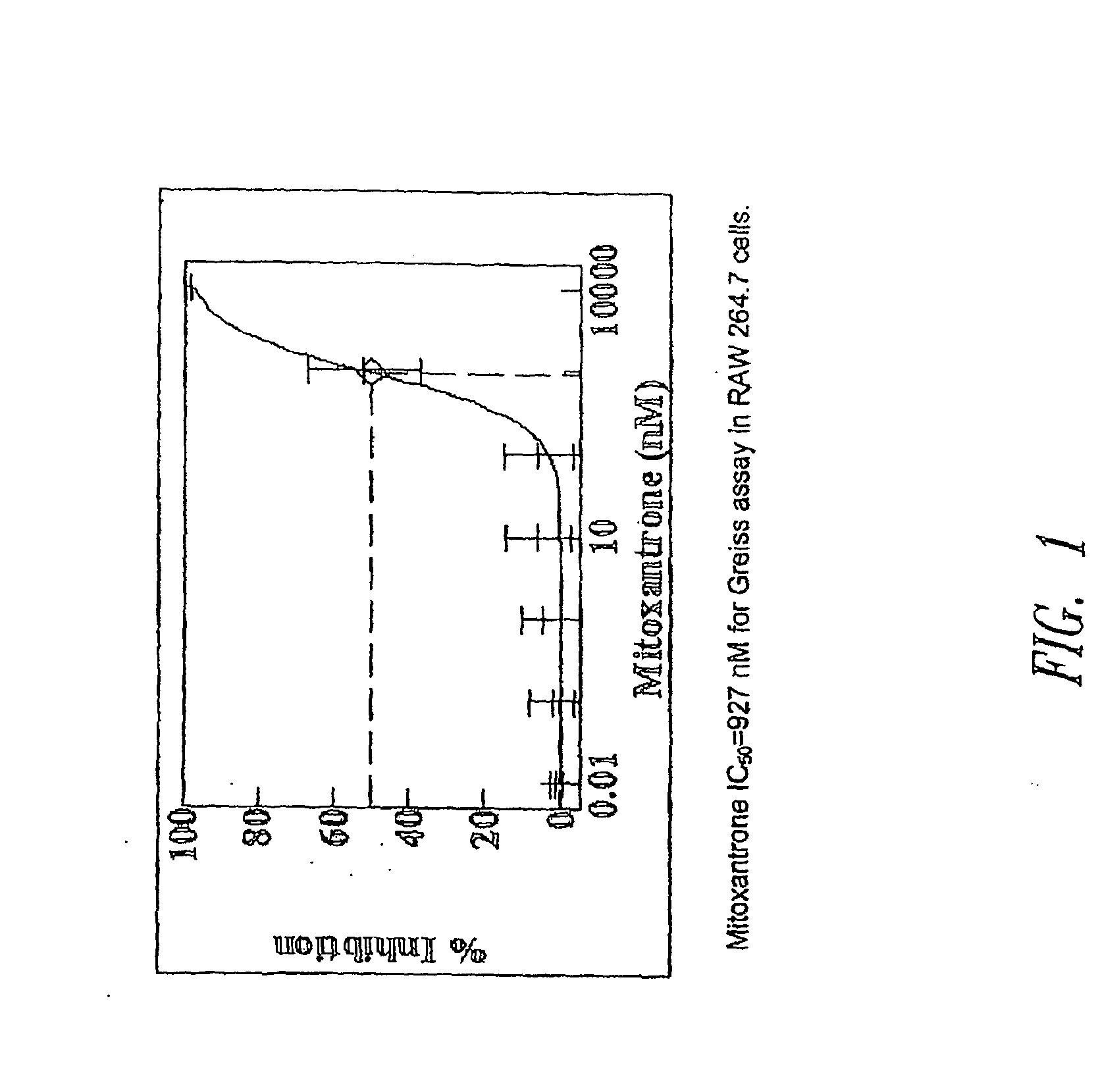
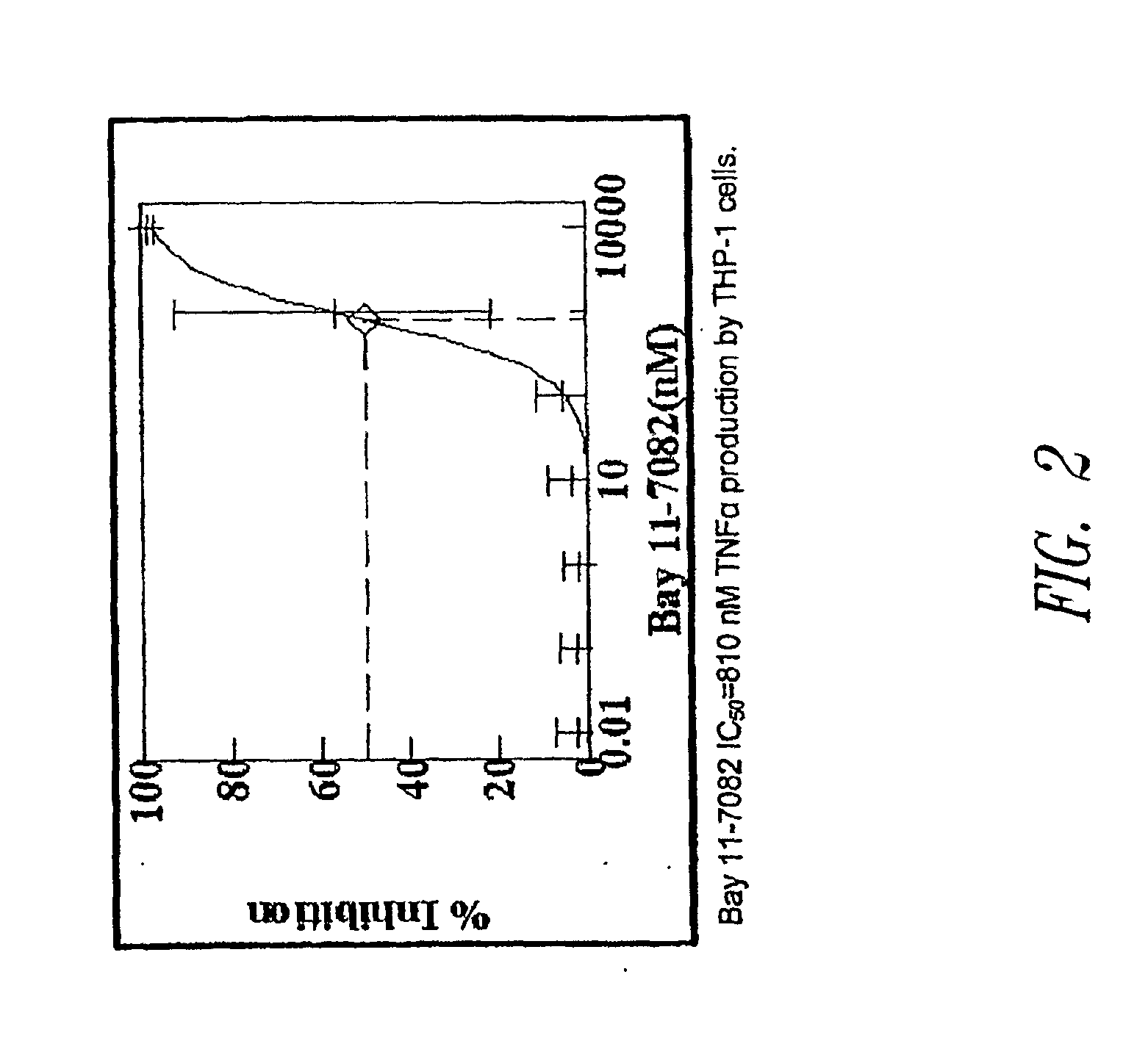
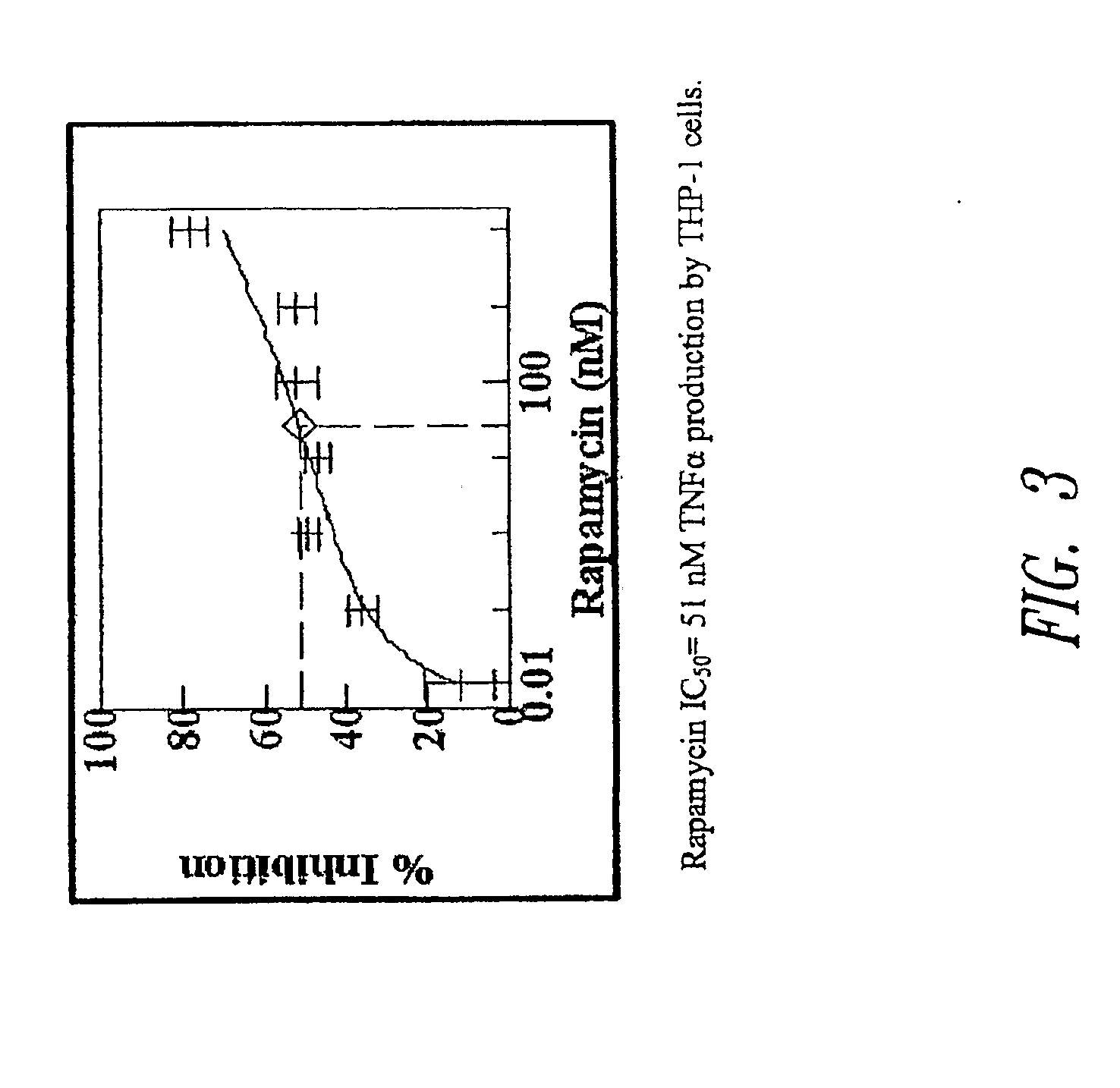
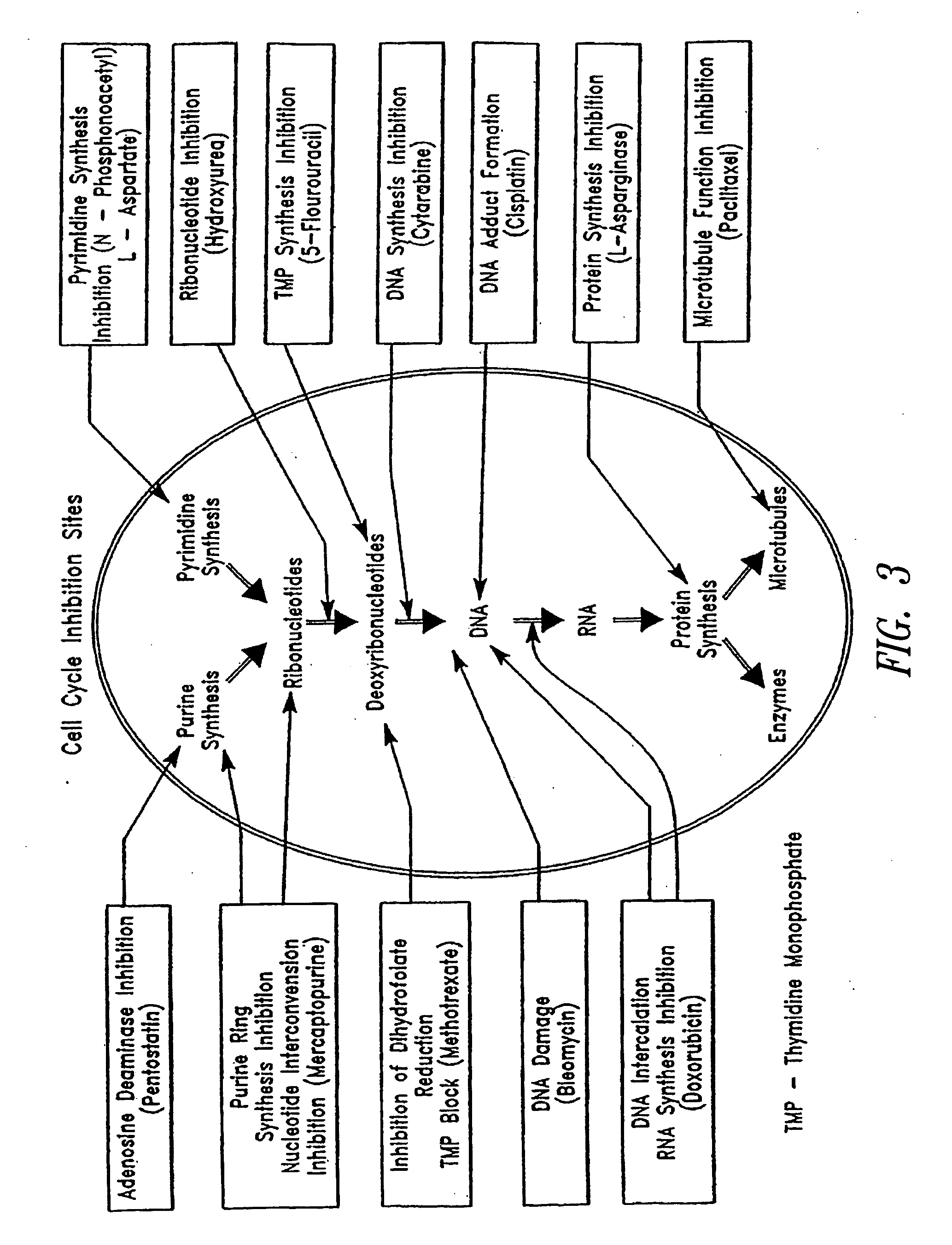
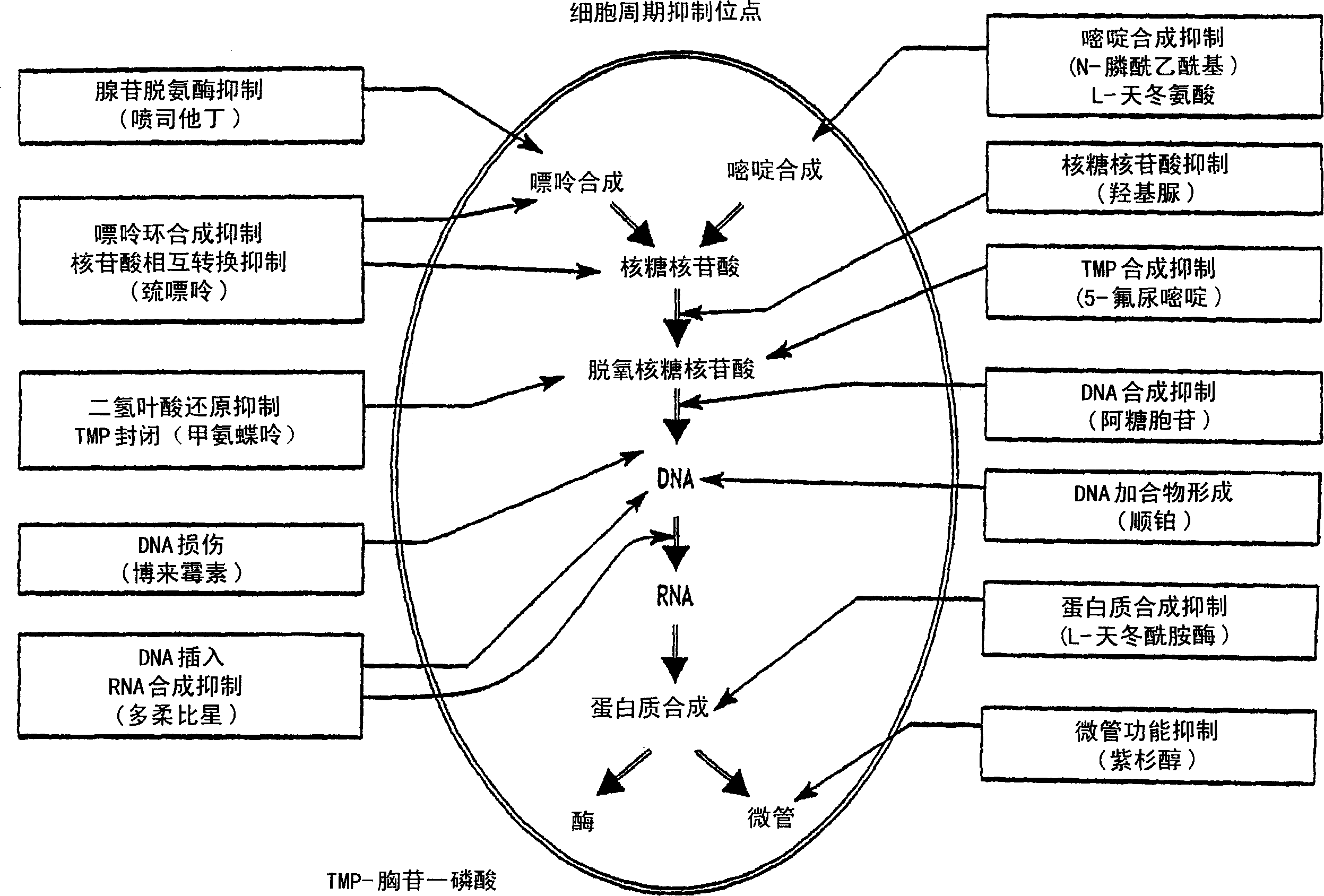
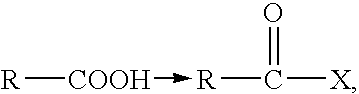Patents
Literature
60 results about "Surgical Adhesions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
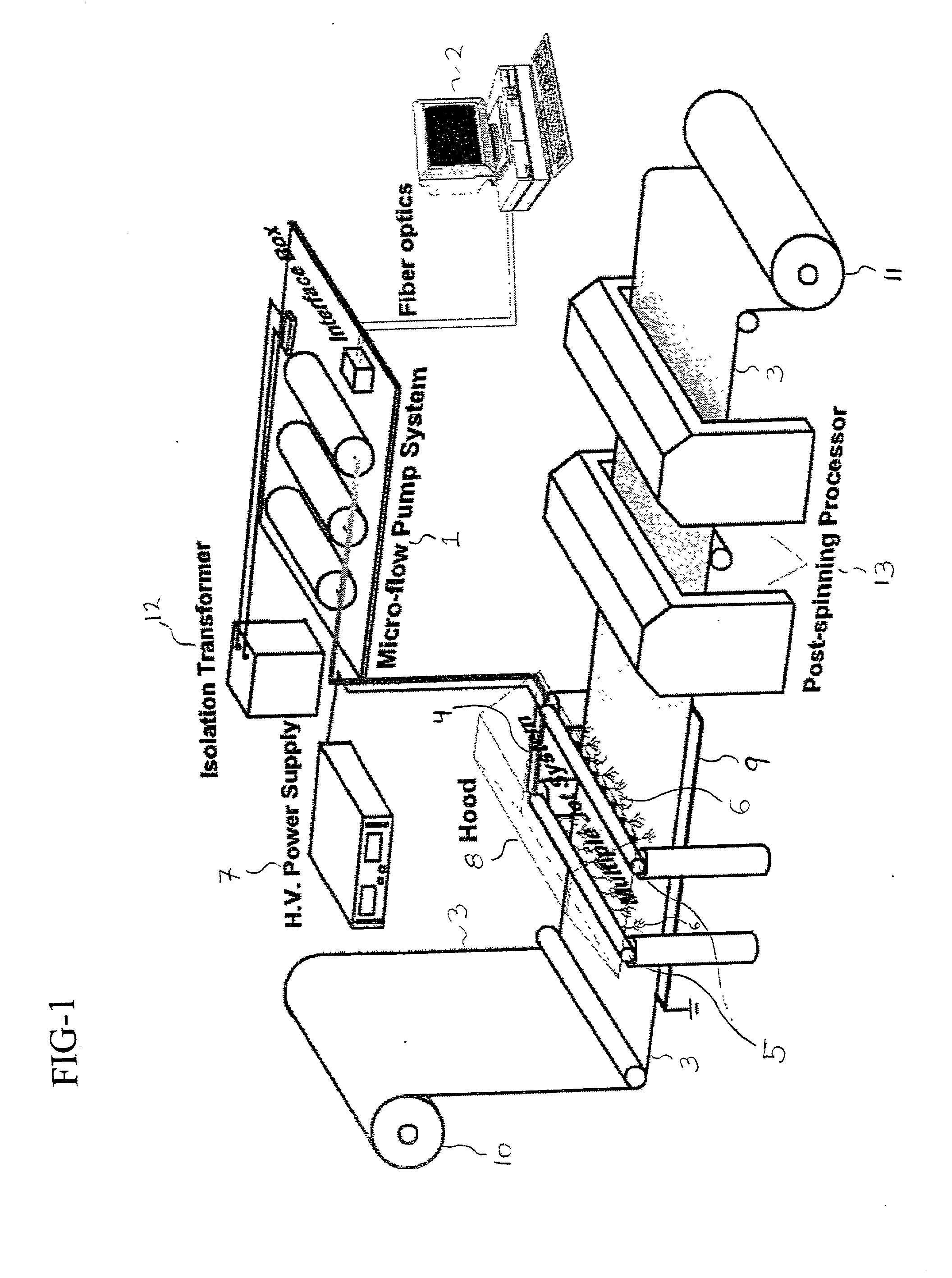
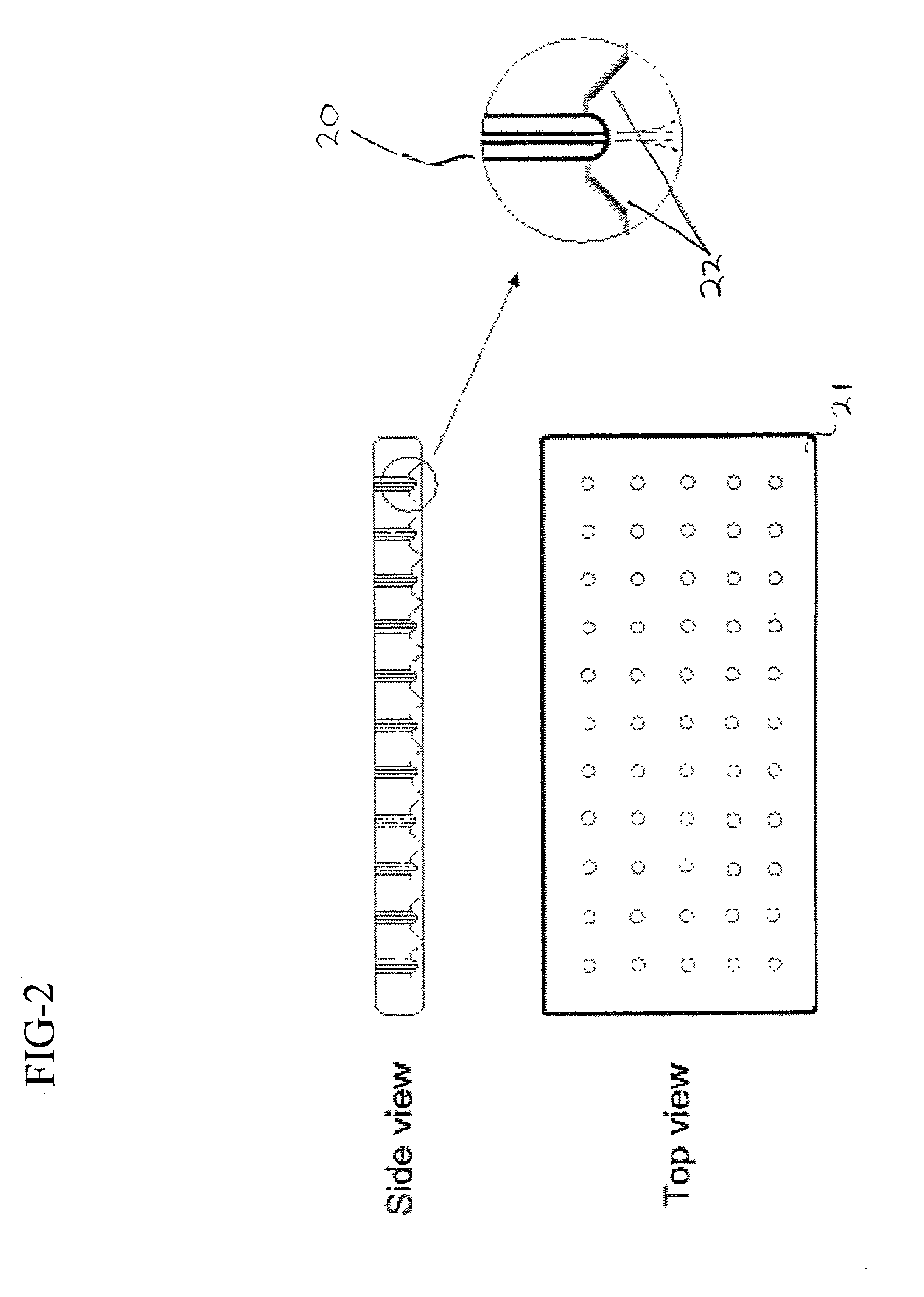
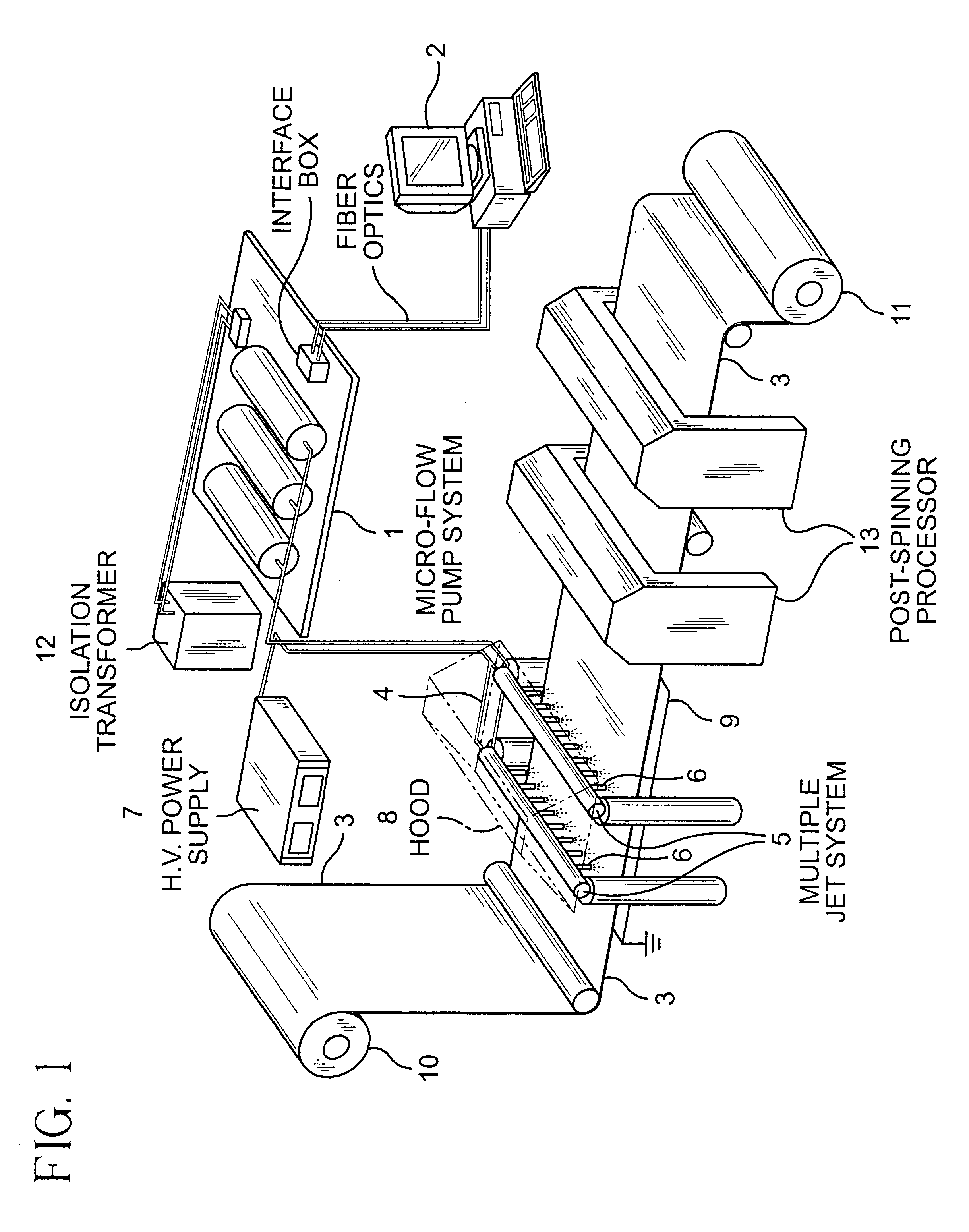
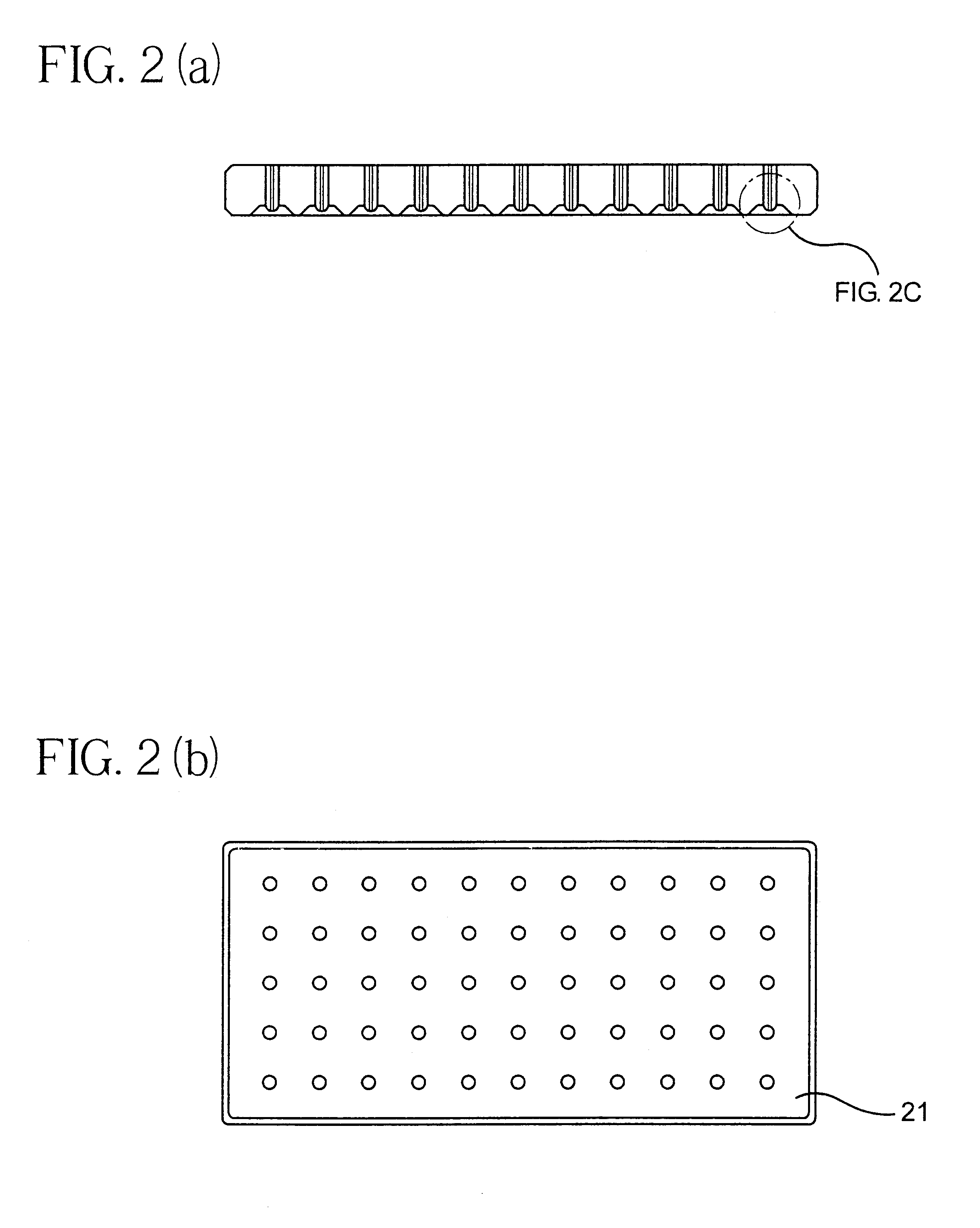
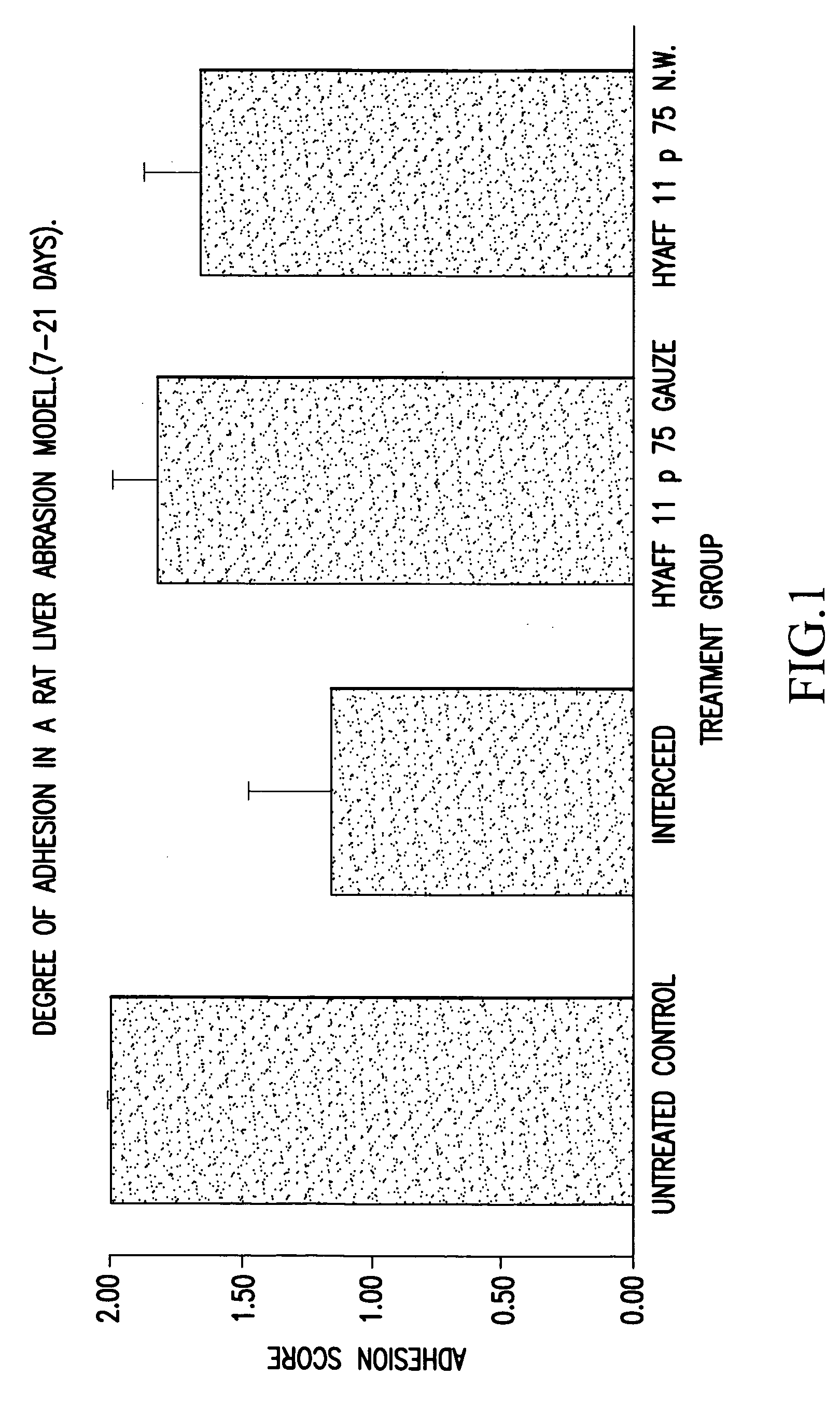
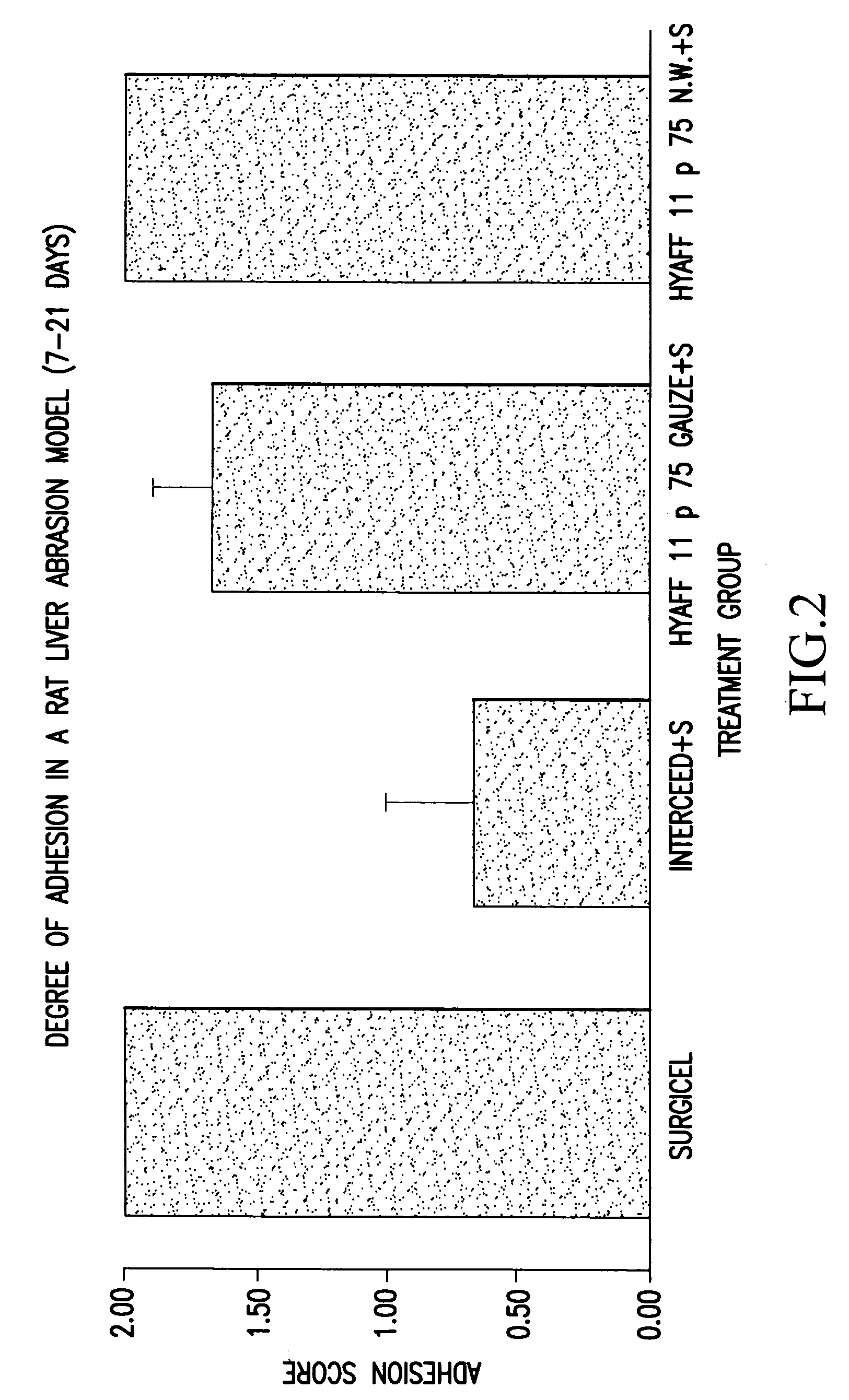
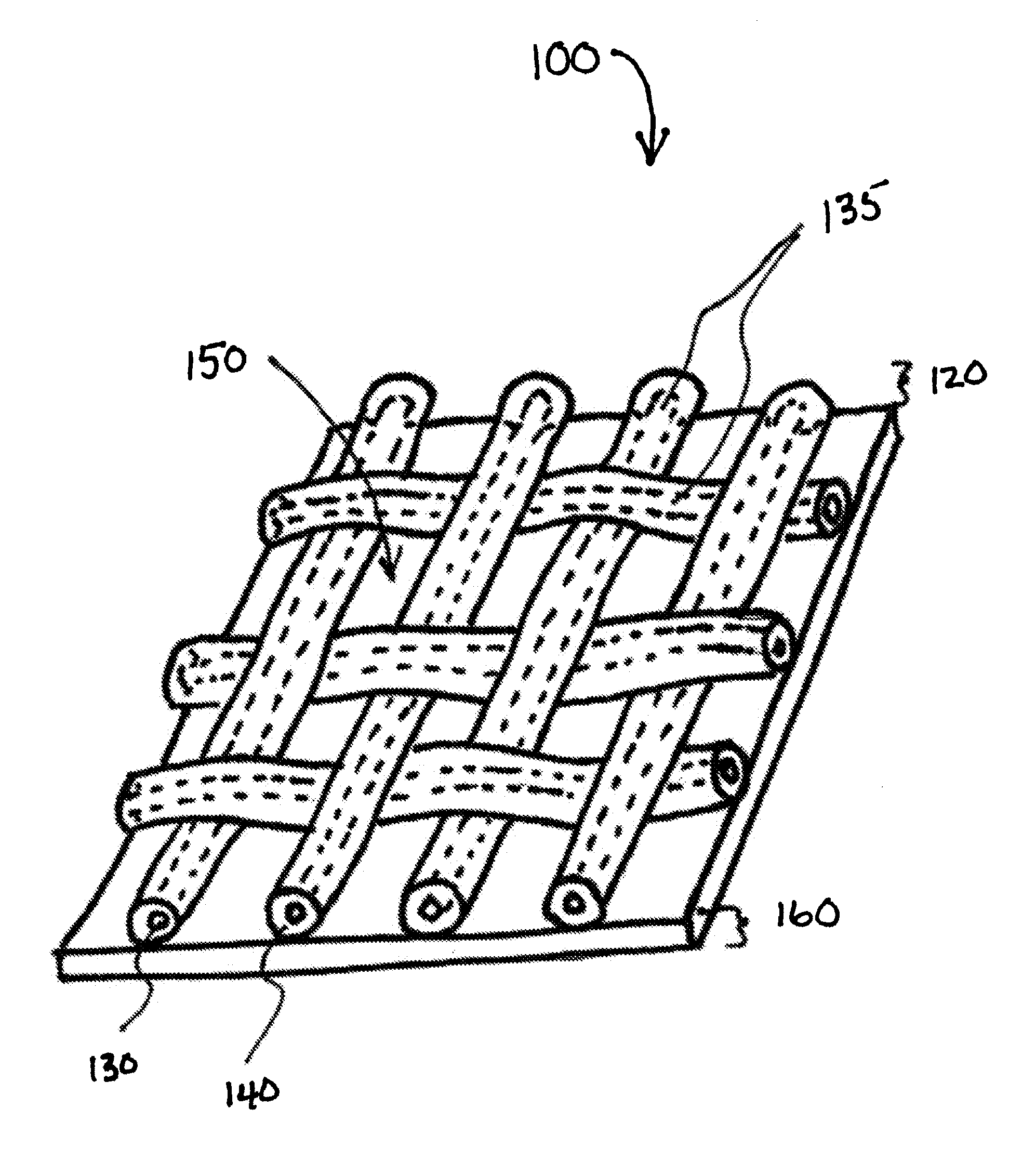
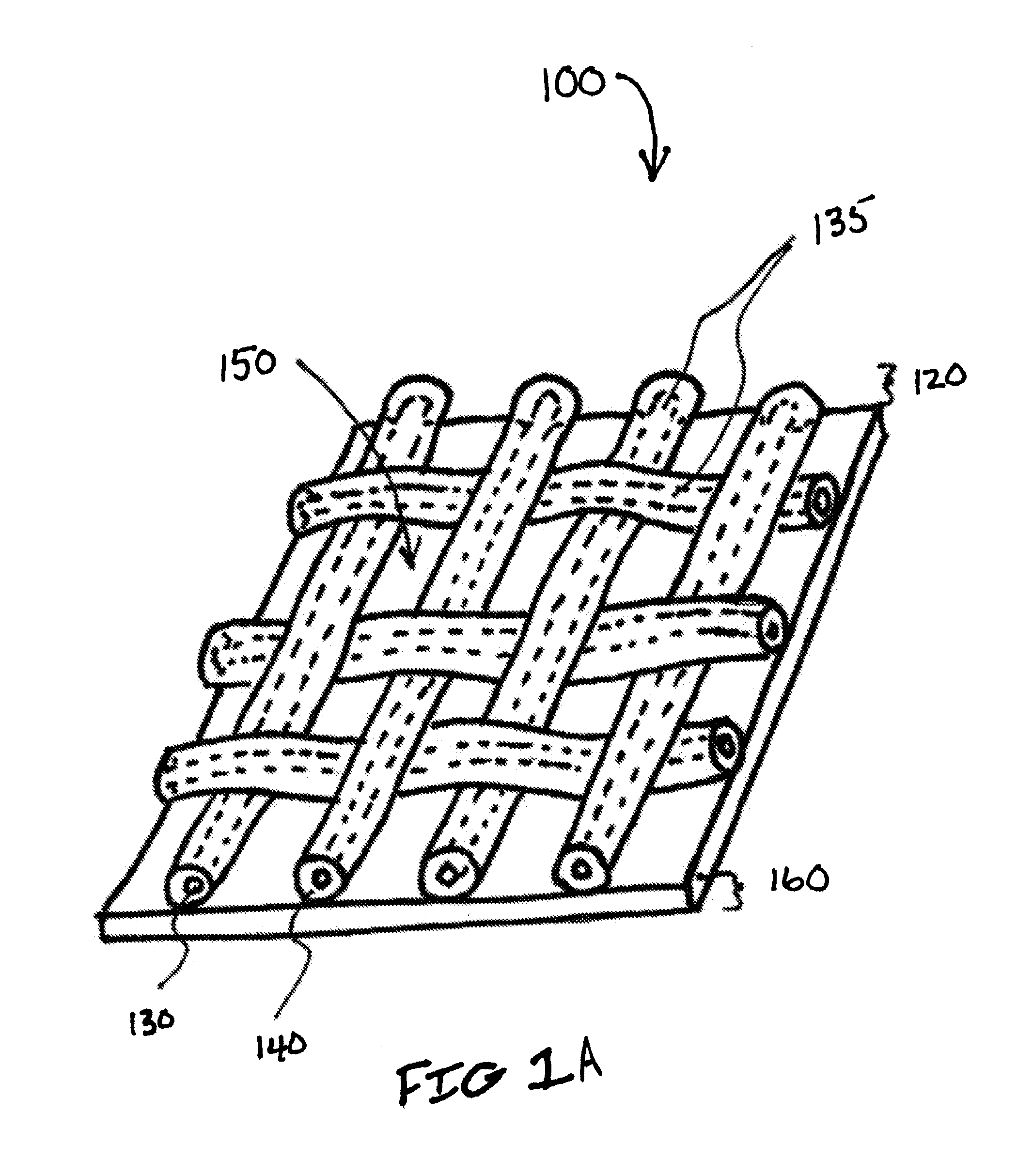
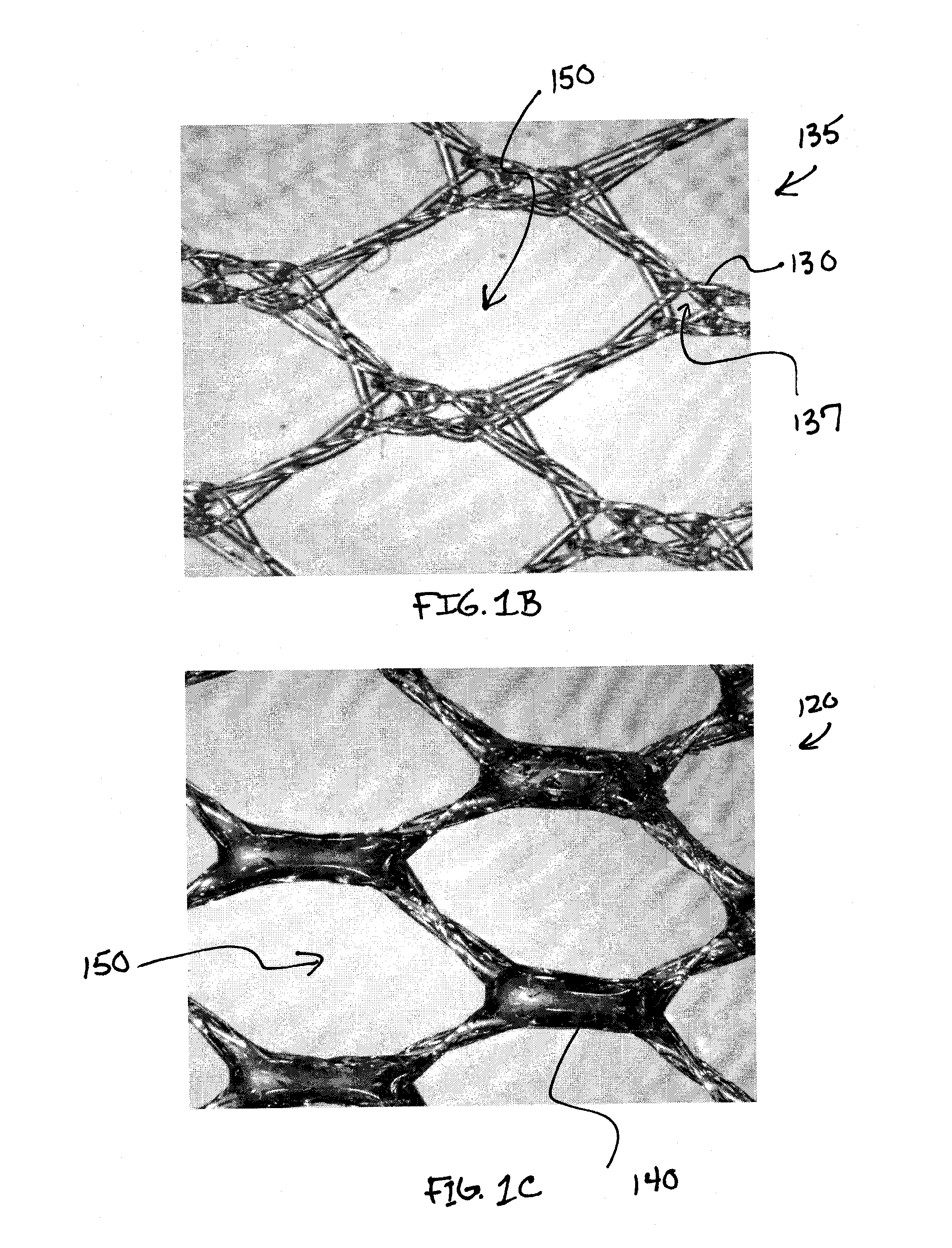
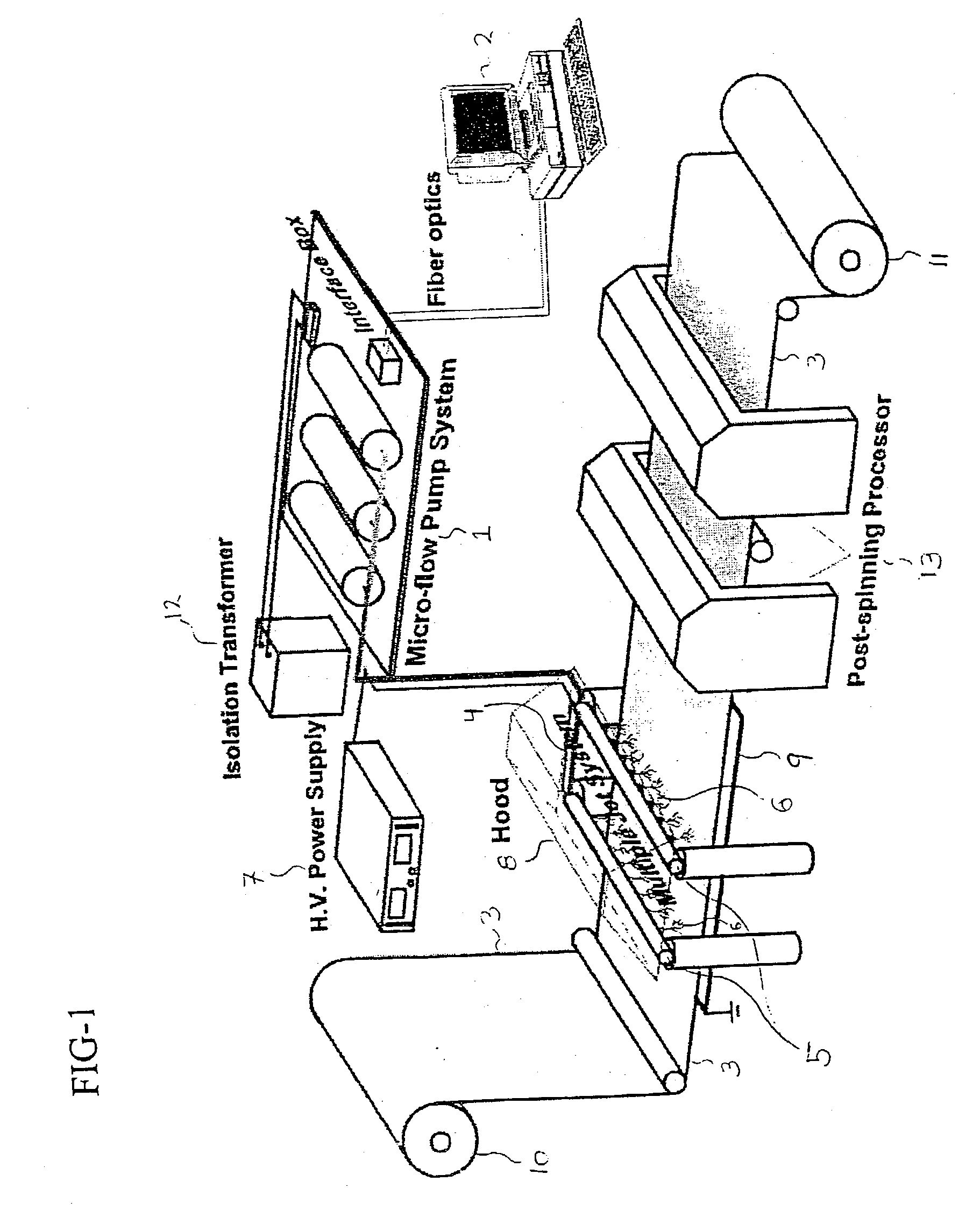
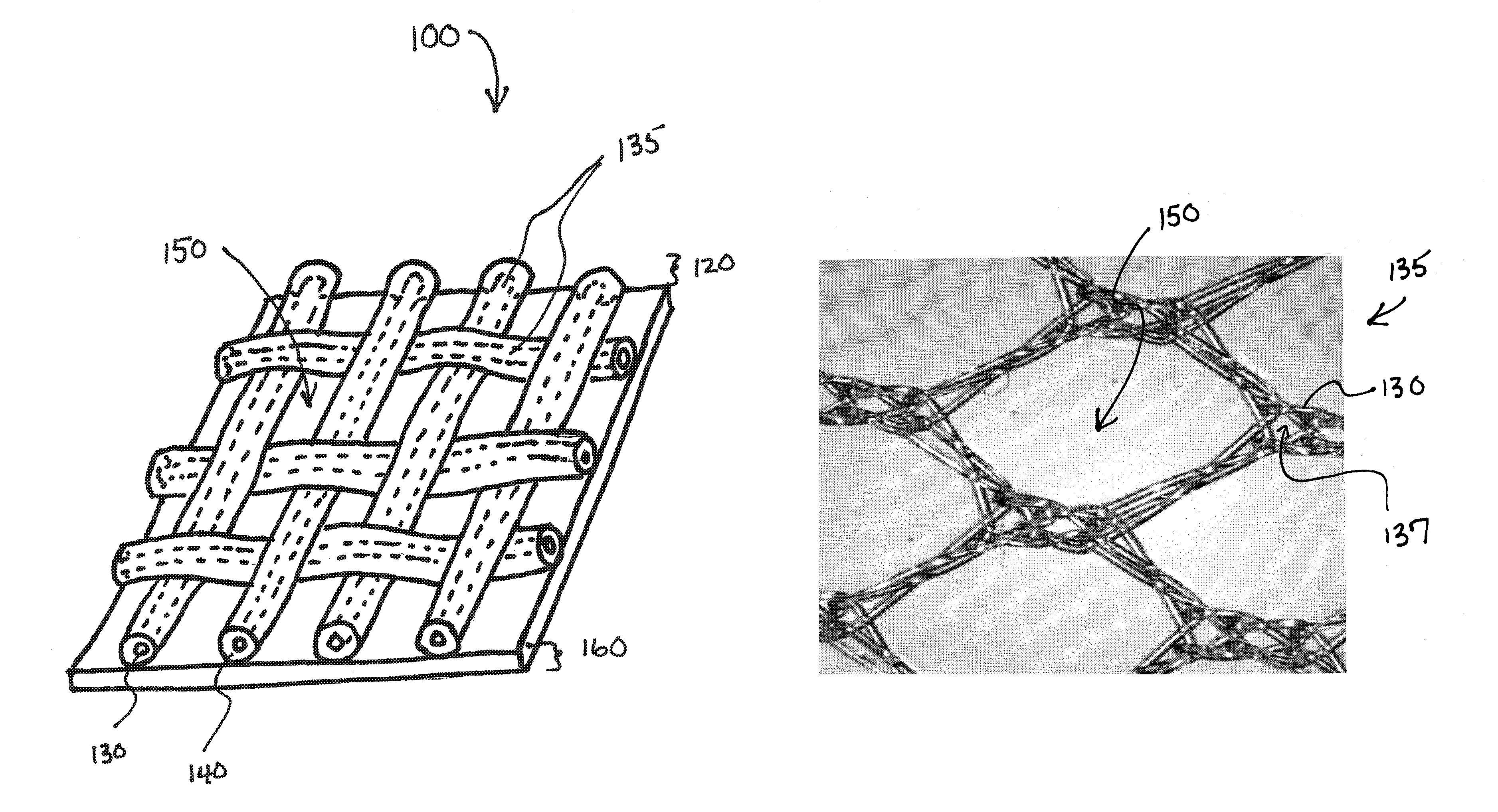
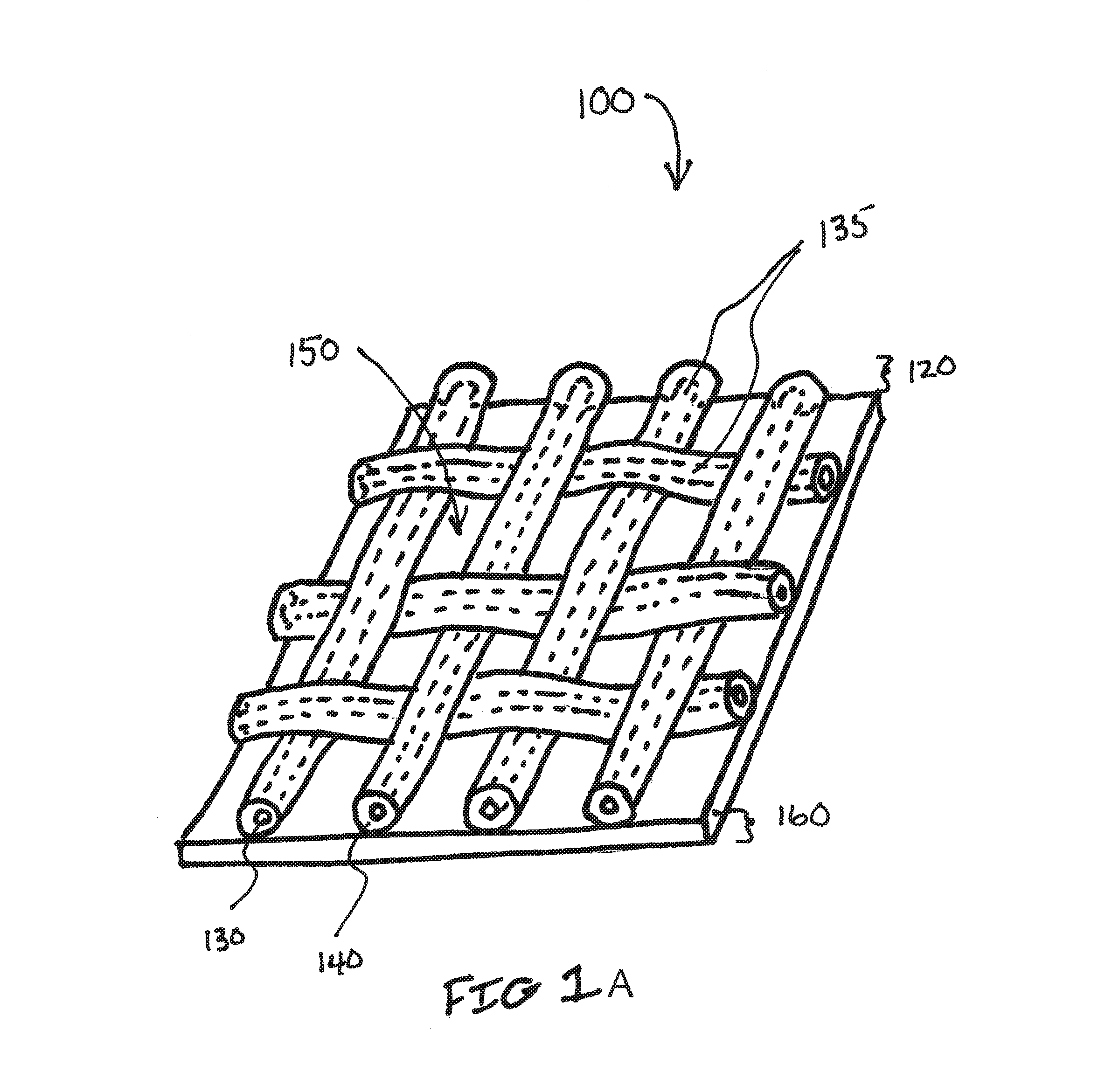
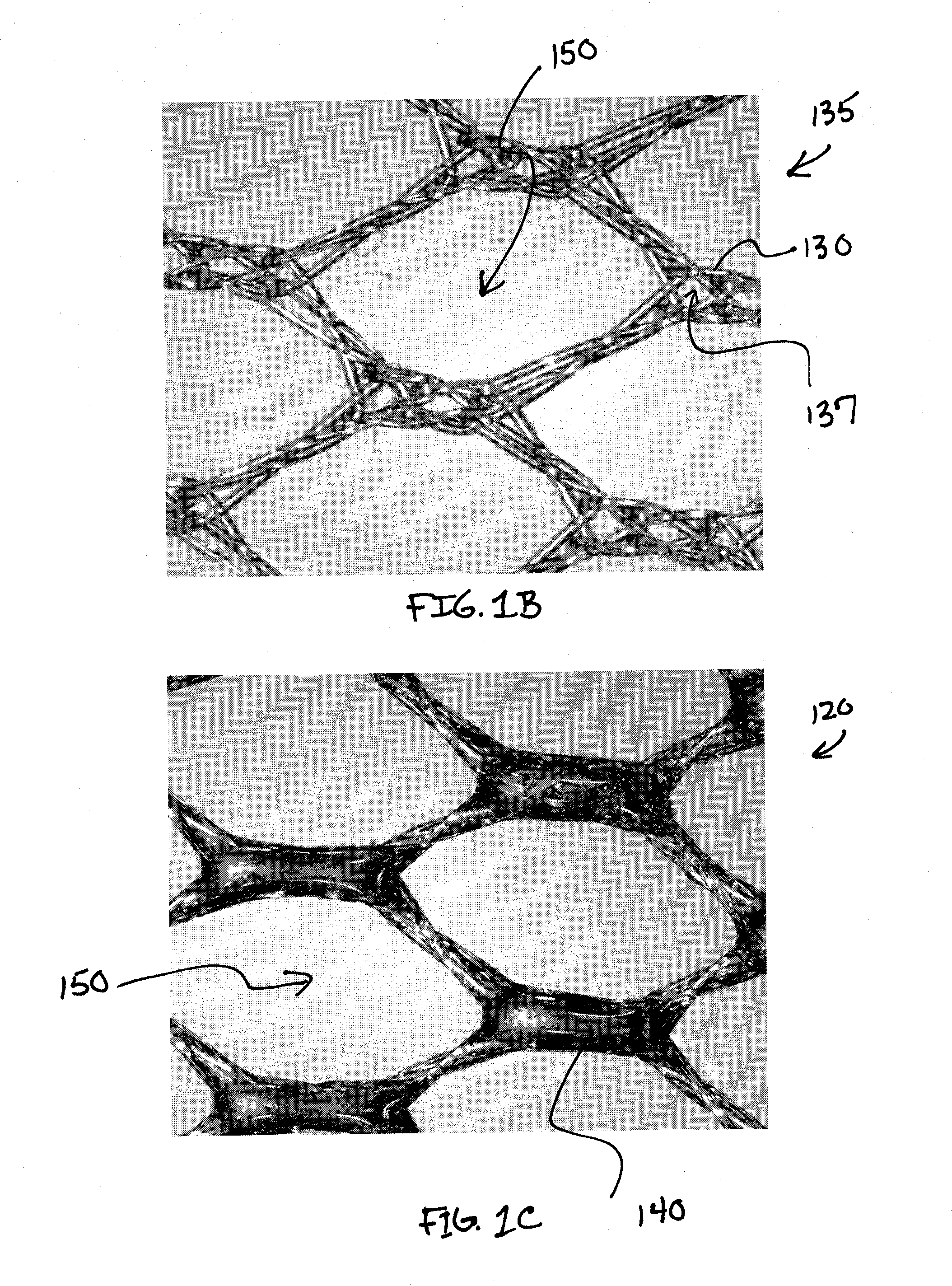
Biodegradable and/or bioabsorbable fibrous articles and methods for using the articles for medical applications
InactiveUS20020173213A1Improved performance and handling characteristicSurgerySynthetic resin layered productsFiberSurgical Adhesions
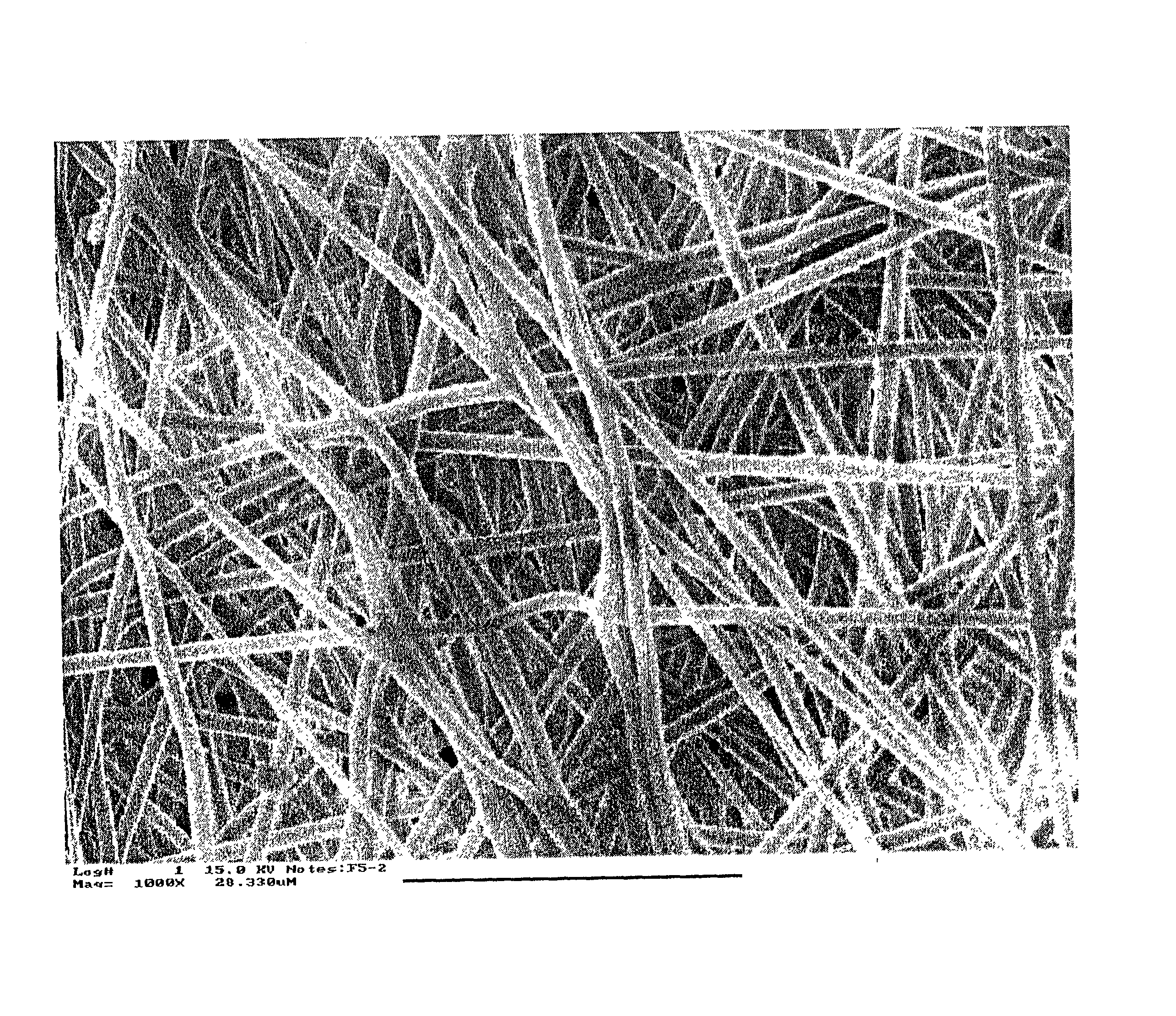
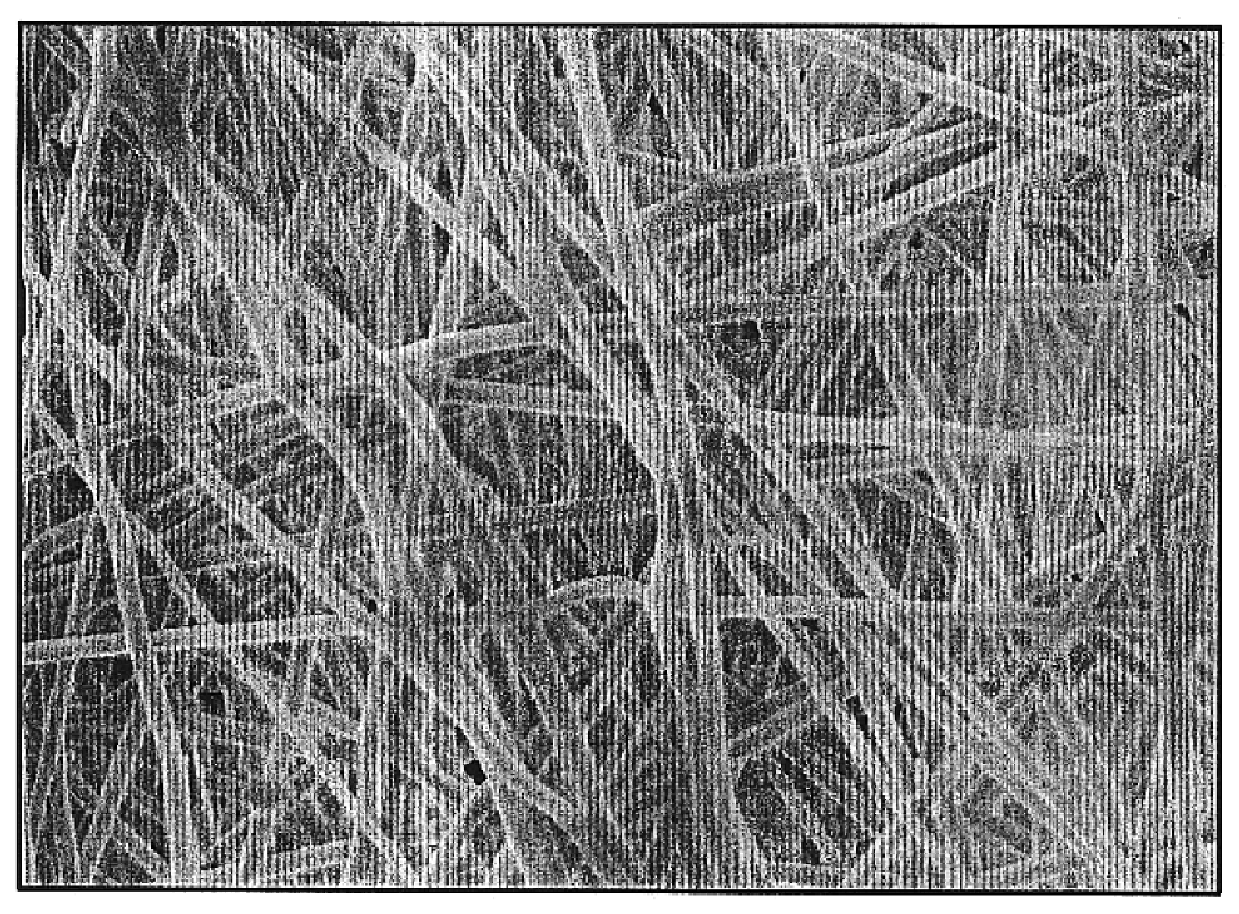
Biodegradable and / or bioabsorable fibrous articles and methods for using the articles in medical applications are disclosed. The biodegradable and / or bioabsorable fibrous articles, which are formed by elctrospinning fibers of biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fiberizable material, comprise a composite (or asymmetric composite) of different biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fibers. Articles having specific medical uses include an adhesion-reducing barrier and a controlled delivery system. The methods include methods for reducing surgical adhesions, controlled delivery of a medicinal agent and providing controlled tissue healing.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Biodegradable and/or bioabsorbable fibrous articles and methods for using the articles for medical applications
InactiveUS6685956B2Improved performance and handling characteristicReduce riskSynthetic resin layered productsSurgeryFiberSurgical Adhesions
Biodegradable and / or bioabsorable fibrous articles and methods for using the articles in medical applications are disclosed. The biodegradable and / or bioabsorable fibrous articles, which are formed by elctrospinning fibers of biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fiberizable material, comprise a composite (or asymmetric composite) of different biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fibers. Articles having specific medical uses include an adhesion-reducing barrier and a controlled delivery system. The methods include methods for reducing surgical adhesions, controlled delivery of a medicinal agent and providing controlled tissue healing.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method of preventing surgical adhesions
The present invention relates to a method and composition for preventing surgical adhesions during surgery. Tissue surfaces and / or surgical articles involved in the surgery are separated by a biomaterial provided in the form of a non-crosslinked, decellularized and purified mammalian tissue (e.g. bovine pericardium). The biomaterial effectively inhibits fibrosis, scar formation, and surgical adhesions, while also serving as a scaffold for recellularization of the tissue site.
Owner:SYNOVIS LIFE TECH
Sutures and Anti-scarring agents
InactiveUS20090226500A1Reducing excessive scarringReducing surgical adhesionSuture equipmentsBiocideHost tissueFibrosis
Sutures are used in combination with anti-scarring agents to inhibit fibrosis between the sutures and the host tissues into which the sutures are inserted. Compositions and methods are described for use in reducing excessive scarring, surgical adhesion, and other disorders.
Owner:ANGIOTECH PHARMA INC
Biomaterials for preventing post-surgical adhesions comprised of hyaluronic acid derivatives
New biomaterials essentially constituted by esterified derivatives of hyaluronic acid or by cross-linked derivatives of hyaluronic acid for use in the surgical sector, particularly for use in the prevention of post-surgical adhesions.
Owner:ANIKA THERAPEUTICS SRL
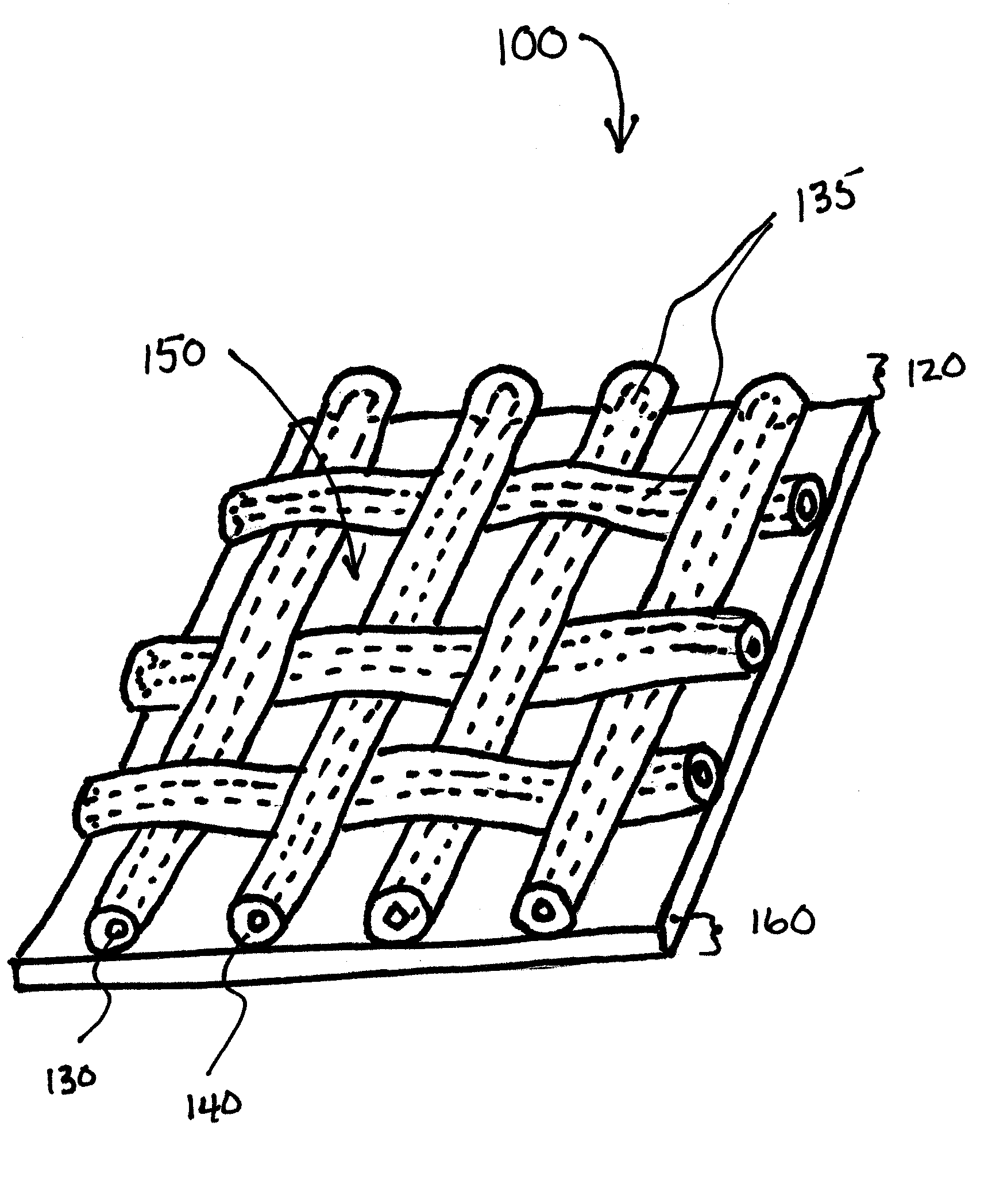
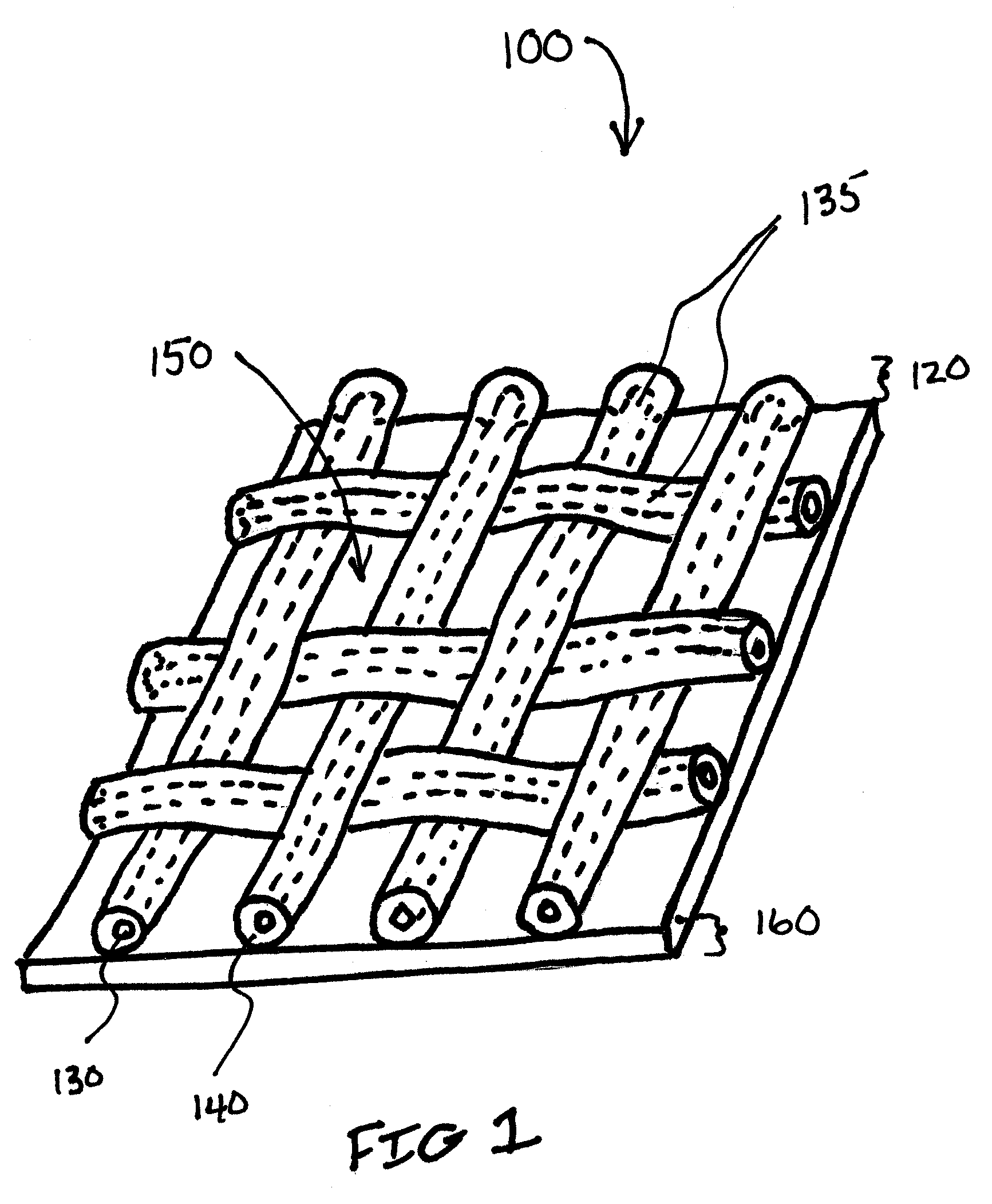
Apparatus and Method for Limiting Surgical Adhesions
A composite prosthesis and method for limiting the incidence of postoperative adhesions. The composite includes a non-inflammatory or coated mesh and a barrier material which prevents exposure of tissue elsewhere in the body to tissue covered by the composite prosthesis. The barrier material is absorbable which allows tissue through-growth and localization of the composite prosthetic. In use, the composite prosthesis is positioned over the tissue defect and may be positioned with the barrier material oriented against the tissue defect or repair site.
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
Methods and compositions based on inhibition of cell invasion and fibrosis by anionic polymers
Owner:TRIAD
Apparatus and method for limiting surgical adhesions
InactiveUS20120179176A1Small surface areaReduce reduction reactionCoatingsProsthesisPolyolBiocompatible coating
The present invention relates to a composite prosthesis including a coated mesh having at least one opening through a first surface and a second surface of the coated mesh; the coated mesh comprising a mesh and a biocompatible coating substantially surrounding each filament of the mesh, wherein the biocompatible coating is formed by coating the mesh with a polyol prepolymer and curing the prepolymer, the prepolymer comprising a polyalkylene oxide polyol end capped with isocyanate, the polyalkylene oxide polyol having from about 70% to about 95% ethylene oxide groups and the remainder propylene oxide; and a barrier material comprising a biocompatible membrane constructed and arranged to cover at least one surface of the coated mesh, wherein the barrier material comprises a biologic material.
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
Method for inhibition of bone growth by anionic polymers
InactiveUS6020326AInhibit bone growthPrevent invasionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCell invasionFibrosis
The present invention relates to the discovery that biocompatible anionic polymers can effectively inhibit fibrosis, scar formation, and surgical adhesions. The invention is predicated on the discovery that anionic polymers effectively inhibit invasion of cells associated with detrimental healing processes, and in particular, that the effectiveness of an anionic polymer at inhibiting cell invasion correlates with the anionic charge density of the polymer. Thus the present invention provides a large number of materials for use in methods of inhibiting fibrosis and fibroblast invasion. Anionic polymers for use in the invention include but are not limited to natural proteoglycans, and the glycosaminoglycan moieties of proteoglycans. Additionally, anionic carbohydrates and other anionic polymers may be used. The anionic polymers dextran sulfate and pentosan polysulfate are preferred. In a more preferred embodiment, dextran sulfate, in which the sulfur content is greater than about 10% by weight, may be used. In a more preferred embodiment, the average molecular weight is about 40,000 to 500,000 Daltons. The present invention provides compositions and methods to inhibit fibrosis and scarring associated with surgery. The invention further provides compositions and methods to inhibit glial cell invasion, detrimental bone growth and neurite outgrowth. In a preferred embodiment, the inhibitory compositions further comprise an adhesive protein.
Owner:TRIAD
Surgical hydrogel
InactiveUS20100291055A1Avoid stickingAffect haemostasisOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCross-linkWound healing
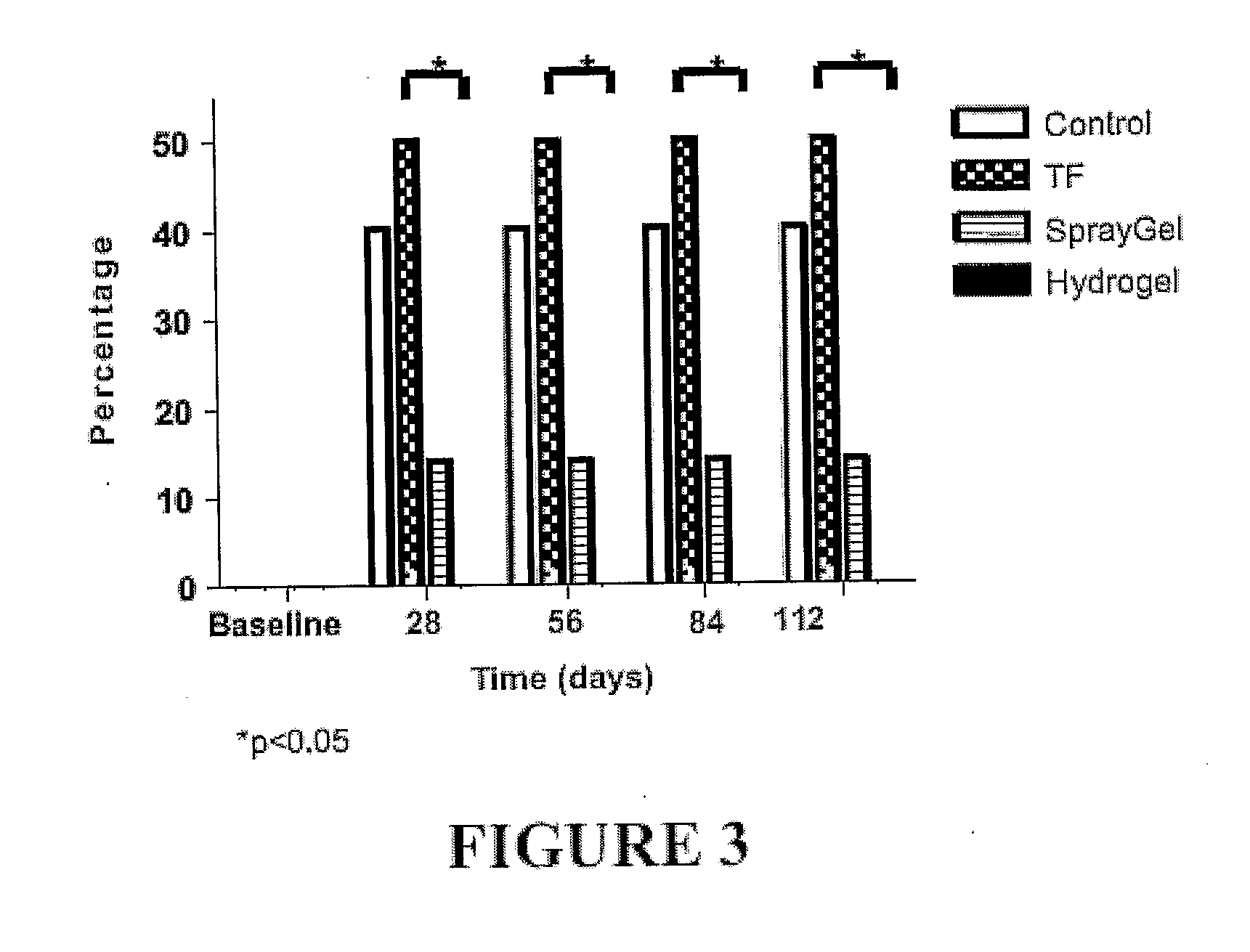
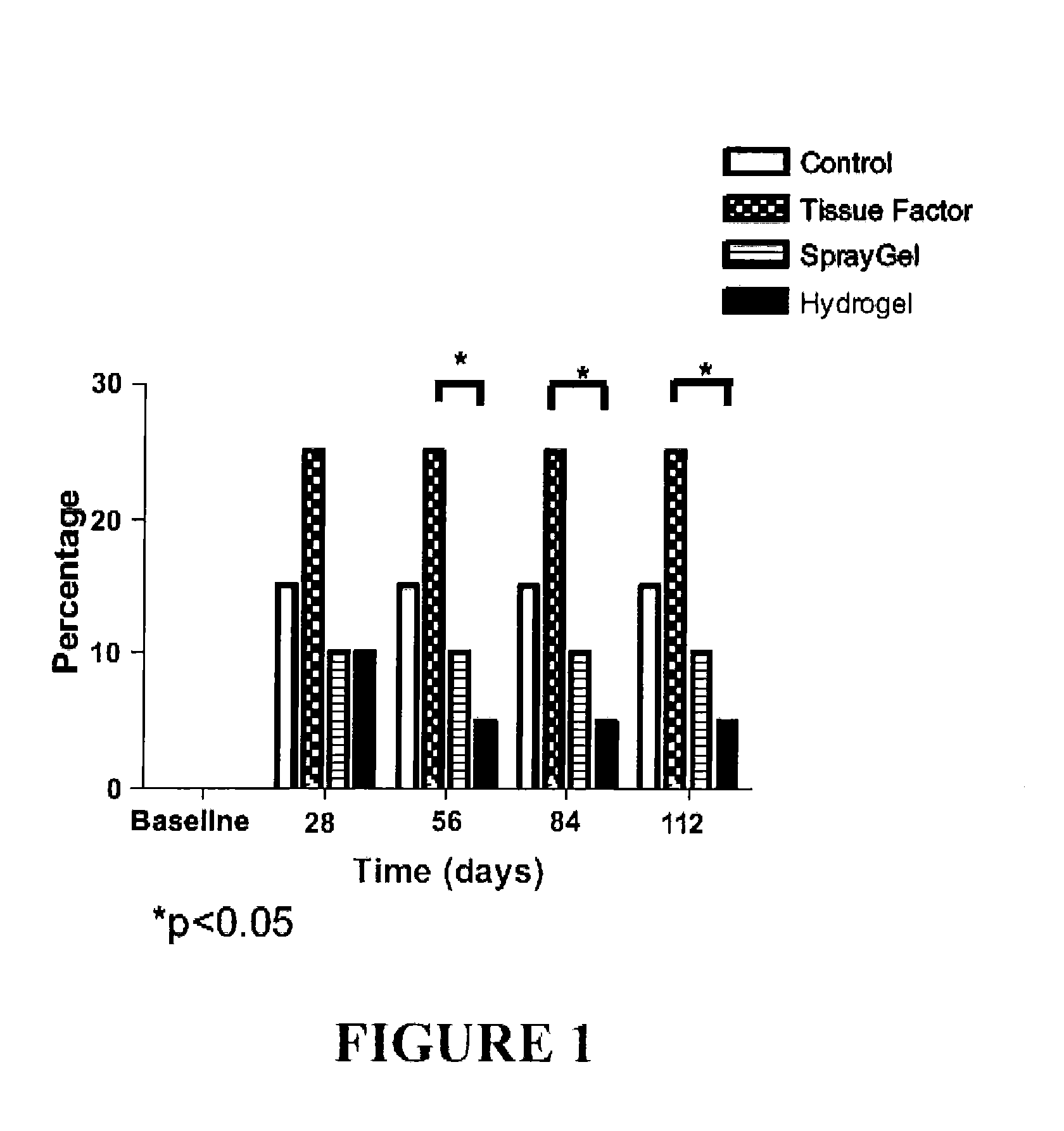
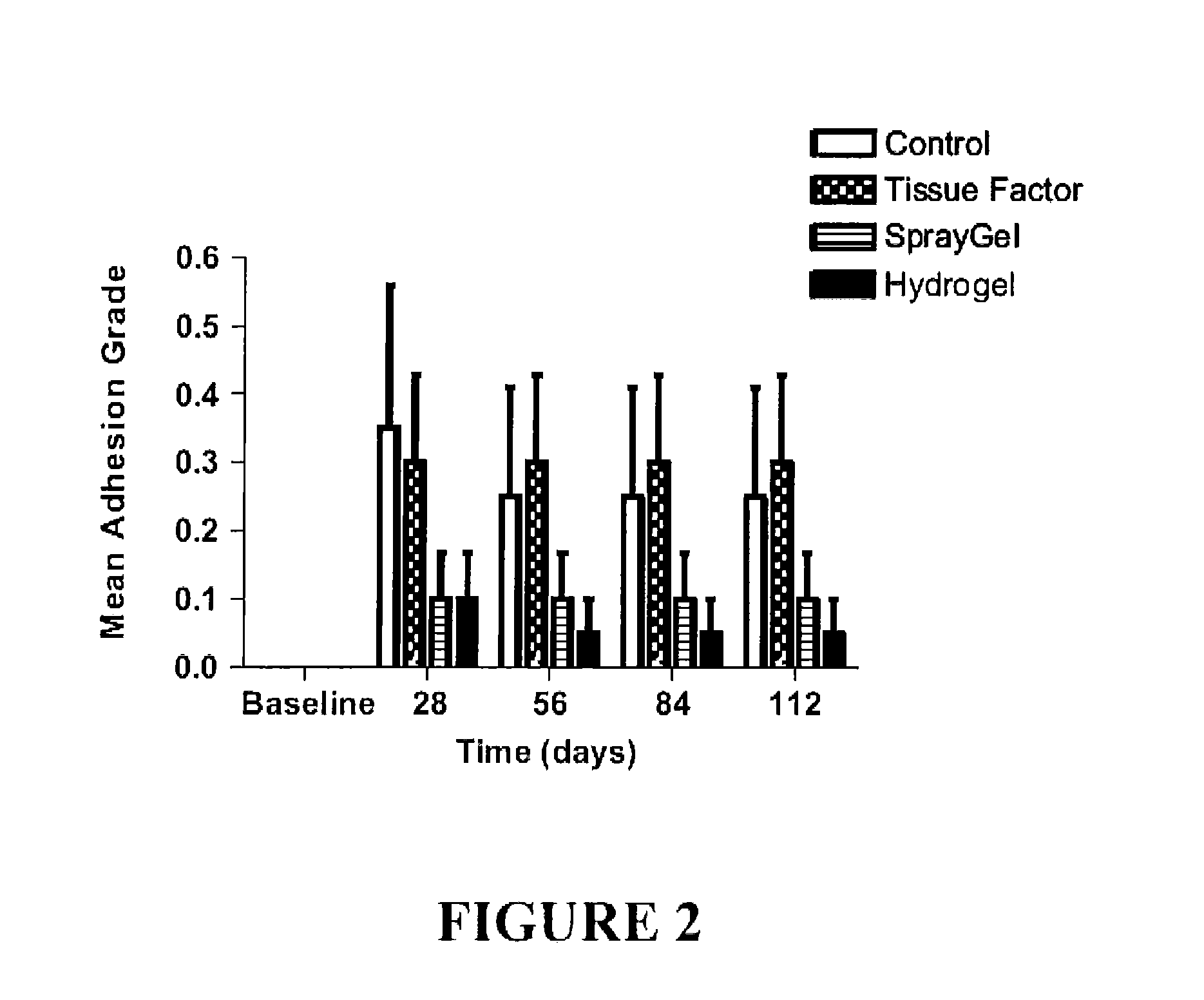
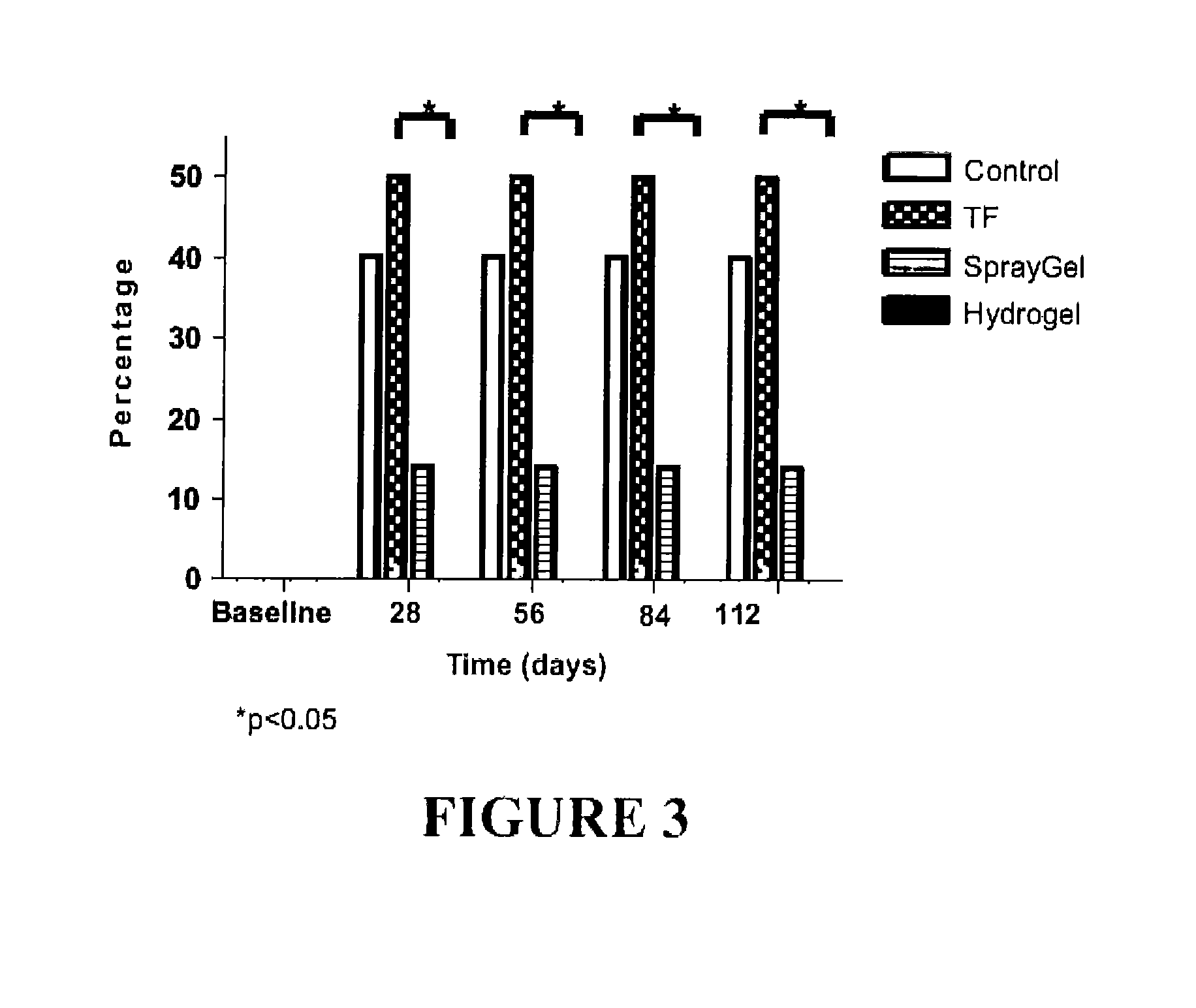
The invention provides a hydrogel suitable for use in wound healing, particularly for reducing post-surgical adhesions. The hydrogel comprises cross-linked derivatives of chitosan and dextran polymers. The hydrogel forms when solutions of the polymers are combined.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
Method of preventing post-operative surgical adhesion
A method for preventing adhesion using a co-polyester comprising the reaction product of a polycondensation polyester and at least one lactone, wherein the polycondensation polyester comprises the reaction product of diglycolic acid and / or a derivative thereof and ethylene glycol; and the co-polyester comprises about 40 to 50% by weight of the polycondensation polyester based on the total weight of the co-polyester.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Immunomodulating polymers
InactiveUS7083777B1Suppressing antibody responseConducive to survivalAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNeutral Amino AcidsDisease
A pharmaceutical composition consisting of identical repeating units, each unit having a charge motif composed of a positively charged free amino moiety and a negatively charged moiety, wherein the positively charged free amino moiety and the negatively charged moiety of each charge motif are separated by at least one neutral amino acid, and wherein the positively charged free amino moiety of one of the charge motifs is separated by a distance of at least 8 amino acids from the positively charged amino moiety of another charge motif, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Said pharmaceutical composition is useful for inducing IL-2, activating T cells to produce a T helper 1 cytokine profile, suppressing IgG antibody response to specific antigen, promoting allograft survival, reducing postoperative surgical adhesion formation, and / or protecting against abscess formation associated with surgery, trauma or diseases that predispose the host to abscess formation.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Immunomodulating polymers
InactiveUS7026285B2Suppressing antibody responseConducive to survivalOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseT cell
Methods and products for inducing IL-2 secretion, inducing IL-10 secretion, activating T cells, suppressing IgG antibody response to specific antigen, promoting allograft survival, reducing postoperative surgical adhesion formation, and protecting against abscess formation associated with surgery, trauma or diseases that predispose the host to abscess formation are provided. The methods of the invention are accomplished using an immunomodulator which is a polymer having at least two repeating charge motifs separated by at least a certain minimum distance.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Compositions and methods of using a transient colorant
This invention relates generally to compositions and systems for forming biomaterials containing a transient colorant for visualizing tissue or surgical materials coated with such biomaterials, to methods of using such compositions as bioadhesives, for tissue augmentation, in the prevention of surgical adhesions, for coating surfaces of synthetic implants, as drug delivery matrices, for ophthalmic applications, and in other applications.
Owner:SURGICAL SPECIALTIES CORP LTD
Biodegradable and/or bioabsorbable fibrous articles and methods for using the articles for medical applications
InactiveUS20030228350A1Improved performance and handling characteristicSurgerySynthetic resin layered productsFiberSurgical Adhesions
Biodegradable and / or bioabsorable fibrous articles and methods for using the articles in medical applications are disclosed. The biodegradable and / or bioabsorable fibrous articles, which are formed by elctrospinning fibers of biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fiberizable material, comprise a composite (or asymmetric composite) of different biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fibers. Articles having specific medical uses include an adhesion-reducing barrier and a controlled delivery system. The methods include methods for reducing surgical adhesions, controlled delivery of a medicinal agent and providing controlled tissue healing.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
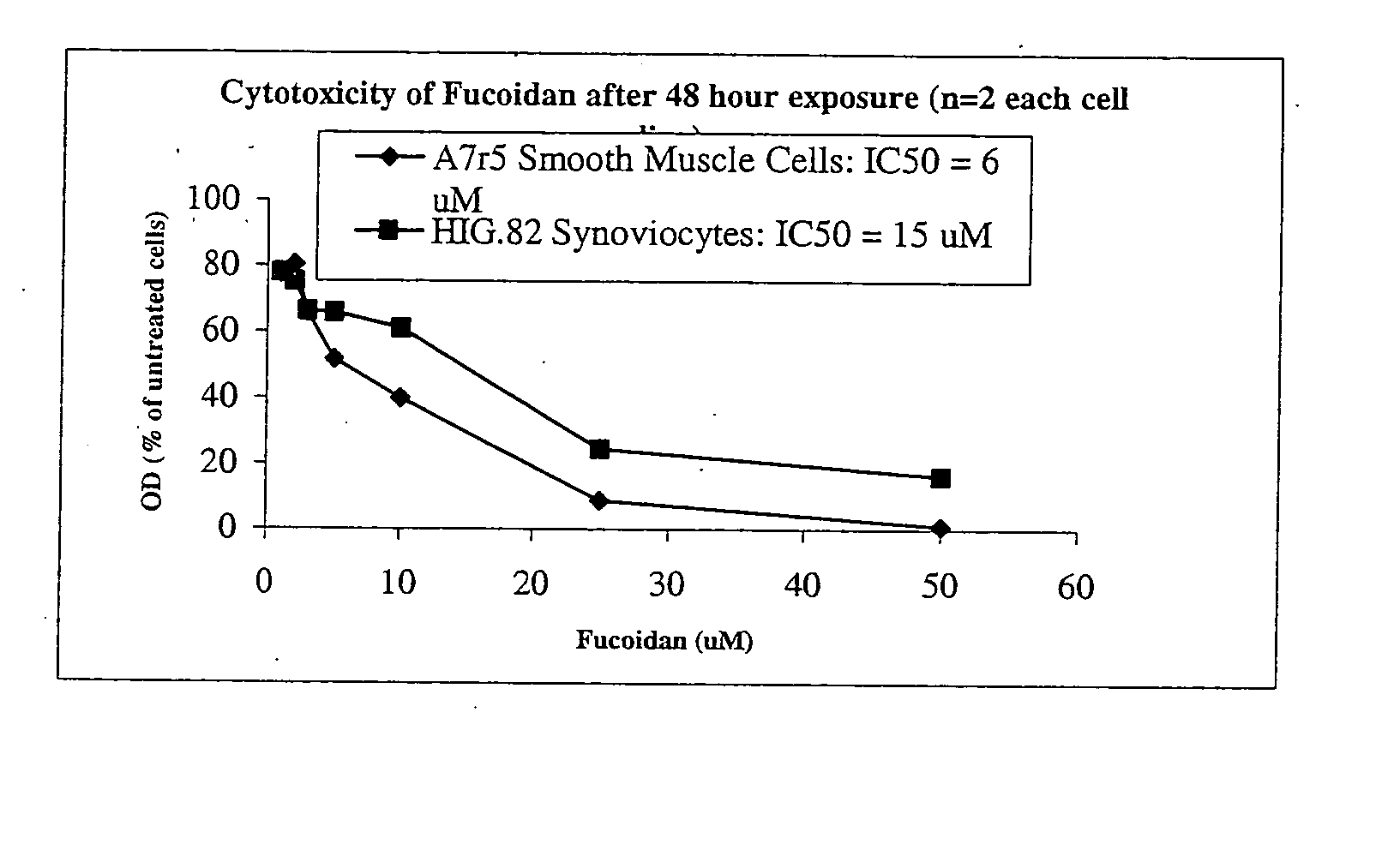
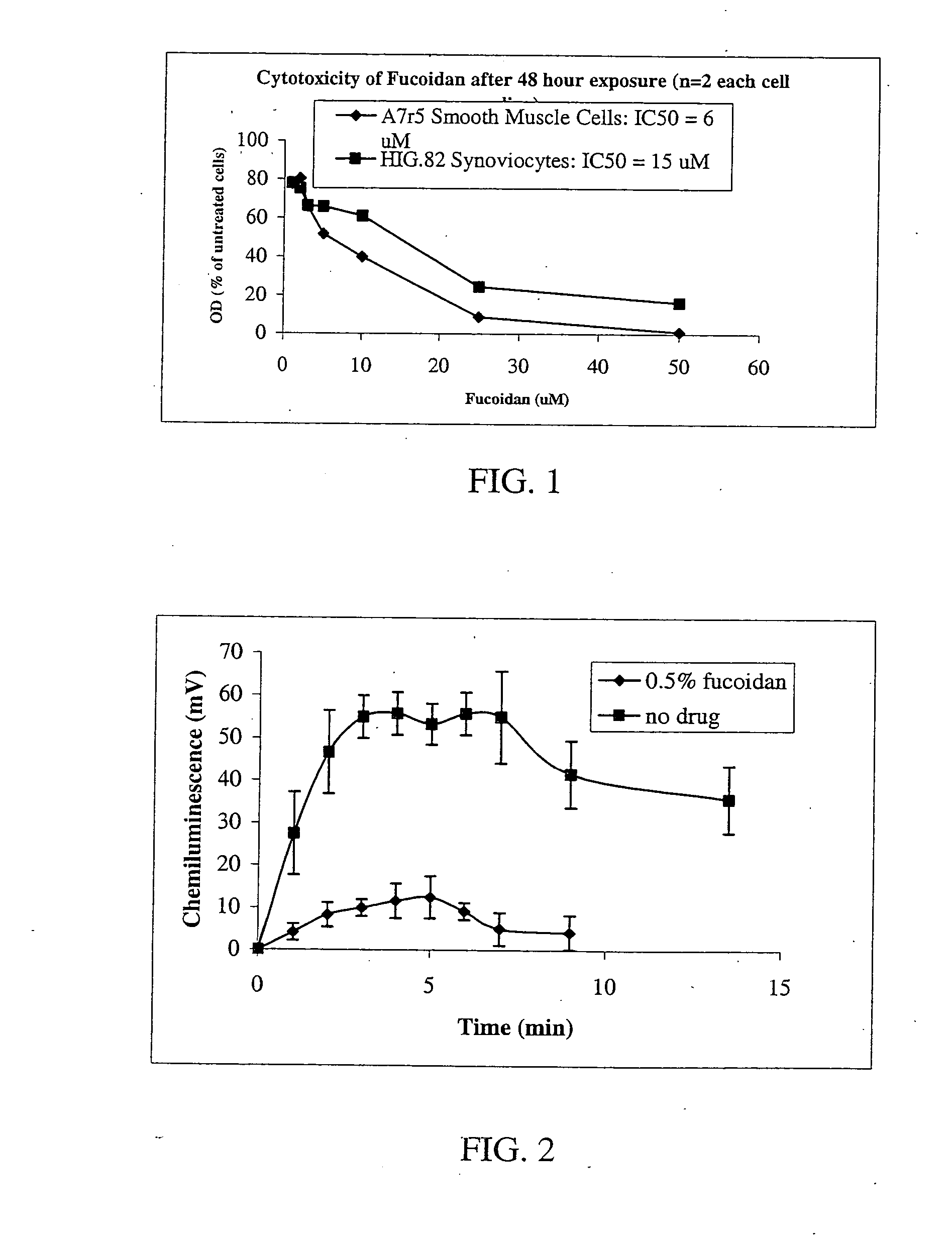
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods relating to fucans
InactiveUS20070238697A1Good treatment effectEliminate side effectsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideFucoidanMedicine
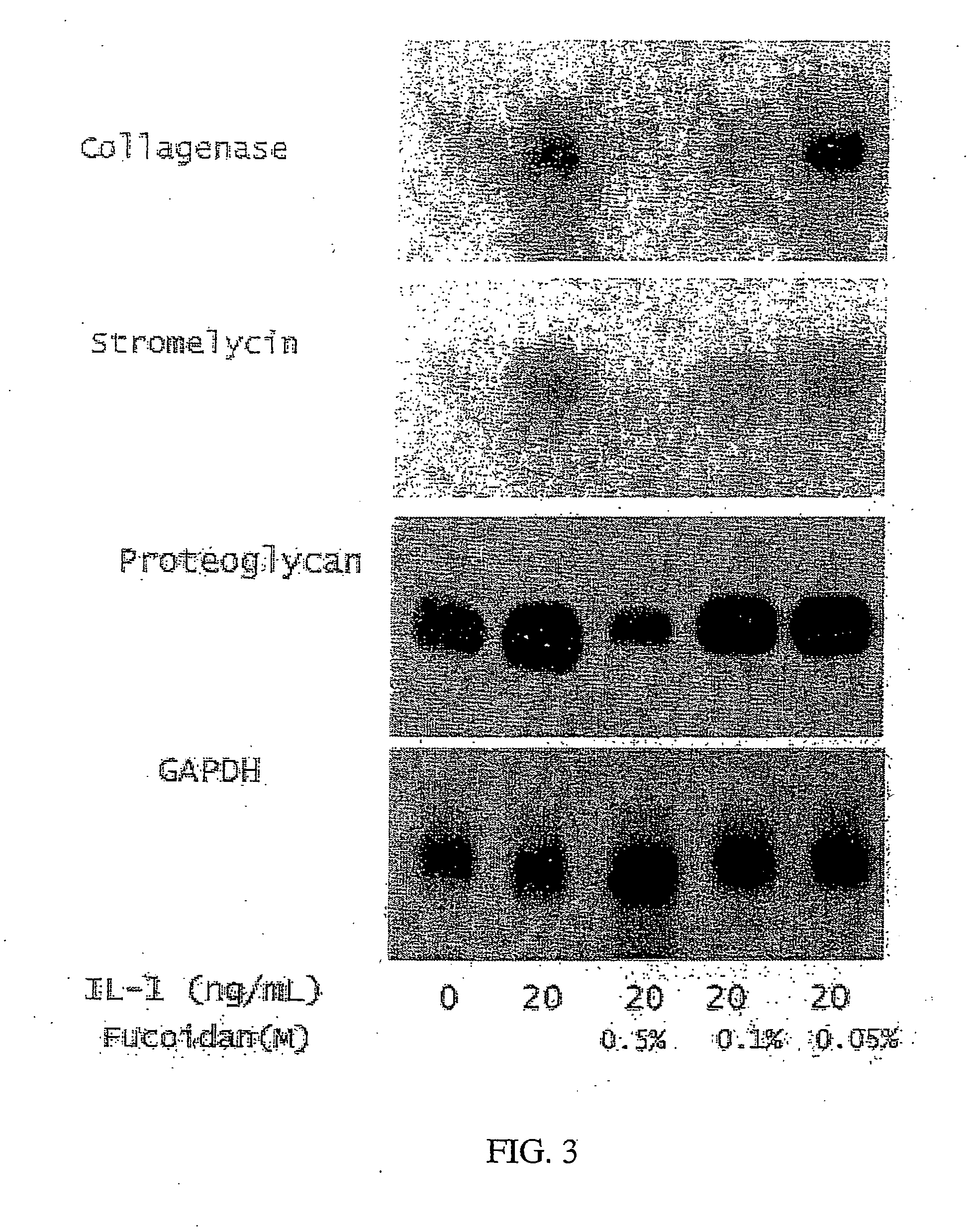
Compositions, methods and the like comprising fucans such as fucoidan to treat surgical adhesions, arthritis, and psoriasis.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Surgical hydrogel
ActiveUS8809301B2Reducing and stopping bleedingAffect haemostasisBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPolymer solutionSurgical Adhesions
A composition suitable for use in wound healing, particularly for reducing post-surgical adhesions, containing cross-linked derivatives of chitosan and dextran polymers. A hydrogel forms when solutions of the polymers are combined.
Owner:ADELAIDE RES & INNOVATION PTY LTD +2
Apparatus and method for limiting surgical adhesions
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
Immunomodulating polymers
InactiveUS20060153832A1Suppressing antibody responseConducive to survivalOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsT cellAbscess
Methods and products for inducing IL-2 secretion, inducing IL-10 secretion, activating T cells, suppressing IgG antibody response to specific antigen, promoting allograft survival, reducing postoperative surgical adhesion formation, and protecting against abscess formation associated with surgery, trauma or diseases that predispose the host to abscess formation are provided. The methods of the invention are accomplished using an immunomodulator which is a polymer having at least two repeating charge motifs separated by at least a certain minimum distance.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Drug delivery from rapid gelling polymer composition
Compositions are disclosed that afford drug delivery from two-part polymer compositions that rapidly form covalent linkages when mixed together. Such compositions are particularly well suited for use in a variety of tissue related applications when rapid adhesion to the tissue and gel formation is desired along with drug delivery. For example, the compositions are useful as tissue sealants, in promoting hemostasis, in effecting tissue adhesion, in providing tissue augmentation, and in the prevention of surgical adhesions.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Method of preventing post-operative surgical adhesion
A method for preventing adhesion using a co-polyester comprising the reaction product of a polycondensation polyester and at least one lactone, wherein the polycondensation polyester comprises the reaction product of diglycolic acid and / or a derivative thereof and ethylene glycol; and the co-polyester comprises about 40 to 50% by weight of the polycondensation polyester based on the total weight of the co-polyester.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Drug delivery from rapid gelling polymer composition
Compositions are disclosed that afford drug delivery from two-part polymer compositions that rapidly form covalent linkages when mixed together. Such compositions are particularly well suited for use in a variety of tissue related applications when rapid adhesion to the tissue and gel formation is desired along with drug delivery. For example, the compositions are useful as tissue sealants, in promoting hemostasis, in effecting tissue adhesion, in providing tissue augmentation, and in the prevention of surgical adhesions.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Polyhydroxystilbenes and stibene oxides as antisoriatic agents and protein kinase inhibitors
Disclosed herein are compositions containing hydroxylstilbenes or their derivatives or analogues. The compositions are useful to inhibit protein kinease, and for the treatment of inflammatory diseases, including psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, rhumatoid arthritis, restinosis, inflammatory bowel disease, and inflammatory lung disease. They are also useful to treat surgical adhesions and graft rejection. Novel derivatives and analogues are also disclosed.
Owner:BEIJING WEN FENG TIANJI PHARMA CO LTD
Treatment of surgical adhesions
InactiveUS20110144182A1Reduce adhesionReduce incidenceOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSurgical AdhesionsTreatment surgery
Connexin modulation for the treatment of surgical adhesions, and associated methods, compositions, and articles.
Owner:BECKER DAVID LAWRENCE +2
Fibrous tissue sealant and method of using same
Disclosed herein is a fibrous tissue sealant in the form of an anhydrous fibrous sheet comprising a first component which is a fibrous polymer containing electrophilic or nucleophilic groups and a second component capable of crosslinking the first component when the sheet is exposed to an aqueous medium, thereby forming a crosslinked hydrogel that is adhesive to biological tissue. The fibrous tissue sealant may be useful as a general tissue adhesive for medical and veterinary applications such as wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures, tissue repair, and to prevent post-surgical adhesions. The fibrous tissue sealant may be particularly suitable for use as a hemostatic sealant to stanch bleeding from surgical or traumatic wounds.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Treatment of surgical adhesions
InactiveUS20110245184A1Preventing and decreasing post-surgical adhesionInhibit intercellular communicationCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineSurgical Adhesions
Owner:CODA THERAPEUTICS INC
Apparatus and Method for Reducing the Occurrence of Post-Surgical Adhesions
A method for inhibiting formation of adhesions following abdominal surgery which involves application of an anti-static fatty acid ethoxylated amide (Cocamide DEA) in a matrix that is placed in the peritoneal cavity at the conclusion of an abdominal surgery and which releases this anti-adhesive chemical over a predetermined time in a range up to seven days. Tests conducted on laboratory rats established that the method reduced the incidence of adhesions from 100 percent (100%) in a test model to near zero in the majority of treated animals. In an alternative embodiment, andrographalide was delivered via a pump with similar results. In still another embodiment, an effective amount of 50% phosphatidylchorene and propylene glycol was delivered, via a pump, into the abdominal cavity, again with similar results.
Owner:ANHESE
Drug delivery from rapid gelling polymer composition
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
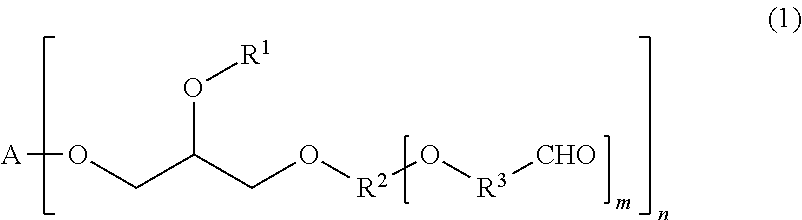
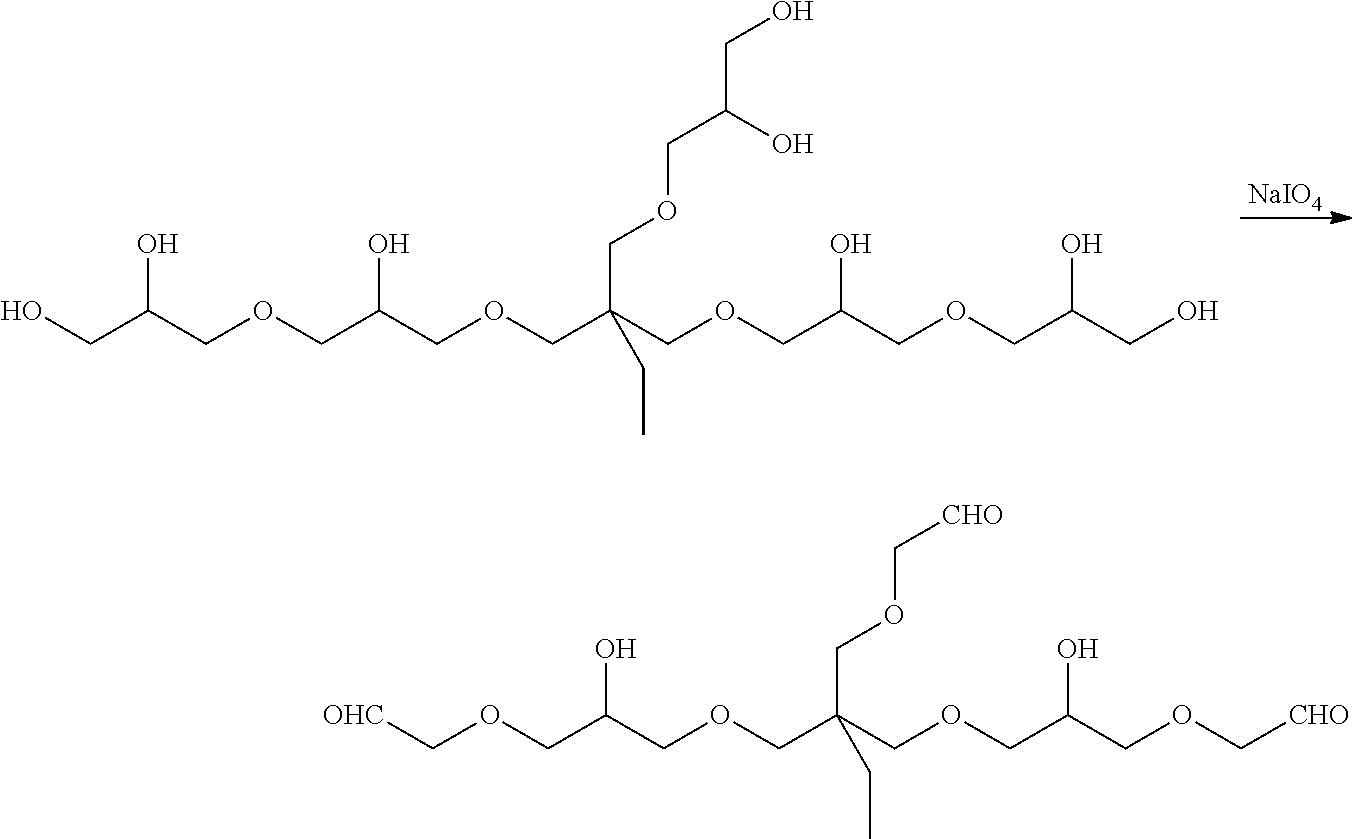
Tissue adhesive and sealant comprising polyglycerol aldehyde
A tissue adhesives and sealant formed by reacting a polyglycerol aldehyde with a water-dispersible, multi-arm amine is described. The tissue adhesive and sealant may be useful for medical and veterinary applications, including, but not limited to, wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, preventing leakage of fluids such as blood, bile, gastrointestinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, and to prevent post-surgical adhesions.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Low swell tissue adhesive and sealant formulations
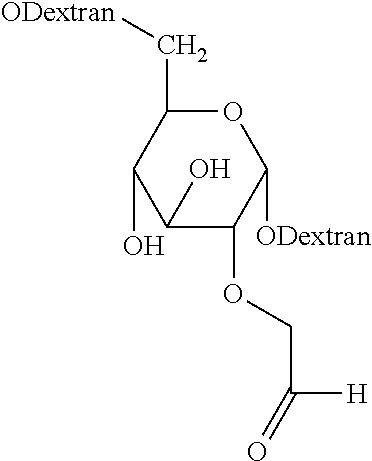
InactiveUS20160184474A1Improve adhesionImprove cohesionSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolyethylene glycolFibrosis
A hydrogel tissue adhesive formed by reacting an aldehyde-functionalized dextran containing pendant aldehyde groups with a multi-arm polyethylene glycol amine is described. The hydrogel exhibits little to no swell upon exposure to physiological conditions. The hydrogel may be useful as a tissue adhesive or sealant for medical applications that require a low swell hydrogel to inhibit complications, such as fibrosis, including scar formation or surgical adhesions.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com