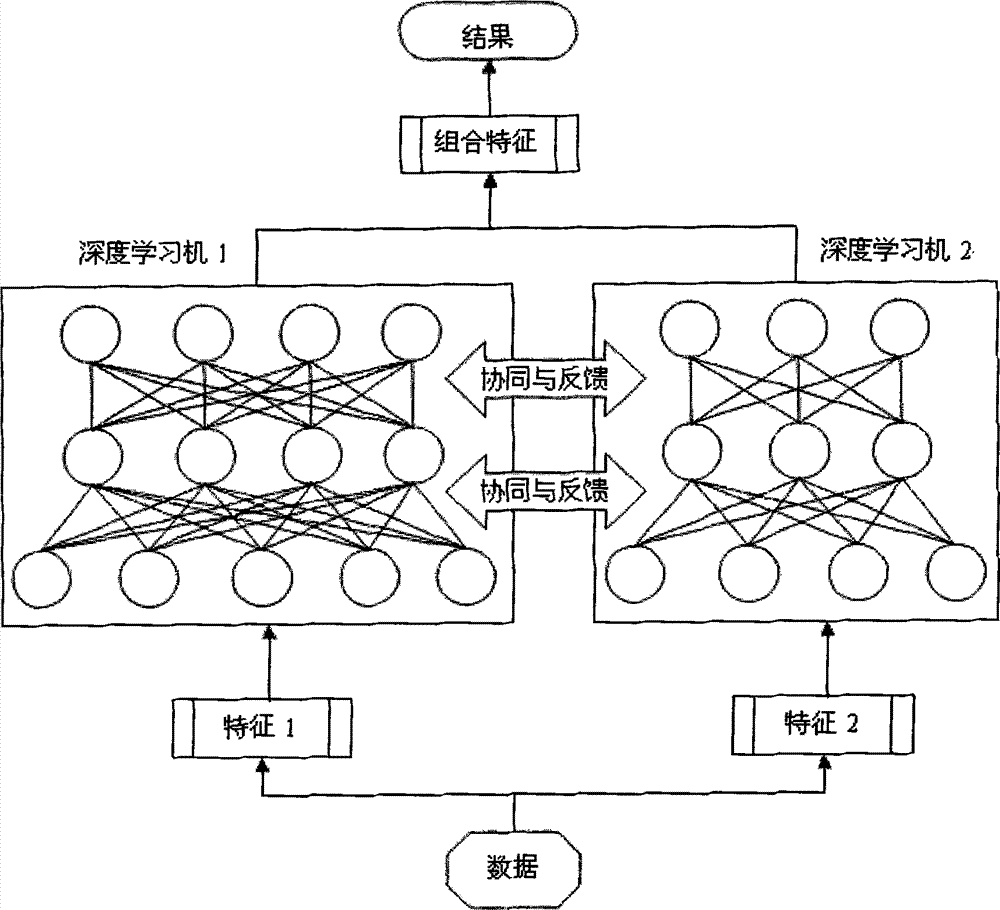
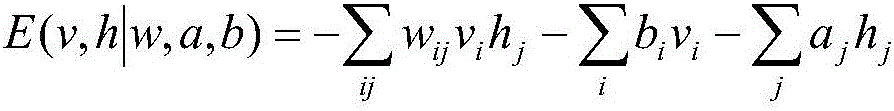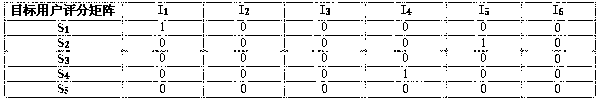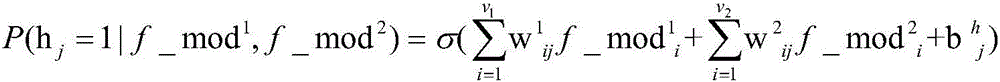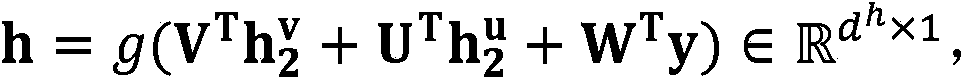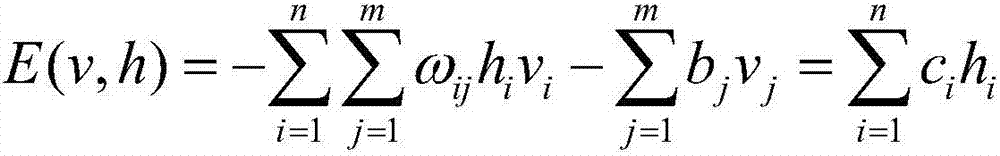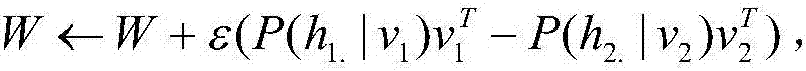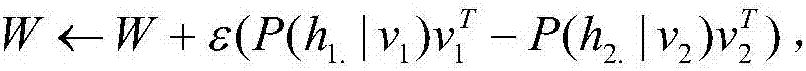Patents
Literature
177 results about "Boltzmann machine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
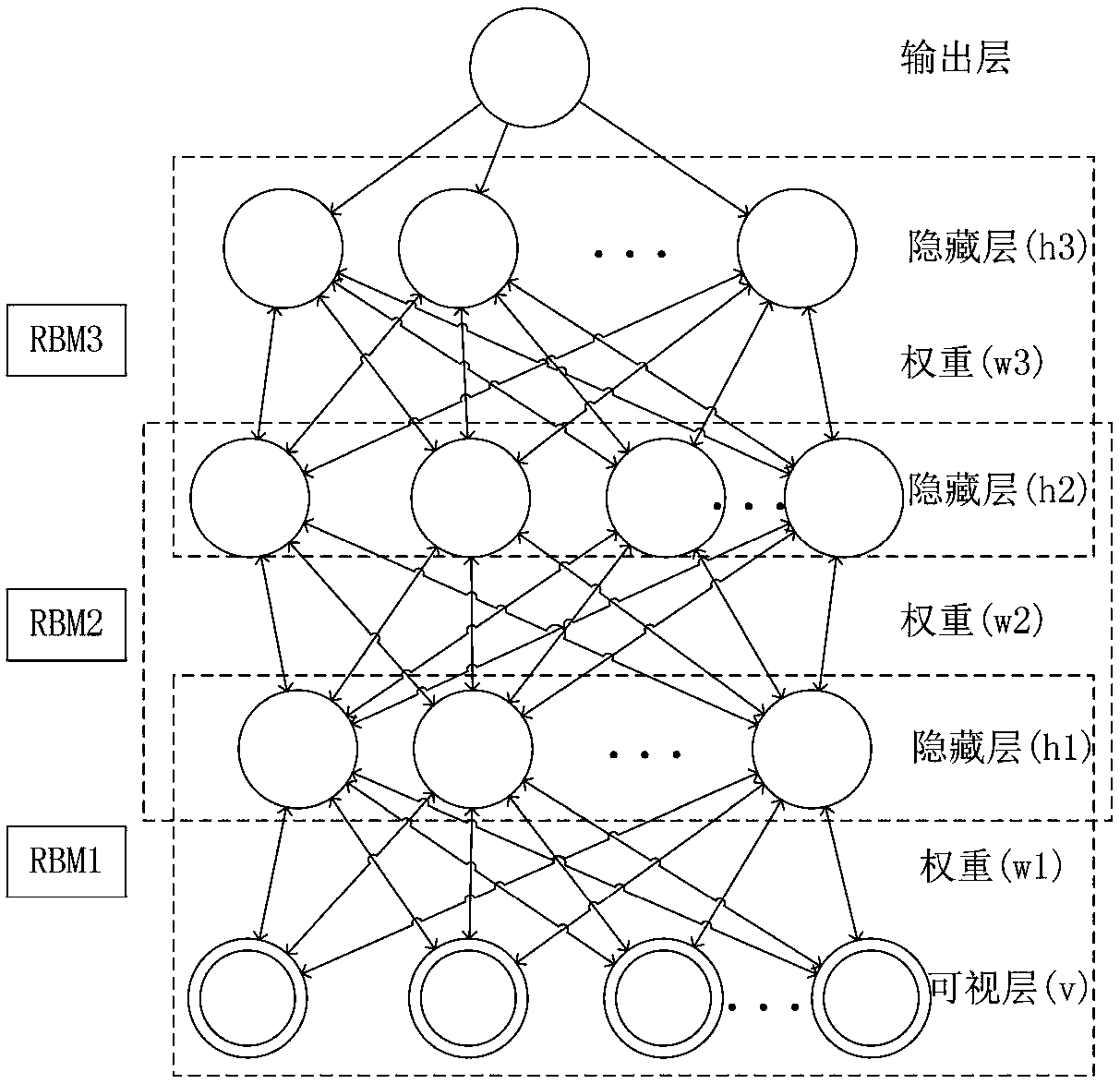
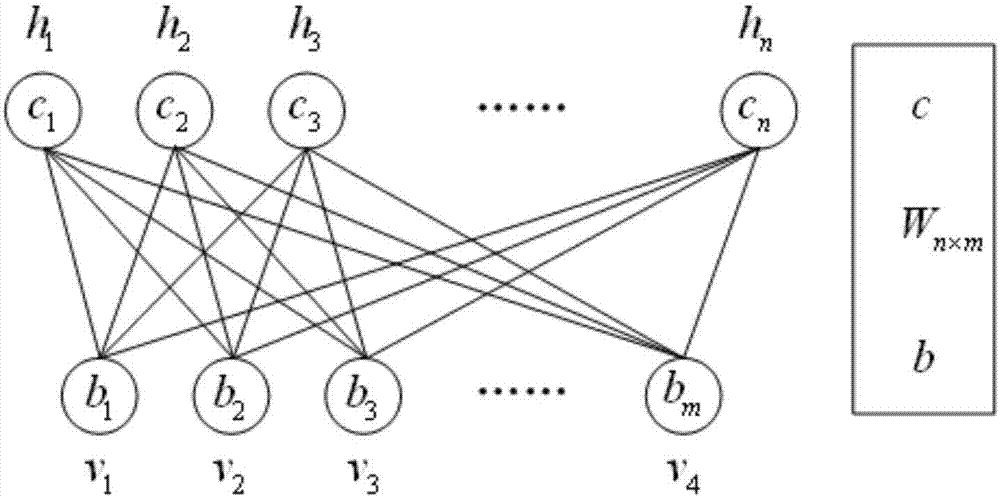
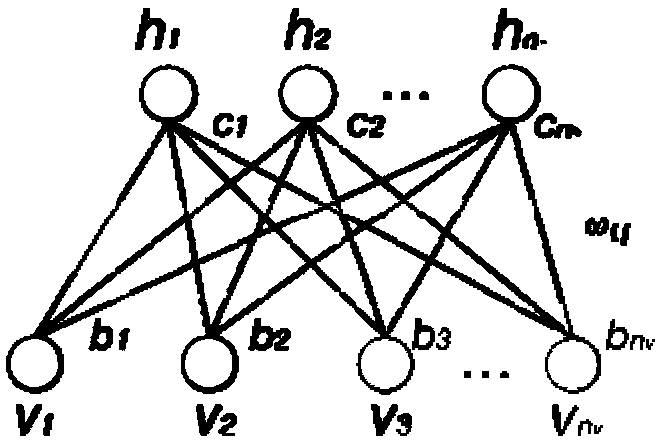
A Boltzmann machine (also called stochastic Hopfield network with hidden units) is a type of stochastic recurrent neural network and Markov random field. Boltzmann machines can be seen as the stochastic, generative counterpart of Hopfield networks. They were one of the first neural networks capable of learning internal representations, and are able to represent and (given sufficient time) solve difficult combinatoric problems.
Speaker recognition method based on depth learning
ActiveCN104157290AImprove recognition rateOvercoming problems such as easy convergence to local minimaSpeech analysisDeep belief networkRestricted Boltzmann machine
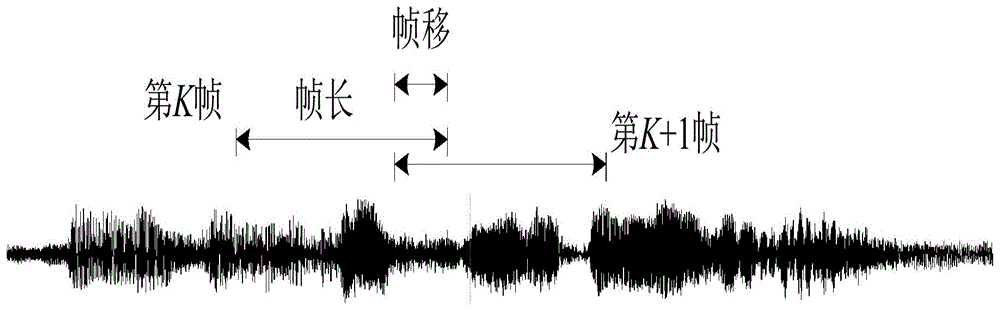
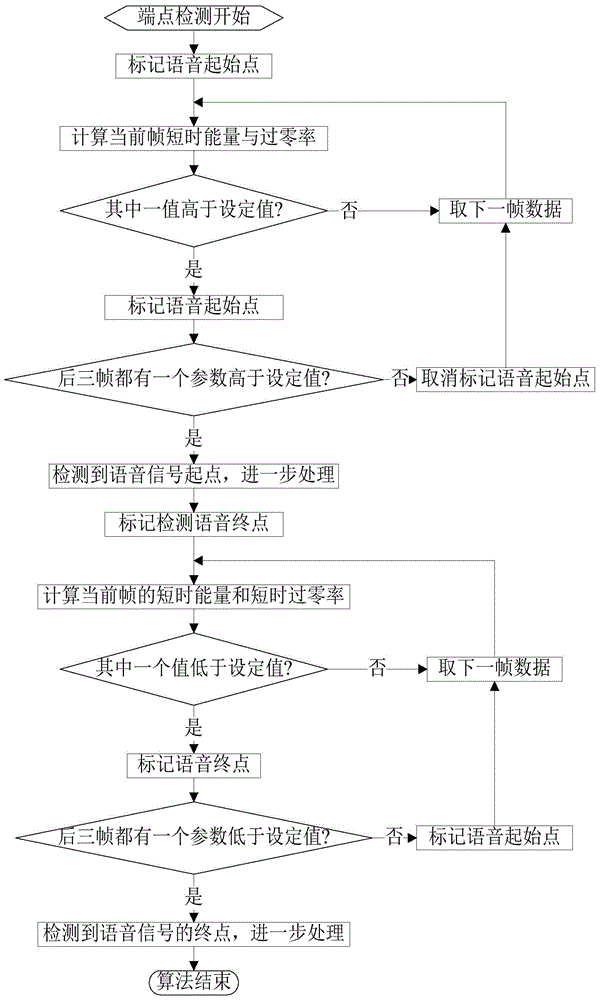
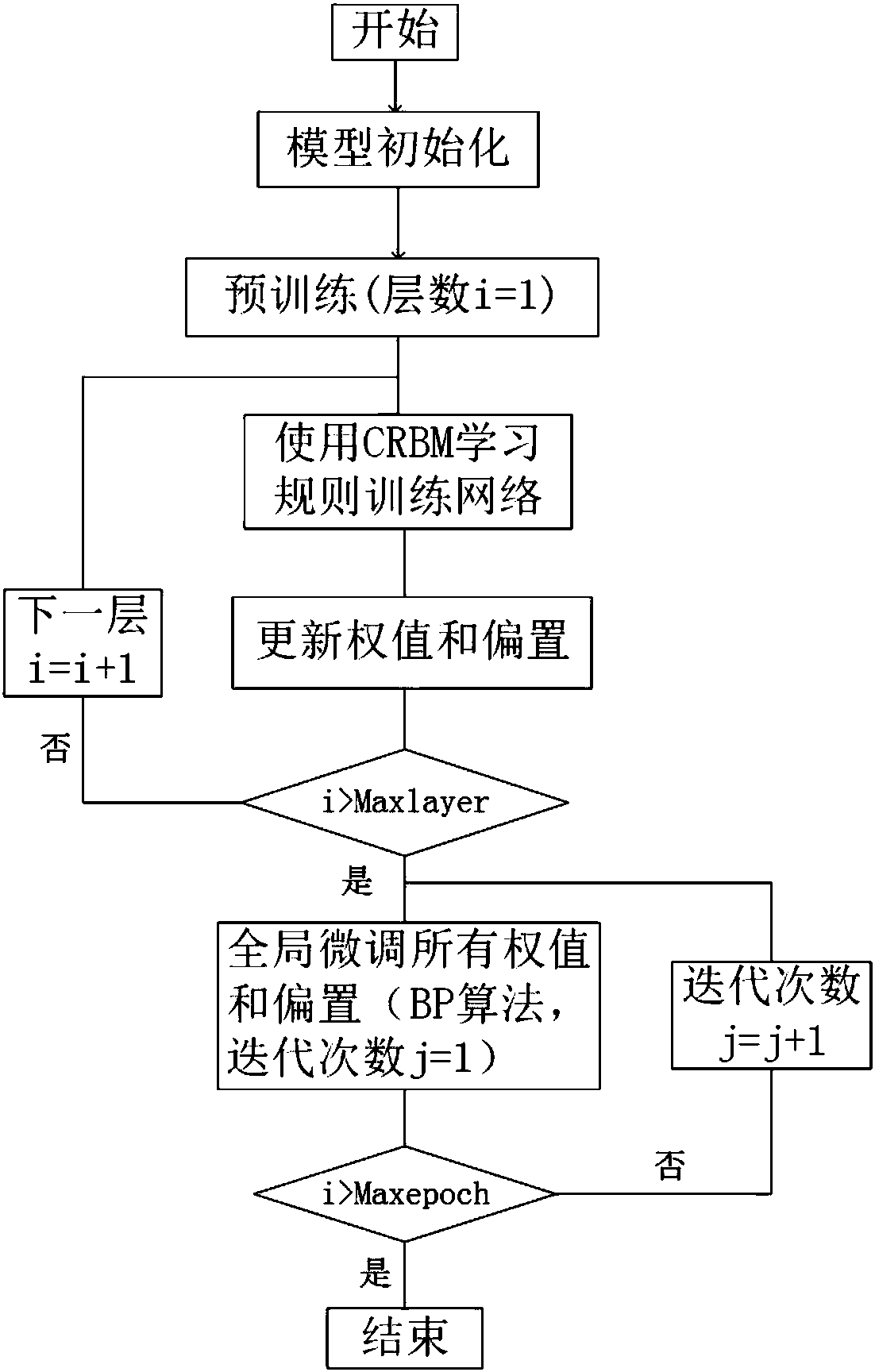
The invention discloses a speaker recognition method based on depth learning. The method comprises the following steps: S1) carrying out pre-emphasis and overlapping-type framing windowing on collected voice signals; S2) carrying out endpoint detection on the collected voice signals by utilizing a dual-threshold endpoint detection method based on short-time energy and short-time zero-crossing rate, and judging and indentifying the staring moment, transition stage , noise section and ending moment of the voice; S3) carrying out feature extraction on the voice signals; S4) forming a depth belief network model based on restricted boltzmann machine hierarchy, training the established depth belief network model by utilizing layer-by-layer greedy algorithm and with speaker voice feature parameters being combined, and adding a Softmax classifier to the top layer of the depth belief network model; and S5) inputting the voice features of a speaker to the depth belief network model obtained after being subjected to training, calculating the probability that the model outputs voice features similar to the voice features of the other speakers, and selecting the speaker corresponding to the maximum probability as recognition result.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
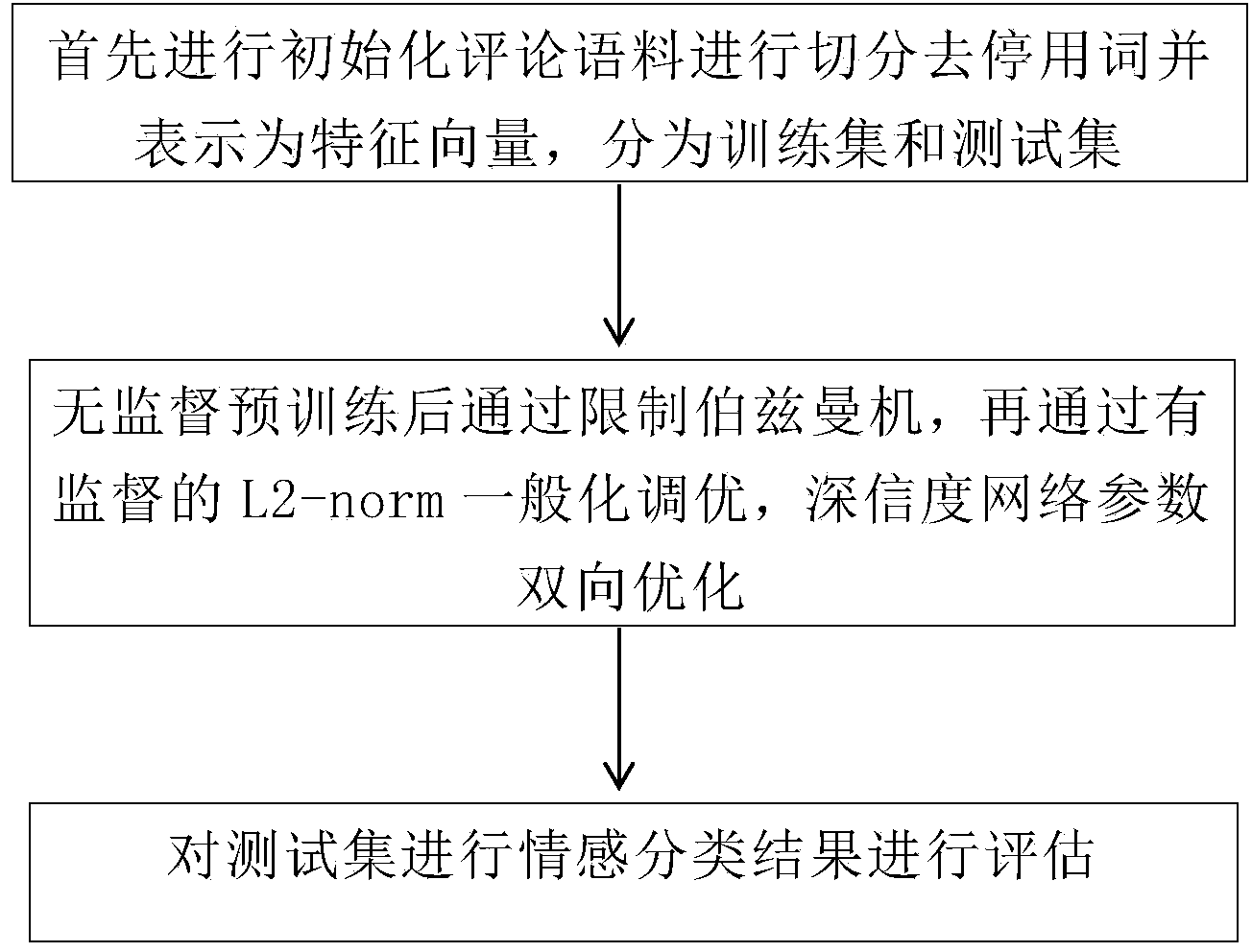
Method for establishing sentiment classification model
InactiveCN103729459AImproved Log ProbabilityReduce training timeNeural learning methodsSpecial data processing applicationsHidden layerNetwork on
The invention provides a sentiment classification method for generating a model deep-convinced-degree network on the basis of the probability of depth study. According to the technical scheme of the method, a plurality of Boltzmann machine layers are stacked, namely, output of this layer is used as input of the next layer. By the adoption of the mode, input information can be expressed in a grading mode, and abstraction can be conducted layer by layer. A multi-layer sensor containing a plurality of hidden layers is the basic study structure of the method. More abstract high layers are formed through combining the characteristics of lower layers and are used for expressing attribute categories or characteristics, so that the distribution type character presentation of data can be discovered. The method belongs to monitoring-free study, and a mainly-used model is the deep-convinced-degree network. The method enables a machine to conduct characteristic abstract better so as to improve the accuracy of sentiment classifications.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
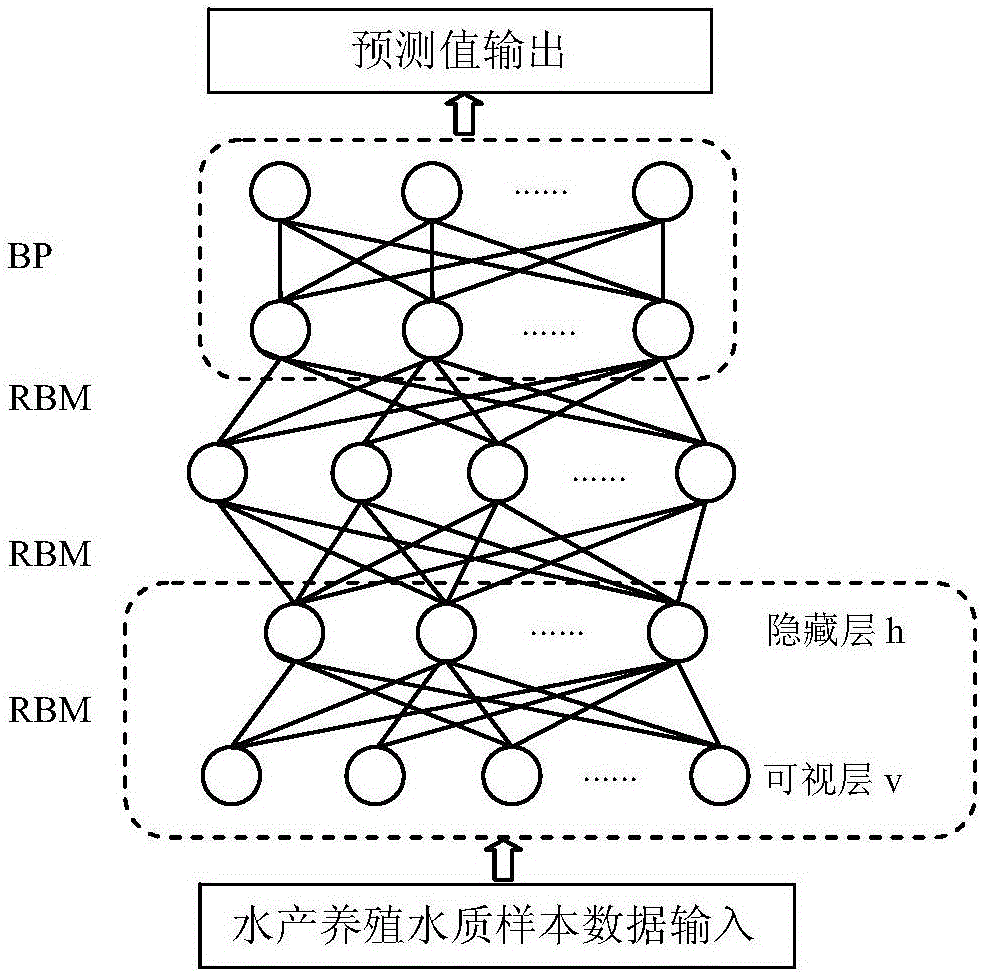
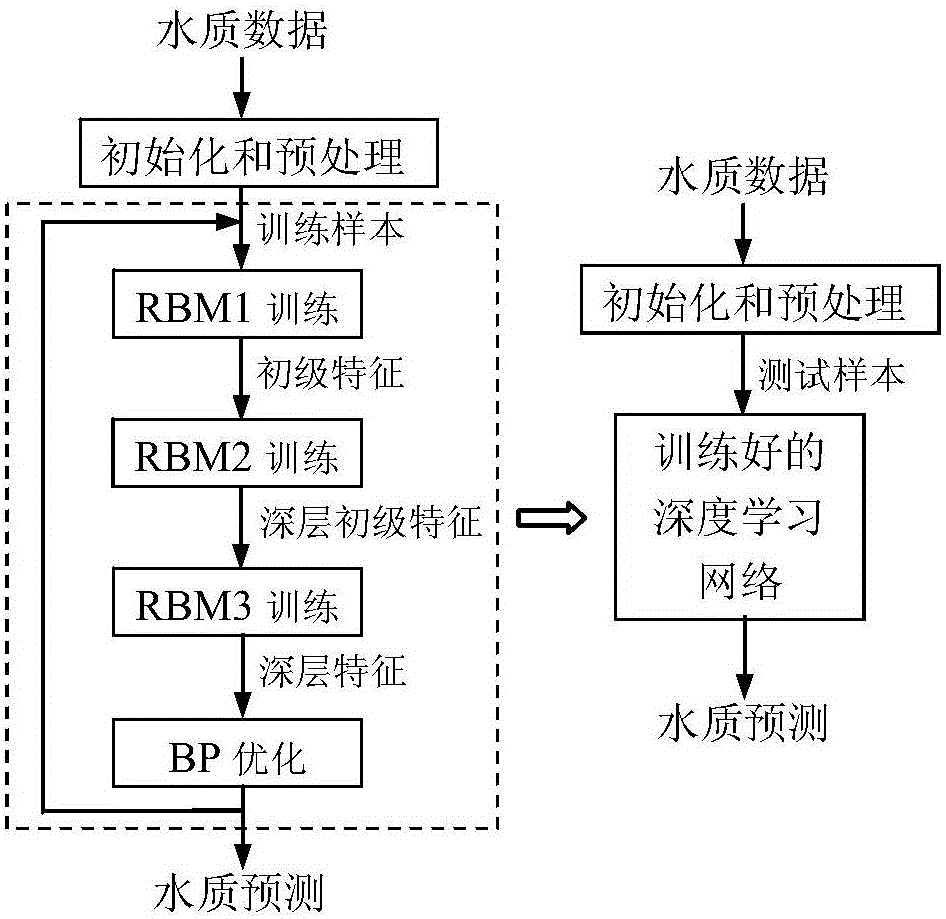
Aquatic product culture water quality prediction method based on deep learning
ActiveCN106198909AGet feature associationImprove accuracyTesting waterNeural learning methodsRestricted Boltzmann machineAquatic product
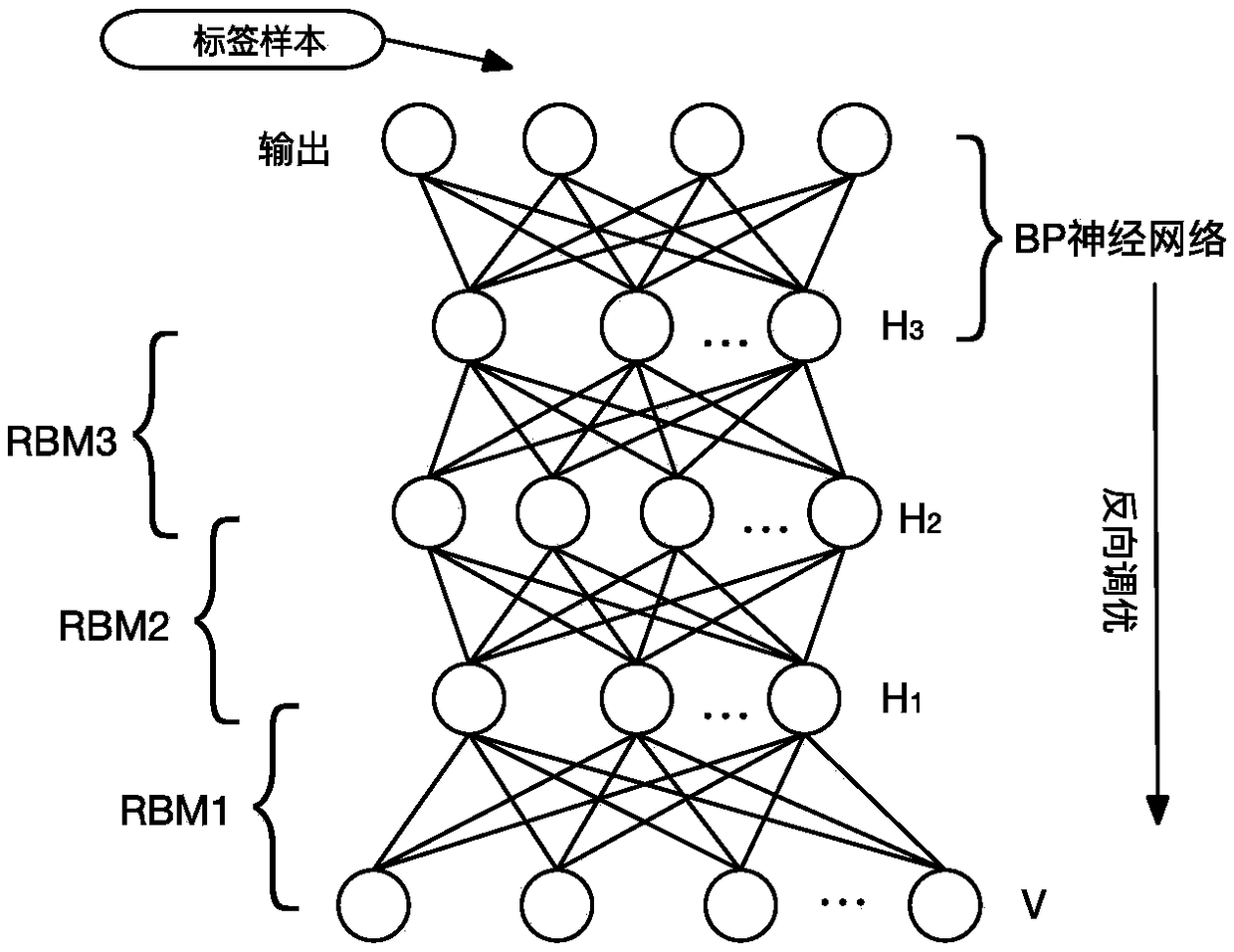
The invention discloses an aquatic product culture water quality prediction method based on deep learning. By building a deep learning network having three-layer limited Boltzmann machine (RBM) and a layer of BP neural network, water quality sample data is used for training three limited Boltzmann machines by specific dispersion learning for extracting the deep characteristics of the water quality sample data, deep learning network parameter is optimized through BP, so that training on the deep learning network is complete. The trained deep learning network is used to the current water quality sample data, and the water quality prediction can be obtained on an output layer. The method can obtain the characteristic relevance between different water quality factors, and the water quality prediction accuracy is increased.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
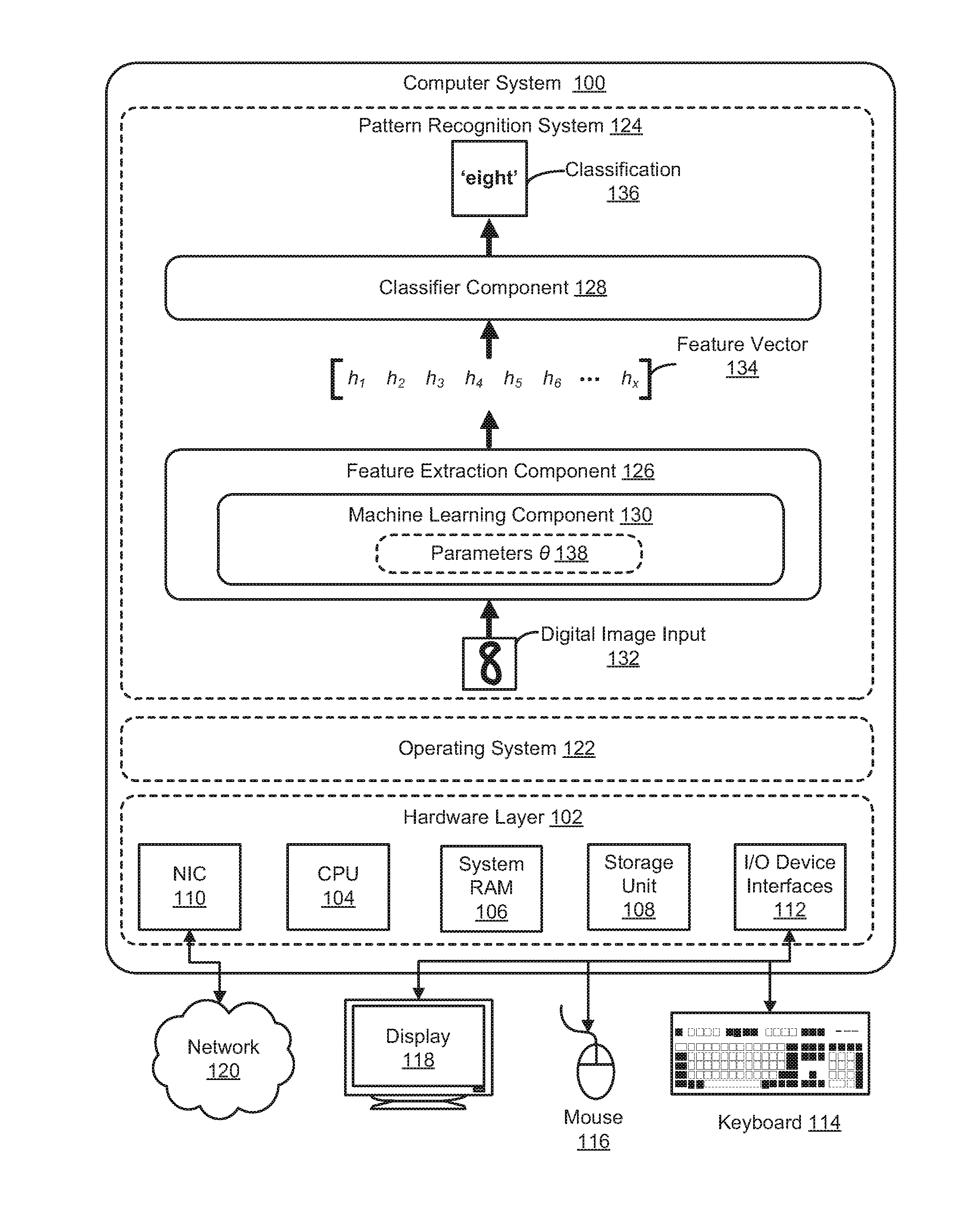
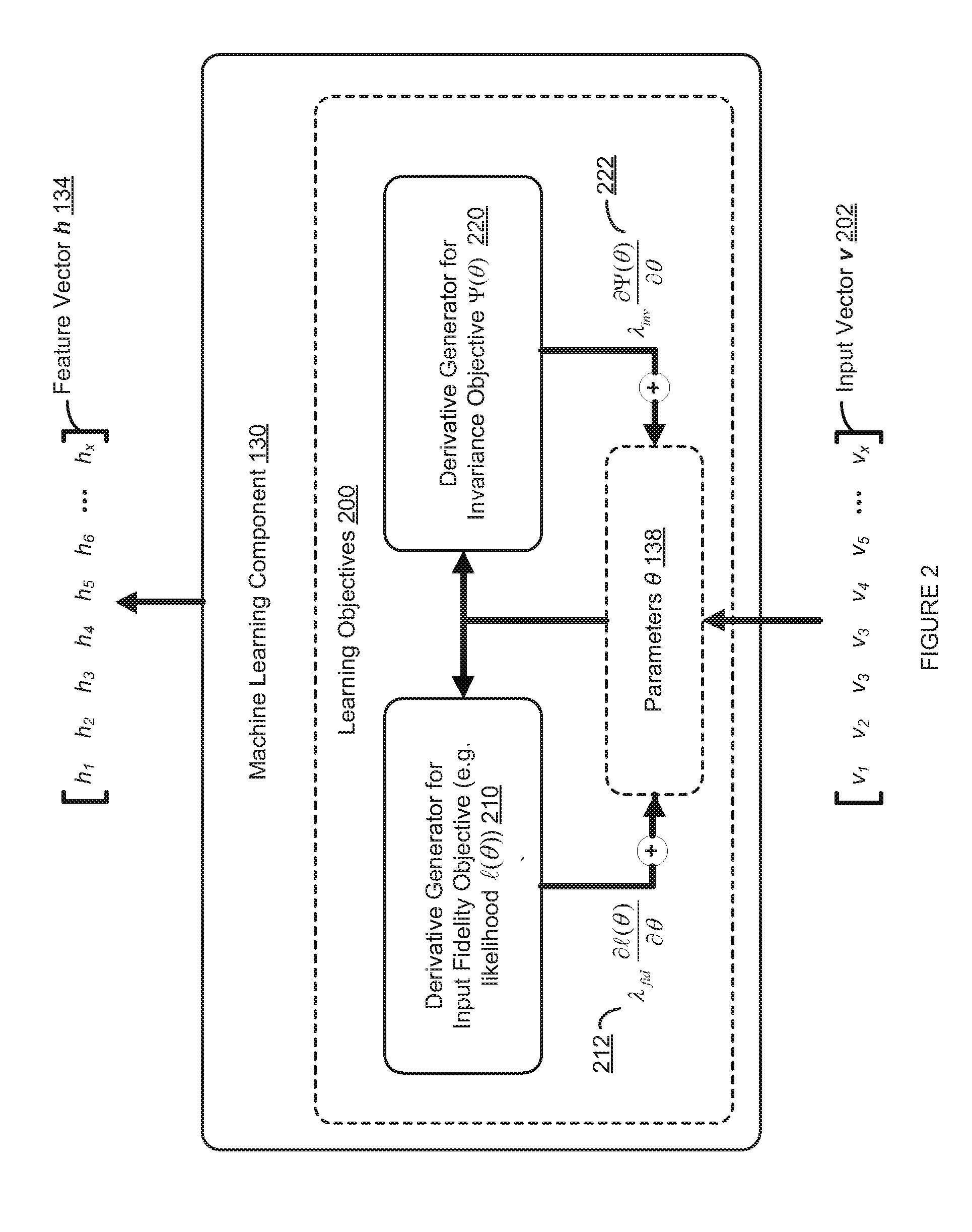
Method and System for Invariant Pattern Recognition
ActiveUS20150227849A1Facilitate invariant pattern recognitionDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionDimensionality reductionSupervised learning
An adaptive pattern recognition system optimizes an invariance objective and an input fidelity objective to accurately recognize input patterns in the presence of arbitrary input transformations. A fixed state or value of a feature output can nonlinearly reconstruct or generate multiple spatially distant input patterns and respond similarly to multiple spatially distant input patterns, while preserving the ability to efficiently evaluate the input fidelity objective. Exemplary networks, including a novel factorization of a third-order Boltzmann machine, exhibit multilayered, unsupervised learning of arbitrary transformations, and learn rich, complex features even in the absence of labeled data. These features are then used to classify unknown input patterns, to perform dimensionality reduction or compression,
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
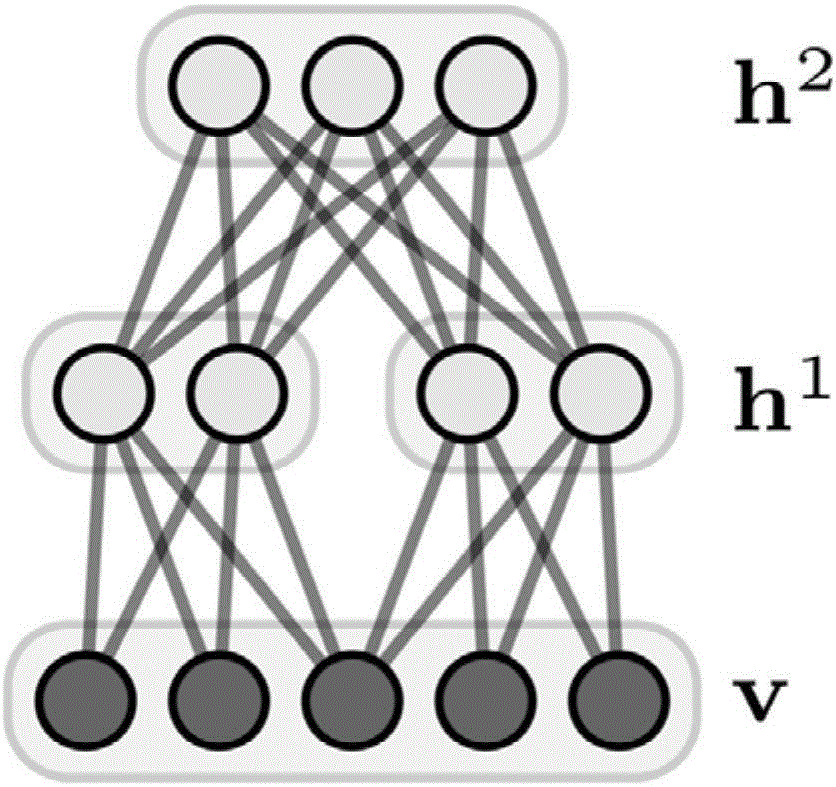
Automatic image annotation method based on deep learning and canonical correlation analysis
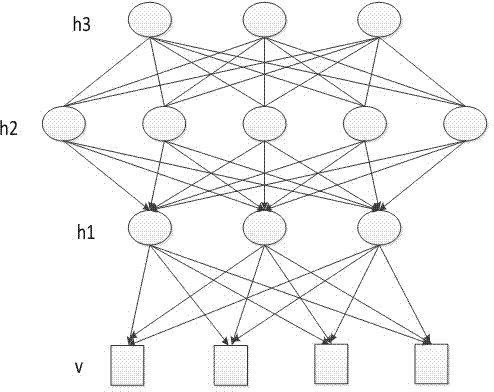
The invention discloses an automatic image annotation method based on deep learning and canonical correlation analysis. The method includes: using a depth Boltzmann machine to extract the high-level feature vectors of images and annotation words, selecting multiple Bernoulli distribution to fit annotation word samples, and selecting Gaussian distribution to fit image features; performing canonical correlation analysis on the high-level features of the images and the annotation words; calculating the Mahalanobis distance between to-be-annotated images and training set images in canonical variable space, and performing weighted calculation according to the distance to obtain high-level annotation word features; generating image annotation words through mean field estimation. The depth Boltzmann machine comprises I-DBM and T-DBM which are respectively used for extracting the high-level feature vectors of the images and the annotation words. Each of the I-DBM and the T-DBM sequentially comprises a visible layer, a first hidden unit layer and a second hidden unit layer from bottom to top. By the method, the problem of 'semantic gap' during image semantic annotation can be solved effectively, and annotation accuracy is increased.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
Method for making human face posture estimation utilizing dimension reduction method
InactiveCN101021900AHigh precisionReduce error rateCharacter and pattern recognitionRestricted Boltzmann machineNerve network
This invention discloses a method for estimating man-face gestures by a dimensionality reduction method including the following steps: 1, preprocessing man-face image trained samples of different gestures, 2, carrying out PCA process to processed data, 3, initializing limited nerve network of a Boltzmann machine, 4, pre-training the limited Boltzmann machine nerve network with the data processed by PCA, 5, adjusting the limited Boltzmqnn nerve network parameters, 6, identifying gestures of new man-face images, which reduces the error rate even further compared with the present technology and reduces its dimensions greatly.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Emotion analysis method for Chinese texts based on computer information processing technology
InactiveCN104965822AHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingRestricted Boltzmann machine
The invention discloses an emotion analysis method for Chinese texts based on computer information processing technology. Comments on Chinese products are subjected to word segmentation. By utilizing a bag-of-words model, vector representations of product comments are generated. The vector of every comment is inputted to a visible unit of a limited Boltzmann machine (RBM) in deep learning. Sentimental characteristics of Chinese texts are extracted by the RBM and the extracted emotional characteristics are inputted to a SVM for text emotion classification. The emotion analysis method for the Chinese texts based on computer information processing technology is capable of improving relevance of emotional semantics of characteristics while the SVM is capable of improving accuracy of emotion classification of comments on Chinese products.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
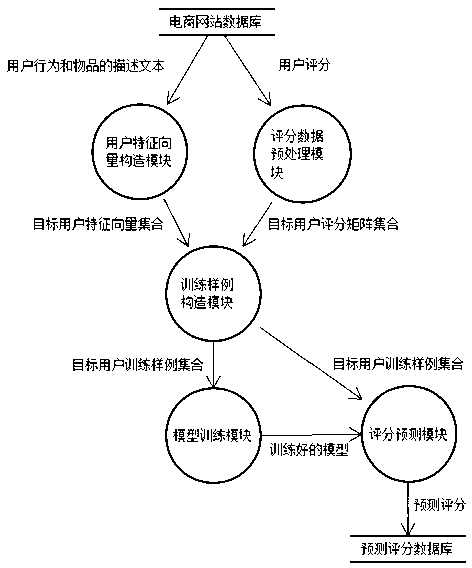
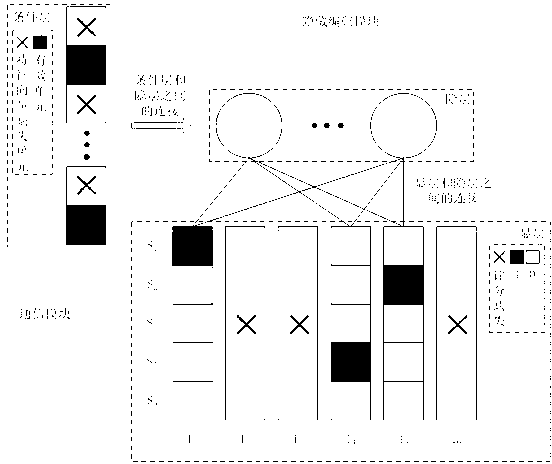
Mixed recommendation method based on factorization condition limitation Boltzmann machine
InactiveCN103324690AFew parametersGood precisionMarketingSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorRestricted Boltzmann machine
The invention provides a mixed recommendation method based on a factorization condition limitation Boltzmann machine. The method includes: constructing a target user feature vector; building a target user grading matrix set; building a target user training sample; building a factorization condition limitation Boltzmann machine model; grading and predicting to recommend results to a target user. The problems of user interest expression inaccuracy caused by pure recommendation based on content and data sparsity caused by recommendation based on behavior are effectively solved.
Owner:FOCUS TECH +1
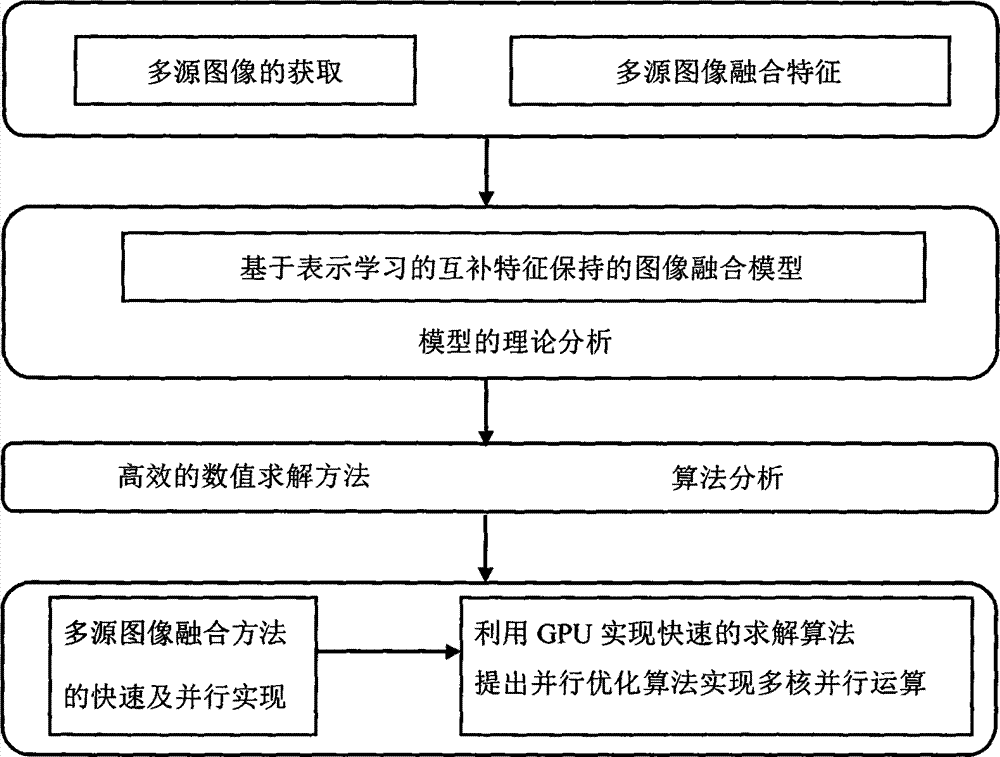
Method for image fusion based on representation learning
InactiveCN104851099AImplement image fusion technologyFast solutionImage enhancementImage analysisImage fusionBoltzmann machine
The invention discloses a method for image fusion based on representation learning, which comprises the steps of acquiring a multi-source image, learning features of the multi-source image through a learning framework of a deep neural network formed by a sparse adaptive encoder, a deep confidence network formed by a Boltzmann machine and a deep convolutional neural network, completing fusion of the multi-source image by using the automatically learned features, and establishing an image fusion model; studying a convex optimization problem of the image fusion model, and carrying out initialization on the networks by using unsupervised pre-training in deep learning, thereby enabling the networks to find an optimal solution quickly in the training process; and establishing a deep learning network for cooperative training according to the features of the multi-source image through two or more deep learning networks, thereby realizing an image fusion technology of representation learning. The method disclosed by the invention studies feature-level fusion of the image by using artificial intelligence and a deep learning based feature representation method. Compared with a traditional pixel-level fusion method, the method disclosed by the invention can better understand image information, and thus further improves the quality of image fusion.
Owner:ZHOUKOU NORMAL UNIV +1
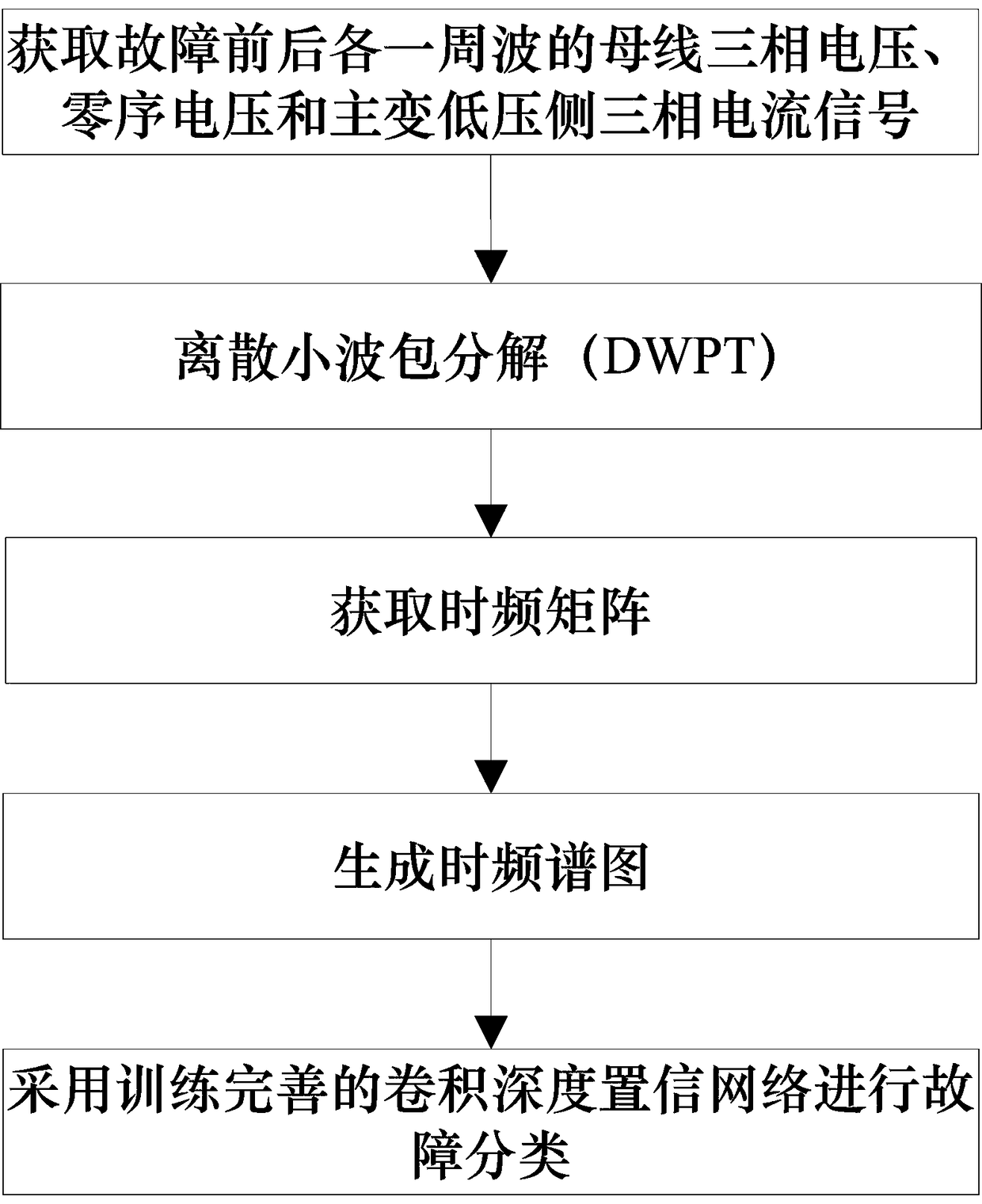
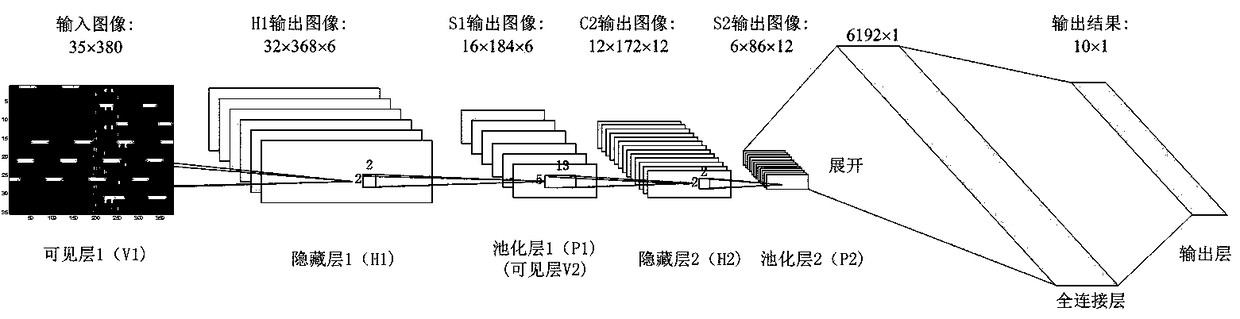
Distribution network fault classification method based on convolution depth confidence network
InactiveCN109325526AAutomatic extraction of fault featuresAccurate Fault Classification RateCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFrequency spectrumLow voltage
The invention relates to a distribution network fault classification method based on a convolution depth confidence network. The method comprises the steps of firstly collecting the three-phase voltage, zero-sequence voltage and three-phase current of a low-voltage bus of a main transformer and a low-voltage side of the main transformer, and respectively interceptting the signal waveform data of one cycle wave before and after each fault condition as training samples; secondly, carrying out the time-frequency decomposition on the training sample data of step S1 by using the discrete wavelet packet transform, and obtaining the time-frequency matrix, then constructing the pixel matrix of the time-frequency spectrum map, and constructing the time-frequency spectrum map as the input of the subsequent CDBN model; then constructing the CDBN model to train two convolution-constrained Boltzmann machines in unsupervised learning mode, and adding the softmax classifier after the second CRBM to train the network model to effectively extract and automatically classify the fault features, and finally, using the trained model to realize the fault classification of distribution network. The method of the invention can realize accurate fault location.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Human behavior recognition method and system based on multi-mode deep Boltzmann machine
ActiveCN107886061AImprove accuracyReduce the impact of comfortCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionHuman behavior
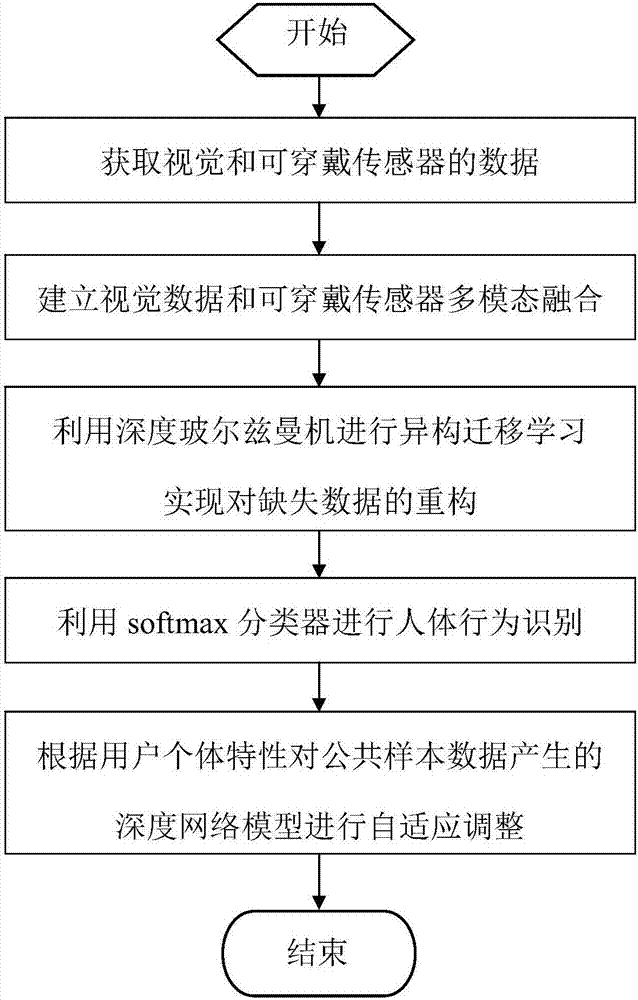
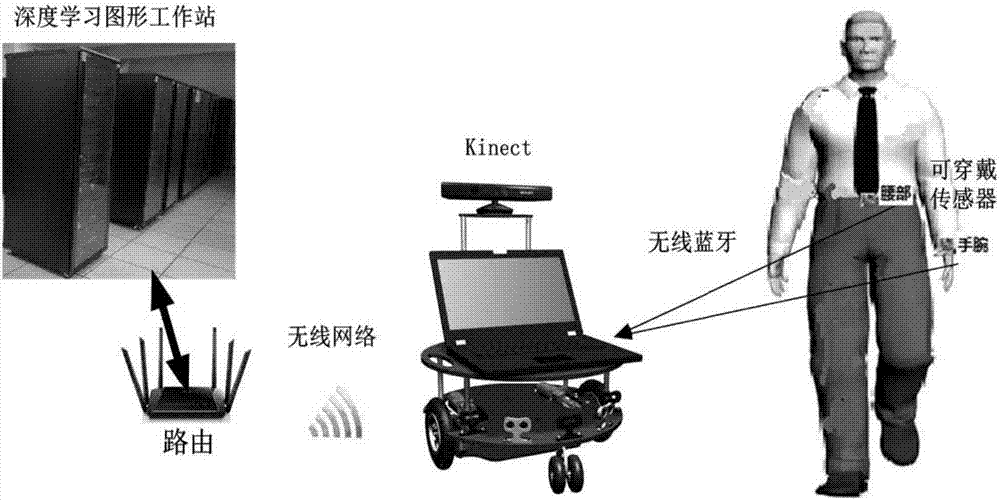
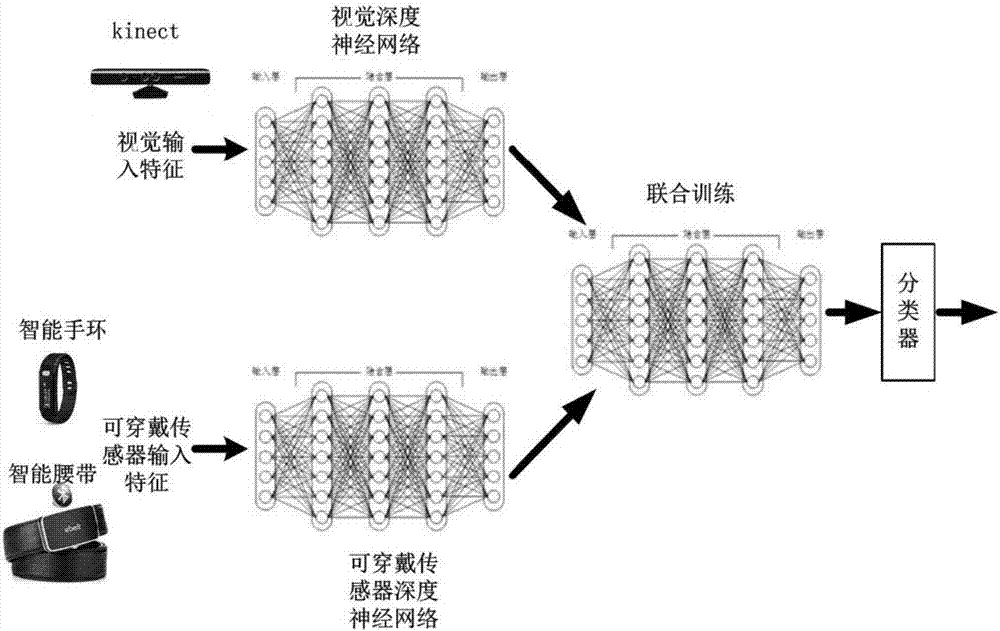
The invention discloses a human behavior recognition method and system based on a multi-mode deep Boltzmann machine. The method includes the following steps: 1) acquiring visual and wearable sensor data; 2) building visual data and wearable sensor multi-mode fusion model; 3) carrying out heterogeneous transfer learning by using a deep neural network to reconstruct missing data; 4) performing classification by using a softmax regression model classifier; 5) adaptively adjusting a deep network model generated by common sample data according to user individual characteristics. The human behaviorrecognition method and system can improve the accuracy of human body recognition in the event of complex scenes and missing data.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
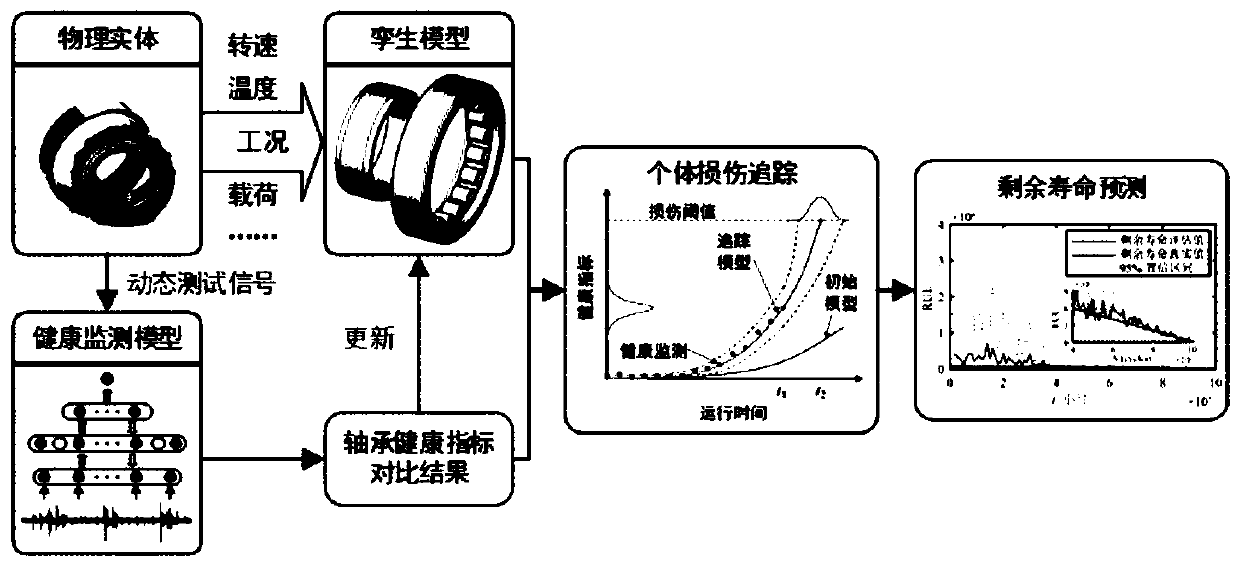
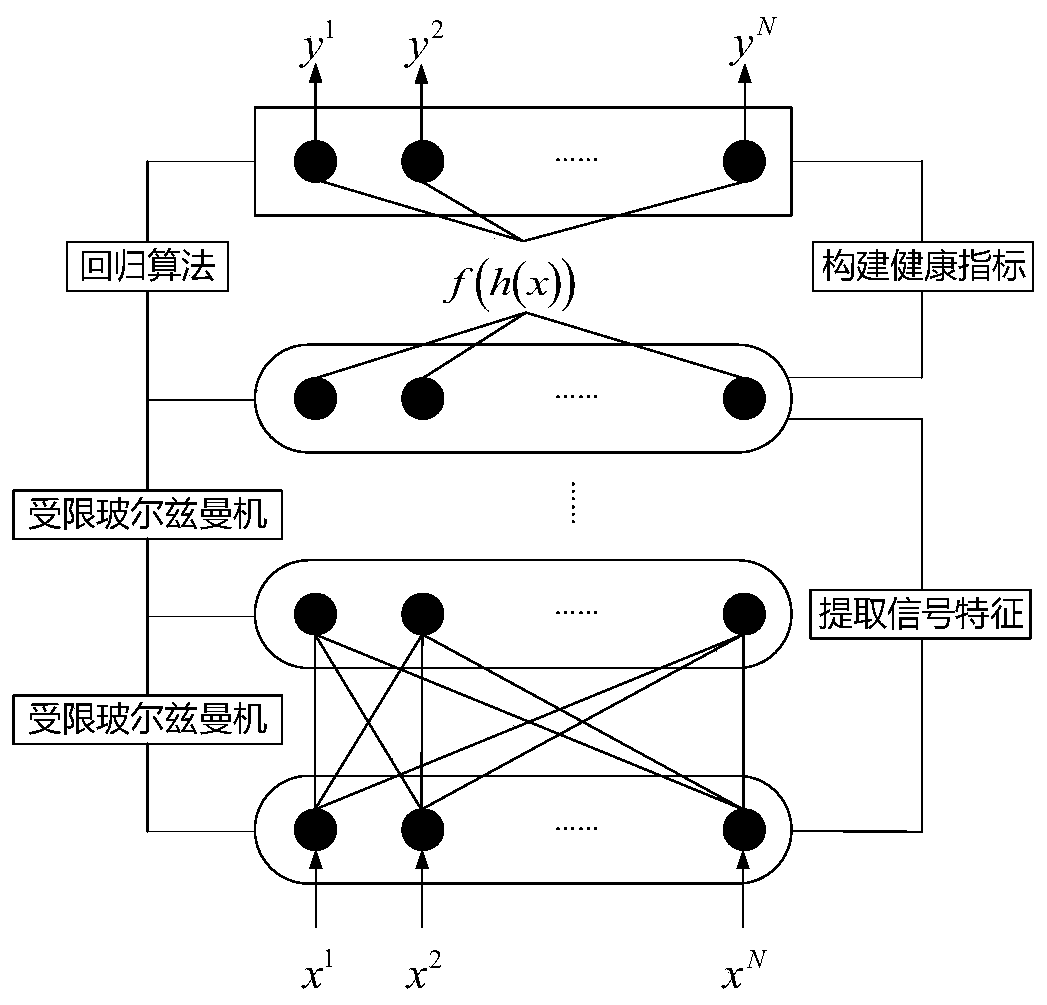
Aero-engine main bearing residual life prediction method based on digital twinning
ActiveCN110532626ASolve the problem of inaccurate prediction results of remaining lifePrediction of remaining life is accurateSustainable transportationNeural architecturesAviationRestricted Boltzmann machine
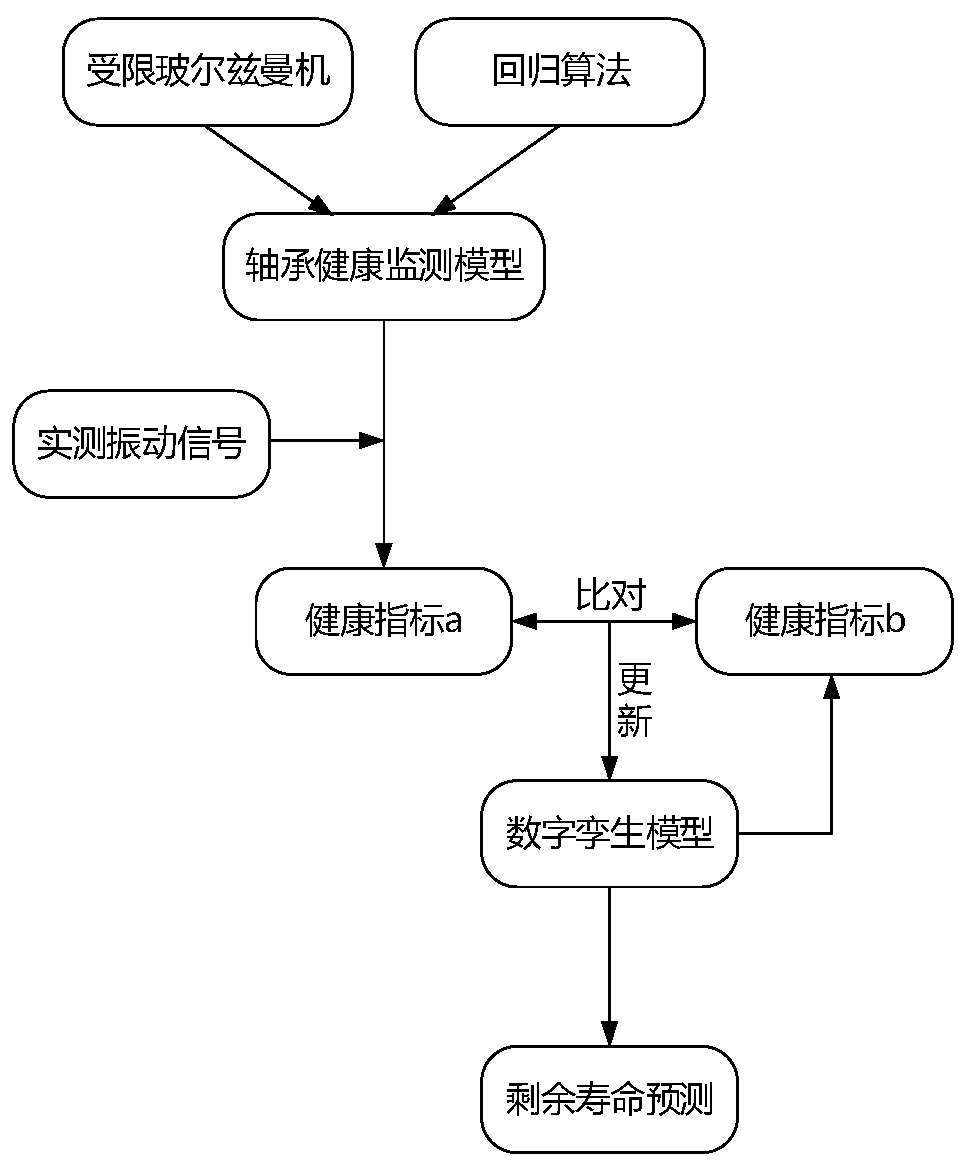
The invention provides an aero-engine main bearing residual life prediction method based on digital twinning. The method comprises: firstly, using a plurality of restricted Boltzmann machines and a regression algorithm to construct a main bearing health monitoring model; comparing the main bearing actual measurement vibration signals with main bearing health state information extracted from the digital twinning model, adjusting and correcting the digital twinning model by utilizing a comparison result, and finally predicting the residual life of the main bearing by utilizing the updated digital twinning model. According to the aero-engine main bearing residual life prediction method based on digital twinning, a digital twinning technology is introduced into the field of main bearing residual life prediction, so that a main bearing digital twinning model applied to the method can be updated in real time along with the change of the working condition of the main bearing of the aero-engine, and a more accurate residual life prediction result can be obtained.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
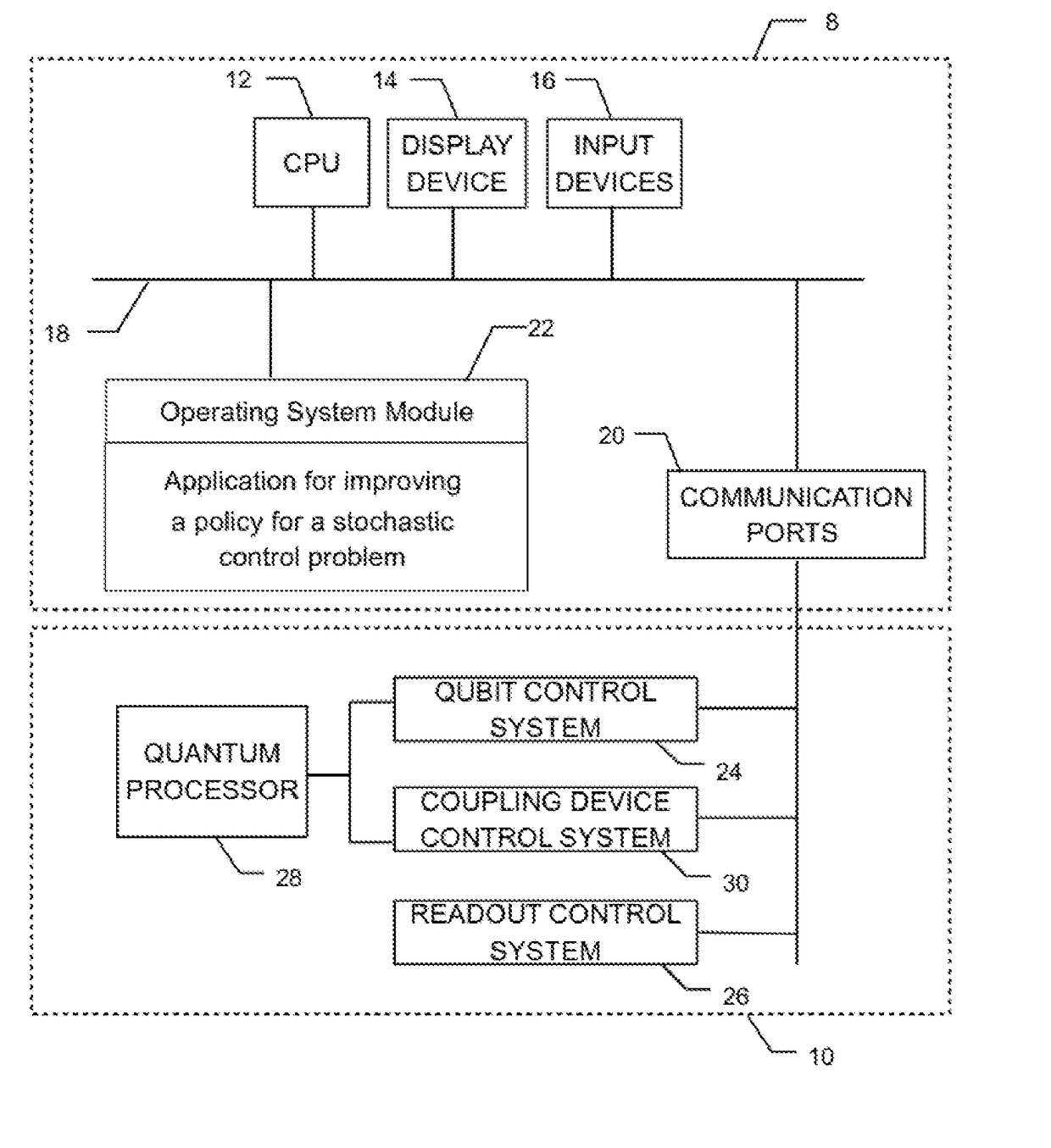
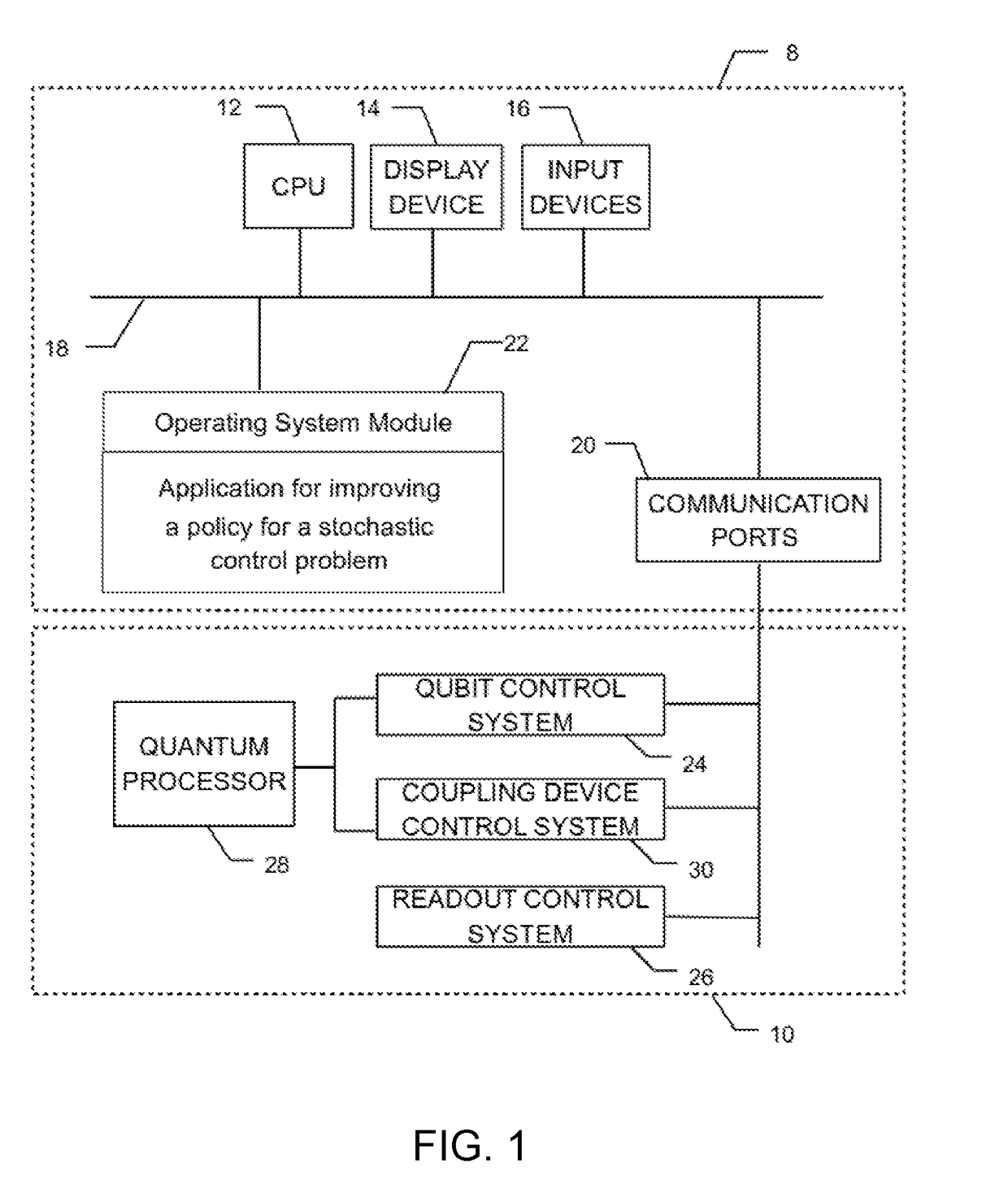
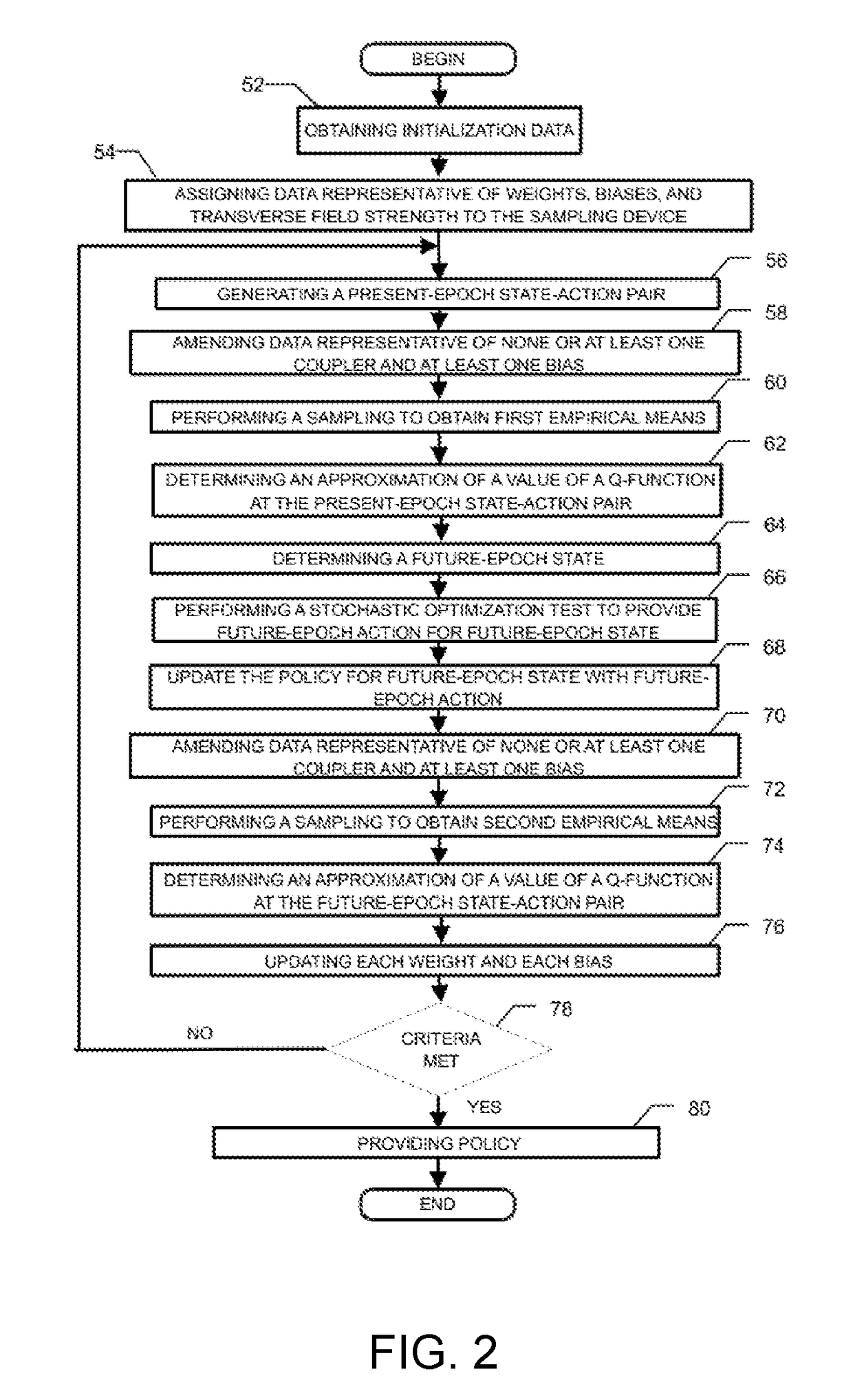
Method and system for improving a policy for a stochastic control problem
ActiveUS20170323195A1Overcome problemsEfficient methodQuantum computersMathematical modelsDecision takingStochastic control
A method and system are disclosed for improving a policy for a stochastic control problem, the stochastic control problem being characterized by a set of actions, a set of states, a reward structure as a function of states and actions, and a plurality of decision epochs, the method comprising using a sampling device obtaining data representative of sample configurations of a Boltzmann machine, obtaining initialization data and an initial policy for the stochastic control problem; assigning data representative of an initial weight and a bias of respectively each coupler and each node and the transverse field strength of the Boltzmann machine to the sampling device; until a stopping criterion is met generating a present-epoch state-action pair, amending data representative of none or at least one coupler and at least one bias, performing a sampling corresponding to the present-epoch state-action pair to obtain first sampling empirical means, obtaining an approximation of a value of a Q-function at the present-epoch state-action, obtaining a future-epoch state-action pair, wherein the state is obtained through a stochastic state process, and further wherein the obtaining of the action comprises performing a stochastic optimization test on the plurality of all state-action pairs comprising the future-epoch state and any possible action to thereby provide the action at the future-epoch and update the policy for the future-epoch state; amending data representative of none or at least one coupler and at least one bias, performing a sampling corresponding to the future-epoch state-action pair, obtaining an approximation of a value of the Q-function at the future-epoch state-action, updating each weight and each bias and providing the policy when the stopping criterion is met.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
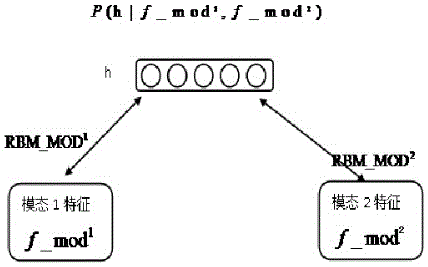
Mammary gland image feature fusion method based on restricted Boltzmann machine
ActiveCN106203488APerfect complementarityPracticalRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsPattern recognitionRestricted Boltzmann machine
The invention relates to a mammary gland image feature fusion method based on a restricted Boltzmann machine. The method first obtains the high-level semantic feature of a mammary gland molybdenum target and a mammary gland B-scan ultrasonography by stacked self-encoder deep learning, and then uses a restricted Boltzmann Machine model to extract the shared feature representation of different modes of image of the mammary gland B-scan ultrasonography and the mammary gland molybdenum target. The mammary gland image feature fusion method based on the restricted Boltzmann machine obtains the united distribution between different modal statistical attributes of the mammary gland B-scan ultrasonography and mammary gland molybdenum target by a unsupervised training mode, and can fully utilize a large amount of unlabeled data, compensates a defect of excessive reliance on sample class labels of a lot of conventional feature fusion method, and has strong practicality.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Aero-engine bearing fault diagnosing method
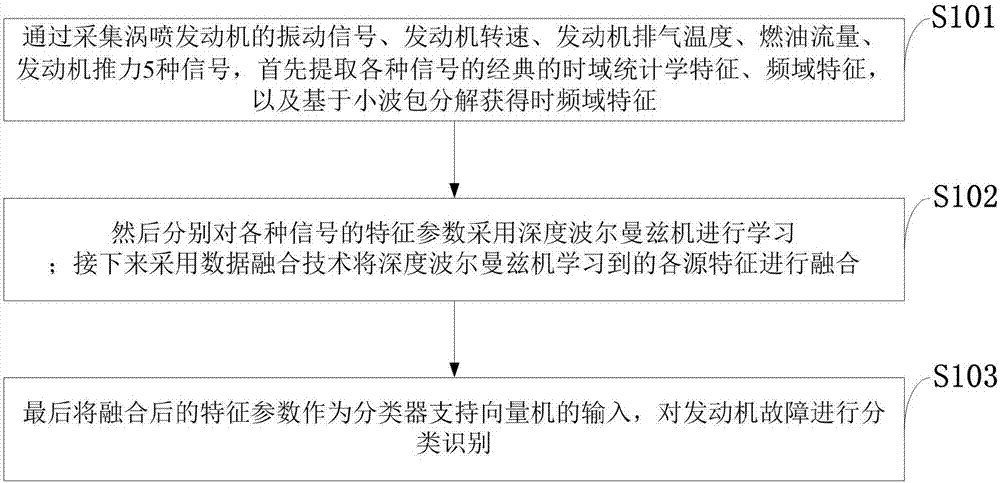
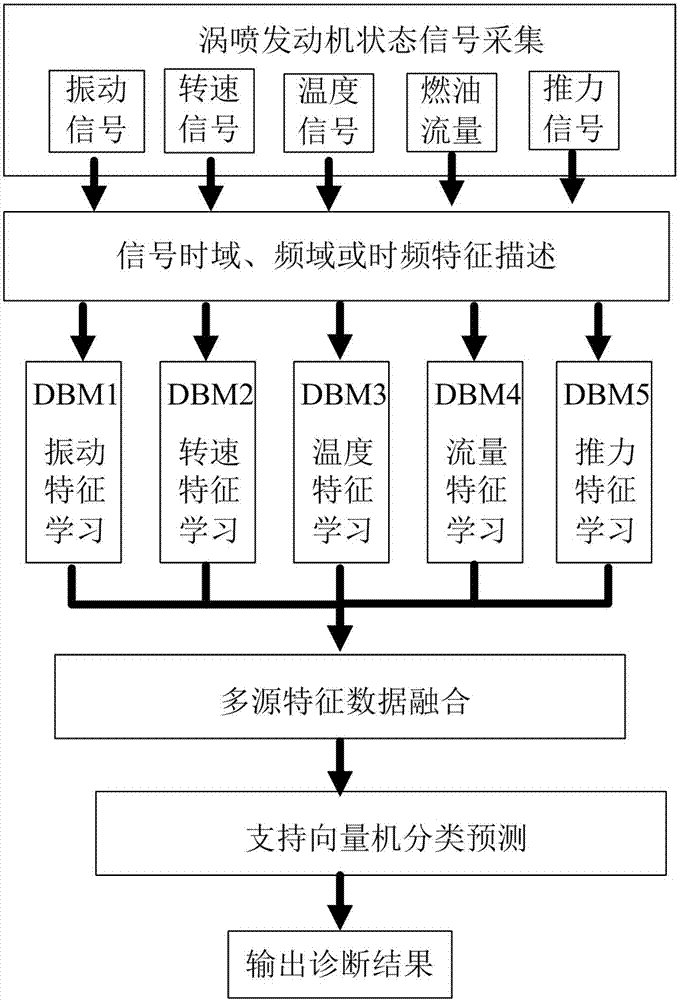
ActiveCN107036816AImprove effectivenessImprove stabilityMachine bearings testingAviationSupport vector machine
The invention discloses an aero-engine bearing fault diagnosing method. The method comprises: first, acquiring the vibration signal of a turbojet engine, the engine speed, the engine rotation speed, the engine exhaust temperature, the fuel flow, and the engine thrust; extracting the classical time-domain statistical characteristics, the frequency-domain characteristics of the various signals and obtaining the time-frequency domain characteristics based on wavelet packet decomposition; then using the deep Boltzmann machine to perform characteristics learning to the characteristic parameters of the various signals; then, proceeding to use the data integration technology to integrate the characteristics of the various sources learned by the deep Boltzmann machine; and finally, using the integrated characteristic parameters as the input of the classifier to the support vector machine, and classifying and identifying the engine fault. The method of the invention improves the identification precision and stability of the turbojet engine bearing fault, effectively mining the essential characteristics of data and greatly increasing the fault precision of the turbojet engine bearing.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
Fan fault detecting method based on depth belief network model
ActiveCN107725283AImplement fault detectionAccurate predictionEngine fuctionsMachines/enginesDeep belief networkSlide window
The invention discloses a fan fault detecting method based on a depth belief network model. The fan fault detecting method comprises that a fan flow forecast model is established by using depth beliefnetwork, state parameters related to the fan flow are selected to be used as the input variable of the model, and the flow of a fan is forecasted. The depth belief network is formed by staking multilayer continuous type limit Boltzmann machines, and an adaptive step length method is used to accelerate the algorithm training process. In addition, residual distribution characteristics are calculated according to a sliding window, when the mean value or standard deviation of the residual exceeds the threshold, alarm is issued. By means of the fan fault detecting method based on the depth beliefnetwork model, the flow of the fan can be accurately forecasted, meanwhile, the abnormal working state of the fan can be detected, and fault detection on the fan is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU FRONTIER ELECTRIC TECH +1
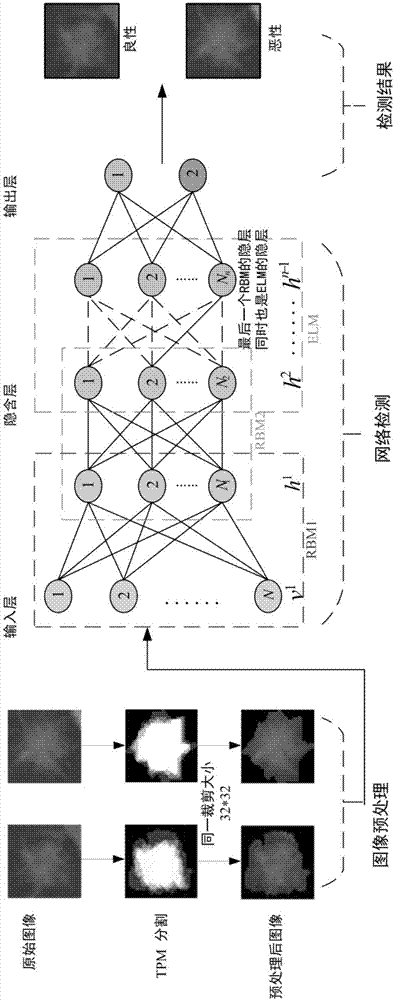
Improved deep Boltzmann machine-based pulmonary nodule feature extraction and benign and malignant classification method
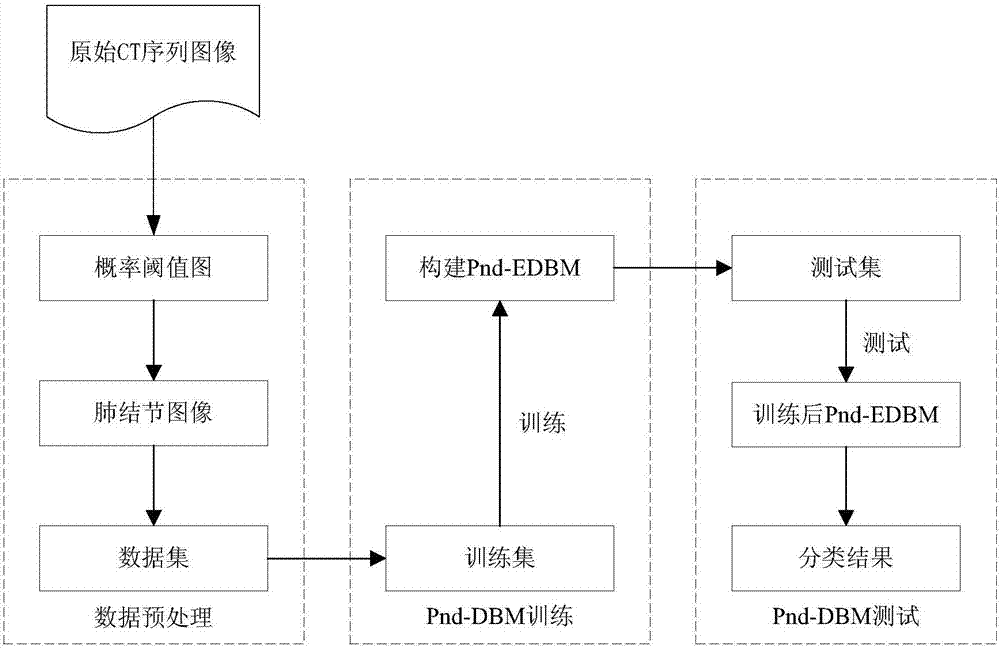
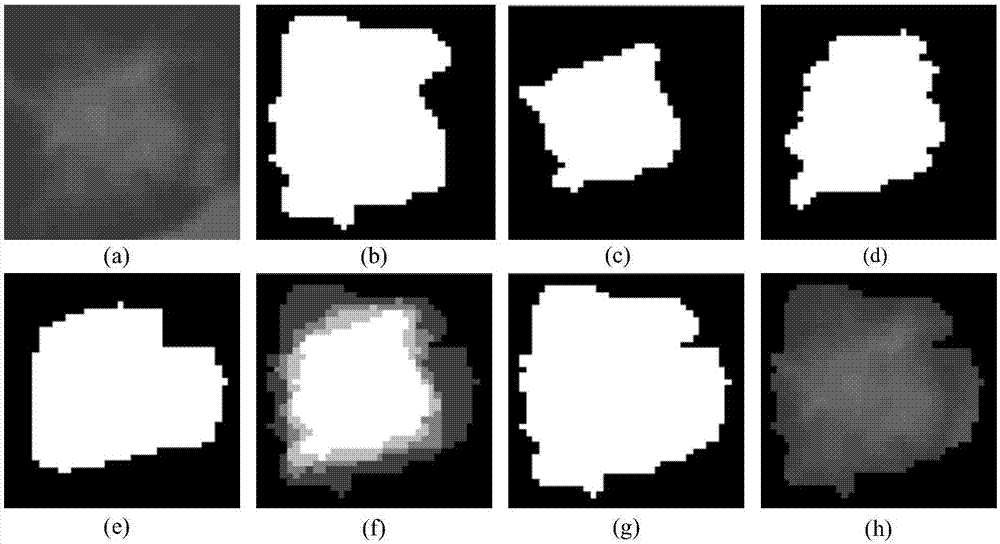
ActiveCN107316294APreserve the original nodule informationGuaranteed accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleLearning machine
The present invention discloses an improved deep Boltzmann machine-based pulmonary nodule feature extraction and benign and malignant classification method. The method includes the following steps that: step A, pulmonary nodules are segmented from CT images through using a threshold probability image graph method, so that regions of interest (ROI) are obtained, and the regions of interest are cut into nodule images of the same size; and step B, a supervised deep learning algorithm Pnd-EBM is designed to realize the diagnosis of a pulmonary nodule, wherein the diagnosis of the pulmonary nodule further includes three major steps: B1, a deep Boltzmann machine (DBM) is adopted to extract the features of the ROI of the pulmonary nodule which have deep expression abilities; B2, a sparse cross-entropy penalty factor is adopted to improve a cost function, so that the phenomenon of feature homogenization in a training process can be avoided; and B3, an extreme learning machine (ELM) is adopted to perform benign and malignant classification on the extracted features of the pulmonary nodule. The improved deep Boltzmann machine-based pulmonary nodule feature extraction method is superior to a traditional feature extraction method. With the method adopted, the complexity of manual extraction and the difference of feature selection can be avoided, and references can be provided for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
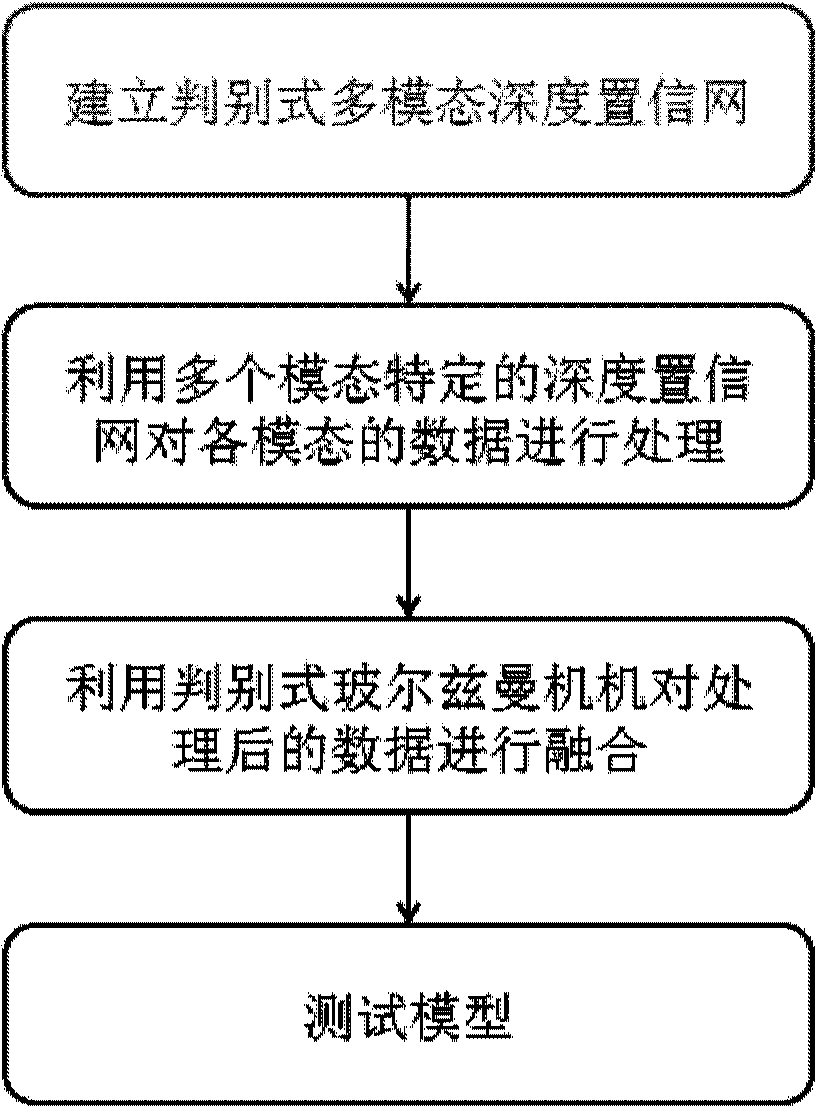
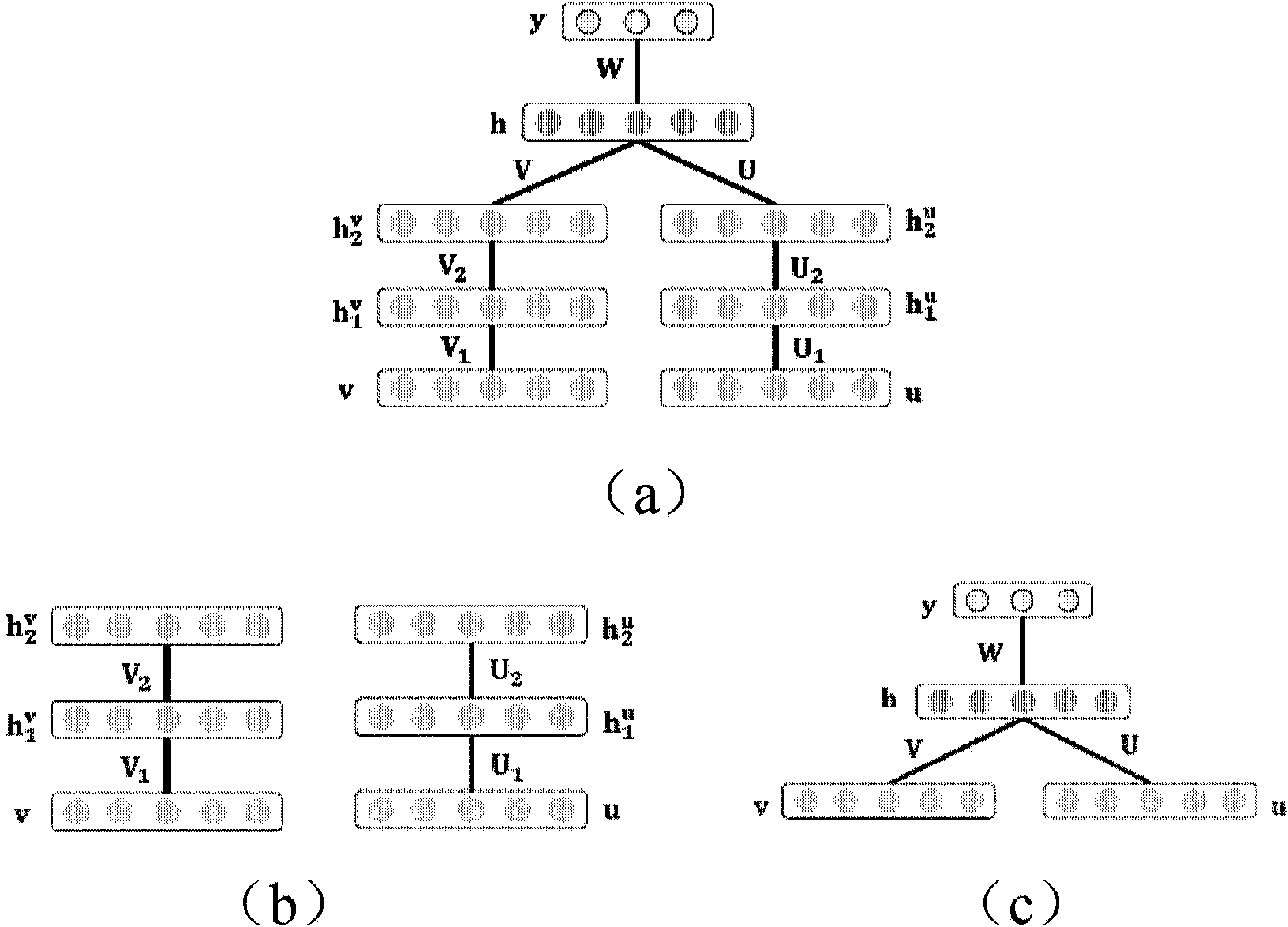
Multi-modal data fusion method and system based on discriminant multi-modal deep confidence network
The invention discloses a multi-modal data fusion method based on a discriminant multi-modal deep confidence network. The multi-modal data fusion method based on the discriminant multi-modal deep confidence network comprises the steps that the discriminant multi-modal deep confidence network is established; for the deep confidence network corresponding to multi-modal data, the weight of the network after the deep confidence network is optimized is obtained by means of limited Boltzmann machines; objective functions of the multi-modal Boltzmann machines are minimized by means of the alternative optimization strategy, the weights of the optimized Boltzmann machines are obtained, and a final discriminant multi-modal deep confidence network model is obtained; the multi-modal data to be fused are input into the deep confidence network model, and then a fusion result is obtained. The invention further discloses a multi-modal data fusion system based on the discriminant multi-modal deep confidence network. According to the multi-modal data fusion method and system based on the discriminant multi-modal deep confidence network, monitored label information is introduced into a traditional multi-modal deep confidence network, the relations between the data with different modals are mined in a discriminant mode, and thus the high accuracy rate can be guaranteed during a large-scale multi-modal data classifying and searching task.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for automatically annotating remote sensing images on basis of deep learning
ActiveCN103823845AImprove visibilityImprove labeling accuracySpecial data processing applicationsHidden layerFeature vector
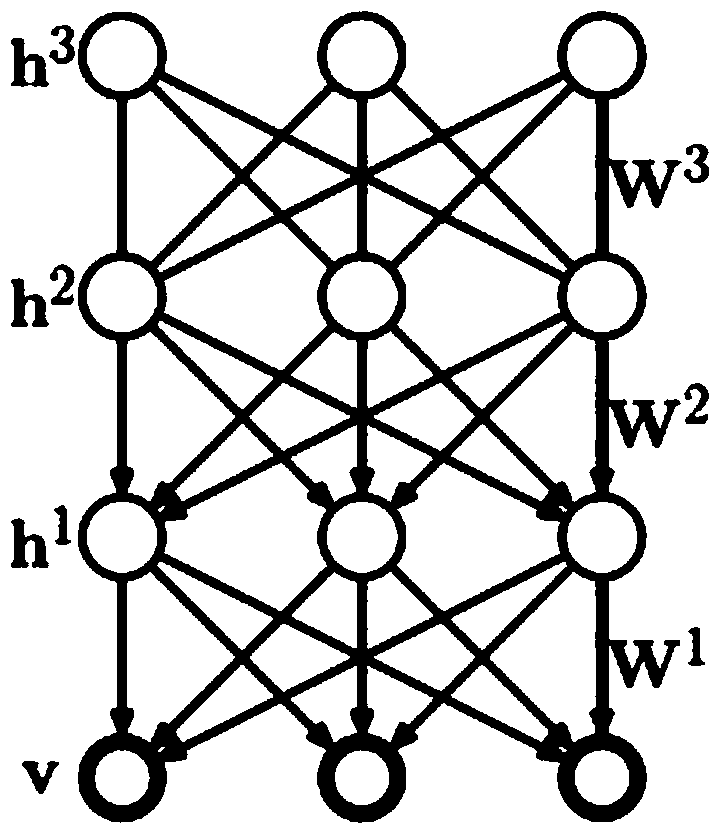
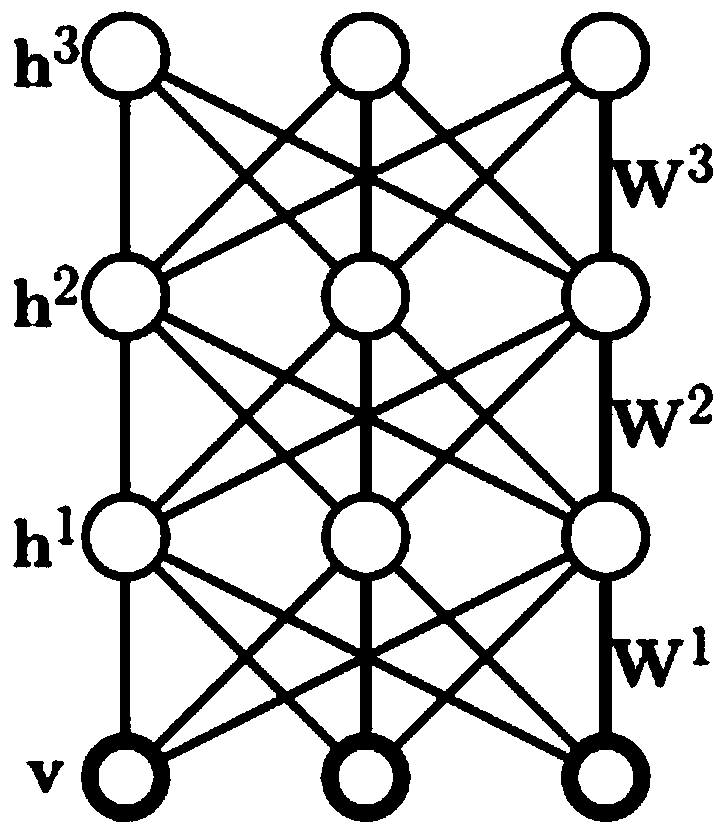
The invention discloses a method for automatically annotating remote sensing images on the basis of deep learning. The method for automatically annotating the remote sensing images includes extracting visual feature vectors of the to-be-annotated remote sensing images; inputting the visual feature vectors into a DBM (deep Boltzmann machine) model to automatically annotate the to-be-annotated remote sensing images. The DBM model implemented in the method sequentially comprises a visible layer, a first hidden layer, a second hidden layer and a tag layer from bottom to top, and is acquired by means of training. The method for automatically annotating the remote sensing images has the advantages that the deep Boltzmann machine model implemented in the method comprises the two hidden layers (namely, the first hidden layer and the second hidden layer respectively), accordingly, the problem of 'semantic gaps' in image semantic annotation procedures can be effectively solved by the two hidden layers, and the integral annotation accuracy can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
CNN-DBN-based partial discharge fault diagnosis method
InactiveCN107449994AImprove recognition rateImprove accuracyTesting dielectric strengthDesign optimisation/simulationRestricted Boltzmann machineAlgorithm
The invention discloses a CNN-DBN-based partial discharge fault diagnosis method, which comprises the following steps: constructing a deep belief learning network based on a deep convolution neural network and a restricted Boltzmann machine model; collecting partial discharge simulation data and actually-measured partial discharge data, mixing a part of the partial discharge simulation data and actually-measured partial discharge data to serve as a training sample set, and mixing the rest partial discharge simulation data and actually-measured partial discharge data to serve as a test sample set; carrying out unsupervised training on the deep belief learning network by utilizing the training sample set, and extracting cross-mode features; inputting the cross-mode features into a logical regression classifier, and carrying out supervised training on the regression classifier by utilizing the test sample set to obtain a trained deep belief learning network; and inputting partial discharge to be tested into the trained deep belief learning network to obtain a partial discharge fault diagnosis result. Accuracy of fault diagnosis is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
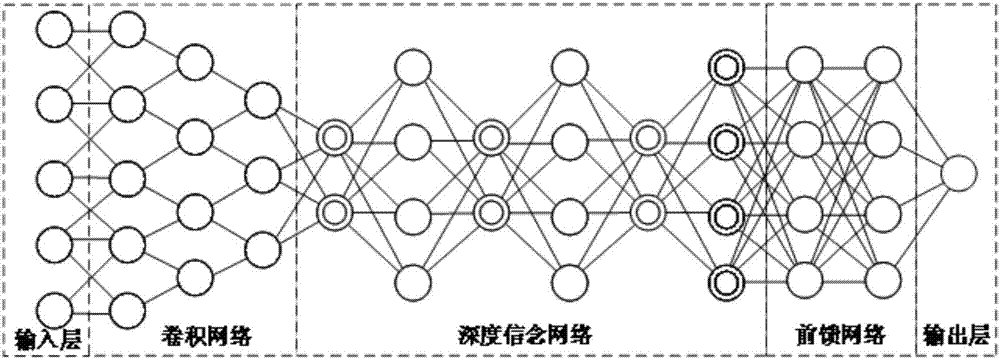
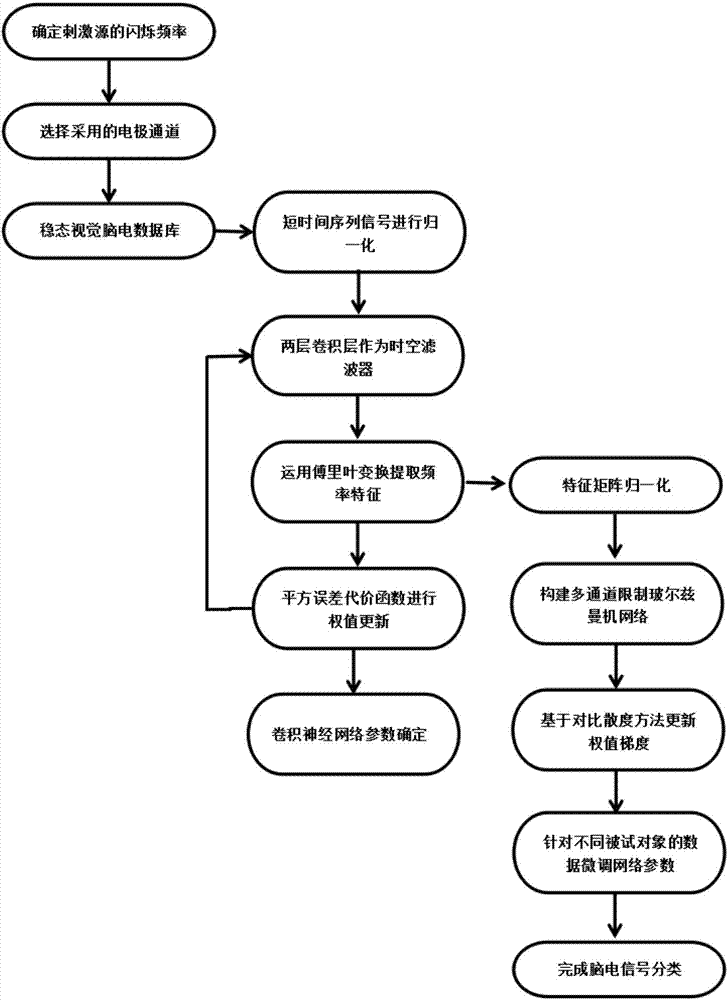
Deep learning mixed model-based steady state visual evoked potential classification method
ActiveCN107168524ARealize automatic extractionPreserve frequency domain featuresInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionSignal classificationClassification methods
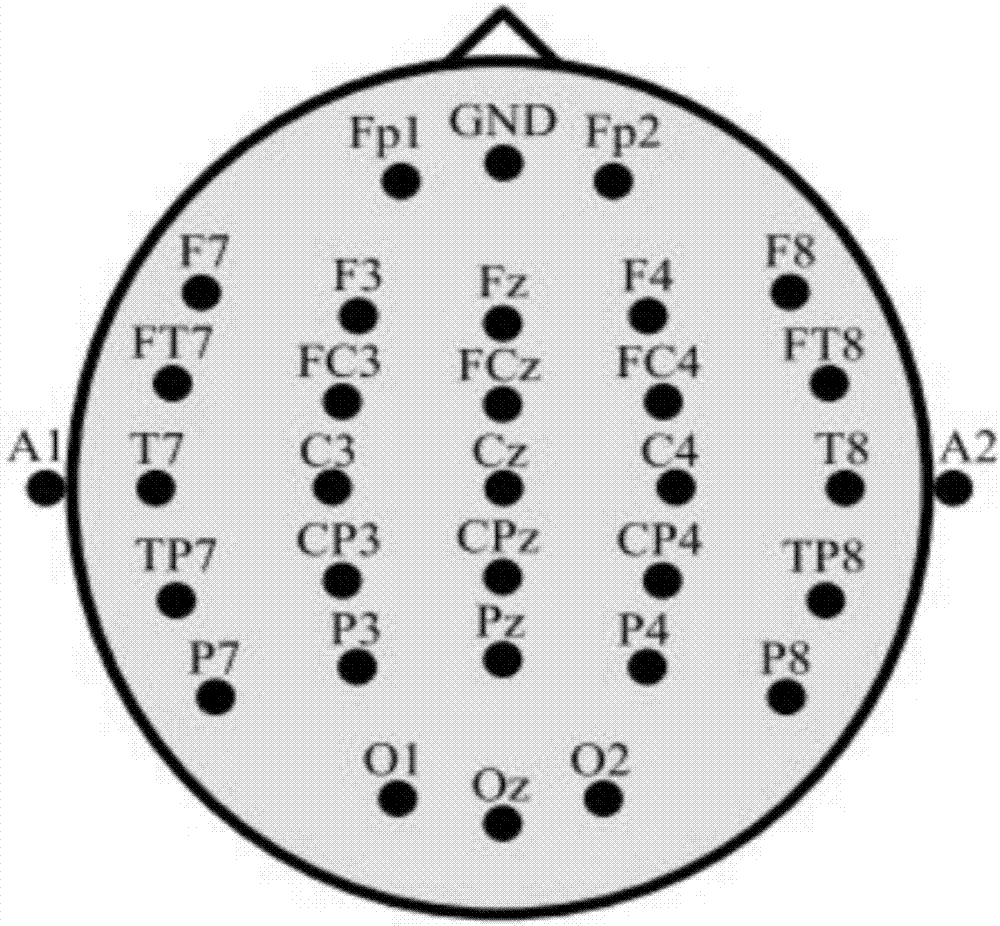
The invention discloses a deep learning mixed model-based steady state visual evoked potential classification method. The method comprises the steps of 1, adopting an LCD display as a stimulation source, determining a flicker frequency, selecting an electrode channel for electroencephalogram collection, carrying out an experiment for multiple different testees, and performing collection to obtain a steady state visual electroencephalogram signal database; 2, based on short-time-sequence electroencephalogram signals in the database, training and determining parameters of a convolutional neural network model, and finishing automatic extraction of features of the electroencephalogram signals; and 3, adopting an output of a convolutional deep learning network as an input of a Boltzmann machine network, performing fine adjustment on parameters of a classification network model for the different testees, and determining parameters of a Boltzmann machine network model. According to the method, the extraction of the generalization features of the electroencephalogram signals can be well realized; the influence of electroencephalogram signal distortion on signal classification is reduced; and the short-time-length electroencephalogram signals can be utilized to well finish the signal classification.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GUANGDA INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
Posture recognition method of human's face based on limited Boltzmann machine neural network
InactiveCN1952953AHigh precisionReduce error rateCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionRestricted Boltzmann machine
This invention relates to Boltzman neutral network for human face identification method in image identification technique field, which comprises the following steps: a, pre-processing human images training samples with different positions; b, initiating limited Boltzman neutral network; c, pre-training limited Boltzman neutral network; d, adjusting limited Boltzman neutral network parameters; e, identifying new human face position. This invention relates to human face testing, mode sorting, human face position identification for re-establish three dimensional human faces and identification.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
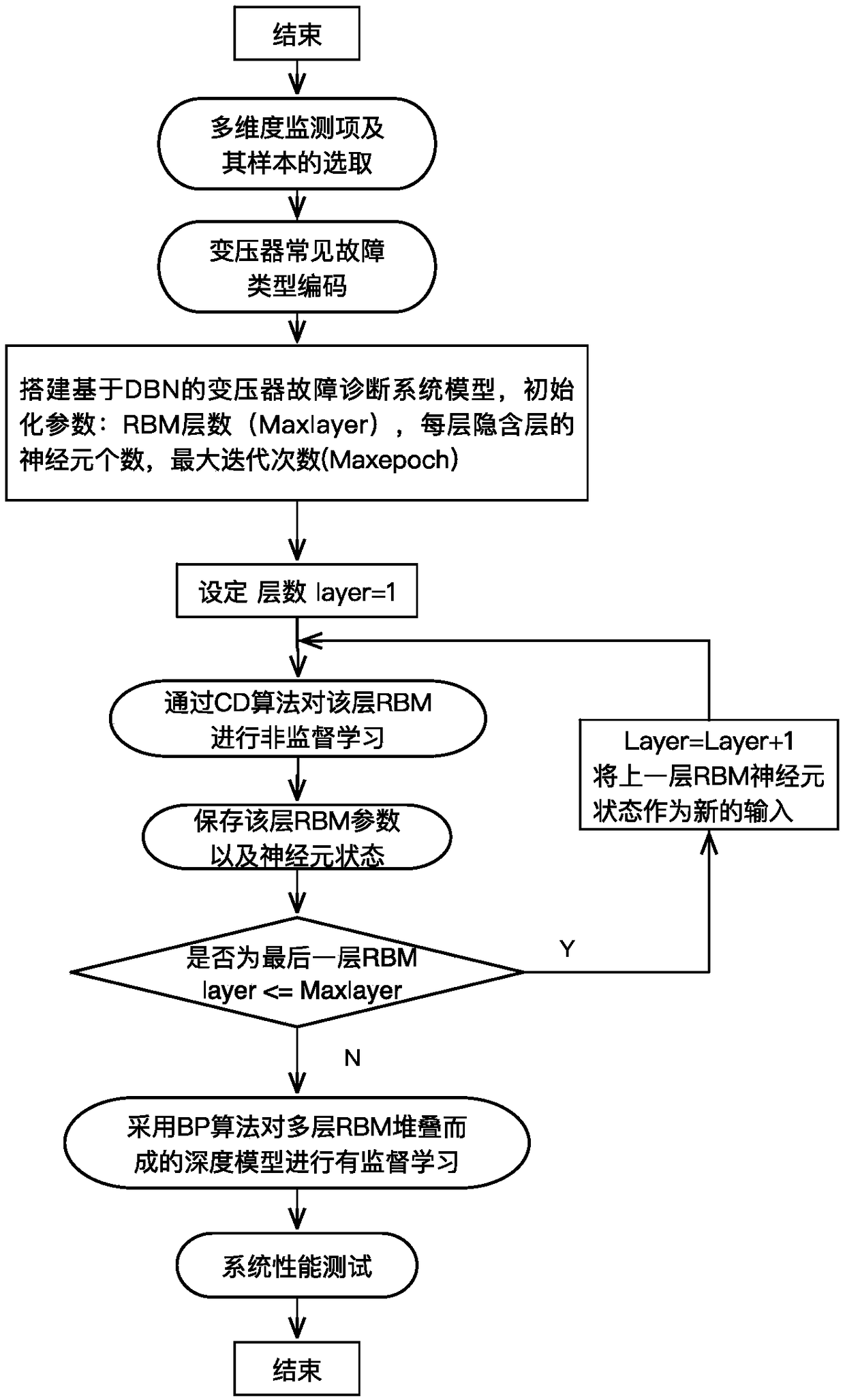
A multi-dimensional information fusion method for transformer fault diagnosis based on depth learning
InactiveCN109214416AReal-time diagnosisAccurate diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesDiagnosis methodsTransformer
The invention provides a multi-dimensional information fusion transformer fault diagnosis method based on depth learning. Firstly, the multi-dimensional state monitor which can best reflect the real operation state of the transformer is selected as the input of the depth learning model for normalization. Secondly, the common transformer faults that need to be identified are coded and classified. Then, based on the depth learning theory, sparse constrained Boltzmann machines are stacked to form the underlying network. Finally, a classifier is added to the top of the depth learning model to forma depth learning model based on sparse depth belief network. The fault diagnosis method can make use of a large number of unlabeled multi-dimensional monitoring data of transformer as learning samples, and only a small number of labeled multi-dimensional monitoring data can be used for optimization. The trained model can make accurate diagnosis of transformer status according to the real-time multi-dimensional monitoring data of transformer. The fault diagnosis method provided by the invention is feasible and effective, and the performance thereof is superior to the existing transformer faultdiagnosis method.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
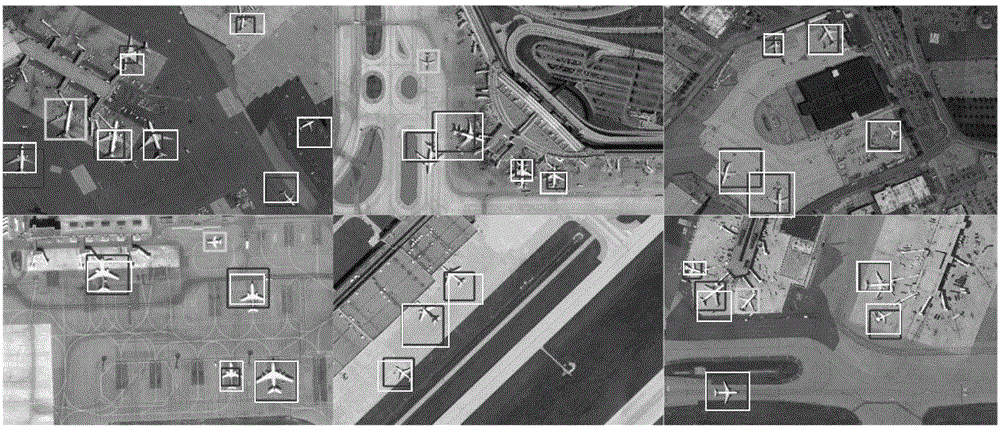
High-resolution remote sensing image airplane detecting method based on high-level feature extraction of depth boltzmann machine
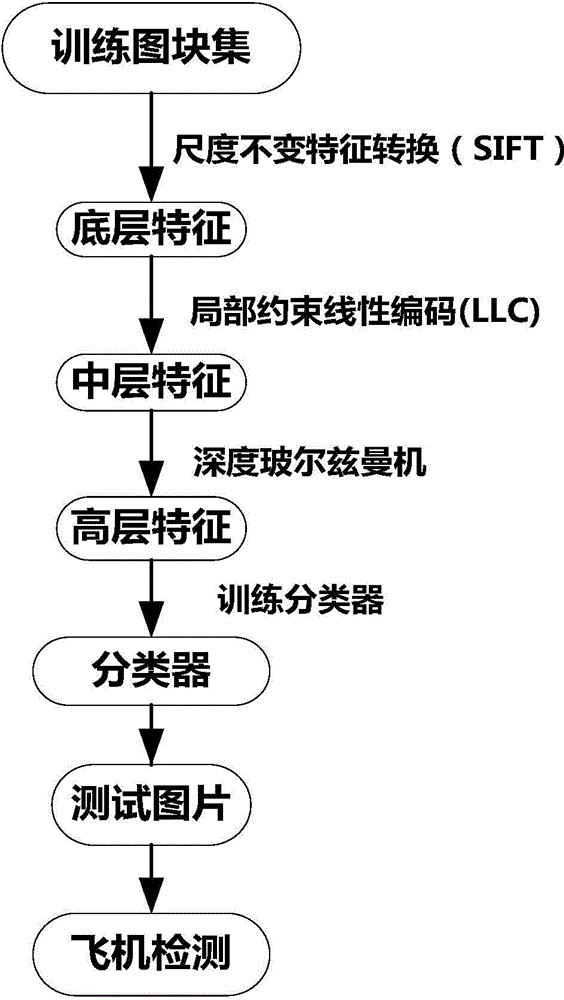
InactiveCN104463248AEnhance expressive abilityExpressiveImage analysisKernel methodsJet aeroplaneScale-invariant feature transform
The invention relates to a high-resolution remote sensing image airplane detecting method based on high-level feature extraction of a depth boltzmann machine. The method comprises the steps that at first, a picture is divided into a plurality of segments, then scale-invariant feature transformation (SIFT) is utilized for extracting key points in the segments, the key points serve as low-level features of the segments, then a local restriction linear coding algorithm is utilized for coding the low-level features to obtain medium-level features, then the three-layer depth boltzmann machine is utilized for obtaining high-level features of the segments from the medium-level features, then the high-level features are utilized for training a support vector machine classifier, finally the classifier is used for detecting an airplane of the detected picture, and the airplane detection result high in accuracy and robustness can be obtained.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
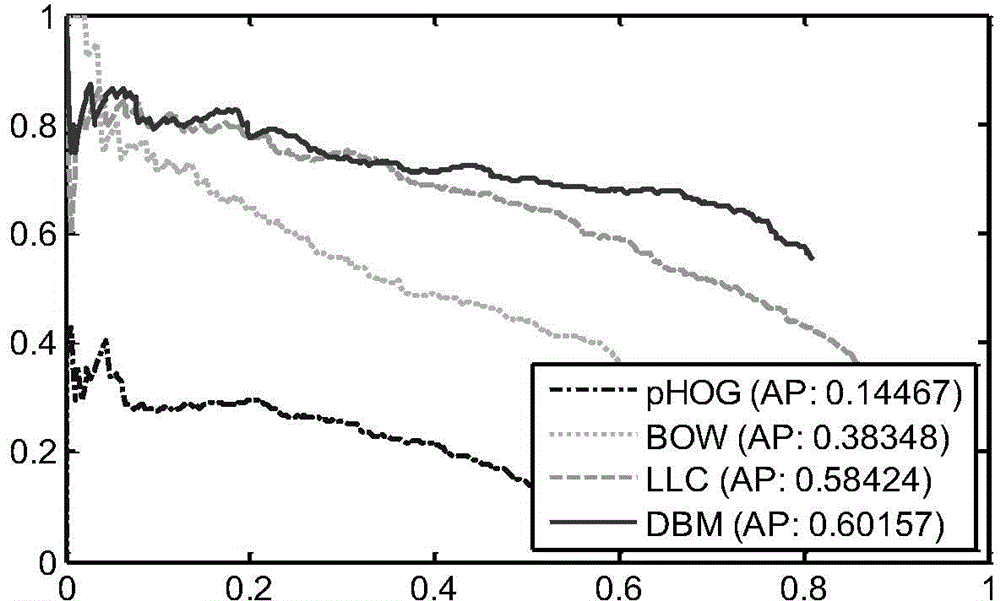
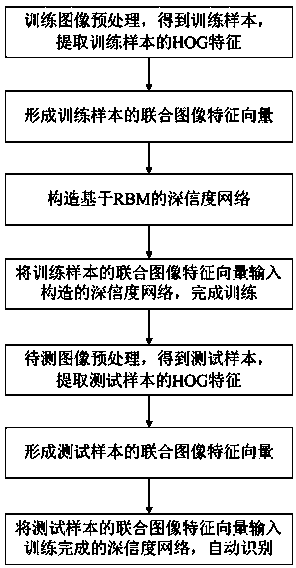
Pest image automatic recognition method based on high-reliability network
InactiveCN104077580AStrong expressive abilityImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorRestricted Boltzmann machine
The invention provides a pest image automatic recognition method based on a high-reliability network. The method includes the following steps that preprocessing is carried out on multiple collected training images to obtain multiple training samples, and HOG feature extraction is conducted on the training samples to form joint image feature vectors of the training samples; the high-reliability network based on a restricted boltzmann machine is constructed, the joint image feature vectors of the training samples are input to the constructed high-reliability network, and training on the high-reliability network is completed; preprocessing is conducted on pest images to be tested to obtain test samples, and HOG feature extraction is carried out on the test samples to form joint image feature vectors of the test samples; the joint image feature vectors of the test samples are input to the high-reliability network after training is finished, and categories of past images to be tested are obtained through recognition. According to the method, the accuracy rate of pest recognition can be improved, and robustness of a pest recognition algorithm is enhanced.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
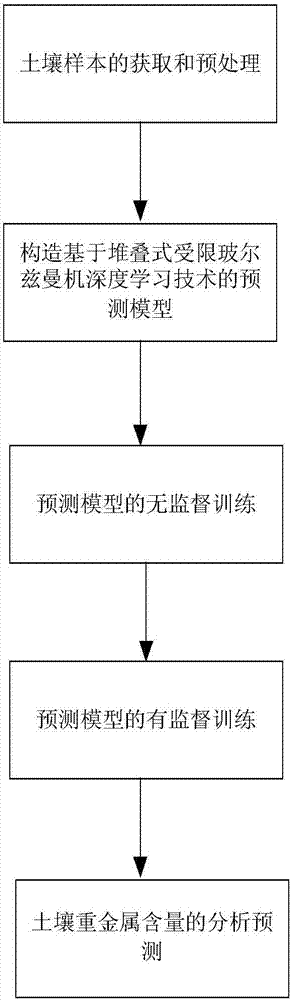
Method for analyzing and predicating content of heavy metals in soil based on LIBS and stacked RBM deep learning technology
InactiveCN107044976AHigh precisionImprove robustnessForecastingAnalysis by thermal excitationRestricted Boltzmann machineSoil heavy metals
The invention relates to a method for analyzing and predicating the content of heavy metals in soil based on LIBS and a stacked RBM deep learning technology. The defect of slow detection speed of the content of the heavy metals in soil in the prior art is overcome in the invention. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining and preprocessing a soil sample; constructing a prediction model based on the stacked restricted Boltzmann machine deep learning technology; carrying out unsupervised training on the prediction model; carrying out supervised training on the predication model; and analyzing and predicating the content of the heavy metals in the soil. The content of the heavy metals in the soil is analyzed and predicated by using the mapping relationship between a laser induced breakdown spectrum and the content of the heavy metals in the soil and combining with the stacked RBM deep learning technology.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
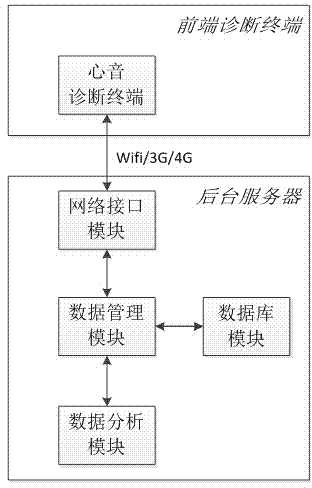
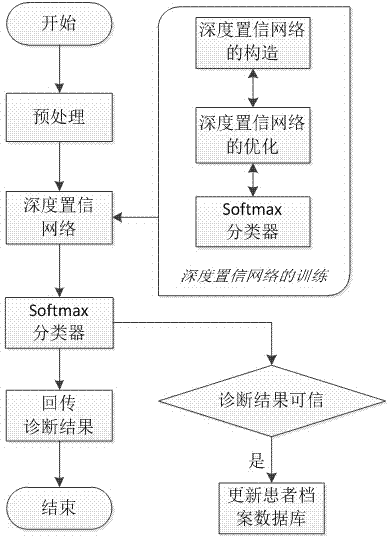
Cardiac sound diagnostic system based on depth confidence network and diagnostic method
InactiveCN104757992ASimple and fast operationImprove auscultation efficiencyStethoscopeRestricted Boltzmann machineNetwork model
The invention discloses a cardiac sound diagnostic system based on a depth confidence network and a diagnostic method of the cardiac sound diagnostic system. The cardiac sound diagnostic system comprises a cardiac sound diagnostic terminal, a network interface module, a database module, a data analyzing module, and a data management module; the data management module is connected with the database module, the data analyzing module and the network interface module at the same time, and the database is connected with the data analyzing module at the same time; the network interface module is in signaling connection with the cardiac sound diagnostic terminal. The diagnostic method is based on a depth confidence network model consisting of restricted Boltzmann machine layering; the diagnostic method comprises the steps: using a patient's cardiac sound file database; training the established depth confidence network by using a layer-by-layer greedy algorithm; inputting the cardiac sound signal to be diagnosed to the depth confidence network model after training; obtaining the final diagnostic result at an output layer and returning to the cardiac sound diagnostic terminal. The cardiac sound diagnostic system based on the depth confidence network and the diagnostic method can realize the remote diagnosis of patient's cardiac sound signals; the operation is convenient and simple, the diagnostic accuracy is high, the cost is low; besides, the device is convenient to maintain and upgrade.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
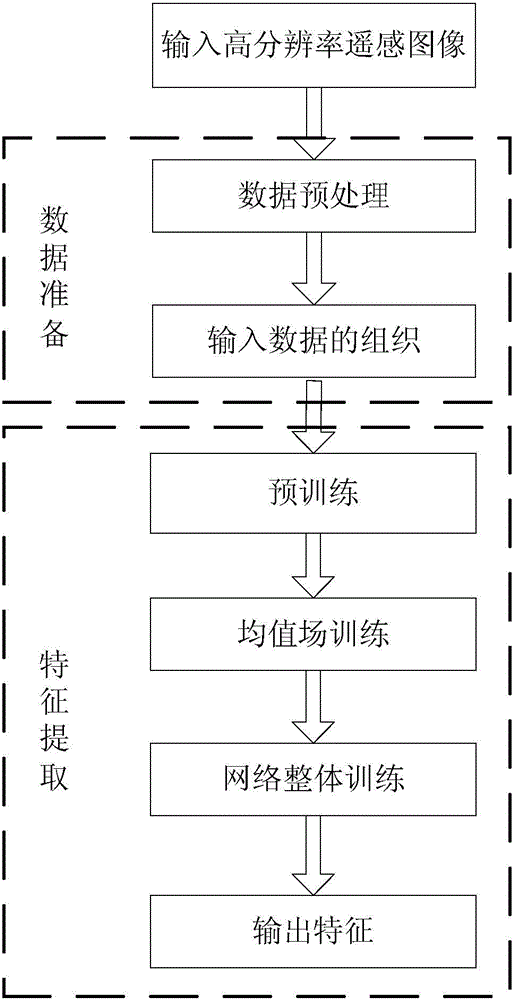
Feature extraction method for high spatial resolution remote sensing big data
InactiveCN104700100AAccurate expressionImprove classification performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionSemantic featureImaging data
The invention relates to a feature extraction method for high spatial resolution remote sensing big data and belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image feature extraction. The feature extraction method for the high spatial resolution remote sensing big data aims to solve the problem that the obtained features of an existing feature extraction for high spatial resolution remote sensing images are low-level features so that the essential can not be expressed accurately. The feature extraction method for the high spatial resolution remote sensing big data comprises the steps of first collecting remote sensing images, pre-processing the remote sensing images and obtaining input data; parting the input data to continuous and non-overlapping 31*31 or 51*51 pixel sub-image data; inputting the sub-image data successively to corresponding nodes of an input layer of a convolution depth Boltzman machine and obtaining low-level semantic features of the sub-image data; taking the low-level semantic features of the sub-image data as a high-level semantic layer of the convolution depth Boltzman machine, and obtaining essential features of the sub-image data; furthermore, obtaining standard 51x contextual information; finally outputting feature extraction results of the input data by a Logistic classifier. The feature extraction method for the high spatial resolution remote sensing big data is used for feature extraction of remote sensing big data.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
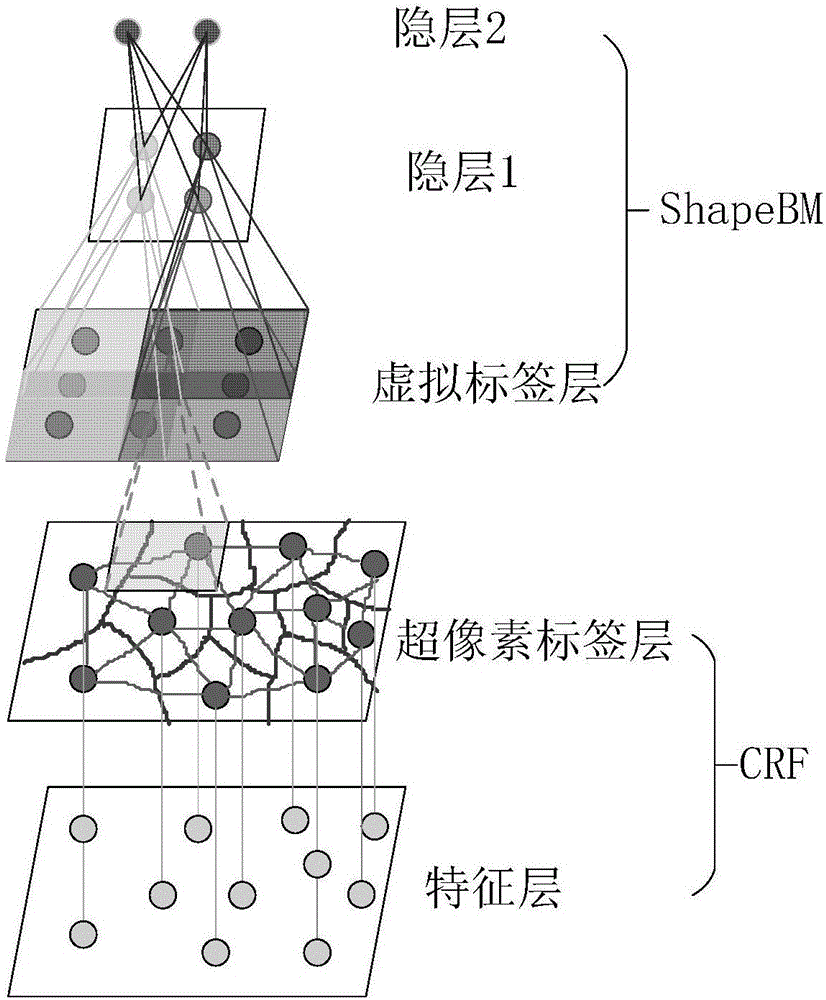
Image marking method combining local image constraint and overall target constraint
ActiveCN106570874AImprove accuracyWide applicabilityImage enhancementImage analysisConditional random fieldComputation complexity
The invention discloses an image marking method combining a local image constraint and an overall target constraint. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring a super pixel area node image of each original image, finding a mask area corresponding to each super pixel area node of the corresponding super pixel area node image in a mask image corresponding to each original image and marking; then, using a characteristic set of the super pixel area node image and an area label set corresponding to the mark image to train a conditional random field model, using a virtual label set corresponding to images acquired after all the mask areas are marked in the mask image to train a shape Boltzmann machine model; and through a grid partitioning technology, effectively combining the conditional random field model and the shape Boltzmann machine model. The local image constraint and the overall target constraint are tightly combined and accuracy of image marking is increased. The method can be suitable for a condition in which a data set is small and image resolution is low. And computation complexity is low.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
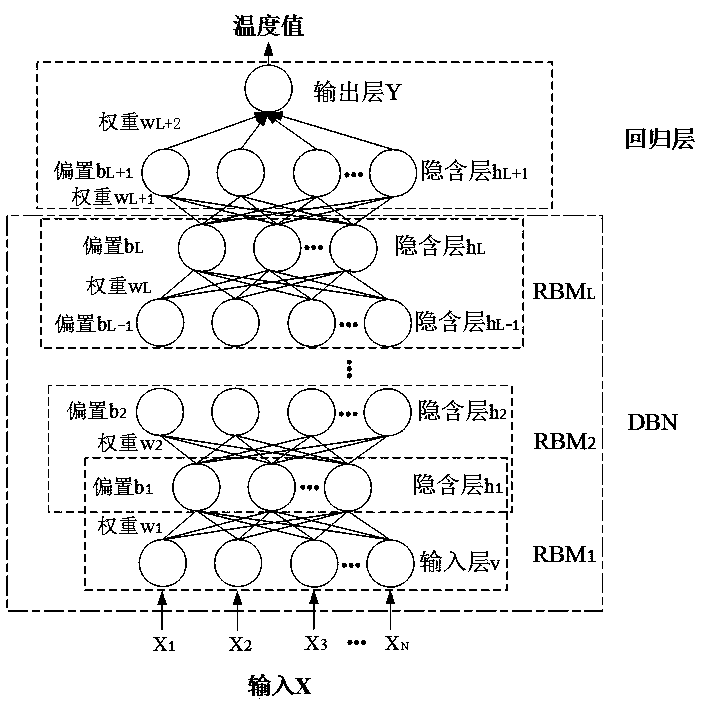
Transformer substation electrical equipment temperature prediction method
ActiveCN110175386ASafe and stable temperatureTemperature prediction, safe and stable operation of the collected electrical equipmentData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationDeep belief networkRestricted Boltzmann machine
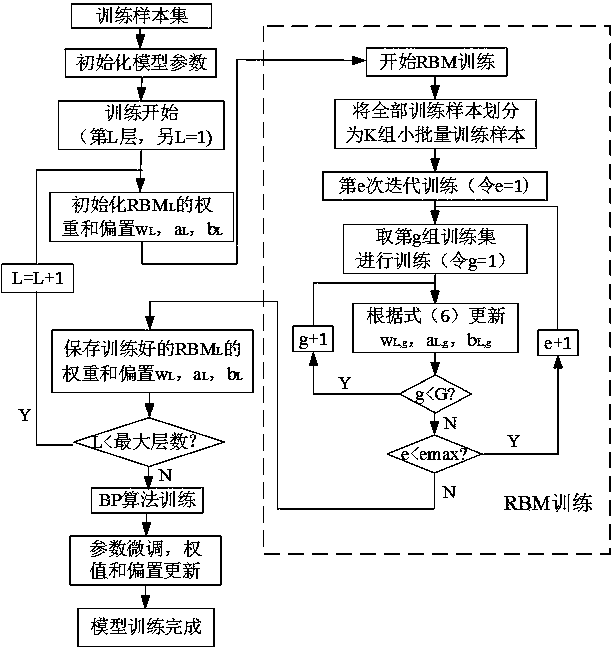
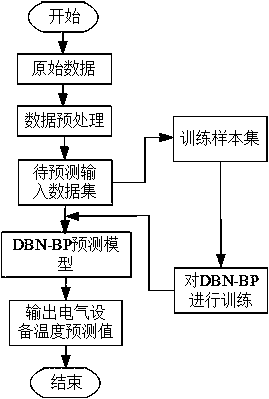
The invention relates to a transformer substation electrical equipment temperature prediction method, which comprises the following steps of taking the collected electrical equipment operation parameters and environment parameters as the input variables, and establishing a prediction model by utilizing a deep belief network (DBN) to predict the temperatures of the electrical equipment. Accordingto the present invention, by firstly carrying out the deep feature extraction on the input electrical equipment parameter data by adopting a deep belief network stacked by a RBM (restricted boltzmannmachine) to complete an unsupervised learning process, taking the high-dimensional characteristic quantity outputted by the last layer of the DBN as the input of the neural network, and carrying out the conventional fitting to obtain a prediction result, and finally, using the trained DBN-NN model for predicting the temperatures of electrical equipment in a transformer substation, through the temperature prediction method provided by the invention, the temperatures of the electrical equipment can be predicted more accurately, so that a new method is provided for solving the prediction estimation problem and reducing the faults of the electrical equipment of the transformer substation.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com