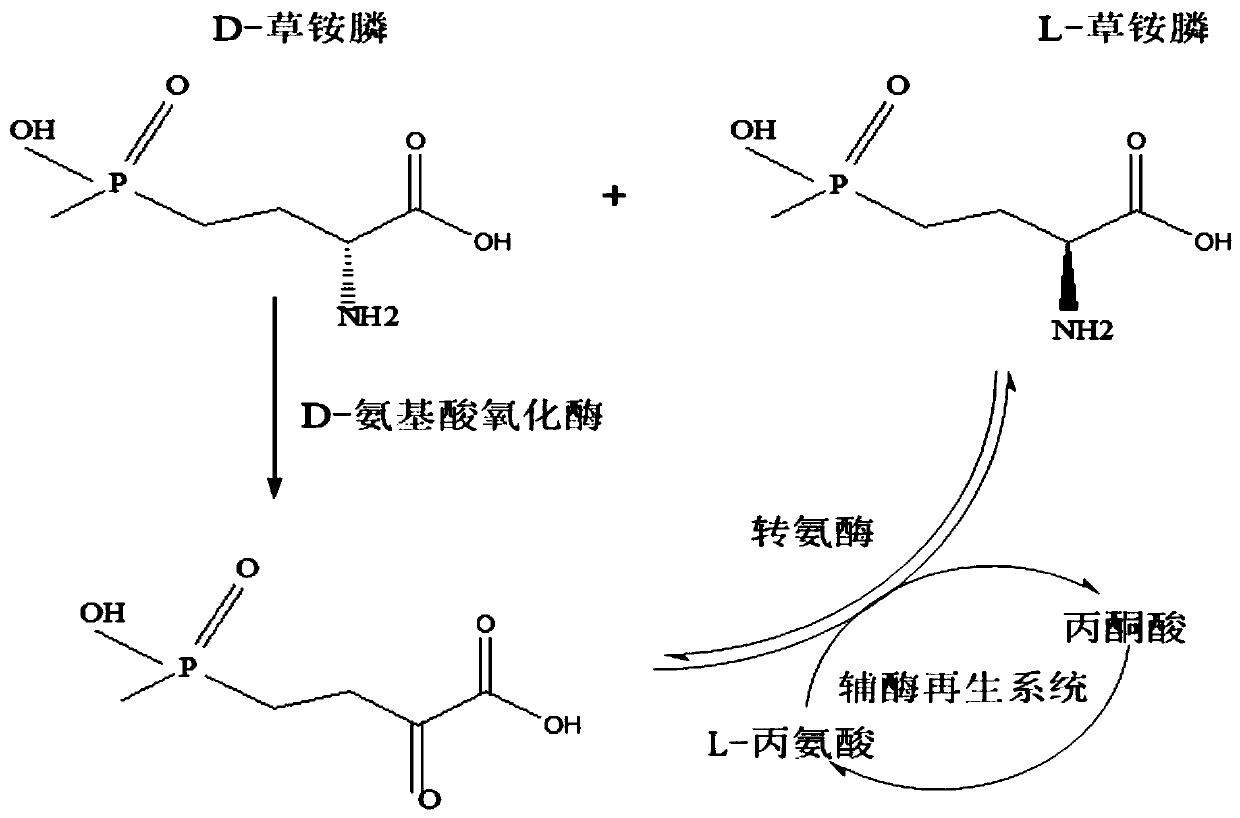
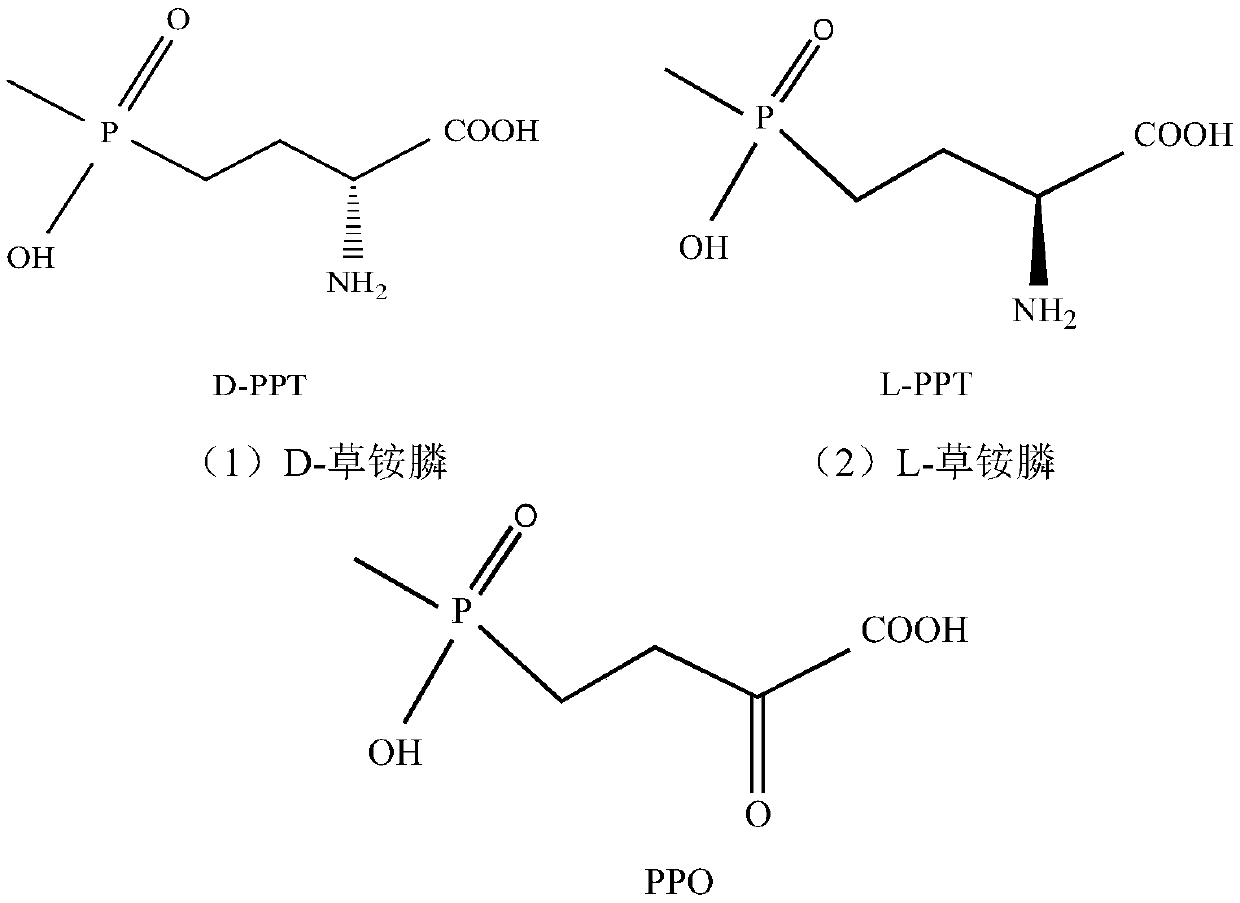
Redox asymmetrical method for preparing L-phosphinothricin by biological multi-enzyme coupling
A technology of glufosinate-ammonium and coupling method, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, oxidoreductase, microorganism and other directions, can solve the problems of complex process, waste of raw materials, expensive chiral resolution reagents, etc., and achieve good catalytic efficiency, The effect of increasing the yield of PPO
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Construction and screening of D-amino acid oxidase mutant library.
[0054] 1. Construction of genetically engineered bacteria
[0055] The gene sequence of D-amino acid oxidase (Gen Bank No.: POY70719.1) from Rhodotorula taiwanensis was codon-optimized and sent to Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. for whole gene synthesis and cloned to the recombinant expression plasmid pET-24a(+). After the recombinant plasmid was verified to be correct by sequencing, it was transferred into the expression host E. coli BL21 (DE3) for subsequent expression of the recombinant D-amino acid oxidase. The codon-optimized D-amino acid oxidase gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.2.
[0056] 2. Construction of D-amino acid oxidase mutant library
[0057] In the first round, the codon-optimized D-amino acid oxidase gene obtained by the above-mentioned whole gene synthesis was used as a template, and the primers used to mutate M213R and M213S in Table 1 were used for site-directed mu...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Construction of Genetically Engineered Bacteria Expressing Transaminase
[0077] 1. Amplification of target gene transaminase
[0078] The transaminase gene was cloned from the Pseudomonas genome, and the corresponding PCR upstream primers and downstream primers were designed according to the corresponding genomic DNA sequence (GenBank accession number WP_076423369.1).
[0079] Upstream primer: ATGAACACCAACAACGCTC
[0080] Downstream primer: TTAAGCCTGTTTAGCTTC
[0081] PCR amplification system:
[0082] 2×Phanta Max buffer: 25 μL;
[0083] dNTPs: 1 μL;
[0084] Upstream primer: 1 μL;
[0085] Downstream primer: 1 μL;
[0086] Template: 1 μL;
[0087] Phanta Super-Fidelity DNA Polymerase: 0.5 μL;
[0088] wxya 2 O: 20.5 μL.
[0089] PCR reaction conditions: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5min; denaturation at 95°C for 30s, annealing at 60°C for 30s, extension at 72°C for 6min, a total of 30 cycles; post-extension at 72°C for 10min; storage at 4°C.
[0090] The P...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Culture of microorganisms
[0095] 1. Bacteria culture
[0096] After the engineering bacteria containing D-amino acid oxidase gene and transaminase gene were respectively activated by streaking on a plate, a single colony was picked and inoculated into 10 mL LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin, and cultured with shaking at 37 °C for 10 h. Transfer to 50mL LB liquid medium also containing 50μg / mL kanamycin according to 2% inoculum amount, and culture with shaking at 37°C until OD 600 When it reaches about 0.8, add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.5mM, and culture with shaking at 28°C for 12h. After the cultivation, the culture solution was centrifuged at 8000rpm for 10min, the supernatant was discarded, the bacteria were collected, and stored in a -80°C ultra-low temperature refrigerator until use.
[0097] 2. Preparation of crude enzyme solution
[0098] After the culture, the collected cells were washed twice with pH 8 phosphate buffer (50 mM). After t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com