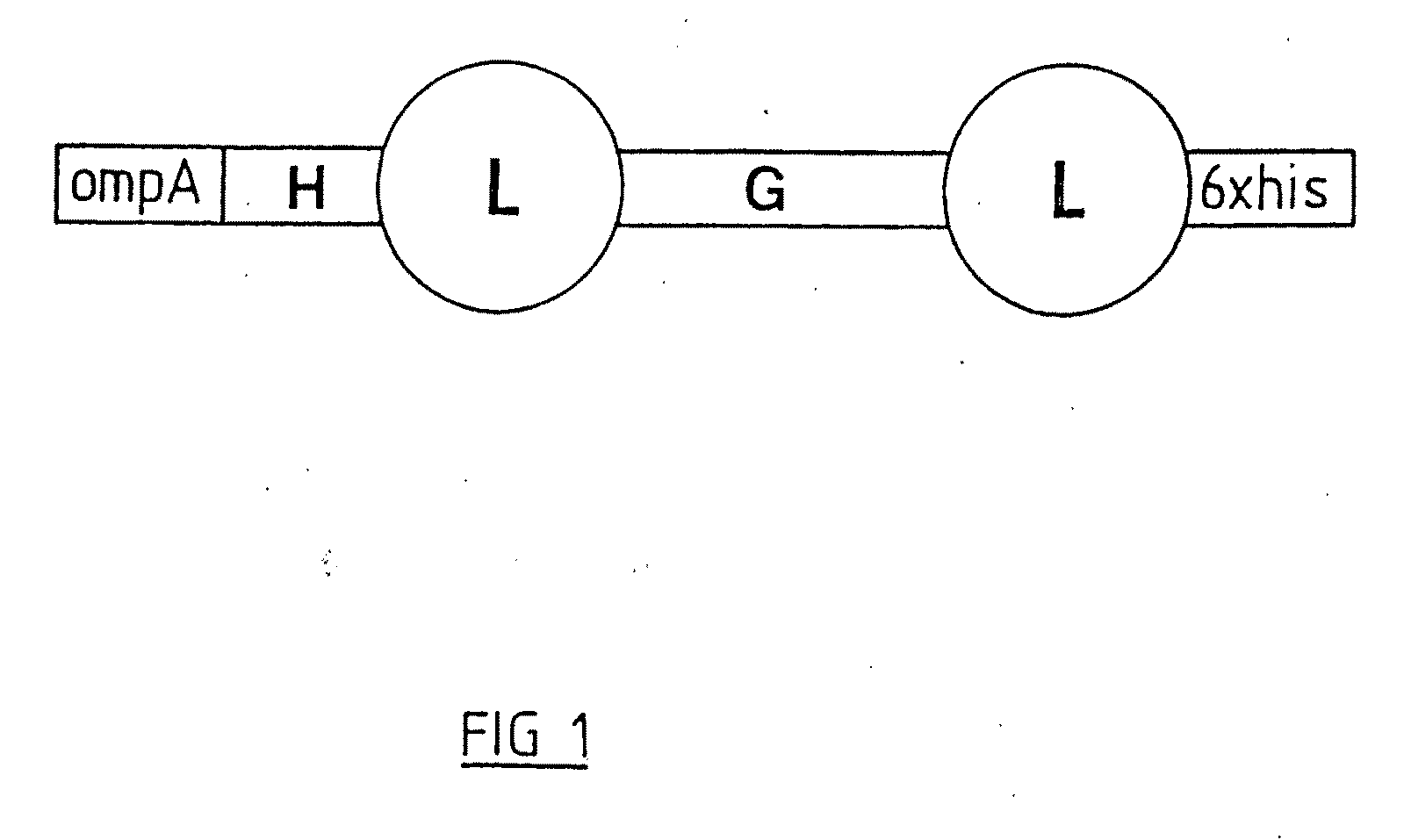
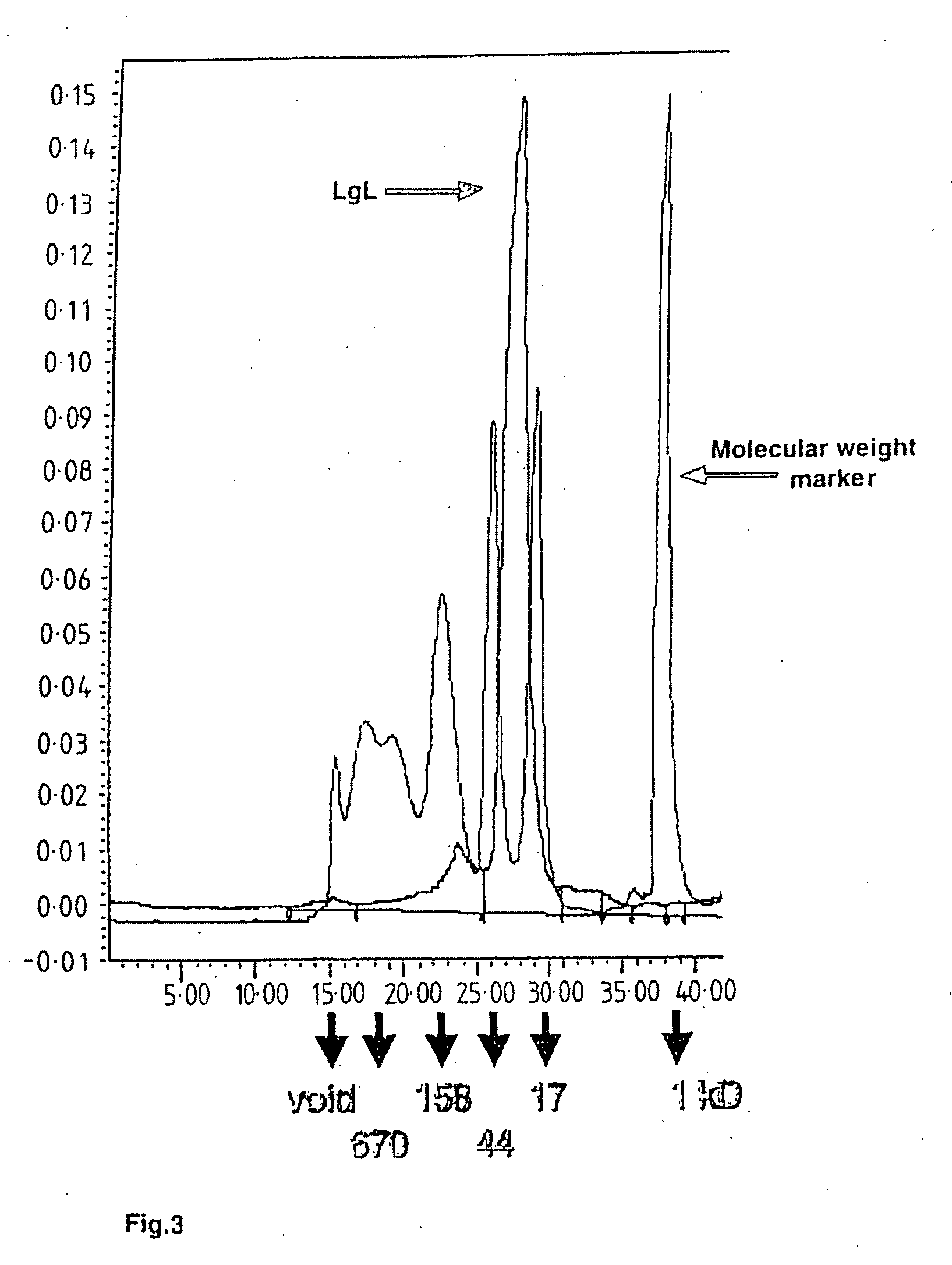
Catalytic antibodies and a method of producing same
a catalytic antibody and antibody technology, applied in the field of growth factor precursors, can solve the problems of difficult to predict the structure of transition state analogs, ineffective recombinant techniques in generating all components of humoral responses, and inefficient immunisation of mice with transition state analogs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Generation of LHL from Synthetic Oligonucleotides
[0152]LHL was generated from three overlapping synthetic oligos, a 115mer, a 116mer and a 105mer, using the proofreading DNA polymerase Pfu in two 20 cycle PCR reactions. The two PCR products (290 bp and 200 bp) were purified and blunt end cloned into the expression vector pASK75. The sequence was verified by automated sequencing. All subsequent PCRs were done in a similar fashion as described in the literature. The nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequence for LHL is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO:2 respectively.
example 2
Expression of LHL in E. coli and Purification Over a Human IgG (huIgG) Affinity Column
[0153]The expression vector pASK75 directs protein expression via the ompA signal peptide into the periplasm of E. coli. Protein expression was induced with 200 ng / ml anhydrotetracycline for 16 hrs in midlog E. coli DH10B cultures. Cells were lysed and soluble LHL purified (>95%) over a huIgG affinity column. Extensive washes with 0.5% v / v Triton X-100 were performed on the affinity column in order to eliminate endotoxins from the preparations. Expression levels were estimated at 200 mg per litre of culture.
example 3
Generation of an LHL Protein Carrying the N-Terminal Flag Epitope and the C-Terminal Strep-Tag
[0154]A form of LHL (referred to herein as “LHL.seq”) was generated by PCR containing the FLAG epitope at its N-terminus and the so called strep-tag at its C-terminus. The nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequence for LHL.seq is shown in SEQ ID NO:7 and SEQ ID NO:8, respectively. The FLAG epitope comprises the amino acids DYKDDDDK (SEQ ID NO:9) and the strep-tag the amino acids AWRHPQFGG (SEQ ID NO: 14). The FLAG epitope is recognised by several anti-FLAG monoclonal antibodies and the strep-tag by streptavidin. The strep-tag was used for purification of LHL.seq over a streptavidin column. LHL.seq was washed with 0.5% v / v Triton X-100, Tween20 and PBS while bound to the column in order to minimise endotoxin levels. LHL.seq was eluted with either 100 mM glycine pH2.0 or with 1 mg / ml diaminobiotin in PBS. In this method LHL.seq was not purified on the basis of binding immunoglobulin, th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Digital information | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com