Method and kit for determining nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase (Nampt) activity
An active, transferase technology, applied in the field of chemistry, which can solve problems such as the inability to achieve high-throughput operations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] The establishment and optimization of embodiment 1 enzyme activity detection method
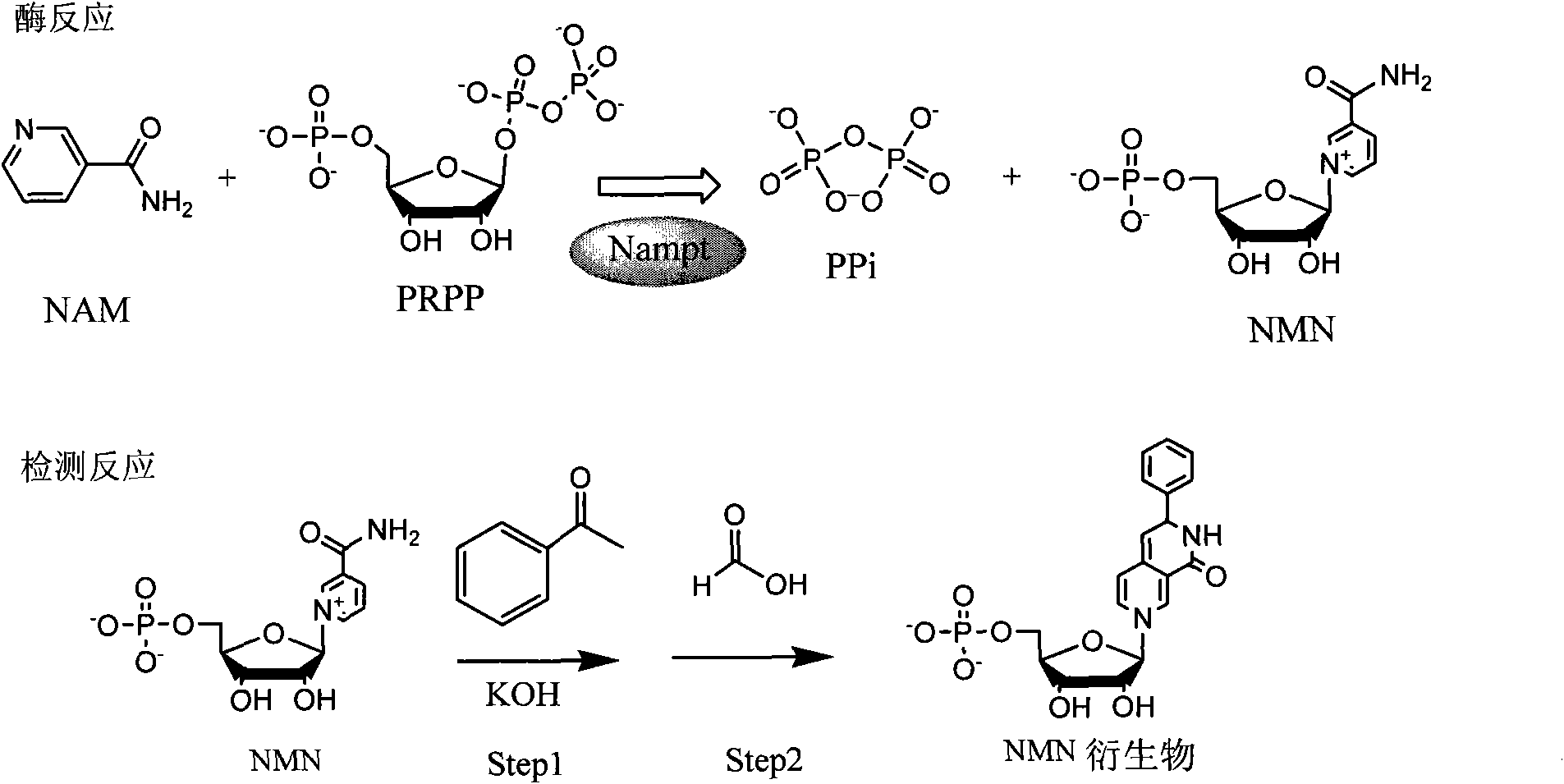
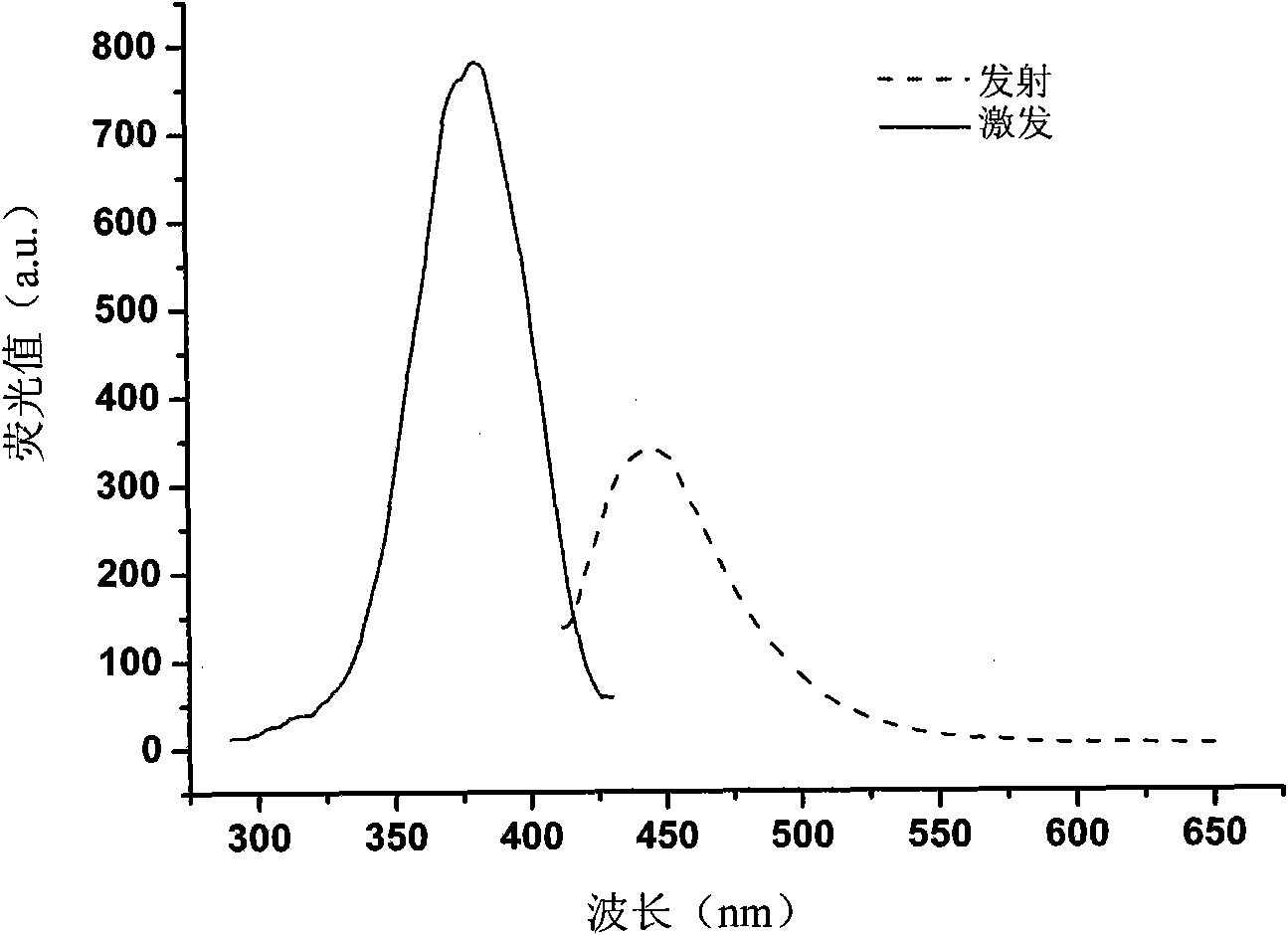
[0072] The present inventor successfully expressed and purified Nampt recombinant protein from the prokaryotic E. coli system, and established a method for detecting Nampt enzyme activity. The reaction principle is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the Nampt enzyme converts the substrate nicotinamide (NAM) into the product nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN); after two simple chemical reactions, NMN is converted into a fluorescent derivative that can be used at an excitation wavelength of 382nm, The maximum fluorescence signal was detected at emission wavelength 445nm ( figure 2 ).
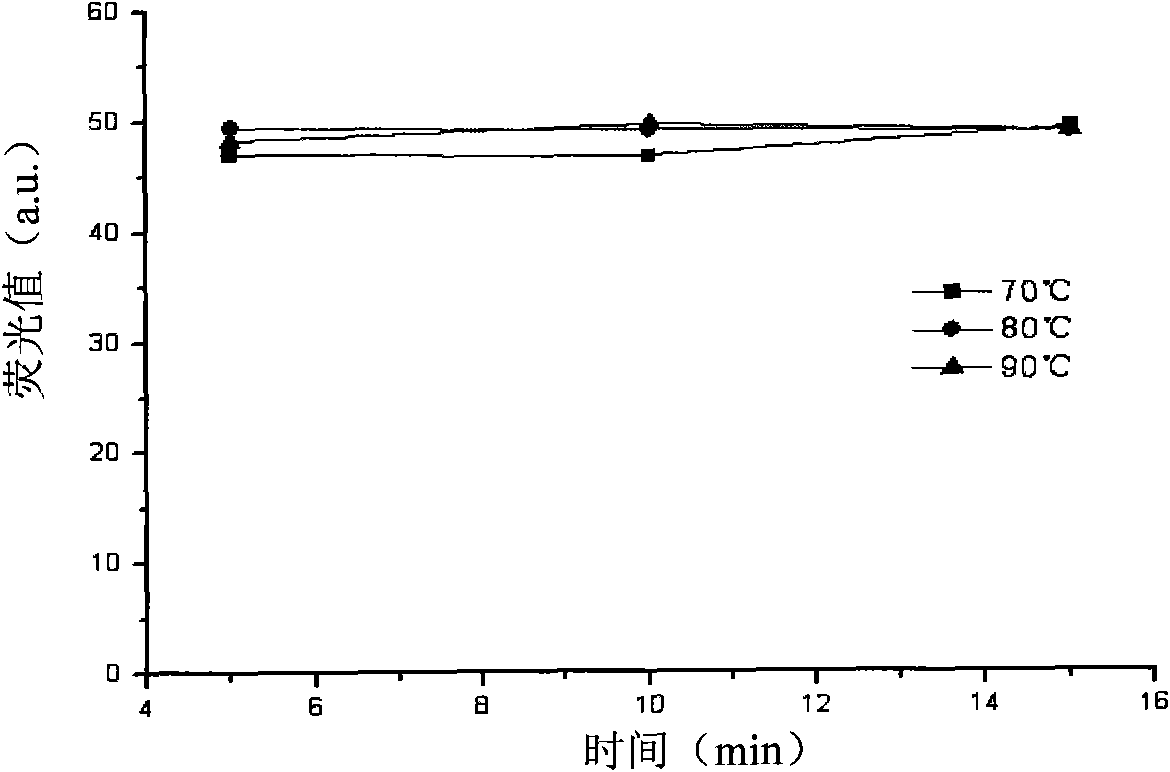
[0073] The inventors investigated the influencing factors of each step of the detection reaction to obtain the optimal reaction conditions for each step. In order to investigate the influence of reaction time and reaction temperature in the second step of the detection reaction, 10 μl of 20% acetophenone and...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Embodiment 2 enzymatic characteristic analysis
[0079] In enzymatic analysis, the Michaelis constant K m It is a basic characteristic constant of an enzyme, which includes the properties of the enzyme binding and dissociation with the substrate. The Mie equation is: v=V max *[S] / (K m +[S]), where v is the reaction rate; K m is the Michaelis constant; V max is the maximum speed of the enzyme reaction; [S] is the substrate concentration. From the Mie equation, it can be seen that the Mie constant K m Equal to the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate reaches half of the maximum reaction rate.
[0080] The inventors investigated the relationship between the concentration of the substrate NAM and the fluorescence intensity of the final product. The substrate NAM was serially diluted and then reacted with 2 μg / ml enzyme at 37°C for 30 minutes, and the fluorescence intensity of the detection reaction product was measured. As shown in the figure, the subst...
Embodiment 3
[0087] The establishment and quality control of embodiment 3 high-throughput screening models
[0088] 3.1 High-throughput screening process:
[0089] The high-throughput screening process is as follows:
[0090] 1. The enzyme reaction system is 25 μl, and the concentration of various components is: 50mM Tris-HCl (pH7.5), 0.02% BSA, 12mM MgCl2, 2mM ATP, 0.4mM PRPP, 2mM DTT, 2μg / mlNampt, 0.2μM NAM, 20 [mu]M candidate compound and 2% DMSO. First add 0.5 μl of the DMSO solution of the candidate compound to the 96-well plate, then add 20 μl of the enzyme reaction mixture solution (enzyme reaction components other than the substrate), pre-incubate at 37°C for 5 minutes, then add 4.5 μl of the substrate NAM solution to Start the reaction, react at 37°C for 15 minutes and then heat at 95°C for 1 minute to terminate the enzyme reaction.
[0091] 2. After the enzyme reaction solution is cooled on ice, add 10 μl 20% acetophenone and 2M KOH in sequence, mix well on a vortex mixer, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Michaelis constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com