Genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and acidogenic fermentation method thereof
A genetically engineered bacteria, a technology for producing succinic acid, applied in the field of bioengineering to achieve the effect of enhancing the range of adaptation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] This example illustrates the use of homologous recombination technology to knock out phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in the starting strain NZN111 ppc gene, resulting in the elimination of apramycin-resistant strains.
[0039] 1. Using LB medium, cultivate Escherichia coli NZN111 to OD at 37°C under aerobic conditions 600 =0.4~0.6, prepared to be electrotransfer competent.
[0040] 2. Electrotransform plasmid pKD46 into competent Escherichia coli NZN111. The electric shock conditions were: 200 Ω, 25 μF, electric shock voltage 2.3 kV, electric shock time 4-5 ms. Immediately after the electric shock, the cells were added to pre-cooled 1 mL SOC medium, cultured at 150 r / min, 30°C for 1 h, and then spread on the LB medium plate with ampicillin (amp) to screen the positive transformant Escherichia coli NZN111 ( pKD46).
[0041] 3. Add 10 mM L-arabinose to LB medium, induce plasmid pKD46 to express λ recombinase at 30°C, and make electroporation competent.
[0042] 4. U...
Embodiment 2
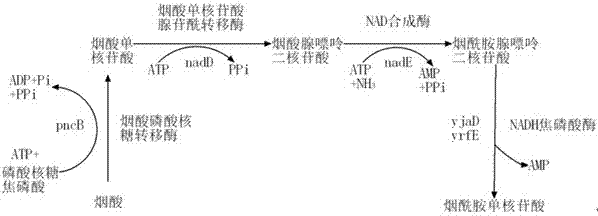
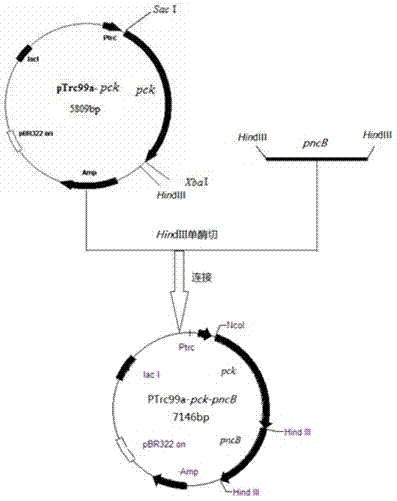
[0053] This example illustrates the construction of an expression plasmid that overexpresses phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase, restores the ability of the recombinant strain to metabolize glucose under anaerobic conditions, and obtains a strain Escherichia coli Methods of BA205.
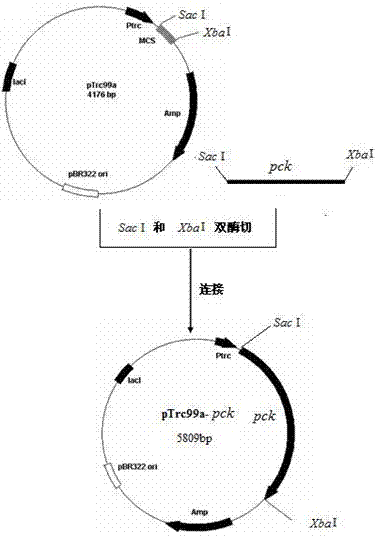
[0054] 1. Construct pTrc99a- pck Plasmids, the process of which involves:
[0055] (1) synthetic with Sac I and Xba Primers for I restriction sites,
[0056] Upstream primer: 5'-CGAGCTCATGAACTCAGTTGATTTGACCG-3'.
[0057] Downstream primer: 5'-GCTCTAGAGCATTCCGTCAATTAAAACAAG -3'.
[0058] (2) with Bacillus subtilis Genomic DNA was used as a template, and the target gene fragment was amplified by PCR. The reaction conditions were: 94°C for 5 min; (94°C for 45 s, 53°C for 45 s, 72°C for 100 s, 35 cycles); 72°C for 10 min. purified amplified pck After the gene, the expression plasmid was used respectively with pTrc99a Sac I and Xba I double...
Embodiment 3
[0066] This example illustrates the co-expression of a newly constructed recombinant E. coli strain Escherichia coli BA205 and the total amount of NAD (H) and NADH / NAD of the apramycin-resistant strain obtained in BA205 and Example 1 + The comparison of the ratio, and the comparison of the sugar consumption and acid production capacity during the fermentation process of the two.
[0067]When the plasmid pTrc99a- pck - pncB Finally, eliminating the overexpression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase in the apramycin-resistant strain restored the redox balance of the recombinant bacteria under anaerobic conditions, and the total amount of NAD(H) was Significantly improved, and also restored the ability to metabolize glucose under anaerobic conditions, while the main product is succinic acid, without the accumulation of formic acid and lactic acid.
[0068] Escherichia coli BA205 was inoculated into the aerobic stage fermentatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com