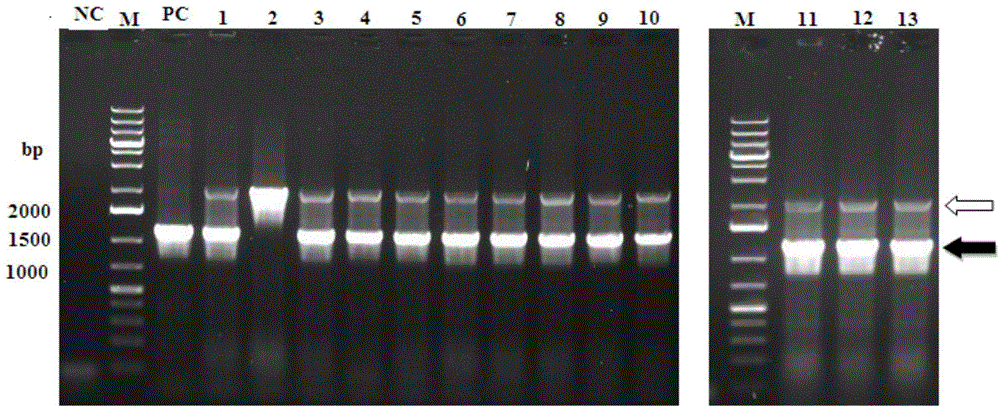
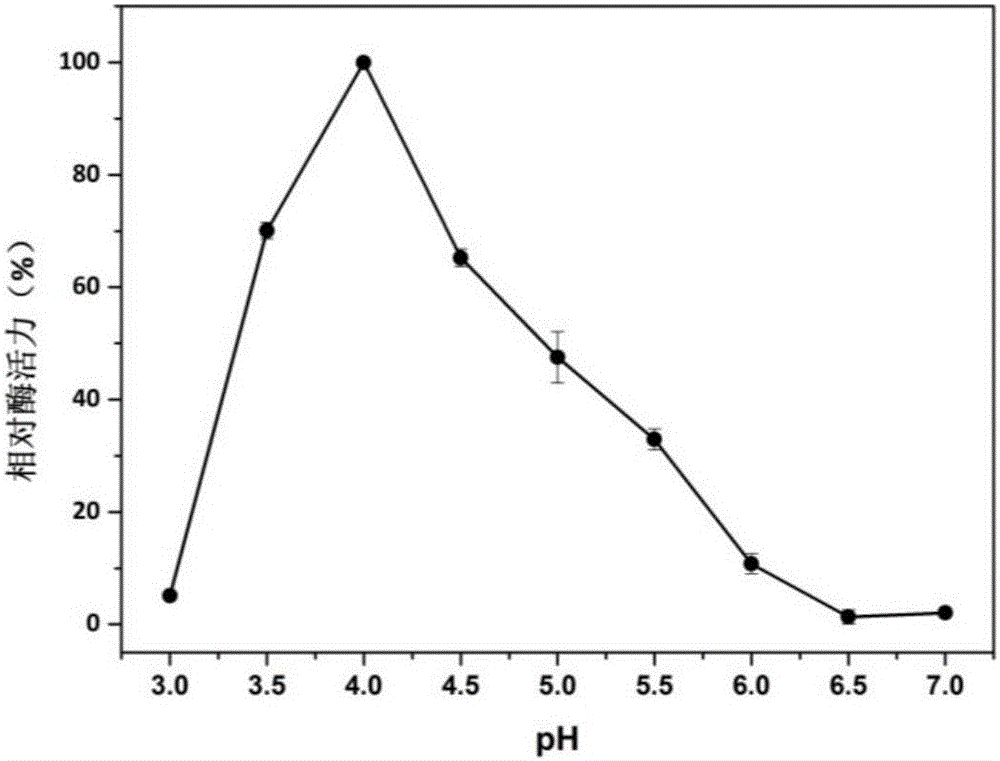
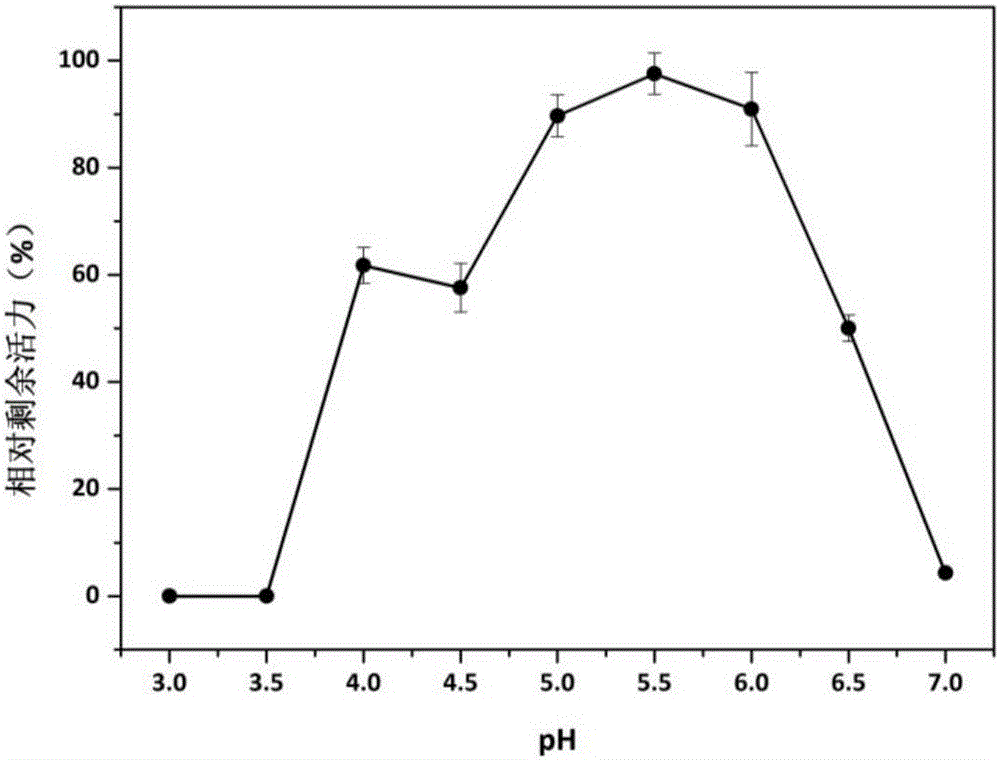
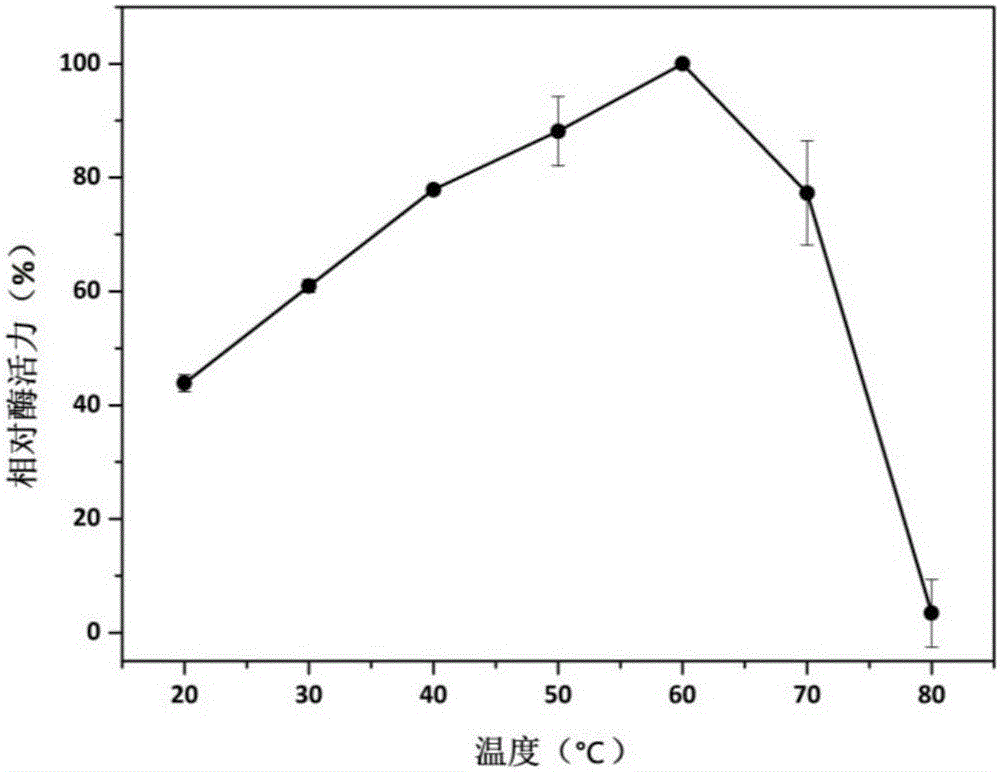
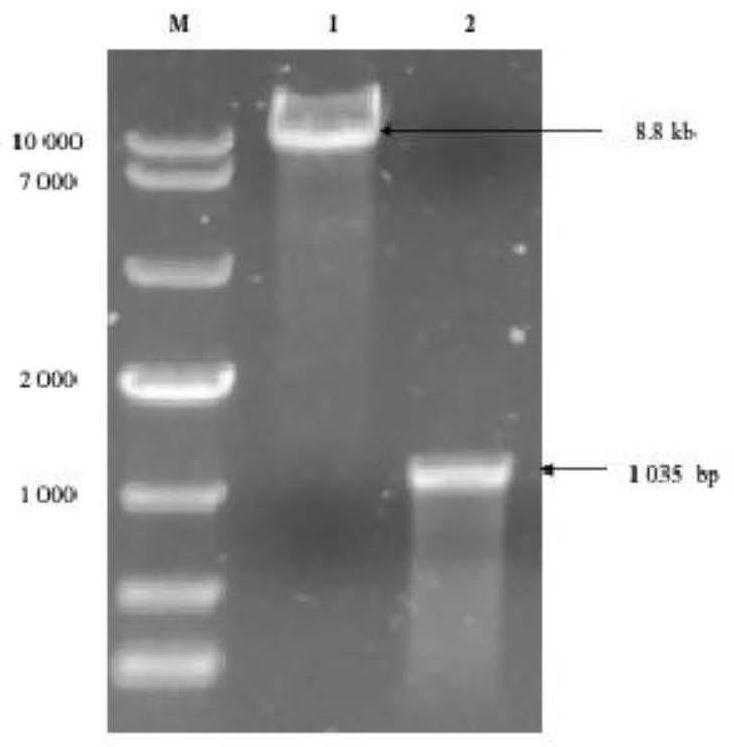
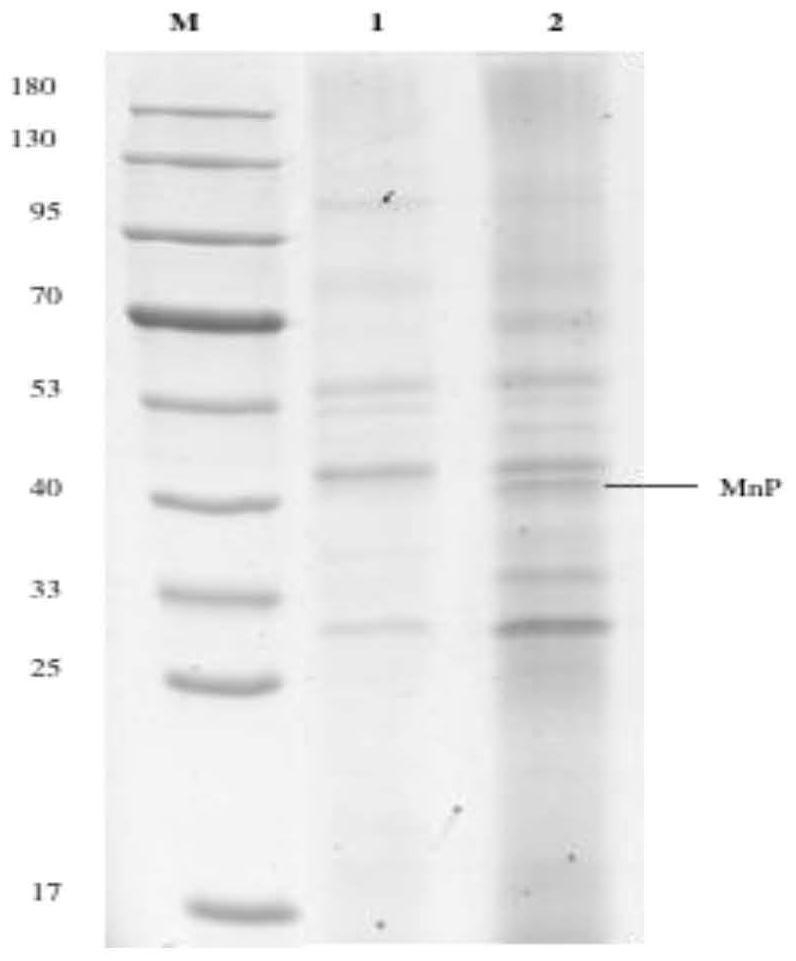
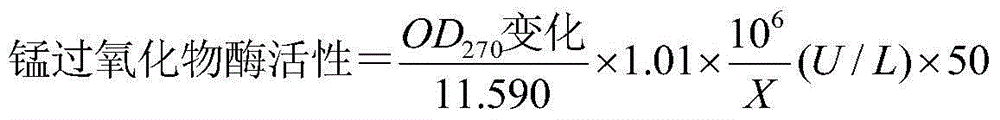Patents
Literature
95 results about "Manganese peroxidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
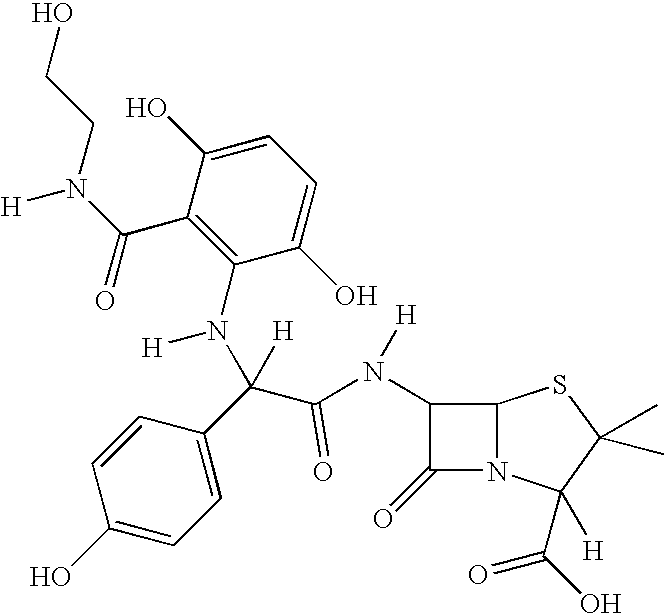
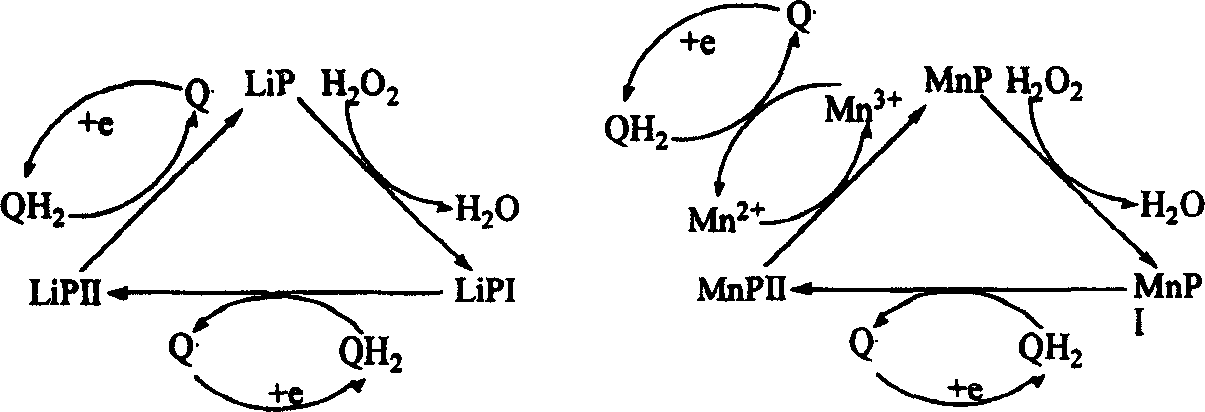
In enzymology, a manganese peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction 2 Mn(II) + 2 H⁺ + H₂O₂ ⇌ 2 Mn(III) + 2 H₂O The 3 substrates of this enzyme are Mn(II), H⁺, and H₂O₂, whereas its two products are Mn(III) and H₂O. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, to be specific those acting on a peroxide as acceptor (peroxidases). The systematic name of this enzyme class is Mn(II):hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase.
Trichoderma harzianum strain and use thereof
InactiveCN101503659APromote growth and reproductionIncrease production capacityFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismLignin peroxidase
The invention relates to Trichoderma harzianum Rifai WRF-2 and use thereof. The bacterium strain was preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 21st, 2009, with a preservation number of CGMCC No.2870. The bacterium belongs to deuteromycetes and is a lower fungus that is short in culture period and quick in growing and propagating speed and produces a large amount of uniform culture liquid for lignin degrading enzyme-generating bacteria in a short time compared with a major part of basidiomycetes to which whiterot fungi belong. The invention also provides a method for culturing and producing lignin peroxydase (Lip) and manganese peroxidase (MnP) by the fermentation of the bacterial strain in a liquid enzyme-generating culture medium, which can produce high-acitivity LiP and MnP in a short time, and is simple in fermentation process, stable, low in cost, and high in yield.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
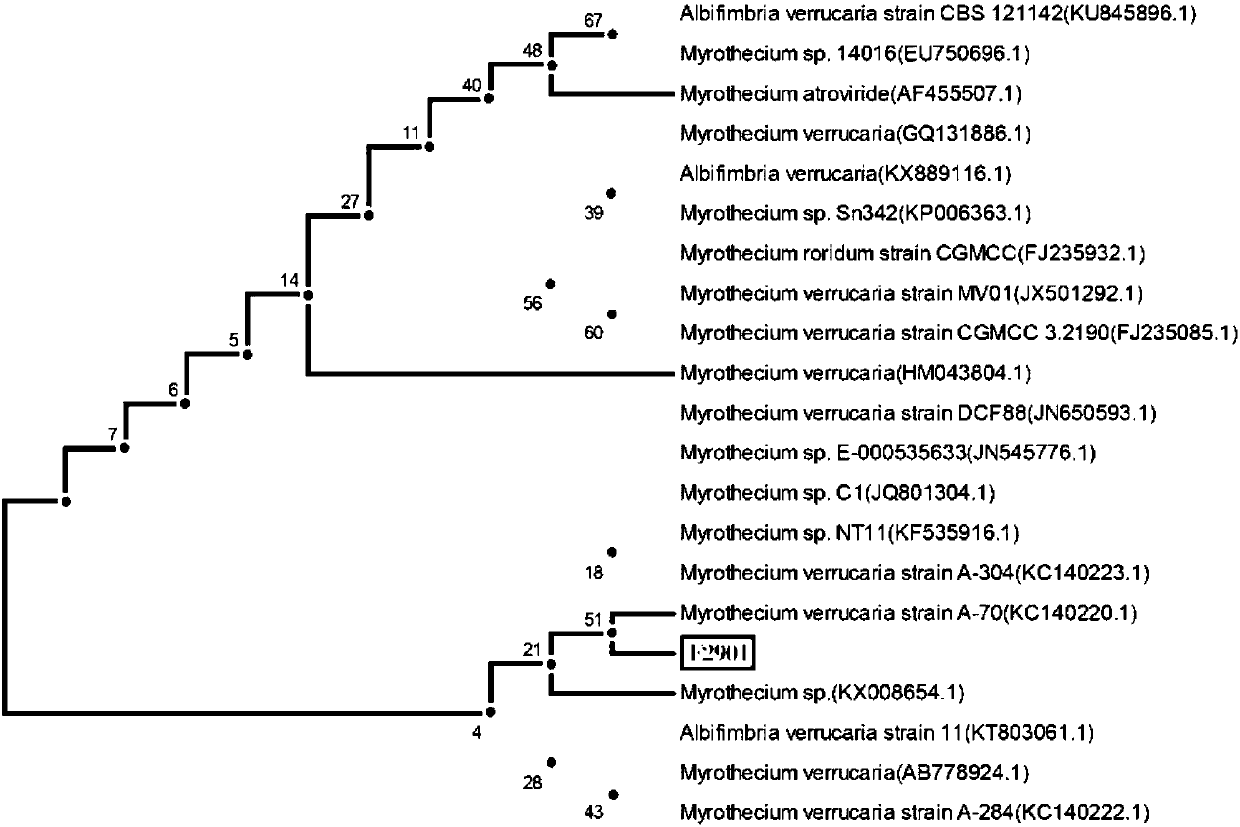
Myrothecium verrucaria mutant strain T2901 and application thereof
The invention discloses a Myrothecium verrucaria mutant strain T2901 with a collection number of CCTCC NO: M2017413. The strain T2901 obtained by separation and mutagenesis can efficiently degrade lignin in corn straw. The strain T2901 can secrete laccase, lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase related to lignin degradation. Studies on impact of microbial pretreatment on structure and composition of the corn straw show that the strain T2901 has no loss of saccharides like cellulose and hemicelluloses, cellulose is retained greatly, and a new path for increasing straw cellulose enzymolysisutilization rate is provided.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Composite biological enzyme preparation for deweighting treatment of domestic sludge, and production and application method thereof
InactiveCN102351321AStable structurePrevents oxidative deactivationBiological sludge treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentManganese peroxidaseNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a composite biological enzyme preparation for the deweighting treatment of domestic sludge, and a production and application method thereof. The invention is characterized in that 100-500 kilograms of composite biological enzyme for the deweighting treatment of domestic sludge are used for 100 thousand tons of municipal domestic sewage, wherein the composite biological enzyme for the deweighting treatment of domestic sludge comprises 25-30 parts of protease, 20-25 parts of one or more of laccase, polyphenol oxidase and manganese peroxidase, 17-21 parts of one or more of xylanase, pentosanase and mannase, 20-25 parts of one or more of cellulase, pectinase and hemicellulase, 10-15 parts of lipase and 12-16 parts of amylase. Compared with the prior art, the invention removes hydrogen sulfide gas and undesirable odor thereof, simultaneously eliminates the inhibiting effect of H2S on the nitrification process, effectively reduces nitrate and ammonia, decomposes proteins, starch, fat, food oil, xylan, cellulose and other organic substances, converts suspended substances, accumulated waste and soluble organic substances in the sludge into carbon dioxide, nitrogengas, oxygen gas, water and sulphate, reduces the TSS (Total Suspended Solids), COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) and BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand), greatly decreases the yield of the sludge, and has the advantages of no poison, no corrosiveness and no secondary pollution production.
Composite biological emzyme/amboceptor system and use for textile scouring process
ActiveCN1986953ABiodegradable solutionRealize comprehensive utilizationHydrolasesBiochemical fibre treatmentCellulosePectinase
Owner:JIANGSU HUAXIN LINEN TEXTILE
Microorganism compound microbial inoculums capable of efficiently degrading straw lignin
ActiveCN108753640AStrong lignin degradation abilityImprovement of industrial utilization efficiencyFungiBacteriaMicroorganismLignin peroxidase
The invention provides microorganism compound microbial inoculums capable of efficiently degrading straw lignin. Floras achieve mutualistic symbiosis and synergistic interaction. In a straw fermentation process, three enzymes relating to the degradation of the lignin can be secreted at the same time; the activities of laccase, lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase are respectively 23.56 U / g,23.02 U / g and 21.74 U / g biomass; the lignin content of the fermented corn straws is reduced by 60.21 percent, and loss of sugar such as celluloses and hemicelluloses is avoided; the conversion rate ofthe celluloses in the pretreated corn straws is greater than that of non-treated corn straws by 142.14 percent; a screened compound bacterial strain is high in lignin degradation capacity, and the industrial utilization efficiency of the straws pretreated by the bacterial strain is obviously improved. The research provides a new pretreatment way for enzymolysis saccharification of lignocellulosesin the straws.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
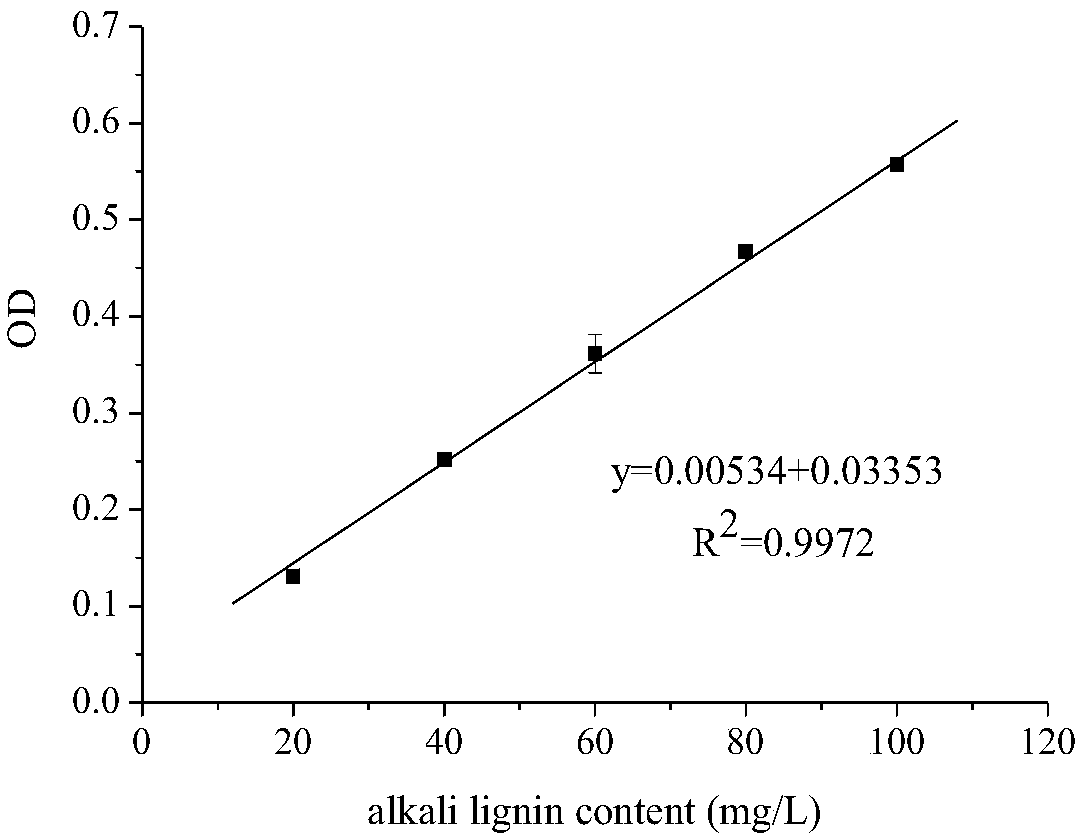
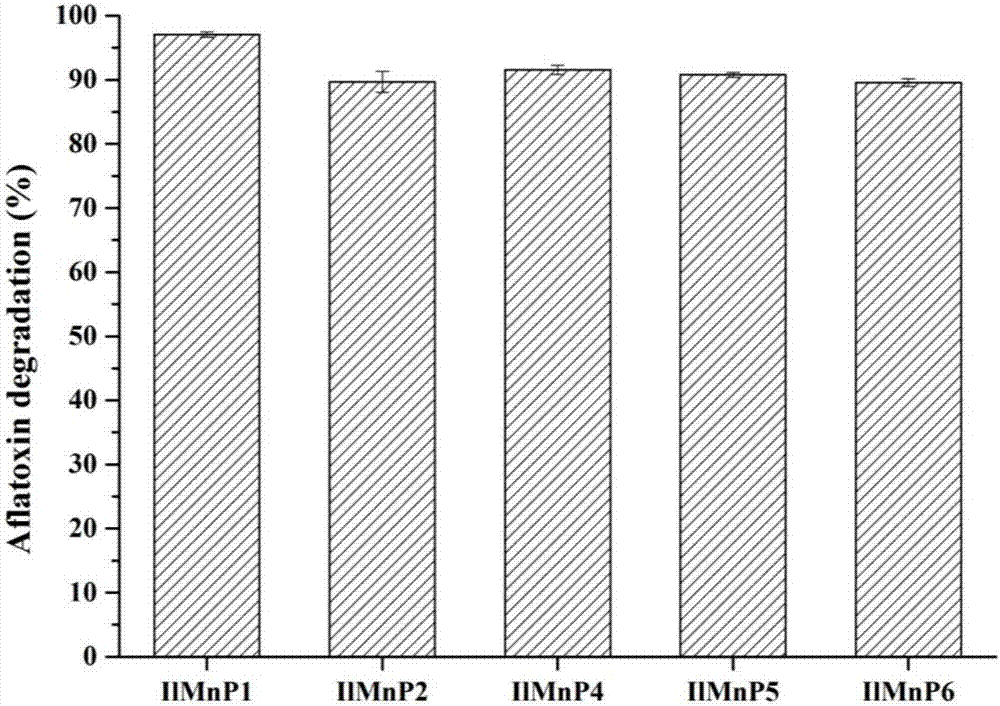
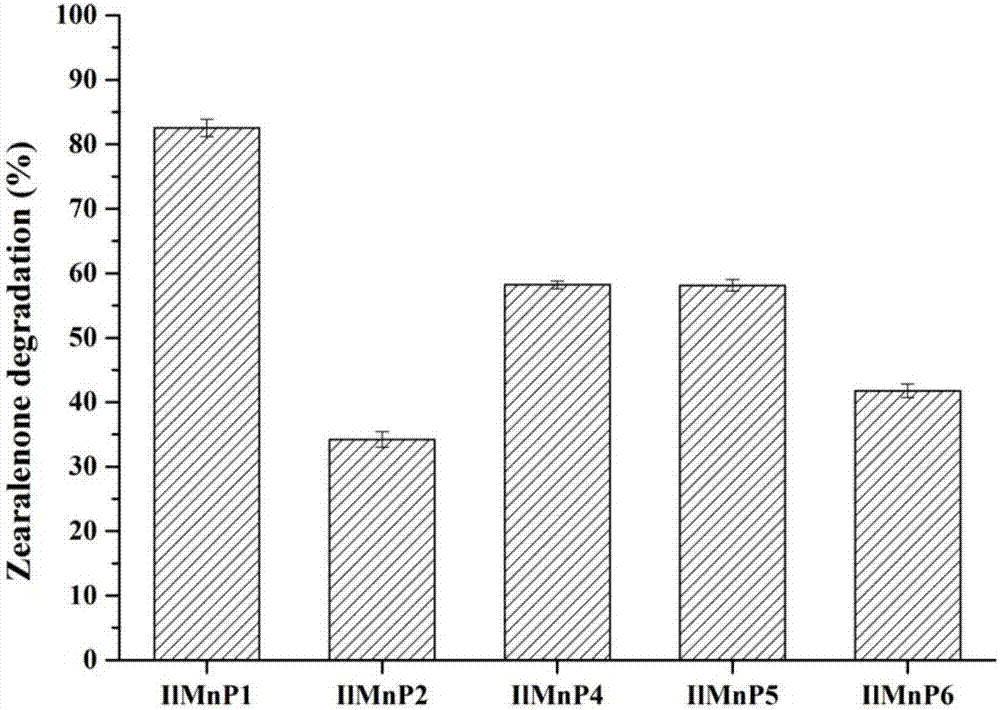
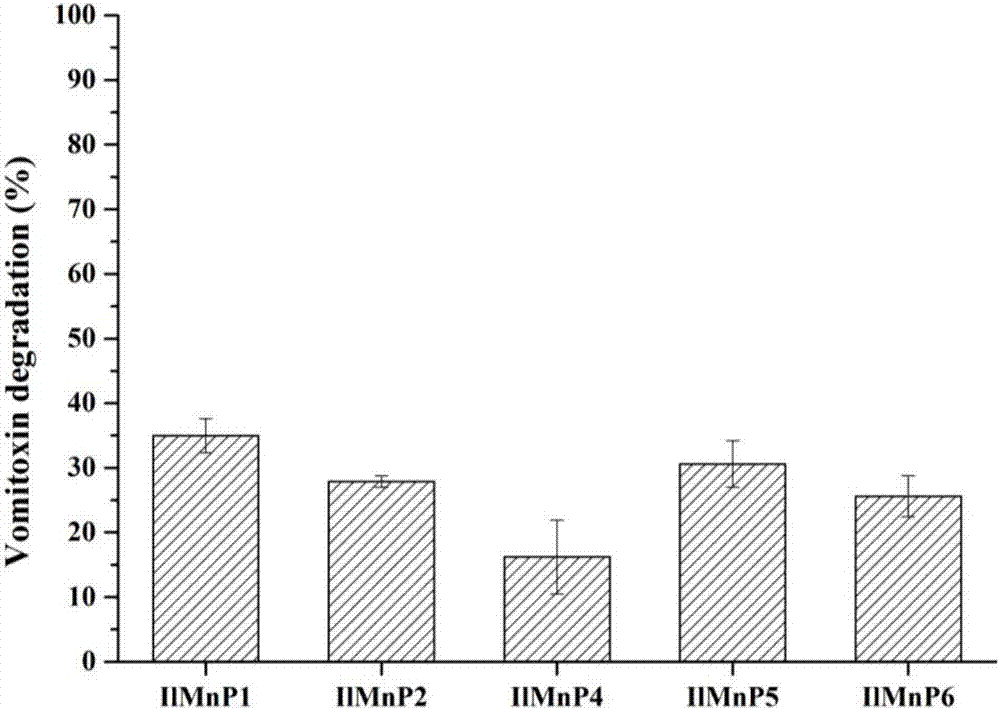
Manganese peroxidase, gene of manganese peroxidase and application of manganese peroxidase to mycotoxin detoxification
The invention relates to application of manganese peroxidase to mycotoxin detoxification, in particular to five kinds of manganese peroxidase (MnP-1, MnP-2, MnP-4, MnP-5 and MnP-6), and a gene and application thereof. The invention provides five kinds of manganese peroxidase (MnP-1, MnP-2, MnP-4, MnP-5 and MnP-6) derived from lignocelluloses degrading bacteria, and the amino acid sequences of the manganese peroxidase are shown as SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.4, SEQ ID NO.7, SEQ ID NO.10 and SEQ ID NO.13. The manganese peroxidase has the following property that mycotoxin of different structure types can be effectively degraded. As a novel enzyme preparation, the manganese peroxidase can be widely applied to the field of food and feed mycotoxin detoxification.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Enzyme producing method for white rot fungus
InactiveCN101260389AContinuous and efficient outputReduce the cost of enzyme productionMicroorganism based processesEnzymesBiotechnologyLignin peroxidase
The invention relates to a white rot fungi continuous high-efficient enzyme producing method, which belongs to the environmental biotechnical field and can be applied in the condition of difficult degradation of organic waste water treatment and environmental repair. In order to realize the aims of the invention, the white rot fungi continuous high-efficient enzyme producing method uses cobs as growth carriers and supplemental nutrition substrates of white rot fungus, utilizes an air-lift fermentation apparatus and optimizes the fermentation conditions, realizes continuous high-efficient output of lignin peroxidases and manganese peroxidases, and simultaneously reduces the enzyme production cost.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Lignin-degrading enzyme regulator and application thereof
ActiveCN104711236AImprove degradation efficiencyIncrease enzyme activityOxidoreductasesLignin peroxidaseManganese peroxidase
The invention discloses a lignin-degrading enzyme regulator and an application thereof. The lignin-degrading enzyme regulator is added by two steps in an aerobic composting process. The lignin-degrading enzyme regulator comprises a manganese peroxidase and lignin peroxidase regulator and a laccase regulator, wherein the manganese peroxidase and lignin peroxidase regulator comprises mixed liquid A of Tween 80, hydrogen peroxide and trace stimulation elements; the laccase regulator comprises mixed liquid B of Tween 80, 1,2-dimethoxybenzene and trace stimulation elements. The lignin-degrading enzyme regulator can be used for regulating secretion of lignin-degrading enzyme in fungi and has the advantages of good promotion effect, simple, economic and practical technology and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
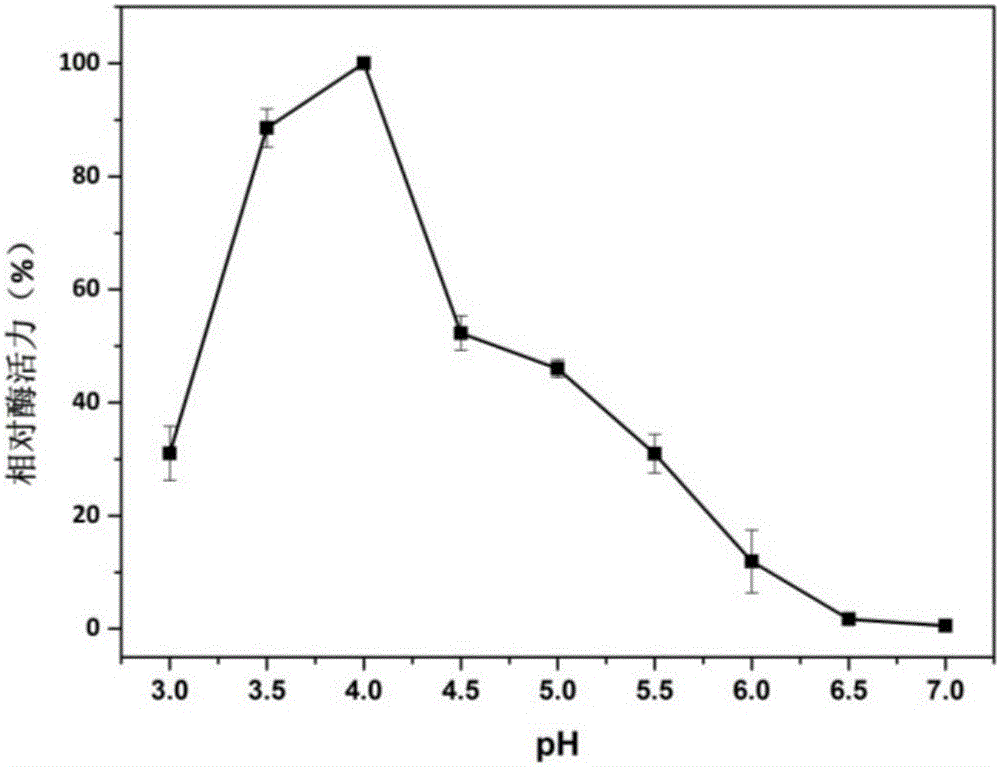
Manganese peroxidase MNP-2, gene and applications thereof
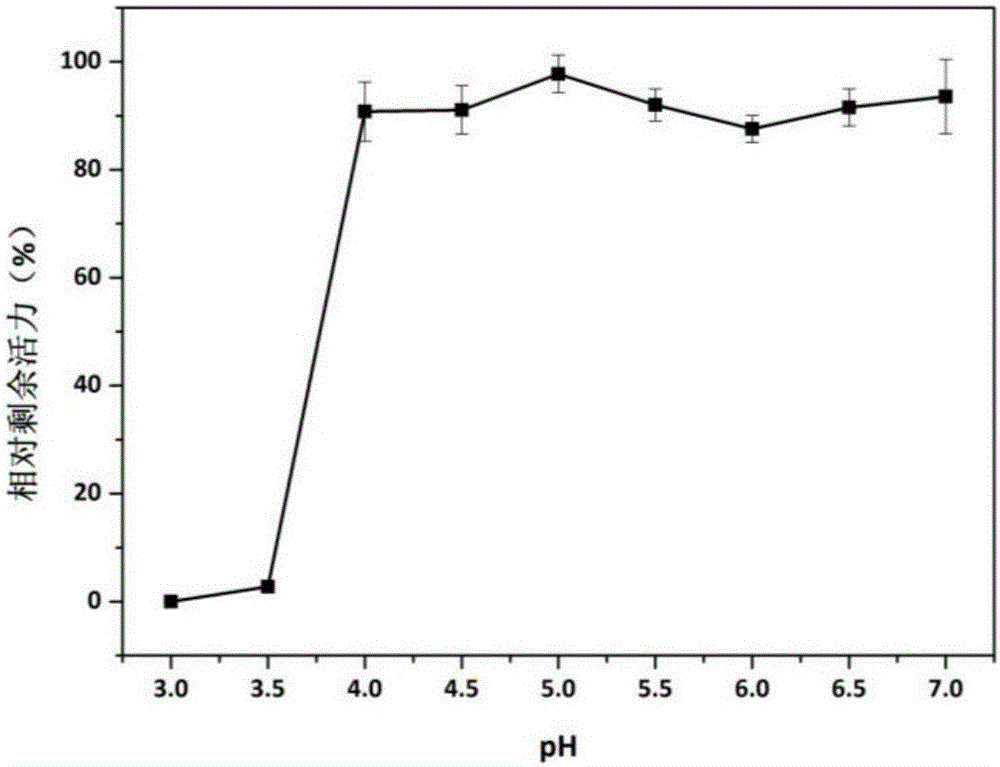
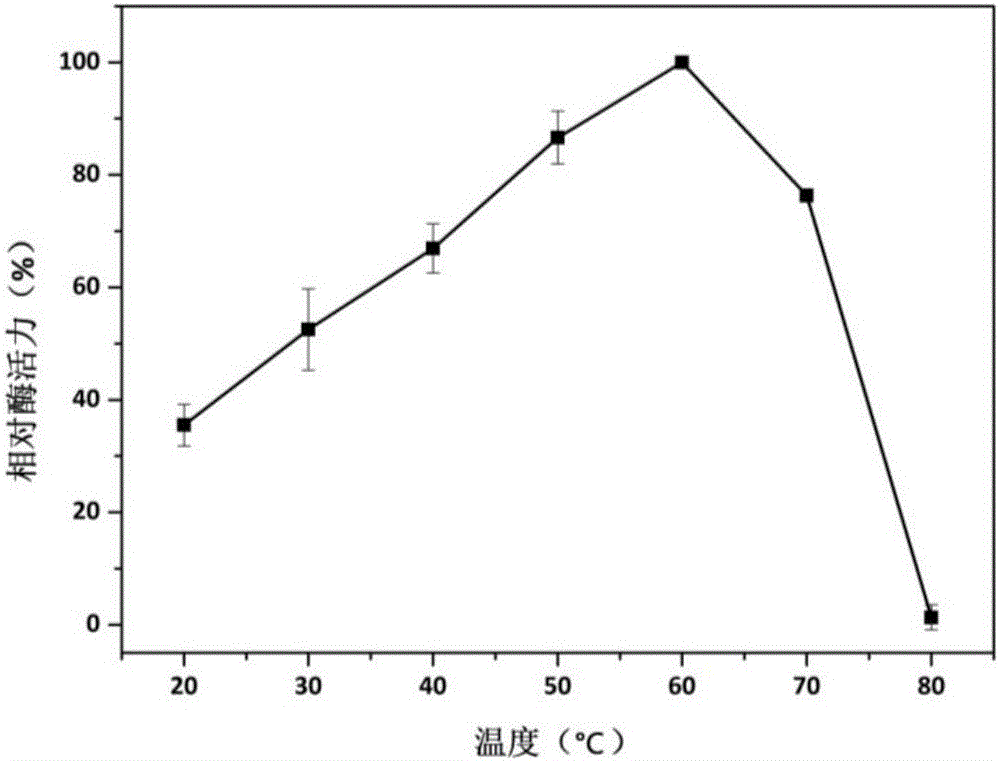
The present invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, particularly to a manganese peroxidase MNP-2, a gene and applications thereof. The present invention provides a manganese peroxidase MNP-2 derived from lignocellulose degradation bacteria, wherein the amino acid sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. According to the present invention, the manganese peroxidase has the following properties that the optimal pH value is 4.0, the optimal temperature is 60 DEG C, the manganese peroxidase MNP-2 can effectively degrade dyes having different structure types, and can be used as the novel enzyme preparation so as to be widely used in the fields of bioremediation, biological energy sources, textile, papermaking, food industry, and the like.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Ultra-Mn2<+>-resistant bacterial laccase, recombinant vector, recombinant bacteria, enzymic preparation, compound enzyme system and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106947748AImprove stabilityImprove degradation rateWater contaminantsOxidoreductasesManganese peroxidaseReaction temperature
The invention relates to ultra-Mn2<+>-resistant bacterial laccase, a recombinant vector, recombinant bacteria, an enzymic preparation, a compound enzyme system and a preparation method and an application thereof and belongs to the biotechnical field. The ultra-Mn2<+>-resistant bacterial laccase is originated from bacterial laccase lac1542 of metagenome, and the gene nucleotide sequence of the laccase is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The optimum pH of the bacterial laccase taking ABTS as a primer is 4.0; the optimum reaction temperature is 75 DEG C and the bacterial laccase is highly stable at a high temperature; 100mmol / L Mn2<+> still can activate the enzyme. Bacterial laccase, manganese peroxidase and coprinus cinereus peroxidase form the compound enzyme system which can degrade 71.5% of lignin at a low concentration; the decolourization ratio of the bacterial laccase and coprinus cinereus peroxidase compound enzyme system on methyl orange can reach 54.8%. The bacterial laccase provided by the invention can be used in the field of papermaking, dyeing and weaving and environmental protection as a novel enzyme source and has a wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Pear branch degrading fungus and fungicide thereof
ActiveCN103992957APromote sustainable developmentSpeed up the ripening processBio-organic fraction processingFungiManganese peroxidaseFermentation
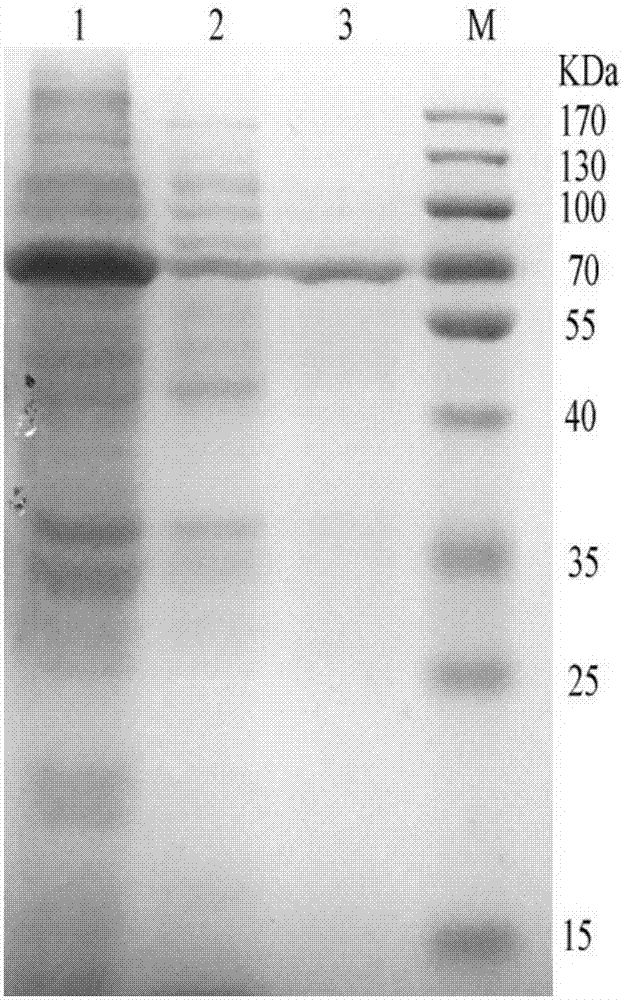
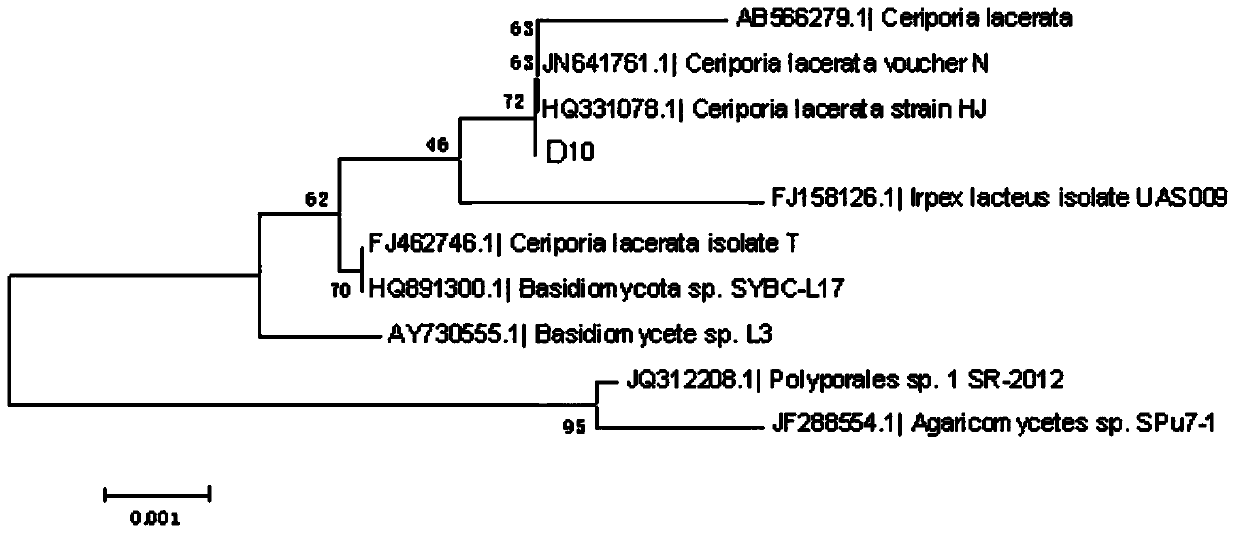
The invention belongs to an agricultural waste recycling technology and discloses a degrading fungus capable of decomposing trimmed pear branches and a fungicide of the degrading fungus. The strain D10 belongs to Ceriporia lacerata which is preserved with the number of CGMCC NO.7852 in China general microbiological culture collection center on July 8th, 2013. The strain can grow on a culture medium with a pear branch as the unique carbon source. The maximum enzyme activity values of laccase, lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase of the strain D10 are respectively 11.03U.Ml<-1>, 36.71U.Ml<-1>and 152.75U.Ml<-1> in the 21d liquid fermentation process. According to the invention, agricultural waste trimmed pear branches are degraded by using a microbial fermentation method and are converted into an organic fertilizer, so that wastes are turned into wealth, the environment is protected, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Sinorhizobium meliloti and method for applying same for fermenting to produce manganese peroxidase
ActiveCN102417890AWith industrial productionHigh biological nitrogen fixation activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyManganese peroxidase
The invention relates to sinorhizobium meliloti and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of microbial fermentation. The sinorhizobium meliloti J09 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with the number of CCTCC NO: M 2011318. A method for applying the strain for producing manganese peroxidase through liquid fermentation comprises the following steps of: (1) slant culture; (2) seed culture; and (3) liquid fermentation culture: inoculating the cultured seed into a fermentation medium with the inoculation rate of 1 percent to 2 percent, and culturing at 32-36 DEG C for 96-136 hours with the rotating speed of a table concentrator of 150rpm. The sinorhizobium meliloti provided by the invention has the advantages that: the CCTCC NO: M 2011318 has the capability of producing the manganese peroxidase and higher biological nitrogen fixation activity. Since the strain is used for producing manganese peroxidase through liquid fermentation, the advantages that the production period is short, the production cost is low, the growth conditions are easy to control, and the like are achieved, and the method has potential for industrialization production. At the same time, the high-efficient biological nitrogen fixation activity shows that the strain has the capabilities of improving soil fertility and promoting high yield of crops.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
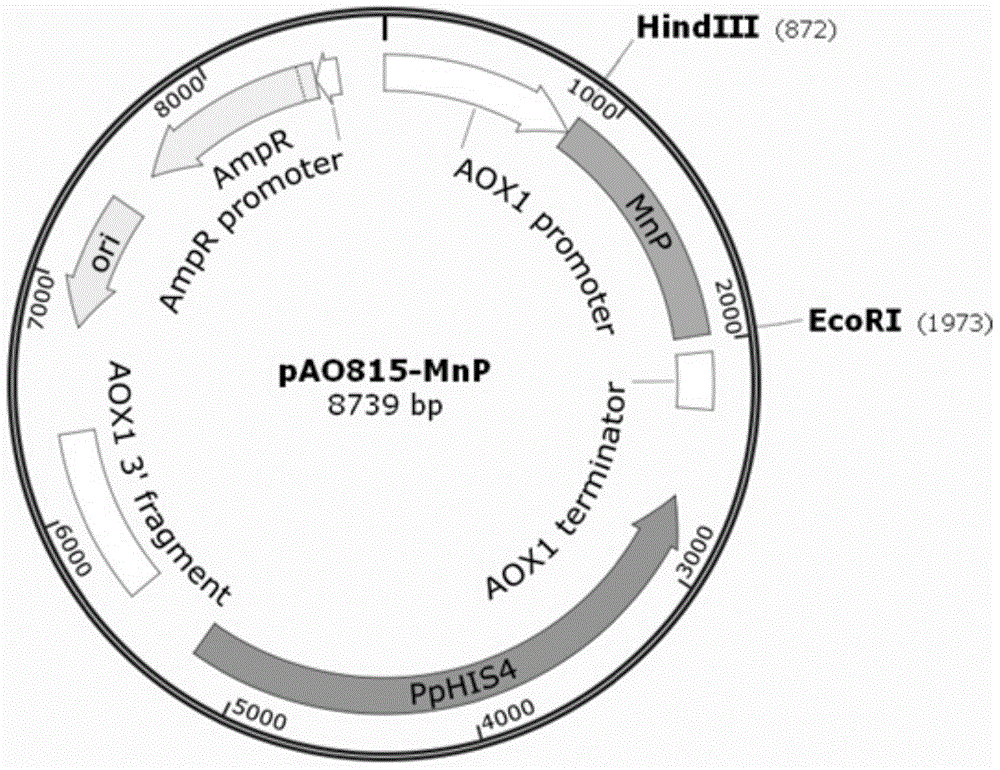
Construction and application of ganoderma manganese peroxidase pichia pastoris gene engineering strain
The invention provides construction and application of a pichia pastoris gene engineering strain in the field of molecular biology and gene engineering. A manganese peroxidase gene GlMnP is cloned from white rot fungus ganoderma, a pichia pastoris expression vector Pao815-GlMnP of an expression cassette containing the manganese peroxidase gene is constructed, the constructed pichia pastoris expression vector is used for converting pichia pastoris (P. pastoris) SMD1168H, and the pichia pastoris engineering strain of the expression cassette containing the manganese peroxidase gene with the expression vector highly copied and recombined by ampicillin resistance screening. The engineering strain is constructed and a biological enzyme is industrially produced in the invention to remove azo dyes in such systems as production, sewage and the like, for example, decoloration of textile industrial wastewater, printing and dyeing industrial wastewater and industrial wastewater related to production and application of dyes.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Wood-rotting basidiomycetes for production of ligninolytic enzymes
The invention relates to the production of ligninolytic enzymes, laccase and manganese peroxidase, from certain white-rot basidiomycetes fungi, using highly efficient fermentation techniques. The aim of this invention is to create a novel economically and time-effective overall procedure comprising use of specific mushroom strains, fermentation process and the isolation-purification techniques, for producing the aforesaid enzymes. In particular, a submerged fermentation of the specific strains on a variety of lignocellulosic substrates from organic wastes like waste of ethanol production from wheat grain, mandarin peels and bran is developed. Culturing conditions can be selected to modify the laccase / manganese peroxidase ratio in favour of the production of either laccase or manganese peroxidase.
Owner:MYCOENZYME
Manganese peroxidase MNP-1 and gene and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to manganese peroxidase MNP-1 and a gene and an application thereof. An amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The manganese peroxidase has the following properties that the most suitable pH (potential of hydrogen) value is 4.0, and the most suitable temperature is 60 DEG C; the different structural types of dyes can be effectively degraded; the manganese peroxidase is used as a novel enzyme preparation, and can be widely applied to the fields of biological restoration, biological energy source, textiles, papermaking and food industry.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fungus with straw degradation capability and application thereof in composting
InactiveCN103468592AHas the ability to decomposeStrong synthetic abilityBio-organic fraction processingFungiBiotechnologyLignin peroxidase
The invention discloses a fungus with straw degradation capability and application thereof in composting and relates to the technical field of biological environmental protection. The straw degradation fungus JSD-17 is penicillium oxalicum (Penicillium oxalicum) and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.7743; the straw degradation fungus is further used for fermenting and composting agricultural waste straw. The penicillium oxalicum disclosed by the invention not only has strong cellulose enzyme synthesis capability, but also has the capability of decomposing hemicellulose and pectin components in the straw. By adopting the fungus disclosed by the invention, laccase (Lac), lignin peroxidase (Lip) and manganese peroxidase (Mnp) can be synthesized; the degradation speed of lignin components in the straw can be greatly increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Chinese yew pulp and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102605667AAlleviate shortagesLow lignin contentNatural cellulose pulp/paperPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsLignin peroxidaseManganese peroxidase
The invention discloses Chinese yew pulp and a preparation method thereof. Chinese yew stalks are used as raw materials, shredded by a rolling and grinding shredding machine and then added into the potassium hydroxide solution for pre-impregnation, water is squeezed out after pre-impregnation, complex enzyme comprising lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase according to the mass ratio of 5:1-4 is added into the solution, the Chinese yew stalks are soaked for 30-40h at the temperature of 35-50 DEG C, alkali cooking is performed after defibrination, total chlorine free bleaching is performed after shoving, cleaning, screening and impurity removal, and then paper is manufactured with pulp after acid treatment, washing and desanding, so that the Chinese yew pulp is prepared. A using approach with a high added value is provided for the Chinese yew stalks, the application field of the Chinese yew stalks is widened, a low-pollution mature production process is provided for preparing dissolving pulp and regenerated cellulose fibers with the Chinese yew stalks, and shortage of regenerated cellulose fiber raw materials at present is relieved.
Owner:潍坊欣龙生物材料有限公司
White rot fungi secretion manganese peroxidase culture medium and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a white rot fungi secretion manganese peroxidase culture medium and a preparation method thereof. The white rot fungi secretion manganese peroxidase culture medium is low-nitrogen asparaginate-succinic acid culture medium, wherein the culture medium comprises a 5-30g / L carbon source, a 5-30mmol / L nitrogen source, 26.7-200mu mol / L manganese ions, 0.25-0.75mL / L Tween 80, 0.1-0.4g / L MgSO4.7H3O, and 10-20ml / L of a mineral element solution; the pH value of a culture liquid is 3.5-5.5. The lignin-degrading enzyme manganese peroxidase in white rot fungi is adopted for biological degradation on lignin, and the lignin can be finally and thoroughly degraded as CO2 and H2O, so that the environment pollution problem of the paper-making industry can be fundamentally solved. Manganese peroxidase can be adopted to degrade lignin and phenol substances, and various organic pollutants including long-lasting solid chemical agricultural pesticide, dye decoloring agents and the like can be attacked.
Owner:ANQING NORMAL UNIV
Engineering bacteria based on manganese peroxidase and implementation method of engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104232555AStable enzymatic propertiesAchieve periplasmic space expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionProtein target
The invention provides engineering bacteria based on manganese peroxidase in the field of the genetic engineering and an implementation method of the engineering bacteria. The genome DNA of the streptomyces griseorubens is taken as a template, and PCR amplification is performed on the template and a primer containing an enzyme digestion site and a polyhistidine label so that the nucleotide sequence coding the manganese peroxidase can be obtained; next, the gene sequence obtained by amplification is connected to an expression vector, and then the obtained connection product is transferred into an escherichia coli expressed strain, and finally, the over-expressed recombinant strain of the manganese peroxidase is obtained. The engineering bacteria based on the manganese peroxidase are used for overcoming the shortage of seriously restricted application range and application effect because the manganese peroxidase mostly is an endoenzyme in vivo and is low in expression amount, and in-vitro mass expression and synthesis of the manganese peroxidase are realized by use of a genetic engineering method; besides, the purity of the purified manganese peroxidase is also guaranteed while the protein activity is improved by use of the method of adding the polyhistidine label to the C end of the expressed recombinant protein; in addition, the periplasmic space expression of the target protein is realized by use of a vector signal peptide and the activity of the manganese peroxidase is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Complex microbial agent for degrading straw, preparation method of complex microbial agent and method for degrading straw
ActiveCN108410753AEfficient degradationFully degradedBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaPectinaseLysinibacillus macroides
The invention discloses a complex microbial agent for degrading straw, a preparation method of the complex microbial agent and a method for degrading the straw. The complex microbial agent for degrading the straw is obtained through mixed culture of lysinibacillus macroides and paenibacillus barcinonensis. Pectinase, cellulase, manganese peroxidase, lignin peroxidase and the like, which are relatively high in activity, can be generated; on the basis of enzyme system components which are on a relatively high amount and cause a coordinated effect on the straw, such components as pectic substances, cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin and the like can be degraded, so that rapid and full degradation of the straw is achieved.
Owner:友美(北京)生物科技有限公司
Biotransformation of biologically active compounds made of various classes of chemical substance by means of laccase and manganese peroxidase enzymes
InactiveUS20030180893A1Altered dissolving behaviorHigh interface activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideManganese peroxidaseSurface-active agents
A process for the preparation of biologically active compounds, wherein active substances having additional functional groups and a modified spectrum of activity and modified application properties are obtainable from medicinal substances and plant protective agents as substrates which bear at least one amino or hydroxy functional group by using a one-electron reaction catalyzed by enzymes or compositions having enzymatic activity and a broad spectrum of substrates, characterized in that free-radical forming enzymes are employed as enzymes and / or supernatants of ligninolytic fungi in solution are employed as compositions having enzymatic activity, wherein the following can be introduced as additional functional groups: A) polyfunctional synthones which provide the active substance with an altered dissolving behavior in aqueous and lipophilic systems and a high interfacial activity; B) aromatic molecules, heteroaromatic compounds; C) heterocyclic compounds; D) active substances having an independent biological activity; E) active substances combining an independent activity and surfactant properties in one molecule; which yield coupling products being covalently linked with the starting materials and having an altered partition behavior which enable polyfunctional interactions with the target organism.
Owner:ERNST MORITZ ARNDT UNIV GREIFSWALD
Method for preparing rice hull ash active carbon by enzymatic pretreatment of rice hull
The invention discloses a method for preparing rice hull ash active carbon by enzymatic pretreatment of rice hull. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, building a lignin degradation enzyme system with a certain enzyme activity ratio to degrade rice hull, wherein the lignin degradation enzyme system is composed of lignin peroxidase, manganese peroxidase and laccase, then degrading the rice hull by a cellulose degradation enzyme system with a certain enzyme activity ratio, wherein the cellulose degradation enzyme system is composed of endoglucanase, exoglucanase and beta-glucosaccharase, and finally distilling to prepare the rice hull ash. The rice hull is subjected to pretreatment by the lignin degradation enzyme system and the cellulose degradation enzyme system; the surface micro-pore structure of the rich hull active carbon is improved; and the adsorptive property is good.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for strengthening white rot fungus to excrete manganese peroxidase
InactiveCN101260388AIncrease productionShorten the fermentation cycleFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySpore
The invention relates to a method for strengthening secretion of manganese peroxidases by white rot fungus which relates to a fermentation method for the white rot fungus. The invention solves the problems in the prior art of long period in secretion (or fermentation) of manganese peroxidases by the white rot fungus and low output of the manganese peroxidases. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the eugonic white rot fungus in a PDA solid medium are inoculated into sterile water, fully oscillated and filtered, and then white rot fungi spores in filtrate are inoculated into a liquid strengthening culture medium which is provided with a foam carrier; secondly, the liquid strengthening culture medium is sealed by a sterilizing sealing membrane and placed into the environment with the temperature of 37+-1 DEG C and the rotary speed of 160 rotates per minute for culture of 3 days, and then strengthening of secretion of the manganese peroxidases by the white rot fungus is realized. The method for strengthening secretion of the manganese peroxidases by the white rot fungus reaches a peak of enzyme activity in fermentation broth on the third day for culture of the white rot fungus and is 3 days in advance compared with the prior method for fermentation of the manganese peroxidases by the white rot fungus, and the fermentation period is half-shortened. The output of the manganese peroxidases of the method is higher than 900 units per liter and is approximately four times of that of the enzyme output of the prior method.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
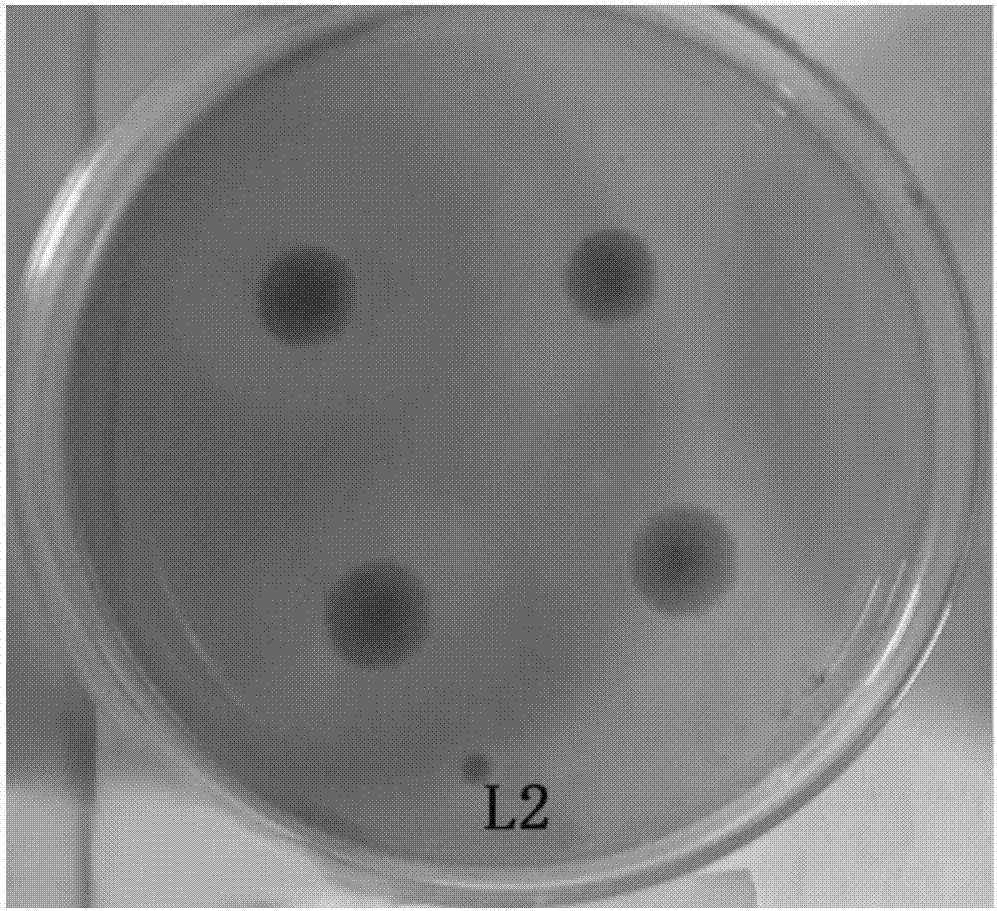
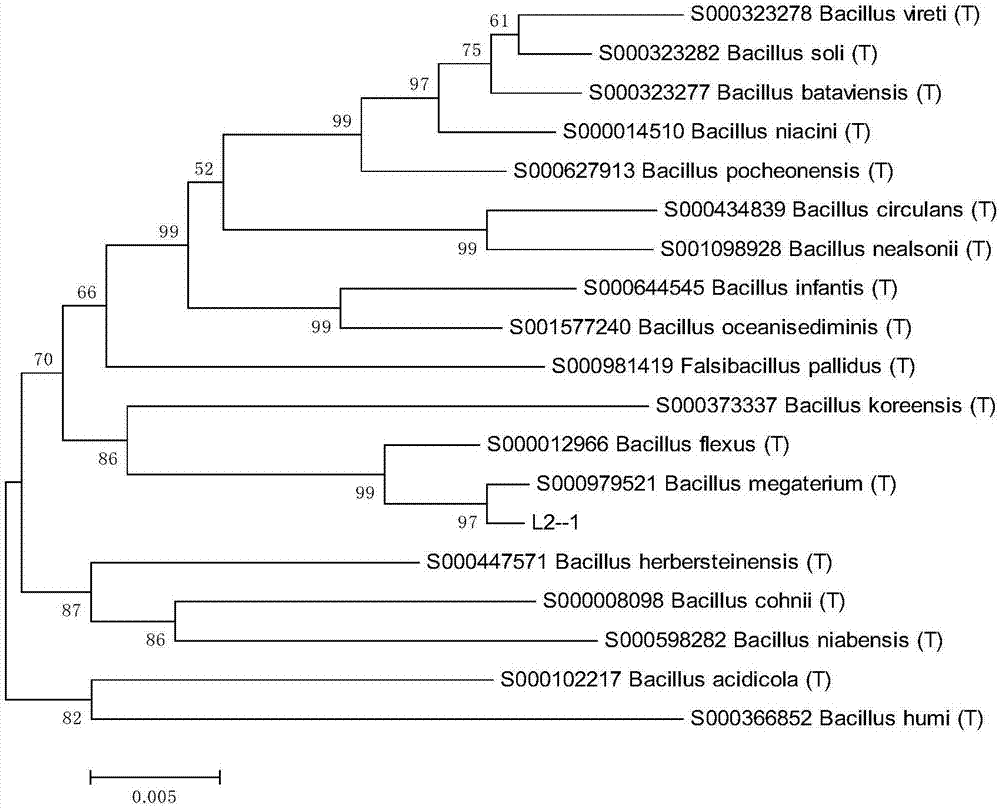
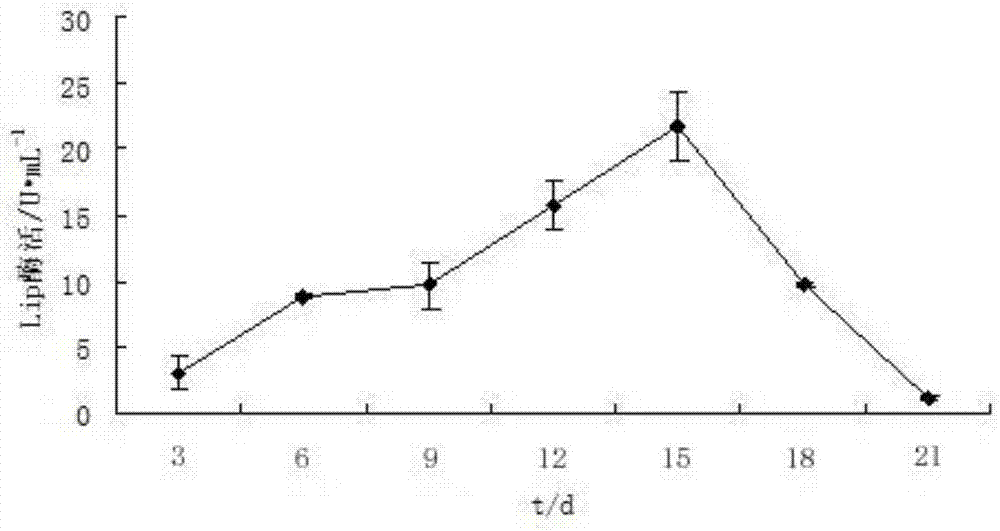
Pear branch degradation bacteria L2 and inoculant thereof
ActiveCN106967637APromote sustainable developmentSpeed up the ripening processBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBacteroidesBacillus megaterium
The invention discloses a bacterium L2 used for degrading pear branches, with a classification name of Bacillus megaterium, preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on 8th, July, 2013, with a culture preservation number of CGMCC NO.7899. The bacterium L2 can grow on a culture medium using analogue of lignin, guaiacol as a unique carbon source or pear branch powder as the unique carbon source, and can generate a fading ring on an LB-aniline blue plate. Experiments show that after culture suspension of the acterium L2 with an inoculation amount of 1% is inoculated on the culture medium, and solid state fermentation is performed for 30d, a weight loss ratio of the culture medium can reach 105. During a liquid state fermentation process on the 21st day, the highest value of activity of generated lignin peroxidase is 21.76U*mL-1, and the highest value of activity of generated manganese peroxidase is 106.36U*mL-1.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
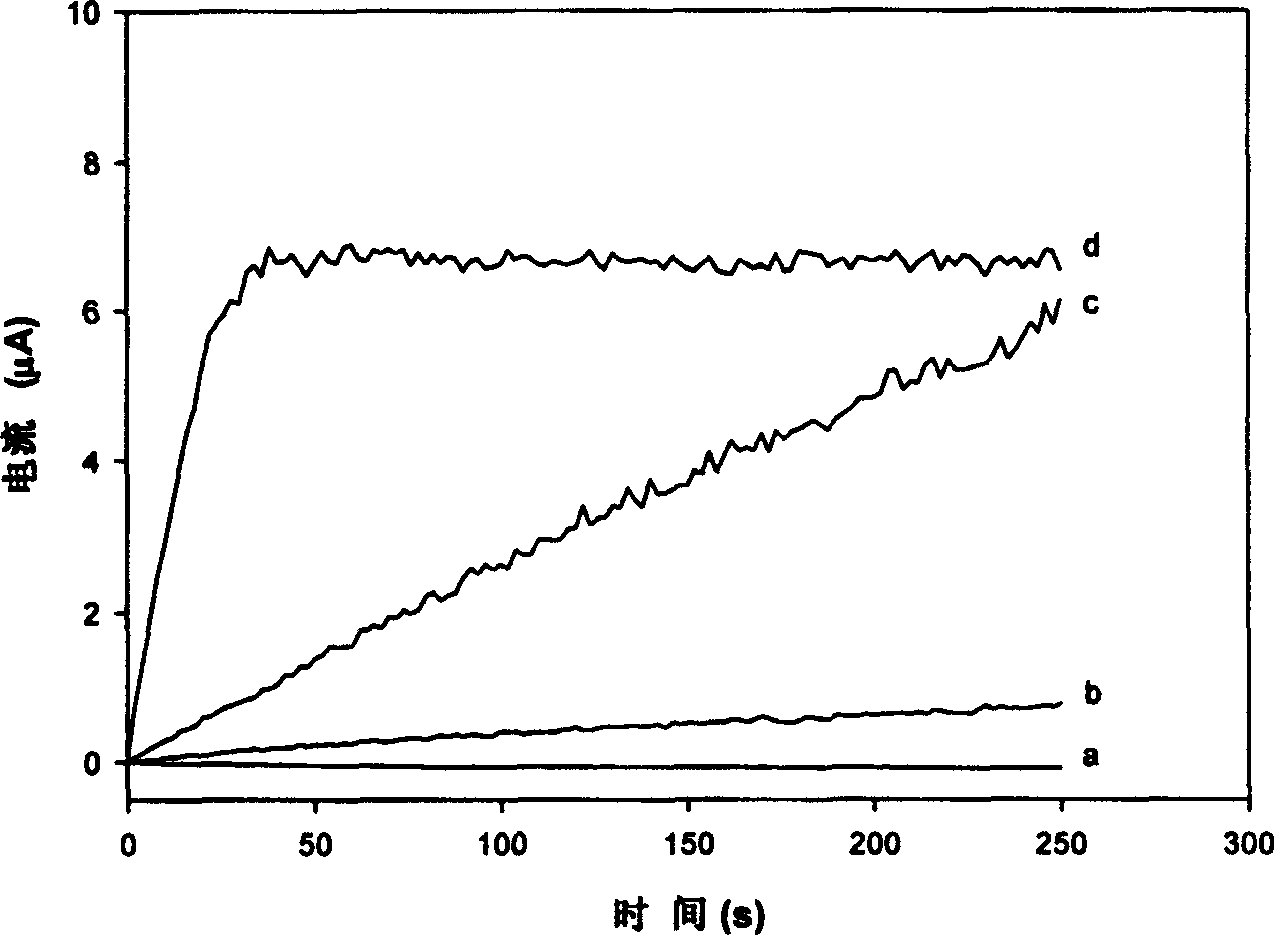
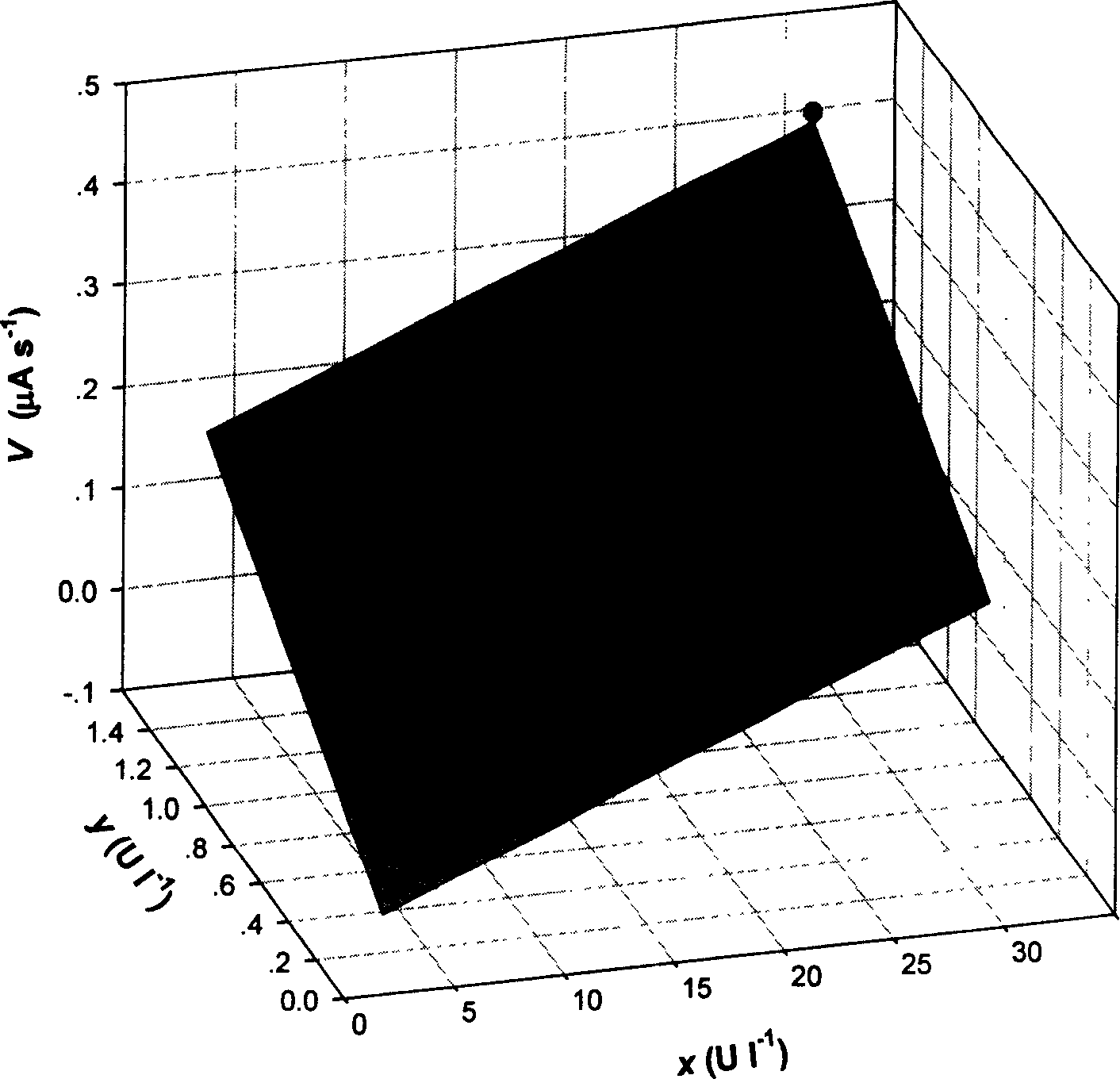
Electrochemical determination method for peroxidase activity in compost
InactiveCN1632551ASolve real-time monitoring problemsIncreased sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesLignin peroxidaseManganese peroxidase
This invention relates to an electrochemistry measurement of the peroxid enzyme activity, the method uses the auricome and eldopaque as the enzyme base and measures the activity of the hyperoxide in the dunghill lixivium with xanthan even bacterium and establishes the linear relation between the current change slope and the enzyme activity. The relation is as following: its peroxide enzyme is 2.27í½29.79U / L and manganese peroxide is 0.085í½1.37U / L.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
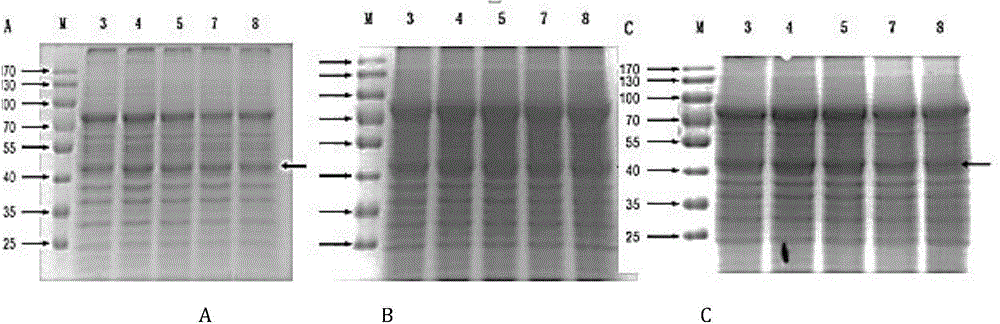
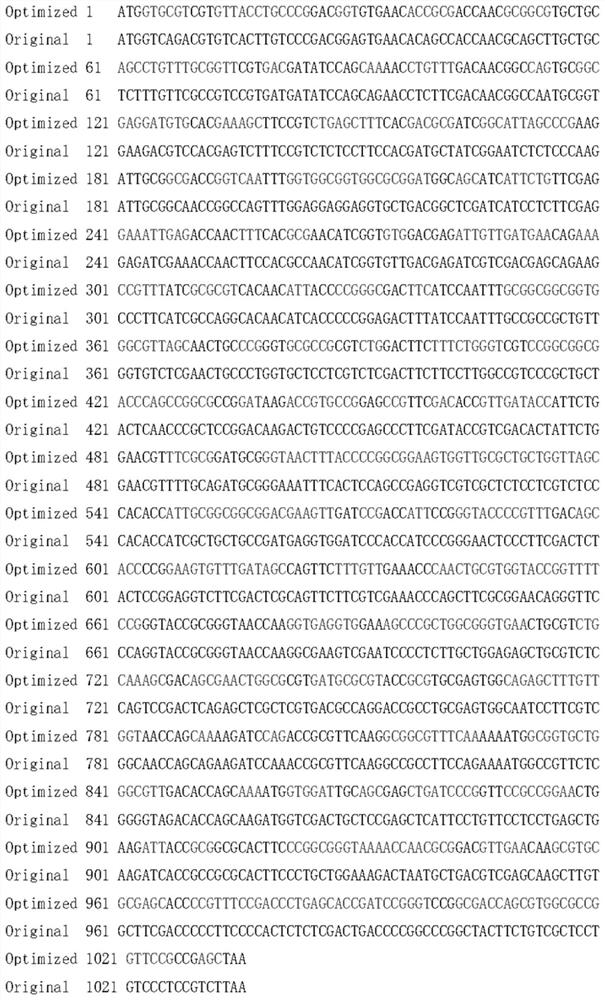
Preparation method of recombinant manganese peroxidase and application of recombinant manganese peroxidase in degradation of Chinese herbal medicine lignin
ActiveCN111808831AEasy accessRealize industrial productionFood processingMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCellulose
The invention belongs to the field of biological feed, and relates to a preparation method of recombinant manganese peroxidase and application of the recombinant manganese peroxidase in degradation ofChinese herbal medicine lignin. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out preference optimization on a gene sequence of manganese peroxidase coming from Irpex lacteus, carryingout PCR amplification by taking the optimized gene as a template, connecting the optimized gene with pREP, then converting the connected gene into escherichia coli competent cells to obtain recombinant shuttle plasmids, and introducing the recombinant shuttle plasmids into defective schizosaccharomyces pombe competent cells to obtain recombinant manganese peroxidase engineering bacteria; and performing culture to obtain a crude enzyme liquid, mixing the crude enzyme liquid with Chinese herbal medicines, and then adding calcium chloride, manganese sulfate, laccase, glucose oxidase and a small molecular substance activator for a multi-enzyme synergistic enzymolysis reaction. According to the method provided by the invention, a large amount of manganese peroxidase can be rapidly obtained, industrial production of the manganese peroxidase is realized, a good and stable peroxidase product is prepared, and effective degradation of Chinese herbal medicine lignin is realized.
Owner:浙江康星生物科技有限公司
Aspergillus oryzae fermentation liquor, corn stalk sugar liquor prepared through same, and preparation method and application of corn stalk sugar liquor
InactiveCN104531640ASolve technical problems that are not easy to degradePollution controlBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesManganese peroxidasePeroxide
The invention provides aspergillus oryzae fermentation liquor and a preparation method of the aspergillus oryzae fermentation liquor. The aspergillus oryzae fermentation liquor contains manganese peroxide with the enzymatic activity being 100-10000U / L, endo-cellulase with the enzymatic activity being 150-3000U / L, beta-dextranase with enzymatic activity being 150-3000U / L, and beta-mannase with enzymatic activity being 50-2000U / L. The invention further provides a process technology of corn stalk sugar liquor. The corn stalk sugar liquor uses corn stalks as main raw materials and is prepared by adding a hydrogen dioxide solution to degrade the corn stalks through the aspergillus oryzae fermentation liquor. The process technology has the advantages of being short in production cycle, small in occupied space, low in production cost and high in sugar yield. In addition, the prepared corn stalk sugar liquor can be used as a carbon source raw material for producing butanol, ethyl alcohol and other fermentation industries.
Owner:BEIJING LYUKE TIANCHENG BIO TECH
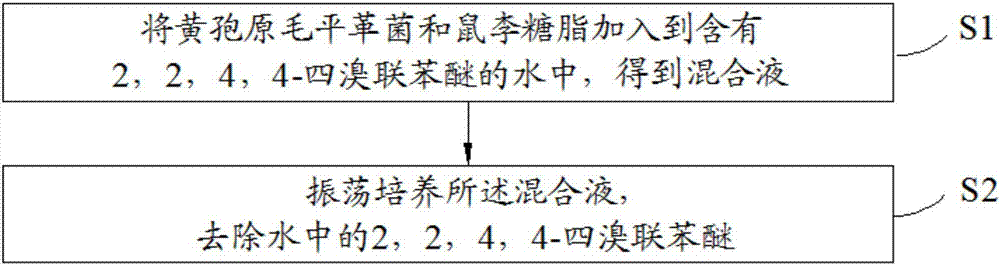
Method for removing 2, 2, 4, 4-tetrabromodiphenyl ether in water
ActiveCN107140748AIncrease enzyme activityGood catalytic degradation effectWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsEnvironmental resistanceManganese peroxidase
The invention discloses a method for removing 2, 2, 4, 4-tetrabromodiphenyl ether in water. The method comprises the following steps: adding phanerochaete chrysosporium and rhamnolipid to water containing 2, 2, 4, 4-tetrabromodiphenyl ether to obtain a mixed solution; shaking and culturing the mixed solution; and removing 2, 2, 4, 4-tetrabromodiphenyl ether in water. The phanerochaete chrysosporium can secrete a plurality of exoenzymes, particularly lignin peroxidase (LiP), manganese peroxidase (MnP) and laccase (Lac); the three enzymes have an excellent catalytic degradation effect on refractory organic compounds; and the biosurfactant rhamnolipid can effectively promote enzymatic activities of three exoenzymes LiP, MnP and Lac, and promote the phanerochaete chrysosporium to remove BDE-47 in a water body. The method provided by the invention has an excellent removal effect on the BDE-47 in the water body, and has a removal rate of 90% or more; and besides, the rhamnolipid is an environment-friendly surfactant which does not cause secondary pollution to environment.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Edible fungus processing feed capable of improving utilization rate of ruminants for rape stalks and preparation method of edible fungus processing feed
InactiveCN104719665AIncrease CP contentImprove degradation rateAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyEnzymatic digestion
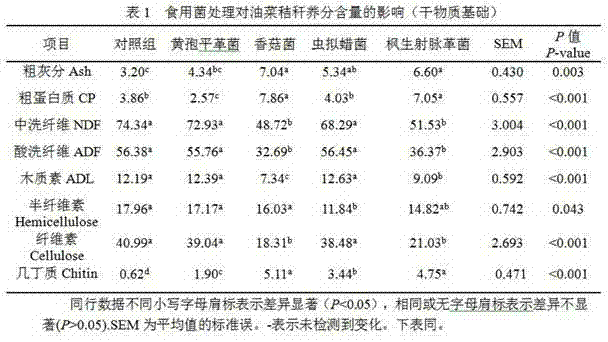
The invention discloses an edible fungus processing feed capable of improving utilization rate of ruminants for rape stalks. The edible fungus processing feed is prepared from 1%-10% of wheat, and 90%-99% of rape stalks and edible fungus. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the edible fungus processing feed. The rape stalks are processed by the edible fungus used by the method; after solid fermentation for 25-75 days, the CP content of the rape stalks, and the degradation rate of nutrients such as DM, OM, NDF, ADF and ADL can be significantly improved; the in-vitro rumen digestibility and the enzymatic digestion rate of organic substances of the rape stalks, and the activity of manganese peroxidase in a fermentation liquid are improved; and the content of a beneficial component chitin in the rape stalks is improved.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Biodegradation method of lignin
InactiveCN112593437ATo achieve the degradation effectPromote degradationCellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymesBiotechnologyManganese peroxidase
The invention discloses a biodegradation method of lignin, and belongs to the technical field of lignin degradation. The method comprises the following operation steps: (1) inoculating a Raoultella ornithinolytica slant strain for dissolving ornithine into an LB solid culture medium so as to obtain an activated strain; (2) inoculating the activated strain into an LB liquid culture medium to obtainfermentation liquor; fermenting the fermentation broth again to obtain a bacterial suspension; (3) drying and crushing the treated lignin; (4) adding the powder into a liquid inorganic salt culture medium for fermentation, adding a fermentation product into the bacterial suspension, and stirring for reaction to obtain a degradation product, wherein the degradation rate of lignin reaches 20%-25%,and the surface of the degradation product is in a loose and porous structure state. Compared with an existing method, the Raoultella ornithinolytica strain for dissolving ornithine has the advantagesthat the adaptability of the Raoultella ornithinolytica strain to the growth environment of bacteria is high, and peroxidase, manganese peroxidase and laccase generated by the bacteria have the excellent characteristics of being better in stability, wider in optimal pH range, more tolerant to chloride ions and the like. The method is mild in reaction and easy to operate.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com