Co-Ni-Si is taken as an example, only thirty-five minutes is needed to melt one furnace of the quinary interalloy AI-Fe-Co-Ni-Si (400kg), while at least one hour is needed to melt Cu-Co, Cu-Ni and the like; and 5, when the interalloy is used, the alloy types are few, so the management is easy.
Owner:武汉泛洲中越合金有限公司
Manufacturing method of ceramic/copper composite material throat insert
InactiveCN102248168AImprove anti-ablationImprove thermal shock resistanceTurbinesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsTungstenLiquid copper
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of a ceramic / copper composite material throat insert, comprising preparation of a ceramic skeleton and infiltration of a copper alloy, wherein the preparation of the ceramic skeleton comprises the steps of ball milling, pelletizing, moulding, presintering and degreasing as well as high temperature sintering, and a porous ceramic skeleton blank used for preparing a throat insert is prepared; and the infiltration of the copper alloy comprises that Cu-Ni-Ag-Au alloy powder accounting for 36-38% of the weight of the porous ceramic skeleton blank is infiltrated into the porous ceramic skeleton blank at a high temperature, and the Cu-Ni-Ag-Au alloy is in composition of Cu-2.5Ni-1.45Ag-0.15Au in percent by weight. The manufacturing method provided by the invention is simple and is convenient to operate, the prepared ceramic / copper composite material has high thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion coefficient, low density and excellent anti-erosion property, a high-strengthen ceramic skeleton material is designed, the proportion of an infiltration agent is adjusted, the wettability of liquid copper / ceramic is improved, the light copper / ceramic throat insert composite material with excellent anti-erosion property can be prepared, and a high-density tungsten-copper throat insert composite material can be replaced, thus the ceramic / copper composite material throat insert is applicable to industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Molten metal casting die
InactiveUS20100243192A1Low costReduce stepsCasting safety devicesFoundry mouldsLiquid copperMaterials science
A molten metal casting die having a modified surface, a method for making such dies, and a method for making articles of manufacture from such dies is disclosed. The methods are designed to protect die steel surfaces from corrosion by molten metals substantially containing liquid copper.
Owner:NONFERROUS MATERIALS TECH DEV CENT
Recovery of residues containing copper and other valuable metals
A process for recovering non-ferrous metals, in particular copper, nickel and cobalt, from metallurgical residues containing these non-ferrous metals at an oxidation state of greater than or equal to zero, in an alternating current type plasma arc electric furnace comprising a plurality of electrodes, containing a liquid copper heel covered by a fluid slag comprising at least one fusion-reduction phase, comprising charging of metallurgical residues comprising the non-ferrous metals onto the heel contained in the plasma arc electric furnace, fusion of the metallurgical residues in the fluid slag or at the slag-metal bath interface, reduction of at least the non-ferrous metals to oxidation state zero, and intense stirring of the copper heel by injection of inert gas, preferably nitrogen and / or argon, so as to avoid crust formation and to accelerate the reduction reaction and to cause the copper-miscible non-ferrous metals to pass into the copper heel.
Owner:PAUL WURTH SA
Method for directly preparing titanium and titanium alloy by titanium-containing waste residue
The invention relates to a method for directly preparing titanium and titanium alloy from titaniferous waste residues, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical metallurgy. The method is characterized in that the titaniferous waste residues are made into an electrolysis electrode, and the electrolysis is performed in a crucible of an electrolytic cell by a solid oxygen permeable membrane in a specific molten salt electrolyte. The method comprises the following process steps: the titaniferous residues is processed by ball milling, then pressed and formed in a mould at 3-6MP, dried in the air, and then sinteredat the temperature of 1000-1100 DEG C for 2h to be made into an electrolysis cathode; molten salt is separated from an anode by an oxygen permeable membrane tube which only conducts oxyanion, the anode is liquid copper or copper alloy with saturated carbon powder, calcium chloride is taken as the molten salt electrolyte, the cathode and the anode are vertically arranged, the electrolytic temperature is 1000-1100 DEG C, the electrolytic voltage is 3.0-3.5V, the electrolysis time is 2-6h, and the cathodic products obtained by the electrolysis are metallic titanium and the titanium alloy. The method has the advantages of simple process, high electrolysis speed and high current efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Process of direct copper exchange into na+-form of chabazite molecular sieve, and catalysts, systems and methods
InactiveCN102946997AShorten the timeHigh copper utilizationNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentMolecular sieveLiquid copper
Disclosed are processes for the preparation of copper containing molecular sieves with the CHA structure wherein the copper is exchanged into the Na+-form of the Chabazite, using a liquid copper solution wherein the concentration of copper is in the range of about 0.001 to about 0.4 molar. Also described are copper containing molecular sieves with the CHA structure, catalysts incorporating molecular sieves, systems and methods for their use.
Owner:BASF CORP
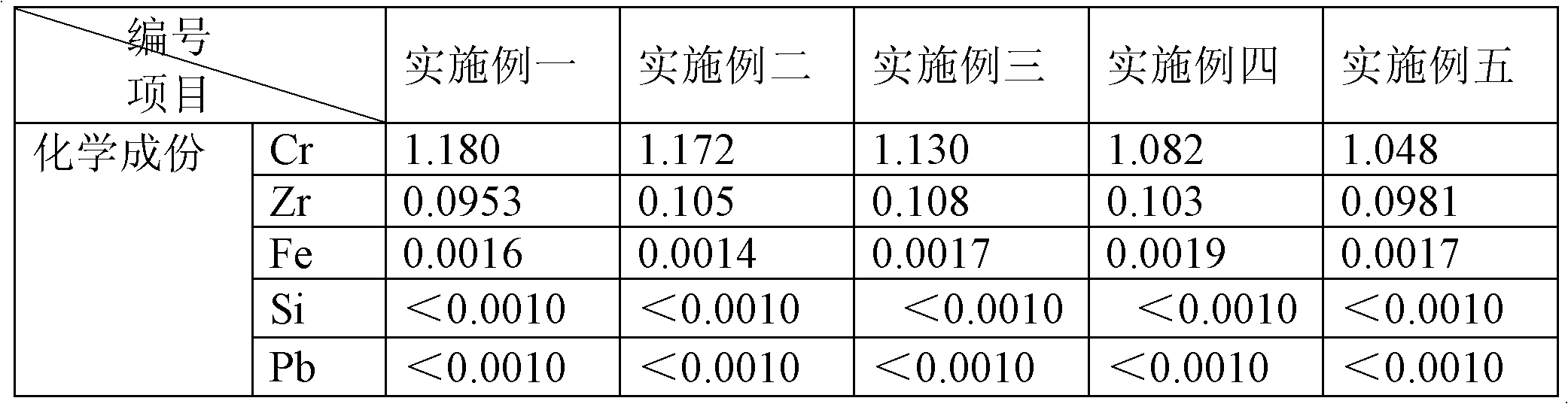
Vacuum semi-continuous method for casting copper chromium zirconium alloy
The invention relates to a vacuum semi-continuous method for casting copper chromium zirconium alloy, which is characterized by following steps of (1) smelting copper zirconium intermediate alloy, (2) sending cathode copper into an intermediate frequency furnace to be smelted, adding deoxidant to deaerate and deoxidize and adding metal chromium into the intermediate frequency furnace after deaeration and deoxidization, (3) heating and drying runner in casting equipment and using gas flame to seal an opening of the runner at the position of the opening above the runner, (4) pouring liquid copper in the intermediate frequency furnace in the heated and dried runner through a furnace opening of the intermediate frequency furnace, (5) pouring the liquid copper in the runner, simultaneously throwing the copper zirconium intermediate alloy into the runner at the position identical with a falling point of the liquid copper, and (6) opening a plug rod switch on the runner to enable the liquid copper to be guided into a water cooling crystallizer through a graphite leakage pipe to be casted ingots. The vacuum semi-continuous method smelts to cast the copper chromium zirconium alloy in the air, thereby being small in investment, simple in operation, stable in ingredient control, safe and reliable.
Owner:江苏隆达超合金股份有限公司
Process for producing anaerobic copper billets in upward continuous casting method
The invention discloses a process for producing anaerobic copper billets in an upward continuous casting method and overcomes difficulties in liquid copper fluidity, electrical property and density.Oxygen content of the anaerobic copper billets produced through the process is not higher than 5ppm, direct-current resistance of the anaerobic copper billets at 20 DEG C is smaller than or equal to 0.017593 / ohm mm<2> / m, the anaerobic copper billets are compact in texture and few in oxide skin and can be directly used in cold rolling production without surface milling, and a large quantity of copper resources are saved. By adopting the process to produce the anaerobic copper billets, ultra-wide anaerobic copper billets can be obtained, and the width of the anaerobic copper billets can be above 20. The process greatly improves yield of the anaerobic copper billets, reduces production cost and improves production efficiency.
Owner:富威科技(吴江)有限公司
Casting method of oxygen-free copper rod
InactiveCN102489510ATemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsLiquid copperCo carbon monoxide
The invention discloses a casting method of an oxygen-free copper rod. The casting method of the oxygen-free copper rod comprises the following steps of: 1) setting a temperature of equipment; 2) feeding a copper raw material; 3) adjusting the content of carbon monoxide; 4) reducing liquid copper; 5) oxygenating the liquid copper; 6) casting a blank by a crystallization wheel trough; and 7) rolling a copper casting blank. The casting method of the oxygen-free copper rod, provided by the invention, has the advantages that: the purity of the copper rod is not less than 99.99%, the yield is more than 1000 tons in one day, the resistivity of the copper rod at 20 DEG C is 0.016888 omegamm<2> / m, the elongation is 42% and the torsion revolution reaches 40; furthermore, the energy and the quantity are saved, and the surface of the copper rod is bright.
Owner:JIANGSU CHENLONG TECH
PCB (Polychlorinated Biphenyl) acidic etching solution
The invention discloses a PCB (Polychlorinated Biphenyl) acidic etching solution which comprises the following components: 130-180 g / L of etching mother liquid copper, 120-200 g / L of hydrochloric acid (the concentration of the hydrochloric acid is 30%-38%), 150-250 g / L of oxidizing agents, 120-250 g / L of industrial salt, 0.5-15 g / L of stabilizing agents, 5-30 g / L of accelerating agents, 0.05-0.2 g / L of buffering agents and the balance of water. According to the PCB acidic etching solution, the acid value of the hydrochloric acid can be controlled to be less than 1.8 N and is greatly lower than the acid value less than 2.5 N in the prior art; the etching uniformity can reach more than 90%; and the etching factor is more than 3.5, so that the accuracy of an etching route figure and the stability of the etching solution are effectively ensured.
Owner:长沙牧泰莱电路技术有限公司
Preparation method for three-dimensional structure graphene reinforced copper matrix composite material
ActiveCN105386003AEvenly dispersedNo agglomerationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingComposite electrodeLiquid copper
The invention provides a preparation method for a three-dimensional structure graphene reinforced copper matrix composite material, and relates to a preparation method for a composite electrode material. The problems that in an existing graphene reinforced copper matrix composite material, the contact of graphene and copper is insufficient, and the thermal conductivity and the electrical conductivity of the prepared graphene reinforced copper matrix composite material are reduced due to the fact that liquid copper is difficult to wet on the surface of the graphene, and holes, defects and the like are easily formed in the interface are solved. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, three-dimensional graphene is prepared on a foam copper matrix through the method of chemical vapor deposition; secondly, a layer of copper is evaporated on the surface of the graphene; and lastly, spark plasma sintering is conducted on the three-dimensional graphene / foam copper material evaporated with the copper and copper powder. The method is used for preparing the three-dimensional structure graphene reinforced copper matrix composite material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
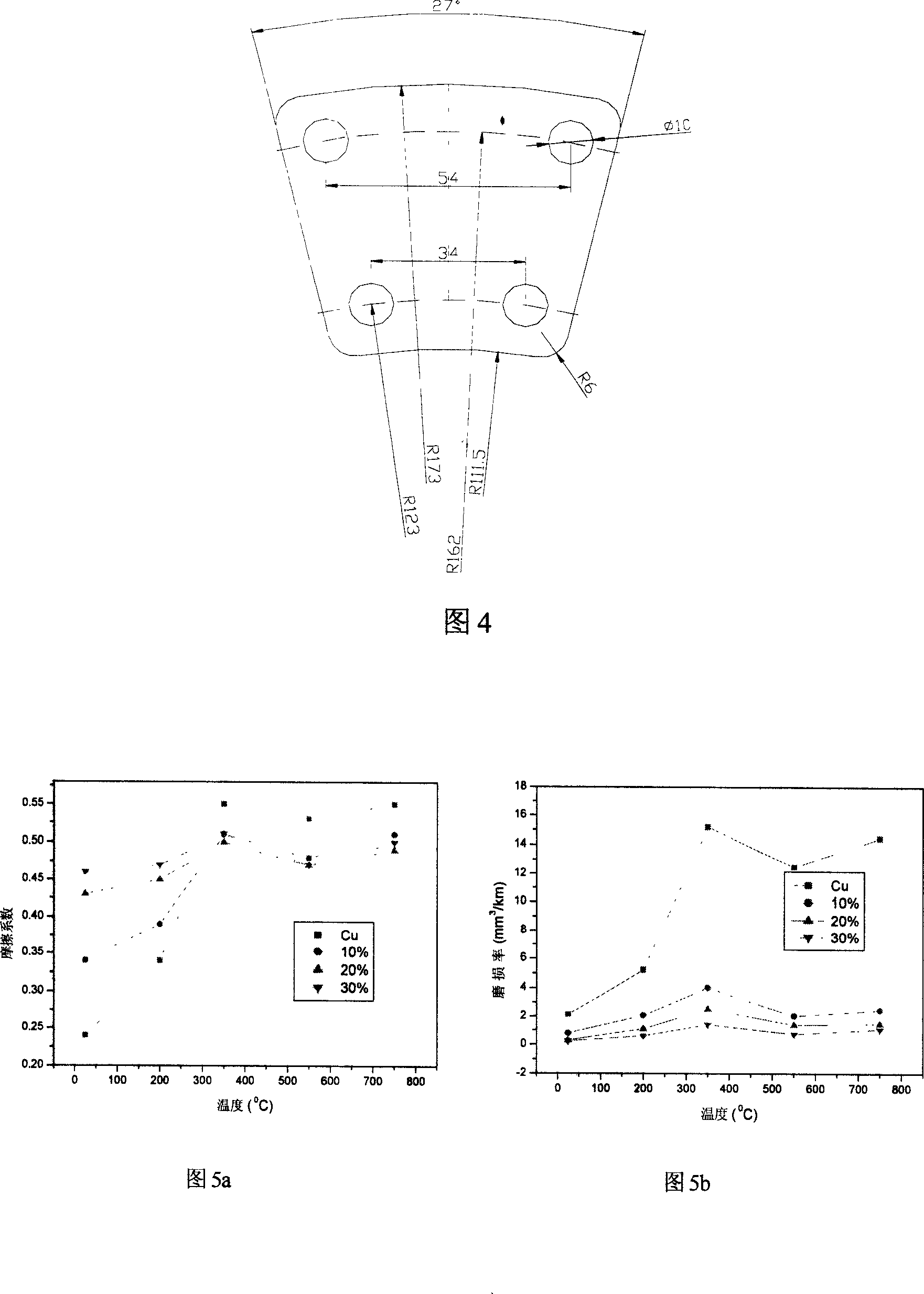
Method for preparing copper-based powder with low oxygen content and low apparent density through atomization
The invention discloses a method for preparing copper-based powder with low oxygen content and low apparent density through atomization, which comprises the following steps: melting metallic coppers into liquid copper; atomizing the liquid copper; carrying out absorption and filtration on the atomized liquid copper so as to obtain the copper-based powder. The invention is characterized in that in the process of atomization, two nozzles are arranged below the liquid copper, and arranged in a same vertical line so as to form two focuses; the diameter of an orifice is 1.2 to 1.5mm; and atomized vertical angles are respectively 28 to 32 degrees and 18 to 22 degrees. The copper-based powder prepared by using the method of the invention has the advantages of low oxygen content, low apparent density and good metallurgical properties.
Owner:铜陵铜基粉体科技有限公司
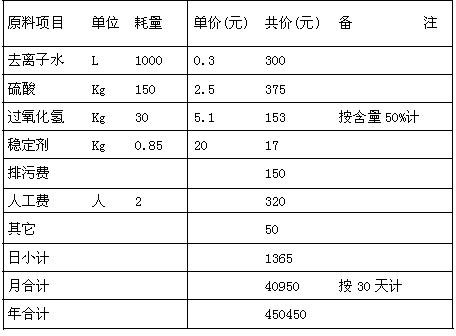
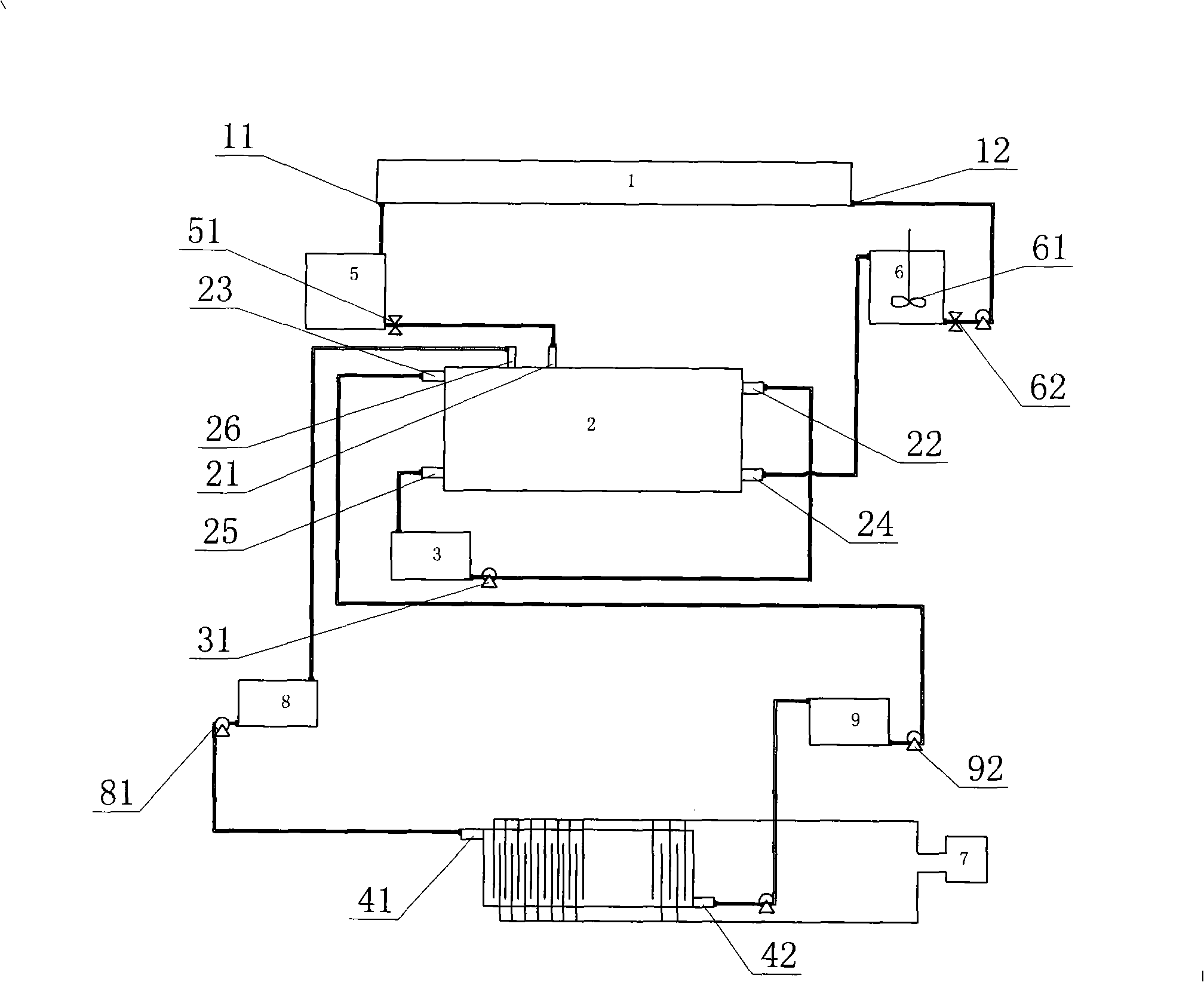
Device for regenerating waste microetching liquid and recovering copper
InactiveCN101974756ASolve the costLow costPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wasteLiquid copper
The invention discloses a device for regenerating waste microetching liquid and recovering copper. A processed workpiece is formed in a microetching groove by a workpiece to be processed of a circuit board; hydrogen peroxide and sulfuric acid solution are taken as microetching liquid in the process; copper oxide and minute quantity of metallic copper on the surface of the workpiece are removed to lead the concentration of microetching liquid copper ion to be increased into the waste microetching liquid; the remnant hydrogen peroxide in the waste microetching liquid is removed; the copper ion is electrodeposited as the metal copper; and the lost components in the microetching liquid are replenished to qualified microetching liquid which is returned to the regenerating cycle process of the microetching groove. The device overcomes the defects that the waste microetching liquid in the circuit board microetching process of the existing circuit board enterprises is only simply processed to be discharged immediately, the processing procedure has large wastes, and serious resource loss; and the device is suitable for the regenerating cycle of copper-containing waste microetching liquid of the circuit board and the copper recovering in the various circuit board production enterprises.
Owner:罗忠凯
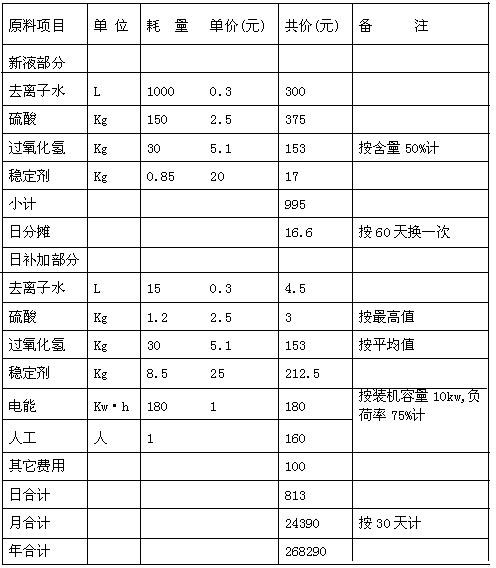
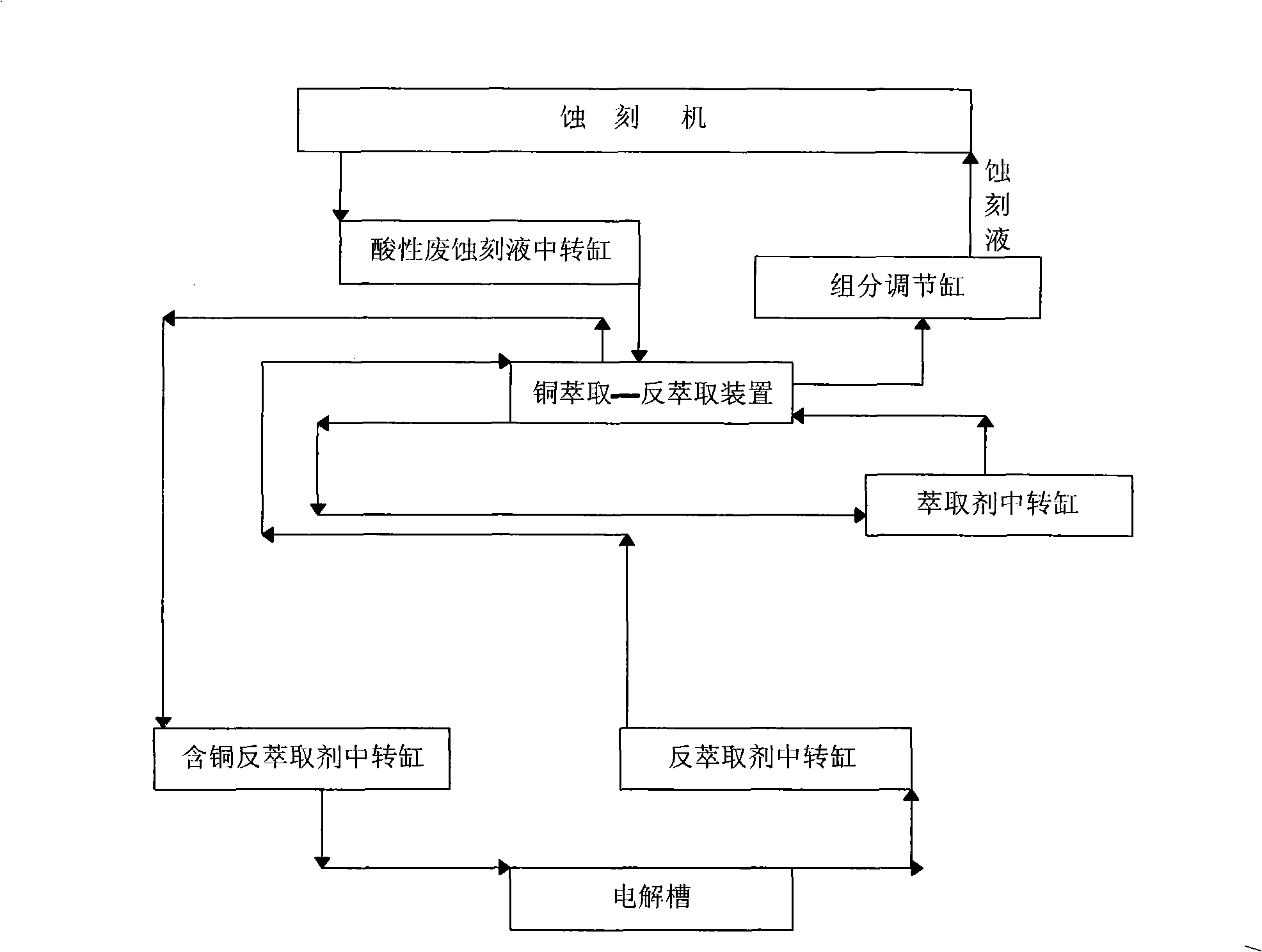
Method and device for circulation and regeneration of acidic waste etching liquid
InactiveCN101492186AEmission reductionReduce pressure on environmental protectionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementAcid etchingElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method and a device for recycling acidic waste etching liquid. The method and the device adopt three closed cycles, namely, an acidic waste etching liquid copper separation and component adjustment cycle, a copper extraction agent cycle, and an electrolytic copper extraction and a back extraction agent cycle. The acidic waste etching liquid from which copper is removed by a copper-extraction and back-extraction mechanism is subjected to component adjustment so as to be circularly used by an acid etching machine, the extraction agent is circularly used in the copper-extraction and back-extraction mechanism, the back extraction agent is returned to the copper-extraction and back-extraction mechanism to be circularly used after copper is removed by electrolyzing deposited copper, and electrolytic copper generated by electrolyzing deposited copper can be sold as a commodity. Therefore, in the whole treatment process, the closed cycles of materials are realized with wastewater discharge avoidance, effective copper recovery and recycling use of waste etching liquid and other materials. In addition, the extraction and back extraction of the copper extraction agent are carried out in the copper-extraction and back-extraction mechanism and liquid in a cell flows in an overflow manner without requiring a pump, so the device is convenient in operation and compact in overall structure.
Owner:陈飙
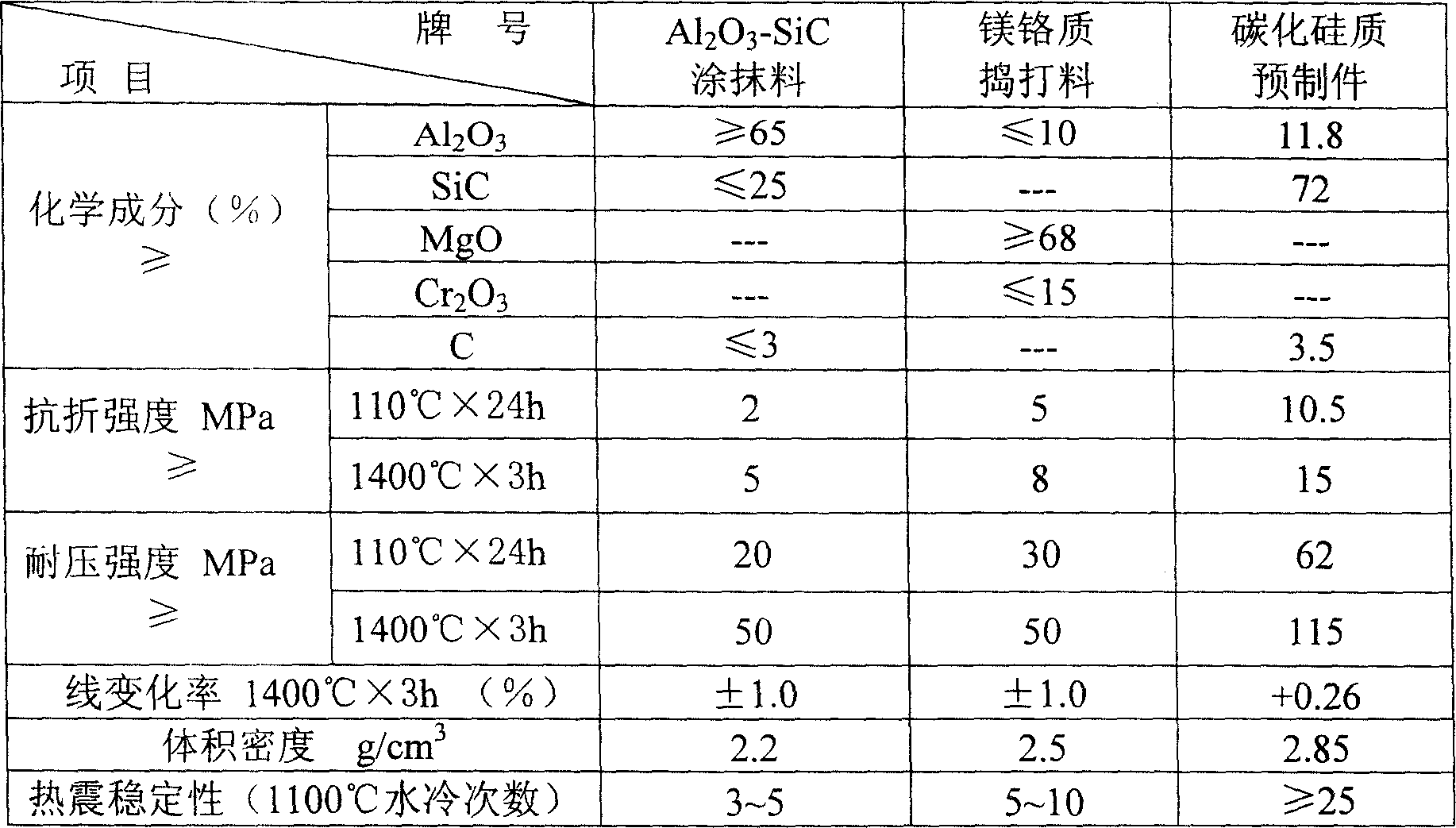
Flame-proof pouring material and launder prefabricated component for copper anode furnace
InactiveCN101152982AReduce labor intensityGood for production turnoverChemical compositionLiquid copper
The present invention provides an improvement of fire-resistant material for copper-anode furnace flow groove. The present invention is characterized in that the basic components are 50 to 80 weight percent of SiC, 0 to 40 weight percent of fire-resistant material containing Al2O3, 1 to 20 weight percent of micro powder, 1 to 4 weight percent of C, 1 to 3 weight percent of Si, 0.5 to 5 weight percent of cement binder. The chemical component after mixing is 48 to 78 weight percent of SiC, 10 to 40 weight percent of Al2O3, 4 to 8 percent of SiO2, less than or equal to 6 weight percent of C, less than or equal to 3 weight percent of CaO, and less than or equal to 6 weight percent of Si. Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the characteristics of good thermal shock resistance, good high-temperature erosion resistance, non-stick liquid copper and copper slag, convenient cleaning, long service life and so on. The one-time service life reaches above 20 furnaces with copper. Besides, the construction is simple and the labor intensity of workers is greatly lowered. When used for the first time, the device should be baked rapidly; when used later, no baking is needed. Thus the present invention saves the baking cost and facilitates the production turnover of copper plants.
Owner:JIANGSU JIANAI HIGH TEMPERATURE MATERIAL
Technological method for producing music bronze drum through hot mould casting
InactiveCN102463321AClear patternCrisp and beautiful voiceFoundry mouldsFoundry coresMetallurgyLiquid copper
The invention relates to a technological method for producing music bronze drum through hot mould casting. With the method, a music bronze drum which can provide the modern equal temperaments can be cast. The method comprises steps that: (1) a music bronze drum template (female mould) is manufactured; (2) a music bronze drum mould is manufactured; (3) liquid wax is injected into the cavity of the mould; the liquid wax is cooled, the mould is opened, and the wax mould is fetched; (4) a paint is brushed on the surface of the wax mould; sand is scattered on the wax mould, such that a mould casing is formed; the mould casing is dried and hardened; the processes are repeated several times, until a mould casing with a certain thickness is obtained; (5) the mould casing is heated; (6) liquid copper is injected into the mould casing being heated.
Owner:DONGLAN MUSIC TONGGU CULTURAL COMM
Technique for preparing tungsten copper heat-sink and electric packaging material
The invention provides a novel process for preparing tungsten-copper heat sink and electronic package materials, in order to overcome the problems that the prior tungsten-copper heat sink and electronic package materials are not excellent enough in quality, high in preparation cost and low in production efficiency. The process comprises the steps of preparing powder, adding inducers, mixing materials, molding for automatic forming, performing isostatic pressing and covering, presintering and infiltrating liquid copper. The process which is adopted to prepare the tungsten-copper heat sink and electronic package materials has the advantages of low cost and high production efficiency; in addition, the prepared tungsten-copper heat sink and electronic package materials are compact in structure and show excellent properties in all aspects.
Owner:安泰天龙钨钼科技有限公司
High-conductivity high-temperature-resisting copper alloy preparing method
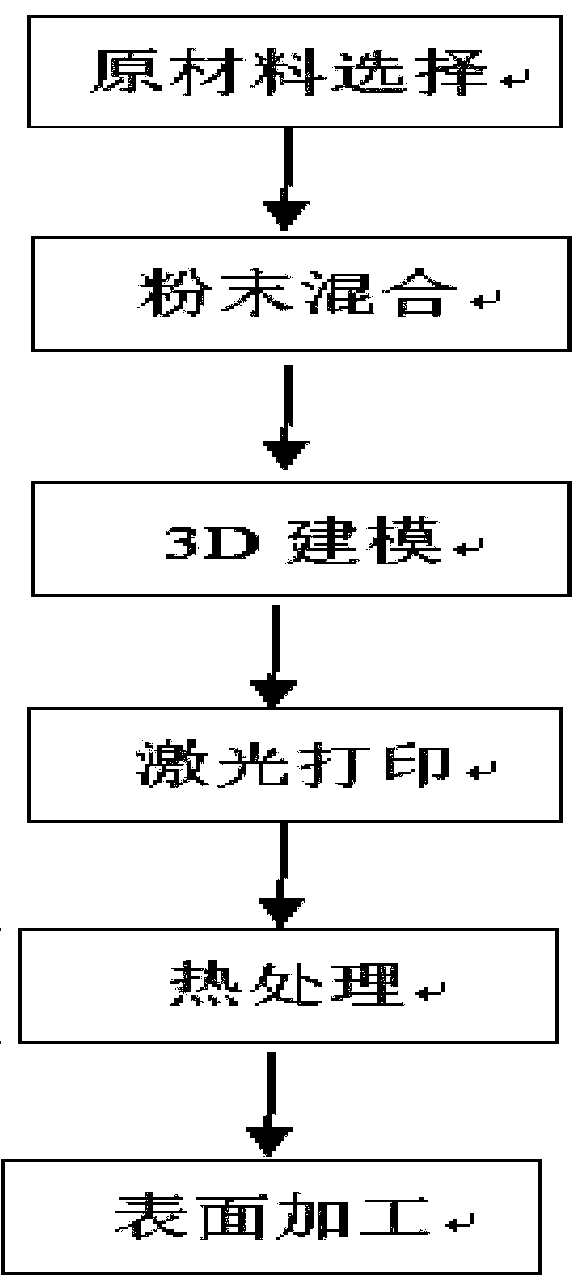
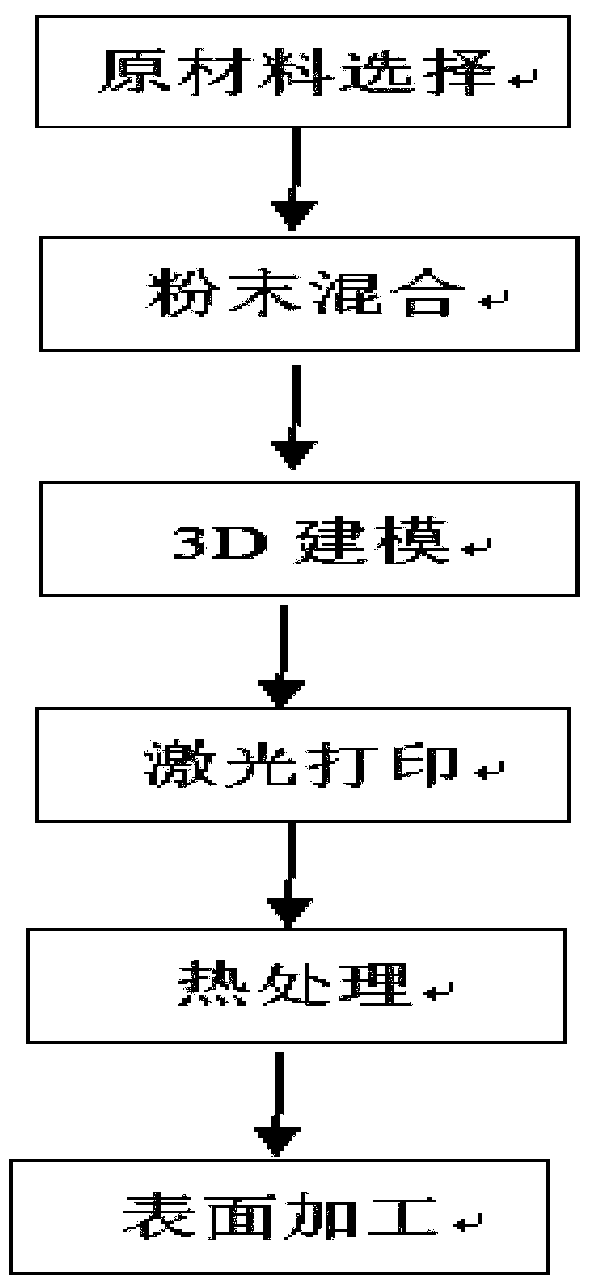
ActiveCN109971989AGood electrical and thermal conductivityHigh temperature resistance and softening performanceLaser printingLiquid copper
The invention discloses a high-conductivity high-temperature-resisting copper alloy preparing method, and belongs to the technical field of nonferrous metal material manufacturing. Prepared atomized copper powder is subjected to reducing into copper powder after being oxidized, roughness of the copper powder surface can be improved, reflectivity of the atomized copper powder surface for lasers during laser printing operation is reduced, and work reliability of laser printing equipment is guaranteed. A supersonic speed gas atomization method is used for preparing the atomized copper powder, andthe advantages that powder granularity is fine, and the degree of sphericity is high; in the smelting process, an electrolysis copper plate can be sufficiently smelted into liquid, and the situationthat due to incomplete smelting of the electrolysis copper plate, residual solid exists in liquid copper, and consequently the prepared atomized copper powder is uneven is avoided; and the copper alloy has high electricity and heat conducting performance and also has high high-temperature resisting softening performance, the mechanical strength can be kept not reduced or slightly reduced in the high-temperature work environment, and the market requirement for high-temperature-resisting high-conductivity copper alloys is met.
Owner:SHAANXI SIRUI ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Recovery of residues containing copper and other valuable metals
InactiveUS20100242676A1Effective volumeHigh recovery rateElectric furnaceProcess efficiency improvementSlagLiquid copper
A process for recovering non-ferrous metals, in particular copper, nickel and cobalt, from metallurgical residues containing these non-ferrous metals at an oxidation state of greater than or equal to zero, in an alternating current type plasma arc electric furnace comprising a plurality of electrodes, containing a liquid copper heel covered by a fluid slag comprising at least one fusion-reduction phase, comprising charging of metallurgical residues comprising the non-ferrous metals onto the heel contained in the plasma arc electric furnace, fusion of the metallurgical residues in the fluid slag or at the slag-metal bath interface, reduction of at least the non-ferrous metals to oxidation state zero, and intense stirring of the copper heel by injection of inert gas, preferably nitrogen and / or argon, so as to avoid crust formation and to accelerate the reduction reaction and to cause the copper-miscible non-ferrous metals to pass into the copper heel.
Owner:PAUL WURTH SA
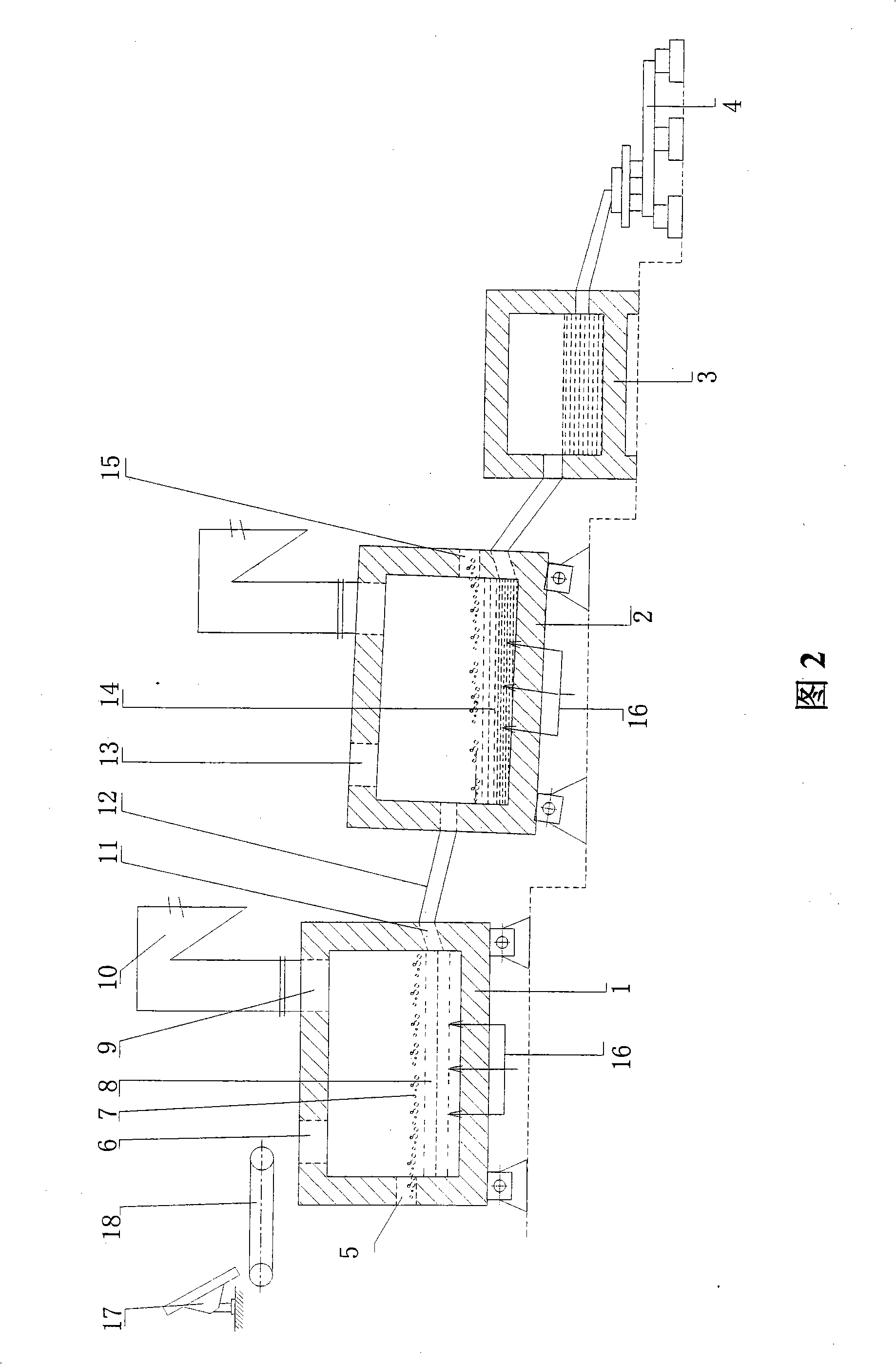
Method for producing bright oxygen-free copper rod
The invention discloses a method for producing a bright oxygen-free copper rod. A copper rod manufactured according to a traditional manufacturing method is high in oxygen content. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: heating and drying a copper material and then melting; keeping the temperature of liquid copper after being molten in a maintaining furnace; penetrating a copper bar bus through a coating chamber communicated with the maintaining furnace and attaching the liquid copper to the surface of the copper bar, thereby forming a thicker copper casting bar; and cooling, hot-rolling, cooling and coiling the copper casting bar in turn, thereby forming a bright oxygen-free copper rod, wherein the temperature of the maintaining furnace for keeping the temperature of the liquid copper is at 1140-1180 DEG C, the temperature after cooling and before hot-rolling the copper rod coated with the liquid copper is at 600-800 DEG C, and the temperature at the moment of coiling is higher than room temperature but lower than 100 DEG C. According to the method provided by the invention, the manufacturing for the high-quality copper bar with oxygen content at 2-10ppm becomes possible. Meanwhile, a specific oxidation film is formed on the surface of the copper bar according to the method provided by the invention, so that the mutual adhesion phenomenon between wire bars during an annealing process at the coiling moment is restrained. No surface scratch or broken wire is caused during the processing process, so that the bright oxygen-free copper rod with excellent surface state and high quality can be produced according to the method.
Owner:HANGZHOU FUTONG ZHAOHE COPPER +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com