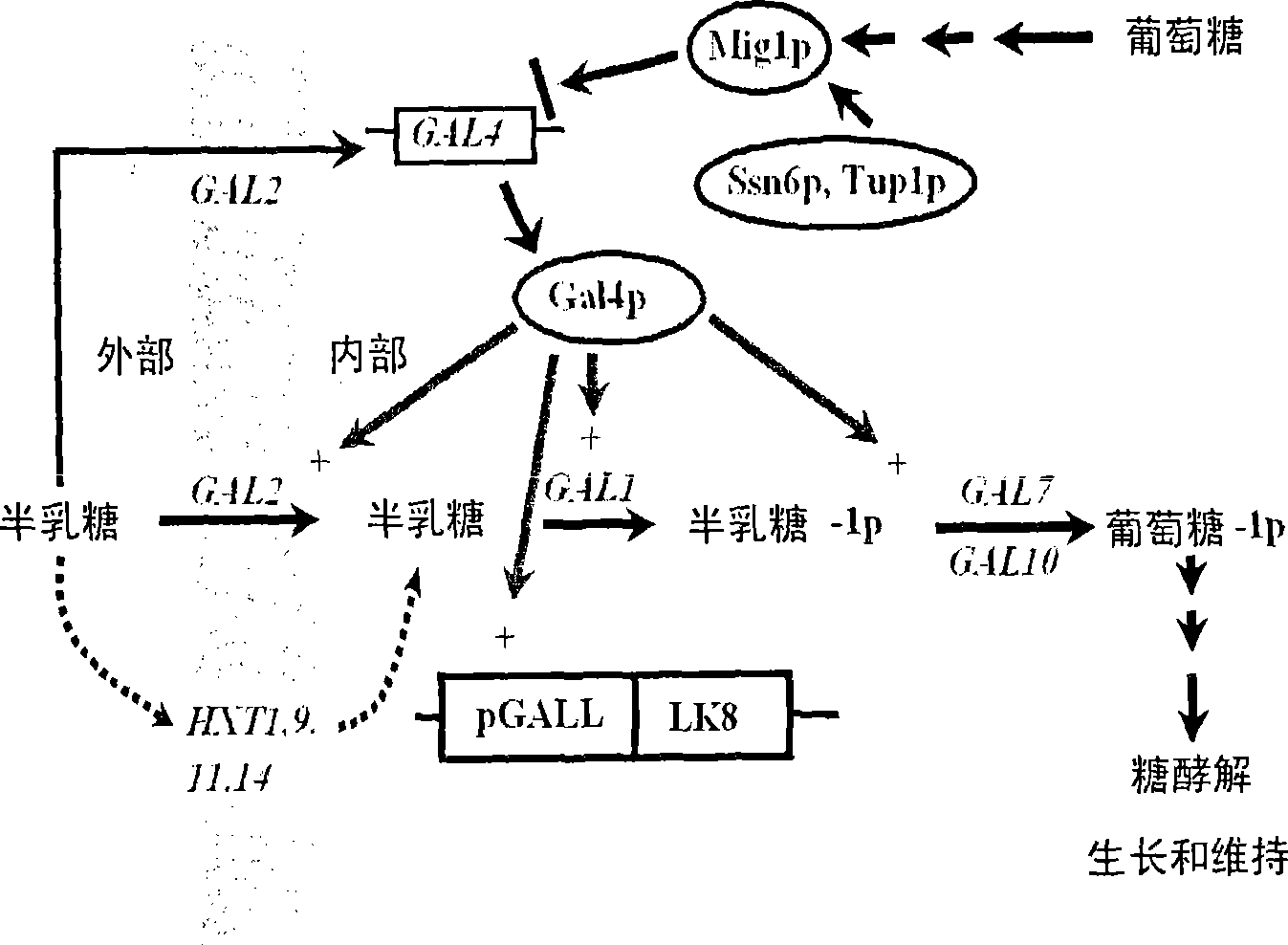
Method for reinforcing secretion efficiency of recombination exogenous protein in sprout fungi expression system
An exogenous protein and high-efficiency technology, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of increased cost of recombinant exogenous protein, prolonged culture period, lower culture temperature, etc., and achieve the goal of secretion efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
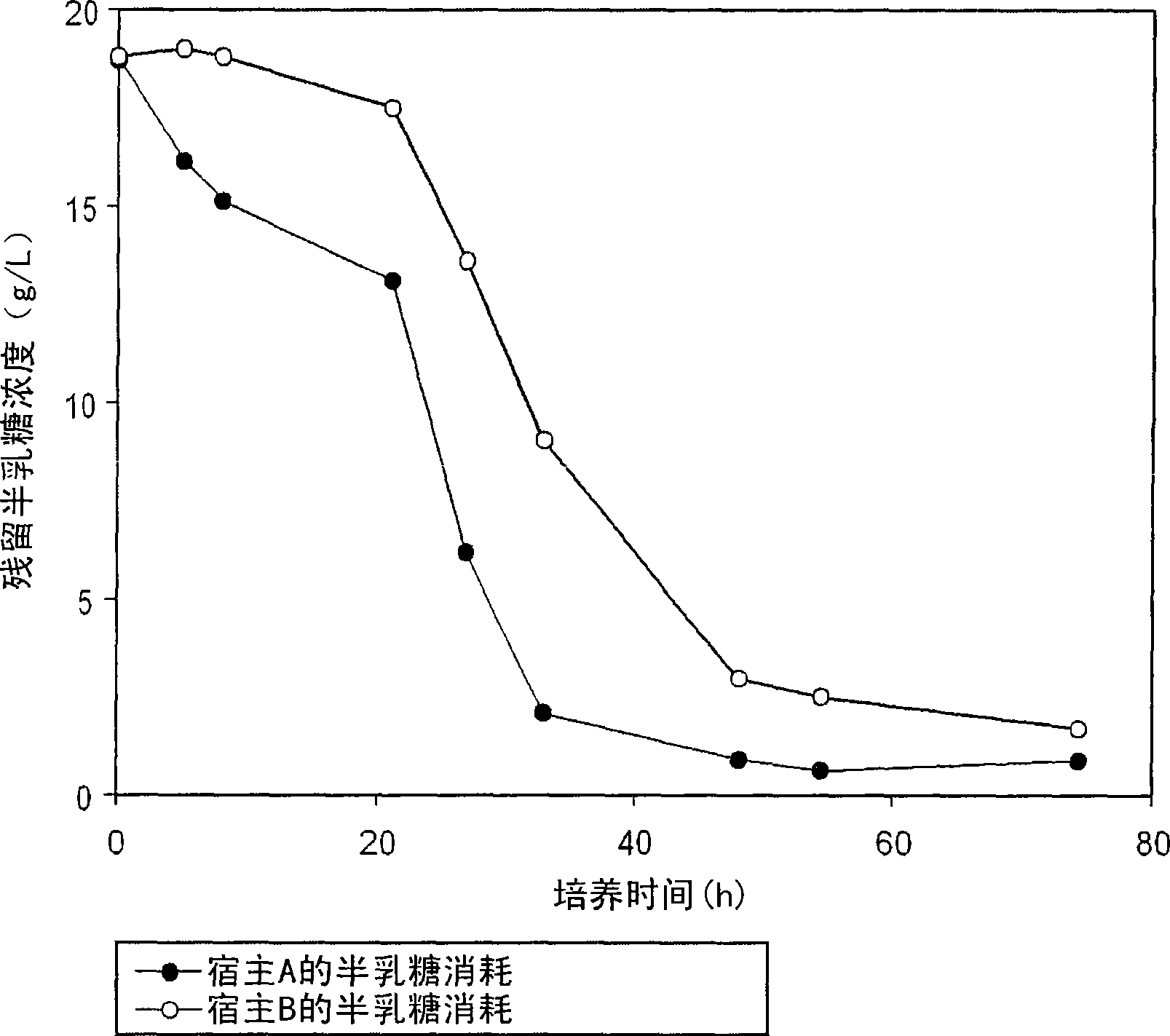
[0062] Example 1: Comparison of intracellular galactose transport capacity between yeast hosts A and B
[0063] Yeast host A (Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2805, genotype: MATα pep4::HIS3 prb1-Δ1.6Rhis3-Δ200 ura3-52 GAL2 can1, Sohn, J.H. et al. Proc. Biochem., 30:653-660, 1995; and Kim , T.H.et al.Biotechnol.Lett.24:279-286, 2002) and yeast host B (Saccharomyces cerevisiae BJ3501, genotype: MATα pep4::HIS3 prb1-Δ1.6R his3-Δ200 ura3-52gal2 can1, ATCC 208280, USA) were streaked on a YPD agar plate and placed in an incubator at 30° C. for about 18 hours, and colonies were isolated. Each colony of yeast hosts A and B was inoculated into separate YPG [yeast extract 1% (w / v), peptone 2% (w / v) and galactose 2% (w / v)] liquid medium and Shake culture in an incubator at 30°C for about 80 hours. To determine the consumption of galactose over time, the residual galactose concentration in the medium was determined by quantifying reducing sugars via 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) analysis (Mo...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2: Construction of Yeast Transformants Secreting Foreign Proteins Using Yeast Hosts A and B
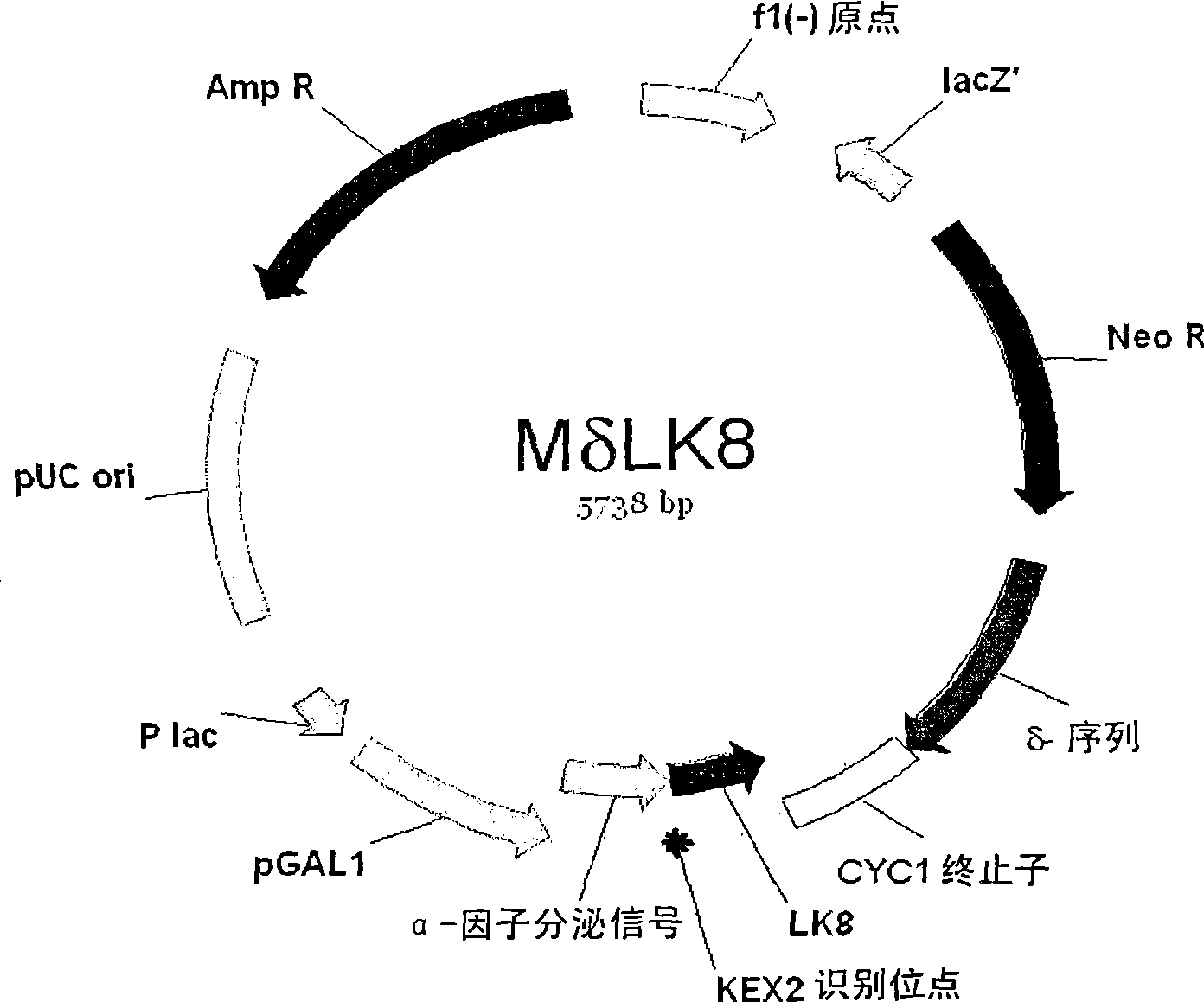
[0066] 2-1. Using Yeast Host A, Construction of Yeast Transformant Saccharomyces cerevisiae 2805 / MδLK8 Secreting Foreign Protein
[0067] Using the expression vector pMBRI-LK8 (Korean Patent Publication Laid-Open Publication No. 2004-0069840) used by the present inventors to produce recombinant LK8 in Pichia pastoris, co-synthesis of the α-factor secretion signal and LK8 cDNA was performed. separate. This application is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. The pMBRI-LK8 vector was treated with EcoR I for 7 hours and washed using a PCR purification kit (Qiagen, USA). Then, the vector was treated with BamHI for 7 hours, and the DNA was separated by gel electrophoresis. Using a gel extraction kit (Qiagen, USA), a DNA fragment having the α-factor secretion signal of SEQ ID NO: 4 and the LK8 cDNA sequence of SEQ ID NO: 16 was obtained. The DNA fragment thus ...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3: Comparison of exogenous protein secretion capacity of transformed yeast strains A and B in fed-batch culture using galactose as carbon source
[0073] In the case of galactose fed-batch culture of the yeast transformants A and B in Example 2, the following analysis was performed to compare the secretion efficiency of the foreign protein. First, the transformed yeast strain as the master seed was treated with YPD [yeast extract 1% (w / v) and peptone 2% ( w / v)] culture medium for 24 hours, so that the desired cell mass and activity (20-fold dilution, OD 600 = 0.8 to 1.2). After seed culture in YPD medium, the seed culture solution was inoculated into the starter medium. First, the batch culture stage is a cell growth stage and an adaptation stage to galactose used as an expression inducer of foreign protein LK8. For this purpose, the cells were given a galactose acclimatization period while the cells were allowed to proliferate by inoculating more than 1% (v / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com