Xylanase mutants
A xylanase mutation and xylanase technology, which is applied in the field of protein engineering transformation, can solve problems such as the inability to meet industrial production needs, and achieve the effects of remarkable heat resistance and improved heat resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] The amplification of embodiment 1 xylanase gene
[0070] Xyn-F1: 5'—CGC GAATTC ACTATTCAACCTGGAACTGGATAC—3' (the underline is the restriction endonuclease ECORI recognition site)
[0071] Xyn-R1: 5'-CT CGCGGCCGC TTATGAGACTGTGATAGAGGCAG—3' (the underline is the restriction endonuclease NOTI recognition site)
[0072] Using the Trichoderma reesei genome as a template, PCR amplification was performed using the above primers Xyn-F1 and Xyn-R1, the PCR product was recovered from the gel, connected to the pEASY-T vector, transformed into E. coli DH5a, and the correct Transformants were sequenced. Sequencing results showed that the nucleotide sequence of the xylanase in the transformant was SEQ ID NO: 2, and the encoded amino acid sequence was SEQ ID NO: 1. Applicants named the xylanase Xyn.
Embodiment 2
[0073] Example 2 Screening and Obtaining of Heat-resistant Mutant Genes
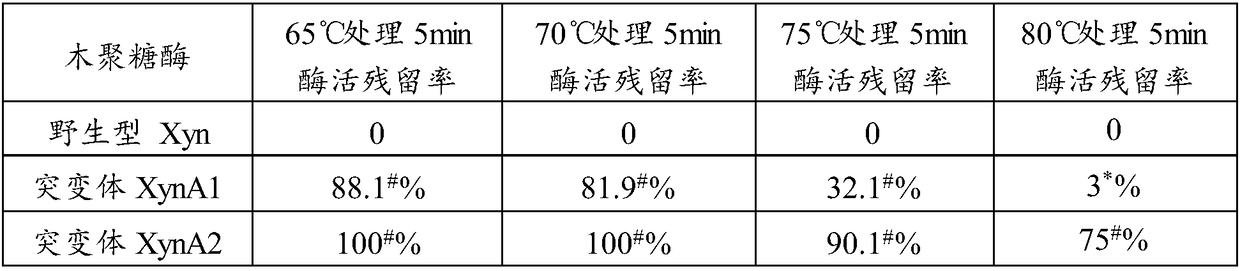
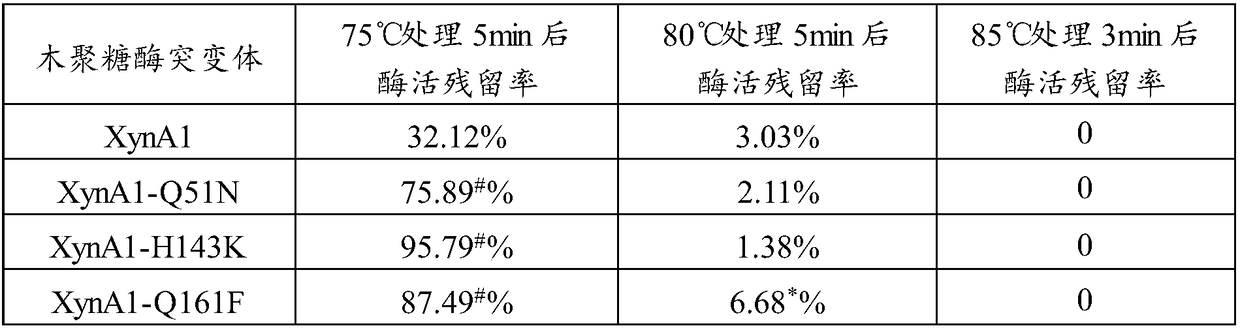
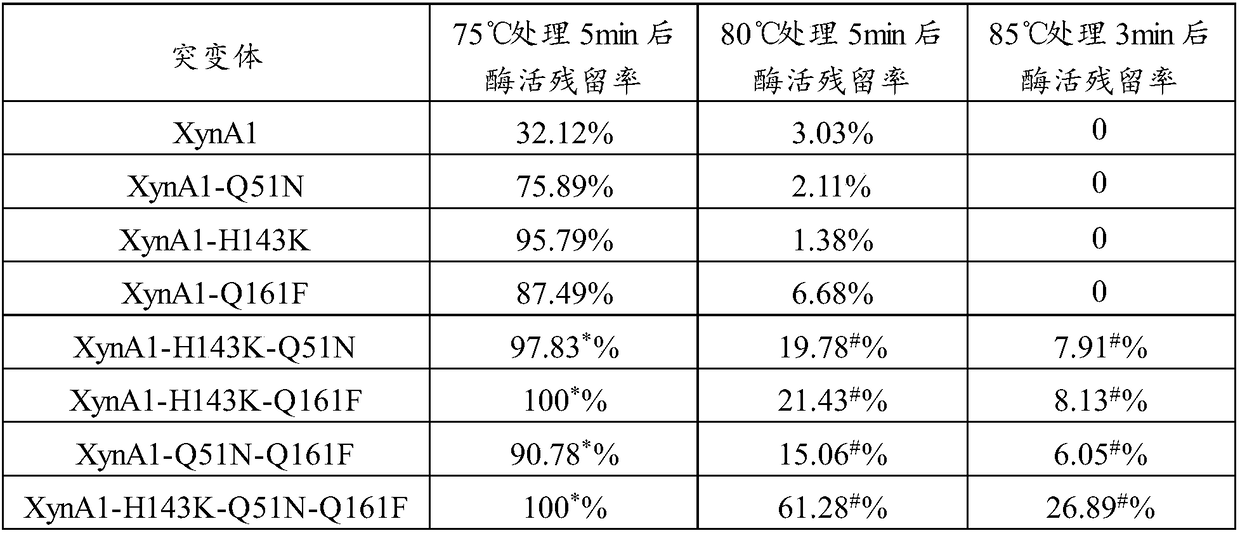
[0074] Disulfide bridges (ie, Cys-Cys bridges) can stabilize the enzyme structure. A certain amount of stabilizing disulfide bridges is necessary to maintain proper stability of the enzyme. By artificially introducing a certain number of disulfide bridges into the protein structure, it is expected that more stable, especially heat-resistant, but possibly less active enzyme mutants can be produced.
[0075] In order to improve the heat resistance of xylanase Xyn, the applicant modified it by analyzing the sequence and structure of xylanase Xyn (crystal structure PDB ID: 2JIC). The modification is to introduce one or more unnatural disulfide bridges by site-directed mutation, for example, introduce unnatural disulfide bridges T1C-T27C to stabilize the N-terminal region of Xyn protein, introduce disulfide bridges S109C-N153C to Stabilizes the α-helical region and introduces a disulfide bridge Q33C-T187C t...
Embodiment 3
[0079] The construction of embodiment 3 pichia pastoris engineering strain
[0080] The xylanase mutant gene XynA1 and XynA2 fragments cloned above were connected to the expression vector pPIC9K through the EcoRI and Not I sites to construct the expression vectors pPIC9K-XynA1 and pPIC9K-XynA2.
[0081]The mutant expression plasmid was linearized with Sal I, and the linearized fragment of the expression plasmid was transformed into Pichia pastoris GS115 by electroporation, and the recombinant strains of Pichia pastoris GS115 / pPIC9K-XynA1 and GS115 / pPIC9K-XynA2 were obtained by screening on MD plates , and then screen multi-copy transformants on YPD plates containing different concentrations of geneticin.
[0082] The positive transformants of the screened recombinant expression xylanase mutants XynA1 and XynA2 were named Pichia pastoris XynA1 (Pichia pastoris XynA1) and Pichia pastoris XynA2 (Pichia pastoris XynA2), respectively, and then respectively transferred to BMGY mediu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com