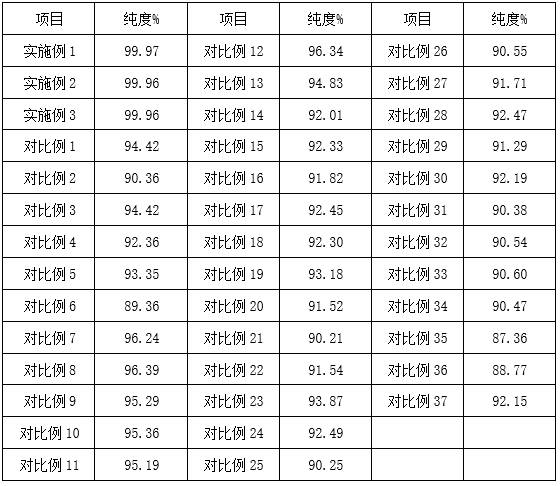
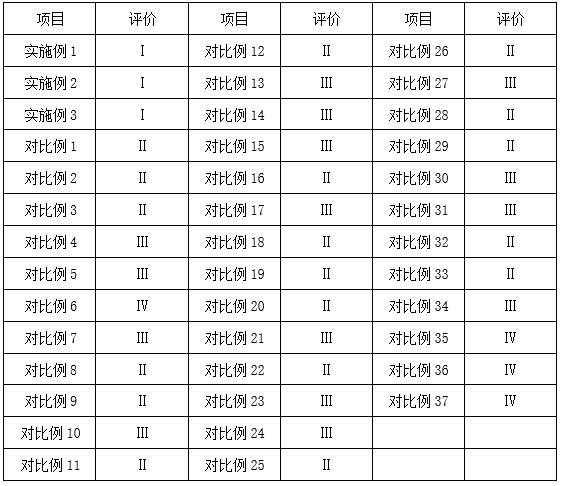
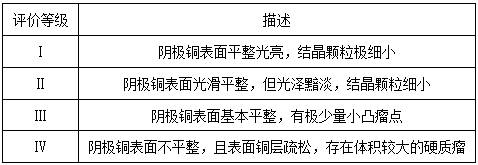
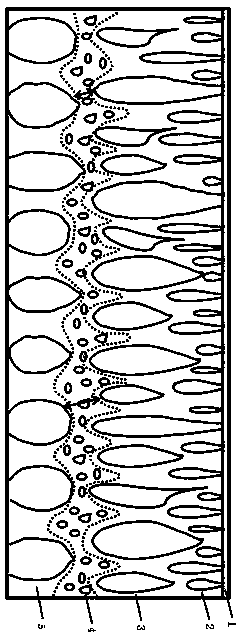
Patents
Literature
50results about How to "Fast electrolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for directly preparing titanium and titanium alloy by titanium-containing waste residue
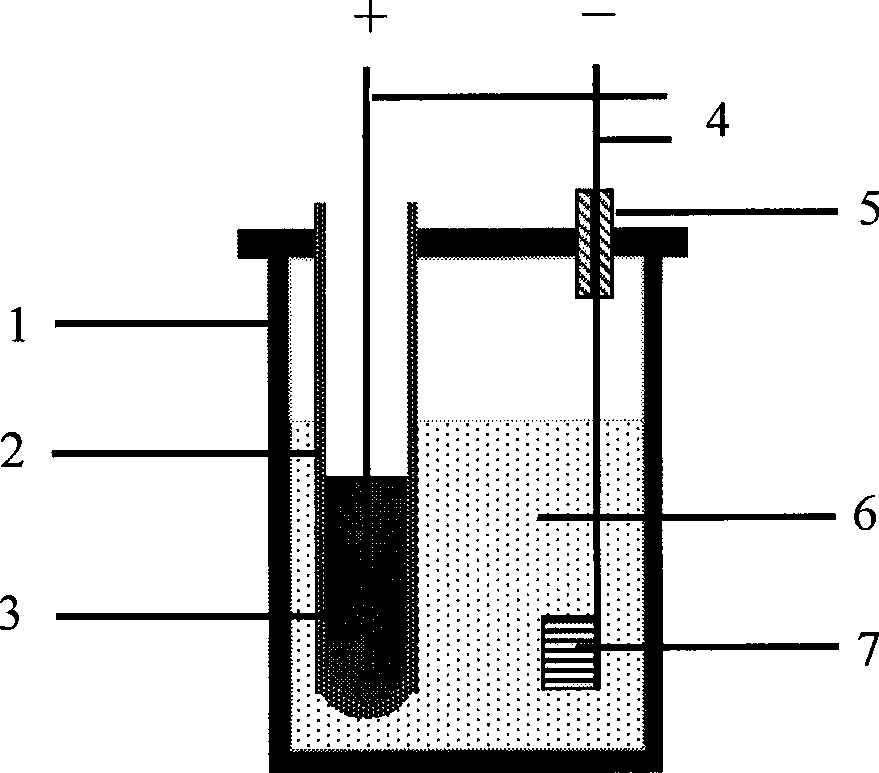
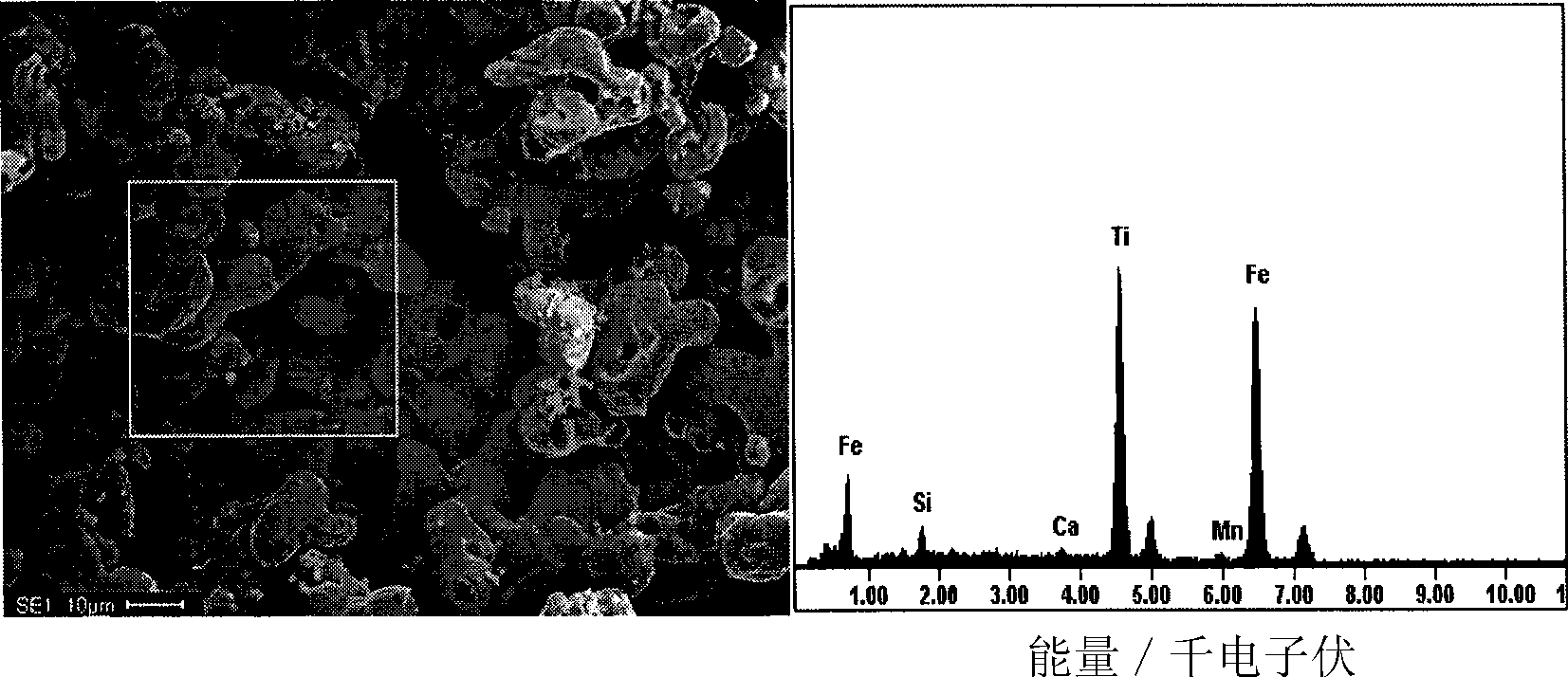
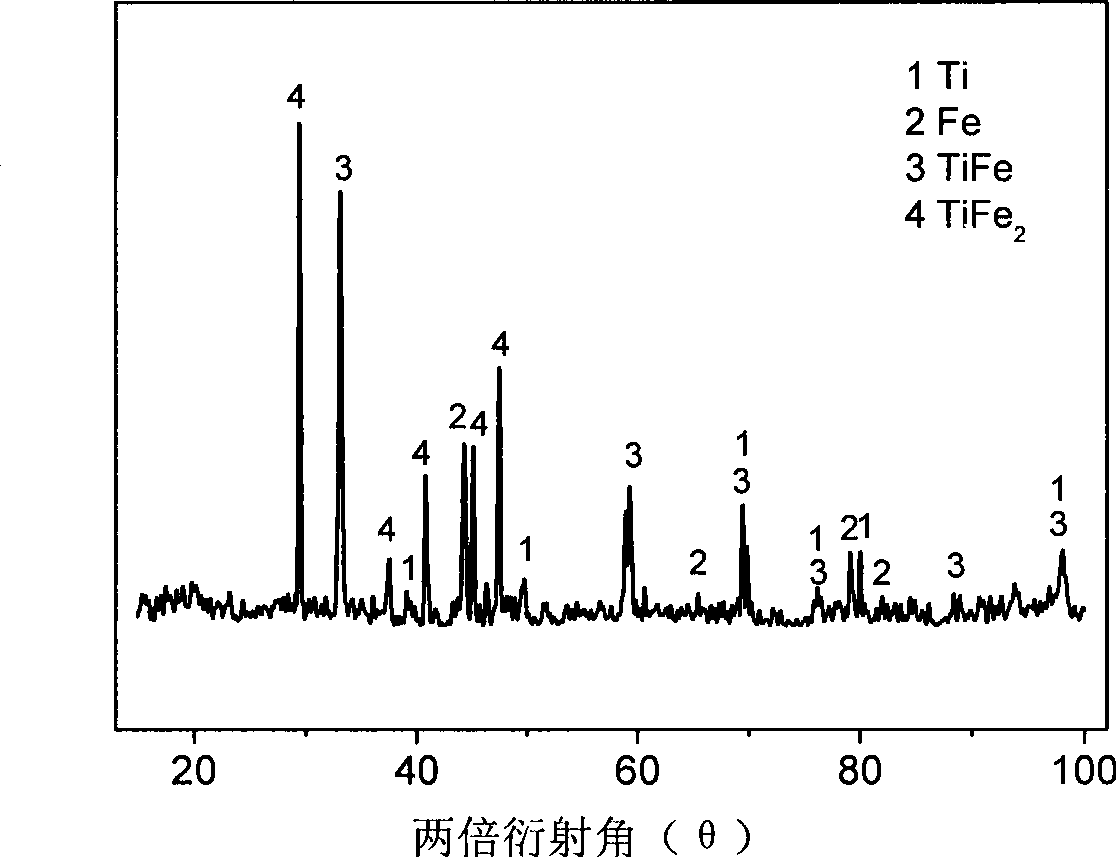
The invention relates to a method for directly preparing titanium and titanium alloy from titaniferous waste residues, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical metallurgy. The method is characterized in that the titaniferous waste residues are made into an electrolysis electrode, and the electrolysis is performed in a crucible of an electrolytic cell by a solid oxygen permeable membrane in a specific molten salt electrolyte. The method comprises the following process steps: the titaniferous residues is processed by ball milling, then pressed and formed in a mould at 3-6MP, dried in the air, and then sinteredat the temperature of 1000-1100 DEG C for 2h to be made into an electrolysis cathode; molten salt is separated from an anode by an oxygen permeable membrane tube which only conducts oxyanion, the anode is liquid copper or copper alloy with saturated carbon powder, calcium chloride is taken as the molten salt electrolyte, the cathode and the anode are vertically arranged, the electrolytic temperature is 1000-1100 DEG C, the electrolytic voltage is 3.0-3.5V, the electrolysis time is 2-6h, and the cathodic products obtained by the electrolysis are metallic titanium and the titanium alloy. The method has the advantages of simple process, high electrolysis speed and high current efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
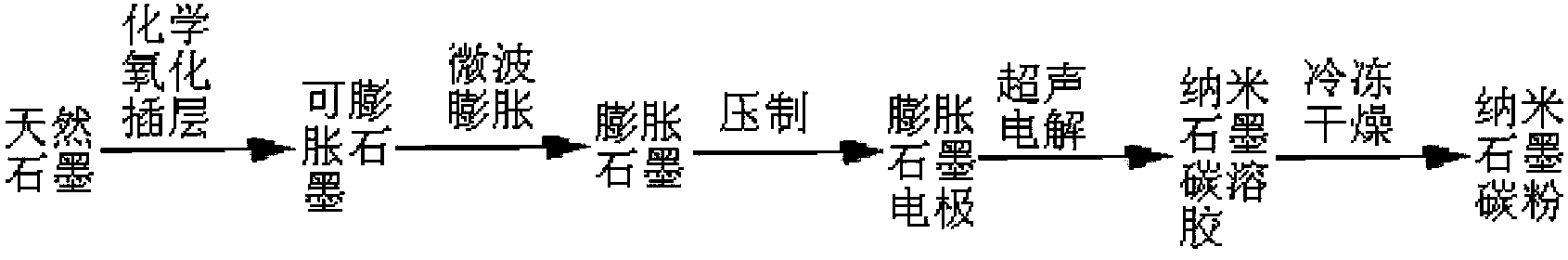
Preparation method of nano-graphite carbon powder
ActiveCN103395777AImprove electrolysis efficiencyShorten electrolysis timeMaterial nanotechnologyGraphiteElectrolysisFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a preparation method of nano-graphite carbon powder. The method comprises the steps of: (1) preparing expansible graphite by a chemical oxidation intercalation process; (2) preparing expanded graphite by a microwave process; (3) pressing the expanded graphite into a expanded graphite sheet, putting it into a microporous filter membrane sieving assembly, conducting pressing and sealing, then placing the assembly at the anode and cathode of an electrolytic bath, taking a chlorate solution as an electrolyte solution, carrying out ultrasonic electrolysis at a temperature below 60DEG C, controlling the electrolytic current at 5-18A / cm<2>, the voltage at 6-20V, the ultrasonic oscillation power at 200-600W, and the frequency at 20-40kHz, inverting the anode and the cathode at an interval of 8-15min, completing electrolysis when the concentration of sol in the electrolytic bath is 2-5%, thus obtaining nano-graphite carbon sol; and (4) adding ammonium sulphate into the nano-graphite carbon sol till the mass concentration of ammonium sulfate reaches 5-8%, stirring them uniformly, then performing freeze drying, thus obtaining the nano-graphite carbon powder. The method has the advantages of mild reaction condition and high speed, thus being suitable for industrialized mass production.
Owner:DATONG XINCHENG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
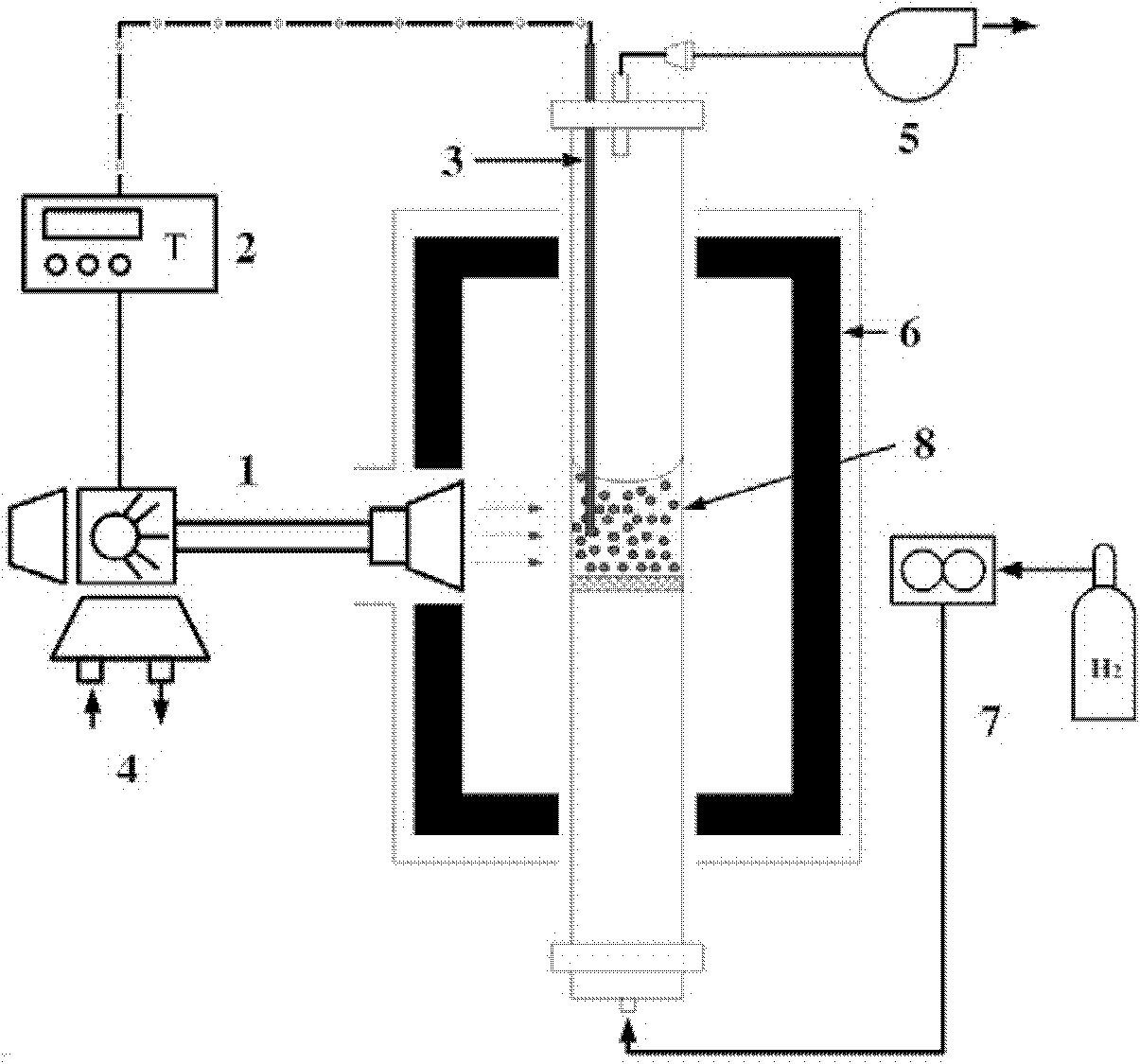
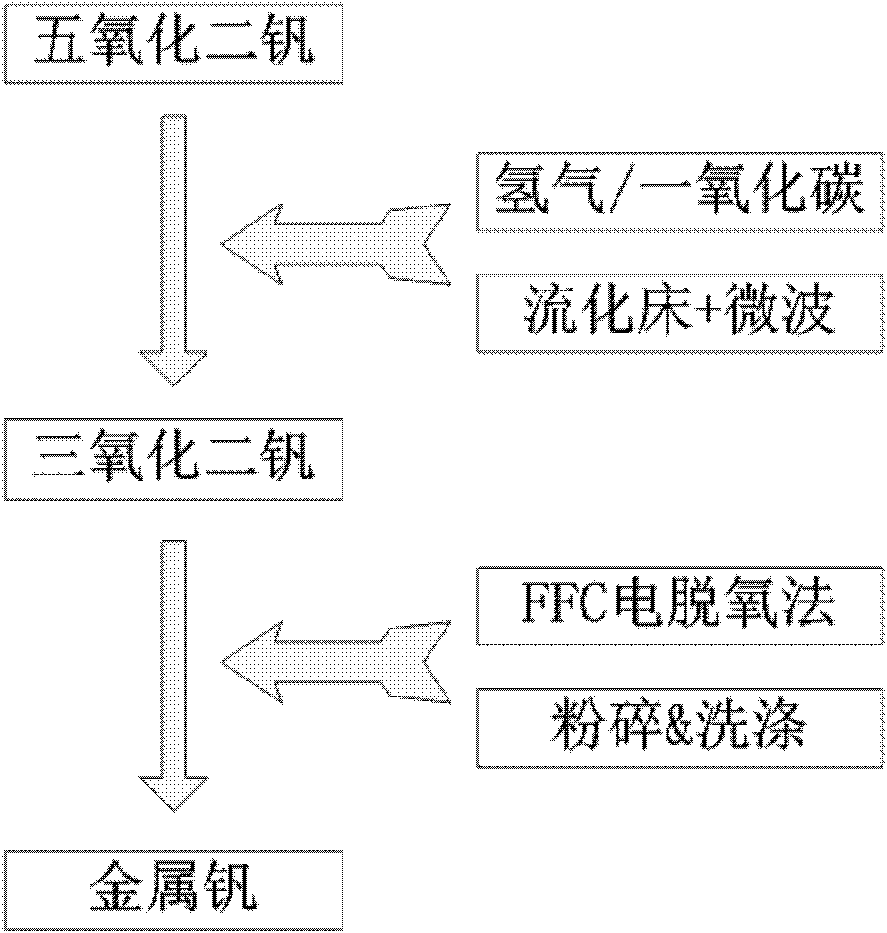
Vanadium metal smelting process
The invention discloses a vanadium metal smelting process. The process prepares vanadium metal by combining a microwave fluidized bed technology and a flexible flat cable (FFC) electric deoxidation technology and using vanadium pentoxide as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: directly reducing the vanadium pentoxide with low melting point (the melting point is 690 DEG C) into vanadium trioxide in short time at the temperature of between 600 and 650 DEG C by using the characteristics of high heating efficiency, quick temperature rise and gas-solid contact of a microwave fluidized bed and adopting hydrogen and / or carbon monoxide as reducing gas; directly preparing the vanadium trioxide which has high melting point into an oxide cathode by molding and sintering processes; and performing FFC electric deoxidation on the oxide cathode in molten salt of calcium chloride or mixed molten salt of calcium chloride and sodium chloride, crushing the electrolyzed cathode by using ultrasonic wave, then performing water washing, acid washing and alcohol washing to remove impurities, and finally obtaining the vanadium metal with purity of over 99 percent, wherein the current efficiency is kept over 70 percent, the energy utilization rate of microwave heating equipment is over 80 percent, and the electrolysis energy consumption is 10kwh to 13kwh / kg.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Fruit-vegetable cleaner utilizing electrolytic ionic water
InactiveCN101579197AIncrease the participating reaction areaExtended use timeKitchen equipmentWater savingWater discharge
The invention provides a fruit-vegetable cleaner utilizing electrolytic ionic water, which comprises a washing bucket, a washing basket and a controller; a main ionic water outlet of an electrolyzer is connected with an electrode chamber of the electrolyzer; the main ionic water outlet is provided with a main water drain valve; a secondary ionic water outlet and a discharge ionic water outlet are connected with the other electrode chamber of the electrolyzer; the secondary ionic water outlet is provided with a secondary water drain valve, and the discharge ionic water outlet is provided with a discharge water drain valve; the main ionic water outlet and the secondary ionic water outlet are communicated with the washing bucket, and the discharge ionic water outlet is communicated with a water discharge pipe; bipolar plate-shaped electrodes of the electrolyzer are twisted and intercrossed; the main water drain valve, the secondary water drain valve and the discharge water drain valve are connected with the controller; and the bipolar electrodes are connected with the controller through an electrolytic drive control panel. Because the bipolar plate type-shaped electrodes of the electrolyzer are twisted and intercrossed, the reaction areas of the electrodes are enlarged, and the electrolytic rate is increased; and because the washing water can be recycled for electrolysis, the utilization time of the washing water is prolonged, the water consumption is reduced, and the cleaning efficiency and effect are improved.
Owner:林修鹏
Diamond synthesis rod purification process
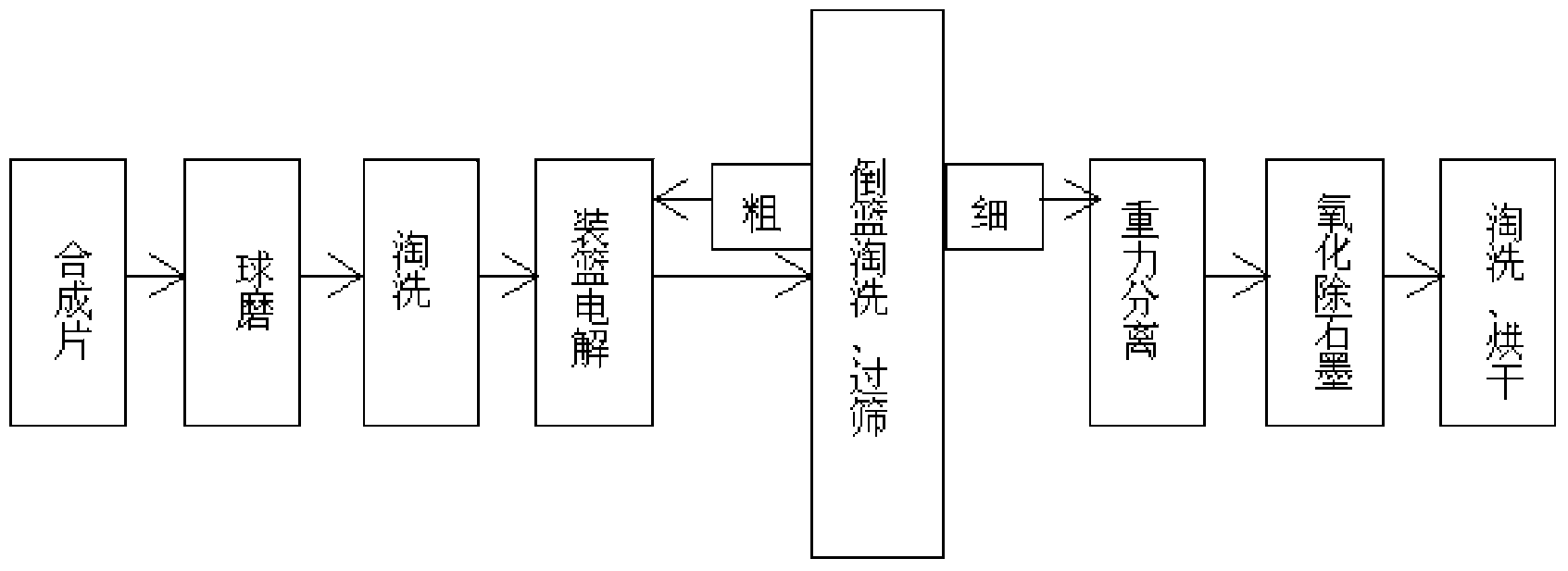
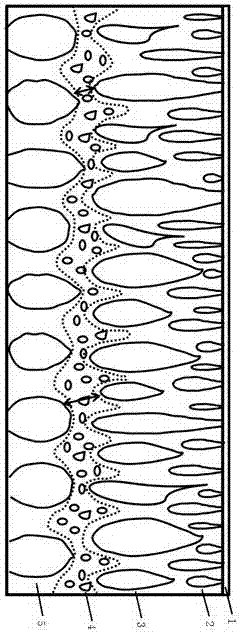
The invention discloses a diamond synthesis rod purification process. A diamond synthesis flake is subjected to ball-milling, elutriation, electrolysis in a basket, pouring out from the basket for elutriation, screening, gravity separation, oxidation to remove graphite, elutriation and drying. The process overcomes the defects of the prior art, the manufacturing process is simple, and due to adoption of the step of ball-milling, a part of the graphite and nearly all pyrophyllite can be abraded, so that both the electrolysis speed is accelerated and a step of removing the pyrophyllite later is canceled; through electrolysis physical screening, coarse particles are fed back to electrolysis, and the situation that catalyzed alloy which is not thoroughly electrolyzed is removed through acid is avoided, so that the economic efficiency is greatly improved, and pollution to the environment is reduced.
Owner:ANQING KAILI DIAMOND TECH
Adsorption pad for TFT thinning and polishing
ActiveCN106903596AIncrease the compression ratioExcellent compression recoverySynthetic resin layered productsLapping toolsThinningDrop-shaped
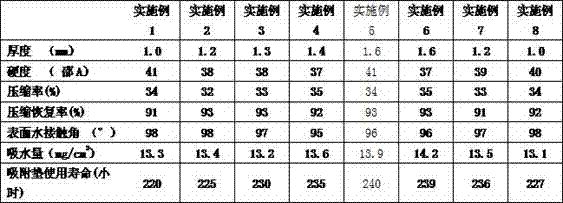
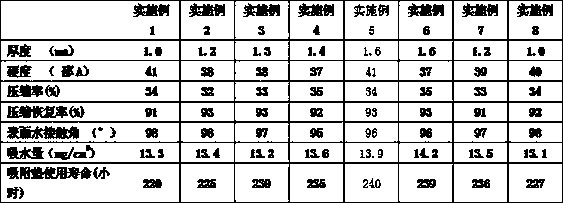
The invention relates to an adsorption pad for TFT thinning and polishing. The adsorption pad is sequentially equipped with release paper, a double faced adhesive tape, a PET film, a double faced adhesive tape, a fluorinated polyurethane porous film and a protective film from bottom to top, wherein the fluorinated polyurethane porous film is sequentially equipped with a surface adsorption layer, a first foaming layer, a second foaming layer, a third isolating layer and a fourth foaming layer from top to bottom; the surface adsorption layer is a compact layer; both the first foaming layer and the second foaming layer are of water drop shaped porous structures; and water drop shaped holes of the second foaming layer are greater than those of the first foaming layer. The adsorption pad for TFT thinning and polishing provided by the invention has relatively high hydrophobicity, so that permeation of a polishing solution can be reduced, heat generated by friction of a polishing disc can be dissipated very well, and the service life of the grinding adsorption pad is 220-240 hours which is prolonged by 25-35 hours in comparison with the service life of an existing adsorption pad for TFT thinning and polishing prepared from polyurethane resin composition.
Owner:ANHUI HECHEN NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Method and device for water-catalytic hydrogen-generation power generation
ActiveCN103456975AFast electrolysisEasy to prepareElectrolysis componentsFuel cellsFuel cellsElectrolysis
The invention discloses a method for water-catalytic hydrogen-generation power generation. The method comprises the following steps of 1, heating water to obtain water vapor, 2, passing the water vapor obtained by the step 1 through negative ion powder used for electrolyzing the water vapor into hydrogen, wherein the negative ion powder is added with a metal catalyst, and 3, feeding the hydrogen produced by the step 2 to a fuel cell or a hydrogen combustion generator, and carrying out power generation. According to the method, the negative ion powder is added with the metal catalyst so that the passing water or the water vapor is electrolyzed into negative ions and hydrogen by the negative ion powder, and the hydrogen is used for power generation of the fuel cell or the hydrogen combustion generator. The method simplifies a hydrogen production process and effectively reduces a hydrogen preparation cost. The invention also discloses a device for water-catalytic hydrogen-generation power generation. The device can prepare a large amount of hydrogen for power generation of a fuel cell and is conducive to fuel cell or hydrogen combustion generator wide application.
Owner:海慧特能源科技(广州)有限公司
Method for extracting tungsten carbide and cobalt from waste hard alloy
ActiveCN108910966AHeating evenlySolve the pollution problemNickel halidesTungsten/molybdenum carbideSpecific gravityStart up
The invention provides a method for extracting tungsten carbide and cobalt from waste hard alloy, and belongs to the technical field. The method comprises the following steps: S1, crushing a hard waste alloy into particles, then loading into an electrolytic small box, placing in an electrolysis tank, electrolyzing, adding hydrochloric acid as an electrolyte solution, starting up a heater, and electrolyzing the electrolyte solution cyclically continuously under the action of an acid-resistant pump; S2, when the specific gravity of cobalt chloride in the electrolyte solution reaches 1.15-1.24 kg / dm<3>, pumping the electrolyte solution containing cobalt chloride into a storage tank, soaking the alloy particles with clear water, and then drying the alloy particles; and S3, carrying out magnetic separation of the dried alloy particles, smashing a cobalt-containing magnetic absorption material into particles with the diameter of 1-6 mm by an air heavy hammer, then loading into the electrolysis tank, electrolyzing again, and separating to obtain tungsten carbide and a cobalt chloride solution. By improvement of the electrolysis tank and the electrolytic process, the cobalt content in thefinished tungsten carbide product after electrolysis is completed is about 0.07%.
Owner:湖南金雕能源科技有限公司
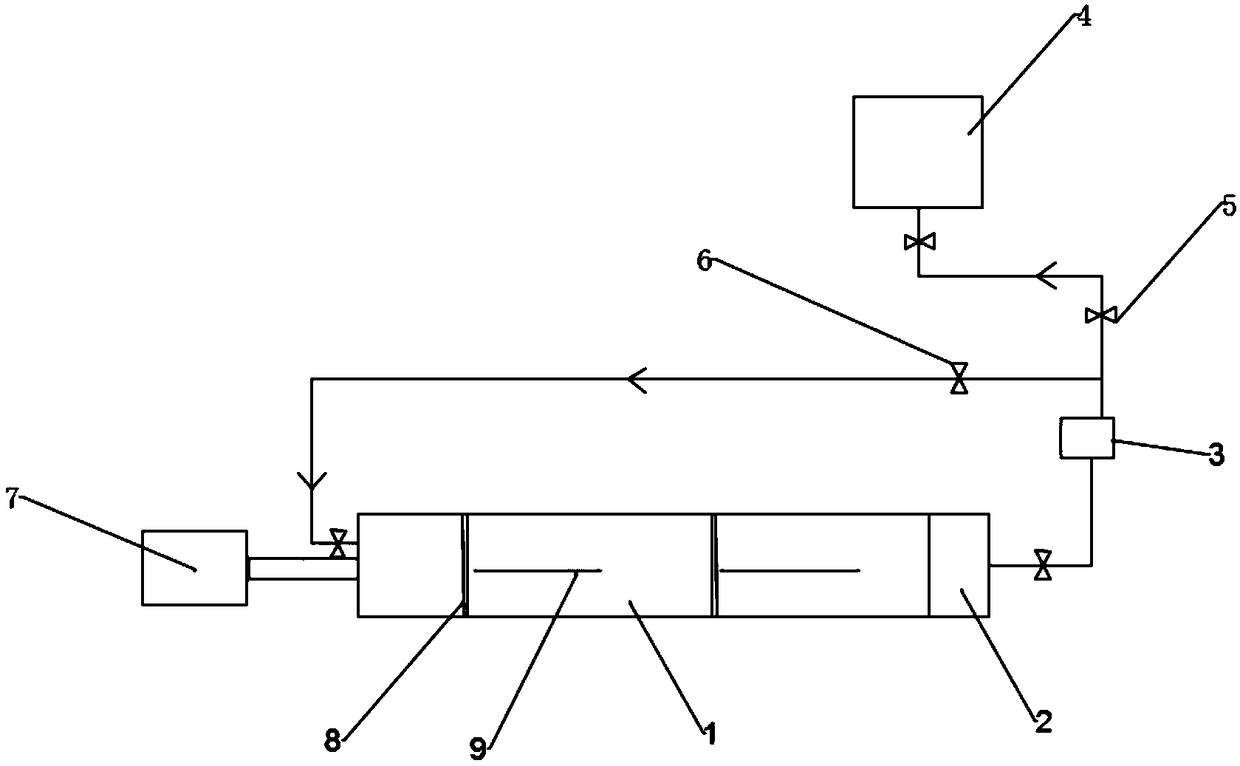
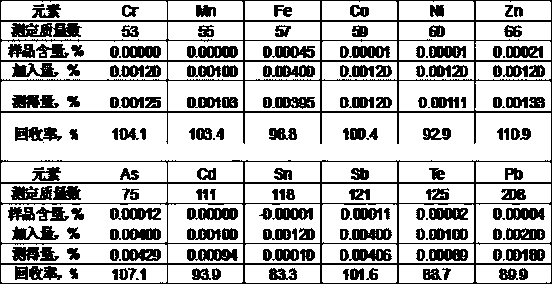
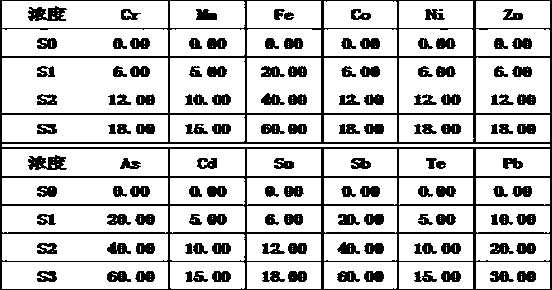
Method for quickly separating copper matrix for ICP-MS analysis of impurity elements in metal copper
InactiveCN110553887AEliminate distractionsMeet the test requirementsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrolysisManganese
The invention relates to a method for quickly separating a copper matrix for ICP-MS analysis of impurity elements in metal copper, which comprises the following steps: digesting a metal copper sampleby using a mixed acid solution of nitric acid and sulfuric acid (a small amount) in a certain ratio, and removing the copper matrix by using a high-current quick electrolysis method to obtain a solution to be detected; and then adopting inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) to realize rapid and simultaneous determination of twelve impurity elements of arsenic, antimony, tellurium,tin, lead, zinc, iron, nickel, cobalt, chromium, cadmium and manganese in the to-be-detected solution under certain instrument working conditions. Compared with the national standard GB / T 5121.28-2010, the method has the advantages that the separation effect is good, the matrix interference is eliminated, the twelve impurity elements of arsenic, antimony, tellurium, tin, lead, zinc, iron, nickel,cobalt, chromium, cadmium and manganese can be rapidly and simultaneously determined, the measurement time is short, and the requirement of rapid analysis of the twelve trace impurity elements in themetal copper is met.
Owner:北矿检测技术股份有限公司
Textile printing and dyeing wastewater advanced treatment method
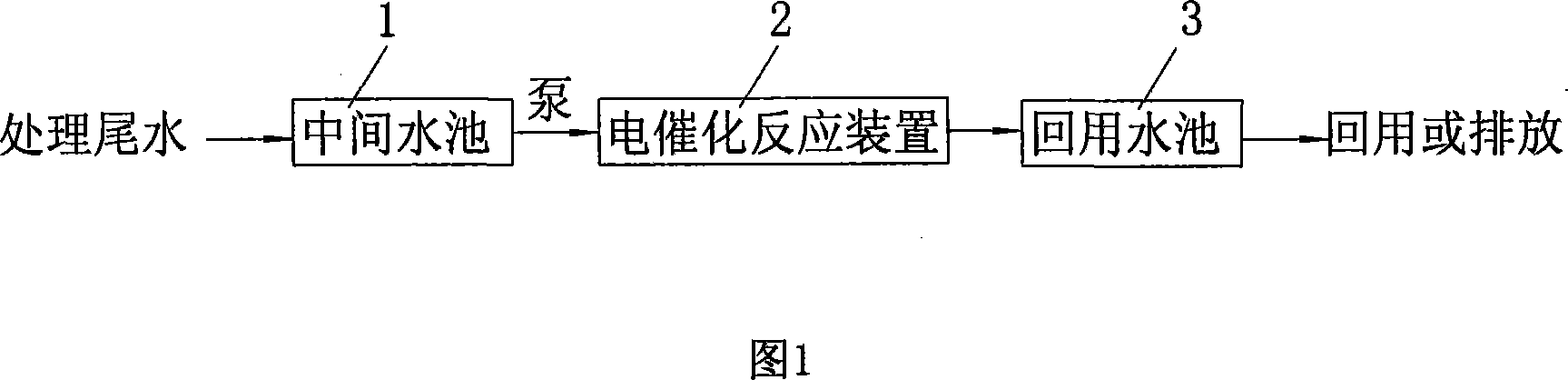
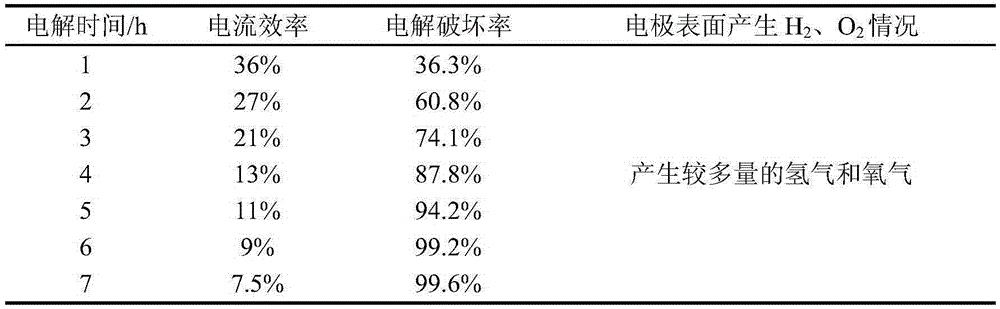
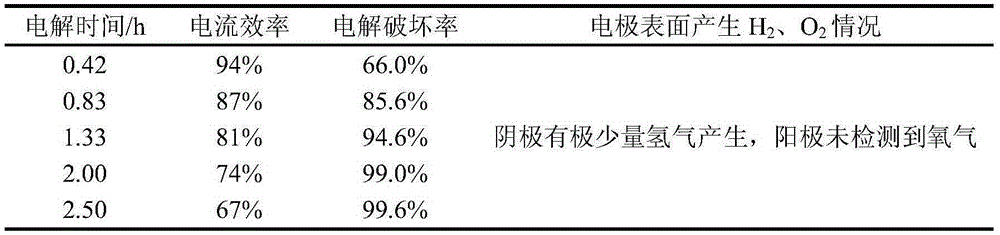
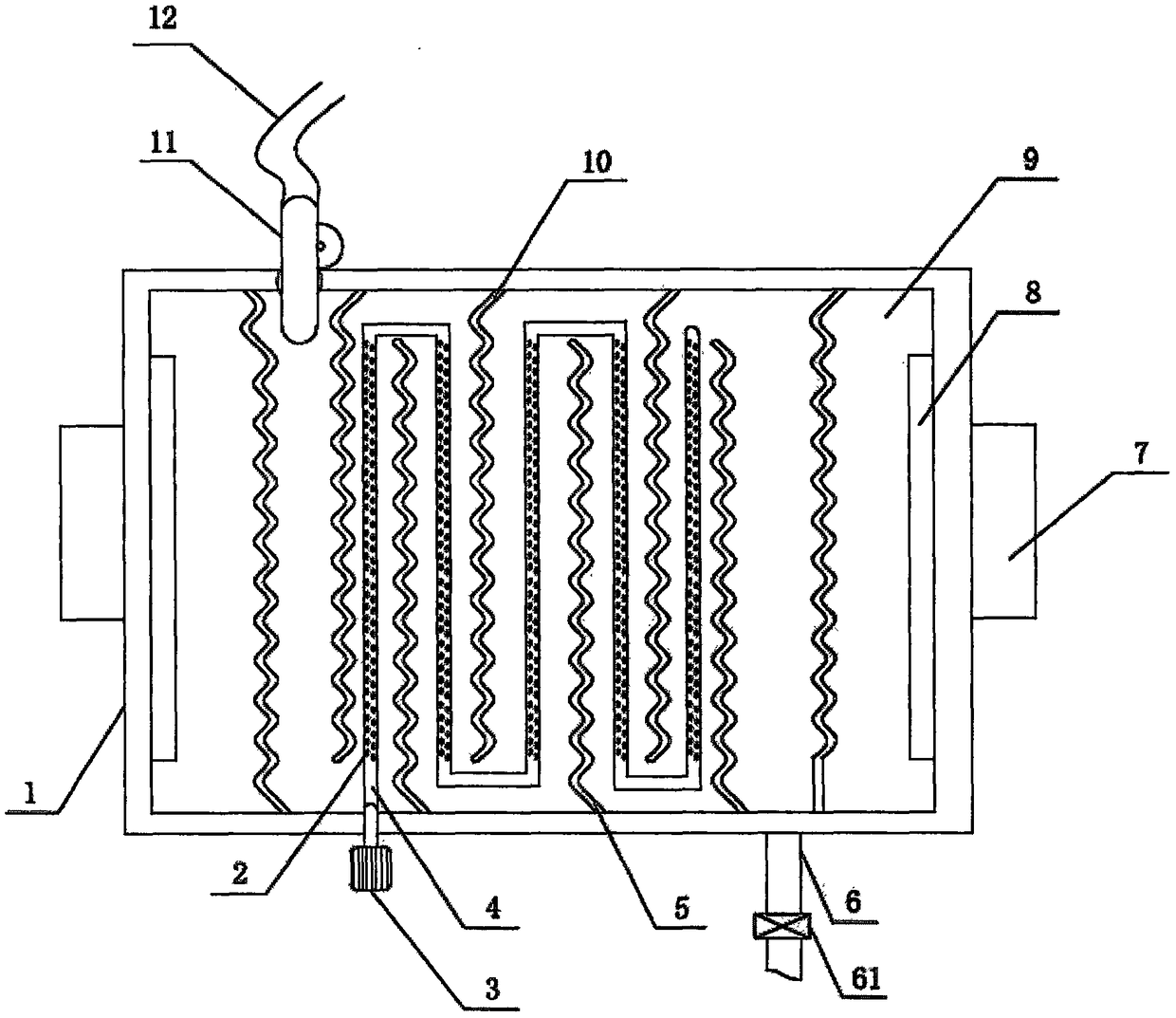
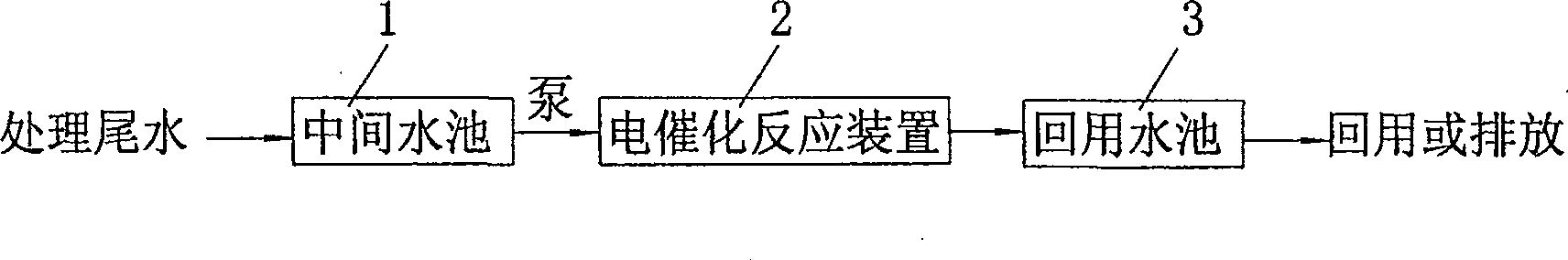
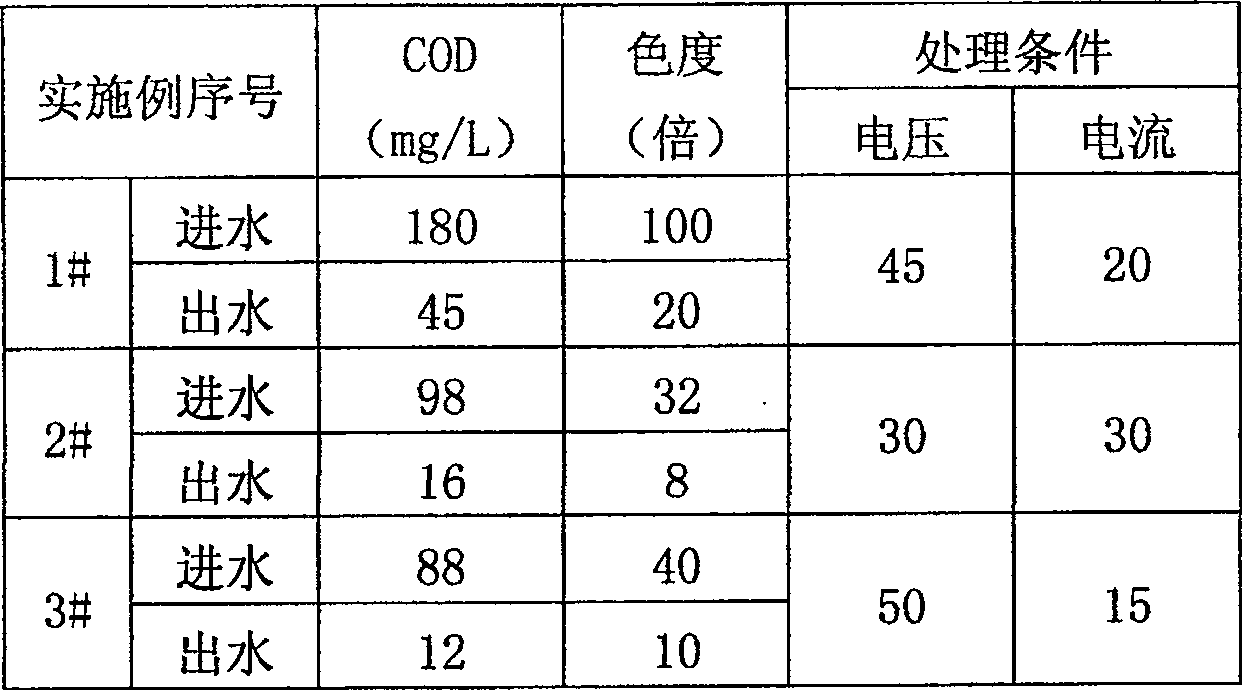
ActiveCN101139156ASolve replacementPromote oxidative degradationTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsTextile printerElectrolysis
The present invention discloses an advanced treatment method of printing and dyeing textile wastewater belonging to treatment method of printing and dyeing wastewater. The treatment method aims at the tail water of the low concentration printing and dyeing wastewater of the traditional after treated. The tail water is conducted into an electrocatalysis reaction device. The voltage to control the device is between 30 volt-amperes to 80 volt-amperes and the current to control the device is between 15 amperes to 50 amperes. The decomposing of persistent organic matters and removing of chroma are accomplished in the electrocatalysis reaction device. The water quality of the tail water after treated is better than primary standard of Discharge Standard of Water Pollutants for Dyeing and Finishing of Textile Industry (GB4287-92) and can reach drainage standard. The tail water after treated can also be applied as production technics water.
Owner:江苏环保产业股份有限公司
Method for destructing oxalic acid in plutonium oxalate sediment mother solution
InactiveCN105274363AImprove electrolysis efficiencyFast electrolysisProcess efficiency improvementFuel reprocessingElectrolysis
The invention belongs to the technical field of spent fuel postprocessing, and discloses a method for destructing oxalic acid in a plutonium oxalate sediment mother solution. The method comprises the following steps that a direct-current power source capable of achieving periodic reverse is utilized for electrolyzing the plutonium oxalate sediment mother solution under the constant-voltage condition, and platinum electrodes or titanium-plated platinum electrodes are adopted as a cathode and an anode, wherein the reverse period of the direct-current power source is the time spent when the anode is passivated, and the constant voltage is an electrolytic oxidation decomposition peak potential value of the oxalic acid in the plutonium oxalate sediment mother solution. The method has the beneficial effects of being capable of effectively avoiding anode passivation and anode oxidation, and being high in electrolytic efficiency and high in electrolysis speed.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Electrochemical treatment method for organic waste water
ActiveCN109467229AFast electrolysisProcessing speedWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater contaminantsElectrolysisDrive motor
The invention discloses an electrochemical treatment method for organic waste water. The electrochemical treatment method for the organic waste water comprises the following steps: S1, checking equipment; S2, adding pure water: injecting the pure water to pure water areas at the two ends of the interior of an insulated water tank; S3, injecting sewage: guiding the sewage into the insulated water tank via a water inlet pipe; S4, electrifying: switching on a power supply to enable a wavy anode plate and a wavy cathode plate to be correspondingly electrified; S5, putting chemicals: putting an environmentally friendly ultrasonic cleaning fluid and a scale inhibitor from a water inlet pipe; S4, starting a driving motor and adjusting forward and backward rotation angles and frequencies of the driving motor; S5, opening a water drain valve to electrolyze the organic waste water in circulation to achieve a purpose of treating the organic waste water. The electrochemical treatment method for the organic waste water, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages that the electrolysis speed of the sewage is increased to increase the sewage treatment speed by using an aeration pipe and an ultrasonic generator to vibrate the sewage; and in the sewage flowing process, the contact areas between the sewage and the electrode plates are increased, and the sewage electrolysis speed is increased.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING
Electrolytic refining system and method for crude copper with high precious metal content
ActiveCN106868543AFast electrolysisIncrease production capacityPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementCopperElectrolytic cell
The invention discloses an electrolytic refining system and method for crude copper with the high precious metal content. The system comprises an electrolytic cell used for containing an industrial electrolyte, an electrolyte low tank, at least one anode and at least one cathode. The anodes are formed by to-be-refined crude copper materials and are positioned to be used for making contact with the industrial electrolyte in the electrolytic cell, the peripheries of the anodes are sleeved with anode bags, and the anodes are wrapped inside the anode bags. The cathodes are positioned to be used for making contact with the industrial electrolyte in the electrolytic cell. The anodes are opposite to the cathodes, and the opening direction of a liquid inlet and the opening direction of an overflow opening are parallel to the fixing direction of the cathodes and the anodes. According to the system, a high tank of a common copper electrolytic technology is removed, the circulation speed of the electrolyte in the cell is increased, the production and operation period of precious metal recycling is shortened by the adoption of the system, and the losses of precious metal in the high-speed copper electrolytic production process are reduced.
Owner:包小玲
Fluid type nanobubble hydrogen-rich water generating device
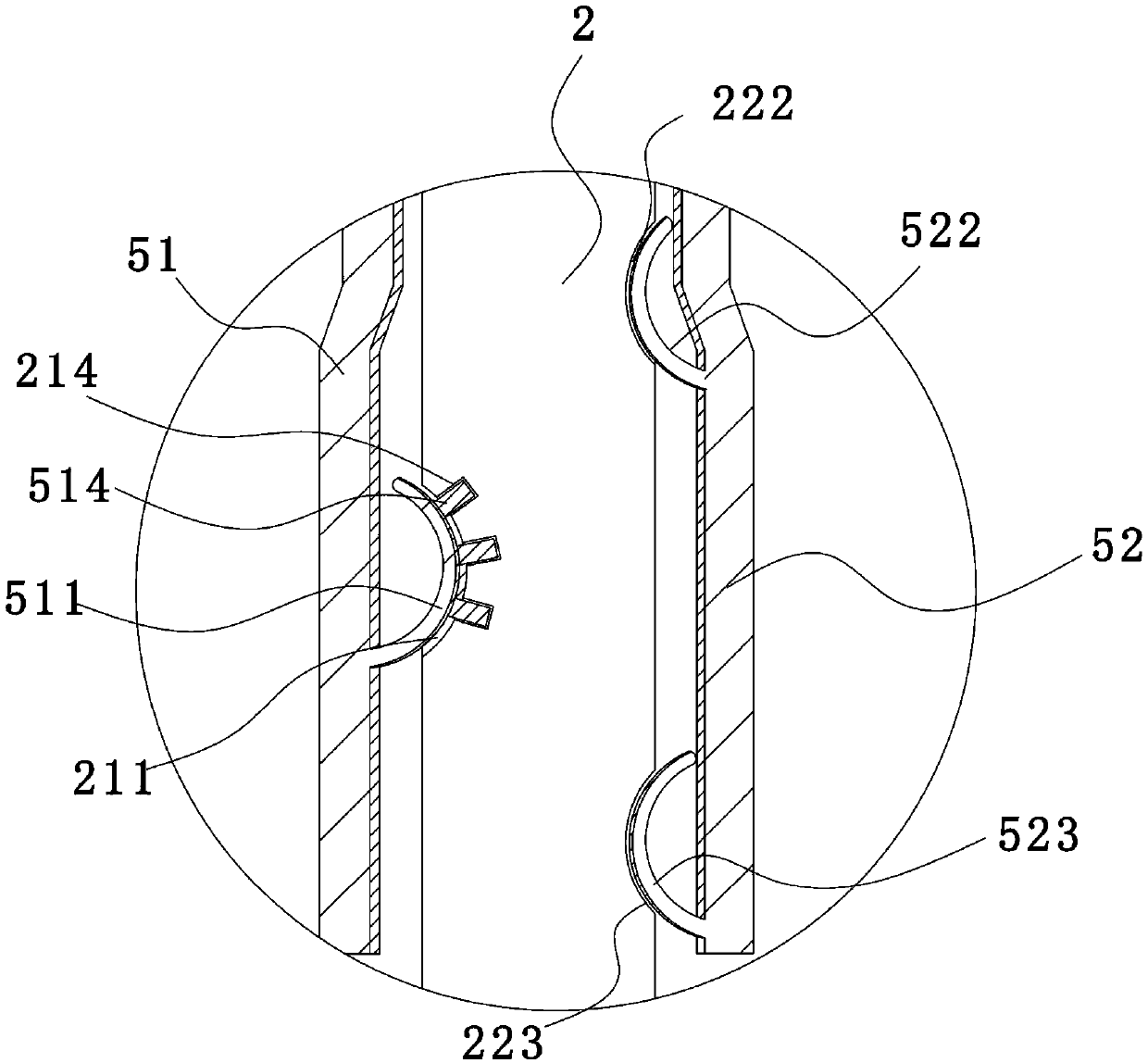
The invention relates to a fluid type nanobubble hydrogen-rich water generating device. An electrolytic cell is arranged inside a device body; an anode component is nested into a cathode component, sothat an annular fluid type electrolytic water reaction channel is formed between the inner wall surface of the cathode component and the outer wall surface of the anode component; water flowing intoa water inlet of the device passes through an incoming water diversion port, uniformly flows into the annular fluid type electrolytic water reaction channel, is electrolyzed, then passes through an outgoing water diversion port and flows out of a water outlet of the device body. According to the fluid type nanobubble hydrogen-rich water generating device disclosed by the invention, fluid type electrolytic water rich in nano-scale bubbles can be generated and is directly utilized by a human body; the diameter of the bubbles can be between 10nm and 100mu m; the electrolytic rate is high and fluid water is instantly electrolyzed, so that continuous electrolytic work is ensured, and the fluid water can be conveniently used by a user; electrodes are convenient to assemble, fix and mount and short circuit of two electrodes can be effectively prevented.
Owner:李向华
Process for extracting metal cobalt from waste hard alloy
InactiveCN1749420AImplement extractionIncrease contact areaProcess efficiency improvementAlloyCemented carbide
The present invention relates to hard alloy recovering and utilizing technology, and is especially the technological process of extracting metal cobalt from waste hard alloy. The technological process includes the following steps: crushing hard alloy with low cobalt content, grinding in ball mill into fine particle of 1-5 microns, dissolving cobalt inside electrolyte, extracting, heating to evaporate, stoving, etc. The technological process can extract cobalt completely from waste hard alloy with cobalt content lower than 9 %.
Owner:段立成
Electrolytic reaction device for preparing graphene
The invention discloses an electrolytic reaction device for preparing grapheme. The electrolytic reaction device for preparing the grapheme comprises an electrolytic cell, graphite plates, discharging mechanisms and graphite paper supporting mechanisms. Each discharging mechanism comprises a pressing roller and a graphite conducting roller connected with a power supply positive pole through a carbon brush. The pressing rollers and the graphite conducting rollers are symmetrically arranged above the electrolytic cell, each graphite paper supporting mechanism is fixed above the corresponding discharging mechanism, and the graphite plates serve as a negative pole and are arranged in the electrolytic cell. According to the purpose of the electrolytic reaction device for preparing the grapheme, the problem that an existing electrolytic device cannot be automated during large-scale preparation of the grapheme is solved.
Owner:DEYANG CARBONENE TECH
Big-belly tank type water electrolysis device and preparation method thereof
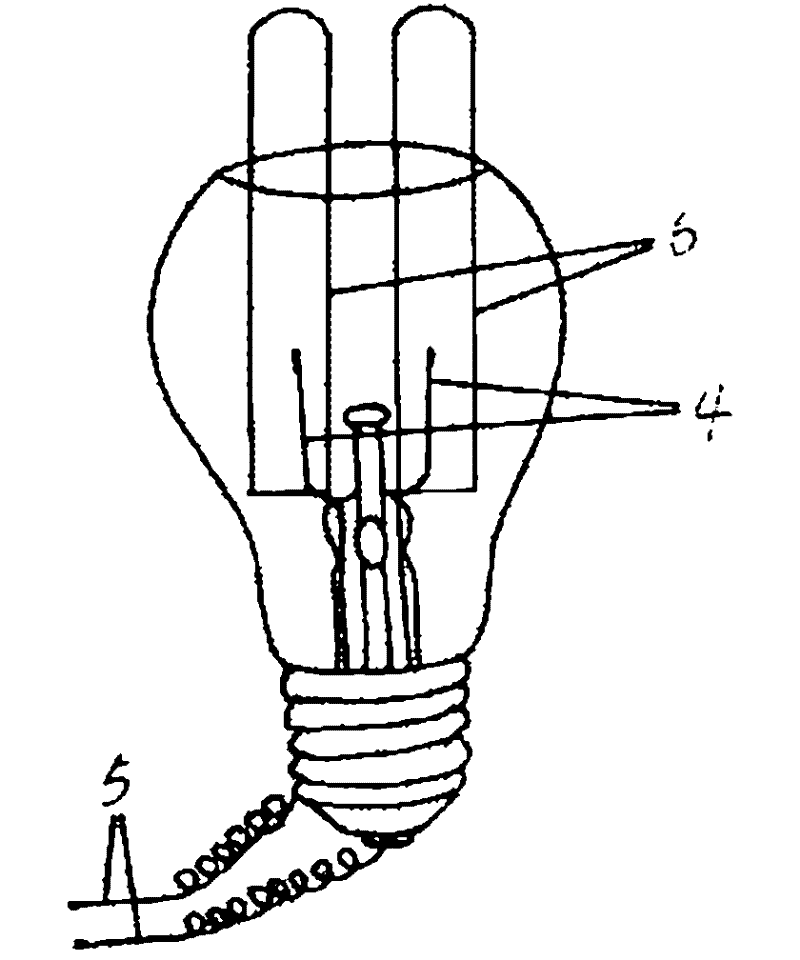
The invention provides a big-belly tank type water electrolysis device and a preparation method thereof. The device comprises a big-belly bulb shaped glass container, wherein, an opening is formed at the upper part of the glass container and two electrodes are arranged at the lower part of the glass container; the two electrodes are connected with an electrolysis power source after extending out of the bottom of the glass container; the bottom of the glass container is sealed with the electrodes; and two gas collecting test tubes respectively buckled on the two electrodes are further arranged in the glass container. The main part of the water electrolysis device provided by the invention, a big-belly tank, is manufactured by completely utilizing a waste bulb which has extensive sources easy to obtain; and the waste is changed into valuables, so that the water electrolysis device is of great benefit to full utilization of the resources, environment protection and experiment cost reduction.
Owner:SHANGLUO UNIV
A quick automatic water electrolyzer
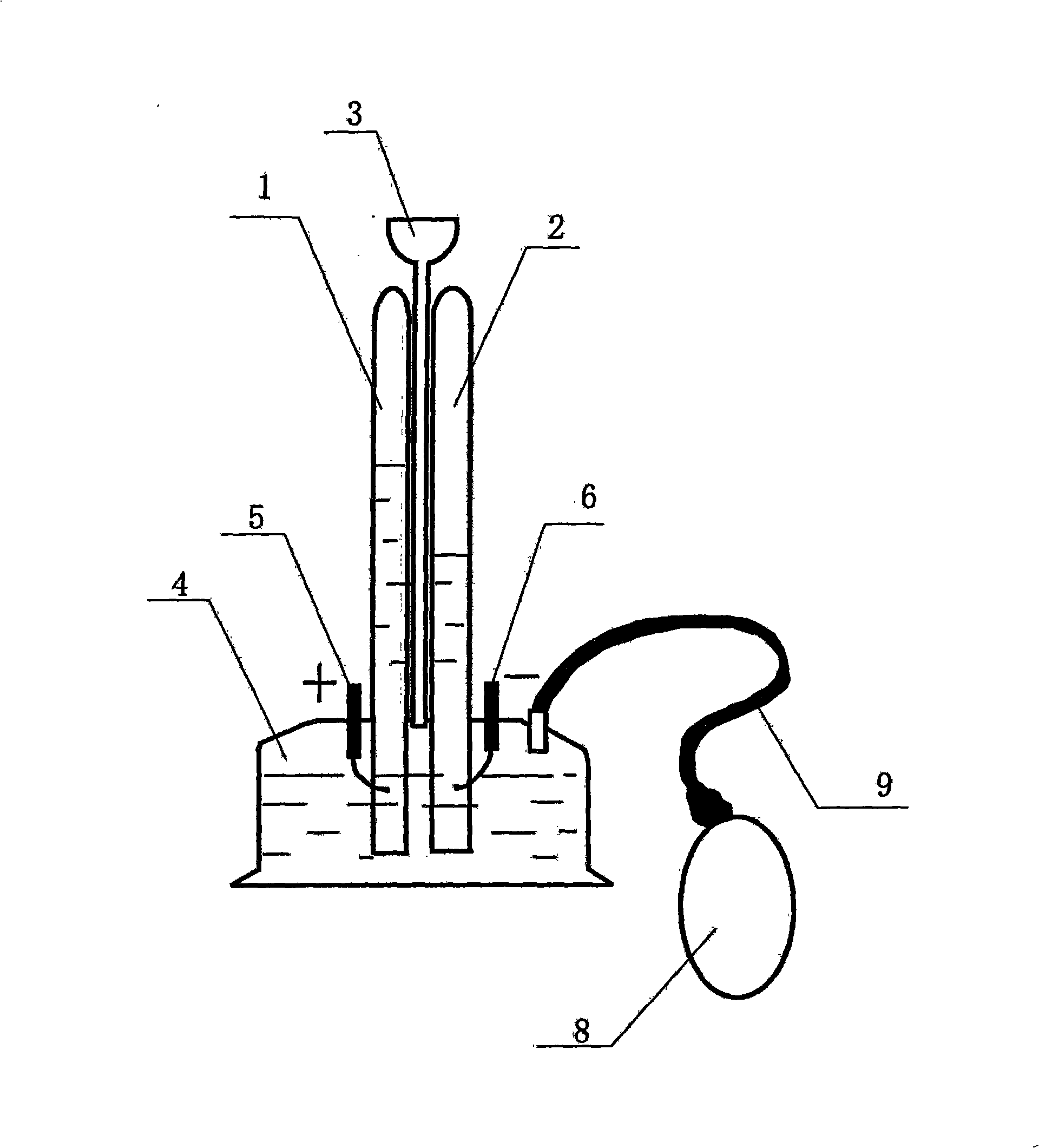
The invention discloses a swift auto water electrolyzer which comprises two burettes (1, 2), a long neck funnel (3), a cylinder body (4), a positive electrode slice (5) and a negative electrode slice (6), wherein the two burettes (1, 2) are inserted into the cylinder body (4) and hermetically connected with the cylinder body (4), the long neck funnel (3) is also inserted into the cylinder body (4) and positioned between the two burettes (1, 2), the positive electrode slice (5) is inserted into one burette (1) after passing through the cylinder body (4), the negative electrode slice (6) is inserted into the other burette (2) after passing through the cylinder body (4), and the positive electrode slice (5) and the negative electrode slice (6) are connected with the power supply. The swift auto water electrolyzer has simple structure and quick electrolysis.
Owner:吉彭才
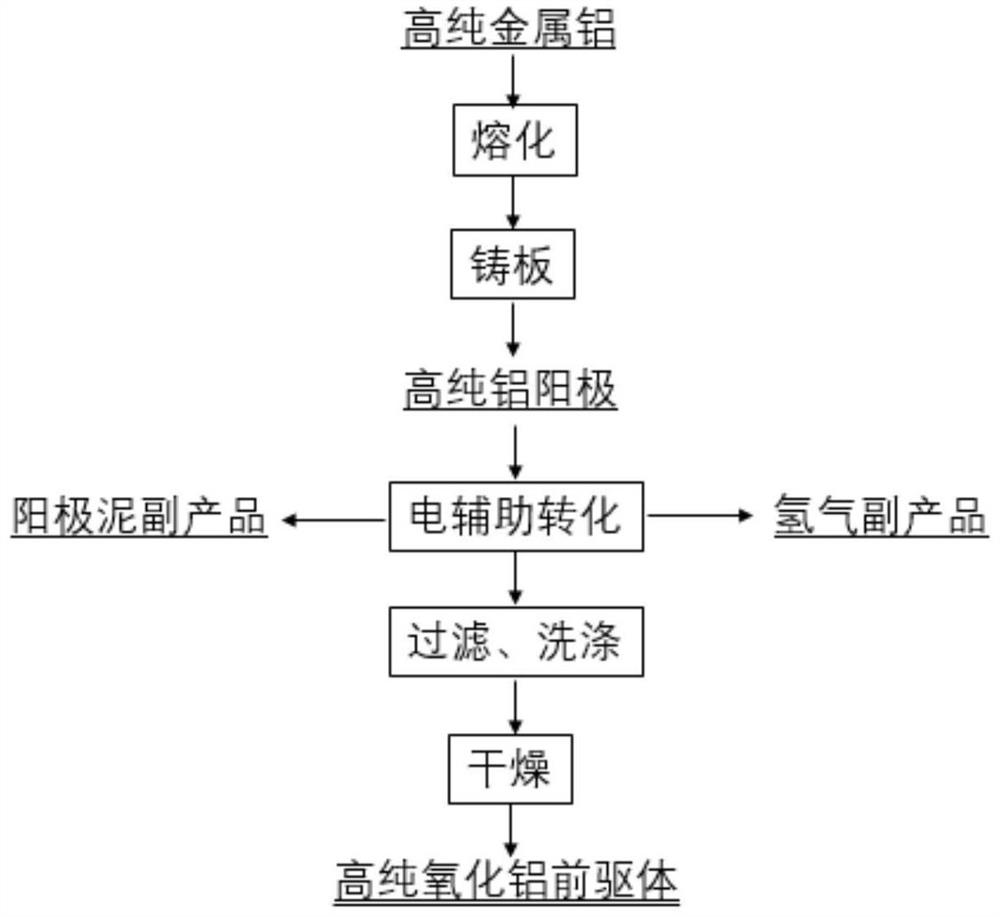
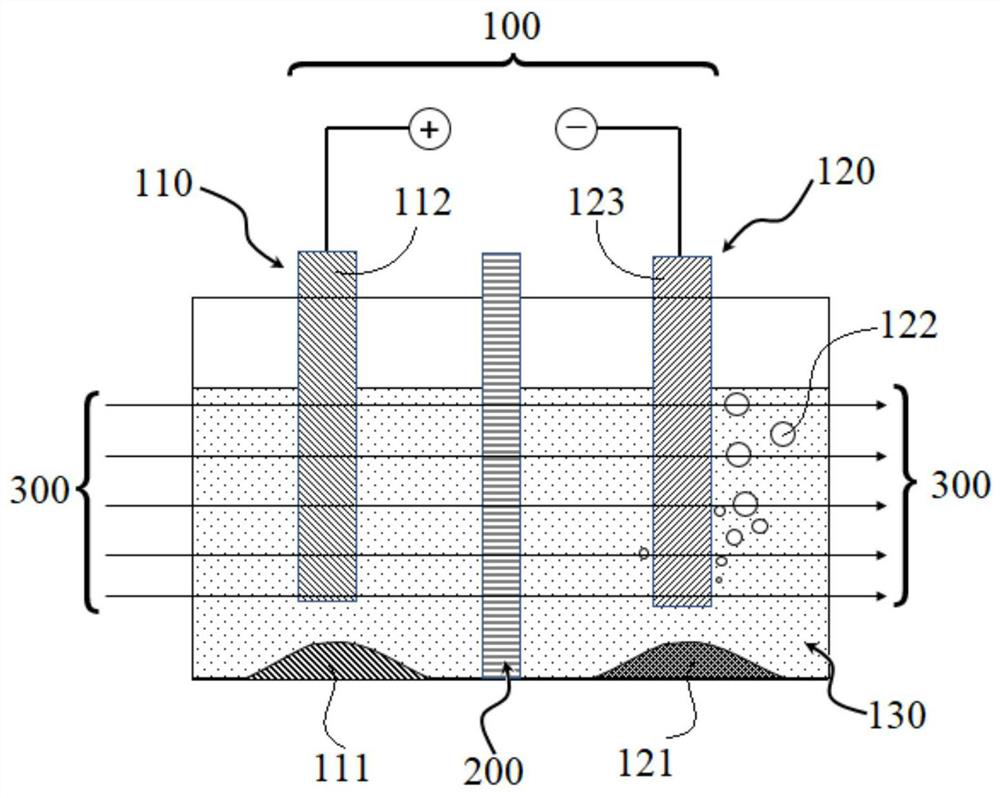
Method for preparing high-purity aluminum oxide precursor Al(OH)3
InactiveCN112877710AControl the dissolution rateGood size controlCellsElectrodesElectrolysisPorous membrane
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-purity aluminum oxide precursor Al(OH)3, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of high-purity aluminum oxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: selecting high-purity aluminum as an anode plate, conducting treatment under the action of electric auxiliary conversion and an external field, meanwhile filtering anode impurities by using a porous membrane, so as to obtain an Al(OH)3 product, and filtering, washing and drying the Al(OH)3 product in sequence to obtain a high-purity aluminum oxide precursor. The porous membrane can prevent anode impurities from polluting an electrolysis product Al(OH)3, an external field not only promotes Al<3+> to penetrate through the porous membrane and improves the electrolysis rate and efficiency, but also can control the opportunity that Al(OH)3 falls off from a cathode, prevent the Al(OH)3 from growing, ensure the uniformity of the size and realize the control on the particle size of generated Al(OH)3 particles, and the purity of the product Al(OH)3 is high. Anode mud generated in the production process can be used for preparing a primary aluminum by-product, and the cathode generates a hydrogen by-product, so that the economical efficiency of the technology can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Electroplating solution with good electroplating effect
The present invention discloses an electroplating solution with a good electroplating effect, wherein the raw material components comprise, by weight, 30-35 parts of nickel sulfate, 25-30 parts of cobalt carbonate, 20-25 parts of cobalt oxide, 25-30 parts of copper sulfate, 15-20 parts of ferrous ammonium sulfate, 13-15 parts of potassium phosphate, 13-15 parts of triethyl phosphite, 6-8 parts of hypophosphorous acid, 5-6 parts of sodium alginate, 8-10 parts of potassium sodium tartrate, 6-8 parts of sodium xylene sulfonate, 6-8 parts of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate, 5-8 parts of sodium lauryl sulfate, 10-12 parts of sodium propionate, 8-10 parts of glacial acetic acid, 6-8 parts of sulfosalicylic acid, 7-10 parts of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt, 5-6 parts of triethanolamine, 3-4 parts of sodium metaborate, 3-6 parts of disodium hydrogen phosphate, and 30-50 parts of deionized water. The electroplating solution of the present invention has characteristics of good electric conduction capability, rapid electrolysis, and good effect.
Owner:陈新棠
Electrolytic reaction device for preparing graphene
The invention discloses an electrolytic reaction device for preparing grapheme. The electrolytic reaction device for preparing the grapheme comprises an electrolytic cell, graphite plates, discharging mechanisms and graphite paper supporting mechanisms. Each discharging mechanism comprises a pressing roller and a graphite conducting roller connected with a power supply positive pole through a carbon brush. The pressing rollers and the graphite conducting rollers are symmetrically arranged above the electrolytic cell, each graphite paper supporting mechanism is fixed above the corresponding discharging mechanism, and the graphite plates serve as a negative pole and are arranged in the electrolytic cell. According to the purpose of the electrolytic reaction device for preparing the grapheme, the problem that an existing electrolytic device cannot be automated during large-scale preparation of the grapheme is solved.
Owner:DEYANG CARBONENE TECH
A method for extracting tungsten carbide and cobalt from waste cemented carbide
ActiveCN108910966BHeating evenlyImprove cycle performanceNickel halidesTungsten/molybdenum carbideElectrolytic agentAlloy
The invention provides a method for extracting tungsten carbide and cobalt from waste hard alloy, and belongs to the technical field. The method comprises the following steps: S1, crushing a hard waste alloy into particles, then loading into an electrolytic small box, placing in an electrolysis tank, electrolyzing, adding hydrochloric acid as an electrolyte solution, starting up a heater, and electrolyzing the electrolyte solution cyclically continuously under the action of an acid-resistant pump; S2, when the specific gravity of cobalt chloride in the electrolyte solution reaches 1.15-1.24 kg / dm<3>, pumping the electrolyte solution containing cobalt chloride into a storage tank, soaking the alloy particles with clear water, and then drying the alloy particles; and S3, carrying out magnetic separation of the dried alloy particles, smashing a cobalt-containing magnetic absorption material into particles with the diameter of 1-6 mm by an air heavy hammer, then loading into the electrolysis tank, electrolyzing again, and separating to obtain tungsten carbide and a cobalt chloride solution. By improvement of the electrolysis tank and the electrolytic process, the cobalt content in thefinished tungsten carbide product after electrolysis is completed is about 0.07%.
Owner:HUNAN GOLDEN EAGLE ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Electroplating solution
The invention relates to an electroplating solution which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 8-14 parts of cobaltous sulfate, 7-11 parts of phosphorous acid, 4-10 parts of sodium citrate, 2-6 parts of citric acid, 3-8 parts of lauryl sodium sulfate, 2-9 parts of sodium acetate, 5-10 parts of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 1-5 parts of sodium perborate, 3-6 parts of citric acid, 1-3 parts of chelator, 2-5 parts of corrosion inhibitor, 5-10 parts of stabilizer and 20 parts of deionized water. The electroplating solution has the advantages of favorable conducting power, high electrolysis speed and favorable effect.
Owner:QINGDAO CHANGANDA PHARMA IND CO LTD
Electrolytic cells for industrial wastewater treatment
ActiveCN108249525BFast electrolysisImprove electrolysis efficiencyWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationPulp and paper industryIndustrial wastewater treatment
The invention discloses an electrolytic tank for treating industrial wastewater. The electrolytic tank for treating the industrial wastewater comprises a tank body, a cathode part, an anode part and aconnecting part, wherein the cathode part and the anode part are arranged at an interval; the connecting part comprises a connecting body, a first connecting part and a second connecting part; the first connecting part is fixedly connected to the anode part; the second connecting part is detachably connected to the cathode part through a fixing part. According to the electrolytic tank for treating the industrial wastewater, the cathode part and the anode part are arranged at an interval, so that the water electrolyzing speed is increased, as a result, the electrolyzing efficiency is improved.
Owner:广东创晟控股集团有限公司
Water fuel generating device and water fuel vehicle using it
ActiveCN107985063BCombination structure is simple and feasibleSimple and fast operationPropulsion by batteries/cellsFuel supplyElectrolysed waterLiquid water
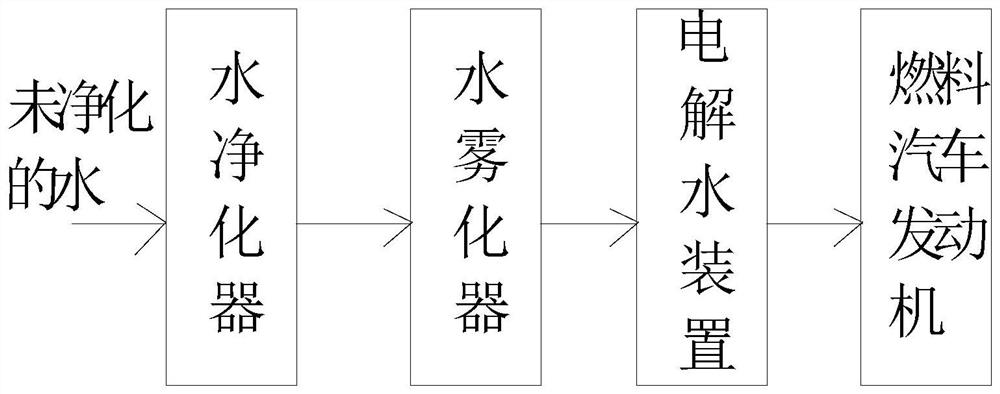
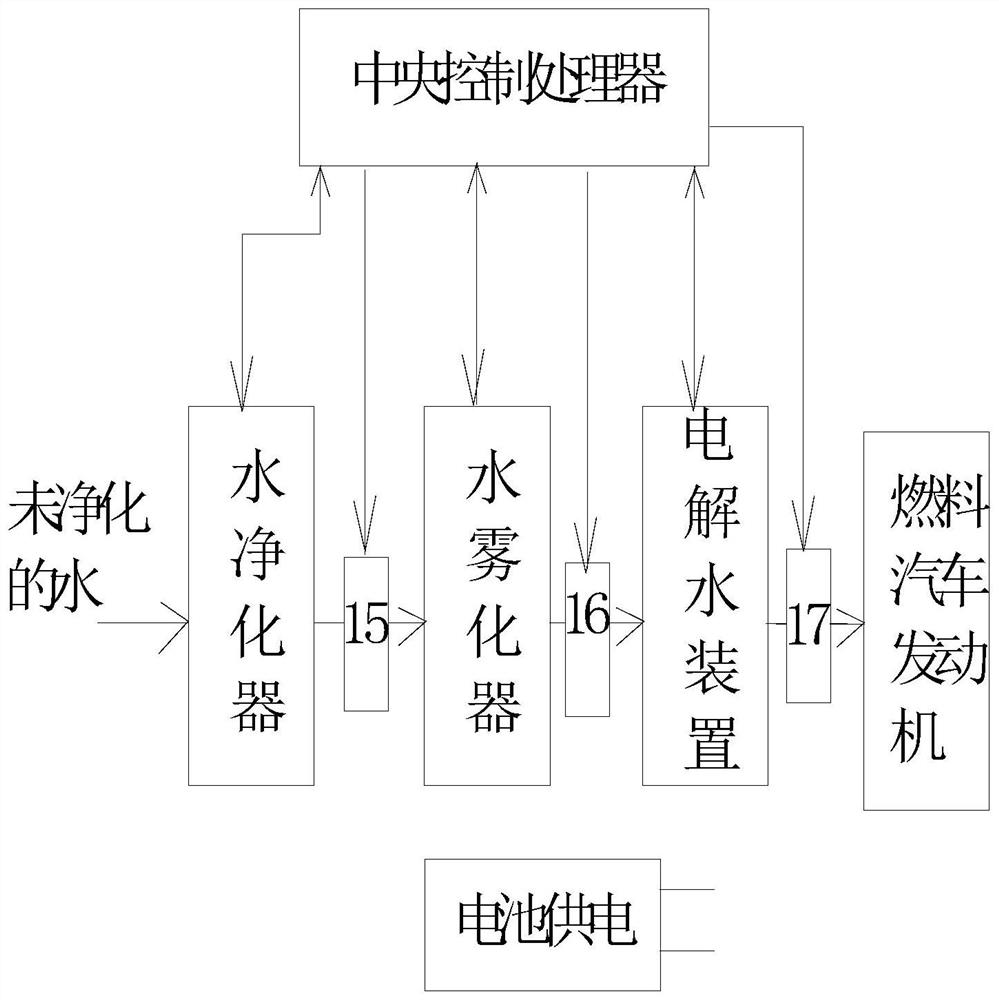
A water fuel generating device and a water fuel vehicle using the same, the water fuel generating device includes an electrolyzed water device, and is characterized in that it also includes a water atomization device, water first enters the water atomization device, and the liquid water passes through the water atomization device. The atomization device turns into water mist of gas, and then the water mist of gas enters the electrolytic water device for electrolytic reduction treatment to become hydrogen and oxygen output. It has a simple structure, is easy to implement, is convenient for large-scale production, and has low cost and small size, and can quickly and efficiently generate sufficient hydrogen and oxygen supply from liquid water.
Owner:易平得
The high nickel copper anode adopts the process of periodic reverse current electrolysis
ActiveCN113652716BEvenly dispersedHigh purityPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEElectrolytic agent
The invention provides a process for electrolysis of high nickel copper anode by periodic reverse current. Among them, the periodic reverse current can ensure the maximum use efficiency of electrolytic copper. By modifying the cathode copper sheet, the impurities and oxide film on the surface of the copper sheet are reduced. The treatment agent contains oxalic acid, which can be complexed by nickel ions. , reduce the concentration of nickel ions in the solution, improve the purity of the cathode copper after electrolysis, and purify the circulating electrolyte to reduce the waste of resources. The leveling agent can control the growth of grains, refine the grains, and make the surface of the cathode copper produced more flat. At the same time, it can effectively promote the reduction of copper ions and speed up the progress of electrolysis. The brightener can improve the brightness of the cathode copper electrode plate and effectively promote the shedding of anode slime, avoid the occurrence of anode polarization, speed up electrolysis, and improve production efficiency.
Owner:江西新金叶实业有限公司
Adsorption pad for tft thinning and polishing
ActiveCN106903596BImprove hydrophobicityExtended service lifeSynthetic resin layered productsLapping toolsThinningPermeation
The invention relates to an adsorption pad for TFT thinning and polishing. The adsorption pad is sequentially equipped with release paper, a double faced adhesive tape, a PET film, a double faced adhesive tape, a fluorinated polyurethane porous film and a protective film from bottom to top, wherein the fluorinated polyurethane porous film is sequentially equipped with a surface adsorption layer, a first foaming layer, a second foaming layer, a third isolating layer and a fourth foaming layer from top to bottom; the surface adsorption layer is a compact layer; both the first foaming layer and the second foaming layer are of water drop shaped porous structures; and water drop shaped holes of the second foaming layer are greater than those of the first foaming layer. The adsorption pad for TFT thinning and polishing provided by the invention has relatively high hydrophobicity, so that permeation of a polishing solution can be reduced, heat generated by friction of a polishing disc can be dissipated very well, and the service life of the grinding adsorption pad is 220-240 hours which is prolonged by 25-35 hours in comparison with the service life of an existing adsorption pad for TFT thinning and polishing prepared from polyurethane resin composition.
Owner:ANHUI HECHEN NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Process for electrolyzing high nickel-copper anode by adopting periodic reverse current
ActiveCN113652716AEvenly dispersedHigh purityPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEElectrolytic agent
The invention provides a process for electrolyzing a high nickel-copper anode by adopting periodic reverse current, wherein the periodic reverse current can guarantee the maximum use efficiency of electrolytic copper, a cathode copper sheet is modified, impurities and an oxidation film on the surface of the copper sheet are reduced, a treatment agent contains oxalic acid components, nickel ions can be complexed through oxalic acid, the concentration of the nickel ions in a solution is reduced, the purity of the electrolyzed cathode copper is improved, and a circulated electrolyte is circularly purified, so that the waste of resources is reduced. A leveling agent can control the growth of crystal grains, so that the crystal grains are refined, and the surface of the produced cathode copper is smoother. Meanwhile, the reduction effect of copper ions can be effectively promoted, and the electrolysis progress is accelerated. A brightening agent can improve the brightness of a cathode copper electrode plate and effectively promote anode mud to fall off, the anode polarization phenomenon is avoided, the electrolysis speed is increased, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:江西新金叶实业有限公司
Textile printing and dyeing wastewater advanced treatment method
ActiveCN100537463CIncrease surface areaReduce migration distanceTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsTextile printerElectrolysis
The present invention discloses an advanced treatment method of printing and dyeing textile wastewater belonging to treatment method of printing and dyeing wastewater. The treatment method aims at the tail water of the low concentration printing and dyeing wastewater of the traditional after treated. The tail water is conducted into an electrocatalysis reaction device. The voltage to control the device is between 30 volt-amperes to 80 volt-amperes and the current to control the device is between 15 amperes to 50 amperes. The decomposing of persistent organic matters and removing of chroma are accomplished in the electrocatalysis reaction device. The water quality of the tail water after treated is better than primary standard of Discharge Standard of Water Pollutants for Dyeing and Finishing of Textile Industry (GB4287-92) and can reach drainage standard. The tail water after treated can also be applied as production technics water.
Owner:江苏环保产业股份有限公司
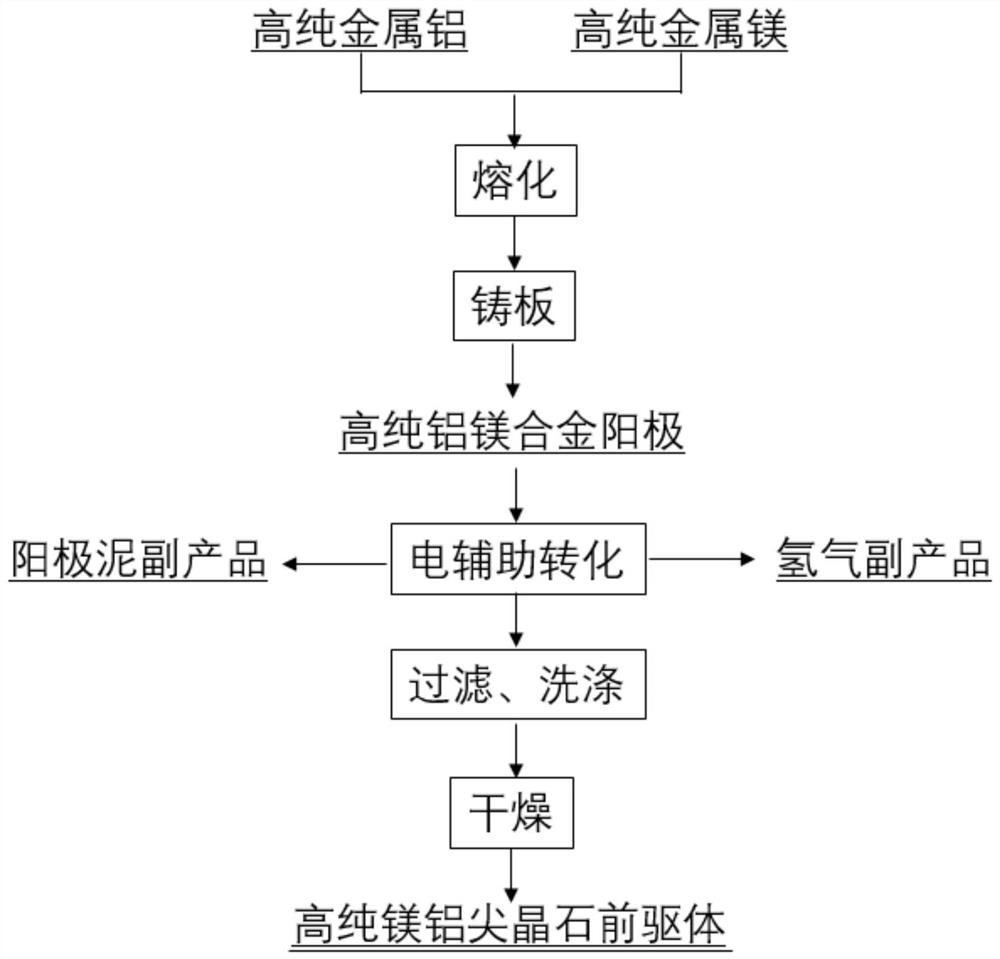
Method for preparing high-purity magnesium aluminate spinel precursor
InactiveCN112877718AAvoid pollutionImprove purityCellsNon-noble metal oxide coatingsMagnesium AluminatePorous membrane
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-purity magnesium aluminate spinel precursor, and belongs to the technical field of high-purity magnesium aluminate spinel preparation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: selecting a high-purity aluminum-magnesium alloy as an anode plate, carrying out electric auxiliary conversion and external field action, filtering anode impurities by using a porous membrane to obtain a magnesium-aluminum hydroxide precipitate, and sequentially conducting filtering, washing and drying on the magnesium-aluminum hydroxide precipitate to obtain a high-purity magnesium-aluminum spinel precursor. The porous membrane can prevent anode impurities from polluting an electrolytic product magnesium-aluminum hydroxide, an external field not only promotes Al<3+> and Mg<2+> to penetrate through the porous membrane and improves the electrolysis rate and efficiency, but also can control the opportunity that the magnesium-aluminum hydroxide falls off from a cathode, prevent the magnesium-aluminum hydroxide from growing and ensure the size uniformity, and control over the particle size of generated magnesium-aluminum spinel precursor powder is achieved. Anode mud generated in the production process can be used for preparing an aluminum-magnesium alloy byproduct, a hydrogen byproduct is generated by a cathode, and the economical efficiency of the technology can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com