Patents
Literature
55 results about "Threshold probability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Probability Threshold means that level of sensitivity determined by Client to be necessary to justify the pursuit of a medical record review of a CEDI Member Medical Record. The Probability Threshold can be set at high, medium, low, or very low.
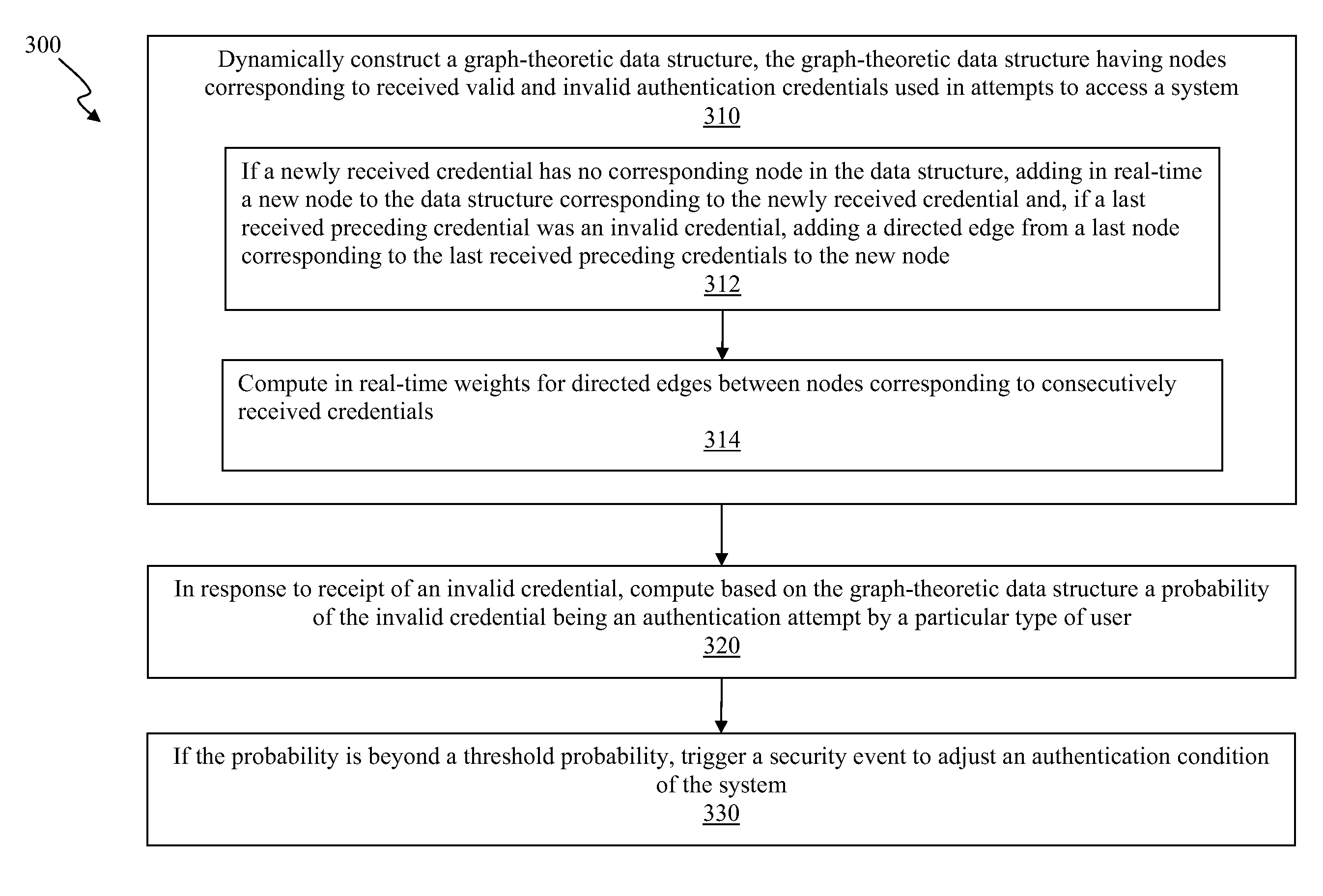
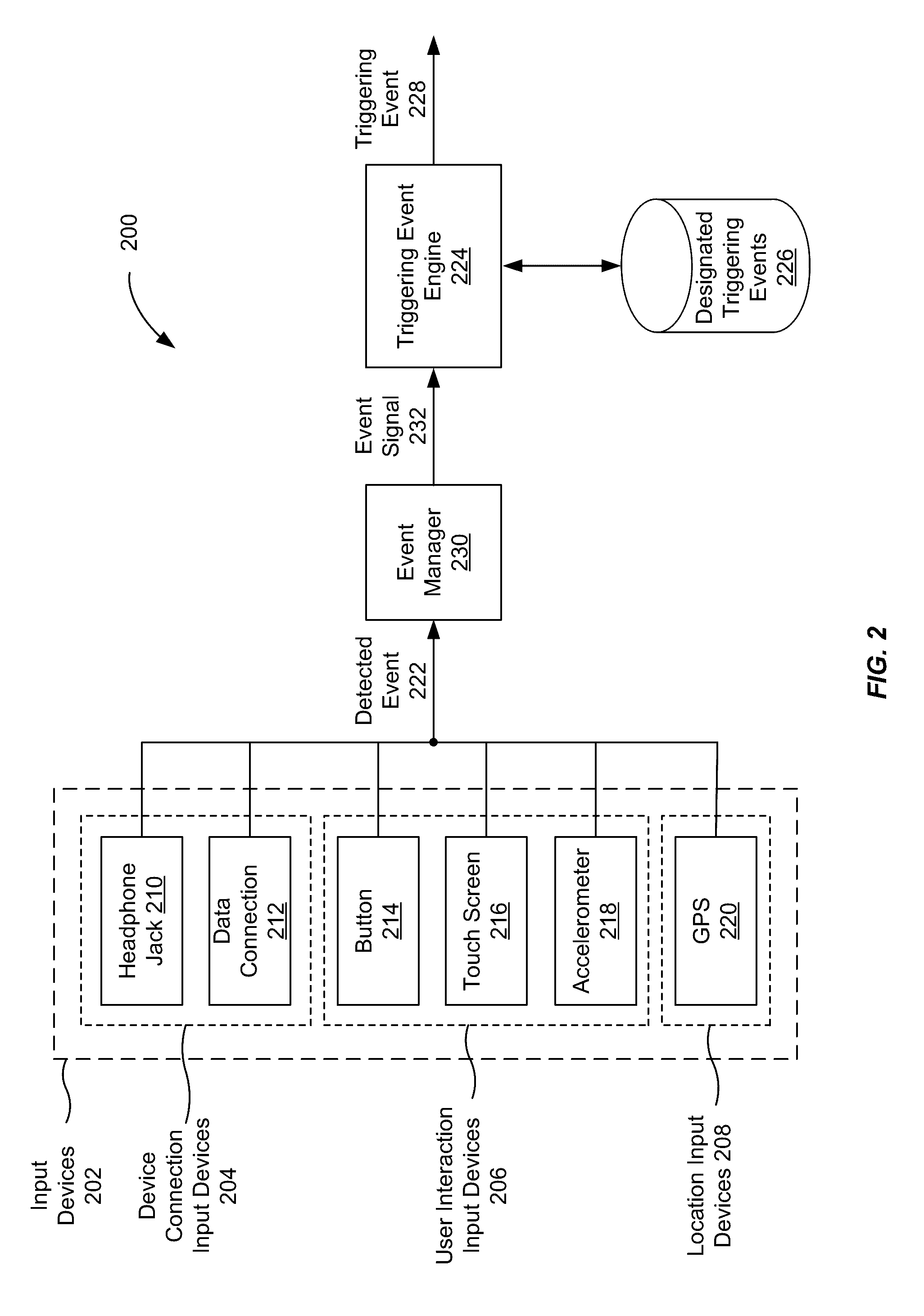
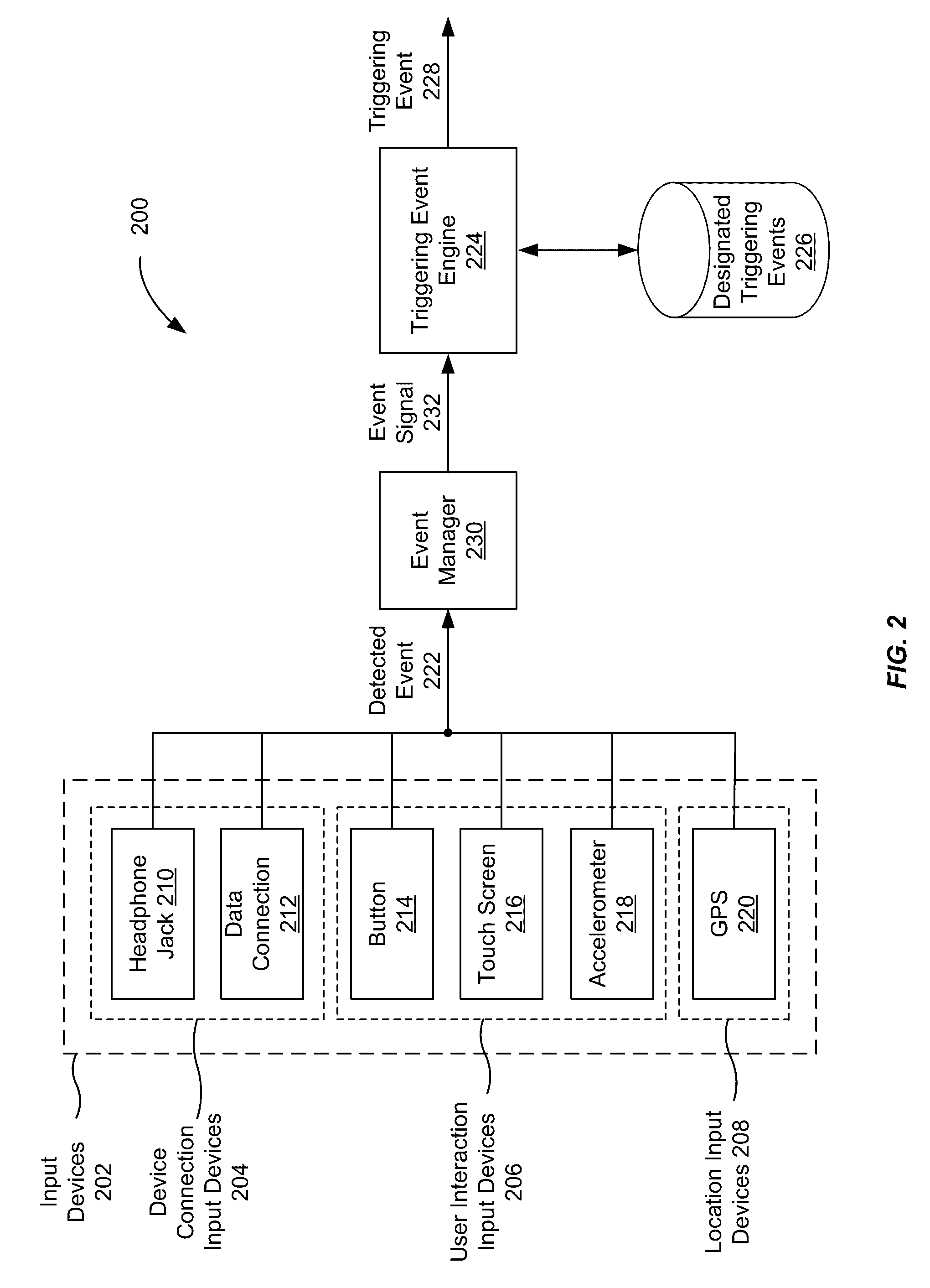
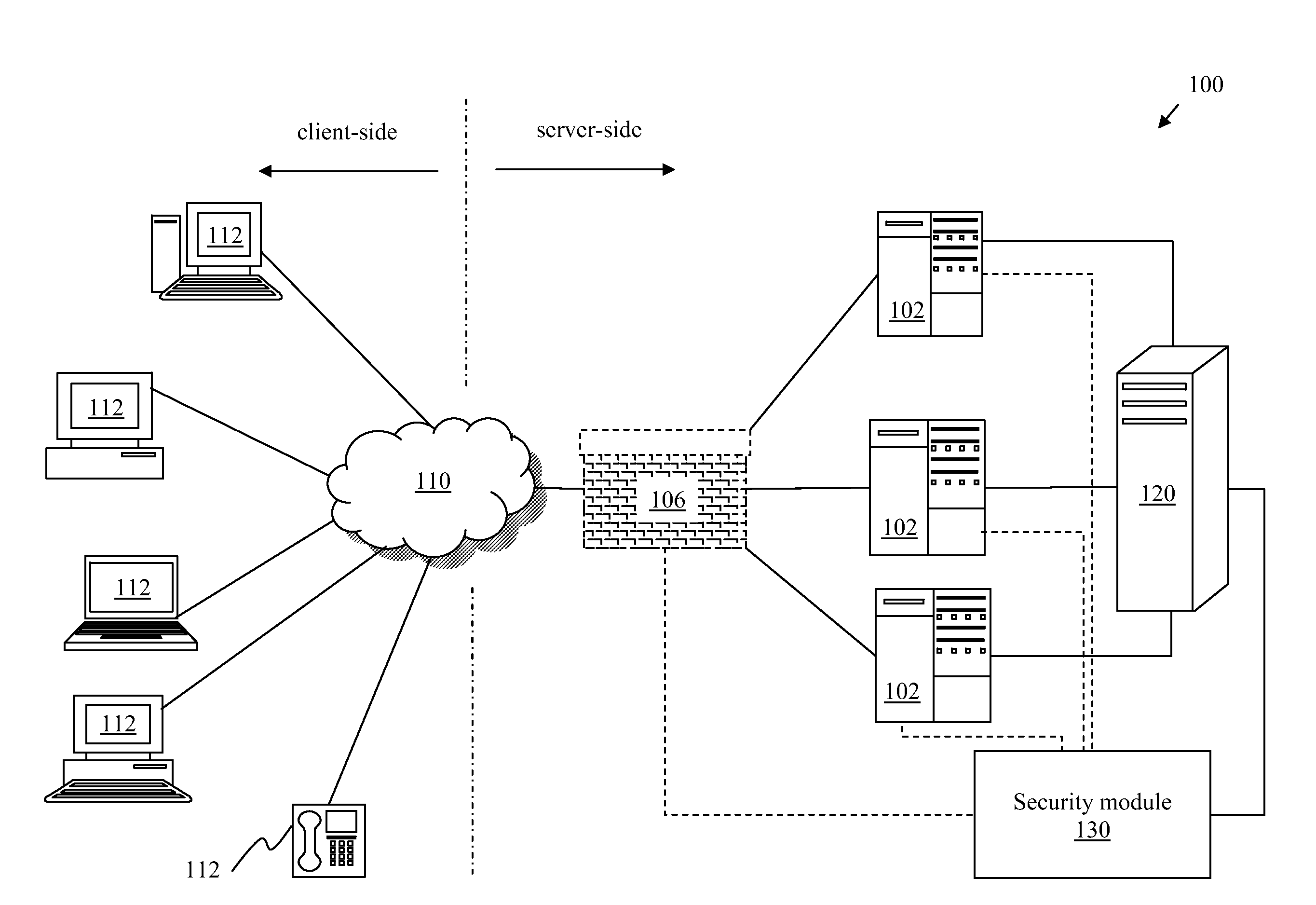
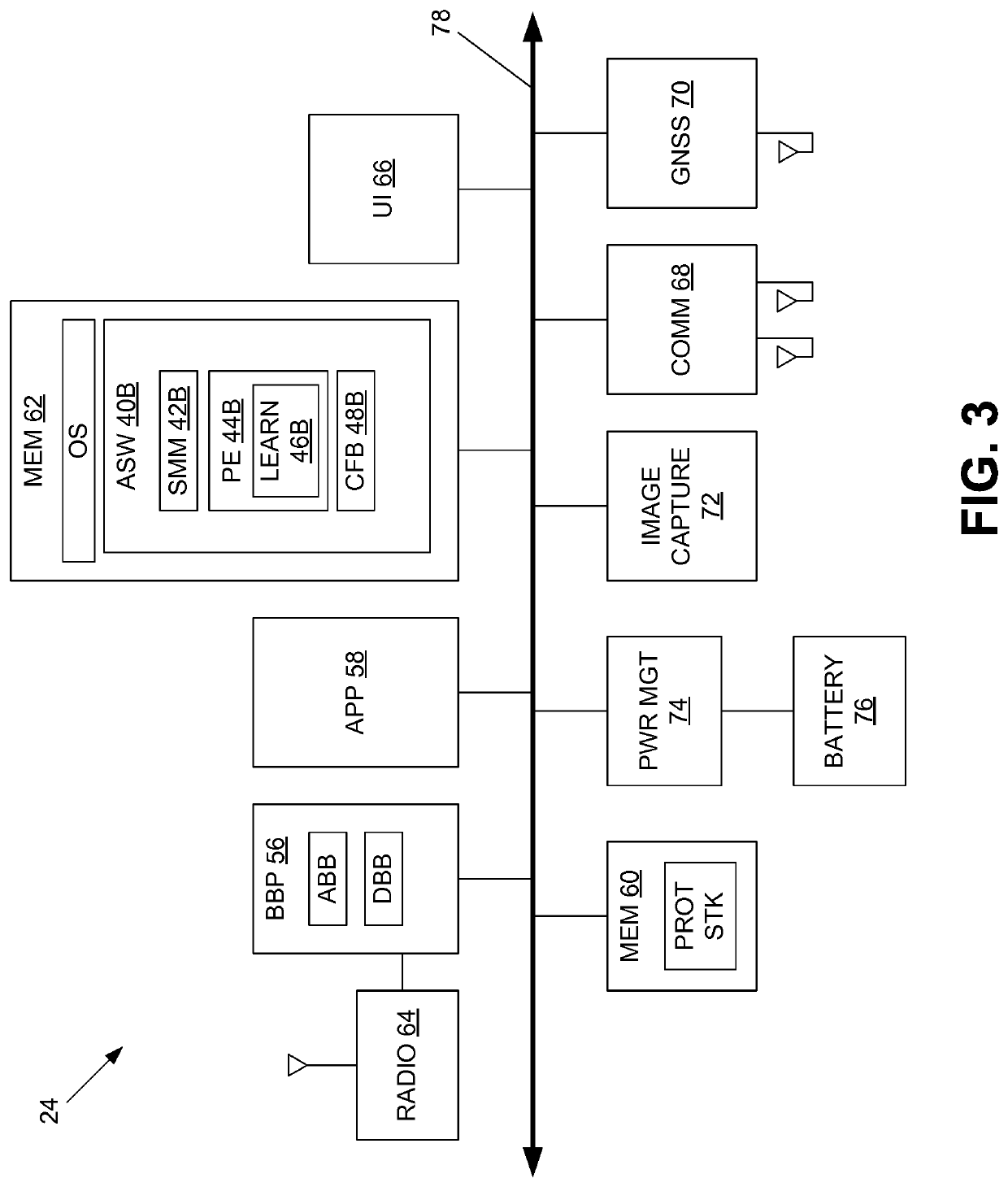
Real-time adjustments to authentication conditions
InactiveUS20110185401A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGraphicsVoucher
Embodiments of the invention provide for adjusting authentication conditions in real-time. A graph-theoretic data structure is dynamically constructing, having nodes corresponding to received valid and invalid authentication credentials used in attempts to access a system. Based on the graph-theoretic data structure, embodiments compute a probability of an invalid credential being an authentication attempt by a particular type of user. If the probability is beyond a threshold probability, embodiments trigger a security event is to adjust an authentication condition of the system, e.g., to increase or decrease a maximum permissible number of failed login attempts within a certain period of time.
Owner:IBM CORP
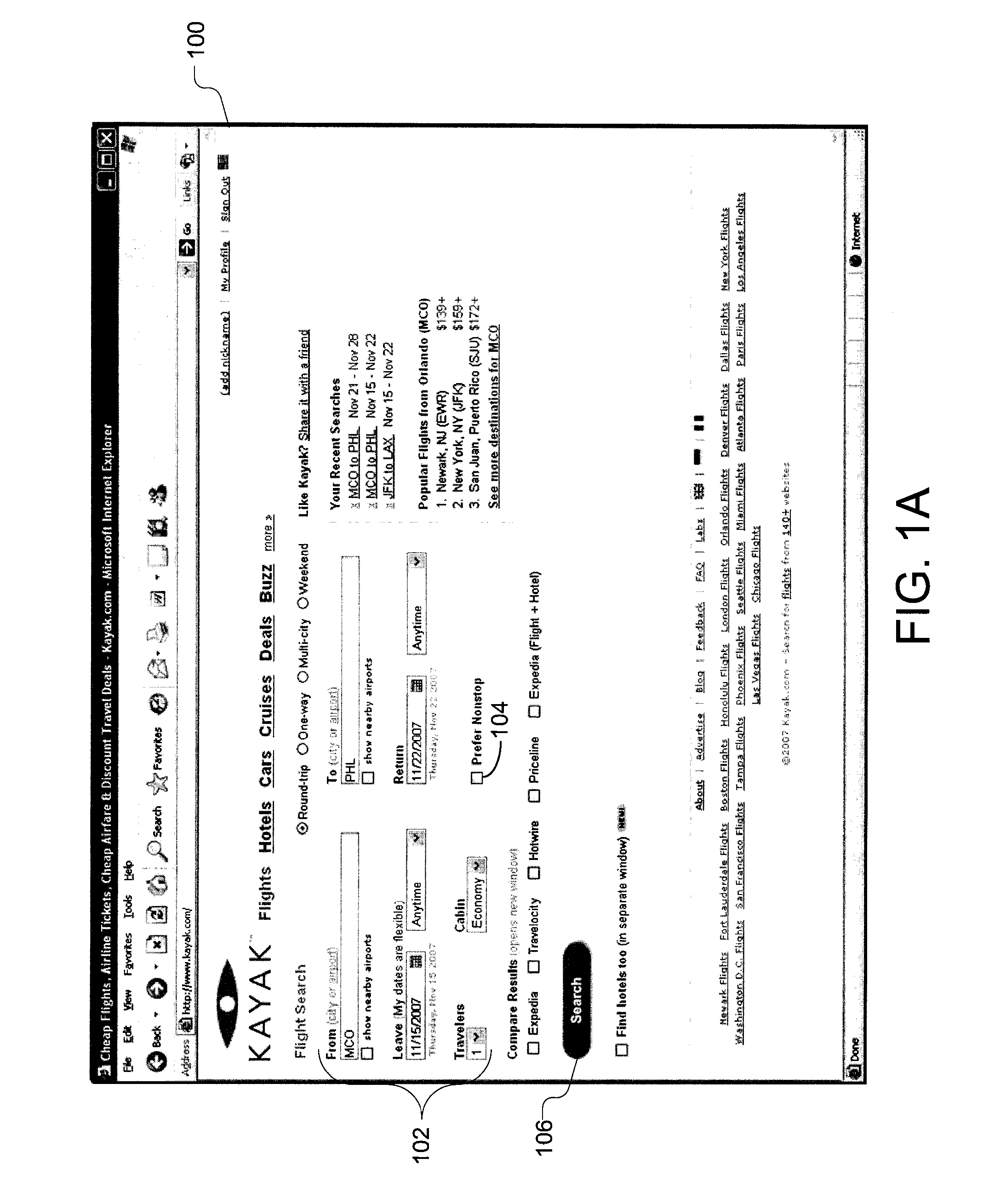
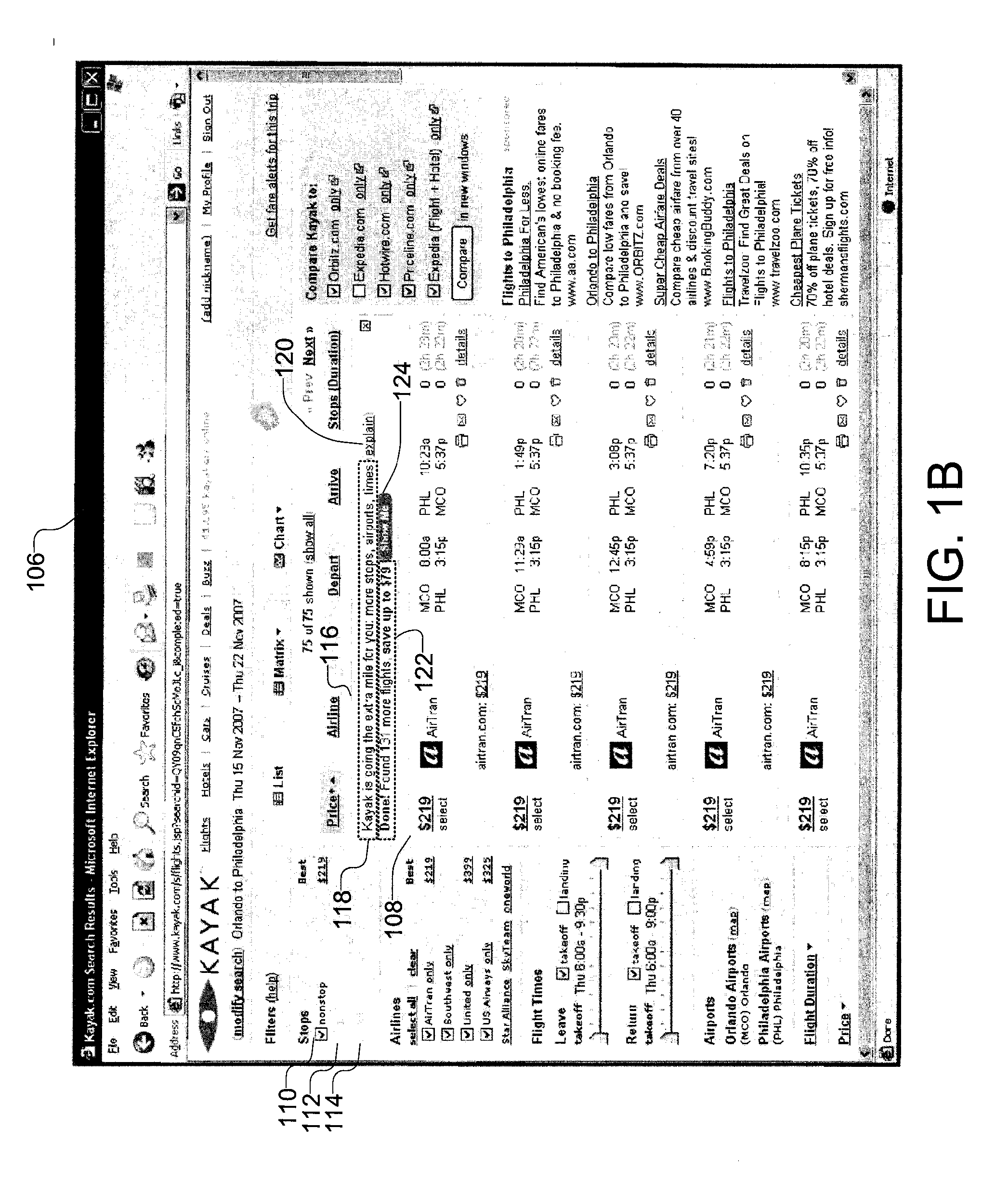
Multi-Phase Search And Presentation For Vertical Search Websites
ActiveUS20090150343A1Presented quicklyEfficiently performing travel reservation queriesWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsPhrase searchMulti phase
The present invention provides a methodology and system for efficiently performing travel reservation queries and presenting significant search results to a user. A travel reservation search engine constructs a first query from one or more constraints. The first query has a threshold probability of returning a first set of search results that will lead to the purchase of a travel reservation. Additionally, if determined necessary by the search engine a second query is constructed from one or more constraints. The second query returns a second set of search results.
Owner:KAYAK SOFTWARE CORP
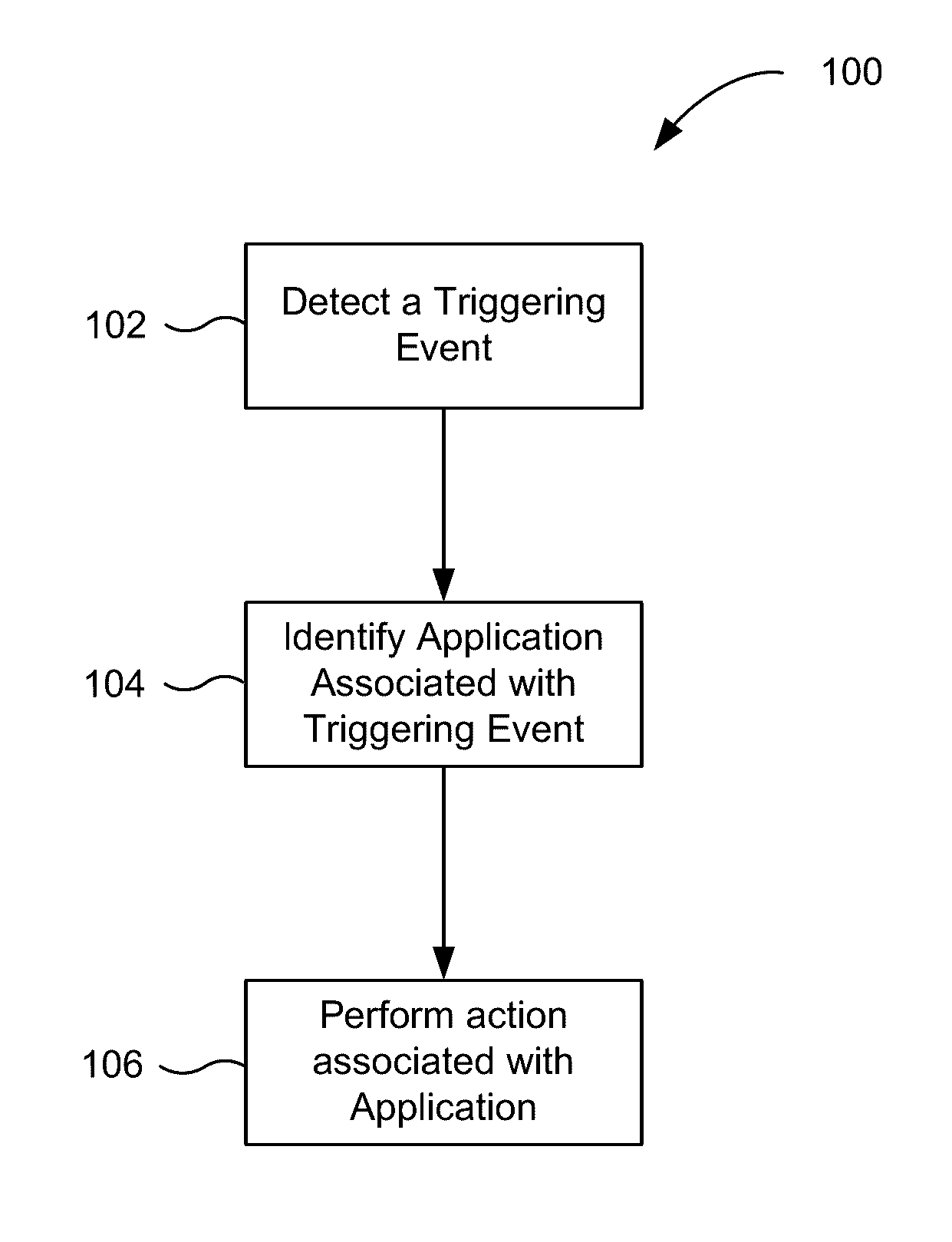
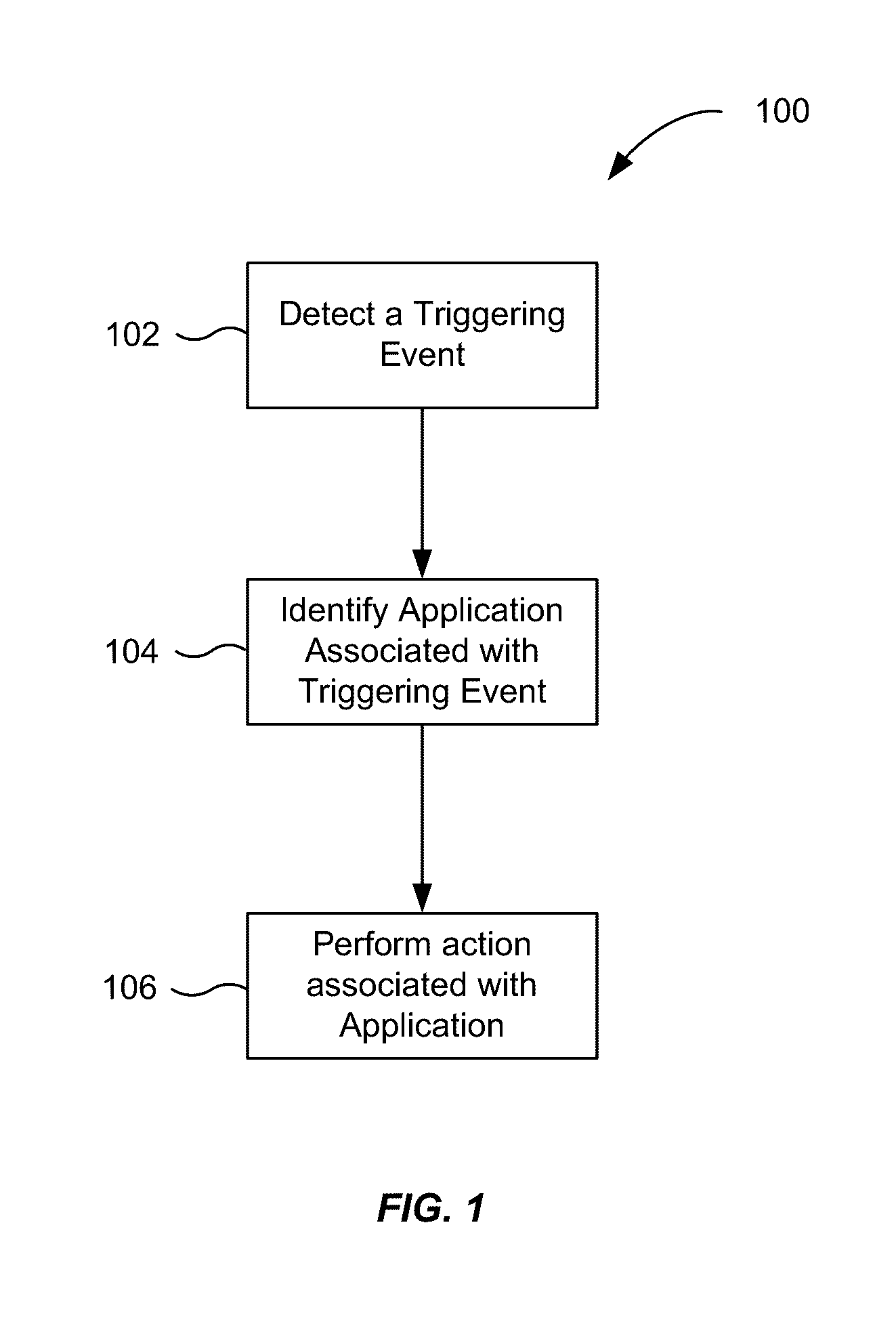
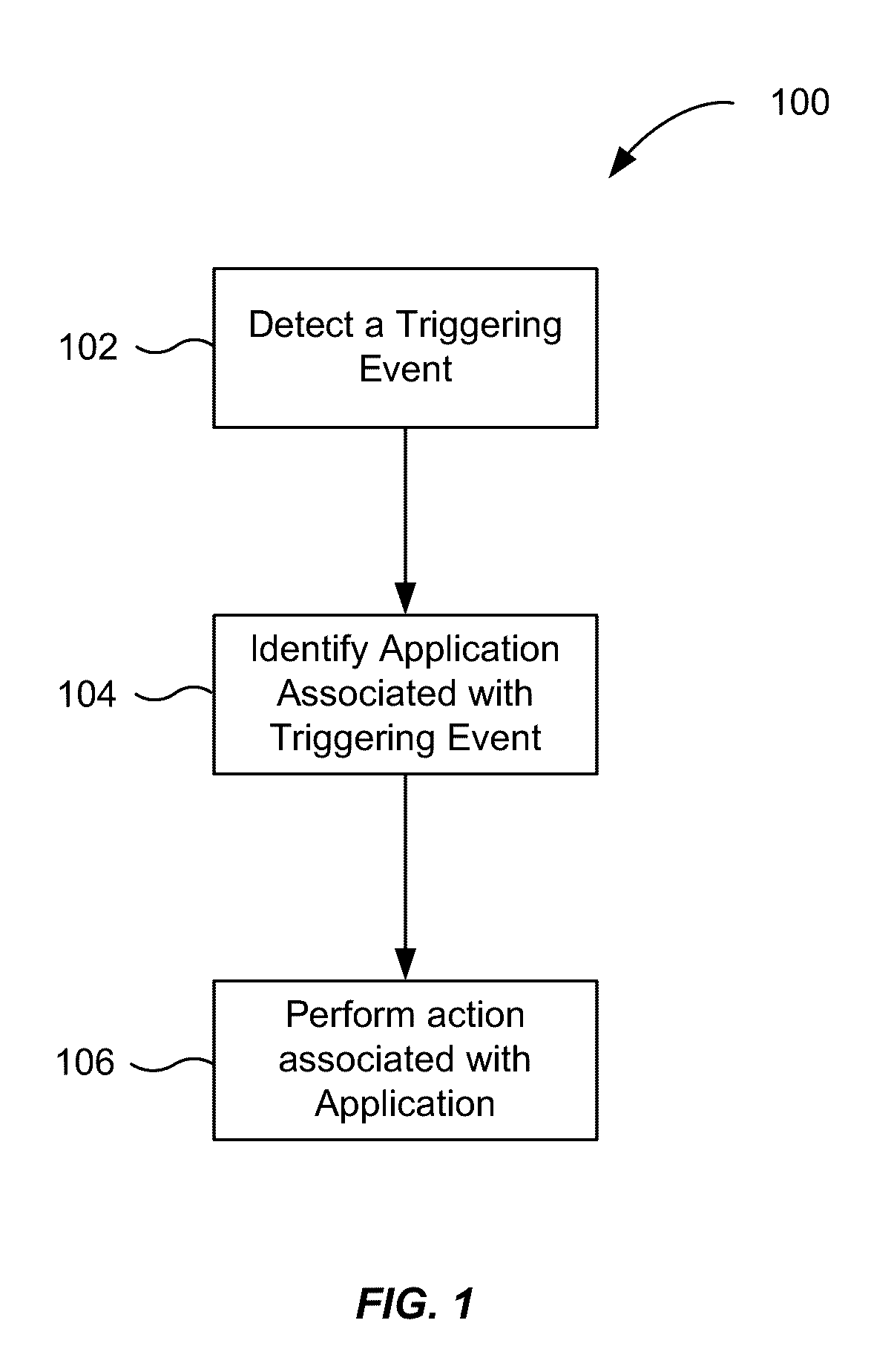
Application recommendation based on detected triggering events
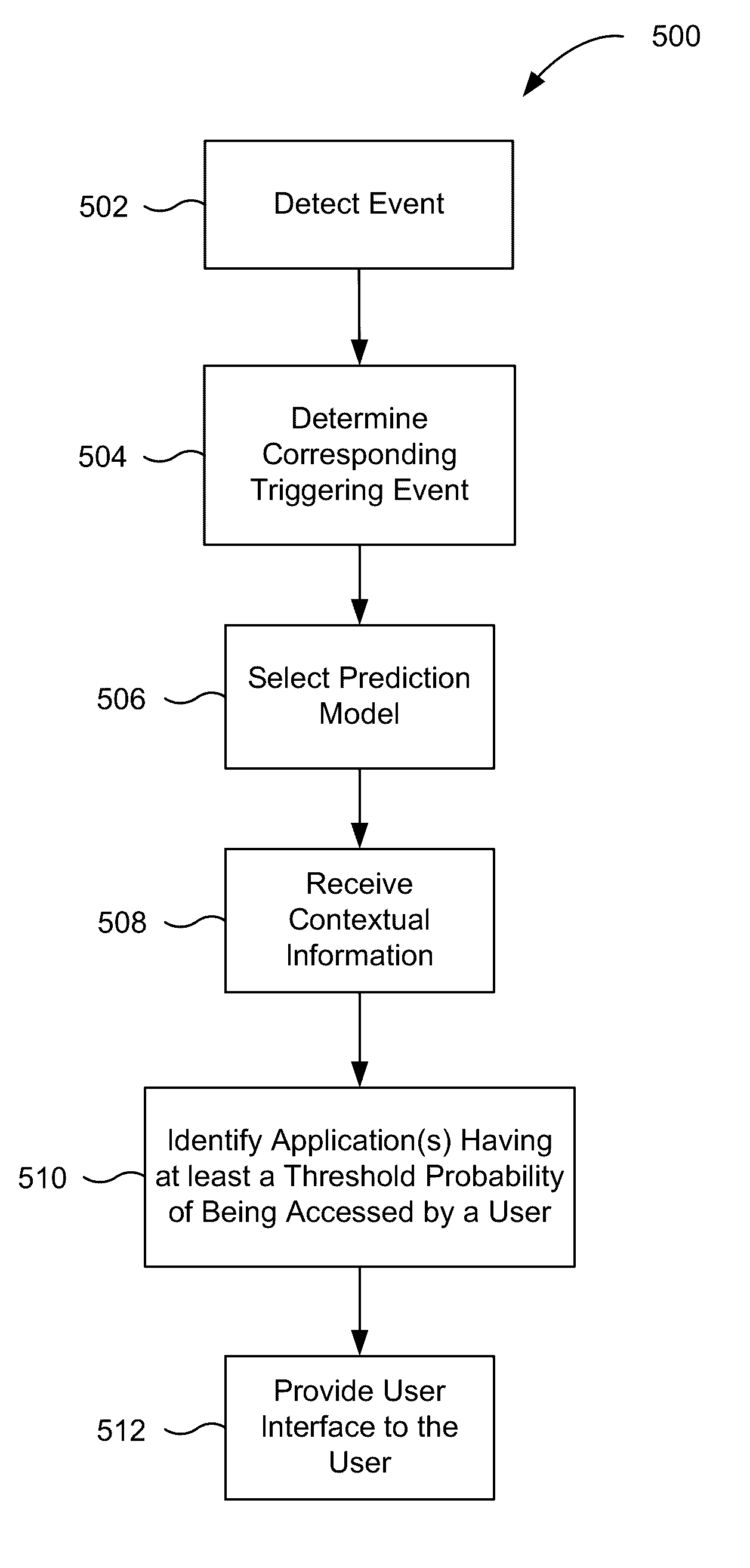
ActiveUS20160357362A1Accurate recommendationEasy accessSubstation equipmentMachine learningComputer scienceThreshold probability
An event can be detected by an input device. The event may be determined to be a triggering event by comparing the event to a group of triggering events. A first prediction model corresponding to the event is then selected. Contextual information about the device specifying one or more properties of the computing device in a first context is then received, and a set of one or more applications is identified. The set of one or more applications may have at least a threshold probability of being accessed by the user when the event occurs in the first context. Thereafter, a user interface is provided to a user for interacting with the set of one or more applications.
Owner:APPLE INC
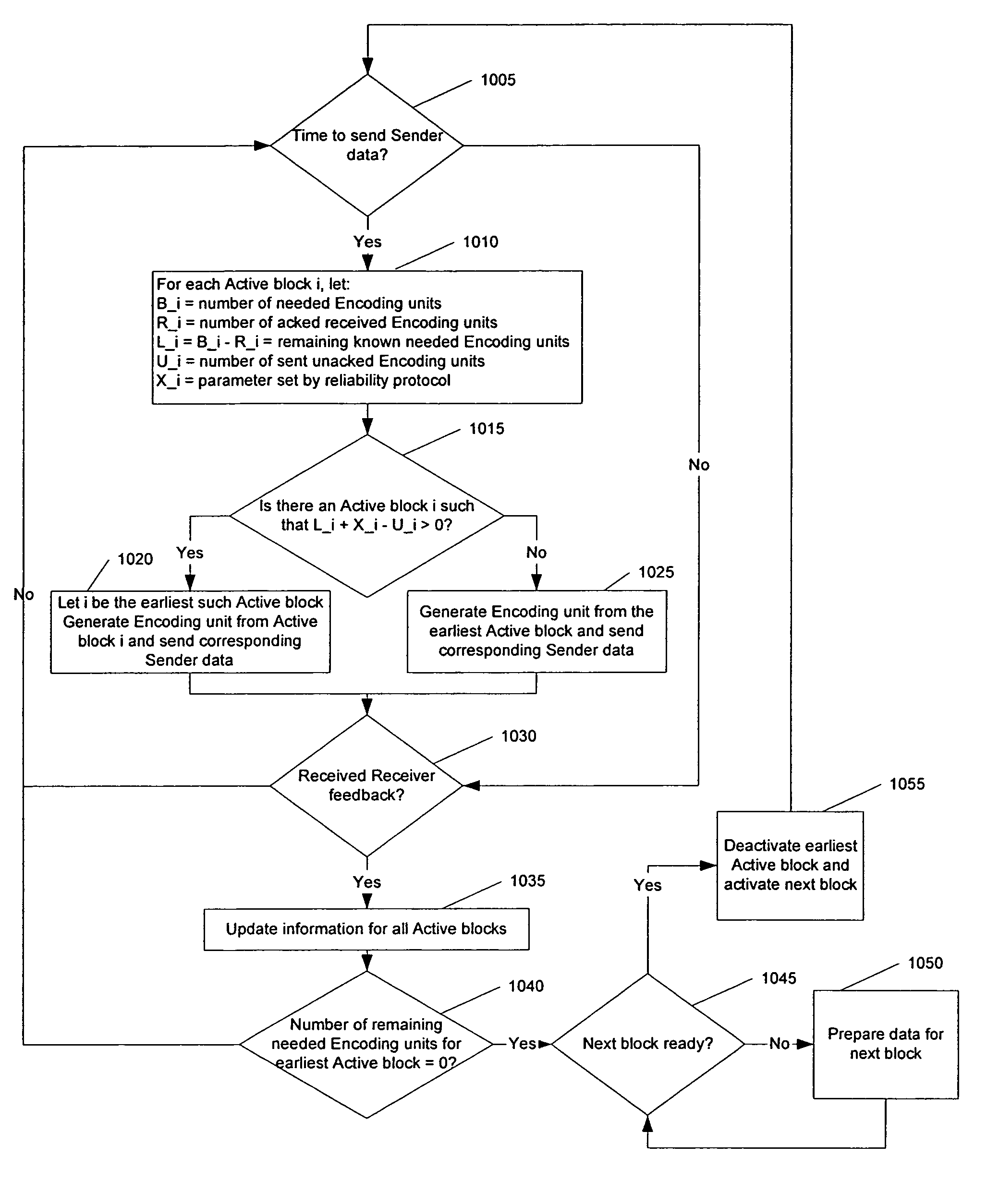
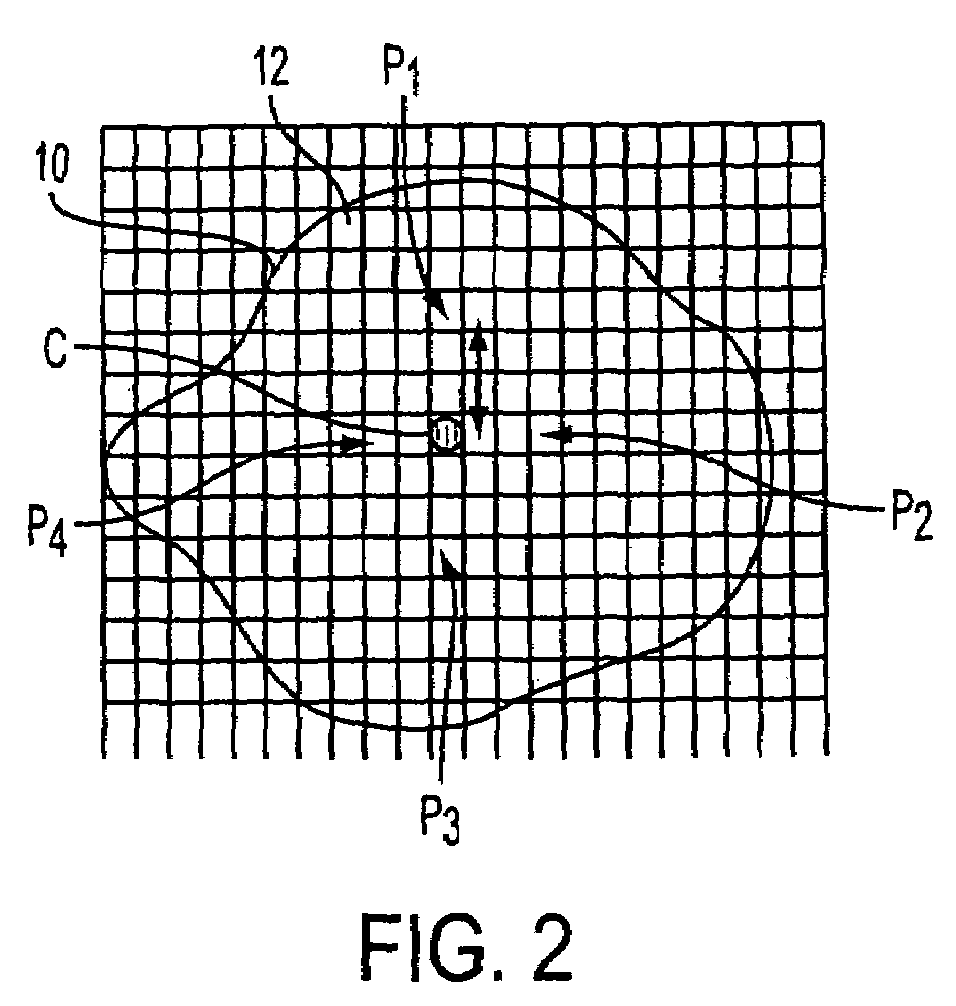
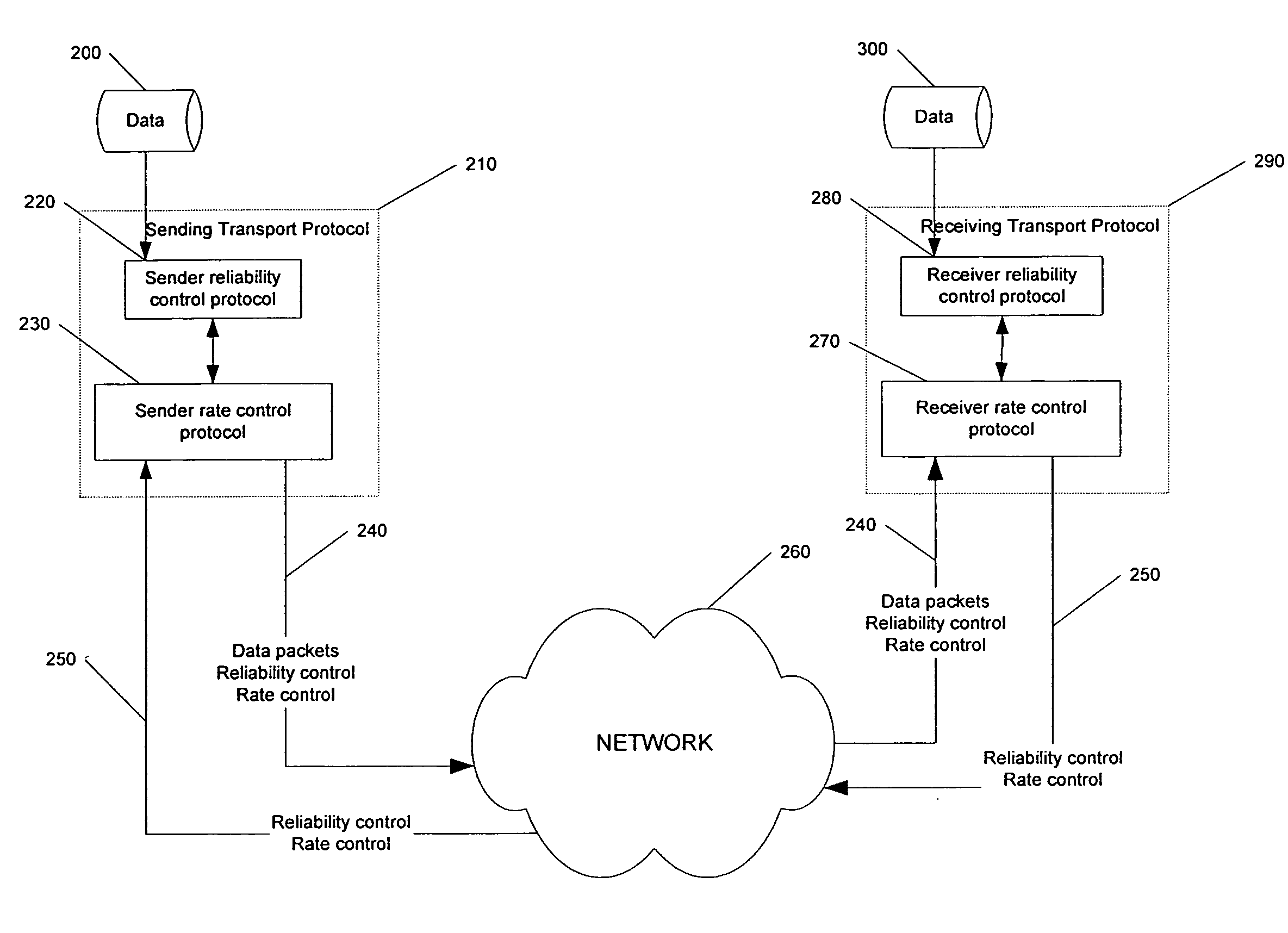
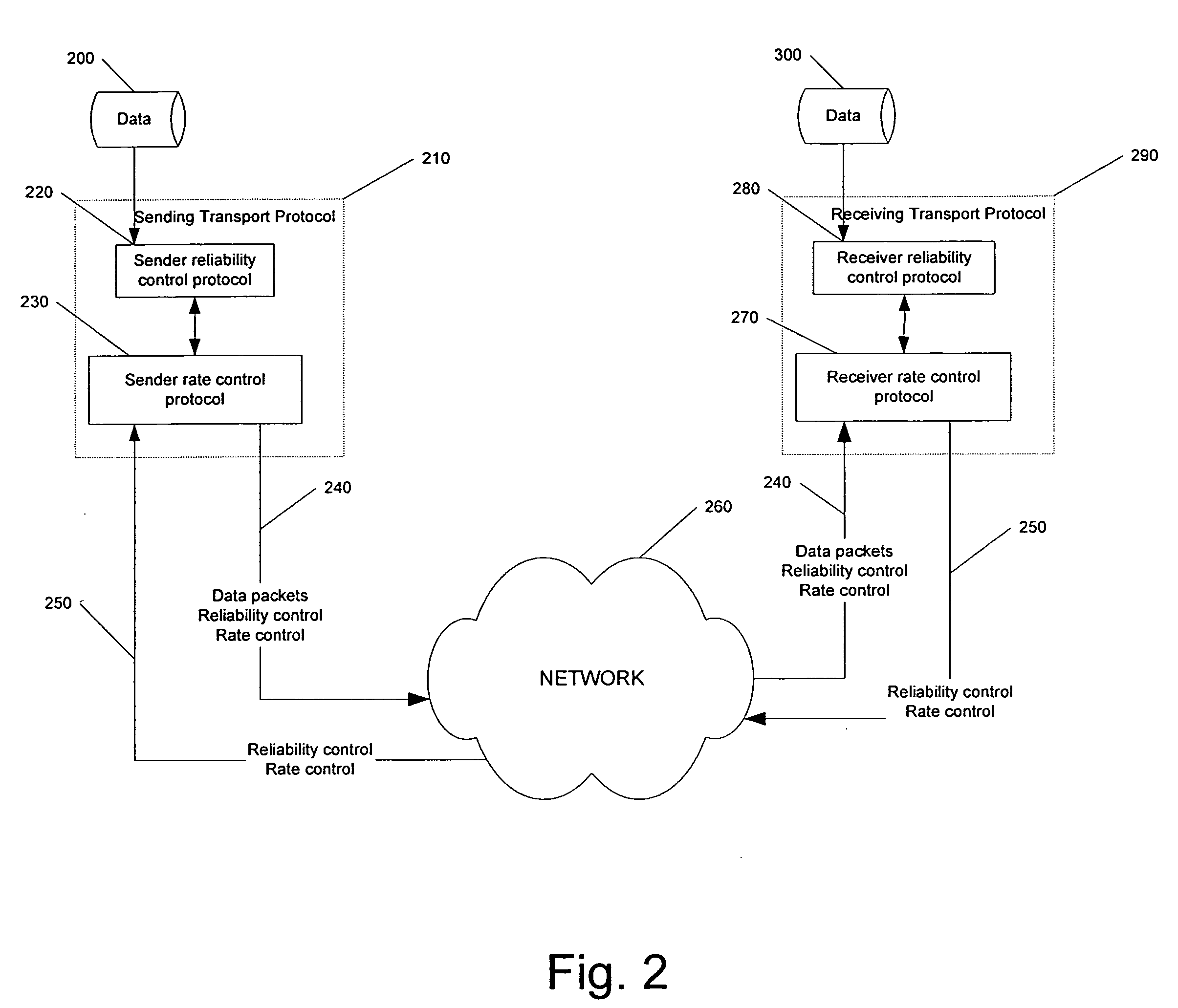
FEC-based reliability control protocols
ActiveUS7447235B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionTransfer systemDependability
In a transport system, data is reliably transported from a sender to a receiver by organizing the data to be transported into data blocks, wherein each data block comprises a plurality of encoding units, transmitting encoding units of a first data block from the sender to the receiver, and detecting, at the sender, acknowledgments of receipt of encoding units by the receiver. At the sender, a probability that the receiver received sufficient encoding units of the first data block to recover the first data block at the receiver is detected and the probability is tested against a threshold probability to determine whether a predetermined test is met. Following the step of testing and prior to the sender receiving confirmation of recovery of the first data block at the receiver, when the predetermined test is met, transmitting encoding units of a second data block from the sender. If an indication of failure to recover the first data block is received at the sender, sending further encoding units for the first data block from the sender to the receiver. In some embodiments, the predetermined test is a comparison of the probability against the threshold probability and the predetermined test is met when the probability is greater than the threshold probability.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
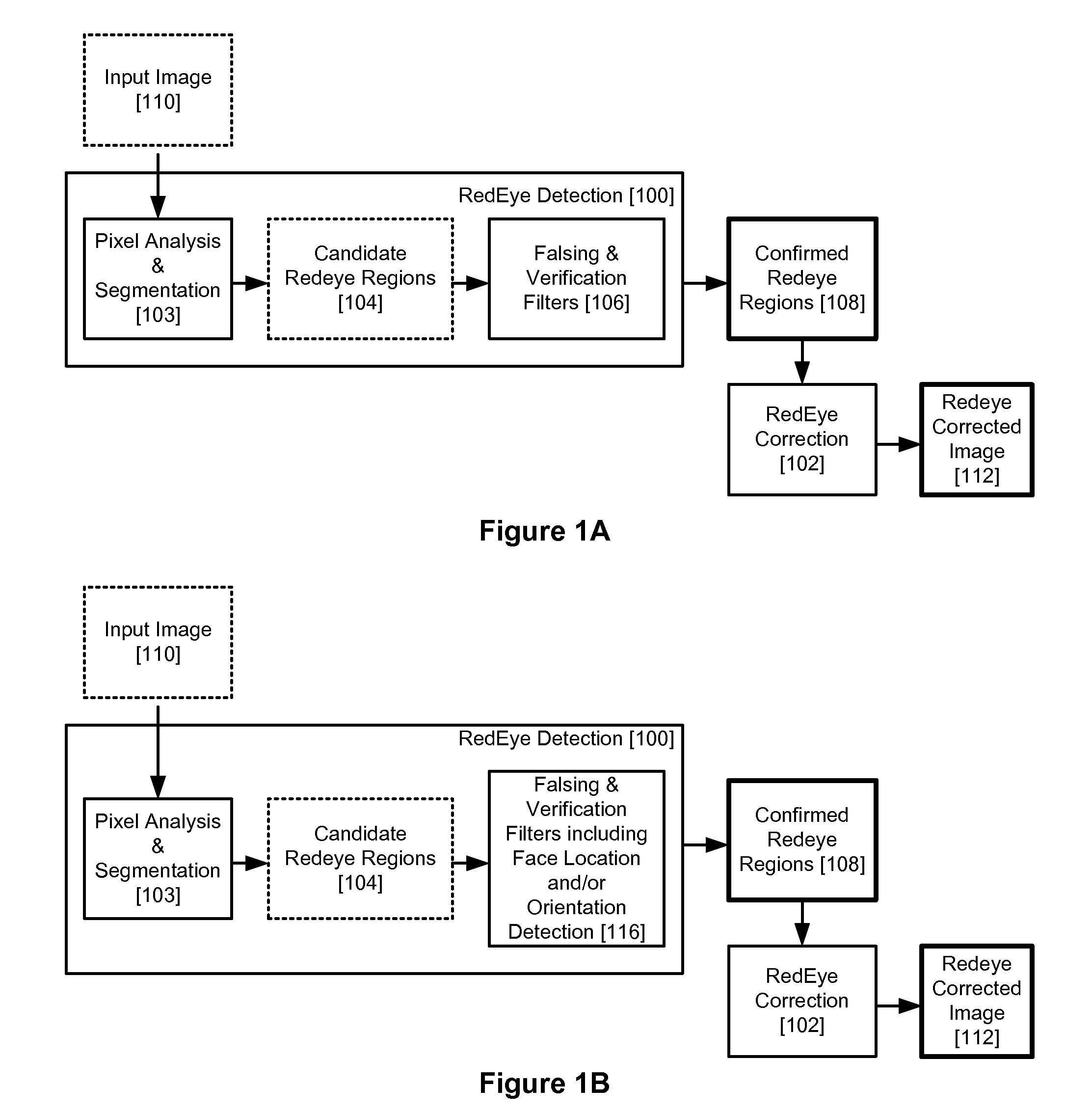
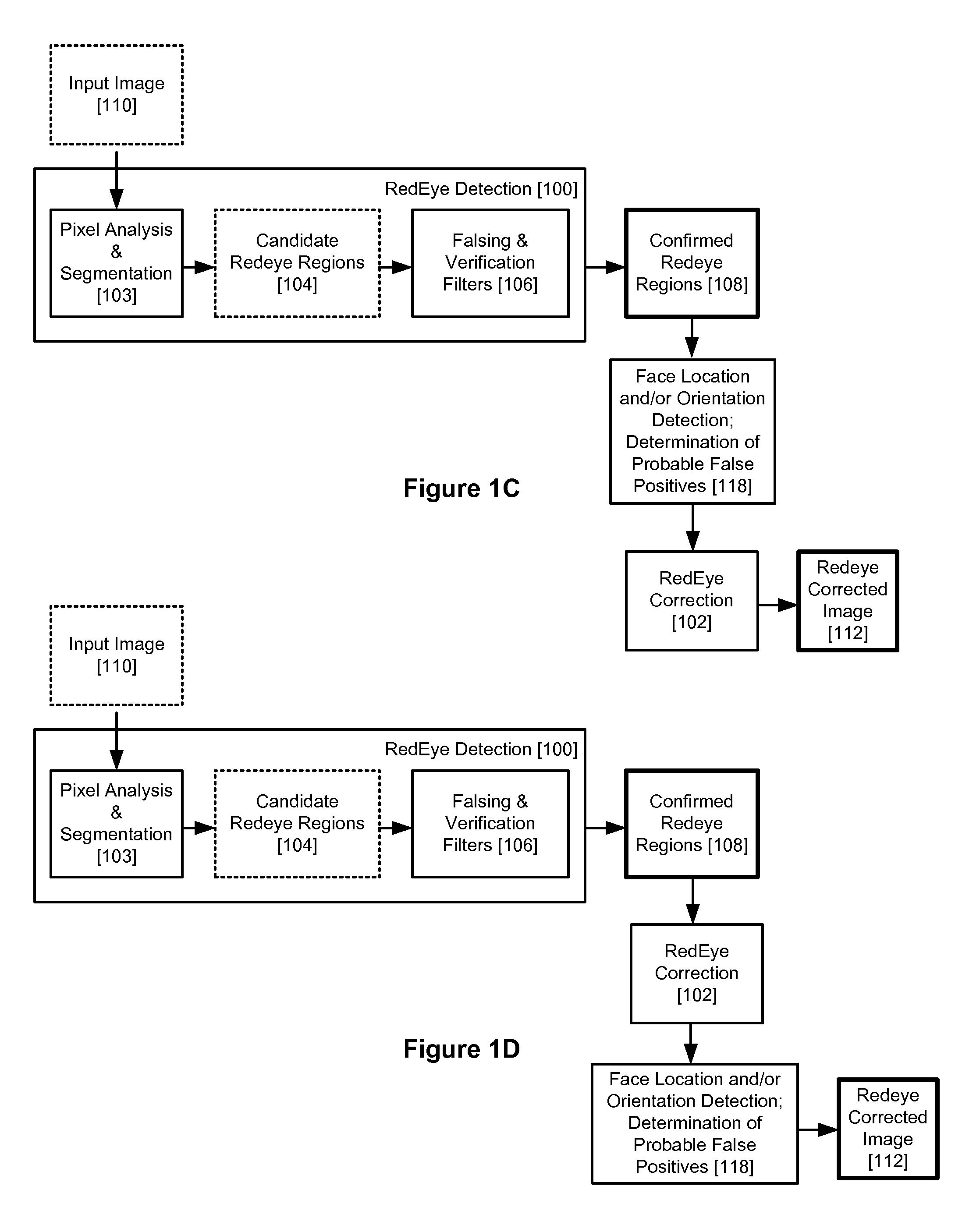
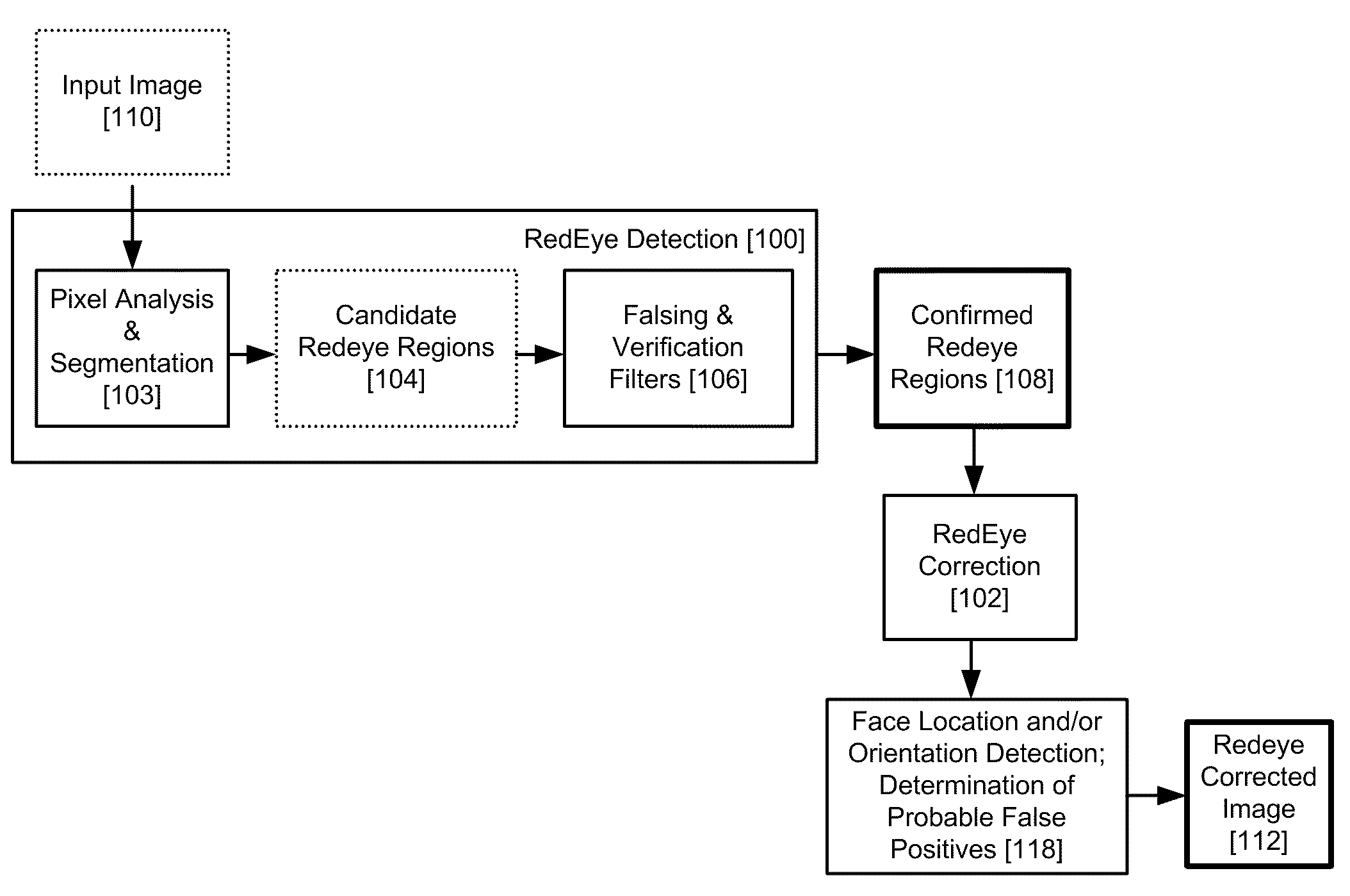
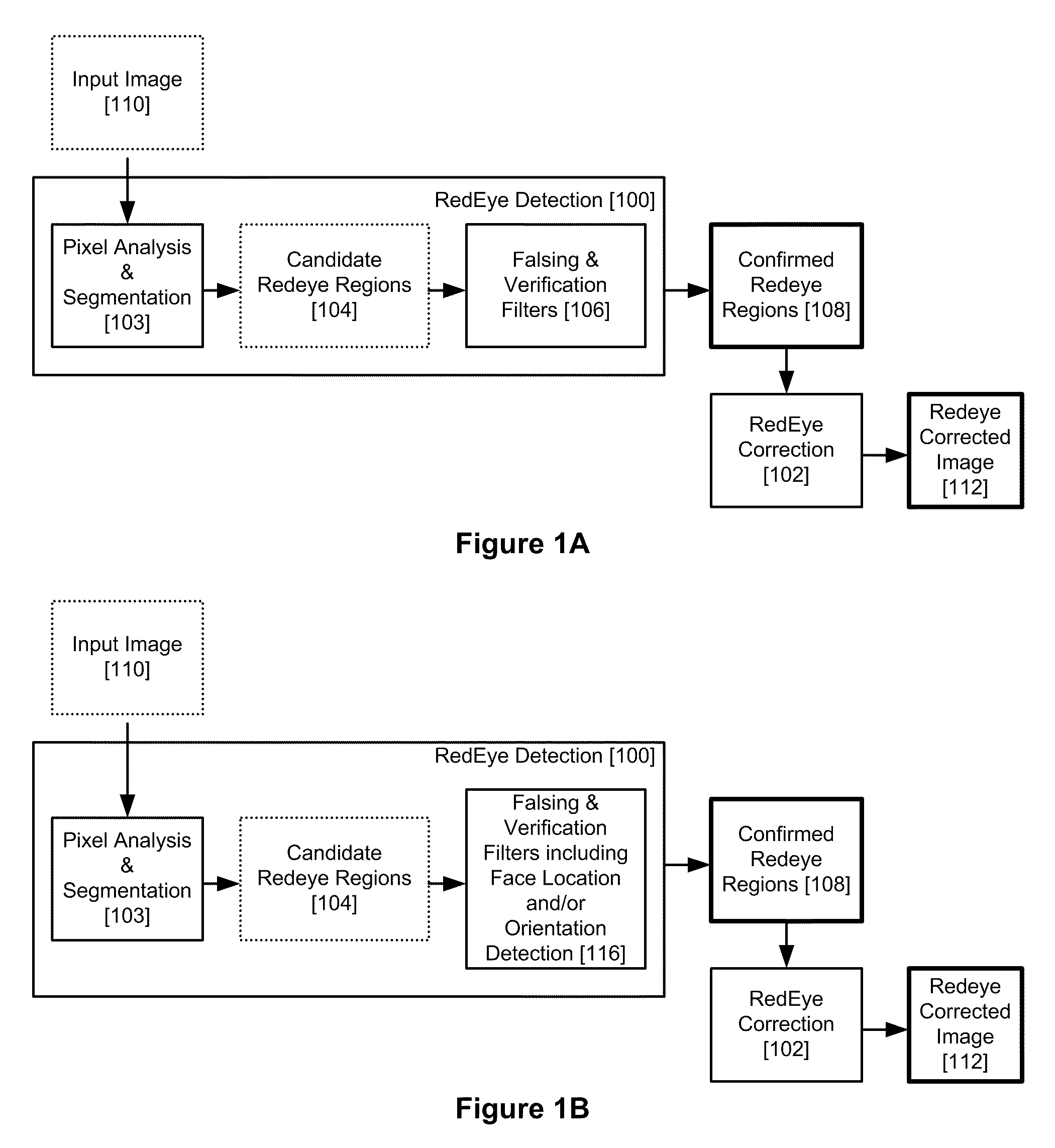
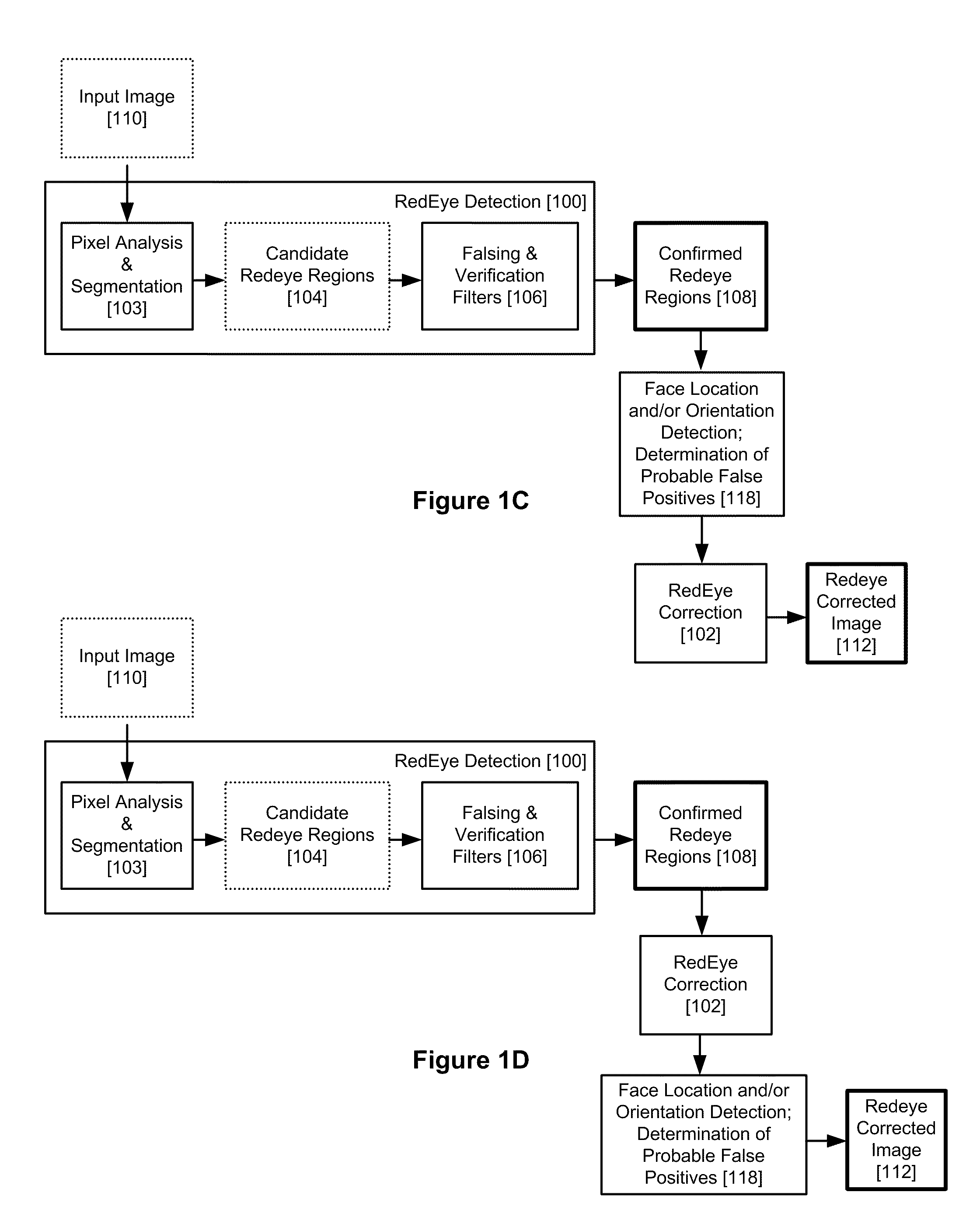
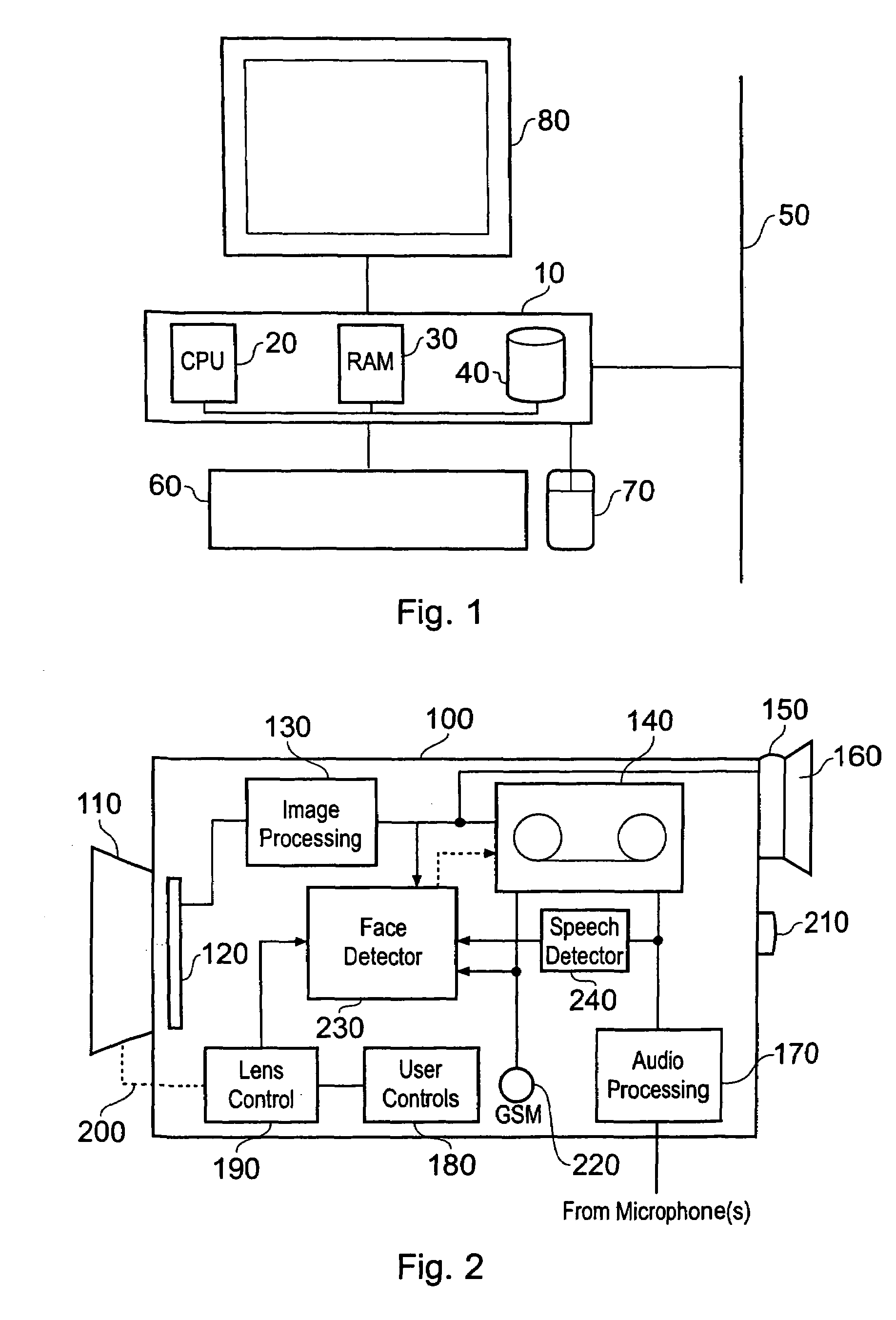
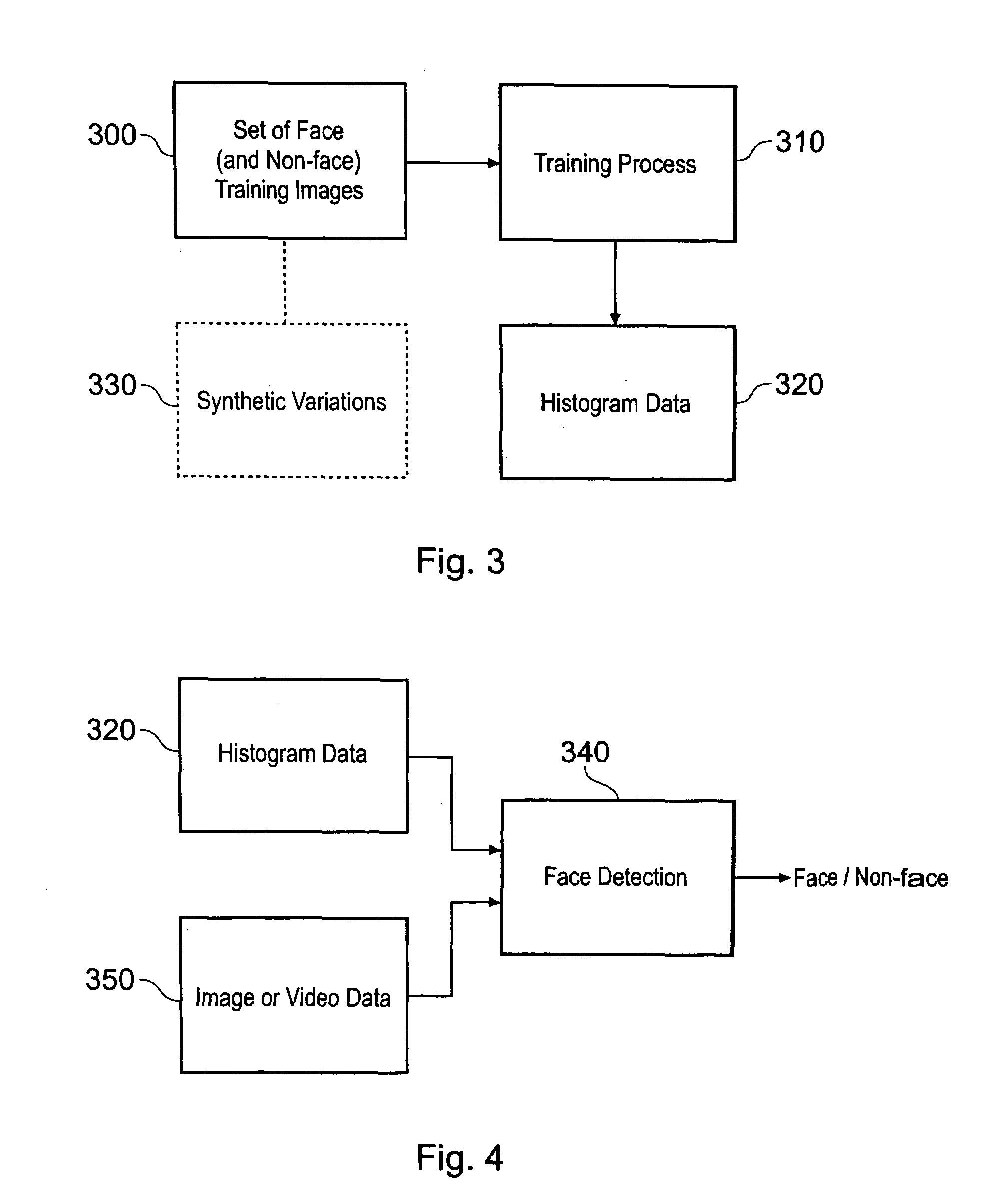
Red Eye False Positive Filtering Using Face Location and Orientation
An image is acquired including a red eye defect and non red eye defect regions having a red color. An initial segmentation of candidate redeye regions is performed. A location and orientation of one or more faces within the image are determined. The candidate redeye regions are analyzed based on the determined location and orientation of the one or more faces to determine a probability that each redeye region appears at a position of an eye. Any confirmed redeye regions having at least a certain threshold probability of being a false positive are removed as candidate redeye defect regions. The remaining redeye defect regions are corrected and a red eye corrected image is generated.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Red eye detection and correction
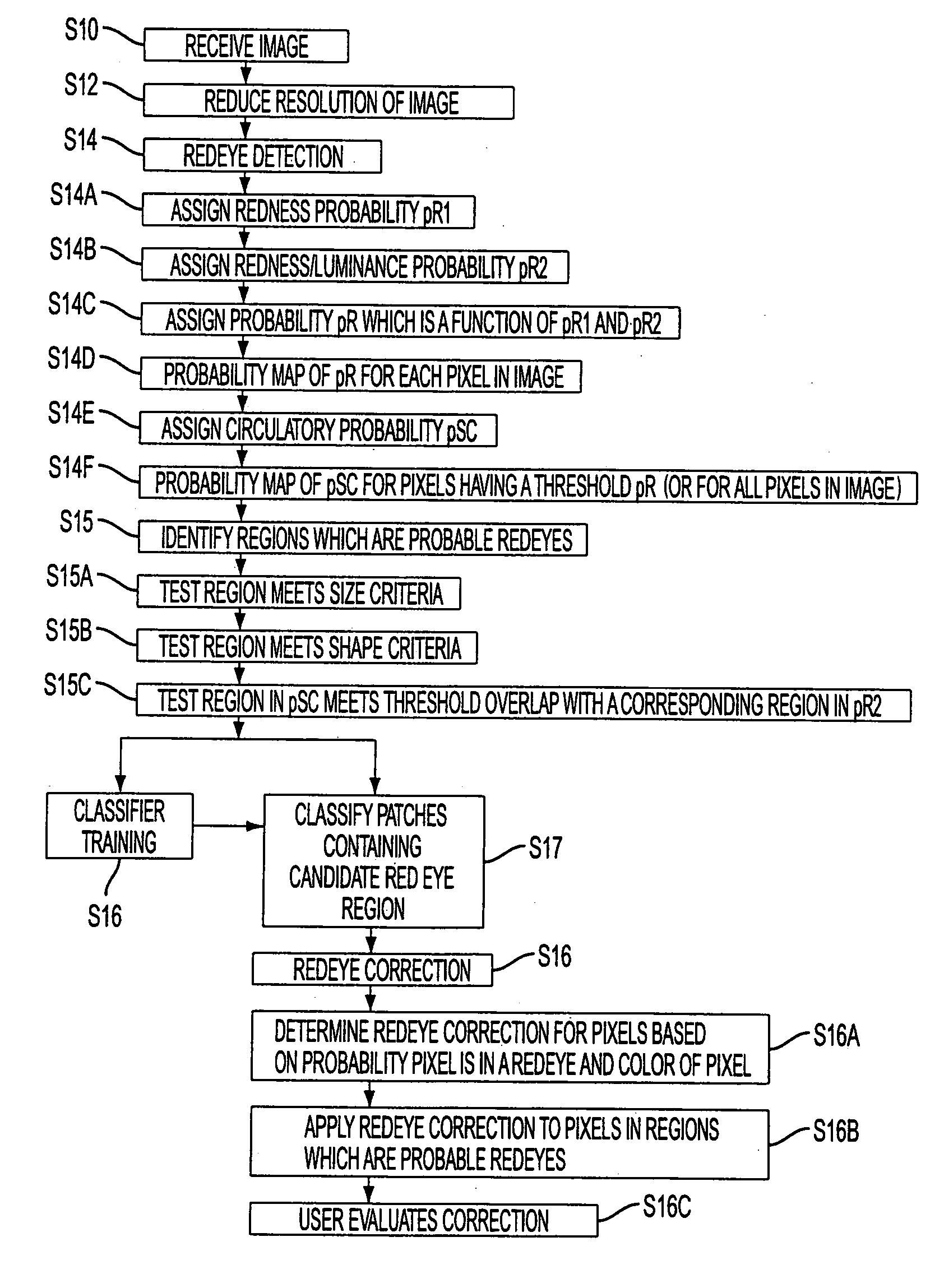
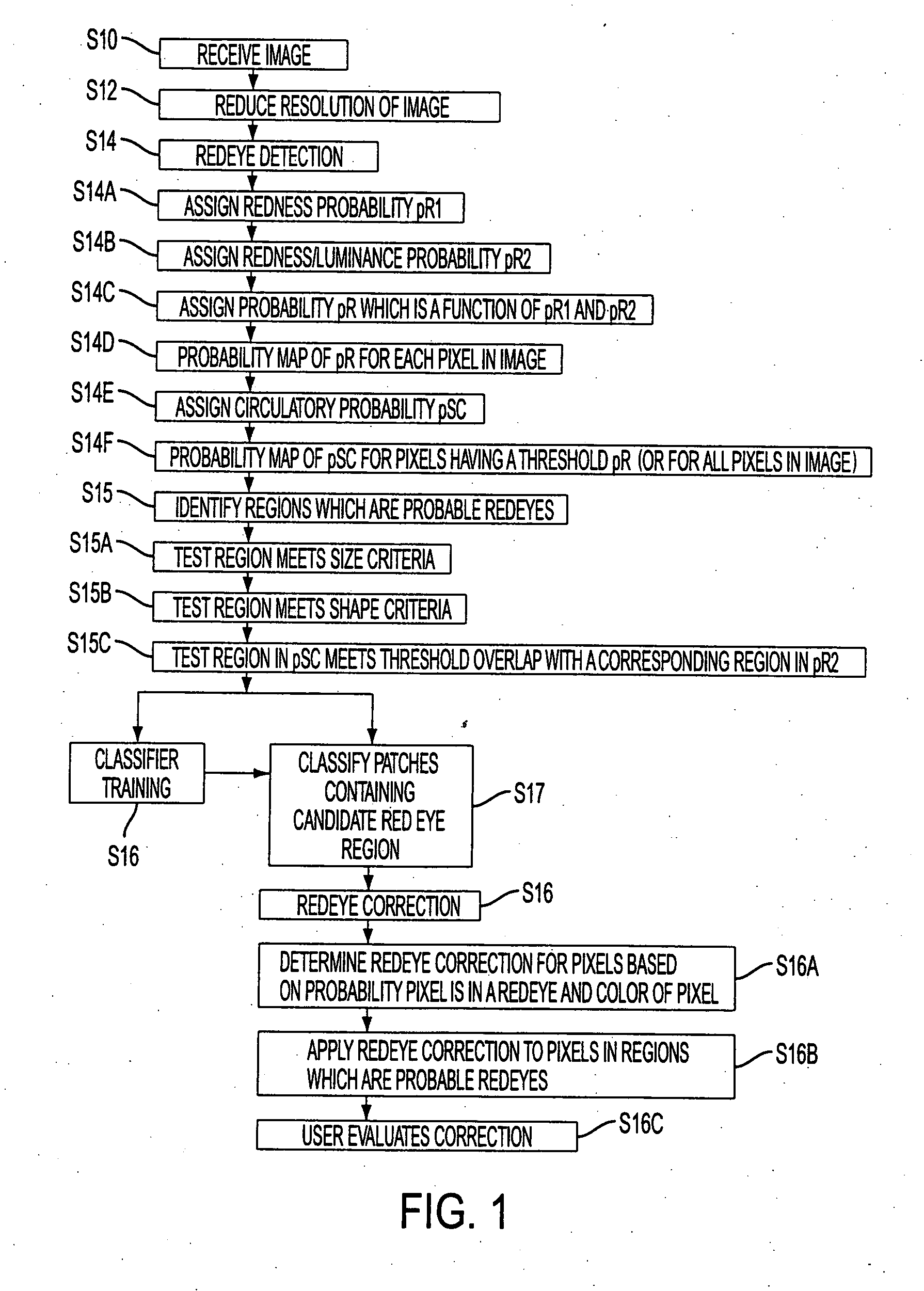
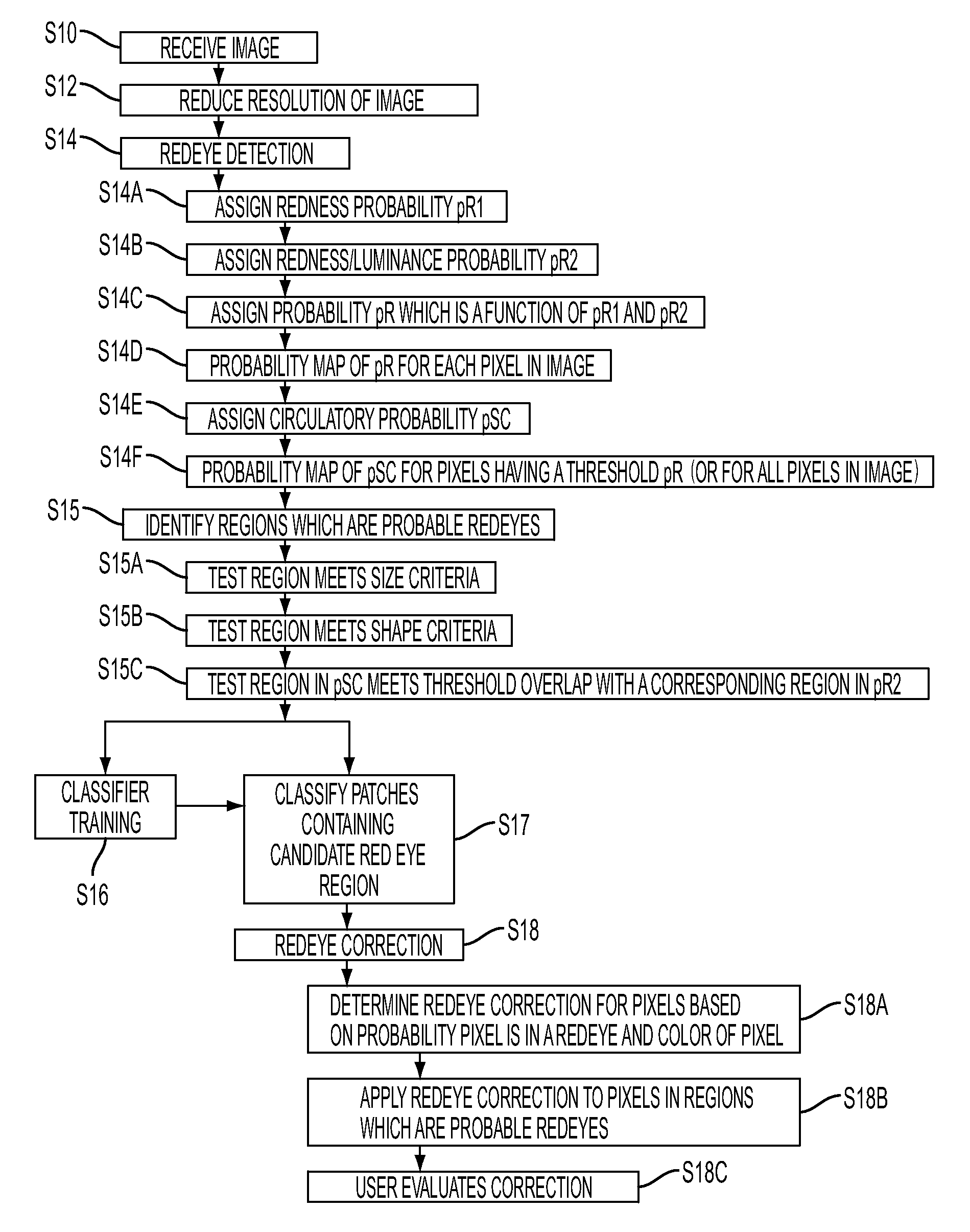
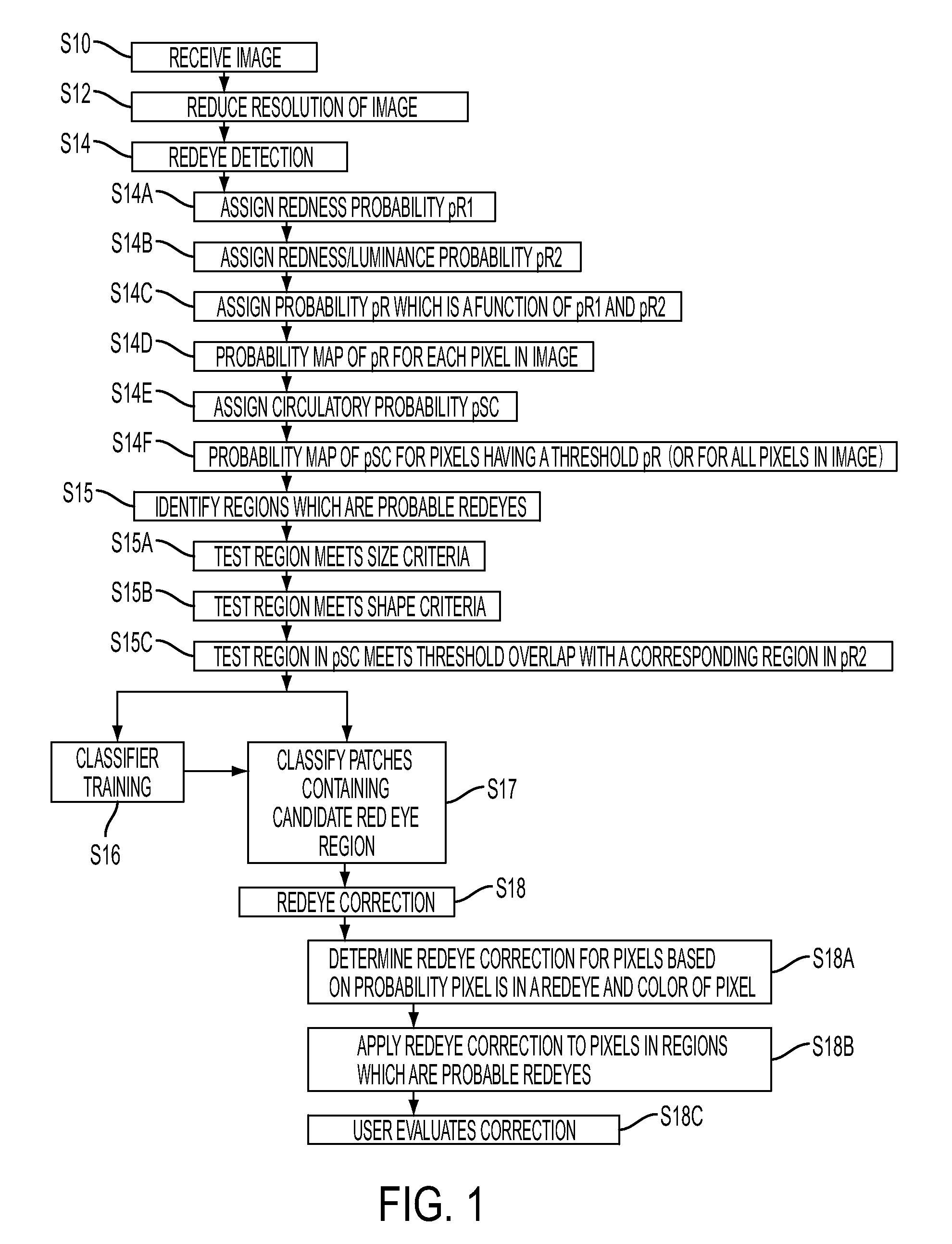
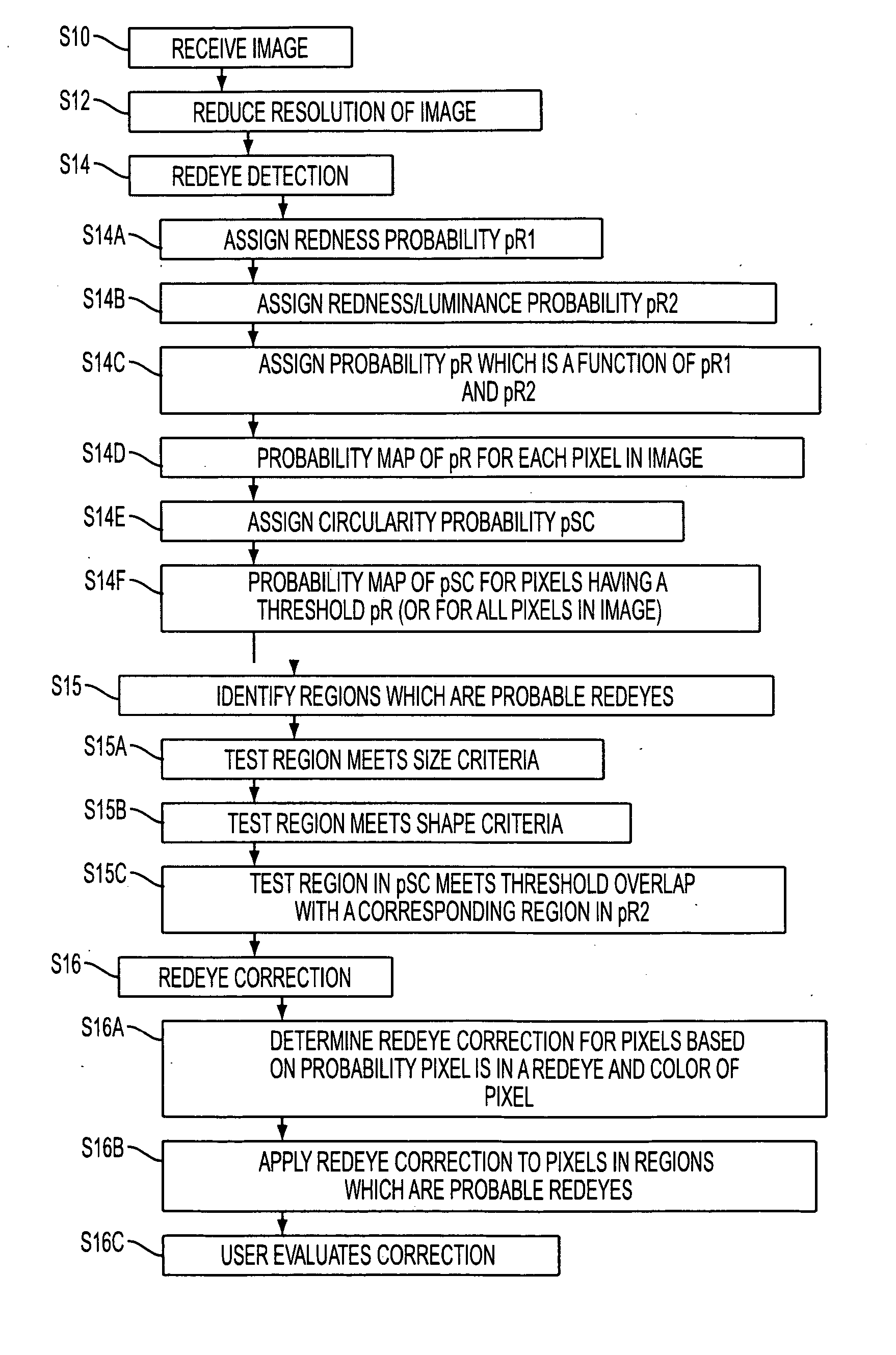
ActiveUS20070140556A1Acquiring/recognising eyesColour-separation/tonal-correctionPattern recognitionDigital image
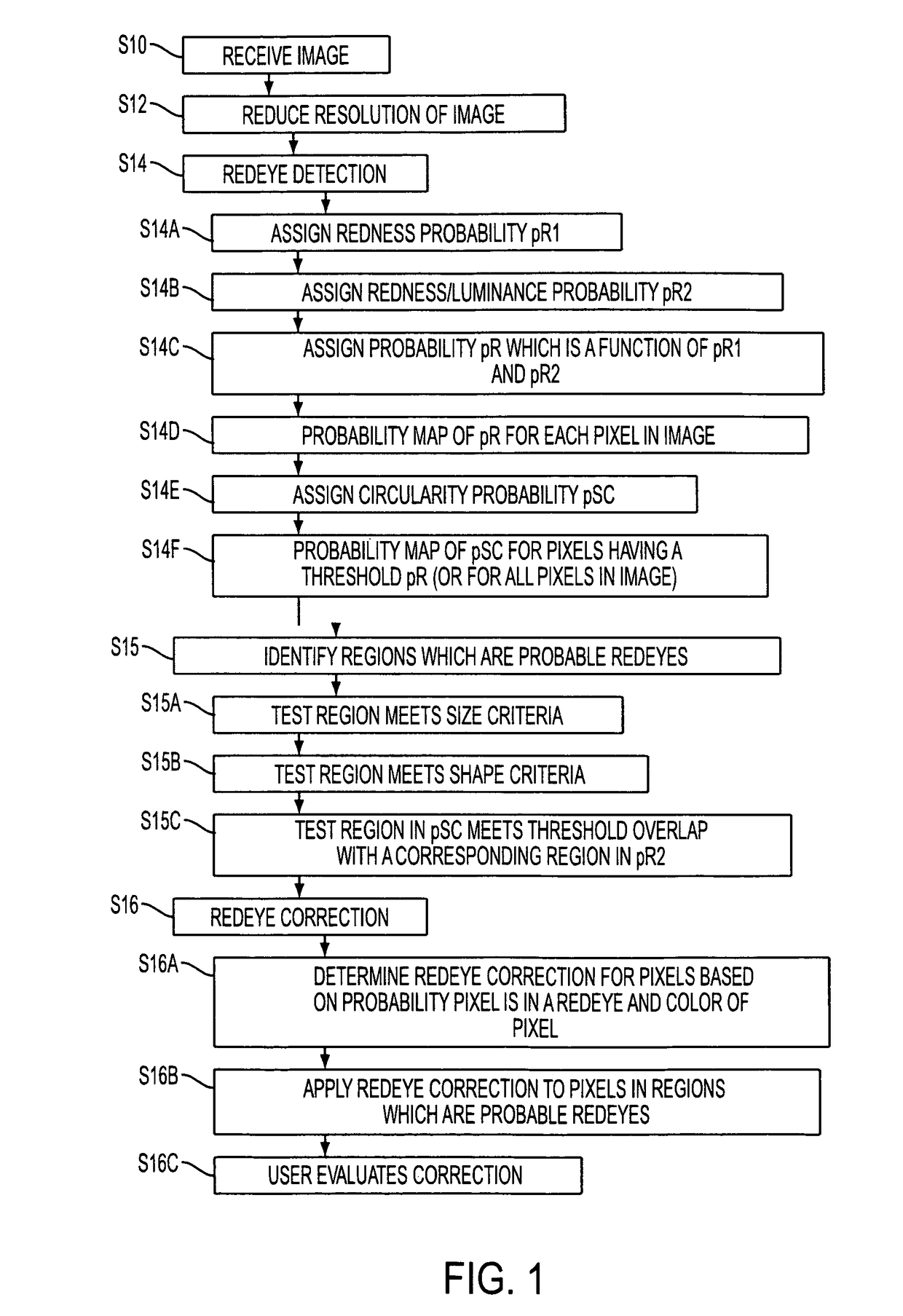
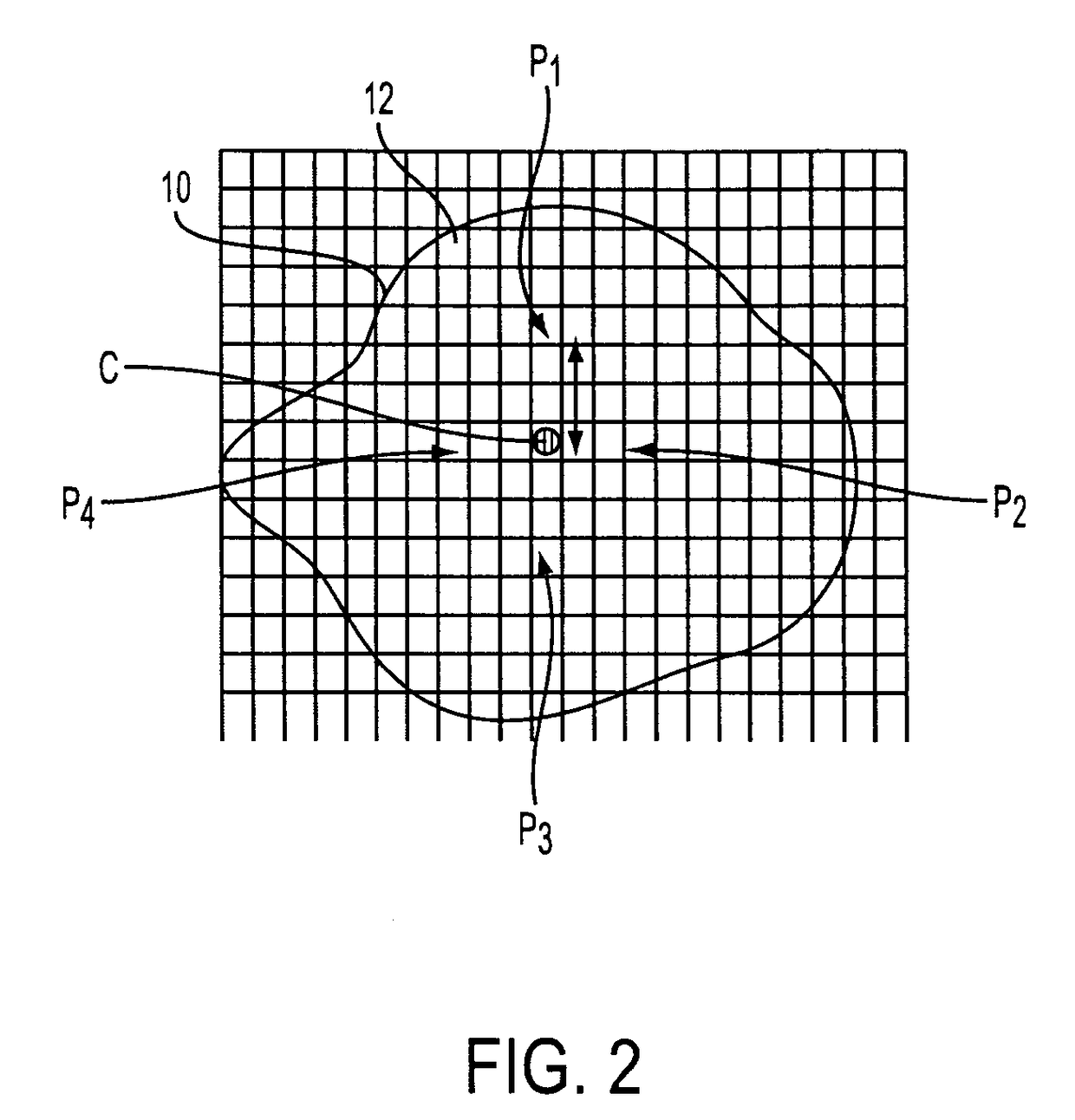
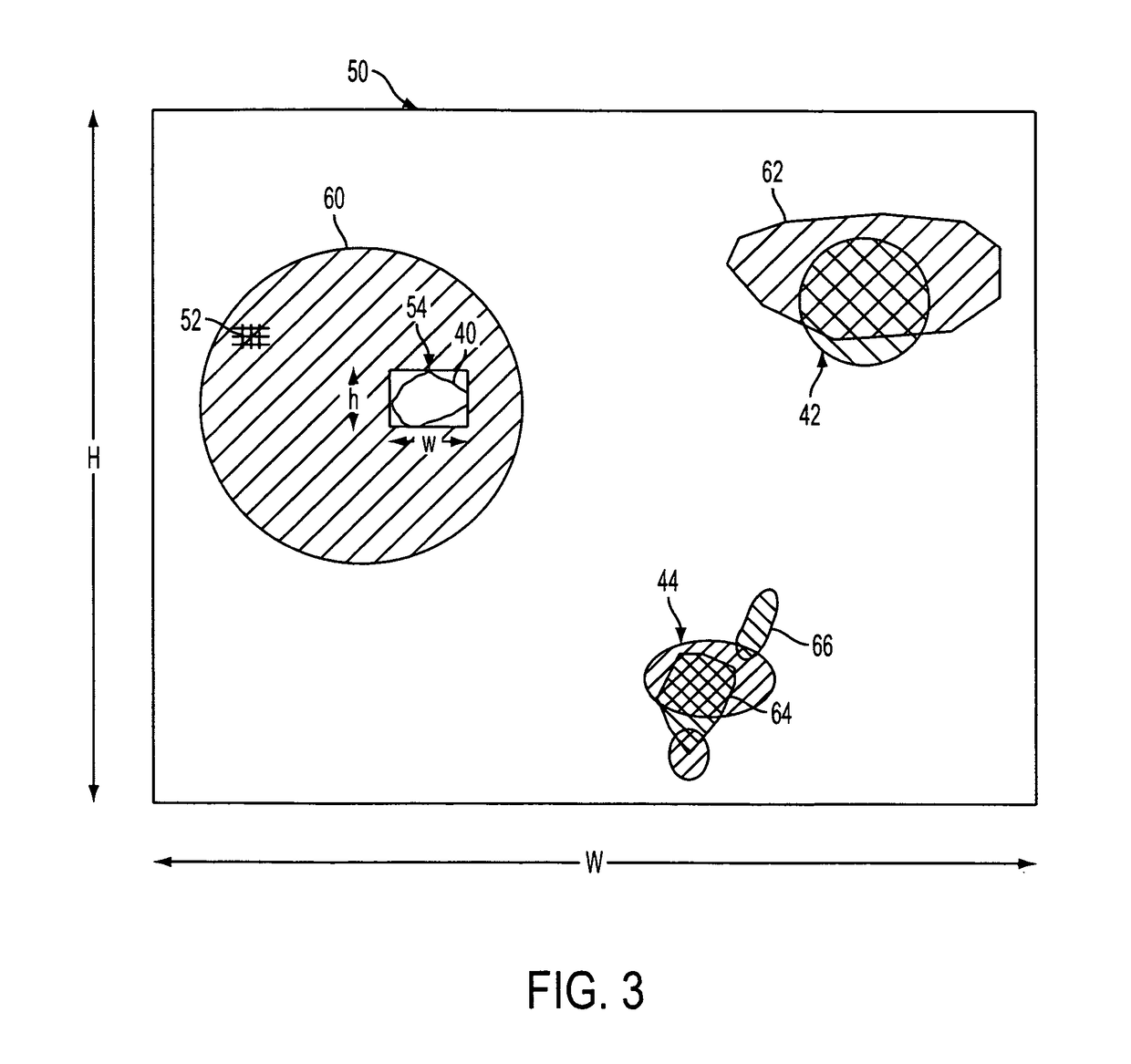
A system suited to correction of red eyes in images includes a detection module which, for a plurality of pixels in a digital image, assigns a probability that a pixel is within a red eye. The probability has a value which may vary from a minimum value to maximum value. A classifier module classifies a patch of the image comprising a region of contiguous pixels which have at least a threshold probability that the pixel is within a red eye. The classifier module distinguishing patches which have a likelihood of including a red eye from other patches which have a likelihood of containing a face or background error rather than a redeye. A correction module assigns a correction to apply to pixels which are in a region of contiguous pixels having at least the threshold probability that the pixel is within a red eye and for which the associated patch has been identified by the classifier as having a probability of including a red eye.
Owner:III HLDG 6
Red eye detection and correction
ActiveUS7567707B2Acquiring/recognising eyesColour-separation/tonal-correctionPattern recognitionDigital image
A system suited to correction of red eyes in images includes a detection module which, for a plurality of pixels in a digital image, assigns a probability that a pixel is within a red eye. The probability has a value which may vary from a minimum value to maximum value. A classifier module classifies a patch of the image comprising a region of contiguous pixels which have at least a threshold probability that the pixel is within a red eye. The classifier module distinguishing patches which have a likelihood of including a red eye from other patches which have a likelihood of containing a face or background error rather than a redeye. A correction module assigns a correction to apply to pixels which are in a region of contiguous pixels having at least the threshold probability that the pixel is within a red eye and for which the associated patch has been identified by the classifier as having a probability of including a red eye.
Owner:III HLDG 6
FEC-based reliability control protocols
In a transport system, data is reliably transported from a sender to a receiver by organizing the data to be transported into data blocks, wherein each data block comprises a plurality of encoding units, transmitting encoding units of a first data block from the sender to the receiver, and detecting, at the sender, acknowledgments of receipt of encoding units by the receiver. At the sender, a probability that the receiver received sufficient encoding units of the first data block to recover the first data block at the receiver is detected and the probability is tested against a threshold probability to determine whether a predetermined test is met. Following the step of testing and prior to the sender receiving confirmation of recovery of the first data block at the receiver, when the predetermined test is met, transmitting encoding units of a second data block from the sender. If an indication of failure to recover the first data block is received at the sender, sending further encoding units for the first data block from the sender to the receiver. In some embodiments, the predetermined test is a comparison of the probability against the threshold probability and the predetermined test is met when the probability is greater than the threshold probability.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Application recommendation based on detected triggering events
An event can be detected by an input device. The event may be determined to be a triggering event by comparing the event to a group of triggering events. A first prediction model corresponding to the event is then selected. Contextual information about the device specifying one or more properties of the computing device in a first context is then received, and a set of one or more applications is identified. The set of one or more applications may have at least a threshold probability of being accessed by the user when the event occurs in the first context. Thereafter, a user interface is provided to a user for interacting with the set of one or more applications.
Owner:APPLE INC
Red eye false positive filtering using face location and orientation
An image is acquired including a red eye defect and non red eye defect regions having a red color. An initial segmentation of candidate redeye regions is performed. A location and orientation of one or more faces within the image are determined. The candidate redeye regions are analyzed based on the determined location and orientation of the one or more faces to determine a probability that each redeye region appears at a position of an eye. Any confirmed redeye regions having at least a certain threshold probability of being a false positive are removed as candidate redeye defect regions. The remaining redeye defect regions are corrected and a red eye corrected image is generated.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Multi-phase search and presentation for vertical search websites
ActiveUS8972434B2Presented quicklyEfficiently performing travel reservation queriesWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsPhrase searchThreshold probability
The present invention provides a methodology and system for efficiently performing travel reservation queries and presenting significant search results to a user. A travel reservation search engine constructs a first query from one or more constraints. The first query has a threshold probability of returning a first set of search results that will lead to the purchase of a travel reservation. Additionally, if determined necessary by the search engine a second query is constructed from one or more constraints. The second query returns a second set of search results.
Owner:KAYAK SOFTWARE CORP
Improved deep Boltzmann machine-based pulmonary nodule feature extraction and benign and malignant classification method
ActiveCN107316294APreserve the original nodule informationGuaranteed accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPulmonary noduleLearning machine
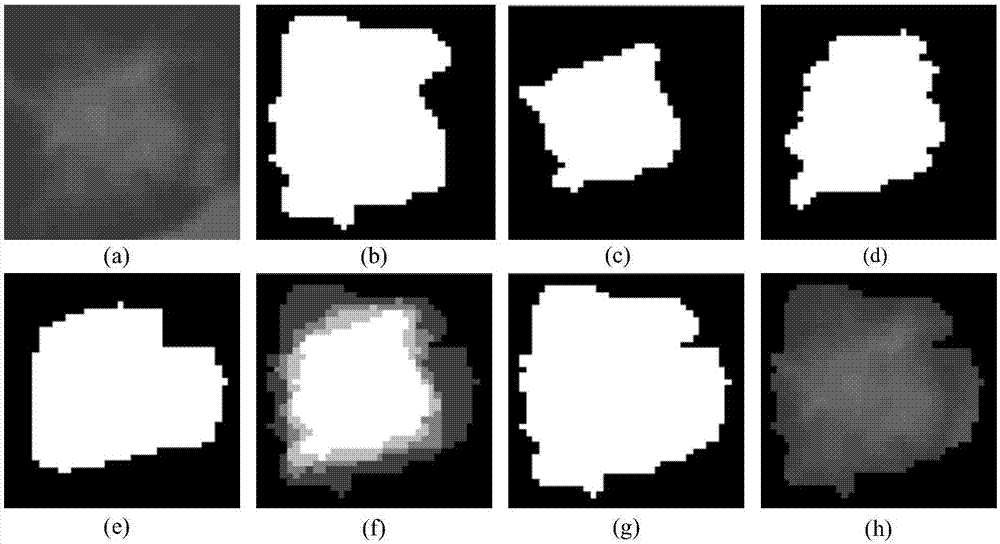
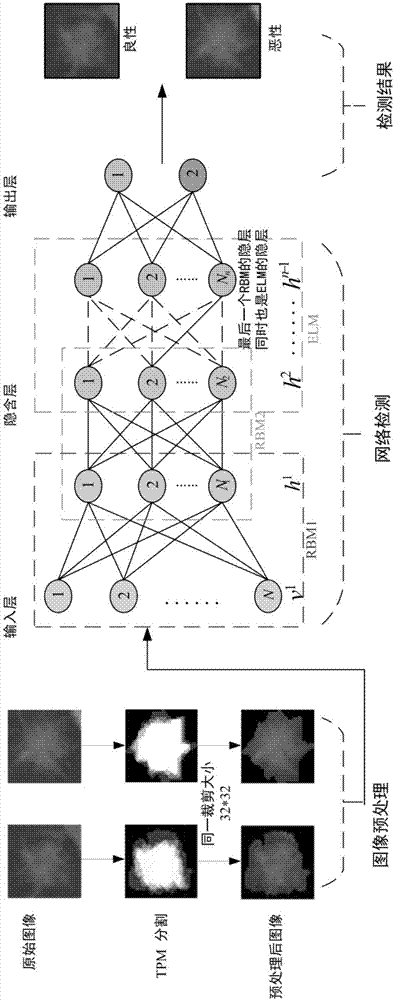
The present invention discloses an improved deep Boltzmann machine-based pulmonary nodule feature extraction and benign and malignant classification method. The method includes the following steps that: step A, pulmonary nodules are segmented from CT images through using a threshold probability image graph method, so that regions of interest (ROI) are obtained, and the regions of interest are cut into nodule images of the same size; and step B, a supervised deep learning algorithm Pnd-EBM is designed to realize the diagnosis of a pulmonary nodule, wherein the diagnosis of the pulmonary nodule further includes three major steps: B1, a deep Boltzmann machine (DBM) is adopted to extract the features of the ROI of the pulmonary nodule which have deep expression abilities; B2, a sparse cross-entropy penalty factor is adopted to improve a cost function, so that the phenomenon of feature homogenization in a training process can be avoided; and B3, an extreme learning machine (ELM) is adopted to perform benign and malignant classification on the extracted features of the pulmonary nodule. The improved deep Boltzmann machine-based pulmonary nodule feature extraction method is superior to a traditional feature extraction method. With the method adopted, the complexity of manual extraction and the difference of feature selection can be avoided, and references can be provided for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Object detection
A system and associated methodology of detecting objects using multiple sets of object probability data relating to different respective expected object sizes relative to the image size. A list of locations in an image where an object has been detected is stored, the list defining a probability data set and a probability value for each detected object. Object locations in a set of object probability data as locations at which a local maximum probability value exceeds a threshold probability value are detected and, if that location is substantially similar to a location previously stored in the list, where the local maximum probability value exceeds that relating to the previously stored location. The storing is repeated successively in respect of each set of probability data.
Owner:SONY UK LTD
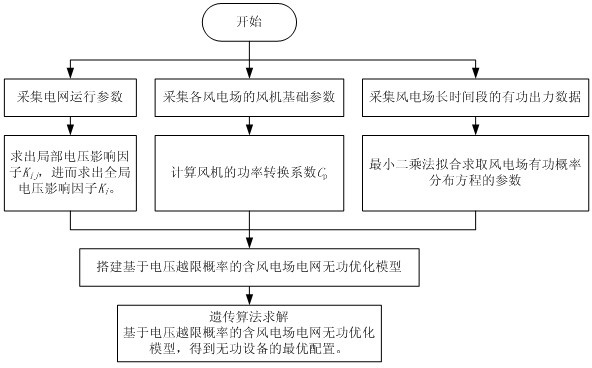
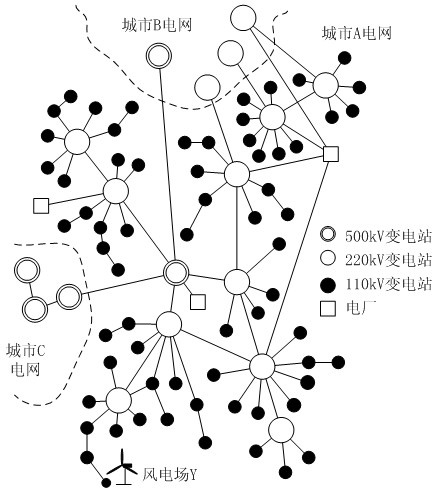
Voltage threshold probability-based reactive power optimizing method for grid containing wind power plant
InactiveCN102684201AImprove adaptabilityGuaranteed voltage qualityAc network voltage adjustmentReactive power compensationConversion coefficientsThreshold probability
The invention provides a voltage threshold probability-based reactive power optimizing method for a grid containing a wind power plant, which aims to solve the problem that under the condition of wind power networking, the effect of the voltage optimizing control to an automatic voltage control system is not ideal. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, collecting grid operation parameters, basic parameters of each wind power generator in the wind power plant, and active power output data of the wind power plant; secondly, acquiring voltage impact factor, power conversion coefficient of the wind power generators and wind power plant active power probability distribution equation through the above parameters, and further obtaining voltage threshold probability; and lastly, establishing a reactive power optimizing model on the basis of the voltage threshold probability, adopting genetic algorithm to solve the model, and obtaining a control instruction of a reactive power device. According to the invention, the voltage threshold probability-based reactive power optimizing method substitutes a conventional reactive power optimizing method for the automatic voltage control system, can enable the voltage optimizing control to the automatic voltage control system to effectively control the reactive power device in the grid under the condition of wind power networking, and ensure the safe and economic operation of the grid.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
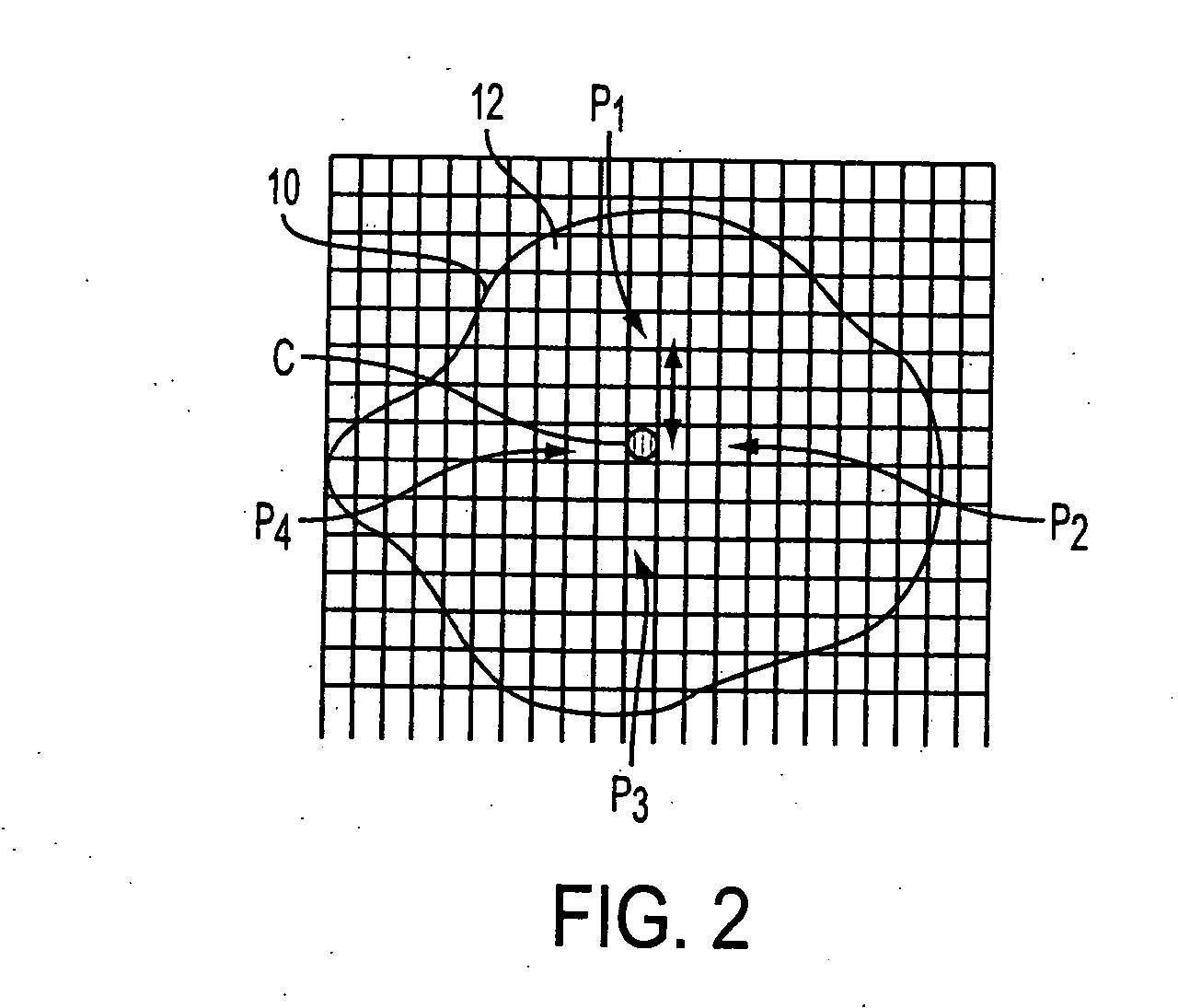
Red-eye detection and correction
A method suited to the detection and correction of red-eyes includes assigning a probability to pixels of a digital image of the pixel being in a red-eye, the probability being a function of a color of the pixel. Optionally, generally circular regions in the image of contiguous pixels which satisfy at least one test for a red-eye are identified. The test may include determining a size or shape of the region or an extent of overlap with a region comprising pixels having at least a threshold probability of being in a red-eye. For each of a plurality of the pixels, such as simply those in identified regions, or for all pixels or a larger group of the pixels, a color correction for the pixel is determined. The correction is a function of the assigned probability that the pixel is within a red-eye and a color of the pixel.
Owner:III HLDG 6
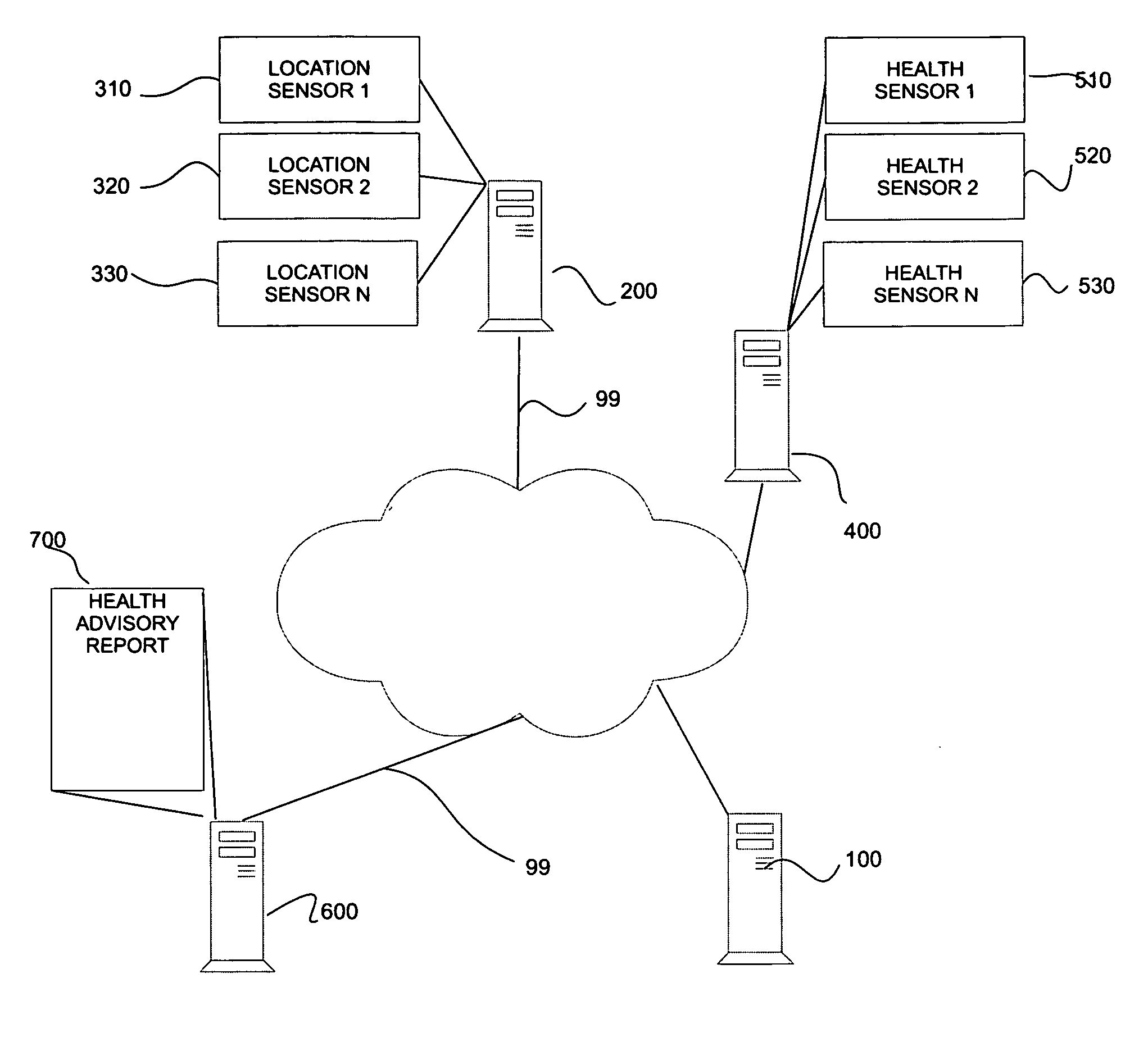
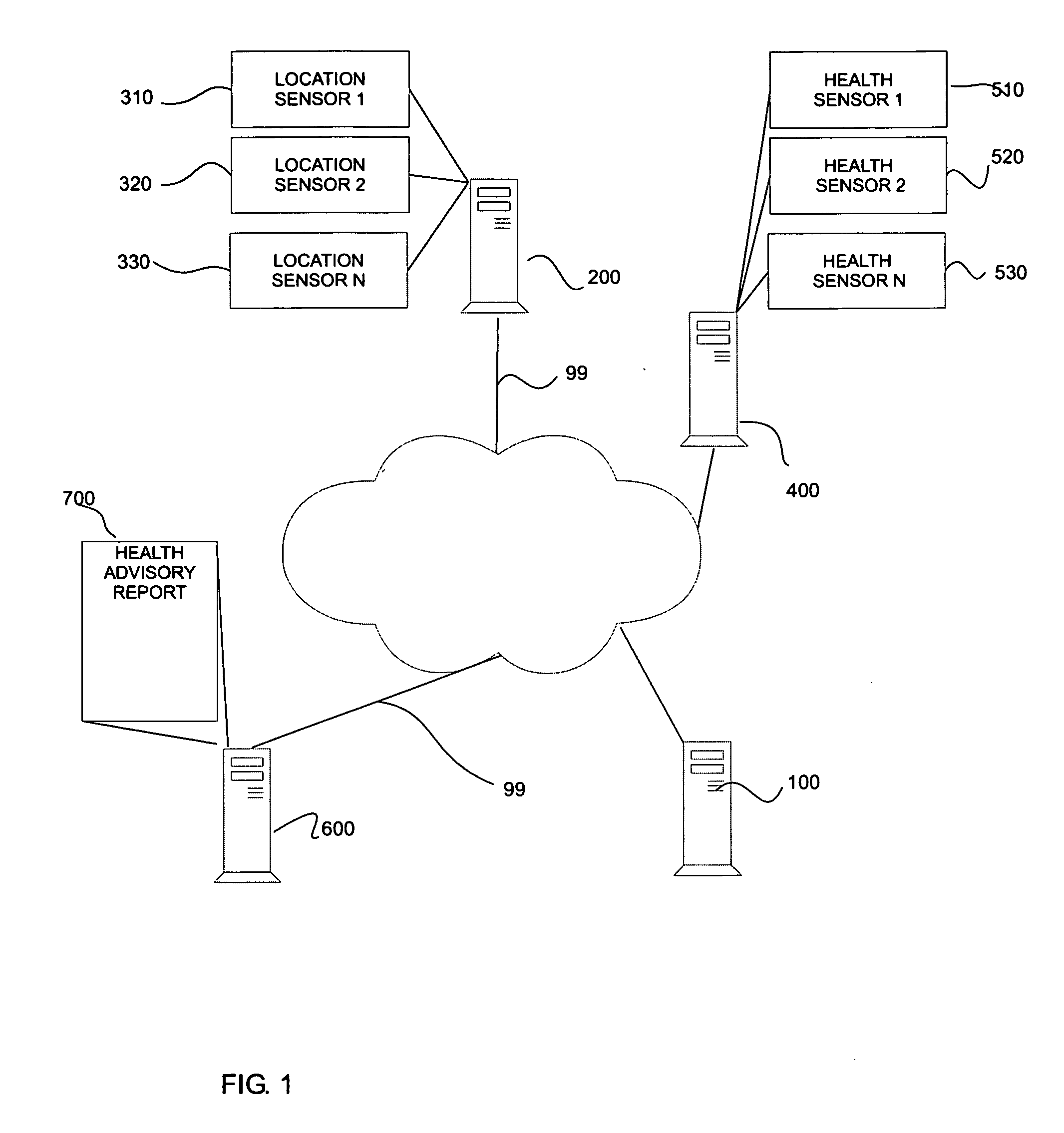
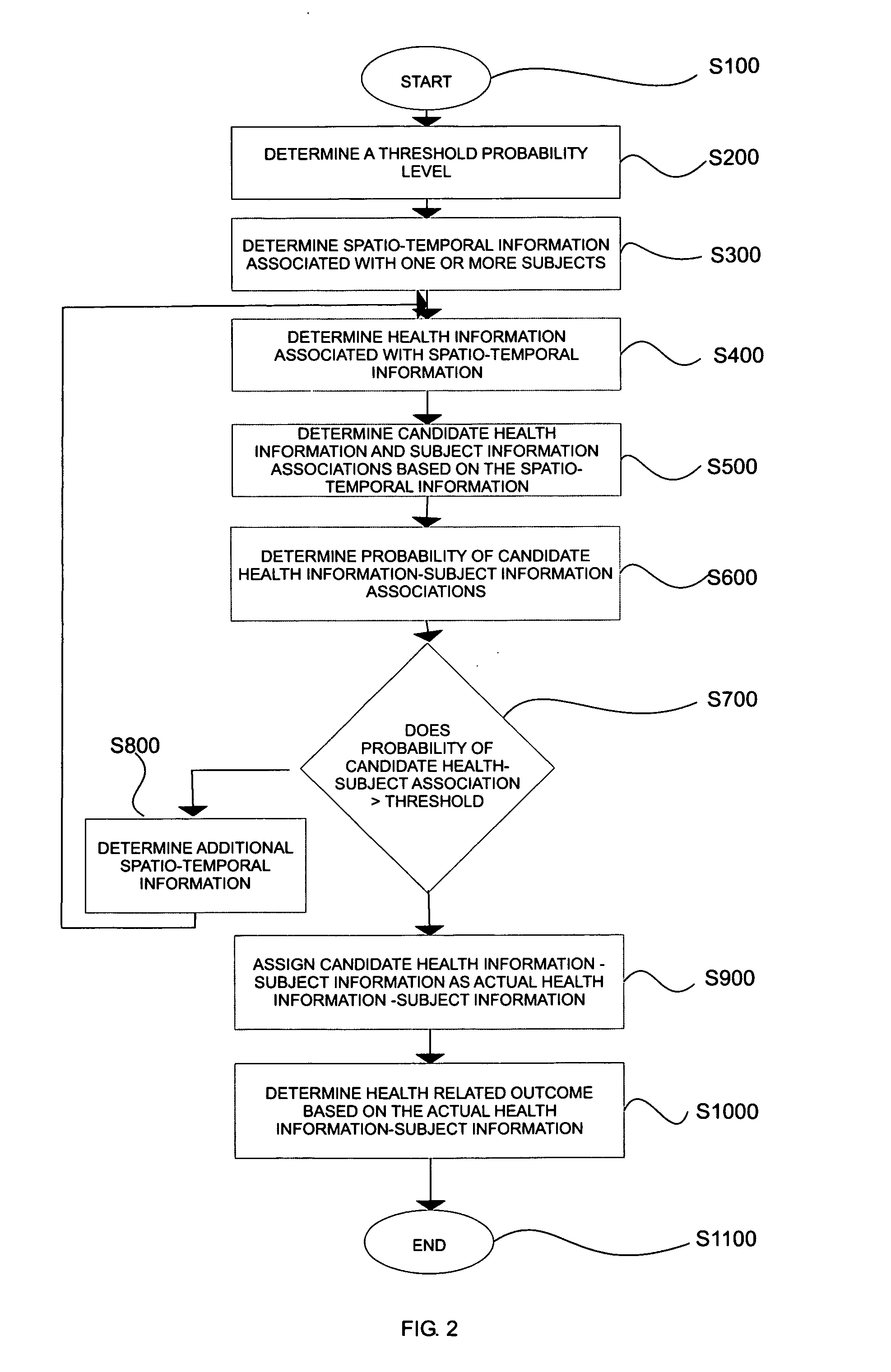
Systems and methods for dynamically determining data-identity information
ActiveUS20080046291A1Data processing applicationsHealth-index calculationTemporal informationData mining
Techniques are presented for determining threshold probability or confidence levels for associating various types of health information with a set of users. Spatio-temporal information associated with one or more of the subjects is determined. Health information associated with spatial-temporal information is also determined. Candidate health-subject associations are associated with probabilities based on the spatio-temporally tagged identity and spatio-temporally tagged health information. Candidate health-subject associations with probabilities exceeding a threshold probability level are assigned as actual health-subject associations. Treatment plans, reports, remedial procedures and or other health related tests, procedures or the like are determined based on the associated health information.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
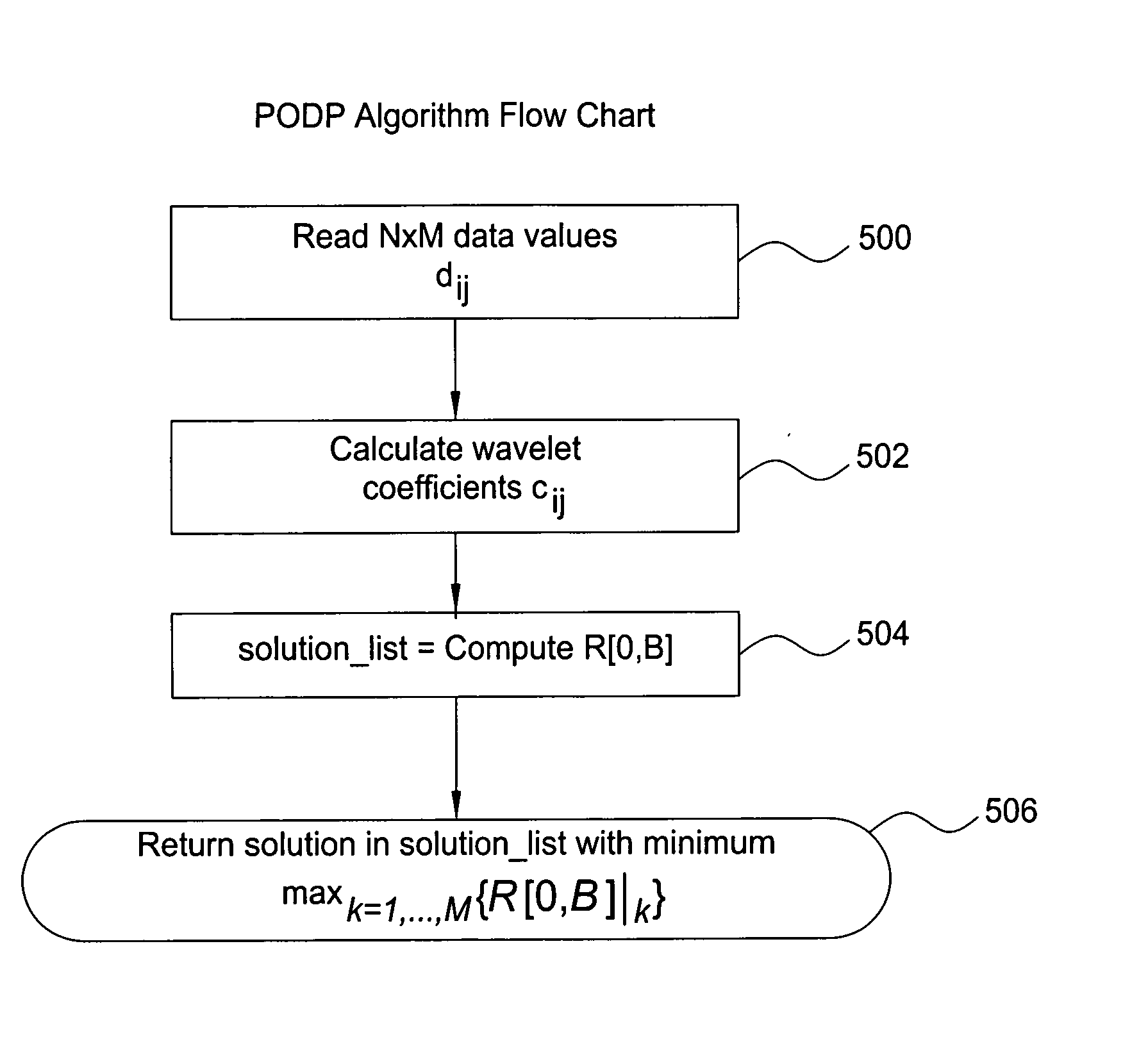
Probabilistic wavelet synopses for multiple measures
InactiveUS20070058871A1Increase profitImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti-dimensional databasesData setWavelet thresholding
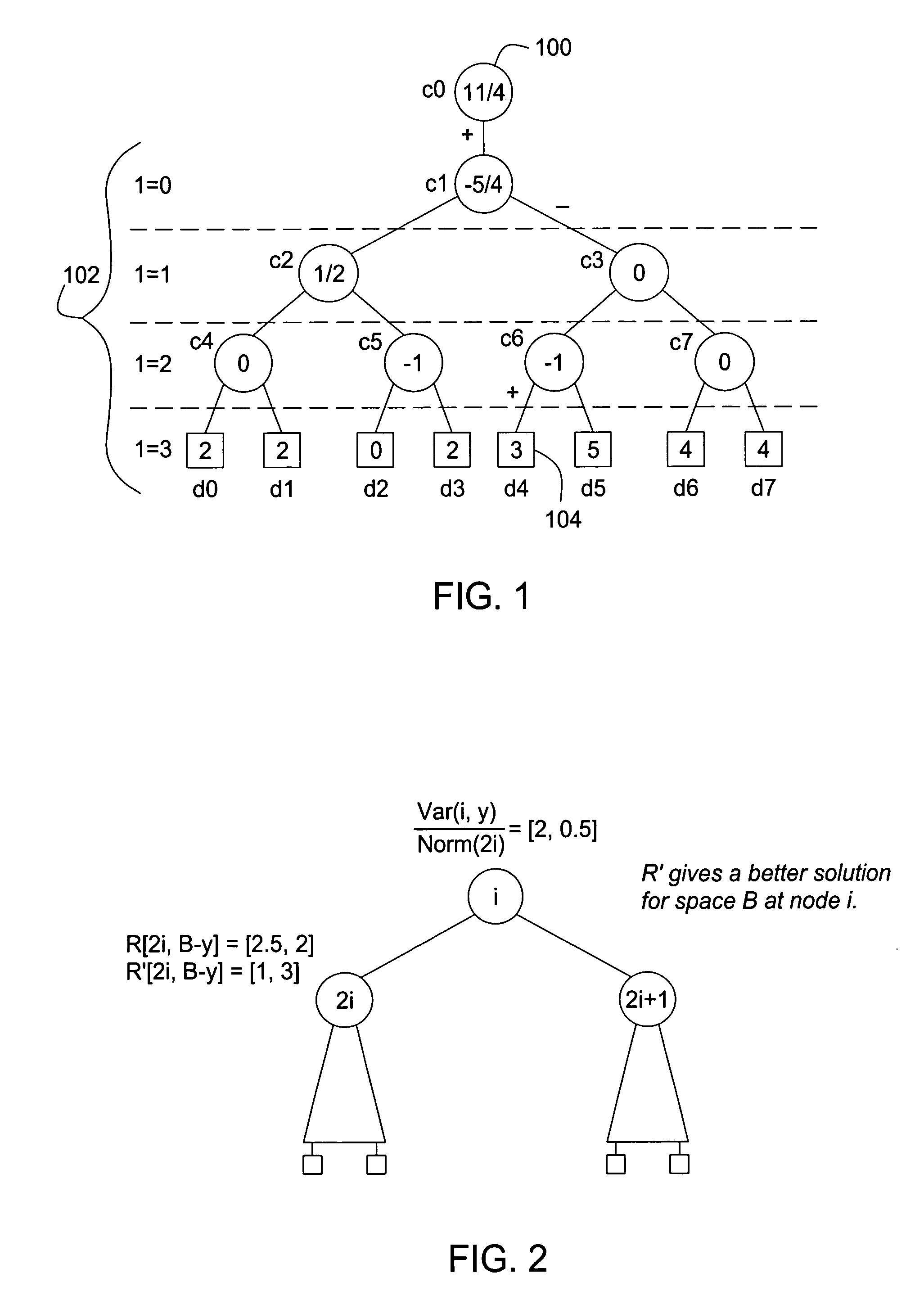
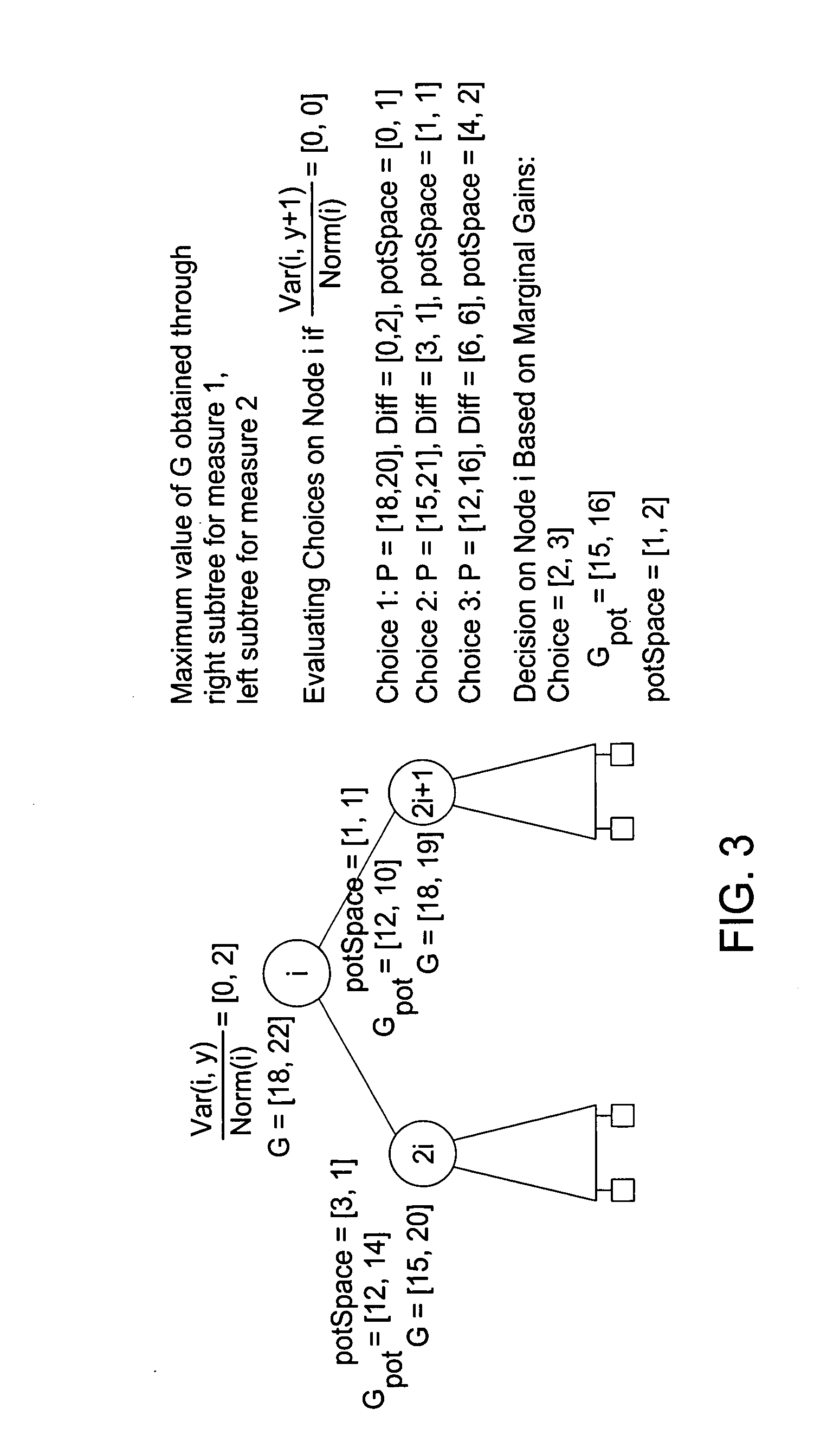
A technique for building probabilistic wavelet synopses for multi-measure data sets is provided. In the presence of multiple measures, it is demonstrated that the problem of exact probabilistic coefficient thresholding becomes significantly more complex. An algorithmic formulation for probabilistic multi-measure wavelet thresholding based on the idea of partial-order dynamic programming (PODP) is provided. A fast, greedy approximation algorithm for probabilistic multi-measure thresholding based on the idea of marginal error gains is provided. An empirical study with both synthetic and real-life data sets validated the approach, demonstrating that the algorithms outperform naive approaches based on optimizing individual measures independently and the greedy thresholding scheme provides near-optimal and, at the same time, fast and scalable solutions to the probabilistic wavelet synopsis construction problem.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Clustering Approach for Detecting DDoS Botnets on the Cloud from IPFix Data
Use machine learning to train a classifier to classify entities to increase confidence with respect to an entity being part of a distributed denial of service attack. The method includes training a classifier to use a first classification method, to identify probabilities that entities from a set of entities are performing denial of service attacks. The method further includes identifying a subset of entities meeting a threshold probability of performing a denial of service attack. The method further includes using a second classification method, identifying similarity of entities in the subset of entities. The method further includes based on the similarity, classifying individual entities.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
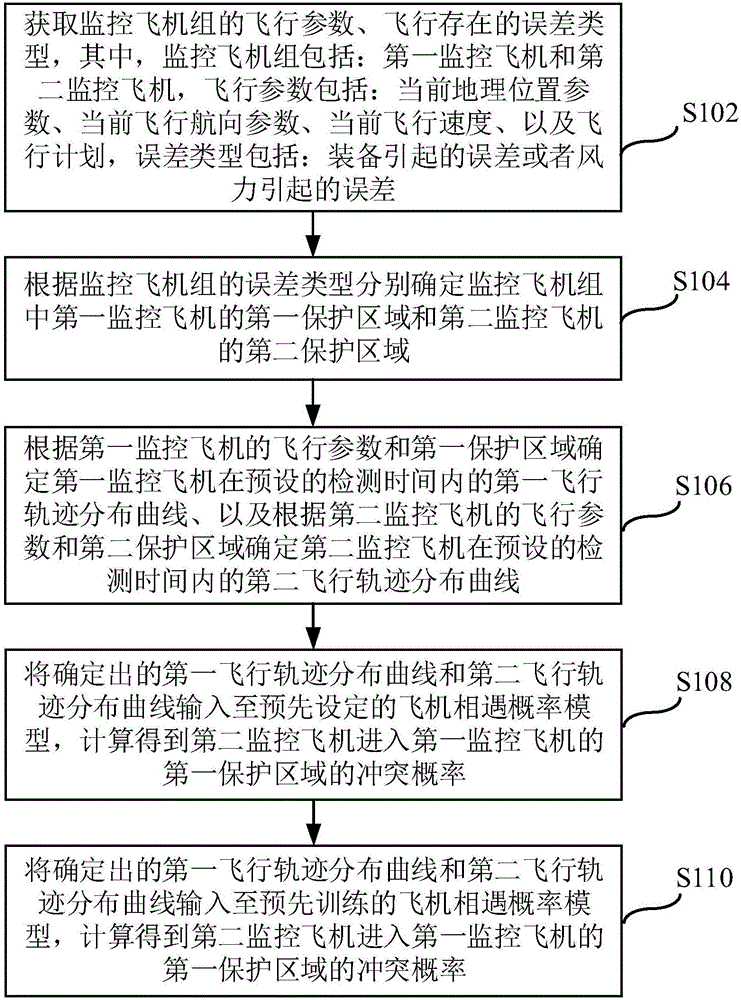
Air traffic control mid-term conflict detection method and device
ActiveCN106601033AImprove forecast accuracyMultiple aircraft traffic managementProbit modelJet aeroplane
The invention provides an air traffic control mid-term conflict detection method and device. The method comprises the following steps: determining a protection region of each airplane according to error type of a monitoring airplane group; determining a flight path distribution curve of each airplane; inputting the determined flight path distribution curves to a preset airplane encounter probability model, and carrying out calculation to obtain collision probability of a second monitoring airplane when entering the protection region of a first monitoring airplane; and determining collision danger level of the monitoring airplane group according to the collision probability and preset threshold probability combination. According to the method and device, by introducing various uncertain factor trajectory distribution curves and calculating the collision probability by utilizing the airplane encounter probability model, and meanwhile, by carrying out comparison on the threshold probability combination and the collision probability to judge the collision danger level, air traffic control mid-term conflict probability prediction accuracy is improved, and reference is provided for an air-traffic controller for airspace conflict resolution.
Owner:INST OF RADAR & ELECTRONICS CONFRONTATION ARMY AIR FORCE EQUIP RES INST OF PLA
Real-time adjustments to authentication conditions
InactiveUS8291472B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGraph theoreticThreshold probability
Embodiments of the invention provide for adjusting authentication conditions in real-time. A graph-theoretic data structure is dynamically constructing, having nodes corresponding to received valid and invalid authentication credentials used in attempts to access a system. Based on the graph-theoretic data structure, embodiments compute a probability of an invalid credential being an authentication attempt by a particular type of user. If the probability is beyond a threshold probability, embodiments trigger a security event is to adjust an authentication condition of the system, e.g., to increase or decrease a maximum permissible number of failed login attempts within a certain period of time.
Owner:IBM CORP
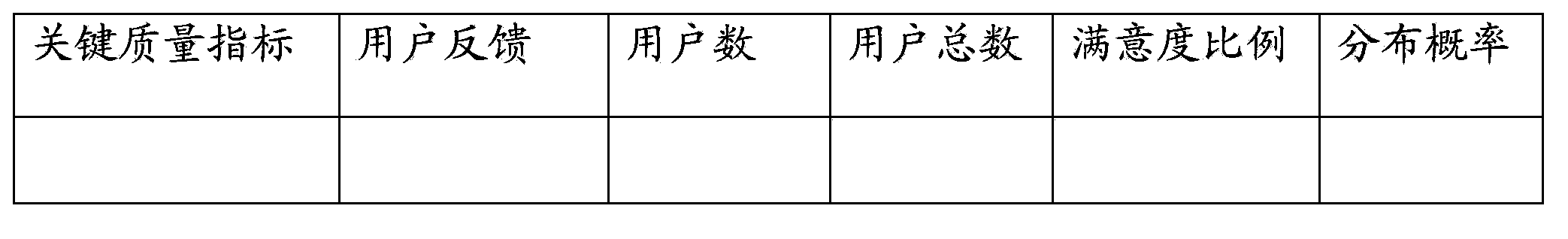
Method and equipment for acquiring KQI threshold
ActiveCN103840978AInvestment protectionPrecise deliveryData switching networksCritical to qualitySimulation
The invention is applicable to the technical field of communication and provides a method and a piece of equipment for acquiring a KQI threshold. The method comprises the following steps: KQI threshold equipment acquires key quality index KQI values of a first user group in a preset period and quality of experience QoE values corresponding to the KQI values; according to the association relationship between the KQI values and the QoE values and by taking each KQI value as the current QoE value, the user satisfaction ratio of each KQI value relative to the current KQI value is acquired first, and then the distribution probability that the user satisfaction ratio meets a preset condition is acquired; and the KQI value of which the distribution probability is lower than a preset threshold probability is acquired, and the KQI value is taken as the KQI threshold. According to the method, the KQI threshold is acquired based on the single-user satisfaction degree, the KQI threshold can make optimization precise and avoid excessive optimization, the KQI threshold can help operators to set an optimization goal toward the single-user satisfaction degree, bad experiences are optimized and good experiences are not optimized, and investment of operators is protected.
Owner:海宁市黄湾镇资产经营有限公司
Abnormal intelligence data recognition machine learning method
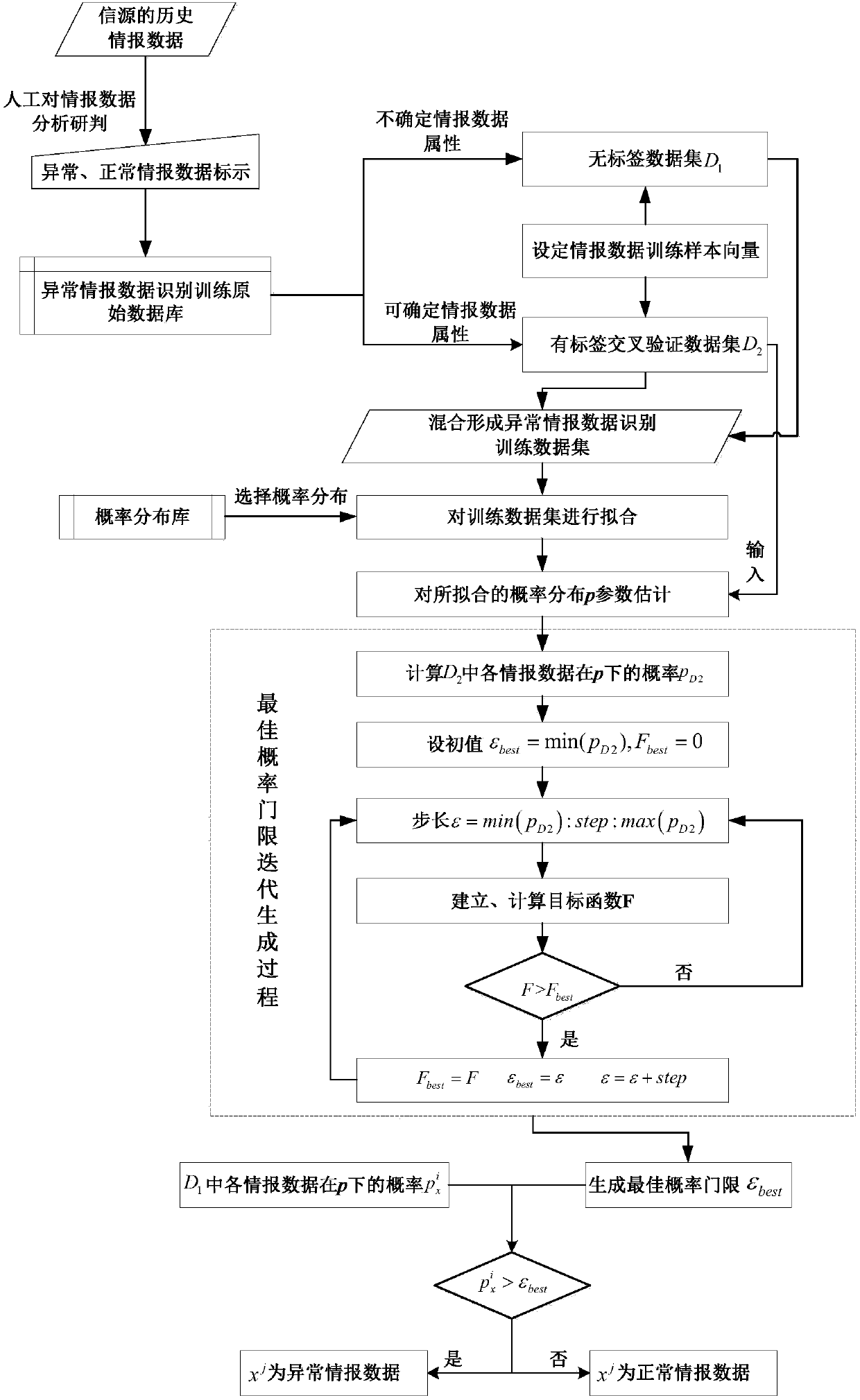
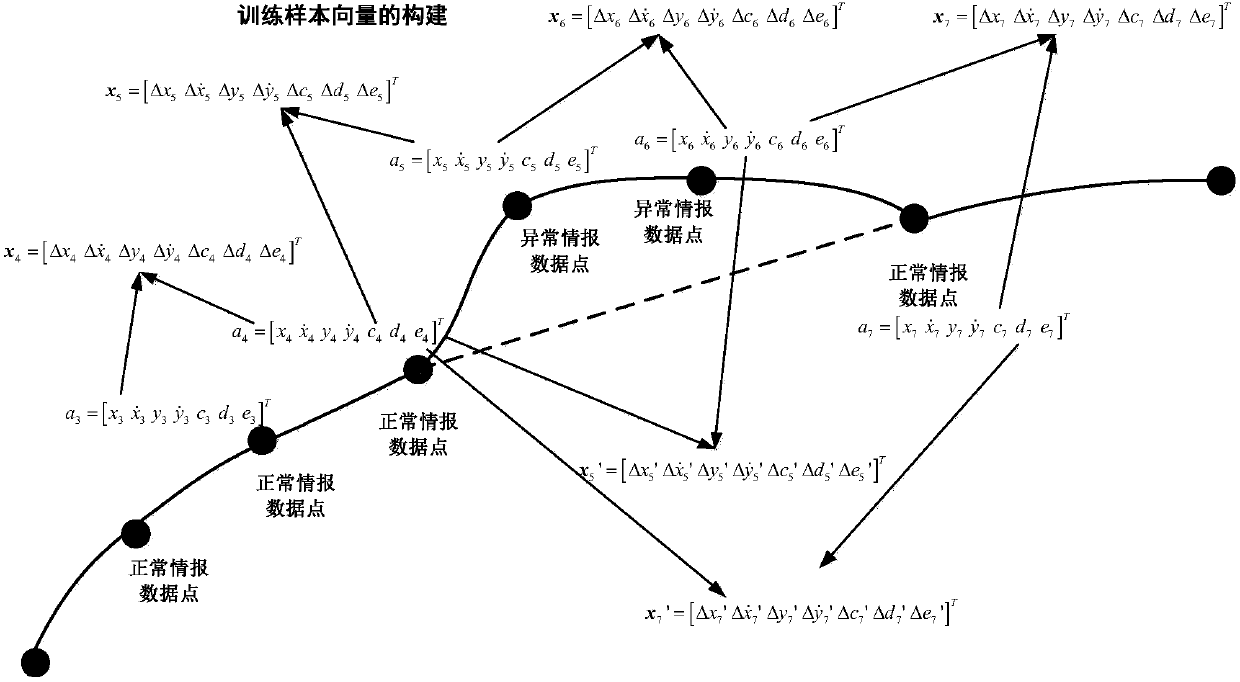
InactiveCN108268632ASolve the discrimination problemAvoid extensive debugging operationsRelational databasesCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionData set
The invention discloses an abnormal intelligence data recognition machine learning method, belongs to the field of intelligence data processing and mainly solves the problem that existing abnormal intelligence data recognition requires a lot of repeated manual debugging in an actual engineering application and data are difficult to directly apply. The method comprises steps as follows: firstly, collecting historical intelligence data of an information source, and performing manual analysis and study on abnormal data to form an original database; setting intelligence data training sample vectorcomposition, and generating an abnormal intelligence data recognition training dataset through feature extraction; further fitting probability distribution of the intelligence data, generating the best threshold probability in combination with label dataset iteration, and generating an abnormal intelligence data recognition model. According to a system, the abnormal intelligence data recognitionmodel is automatically trained and generated, a lot of manual debugging operation of model parameters is completely avoided, and the system has the advantages of high model generation speed and good practical effect.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
Red-eye detection and correction
A method suited to the detection and correction of red-eyes includes assigning a probability to pixels of a digital image of the pixel being in a red-eye, the probability being a function of a color of the pixel. Optionally, generally circular regions in the image of contiguous pixels which satisfy at least one test for a red-eye are identified. The test may include determining a size or shape of the region or an extent of overlap with a region comprising pixels having at least a threshold probability of being in a red-eye. For each of a plurality of the pixels, such as simply those in identified regions, or for all pixels or a larger group of the pixels, a color correction for the pixel is determined. The correction is a function of the assigned probability that the pixel is within a red-eye and a color of the pixel.
Owner:III HLDG 6
Method and apparatus for navigational searching of a website
Methods may display an interactive searching display window on a webpage. Methods may display a search box located on the interactive searching display window, which may enable a user to type in a query. Methods may display an answer box located on the interactive searching display window, which may display an answer to a user's query. Methods may display a minimize button, a maximize button and a pin button, which may allow the user to pin the interactive searching display window to one side of the webpage. Methods may redirect the user to a second webpage in response to the determination that greater than a threshold probability exists that the answer to the user's question may be found on the second webpage. Methods may display the interactive searching display window about a central location on the second webpage for a time period between 1.5 and 3.5 seconds.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
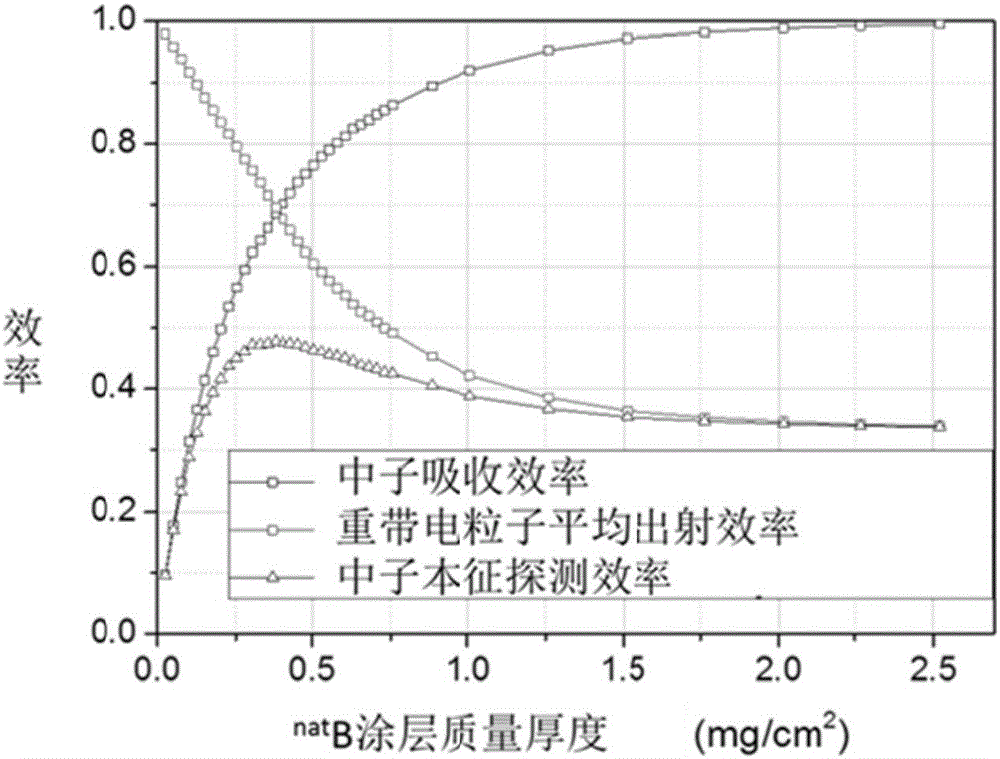
Slow neutron detection device
InactiveCN106199680AReduce drift distanceIncrease the average probability of crossing the thresholdElectric discharge tubesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSlow neutronElectron drift
The invention discloses a slow neutron detection device. The slow neutron detection device comprises a first slow-neutron conversion body, a second slow-neutron conversion body, a reading-out electrode wire set and a negative electrode wire set, wherein the reading-out electrode wire set and the negative electrode wire set are arranged between the first slow-neutron conversion body and the second slow-neutron conversion body. As a reading-out circuit is arranged between the two slow-neutron conversion bodies, and under the condition that the boundary dimension of a detector is invariable, the electron drift distance is reduced by one half, and the average over-threshold probability of signals is increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
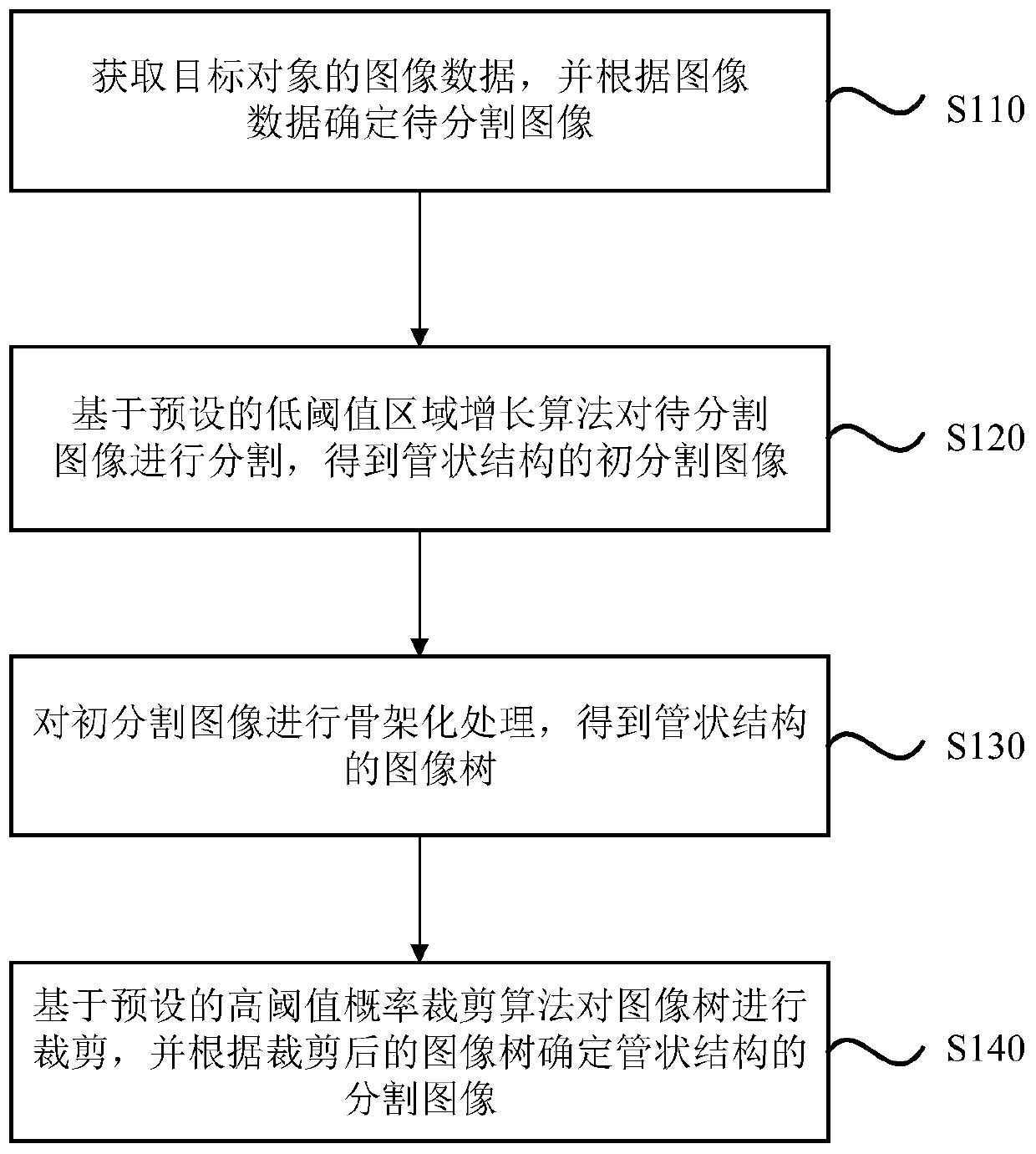
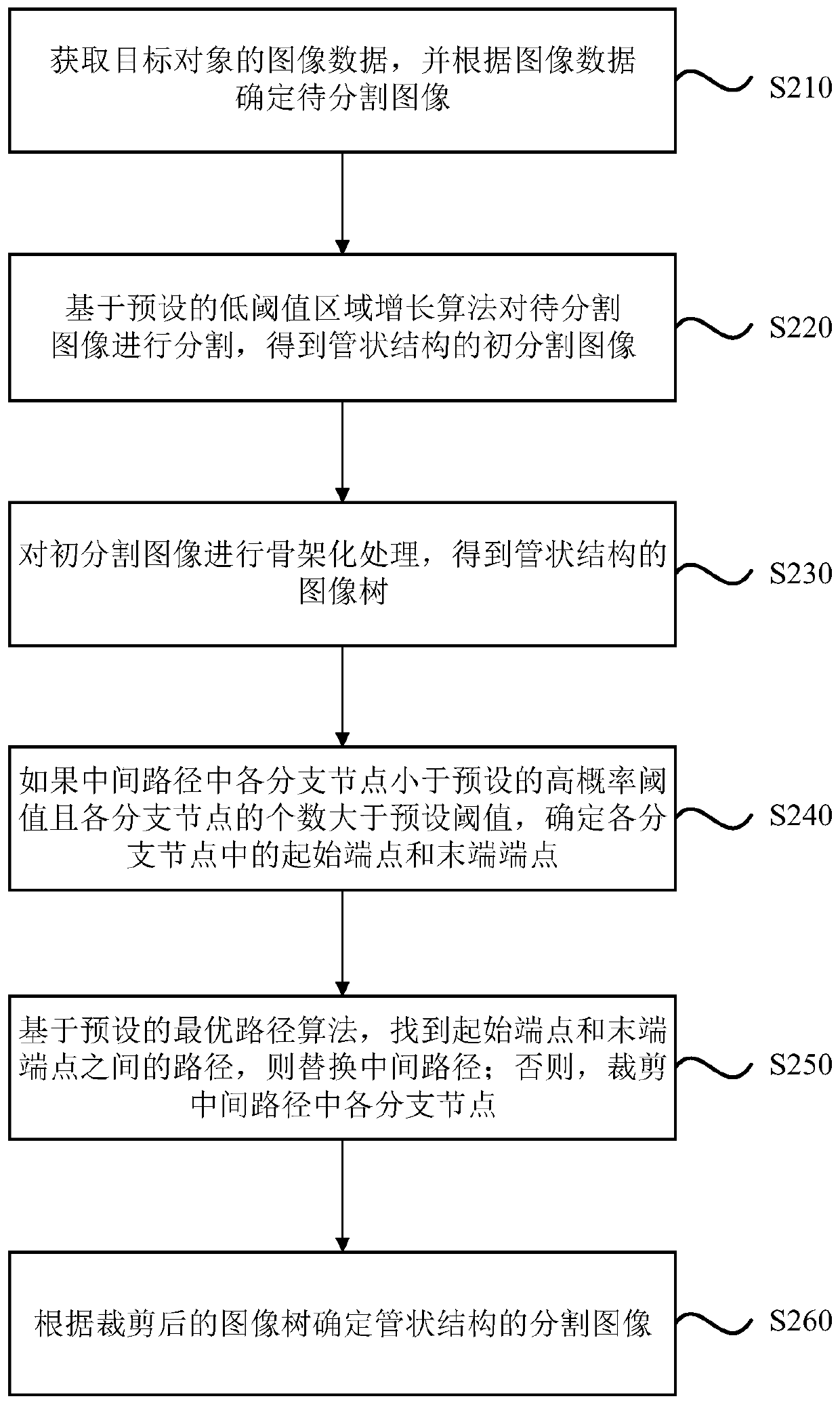
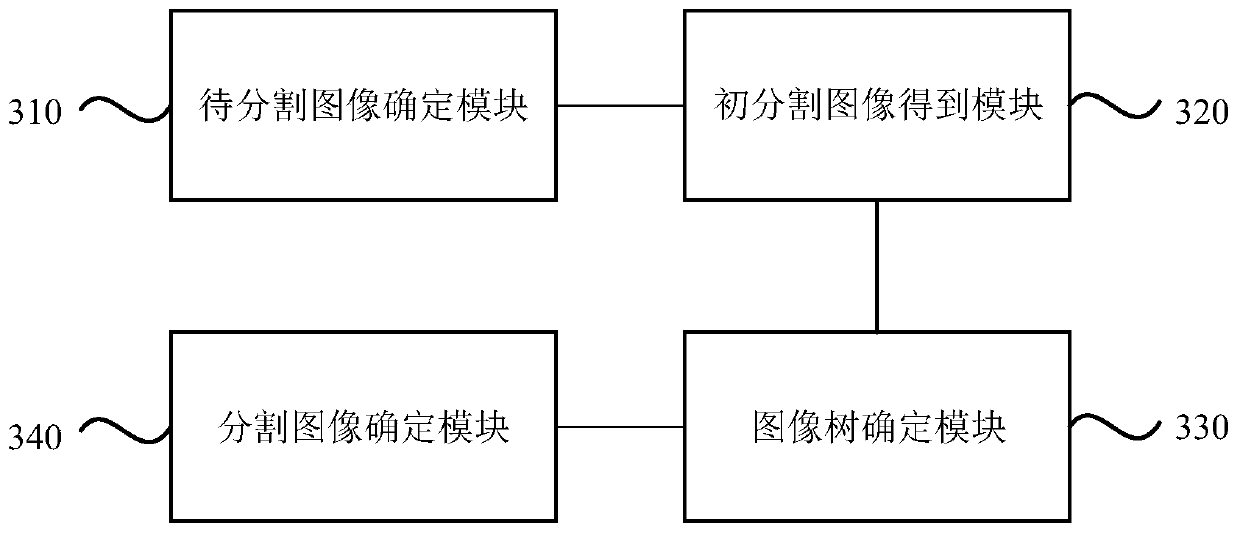
Image segmentation method, device and equipment and storage medium
PendingCN109712161AIntegrity guaranteedThe problem with curbing data breachesImage analysisImage segmentationMedical diagnosis
The embodiment of the invention discloses an image segmentation method and device, equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining image data of a target object, and determining a to-be-segmented image according to the image data; Segmenting the to-be-segmented image based on a preset low-threshold region growing algorithm to obtain an initial segmented image with a tubular structure; performing skeletonization processing on the initial segmented image to obtain an image tree with a tubular structure; and cutting the image tree based on a preset high-threshold probability cutting algorithm, and determining a segmented image of the tubular structure according to the cut image tree. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, theproblem of incomplete segmentation or segmentation leakage in the existing scheme is solved, the tubular structures such as trachea, blood vessels and coronary vessels in the medical image can be accurately segmented, and a basis is provided for medical diagnosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Alert system of the onset of a hypoglycemia even while driving a vehicle
InactiveUS20190382025A1Avoid and mitigate riskAccurate predictionMedical data miningHealth-index calculationHypoglycemiaThreshold probability
In one embodiment, an apparatus (22) is presented that recognizes a user is driving and predicts a hypoglycemic event has reached a threshold probability of occurring based on one or more input parameters and alerts the user or activates a device based on the prediction.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
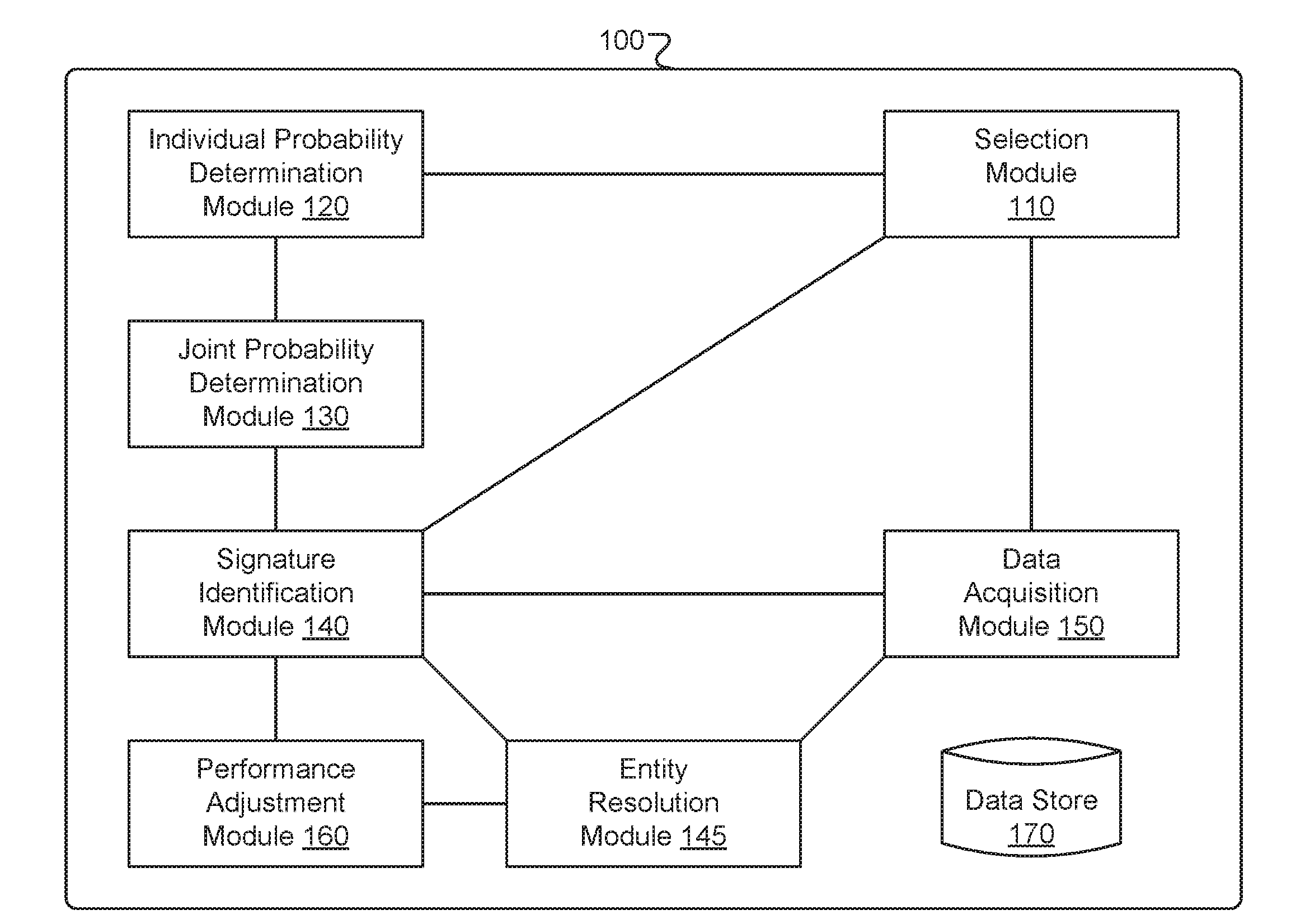
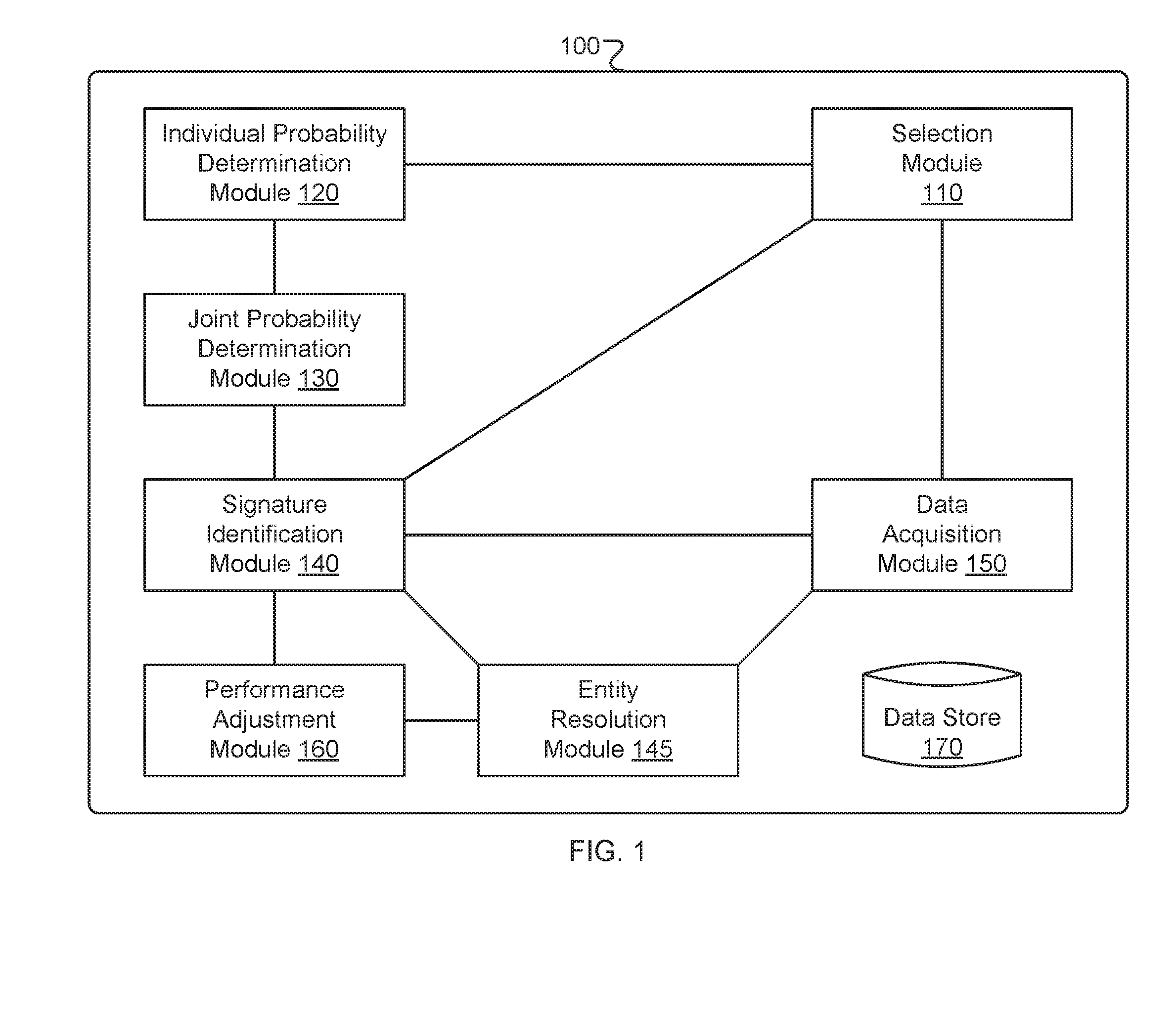
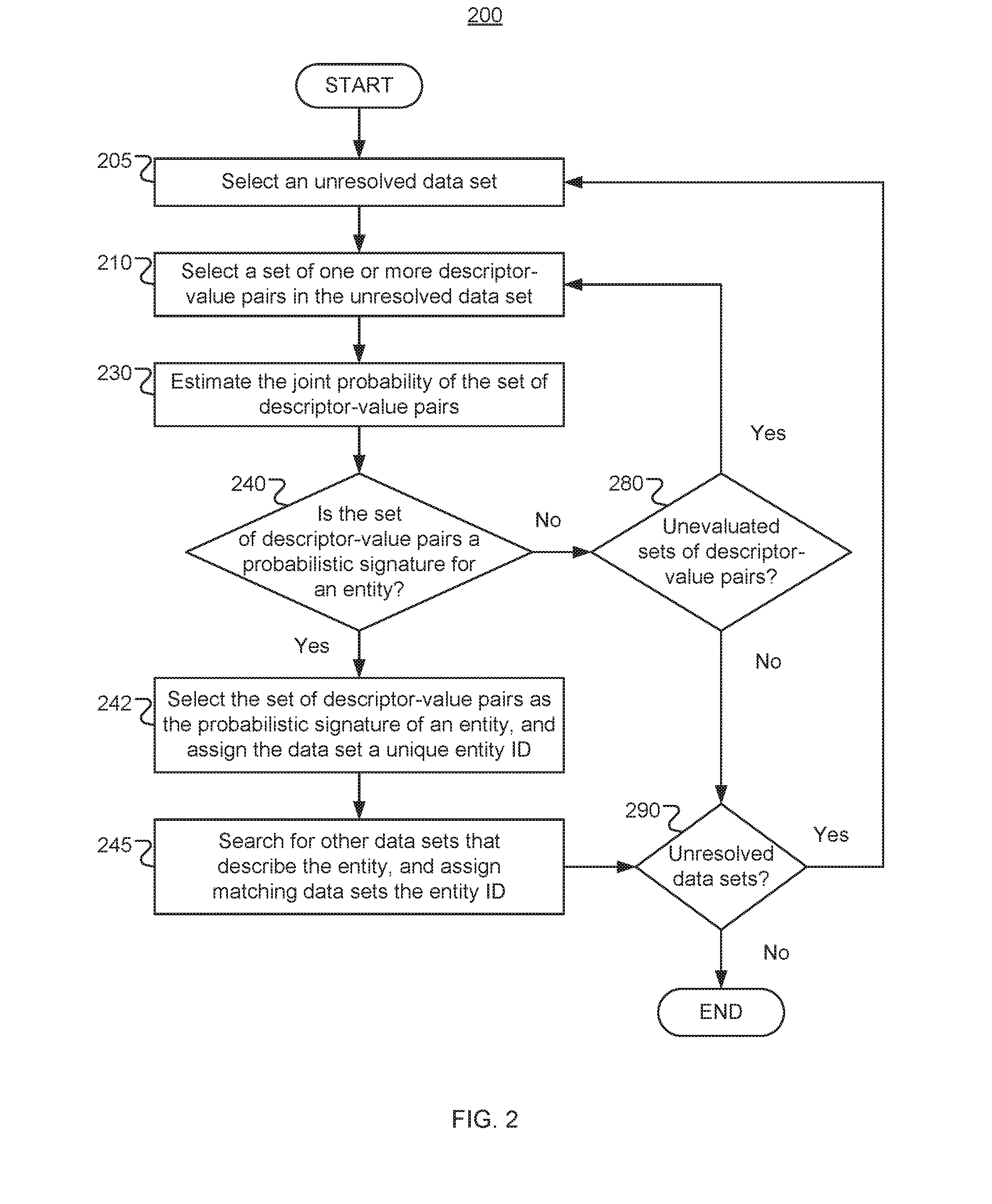
Entity resolution techniques and systems
ActiveUS20160110424A1Improve accuracyFacilitate of entityDigital data processing detailsNatural language data processingData setData mining
Entity resolution techniques and systems are described. An entity resolution method may include estimating a joint probability of occurrence of a plurality of values of a respective plurality of descriptors of an entity. The plurality of descriptor values may be included in a first data set. The method may further include determining that the joint probability of occurrence of the plurality of descriptor values is less than a threshold probability, identifying a second data set including the same plurality of values of the same respective plurality of descriptors, and determining, based at least in part on the joint probability of occurrence of the plurality of descriptor values being less than the threshold probability and on the first and second data sets including the same plurality of descriptor values, that the first and second data sets describe the same entity.
Owner:ENTELO INC
Matching engine
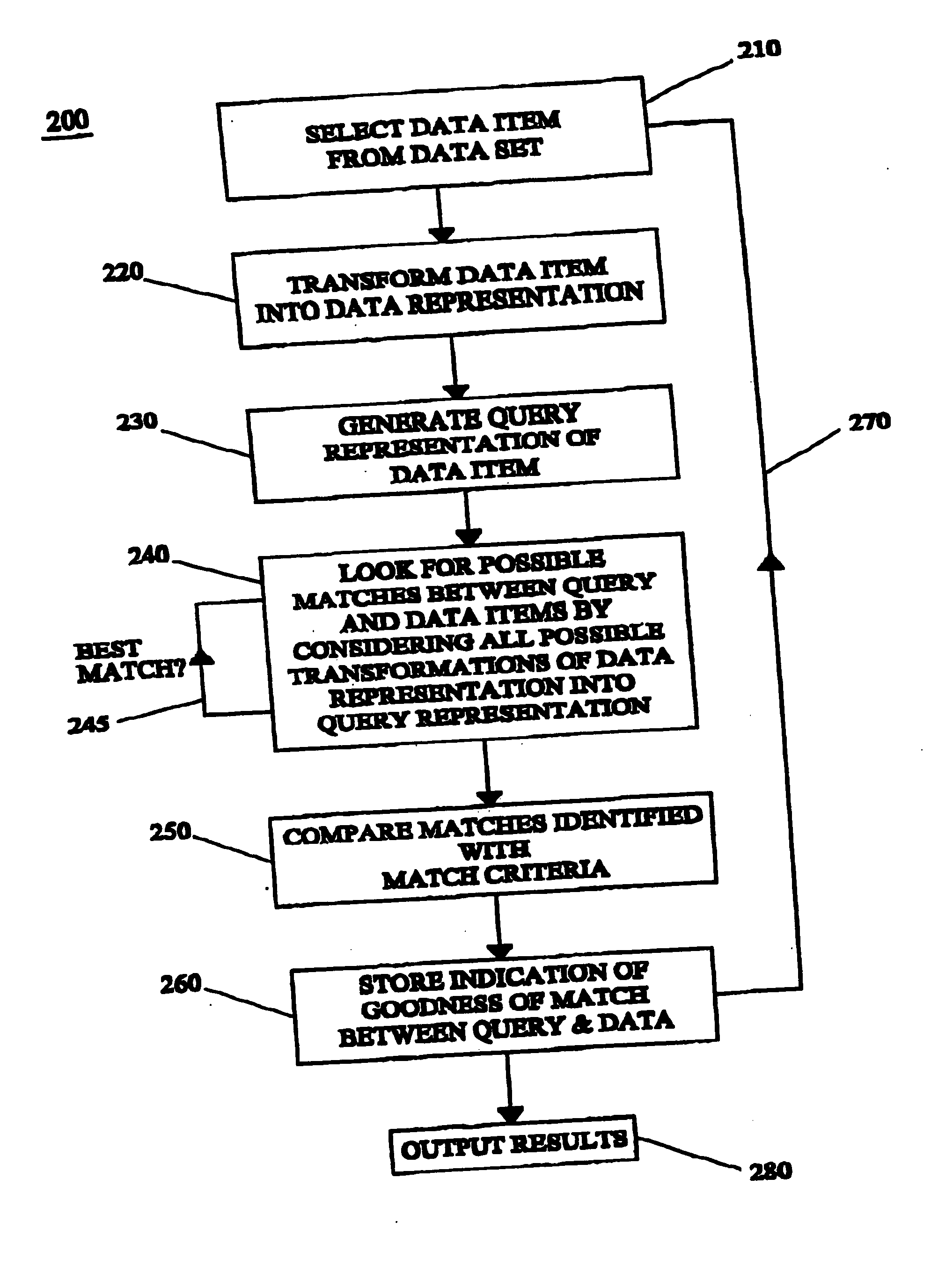
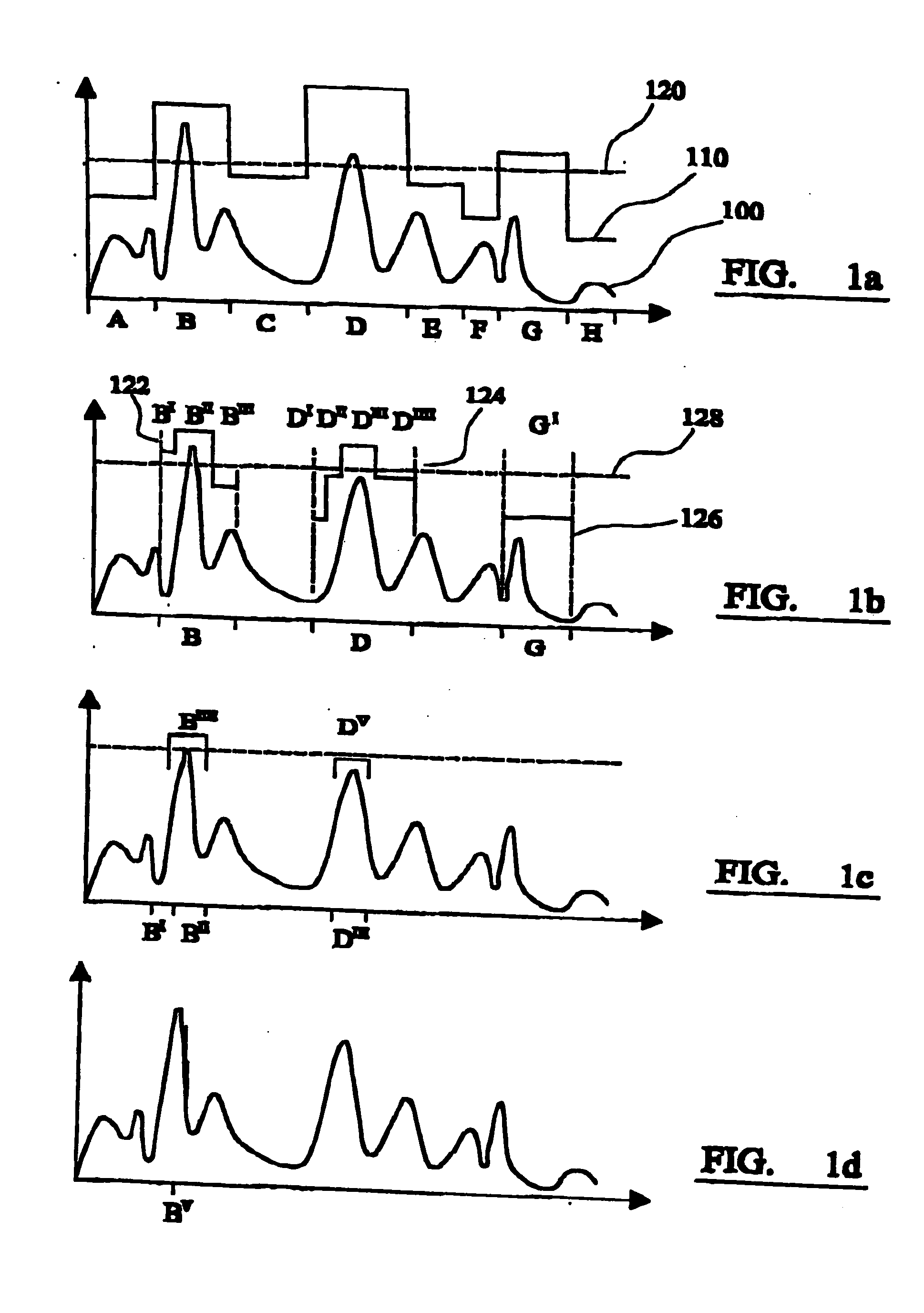
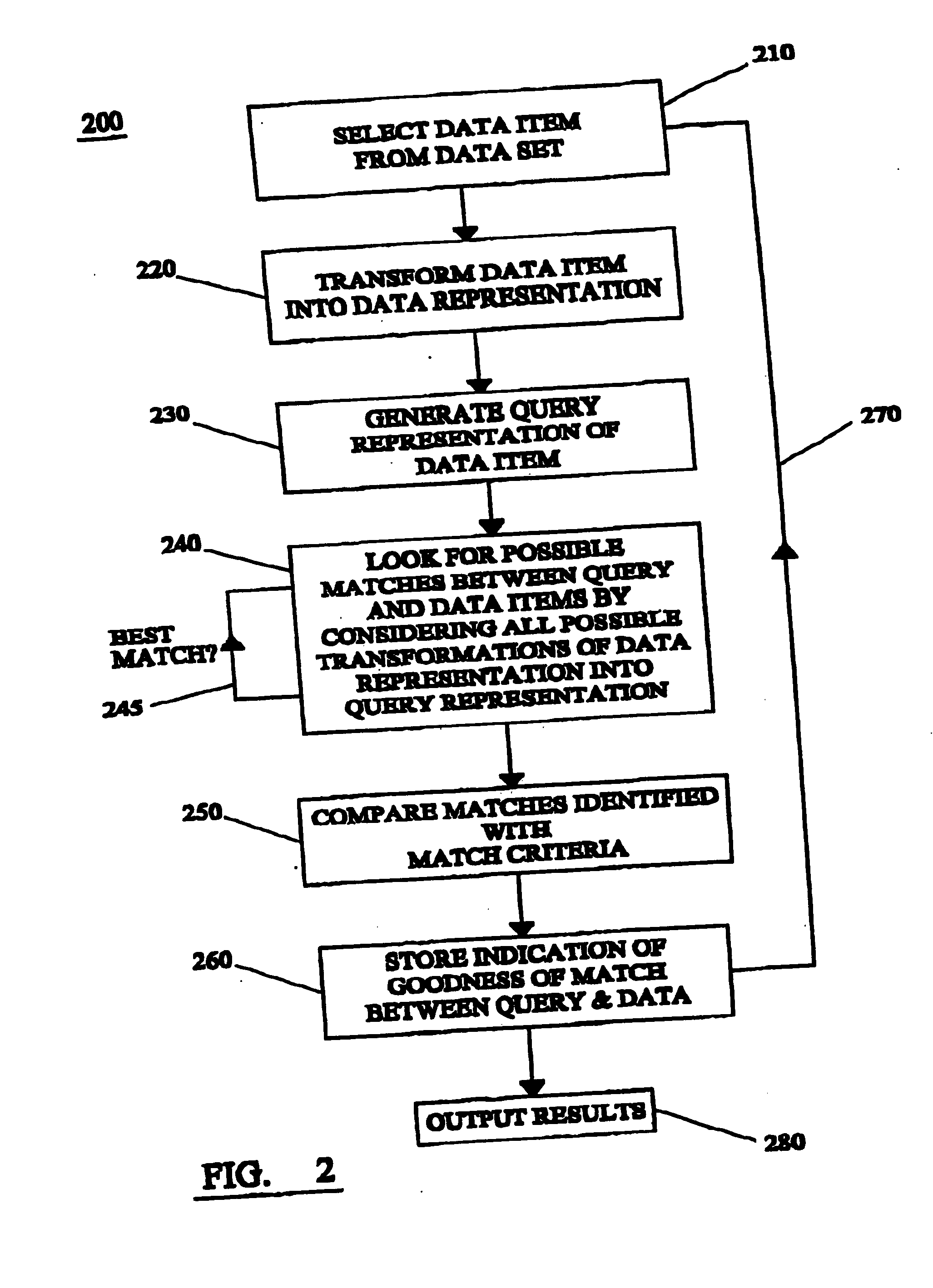
InactiveUS20050246317A1Easy to solveCoverage is ensuredDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData setThreshold probability
A method of identifying the best matches or sets of matches between a query item and an item or items from a data set. The method includes the steps of: (i) providing a data representation for each item in the data set; (ii) providing a query representation of the query item; (iii) defining a transformation space; (iv) for each of a number of regions spanning the entire transformation space, determining an upper bound to the probability of a match between the query representation and a data representation under any transformation in the region; (v) determining a threshold probability; (vi) comparing the upper probability bound of each region with the threshold probability; and (vii) determining regions having an upper probability bound greater than the threshold probability, so as to identify solution regions.
Owner:SQUARE PI
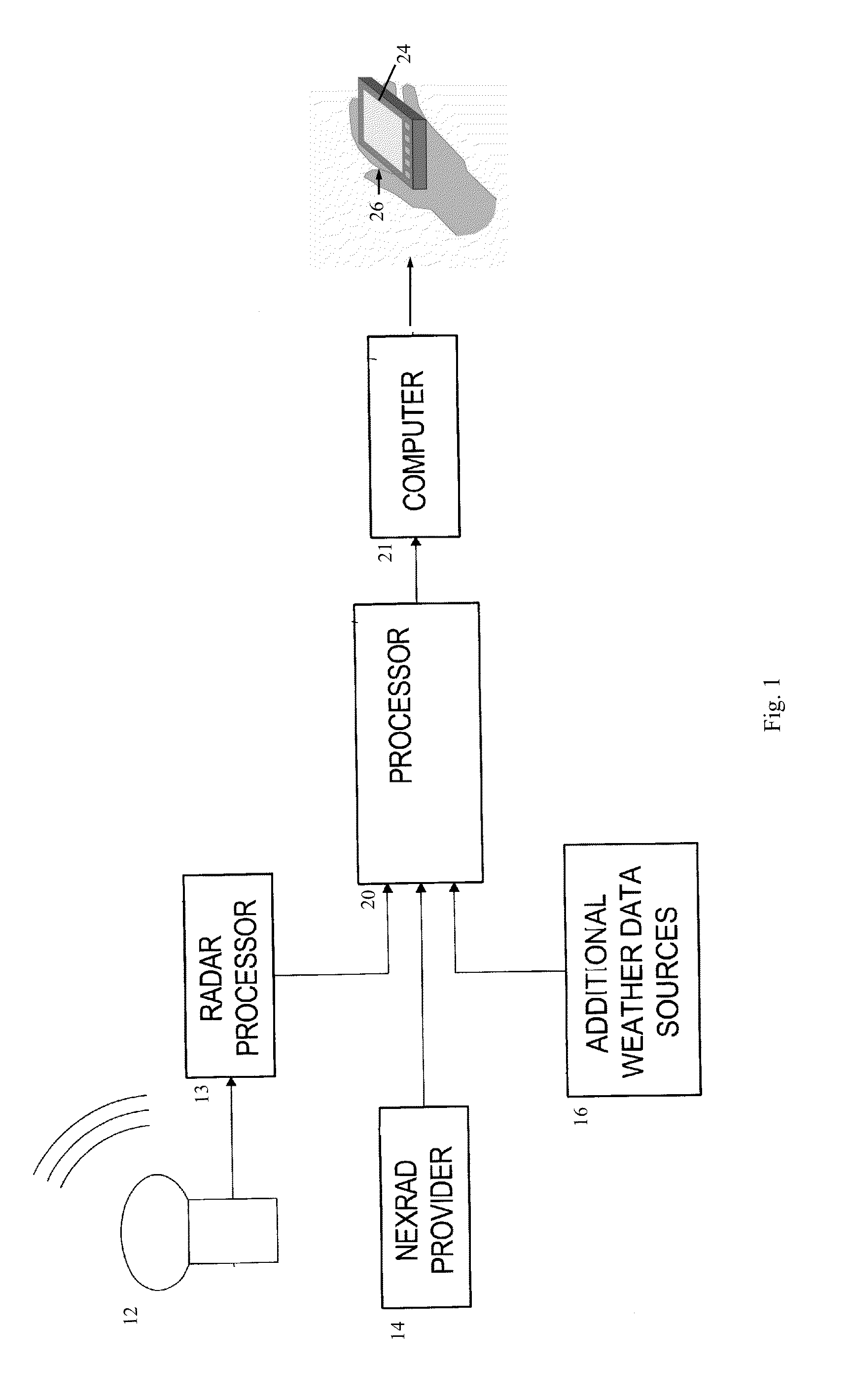
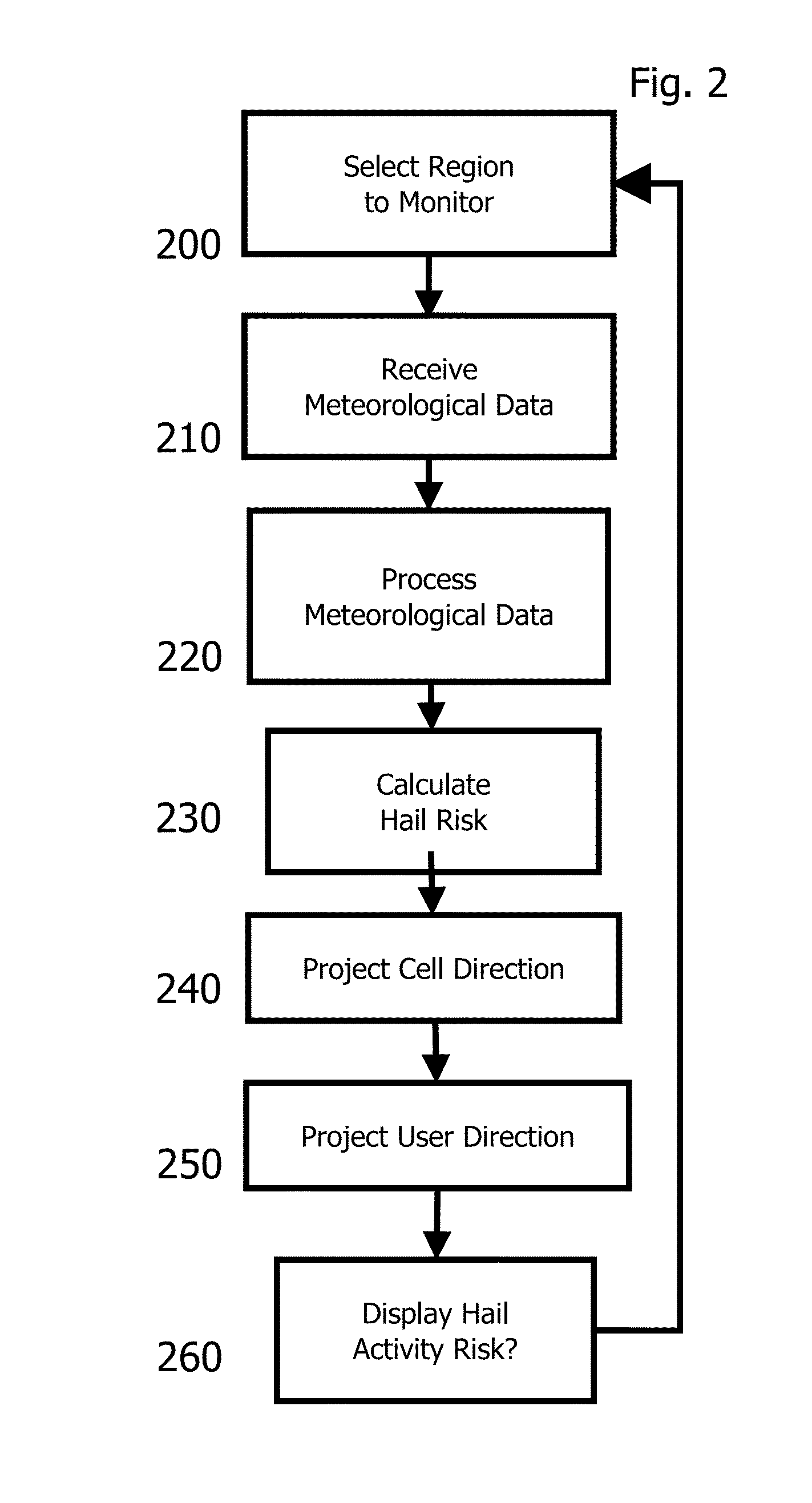
Systems and methods for localized hail activity alerts
InactiveUS20150309208A1Rainfall/precipitation gaugesWeather condition predictionComputer scienceThreshold probability
The present invention is directed to system and method of forecasts, displays, and alerts for localized hail activity. An exemplary method comprises the steps of selecting a region to monitor, receiving meteorological data for that region, processing the meteorological data for storm cell and hail activity in order to determine hail risk activity. The system forecasts the direction of an active storm as well a user position. Probability bands of hail risk activity are created for display. Optionally, an alert is generated when the user position is in or proximate a threshold probability band.
Owner:DYNAMIC WEATHER SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com