Method for recovering tellurium from bismuth telluride base semiconductor refrigeration material
A bismuth telluride-based, semiconductor technology, applied in the field of tellurium recovery, can solve the problems of poor applicability and low recovery rate, and achieve the effects of strong applicability, high recovery rate, and easy scale-up
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
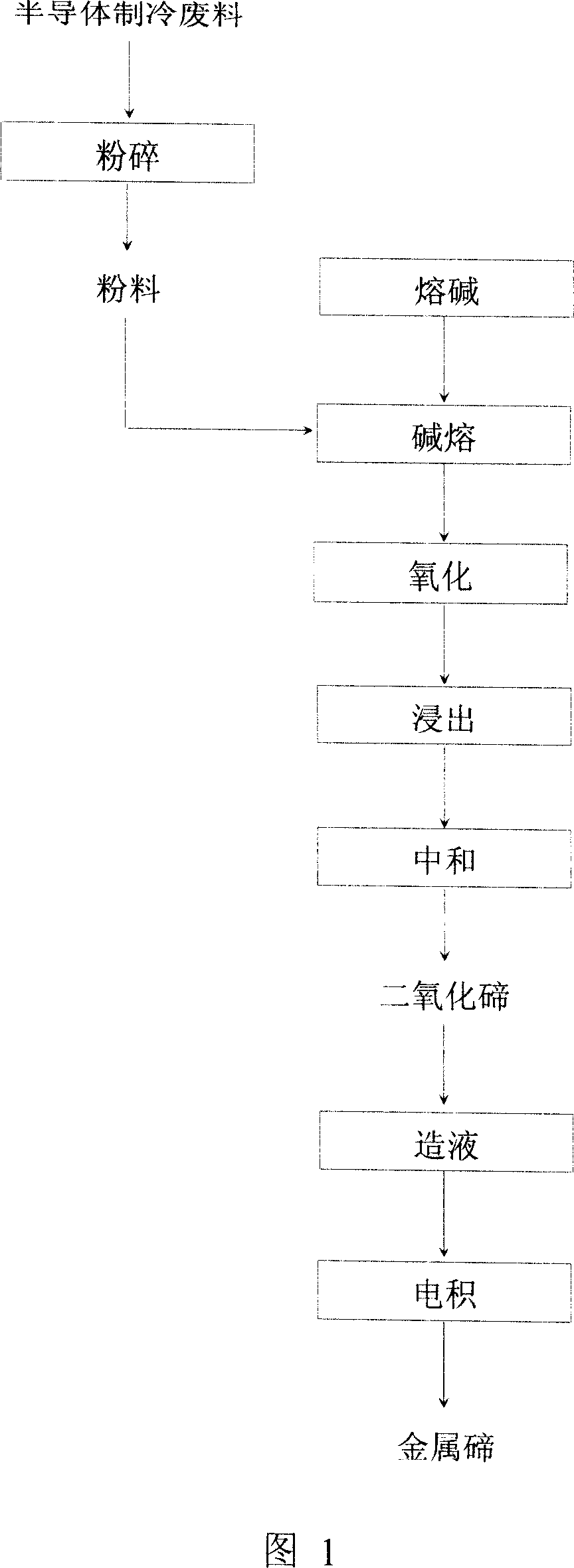
[0021] 100 g of P-type semiconductor refrigeration waste, with a tellurium mass content of 51%, was ball-milled to 0.15 mm for use. Add a mixture of 48g sodium hydroxide and 48g sodium carbonate to the crucible, melt to 650°C; add powdery materials, stir evenly, and alkali-melt for 0.5h; add 20g potassium nitrate in batches, stir the melt, and keep warm for 1h; take out the yellow matter Broken to 0.20mm; leaching with hot water at 95°C, the liquid-solid ratio of the first leaching is 6:1, the second leaching liquid-solid ratio is 3:1, and the time is 1.5h; neutralize the leachate with 3mol / L hydrochloric acid, the temperature is 50°C, The pH at the end of the reaction was controlled to be 6.0, and 55.55 g of white tellurium dioxide with a purity of 99.9% was obtained; the tellurium dioxide was dissolved with dilute lye to obtain a sodium tellurite solution, and electrowinning finally obtained 44.4 g of tellurium metal with a purity of 99.99%. The recovery rate of tellurium wa...
Embodiment 2
[0023] 150g of N-type semiconductor refrigeration bar stock, with a mass content of tellurium of 48%, was ball milled to 0.20mm for later use. Add a mixture of 131.3g sodium hydroxide and 56.2g sodium carbonate to the crucible, melt to 640°C; add powdery materials, stir evenly, and alkali-melt for 1 hour; add 37.5g sodium nitrate in batches, stir the melt, and keep warm for 1.5 hours; Take out the yellow matter and break it to 0.15mm; leaching with hot water at 90°C, liquid-solid ratio 4:1, time 1.5h; 3.6mol / L sulfuric acid to neutralize the leachate, temperature 70°C, control the reaction end pH to 6.0, 81.16g purity It is 99.8% white tellurium dioxide; dissolving tellurium dioxide with dilute lye to obtain sodium tellurite solution, and electrowinning to finally obtain 64.8g of metal tellurium with a purity of 99.97%, and the recovery rate of tellurium is 90.00%.
Embodiment 3
[0025] 120g of mixed semiconductor refrigeration waste, with a mass content of tellurium of 49%, was ball milled to 0.125mm for later use. Add 96g of sodium hydroxide to the crucible and melt to 660°C; add powdery materials, stir evenly, and alkali-melt for 0.5h; add 24g of sodium nitrate in batches, stir the melt, and keep warm for 2h; take out the yellow matter and break it to 0.20mm; Hot water leaching at 95°C, liquid-solid ratio 6:1, time 1.5h; 3mol / L hydrochloric acid to neutralize the leachate, temperature 50°C, control the pH of the reaction end point to 6.0, and obtain 67.05g of white tellurium dioxide with a purity of 99.8%; Tellurium dioxide was dissolved in dilute lye to obtain sodium tellurite solution, and electrowinning was performed to finally obtain 53.5 g of metallic tellurium with a purity of 99.99%, and the recovery rate of tellurium was 90.98%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com