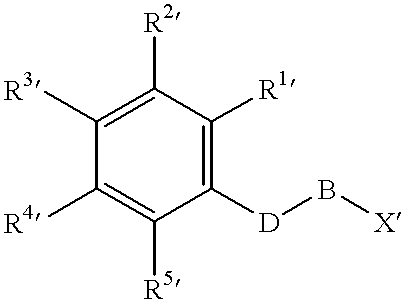
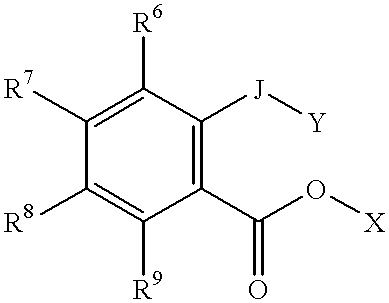
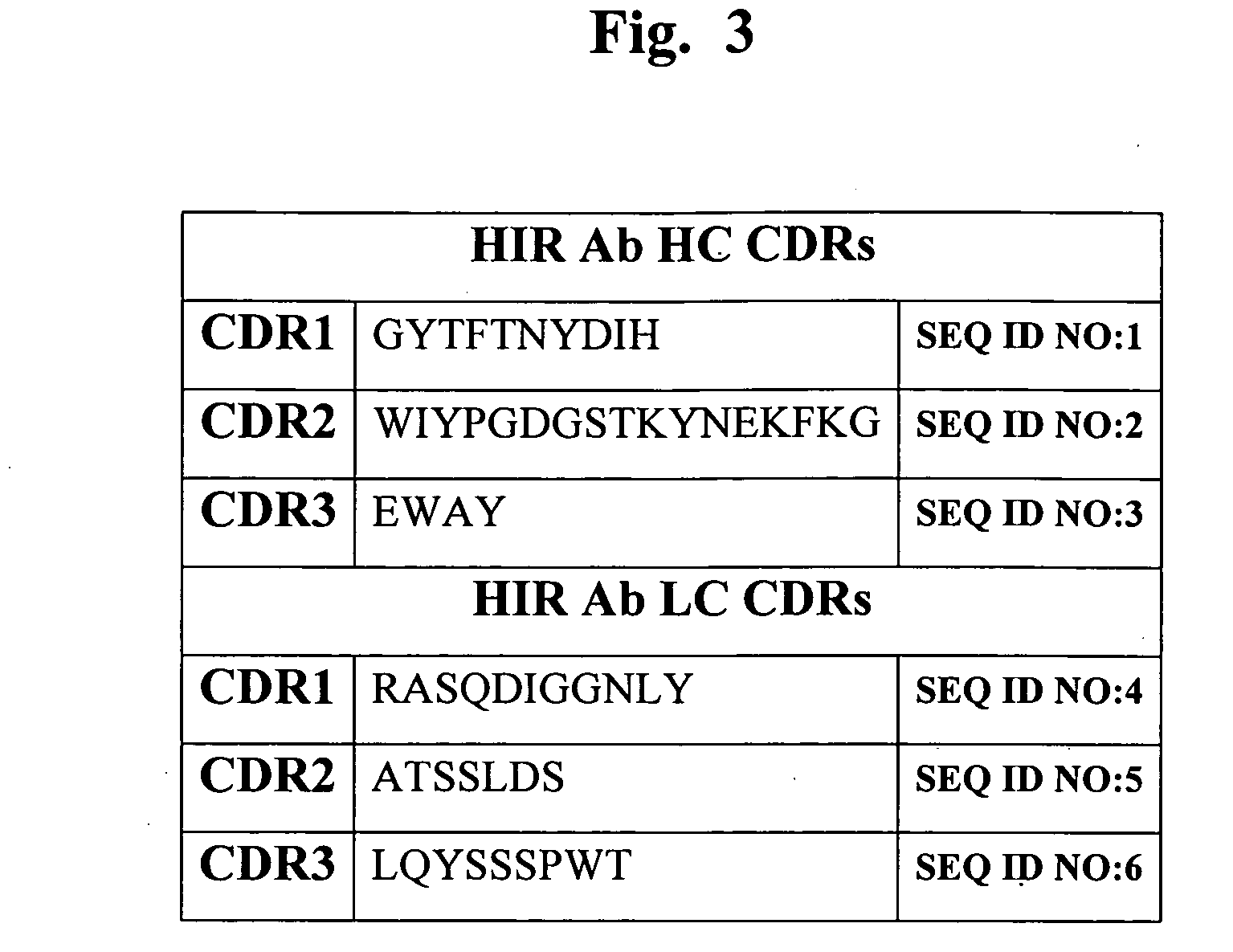
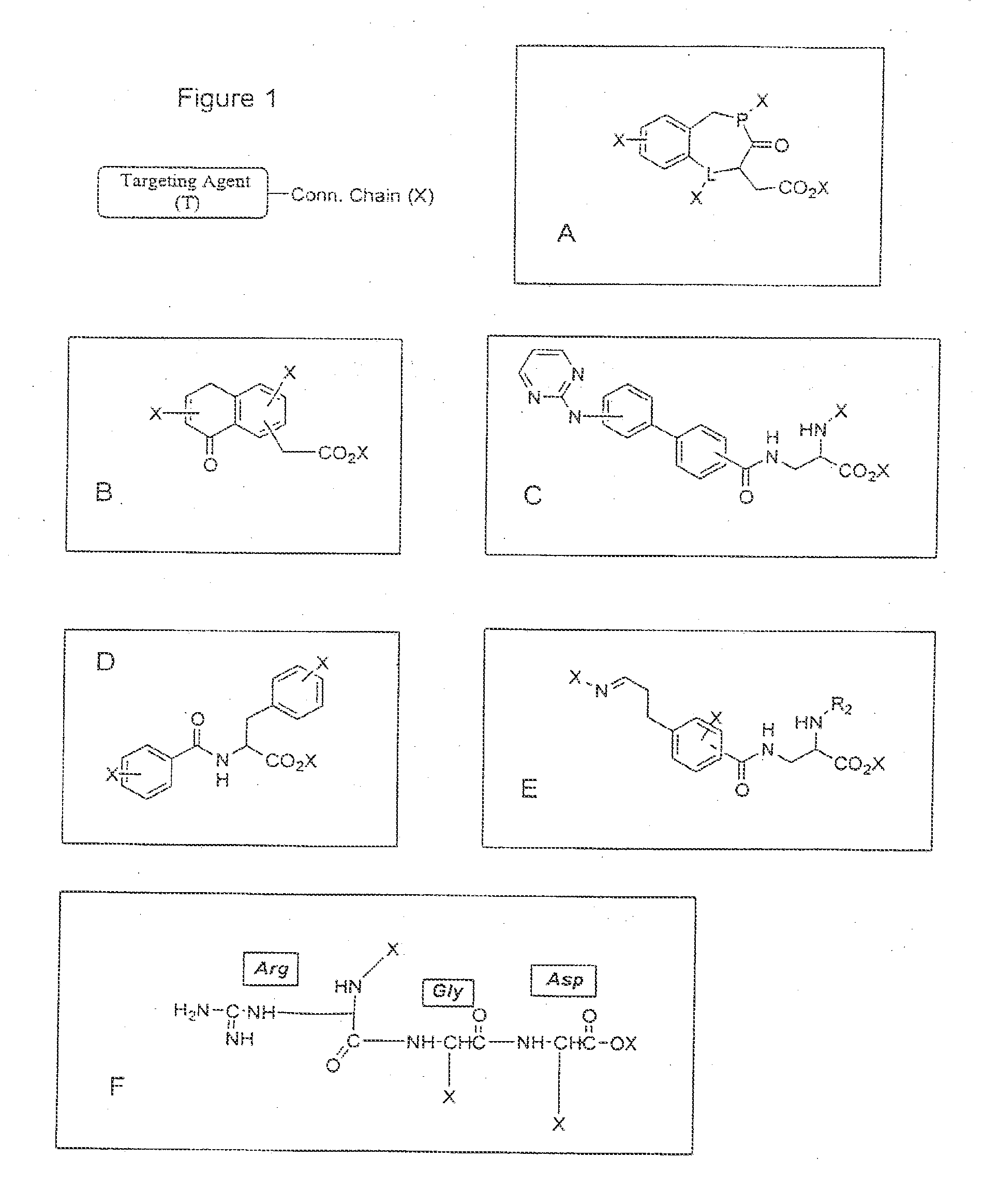
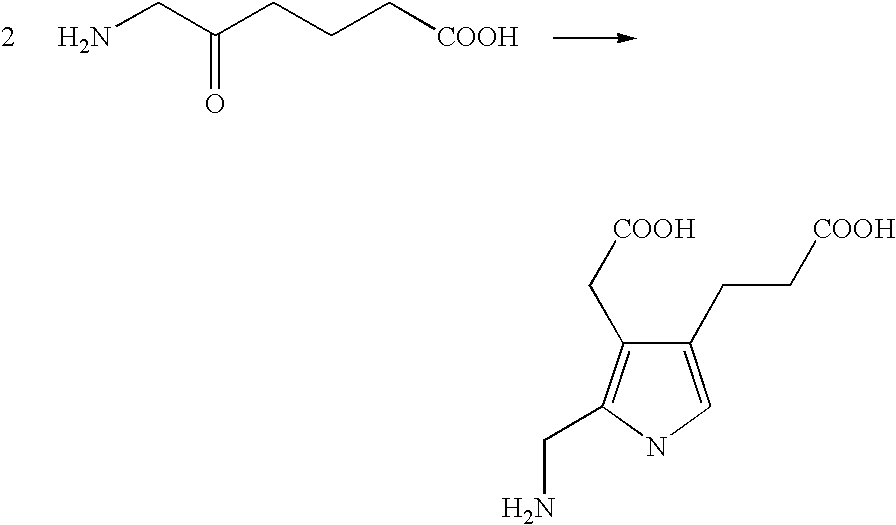
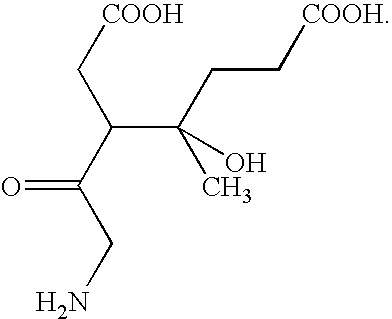
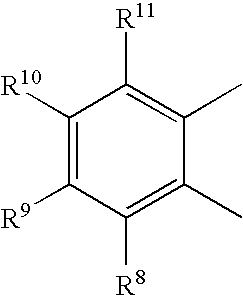
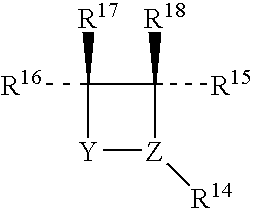
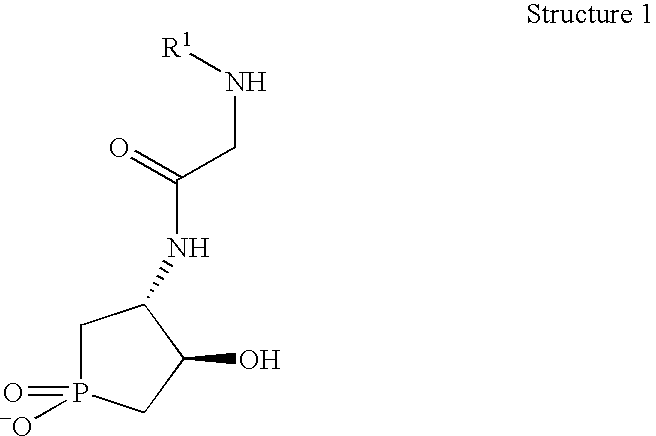
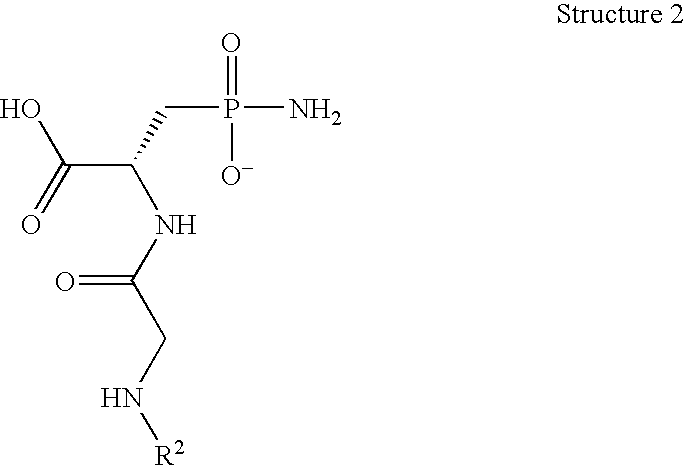
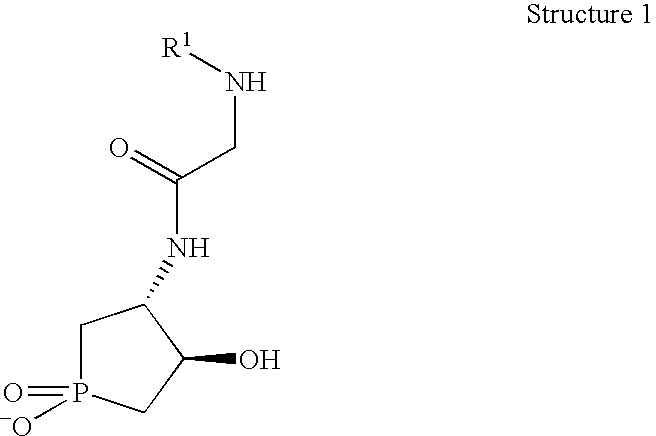
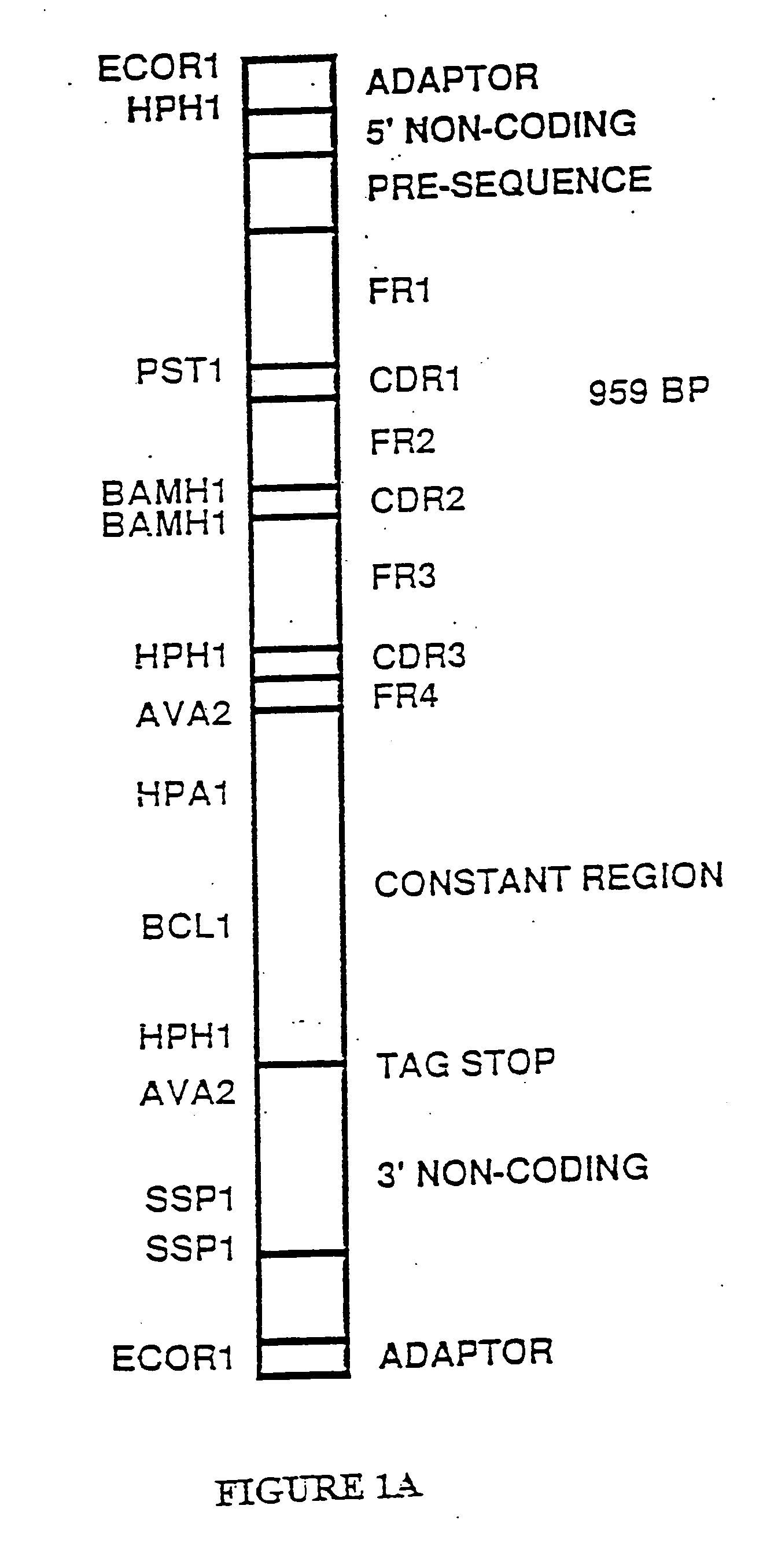
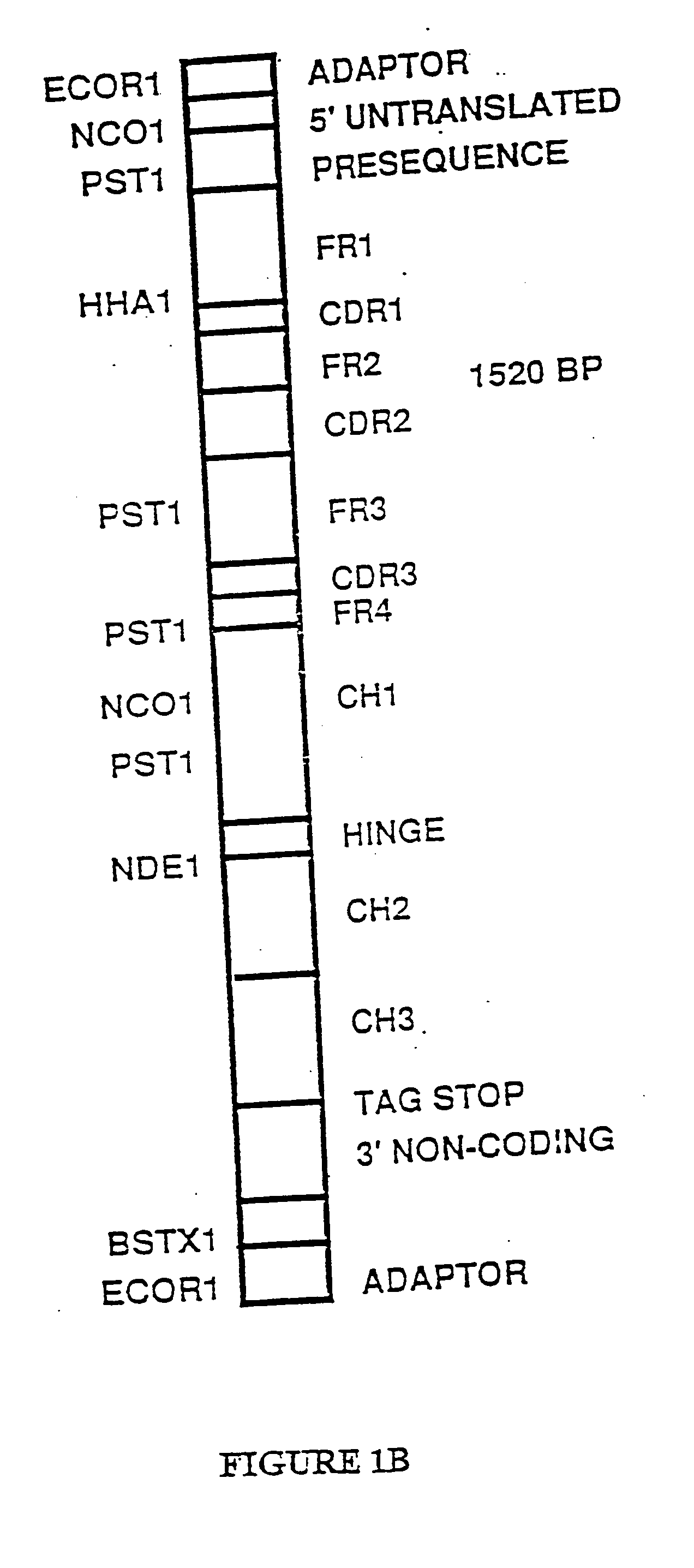
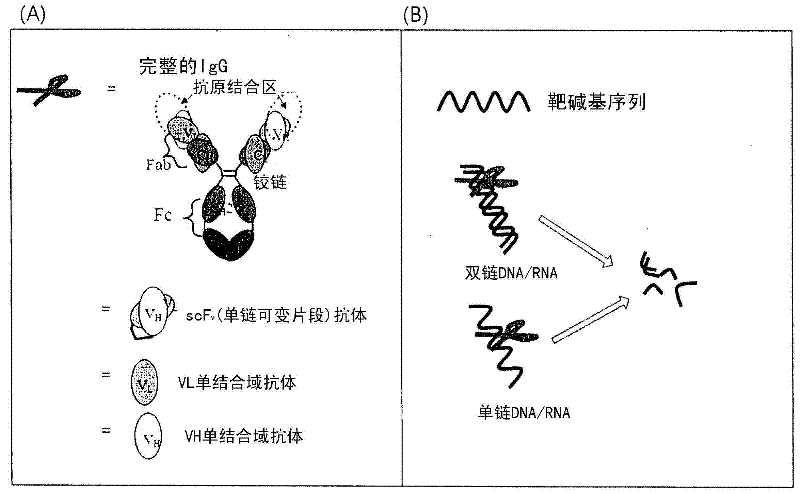
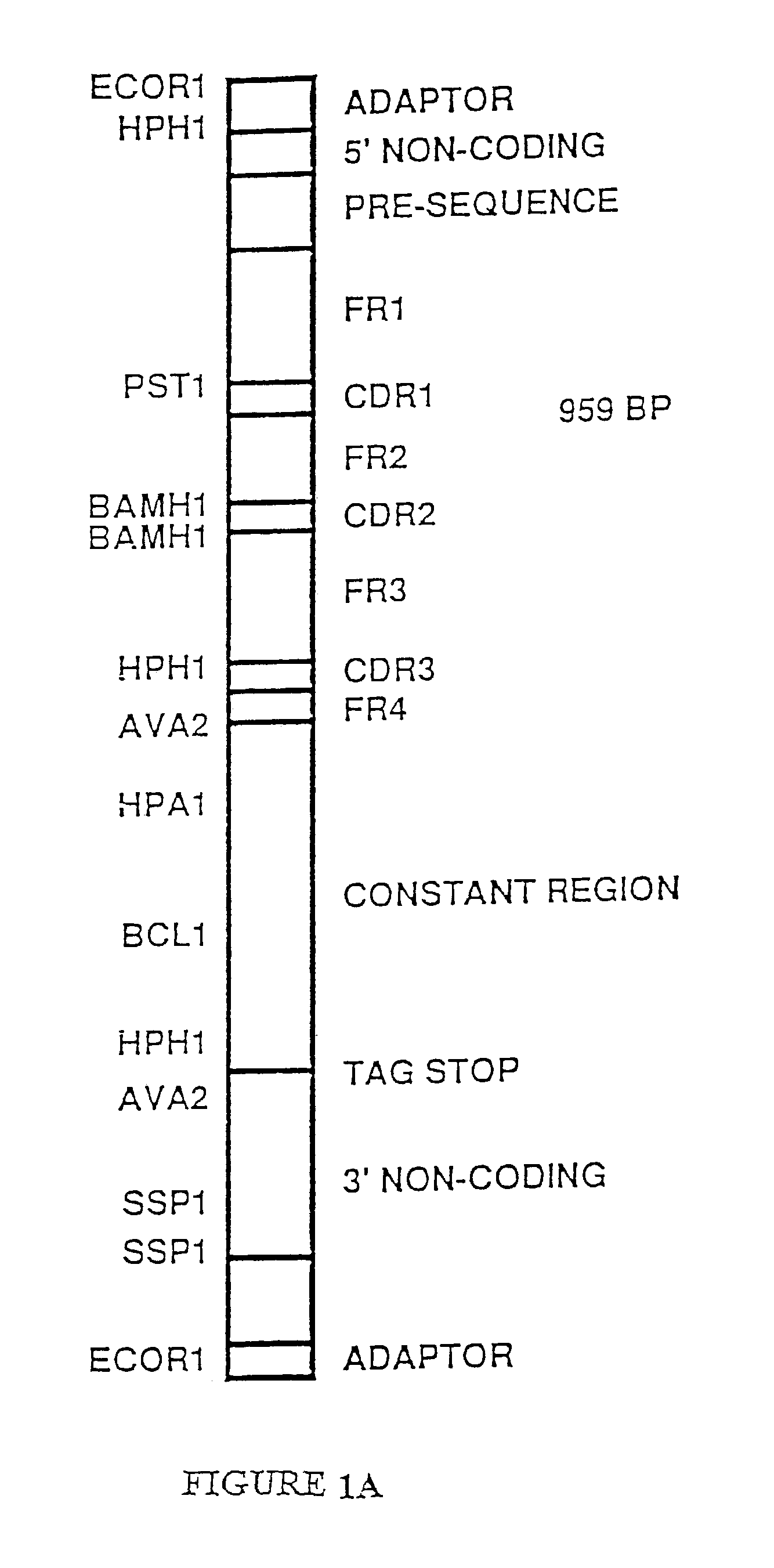
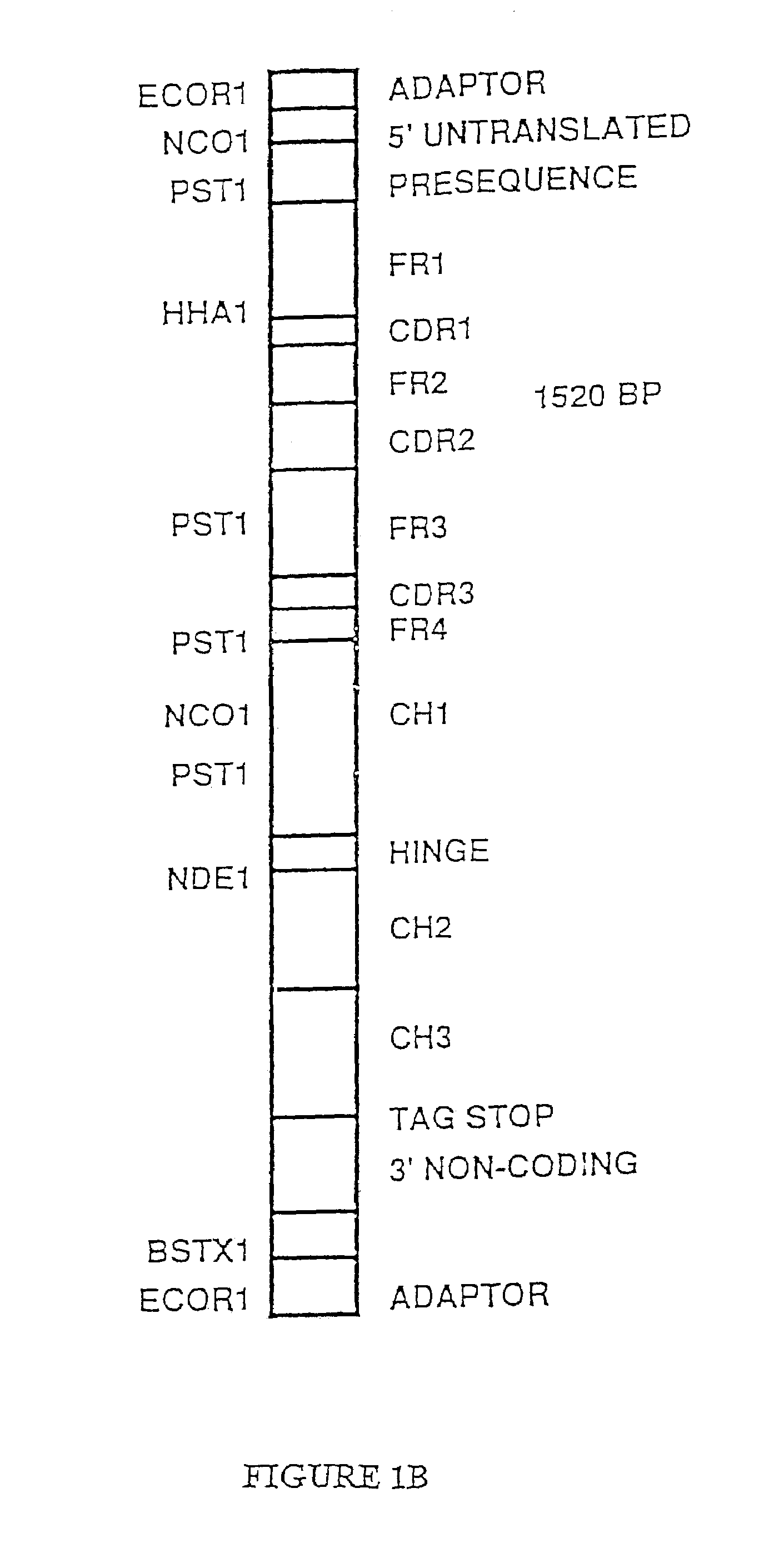
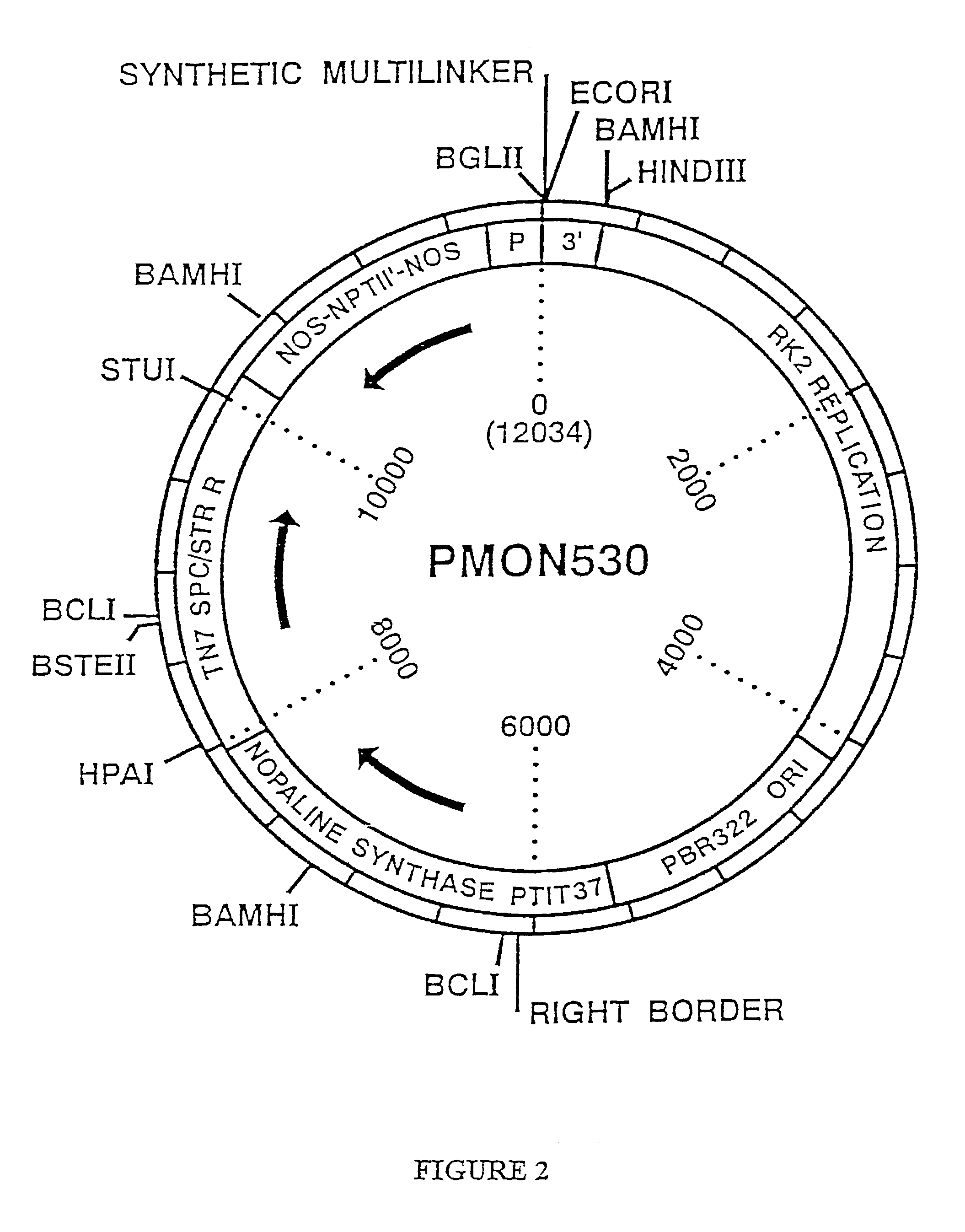
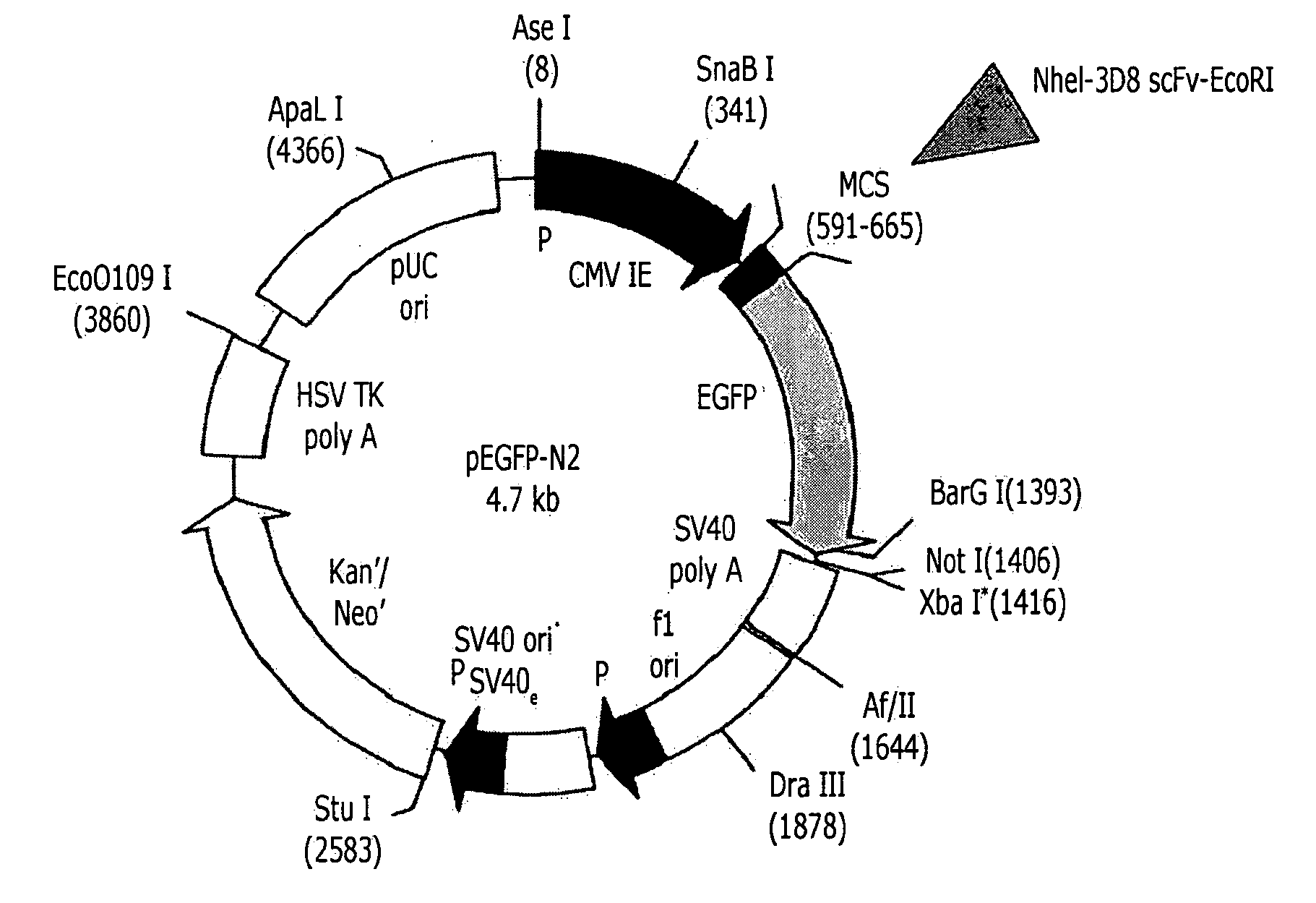
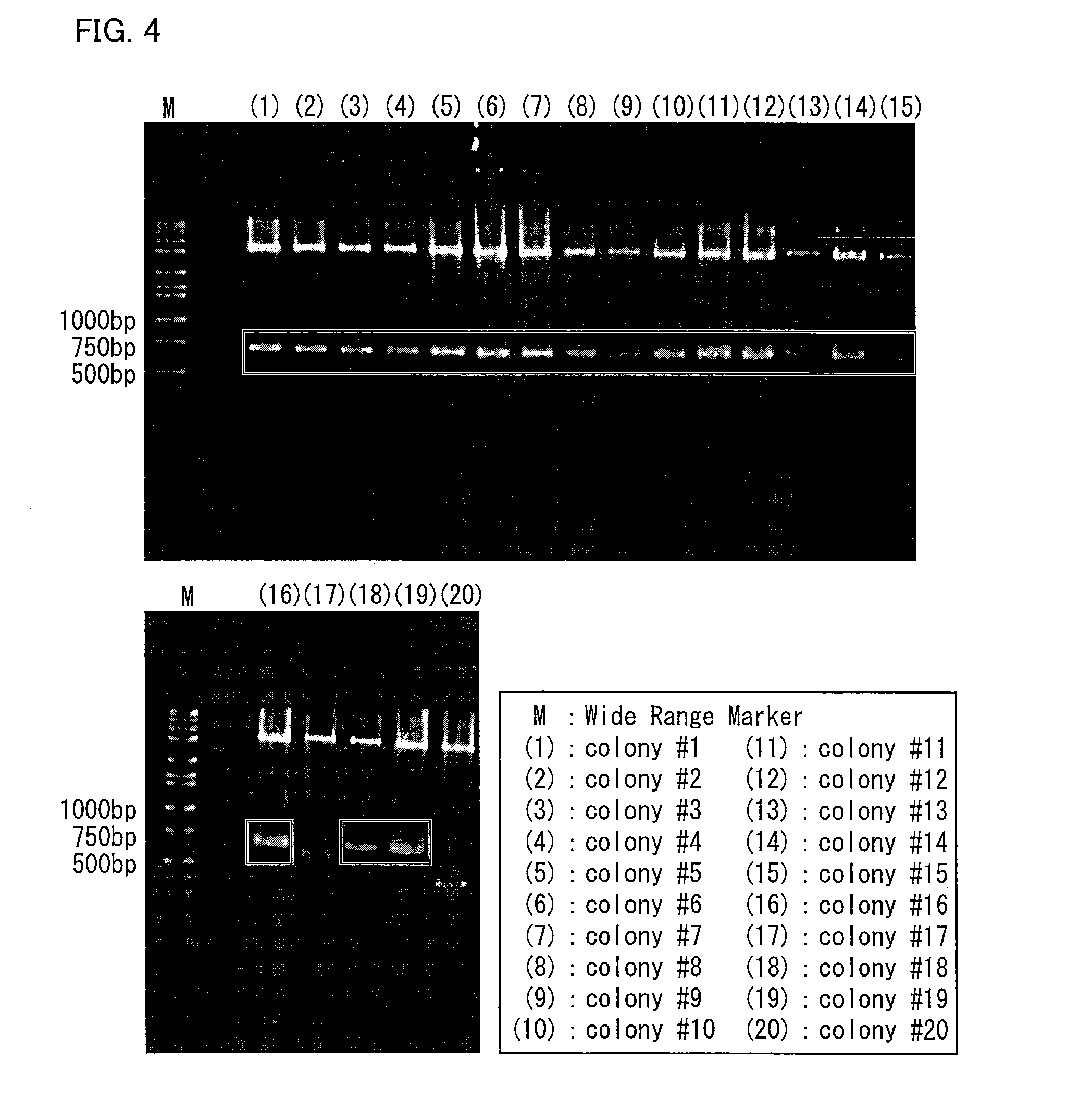
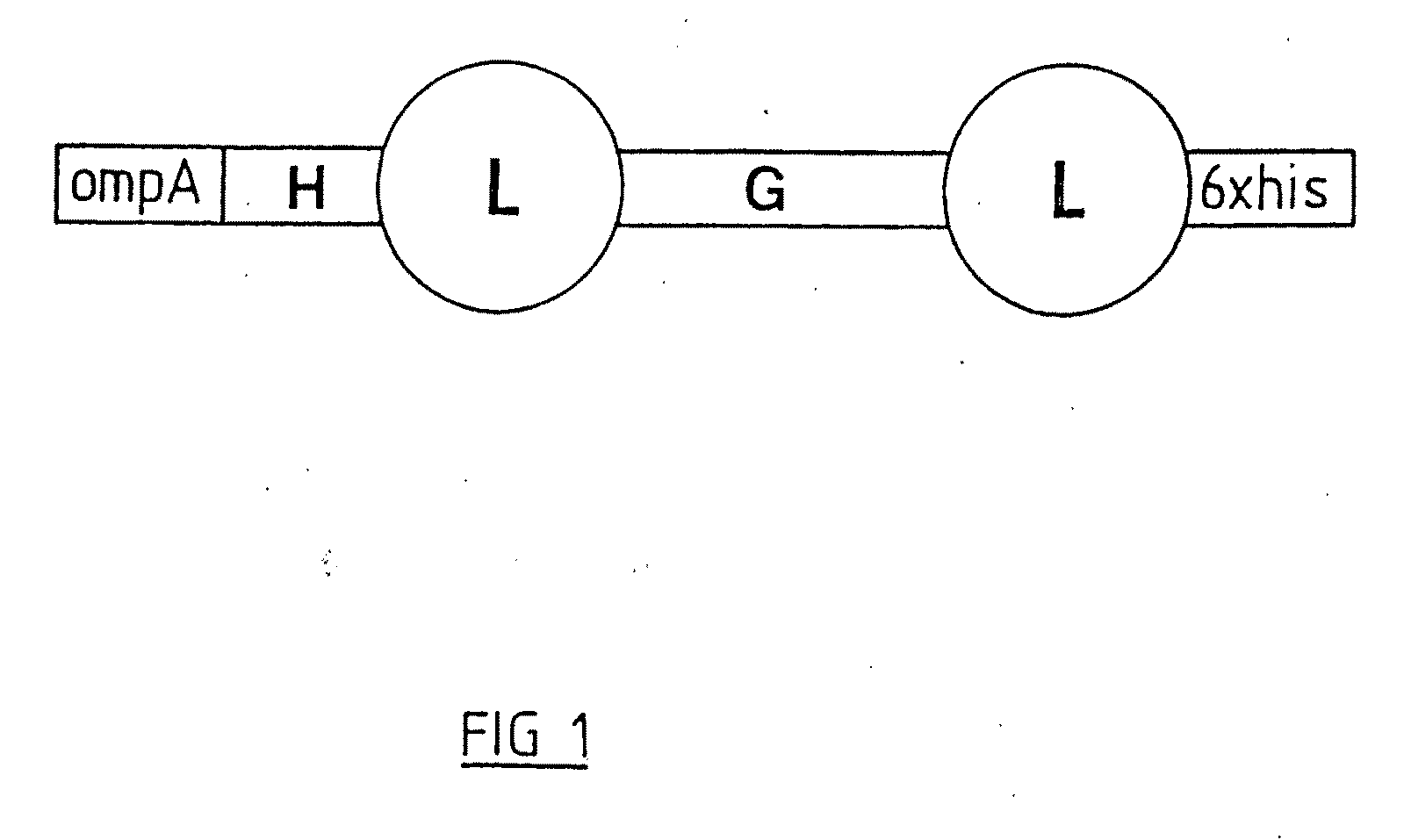
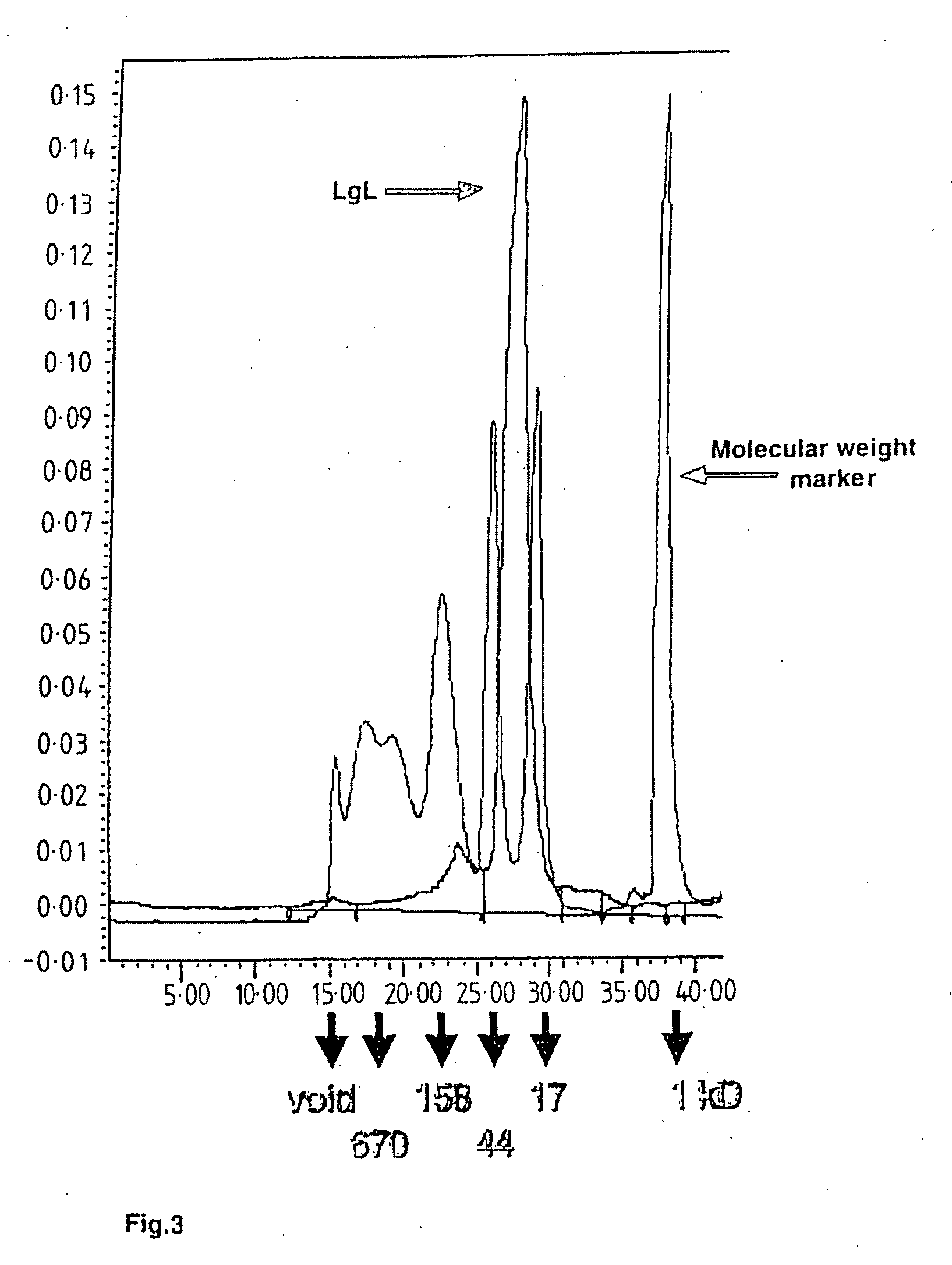
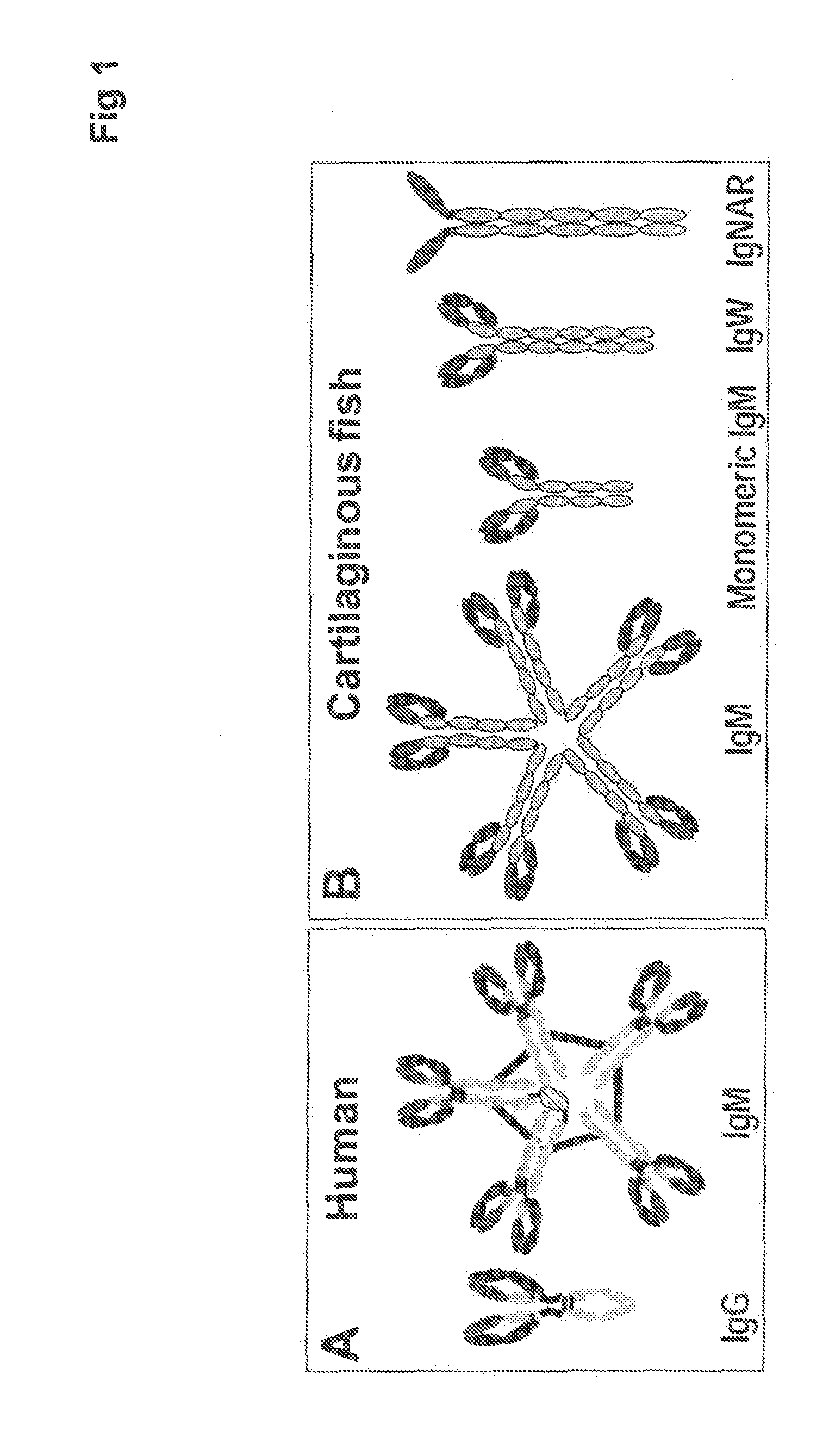
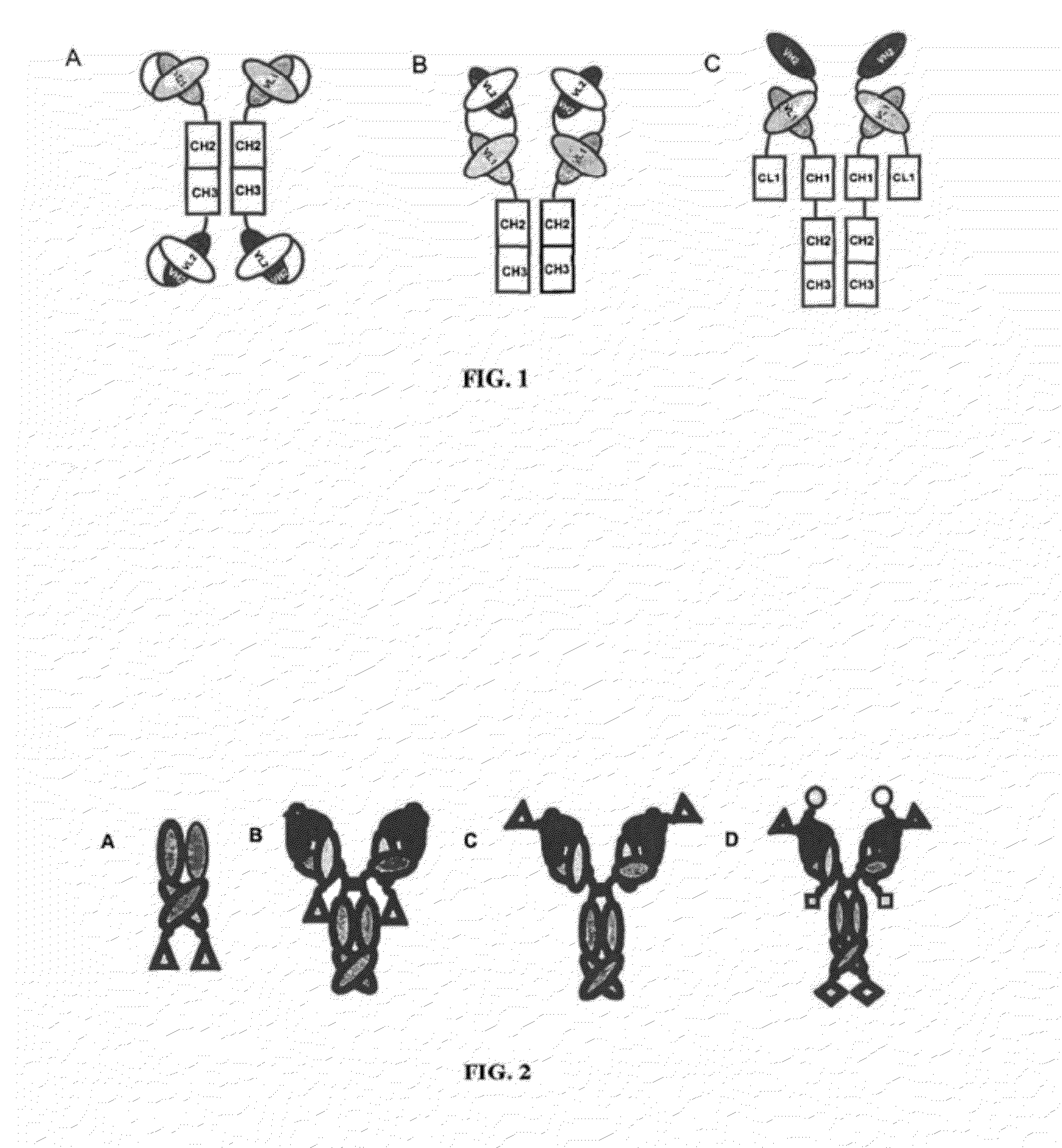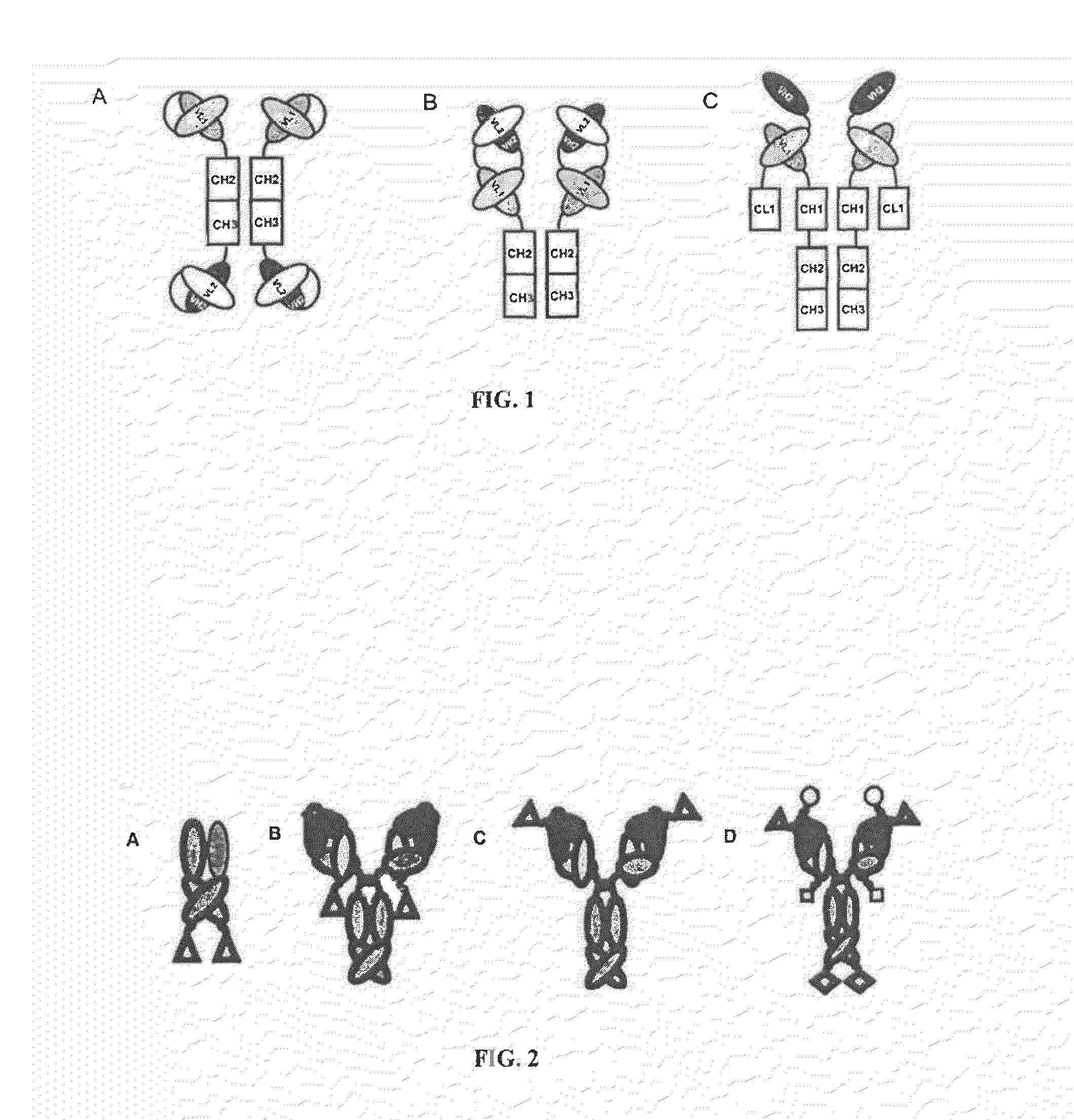Patents
Literature
49results about "Antibodies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Catalytic monoclonal antibodies with protease activity for selective lysis of protein component of plaques aggregates pathological conditions
InactiveUS6387674B1Reduce usageUseful in treatmentNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAbzymeDisease
Catalytic monoclonal antibodies (abzymes) with selective protease activity in the pathologies characterized by the presence of plaques and fibrillar aggregates with protein component; methods for the preparation thereof and the use thereof as medicaments in the treatment of pathologies such as Alzheimer's disease, amyloidosis, atherosclerosis, prions diseases.
Owner:ABIOGEN PHARMA SPA
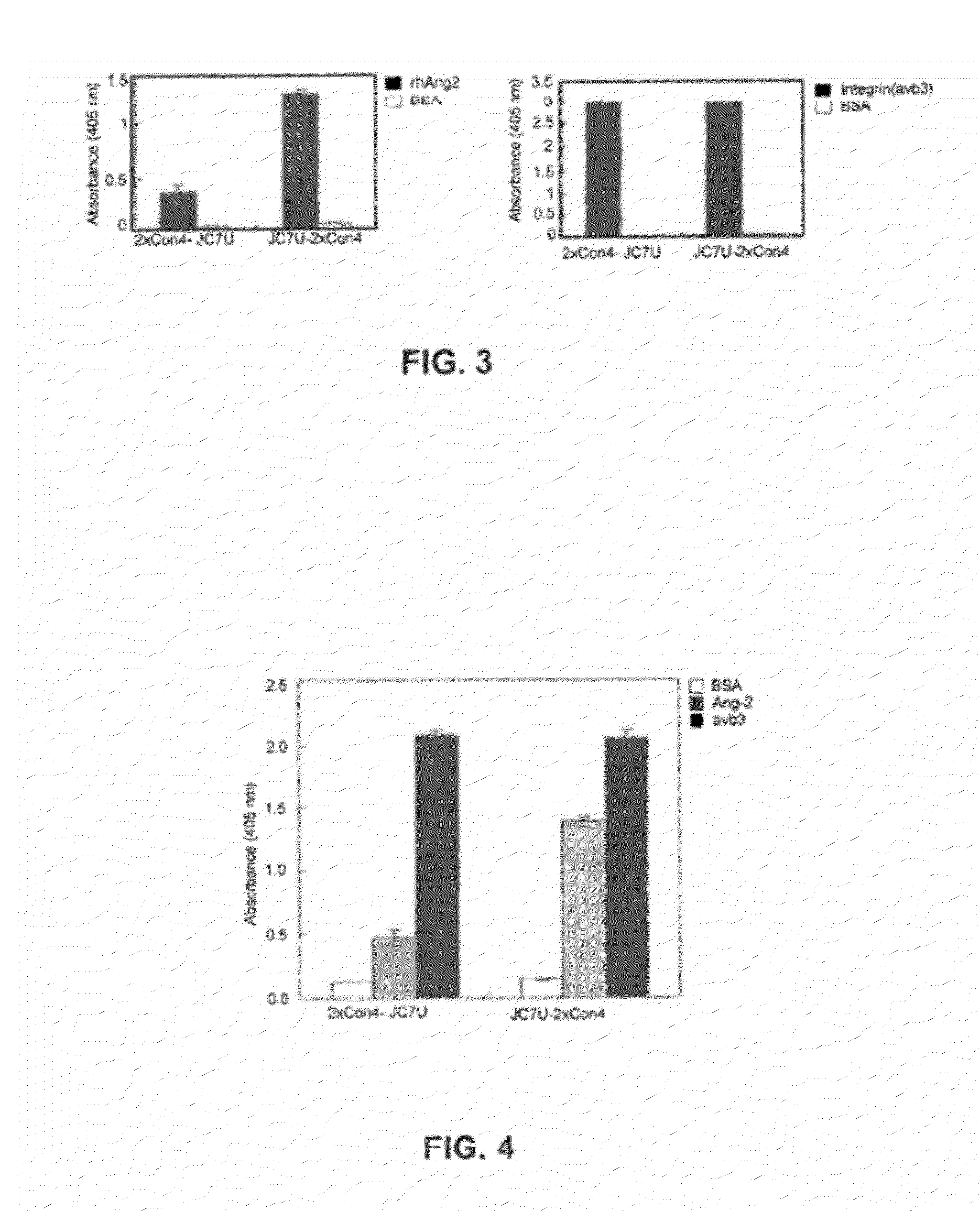
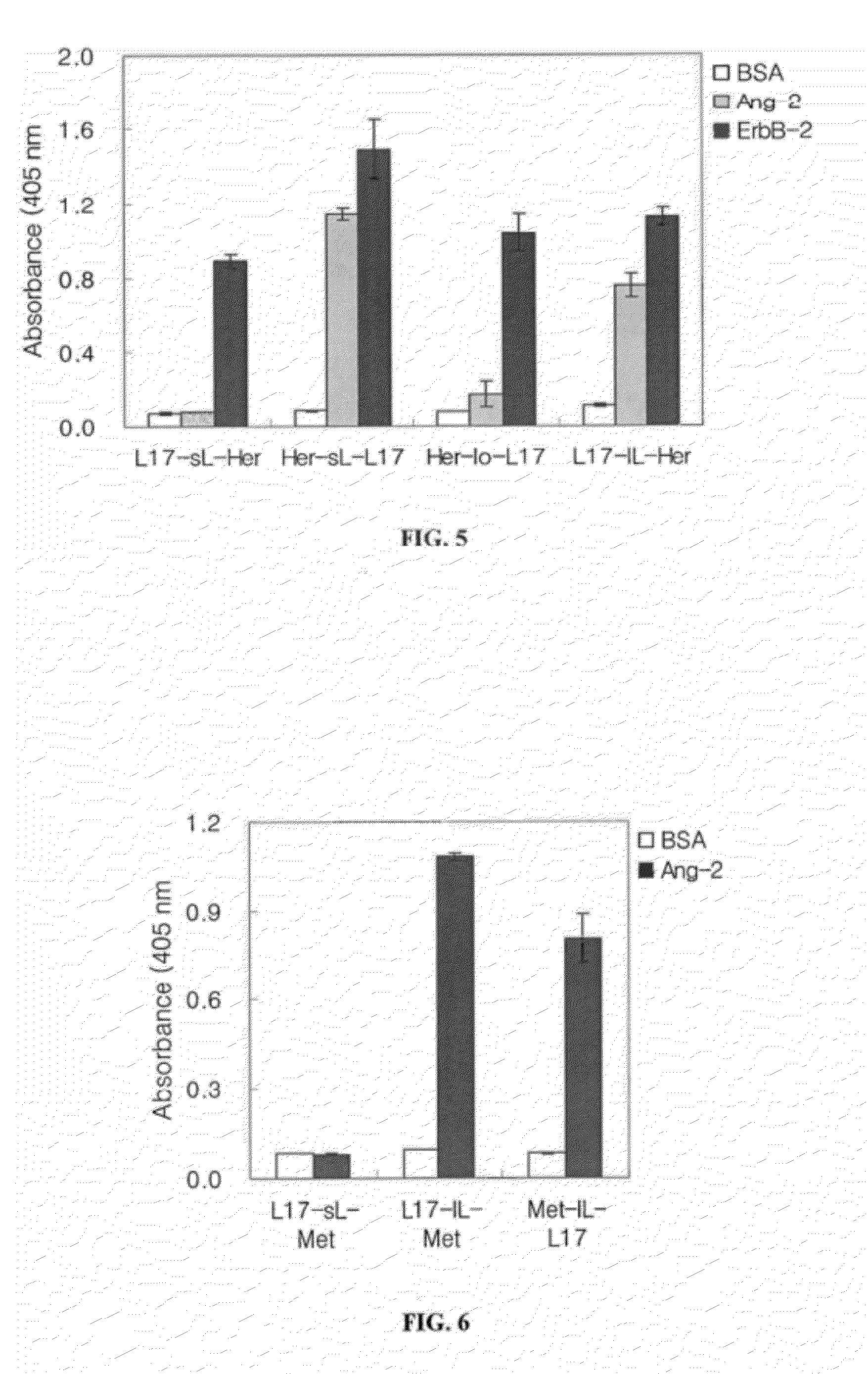
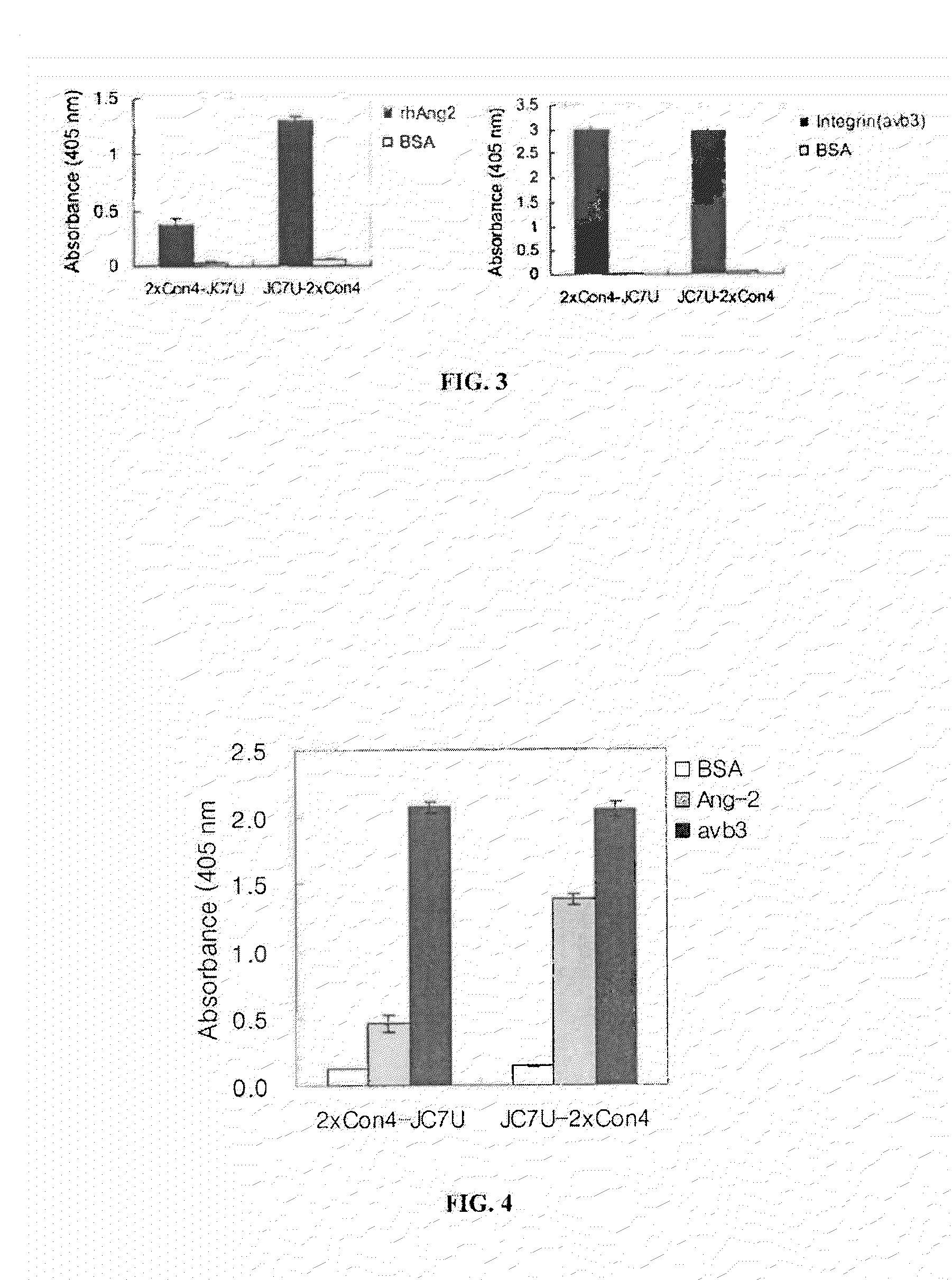
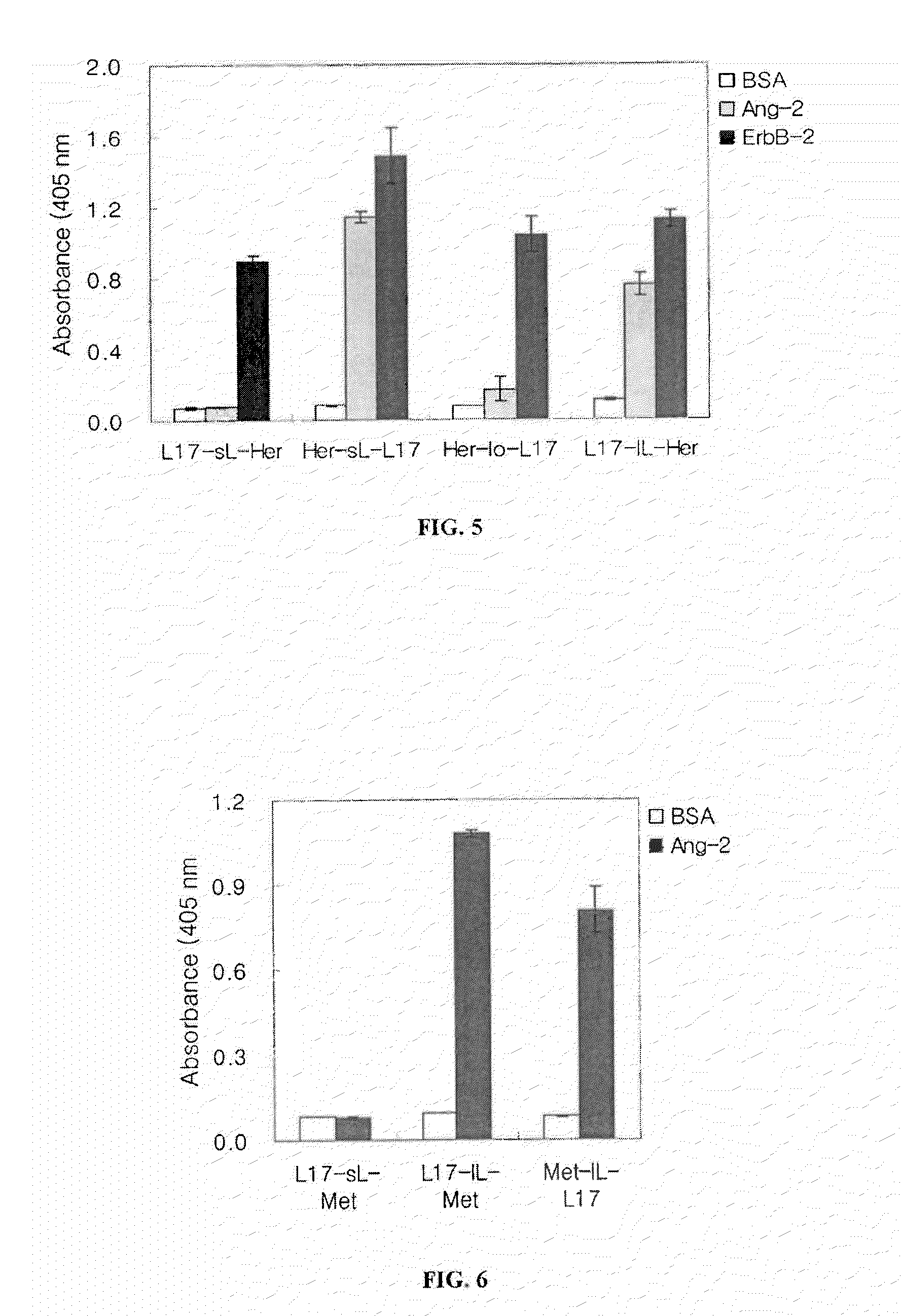
Ang-2 Binding Complexes and Uses Thereof
Owner:ZYNGENIA
Prodrugs activated by targeted catalytic proteins
InactiveUS6258360B1Minimal systemic exposureIncrease concentrationOrganic active ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCatalytic antibodyProtein C
Prodrugs that are activated by and conjugated to a catalytic antibody conjugated to a moiety that binds to a tumor cell population are provided.
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOCATALYSIS
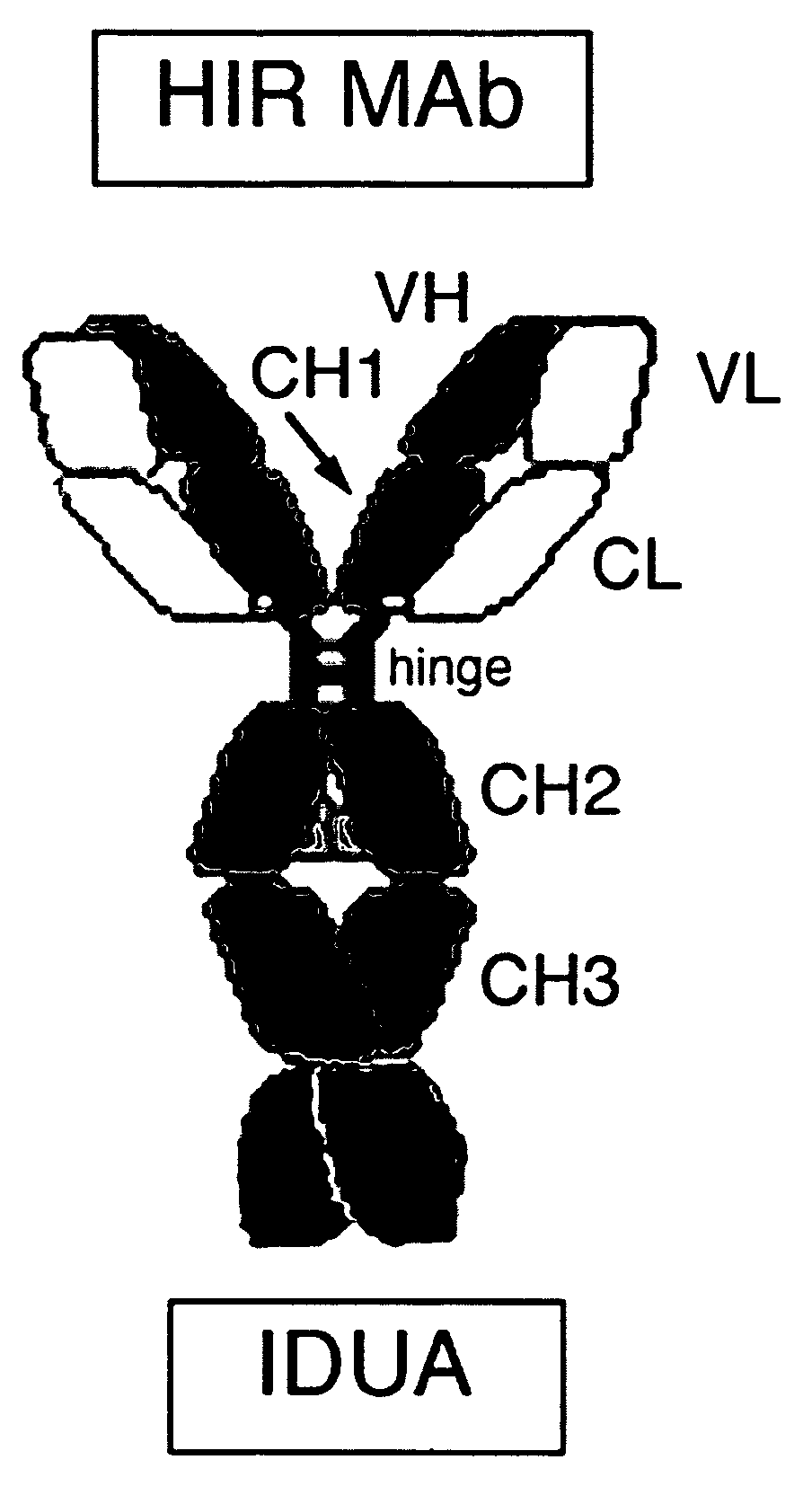
Methods and compositions for increasing alpha-l-iduronidase activity in the CNS
Provided herein are methods and compositions for treating a subject suffering from a deficiency in α-L-Iduronidase in the CNS. The methods include systemic administration of a bifunctional fusion antibody comprising an antibody to a human insulin receptor and an α-L-Iduronidase. A therapeutically effective systemic dose is based on the specific CNS uptake characteristics of human insulin receptor antibody-α-L-Iduronidase fusion antibodies as described herein.
Owner:ARMAGEN INC +1
Targeting compounds
InactiveUS20130171074A1Increase in sizeExtended half-lifeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAntibacterial agentsBinding siteBiological agent
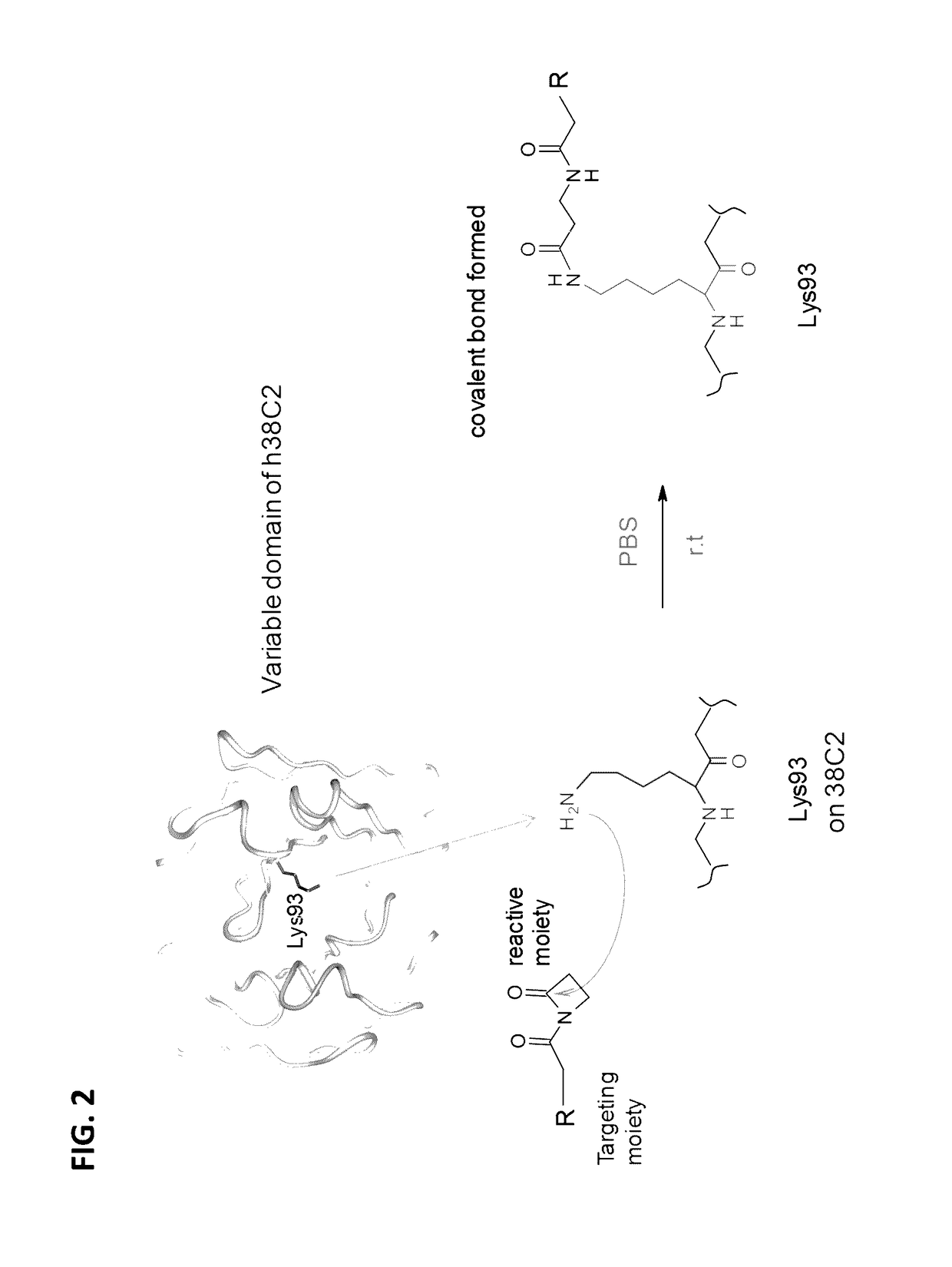
The present invention provides antibody targeting compounds in which the specificity of the antibody has been reprogrammed by covalently or noncovalently linking a targeting agent to the combining site of an antibody. By this approach, the covalently modified antibody takes on the binding specificity of the targeting agent. The compound may have biological activity provided by the targeting agent or by a separate biological agent. Various uses of the invention compounds are provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Novel process for producing antibody enzyme, novel antibody enzyme and utilization thereof
InactiveUS20060030015A1Reduce developmentInhibition of disease progressionAnimal cellsFungiStructure analysisHelicobacter pylori
A process for producing an antibody enzyme which involves an antibody structure analysis step of confirming the presence of a catalyst triplet residue structure wherein a serine residue, an aspartate residue and a histidine residue or a glutamate residue are located stereostructurally close to each other in the stereostructure of an antibldy anticipated based on its amino acid sequence. Since the above-described catalyst triplet residue structure is a structure specific to an antibody enzyme, an antibody enzyme can be efficiently screened by using the same. Examples of the antibody enzyme as described above include an antibody enzyme against Helicobacter pylori urease and an antibody enzyme against chemokine receptor CCR-5.
Owner:TOWA KAGAKU CO LTD
Ang-2 Binding Complexes and Uses Thereof
Complexes containing one or more modular recognition domains (MRDs) and MRDs attached to scaffold's including antibodies are described. The manufacture of these complexes are the use of these complexes to treat and diagnose diseases and disorders are also described.
Owner:ZYNGENIA
Catalytic antibodies
ActiveUS7205136B1Strong specificityConstant and inexpensiveMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisChemical reactionReaction rate
A method for increasing the rate of chemical reactions involving the conversion of at least one reactant to at least one product involves contacting the reactant with an appropriate monoclonal antibody under conditions permitting the formation of a complex between the antibody and the reactant. The complexed reactant is converted to the product which is then released from the complex. The monoclonal antibody may employ a cofactor and may be directed to a known substrate of an enzyme. Methods for preparing such monoclonal antibodies are also disclosed.
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOCATALYSIS
Prodrugs activated by targeted catalytic proteins
InactiveUS6702705B1Minimal systemic exposureIncrease concentrationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCatalytic antibodyProtein C
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOCATALYSIS
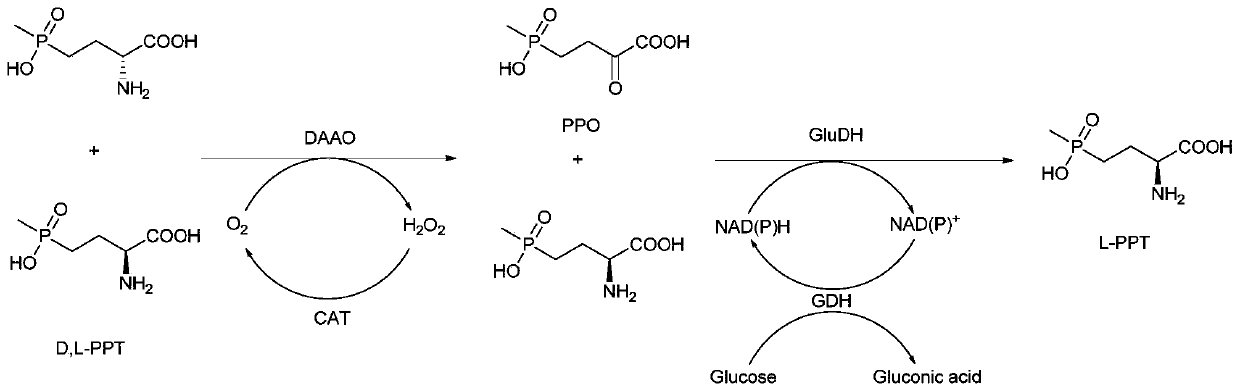
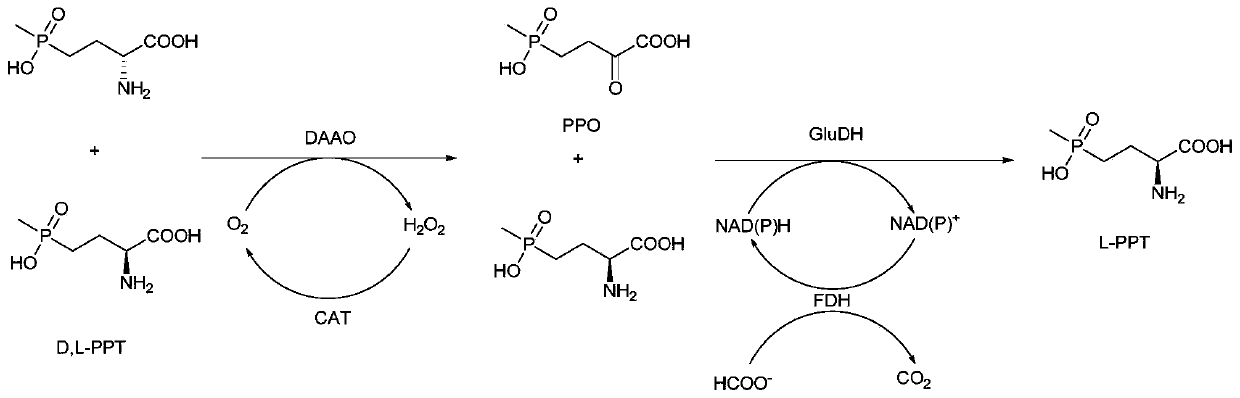
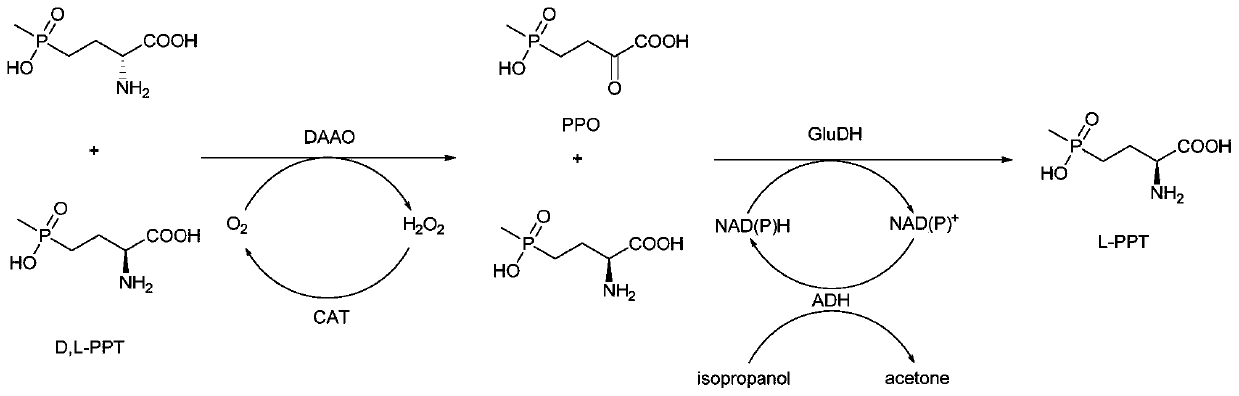
Method for preparing L-phosphinothricin through de-racemization by biological enzyme method, phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant and application
ActiveCN111363775AHigh catalytic efficiencyImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesAntibodiesAcid catalysisOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-phosphinothricin through de-racemization by a biological enzyme method, a phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant and an application. According to the method for preparing L-phosphinothricin through de-racemization by a biological enzyme method, D,L-phosphinothricin is used as a raw material, through catalysis with a multienzyme catalysis system, theL-phosphinothricin is obtained, wherein the enzyme catalysis system comprises D-amino acid oxidase which is used for catalyzing D-phosphinothricin in the D,L-phosphinothricin into 4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-2-oxobutanoic, and the phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant which is used for performing catalytic reduction on the 4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-2-oxobutanoic to obtain the L-phosphinothricin,the phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant is obtained through mutation of phosphinothricin dehydrogenase in wild mushrooms Thiopseudomonas denitrificans, and a mutation site is V377S. The phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant disclosed by the invention has better catalysis efficiency, when a catalytic reaction is performed by using racemation D,L-phosphinothricin as a substrate, the conversion rate is far higher than that of a catalytic reaction performed by using a wild type enzyme as a substrate, and the PPO yield is also substantially increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Methods and compositions for increasing α-L-iduronidase activity in the CNS
Provided herein are methods and compositions for treating a subject suffering from a deficiency in α-L-Iduronidase in the CNS. The methods include systemic administration of a bifunctional fusion antibody comprising an antibody to a human insulin receptor and an α-L-Iduronidase. A therapeutically effective systemic dose is based on the specific CNS uptake characteristics of human insulin receptor antibody-α-L-Iduronidase fusion antibodies as described herein.
Owner:ARMAGEN INC +1
Antibody targeting compounds
InactiveCN1606454AEasy to measurePromote exchangeAntibacterial agentsVirusesAntibody targetingCovalent modification
The present invention provides antibody targeting compounds in which the specificity of the antibody has been reprogrammed by covalently or non-covalently linking a targeting agent to the antibody binding site. By this approach, covalently modified antibodies exhibit binding specificity for the targeted agent. Compounds may have biological activity provided by targeted agents or separate biological agents. Various uses of the compounds of the invention are provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Asparagine deaminase catalytic antibodies
InactiveUS20050084488A1Group 5/15 element organic compoundsAntibody ingredientsCatalytic antibodyAspartic acid
Transition state analogs are described which may be used to elicit antibodies that catalyze the conversion of asparagine to aspartic acid. Synthetic schemes are disclosed for making the transition state analogs which can than be attached to a carrier molecule to form an immunoconjugate. Immunoconjugates can be administered to an animal for the purpose of raising antibodies. Antibodies can in turn be used in pharmaceutical compositions which can be given to patients as part of a method of treating various conditions, particularly cancer.
Owner:AMGEN FREMONT INC
Transgenic plants expressing assembled secretory antibodies
InactiveUS20050241023A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsForeign matterTransgene
The present invention relates to expression and assembly of foreign multimeric proteins—e.g., antibodies—in plants, as well as to transgenic plants that express such proteins. In one of several preferred embodiments, the generation and assembly of functional secretory antibodies in plants is disclosed. The invention also discloses compositions produced by the transgenic plants of the present invention and methods of using same.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
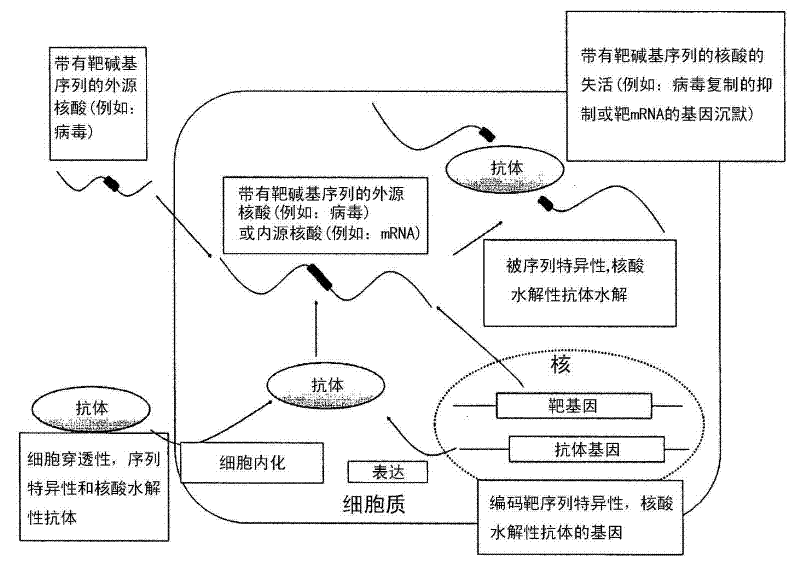
Cell-penetrating, sequence-specific and nucleic acid-hydrolyzing antibody, method for preparing the same and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same
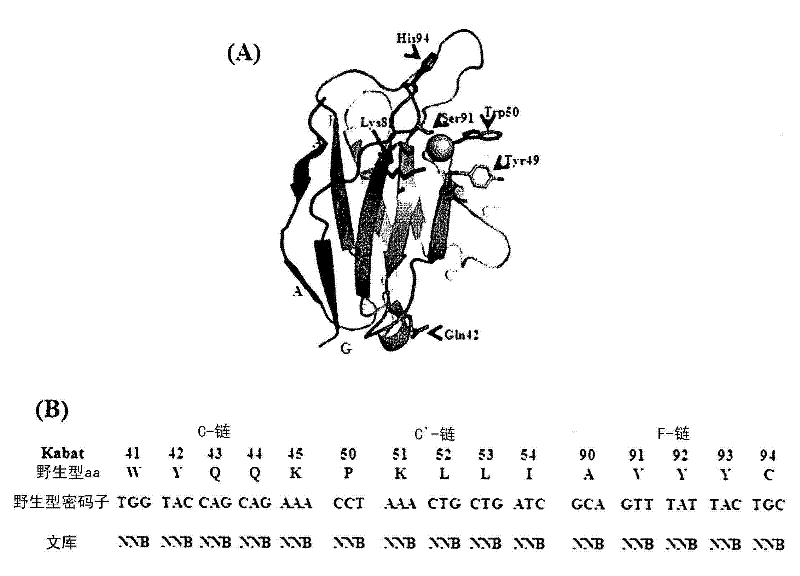
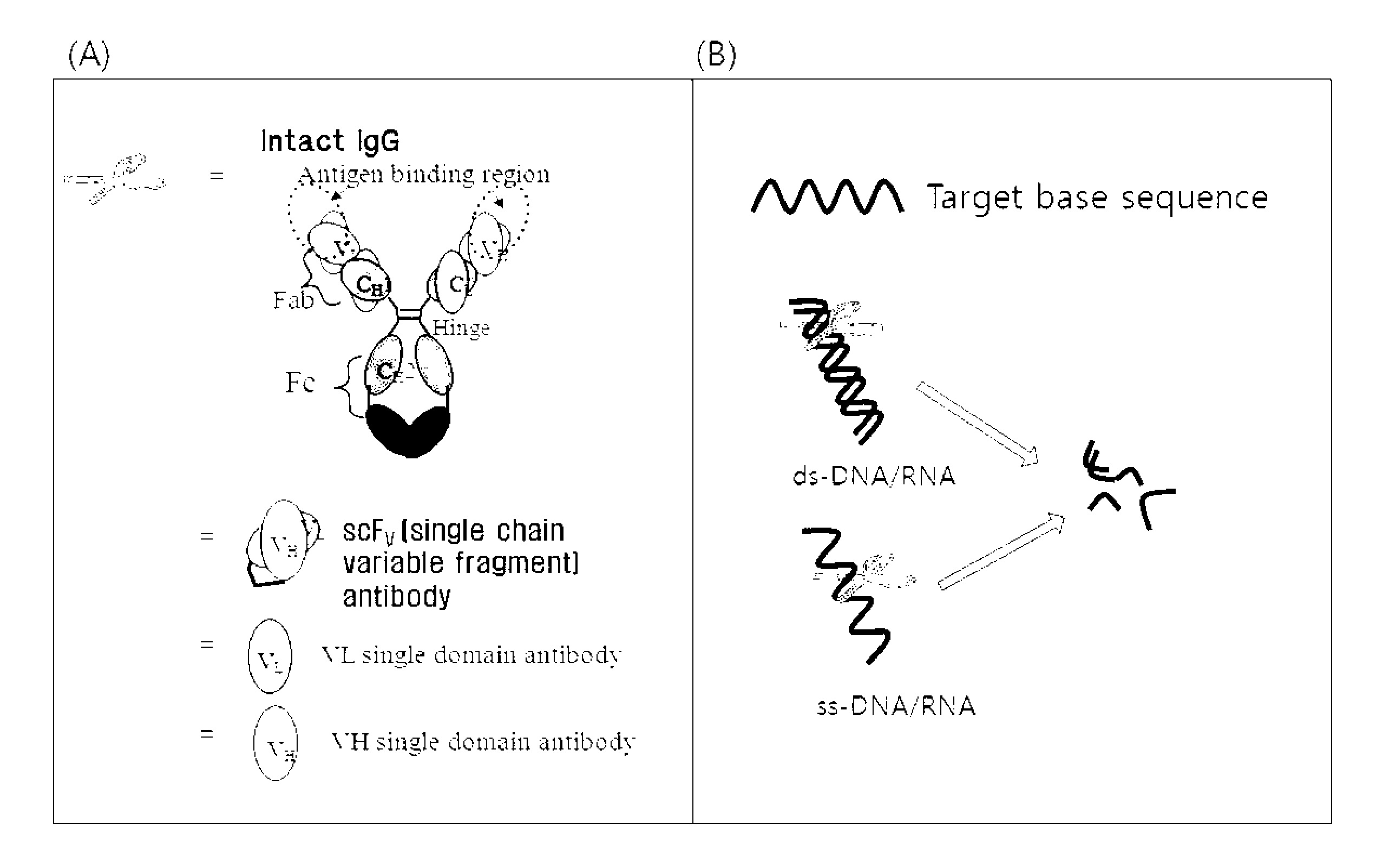
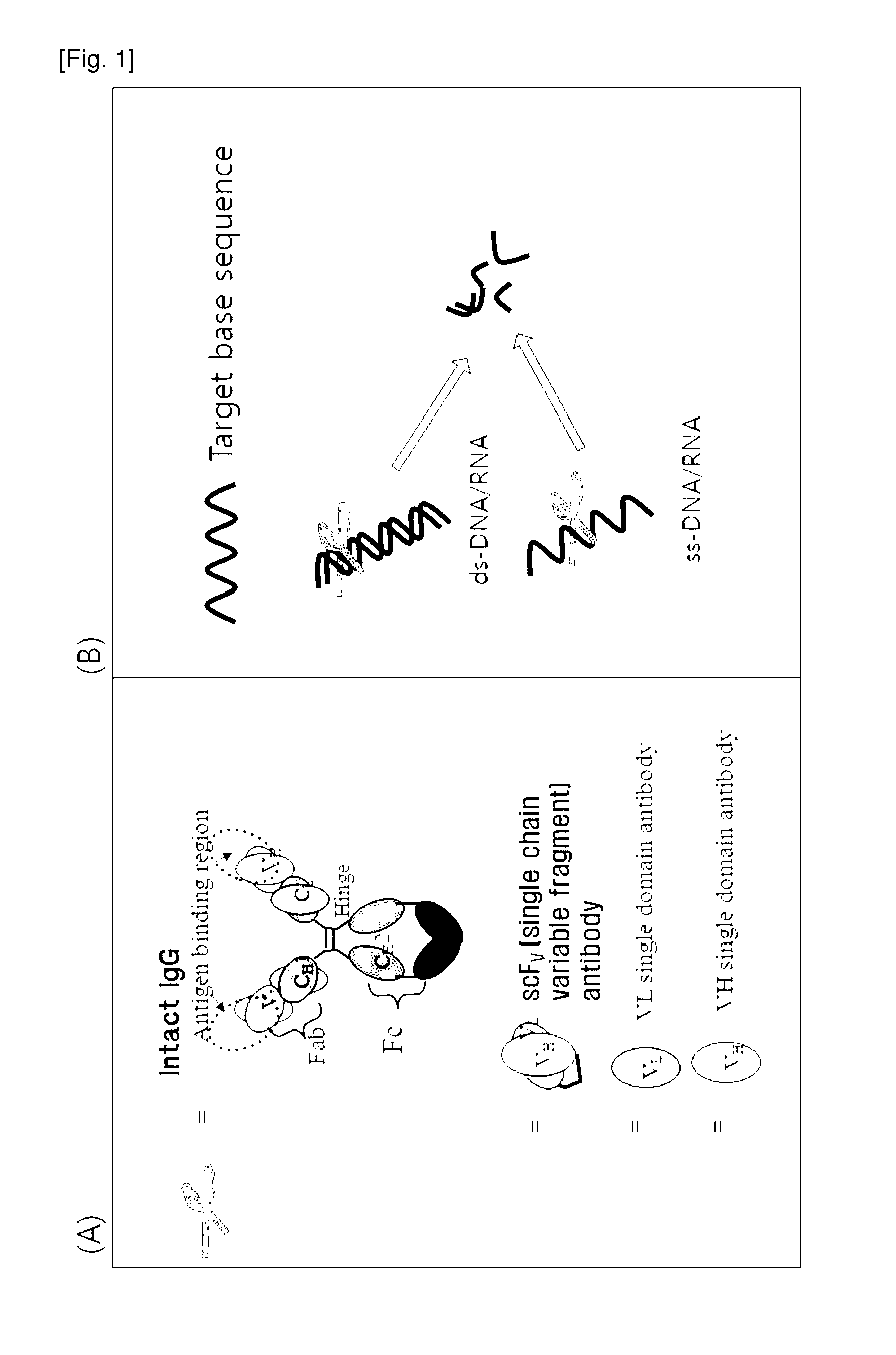
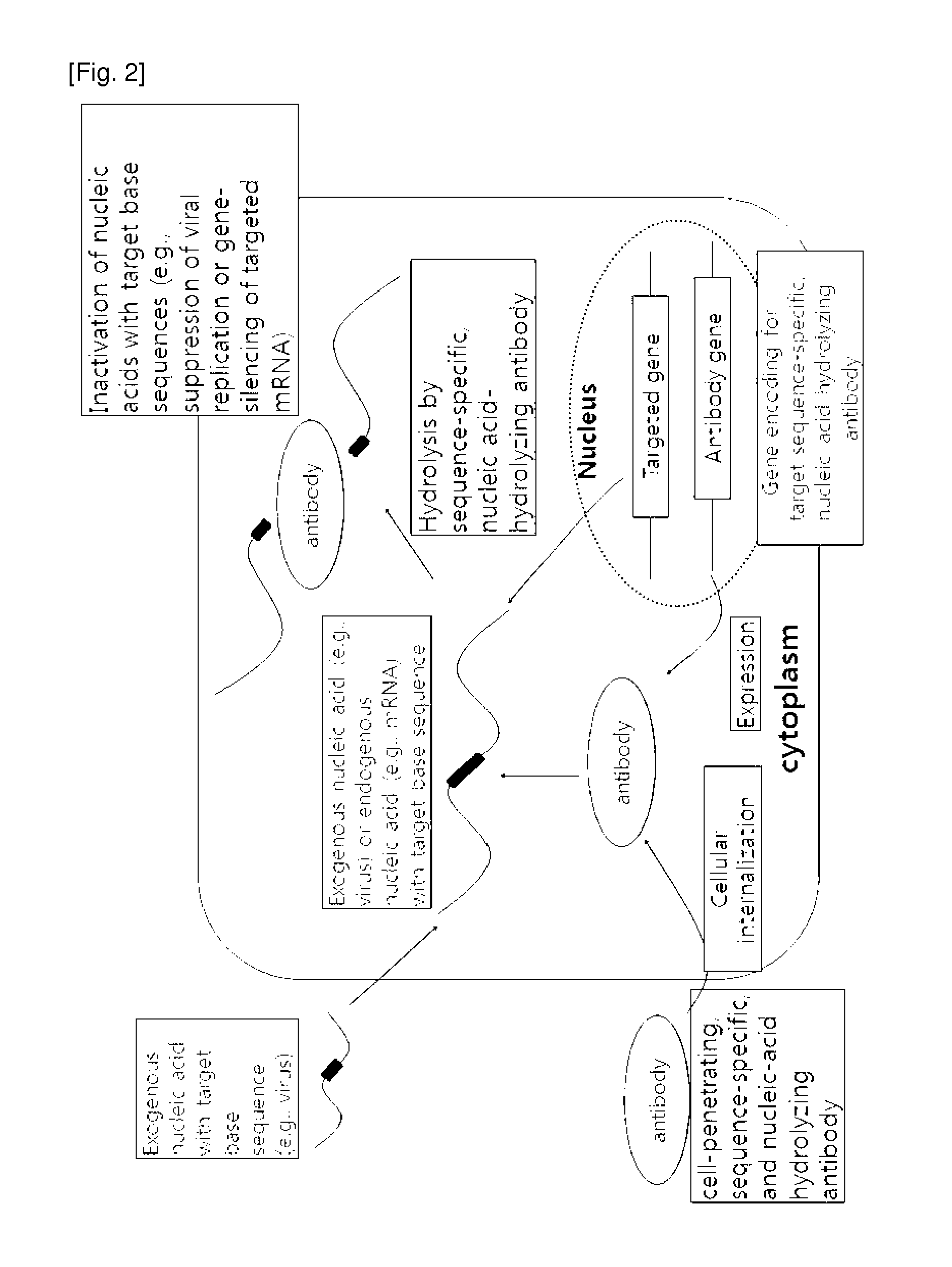
InactiveCN102209726AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibodiesDouble strandedSubstrate specificity
Disclosed are a cell-penetrating, base sequence-specific, nucleic acid-hydrolyzing antibody, a method of preparing the same, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same. The antibody can be prepared by modifying a particular site of a cell-penetrating, nucleic acid-hydrolyzing antibody which lacks substrate specificity to impart sequence specificity thereto without alteration in nucleic acid-hydrolyzing ability. The antibody, when penetrating into cells by itself or ectopically expressed within cells, binds specifically to single- or double-stranded nucleic acid targets and hydrolyzes them, thus downregulating the expression of the targeted genes.
Owner:亚州大学校产学协力团
Cell-penetrating, sequence-specific and nucleic acid-hydrolyzing antibody, method for preparing the same and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same
InactiveUS20110263829A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide preparation methodsDouble strandedSubstrate specificity
Disclosed are a cell-penetrating, base sequence-specific, nucleic acid-hydrolyzing antibody, a method of preparing the same, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same. The antibody can be prepared by modifying a particular site of a cell-penetrating, nucleic acid-hydrolyzing antibody which lacks substrate specificity to impart sequence specificity thereto without alteration in nucleic acid-hydrolyzing ability. The antibody, when penetrating into cells by itself or ectopically expressed within cells, binds specifically to single- or double-stranded nucleic acid targets and hydrolyzes them, thus downregulating the expression of the targeted genes.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
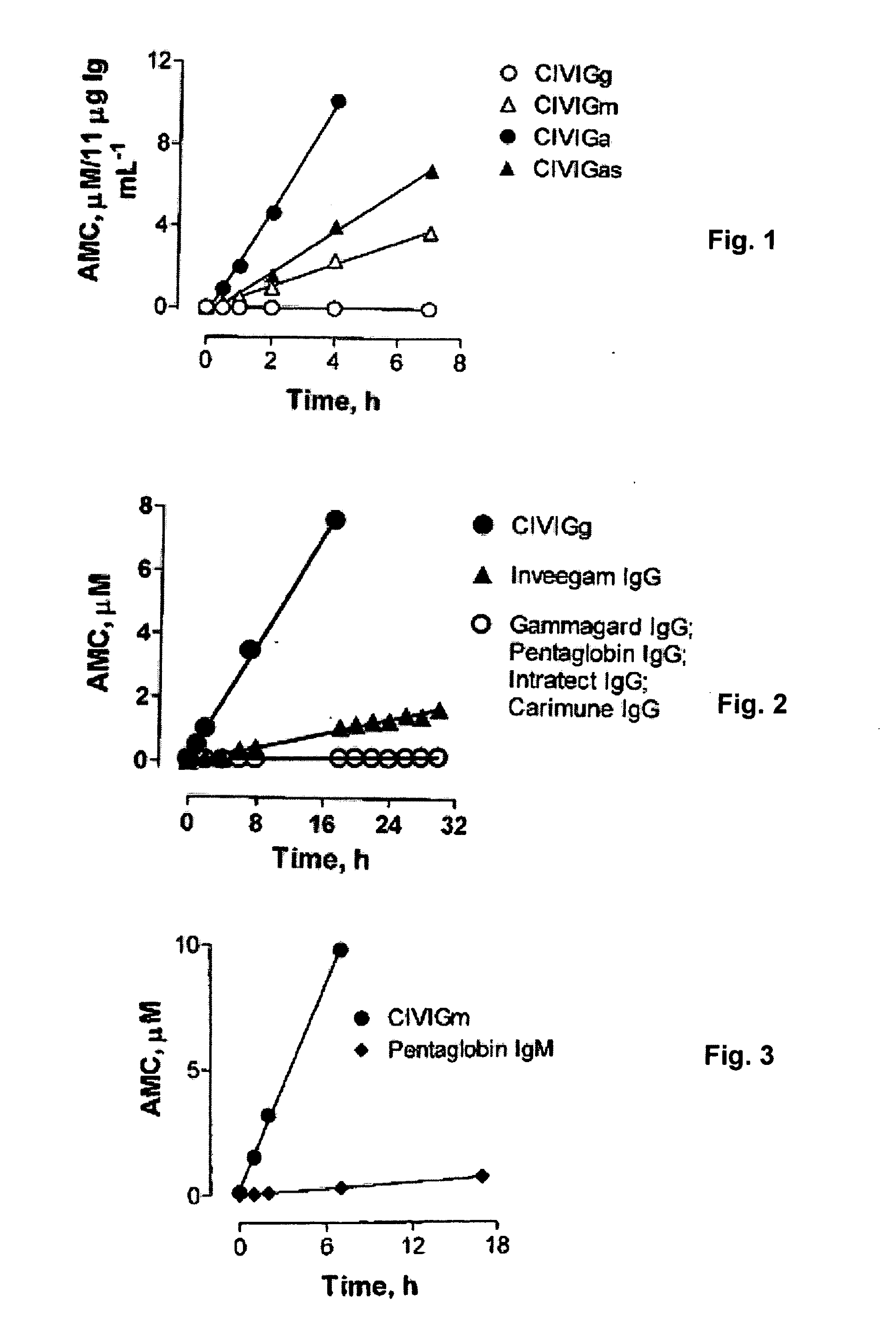
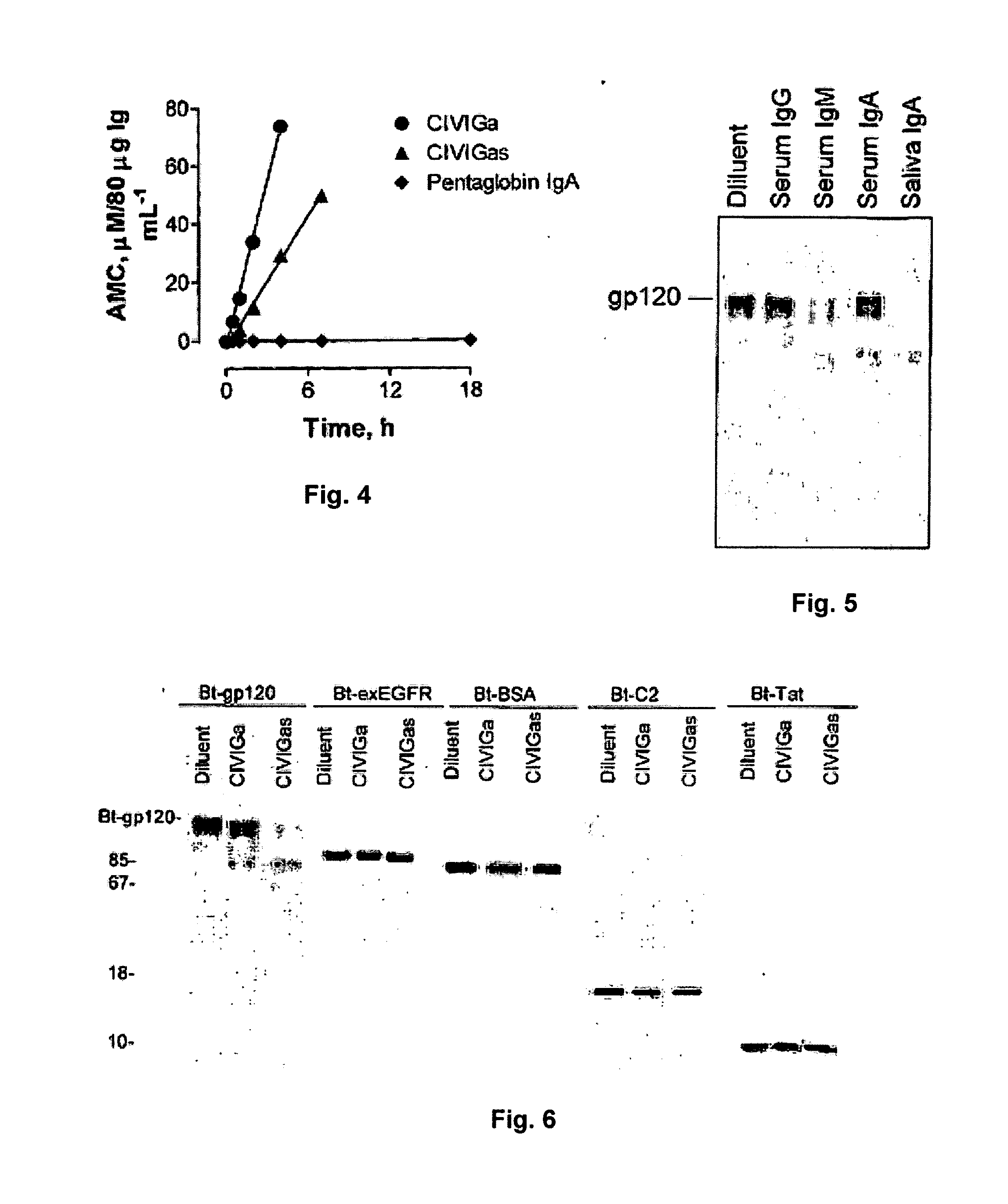
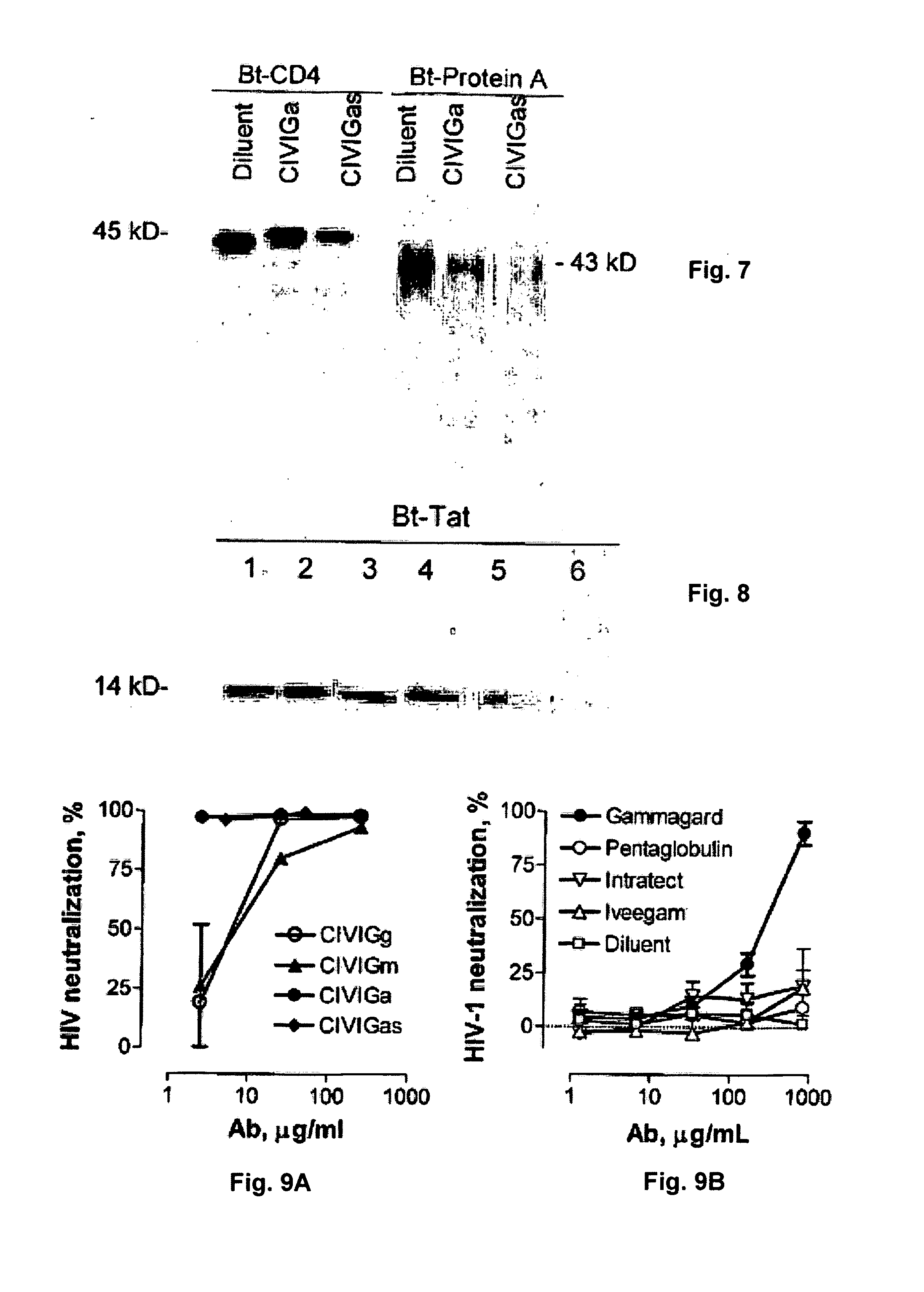
Catalytic Immunoglobulins BBK32 and Uses Therefor
InactiveUS20090297534A1Delay progressReduce resistanceAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderHuman immunoglobulinsStereochemistry
The present invention describes the composition of class and subclass selected pooled human immunoglobulins with catalytic activity, methods of preparation thereof, and therapeutic utility thereof.
Owner:PAUL SUDHIR +3
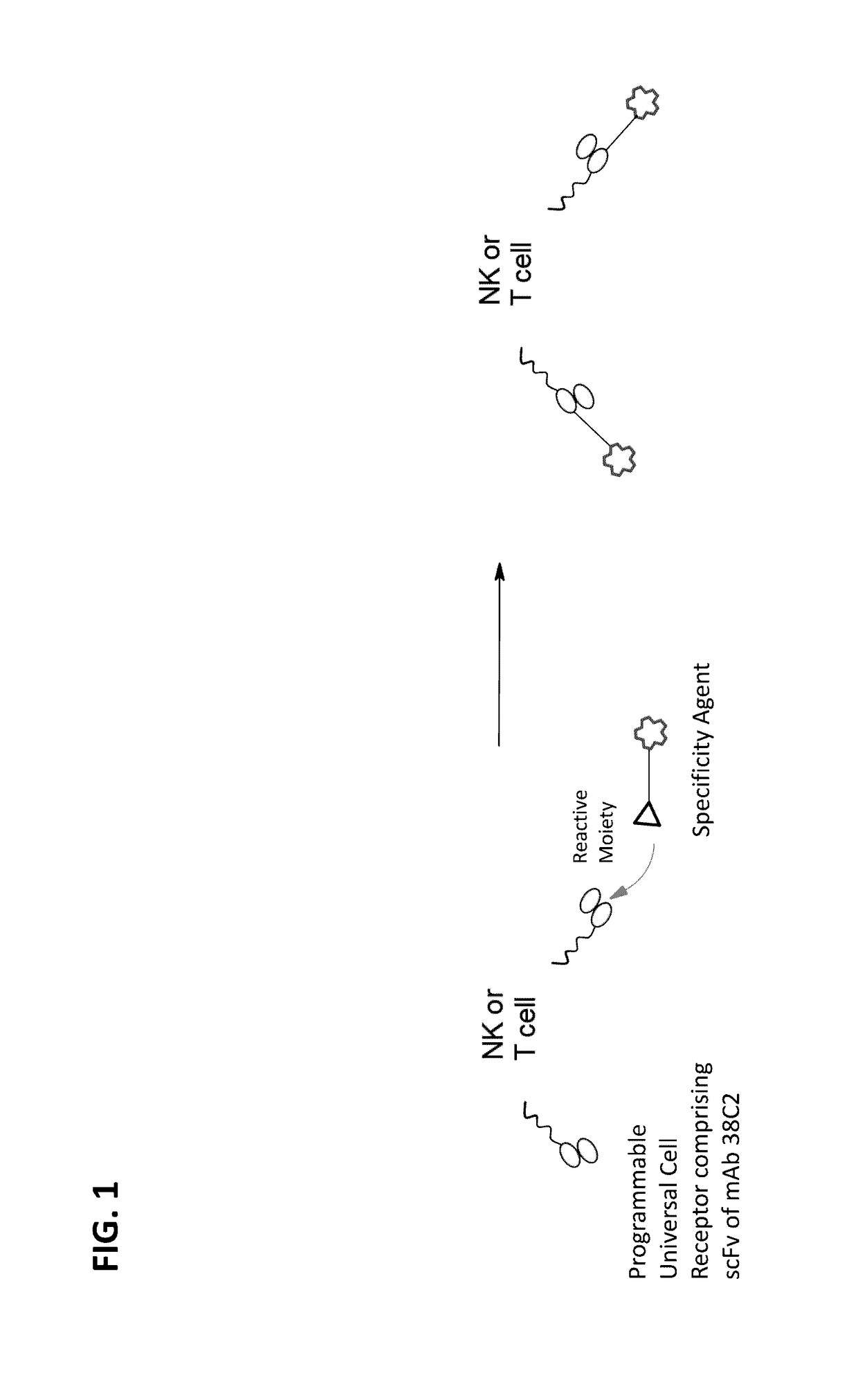
Programmable universal cell receptors and method of using the same
InactiveUS20170112878A1Effective treatmentPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyDiseaseCatalytic antibody
The present invention provides programmable universal cell receptors (PUCRs) comprising a catalytic antibody region, a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic domain. The PUCRs disclosed herein may be conjugated to a specificity agent in order to program the receptor for specificity to any molecule of interest. Also provided are nucleic acids encoding such PUCRs, and cells expressing the PUCRs. Such cells may be used in treating a variety of medical conditions and diseases including cancer and infectious diseases.
Owner:SORRENTO THERAPEUTICS INC
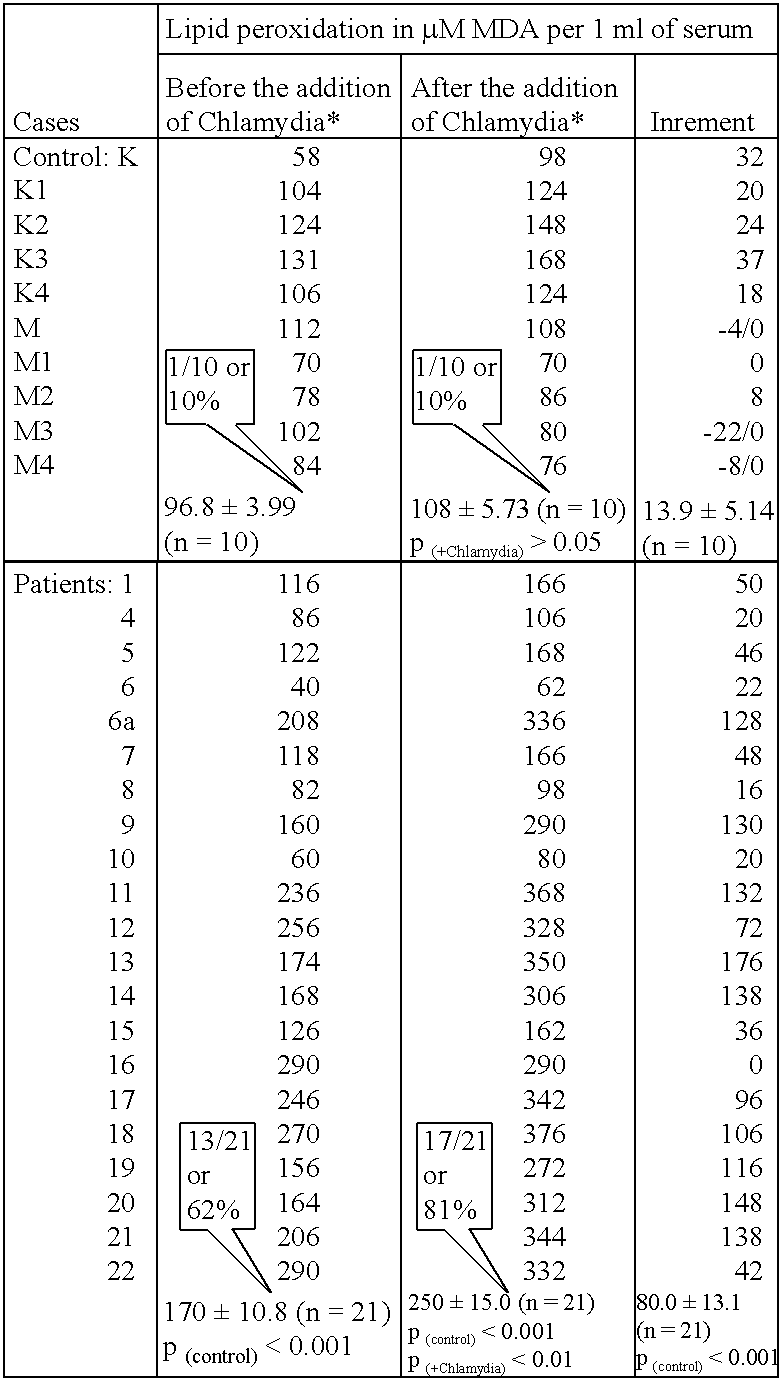
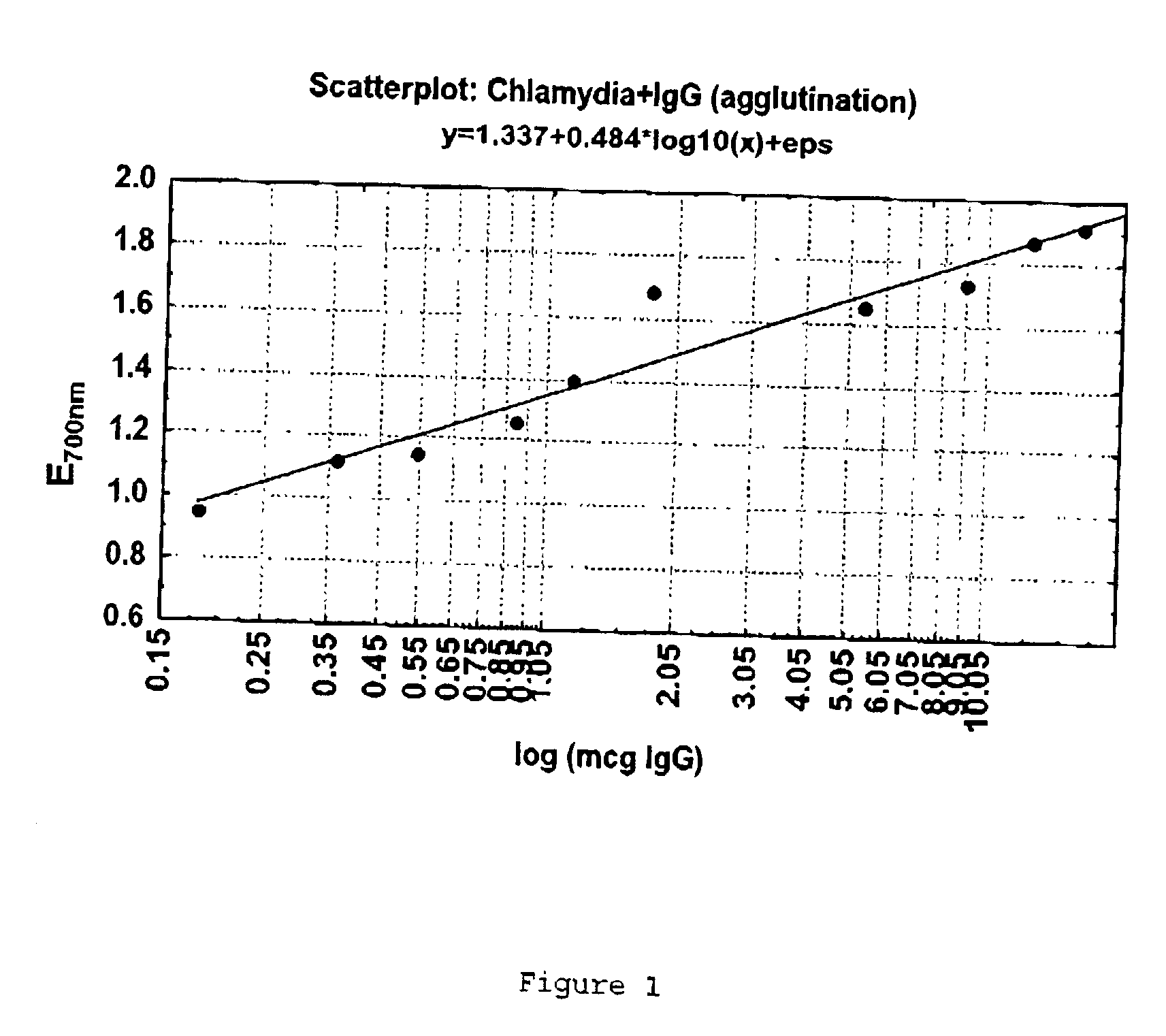
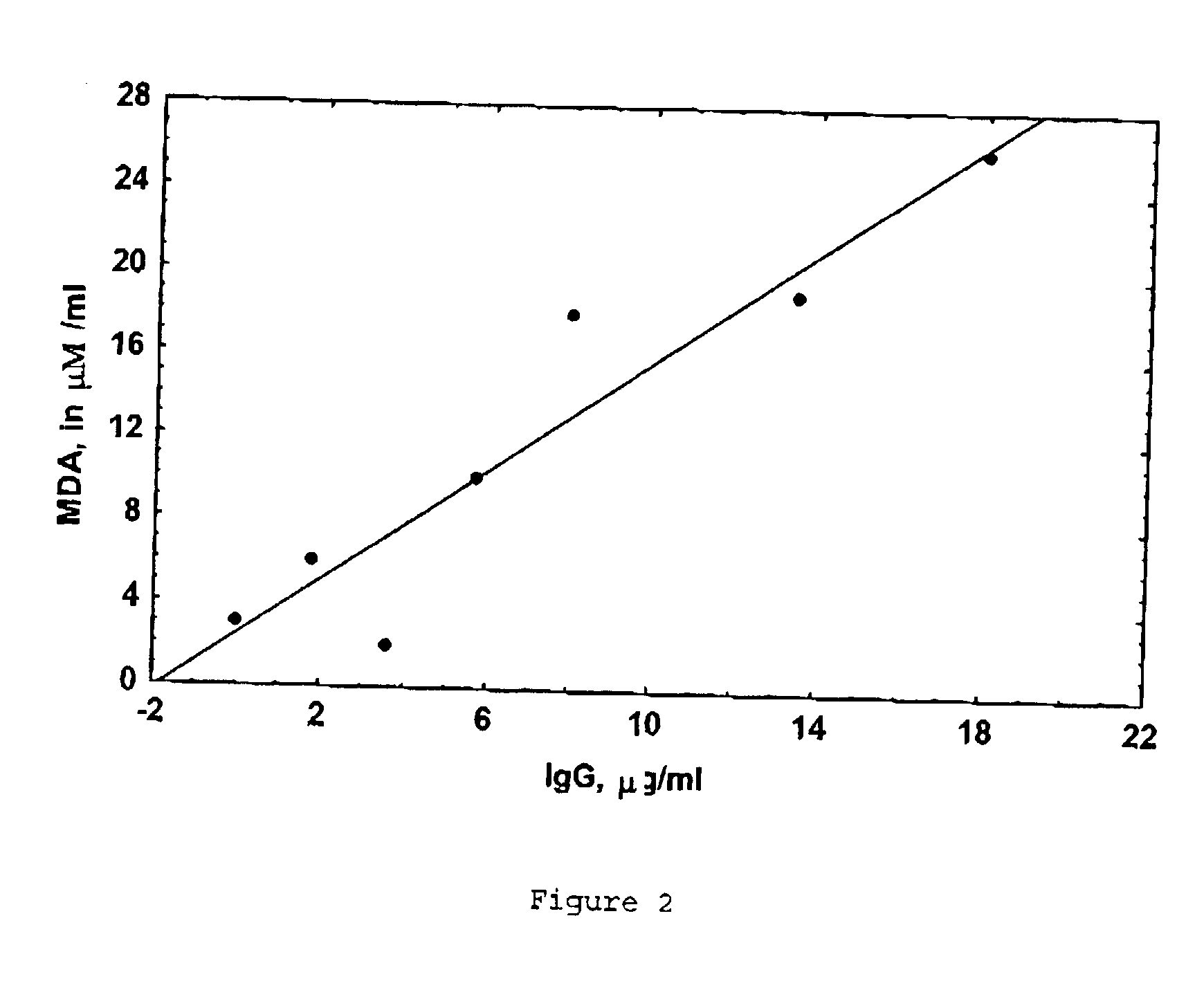
Treatment of atherosclerotic disorders
The present invention relates to the identification of lipid oxidising abzymes as a key pathogenic factor in atherosclerotic disorders. Methods and means for the reduction of abzyme mediated lipid oxidation in the vascular system are provided as therapeutic approaches for the treatment of atherosclerotic disorders.
Owner:CAMNUTRA
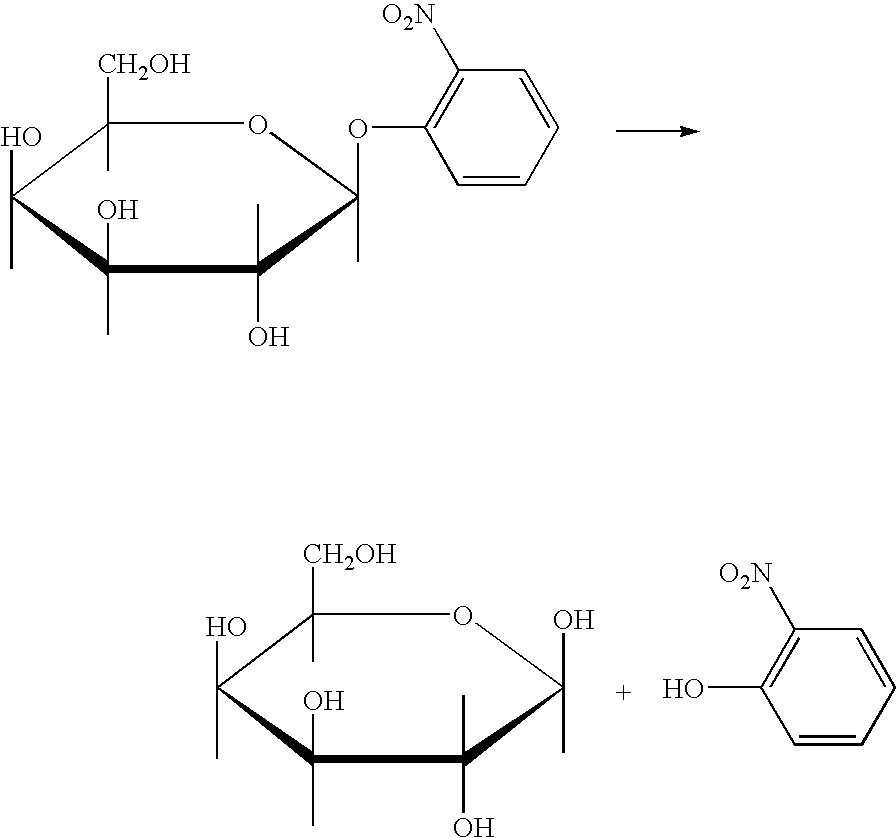
Transition state analogs
InactiveUS6946272B1Improve stabilityProfound effect on chiralityMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsChemical reactionBoron
Antigens capable of eliciting antibodies which can catalyze chemical reactions, in particular, the cleavage or formation of a peptide linkage, comprising a hapten or a hapten and a suitable carrier molecule are disclosed. Haptens include, among others, silicon and boron containing compounds. Antibodies which are catalytically active for chemical reactions, in particular, the cleavage or formation of a selected peptide linkage or an ester bond, and which are elicited by such antigens are disclosed as well as methods for producing the antibodies and methods for catalyzing the cleavage or formation of a peptide linkage or in ester bond in a molecule.
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOCATALYSIS
Method of producing heteromultimeric mammalian proteins in plants
InactiveUS7101688B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesForeign matterTransgene
The present invention relates to expression and assembly of foreign multimeric proteins—e.g., antibodies—in plants, as well as to transgenic plants that express such proteins. In one of several preferred embodiments, the generation and assembly of functional secretory antibodies in plants is disclosed. The invention also discloses compositions produced by the transgenic plants of the present invention and methods of using same.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Anti-nucleic acid antibody inducing cell death of cancer cells and composition for preventing or treating cancers comprising the same
InactiveUS20110159569A1Good choiceShow cytotoxicitySugar derivativesHydrolasesCancer cellNormal cell
There are provided an anti-nucleic acid antibody inducing cell death of cancer cells by invading normal cells; and a composition for preventing or treating cancers comprising the anti-nucleic acid antibody, which shows anticancer effect of an anti-nucleic acid antibody that shows cytotoxicity by damaging nucleic acid strands, that is, genetic information of a cancer cell when the anti-nucleic acid antibody, which has binding activity and degrading activity to the nucleic acid strands in cells at the same time, is overexpressed in the cancer cell, or flows in the cancer cell. Therefore, the composition for treating cancers may be useful to induce the selective cell death in cancer cells than in normal cells since the anti-nucleic acid antibody very easily permeates into the cancer cells due to the excellent selectivity, compared to the normal cells.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Antiviral agent, abzyme, primer set, method for producing polynucleotide, and method for producing polypeptide
ActiveUS20120322135A1Efficiently obtainedEffective lightingImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsAbzymePolynucleotide
The present invention provides: a novel antiviral agent containing a human antibody κ light chain, a novel human abzyme containing a human antibody κ light chain; a polynucleotide, a vector, and a transformant, each of which relating to the containing a human antibody κ light chain of the above; a primer set for effectively obtaining a human antibody κ light chain having a function as an antiviral agent or abzyme; and a method for producing a polynucleotide and a method for producing a polypeptide, each of which method utilizes the primer set.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Catalytic antibodies and a method of producing same
InactiveUS20090269355A1Avoid interactionSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAdjuvantCatalytic antibody
The present invention relates generally to a growth factor precursor and its use to select production of antigen specific catalytic antibodies. Such catalytic antibodies are produced following B cell activation and proliferation induced by catalytic cleavage products of a target antigen portion of the growth factor precursor of the present invention. A particularly useful form of the growth factor precursor is as a nucleic acid vaccine. The nucleic acid vaccine of the present invention preferably further comprises a molecular adjuvant. Another aspect of the present invention comprises a growth factor precursor in multimeric form. The growth factor precursor of the present invention is useful for generating catalytic antibodies for both therapeutic, diagnostic and industrial purposes.
Owner:KOENTGEN FRANK
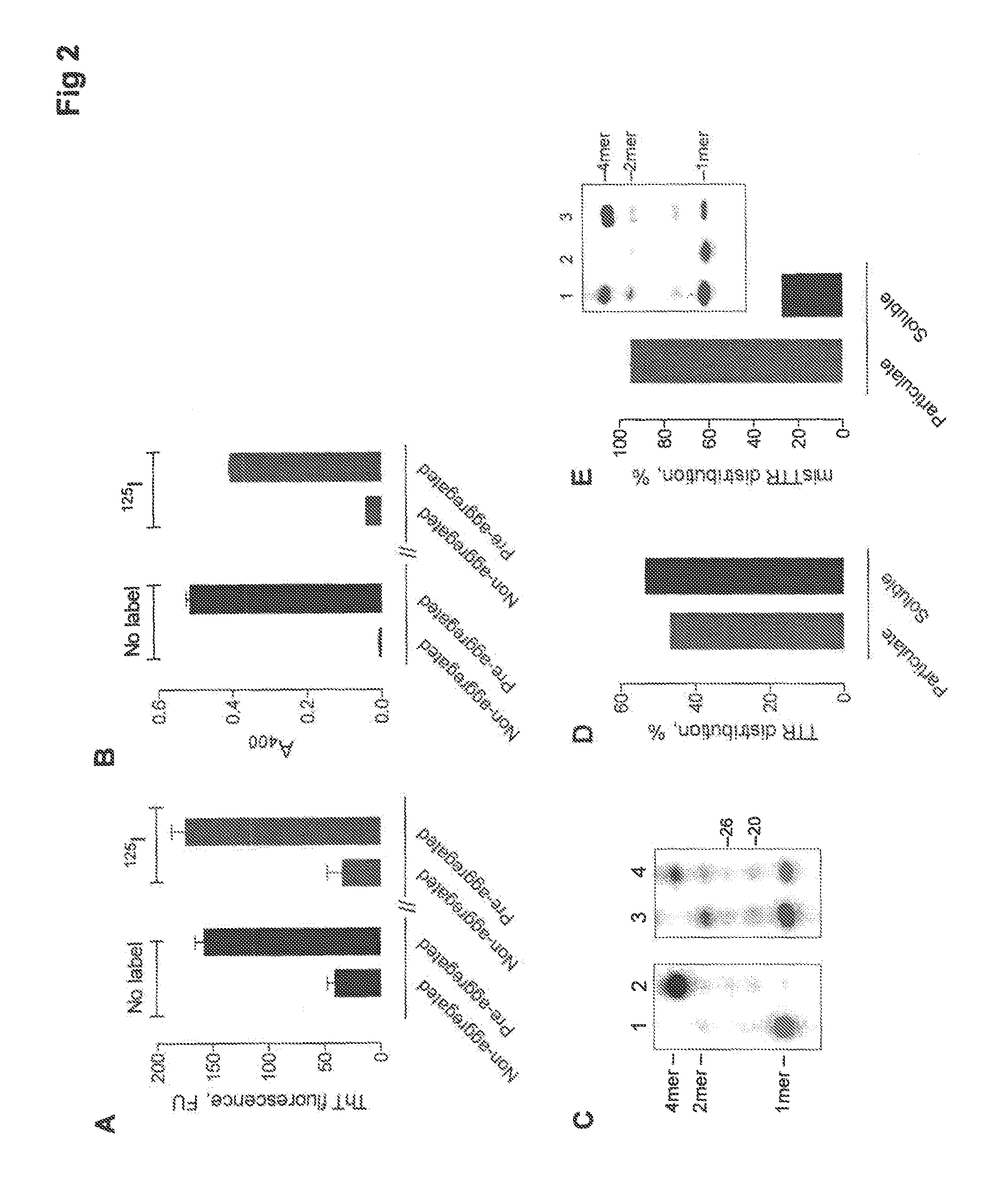
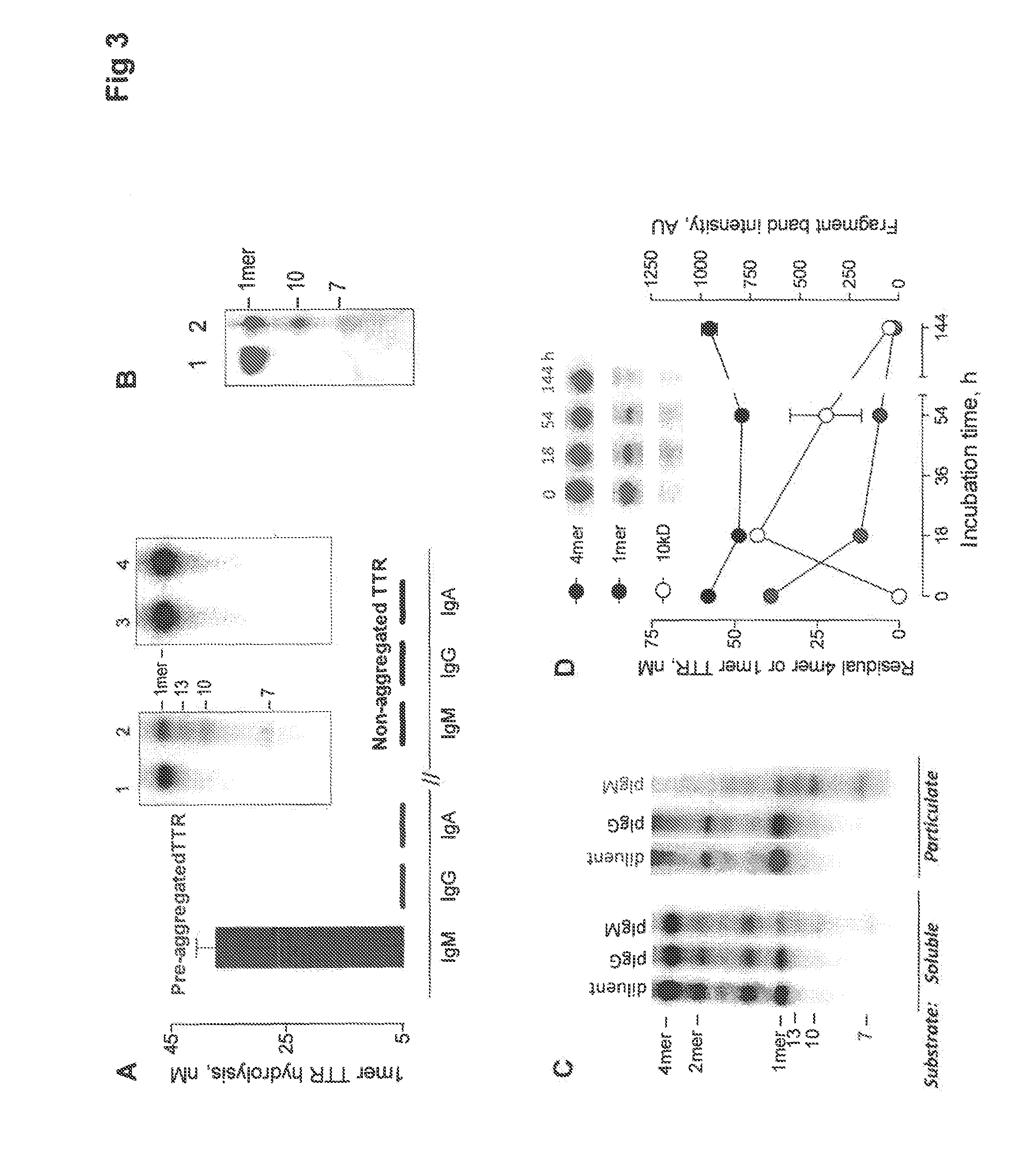
Transthyretin amyloid-selective and polyreactive catabodies
PendingUS20160168235A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAmyloidCancer research
The present invention provides transthyretin amyloid-selective and polyreactive catabodies and method of use thereof.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Random chemistry for the generation of new compounds
InactiveUS20050037435A1Microbiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsChemical reactionChemical composition
Methods for the generation of new compounds are disclosed. The present invention eliminates the need to know in advance the structure or chemical composition of a compound having a desired property. The disclosure of the present invention provides that diversity of unknown compounds may be produced by “random” chemistry, and such a diversity of unknown compounds may be screened for one or more desired properties to detect the presence of suitable compounds. In one aspect, a starting group of organic compounds is caused to undergo a series of chemical reactions to create a diversity of new organic compounds that are screened for the presence of organic compounds having the desired property. In another aspect of the present invention, a diversity of compounds is generated from a group of substrates which are subjected to a group of enzymes representing a diversity of catalytic activities.
Owner:GENESIS MOLECULAR DISCOVERY
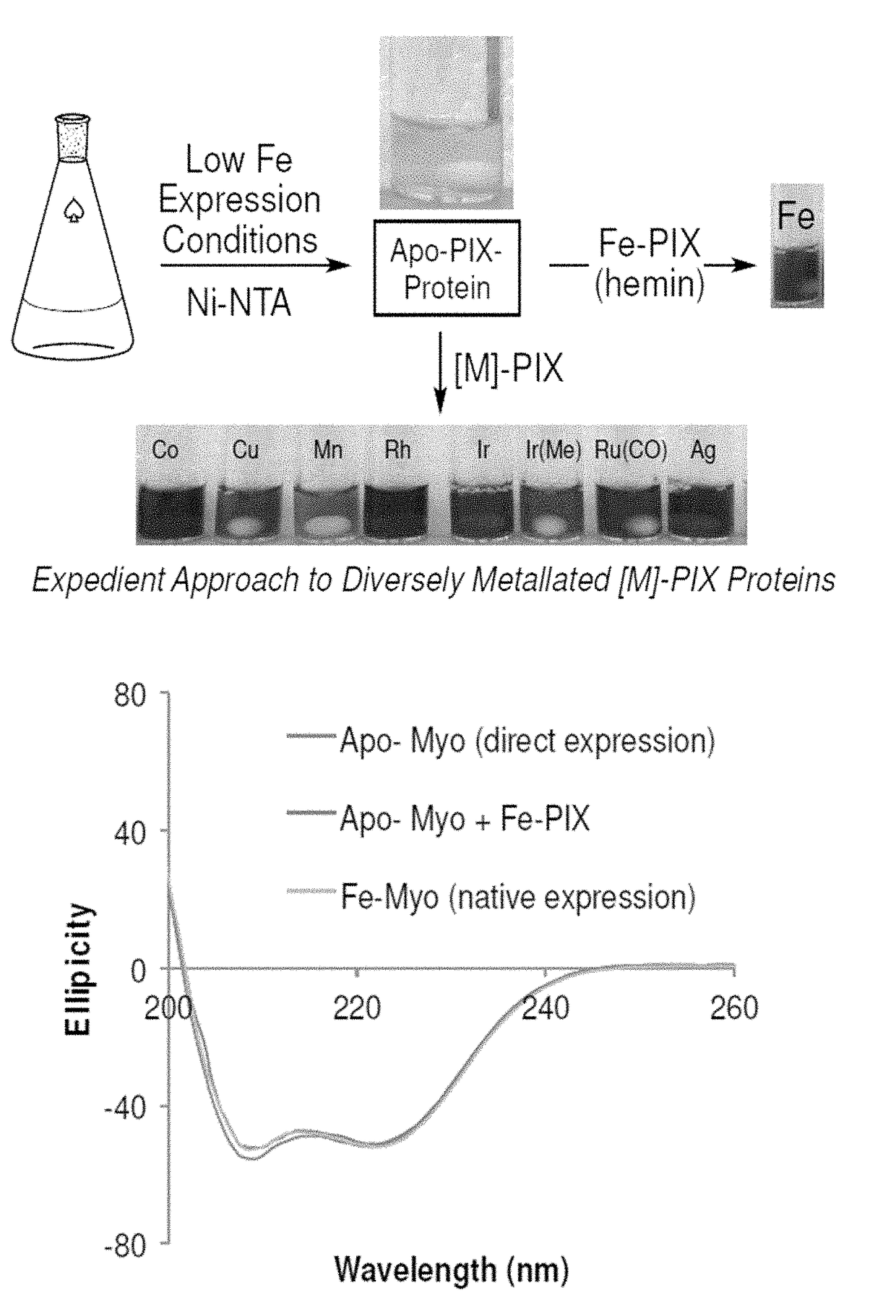
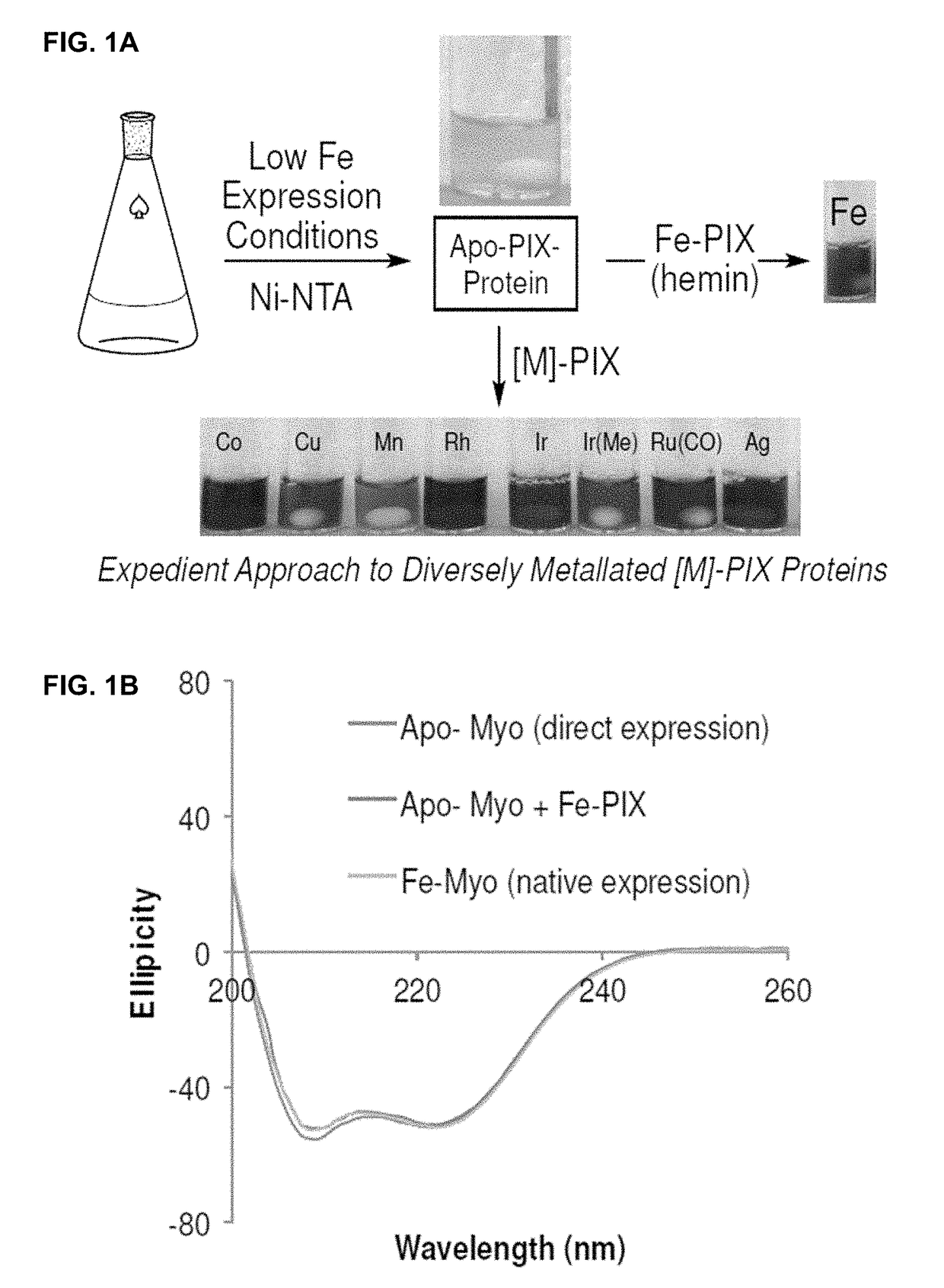
Artificial metalloenzymes containing noble metal-porphyrins
ActiveUS20180305368A1High activityHigh selectivityHaemoglobins/myoglobinsCytochromesPorphyrinCyclopropanation
The present invention is drawn to artificial metalloenzymes for use in cyclopropanation reactions, amination and C—H insertion.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for producing catalytic antibodies (variants), antigens for immunization and nucleotide sequence
A method for producing catalytic antibodies to proteins and peptides, in particular to gp120, using animals having spontaneous and induced autoimmune pathologies. The method makes it possible to create a catalytic vaccine which can when injected to a patient to exhibits adhesive properties in relation to antigen simultaneously with a destructive function, thereby suspending the progression of disease. The method for the autoimmunisation of animal lines SJL by fused proteins containing classical peptide epitope which develops pathology of an animal by protein fragments gp120 accompanied with an interest target catalytic antibody is disclosed. Also the method for immunising autoimmune animals by highly reactive chemical compositions which can perform a covalent selection of catalytic clones containing peptide fragments of potential resected portions gp120 is disclosed.
Owner:LIFEBIO LAB
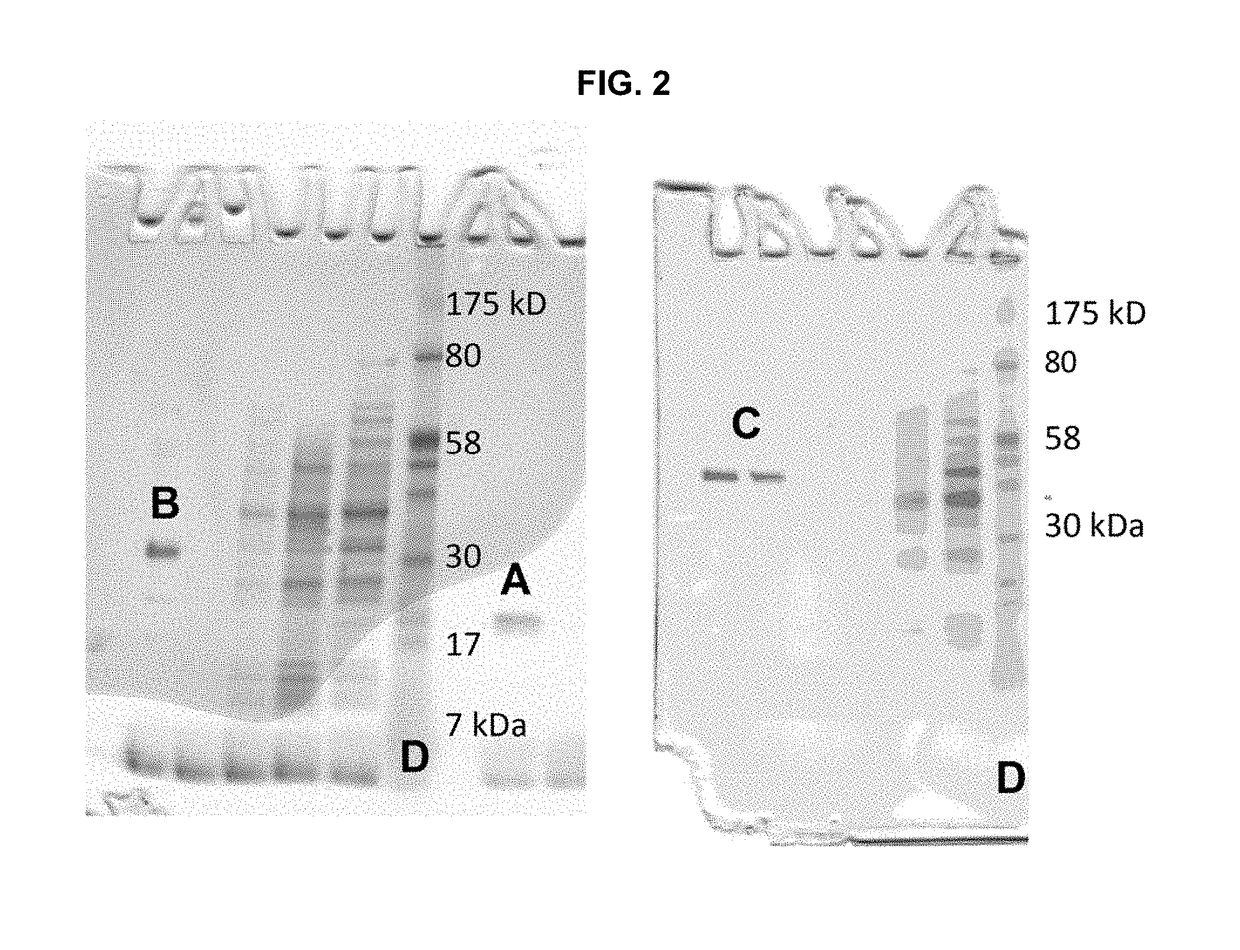
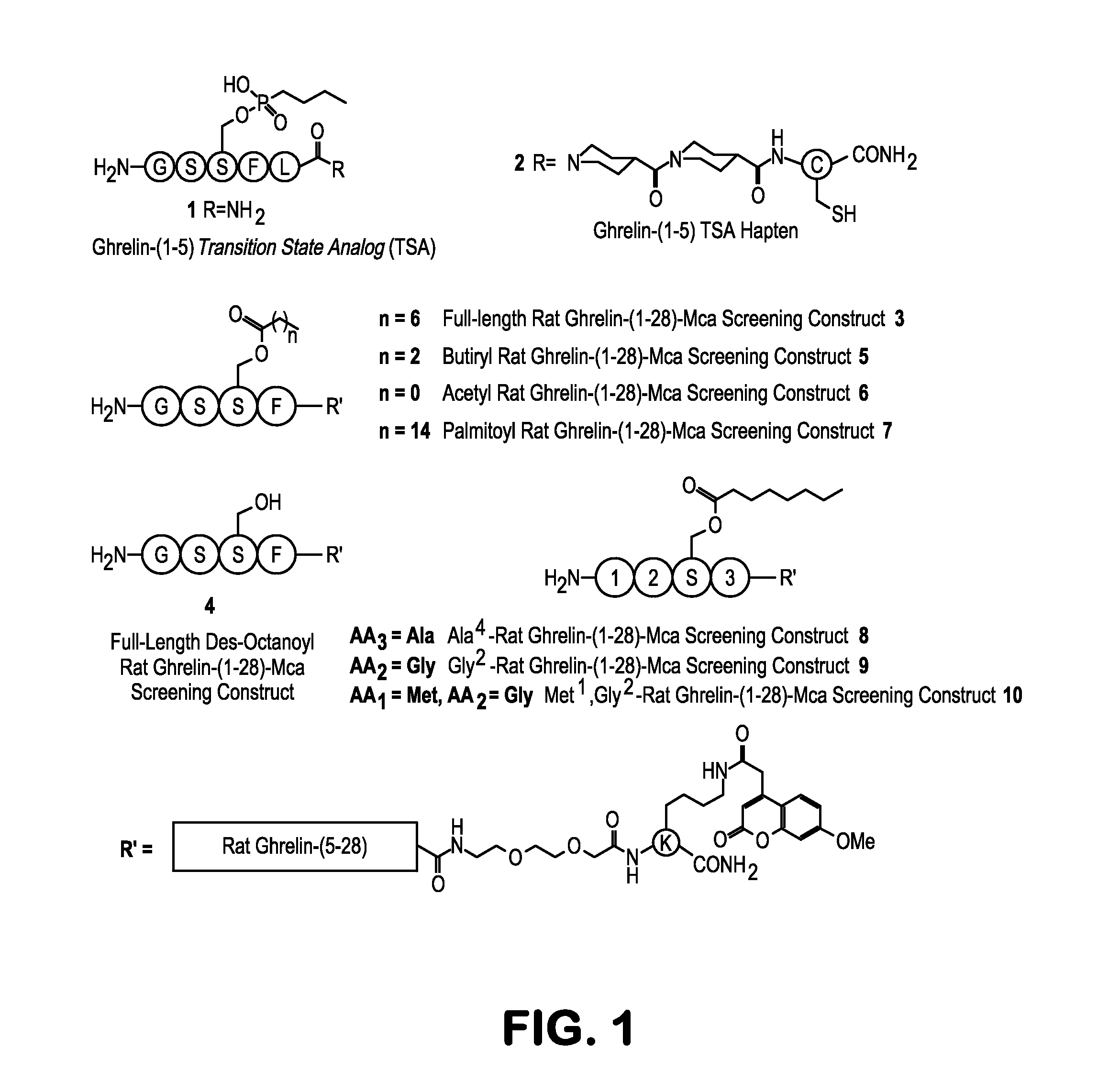
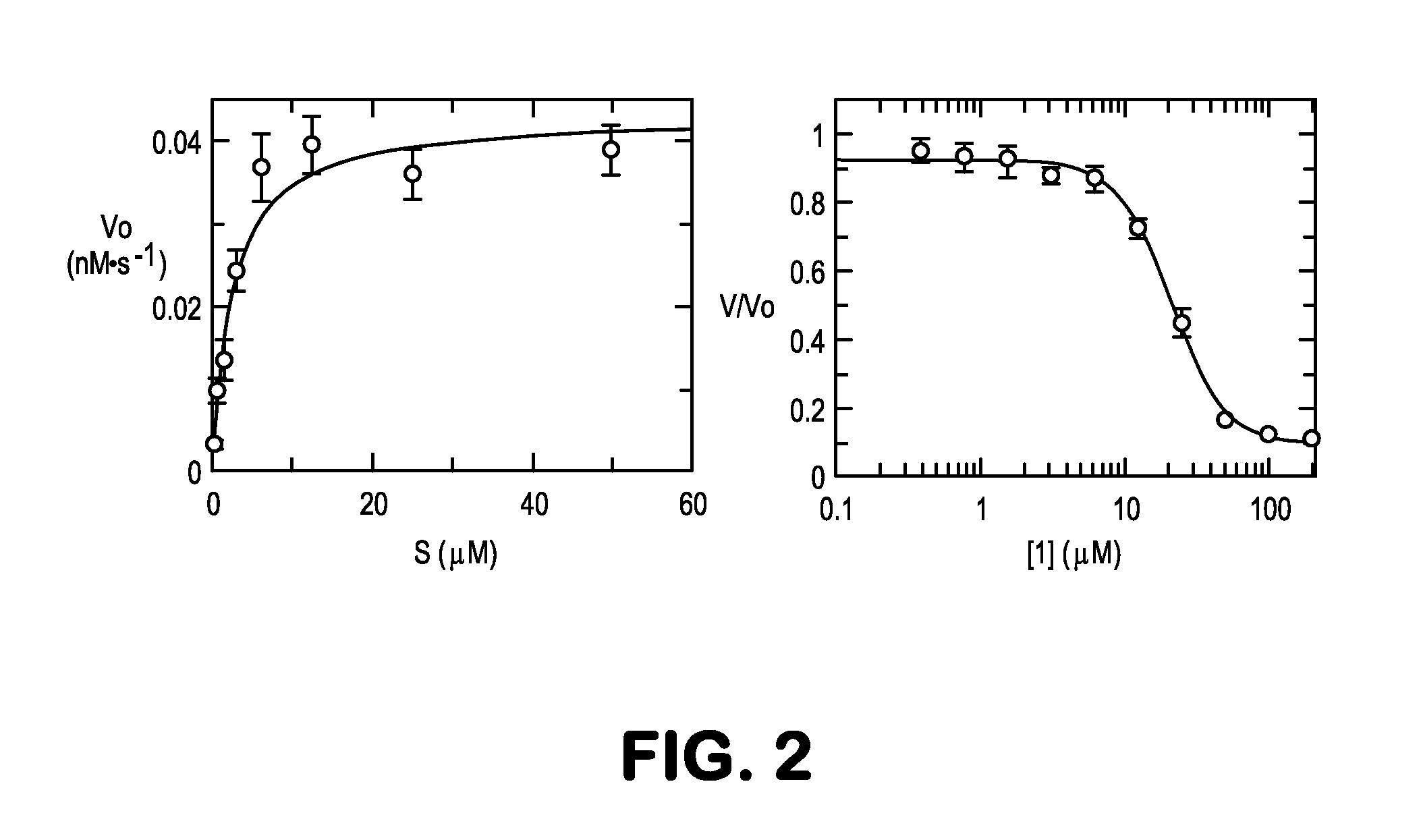
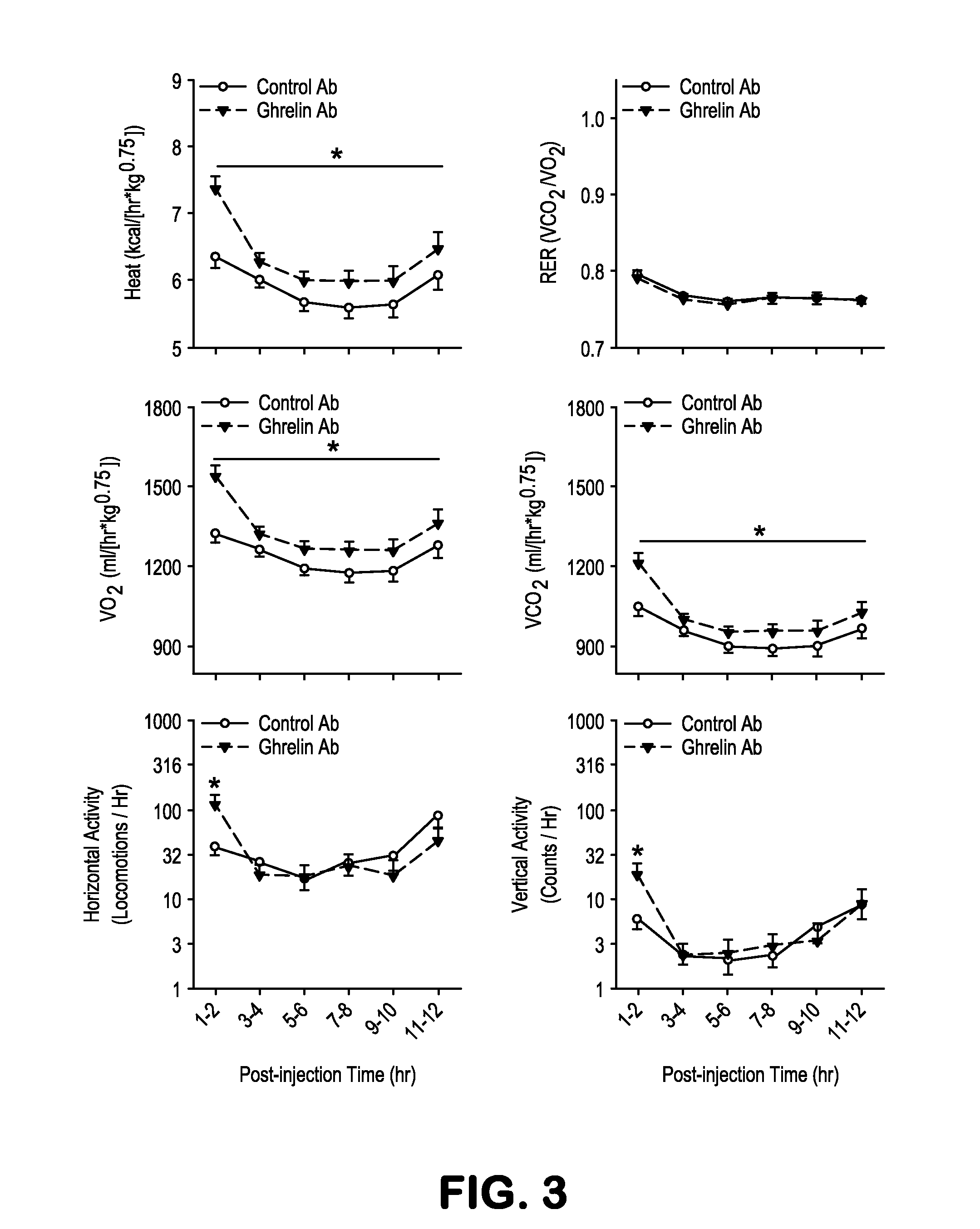
Methods and Compositions for Treating Obesity
The present invention provides anti-ghrelin antibodies or antigen-binding molecules that are capable of degrading ghrelin and inhibiting ghrelin-mediated cellular activities. Also provided in the invention are therapeutic applications of combinations of these antibodies, e.g., to treat or prevent obesity.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Methods relating to treatment of atheroaclerosis
InactiveUS20030166029A1Abzyme activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionLipid oxidationPathogenic factor
The present invention relates to the identification of lipid oxidising antibodies as a key pathogenic factor in atherosclerotic disorders. These disorders may be treated by inhibiting this antibody mediated lipid oxidation and methods and means for identifying and producing inhibitory agents are provided.
Owner:CAMNUTRA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com