Three-generation sequencing-based whole genome structure variation analysis method and system
A structural variation, whole-genome technology, applied in the field of whole-genome structural variation analysis based on third-generation sequencing, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, high single-base error rate, and good randomness of errors in the second-generation technology, and meet the accuracy requirements. or sensitivity requirements, time-consuming, and the effect of improving detection speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
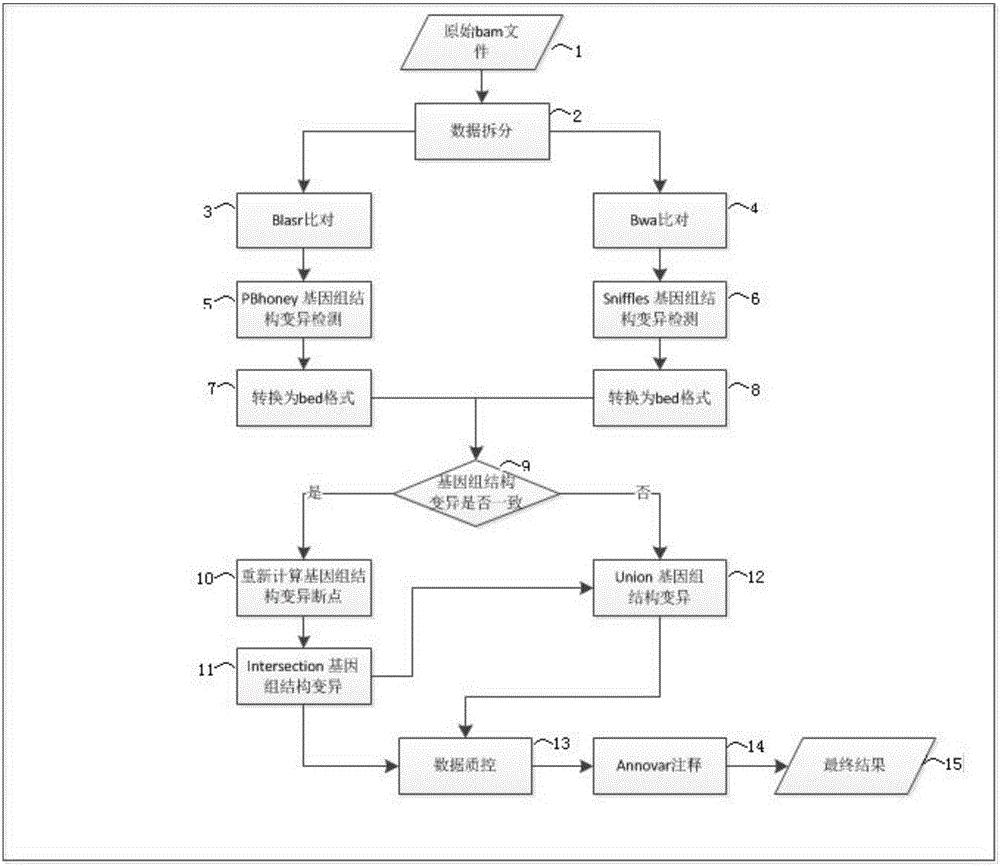
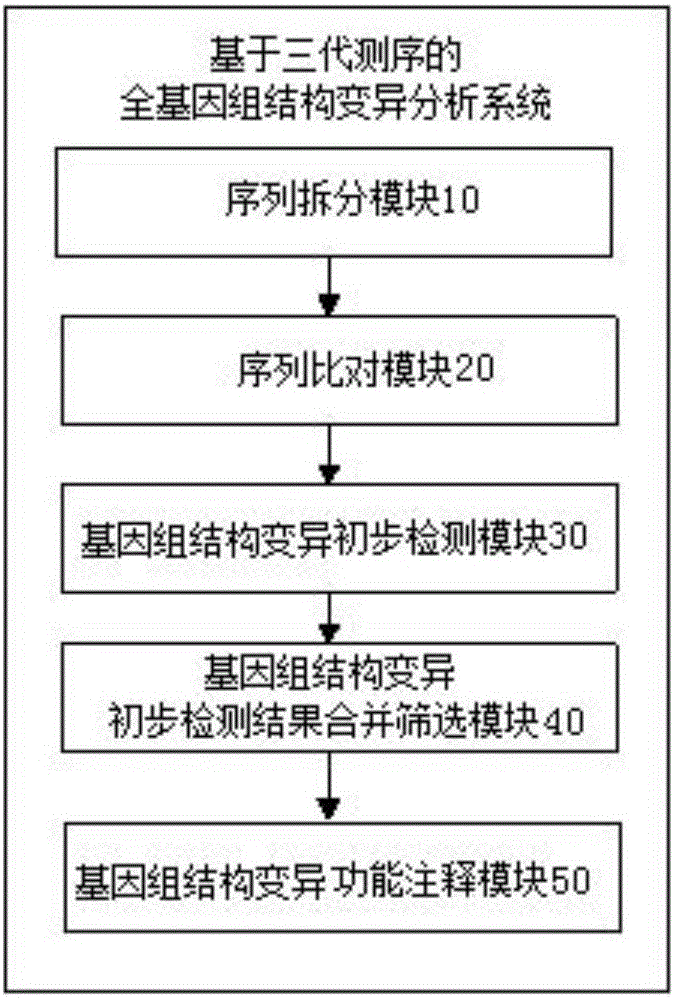
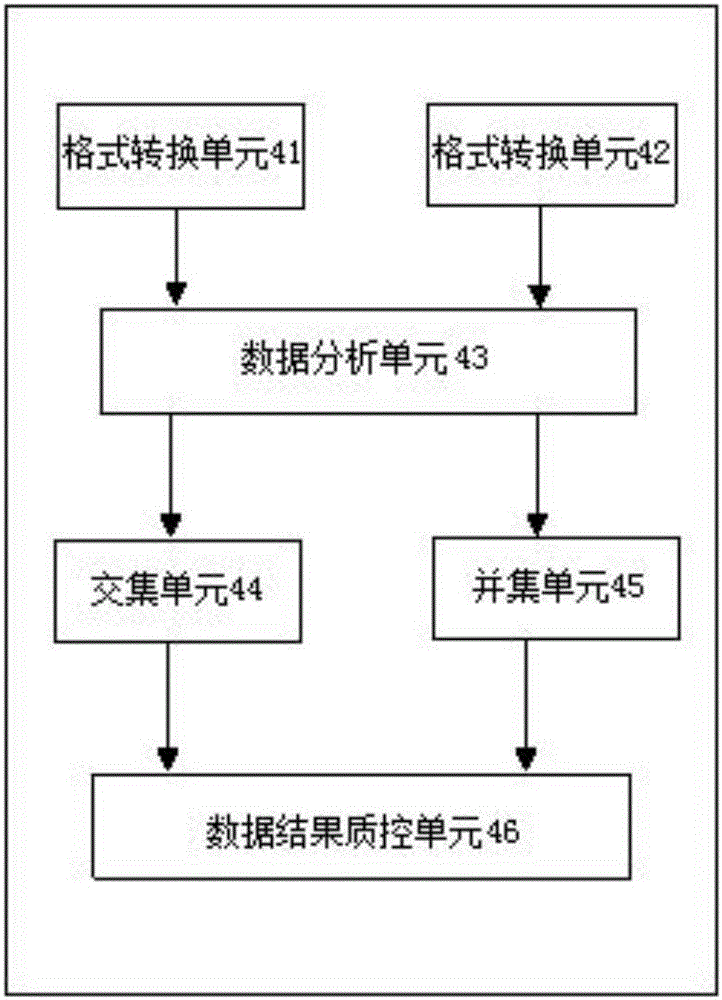
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Sample: This sample comes from a voluntary donor of our company. This sample has a good research basis for first-generation and next-generation sequencing. Therefore, this example uses this sample as a demo case to illustrate the accuracy of this system.
[0092] Data analysis and result statistics:
[0093] raw data statistics
[0094] Table 1 Raw data statistics
[0095] Number of sequencing bases
34.28G
Number of polymer reads
3.59M
Polymer read average length
9,441
polymer read length N50
16,694
number of subreads
12.88M
subread average length
2,624
subread average N50
3,208
[0096] Comparison result statistics
[0097] Through blasr alignment, 12.85M reads were finally aligned to the genome (version number hg19).
[0098] Compare with standard data
[0099] It is currently known that there are 2194 and 68 deletion sequences and insertion sequences longer than 200 bp in the samples use...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Sample: This sample is a whole-genome sequencing sample completed by our company using three-generation sequencing technology. The sequencing depth of this sample is as high as 100X, so the detection result of the genome structure variation of this sample has high reliability. In this embodiment, the genomic structural variation detected by various systems under high-depth conditions is used as a standard set, and 10X data is randomly selected as test data to test the accuracy of the present invention.
[0107] Data analysis and result statistics:
[0108] The statistical results of the test data in this embodiment are as follows
[0109] Table 4 Raw data statistics
[0110] Number of sequencing bases
34.22G
Number of polymer reads
2.39M
Polymer read average length
14,344
polymer read length N50
12,169
number of subreads
3.03M
subread average length
11,294
subread average N50
9,954
[0111] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com