Method for increasing yield of L-histidine
A histidine and amino acid technology, applied in the field of metabolic engineering, can solve problems such as difficulty in consumer acceptance and approval
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1: Determination of the critical lethal 6-MP concentration of S. marcescens ATCC 31026
[0033] Inoculate a single colony of S.marcescens ATCC 31026 before mutagenesis into 2mL LB medium (yeast powder 5g / L, tryptone 10g / L, NaCl 10g / L), culture at 37°C, 220r / min, for 10-12h, Centrifuge the bacteria, wash 2-3 times with sterile normal saline, then dilute 100,000-fold with sterile normal saline, and then take 100 μL of the bacteria solution and spread them respectively to 1.5 mg / mL MET and different concentrations of 6-MP Resistance plate (glucose 5.0g / L, beef extract 10g / L, peptone 10g / L, yeast extract 5.0g / L, sodium chloride 2.5g / L, agar 20g / L, pH adjusted to 7.0, extinguished at 121°C Bacteria 15min), the critical lethal concentration of 6-MP was determined to be 1.5mg / mL, so 1.5mg / mL was selected as the experimental concentration. As shown in table 2.
[0034] Table 2
[0035]
[0036] Note: ++ means more single colonies; + means a few single colonies; - ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Mutagenesis of S. marcescens ATCC 31026 by ARTP
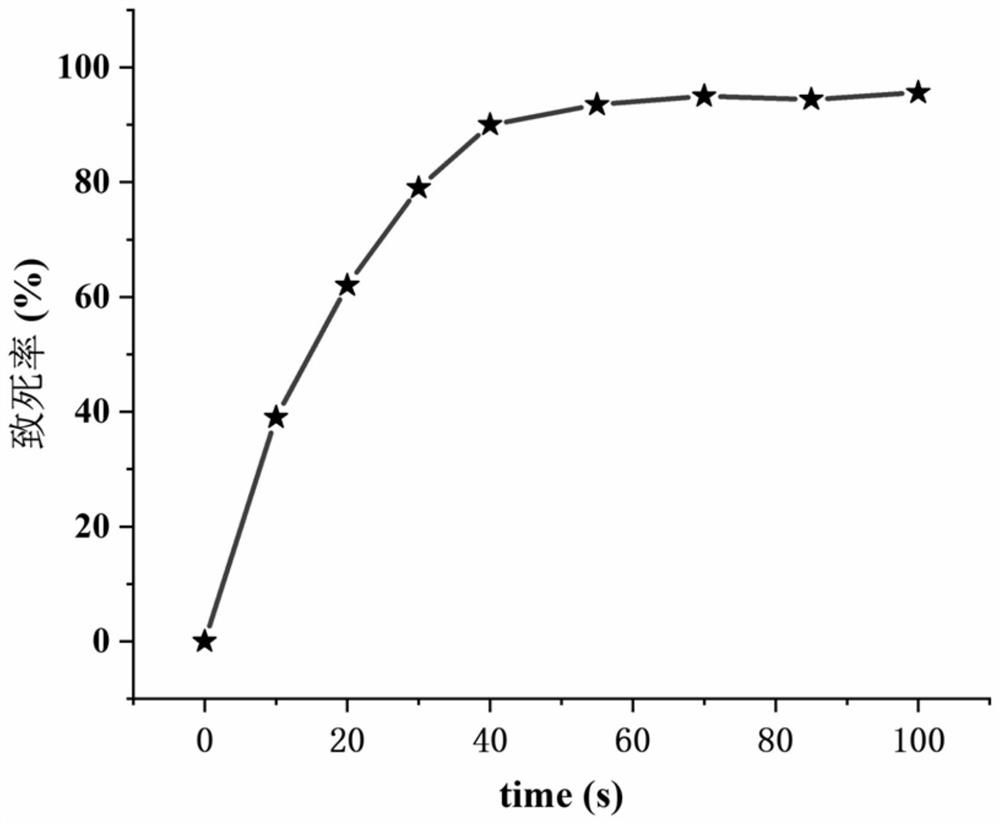
[0038] Select S.marcescens ATCC 31026 for ARTP mutagenesis. Firstly, prepare the bacterial suspension, put the single colony of S.marcescensATCC 31026 in LB medium into a 14mL shaking tube, 37°C, 220r / min, after overnight culture, use 1% inoculum Transfer to LB shaker flask, 37°C, 220r / min, and cultivate for 4-6h. Collect the cultured bacteria by centrifugation, wash 2-3 times with sterile normal saline, and then dilute to OD with sterile normal saline. 600 For the bacterial suspension with a value of 0.6-0.8, take 10 μL of the bacterial suspension and apply it on a glass slide for processing. The parameters of the ARTP mutagenesis treatment were as follows: the slide was positioned 2mm from the airflow port, the power was 120W, the airflow was 10SLM, and the action time was 35s.
[0039] Spread the bacterial suspension treated with ARTP mutagenesis on MET (1.5 mg / mL) and 6-MP (1.5 mg / mL) resistant plates, and...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: Fermentative synthesis of L-histidine
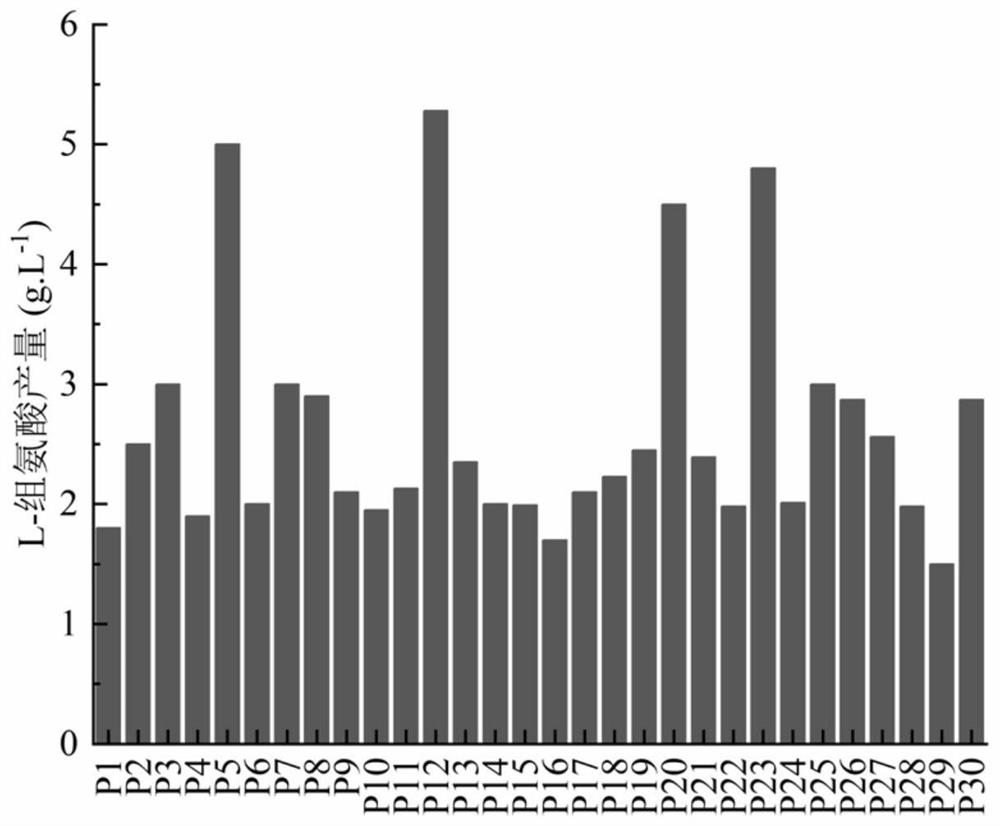
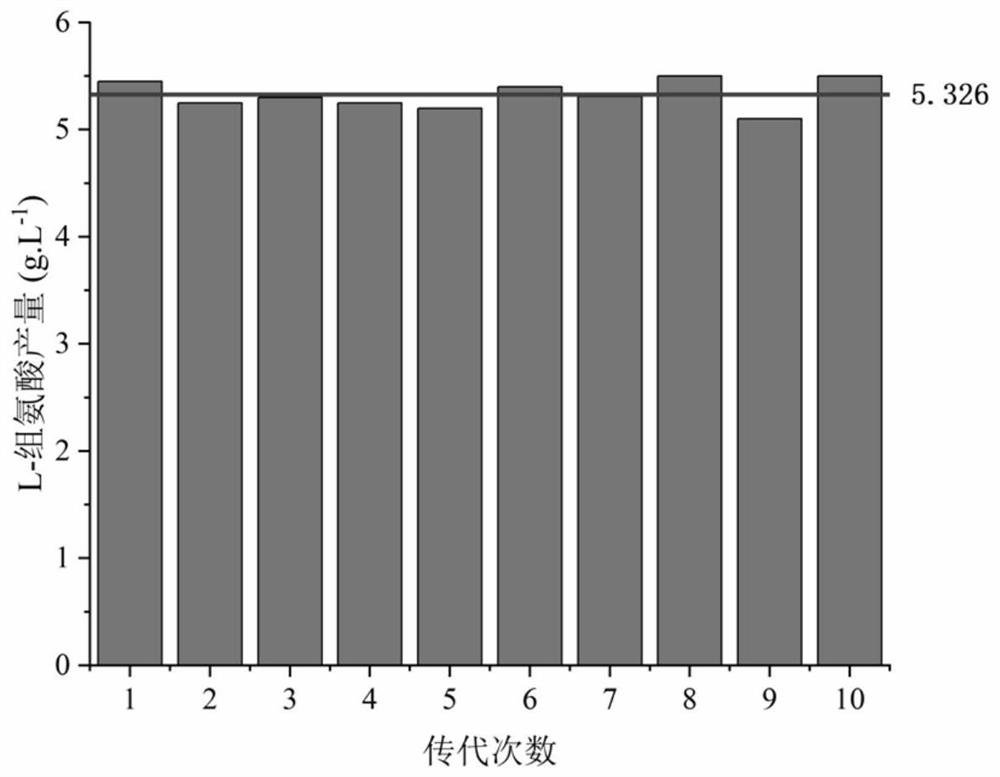
[0041] Pick a single colony of the thirty mutagenized strains of S.marcescens P1--30 obtained and inoculate them into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask with a liquid volume of 500mL, 30°C, 220r / min, and cultivate for 18h. The formulation of the seed medium For: glucose 25g / L, corn steep liquor 20g / L, urea 1.25g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.0g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.5g / L, pH adjusted to 7.0, sterilized at 121°C for 15min, glucose was sterilized separately Bacteria (115°C, 15min); draw 1.5mL of seed culture medium with 10% inoculum volume into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, fill liquid volume 15mL, 30°C, 220r / min, cultivate for 72h, the formula of the fermentation medium is: glucose 130g / L, ammonium sulfate 35g / L, corn steep liquor 15g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.0g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.5g / L, calcium carbonate 20g / L (disinfection), pH adjusted to 7.0, extinguished at 115°C Bacteria, 15min.
[0042] Liquid phase an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com