Antibody targeting compounds
一种抗体靶向、化合物的技术,应用在靶向生物分子的化合物领域,能够解决限制等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
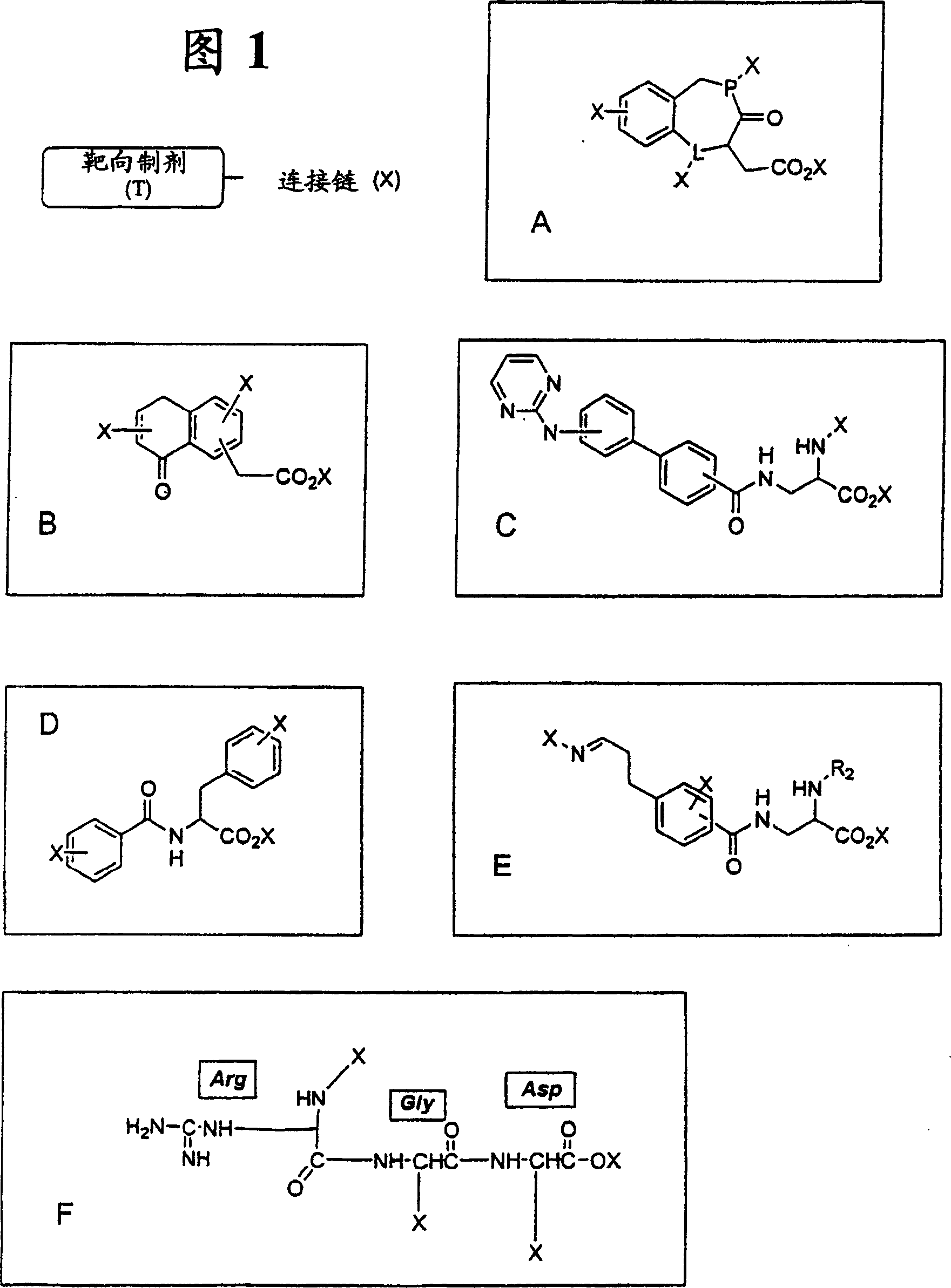
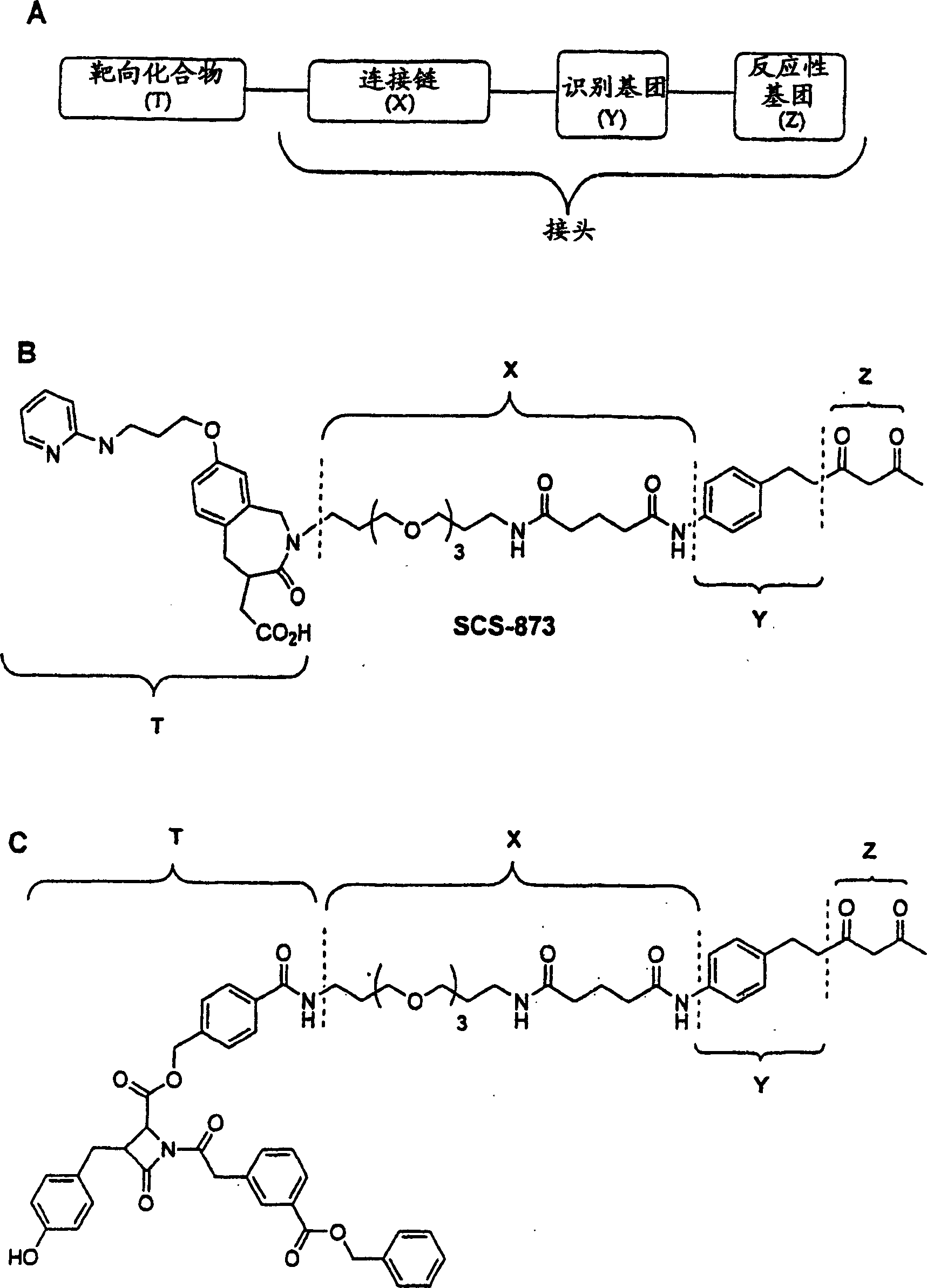
[0209] Example 1: Antibody Targeting Compounds Containing RGD Peptidomimetic Targeting Formulations Covalently Linked to the Binding Site of Aldolase Monoclonal Antibody 38C2
[0210]Integrin-targeting compounds were formed based on the formation of a reversible covalent bond between a diketone linker derivative of the RGD peptidomimetic and the active lysine of mouse mAb 38C2. The mouse mAb 38C2 is the prototype of a new class of catalytic antibodies generated by reactive immunization and mechanistic mimicry of natural aldolases (Barbas et al., Science 278, 2085-2092, 1997). Using the enamine mechanism of natural aldolases, these antibodies catalyze aldol and retro-aldol reactions via active lysine (Wagner et al., Science 270, 1797-1800, 1995; Barbas et al., Science 278, 2085 -2092, 1997; Zhong et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 38, 3738-3741, 1999). In addition to their versatility and effectiveness in synthetic organic chemistry, aldolase antibodies have been used as anticancer...
Embodiment 2
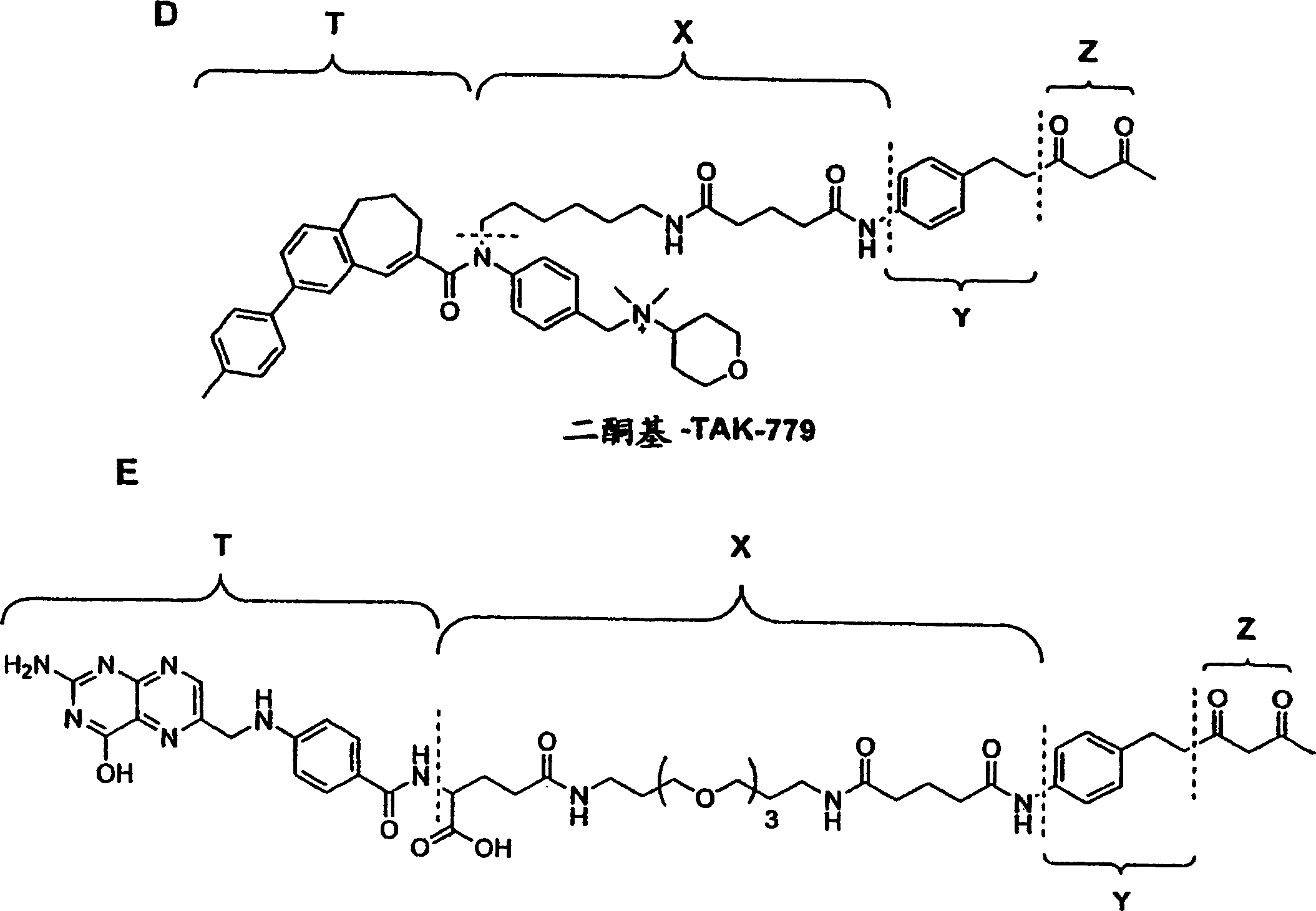
[0215] Example 2: Antibody Targeting Compounds Containing IL-4 as a Targeting Agent Covalently Linked to the Binding Site of Aldolase Monoclonal Antibody 38C2
[0216] Among other human endothelial tumor cells, Kaposi's sarcoma tumor cells express the interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptor, which uses a recombinant chimeric protein consisting of IL-4 and endotoxin called Pseudomonas A truncated form of the bacterial toxin can be targeted to a target (Husain et al., 1999, Nat. Med. 5, 817-822). Based on these studies, IL-4 targeting compounds for targeting mAb 38C2 to Kaposi's sarcoma tumor cells were prepared. A linker bearing a diketone reactive group is conjugated to the lysine side chain of IL-2 using a lysine reactive moiety such as N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS). Alternatively, recombinant IL-4 with added free cysteine is used conjugated to a cysteine active moiety such as maleimide. In order to reduce the immunogenicity associated with the linker portion of the targeting compou...
Embodiment 3
[0217] Example 3: Antibody Targeting Compounds Containing VEGF-R2 Binding Peptides Covalently Linked to the Binding Site of Aldolase Monoclonal Antibody 38C2 as Targeting Agents
[0218] Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a key regulator of tumor angiogenesis. Induced by hypoxia, upregulation of VEGF expression is induced via VEGF mRNA transcription in tumors. After production and release by tumors, VEGF diffuses to endothelial cells adjacent to pre-existing blood vessels, which display VEGF (VEGFR) receptors. VEGF binds two tyrosine kinase receptors, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2, which are mainly expressed on endothelial cells. Activation of endothelial cells is associated with VEGF binding to VEGFR-2, and VEGR-1 may function as a decoy receptor regulating local concentrations of VEGF (Neufeld et al., 1999, FASEB J.13, 9-22). Upon activation, endothelial cells proliferate, migrate directly to the tumor, and finally wind up and connect with each other to form new blood vess...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com