Rapid identification method and kit for MTBC (mycobacterium tuberculosis complex)
A technology of mycobacterium tuberculosis and mycobacteria, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, material stimulation analysis, microbial measurement/testing, etc., can solve problems such as inability to meet rapid clinical diagnosis, time-consuming and labor-intensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Embodiment 1. Primer and probe design
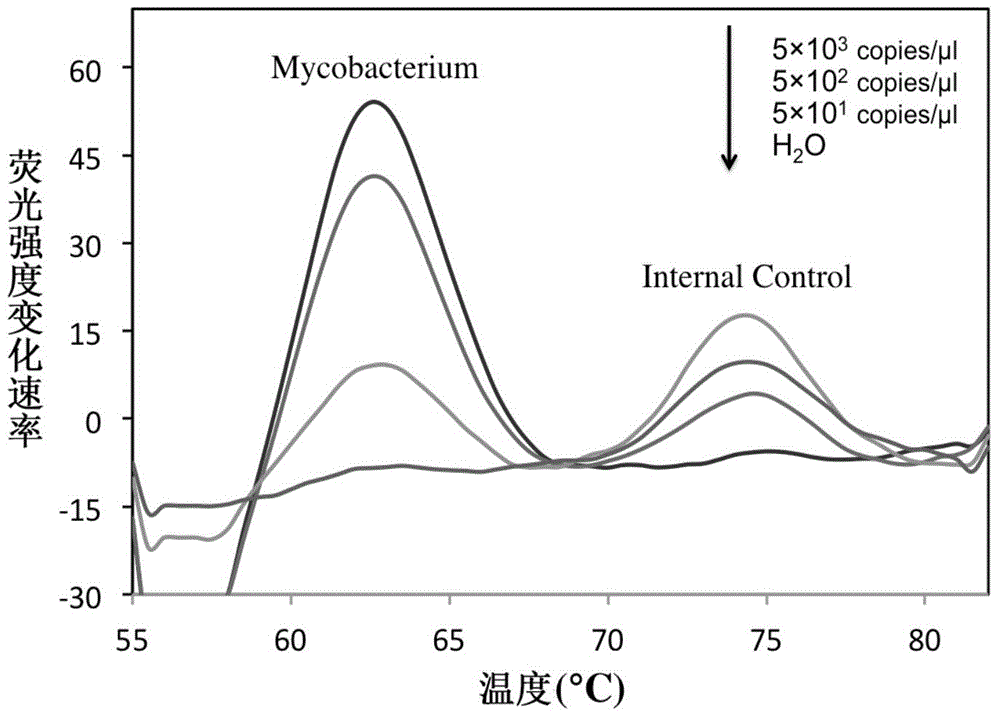
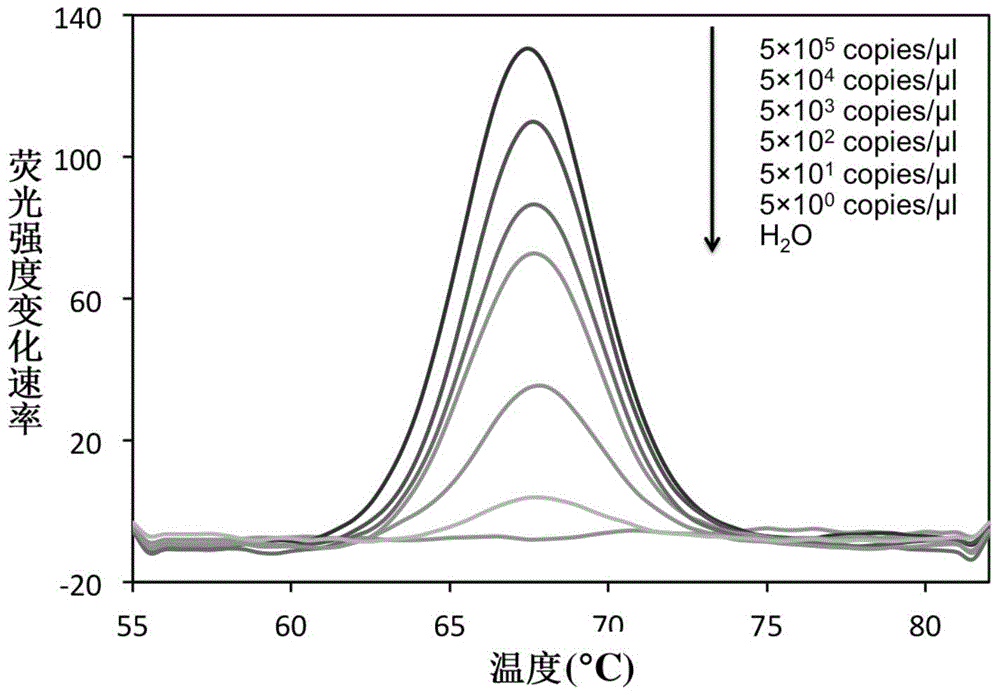
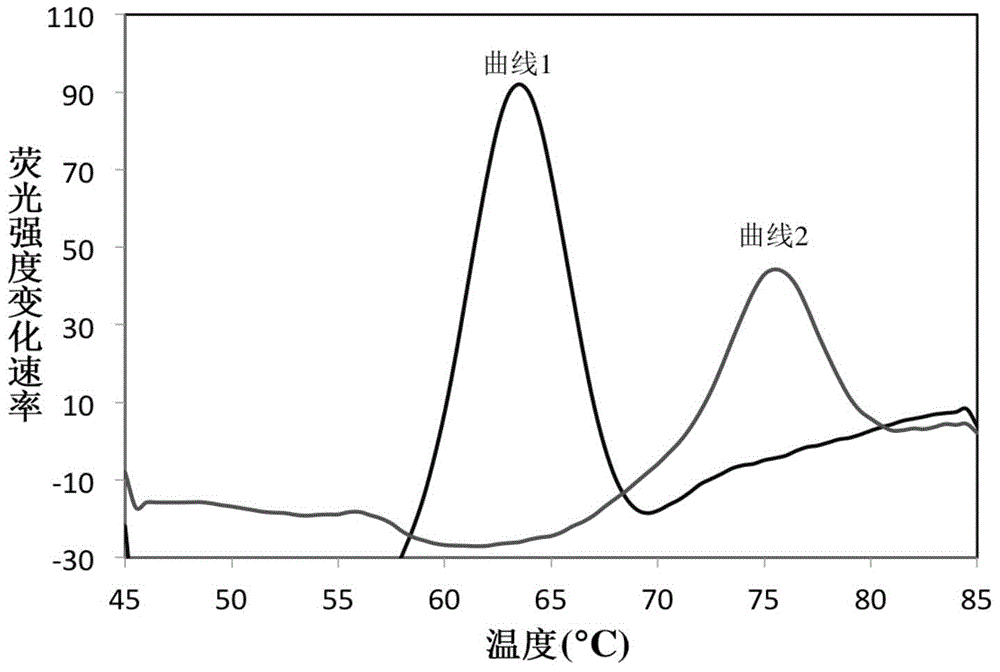
[0062] The 16S rRNA gene sequences of common mycobacteria (including MTBC and NTM) and common non-mycobacteria were searched in the NCBI database, and bioinformatics comparison analysis was performed to select the bacteria with the ability to identify and distinguish mycobacteria from non-mycobacteria. Bacillus and the conserved sequence fragments of MTBC and NTM are used as target sequences, among which, target sequence one (rrs1022-1046) is used to identify Mycobacterium bacteria and non-Mycobacterium bacteria. In this sequence region, Mycobacterium bacteria show Sequence identity, non-mycobacteria have different mutations in this region, so mycobacteria can be distinguished from non-mycobacteria by detecting this region; target sequence two (rrs1269-1291) is used to distinguish MTBC from NTM, In this sequence region, MTBC bacteria show sequence consistency, while NTM bacteria have different mutations in this region, and the ide...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2: Construction and preparation of internal reference plasmids and positive control plasmids
[0069] 1. Construction of internal reference plasmids and positive control plasmids
[0070] Internal reference plasmid construction: artificially synthesize a DNA single-stranded fragment, which contains the binding sequence of the upstream and downstream primers (16sR, 16sL) and the sequence that is completely complementary to the probe Probe-Myco, and uses this sequence as a template to perform PCR amplification reaction to obtain The double-stranded product was cloned into the pMD19-T vector, and the DNA sequence was determined. The recombinant plasmid was used as an internal reference standard and named 16s-IC. The internal reference plasmid was added to each reaction system at a low concentration (50 copies / reaction), in order to monitor whether the entire reaction system is working properly: 1) When the test sample is non-mycobacterial DNA, the internal referen...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Example 3: Clinical Mycobacterium Genomic DNA Extraction
[0079] Extract mycobacterial genomic DNA by thermal lysis: 1) Scrape 1-2 inoculum loops of mycobacteria from the solid medium, resuspend in 100uL TE, inactivate at 80°C for 30 minutes, 2) inactivate the strain Take out the P3 laboratory and perform the following operations: boil at 100°C for 1 minute, immediately put it on ice for 2 minutes, centrifuge at 12000r / min for 10 minutes, take the supernatant and put it in another sterile EP tube, store it at -20°C, and put it on ice for 2 minutes. The supernatant is the template DNA for PCR amplification.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com