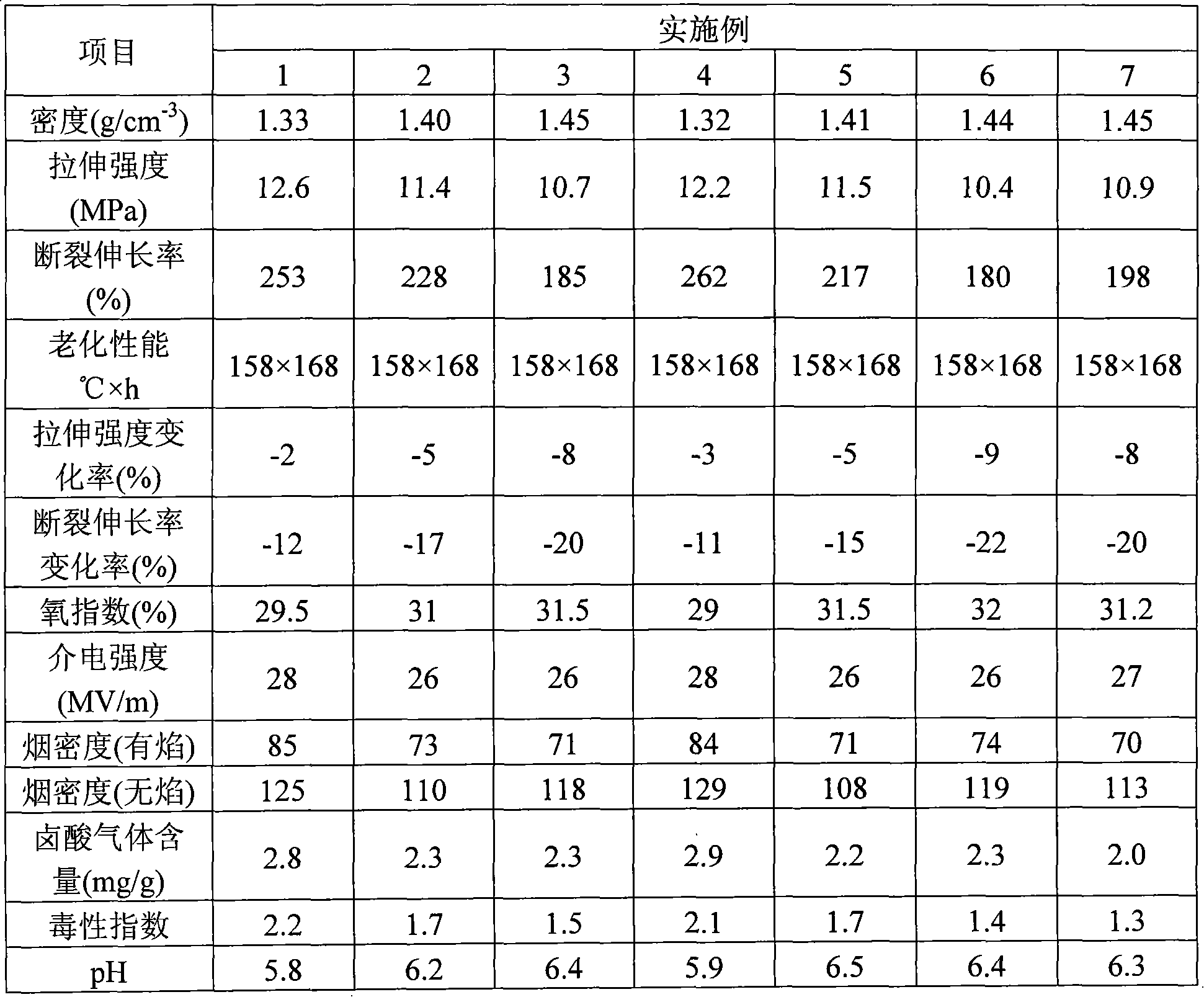
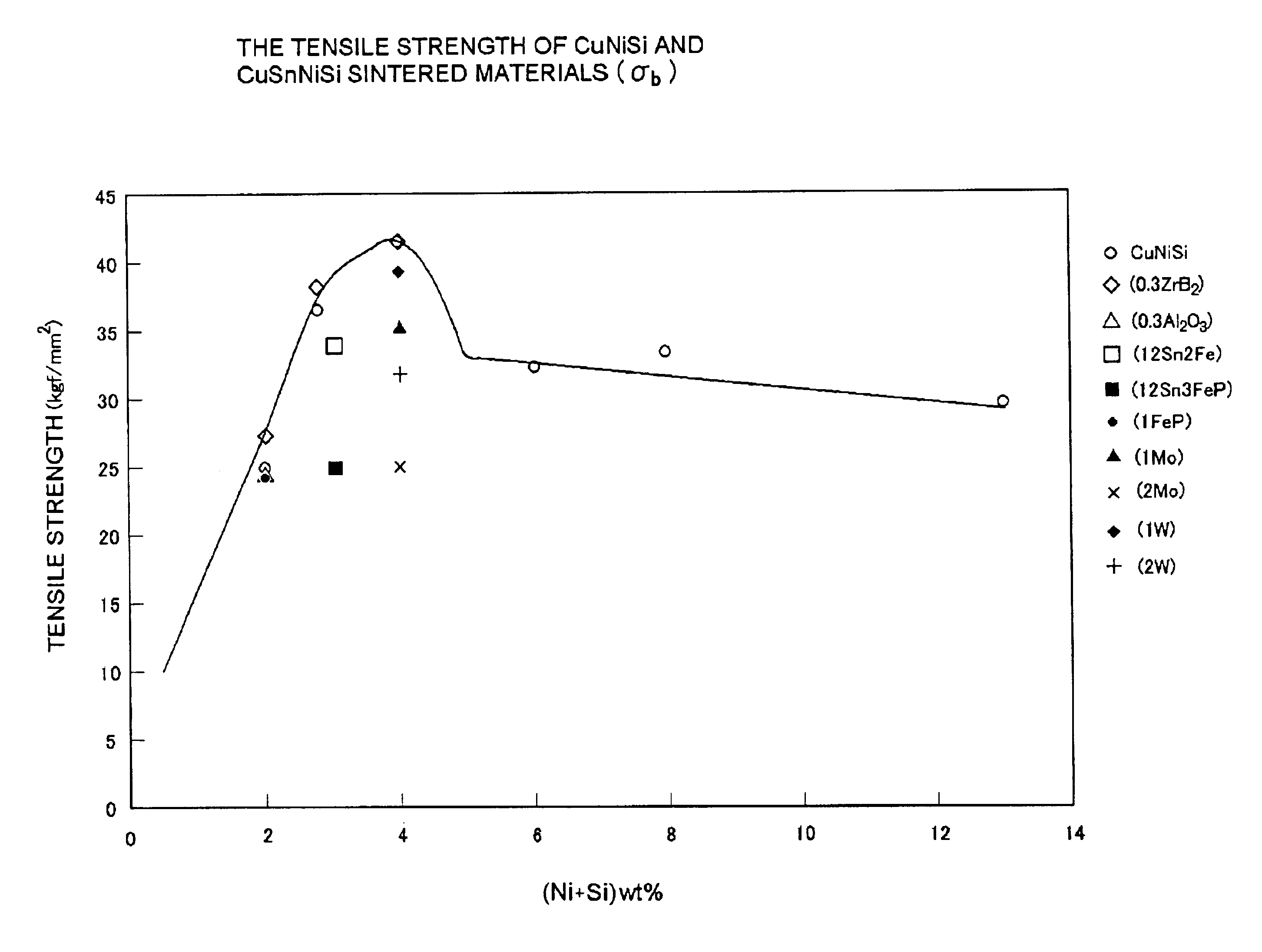
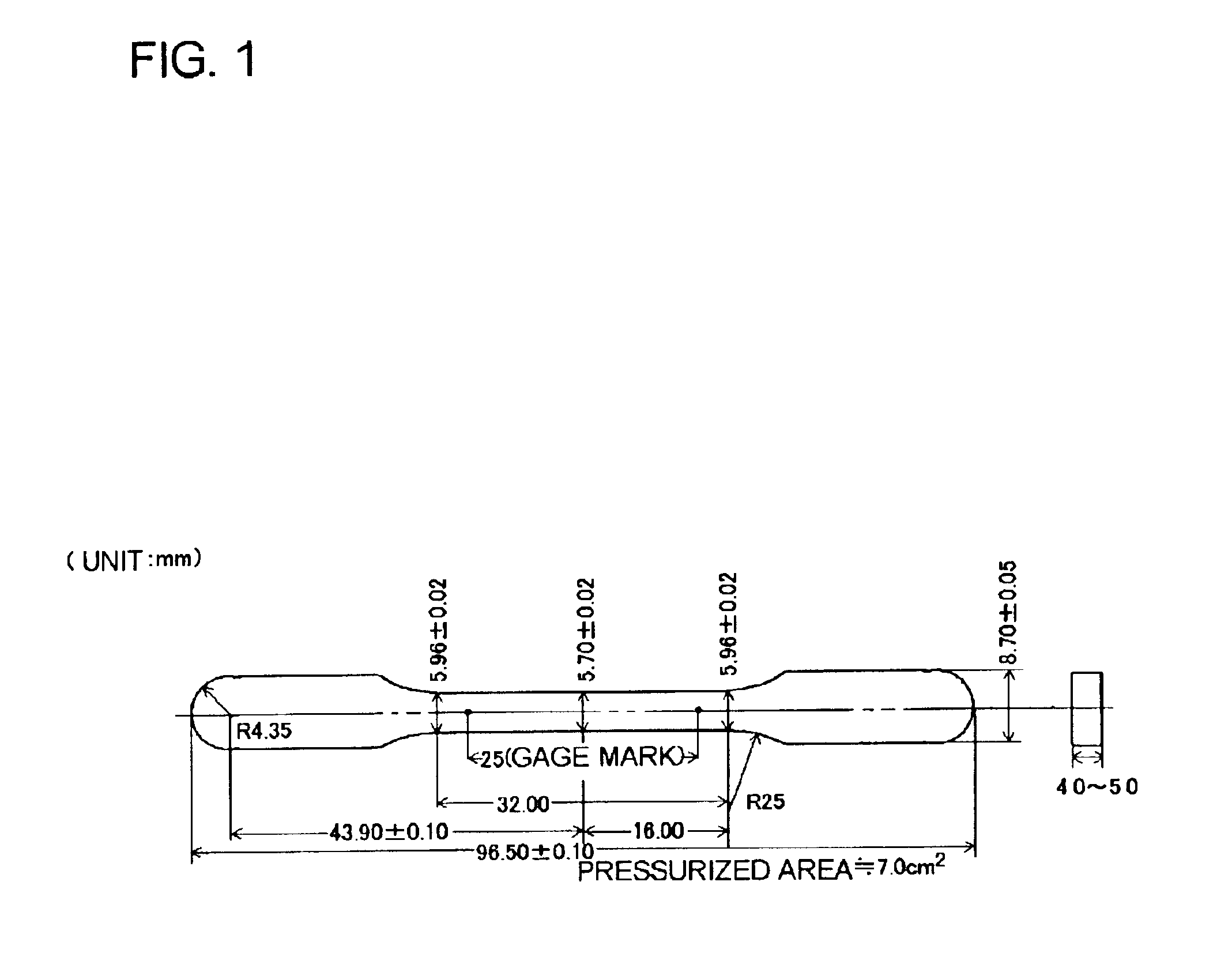
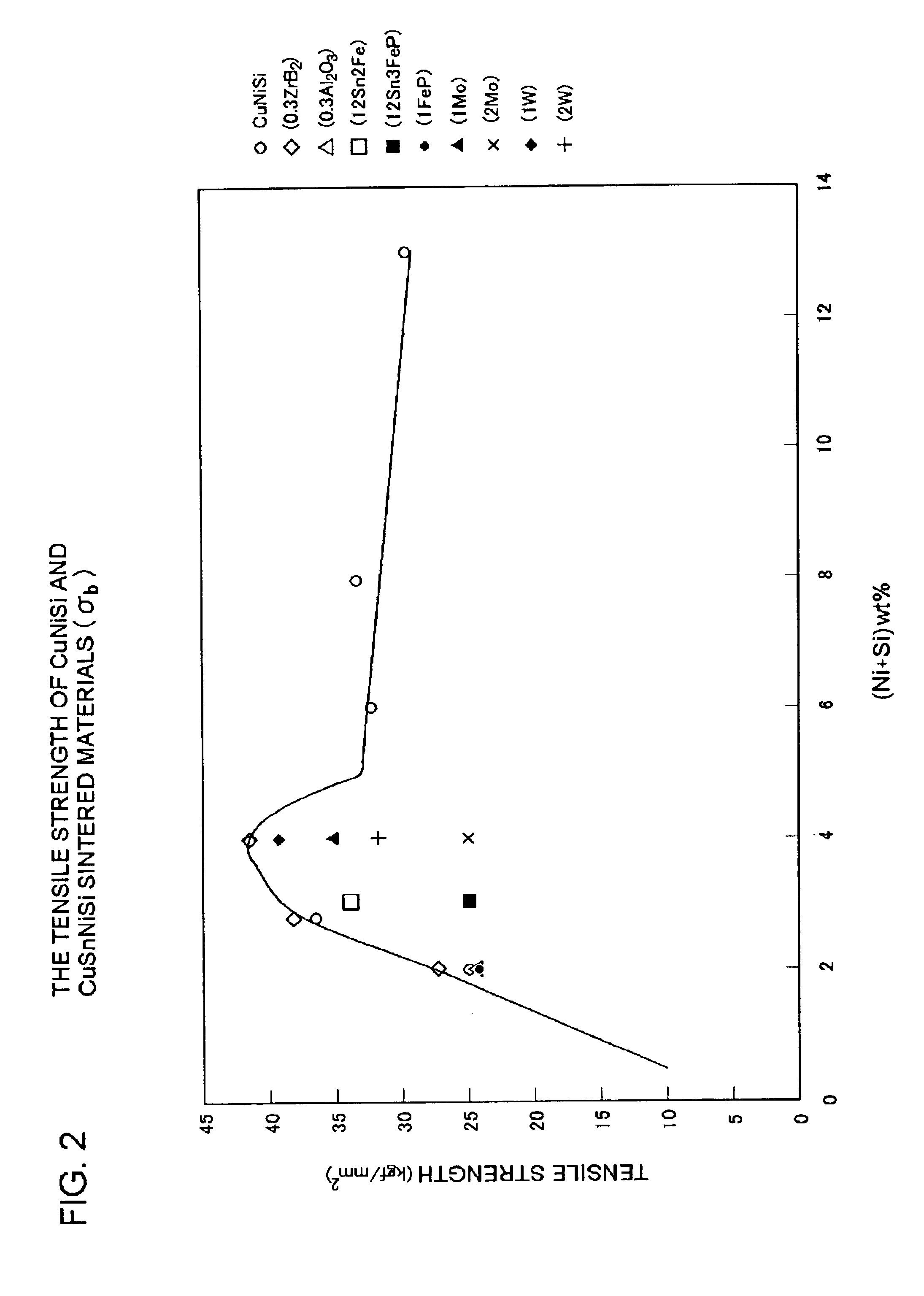
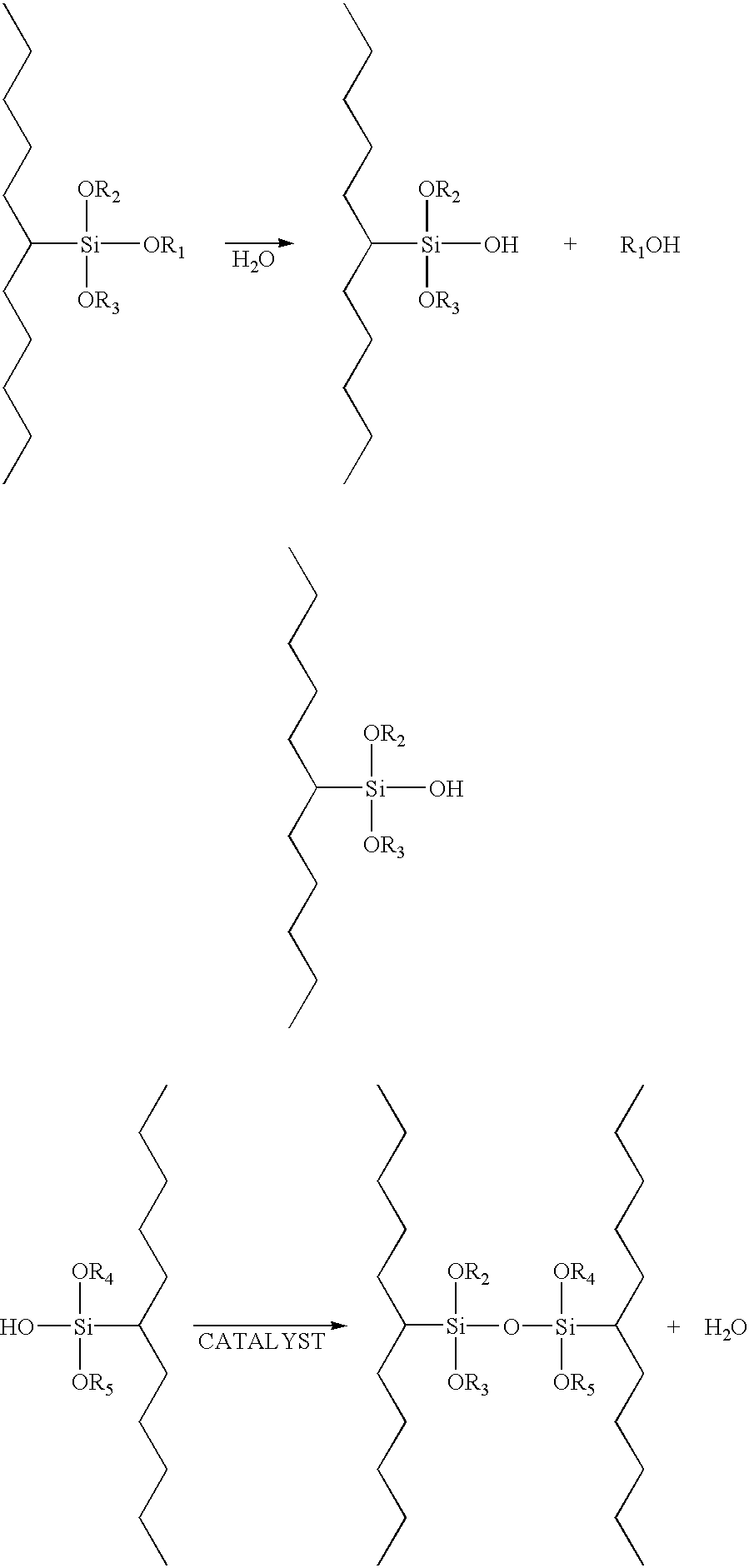
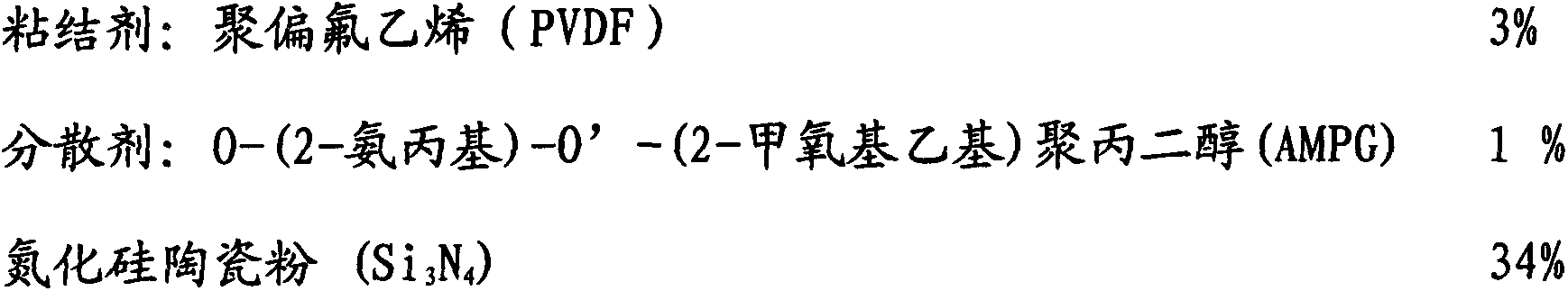Patents
Literature
4955results about How to "Improve thermal shock resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Strontium feldspar aluminum titanate for high temperature applications
InactiveUS6620751B1Improve stabilityReduce bloatInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle filtrationMicrometerRoom temperature
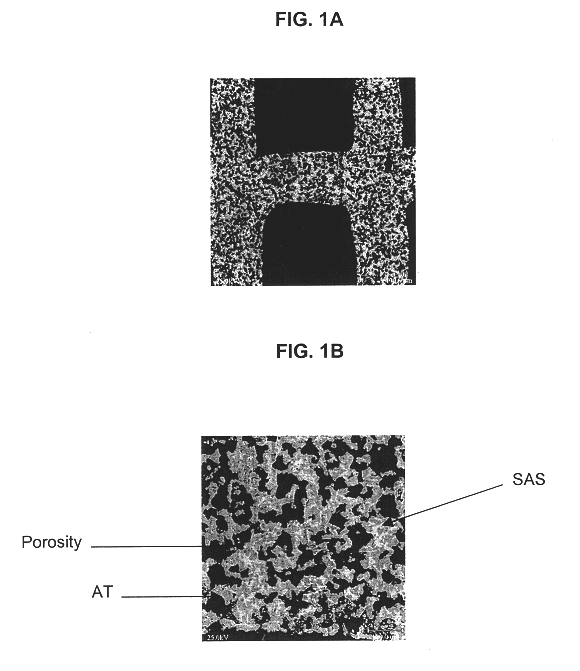
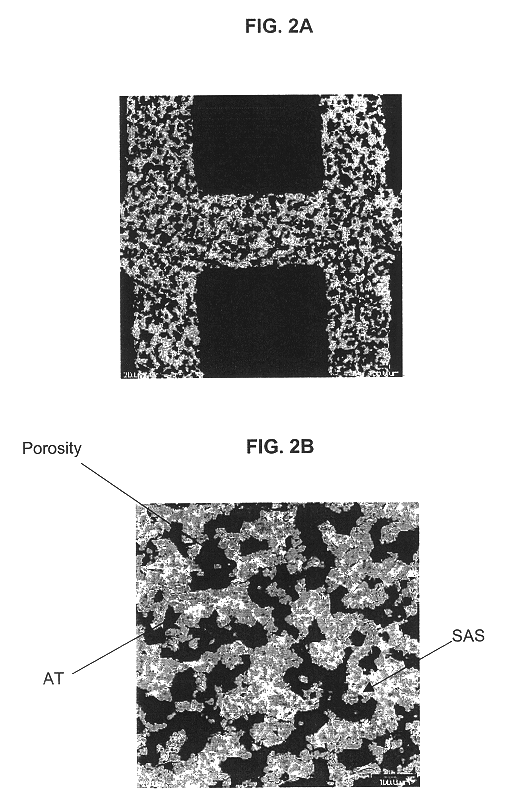
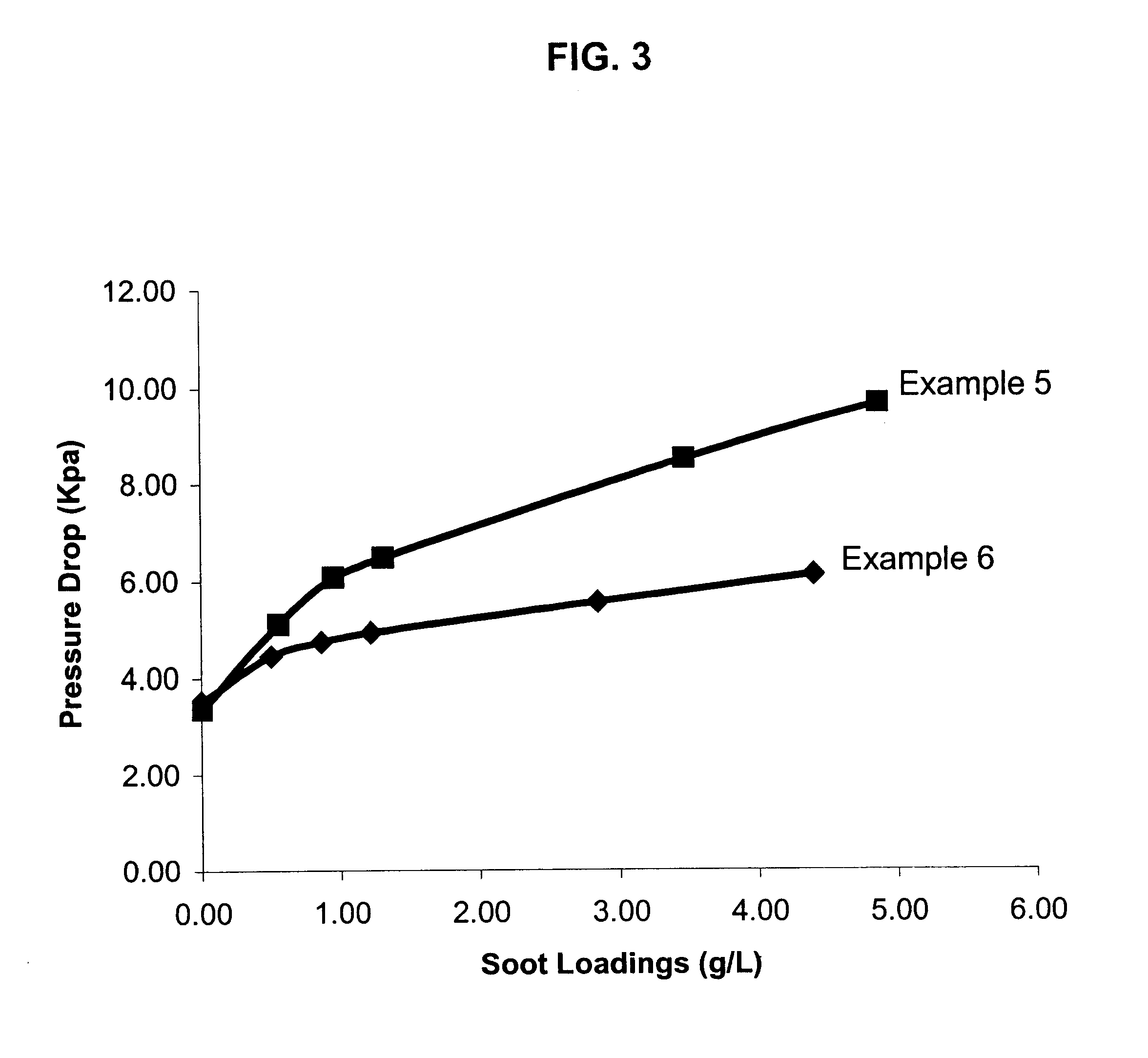
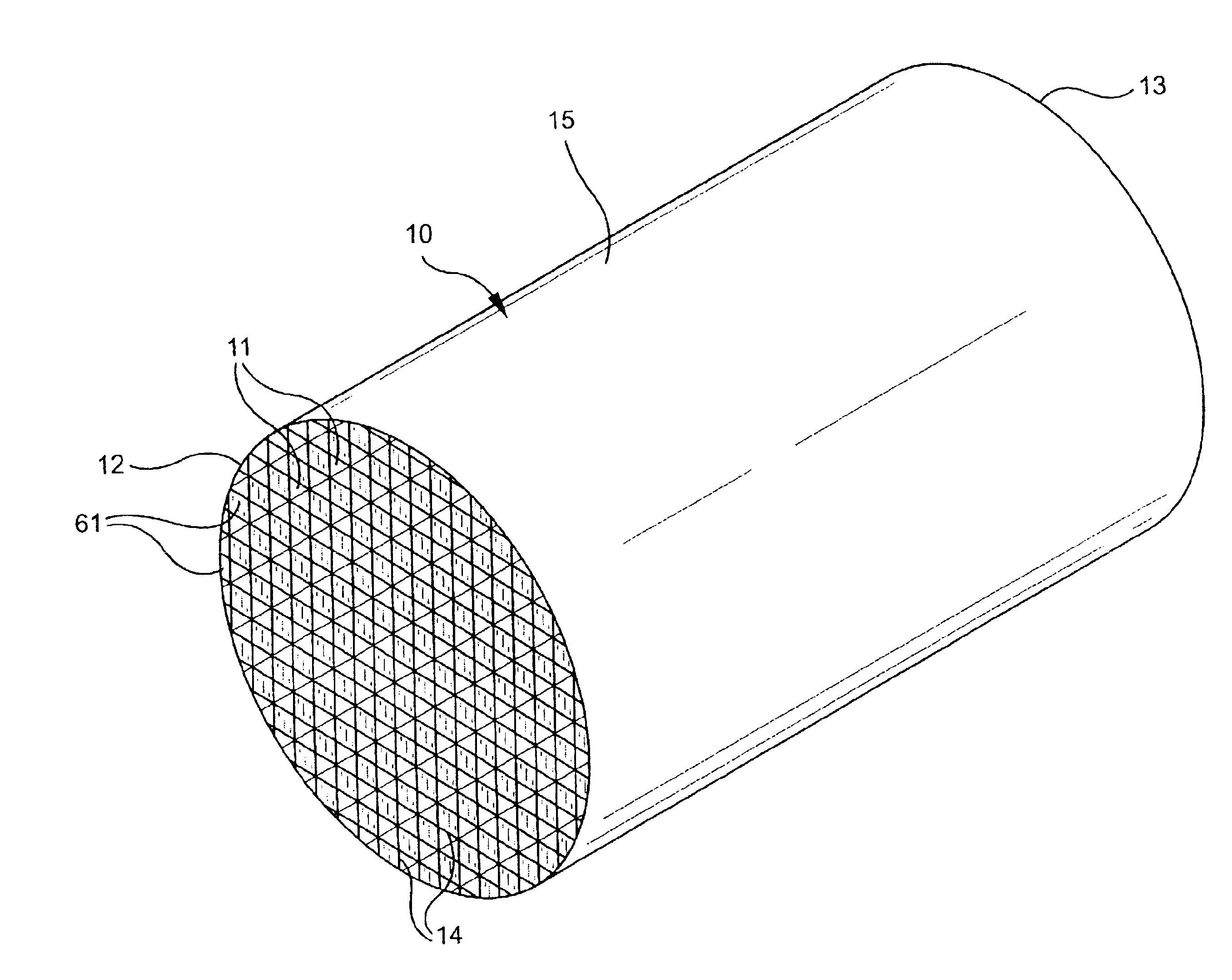
A structure for use in high temperature applications and including a porous ceramic material consisting essentially of about 50-90 percent by weight iron or magnesium stabilized aluminum titanate (AlTiO5) and about 10-50 percent by weight strontium feldspar (SrO.Al2O3.2SiO2), and having a coefficient of thermal expansion over a temperature range from room temperature to 1000° C. of about -10x10-7 / ° C. to +15x10-7 / ° C., a heat capacity at 500° C. greater than 3.2 J / cm3K, a porosity of about 15-50 percent by volume, preferably 40-50 percent by volume, and a median pore size of about 5-50 micrometers, preferably 8-15 micrometers. The structure is especially useful as a diesel exhaust particulate filter.
Owner:CORNING INC
Mullite-aluminum titanate diesel exhaust filter
InactiveUS6849181B2High porosityLarge apertureIron oxides/hydroxidesExhaust apparatusFiltrationMullite
The invention is directed at a mullite-aluminum titanate porous diesel particulate filter constituting a porous ceramic body containing, expressed in terms of weight percent of the total body, of 60-90%, preferably 70-80%, most preferably 70% iron-aluminum titanate solid solution having a stoichiometry of Al2(1−x)Fe2xTiO5, where x is 0-0.1, and 10-40%, preferably 20-30%, most preferably 30% mullite (3Al2O3.2SiO2), and consists essentially, expressed in terms of weigh percent on the oxide basis, of 3 to 15% SiO2, 55 to 65% Al2O3, 22 to 40% TiO2, and 0 to 10% Fe2O3, and being useful for filtration of diesel exhaust. The inventive diesel particulate filter exhibits high interconnected open porosity and large median pore size, in combination with high permeability when fired to a temperature of between 1650° to 1700° C., along with high thermal shock resistance and good filtration capability.
Owner:CORNING INC
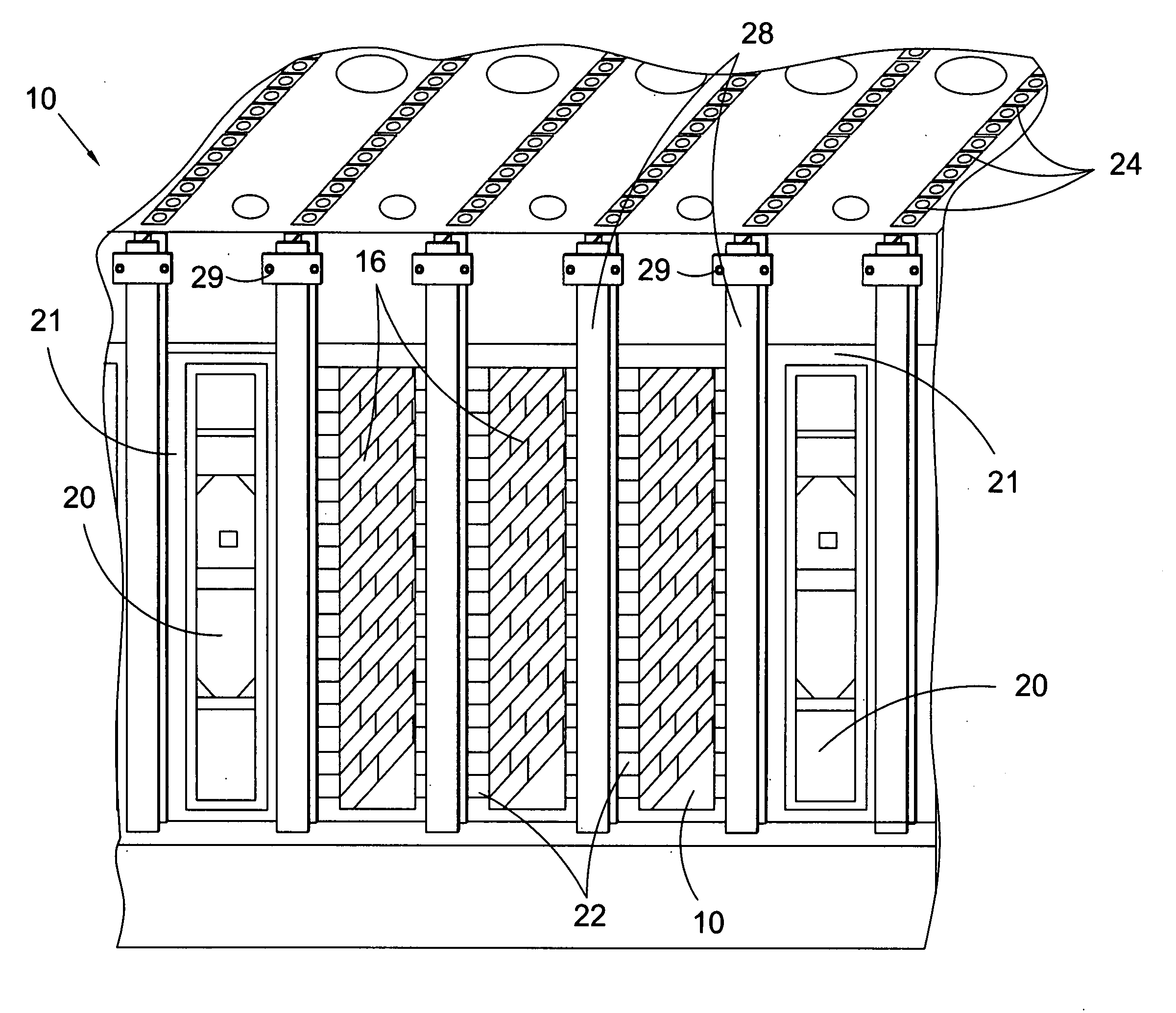
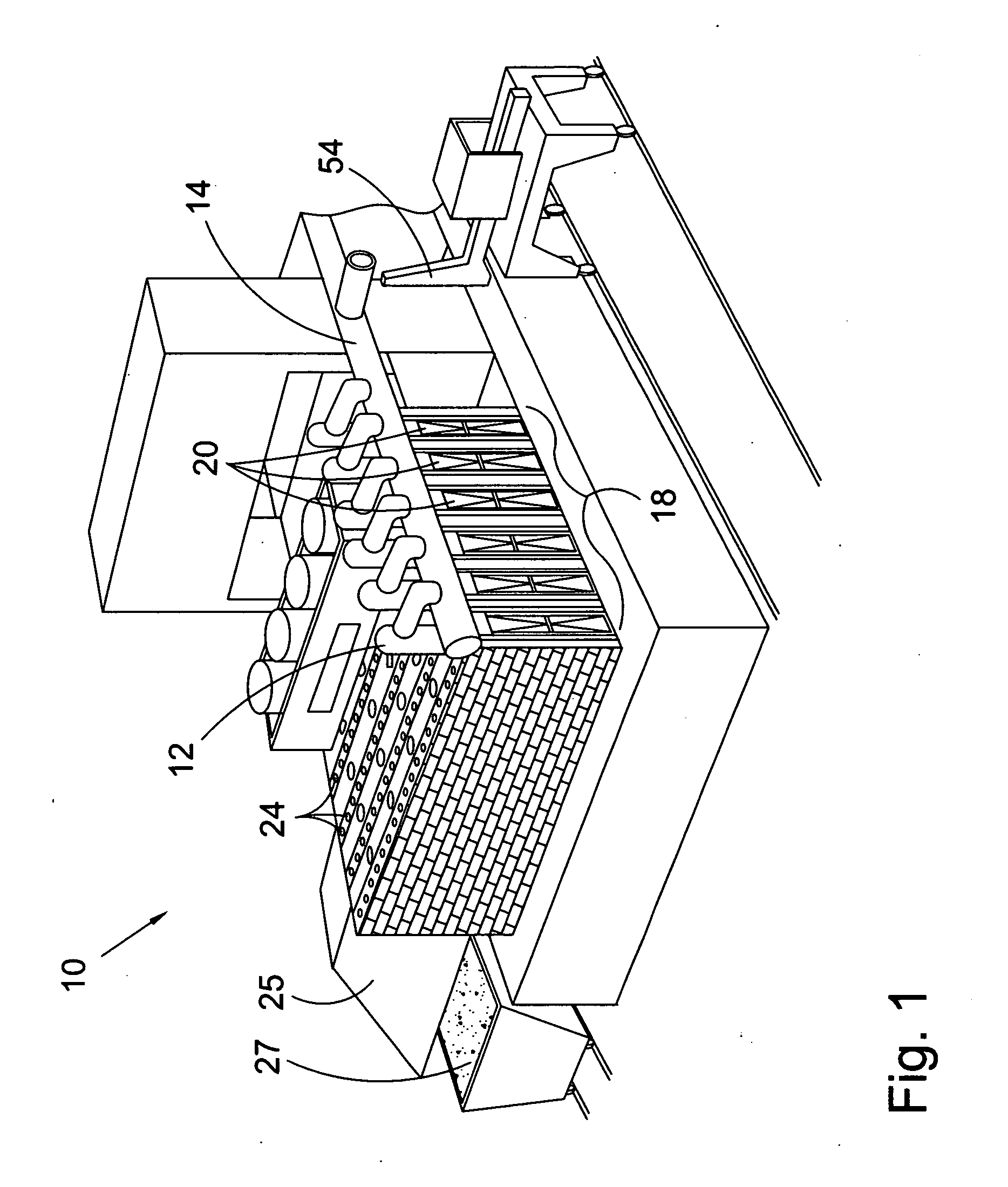
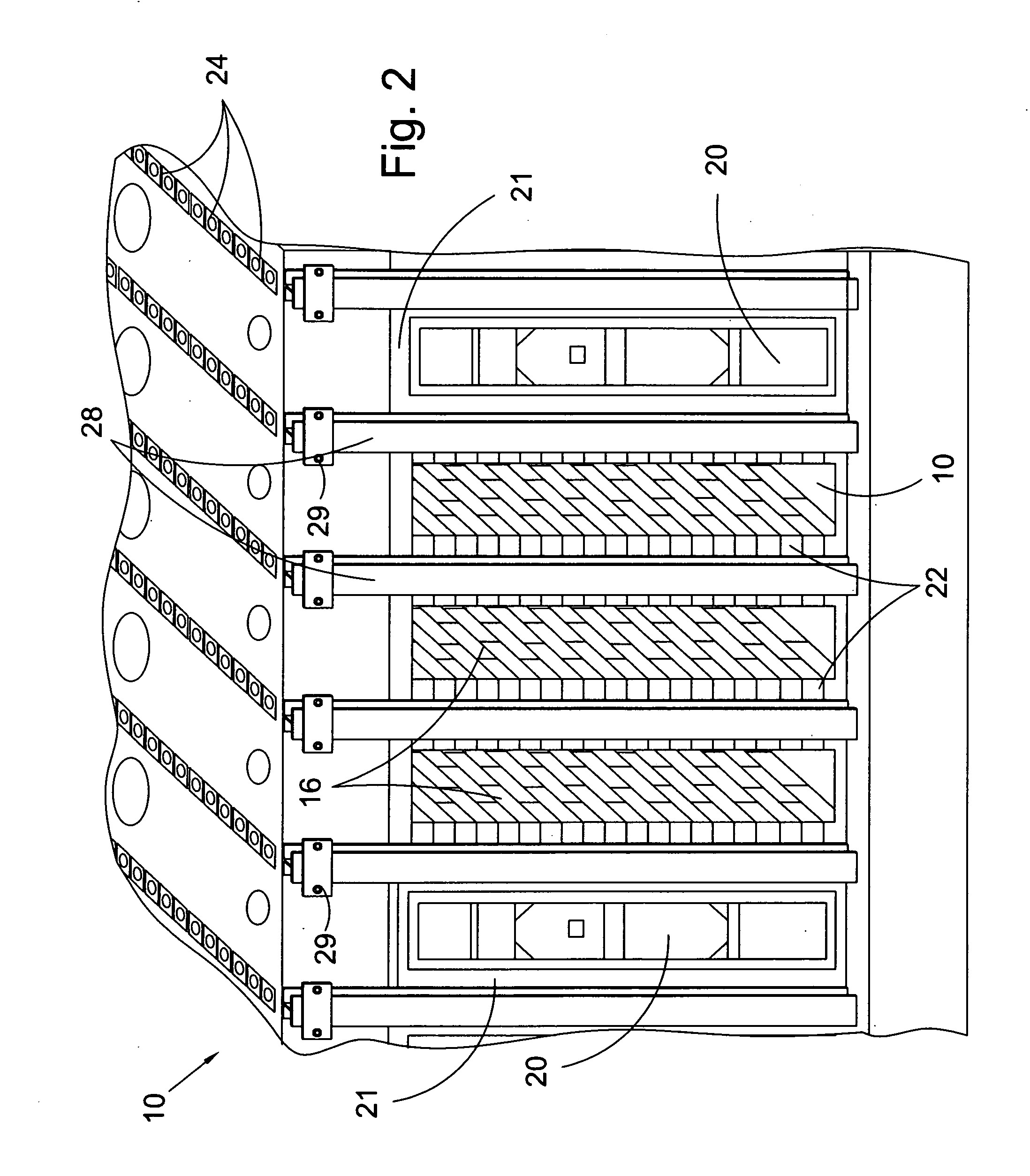
Honeycomb structured body, method for manufacturing honeycomb structured body and honeycomb structured body manufacturing apparatus
ActiveUS20080138567A1High bonding strengthImprove thermal shock resistanceInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle filtrationFiberCell wall
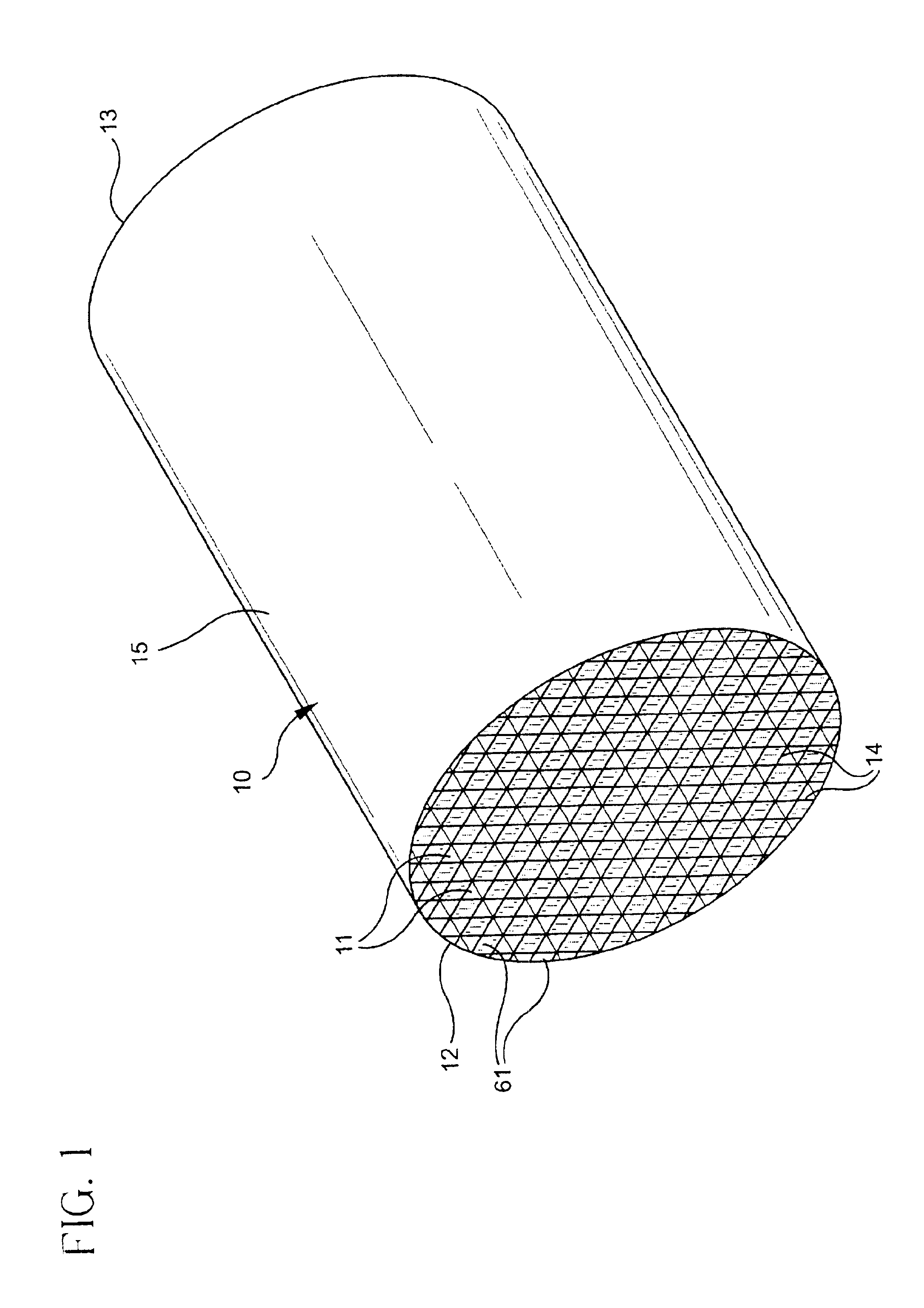
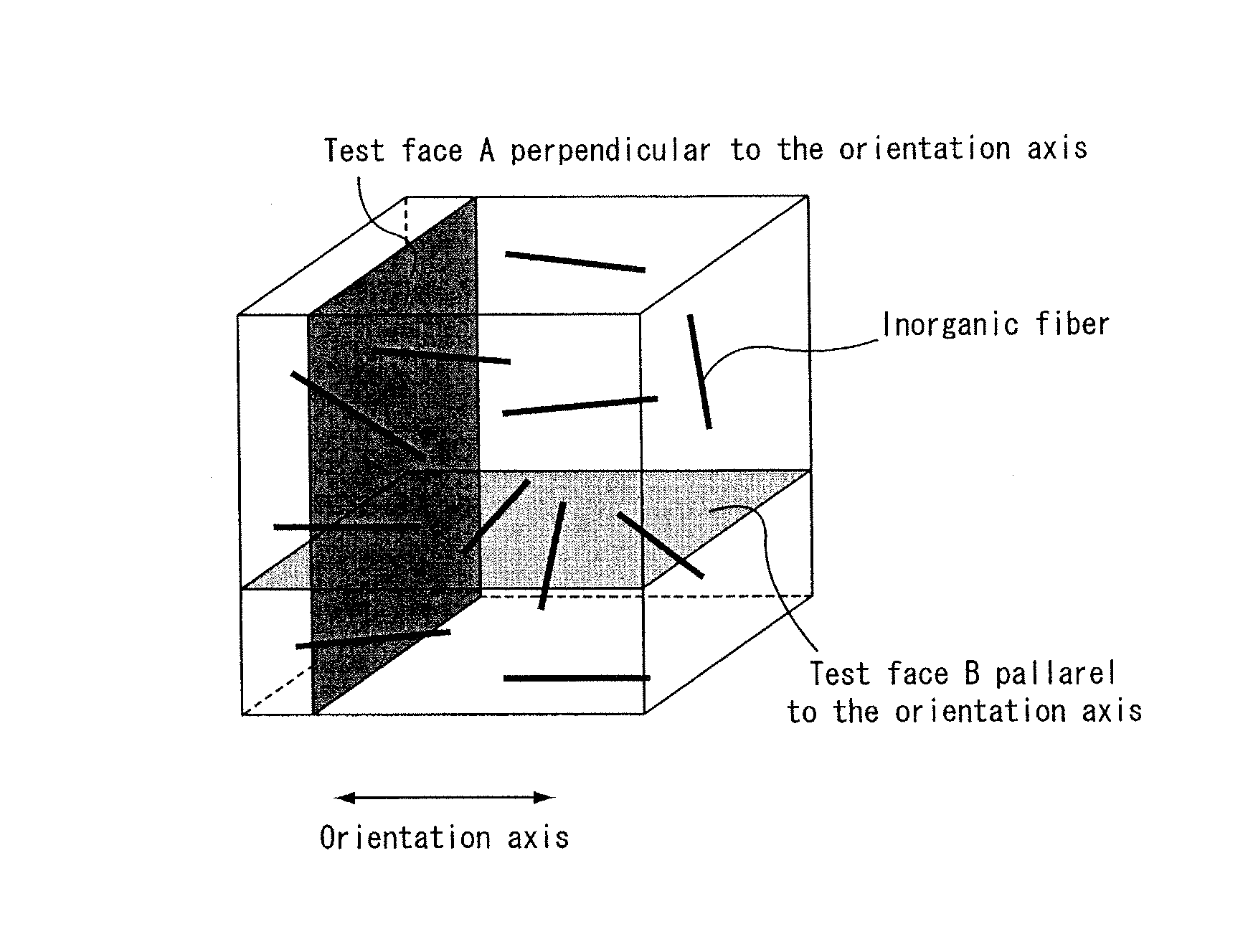
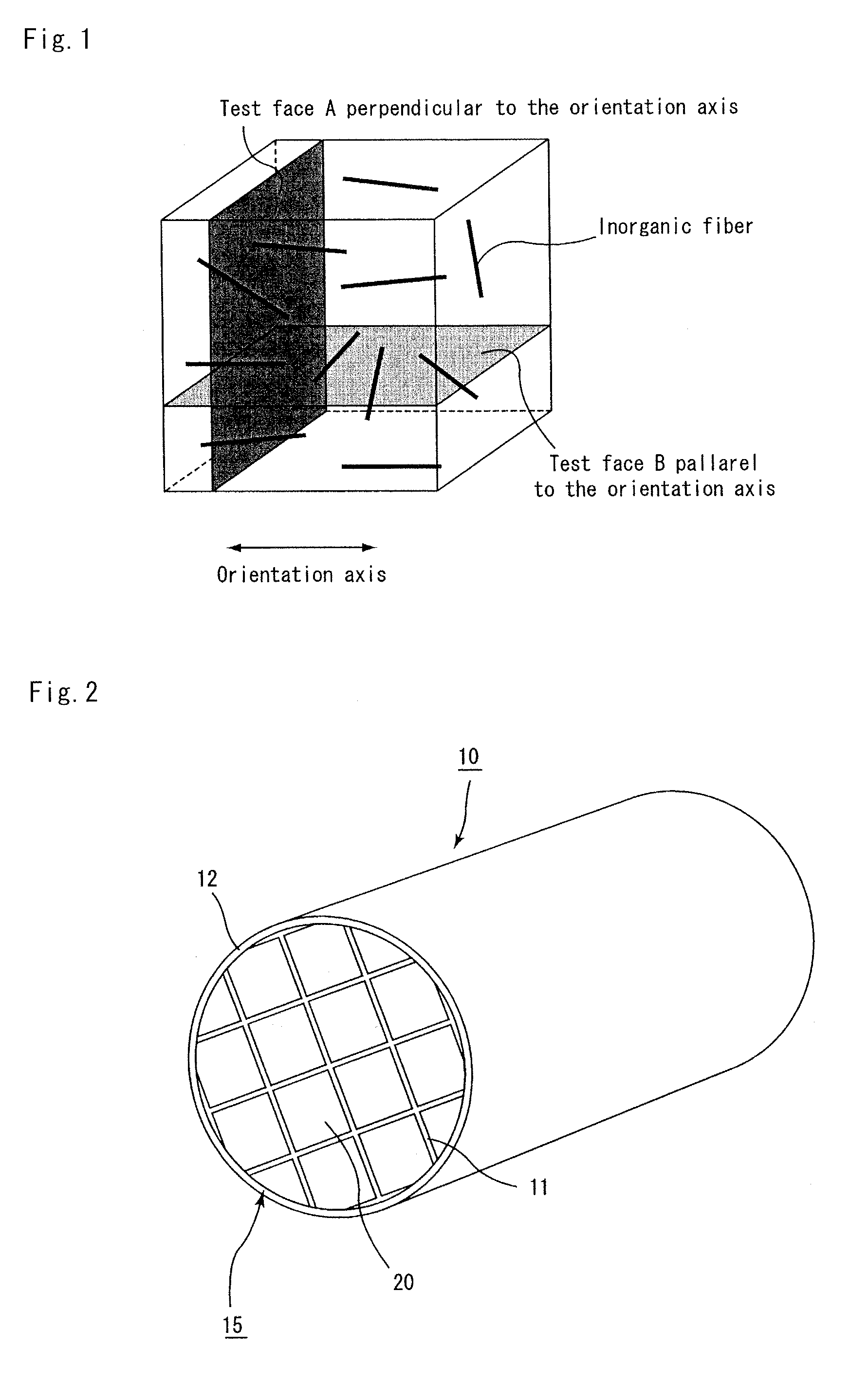
A honeycomb structured body includes a plurality of honeycomb members which are bonded to one another by interposing an adhesive layer. Each of the honeycomb members has a number of cells placed in parallel with one another in the longitudinal direction with a cell wall therebetween. When the longitudinal direction is defined as the orientation axis, the degree of orientation Ω of the inorganic fibers in the adhesive layer obtained by the Saltykov method is set in the range of about 0.2≦Ω≦about 0.7 or in the range of about −0.7≦Ω≦about −0.2 in the adhesive layer.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Mullite-aluminum titanate diesel exhaust filter
InactiveUS20040020846A1High interconnected porosityReduce back pressureIron oxides/hydroxidesExhaust apparatusFiltrationWhole body
The invention is directed at a mullite-aluminum titanate porous diesel particulate filter constituting a porous ceramic body containing, expressed in terms of weight percent of the total body, of 60-90%, preferably 70-80%, most preferably 70% iron-aluminum titanate solid solution having a stoichiometry of Al2(1-x)Fe2xTiO5, where x is 0-0.1, and 10-40%, preferably 20-30%, most preferably 30% mullite (3Al2O3.2SiO2), and consists essentially, expressed in terms of weigh percent on the oxide basis, of 3 to 15% SiO2, 55 to 65% Al2O3, 22 to 40% TiO2, and 0 to 10% Fe2O3, and being useful for filtration of diesel exhaust. The inventive diesel particulate filter exhibits high interconnected open porosity and large median pore size, in combination with high permeability when fired to a temperature of between 1650° to 1700° C., along with high thermal shock resistance and good filtration capability.
Owner:CORNING INC
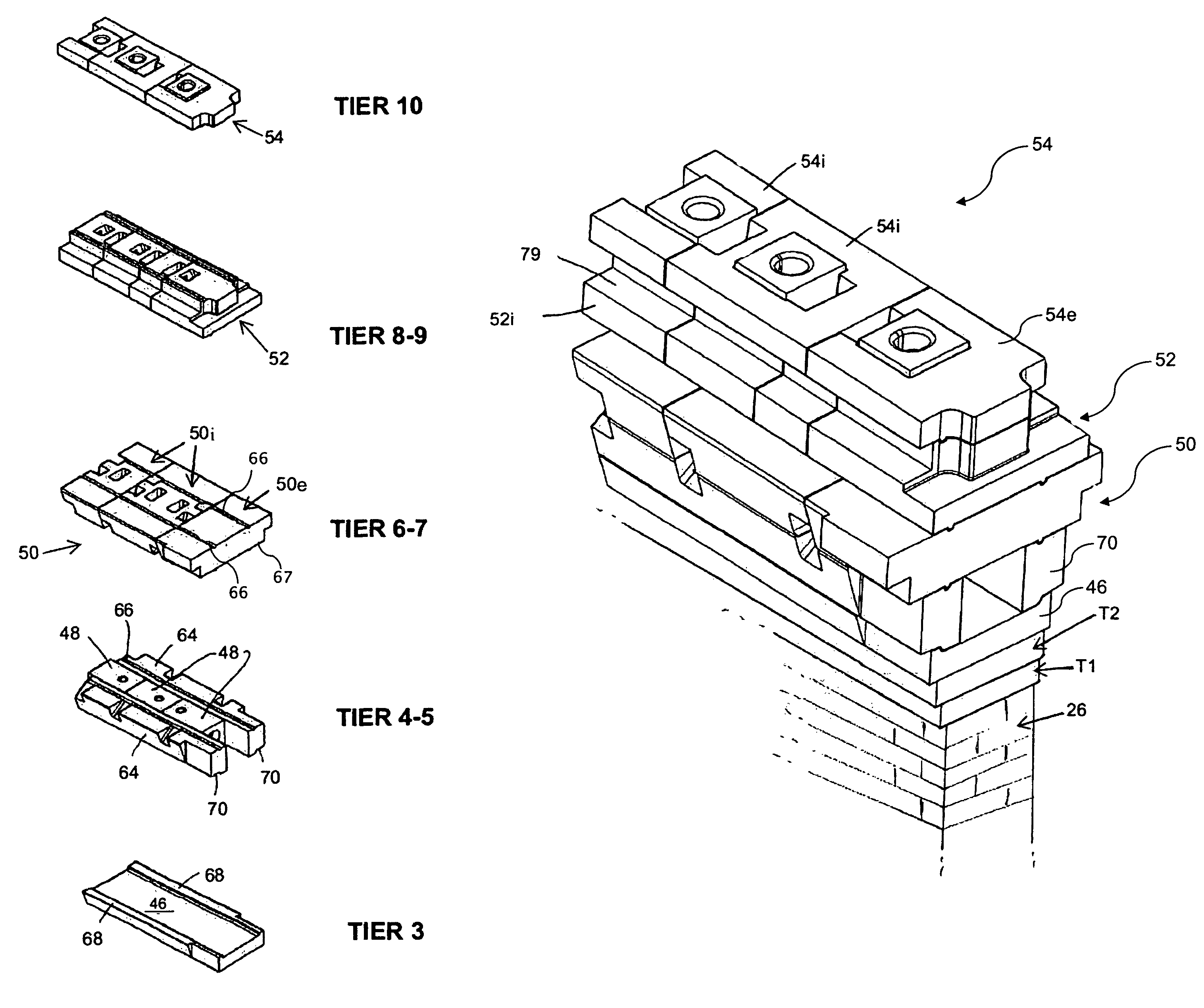
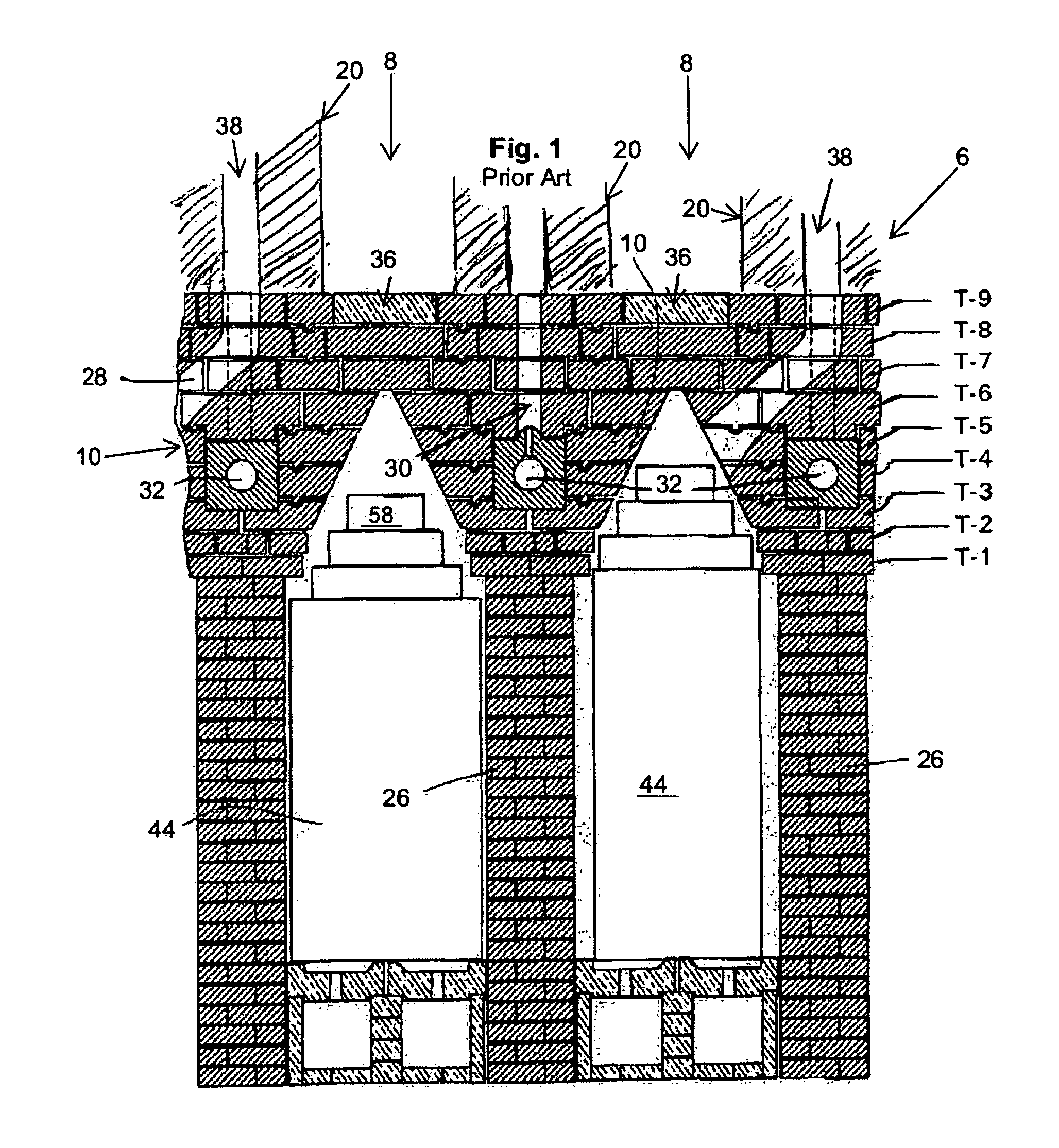
Corbel repairs of coke ovens
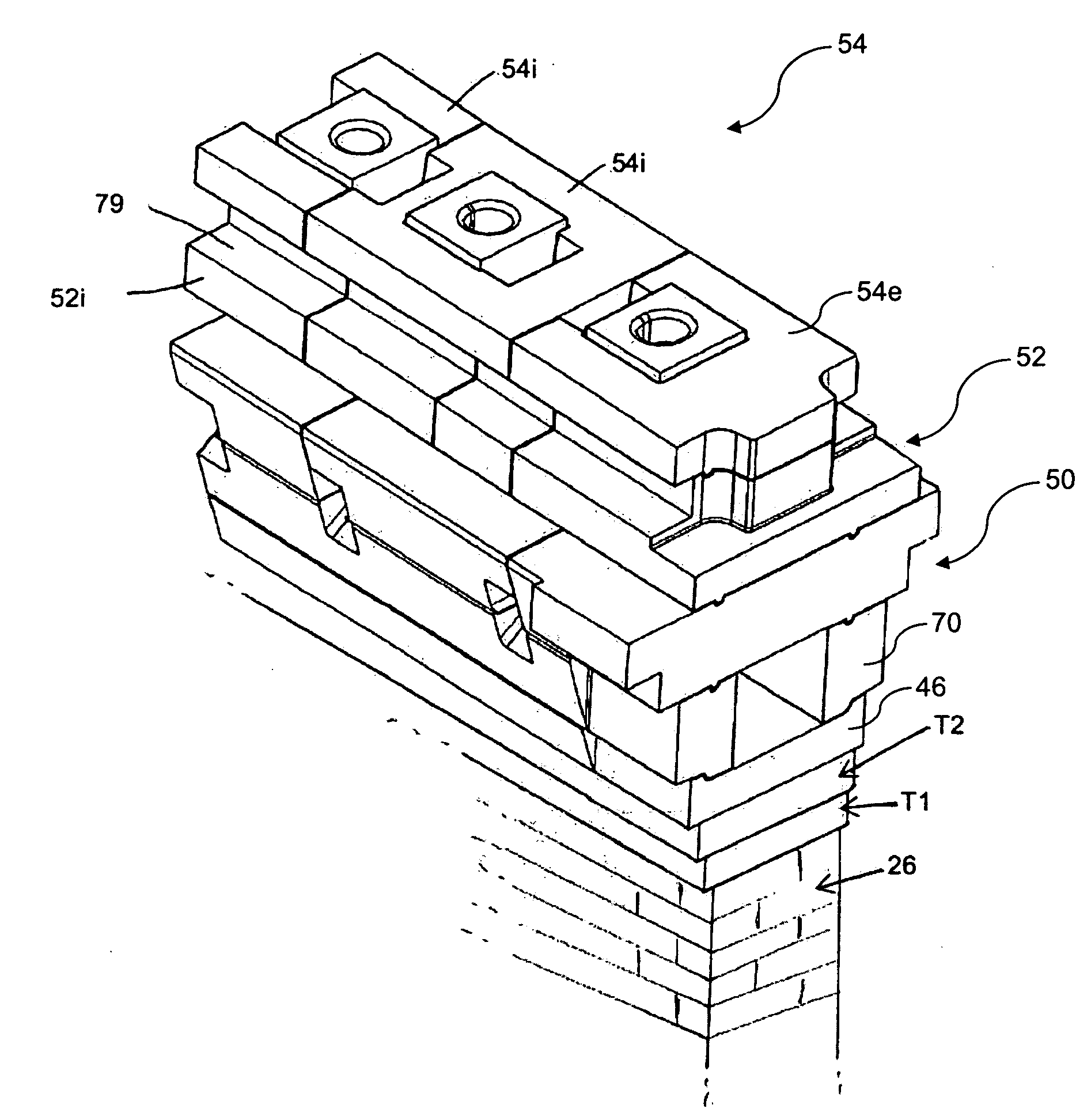
ActiveUS8266853B2Cost-effective constructionSave significant amountFurnace componentsFloorsEngineeringCoke oven
An improved corbel includes a first tier having first blocks and a second tier having second blocks. Each of the first blocks includes a first aperture extending through the block from a first surface to a back surface and a second aperture formed through a top surface of the block, extending into the first aperture. The first blocks are arranged on a substantially planar surface to align the respective first apertures to define a first passageway. Each of the second blocks includes a third aperture extending through the second block from a top surface to a bottom surface. The second blocks are disposed above the first tier to align the third aperture of each of the second blocks with the second aperture of the first blocks to form a second passageway.
Owner:VANOCUR REFRACTORIES LLC
Mullite-aluminum titanate body and method for making same
InactiveUS20060021308A1Low thermal expansionHigh thermal shock resistanceInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle filtrationYttriumBismuth preparation
This invention relates to a mullite-aluminum titanate body having a low coefficient of thermal expansion of less than 15×10−7 C−1, a high porosity of at least 38% by volume, a median pore diameter of at least 8 microns, and a narrow pore size distribution as characterized by the relation (d50-d10) / d50 being less than 0.50 corresponding to a high degree of interconnected porosity. The inventive ceramic body also contains at least 0.10% by weight metal oxide, the metal being either yttrium, calcium, bismuth, a lanthanide metal or combinations of thereof. The inventive ceramic body is particularly useful as a wall-flow filter for diesel exhaust. A method of fabrication is provided where the sintering temperature is between 1375°-1550° C.
Owner:CORNING INC
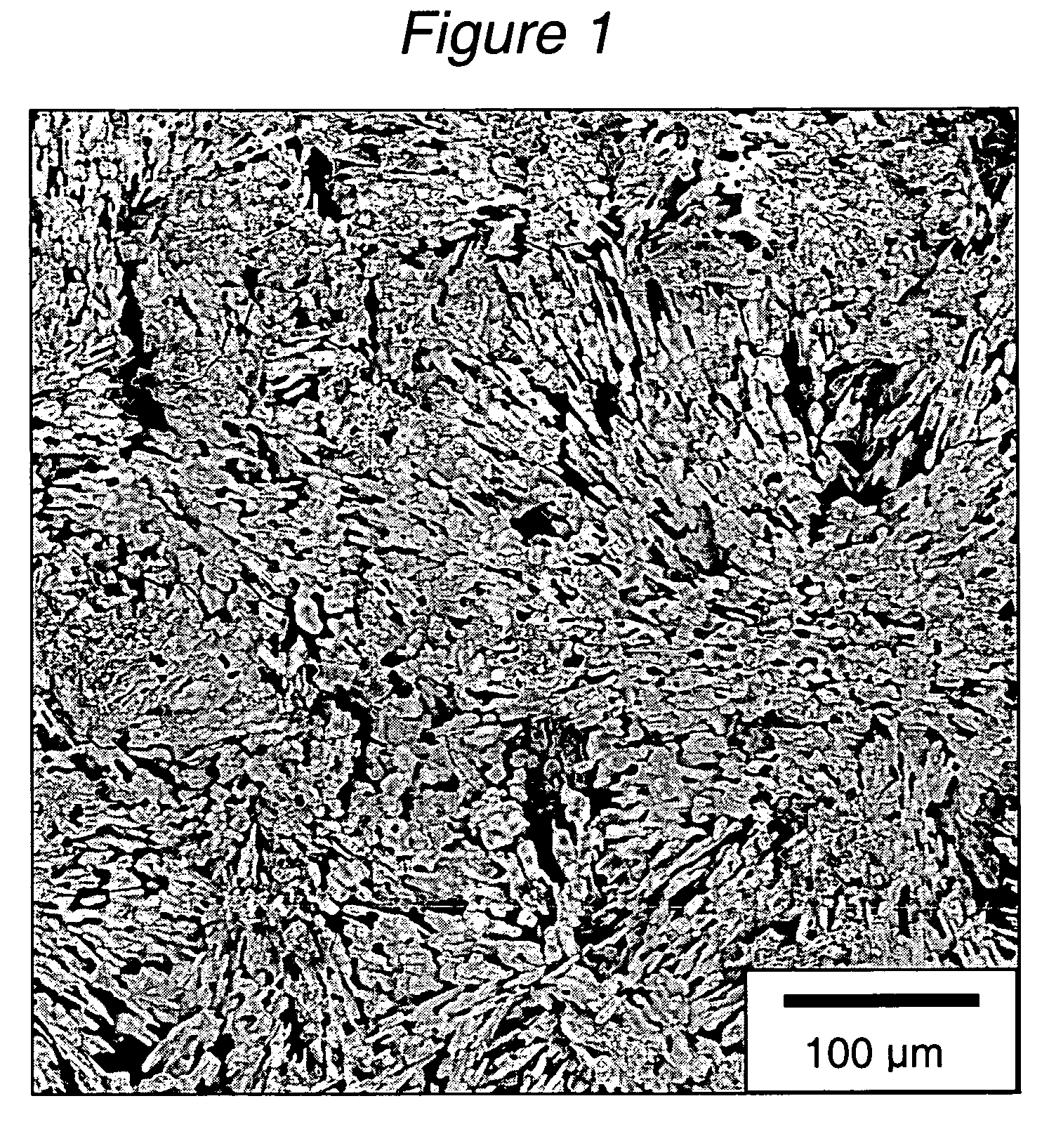
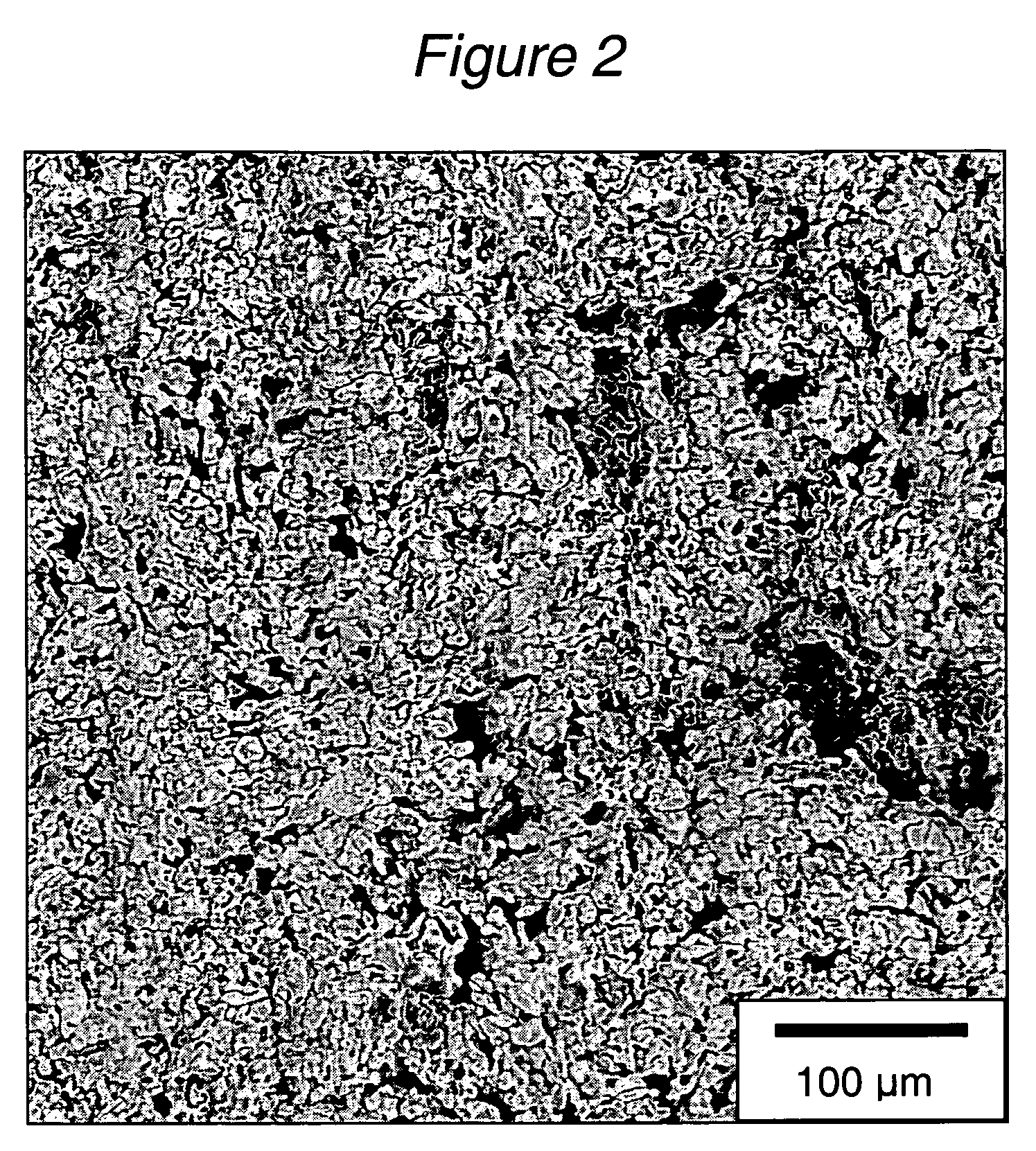
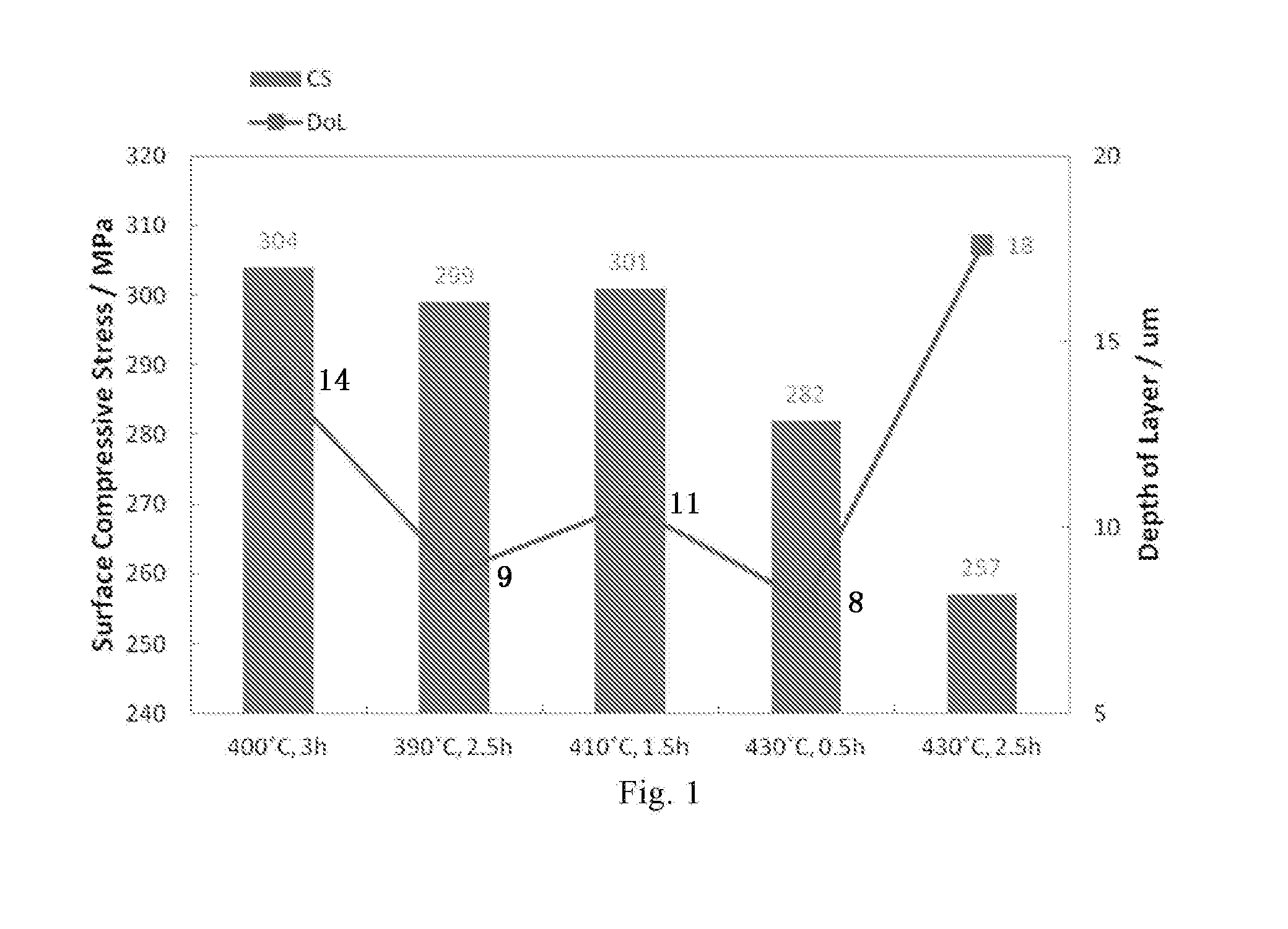
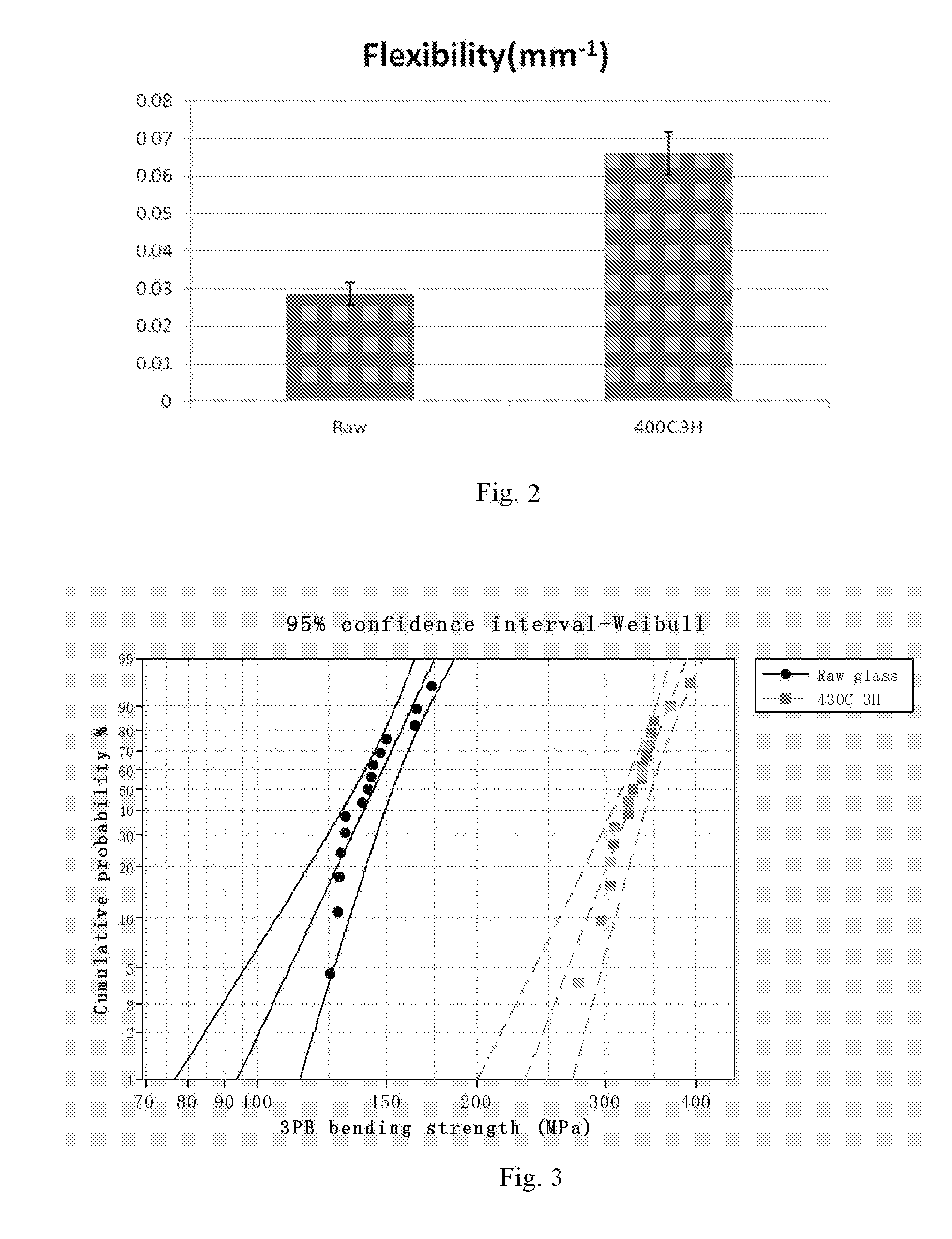
Chemically Toughened Flexible Ultrathin Glass
ActiveUS20160002103A1Reduce compressive stressIncrease flexibilityFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsGlass sheetThermal shock
A chemically toughened ultrathin glass is provided. The glass has a thickness less than 500 μm and a surface compressive layer having a depth of at most 30 μm. The toughened ultrathin glass sheet is more flexible and has extraordinary thermal shock resistance with the glass being easier to handle for processing.
Owner:SCHOTT GLASS TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
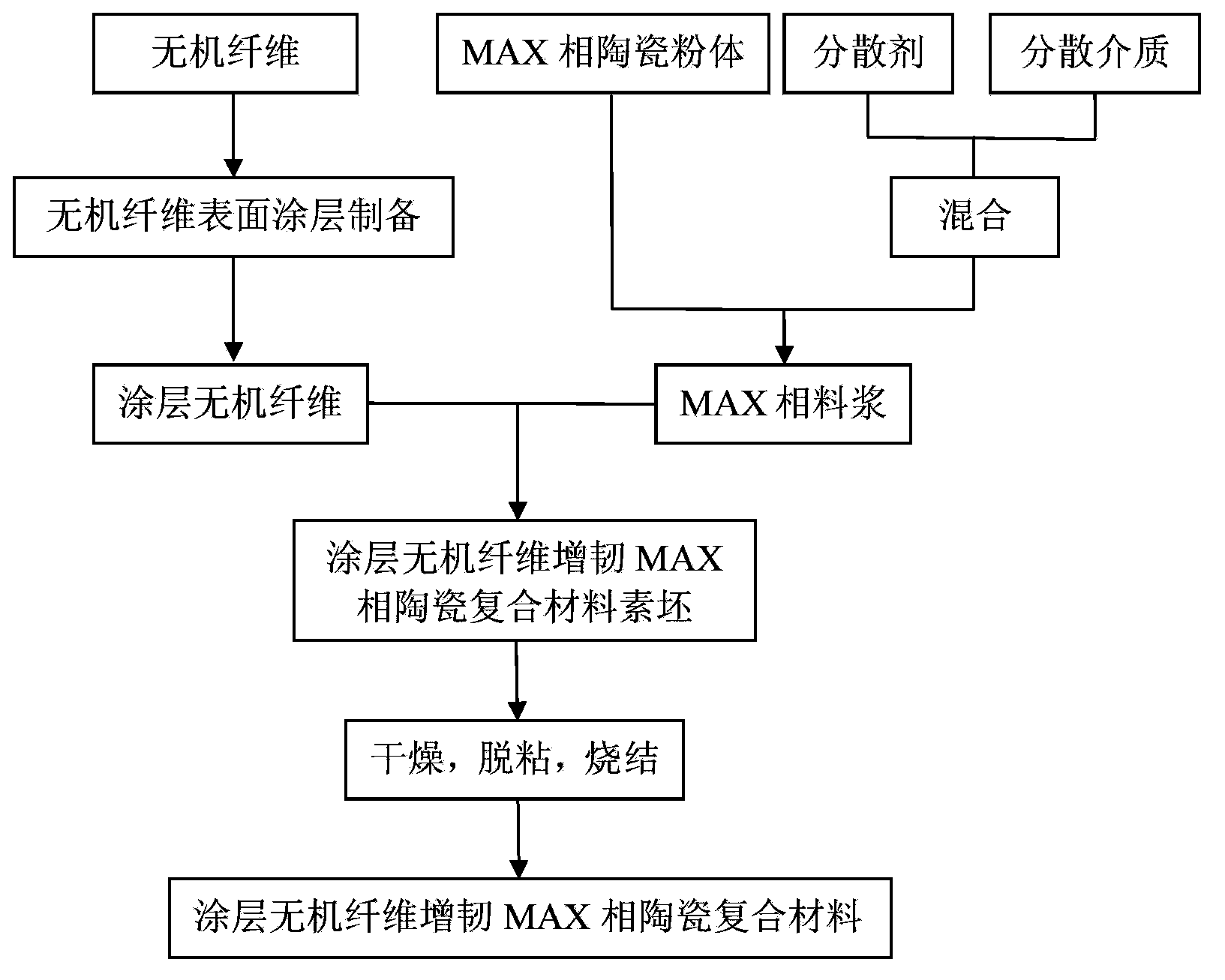
Coating inorganic fiber toughened MAX phase ceramic composite material, preparation method and uses thereof
ActiveCN103910532AAppropriate bonding interface strengthFree control of interface strengthNuclear energy generationContainmentAviationFiber
The present invention provides a coating inorganic fiber toughened MAX phase ceramic composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material adopts a MAX phase ceramic material as a matrix and adopts coating inorganic fibers as a toughening phase, wherein the coating inorganic fiber content is 0.5-90% (by volume), and the coating inorganic fibers are completely dispersed in the matrix and are inorganic fibers with the surface coated with the coating. Compared with the composite material in the prior art, the composite material of the present invention has the following characteristics that: the interface reaction between the inorganic fibers and the MAX phase ceramic can be effectively inhibited, the thermal expansion coefficient and elasticity modulus matching degree between the inorganic fibers and the MAX phase ceramic can be effective regulated, the effective improvement of the fracture toughness and the high temperature resistance of the MAX phase ceramic composite material can be achieved, the problems of high brittleness and insufficient use reliability of the MAX phase ceramic can be fundamentally solved, and the coating inorganic fiber toughened MAX phase ceramic composite material has potential application prospects in the high technology fields of civil use, aviation, aerospace, nuclear industry and the like, and is especially for the fission and fusion reactor nuclear power plant inner wall structure material.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Coke oven reconstruction
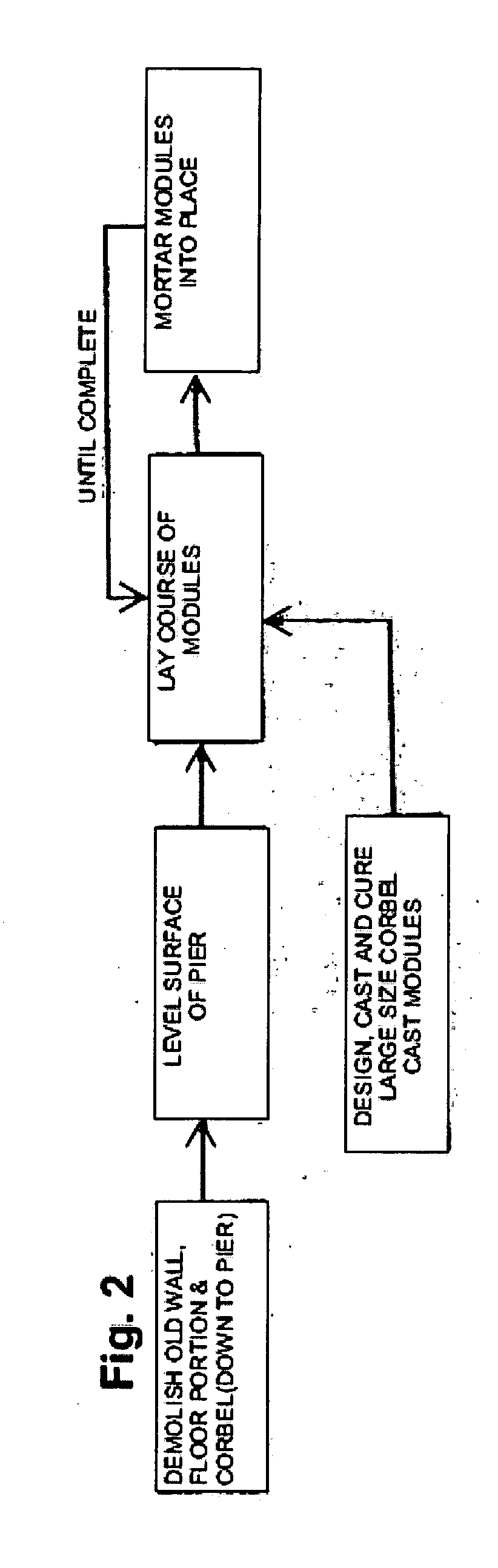
ActiveUS7827689B2Good dimensional stabilityNegligible heatingConstruction materialCoke oven brickworkComputer moduleEngineering
A new, faster and more efficient process to replace heating walls and ceilings in coke oven batteries. Thus, when replaced, at least one heating wall is constructed of thermally stable non-expanding large size modular cast modules from end to end and the ceiling adjacent the heating wall is constructed of thermally stable non-expanding large modular cast blocks.
Owner:VANOCUR REFRACTORIES LLC
Corbel repairs of coke ovens
ActiveUS20100287871A1Cost-effective constructionSave significant amountFurnace componentsWallsEngineeringCoke oven
An improved corbel includes a first tier having first blocks and a second tier having second blocks. Each of the first blocks includes a first aperture extending through the block from a first surface to a back surface and a second aperture formed through a top surface of the block, extending into the first aperture. The first blocks are arranged on a substantially planar surface to align the respective first apertures to define a first passageway. Each of the second blocks includes a third aperture extending through the second block from a top surface to a bottom surface. The second blocks are disposed above the first tier to align the third aperture of each of the second blocks with the second aperture of the first blocks to form a second passageway.
Owner:VANOCUR REFRACTORIES LLC
Microwave regenerated diesel particular filter and method of making the same
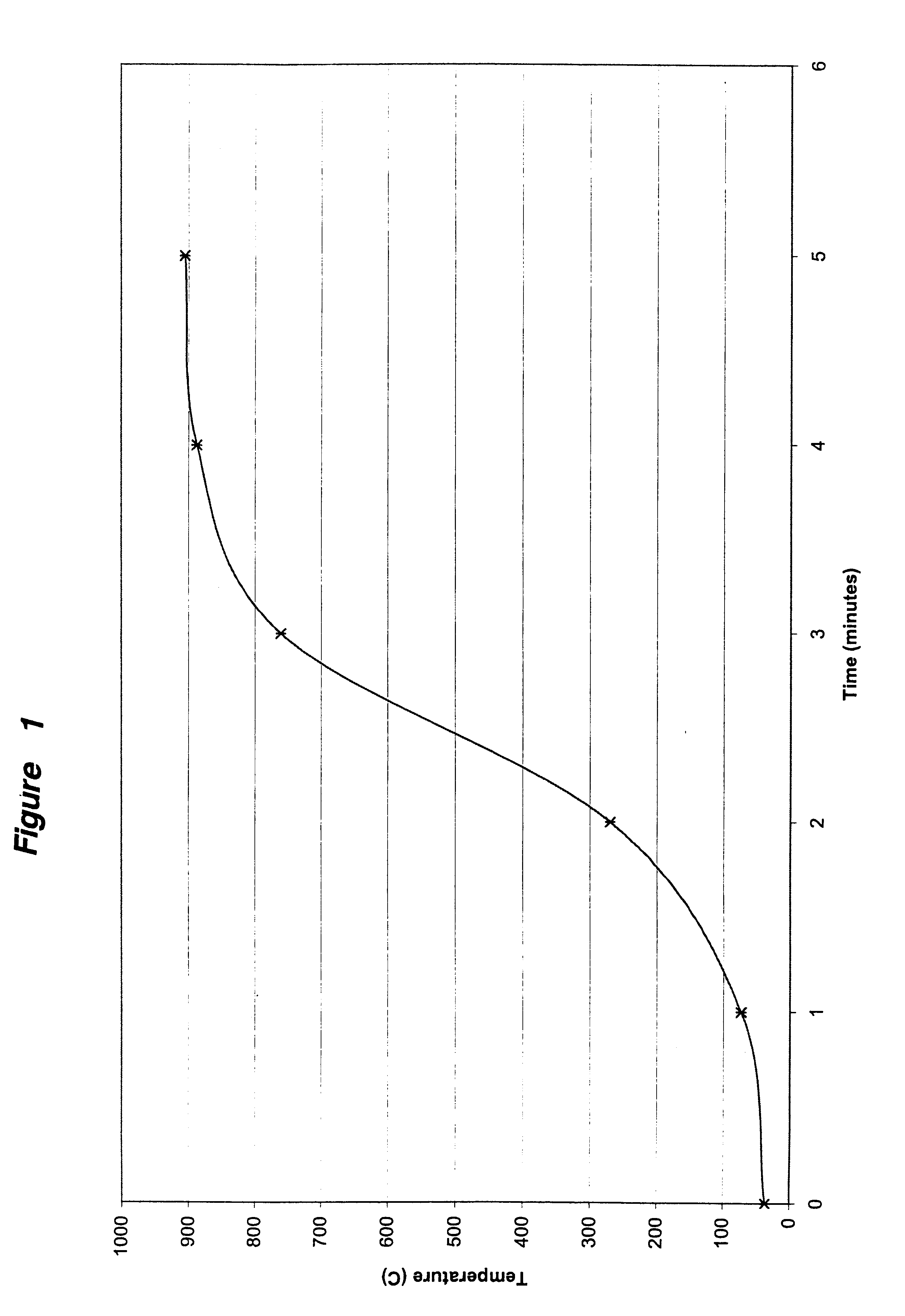
A filter for trapping and combusting diesel exhaust particulates and method of making the same. The filter comprises a monolithic substrate coated with a refractory oxide material which at a frequency of 2.45 GHz heats up said filter from room temperature to about 600° C. in 5 minutes or less, and wherein said refractory oxide material has a loss tangent which decreases with increasing temperature such that an equilibrium in said filter temperature is reached at no greater than 1100° C. The microwave-absorbing material having a composition selected from the group consisting of A1-xMxB1-yM'yO3-alpha, where A and M are selected from the group consisting of Na, K, Rb, Ag, Ca, Sr, Ba, Pb, La, Pr, Nd, Bi, Ce, Th and combinations thereof; where B and M' are selected from the group consisting of Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Rh, Ru, Pt, Zn, Nb, Ta, Mo, W and combinations thereof; wherein, the chemical formula is electrostatically balanced; (A'aRrM''m)(Z)4(X)6O24, where A' is from Group IA metals; where R is selected from Group IIA metals; where M'' is selected from the group consisting of Mn, Co, Cu, Zn, Y, lanthanides and combinations thereof; where Z is selected from the group consisting of Zr, Hf, Ti, Nb, Ta, Y, lanthanides, Sn, Fe, Co, Al, Mn, Zn, Ni, and combinations thereof; where X is selected from the group consisting of P, Si, As, Ge, B, Al, and combinations thereof.
Owner:CORNING INC
Coke oven reconstruction
ActiveUS20080169578A1High dimensional stabilityRepair time be approximately halvedConstruction materialCoke oven brickworkEngineeringCoke oven
A new, faster and more efficient process to replace heating walls and ceilings in coke oven batteries. Thus, when replaced, at least one heating wall is constructed of thermally stable non-expanding large size modular cast modules from end to end and the ceiling adjacent the heating wall is constructed of thermally stable non-expanding large modular cast blocks.
Owner:VANOCUR REFRACTORIES LLC
Method with functions of preheating and postheating for forming crack-free coating with high efficiency by three-light-beam laser-cladding technique
InactiveCN102383126ALow and adjustable dilution rateSmall heat affected zoneMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusMelting tankHeat-affected zone
The invention discloses a method with functions of preheating and postheating for forming crack-free coating with high efficiency by a three-light-beam laser-cladding technique. The method comprises the following steps of: splitting a laser beam emitted by an Nd: YAG laser into two laser beams by using a laser beam splitter, namely a preheating laser beam for preheating the surface of a base material and a postheating laser beam for postheating the formed coating; then blowing alloy powder into a molten pool which is formed by focusing a laser beam emitted by a CO2 laser and acting the focused laser beam on the surface of the base material by using a powder nozzle, wherein after the CO2 laser beam moves away, a molten layer is cured and crystallized quickly to form the coating; and postheating the formed coating by adopting the postheating laser beam. The method has the advantages that: (1) the dilution rate of the coating is low and adjustable, and the coating is metallurgically combined with the base material, so the base material has a small thermal influence area and is deformation-free and crack-free; (2) residual inner stress in the coating can be eliminated effectively, a tissue can be improved, and the coating has high abrasion resistance, high corrosion resistance, high anti-cracking performance and high thermal shock resistance; and (3) relative to the processing efficiency in the conventional laser cladding technology, the processing efficiency in the method can be improved by 50 times to the maximum extent, so the processing cost is reduced greatly, and a large-scale industrialized application potential is realized.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
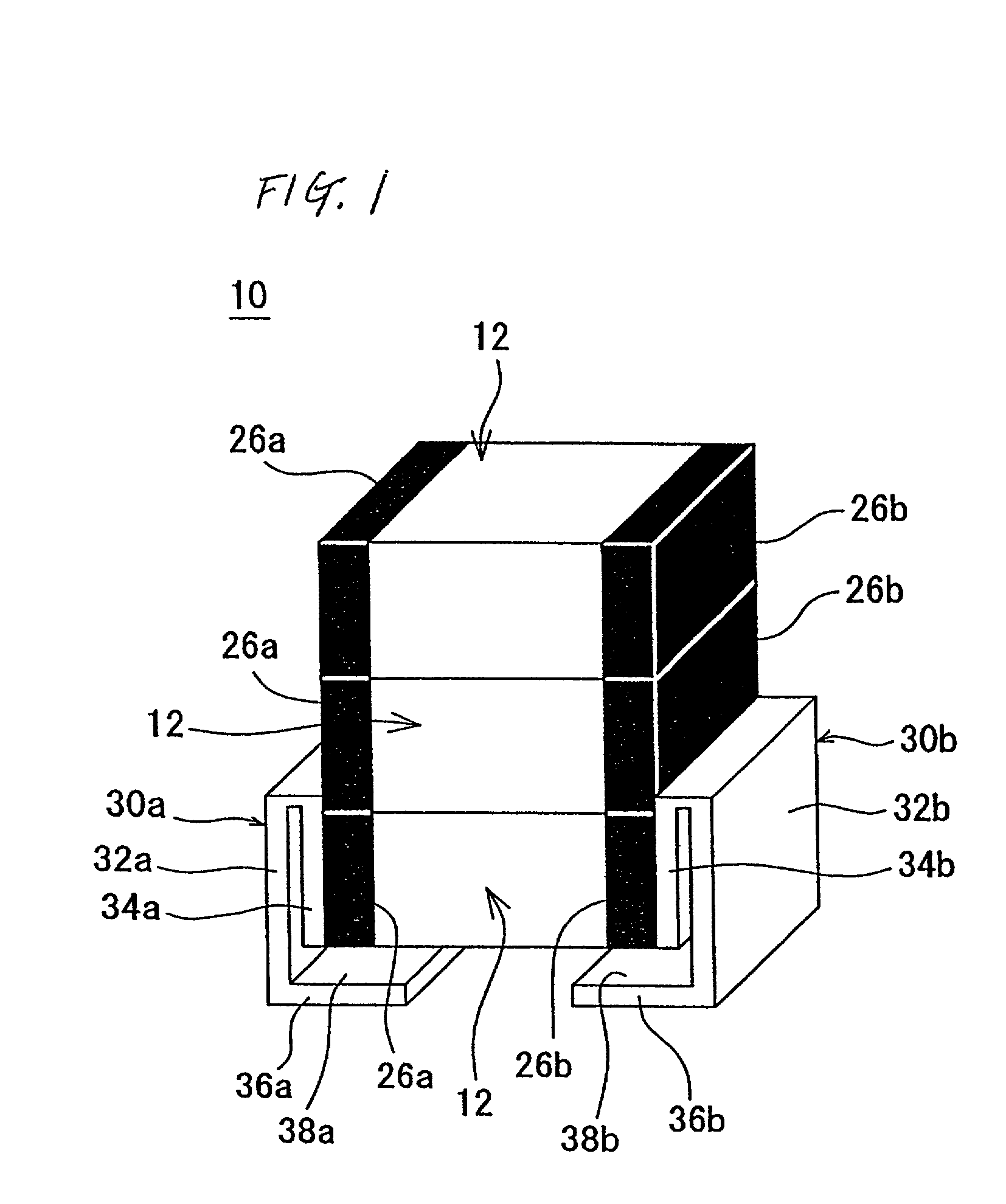
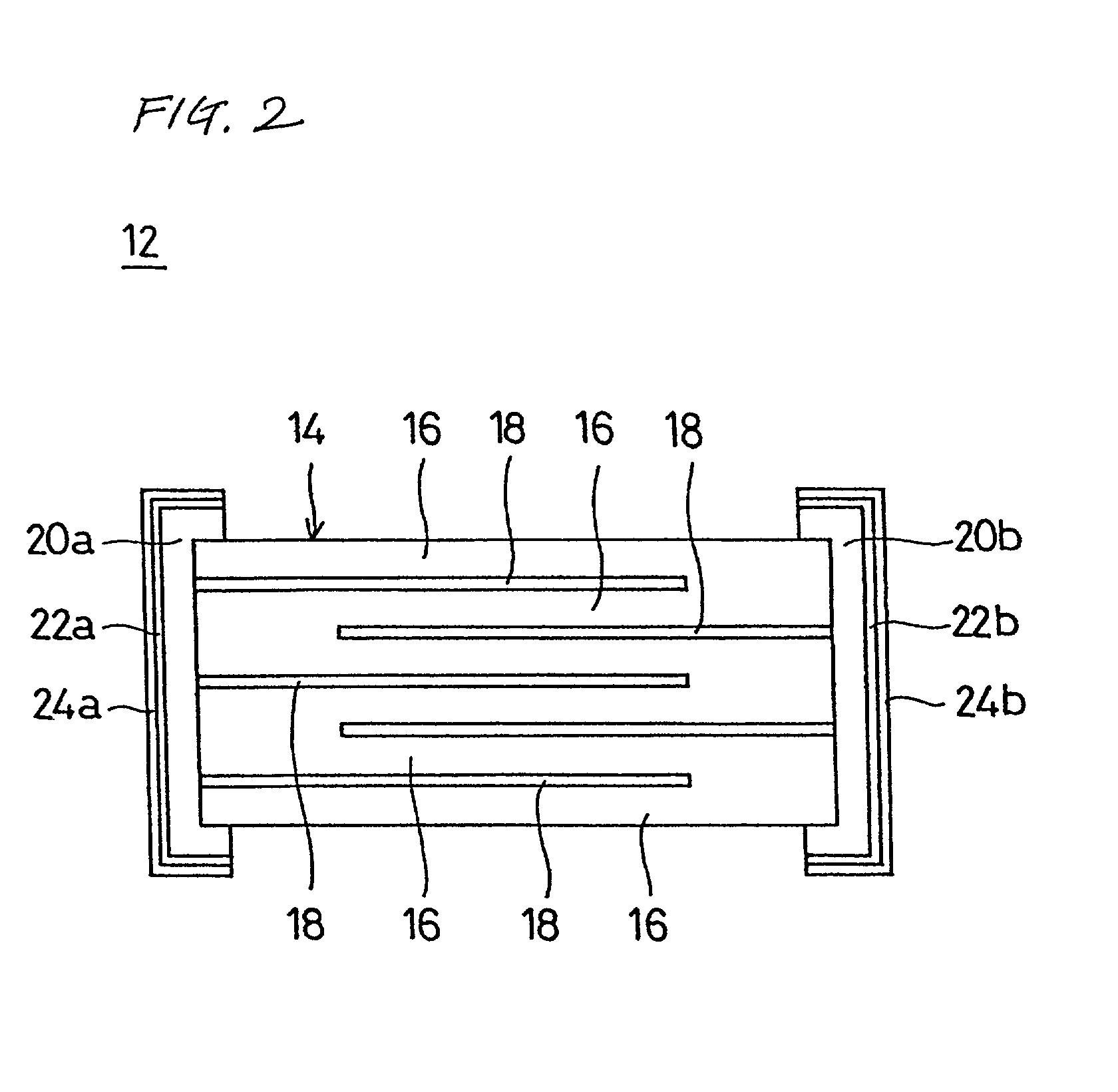
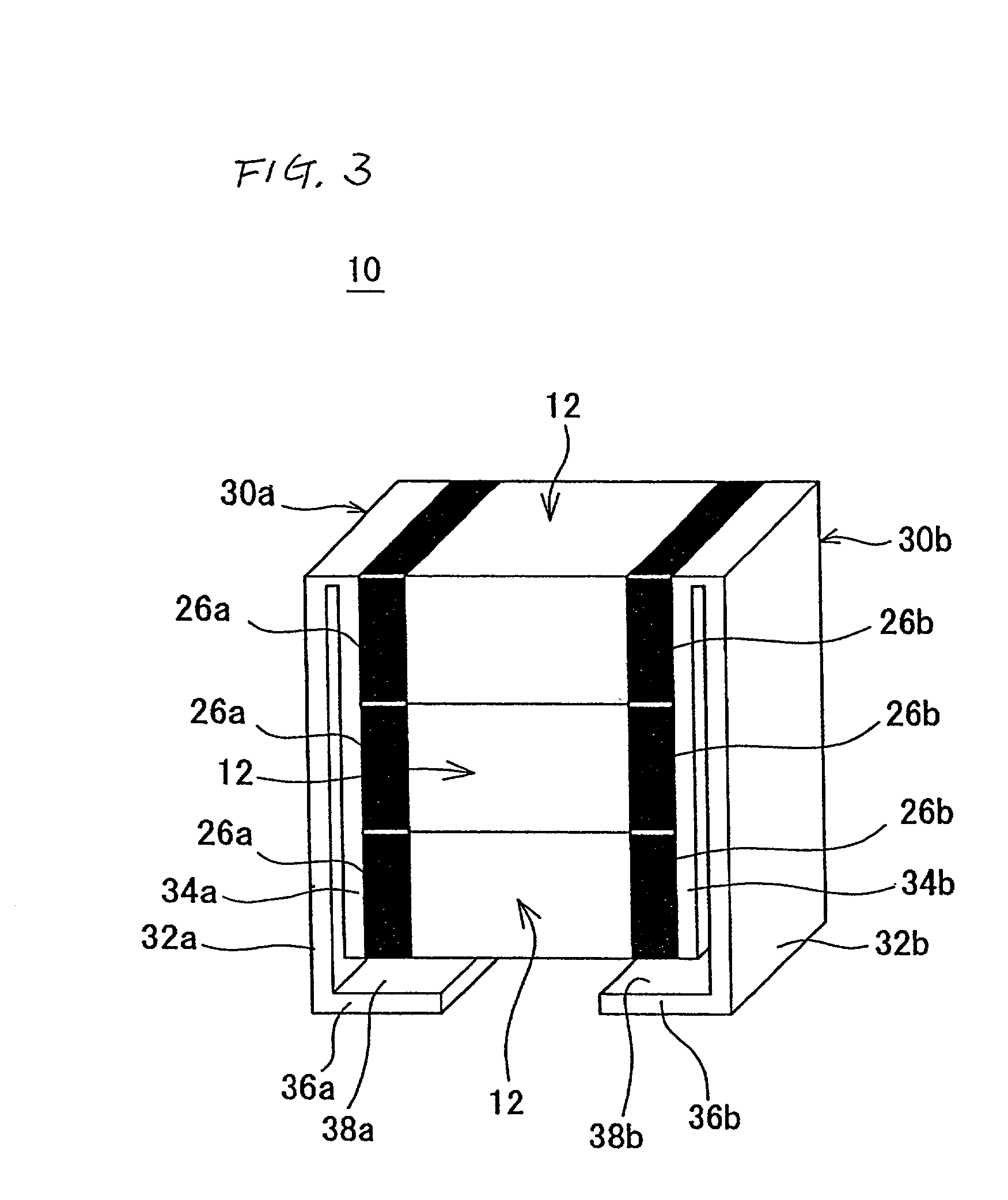
Multilayer ceramic capacitor
InactiveUS20160293331A1Reduce the effective areaReduce capacitanceFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsCapacitanceCeramic capacitor
A multilayer ceramic capacitor includes an element body of roughly rectangular solid shape which is constituted by dielectric layers alternately stacked with internal electrode layers having different polarities, with a pair of cover layers formed on it to cover the top and bottom faces in the direction of lamination of the foregoing, and which has a pair of principal faces, a pair of end faces, and a pair of side faces, wherein external electrodes are formed on the pair of end faces and at least one of the pair of principal faces of the element body, and Tt representing the thickness of the external electrode and Tc representing the thickness of the cover layer satisfy the relationship of Tt≦Tc. The multilayer ceramic capacitor has large capacitance and also exhibits excellent thermal shock resistance while sufficiently suppressing generation of cracks.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
Monolithic capacitor
InactiveUS20010007522A1Improve thermal shock resistancePrinted circuit assemblingMultiple fixed capacitorsCeramic capacitorMaterials science
A monolithic capacitor includes a plurality of monolithic ceramic capacitor elements provided with external electrodes at both ends thereof, solder layers arranged on the entire surfaces of the external electrodes of the monolithic ceramic capacitor elements, and metal terminals electrically connected to the external electrodes of the monolithic ceramic capacitor elements. The monolithic ceramic capacitor elements are joined to each other by the solder layers and are stacked on each other. The external electrodes of the monolithic ceramic capacitor elements are electrically connected to each other by the solder layers.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Nanoclay modified waterborne compositions for coating plastic and methods for making the same
InactiveUS20050059765A1Improve thermal shock resistanceMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresWater dispersibleWater insoluble
The present invention provides aqueous dispersion compositions comprising one or more than one of each of aqueous dispersions of water-dispersible polymers and aqueous nanocomposite dispersions of at least partially exfoliated layered silicates and water-insoluble polymers to enhance the thermal shock resistance of a waterborne coating, film, or article comprising the composition. Only 2 to 10 phr of the layered silicate, e.g. sodium montmorillonite surprisingly enhances thermal shock resistance. Optional fillers, such as nepheline syenite, may be added. Such compositions may be coated on automotive plastic, TPO or resinous substrates, and provide coatings having a 19 or greater thermal shock resistance according to Ford laboratory test method BI 107-05 when coated on TPO and baked for 15 minutes at from 74 to 90° C. Further, the present invention provides methods of making aqueous nanocomposite dispersions comprising mixing unmodified layered silicate and water insoluble neat resin in water to at least partially exfoliate the clay and subjecting the resulting mixture to high shear.
Owner:NIPPON PAINT USA
High-temperature far infrared paint and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN1552779AImprove adhesion strengthImprove thermal shock resistanceCellulose derivative coatingsFire clayBrown iron oxide
A refractory far infrared paint is prepared from zirconium oxide, Cr2O3, refractory clay, bentonite, TiO2 powder, brown corundum, iron oxide, silicon carbide, adhesive PA80 or water glass and carboxymethyl cellulose through proportional mixing, and nano-class superfine processing. Its advantage is high emissivity (0.93) at high temp.
Owner:山东慧敏科技开发有限公司
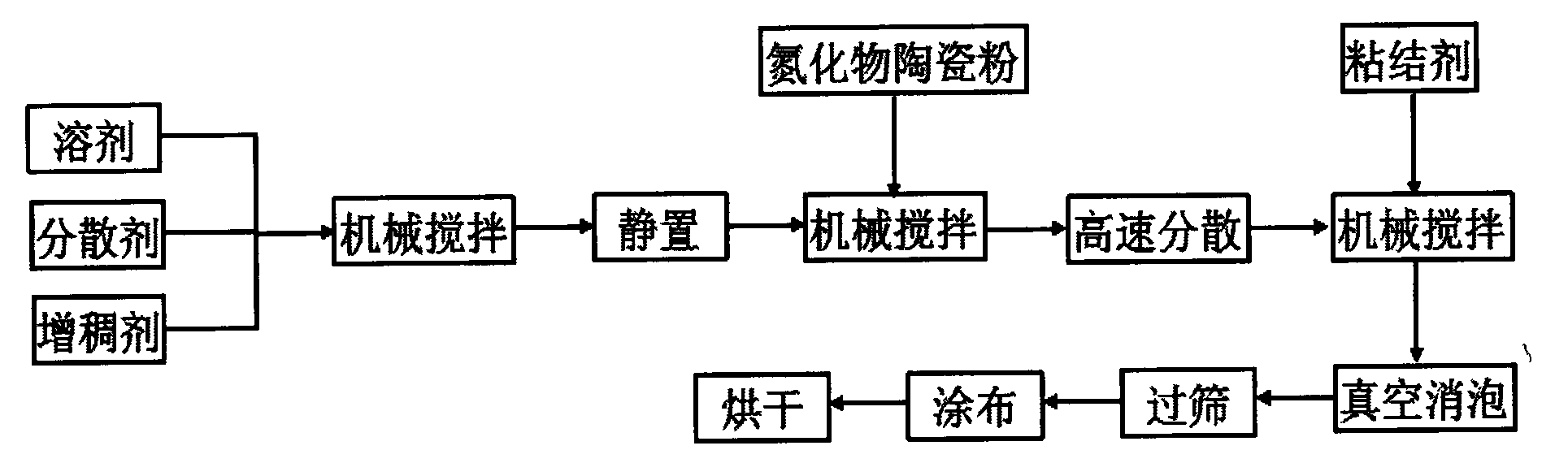
Method for preparing nitride ceramic coating applied to lithium ion battery
InactiveCN103647034AImproves liquid absorption and retentionImproved hydrofluoric acid resistance and thermal shock resistanceNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesCell component detailsSolventCeramic particle
The invention discloses a nitride ceramic coating applied to a lithium ion battery. The nitride ceramic coating consists of the following components in parts by weight: 2-10 parts of adhesive, 10-40 parts of nitride ceramic particles, 0.5-3 parts of thickening agent, 0.05-2 percent of dispersing agent and the balance of solvent. The nitride ceramic coating is prepared by the following steps: (1) preparing slurry, namely uniformly mixing and stirring the solvent, the dispersing agent and the thickening agent, standing, defoaming, adding the nitride ceramic particles, uniformly dispersing and forming slurry A; (2) dispersing at high speed, namely dispersing the slurry A at high speed, then adding the additive, uniformly stirring, performing vacuum defoaming, and screening to form slurry B; (3) coating, namely coating the slurry B on an edge of the anode and / or the surface of the cathode and / or a diaphragm in the lithium ion battery, and drying at the temperature of 60-120 DEG C. According to the nitride ceramic coating, the liquid absorption capacity and liquid retaining capacity of the diaphragm or the pole piece can be effectively improved, the hydrofluoric acid resistance and thermal shock resistance of the pole piece or the diaphragm are improved, and a better heat barrier effect is achieved.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
Dedicated pouring material for cement kiln outlet and jetting coal pipe and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101445379AImprove thermal shock performanceGood alkali resistanceCarbide siliconCement factory
The invention discloses a dedicated pouring material for a cement kiln outlet and a jetting coal pipe, which comprises the following components by the weight percentage: 20 to 30 percent of sintered plate-shaped corundum, 20 to 30 percent of sintered and synthesized mullite, 10 to 15 percent of chrome corundum, 5 to 10 percent of silicon carbide, 3 to 5 percent of silicon carbide superfine powder, 3 to 5 percent of magnesia alumina spinel, 5 to 8 percent of zircon sand, 2 to 5 percent of activated Al2O3 micro powder, 2 to 5 percent of silicon micro powder, 3 to 5 percent of pure calcium aluminate cement, 1 to 2 percent of stainless steel fiber, 5 to 10 percent of synthesized zirconium mullite grinding powder, 0.1 to 0.15 percent of composite additives and 0.01 to 0.1 percent of explosion proof fiber. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the pouring material. The pouring material is applicable to the dry-process cement kiln outlets and the jetting coal pipes in large-scale cement plants and has the advantages of high wear resistance, good anti-stripping resistance and long service life.
Owner:JIANGSU GUOHAO REFRACTORY TECH
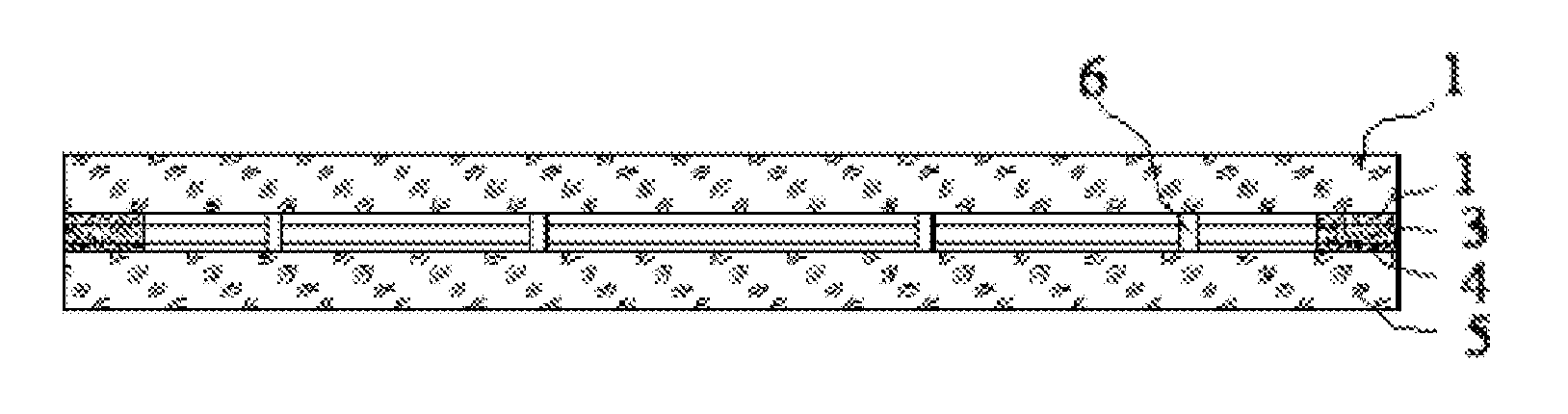
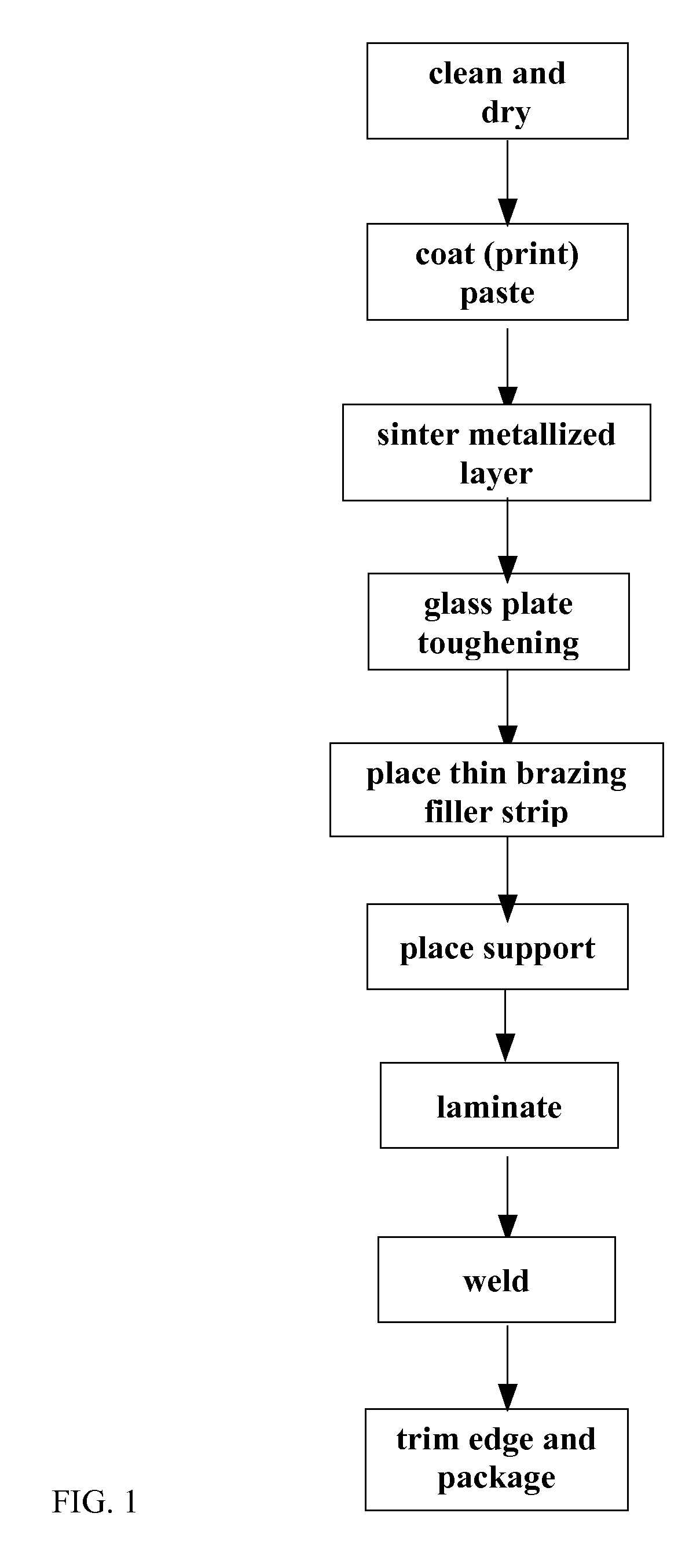
Compound Sealing Method for Vacuum Glass
ActiveUS20120321822A1Excellent brazeabilityPrevent annealingClimate change adaptationSoldering apparatusThermal shockBrazing
The invention relates to a compound sealing method for glass plates, which is characterized by realizing the air-tight joint between compounded glass plates in a preset position by using a metal brazing technology. The invention provides a brand new technological method for the compound sealing between glass plates. The method has the advantages of firm connection in sealing positions, high air tightness, favorable thermal shock resistance and the like, and the annealing of toughened glass are avoided because of a lower brazing temperature used, thereby providing convenience to the processing of toughened vacuum glass, toughened insulated glass and other toughened compound glass products
Owner:LUOYANG LANDGLASS TECH CO LTD
High temperature resistant ceramic matrix composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an ultra-high temperature resistant ceramic-based composite and a preparation method, which adopts carbon or boron nitride fabric cloth as reinforcing phases, ceramic powders of high melting point or high-temperature resistant metal powders as the stuffing, and carbon / silicon carbide as the base. Through the blending and ball milling of the adhesives and the powder stuffing, the sizing agent thus acquired is coated on the reinforcing phase fabric cloth, and then overlapping, molding, cross-bonding, high-temperature pyrolysis, and repeated densification are carried out in preparing the composite. The ultra-high temperature resistant ceramic composite has the advantages of excellent thermal shock resistance, low density, and low ablating rate under ultra-high temperature.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Combustion chamber wall construction for high power engines and thrust nozzles
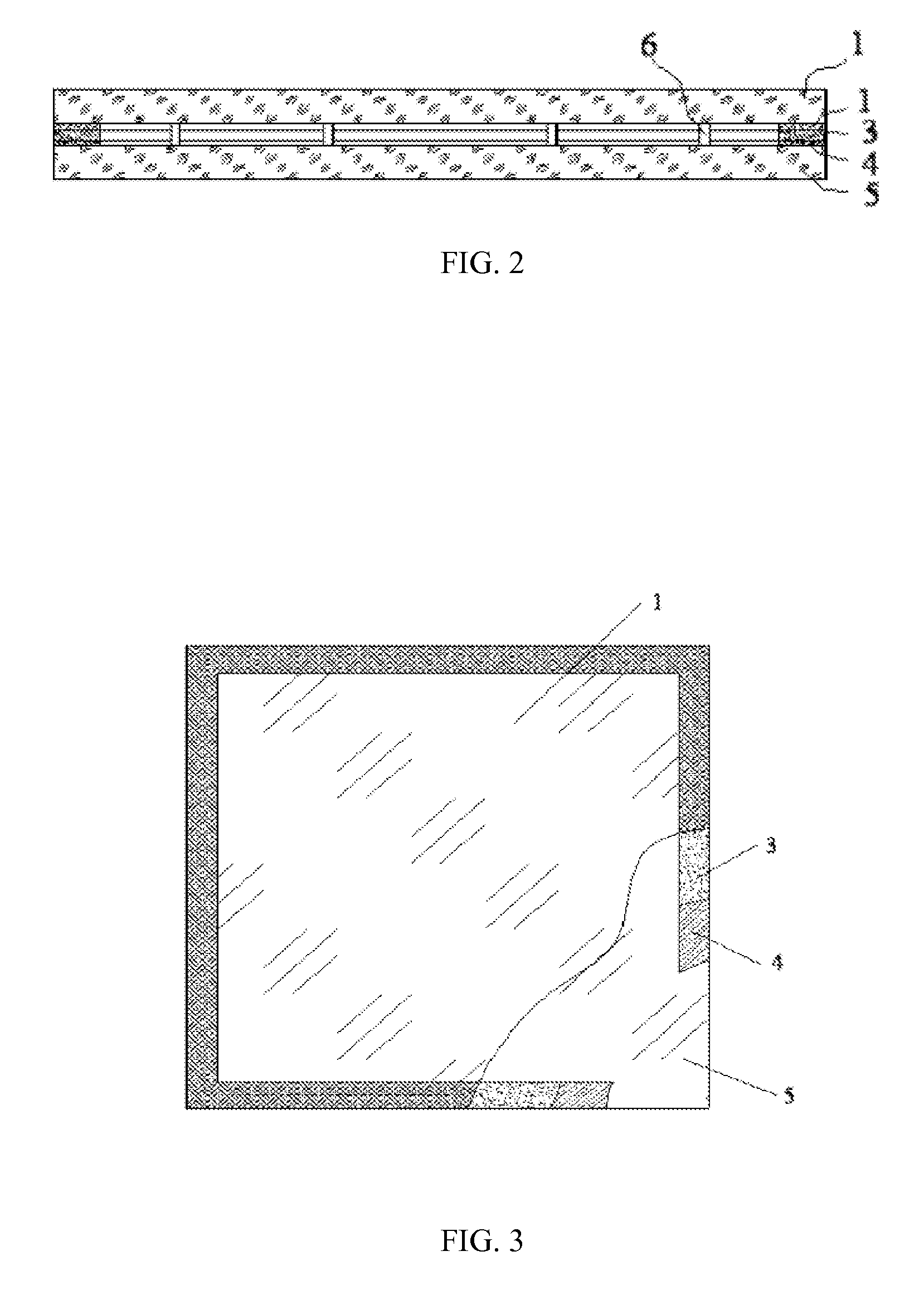
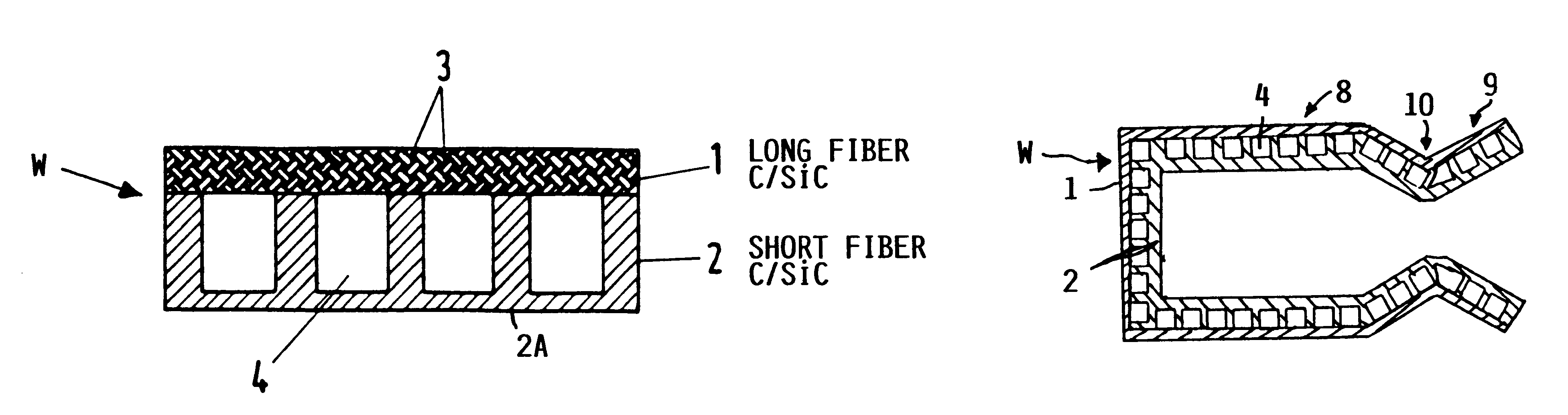
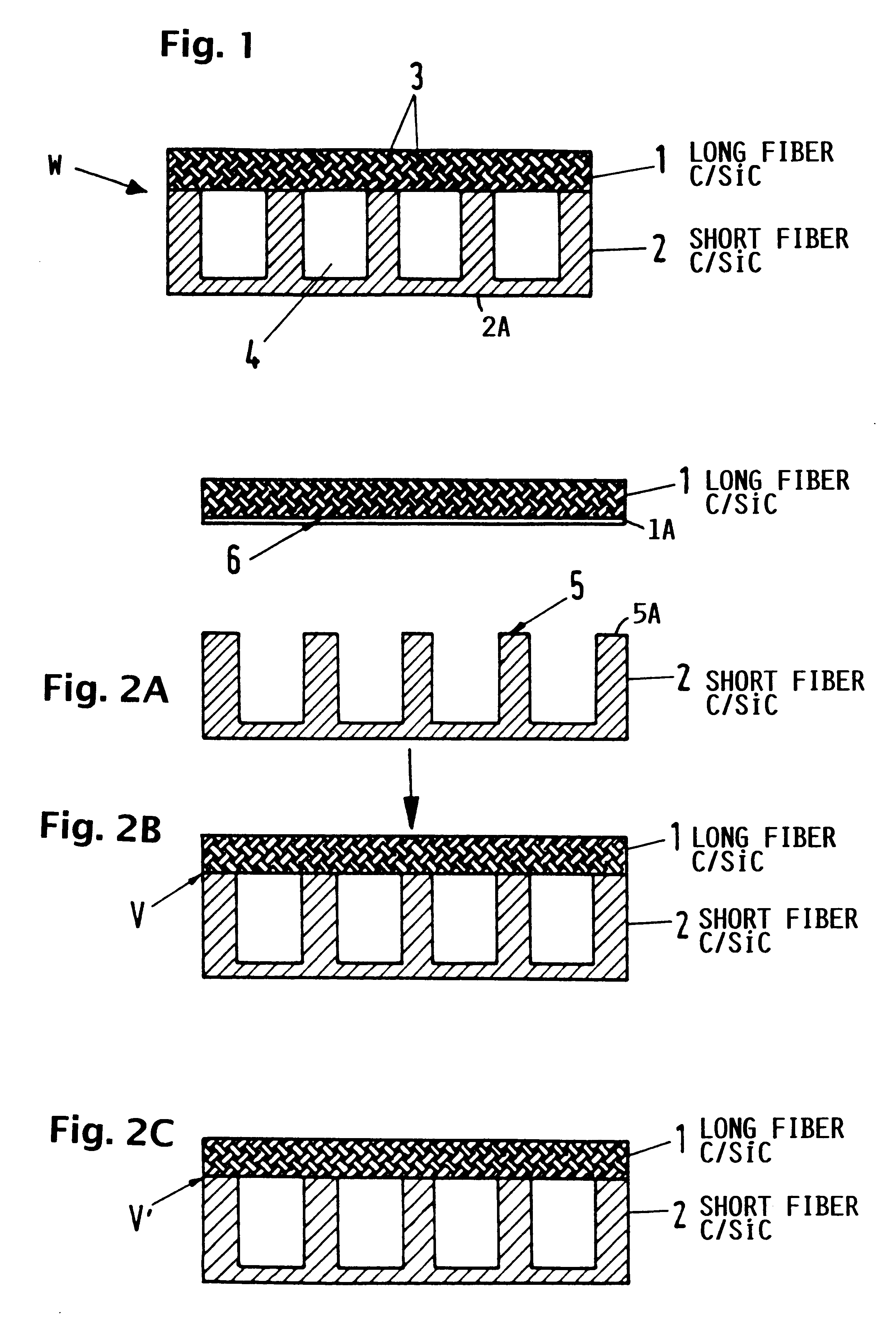
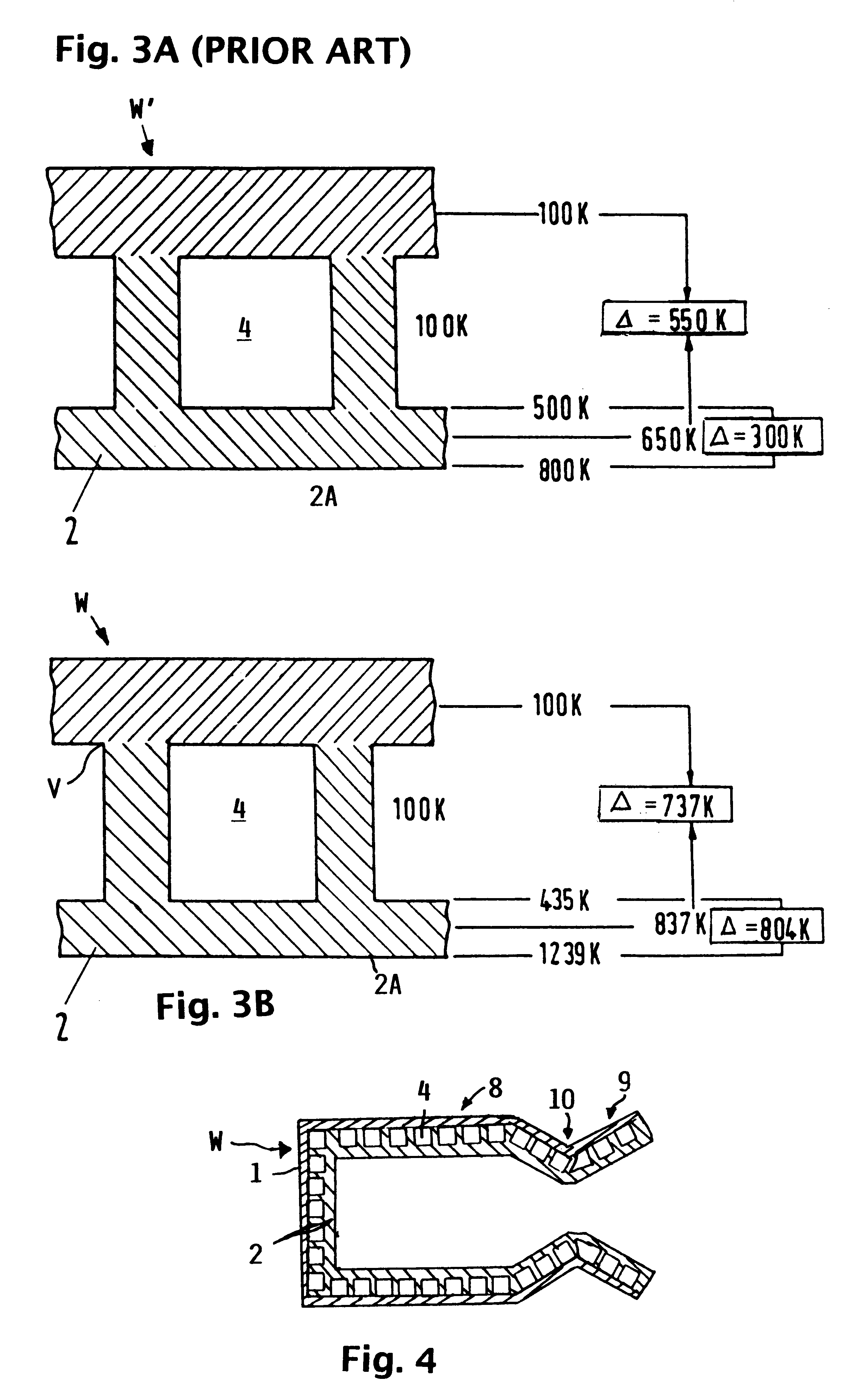
InactiveUS6182442B1Long lastingReduce quality problemsContinuous combustion chamberPower plant exhaust arrangementsFiberCombustion chamber
A wall construction for a combustion chamber or thrust nozzle of a high power engine of a flying body includes an inner wall body that is subjected to the hot gases within the combustion chamber, and an outer jacket that surrounds the inner wall body and carries the mechanical loads. The inner wall body has a plurality of cooling channels through which a cooling medium may flow. The outer jacket is made of a long-fiber C / SiC composite material, while the inner wall member is made of a short fiber C / SiC composite material. The reduced thermal expansion coefficient of this ceramic composite material in comparison to metal alloys leads to a reduced straining and reduced deformation of the wall construction and therewith an increased operating life.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Abrasion resistant ceramic coating
The invention discloses a brushing-proof abrasion-proof and erosion-proof ceramic paint, which is characterized by the following: selecting at least one of electric-melting brown corundum, electric-melting subwhite corundum, electric-melting white corundum, carborundum and electric melting mullite with different grain sizes as main material and at least one of compact corundum, electric-melting subwhite corundum, electric-melting white corundum, carborundum, silicon nitride and boron nitride as auxiliary material; using CA50 calcium aluminate cement or pure calcium aluminate cement as binder and nanometer micro-silica powder and active alpha-Al2O3 micropowder as reinforcer; making hyperdrying active high-effective dehydragent, sodium citrate and sodium hexametaphosphate as composite additive; loading in the strength stirrer to stir 12-17min; blending evenly; packing.
Owner:CHONGQING LUOMAN NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Fast ceramic flame-resistant cable and its production method
ActiveCN101404189ASimple processEasy constructionPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesCeramicSurface finishing
The invention discloses a quickly vitrified fireproof cable material and a preparation method thereof. According to the weight parts, the raw material of the ceramic fireproof cable material comprises 60-70 of ethane-vinyl acetate copolymer, 30-40 of polyethylene, 50-100 of ceramic filler, 0.5-2.5 of coupling agent, 80-100 of flame retardant A, 10-20 of flame retardant B, 1-2 of lubricant and 1-3 of antioxidant. The preparation process of the cable material comprises the steps as follows: surface disposing of the ceramic filler, compounding, mixing, granulating, drying and the like. The fireproof cable material is polymer-based composite material and has the same behaviors (namely excellent processability and convenient construction) with normal extrusion cable insulation material under normal environment, and can be vitrified within 10 minutes under the temperature of 750 DEG C or higher; the ceramics can ensure that the normal running time of the line under the temperature of 750-950 DEG C for more than 90min.
Owner:LUOYANG ZHONGCHAO NEW MATERIAL SHARES CO LTD
Open-celled silicon carbide foam ceramic and method for production thereof
InactiveUS6887809B1Improve thermal shock resistanceHigh strengthSolar heating energySolar heat devicesThermal shockCeramic
The invention relates to the field of ceramics and open-celled silicon carbide foam ceramics, which can find application, for example, as high temperature- and thermal shock-resistant silicon carbide foam. The aim of the invention is to disclose an open-celled silicon carbide foam ceramic with improved thermal shock resistance, which may be produced by a simple method. Said aim is achieved with an open-celled silicon carbide foam ceramic, the structure of which is made up of sintered silicon carbide with a 5 to 30% pore volume of closed pores with an average diameter of <20 μm. The invention further relates to a method for the production of an open-celled silicon carbide foam ceramic, whereby coarse and fine silicon carbide powder in the ratio 20:80 to 80:20 parts are mixed and a suspension produced therefrom. An open-celled foam or open-celled network is then coated with said suspension, the foam or network material removed and sintering carried out at a temperature of >1800° C. under a protective atmosphere or in vacuo.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Copper based sintered contact material and double-layered sintered contact member
With the objectives of alleviating the property of attacking on the mating member by scratching-off of local agglutinates on the sliding contact surface, achieving improved wear resistance, and achieving improved seizure resistance through restraint of frictional heat generation by a hard phase, a copper based sintered contact material contains shock-resistant ceramics in an amount of 0.05 to less than 0.5 wt % as non-metallic particles composed of one or more substances selected from pulverized oxides, carbides and nitrides. The shock-resistant ceramics are comprised of SiO2 and / or two or more substances selected from SiO2, Al2O3, LiO2, TiO2 and MgO.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Organic PTC thermistor
InactiveUS6607679B2Improve reliabilityImprove stabilityPrimary cell maintainance/servicingConductive materialThermoplastic elastomerThermistor
In an organic PTC thermistor comprising a matrix of at least two high-molecular weight compounds, a low-molecular weight organic compound, and conductive particles having spiky protuberances, a thermoplastic elastomer is contained in the matrix whereby the thermistor is improved in reliability and performance stability.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
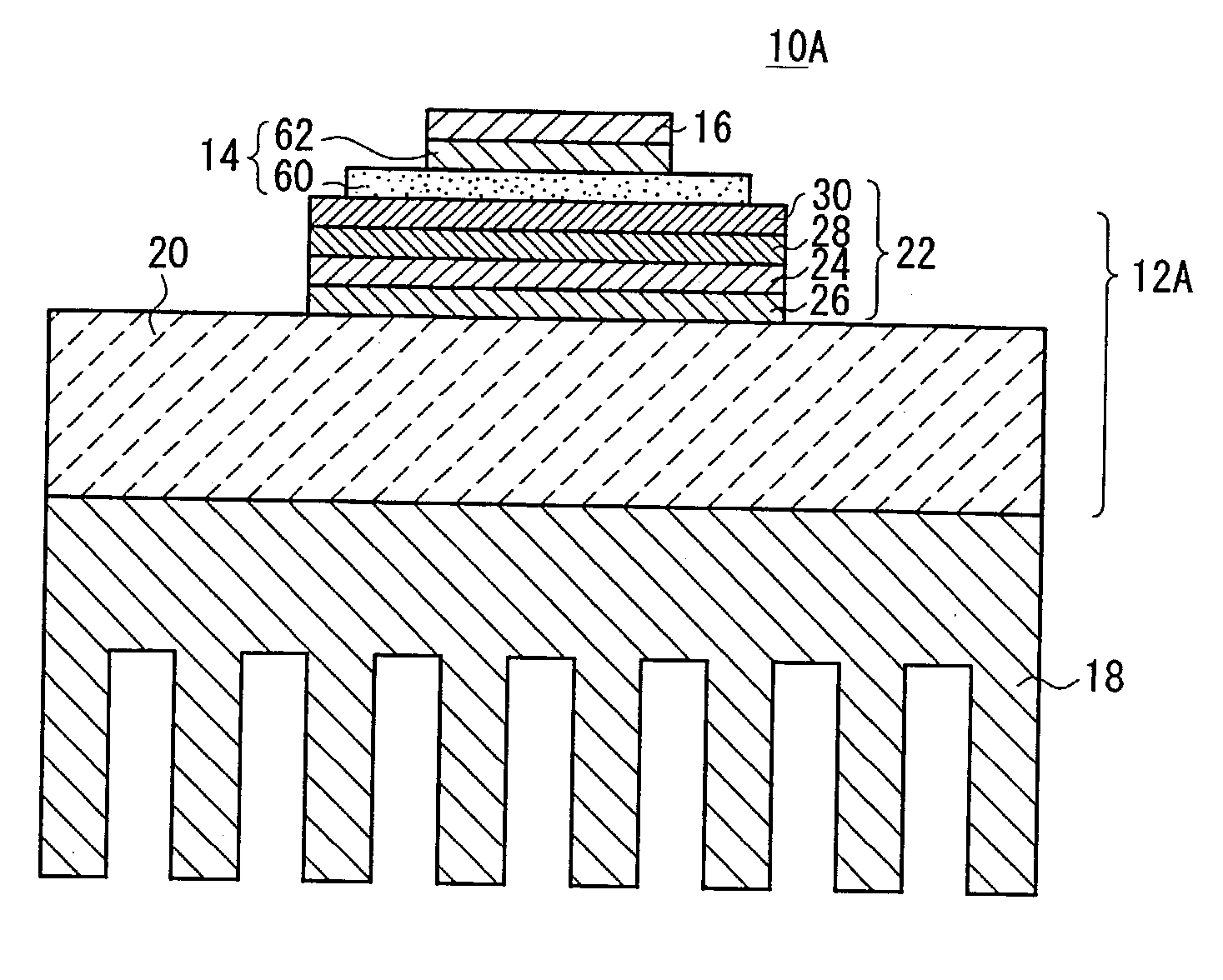
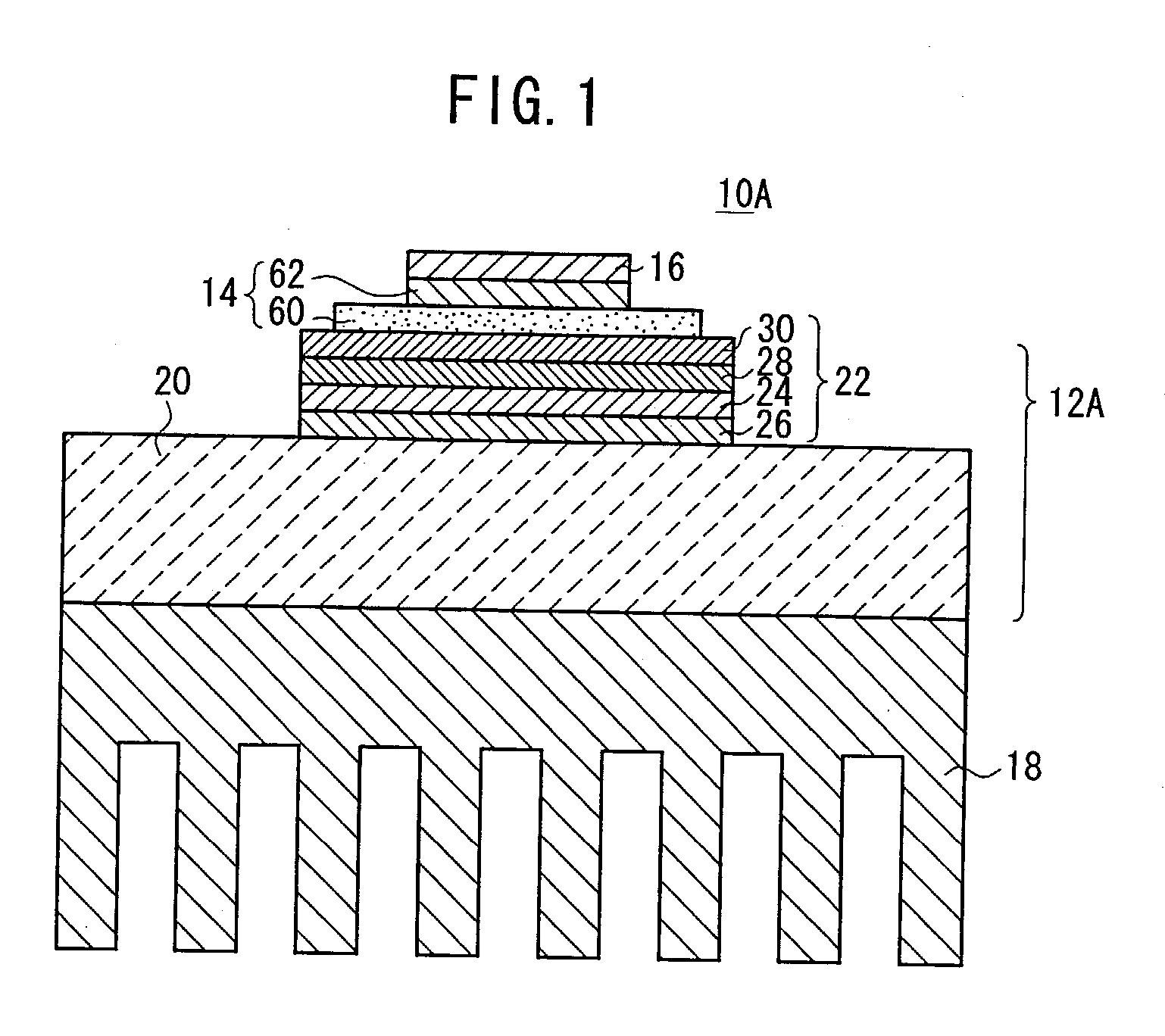
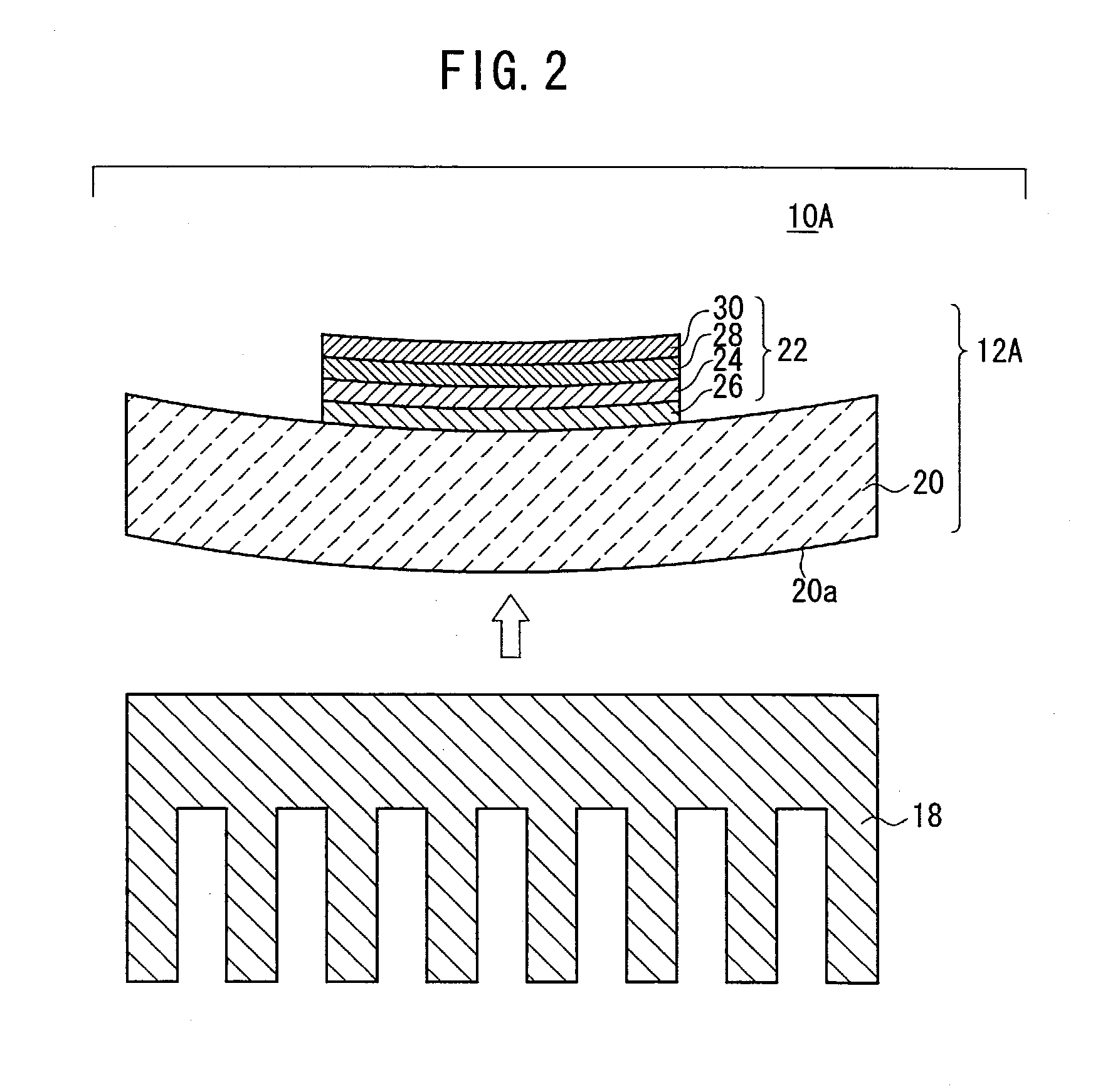
Member for electronic circuit, method for manufacturing the member, and electronic part
InactiveUS20030102553A1Reduce manufacturing stepsReduce manufacturing costInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsJoint componentEngineering
A member (12A) for use in an electronic circuit has a thermally conductive layer (22) mounted on a heat sink (20). The thermally conductive layer (22) comprises an insulating substrate (24), a first joint member (26) joining the insulating substrate (24) to the heat sink (20) and containing an active element, a second joint member (28) disposed on the insulating substrate (24), and an electrode (30) disposed on the second joint member (28). The insulating substrate (24) comprises an AlN layer or an Si3N4 layer. Each of the first and second joint members (26, 28) is made of a hard brazing material containing an active element. The heat sink (20) is made of an SiC / Cu composite material or a C / Cu composite material.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Method of laser induction composite cladding gradient function thermal barrier coating
InactiveCN101748402AImprove cladding efficiencyImprove thermal shock resistanceMetallic material coating processesNumerical controlLaser scanning
The invention discloses a method of a laser induction composite cladding gradient function thermal barrier coating, which is characterized in that the methods and steps are as follows: (1) the surface of base material is provided with processing of rust removing, oil removing, cleaning and sand spraying; (2) meanwhile, the inert protective gas is blown into an induction heating zone through utilizing a copper pipe, which prevents the high-temperature oxidation; (3) a focused laser beam and a powder nozzle of an automatic double-hopper powder feeder are located in the induction heating zone, and the composition of the laser heat source and the induction heating source can be realized; (4) a numerical control machine is moved 70-30% of the laser spot diameter along the vertical direction of the laser scanning speed; (5) the mass percentage content of a ceramic phase in the composite powder is led to be increased by 0-90 wt.%; (6) steps (2)-(5) are repeated until the required thickness of the coating is achieved; otherwise, the work is ended. The advantages of the invention are as follows: (1) the size, the shape and the part needing to process of the base material are not limited; (2) for the gradient function thermal barrier coating, the content of the ceramic phase in the coating presents change of gradient and is controllable along the thickness direction of the coating; (3) the whole gradient function thermal barrier coating has no air hole and crack; (4) the service life is greatly increased.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Device and method for controlling glass-board thickness evenness
InactiveCN101028964AControl the degree of heat transferHigh blacknessGlass forming apparatusThermal energyBrick
An apparatus for controlling the thickness uniformity of glass plate is composed of supporting frame, the upper, lower, left and right insulating refractory brick layers for enclosing whole apparatus, and two closed cavities containing at least one fluid tube and arranged at both sides of glass plate for collecting the heat to heat the fused glass in irradiation mode. Its method features that the distance between said apparatus and fused glass and the relative position between fused glass and heating element are regulated for controlling the temp of fused glass.
Owner:HENAN ANCAI HI-TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com