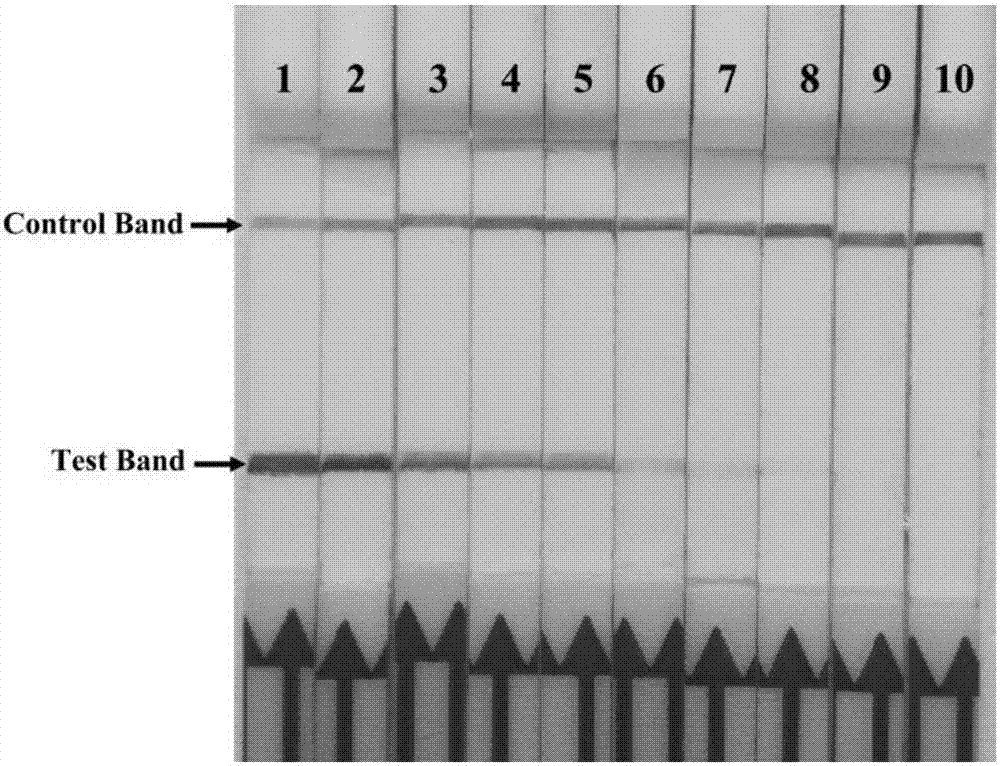
Patents
Literature
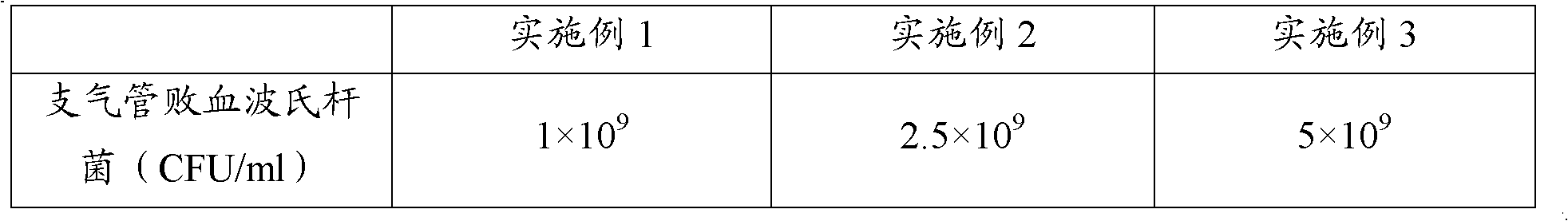
205 results about "P. multocida" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
P. multocida is the cause of a range of diseases in mammals and birds, including fowl cholera in poultry, atrophic rhinitis in pigs, and bovine hemorrhagic septicemia in cattle and buffalo. It can also cause a zoonotic infection in humans, which typically is a result of bites or scratches from domestic pets.
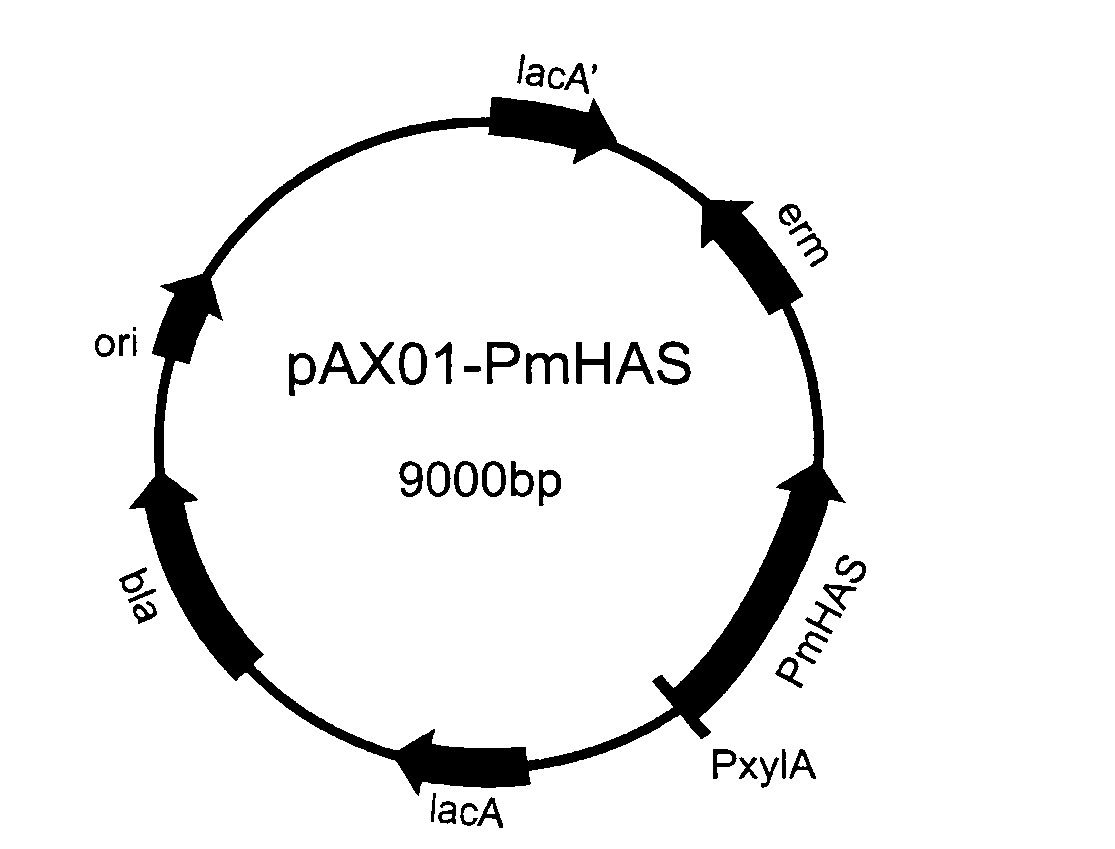
Polymer grafting by polysaccharide synthases
InactiveUS20060183203A1Reduce immunoreactivityReduce inflammationSugar derivativesBacteriaP. multocidaPolysaccharide
The present invention relates to methodology for polymer grafting by a polysaccharide synthase and, more particularly, polymer grafting using the hyaluronate synthase from Pasteurella multocida.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Natural, chimeric and hybrid glycosaminoglycan polymers and methods of making and using same
InactiveUS20060188966A1Difficult to controlModerate yieldSurgical adhesivesSaccharide librariesP. multocidaSugar
The present invention relates to methodology for polymer grafting by a polysaccharide synthase and, more particularly, polymer grafting using the hyaluronate or chondroitin or heparin / heparosan synthases from Pasteurella multocida, in order to create a variety of glycosaminoglycan oligosaccharides having a natural or chimeric or hybrid sugar structure.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Polymer grafting by polysaccharide synthases using artificial sugar acceptors
InactiveUS20060105431A1Reduce immunoreactivityReduce inflammationHydrolasesFermentationUDP-GalNAcP. multocida
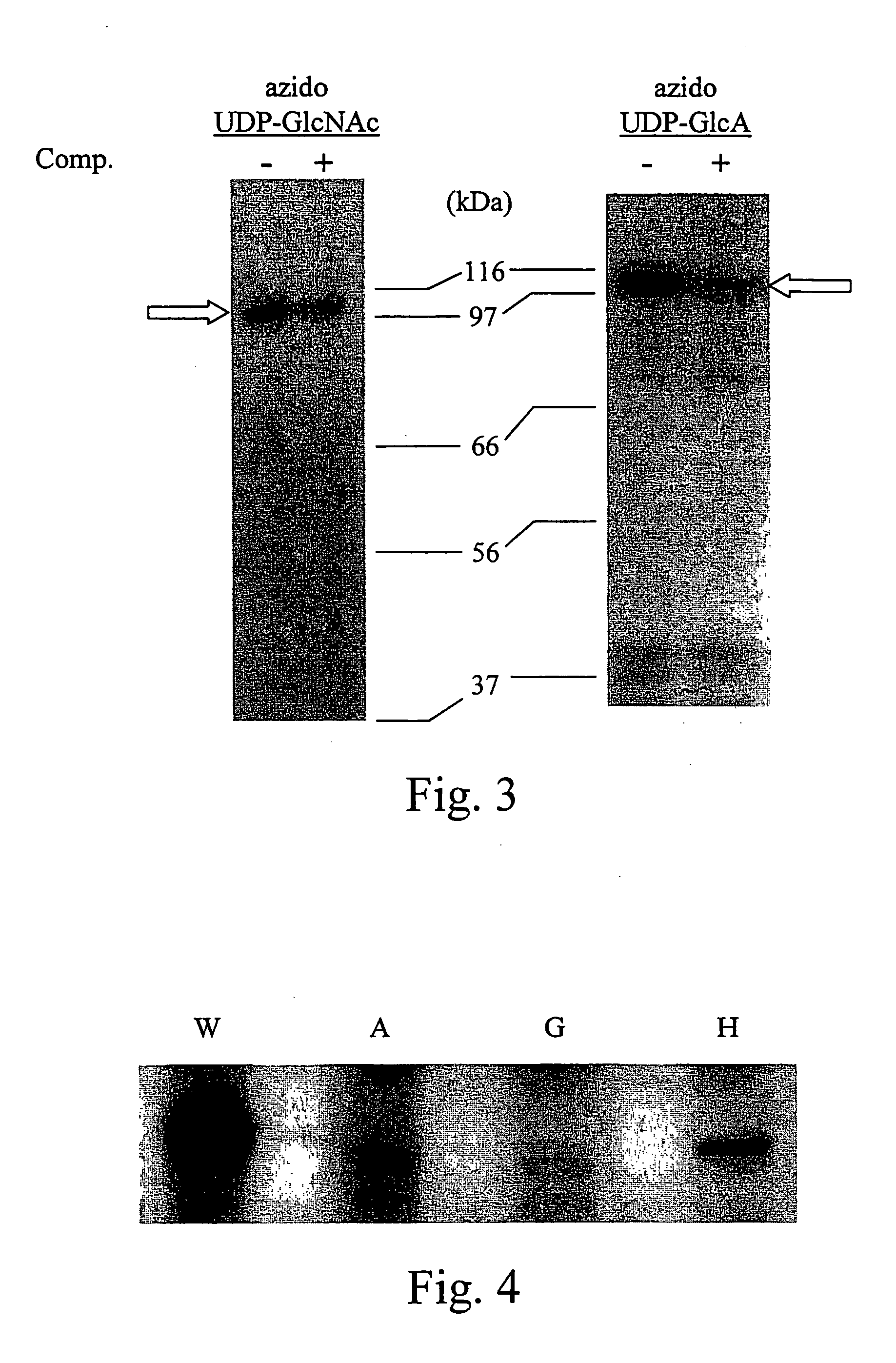
The present invention relates to methodology for polymer grafting by a polysaccharide synthase and, more particularly, polymer grafting using the glycosaminoglycan synthases from Pasteurella multocida. The methodology of the present invention includes providing an enzymatically active glycosaminoglycan synthase enzyme from Pasteurella multocida, providing a synthetic, artificial acceptor for the glycosaminoglycan synthase enzyme; combining the synthetic, artificial acceptor with the glycosaminoglycan synthase enzyme within a reaction medium, wherein the reaction medium contains at least one sugar precursor selected from the group consisting of UDP-GlcA, UDP-GlcNAc, UDP-GalNAc, and reacting the glycosaminoglycan synthase enzyme with the synthetic, artificial acceptor to produce an oligosaccharide or polysaccharide polymer. The glycosaminoglycan synthase enzyme may be hyaluronan synthase, chondroitin synthase, or heparosan synthase from P. multocida, and the oligosaccharide or polysaccharide polymer may be hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan), chondroitin, heparosan, or combinations thereof.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OK THE
Primer, probe and kit for rapidly detecting pasteurella mutocida on site
InactiveCN106811541AExcellent detection timeNo cross reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerCrude lysate
The invention discloses a combination of primer and probe for rapidly detecting pasteurella multocida on site by RPA-LFD. A forward primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID No. 1; a reverse primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID No. 2; a probe sequence is shown in SEQ ID No. 3. The invention also discloses a kit for detecting pasteurella multocida. The pasteurella multocida RPA-nfo detection combination of primer and probe and kit have high sensitivity and strong specificity, at least can detect six copied / reacted Pasteurella multocida DNAs, and can perform sensitive, specific and rapid detection of Pasteurella multocida DNA on crude lysate of a sample to be detected within 25 min by means of a constant-temperature water bath kettle or human armpit temperature without special instrument and equipment, so as to be suitable for the diagnosis of the pasteurella mutocida disease on site or base.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Rabbit triple inactivated vaccine, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101708332AImprove immune efficiencyImprove securityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseSide effect
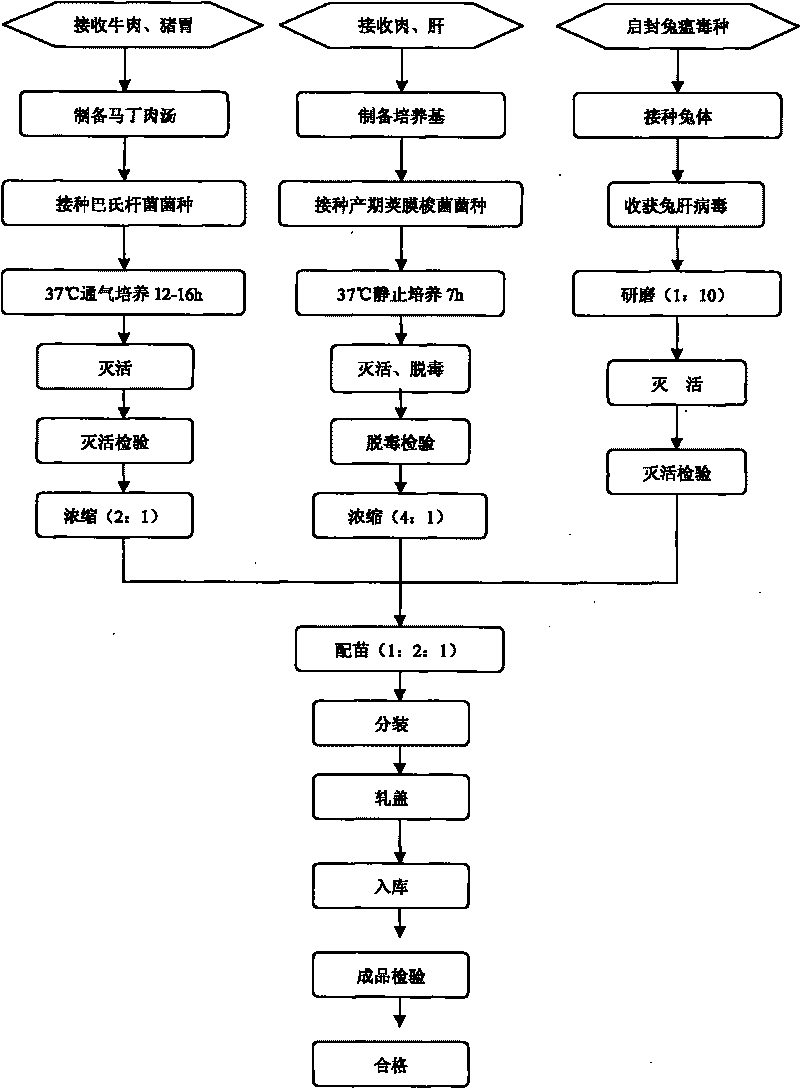
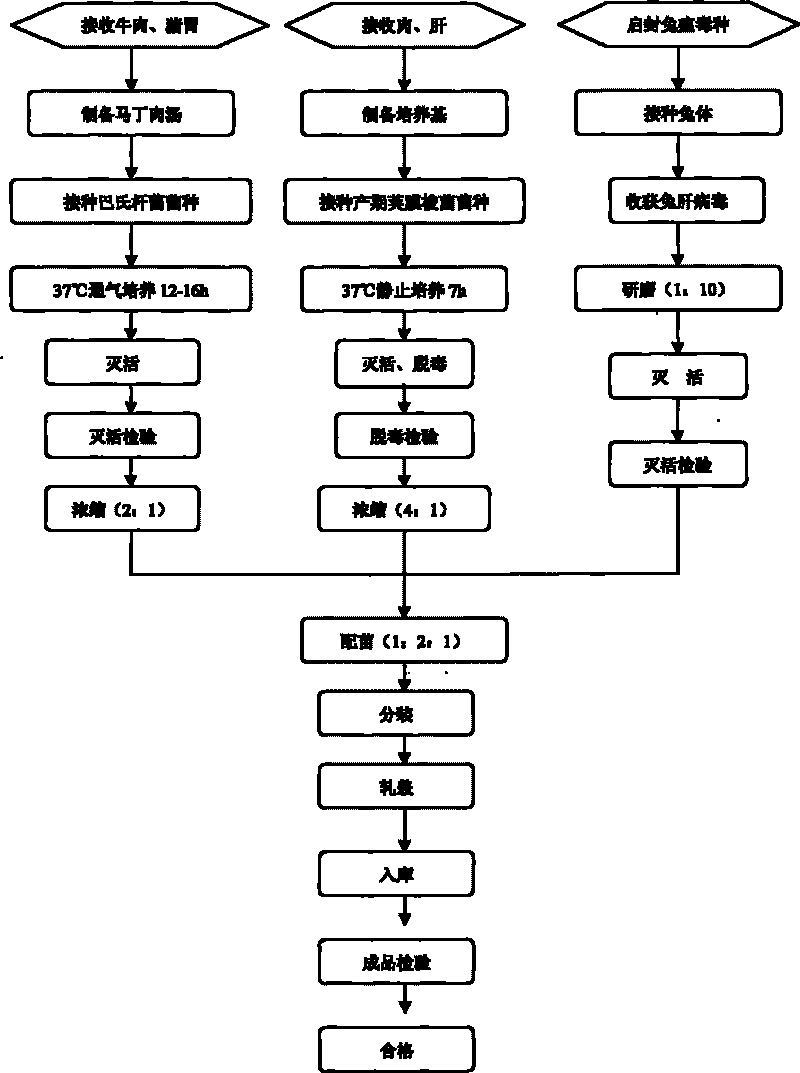
The invention discloses a rabbit triple inactivated vaccine, a preparation method and the application thereof; the rabbit triple inactivated vaccine is formed mainly by rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus liquid which is inactivated and detoxified, rabbit pasteurella multocida liquid and rapid A type clostridium perfringens liquid which have 1:1:2 volume ratio; in the invention, by optimizing culture technology, concentration technology and immunizing dose and other measures, the rabbit triple inactivated vaccine which has good immunity effect and safety is obtained and can effectively control the rabbit hemorrhagic disease, the pasteurella multocida disease and the pasteurella multocida disease (A type) and reduce vaccine injection times of farmers, so as to reduce the stress reaction of animals and improve the production performance. The clinical application proves that the immunization effect of the rabbit triple inactivated vaccine is ideal, each rabbit is vaccinated with 2ml and has immunity after 5-7 days, the immune period is at least 180 days, and the immune safety is good without toxic and side effect.
Owner:哈药集团生物疫苗有限公司
Polyvalent inactivity vaccine for preventing and treating atrophic rhinitis of swine
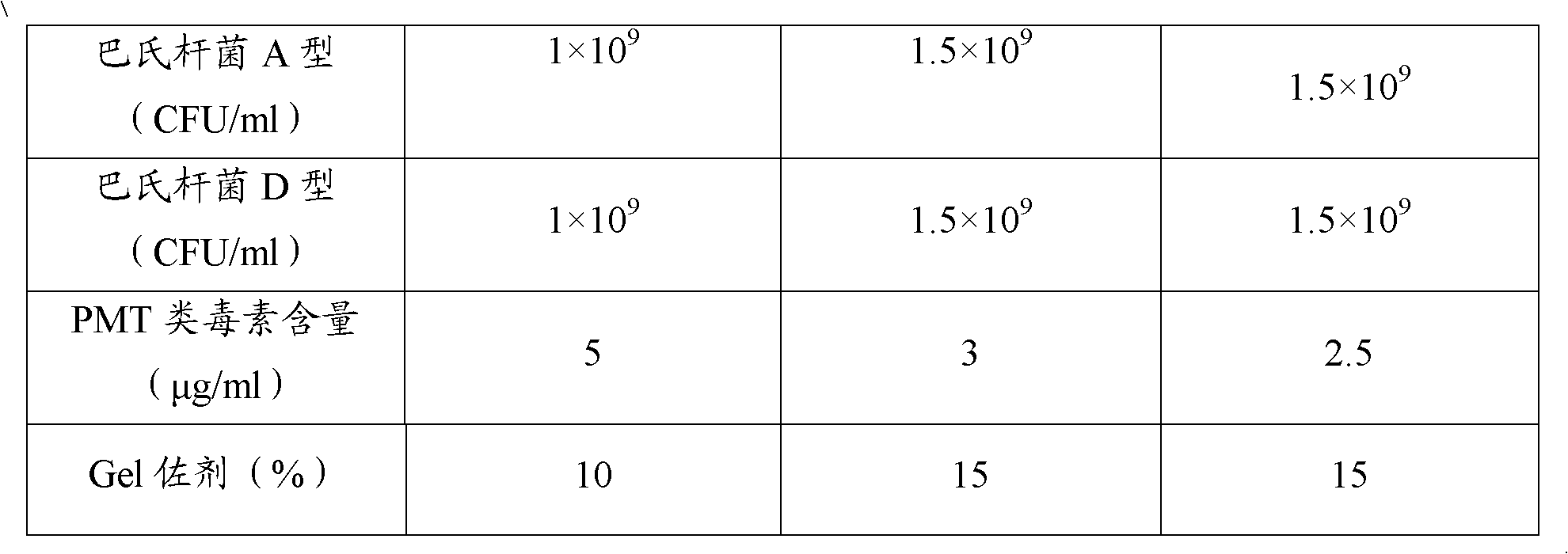
ActiveCN102302771AEffective therapeuticEffective preventionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPasteurella multocida toxinImmune effects
The invention provides a polyvalent inactivity vaccine for preventing and treating atrophic rhinitis of a swine and a preparation method thereof. The polyvalent inactivity vaccine contains inactivated Bordetella bronchiseptica, Pasteurella multocida A, Pasteurella multocida D and PMT (Pasteurella Multocida Toxin) anatoxin. The invention further provides a novel method for culturing and extractingPMT. Compared with the traditional atrophic rhinitis of the swine, the polyvalent inactivity vaccine for the atrophic rhinitis of the swine, provided by the invention, can be used for more generally and effectively treating and preventing the atrophic rhinitis of the swine by comprehensive antigen protection. Finally, in the polyvalent vaccine provided by the invention, the vaccine with a plurality of antigens in a reasonable proportion can be used for solving the problem that the plurality of the antigens interfere each other, thereby improving an immune effect. Furthermore, the inventor provides a water adjuvant by which defects such as incomplete absorption, large side reaction and the like after the traditional alumina gel adjuvant, Freund adjuvant and water-in-oil adjuvant are injected into the water adjuvant can be overcome.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
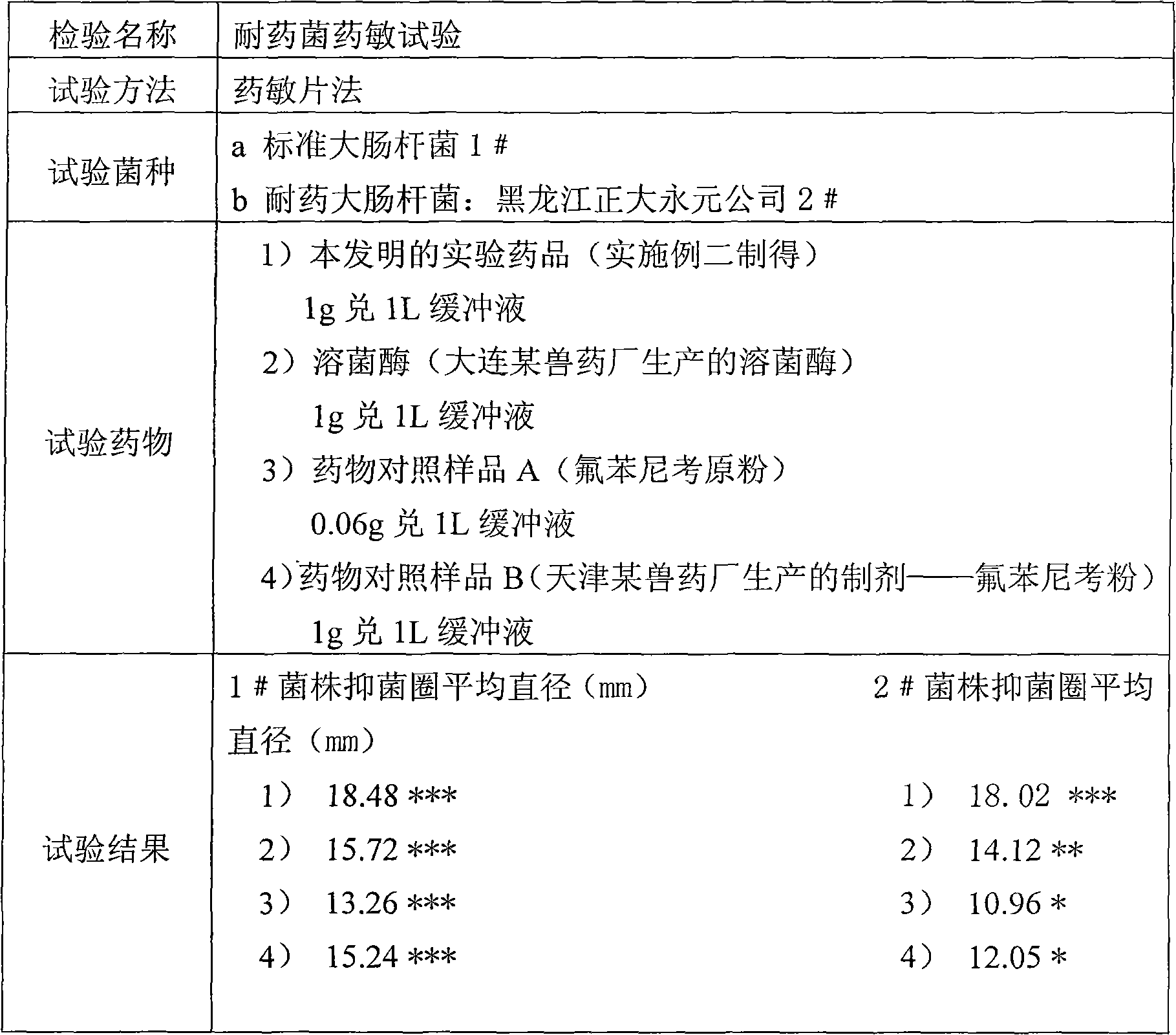
Veterinary antibacterial drug composition containing lysozyme and oligosaccharide and application thereof
InactiveCN101934070ALower resistanceBroad spectrum antibacterialAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a veterinary antibacterial drug composition containing lysozyme and oligosaccharide and an application thereof. The composition can be prepared into powder, granules, premixes, suspensions and oral solutions by mixing a pharmaceutically acceptable drug carrier with the main drugs of the lysozyme, the oligosaccharide and an antibacterial drug, as well as the auxiliary ingredients of biotin, phytic acid, trehalose, glycine and the like which are used for coordination, according to a conventional preparation method. The composition not only can enhance the self immunity of animals, equalize the absorption of amino acids and mineral substances in vivo and broaden the antimicrobial spectrum, but also has high efficiency, safety and no toxic and side effect and is not easy to lead to drug tolerance and drug resistance. The composition is used for preventing and treating intestinal diseases and respiratory diseases, such as colibacillosis, salmonellosis, pasteurella multocida, staphylococosis and the like, of livestock and poultry. Meanwhile, the developed drugs can be used for effectively substituting the traditional veterinary antibiotic drugs which are easy to lead to drug tolerance.
Owner:TIANJIN RINGPU BIO TECH
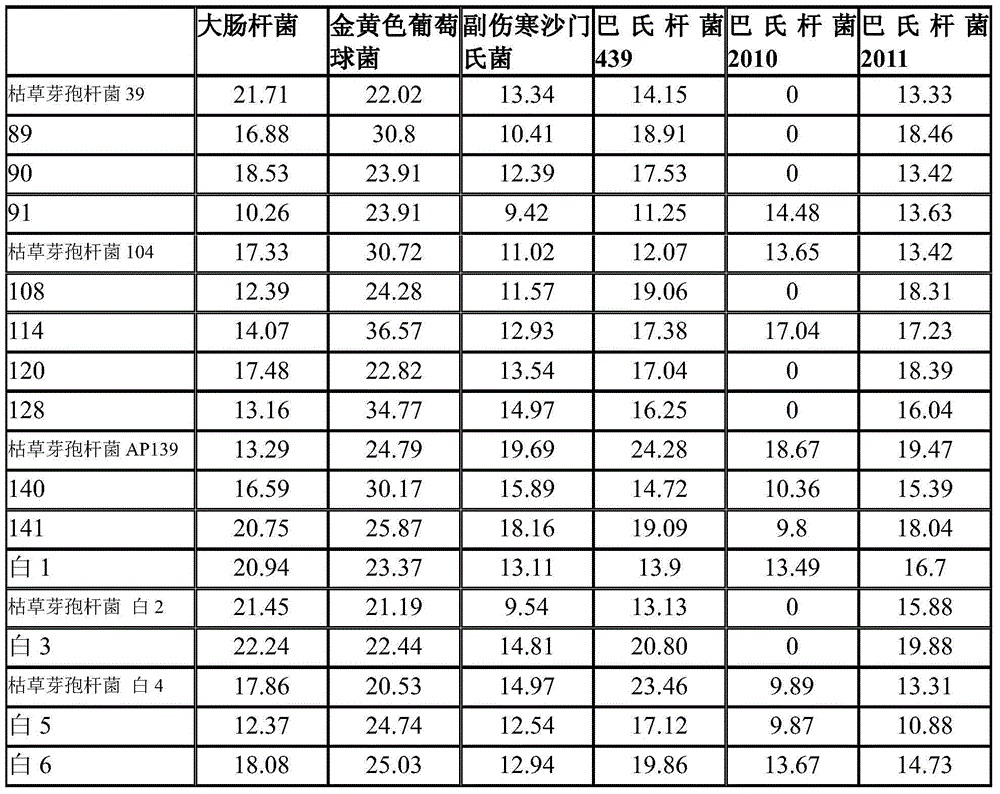
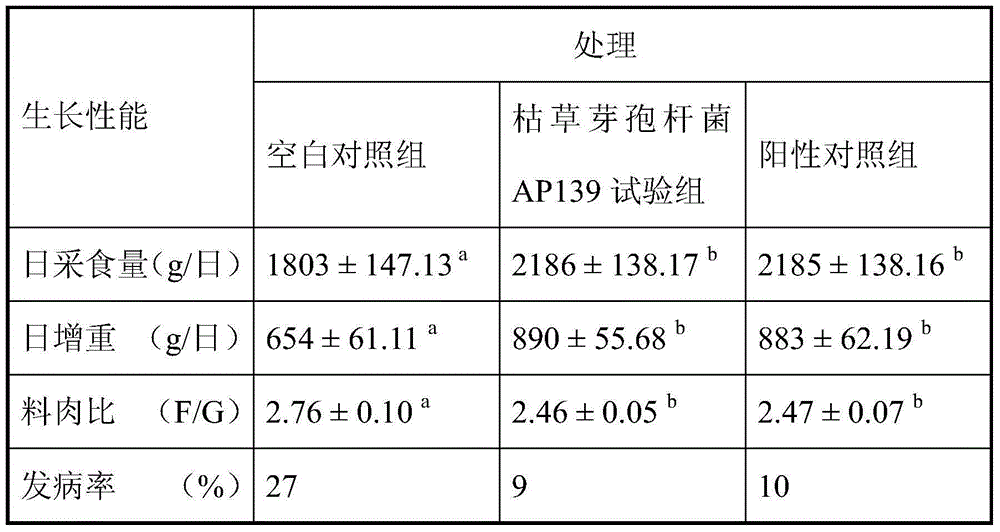
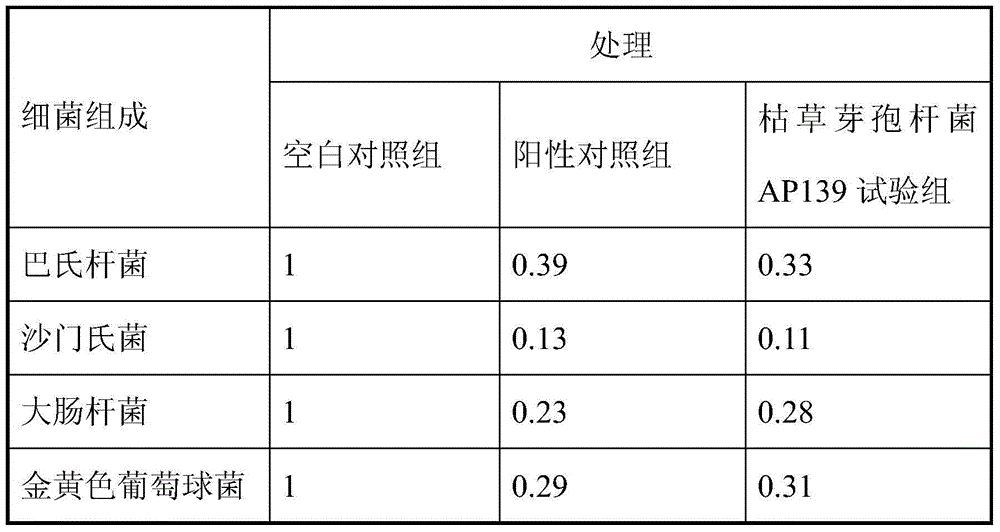
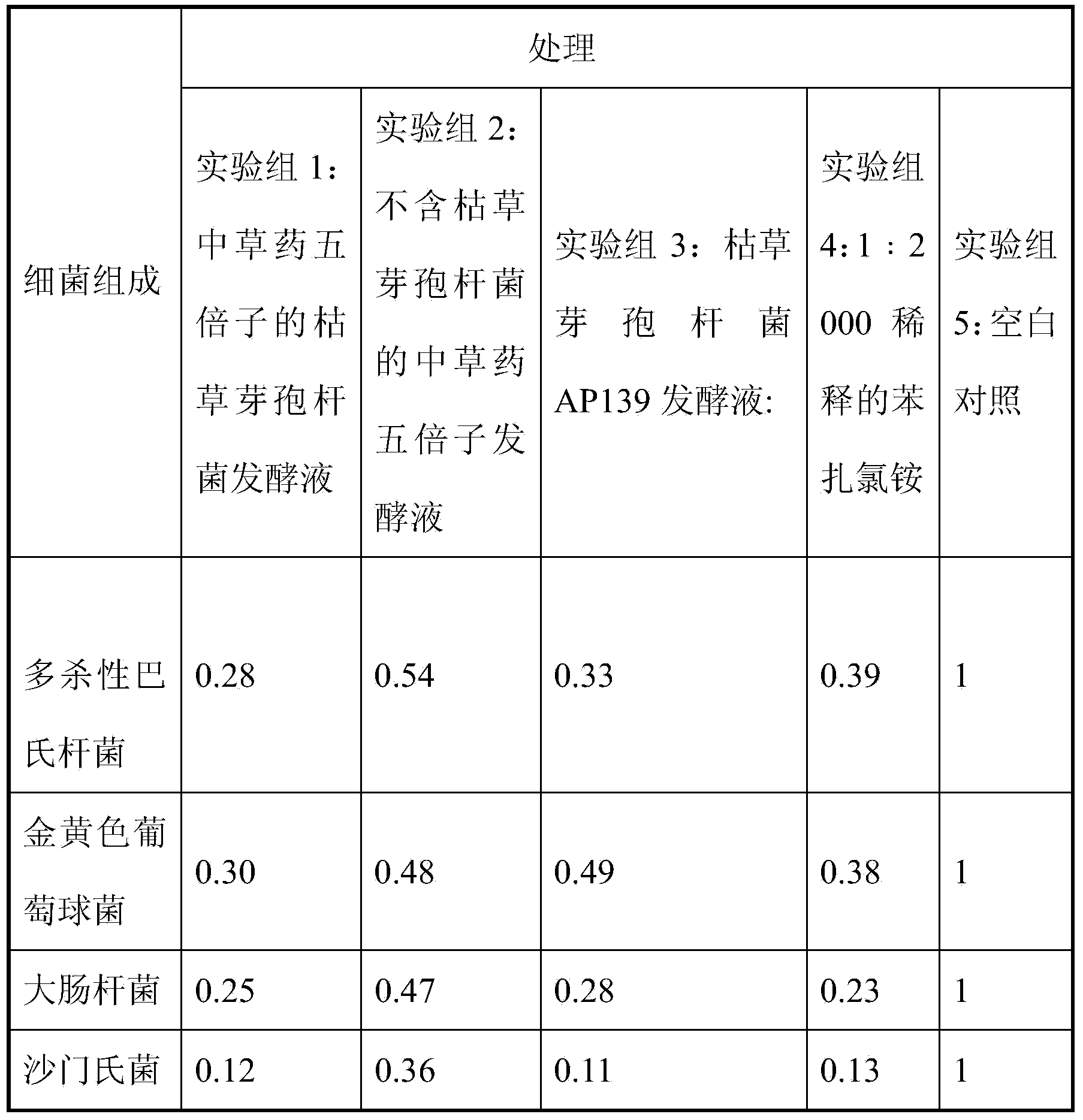
Bacillus subtilis AP139 and fermented microbial inoculum thereof, and application method of bacillus subtilis AP139 and fermented microbial inoculum
ActiveCN104099276AReduce morbidityHarm reductionBiocideBacteriaEscherichia coliStaphylococcus aureus
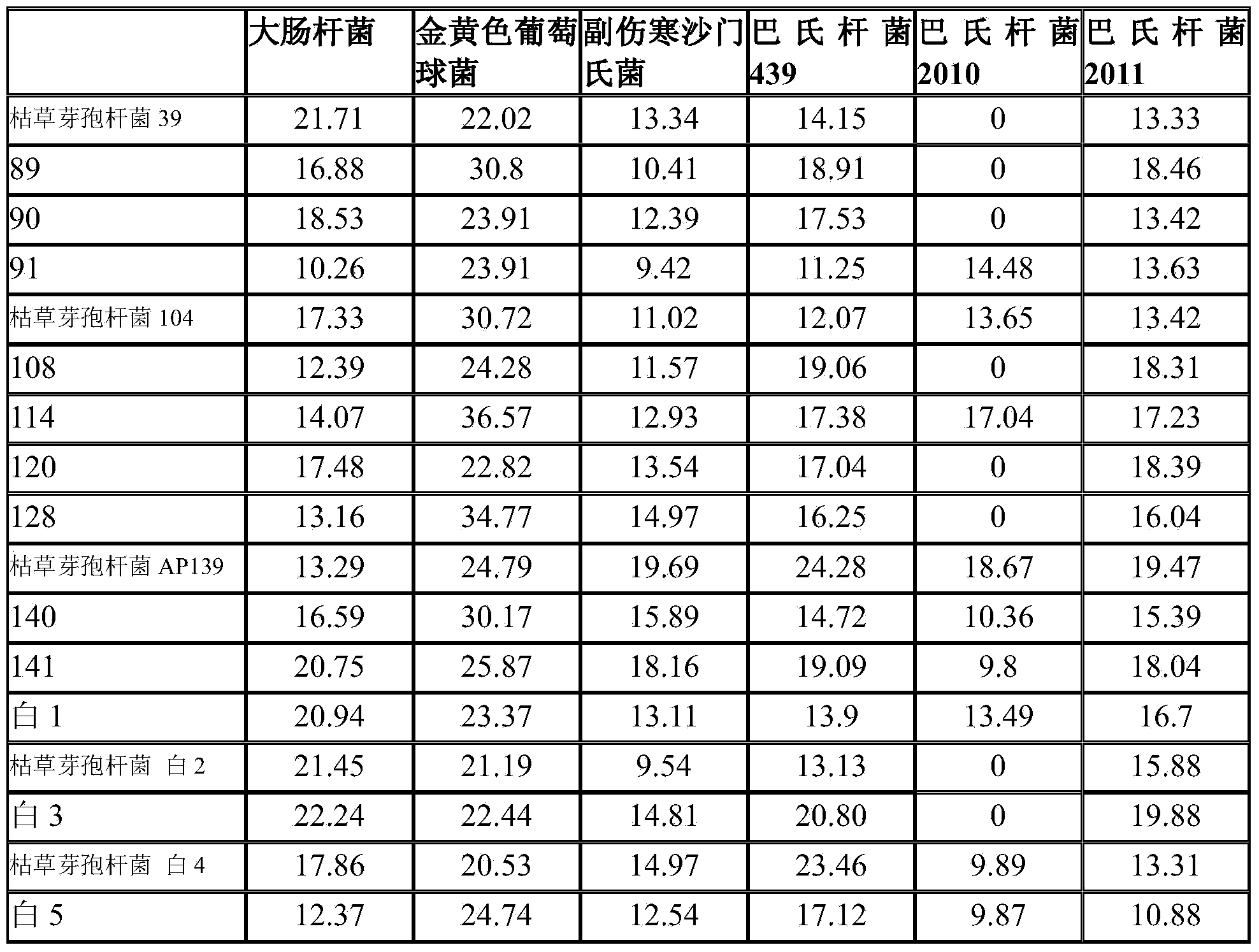
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis AP139 and fermented microbial inoculum thereof, and an application method of the bacillus subtilis AP139 and the fermented microbial inoculum. The bacillus subtilis is preserved in the China Center For Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2014053. The bacterial strain can restrain the growth and the propagation of porcine toxigenic pasteurella multocida in a culture dish experiment by screening porcine toxigenic pasteurella multocida resistance. The bacillus subtilis AP139 is atomized in an animal breeding shed, the bacillus subtilis AP139 has an obvious characteristic of restraining the growth of pasteurella multocida in air, the pasteurella multocida attack rate in a breeding farm is reduced, at the same time, the bacillus subtilis AP139 also has a good effect on restraining escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus and salmonella, and the bacillus subtilis AP139 has a favorable application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
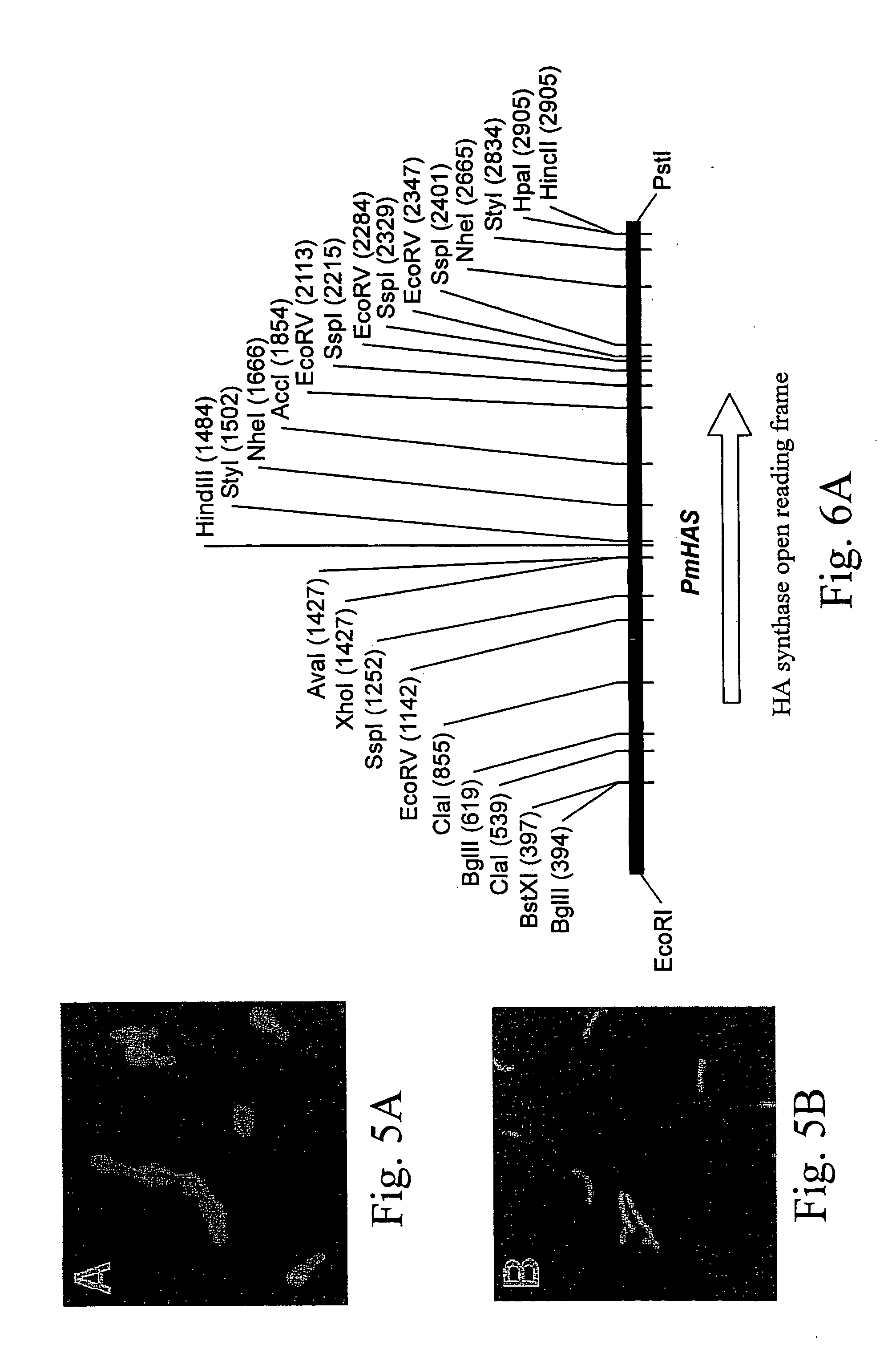
DNA encoding hyaluronan synthase from Pasteurella multocida and methods of use
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid segment having a coding region segment encoding enzymatically active Pasteurella multocida hyaluronate synthase (PmHAS), and to the use of this nucleic acid segment in the preparation of recombinant cells which produce hyaluronate synthase and its hyaluronic acid product.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Bivalent inactivated vaccine for bovine multocida pasteurellosis and preparation method of bivalent inactivated vaccine
ActiveCN107569681AImprove securityImprove packaging utilizationAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmune effectsCapsular type
The invention relates to a bivalent inactivated vaccine for bovine multocida pasteurellosis, belonging to the technical field of preparation of veterinary biological products. The bivalent inactivatedvaccine provided by the invention is composed of antigens and a vaccine adjuvant, wherein the antigens are a bovine multocida pasteurellosis capsular type-A Pm-TJ strain and a bovine multocida pasteurellosis capsular type-B C45-2 strain. For the bivalent inactivated vaccine prepared by adopting the method provided by the invention, the concentration purifying process is adopted, the fermentationculture process of the bovine multocida pasteurellosis capsular type-B C45-2 strain is optimized, so that the fermentation time is shortened by one half, and the production efficiency is improved. Forthe bivalent inactivated vaccine provided by the invention, the bovine fibrinous and suppurative pneumonia and bovine hemorrhagic septicemia caused by bovine pasteurella multocida infection can be prevented through one-time injection immunization, and the bivalent inactivated vaccine has the features of safety, reliability and good immune effect.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Polymer grafting by polysaccharide synthases
InactiveUS20060116348A1Reduce immunoreactivityReduce inflammationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideElectrical devicesBioadhesive
The present invention relates to methodology for polymer grafting by a polysaccharide synthase and, more particularly, polymer grafting using the hyaluronate synthase from Pasteurella multocida. The present invention also relates to coatings for biomaterials wherein the coatings provide protective properties to the biomaterial and / or act as a bioadhesive. Such coatings could be applied to electrical devices, sensors, catheters and any device which may be contemplated for use within a mammal. The present invention further relates to drug delivery matrices which are biocompatible and may comprise combinations of a biomaterial or a bioadhesive and a medicament or a medicament-containing liposome. The biomaterial and / or bioadhesive is a hyaluronic acid polymer produced by a hyaluronate synthase from Pasteurella multocida. The present invention also relates to the creation of chimeric molecules containing hyaluronic acid or hyaluronic acid-like chains attached to various compounds and especially carbohydrates or hydroxyl containing substances. The present invention also relates to a chondroitan synthase from Pasteurella multocida which is capable of producing polysaccharide polymers on an acceptor or primer molecule.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Inactivated vaccine for streptococcus suis and pasteurella multocida diseases and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101745105AAvoid infectionAchieve the effect of multiple defenses with one injectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseSerum ige
The invention provides an inactivated vaccine for streptococcus suis and pasteurella multocida diseases and a preparation method thereof, which can prevent streptococcus suis infection caused by a plurality of different sero-group streptococcus and infection caused by a plurality of different capsular serotype pasteurella multocida, achieves multiple preventions with one injection clinically, and is lowered in cost, free from the hidden hazard of virus dispersion, safe and reliable. The invention further provides a method for preparing the inactivated vaccine for streptococcus suis and pasteurella multocida diseases.
Owner:广东永顺生物制药股份有限公司
Natural, chimeric and hybrid glycosaminoglycan polymers and methods making and using same
InactiveUS20070117188A1Reduce immunoreactivityReduce inflammationSugar derivativesBacteriaSugarP. multocida
The present invention relates to methodology for polymer grafting by a polysaccharide synthase and, more particularly, polymer grafting using the hyaluronate or chondroitin or heparin / heparosan synthases from Pasteurella multocida, in order to create a variety of glycosaminoglycan oligosaccharides having a natural or chimeric or hybrid sugar structure.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Prevention, treatment and detection of pig progressive atrophic rhinitis
Disclosed is the animal vaccine for the prevention, treatment and detection of pig progressive atrophic rhinitis, which comprises three polypeptides generated by antibody against Pasteurella multocida related to progressive atrophic rhinitis, these polypeptides all have a amino acid sequence, which mainly corresponds to the 2-486, 486-986 or 986-1281 amino acid residue of the PMT protein. The invention also discloses the multivalent vaccine for the prevention and treatment of at least PAR for animals.
Owner:简茂盛
Novel pasteurella multocida bacteriophage pas-mup-1 and use thereof for inhibiting proliferation of pasteurella multocida
ActiveUS20180369300A1Strong specificityLess side effectsAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsPasteurella caballiBacteriophage
The present invention relates to: Myoviridae bacteriophage Pas-MUP-1 (accession number KCTC 12706BP) which has the capability to specifically destroy Pasteurella multocida, is characterized by having a genome represented by SEQ ID NO: 1, and is isolated from nature; and a method for preventing and treating Pasteurella multocida infections, using a composition containing bacteriophage Pas-MUP-1 as an active ingredient.
Owner:INTRON BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus baculovirus vector and pasteurella multocida bivalent inactivated vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108904796AFermentation culture process is matureImprove securityAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses positive-senseAdjuvantP. multocida
The invention relates to a rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus baculovirus vector and pasteurella multocida bivalent inactivated vaccine and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of immune technology. Recombinant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus VP60 baculovirus is inoculated into Sf9 insect cells and cultured at 27-28 DEG C. When cell lesion reaches 85% or more, a cell culture is harvested and inactivated, and the inactivated cell culture is used as a rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus antigen. Rabbit Pasteurella multocida capsular serotype A C51-17 strain is amplified and cultured, a bacterial solution is inactivated, and the inactivated bacterial solution is used as a Pasteurella multocida antigen. The rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus baculovirus vector and pasteurella multocida bivalent inactivated vaccine can be prepared by mixing the rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus antigen and the Pasteurella multocida antigen with adjuvants in proportion. The rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus baculovirus vector and pasteurella multocida bivalent inactivated vaccine has high safety, good immune effect and simple process, and can be used for preventing and controlling Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease (Rabbit Plague) and Rabbit Pasteurella multocida.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Primers, probes and kit for rapidly detecting mycoplasma bovis on site
InactiveCN106868167AExcellent detection timeStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerBacteroides
The invention discloses primers, probes and a kit for rapidly detecting mycoplasma bovis on site. The kit comprises a forward primer sequence shown as SEQ No.1, a reverse primer sequence shown as SEQ No.2, and a probe sequence shown as SEQ No.3, wherein the 5'-terminal of the reverse primer sequence is labeled by biotin; the 5'-terminal of the probe sequence is labeled by FAM, dSpacer is arranged at the position away from the 5'-terminal by 30 basic groups, and the 3'-terminal is blocked by C3-spacer. The primers, the probe assembly and the kit for detecting the mycoplasma bovis RPA-nfo are high in sensitivity and strong in specificity, the mycoplasma bovis DNA of 10 copies / reaction can be detected at the minimum, and the primers and the probes for detecting RPA-nfo respectively have no cross reaction with other mycoplasmas, as well as the bacteria including pasteurella multocida, mannheimia haemolytica, arcanobacterium pyogenes, histophilus somni, and streptococcus pneumoniae.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Plasmid, recombinant engineering bacteria and preparation method of hyaluronic acid with uniform molecular weight
A plasmid, recombinant engineering bacteria and a preparation method of hyaluronic acid with uniform molecular weight belong to the technical field of gene engineering. A first expression plasmid containing a Pasteurella multocida hyaluronan synthase gene (SEQ NO.1 in the sequence table) and a second recombinant expression plasmid containing hyaluronic acid precursor synthesis related genes (SEQ NO.2, SEQ NO.3, SEQ NO.4 and SEQ NO.5 in the sequence table) cloned from Bacillus subtilis are introduced into gram positive safe microorganisms, and an expression regulation and control system consisting of the two recombinant expression plasmids respectively controls hyaluronan synthase and hyaluronic acid precursor synthesis related enzyme, so as to obtain hyaluronic acid with uniform molecular weight by a biosynthesis method. The method provided by the invention not only improves the capability of the host strains to synthesize hyaluronic acid, but also can obtain several varieties of sufficient pure hyaluronic acid with uniform molecular weight.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Multiplex PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection primer group for avian pathogenic escherichia coli and the like, method and kit
ActiveCN108251548AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention provides a multiplex PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer group for avian pathogenic escherichia coli, pasteurella multocida, proteus mirabilis, pseudomonas aeruginosa, salmonella andstaphylococcus aureus, a multiplex PCR detection kit comprising the primer group, and a multiplex PCR detection method using the primer group. The primer group comprises primer pairs PhoA-F and PhoA-Rfor specifically amplifying a gene phoA of the avian escherichia coli, primer pairs KMT-F and KMT-R for specifically amplifying a gene KMT1 of the pasteurella multocida, primer pairs AtpD-F and AtpD-R for specifically amplifying a gene AtpD of the proteus mirabilis, primer pairs PETA-F and PETA-R for specifically amplifying a gene PETA of the pseudomonas aeruginosa, primer pairs InvA-F and InvA-Rfor specifically amplifying a gene InvA of the salmonella, and prier pairs NuC-F and NuC-R for specifically amplifying a gene nuc of the staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
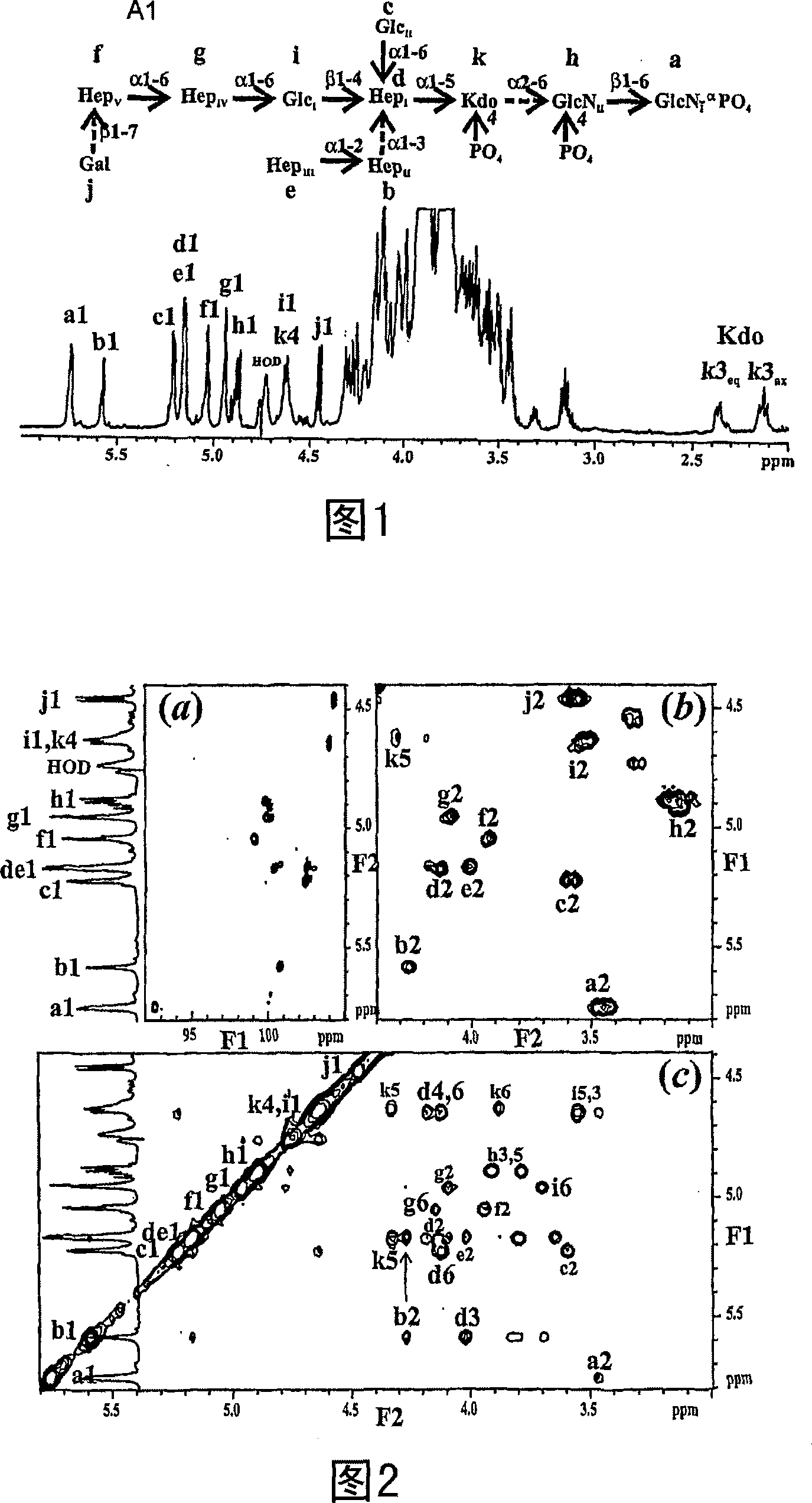
Conserved inner core lipopolysaccharide epitopes as multi-species vaccine candidates
InactiveCN101014698AEsterified saccharide compoundsAntibacterial agentsDiseaseMANNHEIMIA HAEMOLYTICA
A conserved inner-core oligosaccharide epitope expressed on the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of a range of disease causing pathogenic bacterial isolates, including Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (Ap), Mannheimia haemolytica (Mh) and Pasteurella multocida (Pm), is disclosed. Construction of a mutant bacterial strain exclusively expressing the conserved inner core OS epitope as a terminally exposed structure has allowed the identification, production and isolation of an inner core LPS which is common to all three organisms. Further provided are associated vaccines, antibodies raised against the conserved LPS inner core and glycoconjugates comprising the LPS inner core linked to an immunogenic carrier.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Swine pasteurellosis bivalent inactivated vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101766814AAvoid infectionPreventive Immunization SafetyAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsSerotypeP. multocida
The invention provides a swine pasteurellosis bivalent inactivated vaccine, which can prevent infection caused by two different capsule serotypes of pasteurella multocida, reaches the effect that one stitch of vaccine can prevent multiple infections, reduces the cost, does not have the hidden trouble of dispersing toxin and is safe and reliable. The invention also provides a preparation method for the swine pasteurellosis bivalent inactivated vaccine.
Owner:广东永顺生物制药股份有限公司
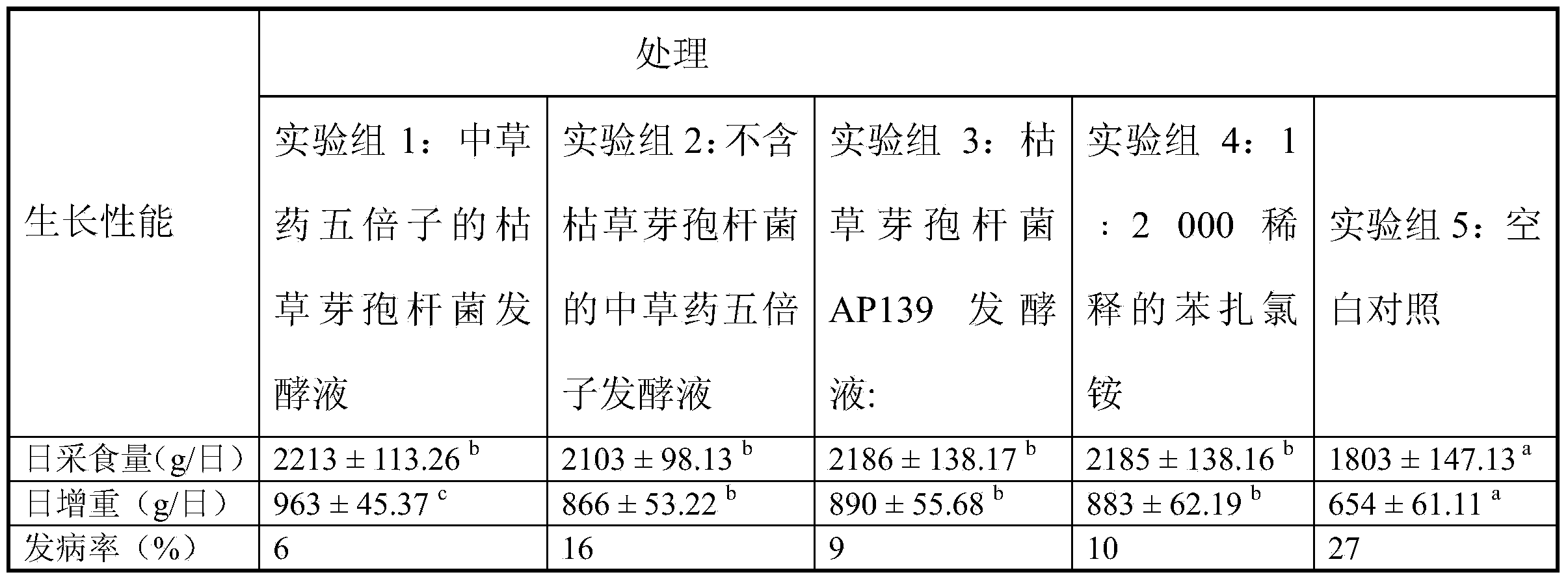
Bacillus subtilis fermentation broth of Chinese herbal medicine as well as preparation and application of bacillus subtilis fermentation broth
InactiveCN104351472AReduce morbidityHarm reductionAntibacterial agentsBiocideStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus aureus
The invention relates to bacillus subtilis fermentation broth of a Chinese herbal medicine as well as preparation and an application of the bacillus subtilis fermentation broth. The Chinese herbal medicine refers to Chinese gall; according to pasteurella multocida and staphylococcus aureus inhibiting screening tests, the Chinese gall can inhibit growth of the pasteurella multocida and the staphylococcus aureus, bacillus subtilis AP139 is used for fermenting the Chinese gall, spraying is performed in an animal breeding shed, the fermented Chinese herbal medicine remarkably inhibits the growth of the pasteurella multocida and the staphylococcus aureus in the air, the effect is superior to those of a bacillus subtilis AP139 separate fermentation group and a Chinese herbal medicine control group, and the fermentation broth has the broader application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
Vaccine composition, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104208666ASmall dose of immunizationGood immune effectAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBordetella bronchiseptica antigenPasteurella multocida toxoid
The invention provides a vaccine composition, and the vaccine composition comprises immunization amount of a bordetella bronchiseptica antigen, immunization amount of pasteurella multocida toxoid antigen and an adjuvant acceptable in veterinary medicine. The vaccine composition is capable of effectively controlling co-infected swine atrophic rhinitis caused by bordetella bronchiseptica and pasteurella multocida, and further comprises other antigen compositions for controlling respiratory syndrome caused by secondary infection of swine atrophic rhinitis. By reducing the antigen composition and using pasteurella multocida toxoid to replace pasteurella multocida antigens with different serotypes, the purpose of preventing swine atrophic rhinitis is realized. Also by improving the antigen content in per volume of the vaccine composition, the immunization dosage of the vaccine composition is reduced to 1 / 4 of the dosage of a conventional vaccine without reducing the immunization effect. Therefore, the vaccine composition is relatively low in immunization dosage, relatively less in antigen compositions, relatively low in immunization cost and convenient to use.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Geotechnical material of microbial granule and production method thereof
InactiveCN106631127ALight weightIncrease in sizeBacteriaSolid waste managementCalcareous soilsP. multocida
The invention discloses a geotechnical material of microbial granule and a production method thereof. The material comprises, by weight, 1-5 parts of foam plastic particles or fragments, 80-95 parts of calcareous soil and 5-9 parts of Pasteurella multocida fluid. The geotechnical material prepared by the method has the advantages of being light in mass, medium in strength, and good in stability. The geotechnical material of microbial granule can be produced by using discarded foam material and calcareous material, thus the cost is low. The geotechnical material can be used as the filler material for man-made islands of roadbed and pipe, and can also be used for preparing building materials such as light building blocks.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Treble PCR method for simultaneously detecting mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, porcine pasteurella multocida and haemophilus parasuis
InactiveCN104263845AQuick checkShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeP. multocida
The invention discloses a treble PCR method for simultaneously detecting mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, porcine pasteurella multocida and haemophilus parasuis. A treble PCR detection method for directly detecting 3 pathogens once from a sample is established through the following steps: firstly, screening out conservative genetic fragments with the gene type characteristics of the pathogens, using the conservative genetic fragments as 3 gene target points for PCR detection, respectively synthetizing and amplifying primers of the target point genes, and then putting 3 pairs of the primers of the 3 genetic fragments in a PCR reaction system. Through the adoption of the treble PCR method disclosed by the invention, on one hand, the pathogens can be accurately detected, and a mixed infection condition can be analyzed, so that the epidemic and development trend of an epidemic situation can be controlled, and the treble PCR method has double effects; on the other hand, compared with the conventional PCR method, the detecting time is shortened by 24 hours, so that the purpose of quickly detecting actual samples is achieved, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Prevention, treatment and detection of progressive atrophic rhinitis of pig
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a vaccine for animals with progressive atrophic rhinitis (PAR), which comprises the following steps that: nucleic acid fragments of polypeptides with three respective amino acid sequences encoded by which are 2-486, 486-986 or 986-1281 amino acid residues corresponding to Pasteurella multocida toxin (PMT) protein are expressed in Escherichia coli in a large amount respectively, and the polypeptides are separated and used for preparing a vaccine which can excite the generation of an antibody against Pasteurella multocida (related to the progressive atrophic rhinitis). The invention also discloses a method for manufacturing a multivalent vaccine capable of at least preventing the PAR for the animals, which comprises the following steps that: the multivalent vaccine is obtained by mixing the three polypeptides for the PAR prepared by the method and at least one pathogenic antigen related with other animal diseases or an epitope thereof.
Owner:简茂盛
Indirect ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) detection reagent kit and detection method for bovine-derived pasteurella multocida antibodies
ActiveCN106053807AImprove featuresImproved conservatismMaterial analysisPasteurella multocida antibodyPositive control
The invention discloses an indirect ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) detection reagent kit and a detection method for bovine-derived pasteurella multocida antibodies. The indirect ELISA detection reagent kit comprises solid-phase carriers enveloped by bovine-derived pasteurella multocida specific protein 0230, HRP (horse radish peroxidase)-labeled IgG (immunoglobulin G) enzyme-labeled second antibodies, standard positive control serum, standard negative control serum, sample diluent, concentrated washing solution, color developing solution and stop solution. The detection method is implemented by the aid of the indirect ELISA detection reagent kit, and includes enabling to-be-detected serum samples to be in contact with the enveloping bovine-derived pasteurella multocida specific protein 0230 on the solid-phase carriers and carrying out heat-insulation incubation; specifically capturing specific antibodies combined on 0230 protein antigens by the aid of the HRP-labeled IgG enzyme-labeled secondary antibodies; developing colors by the aid of color developing agents so as to measure 0230 protein antibody level of the to-be-detected serum samples. The indirect ELISA detection reagent kit and the detection method have the advantages of good specificity and repeatability, high sensitivity and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Compound doxycycline-hydrochloride florfenicol sustained-release microsphere suspension injection for veterinary use
ActiveCN105287607AImprove clinical efficacyReduce clinical dosageAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsSuspending AgentsVeterinary Drugs
The invention belongs to the technical field of veterinary drug preparation, and relates to a compound doxycycline-hydrochloride florfenicol sustained-release microsphere suspension injection for veterinary use. The suspension injection is produced through a preparation technology combining an inclusion technology, a microcapsule technology and a high-pressure homogenization technology. The suspension injection comprises the following ingredients according to W / V: 10-30% of an inclusion material, 5-20% of doxycycline hydrochloride, 5-20% of florfenicol, 2.5-7.5% of a high-molecular capsule material, 0.2-1% of a suspending agent, 0.25-1% of an anti-oxidant, 0.05-0.2% of a metal chelator, 0.1-0.4% of an antiseptic, and the balance injection water. The active ingredients in the injection possess synergic antibacterial effects and obvious sustained release effect, clinic dosing frequency is reduced, the injection does not contain organic solvents, does not stimulate target animals, is small in toxic and side effects, and is capable of controlling respiratory diseases caused by streptococcus suis, actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, pasteurella multocida, haemophilus parasuis, mycoplasma and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Subunit vaccine immunologic adjuvant and application thereof
InactiveCN102178950AImproving immunogenicityGood immune effectAntibacterial agentsAntibody medical ingredientsPasteurella caballiP. multocida
The invention provides a subunit vaccine immunologic adjuvant and application thereof. The adjuvant is a fusogenic peptide of antibacterial peptide and allanoin tripeptide and has an amino acid sequence of SEQ.ID.NO.1 and a nucleotide sequence of SEQIDNO.2. In the invention, PG-1-GGGGS-3BS fusogenic peptide is used as a molecular adjuvant, and the immunogenicity of the outer membrane protein of chicken pasteurella multocida can be enhanced effectively; when the PG-1-GGGGS-3BS fusogenic peptide is used as a molecular adjuvant, a eukaryotic yeast expression vector is selected, the fusogenic peptide can be expressed and purified easily, can be modified by glycosylation and the like, and is easy for mass production; the fusogenic peptide expressed by yeast has modifier genes of eukaryotic cells, is similar to the structure of PG-1 expression in a mammal body and has good biological activity.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for extracting lipopolysaccharides from avian pasteurella multocida and preparing lipopolysaccharide vaccine
InactiveCN102120028AIncrease concentrationHigh purityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAnimal virusMedicine
The invention provides a method for extracting lipopolysaccharides from avian pasteurella multocida and preparing a lipopolysaccharide vaccine. The method comprises the following eight steps of: 1, preparing culture solution of avian pasteurella multocida; 2, collecting the avian pasteurella multocida from the culture solution of avian pasteurella multocida; 3, crushing the avian pasteurella multocida by using ultrasonic wave; 4, crudely extracting solution of lipopolysaccharides from the avian pasteurella multocida crushed by the ultrasonic wave; 5, extracting concentrated solution of lipopolysaccharides from the crudely extracted solution of lipopolysaccharides; 6, performing enzymolysis on deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the concentrated solution of lipopolysaccharides by using DNA and RNA enzymes; 7, preparing the purified lipopolysaccharides; and 8, preparing the lipopolysaccharide vaccine of avian pasteurella multocida from the purified lipopolysaccharides. According to animal immunization experiments and animal virus attacking experiments, after the lipopolysaccharide vaccine of avian pasteurella multocida, prepared by the method, is used for immunizing chickens for three times, the immunized chickens can be effectively prevented from suffering from avian pasteurella multocida disease.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com