Method for directly preparing titanium and titanium alloy by titanium-containing waste residue
A technology of titanium waste slag and titanium alloy, which is applied in the field of electrochemical metallurgy, can solve the problems of waste slag discharge, waste slag ratio limitation, poor activity and viscosity, etc., and achieve the effect of improving current efficiency, avoiding re-oxidation, and increasing reduction speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
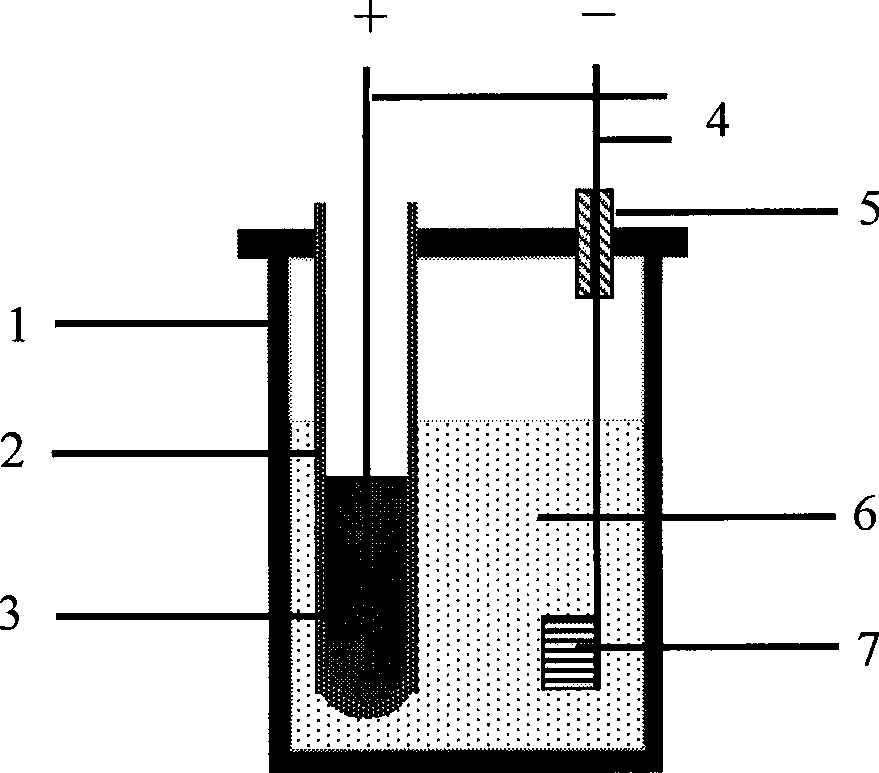
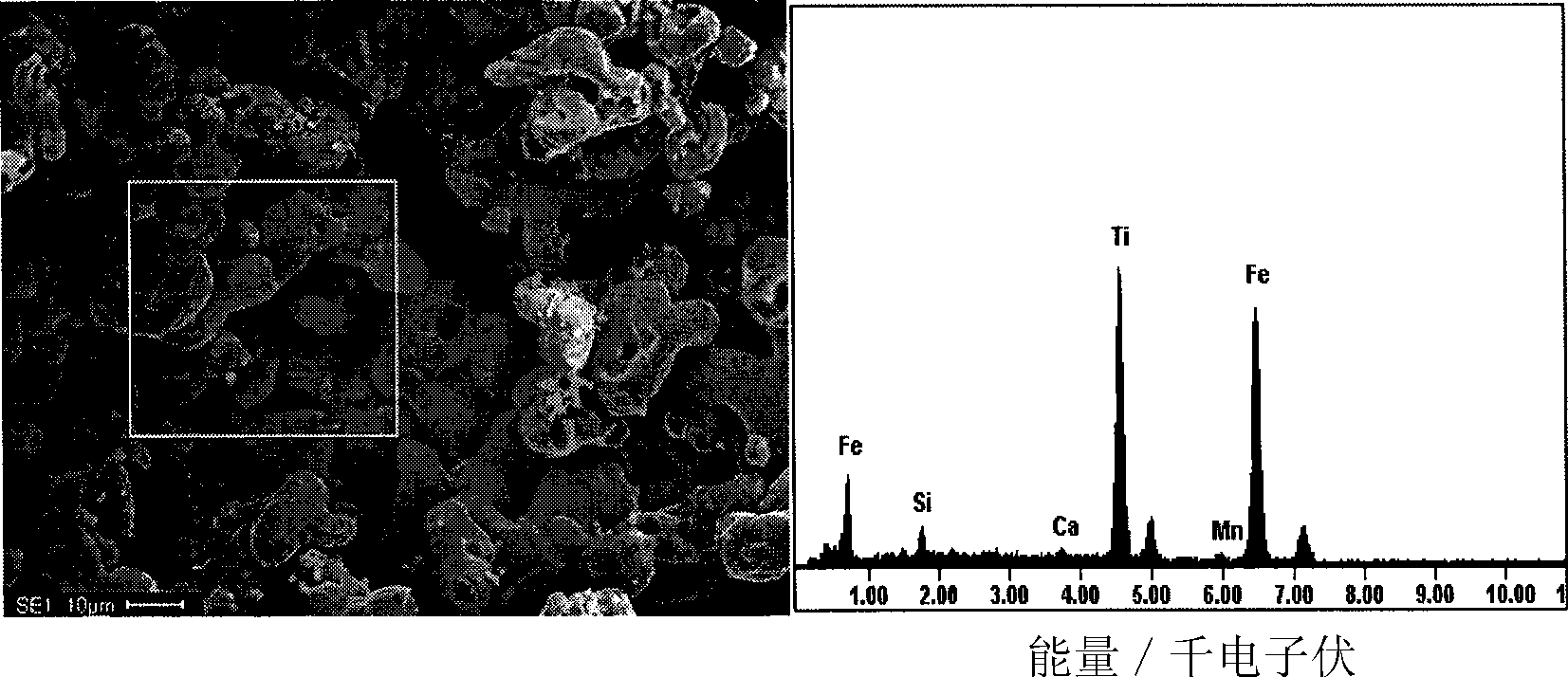
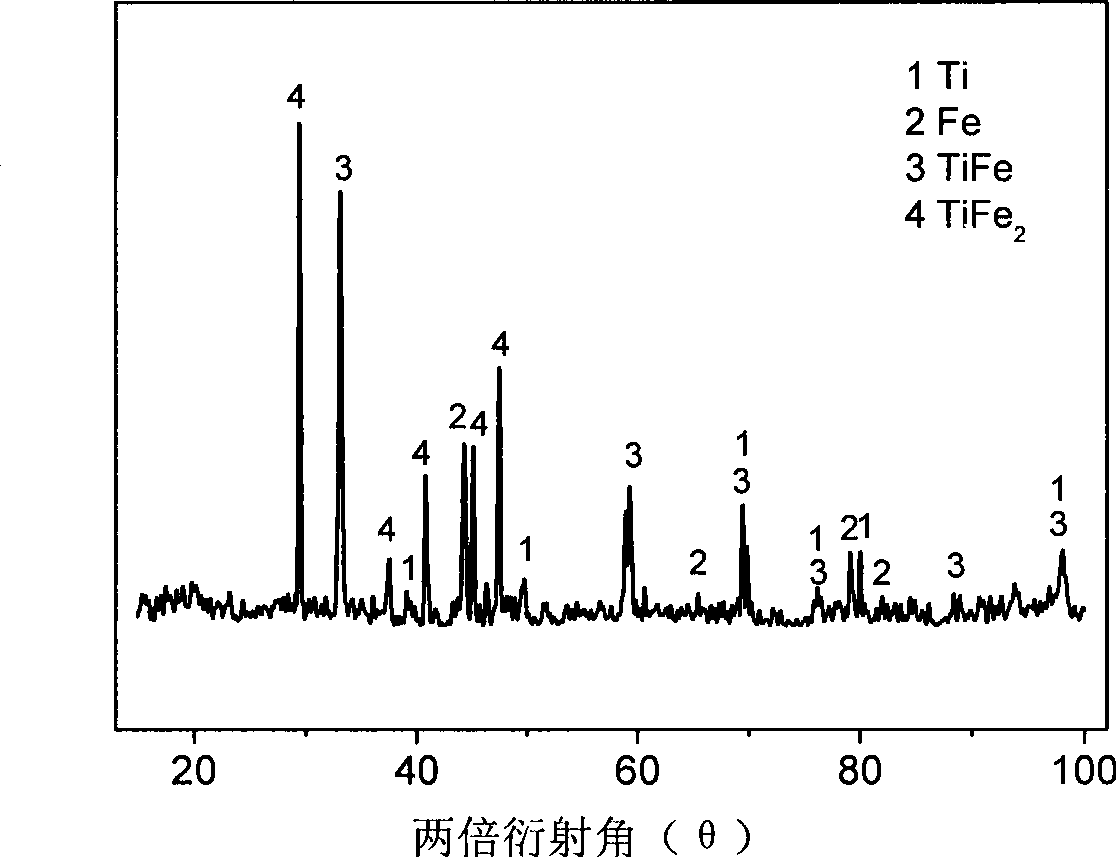
[0032] Example 1: The iron-titanium slag in the waste slag was ball-milled in a high-energy ball mill for 2 hours, using liquid paraffin as a binder, and using a 24T powder press to press 2.5 g of slag powder into a disc with a diameter of 10 mm under a pressure of 6 MPa. After natural drying at room temperature, it was sintered in an oxidizing atmosphere at 1100°C for 2 hours. A molybdenum wire with a diameter of 0.2 mm is used to wind the disc on a molybdenum rod with a diameter of 1.5 mm to make a cathode; the anode is a copper liquid saturated with carbon powder in a yttria-stabilized zirconia tube, and the CaCl 2 It is a molten salt electrolyte, and the graphite crucible is a reaction vessel. When the temperature of the furnace reaches 1100°C, insert the cathode into the molten salt in the crucible, and apply a voltage of 3.0-3.5V to the two poles for electrolysis. The electrolysis time is 6 hours. The electrolysis cathode product is rinsed and dried for detection. figu...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: Mill the high-titanium slag in the waste slag for 2 hours in a high-energy ball mill, use liquid paraffin as a binder, and use a 24T powder press to press 2.5 g of slag powder into a circle with a diameter of 10 mm under a pressure of 3 to 4 MPa. After natural drying at room temperature, the sheets were sintered in an oxidizing atmosphere at 1100°C for 2h. A molybdenum wire with a diameter of 0.2 mm is used to wind the disc on a molybdenum rod with a diameter of 1.5 mm to make a cathode; the anode is a copper liquid saturated with carbon powder in a yttria-stabilized zirconia tube, and the CaCl 2 It is a molten salt electrolyte, and the graphite crucible is a reaction vessel. When the temperature of the furnace reaches 1100°C, insert the cathode into the molten salt in the crucible, and apply a voltage of 3.0-3.5V to the two poles for electrolysis. The electrolysis time is 6 hours. The electrolysis cathode product is rinsed and dried for detection. Figure 4...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: Mill the high-titanium slag in the waste slag for 2 hours in a high-energy ball mill, use liquid paraffin as a binder, and use a 24T powder press to press 2.5 g of slag powder into a circle with a diameter of 10 mm under a pressure of 3 to 4 MPa. After natural drying at room temperature, the sheets were sintered in an oxidizing atmosphere at 1100°C for 2h. A molybdenum wire with a diameter of 0.2 mm is used to wind the disc on a molybdenum rod with a diameter of 1.5 mm to make a cathode; the anode is a copper liquid saturated with carbon powder in a yttria-stabilized zirconia tube, and the CaCl 2 It is a molten salt electrolyte, and the graphite crucible is a reaction vessel. When the furnace temperature reaches 1100°C, the cathode is inserted into the molten salt in the crucible, and a voltage of 3.0-3.5V is applied to the two poles for electrolysis. The electrolysis time is 4 hours. The electrolysis cathode product is washed and dried before detection. Im...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com