Patents
Literature
66results about How to "Increase methane production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
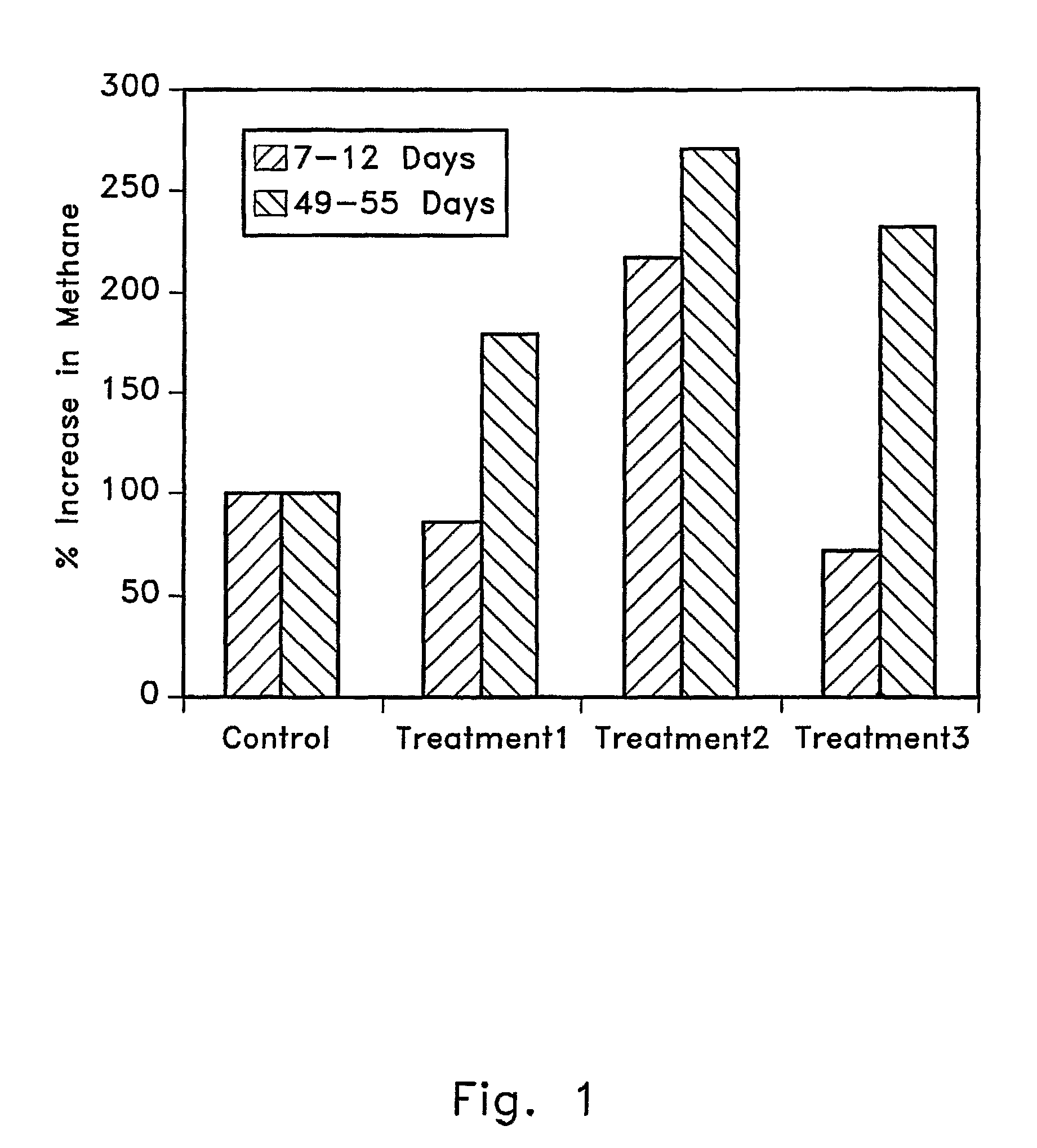
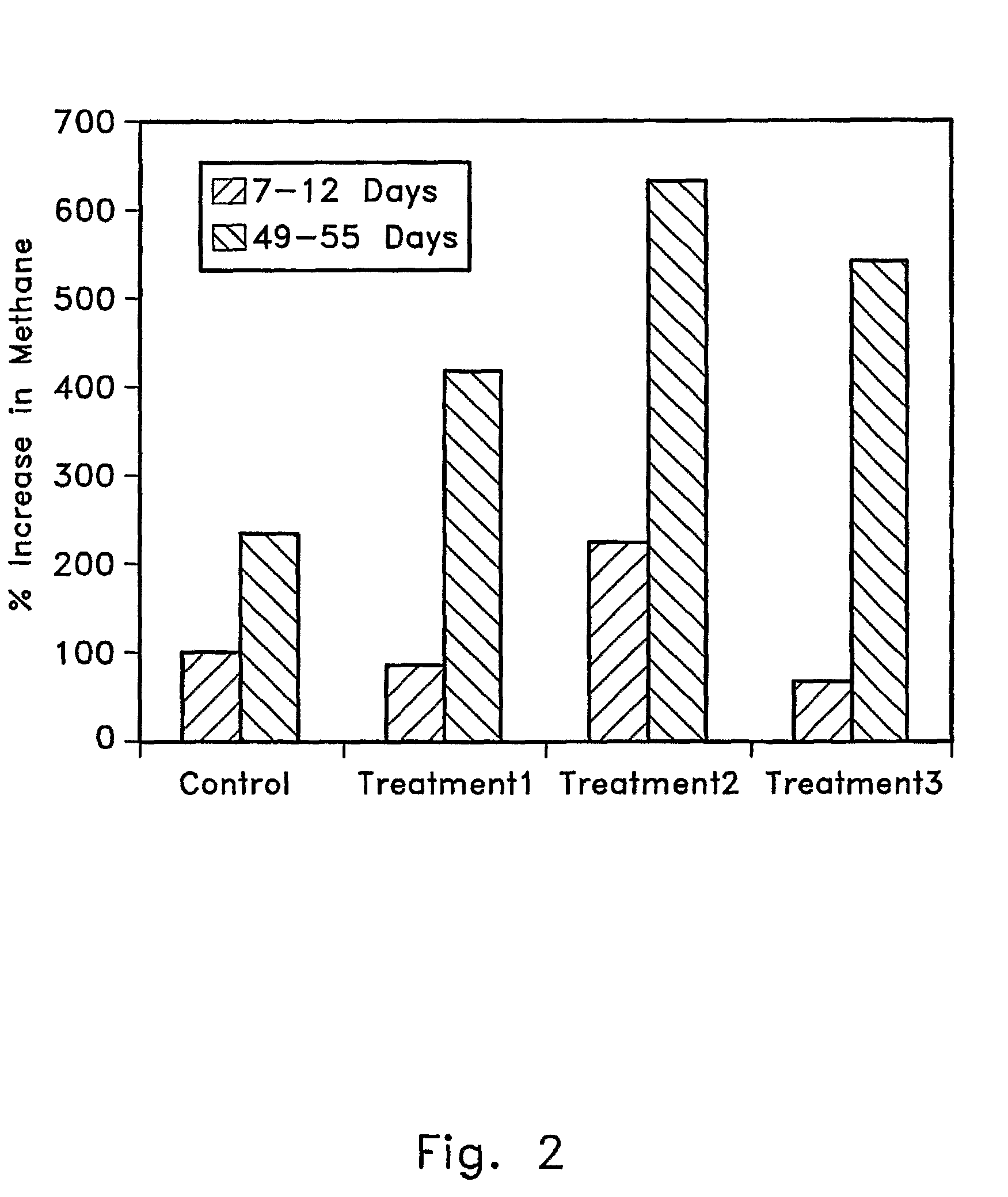
Bio-recycling of carbon dioxide emitted from power plants
InactiveUS20070298478A1Enhance biogas methane productionReduce carbon dioxide emissionsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFermentationFossil fuel
The invention provides a method to decrease emission of carbon dioxide from combustion of fossil fuels or other hydrocarbons and to enhance the efficiency of methane production from anaerobic biodigesters. The invention involves feeding carbon dioxide from the exhaust gas of hydrocarbon fuel combustion to an anaerobic biodigester where biomass is anaerobically fermented to produce methane. Carbon dioxide is an electron acceptor for anaerobic fermentation, and thus some of the carbon dioxide is reduced to methane, which can again be used for fuel. In this way, at least a portion of the exhaust gas CO2 is recycled to form fuel methane instead of being released into the atmosphere. Thus, the net CO2 emission from burning a given amount of fossil fuel is decreased. Adding carbon dioxide to an anaerobic fermentation also increases the efficiency and amount of methane production in the fermentation.
Owner:VIRESCO AD LLC
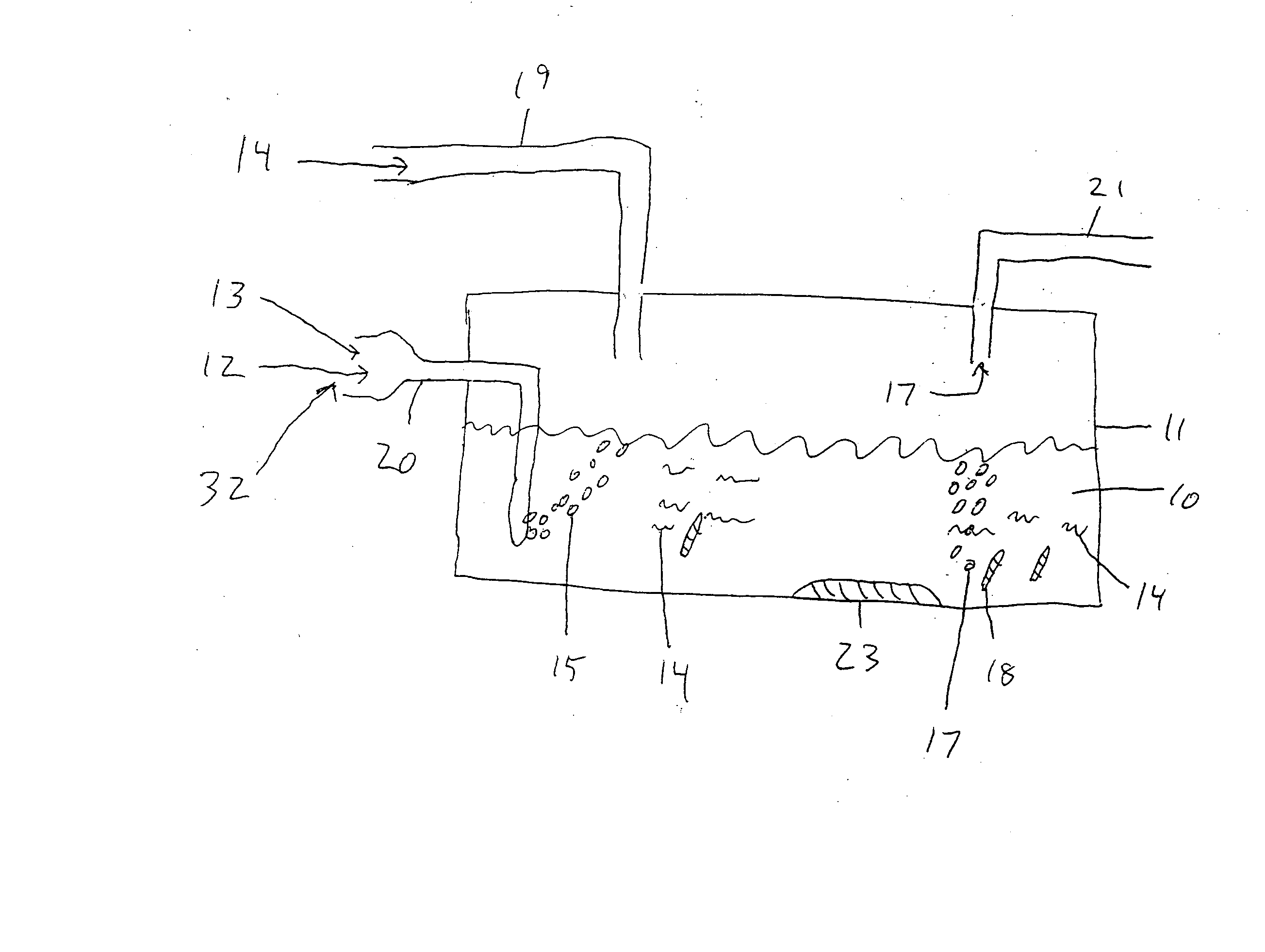
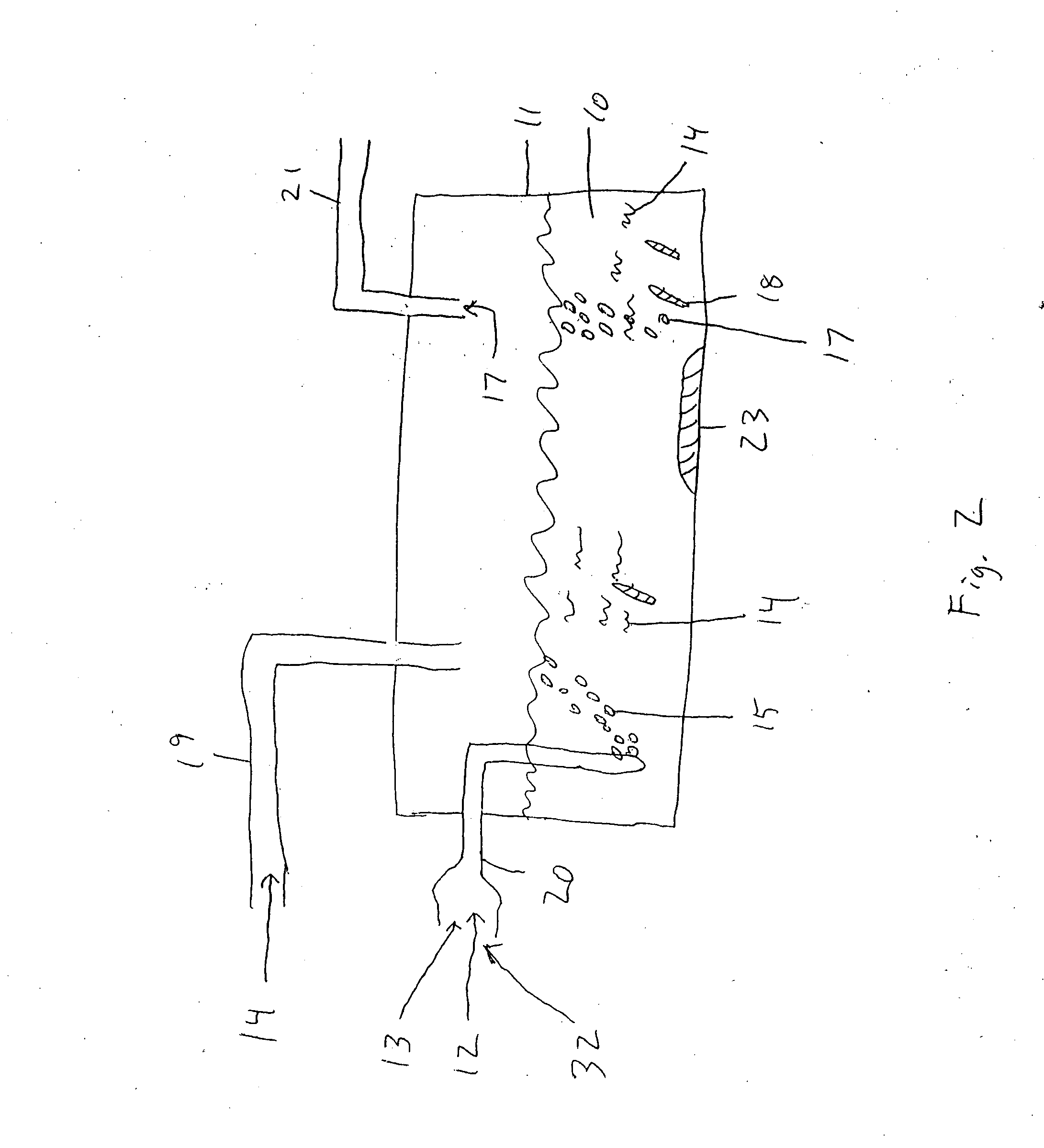
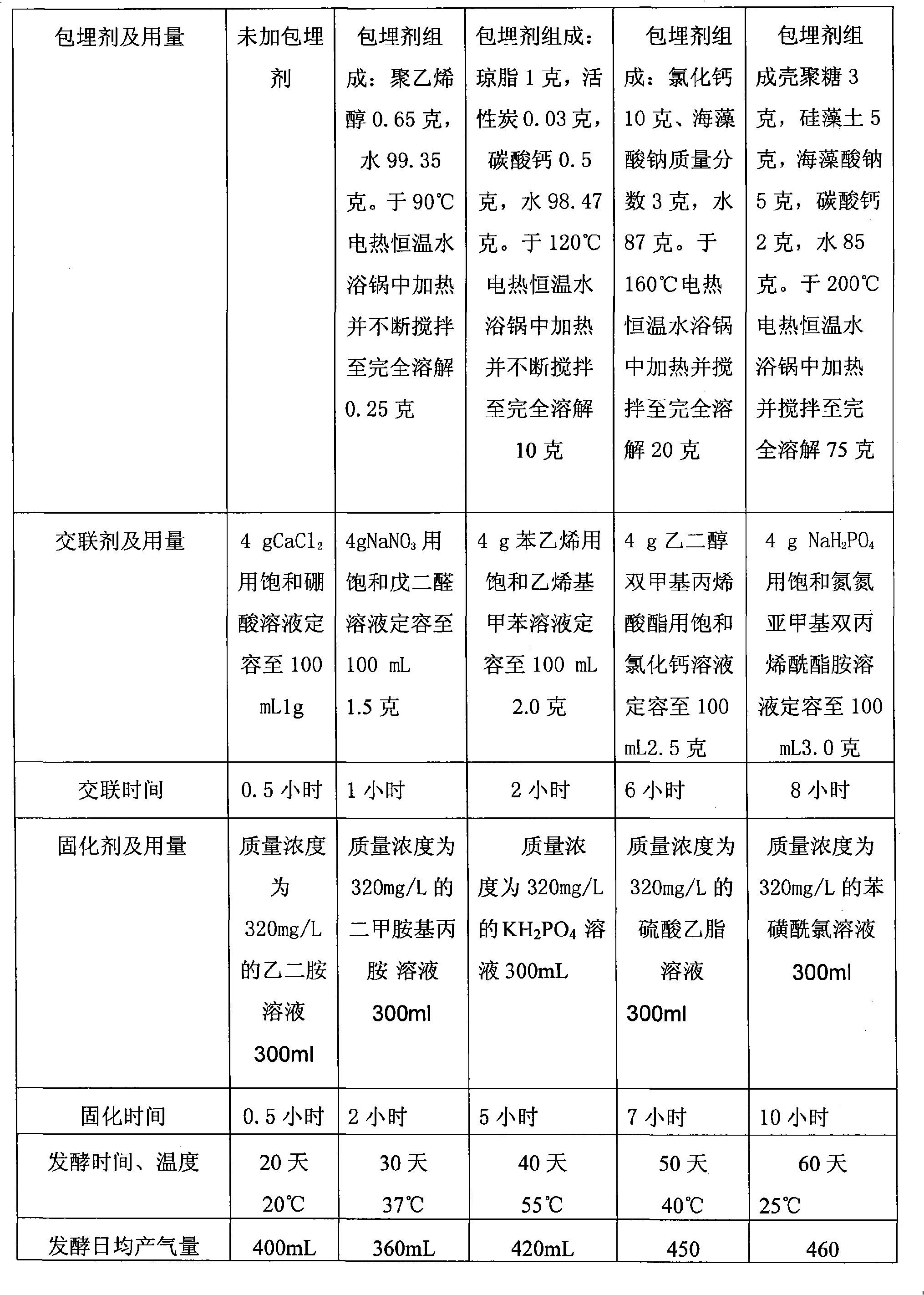
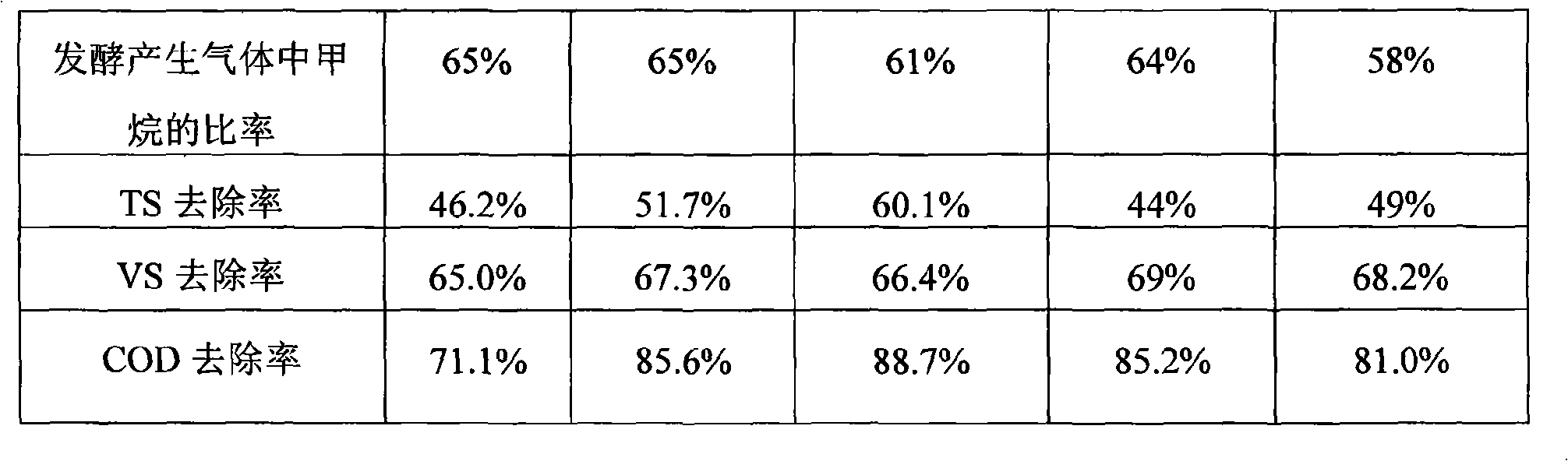
Immobilization method for anaerobic fermentation bacterial active sludge
InactiveCN101319212AExcellent fermentation and COD removal propertiesThe preparation method is simple and easy to useOn/in organic carrierFermentationChemistryWater treatment
The invention provides an immobilization method for anaerobic fermentation strain activated sludge, and belongs to the anaerobic fermentation field. The prior activated sludge immobilization study mainly focuses on organic waste water treatment, while the activated sludge immobilization study on the anaerobic fermentation is not taken up. The method comprises the following steps of: taking concentrated activated sludge, and then adding a solid carrier into the sludge with a mass ratio of the solid carrier to the concentrated activated sludge being 1 to 0.5-10; fully mixing the solid carrier and the concentrated activated sludge, then putting the solid carrier absorbing the activated sludge in a cross-linking agent, and drying to produce immobilized particles; and carrying out cross linking of the produced immobilized particles for 0.5 to 8 hours, and then putting the immobilized particles after cross linking in a curative agent to carry out solidification for 0.5 to 10 hours. The obtained immobilized activated sludge can be widely applied to the anaerobic fermentation of catering organic wastes, straws, animal droppings on cultivation farms and other organic wastes for preparing the clean energy of methane.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
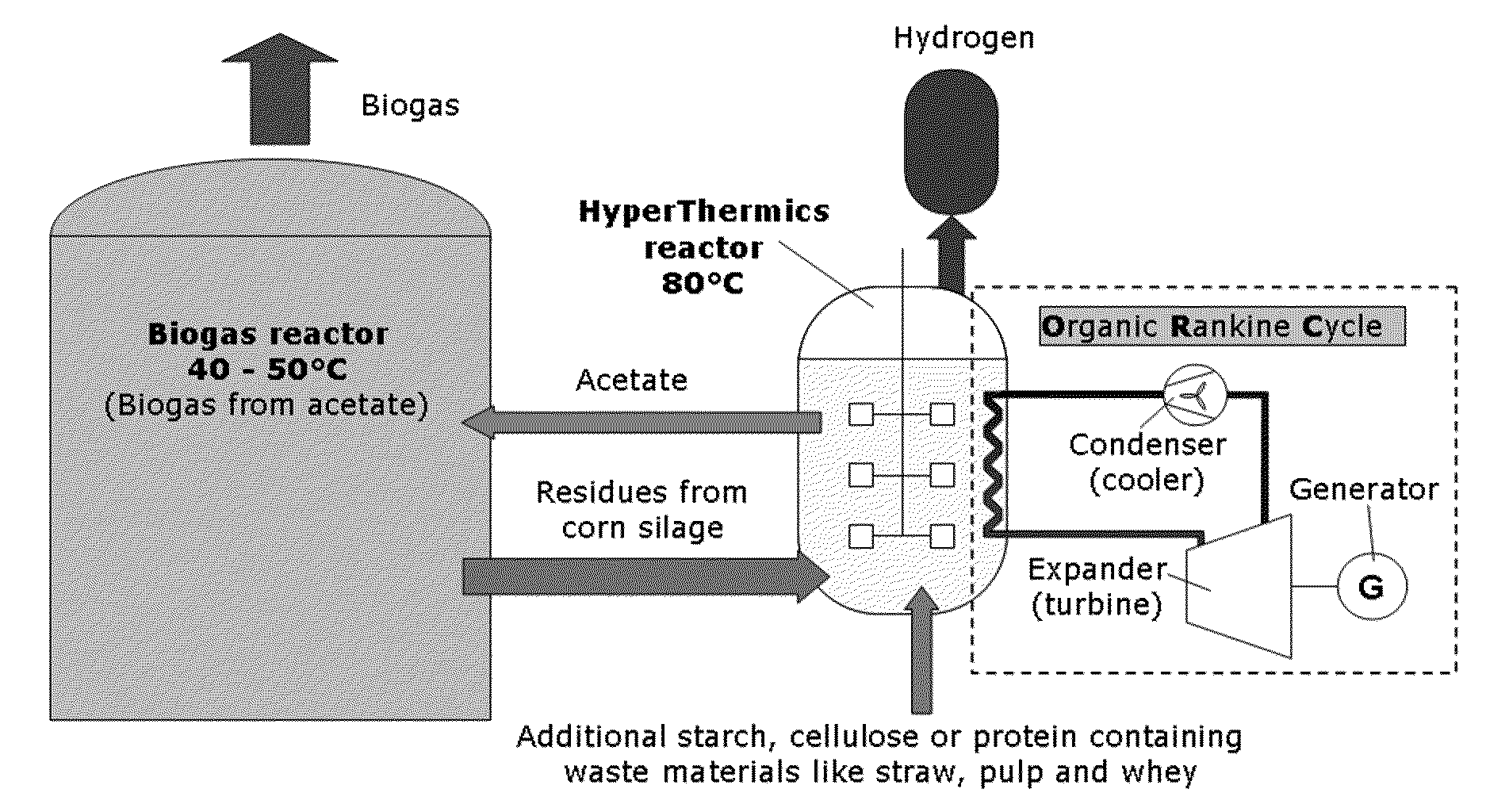
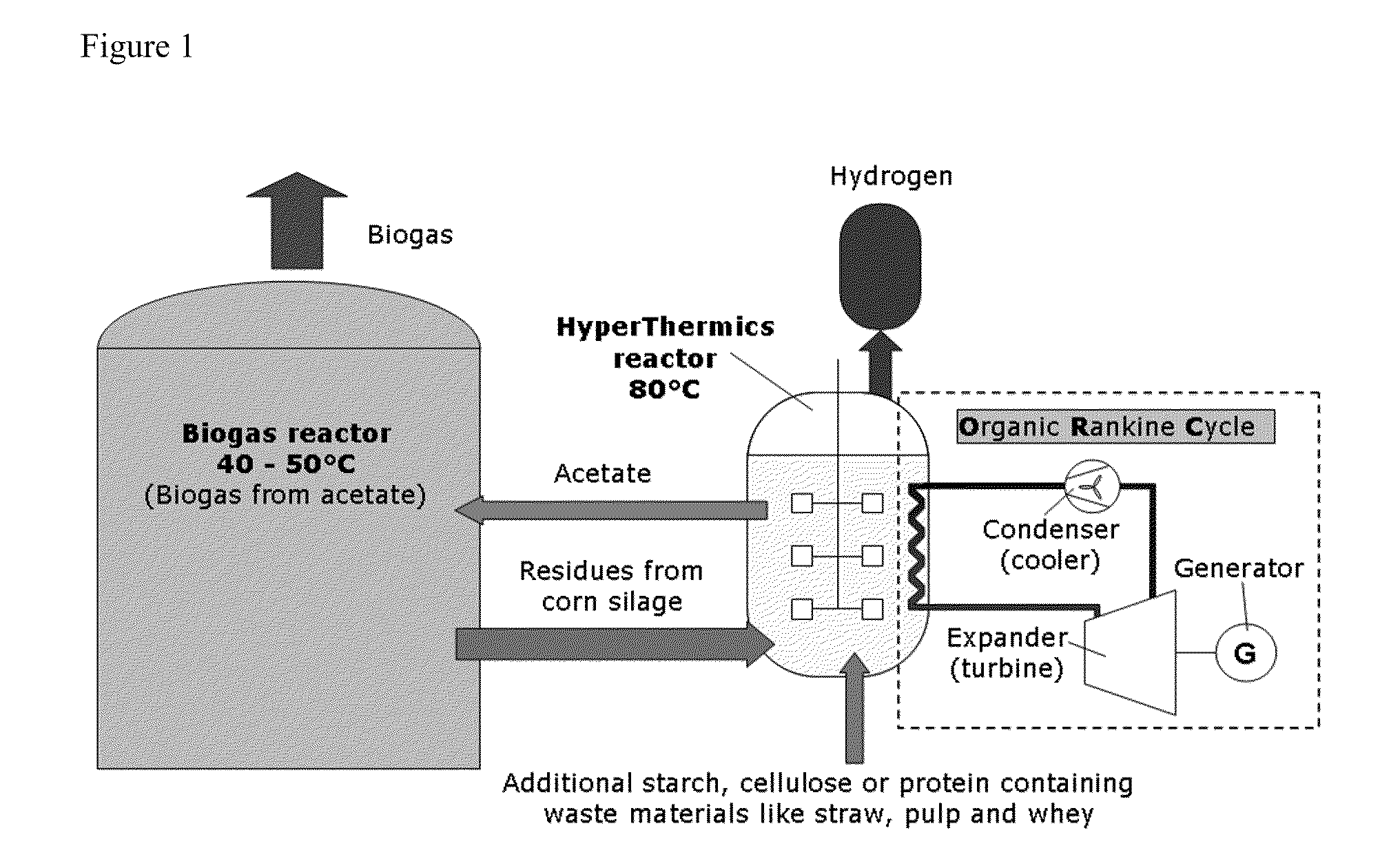
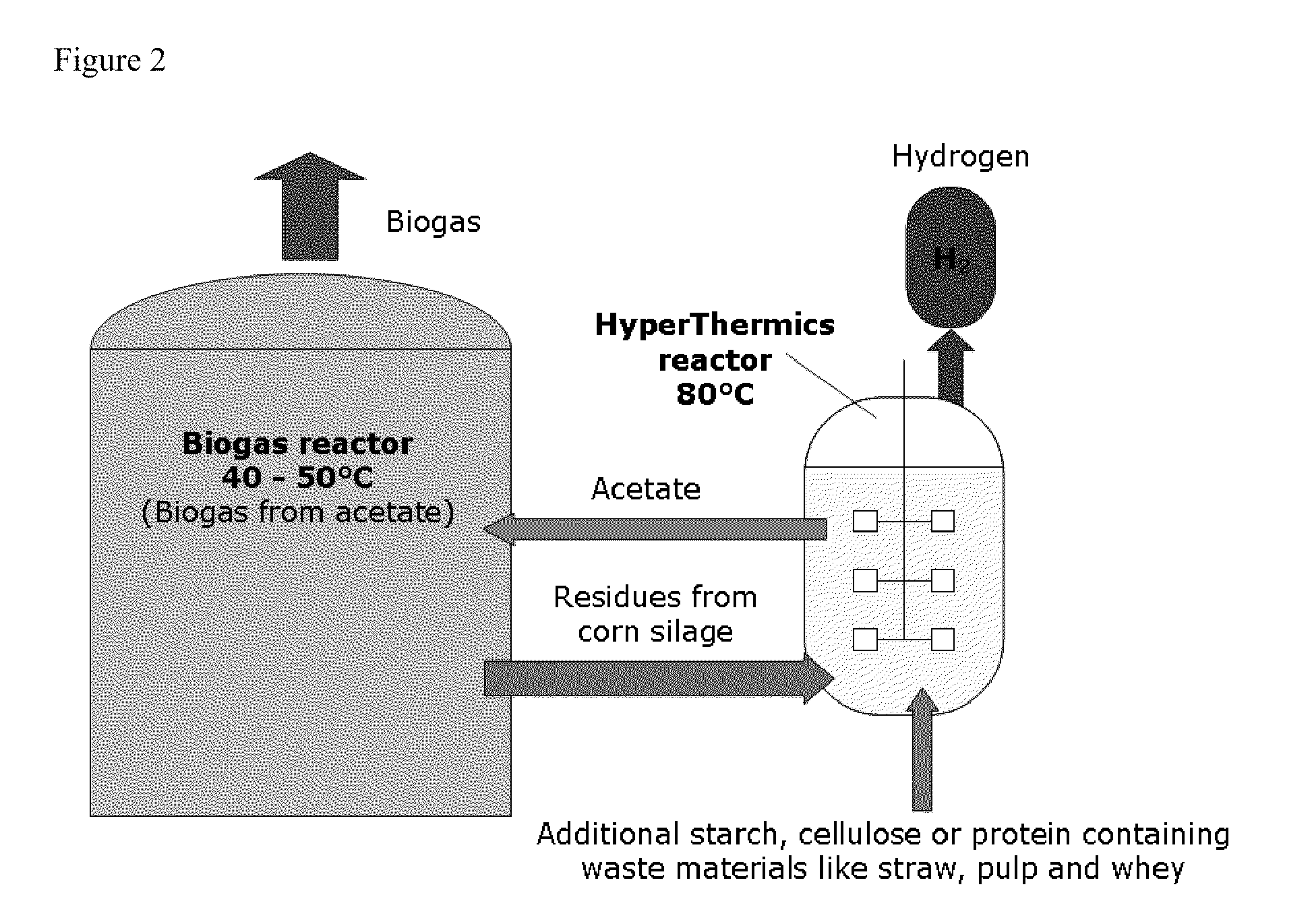
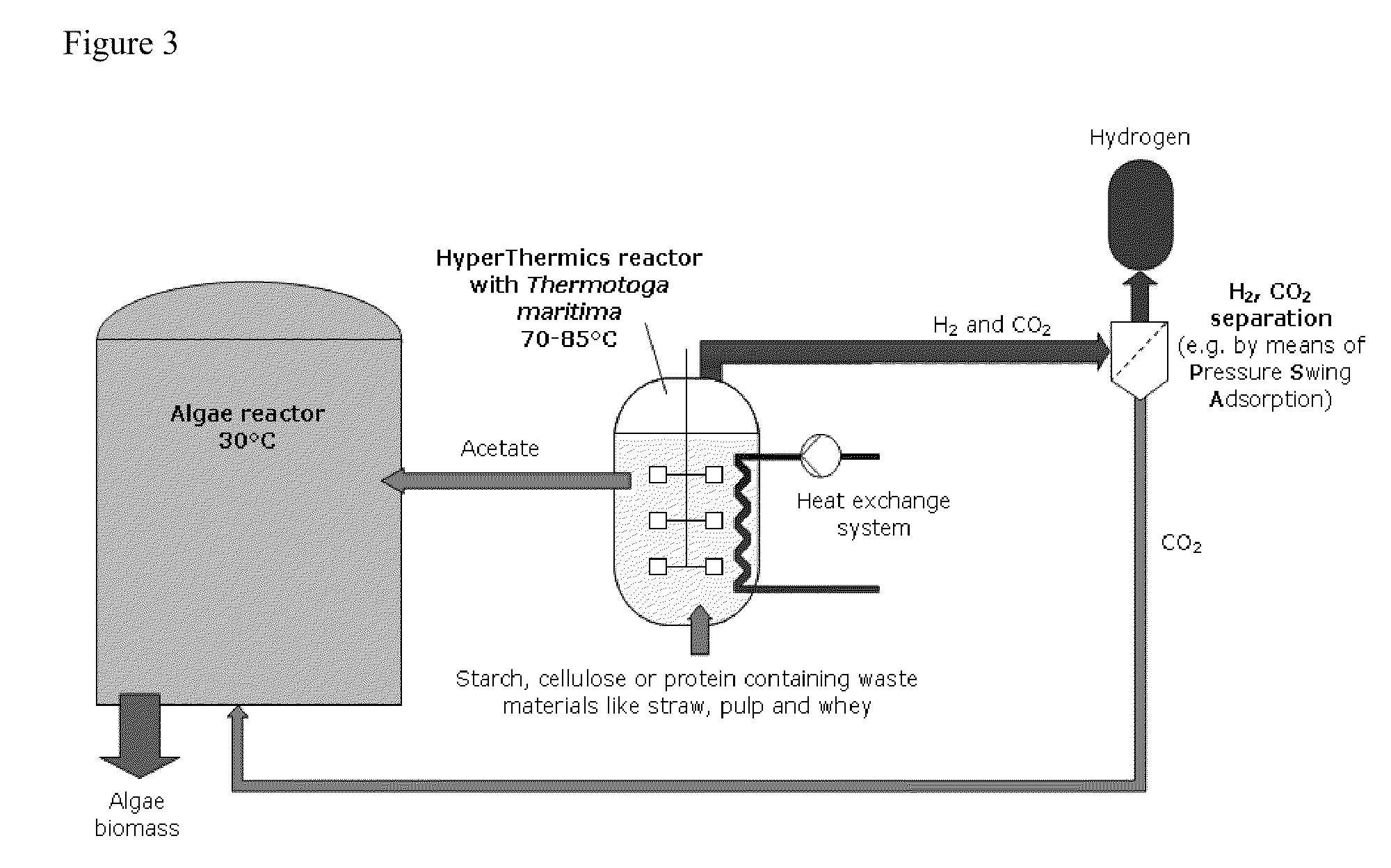
Energy production with hyperthermophilic organisms
ActiveUS20100093046A1Increase methane productionReduce oxygenBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRadiant heatOrganism
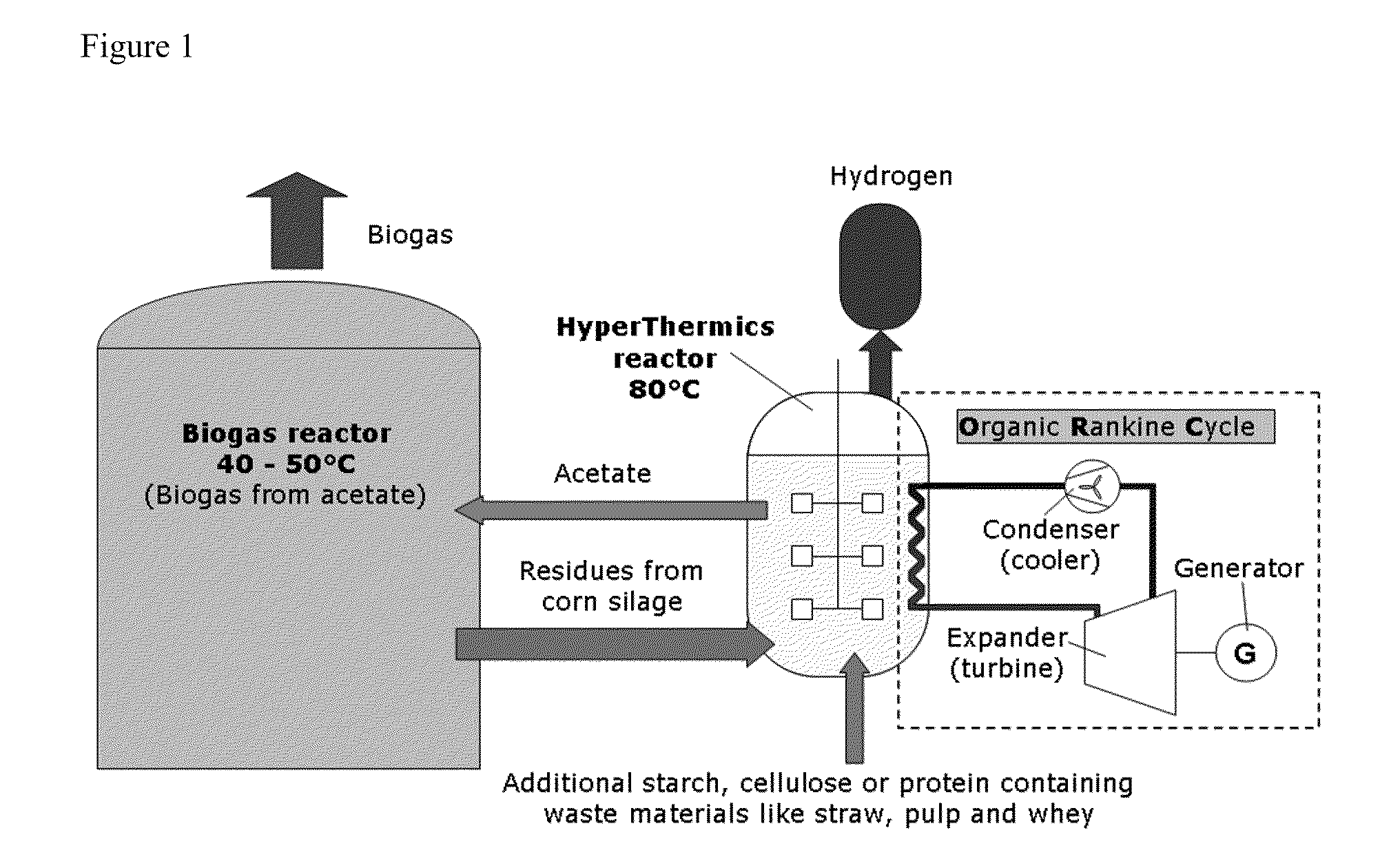
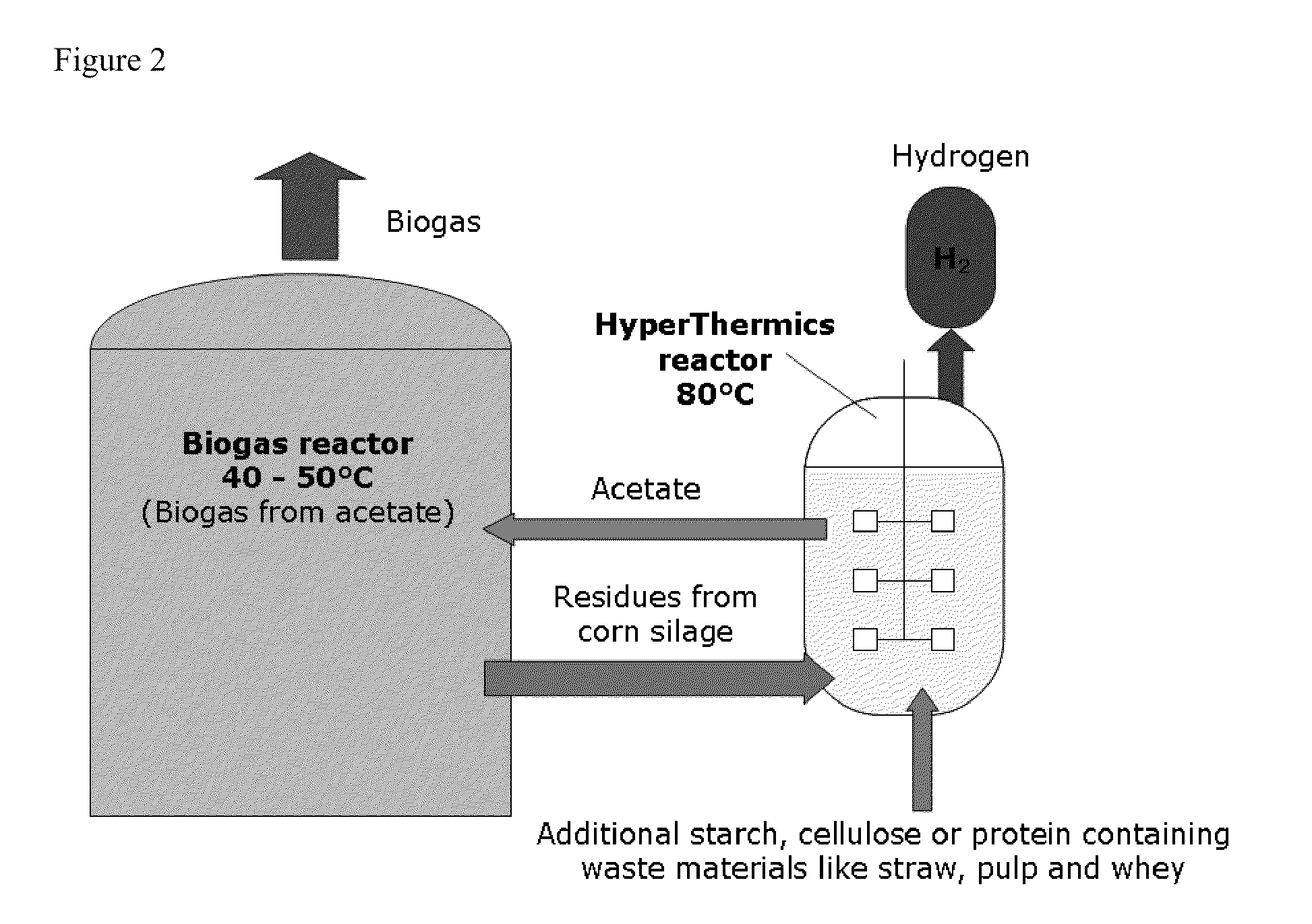
The present invention relates to the field of degradation with hyperthermophilic organisms, and in particular to the use of hyperthermophilic degradation to produce heat and energy rich components including hydrogen and ethanol from a biomass. In some embodiments, a biomass is fermented in the presence of hyperthermophilic organisms to produce heat. The heat is used to heat a liquid which is used directly in a heat pump or radiant heat or to produce electricity or drive a steam turbine. In some embodiments, acetate is utilized as a substrate to produce energy by methanogenesis.
Owner:HYPERTHERMICS HLDG
Combined pre-treatment method for improving sludge disintegration effect and strengthening subsequent anaerobic digestion
InactiveCN101565262AIncreased concentration of dissolved CODIncrease methane productionSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningGas production bioreactorsSolubilityHigh energy
The invention belongs to the technical field of solid waste treatment, in particular relates to a combined pre-treatment method for improving sludge disintegration effect and strengthening subsequent anaerobic digestion, comprising the following concrete steps of: gravity settling and thickening residual sludge generated in a secondary settling tank of a municipal sewage treatment plant, sending the thickened sludge into an ultrasonic reactor for ultrasonic irradiation and adding NaOH; sending the sludge into a sludge anaerobic digestion reactor for subsequent medium temperature anaerobic digestion after the combined action of ultrasonic and NaOH; and collecting methane generated by digestion and measuring the yield of the methane with a gas collection device. The method firstly uses ultrasonic and NaOH jointly for sludge treatment, the soluble COD concentration in sludge liquid phase after treatment is improved by about 52 times, the methane yield is improved by 40.6 percent, and the problem of limited application of ultrasonic due to high energy consumption is largely overcome; and the method is applicable to the treatment of residual sludge in sewage treatment plants, and can be achieved by making corresponding modification on the current treatment facilities of sewage treatment plants for different-scale sewage treatment plants, thus having wide application prospect.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
Bio-recycling of carbon dioxide emitted from power plants
InactiveUS7608439B2Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsImprove methane production efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFermentationFossil fuel
The invention provides a method to decrease emission of carbon dioxide from combustion of fossil fuels or other hydrocarbons and to enhance the efficiency of methane production from anaerobic biodigesters. The invention involves feeding carbon dioxide from the exhaust gas of hydrocarbon fuel combustion to an anaerobic biodigester where biomass is anaerobically fermented to produce methane. Carbon dioxide is an electron acceptor for anaerobic fermentation, and thus some of the carbon dioxide is reduced to methane, which can again be used for fuel. In this way, at least a portion of the exhaust gas CO2 is recycled to form fuel methane instead of being released into the atmosphere. Thus, the net CO2 emission from burning a given amount of fossil fuel is decreased. Adding carbon dioxide to an anaerobic fermentation also increases the efficiency and amount of methane production in the fermentation.
Owner:VIRESCO AD LLC
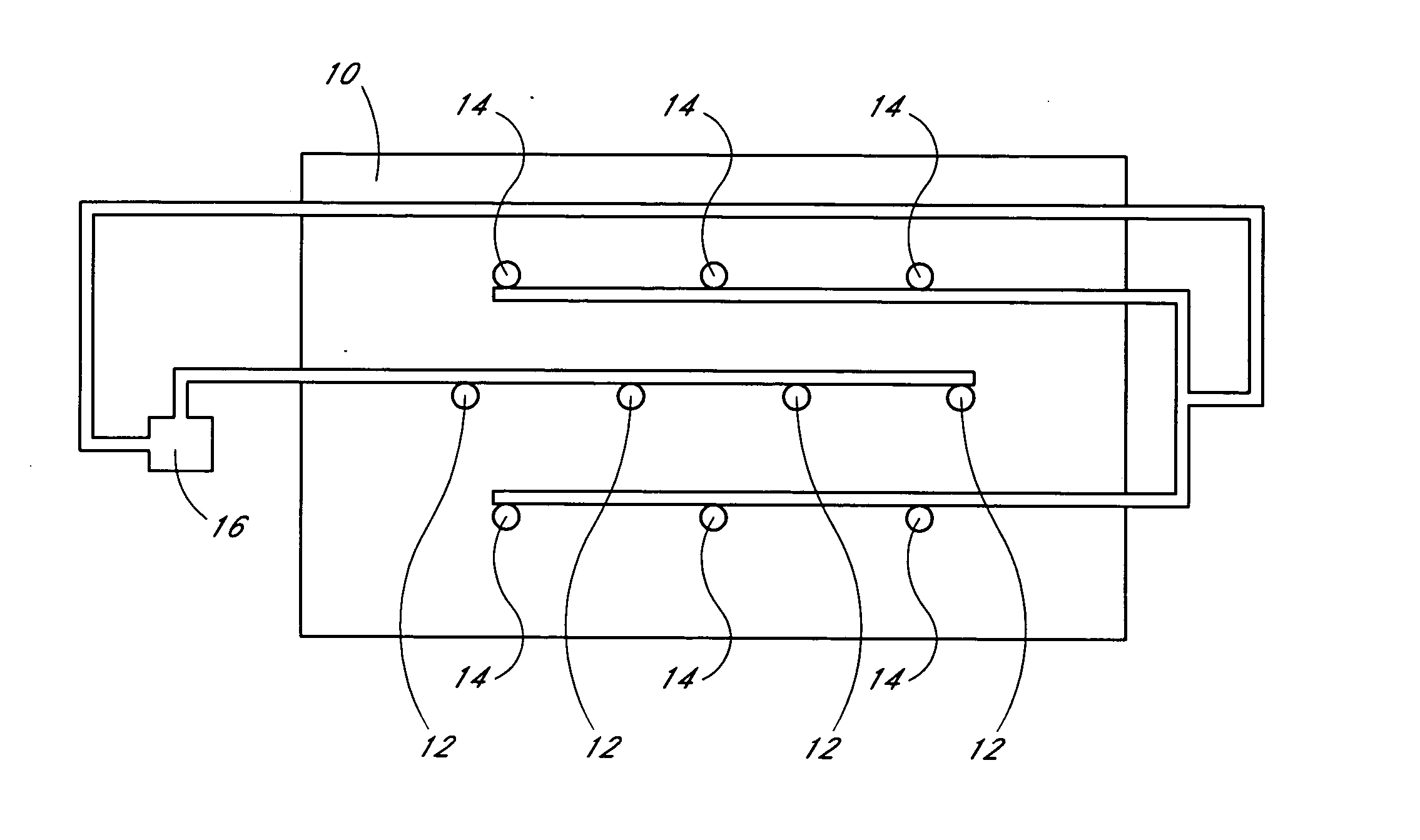
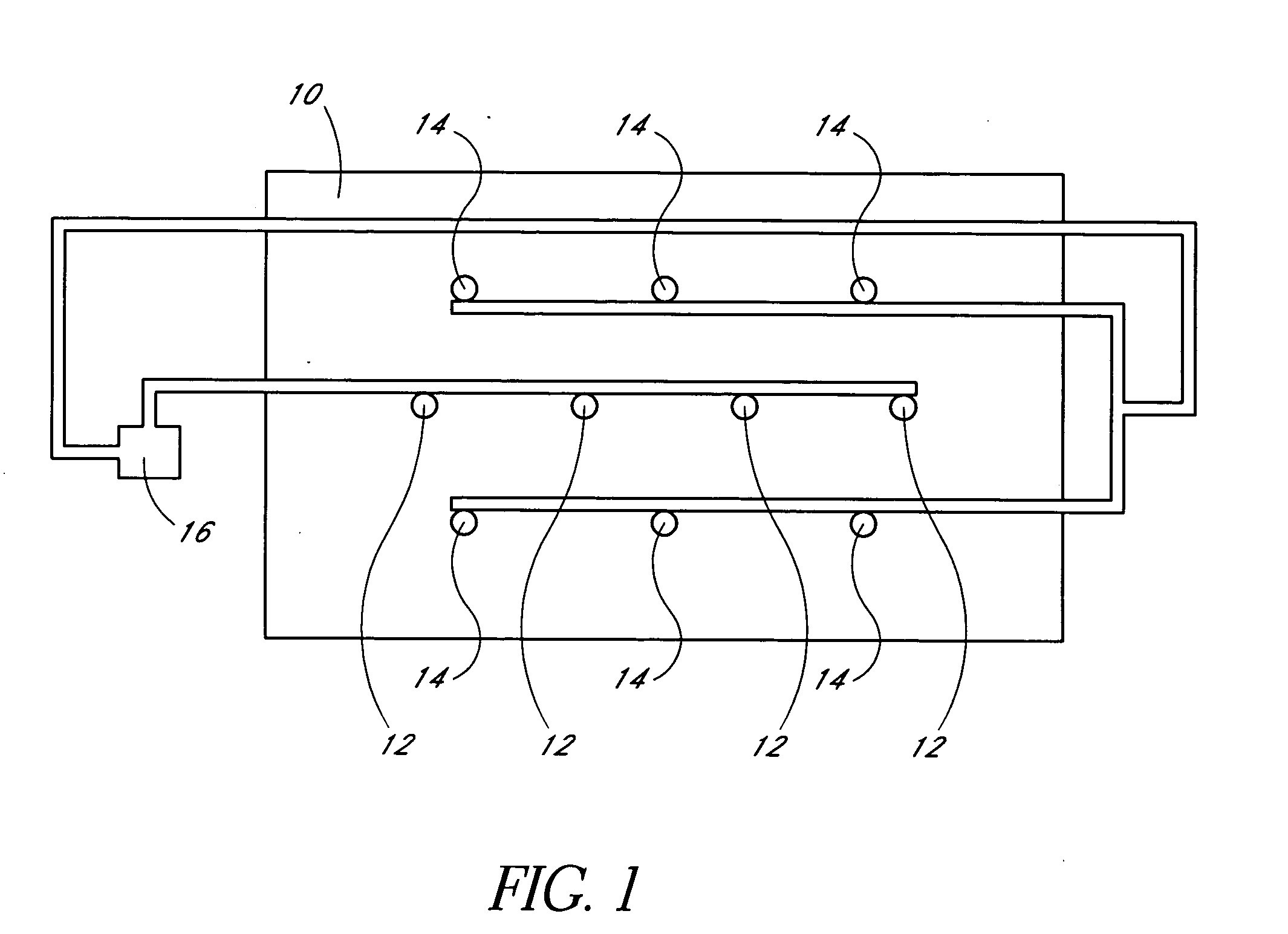
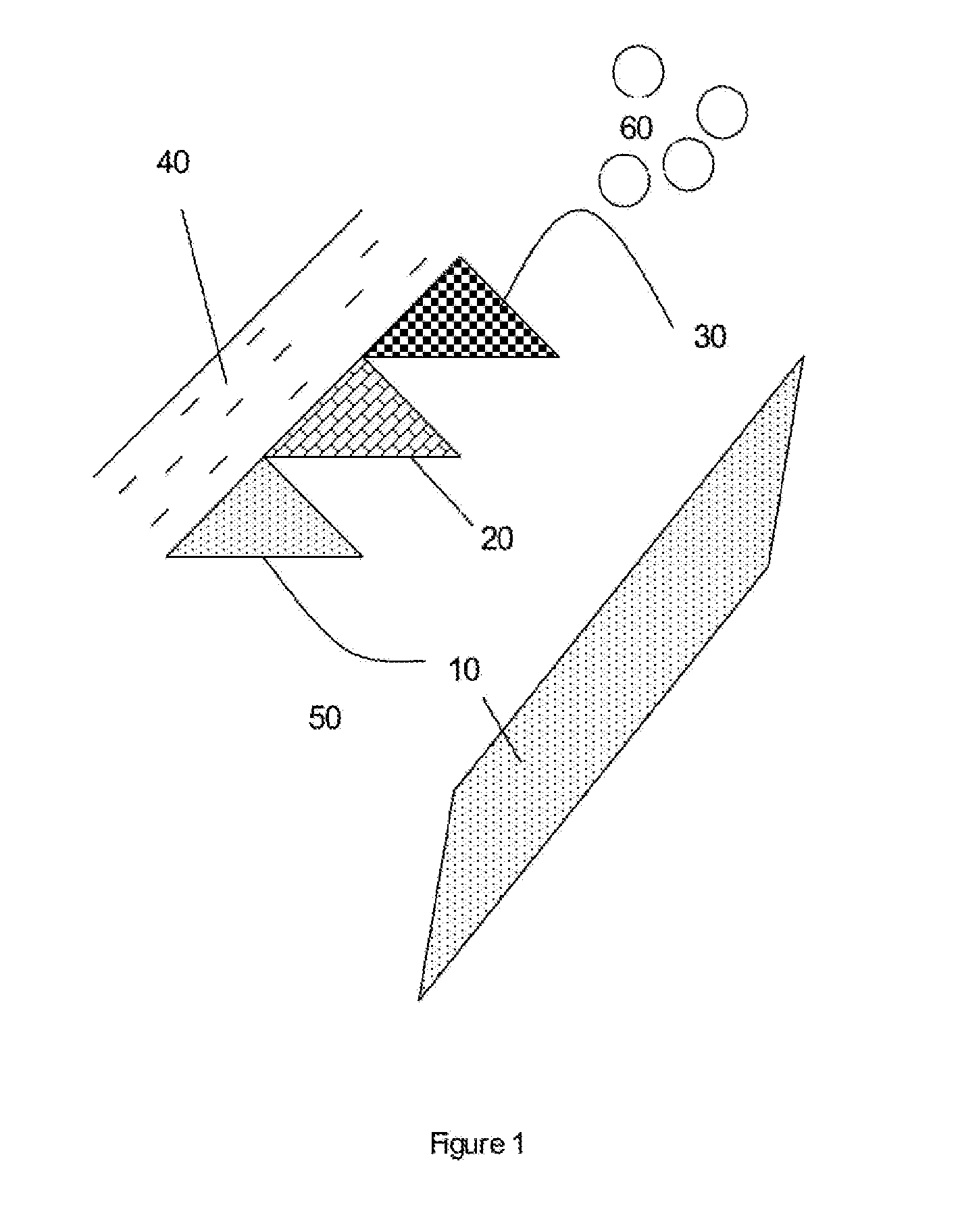
Biogenic Methane Production Enhancement Systems
InactiveUS20090246849A1Increase methane productionReduce competitionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSulfateMethane production
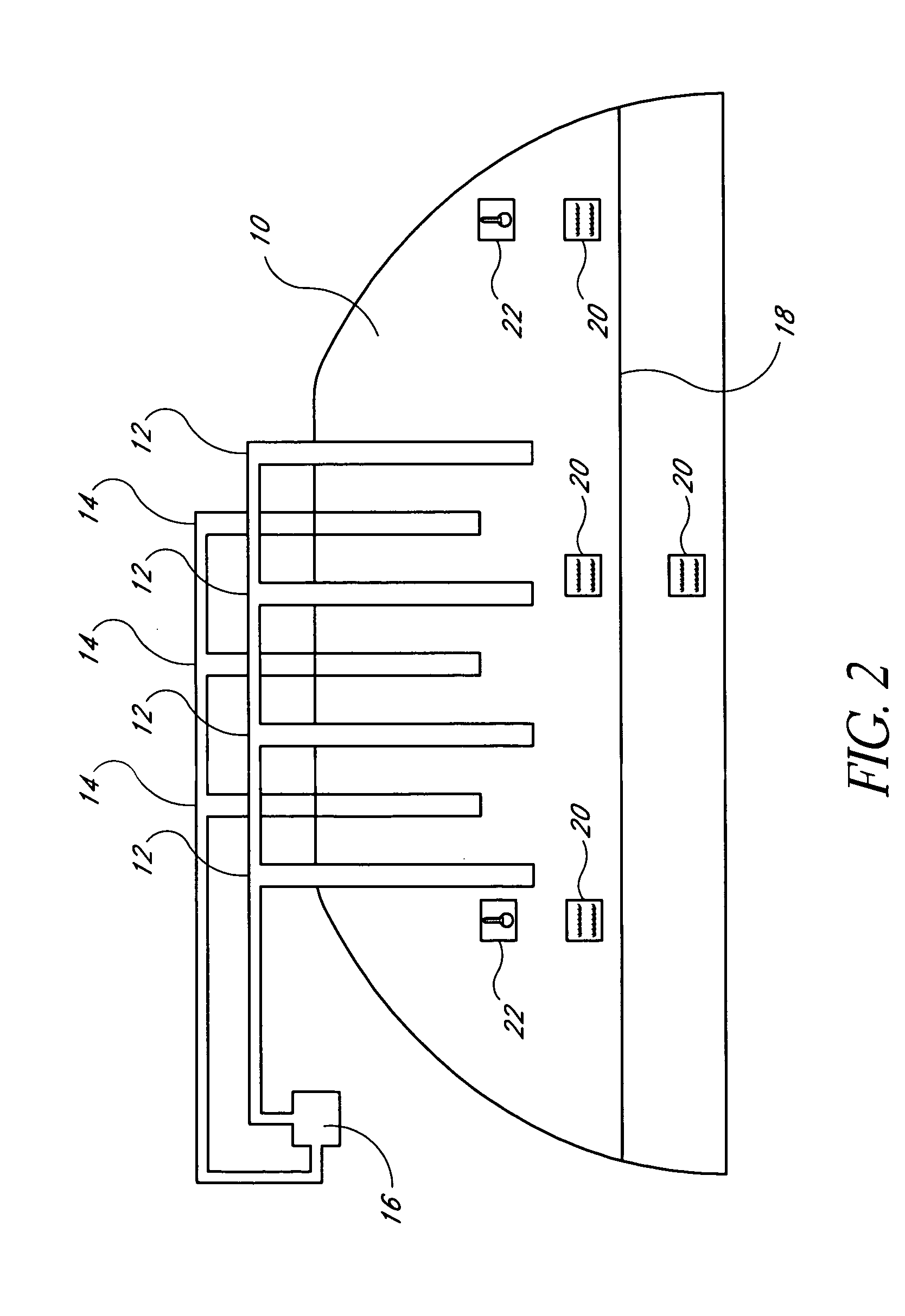
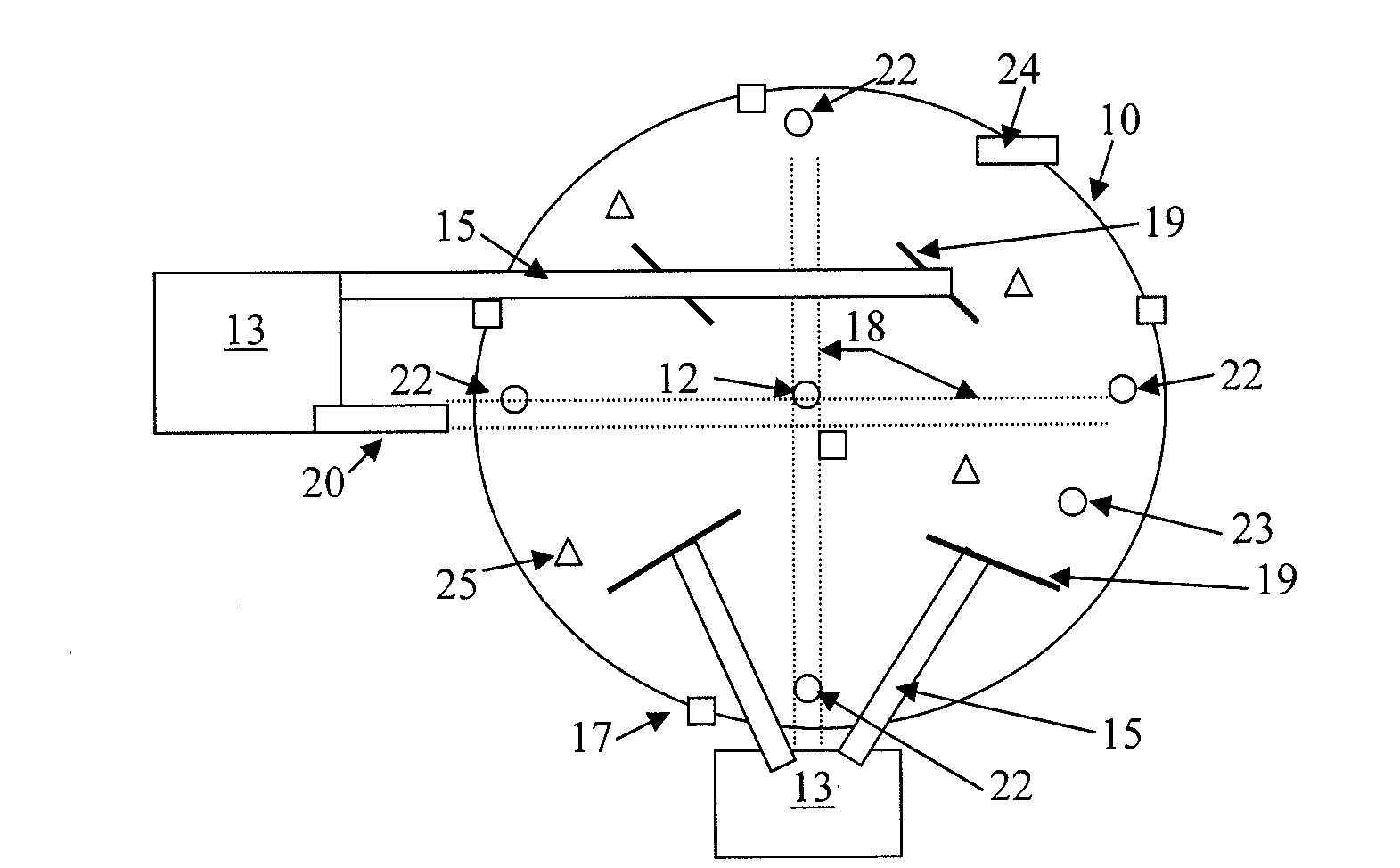
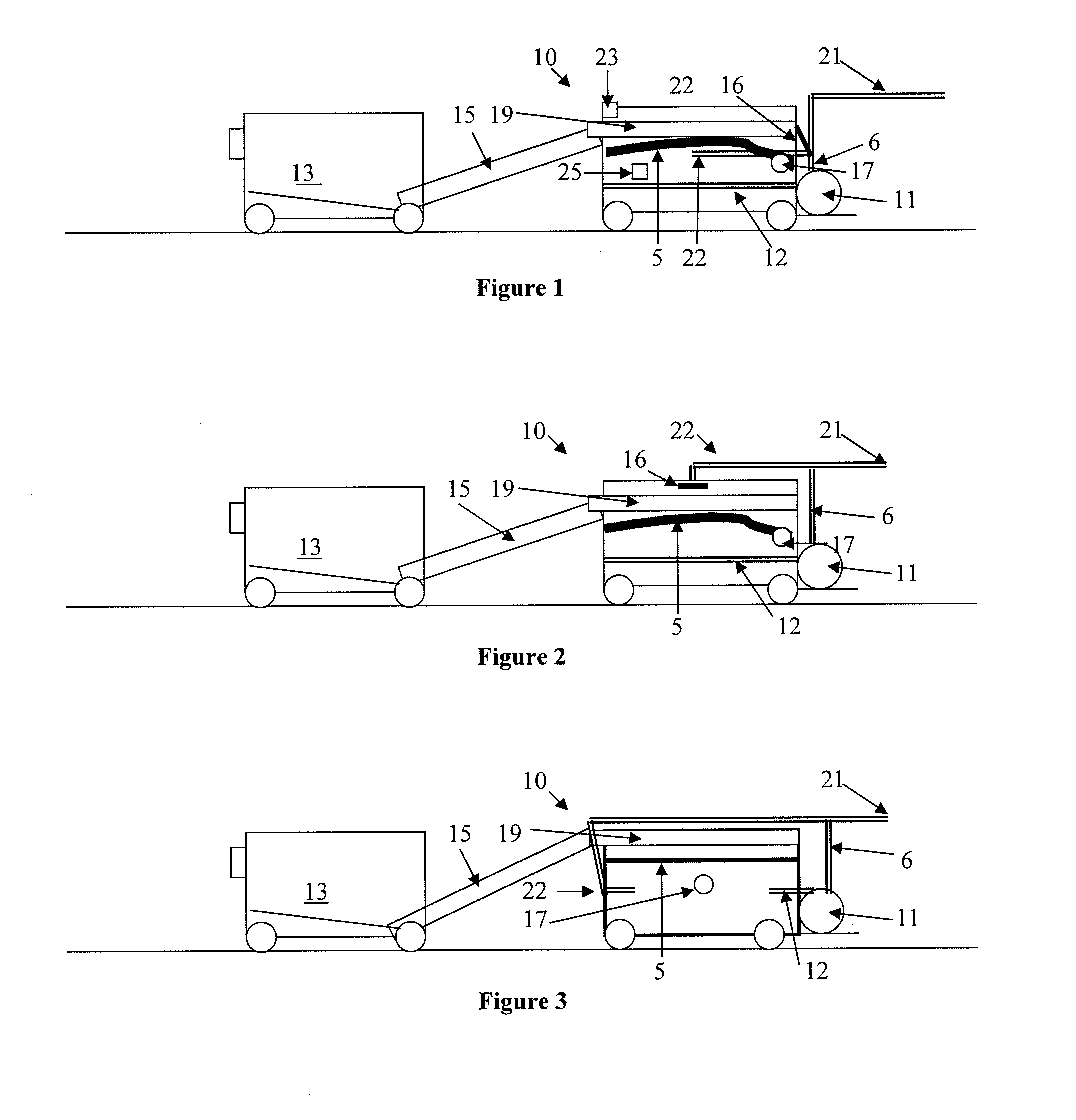
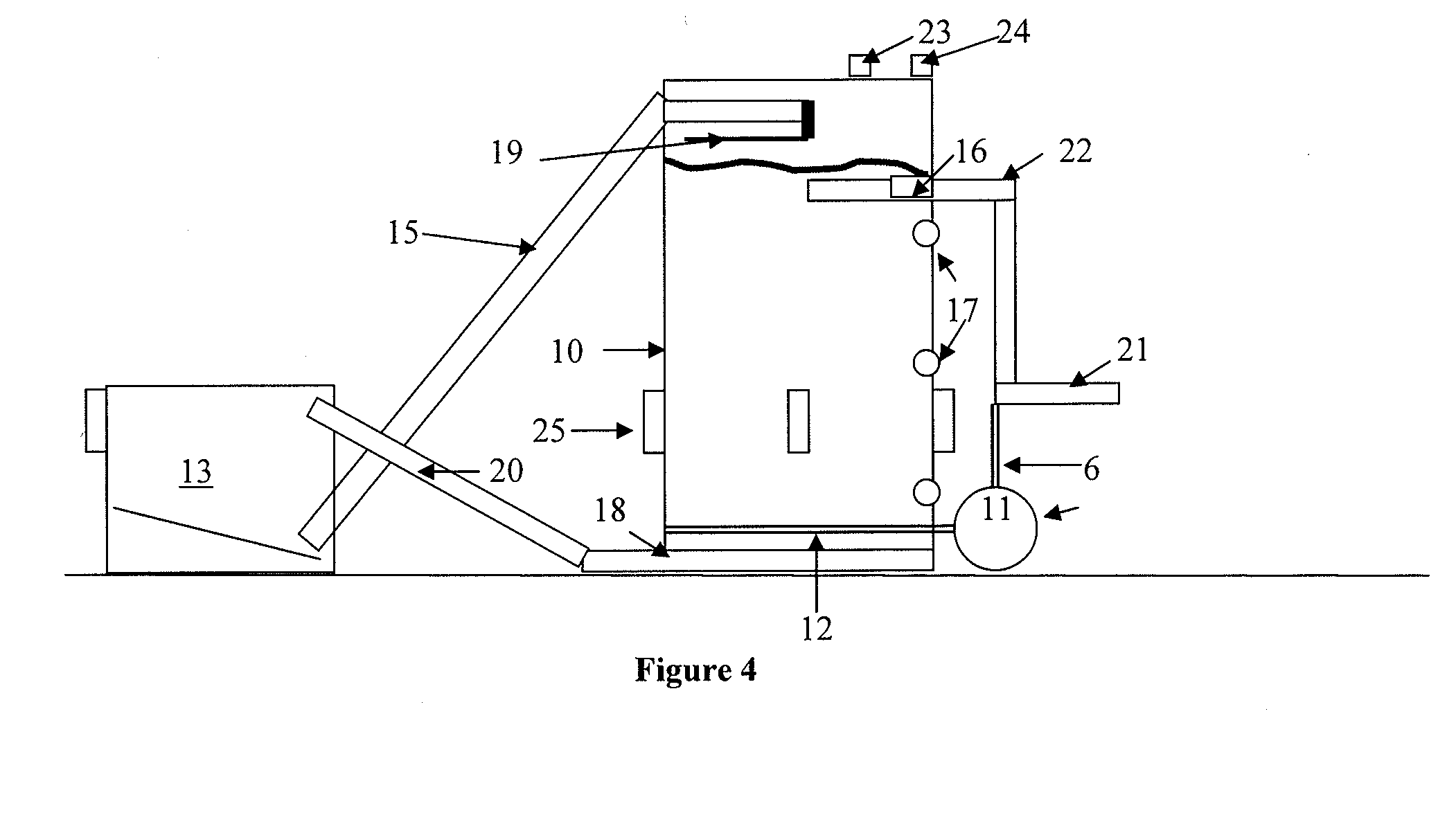
Systems for enhanced in-situ or perhaps even ex-situ biogenic methane production from hydrocarbon-bearing formations (1) including coal seam, oil shale, coal, coal derivates and the like are presented in embodiments such as but not limited to: increasing and perhaps even selection of microbial populations (2), amending CBM water and other microbe-containing media, diminishing sulfate reduction competition, enhancing organic matter concentrations and generation of biogenic methane (10), universally treating hydrocarbon-bearing formations, and introducing amendments (3) to hydrocarbon-bearing formations.
Owner:WESTERN RES INST INC
Biogenic methane production enhancement systems
InactiveUS7832475B2Increase methane productionReduce competitionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSulfateMethane production
Systems for enhanced in-situ or perhaps even ex-situ biogenic methane production from hydrocarbon-bearing formations (1) including coal seam, oil shale, coal, coal derivates and the like are presented in embodiments such as but not limited to: increasing and perhaps even selection of microbial populations (2), amending CBM water and other microbe-containing media, diminishing sulfate reduction competition, enhancing organic matter concentrations and generation of biogenic methane (10), universally treating hydrocarbon-bearing formations, and introducing amendments (3) to hydrocarbon-bearing formations.
Owner:WESTERN RES INST INC
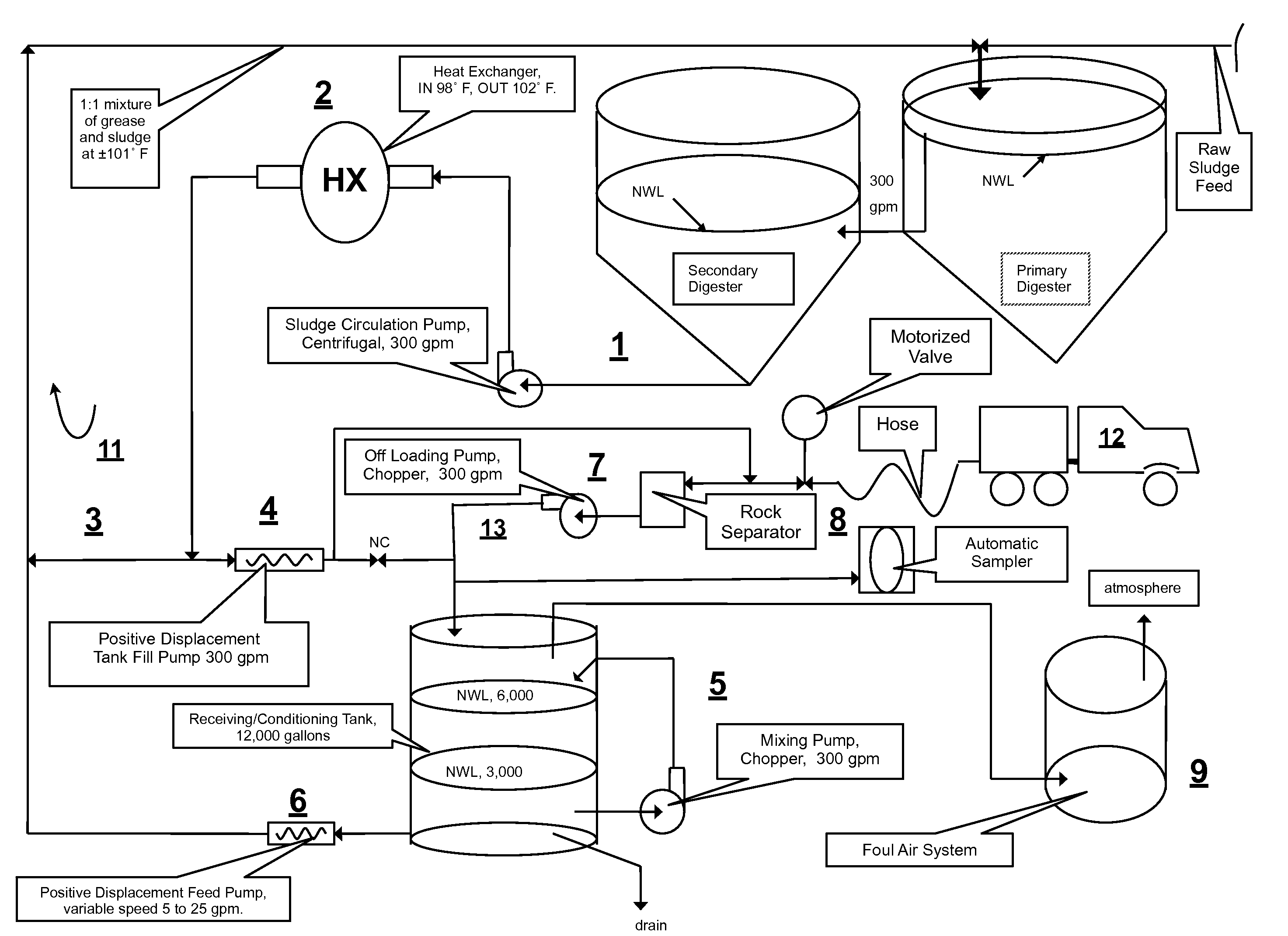
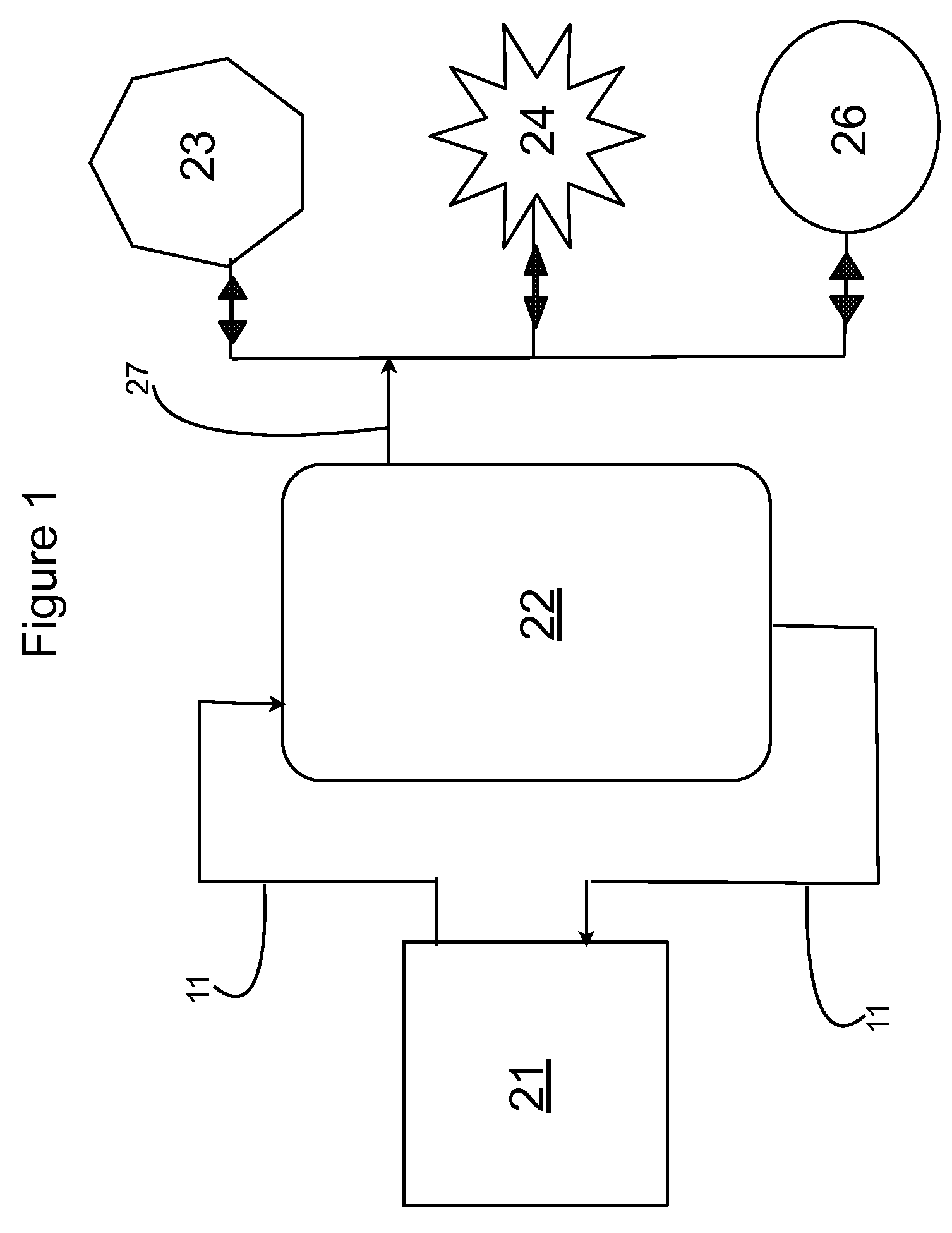
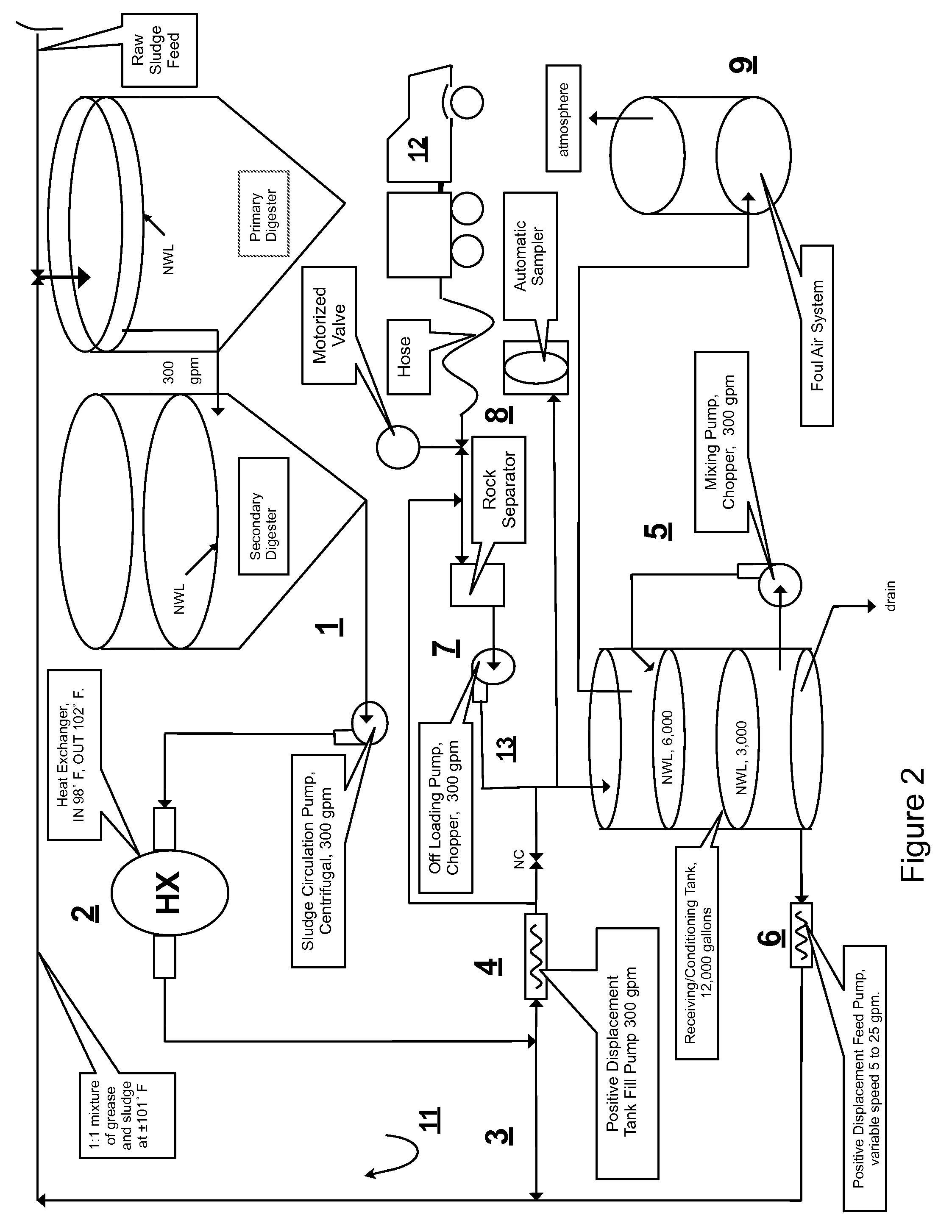
Integrated cogeneration wastewater sewage and waste polar fats/ oils/ greases/waxes (FOG) waste treatment method and facility
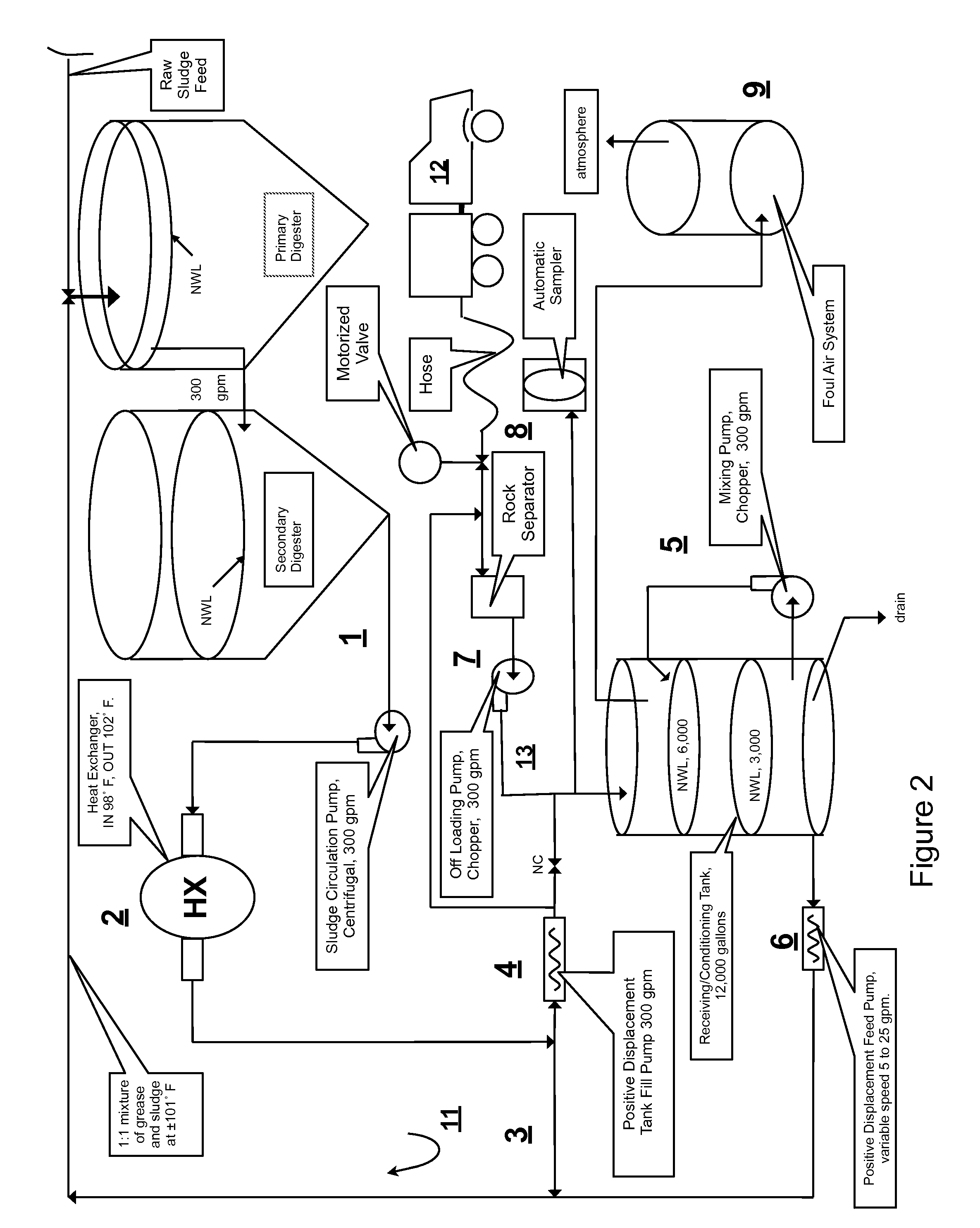
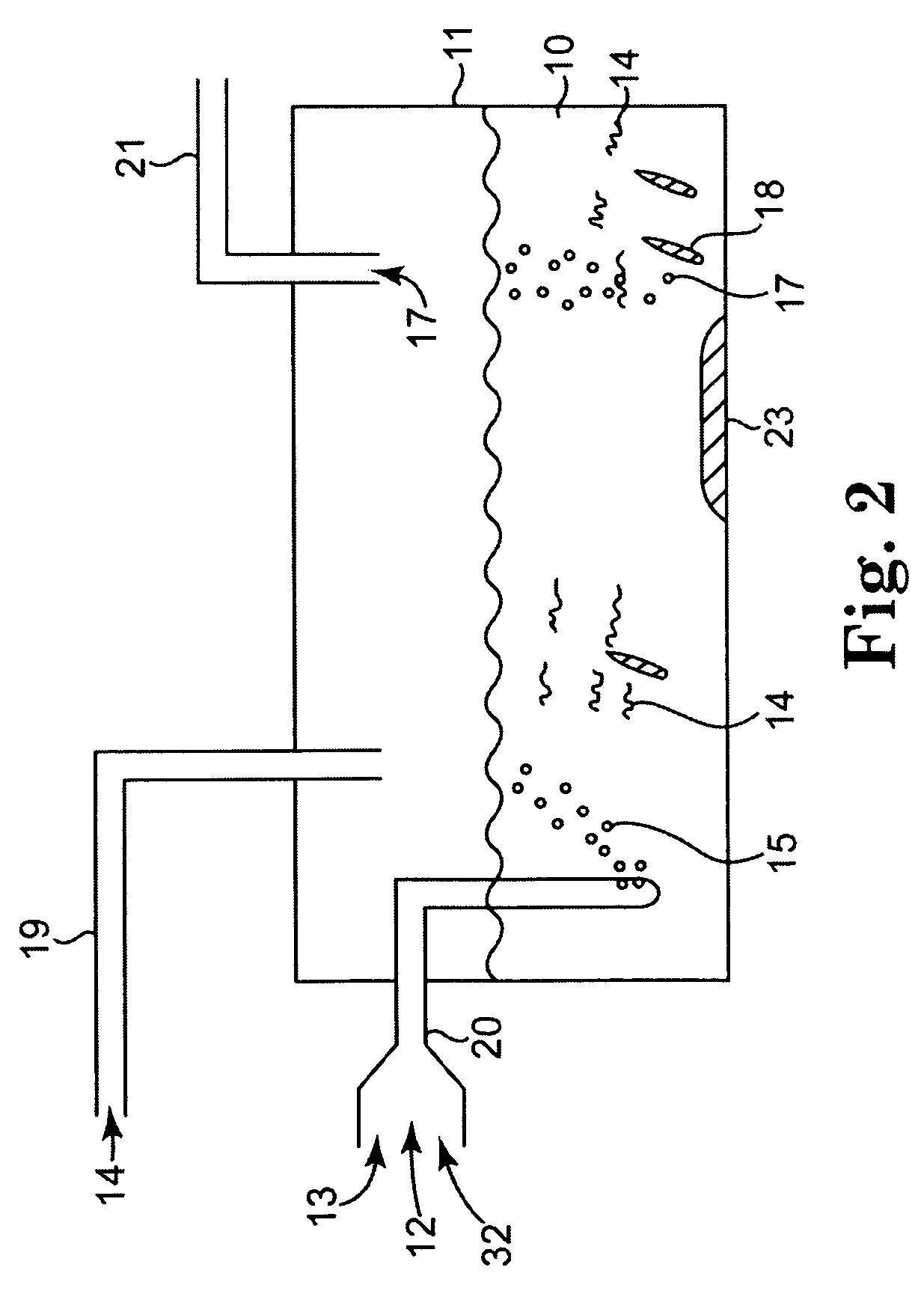
InactiveUS20080203014A1Rule out the possibilityLow solidsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGeneral water supply conservationOil and greaseVolatile fatty acids
Integrated sewage or digestible wastes, and fats, oils, greases and waxes (FOG) waste treatment methods, systems and facilities include a slipstream loop incorporating circulation pumps, hot water heat exchangers and conventional anaerobic digesters for continuously circulating actively digesting sludge at a rate to preclude solid settlement accumulation as a warm flowable slurry source. The warmed actively digesting sludge is pumped from the slipstream loop through a rock trap into a delivery / input loop both for aiding transport or delivery of FOG waste to, and for partially filing a closed receiving / conditioning holding tank, where the warmed actively digesting sludge softens and liquefies the FOG wastes offloaded into the holding tank for further treatment at a desired treatment temperature range (whether psychrophilic, mesophilic, or thermophilic). The contents of the closed receiving / conditioning holding tank are continuously mixed by a bottom-top recirculation chopper pump to pre-treat the FOG wastes, liquefying and decreasing solids particle size allowing acidogens in the actively digesting sludge to pre-digest such wastes producing volatile fatty acids, some biogas and a highly bioreactive, flowable feedstock slurry. The produced highly bioreactive, flowable feedstock slurry can then injected back into the actively digesting sludge slipstream loop at a controlled rate where the resultant mixture then is introduced, together with raw sewage or other digestible wastes, into input or head ends of waste treatment systems having anaerobic digesters for digestion of solids and steady-state methane production. Advantages of the integrated system relate to a partial digestion of the FOG in the reaction / holding tank generating volatile fatty acids that suppress expression of methane producing methagens in the holding tank, increased steady-state methane production and significantly reduced solids volume of treated digestible wastes (sewage) and FOG wastes.
Owner:MAGNER JOSEPH A +1
Method for producing methane as clean energy source by utilizing catering organic waste
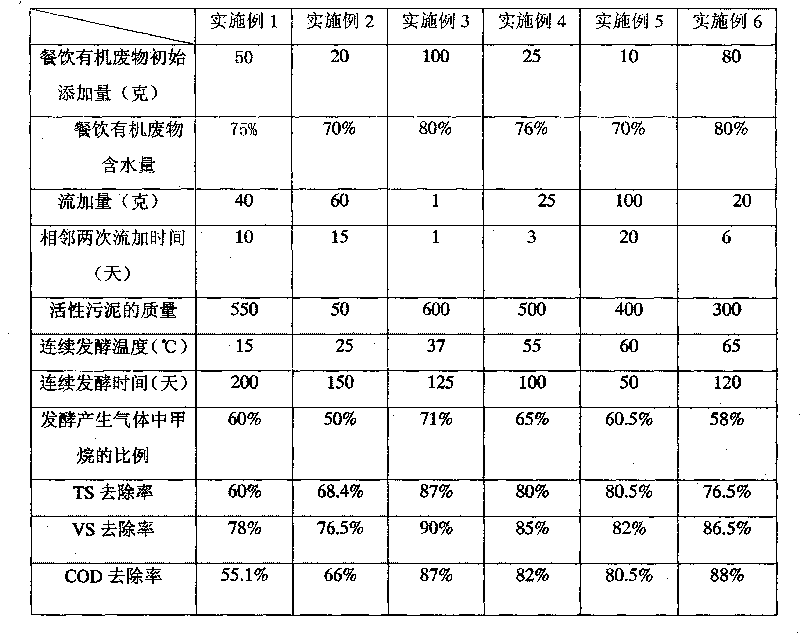
ActiveCN101724655AReduce processing costsThe process steps are simpleWaste based fuelFermentationActivated sludgeClean energy
The invention relates to a method for producing a clean energy source by a continuous feeding type anaerobic fermentation method, particularly to a continuous feeding type anaerobic fermentation method for preparing methane by fermenting catering organic waste. The method for producing the clean energy source through continuous feeding type anaerobic fermentation can be widely used for preparing the methane which is a clean energy source through the anaerobic fermentation of the catering organic waste, straws, animal excreta in farms and other organic waste. The method comprises the following steps of: draining partial moisture of the collected catering organic waste to enable the water content thereof to be not more than 80 percent, and then adding the processed catering organic waste and acclimated anaerobic activated sludge in a definite proportion into a reactor for fermentation. The catering organic waste is added into the reactor by adopting a continuous feeding method in the fermentation process, and a fermentation raw material is added once at regular intervals. An addition period is a gas production vigorous period. The addition is 0.1-10 percent of the volume of the reactor. An anaerobic state is strictly controlled in the whole process so as to facilitate the growth of anaerobes.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
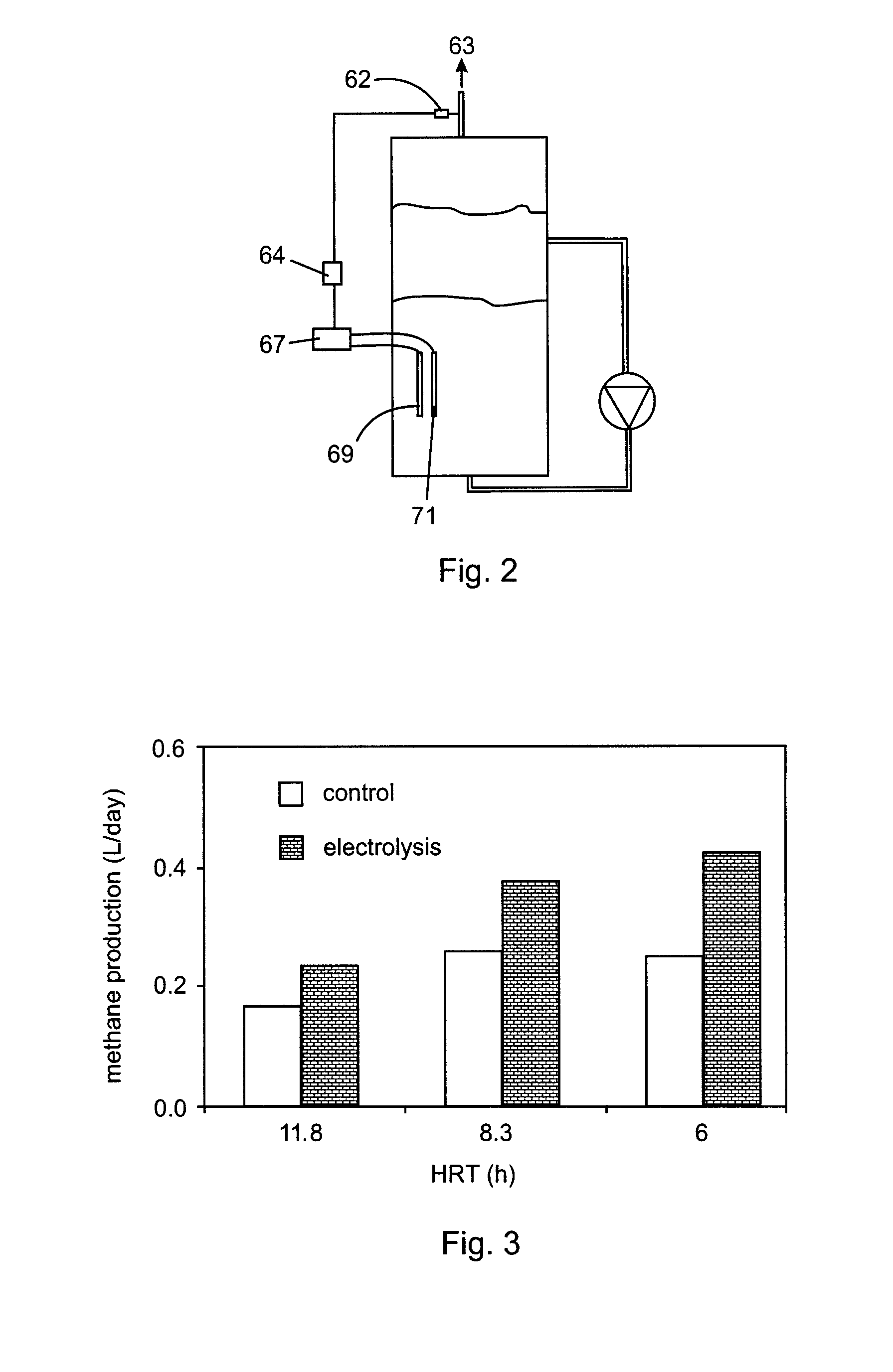
Microbially-assisted water electrolysis for improving biomethane production
InactiveUS20120100590A1Increase surface areaReduce the amount requiredBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsElectrochemistryAnaerobic microorganisms
A method of producing in a bioreactor a biogas rich in methane involves electrolyzing water in an aqueous medium at a voltage in a range of from 1.8 V to 12 V in the presence of electrochemically active anaerobic microorganisms that biocatalyze production of hydrogen gas, and, contacting a species of hydrogenotrophic methanogenic microorganisms with the hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide to produce methane. Volumetric power consumption is in a range of from 0.03 Wh / LR to 0.3 Wh / LR. Current density is 0.01 A / cmE2 or lower. The voltage is sufficient to electrolyze water without destroying microbial growth. Such a method results in improved electrolysis efficiency while avoiding the use of noble metal catalysts. Further, a combination of water electrolysis with anaerobic degradation of organic matter results in increased biogas quality and in increased biogas quantity and yield. Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide contributes to the increased quality, while an increase in the rate of organic matter hydrolysis and an increase in the production of methane from hydrogen contributes to the increased quantity and yield.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Method and device for cultivating anaerobic granular sludge
InactiveCN103043792AEasy to transportGuaranteed uptimeTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSludgeEngineering
The invention discloses a device for cultivating anaerobic granular sludge. The device is characterized in that an artificial sludge bed is arranged inside a body and is formed in a manner that a packing support pipe is fixed between an upper support plate and a lower support plate in a penetrating manner; the upper support plate and the lower support plate are fixed together with the body through a lower fixing frame; radial packings are evenly distributed on the pipe wall of the packing support pipe; a plurality of paths of inlet water distributors are arranged at the bottom part of the body and are connected with a water inlet pump; a water outlet pipe is arranged at the upper part of the body; an overflow weir is arranged on the body above the water outlet pipe; an exhaust pipe is arranged on the body above the overflow weir and is connected with an air collector; and a sludge pump connected to the lateral wall of the bottom part of the body is connected with a sludge collecting tank. The invention also provides a method for cultivating the anaerobic granular sludge. A strain cultivated by the device and the device is stable in performance and has a strong capacity of adapting to changes of an external environment, an expansion coefficient of the anaerobic granular sludge bed is high, a cultivation period of the anaerobic granular sludge is short, the cultivation efficiency is high, and the performance of the anaerobic granular sludge is stable.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
Composite bacterial agent for methane fermentation
ActiveCN101948752AEasy to combineIncrease the average daily gas production rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyClostridium pasteurianum
The invention discloses a composite bacterial agent for methane fermentation, which relates to a composite preparation of microbial fermentation bacterial liquid. In the invention, the problem of lacking bacterial gent applicable to methane fermentation using cow dung as a main raw material and bacterial agent applicable to medium and large methane fermentation projects is solved. The composite bacterial agent comprises 8 to 15 weight parts of bacteroides cellulosolvens fermentation liquor, 12 to 20 weight parts of clostridium pasteurianum fermentation liquor, 30 to 45 weight parts of methanoculleussubmarinua fermentation liquor and 20 to 50 weight parts of methanosarcina mazei fermentation liquor. The number of the active bacteria of 1 milliliter of the fermentation liquor of each of the four kinds of bacteria is greater than 10<9>. The composite bacterial agent for the methane fermentation using the cow dung as the main raw material can make gas production earlier and improve gas yield and methane yield effectively.
Owner:黑龙江省昊千生物科技有限公司
Bio-recycling of carbon dioxide emitted from power plants
InactiveUS20090162914A1Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsImprove methane production efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFermentationFossil fuel
The invention provides a method to decrease emission of carbon dioxide from combustion of fossil fuels or other hydrocarbons and to enhance the efficiency of methane production from anaerobic biodigesters. The invention involves feeding carbon dioxide from the exhaust gas of hydrocarbon fuel combustion to an anaerobic biodigester where biomass is anaerobically fermented to produce methane. Carbon dioxide is an electron acceptor for anaerobic fermentation, and thus some of the carbon dioxide is reduced to methane, which can again be used for fuel. In this way, at least a portion of the exhaust gas CO2 is recycled to form fuel methane instead of being released into the atmosphere. Thus, the net CO2 emission from burning a given amount of fossil fuel is decreased. Adding carbon dioxide to an anaerobic fermentation also increases the efficiency and amount of methane production in the fermentation.
Owner:OFFERMAN JOHN D +1
Method for treating crop straws by utilizing acidizing fermentation liquor backflow and applications thereof
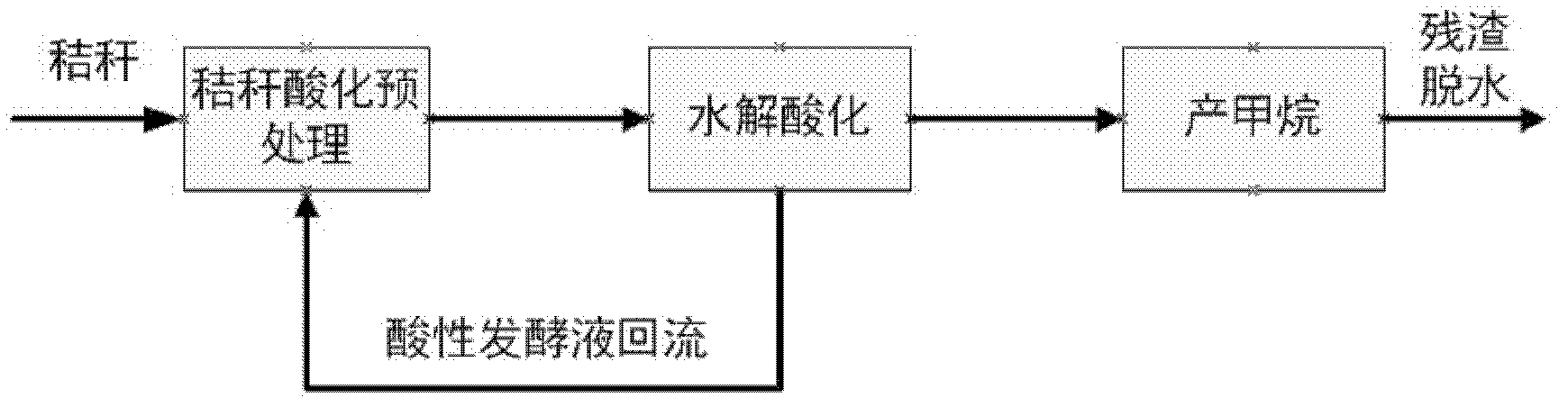
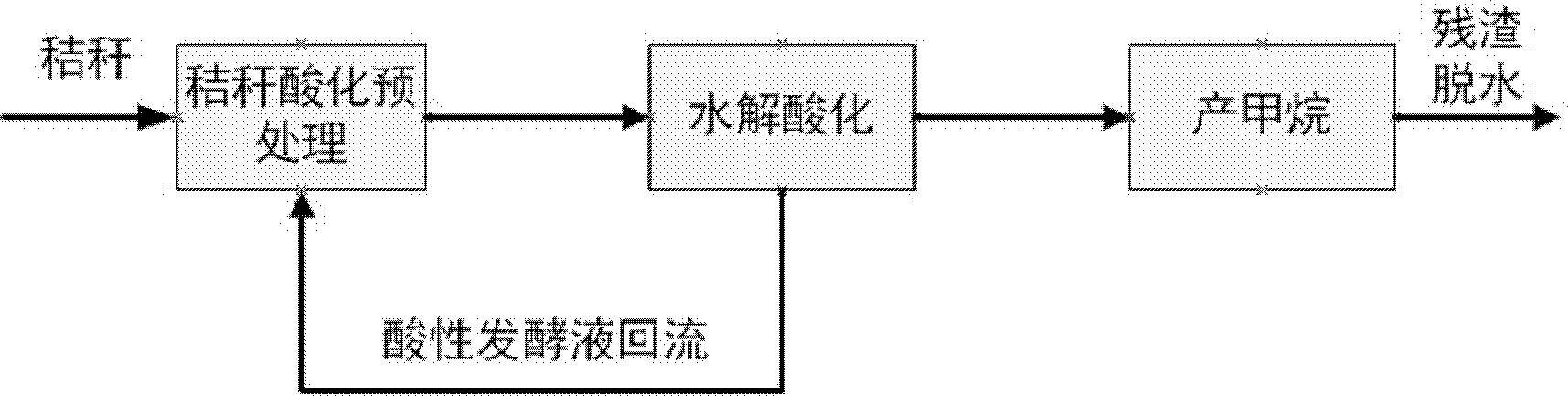
InactiveCN102533871AIncrease productionReduce pretreatment costsWaste based fuelFermentationAgricultural scienceAgricultural engineering
The invention discloses a method for treating crop straws by utilizing acidizing fermentation liquor backflow and applications thereof. The method for treating the crop straws by utilizing the acidizing fermentation liquor backflow comprises the following steps: performing hydrolytic acidification on the crop straws; then, enabling the acidizing fermentation liquor of the crop straws to flow back to perform acidolysis pretreatment on the crop straws; then, performing hydrolytic acidification fermentation on the pretreated crop straws; and finally, producing methane by utilizing the crop straws. According to the method for treating the crop straws by utilizing the acidizing fermentation liquor backflow, the acidolysis pretreatment is performed on the crop straws by utilizing the fermentation liquor of the crop straws, thereby, the time required by anaerobic digestion is shortened, the gas production rate is increased, and the operating cost is reduced. The invention provides a method for increasing the two-phase anaerobic digestion efficiency through pretreating the crop straws by utilizing the fermentation liquor backflow of the crop straws.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Integrated cogeneration wastewater sewage and waste polar fats/ oils/ greases/waxes (FOG) waste treatment method and facility
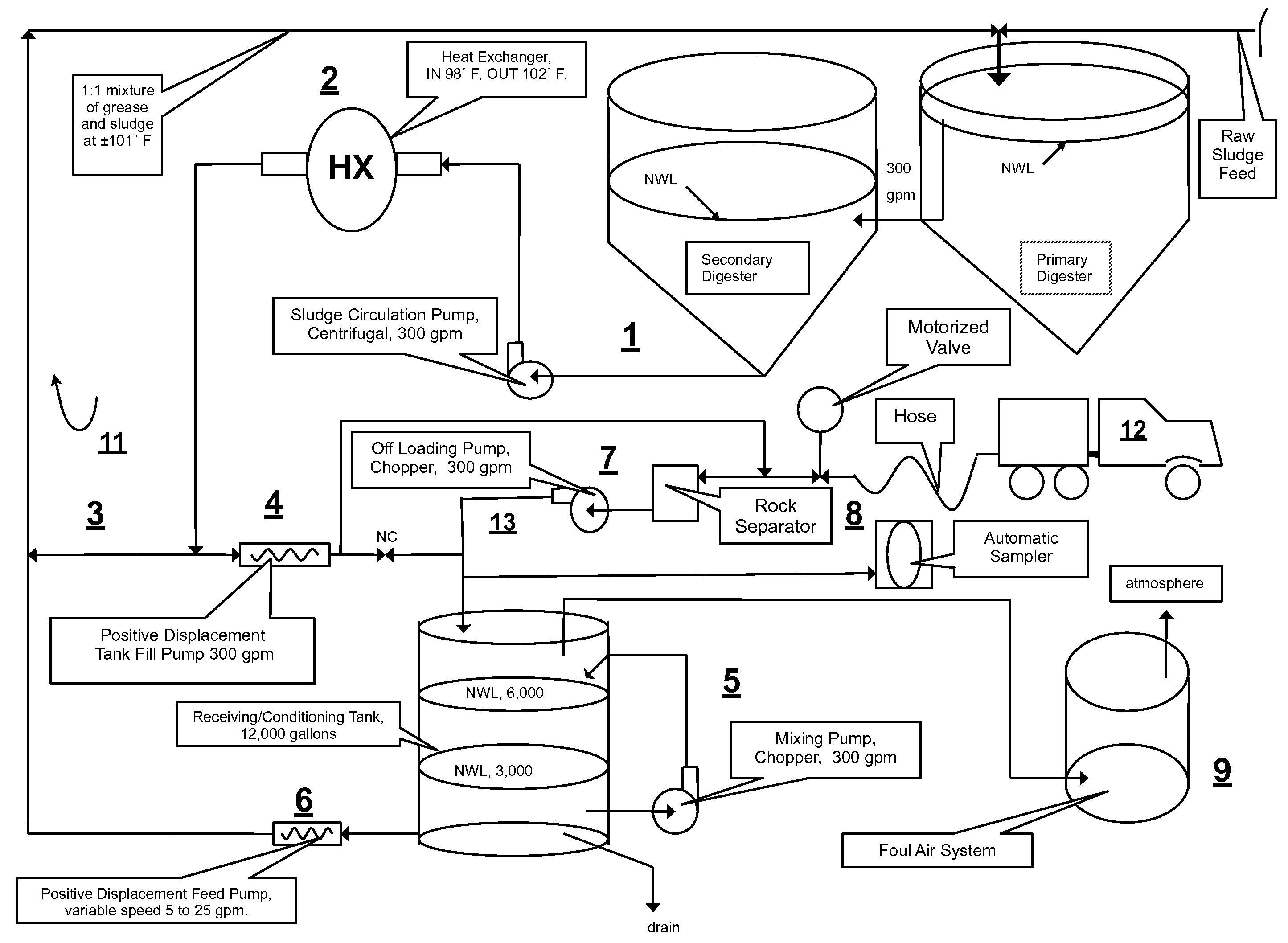
InactiveUS7485230B2Low solidsHigh energyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGeneral water supply conservationVolatile fatty acidsCogeneration
A system and method integrating treatment of waste, polar Fats / Oils / Greases (FOG) with conventional anaerobic wastewater treatment facilities for biologically fueling digestion of solids in, and steady state production of methane from treated wastewater streams that includes a slipstream loop circulating warmed, actively digesting sludge from the base to the head of the anaerobic wastewater treatment facility, a conditioning tank with input screened by a rock trap, actively digesting sludge pumped from the slipstream loop into the tank via the rock trap, before and after FOG wastes are pumped from a hauler tank via a hose connecting to the rock trap into the conditioning tank and mixed with actively digesting sludge in the tank to produce a feedstock slurry rich in volatile fatty acids for injection at a metered rate back into the actively digesting sludge slipstream loop for introduction at the head of the anaerobic wastewater treatment facility.
Owner:MAGNER JOSEPH A +1
Method and apparatus for treating refuse with steam
InactiveUS20070144027A1Increase humidityIncrease methane productionDrying solid materials with heatTransportation and packagingLitterDecomposition
A method of injecting steam into a landfill is provided. The steam enhances methane gas production in the landfill during the anaerobic phase, accelerates decomposition / biodegradation of the organic component of the trash prism during both the aerobic and anaerobic phases, and increases the rate of settlement of the landfill. A method of introducing a gaseous anaerobic fertilizer into the landfill is also provided. The fertilizer accelerates the decomposition / biodegradation of the organic component of the trash prism. A method of reducing the volume of a plastic component of the trash prism is provided, wherein the temperature and pressure of injected steam are raised to a level sufficient to melt plastic. Methods and apparatus for reducing the volume of a quantity of refuse prior to placing the refuse in a landfill are provided. The refuse is heated with steam and also compacted. The heat melts plastic in the refuse, and the compaction increases the quantity of refuse that can be placed into a given landfill.
Owner:RENAUD REGIS P
Method for strengthening autotrophic denitrification effect of urban sewage by using oxidation ditch
ActiveCN103102044AImprove phosphorus removal effectIncrease methane productionMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeMethanogenesis
The invention relates to a method for strengthening the autotrophic denitrification effect of urban sewage by adopting an oxidation ditch and belongs to the field of sewage treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: feeding the urban sewage into an aerobic zone of a high-load activated-sludge reactor so as to be subjected to anaerobic phosphorus release, feeding the urban sewage into an aerobic zone, adsorbing organic matters in the urban sewage onto activated sludge under the adsorbing action of the activated sludge, removing the phosphorus in the urban sewage by the way of aerobic phosphorus adsorbing, feeding the urban sewage in which the organic matters and the phosphorus are removed into the oxidation ditch, carrying out short-time nitrification and anaerobic ammonium oxidation to the urban sewage in a hypoxic zone, carrying out anaerobic ammonium oxidation to the urban sewage in an anoxic zone, and carrying out autotrophic nitrogen removal to the urban sewage by carrying out short-time nitrification and short-time anaerobic ammonium oxidation in the hypoxic zone and the anoxic zone repeatedly. By utilizing the method, the organic matters in the sewage can be enriched into the sludge in the process of removing the phosphorus biologically, the sludge can be used for the anaerobic methanogenesis, and the energy in the sludge can be recovered. In addition, the autotrophic nitrogen removal is realized by carrying out nitrification and anaerobic ammonium oxidation in the hypoxic zone and the anoxic zone repeatedly, and the energy consumed for treating the sewage can be reduced greatly.
Owner:SHANDONG ZIER ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Energy production with hyperthermophilic organisms
ActiveUS8278087B2Reduce oxygenIncrease methane productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityHydrogen
Owner:HYPERTHERMICS HLDG
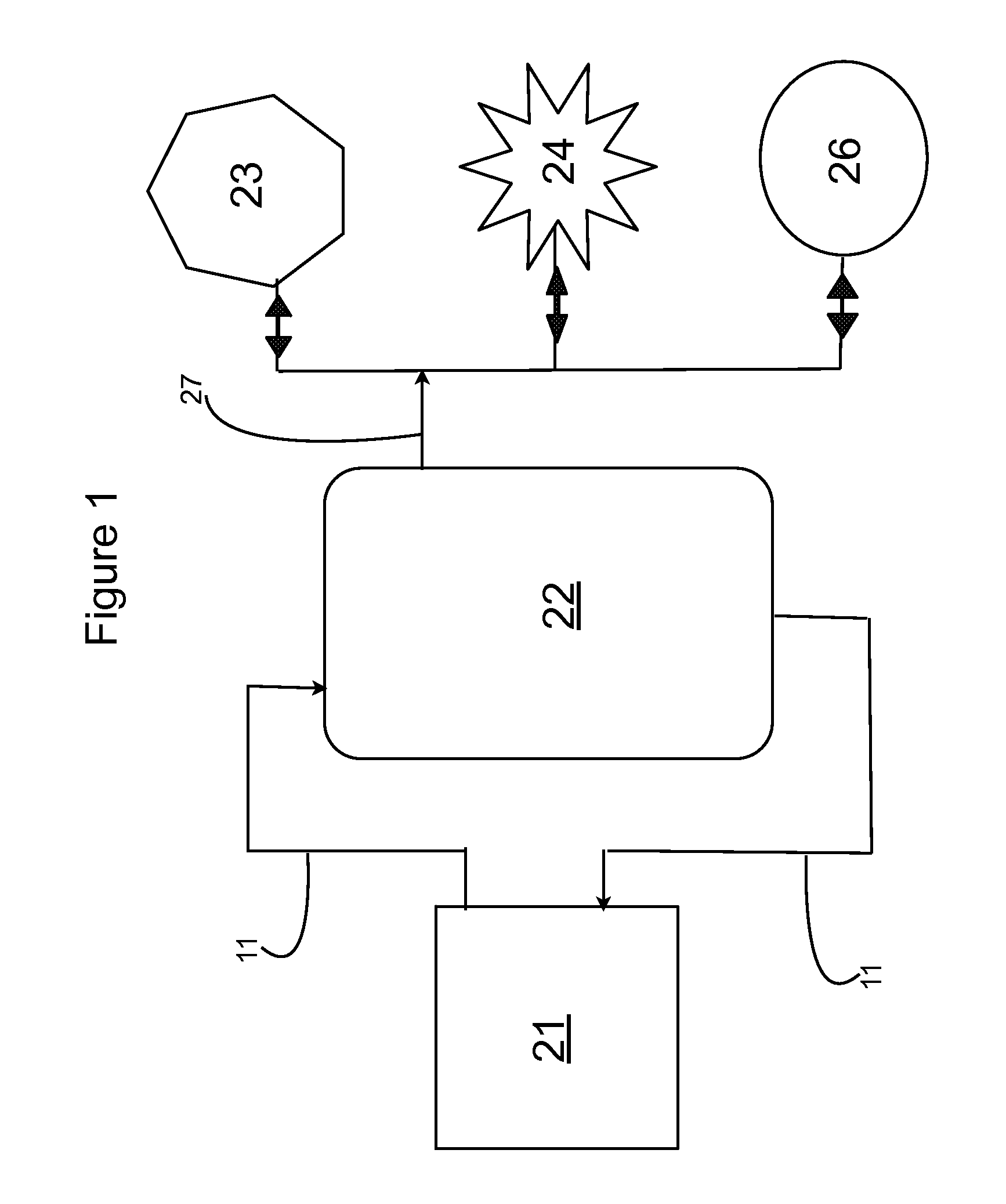
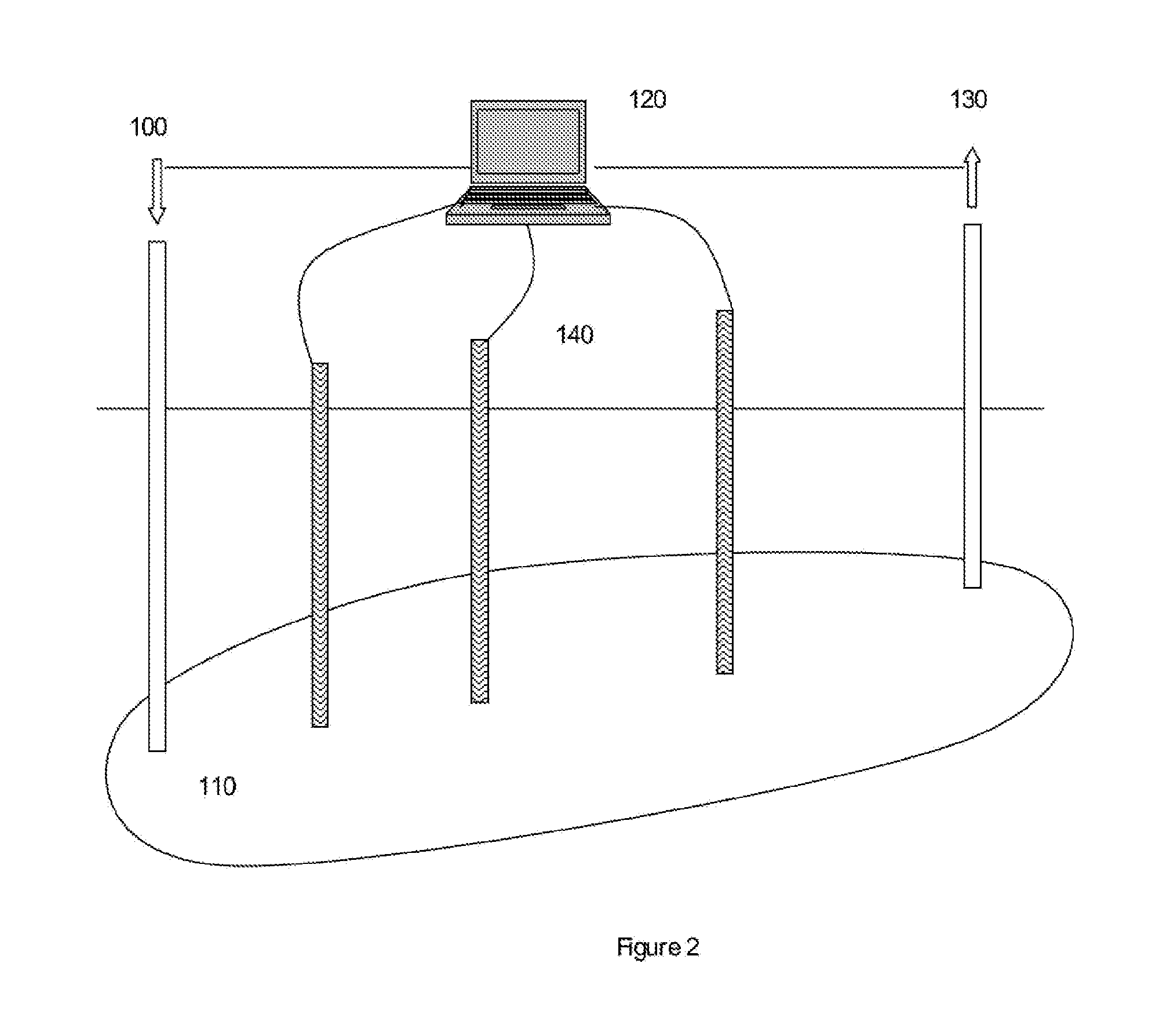
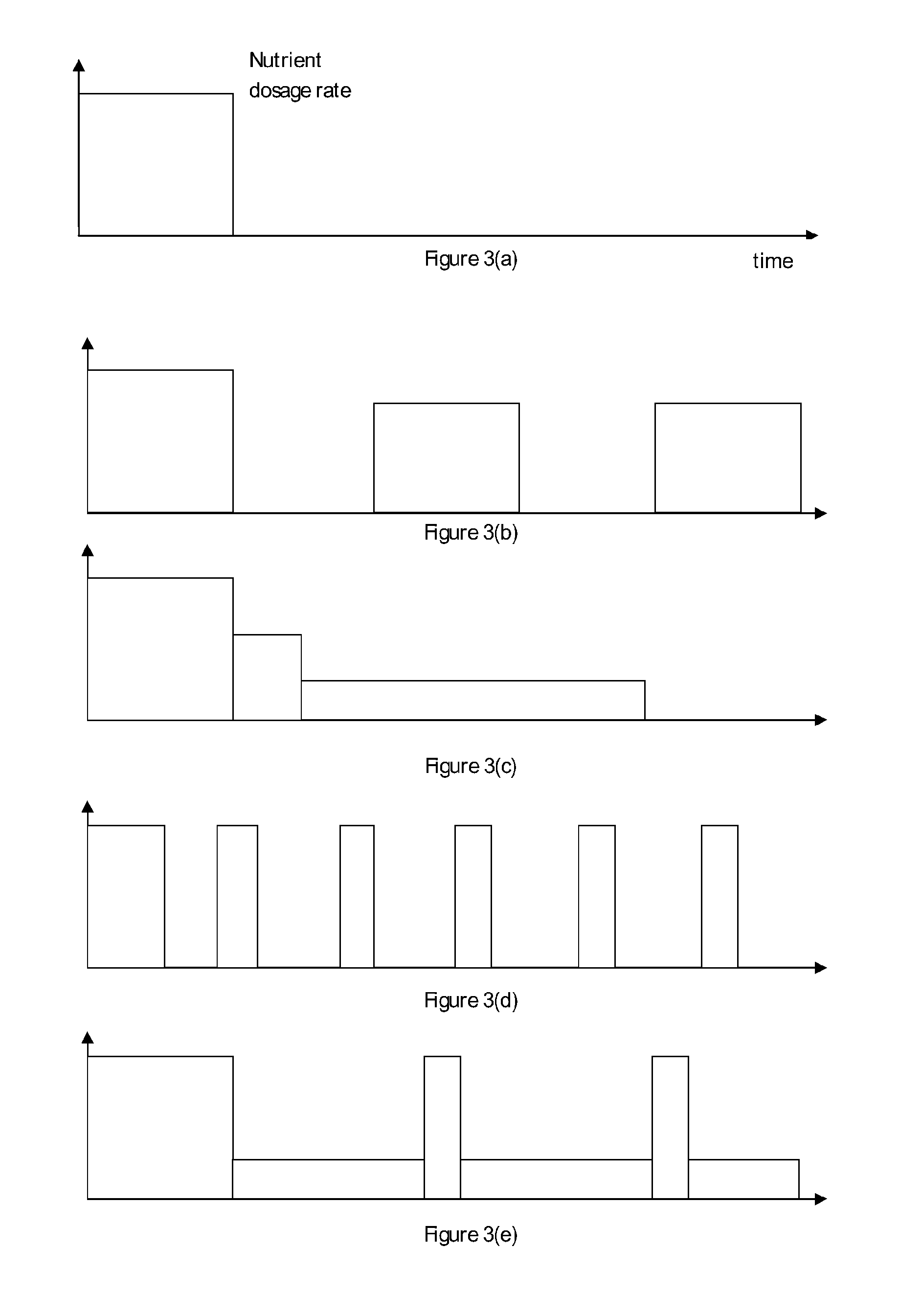
Process of sustaining methane production in a subterranean carbonaceous medium
ActiveUS20160319643A1Effective meanIncrease methane productionSurveyWaste based fuelMethane productionBiology
Process for stimulating and maintaining the activity of a microbial consortia within a subterranean solid carbonaceous medium to produce methane are described. The process comprises the steps of: (A) dosing a first nutrient composition into the microbial consortia environment, (B) monitoring the microbial consortia environment, including the generation of methane therein; (C) dosing a second nutrient composition into the microbial consortia based upon the results of step (B); and (D) repeating steps (B) and (C) and, if required, (E) dosing a further nutrient composition into the microbial consortia environment based upon the results of step (D).
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Methods and systems for biodegradable waste flow treatment using a transport fluid nozzle
InactiveUS20150096343A1Improve balanceFocusBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersWaste streamSewage
The present invention is directed to methods and systems for pre-treating sewage sludge in a sewage treatment works (STW) to facilitate anaerobic digestion. These methods include (a) passing sewage sludge through one or more pre-treatment devices, wherein each pre-treatment device comprises (i) a passage of substantially constant diameter having an inlet in fluid communication with the STW and an outlet; and (ii) a transport fluid nozzle communicating with the passage and adapted to inject high velocity transport fluid into the passage; (b) passing the sewage sludge treated in step (a) to an anaerobic digester; and (c) collecting methane produced in step (b). Other methods are also provided for pre-treating a bio-degradable waste flow. Such methods include (a) passing bio-degradable waste flow through one or more pre-treatment devices, wherein each pre-treatment device comprises (i) a passage of substantially constant diameter having an inlet in fluid communication with the bio-degradable waste flow and an outlet; and (ii) a transport fluid nozzle communicating with the passage and adapted to inject high velocity transport fluid into the passage; (b) dewatering the bio-degradable waste flow from step (a); and (c) optionally compacting the material resulting from step (b).
Owner:PURSUIT MARINE DRIVE
Method for accelerating anaerobic propionic acid and butyric acid decomposition by utilizing ethanol and charcoal
ActiveCN106830308AImprove decomposition rateReduce inhibitionWater contaminantsWaste based fuelChemical oxygen demandPropanoic acid
The invention discloses a method for accelerating anaerobic propionic acid and butyric acid decomposition by utilizing ethanol and charcoal. The method comprises the following steps: adding ethanol into wastewater containing propionic acid or butyric acid according to a ratio 4:1 to 1:1 of chemical oxygen demand, and operating an anaerobic digestion device; controlling the hydraulic retention time of the device as well as the pH value and temperature in the device; adding charcoal into a charcoal filling layer in the device, and sealing the device; gradually reducing the addition amount of ethanol after the device is operated until the wastewater does not contain any ethanol, and monitoring the concentration of the propionic acid or butyric acid in the effluent of the device and methane yield in the device. According to the technical scheme, the method can achieve the technical effects that the decomposition rate of the anaerobic propionic acid or butyric acid is accelerated, a methane production acid balance is maintained, and the methane yield is improved. The technology is low in investment cost and simple to operate, and the effect is obviously improved. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for the anaerobic digestion device which is positioned in acidification state or in which methanation is inhibited, and can also be used for upgrading and rebuilding of the anaerobic digestion device for resisting high wastewater inlet load impact.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving production of methane from surplus sludge of wastewater treatment plant
InactiveCN103193369AIncrease fatty acid content and methane productionFully Recycle and ReuseWaste based fuelBiological sludge treatmentChemistryAcid production
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental protection and relates to a method for improving production of methane from surplus sludge of a wastewater treatment plant. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) thoroughly mixing sludge with ryegrass for fermentation, hydrolysis and acid production; and (2) performing anaerobic fermentation on the mixture obtained in the step (1) to generate methane. The method for prompting the production of methane from surplus sludge of the wastewater treatment plant with energy grass is capable of improving the yield of short chain fatty acids and the yield of methane from sludge at the same time, and also capable of recovering and reutilizing organic matters in the sludge more thoroughly; and pollution of sludge on the environment is reduced.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method and apparatus for steam biomass reactor
ActiveUS20090314625A1Facilitate of organic materialMaterial is delayedGas treatmentGas production bioreactorsDecompositionProcess engineering
A method and apparatus for a steam biomass reactor converts organic waste placed inside a sealed steam injected reactor to biogas (methane CH4 and carbon dioxide CO2). The amount of liquid introduced into the reactor can be minimized, increased methane and CO2 can be produced, and the methane produced can have higher Btu values as compared to methane produced in other reactors. Some embodiments provide a method of injecting steam into a sealed vessel that is loaded with organic waste and collecting the methane produced by accelerated decomposition / biodegradation of the organic component of the waste within the vessel. The steam accelerates the decomposition of the organic refuse, thereby enhancing the production of methane gas and CO2.
Owner:RENAUD REGIS P
Coal bed methane borehole pipe liner perforation system
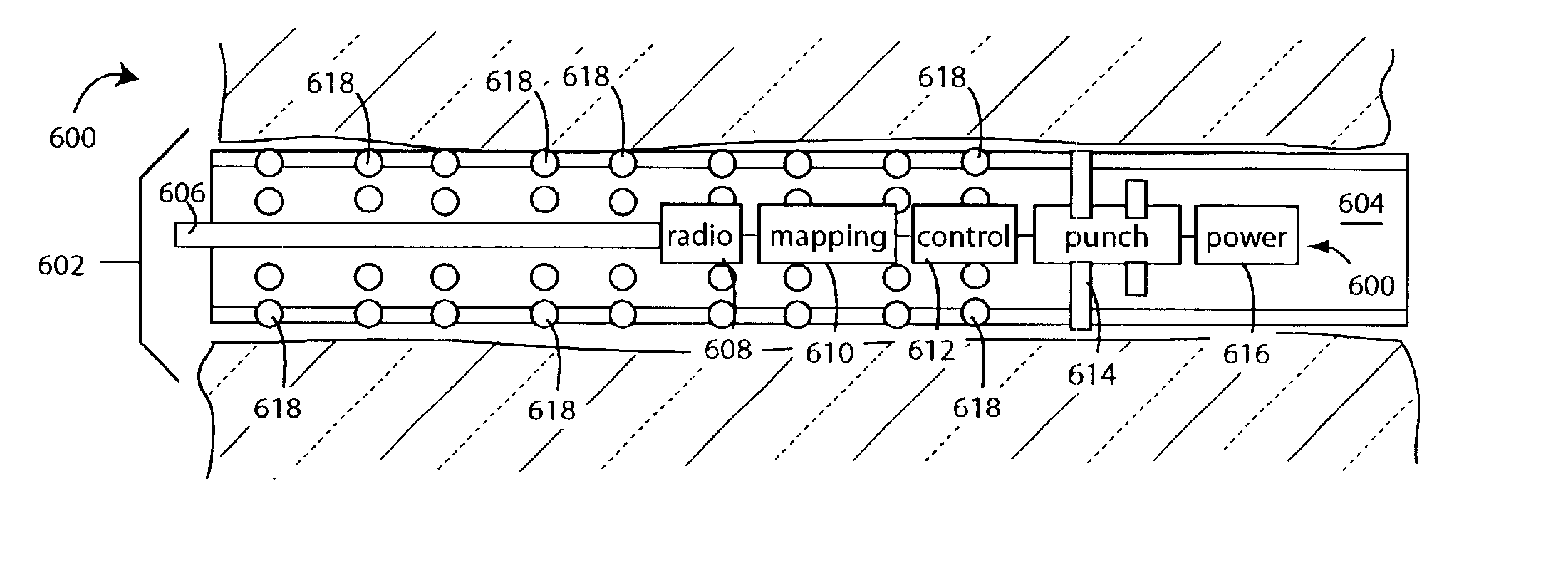
InactiveUS6892815B2Increase coalbed methane production profitIncrease methane productionDefence devicesElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPunchingPlastic pipework
A coalbed methane borehole pipe liner perforation system comprises a plastic pipe punch that slips down inside a coalbed methane production borehole lined with a non-perforated plastic pipe. A ground-penetrating radar is used inside the plastic-pipe lined borehole to determine which sections of the pipe are in contact with groundwater. The punch is then operated along the length of the plastic-pipe lined borehole to perforate it for methane-gas collection wherever such groundwater is not present. A radar survey to determine groundwater contact can be made simultaneously in combination with the punching of liner pipe perforations, or earlier in a separate operation.
Owner:STOLARCZYK LARRY G
Reactor for producing acid phase from urban solid waste through two-phase anaerobic digestion
PendingCN106929410AReduce lossEfficient use ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlMethanogenesis
The invention belongs to the field of solid waste treatment devices and discloses a reactor for producing an acid phase from urban solid waste through two-phase anaerobic digestion. The reactor comprises a pretreatment device, a hydrolytic acidification region and a methanogenesis region which are distributed from top to bottom, wherein a crusher and a heating device are arranged in the pretreatment device, and a feeding channel is arranged in the pretreatment device and is connected with the hydrolytic acidification region; a rotatable semi-closed roller reactor and a heating device are arranged in the hydrolytic acidification region, and a multi-layer push type spiral stirrer is arranged in the roller reactor; the hydrolytic acidification region and the methanogenesis region are separated through a partition board and are communicated through a flow guide pipe; a heating device is arranged in the methanogenesis region. The reactor is of an integrated design, is integrated with functions of pretreatment, reaction fermentation, temperature control and air collection and is multifunctional equipment, the loss in a material transfer process can be reduced, and each space is effectively utilized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Organic waste anaerobic digestion method
ActiveCN111826403AIncrease speedHigh organic loadSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWaste based fuelBiofilmMicroorganism
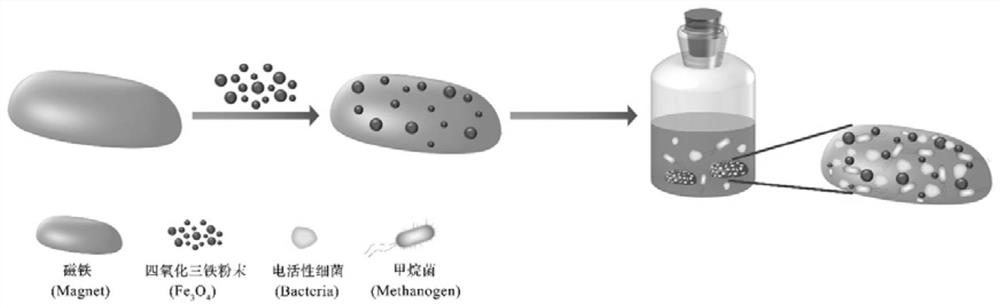
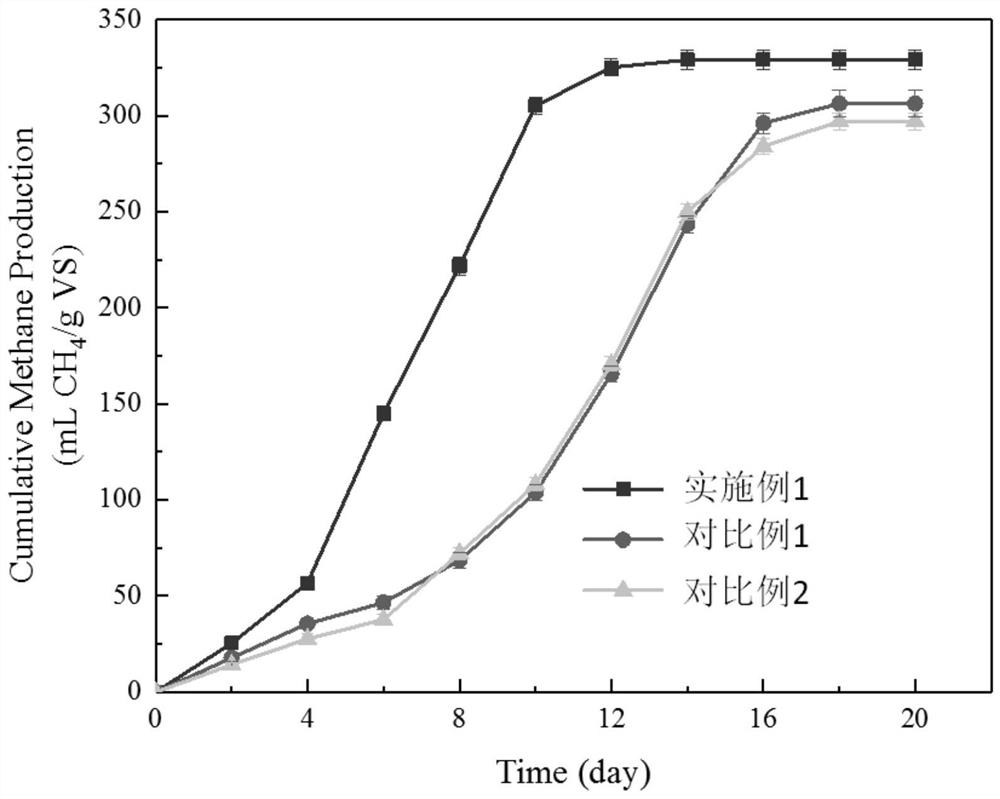
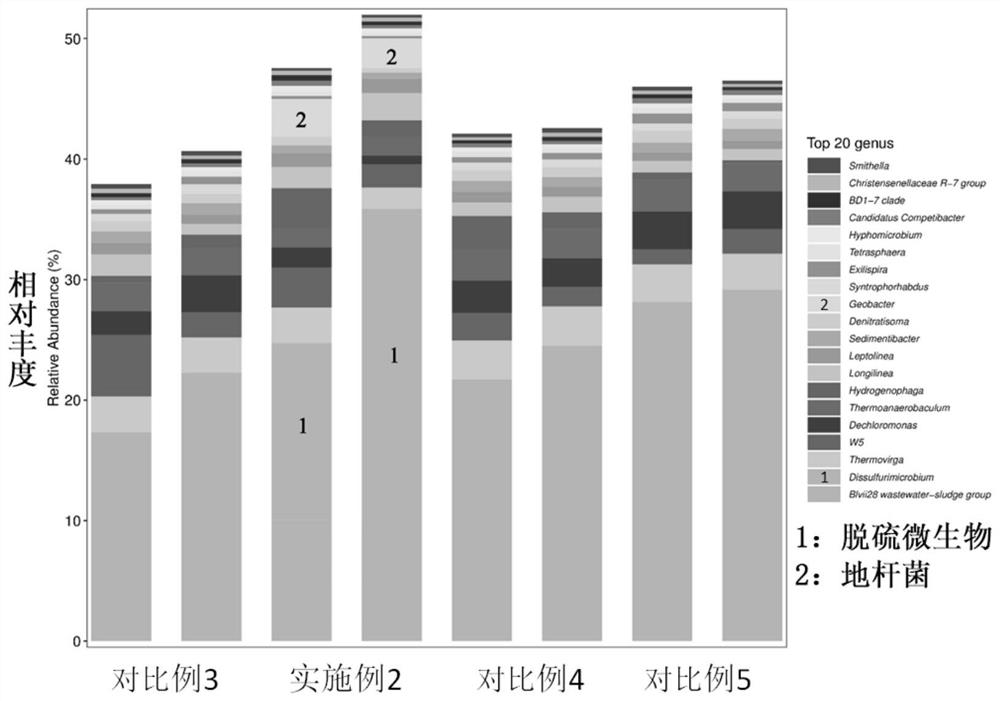
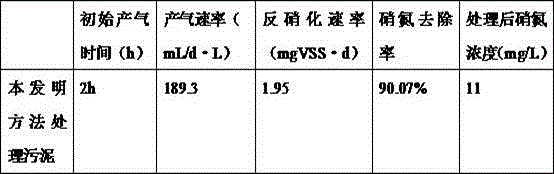
The invention relates to an organic waste anaerobic digestion method. The method comprises the steps of adding organic waste, inoculum and a catalyst rich in high efficiency microorganisms to a reactor, and performing stirring for a reaction to generate methane. The catalyst adopts a magnet as a basal body and ferroferric oxide as a surface adsorber to enrich electrical activity microorganisms capable of realizing efficient anaerobic transformation of the organic waste and enable the microorganisms to be quickly combined with the ferroferric oxide on the surface of the magnet to form a biomembrane, the rate for generating the methane through anaerobic digestion is increased, the organic loading and the methane generating amount of an anaerobic digestive system can be increased, and the reaction period can be shortened. Compared with the prior art, the catalyst is used for enriching the electrical activity microorganisms capable of realizing efficient anaerobic transformation of the organic waste and enabling the microorganisms to be quickly combined with the ferroferric oxide on the surface of the magnet to form the biomembrane, the rate for generating the methane through anaerobicdigestion is increased, the organic loading and the methane generating amount of the anaerobic digestive system can be increased, and the reaction period can be shortened.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Microbial preparation for sludge anaerobic fermentation
InactiveCN106754543ALower initial costAdaptableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus amyloliquefaciensSludge
The present invention belongs to the field of microbial technology and discloses a microbial preparation for sludge anaerobic fermentation. The microbial preparation comprises a mixed bacteria liquid and a carrier, wherein the mixed bacteria liquid is prepared from Bacillus pumilus, enterobacter cloacae, denitrifying bacteria, paracoccus denitrificans, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and lactococcus lactis. The microbial preparation can greatly increase the amount of methane generated by sludge, increase the utilization rate of the sludge, and recycle the sludge.
Owner:王筠涵
Dye wastewater treatment apparatus and method thereof
ActiveCN107010794AImprove processing efficiencyImprove the efficiency of COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) removalTreatment using aerobic processesWater contaminantsAnthraquinonesAcetic acid
The invention discloses a dye wastewater treatment apparatus and a method thereof. Phosphorus / cyanogen (CN)-containing wastewater, gypsum wastewater, anthraquinone substance-containing wastewater and alcohol / acetic acid degradable wastewater are classified from the source, enters different devices in the apparatus according to different water properties and are treated to eliminate the pollution from the source, and the method is improved to increase the resource utilization efficiency, greatly reduce the instability and the toxicity of raw water, reduces the impact of wastewater to a biochemical system and realize strong adaptation to the sudden change of the water quality and the water volume, less residual sludge and the recycling and the long-period stable running of the apparatus. The apparatus and the method have the advantages of small investment, high treatment efficiency, stable outlet water quality, and convenience in operation.
Owner:宁波德欣科技有限公司
Method and system of treating biomass wastes by biochemistry-thermochemistry multi-point interconnection
ActiveUS20160376205A1Enhance enrichment growingImprove stabilityBio-organic fraction processingCombustible gas coke oven heatingLiquid productLiquid fuel
The present invention discloses a method and a system of treating biomass wastes by biochemistry-thermochemistry multi-point interconnection. The present invention applies solid, gas and liquid products of the thermochemical treatment subsystem to the biochemical treatment subsystem and applies heat produced by the biochemical treatment subsystem to the thermochemical treatment subsystem, forming multi-point and two-way interconnection between the biochemical treatment subsystem and the thermochemical treatment subsystem, thereby increasing the yield and stability of energy gas of the biochemical treatment subsystem and reducing pollution and energy consumption of the thermochemical treatment subsystem respectively. The present invention is suitable for treating biomass wastes with high and low water contents at the same time, producing soil amendment, liquid fuel and biogas, having properties of low secondary pollution and significant reduction of greenhouse gas emission and so on. The bio-stability, humus content and nitrogen content of the solid product are as high as soil amendment, making it easy to store and transport.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method and device for improving treatment efficiency of anaerobic reactor in pharmaceutical wastewater treatment process
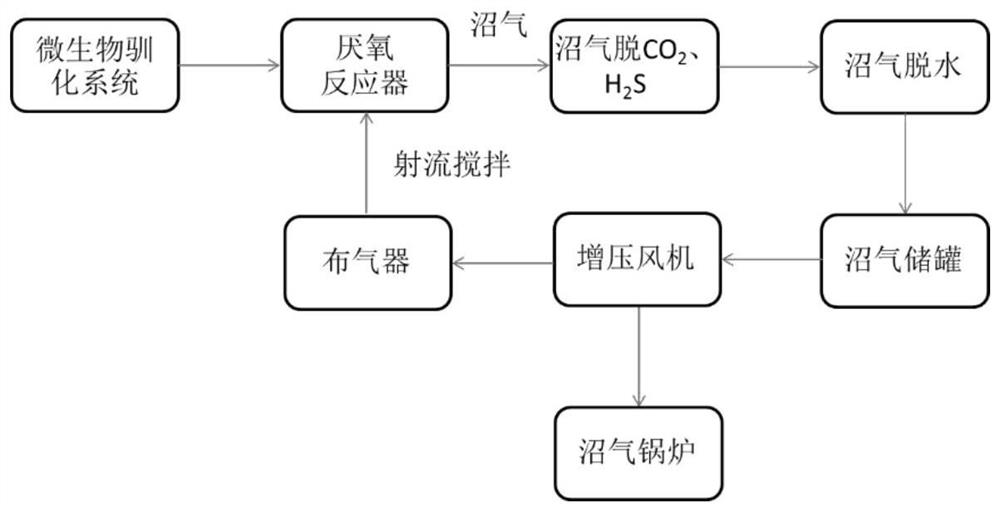
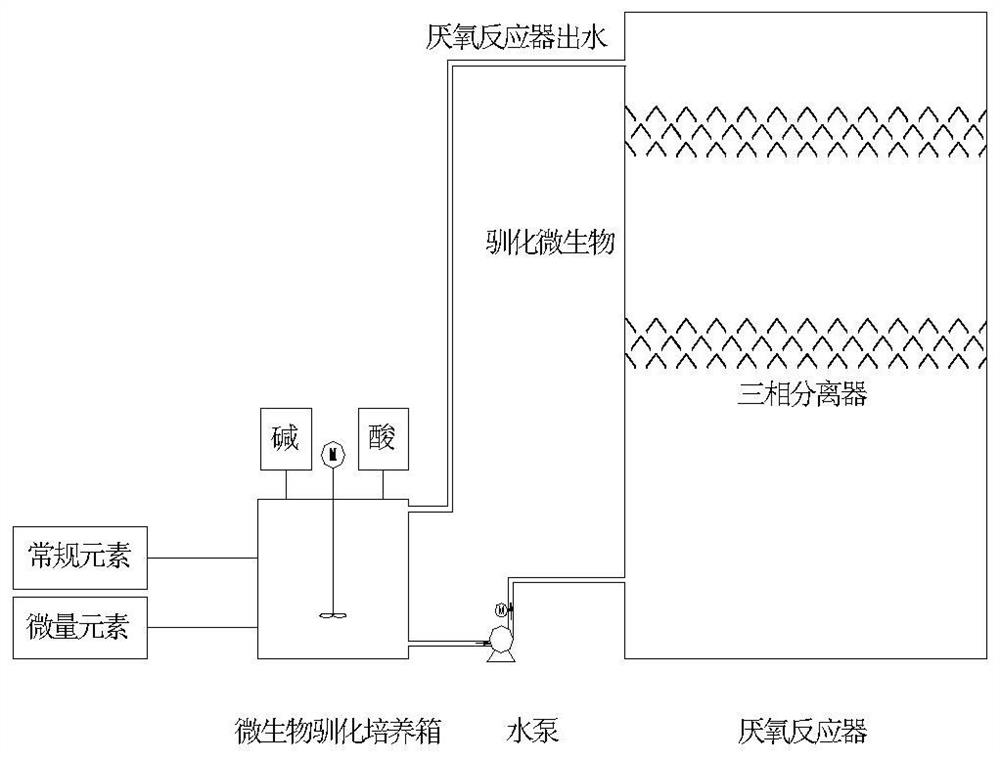
ActiveCN112707504AHigh activityGood removal effectWater contaminantsDispersed particle separationMicroorganismChemical oxygen demand
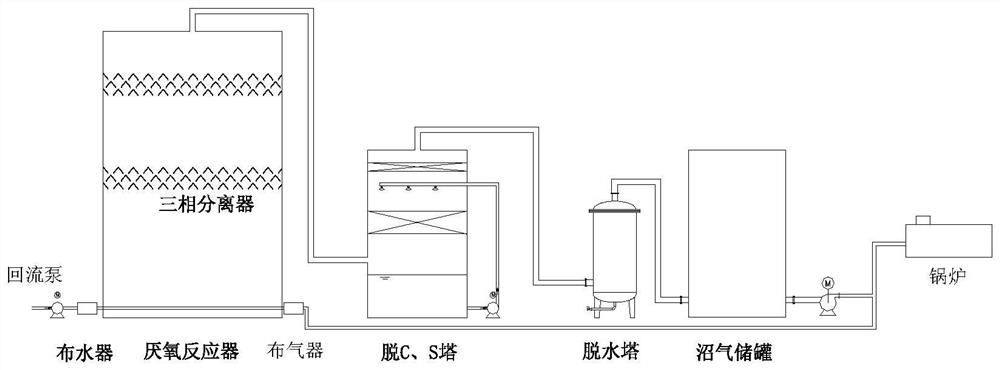
The invention belongs to the technical field of industrial sewage treatment, and particularly discloses a method and a device for improving the treatment efficiency of an anaerobic reactor in a pharmaceutical wastewater treatment process, and the device comprises the following two systems: a microorganism domestication system which is used for carrying out domestication culture on microorganisms in an anaerobic reactor, and pumping the domesticated microorganisms into the anaerobic reactor; and a biogas impurity removal and utilization system which is used for enabling biogas to sequentially pass through a CO2 and H2S removal system, a dehydration system and a biogas storage tank; feeding part of biogas into a boiler for combustion through a booster fan; and enabling the other part of the biogas to be mixed with effluent of an anaerobic reflux pump and to enter the anaerobic reactor, so that the aims of mixing and stirring gas and liquid and reducing the concentration of CO2 in an anaerobic system are fulfilled. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) removal rate of the anaerobic reactor is increased by about 10% and the methane yield is increased by about 15% by combining the microbial acclimation system, the marsh gas impurity removal system and the anaerobic reactor, so that the treatment efficiency of the anaerobic reactor is greatly improved, and favorable conditions are provided for subsequent working sections.
Owner:湖北金润德环保技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com