Patents
Literature
105 results about "Total suspended solids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
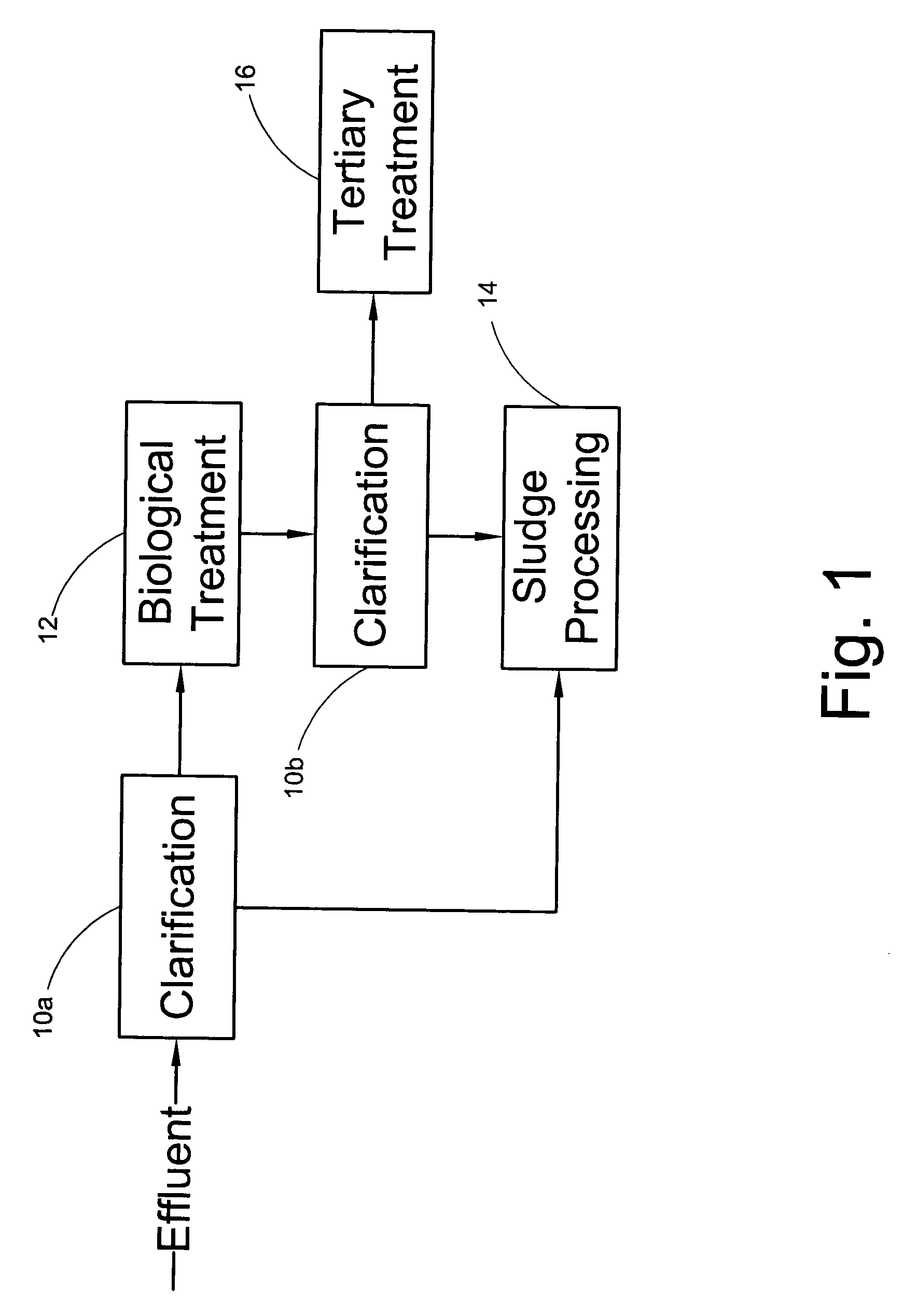
Total suspended solids (TSS) is the dry-weight of suspended particles, that are not dissolved, in a sample of water that can be trapped by a filter that is analyzed using a filtration apparatus. It is a water quality parameter used to assess the quality of a specimen of any type of water or water body, ocean water for example, or wastewater after treatment in a wastewater treatment plant. It is listed as a conventional pollutant in the U.S. Clean Water Act. Total dissolved solids is another parameter acquired through a separate analysis which is also used to determine water quality based on the total substances that are fully dissolved within the water, rather than undissolved suspended particles.
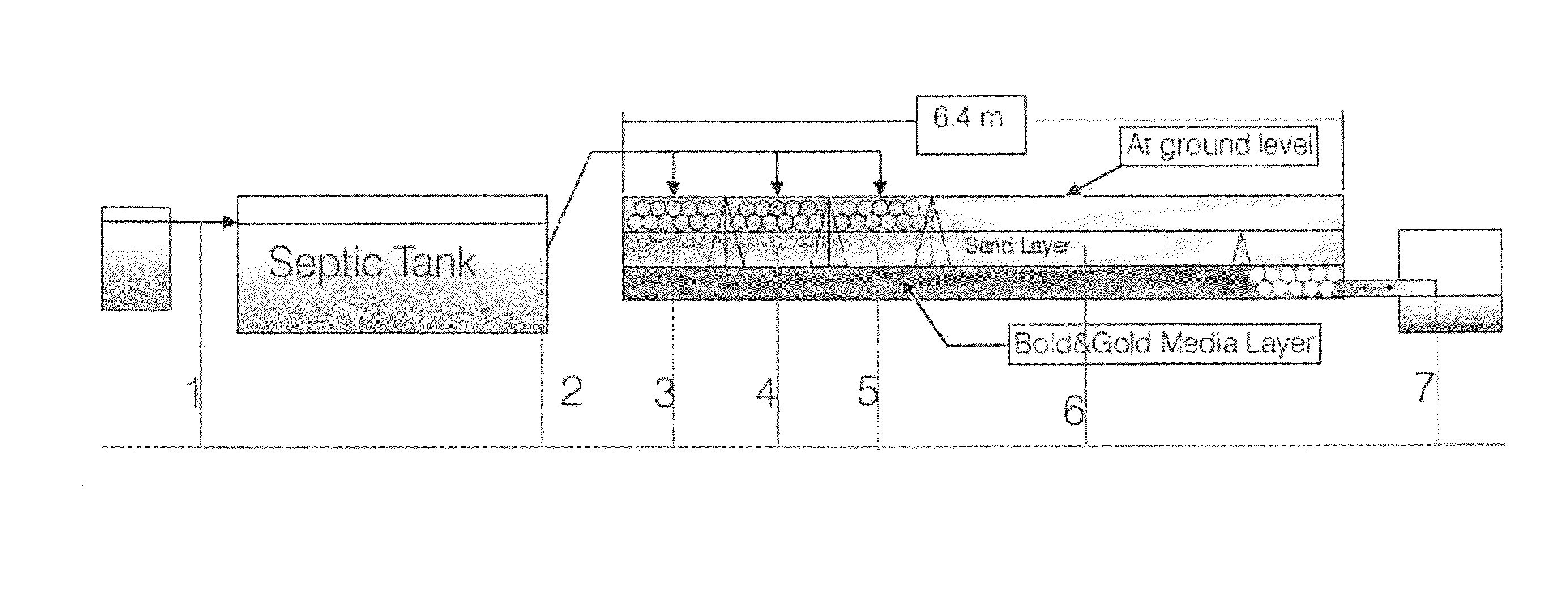
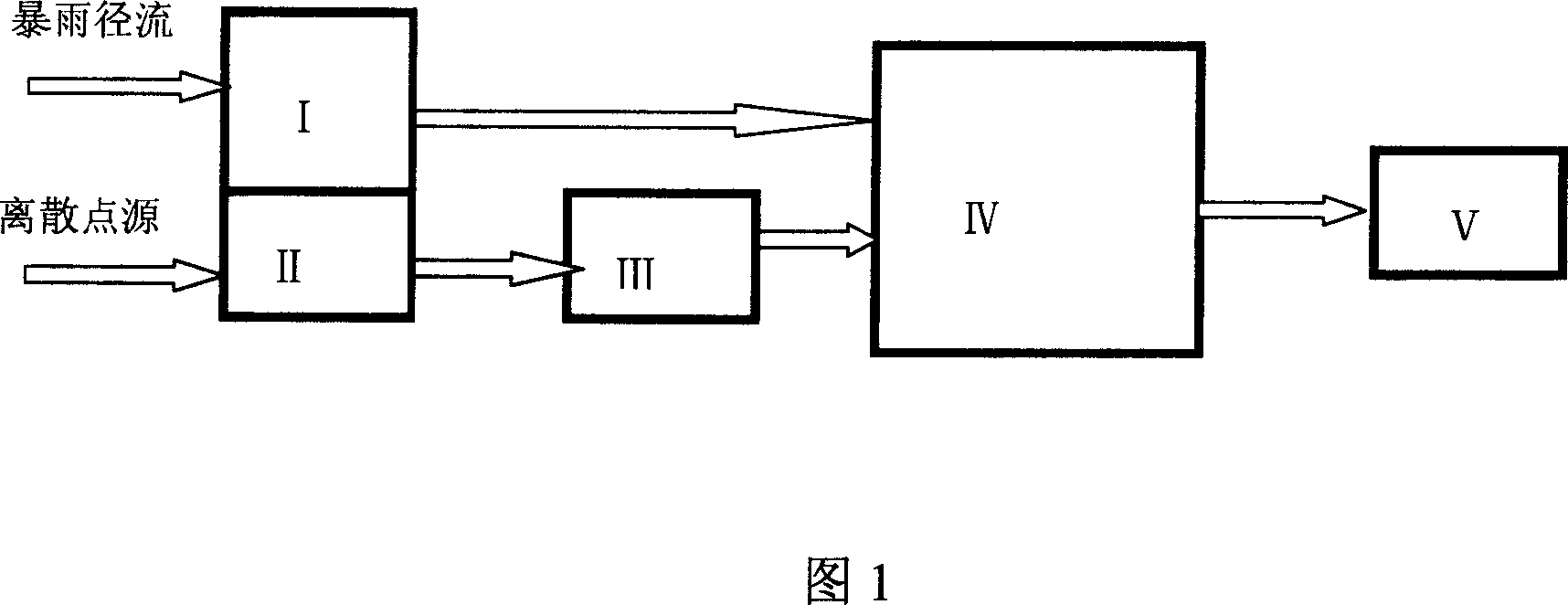
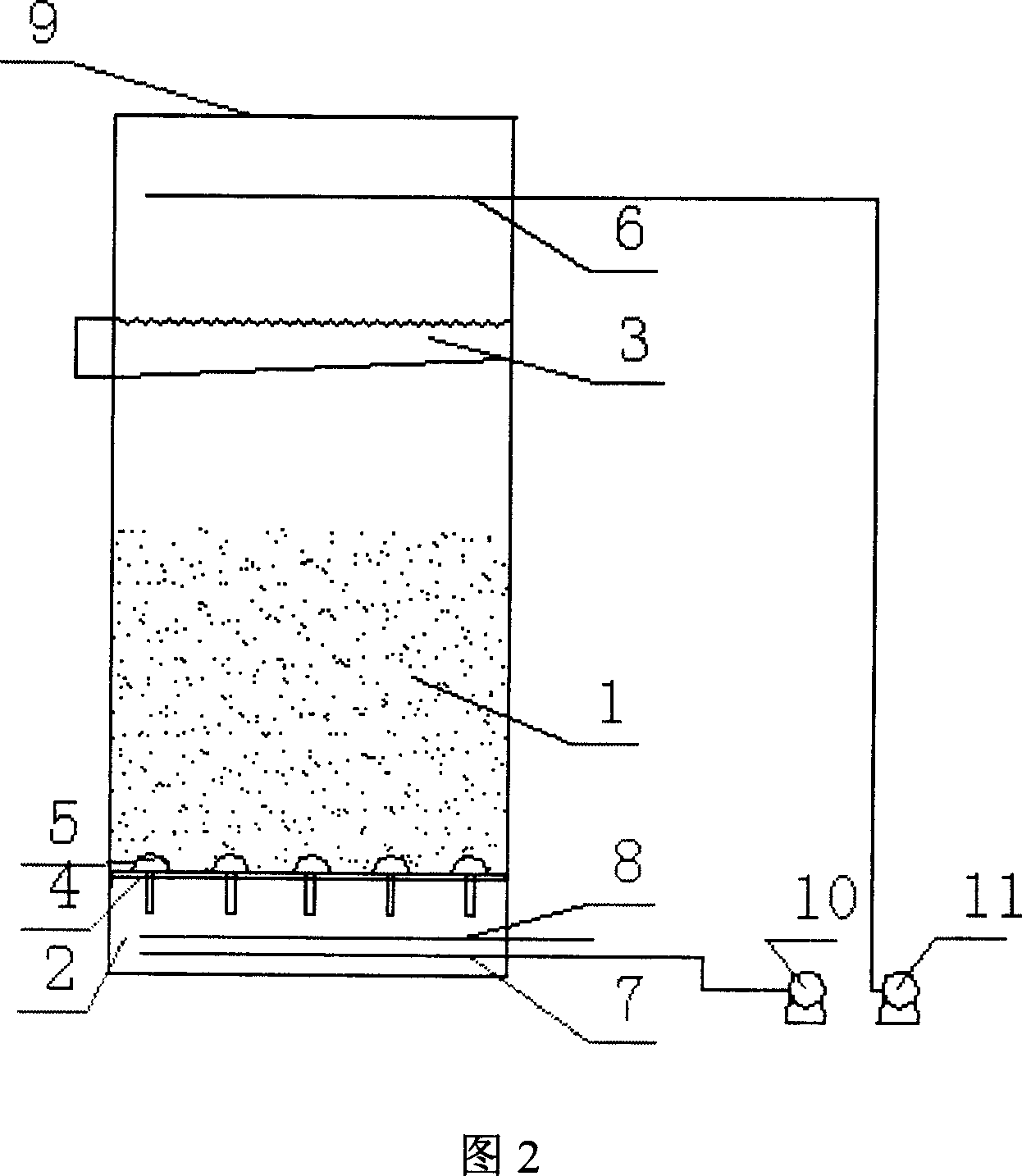
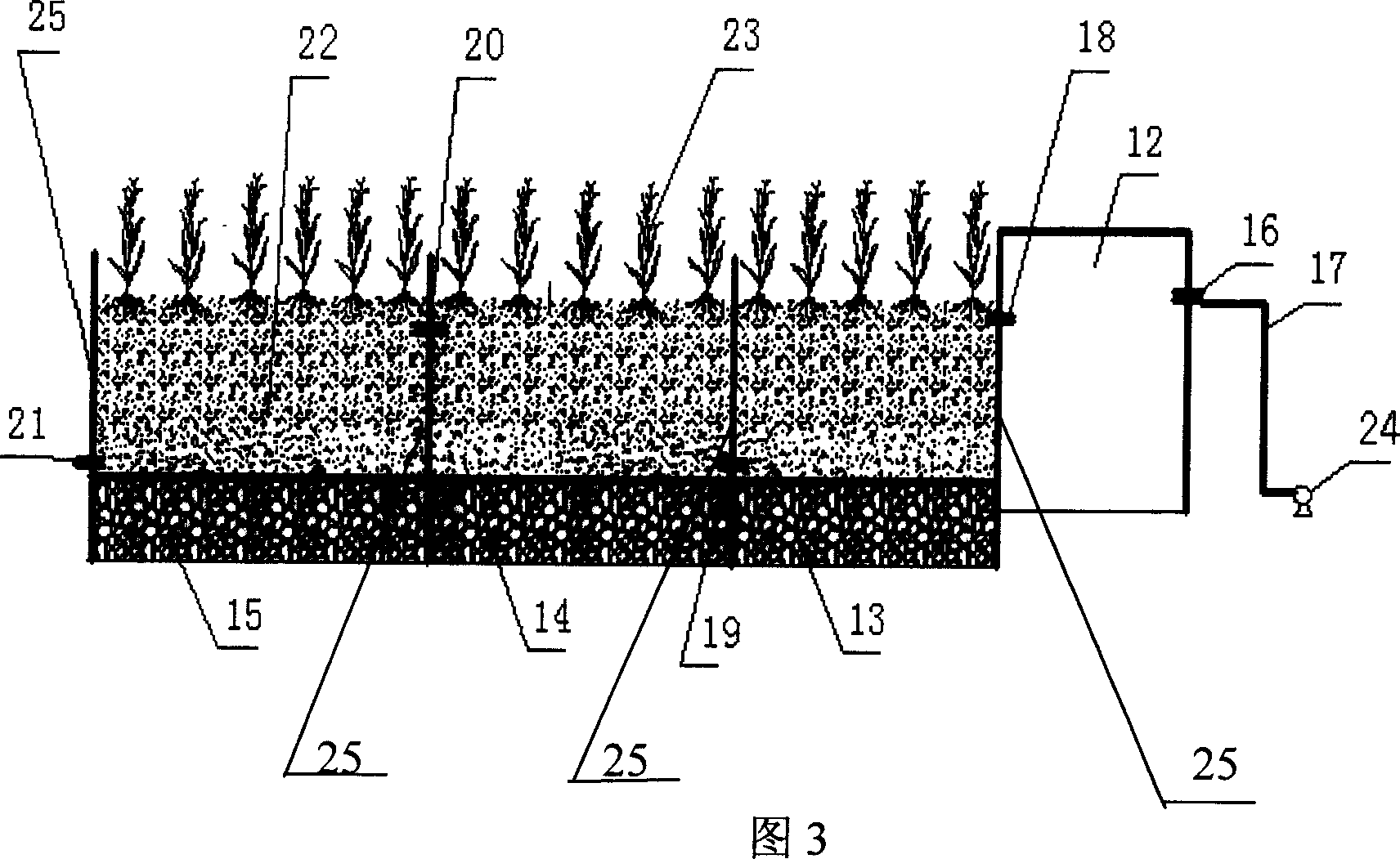
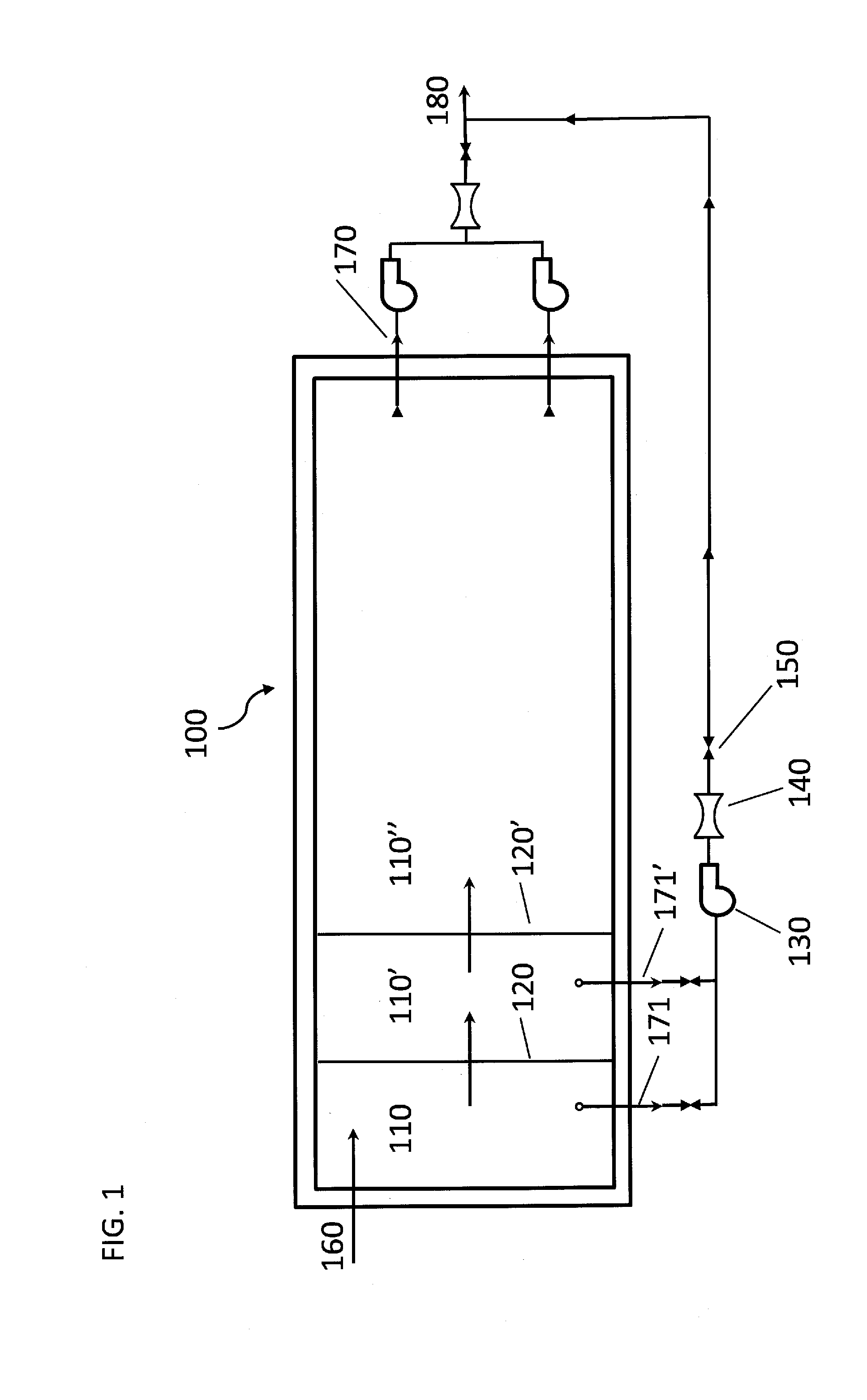
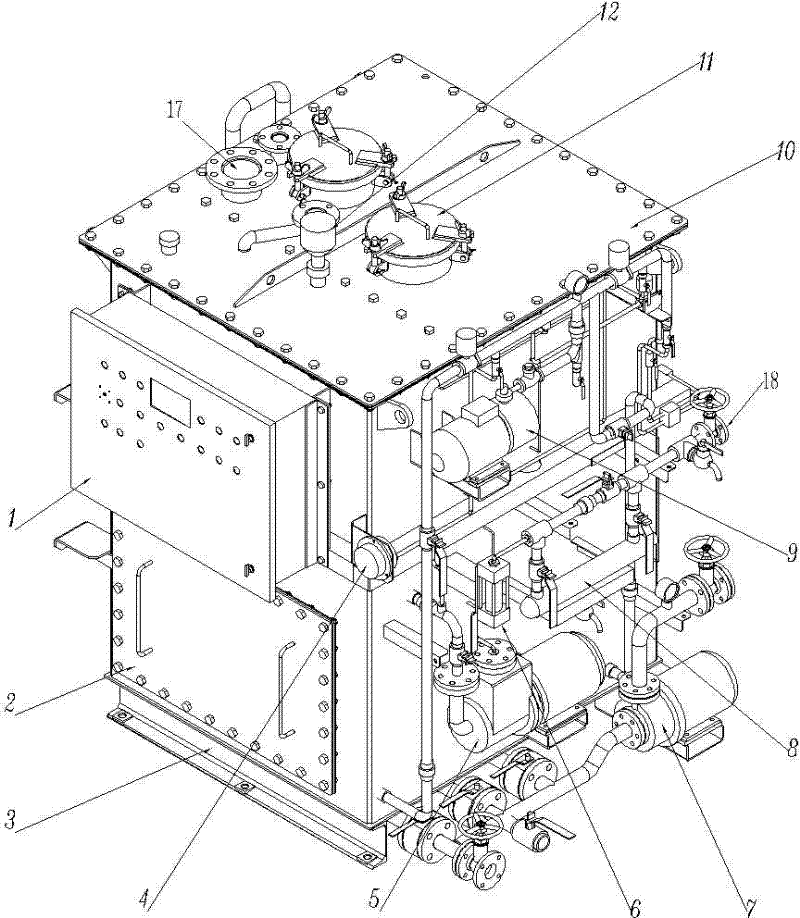
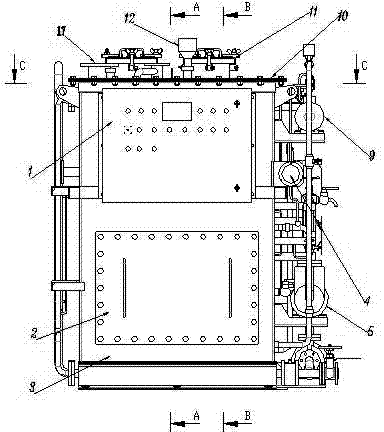
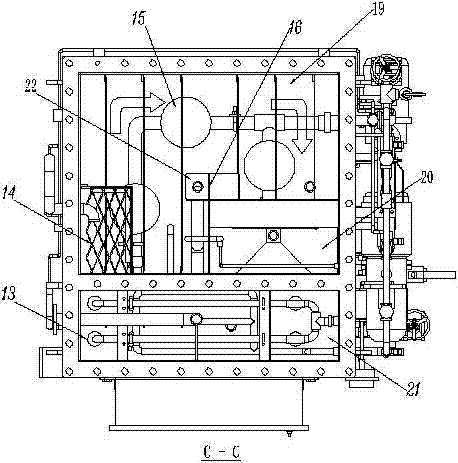
Subsurface upflow wetland system for nutrient and pathogen removal in wastewater treatment systems
ActiveUS8252182B1Low maintenance burdenHigh benefit cost ratioWater cleaningContaminated soil reclamationFecesTotal suspended solids
Methods and systems for a subsurface upflow wetland for wastewater treatment that includes a series of parallel treatment cells, each cell including from bottom to top, a layer of gravel, a layer of sand over the gravel to remove pathogens from a septic effluent, a pollution control medium above the sand layer to remove nutrients, total suspended solid, and biochemical oxygen demand and a growth media mixture layered on top of the pollution control media to grow plants, and a gravity distribution system to distribute effluent to the series of parallel treatment cells. The pollution control medium includes at least one recycled material and at least one naturally occurring material. In an embodiment it includes recycled tire crumb, sand and limestone or recycled tire crumb, compost, sand and limestone.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
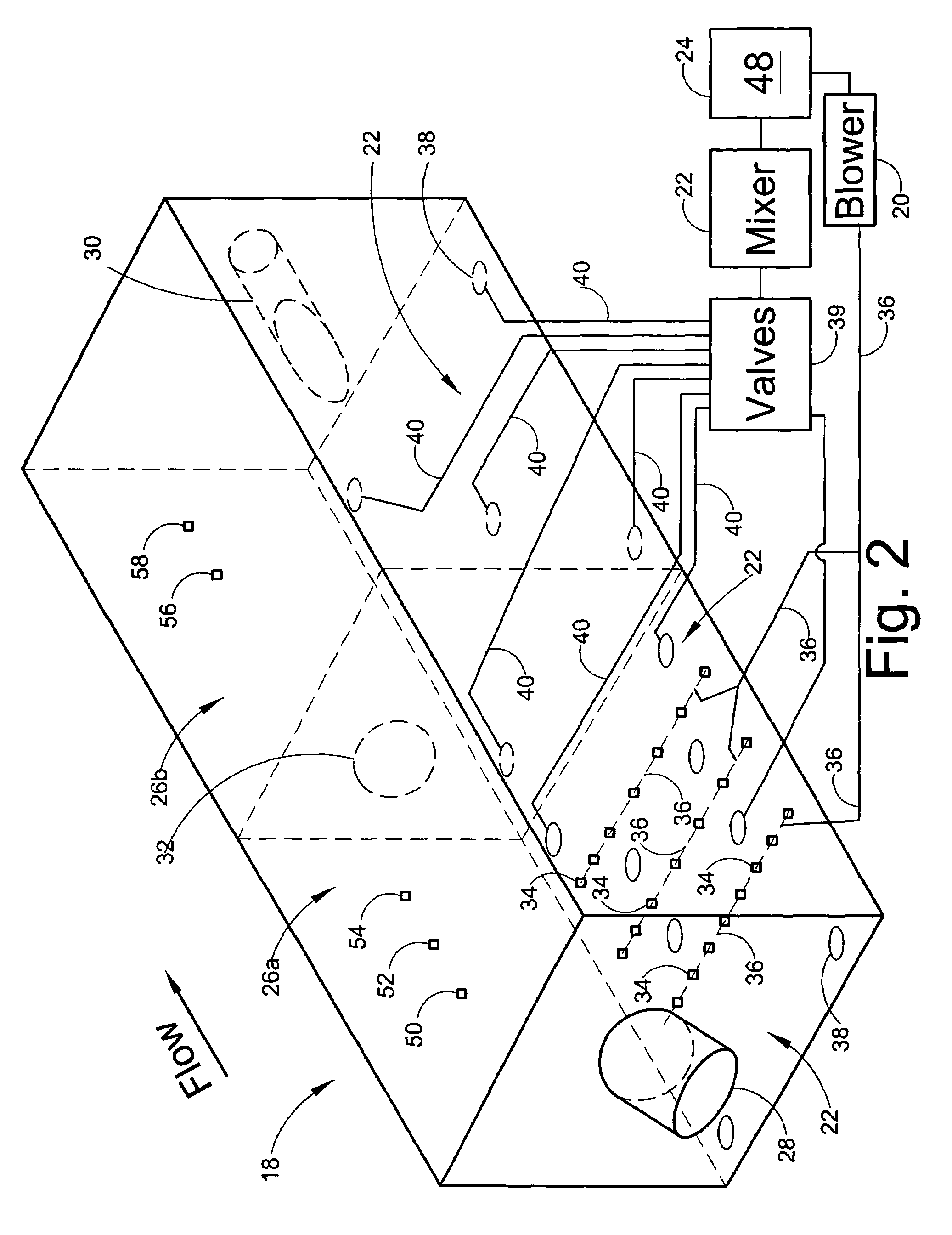
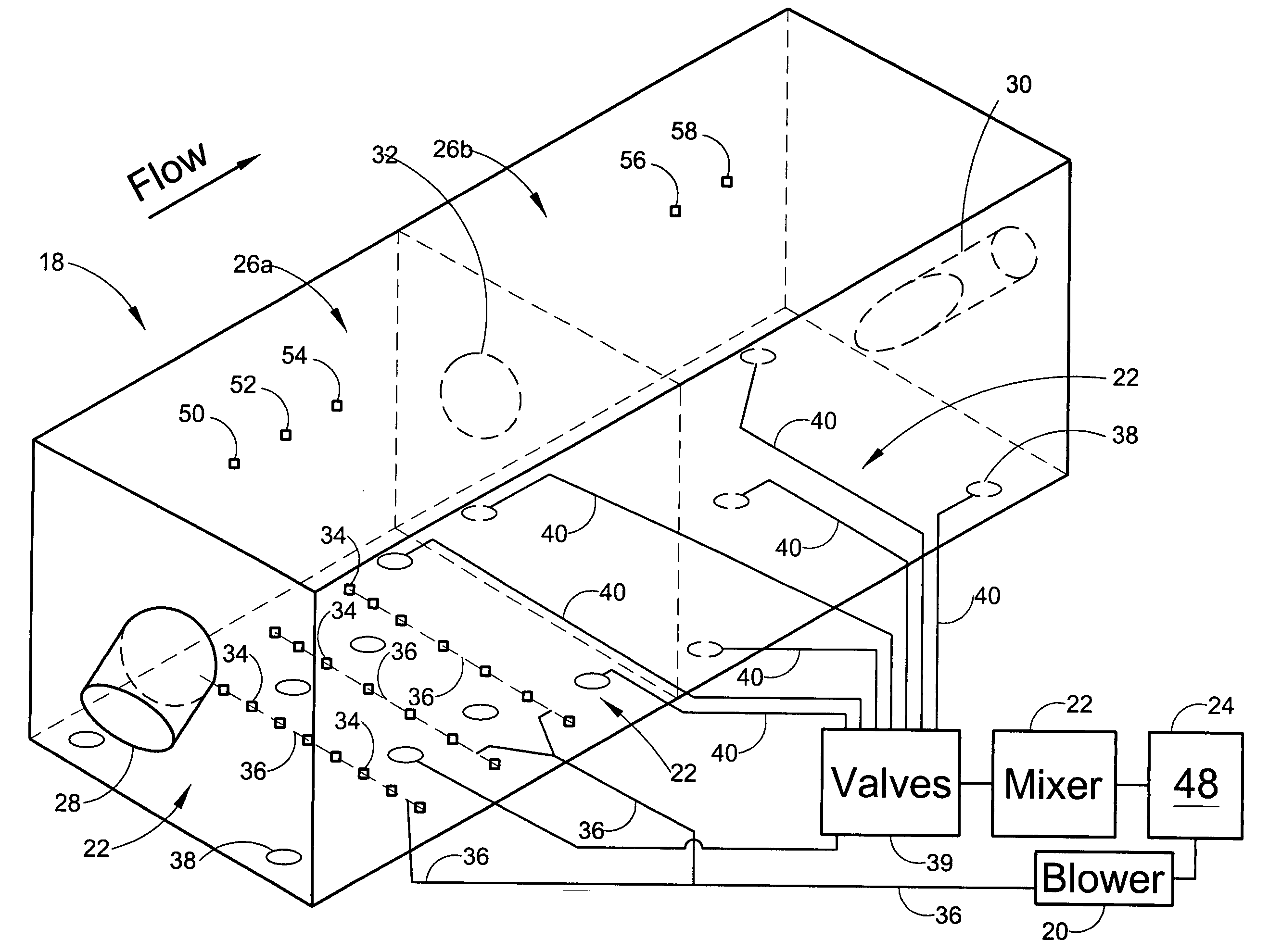
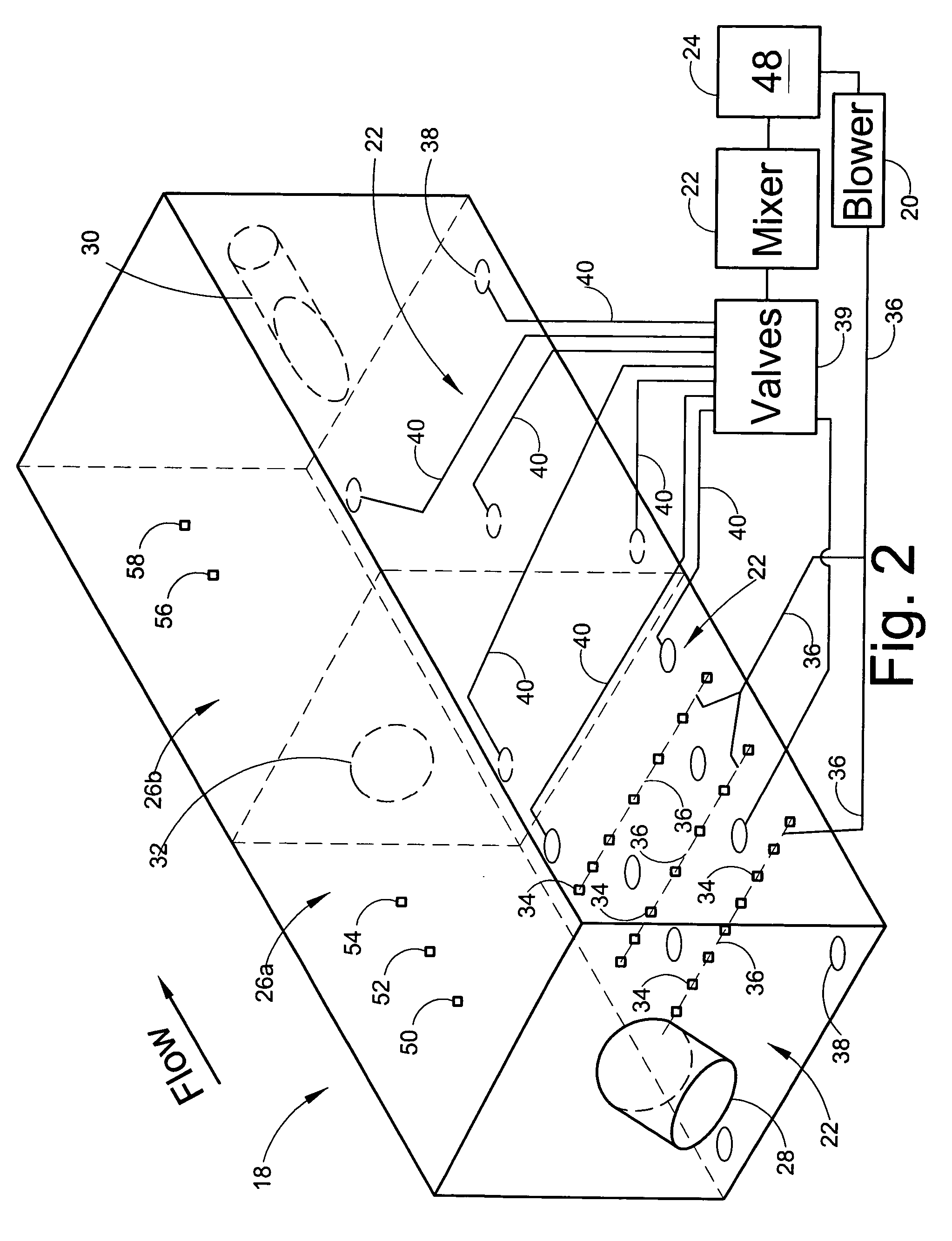
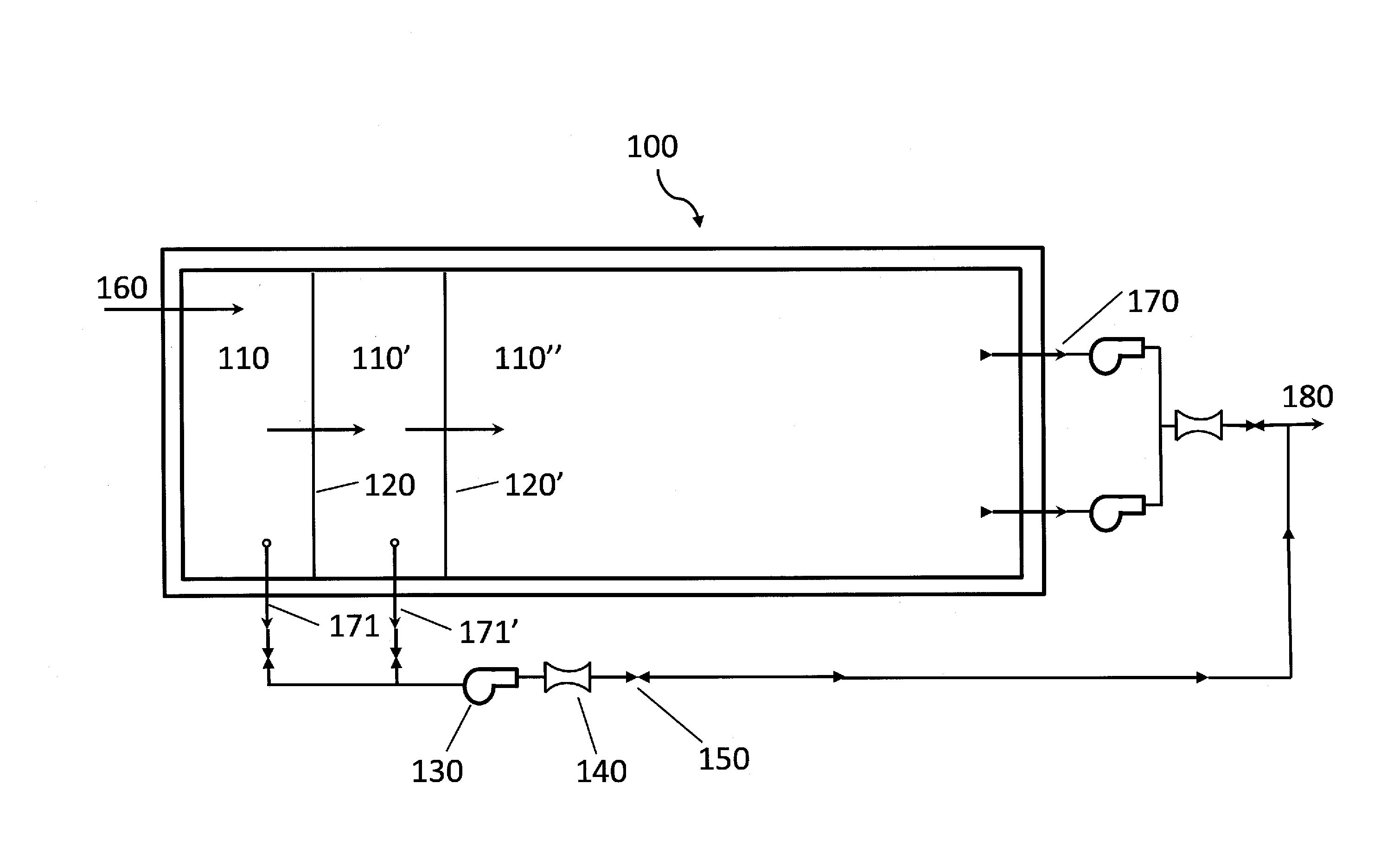
Mixer and process controller for use in wastewater treatment processes
ActiveUS7282141B2Less energyReduce stepsWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesNitrateOxygen
Owner:KOOPMANS RICHARD J +1
Mixer and process controller for use in wastewater treatment processes
ActiveUS20060254979A1Less energyReduce stepsWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesNitrateNitrite concentration
A system and method of wastewater treatment in a tank provides large mixing bubbles generated in the lower portion of the tank. In embodiments providing aerobic wastewater treatment, the system further provides oxygen to the wastewater by way of tiny aerating bubbles provided by diffusers. At least one sensor in the tank provides measurements of at least one wastewater treatment parameter such as total suspended solids, dissolved oxygen, ammonium or nitrate. An automatic controller in the system, responsive to measurements provided by the sensor, adjusts the rate of mixing provided by the large mixing bubbles. In some aerobic embodiments, the controller, responsive to measurements from the sensor, further adjusts the rate of oxygenation supplied to the wastewater by the tiny aerating bubbles.
Owner:KOOPMANS RICHARD J +1
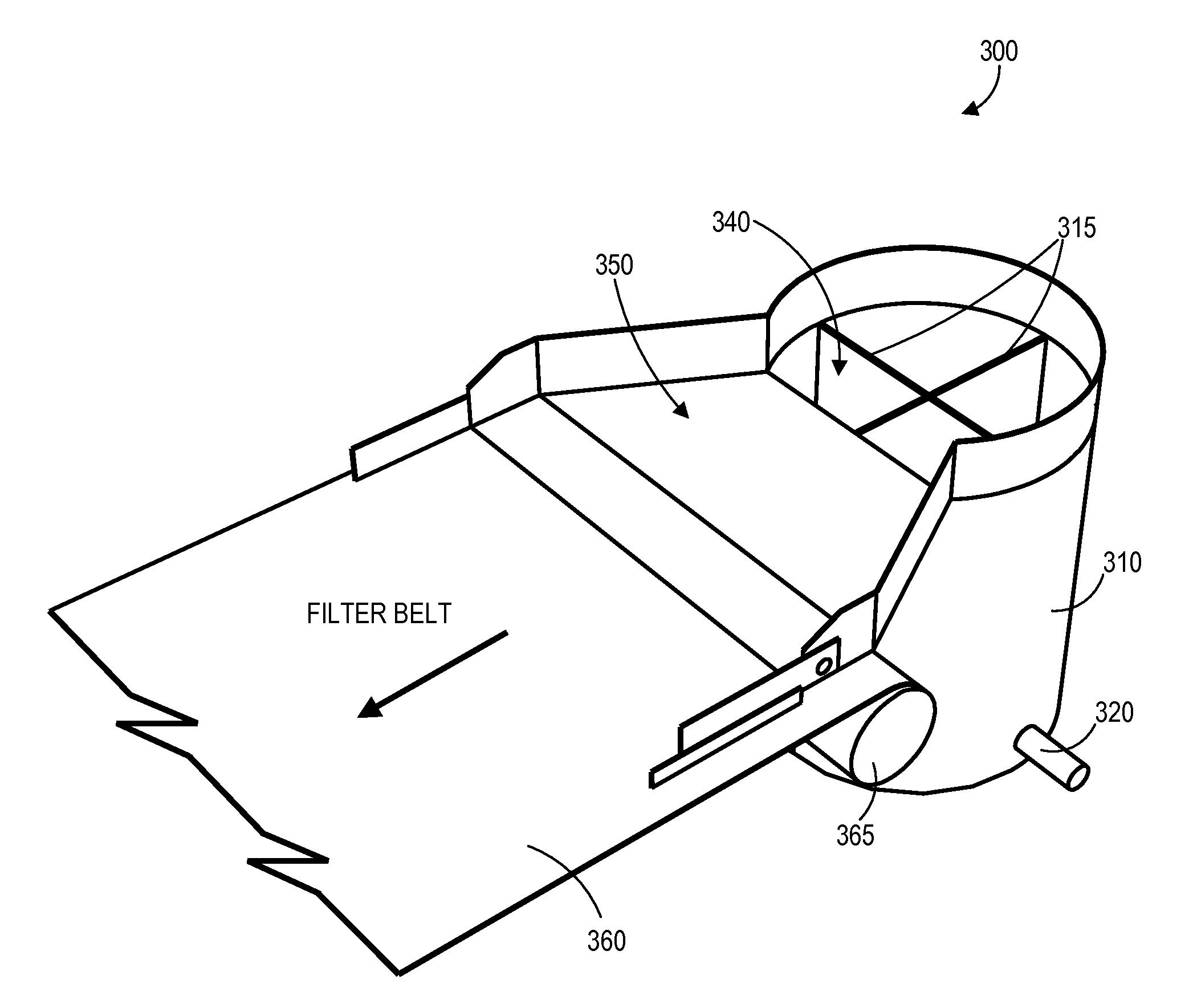
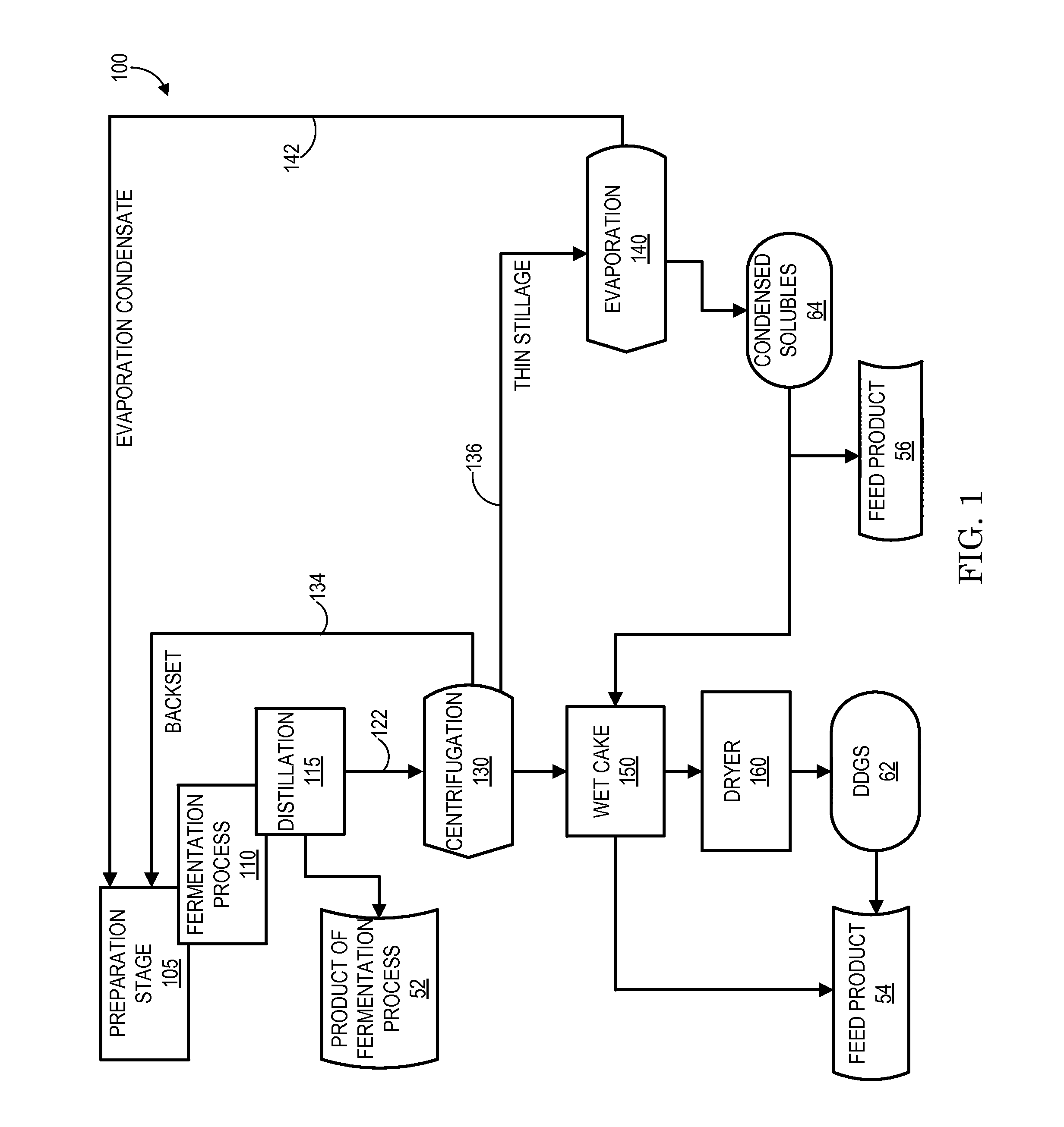
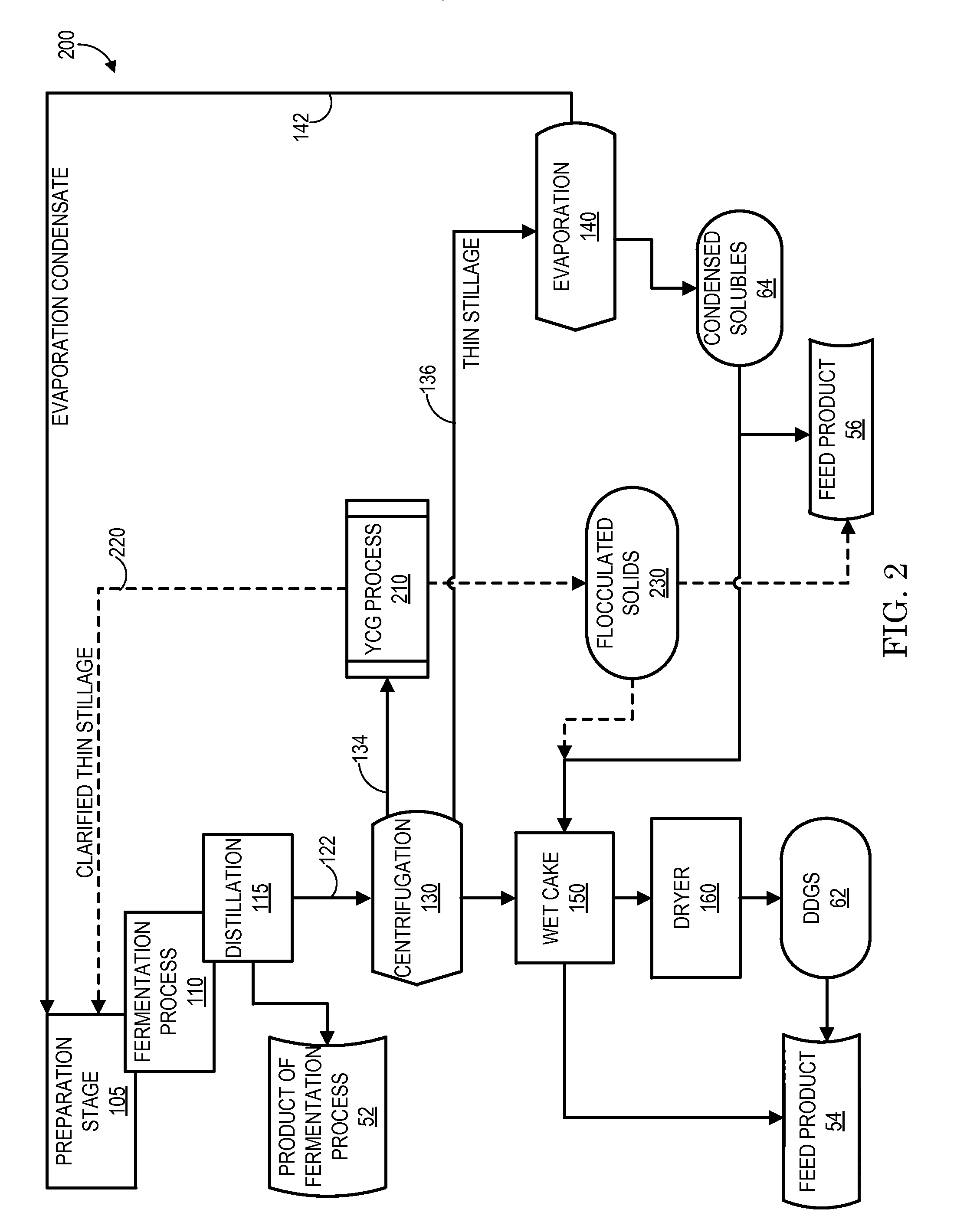
Thin Stillage Clarification
InactiveUS20140319066A1Efficiently processing and recoveringQuality improvementBy-product recoveryWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationEvaporationFatty acid
Systems and methods for improving the quality of solids and liquids recovered at atmospheric pressure and temperature from a stillage stream generated as a by-product of an ethanol production process, the recovered solids having higher bio-available amino and fatty acids than evaporation-produced condensed solubles, the recovered liquids having less total solids and total suspended solids than evaporation-produced condensate. A static mixer includes an input for receiving the stillage stream combined with a GRAS anionic polymer, a cylindrical mixing chamber that controllably mixes the stillage stream and the polymer to generate wet flocculated solids and liquid co-product, and a discharge chute that outputs the wet flocculated solids and liquid co-products onto a moving, gravity filter belt having a membrane surface that separates the output from the static mixer into recovered liquids in the form of clarified, thin stillage and recovered solids in the form of dry flocculated solids.
Owner:YIELD & CAPACITY GRP
Compositions and Methods for Wastewater Treatment
Methods and compositions utilizing aluminum, magnesium, and calcium-based additives for the treatment and neutralization of wastewater are described for removing contaminants from wastewater, including reducing phosphorous-containing compounds, total suspended solids (TSS), biological oxygen demand (BOD), fats, oils, and greases (FOG), and total Kjedahl nitrogen (TKN) are described. Methods and compositions to control pH, sulfur and sodium loads present in wastewater and precipitatable solids are described. Concentrations of aluminum, magnesium, and calcium-based additives are maintained at mass action concentrations to the wastewater component levels present in the wastewater and bracketed approximately + / −0.5 pH units about the pK value of the soluble, buffering species.
Owner:INLAND ENVIRONMENTAL RESOURCES
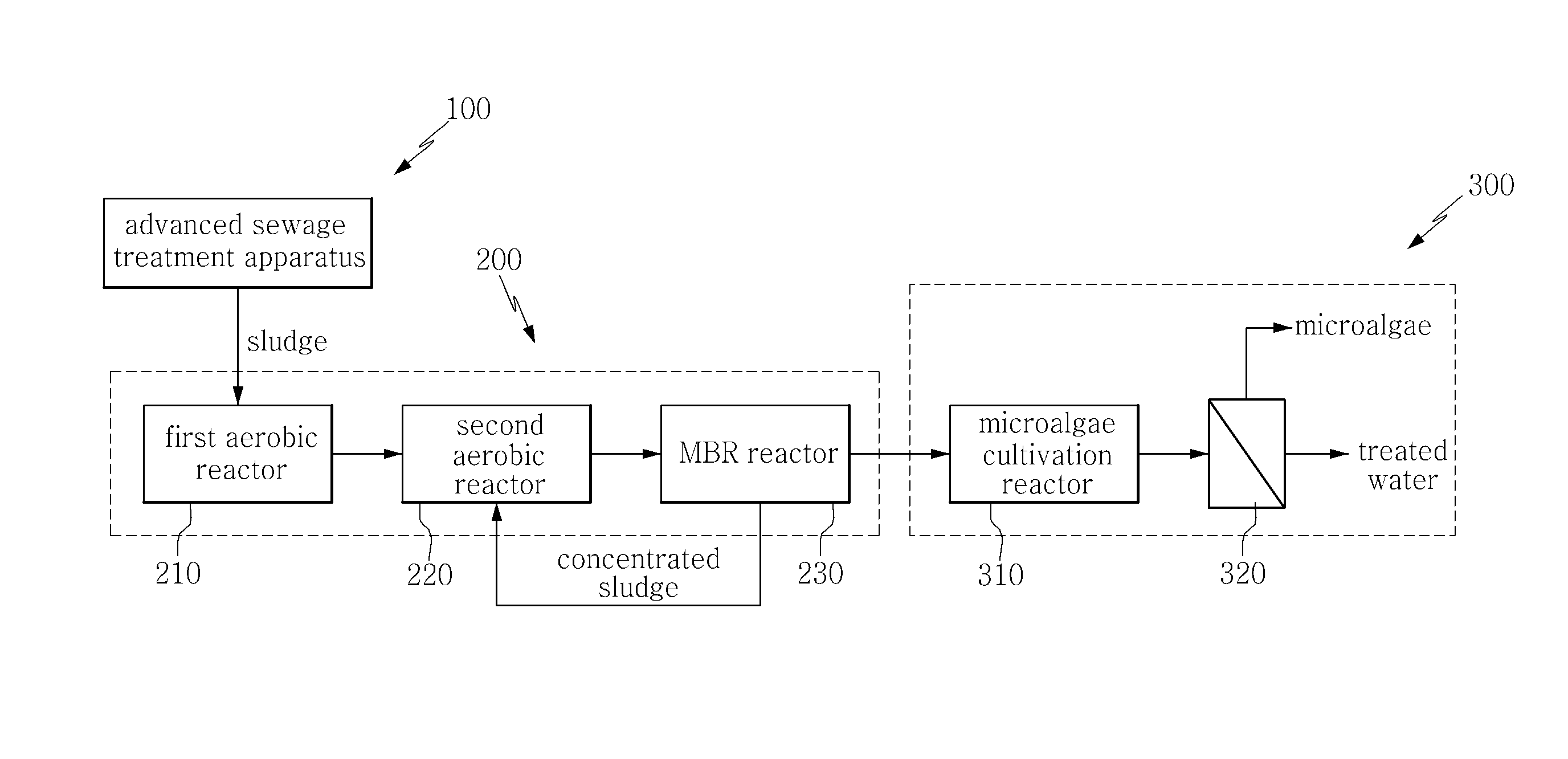
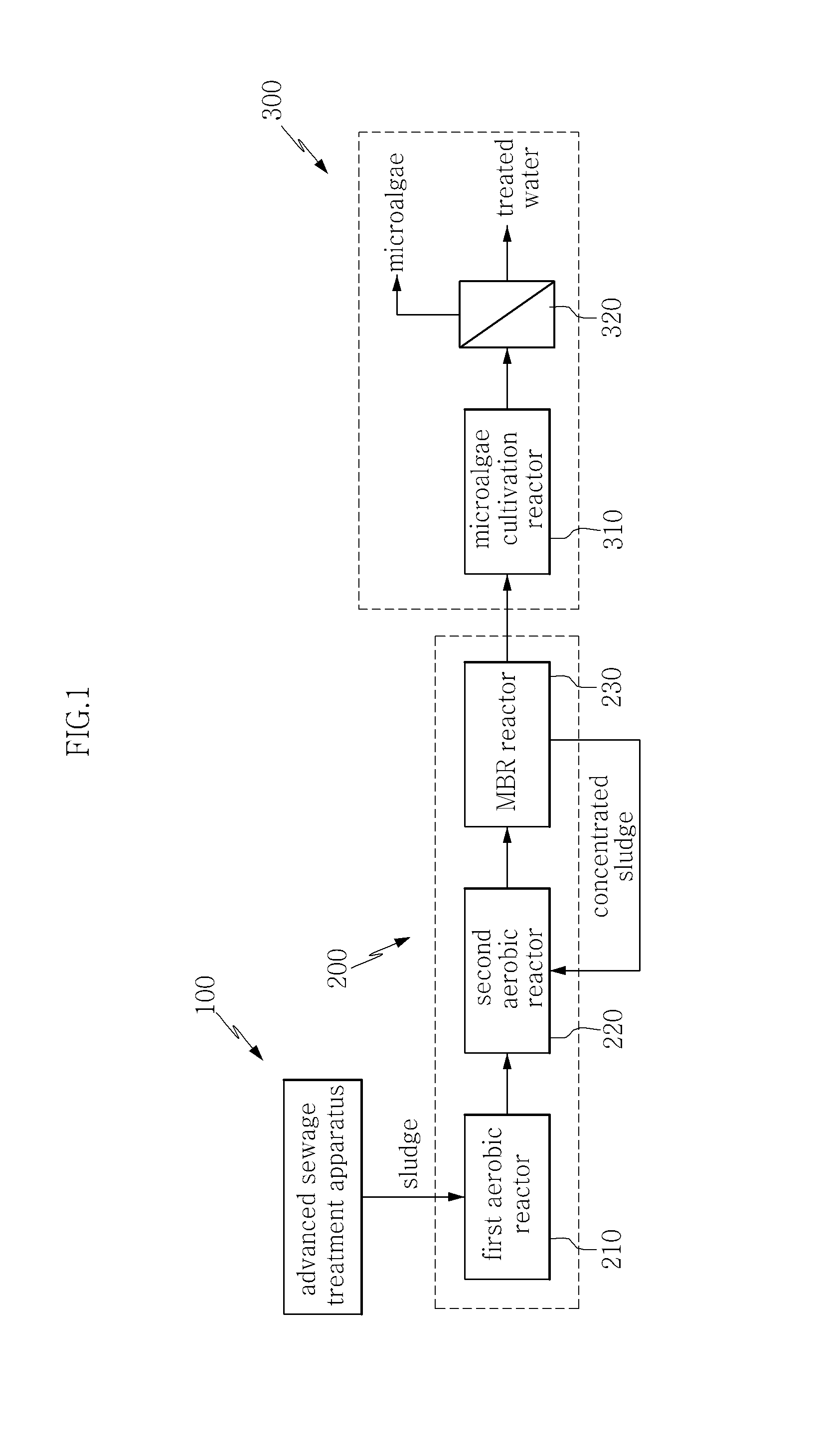
Apparatus and method for cultivating microalgae using effluent from sludge treatment
InactiveUS20140144839A1Improve efficiencyEasy dischargeTreatment using aerobic processesUnicellular algaeMicroorganismHigh concentration
Disclosed herein are an apparatus and method for cultivating microalgae using effluent from sludge treatment. The apparatus includes an advanced sewage treatment apparatus, a sludge treatment apparatus and a microalgae cultivation apparatus, the sludge treatment apparatus including: a first aerobic reactor which is operated under aerobic conditions and serves to ferment sludge; a second aerobic reactor which is operated in a state in which air is injected in an amount larger than that in the first aerobic reactor, and serves to increase the fermentation activity of microorganisms in the sludge and degrade the sludge; a membrane bio-reactor (MBR) which serves to receive effluent from the second aerobic reactor and biologically remove high-concentration organic matter from the effluent by the action of aerobic microorganisms while removing total suspended solids using a membrane, wherein the effluent discharged from the MBR reactor is supplied to the microalgae cultivation apparatus.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
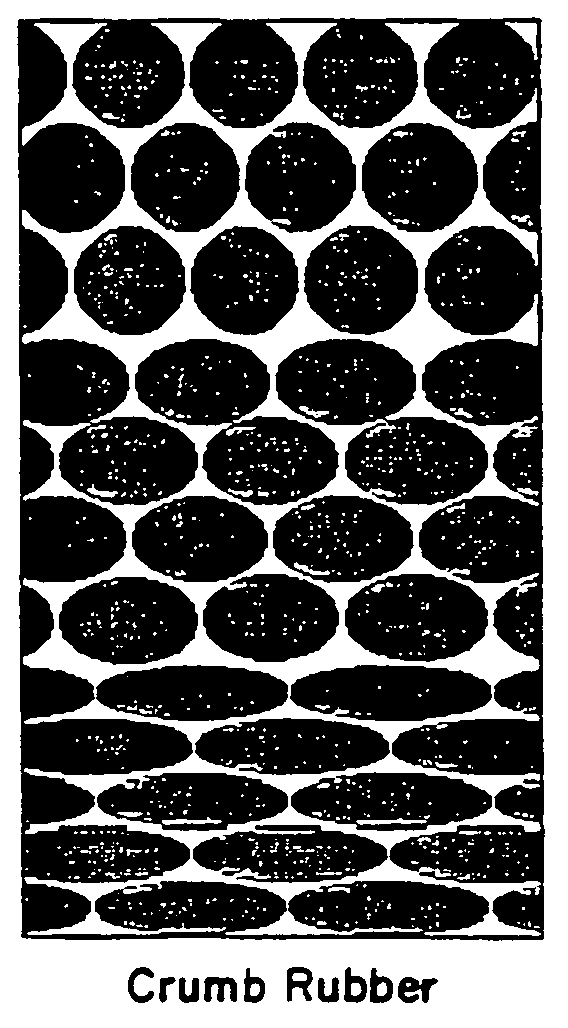
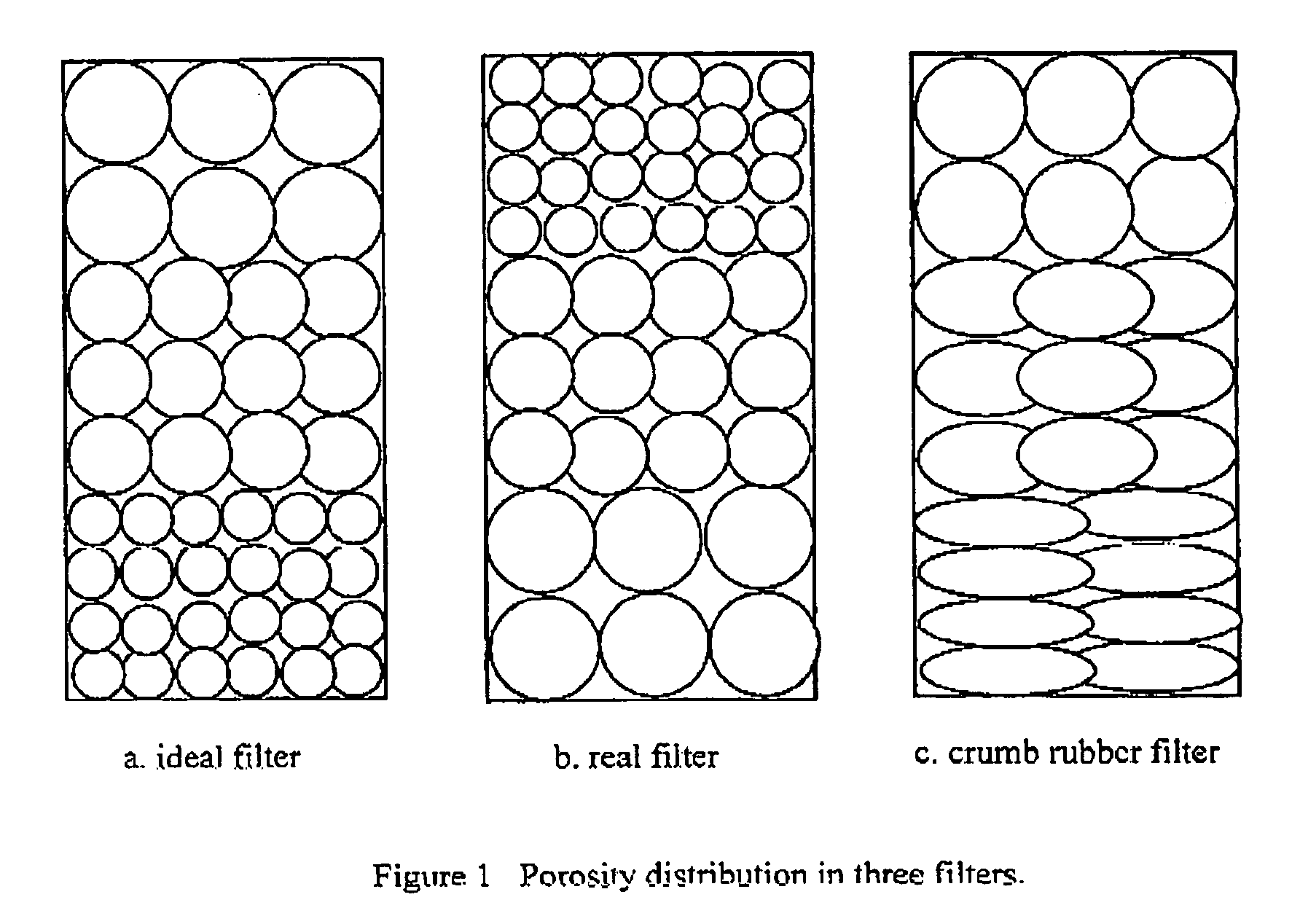
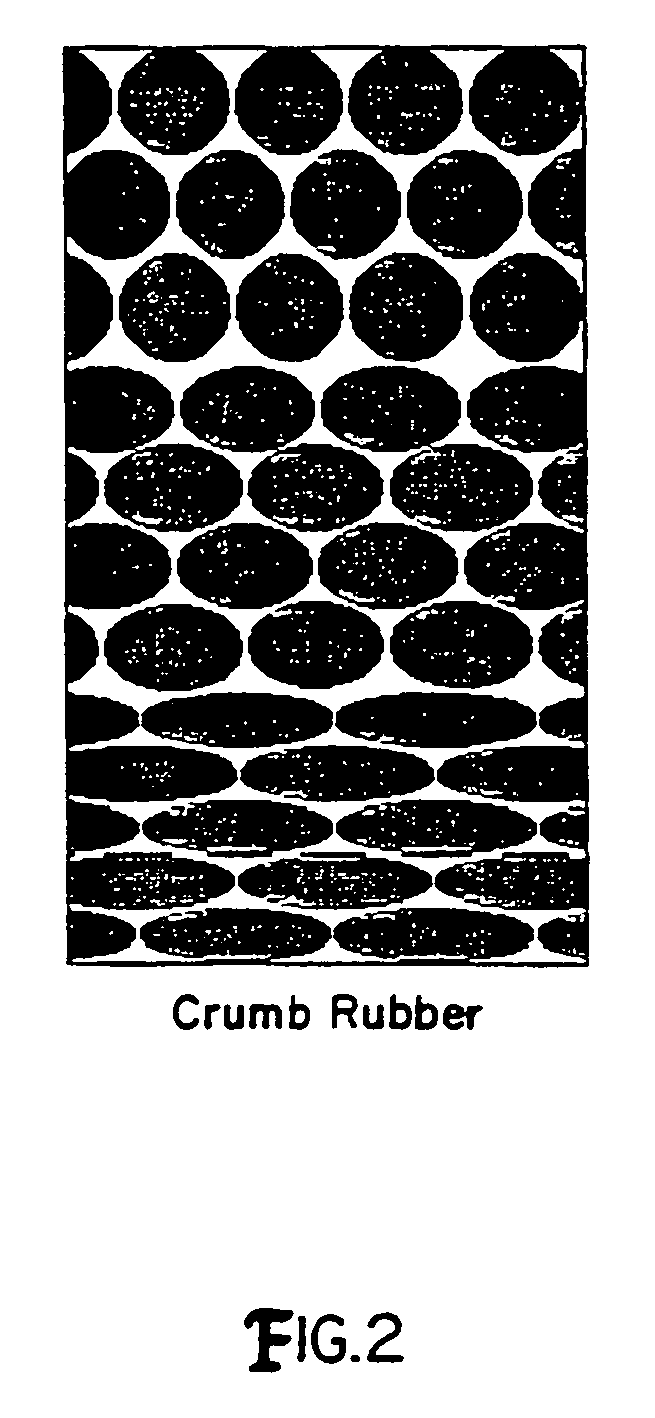
Method of using waste tires as a filter media
InactiveUS6969469B1Improve effluent qualityGreat depth filtrationWater/sewage treatmentMembrane filtersWaste tiresTotal suspended solids
The present invention is a method of using crumb rubber from recycled tires as a filter media. The use of crumb rubber as a media differs from conventional sand or anthracite filters in several ways. The crumb rubber media is compressible which allows the porosity between rubber particles to decrease through the filter bed. The crumb rubber media compresses as headloss increases, allowing for better effluent quality late in the run. The crumb rubber media allows greater depth filtration. The crumb rubber media can be used at high filter rates, greater than 20 gpm / ft2. The crumb rubber media performs similarly to other traditional filter media in respect to turbidity and total suspended solids removal. The crumb rubber media properties are closely tied to media size and shape, with smaller media providing better effluent qualities and larger media allowing longer filter runs at higher flow rates.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Composite biological enzyme preparation for deweighting treatment of domestic sludge, and production and application method thereof
InactiveCN102351321AStable structurePrevents oxidative deactivationBiological sludge treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentManganese peroxidaseNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a composite biological enzyme preparation for the deweighting treatment of domestic sludge, and a production and application method thereof. The invention is characterized in that 100-500 kilograms of composite biological enzyme for the deweighting treatment of domestic sludge are used for 100 thousand tons of municipal domestic sewage, wherein the composite biological enzyme for the deweighting treatment of domestic sludge comprises 25-30 parts of protease, 20-25 parts of one or more of laccase, polyphenol oxidase and manganese peroxidase, 17-21 parts of one or more of xylanase, pentosanase and mannase, 20-25 parts of one or more of cellulase, pectinase and hemicellulase, 10-15 parts of lipase and 12-16 parts of amylase. Compared with the prior art, the invention removes hydrogen sulfide gas and undesirable odor thereof, simultaneously eliminates the inhibiting effect of H2S on the nitrification process, effectively reduces nitrate and ammonia, decomposes proteins, starch, fat, food oil, xylan, cellulose and other organic substances, converts suspended substances, accumulated waste and soluble organic substances in the sludge into carbon dioxide, nitrogengas, oxygen gas, water and sulphate, reduces the TSS (Total Suspended Solids), COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) and BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand), greatly decreases the yield of the sludge, and has the advantages of no poison, no corrosiveness and no secondary pollution production.
Novel compound microbial agent used for sludge reduction treatment
InactiveCN103910477AReduce mud accumulationReduce corrosionBiological sludge treatmentBacteroidesMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a novel compound microbial agent used for sludge reduction treatment. The compound microbial agent consists of photosynthetic bacteria, lactic acid bacteria and saccharomycetes, and comprises bacillus subtilis, bifidobacterium animals, bifidobacterium bifidum, bifidobacterium longum, lactobacillus acidophilus, lactobacillus casei, lactobacillus delbrueckii, lactobacillus fermentium, lactobacillus plantarum, lactococcus lactis, rhodopseudomonas palustris, streptococcus thermophilus and saccharomyces cerevisiae which are 13 different microorganisms in total. The compound microbial agent can reduce BOD (biochemical oxygen demand), COD (chemical oxygen demand) and TSS (total suspended solids) to expected values, effectively reduces sludge deposit in a treatment plant, and reduces corrosion on equipment to lower maintenance cost; and besides, bacteria can decompose an organic compound and can generate byproducts beneficial to environment.
Owner:XIAMEN EPIGENESIS TECH
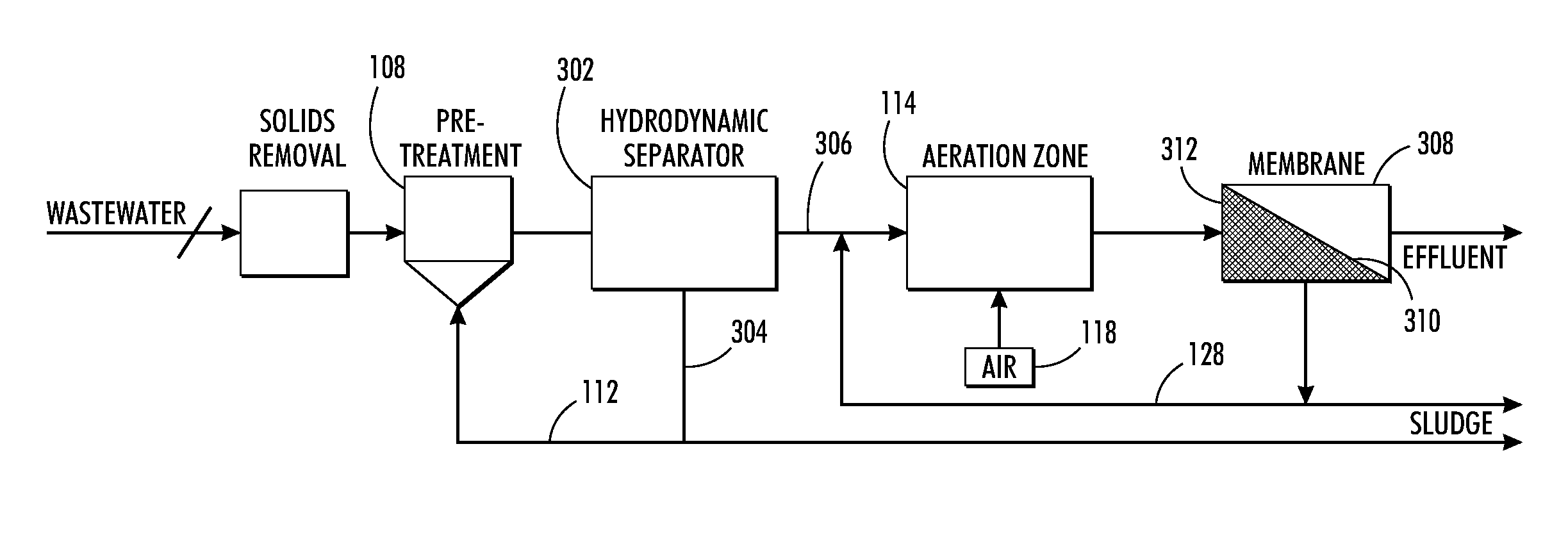
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) and moving bed bioreactor (MBBR) configurations for wastewater treatment
ActiveUS20120152814A1Reduce loadReduce energy costsSemi-permeable membranesTreatment using aerobic processesWater treatment systemFiltration
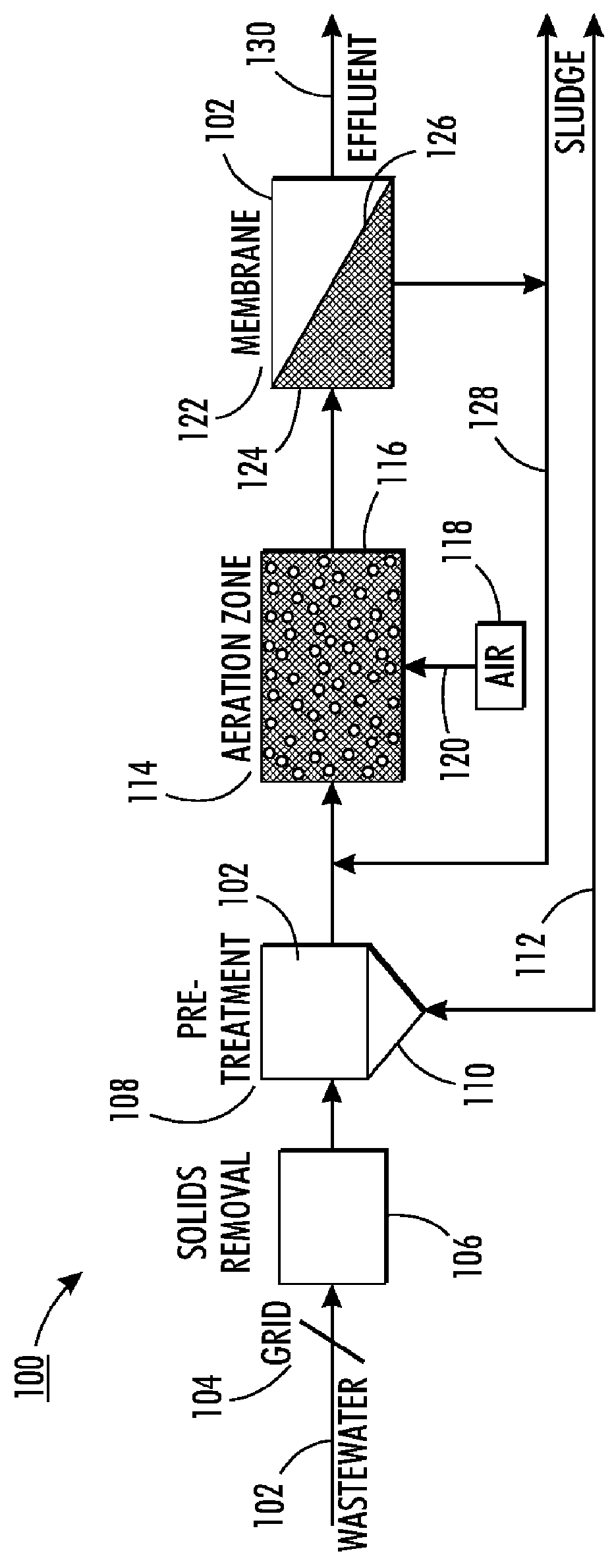
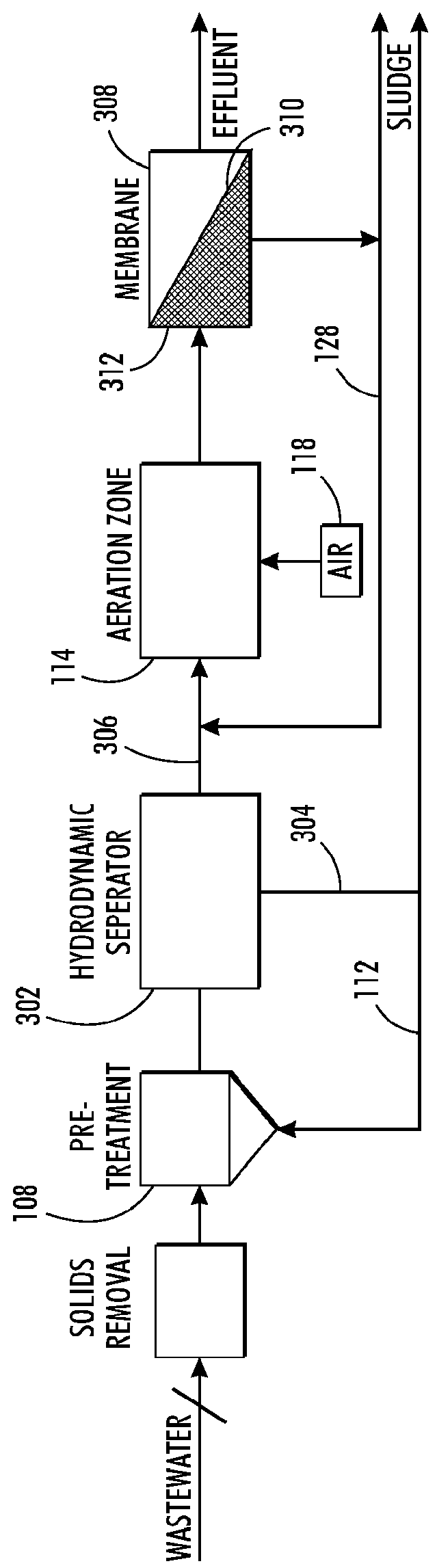
The water treatment system and method incorporating the use of a hydrodynamic separator to remove most of the total suspended solids (TSS) in source water being treated to thereby lighten the load on membrane filtration in the water treatment system and lower energy costs.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for strengthening electricity generating performance of MFC (micro-function circuit) by taking excess sludge as fuel and strengthening sludge reduction by enzyme
InactiveCN102569860AHigh removal rateImprove power generation performanceBiochemical fuel cellsBiological sludge treatmentNeutral proteaseSludge
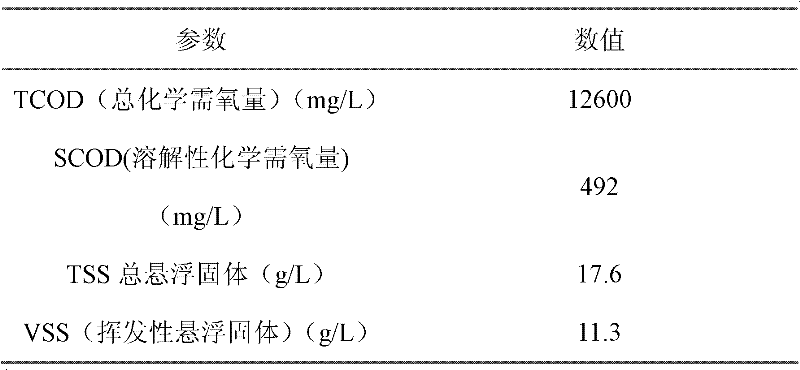
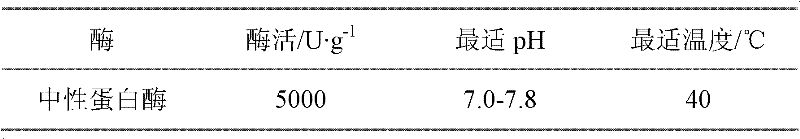
The invention belongs to the filed of microbiological fuel cells, and provides a method for strengthening electricity generating performance of an MFC (Microbial Fuel Cell) by taking excess sludge as fuel and strengthening sludge reduction by enzyme. The method comprises the steps of adding 20mM of NaCl in the excess sludge for strengthening the electrical conductivity of solution, adding neutral protease and Alpha-amylase, and generating electricity by directly using electricity generating microorganisms in the excess sludge for one day so as to start the MFC and obtain higher electric energy, wherein the strengthening effect of the neutral protease and the Alpha-amylase on an SMFC (Sediment Microbial Fuel Cell) at 40 DEG C is the most obvious. Under a condition that the total concentration of the enzyme is not changed, the mass concentration ratio of the neutral protease and the Alpha-amylase is 2:3, at the moment, the power density is the largest (776mW*m-2), and the removal rates of TCOD (total chemical oxygen demand), TSS (total suspended solids) and VSS (volatile suspended solids) reach 87.29%, 91.75% and 95.01% respectively. The method is fast in starting, simple in process, convenient to operate, and low in cost, and can treat the excess sludge in an urban domestic sewage treatment plant.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) and moving bed bioreactor (MBBR) configurations for wastewater treatment
ActiveUS8268169B2Reduce loadReduce energy costsSemi-permeable membranesOther chemical processesWater treatment systemFiltration
The water treatment system and method incorporating the use of a hydrodynamic separator to remove most of the total suspended solids (TSS) in source water being treated to thereby lighten the load on membrane filtration in the water treatment system and lower energy costs.
Owner:XEROX CORP
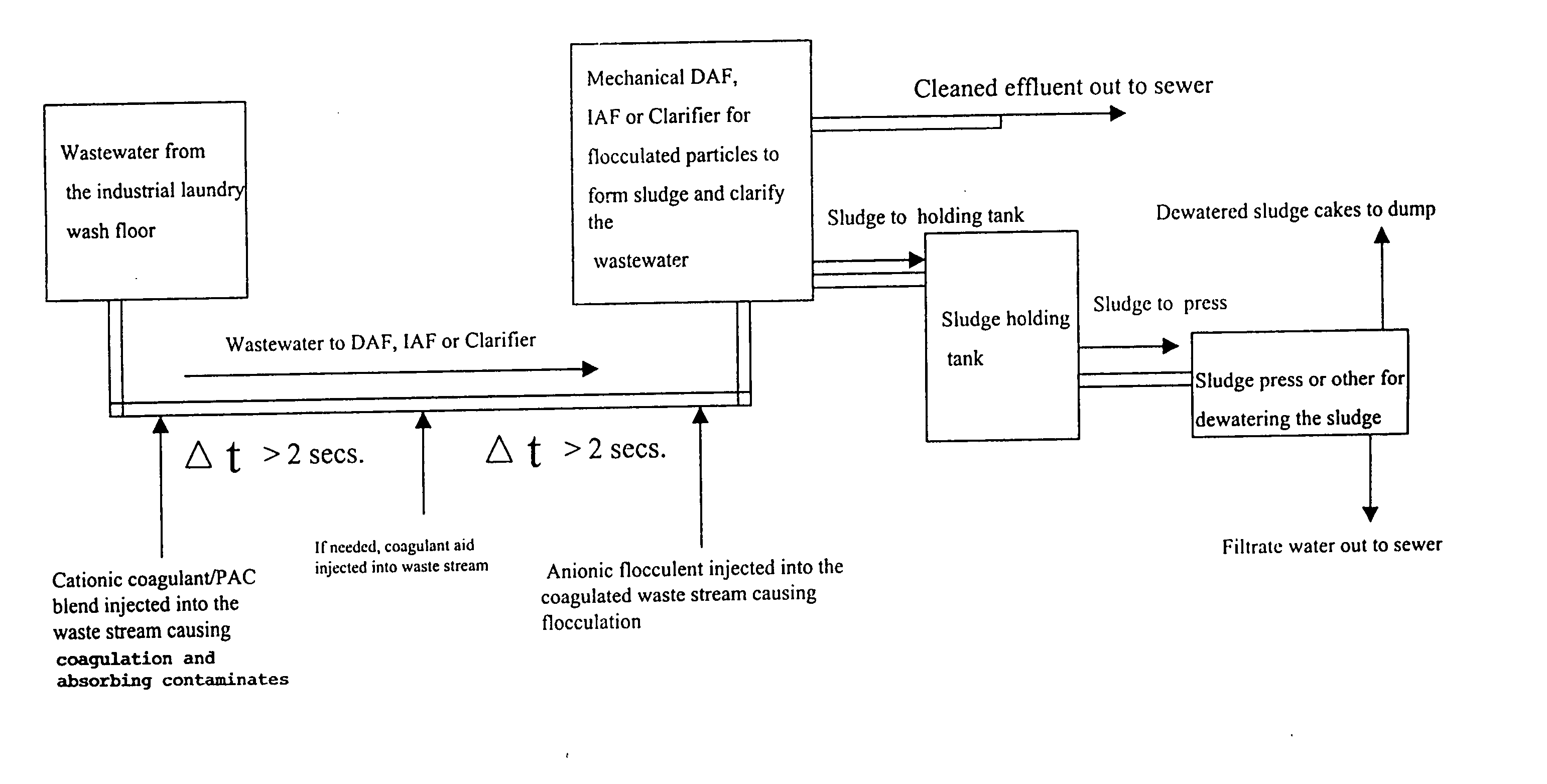
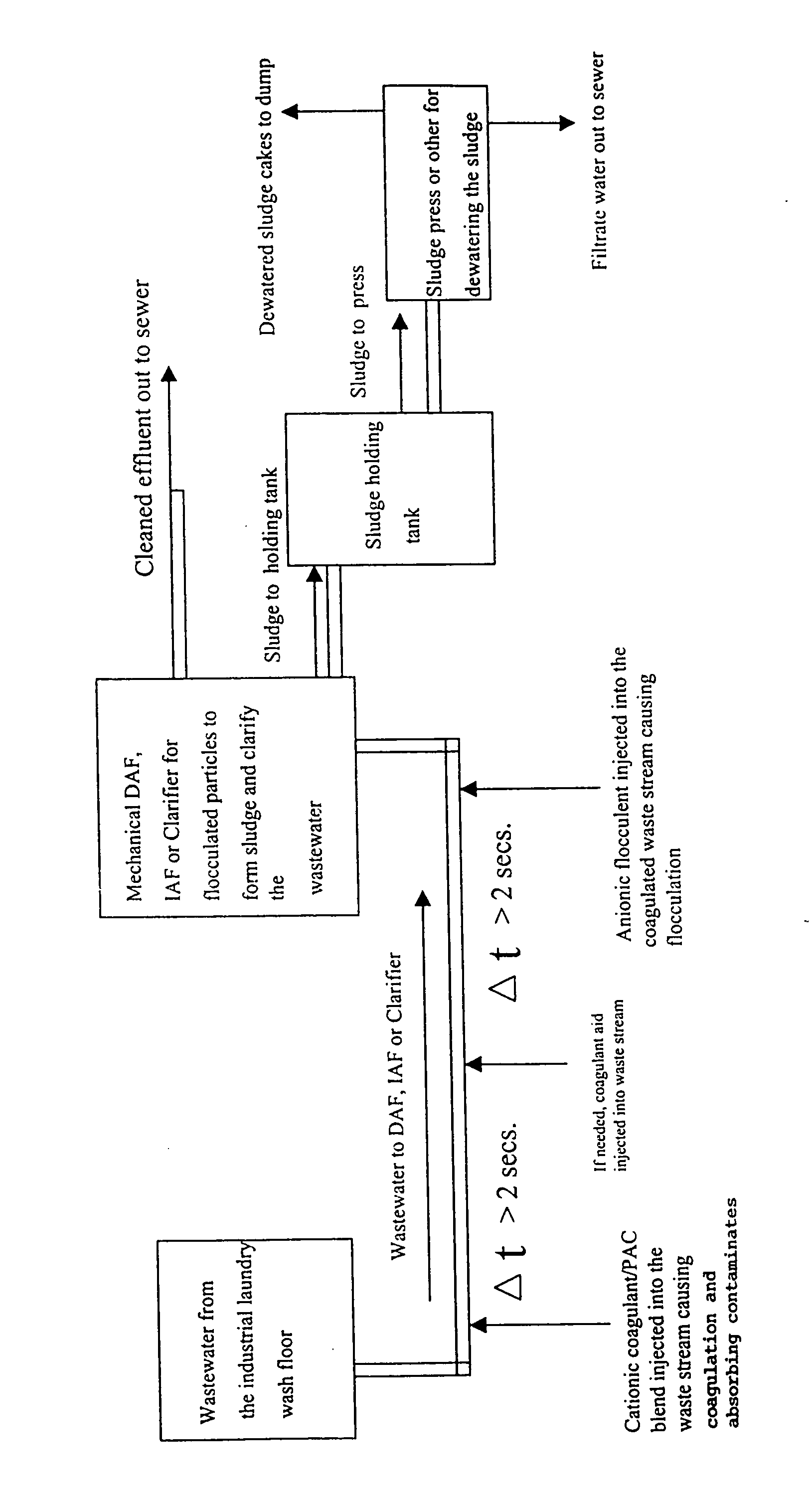
Method of clarifying industrial wastewater for the reduction of organic waste content using cationic dispersion polymers combined with powdered activated carbon and anionic flocculent polymers
ActiveUS20070187334A1Cleans wastewaterImprove the ability to solveWater treatment parameter controlSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningActivated carbonOil and grease
Methods are described for removing contaminates from aqueous industrial wastewater process streams, to yield a less contaminated aqueous specifically in the area of soluble organic containing effluent for discharge. A premixed medium / high molecular weight and medium / high charged cationic coagulant solution polymer and a powered activated carbon (PAC) is injected into the wastewater, and after a delay on the order of about ten seconds or greater, a high molecular weight highly charged anionic flocculent polymer solution is injected into the wastewater which reduces oil and grease (FOG), (BOD). (COD), volatiles total suspended solids (TSS), and other contaminants.
Owner:DAVIS STUART G +1
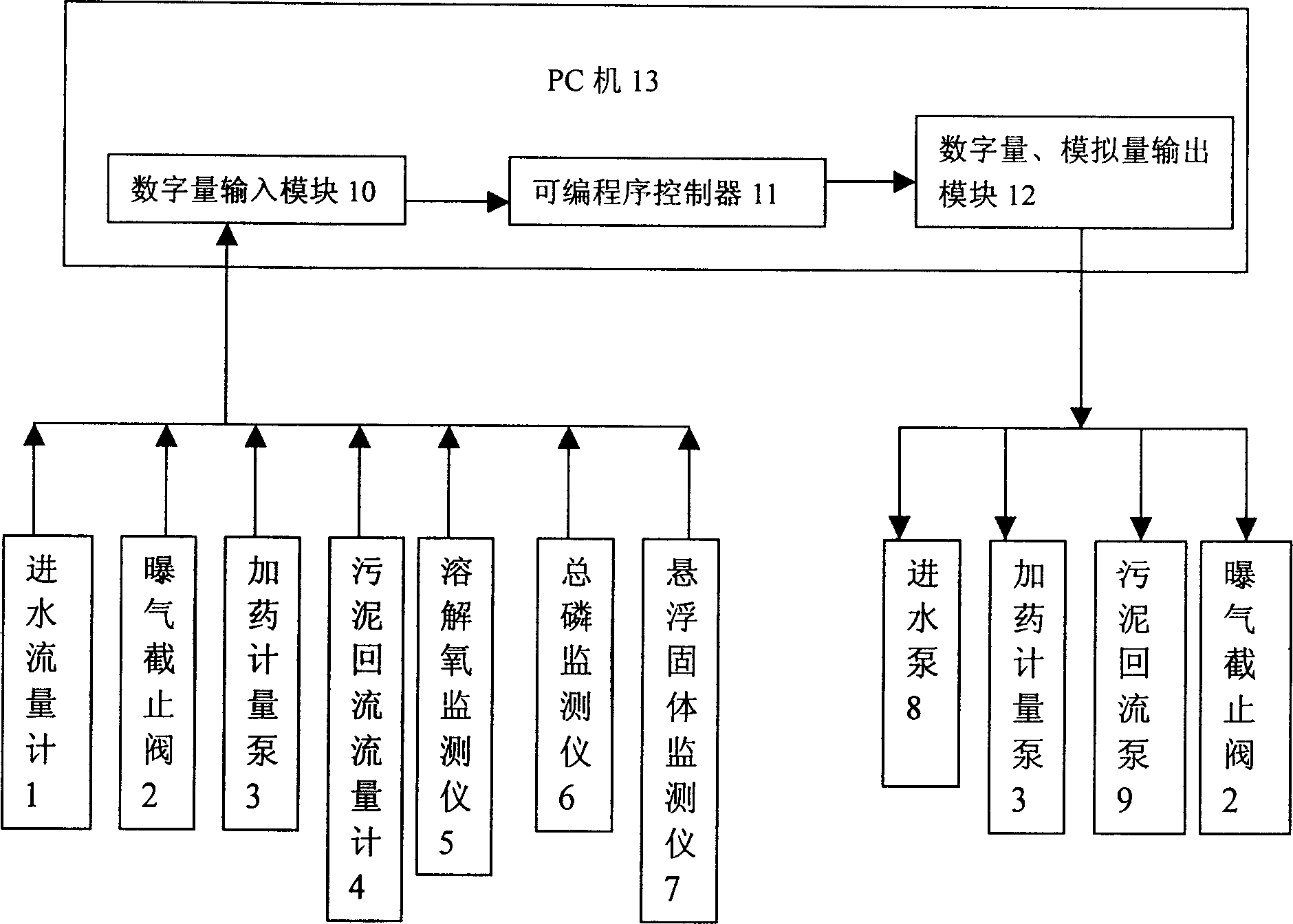
Automatic controlling method and cotnroller for treating urban waste water by chemical biological flocculation
InactiveCN1583592ATimely controlSimplify operational complexityWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSuspended particlesAutomatic control
An automatic control equipment for the biochemical flocculating treatment of city sewage features use of PC for in-line monitor and control to whole treating procedure. Its automatic control method features that the total content of P in output water is used as control target for automatically controlling the amount of added chemical, the in-line DO monitor system is used to automatically control the aeration, and the amount of total suspended particles is monitored for automatically controlling the reflux amount of sludge.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
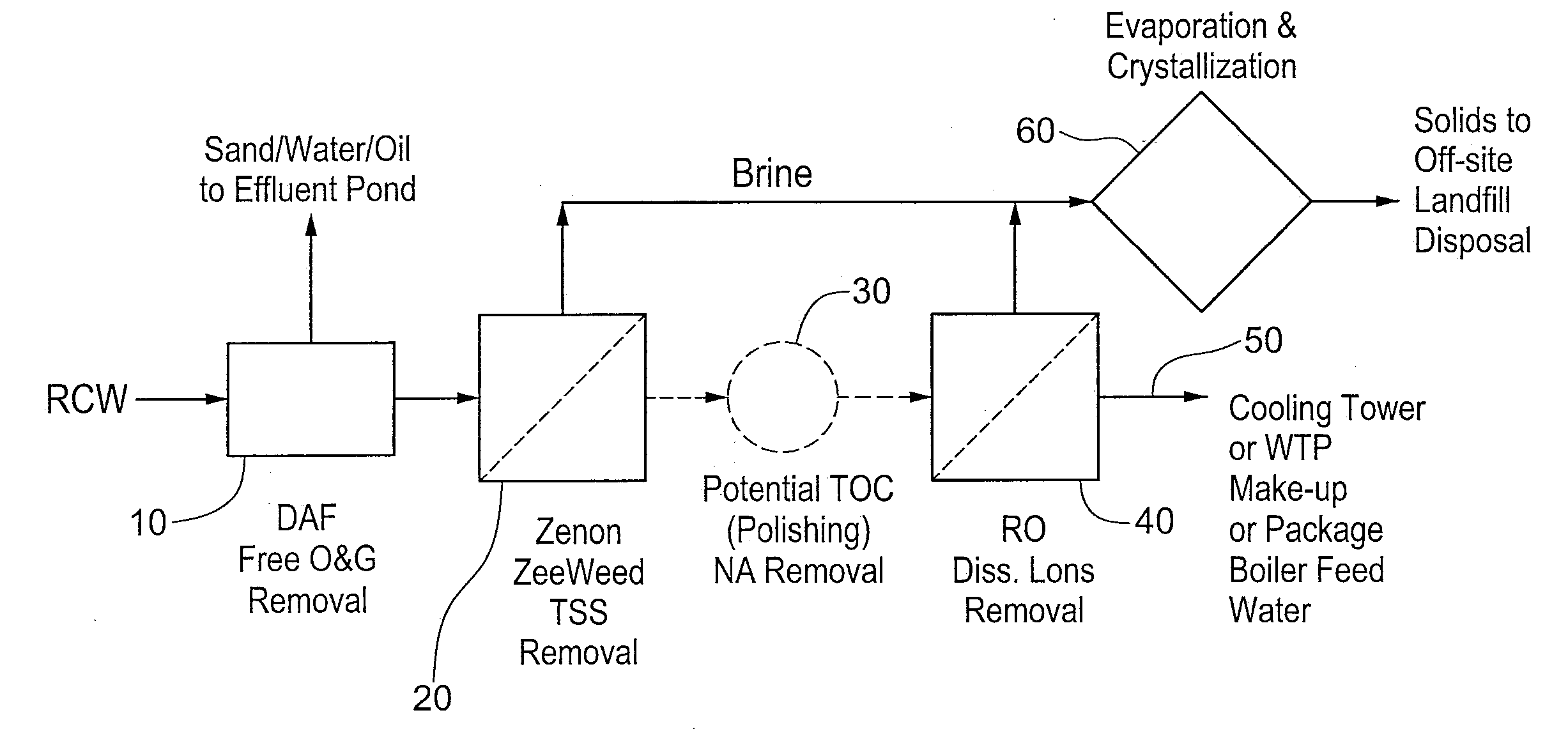
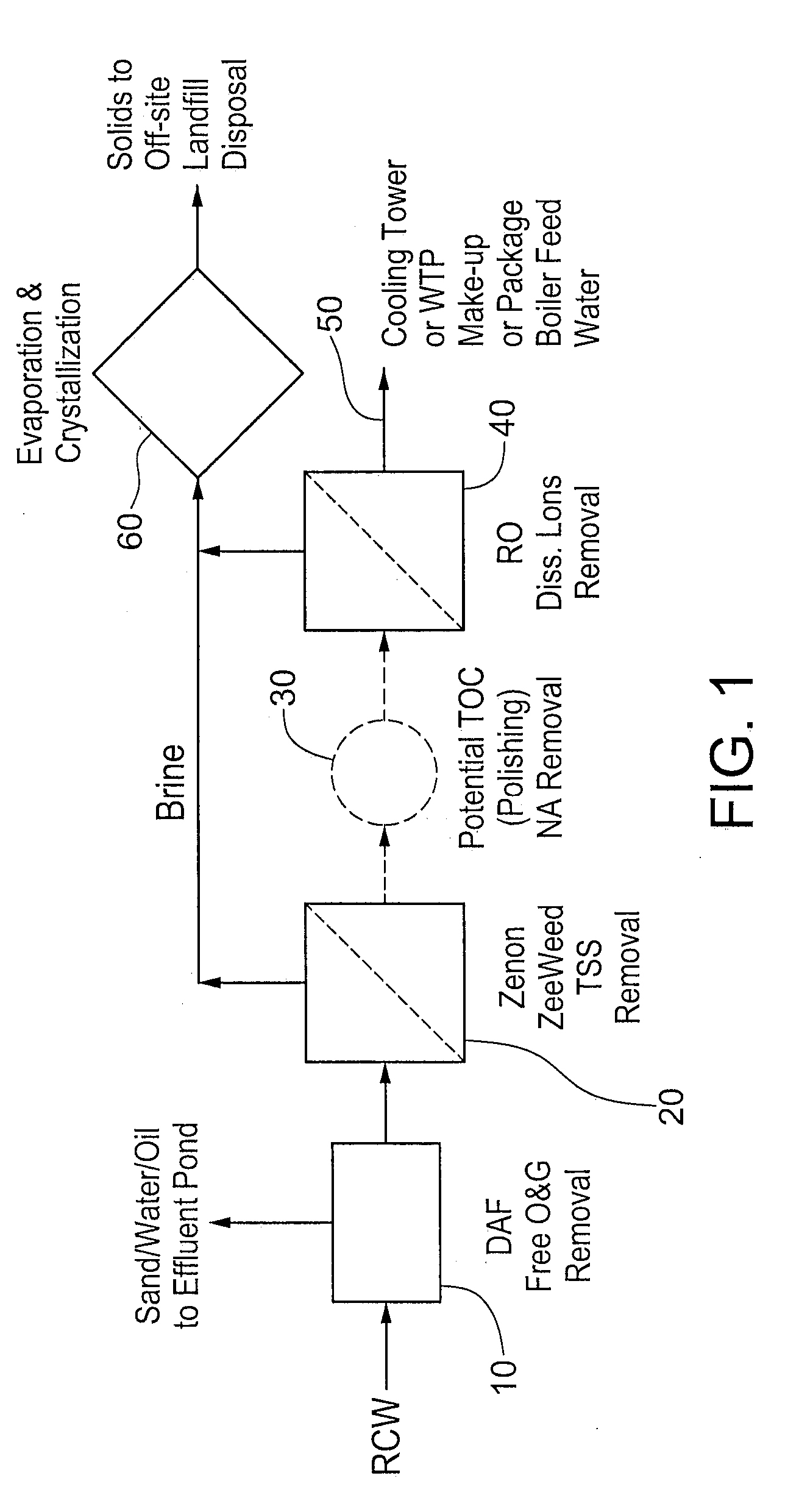
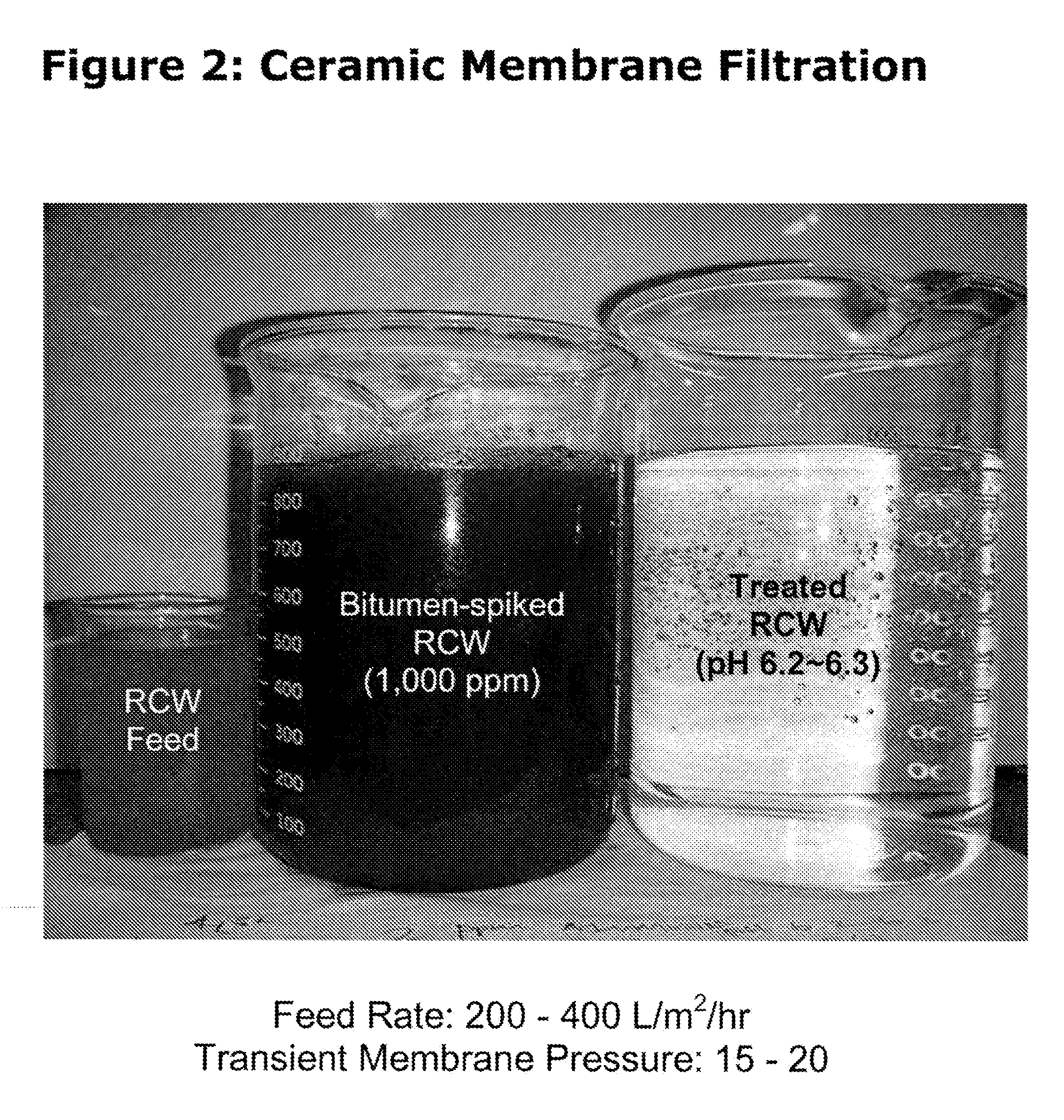
Oil sands process water treatment for reuse
InactiveUS20110127217A1Reduce usageReduce TSSWaste water treatment from quariesSemi-permeable membranesOil and greaseFiltration
A process for treating oil sands process water is provided, comprising removing free oil and grease from the oil sands process water to produce de-oiled process water; reducing the total suspended solids by subjecting the de-oiled process water to filtration using a membrane system to produce filtered process water; and removing dissolved ions such as chloride ions and sulfate ions present in the filtered process water by reverse osmosis to produce a treated water stream and a concentrated salt stream.
Owner:SYNCRUDE CANADA LTD
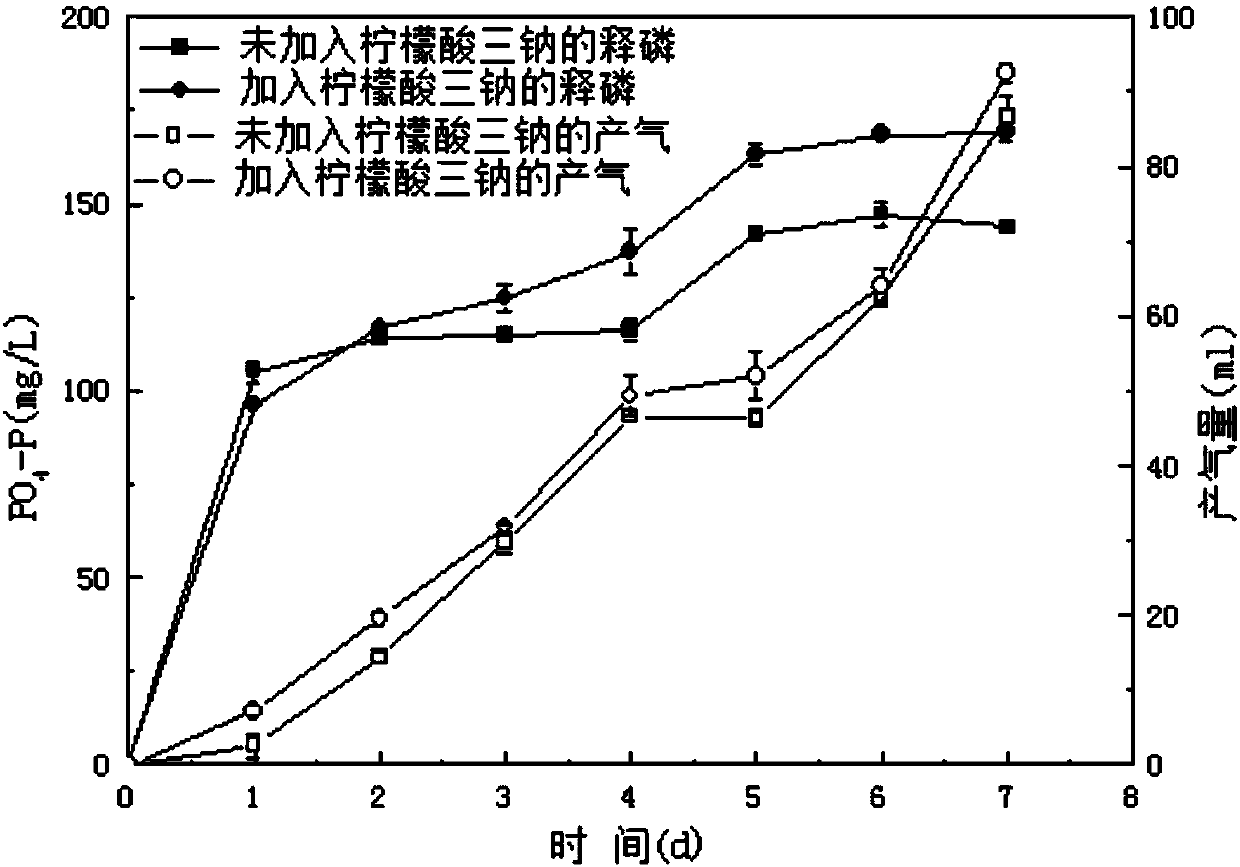
Method for promoting phosphorus release and gas production of phosphate-precipitate-containing sludge under room temperature condition
ActiveCN108046557AIncrease phosphorus release rateIncrease methane productionWater contaminantsWaste based fuelPhosphateSludge
The invention relates to a method for promoting the phosphorus release and the gas production of phosphate-precipitate-containing sludge under a room temperature condition. The method comprises: placing phosphate-precipitate-containing sludge in a reactor, carrying out static precipitation at a room temperature, and discharging the supernatant to obtain concentrated mixed sludge; adding trisodiumcitrate according to the total suspended solid content of the sludge, sealing the reactor, and carrying out anaerobic fermentation for more than 7 days under a room temperature condition, wherein thephosphorus release rate of the sludge can be increased, and the anaerobic fermentation of the sludge can be promoted so as to produce acid and methane. Compared to the method in the prior art, the method of the present invention has the following characteristics that the phosphorus release in the phosphate-precipitate-containing sludge can be promoted sp as to improve the recovery rate of the phosphorus resource at the late stage and promote the anaerobic fermentation of the sludge to produce acid and gas, and achieve the resource utilization of the residual sludge, and the operation is performed at the room temperature, such that the economic cost is low.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Calculation method of performance evaluation index of sponge city based on measured value
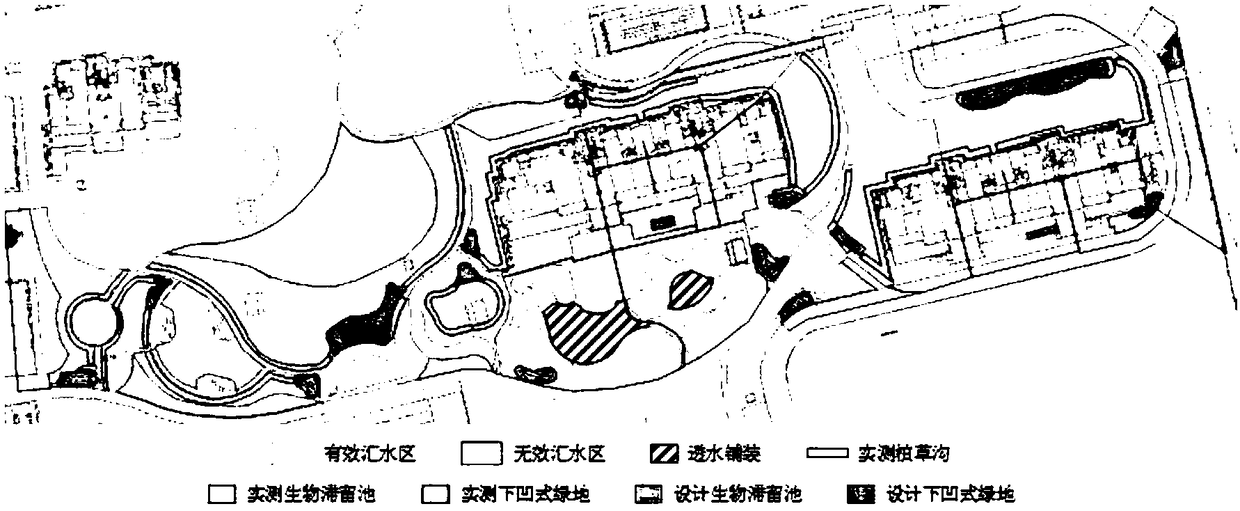
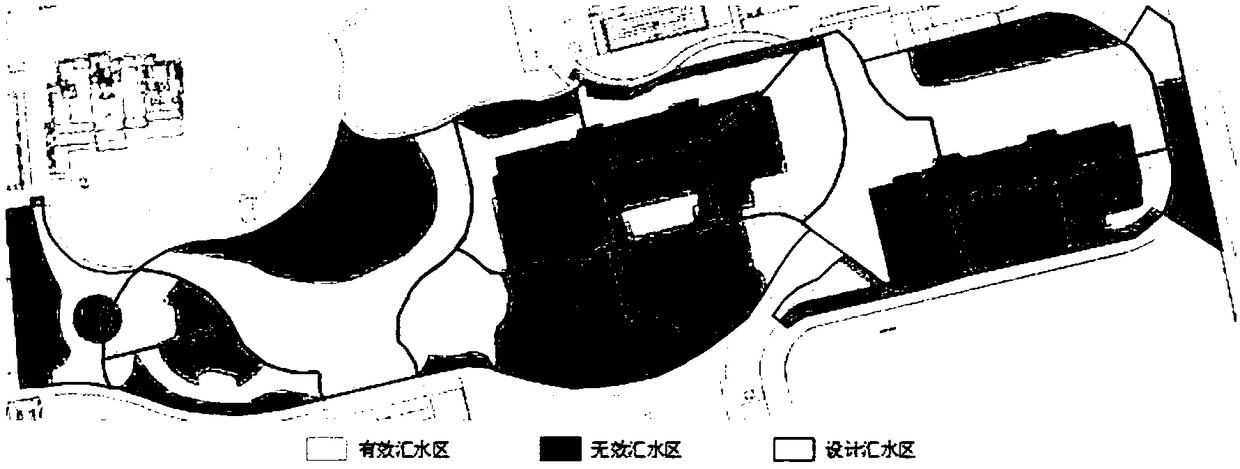
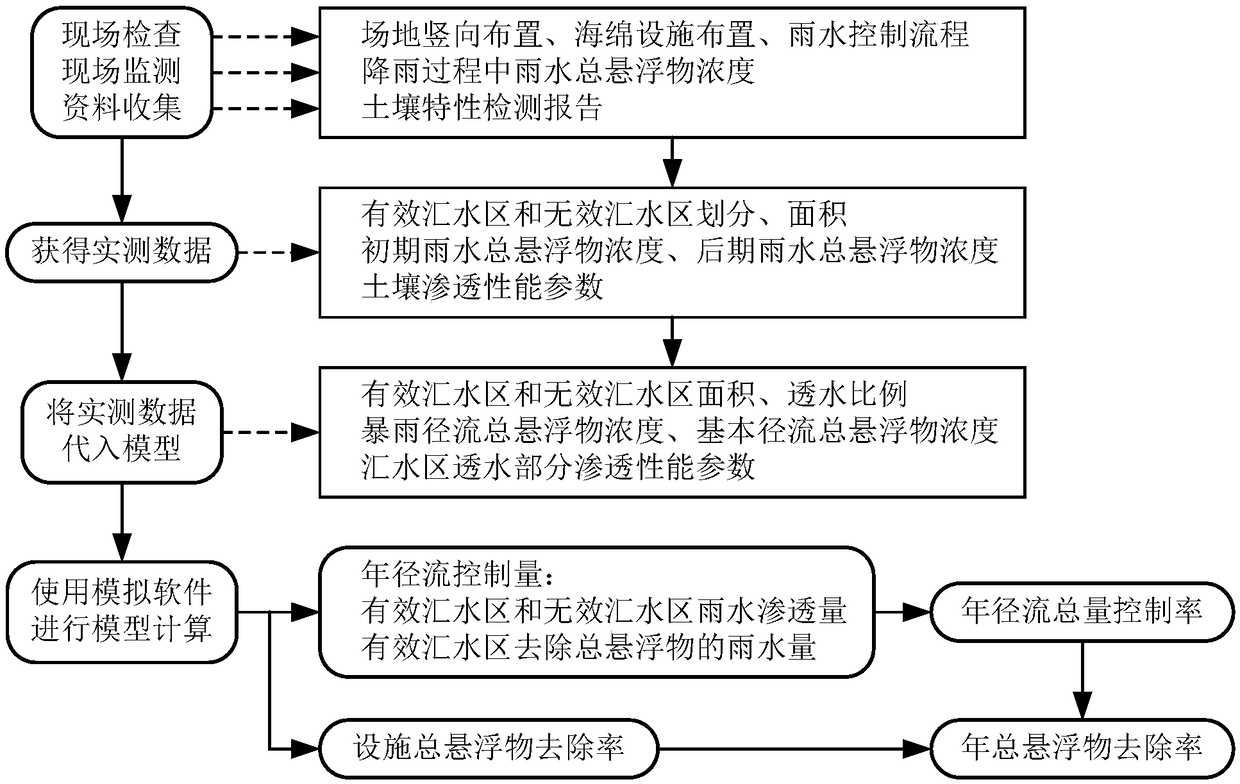
ActiveCN109409694AAccurate assessmentPromote improvementClimate change adaptationResourcesSite monitoringControl flow
The invention discloses a method for calculating the performance evaluation index of sponge city based on the measured value of the plot. Firstly, the site vertical arrangement, the sponge facility arrangement and the rainwater control flow field inspection are carried out, and the concentration of the total suspended solids of the initial and later rainwater runoff and the actual soil permeability parameters are obtained through the on-site monitoring and the actual data collection. Rezoning catchment zones; the topological structure model between catchment area, sponge facility and drainagenode is established, and the effective catchment area, ineffective catchment area, permeability ratio, initial runoff total suspended solids concentration, later runoff total suspended solids concentration and soil permeability parameters are substituted into the rainfall-flood model software. The operation model obtains the annual runoff control quantity and the facility annual total suspended matter removal rate, and then calculates the annual runoff total amount control rate and the annual total suspended matter removal rate. The invention can ensure the accurate evaluation of the performance evaluation index of the land sponge city, and is beneficial to the improvement of the land sponge city.
Owner:KUNSHAN CONSTRUCT ENG QUALITY TESTING CENT +1
Sludge anaerobic fermentation treatment method synchronously enhancing acid production and phosphorus removal
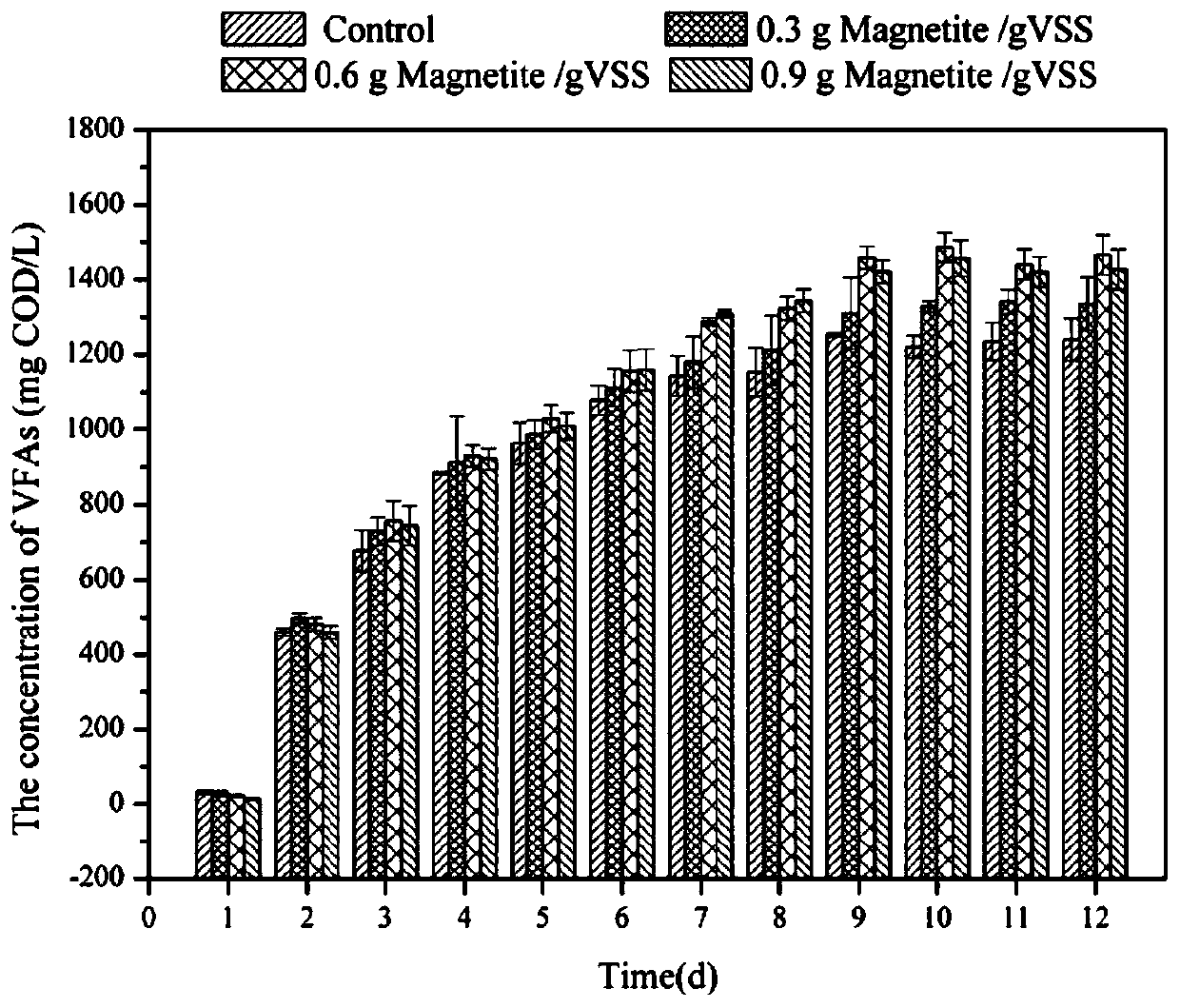
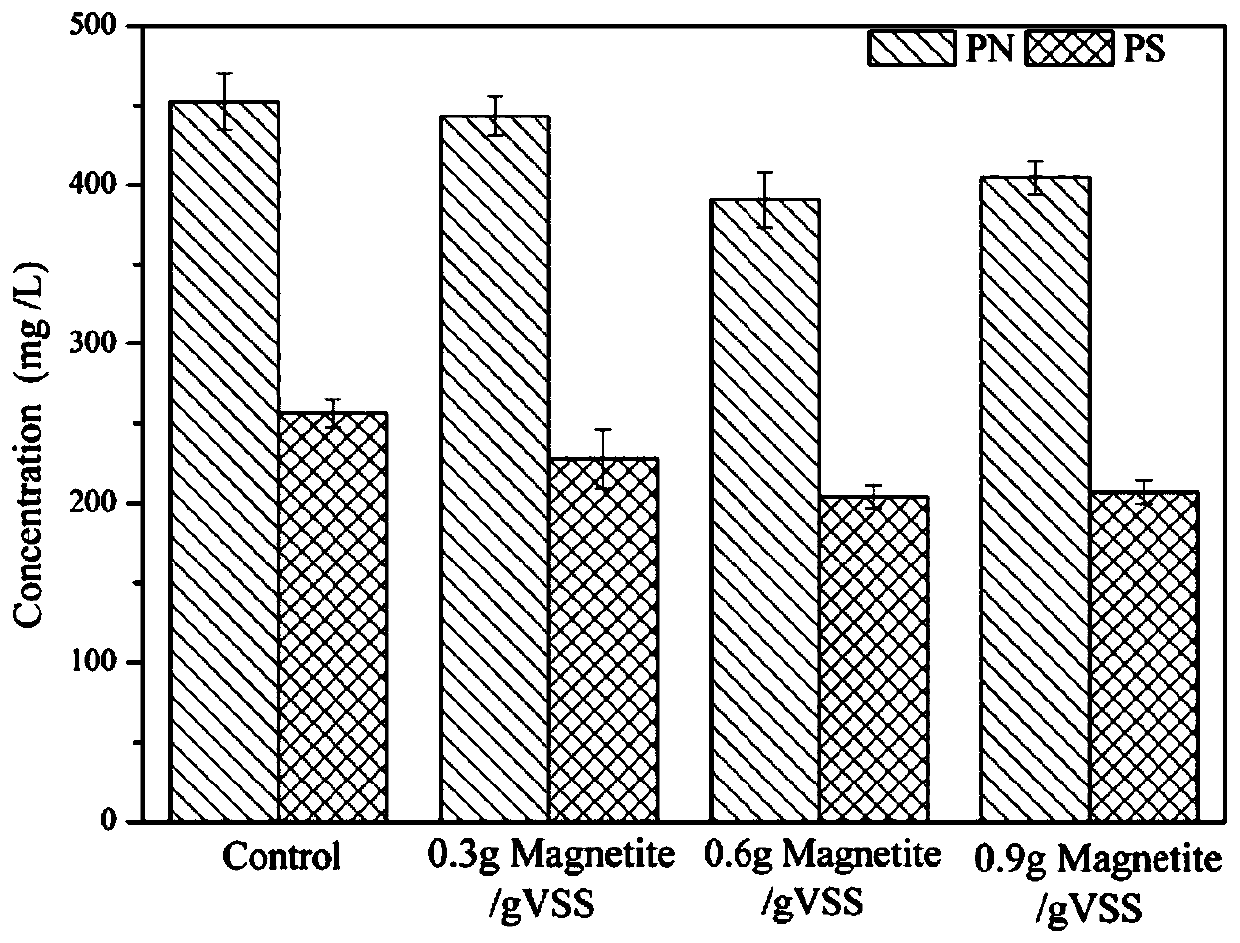
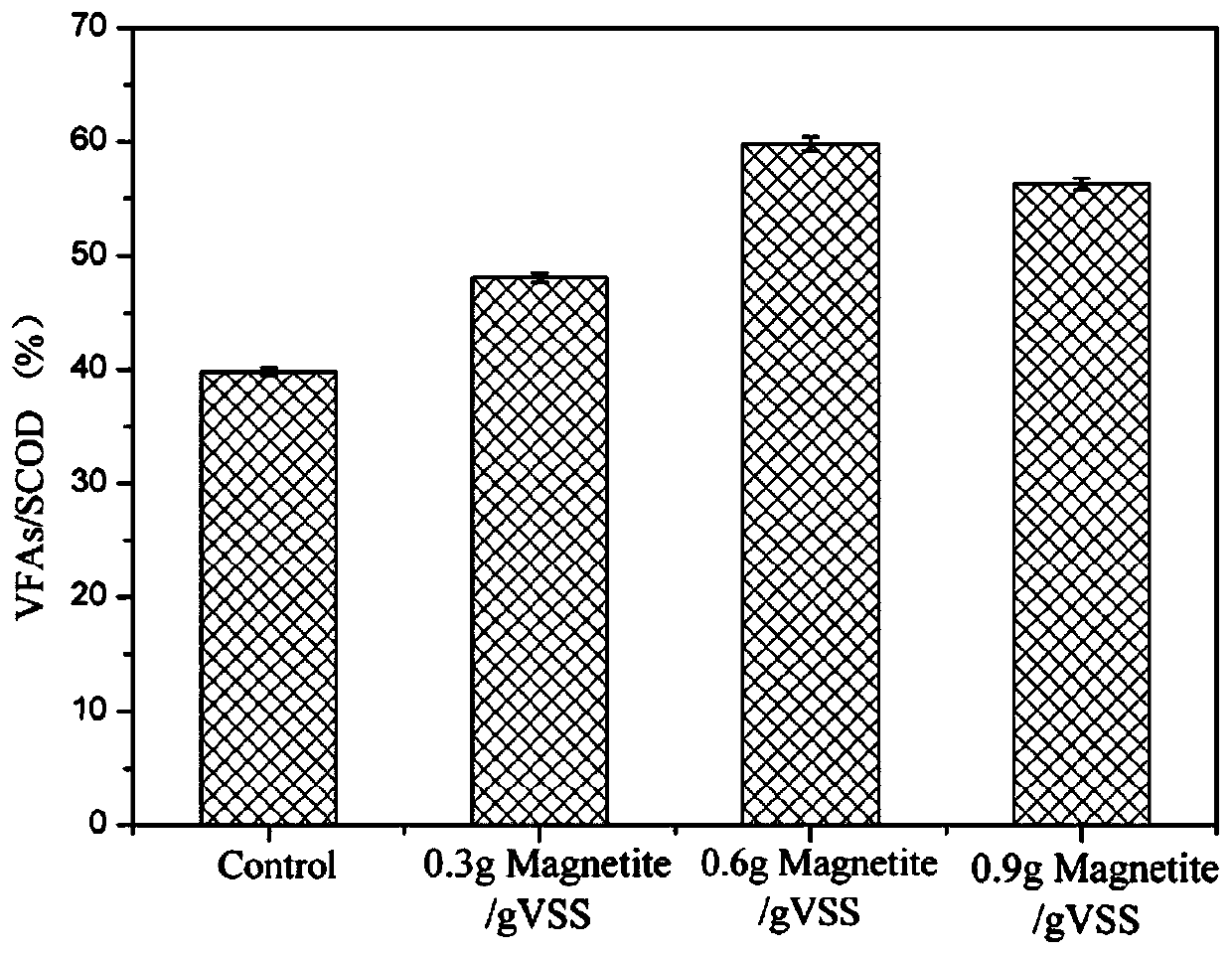
ActiveCN110066082APromote accumulationPromote acid production by anaerobic fermentationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater treatment parameter controlMagnetiteVolatile suspended solids
The invention discloses a sludge anaerobic fermentation treatment method synchronously enhancing acid production and phosphorus removal, and belongs to the field of sludge and sewage treatment. The method includes the steps that (1) excess sludge is added to an anaerobic reaction system, wherein the concentration of total suspended solids (TSS) of the excess sludge is 10000-15000 mg / L, and the concentration of volatile suspended solids (VSS) is 6000-9000 mg / L; (2) the pH value of the excess sludge is adjusted to be 10+ / -0.1 with a sodium hydroxide solution; magnetite is added to the excess sludge with the addition amount of the magnetite being 0.3-0.9 g / gVSS; after air in a reactor is removed, the reactor is sealed, anaerobic fermentation is carried out for 10-15 days in the stirring state, and the pH of the excess sludge is maintained at 10+ / -0.1 all the time in the stirring fermentation process. Compared with a simple alkaline condition, under the condition of the method, the accumulation of short-chain fatty acid is increased by 20% or above, and acid production by anaerobic fermentation of the excess sludge is effectively promoted; besides, the content of orthophosphoric acid in excess sludge fermentation liquor is reduced by 10% or above, and the influence of the fermentation liquor as a carbon source on biological phosphorus removal is alleviated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Anaerobic lagoon or tank design for eflluent carbon to nitrogen ratio control
ActiveUS20130327710A1Reduce concentrationHigh BOD/TKN ratioWater treatment parameter controlWater cleaningOil and greaseWater treatment system
An anaerobic lagoon wastewater treatment system, which includes a plurality of wastewater treatment zones. The treatment zones are either formed by providing a plurality of separate lagoons or by providing one or more partitioning elements within one lagoon. One or more treatment zones may also be provided in the form of a tank. The first wastewater treatment zone in the direction of wastewater flow has a smaller volume than the second wastewater treatment zone. Further, the first wastewater treatment zone achieves a significant reduction in fat, oil and grease removal, as well as in total suspended solids removal, but only a modest reduction in biological oxygen demand. An effluent from the first wastewater treatment zone is mixed with an effluent from the second wastewater treatment zone such that a predetermined ratio of carbon to nitrogen is maintained within the mixture of first and second effluents.
Owner:REID JOHN H
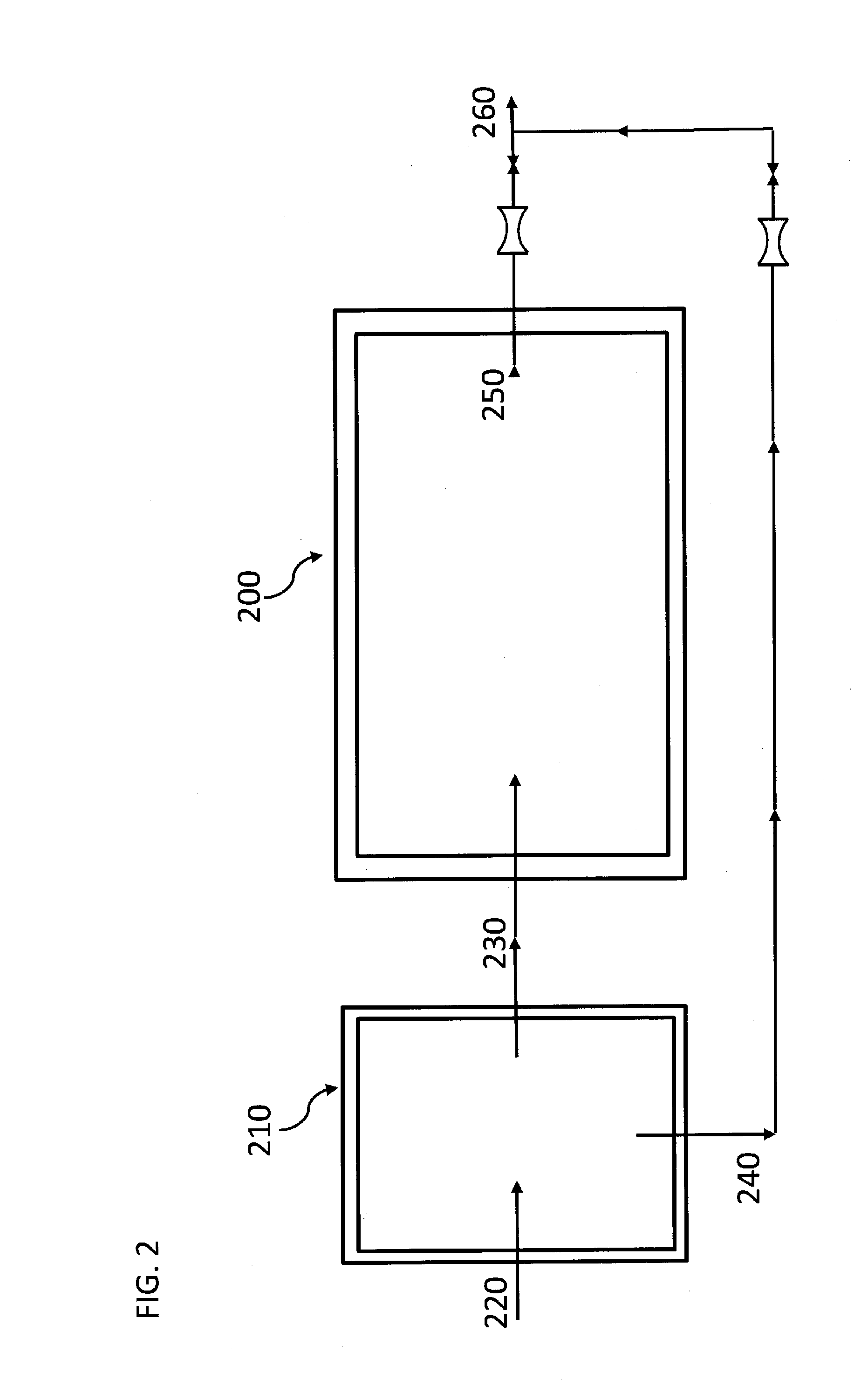
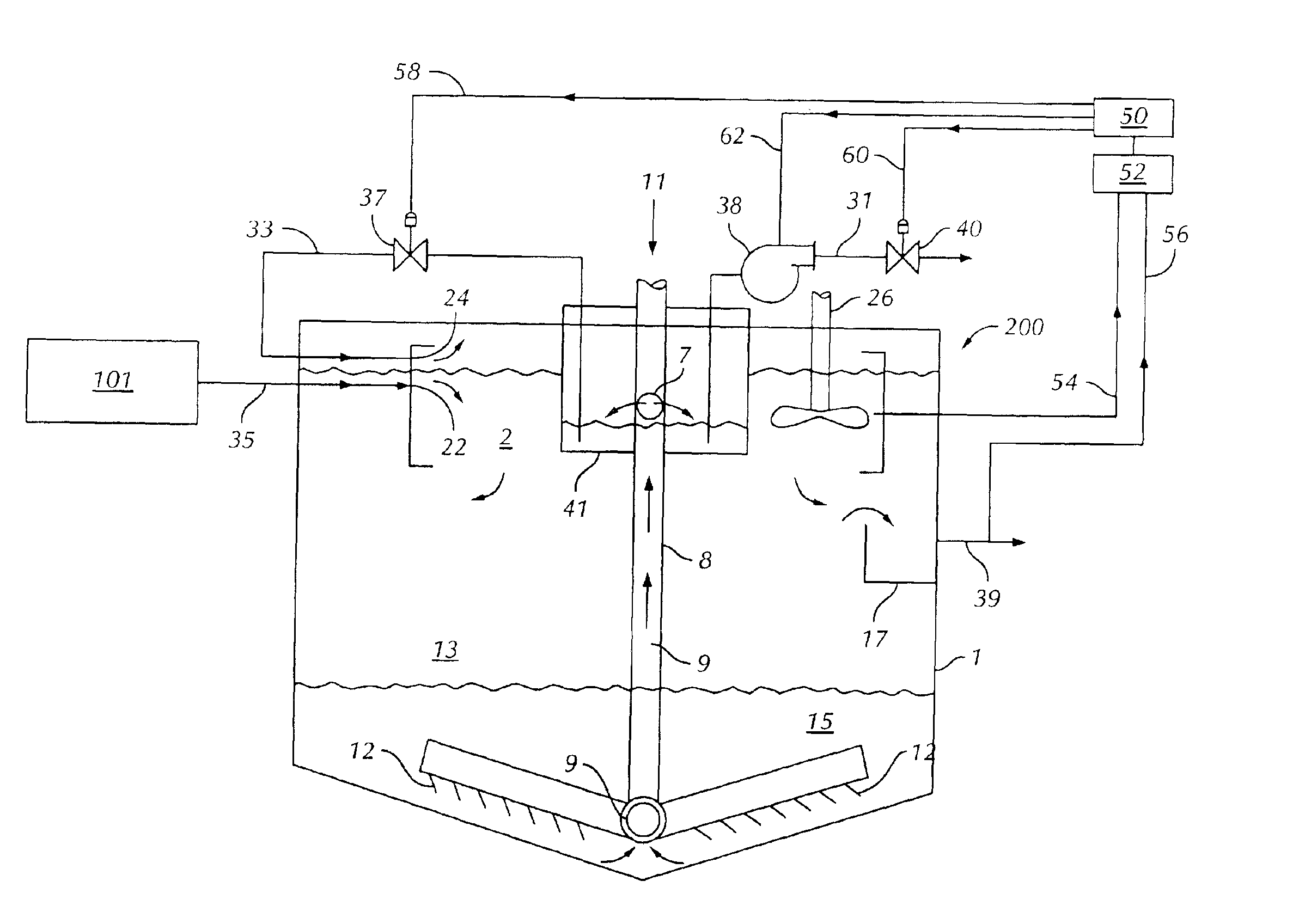
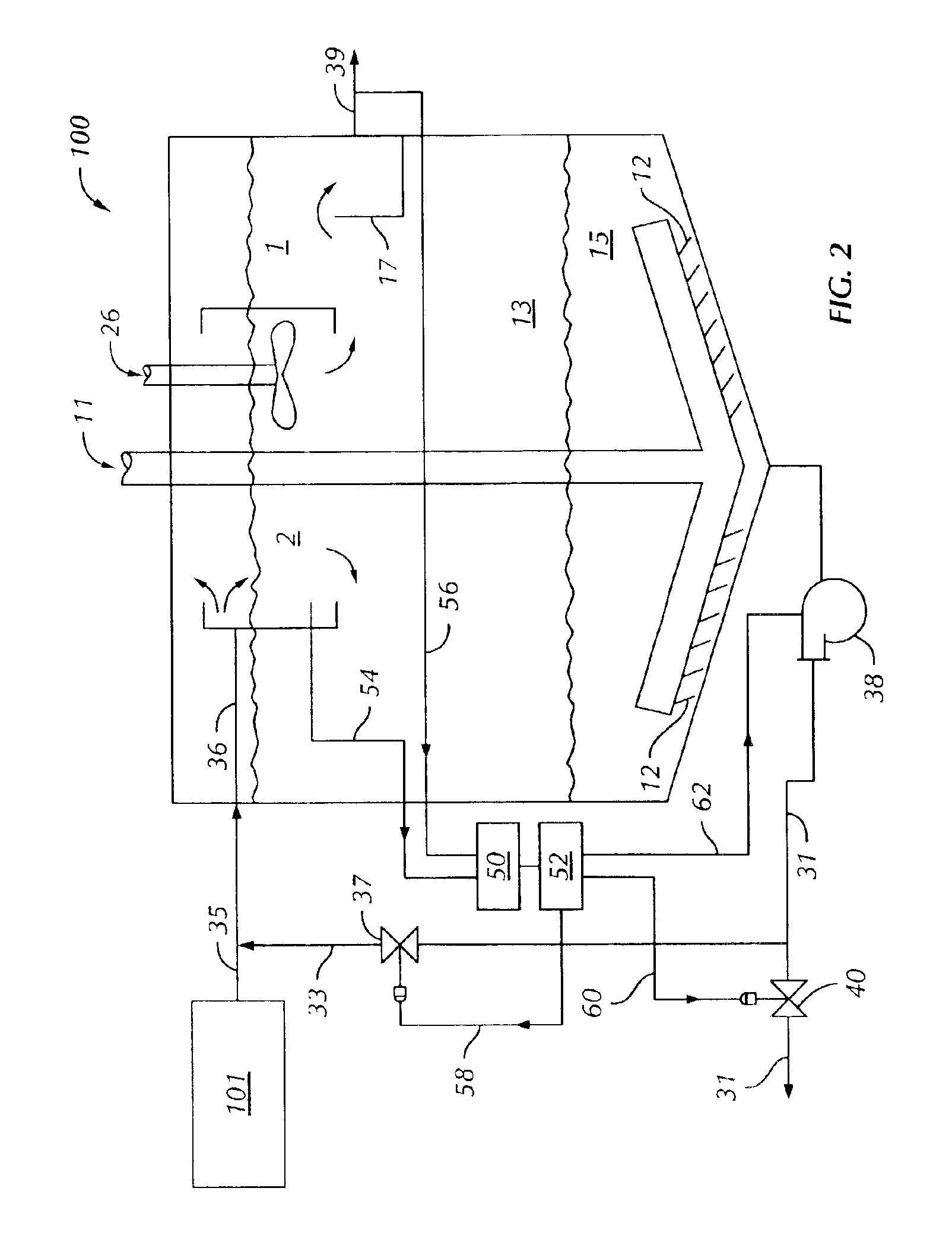
Wastewater clarification methods and apparatus
InactiveUS6878280B2Lower levelTreatment using aerobic processesSettling tanks feed/dischargeWater treatment systemCombined use
The invention relates to a liquid clarifier useful for removing solids suspended in a wastewater stream. Settled biological solids are taken from the clarifier and combined in a mixing chamber with a wastewater stream. The combined liquid is provided to a settling region of the clarifier, and suspended solids settle in a biological solids collection region, from which the solids are taken. Clarified liquid can be withdrawn or permitted to overflow from an outlet region in the settling region of the clarifier. The clarifier can enhance the degree of solids removal from wastewater streams having relatively low total suspended solids values, such as outlet streams from fixed film-type digesters. The clarifier is suitable for use in combination with other components of wastewater treatment systems, and can be included as a module in many kinds of wastewater treatment systems.
Owner:BRENTWOOD INDS
Method for improving phosphorus release rate of iron phosphate-containing sludge during anaerobic fermentation
InactiveCN104609688APrevent re-precipitationIncrease phosphorus release rateWater contaminantsBiological sludge treatmentSludgeIron phosphate
The invention relates to a method for improving the phosphorus release rate of iron phosphate-containing sludge during anaerobic fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: placing concentrated iron phosphate-containing sludge into a reactor; adding a certain amount of Na2S into the reactor according to the total content of suspended solids in the concentrated iron phosphate-containing sludge; closing the reactor for 5-10 days' anaerobic fermentation at 30-40 DEG C, so that a large amount of phosphorus can be released from the iron phosphate-containing sludge generated during chemical phosphorus removal, and especially the release of chemical phosphorus can be promoted. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that the phosphorus release rate of the iron phosphate-containing sludge during anaerobic fermentation can be improved, the release of organics can also be promoted, the phosphorus recovery rate in the later period can be improved, and the sludge can be further recycled and reduced. Meanwhile, the defects that the accumulated concentration of phosphorus in a surplus sludge supernatant obtained according to a pure fermentation method is low, much biological phosphorus is released during anaerobic fermentation according to a pH adjustment method, but the release of chemical phosphorus during anaerobic fermentation according to the pH adjustment method is restricted, and released phosphorus is easy to re-precipitate can be overcome. The method is higher in operability and controllability.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for improving anaerobic fermentation phosphorus release rate of phosphorus-containing chemical-biological mixed sludge
ActiveCN103936249APrevent re-precipitationAvoid corrosionBiological sludge treatmentSludgeResource utilization
The invention relates to a method for improving anaerobic fermentation phosphorus release rate of phosphorus-containing chemical-biological mixed sludge. The method comprises the following steps: placing the phosphorus-containing chemical-biological mixed sludge in a reactor, performing static settling at room temperature for 24h, and discharging supernatant fluid to obtain the concentrated mixed sludge; adding a certain amount of EDTA-2Na according to the content of total suspended solids in the sludge aiming at the chemical-biological mixed sludge produced by using different chemical reagents to remove phosphorus, maintaining the pH value in the anaerobic fermentation process of the mixed sludge at 6.5-7.5, closing the reactor and performing anaerobic fermentation for 5-10 days at the temperature of 30-50 DEG C. According to the method, a large amount of phosphorus in the chemical sludge produced by chemical phosphorous removal is released, the re-precipitation of phosphorous released by anaerobic fermentation of the sludge can be further prevented, and the phosphorous release rate of the mixed sludge can be further improved. Compared with the prior art, by adopting the method provided by the invention, the total phosphorous release rate of the phosphorus-containing chemical-biological mixed sludge can be improved so as to be conductive to improving the recovery rate of later-stage nitrogen and phosphorous resources, and the resource utilization of the remaining sludge can be realized.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Organism-ecology filtration system of purifying rain/sewage and operational method thereof
InactiveCN1927737AReduce areaEasy to useSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentWater savingFiltration
The present invention belongs to the field of rain water / sewage treating environment engineering and ecological engineering technology, and is especially one rain water / sewage purifying biological and ecological filtering system and its operation process. The system consists of biofilters as environment engineering units and ecological filters as ecological engineering units. The biofilters can eliminate organic pollutant, ammonia nitrogen, suspended solid, etc from sewage and needs no aerator. The serially connected ecological filters have high treating effect, front settling tank to reduce the load of the subsequent ecological filters, and plant growing to further purify water. The present invention has the features of obvious water purifying effect, low running cost, environment friendship, water saving, etc. The treated rain water / sewage may be used in irrigation or for other purpose.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anaerobic lagoon or tank design for eflluent carbon to nitrogen ratio control
ActiveUS9005442B2Raise the ratioEasy to controlWater treatment parameter controlWaste water treatment from animal processingOil and greaseWater treatment system
An anaerobic lagoon wastewater treatment system, which includes a plurality of wastewater treatment zones. The treatment zones are either formed by providing a plurality of separate lagoons or by providing one or more partitioning elements within one lagoon. One or more treatment zones may also be provided in the form of an anaerobic tank. The first wastewater treatment zone in the direction of wastewater flow has a smaller volume than the second wastewater treatment zone. Further, the first wastewater treatment zone achieves a significant reduction in fat, oil and grease removal, as well as in total suspended solids removal, but only a modest reduction in biological oxygen demand. An effluent from the first wastewater treatment zone is mixed with an effluent from the second wastewater treatment zone such that a predetermined ratio of carbon to nitrogen is maintained within the mixture of first and second effluents.
Owner:REID JOHN H
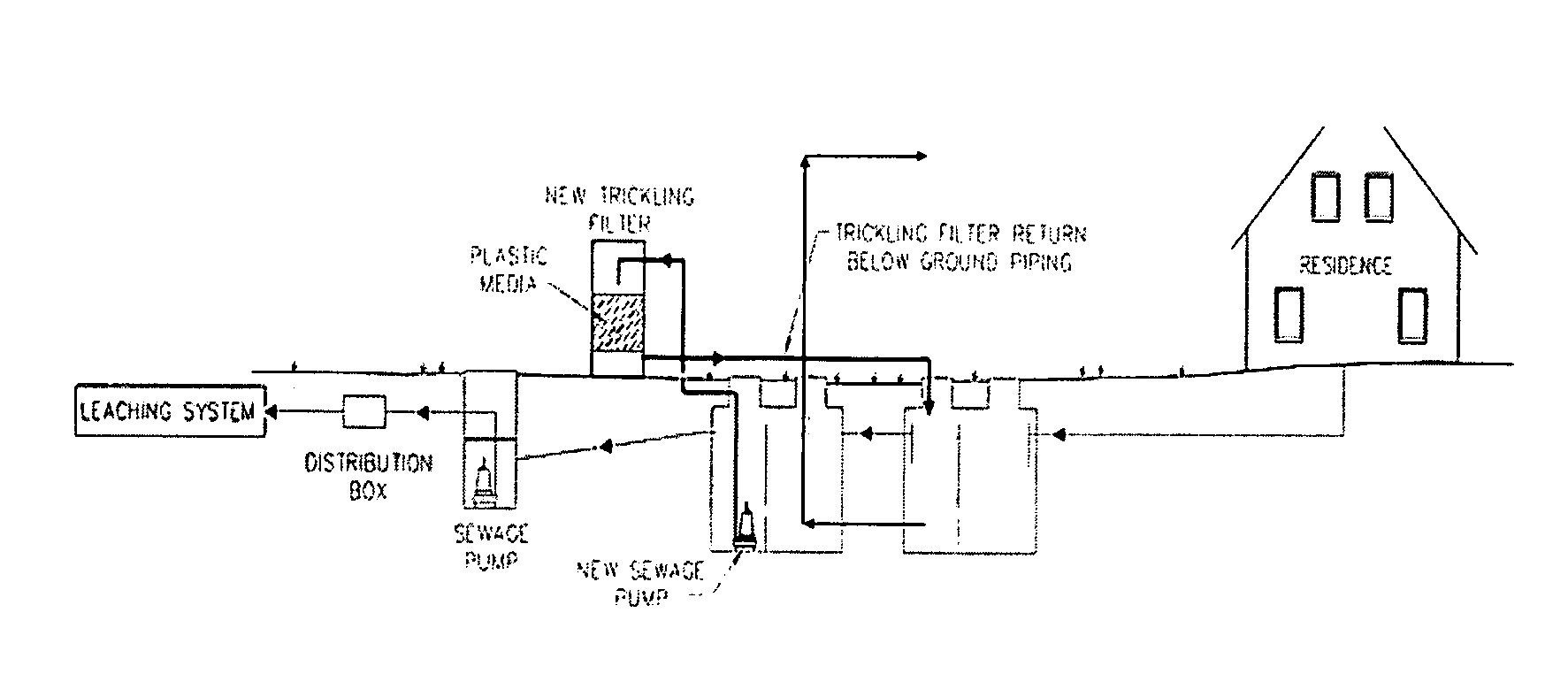
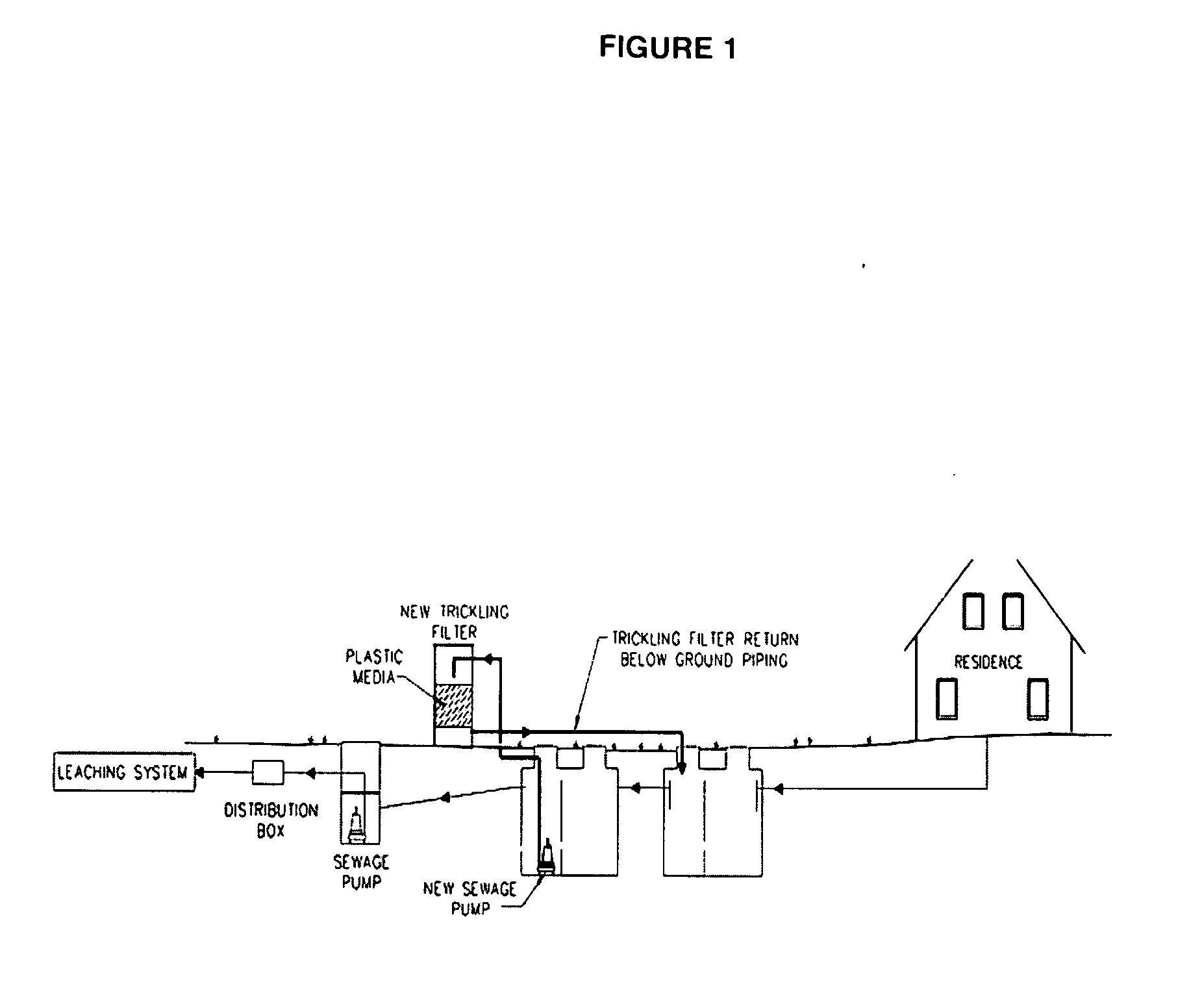
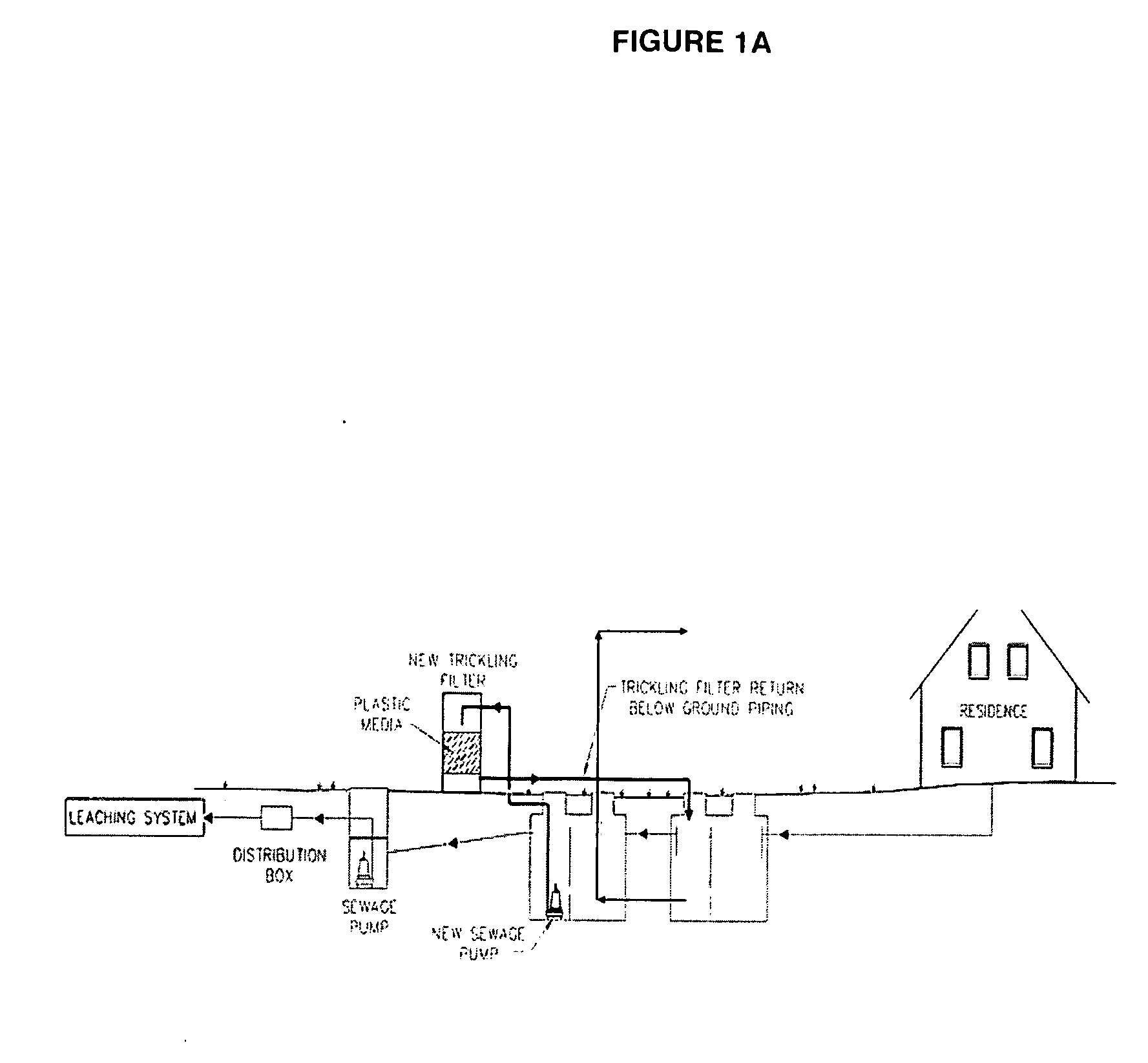
Wastewater Treatment System and Methods
Disclosed are wastewater treatment systems and methods of treating wastewater. In particular, this disclosure provides a method of lowering the biological oxygen demand, total nitrogen, total suspended solids, and phosphorous within wastewater containing human excrements. In addition to improving the quality of the wastewater on a per Liter basis, this disclosure also provides methods and systems that reduce the absolute quantity of total nitrogen, total suspended solids, and phosphorous released into the environment through effluent. The disclosed methods and systems also provide ways of reintroducing water into the environment.
Owner:SOSYST INC
Method for pond culture of cynoglossus semilaevis gunther by means of biofloc technique
InactiveCN105052799AReduce diseaseIncrease productionClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffNitrogen sourceOxygen
The invention discloses a method for pond culture of cynoglossus semilaevis gunther by means of the biofloc technique. The method comprises the steps of biofloc cultivation and breeding. In the biofloc cultivation process, aquaculture water is extracted to a cultivation unit; a carbon source and / or nitrogen source is added to a culture pond to enable the total content of carbon in water to be 5.5-45 mg / L, the total content of nitrogen in water to be 0.55-2.25 mg / L and carbon nitrogen ratio to be 10-20:1; water in the culture pond needs to be fully aerated, dissolved oxygen in water is maintained to be 5.5-8.5 mg / L, pH value is maintained to be 6-8, and temperature is maintained to be over 20 DEG C; when the total suspended solid in water in the culture pond reaches 100-500 mg / L, water is prepared for use. In the breeding process, cynoglossus semilaevis gunther is placed in the cultivation unit with released density being 10-150 pieces / m<2>. Compared with ordinary methods, the method has the advantages that water changing frequency is low, bait feeding amount is small, and obtained cynoglossus semilaevis gunther rarely gets sick and is high in yield.
Owner:DALIAN BAOFA SEAFOOD
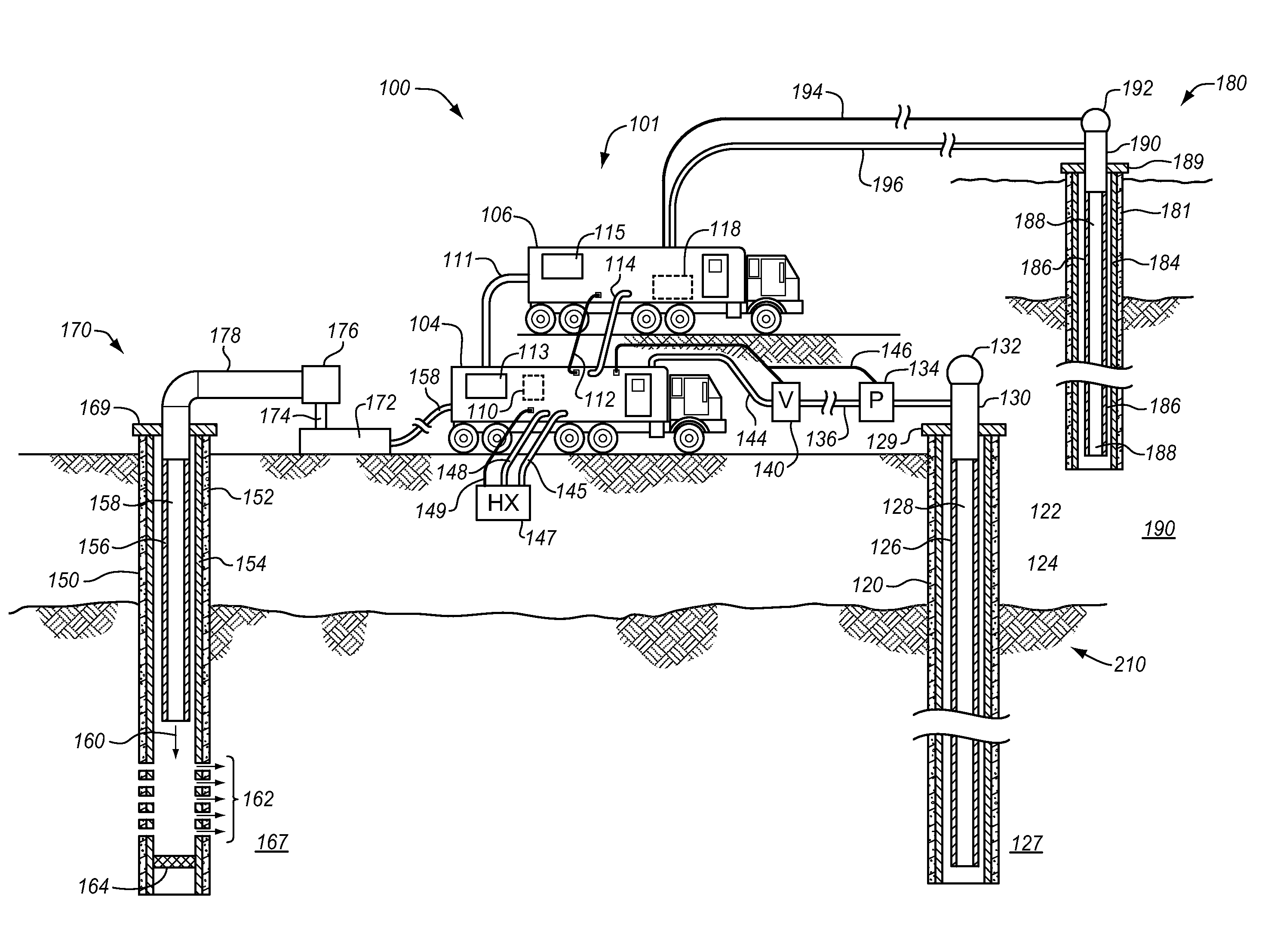
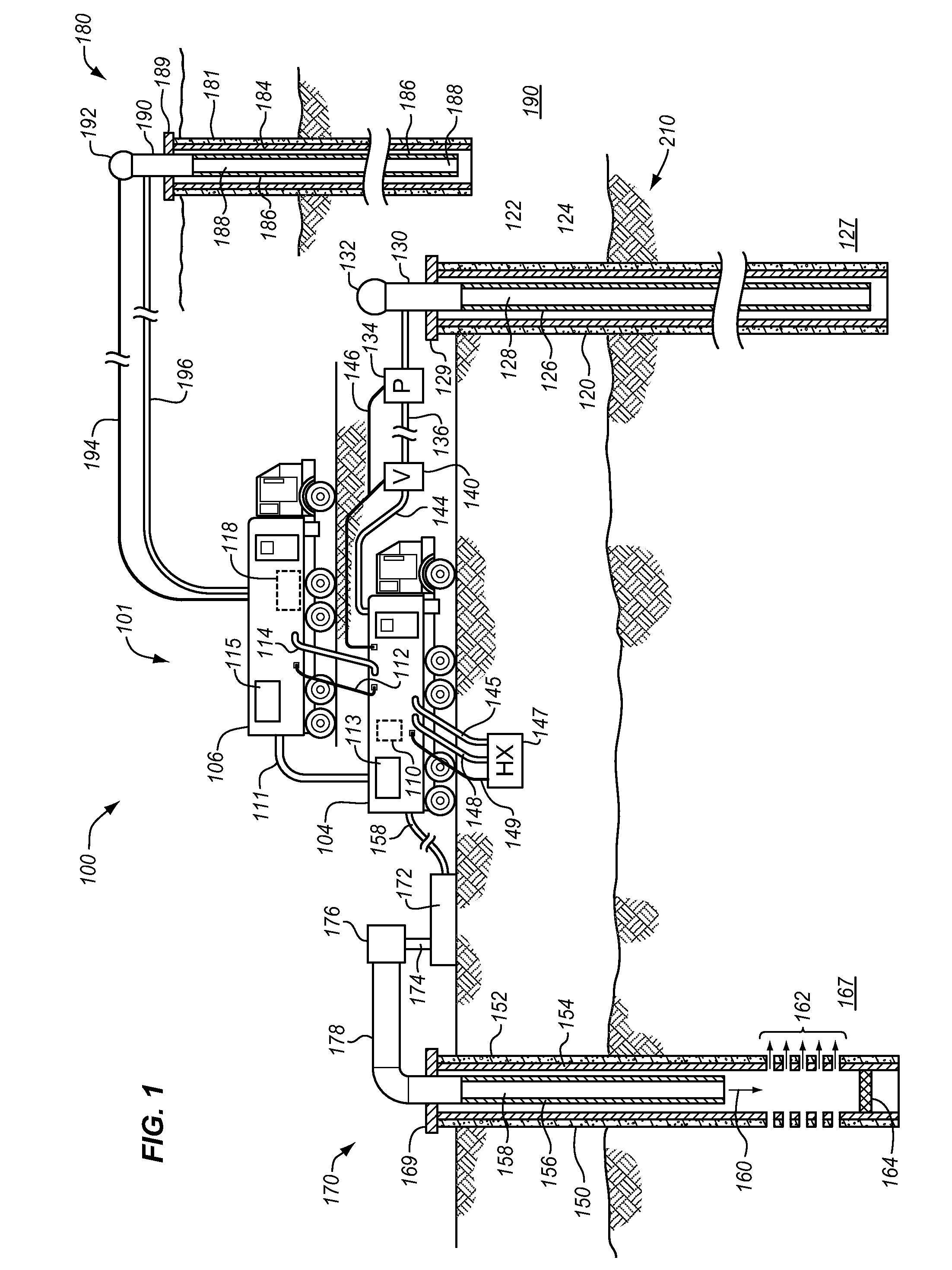
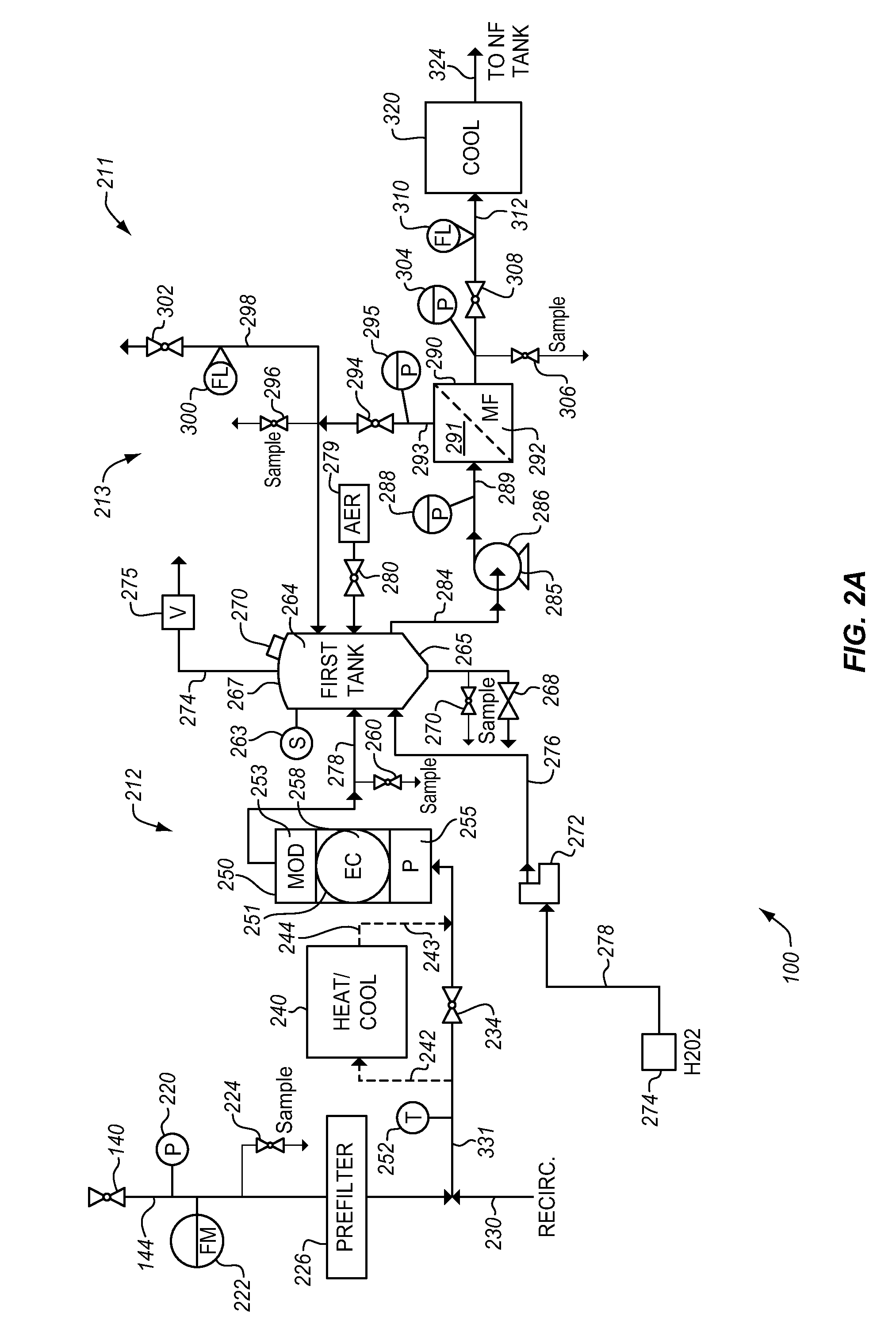
Water conversion system
ActiveUS9322258B2Improve efficiencyReducing sodium brine contentOther heat production devicesGeothermal energy generationElectro coagulationReverse osmosis plant
Owner:ADVANCED AQUA GRP
Domestic sewage treatment device for ship
ActiveCN102417280ASufficient and uniform biological oxidation reactionImprove the efficiency of biochemical reactionsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMultistage water/sewage treatmentStable stateSewage
The invention relates to a domestic sewage treatment device for a ship. An aeration chamber, a precipitation chamber and a membrane chamber are formed in the body of the device respectively; the membrane chamber is a flat cube and is positioned on one side of the body; the aeration chamber and the precipitation chamber form a box type cube which is positioned on the other side of the body; a clapboard of which a half is isolated is arranged in the aeration chamber; the bottom of the precipitation chamber is funnel-shaped, and the top of the precipitation chamber is trumpet-shaped; and a wateroutlet cavity on the upper part of the precipitation chamber is positioned at the central position of the box type cube. Due to the design of the clapboard in the aeration chamber, a plug flow movement locus is formed while sewage is aerated by using an aerator at the bottom of the aeration chamber, so that higher biochemical reaction efficiency is realized for sewage; and by improving the structure of the precipitation chamber, the chemical oxygen demand (COD), biochemical oxygen demand after 5 days (BOD5) and total suspension solid (TSS) value can be lowered effectively. By improving the water outlet cavity of the precipitation chamber, a liquid in the precipitation chamber can keep in stable state no matter which direction the device is inclined in, and the stability of the device is further enhanced.
Owner:安庆泰邦船舶科技有限公司
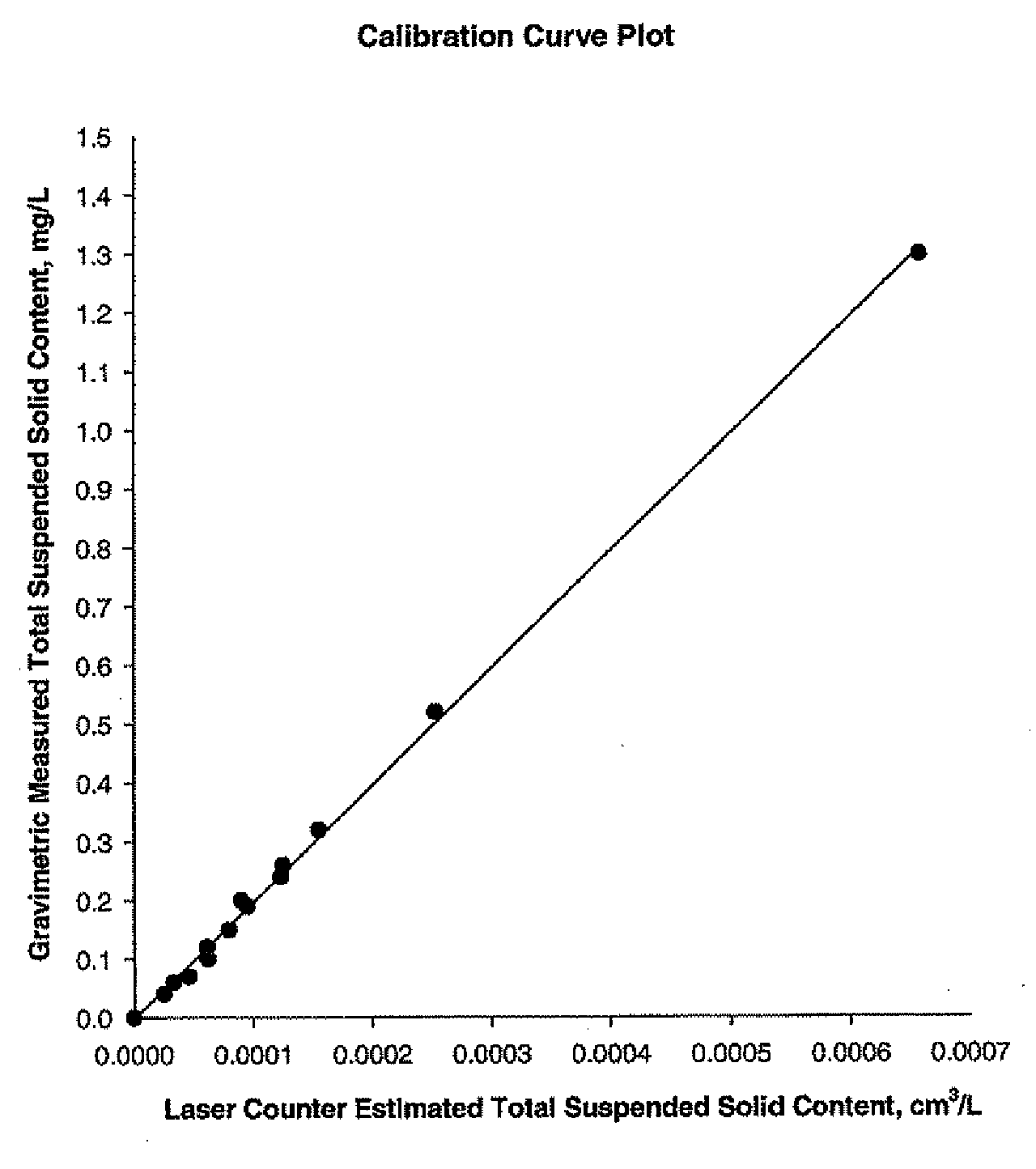
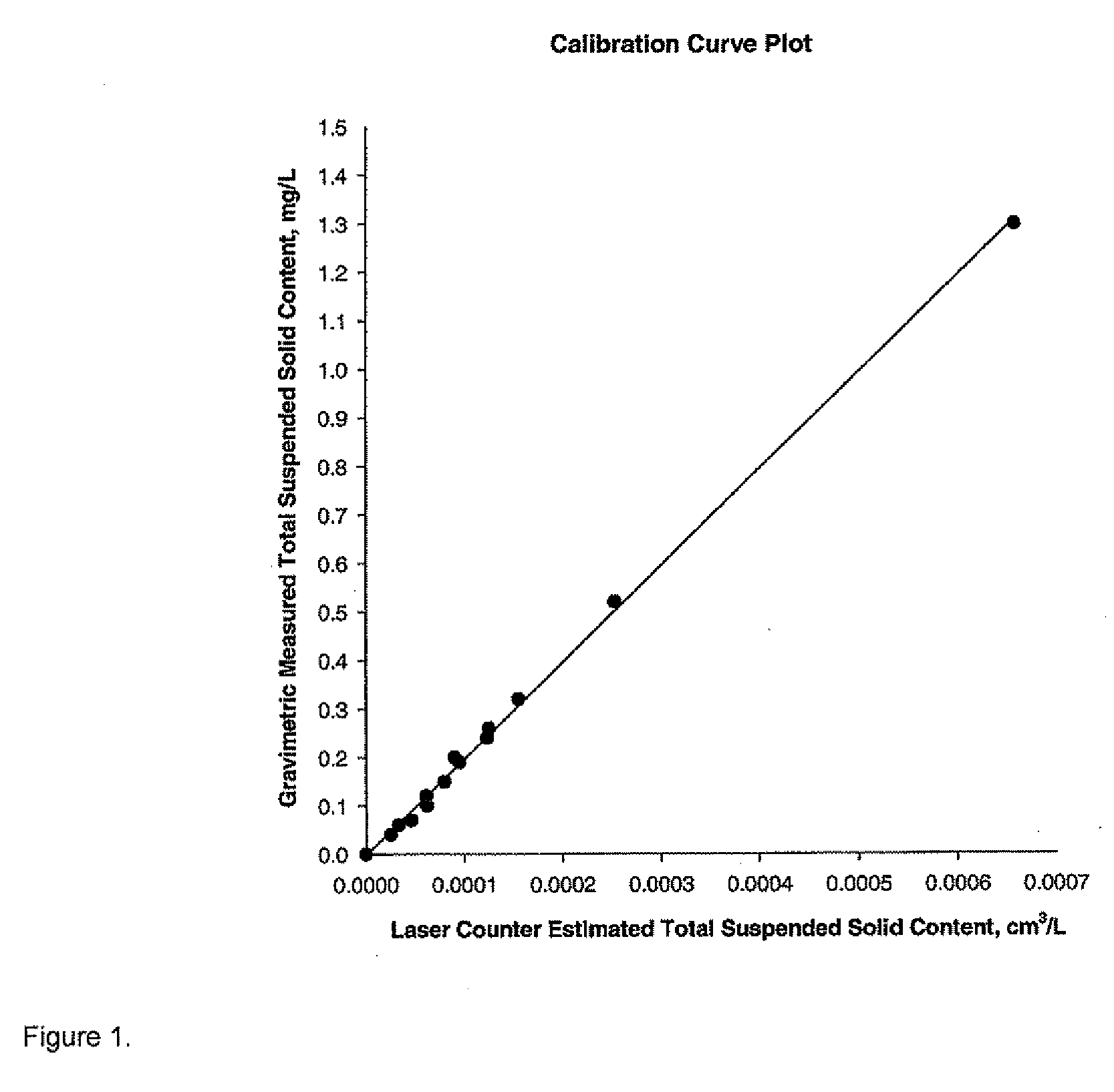
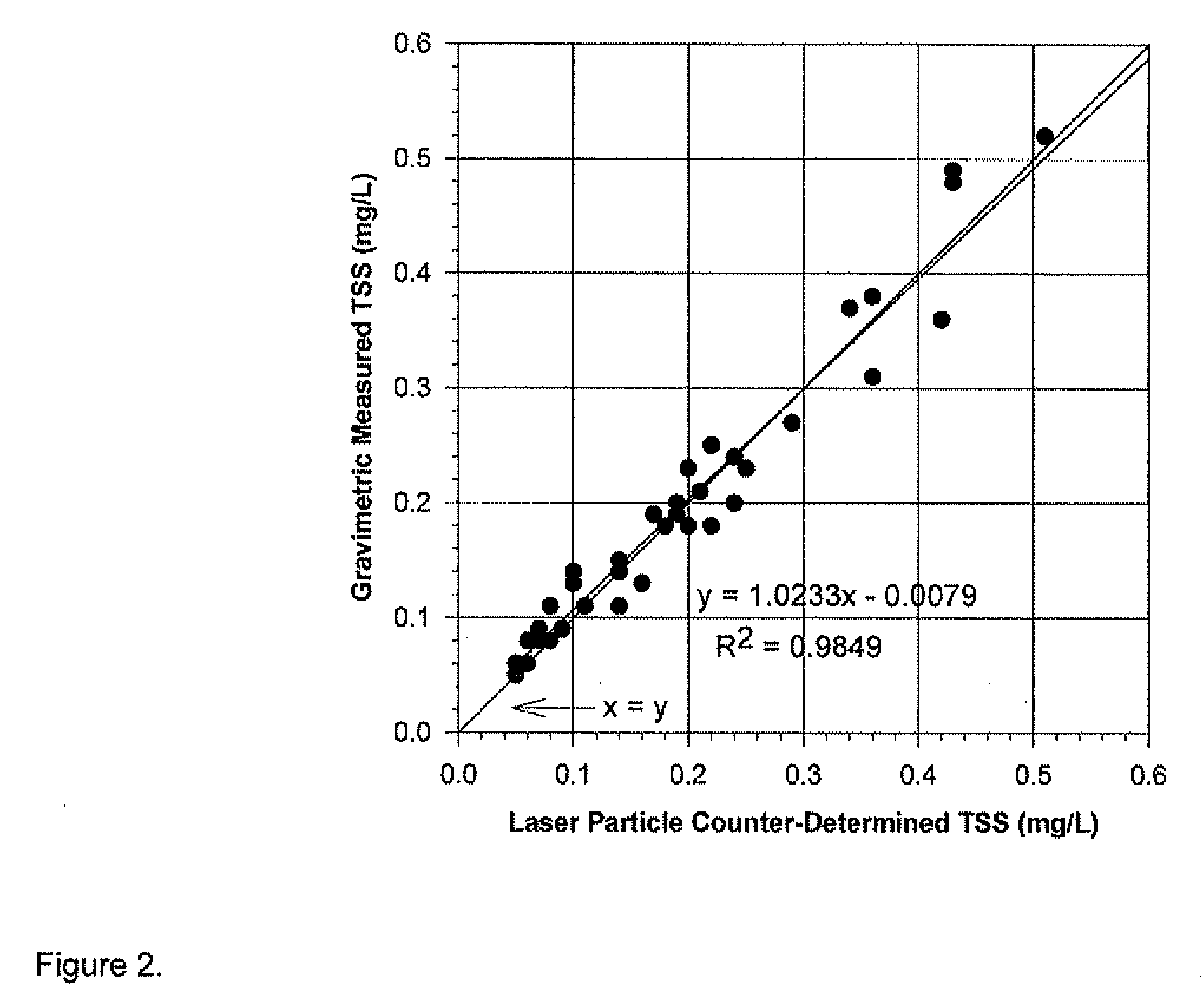
Optical Method for Determination of the Total Suspended Solids in Jet Fuel
ActiveUS20110013184A1Testing/calibration apparatusScattering properties measurementsTotal solid contentQuantitative determination
The invention provides a method for the quantitative determination of total suspended solid particles in a liquid. The method includes providing a liquid sample that includes solids suspended therein, illuminating the solids with a light source, collecting light scattered by the solids and correlating the light scattered by the solids with a total solids content
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Commercial laundry waste water treatment system
InactiveUS20180347100A1Treatment involving filtrationWater distributersAfter treatmentWater treatment system
The present invention provides a method of treating a commercial or industrial laundry wastewater stream. The method and apparatus treats a commercial laundry waste stream from a commercial washing machine or machines wherein the waste includes total suspended solids, chemical oxygen demand, biological oxygen demand, turbidity, and bacteria. The waste stream is transmitted to a first treatment unit that has a membrane filter that filters particles of between about 6 and 40 nanometers. At the first treatment unit, the waste stream is separated into a permeate stream and a retentate component. The retentate component is transmitted to a second treatment unit that filters particles of between about 3 and 10 nanometers. The permeate stream is then transmitted to a permeate holding vessel after treatment in the second treatment unit. The retentate component is placed in a mixing vessel where it is mixed with a polymer to form a solid waste.
Owner:WATER RECOVERY SYST LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com