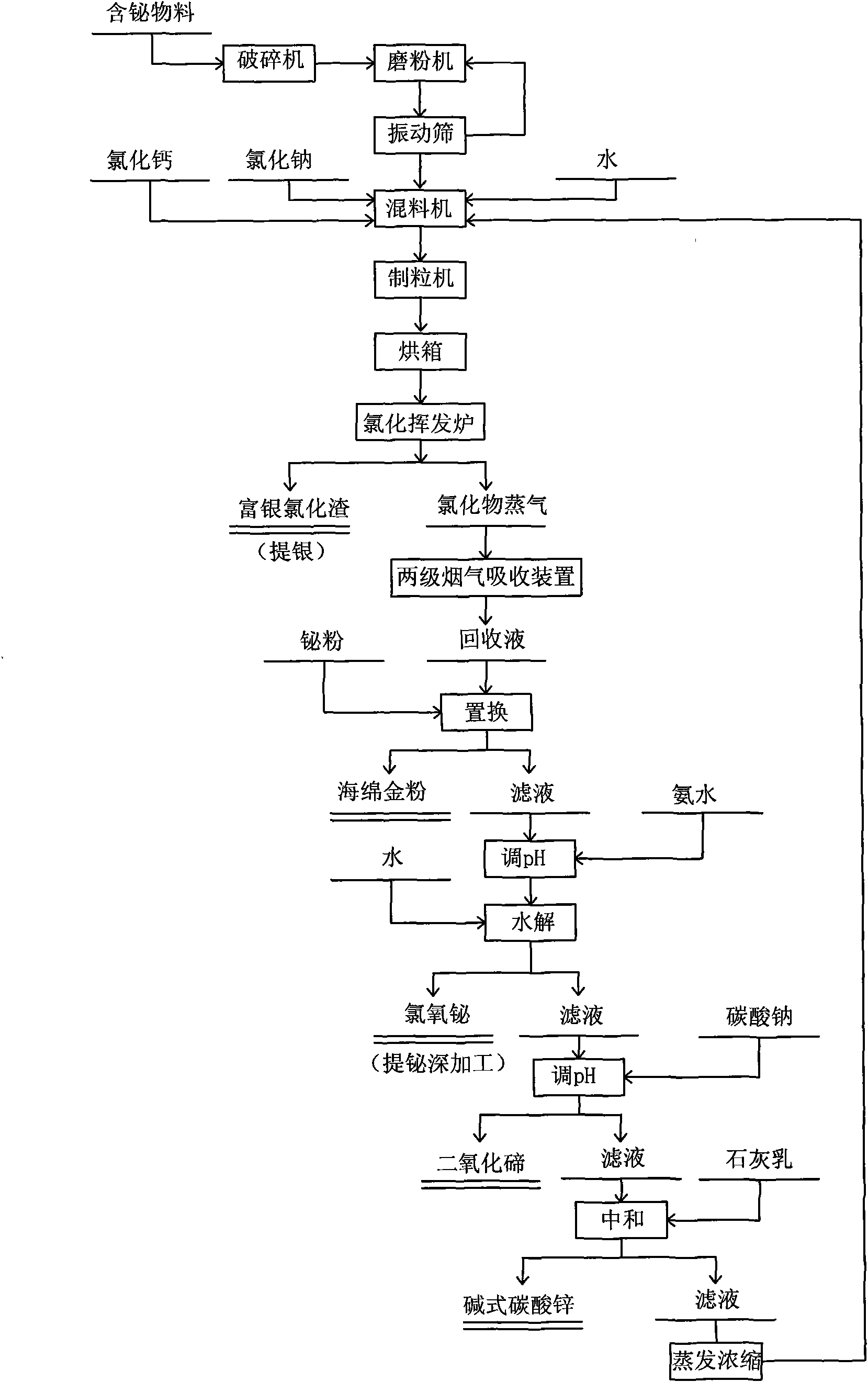
Process for recovering valuable metals in bismuth-containing material by selective chloride volatilizing method
A technology for chlorinated volatilization and valuable metals, applied in the field of non-ferrous metallurgy, can solve the problems of long process flow and lack of universal applicability, and achieve the effects of short process flow, accelerated capital turnover and low requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The materials used in this embodiment are mainly industrial grade anhydrous calcium chloride, common salt, soda ash, bismuth powder and silver-zinc slag.
[0021] The multi-element test results of silver-zinc slag are shown in Table 1.
[0022] Table 1
[0023] the element
Bi
Zn
Fe
Pb
Te
Cl
Au g / t
Ag g / t
Content%
55.34
7.69
0.22
0.10
0.16
1.15
11.8
2778
[0024] In view of the properties and characteristics of the above-mentioned silver-zinc slag, this embodiment studies the effects of the type of chlorinating agent, roasting atmosphere, roasting temperature, and roasting time on the volatilization rate of valuable metals. Precipitating zinc with zinc and milk of lime is a relatively mature process, and the work in this example mainly focuses on the selective chlorination of volatile parts.
[0025] The main equipment used in this embodiment is shown in Table 2.
...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The batching ratio of the process step ② of the present embodiment is according to: bismuth-containing powder / calcium chloride / sodium chloride / water or return concentrated solution=100 / 3 / 8 / 7; the rest are the same as in embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0038] The batching ratio of the process step ② of the present embodiment is according to: bismuth-containing powder / calcium chloride / sodium chloride / water or return concentrated solution=100 / 6 / 5 / 9; the rest are the same as in embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com