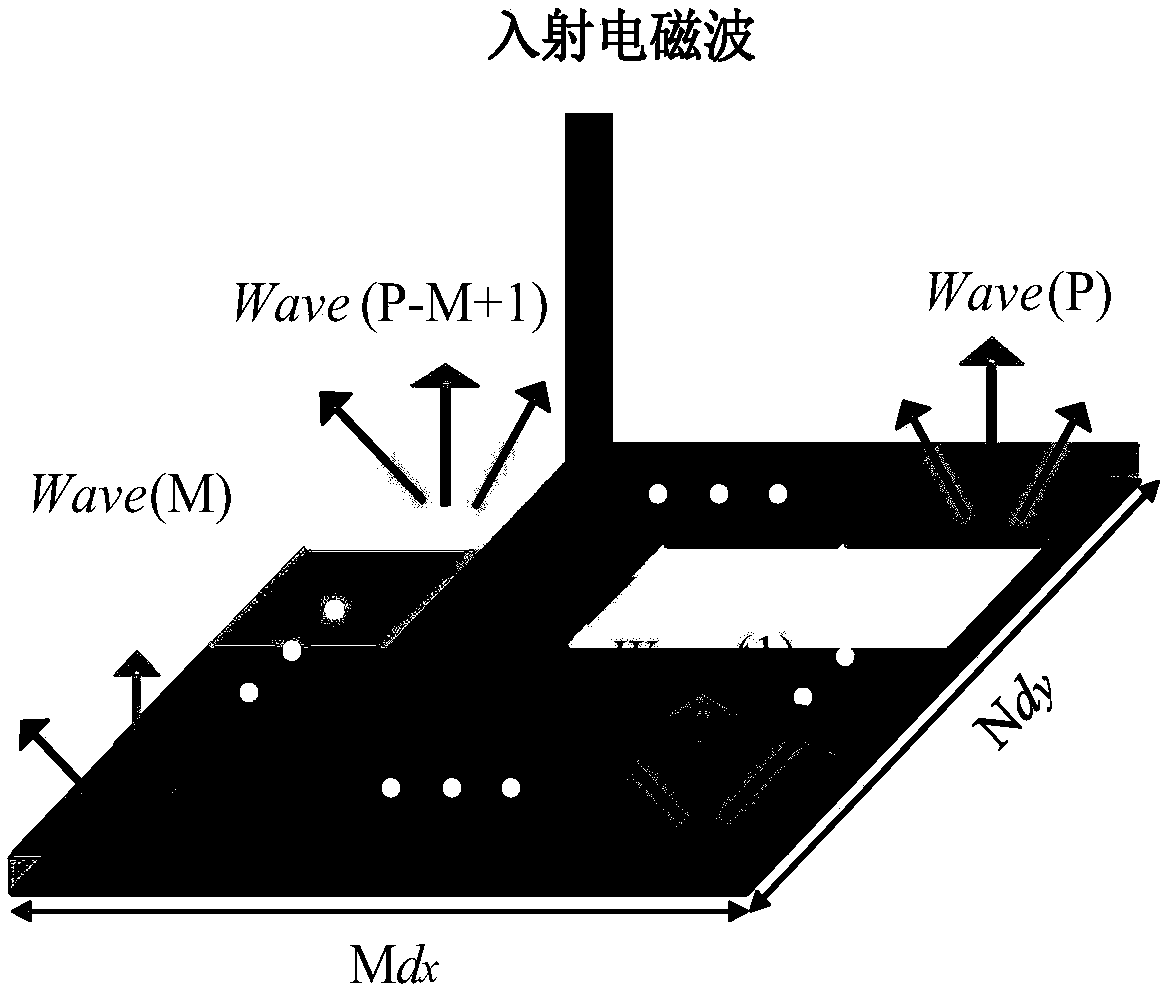
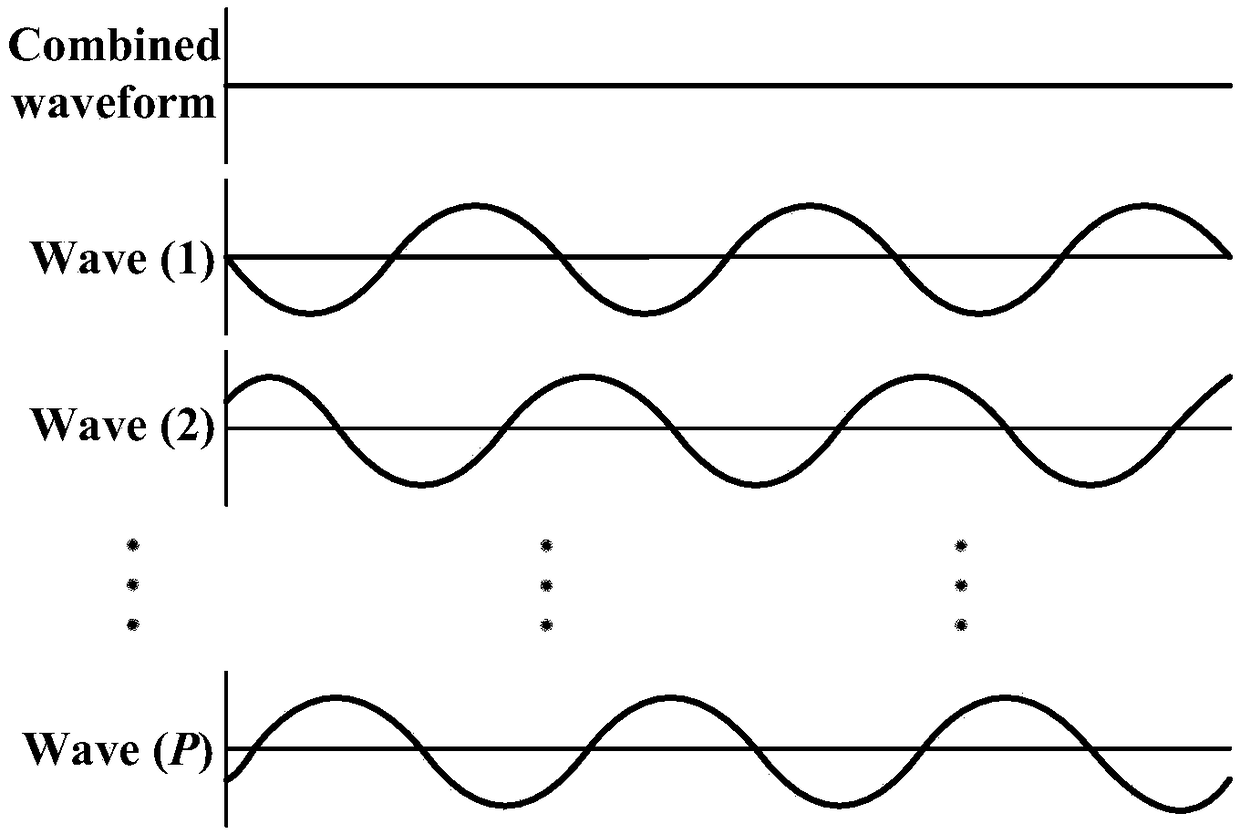
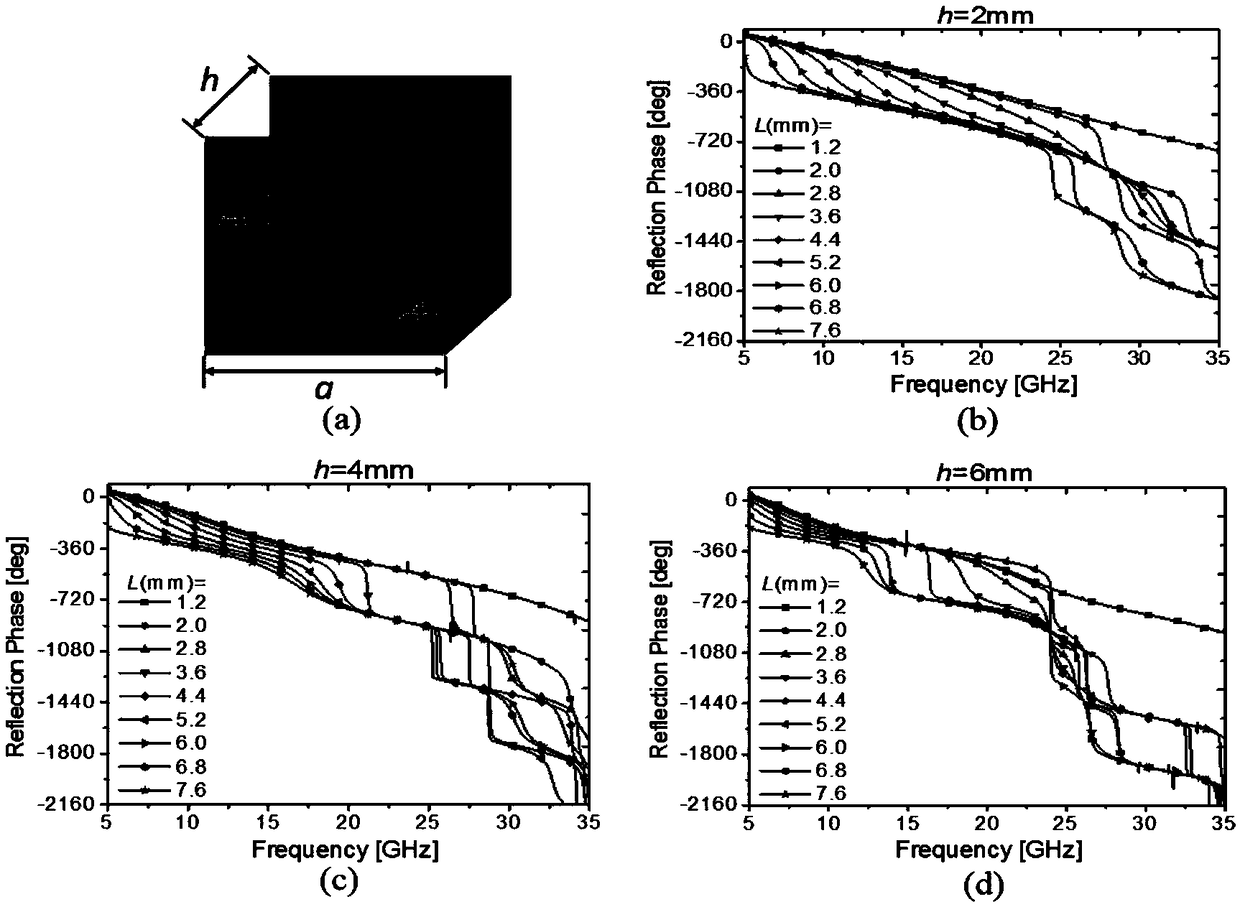
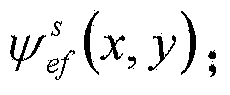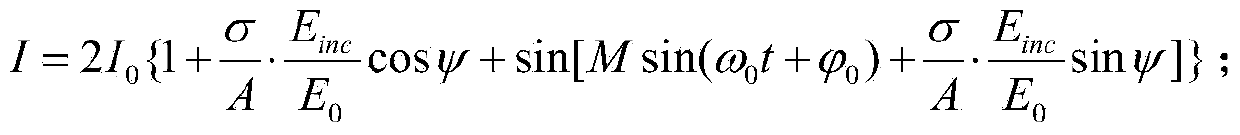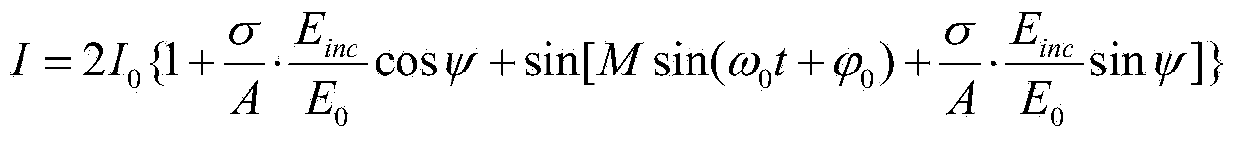Patents
Literature
271 results about "Scattering cross-section" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
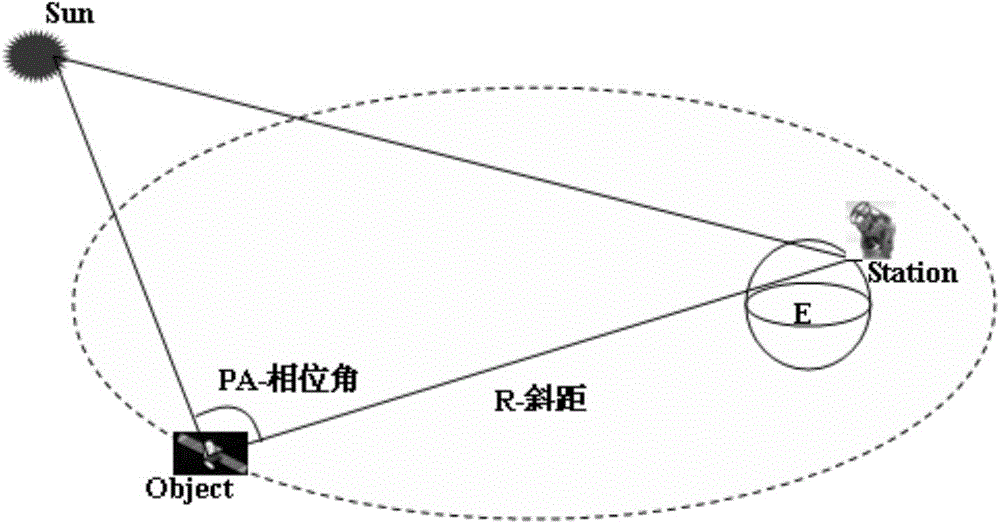
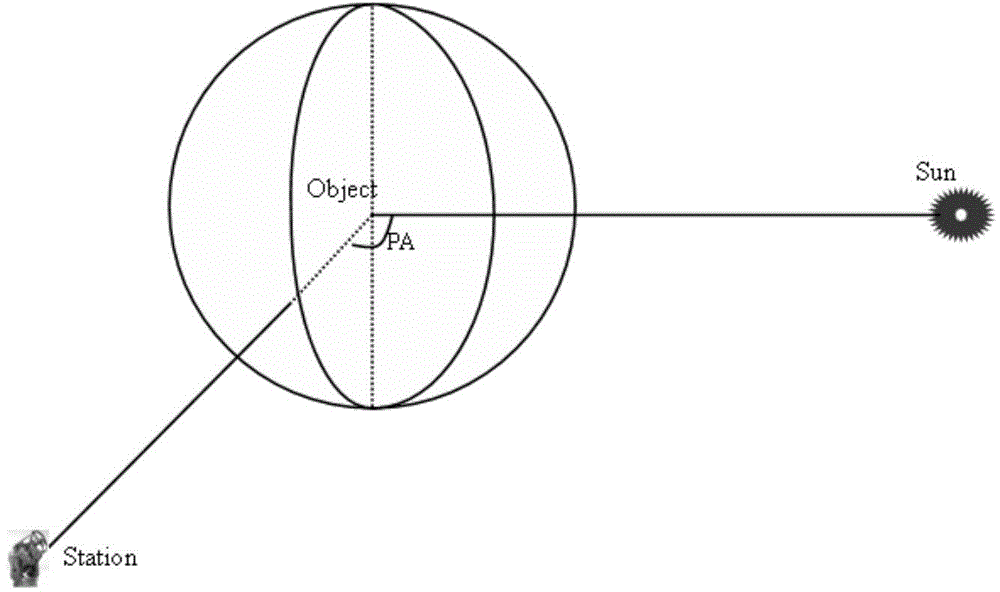
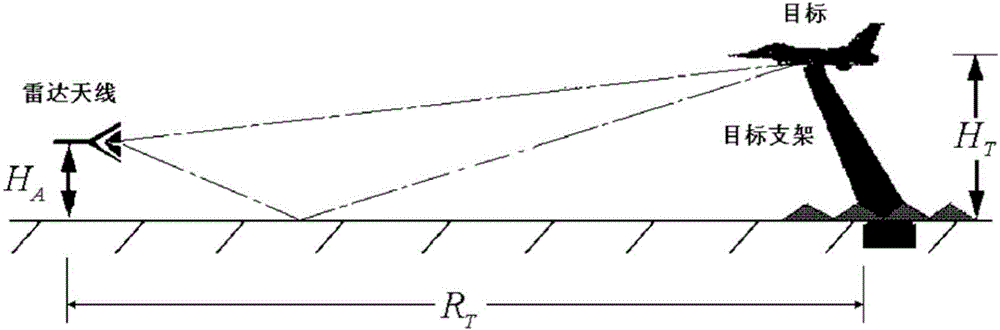
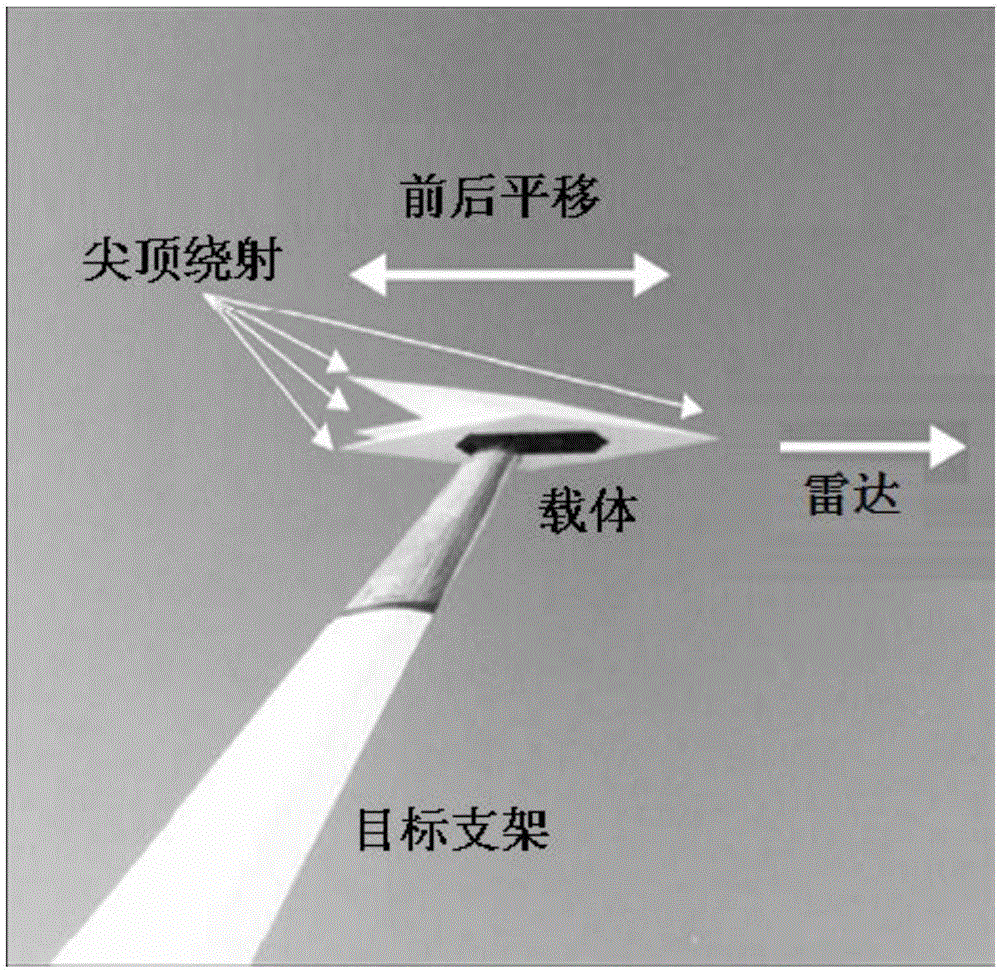
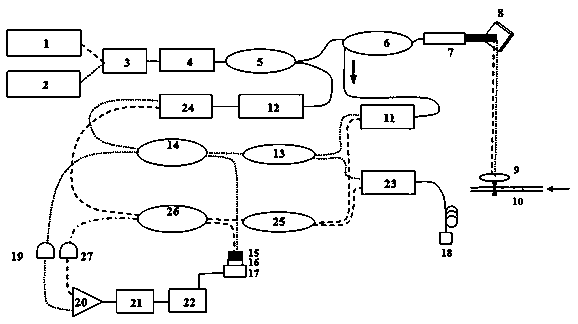
The scattering cross-section is a hypothetical area which describes the likelihood of light or other radiation being scattered by a particle, the scattering center. It is a measure of the strength of the interaction between the scattered particle and one or several scattering centers.
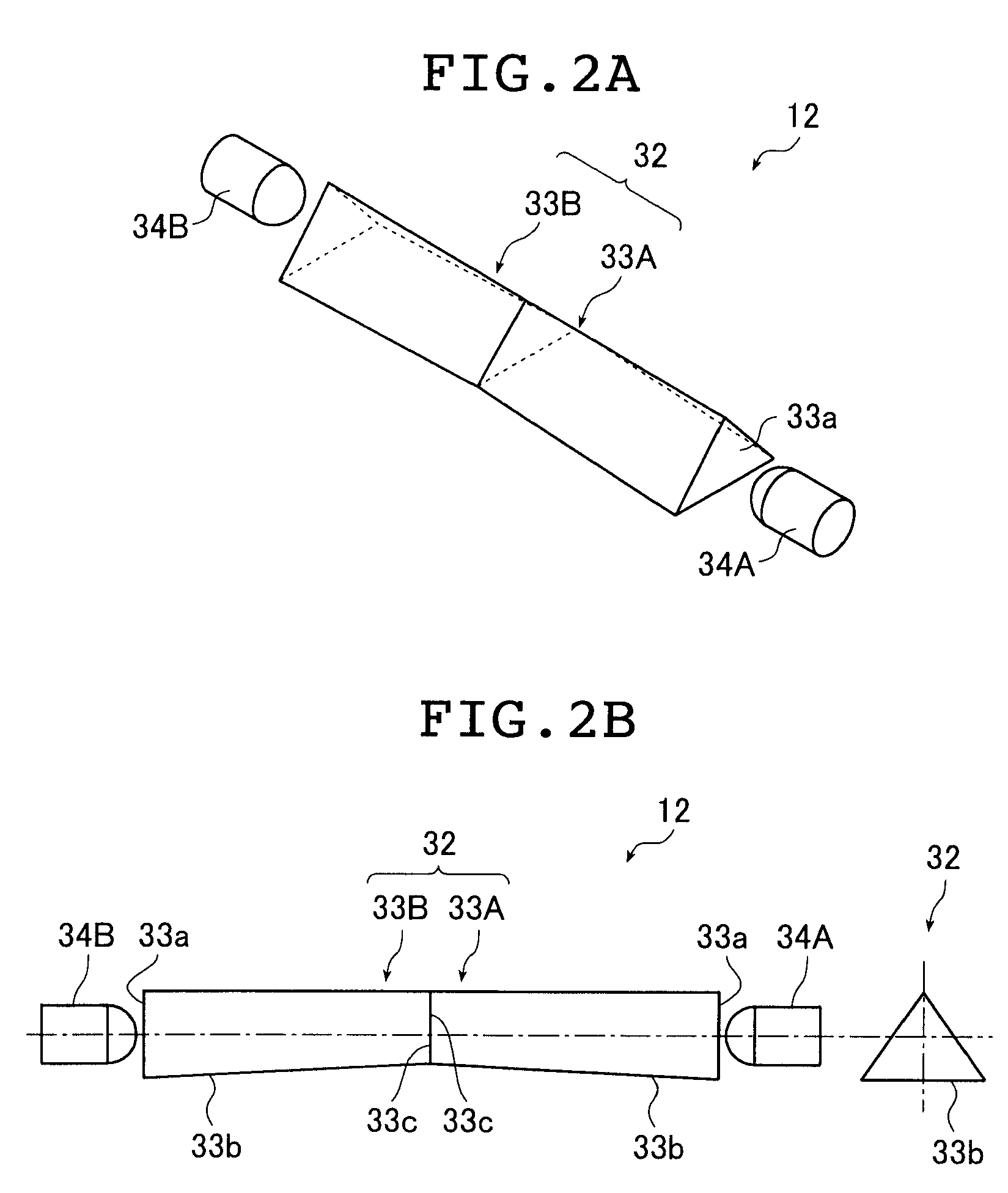
Apparatus and method for non-invasive and minimally-invasive sensing of venous oxygen saturation and pH levels
InactiveUS20060224053A1Easy to useCost effectiveOrgan movement/changes detectionSensorsSonificationScattering cross-section
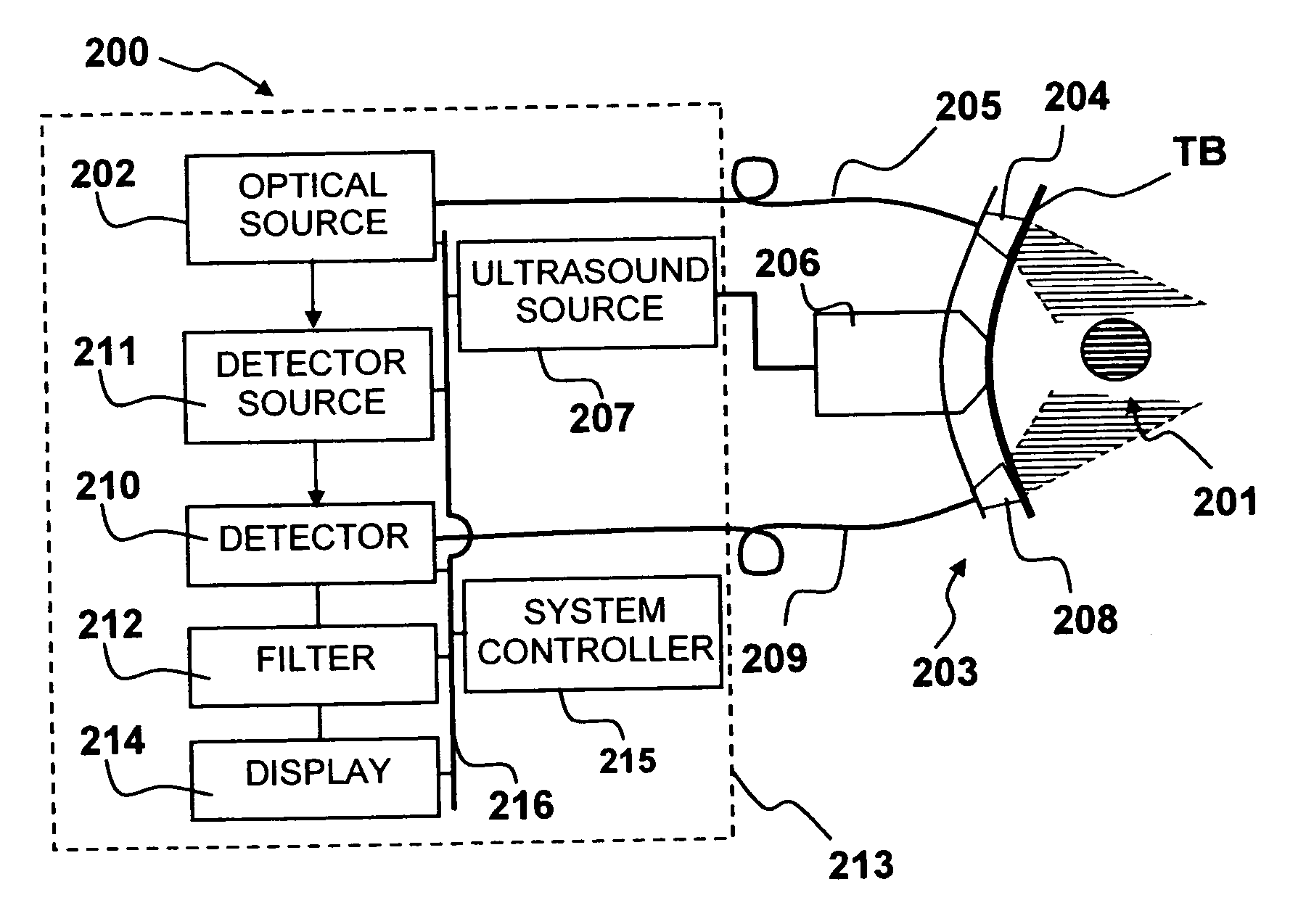
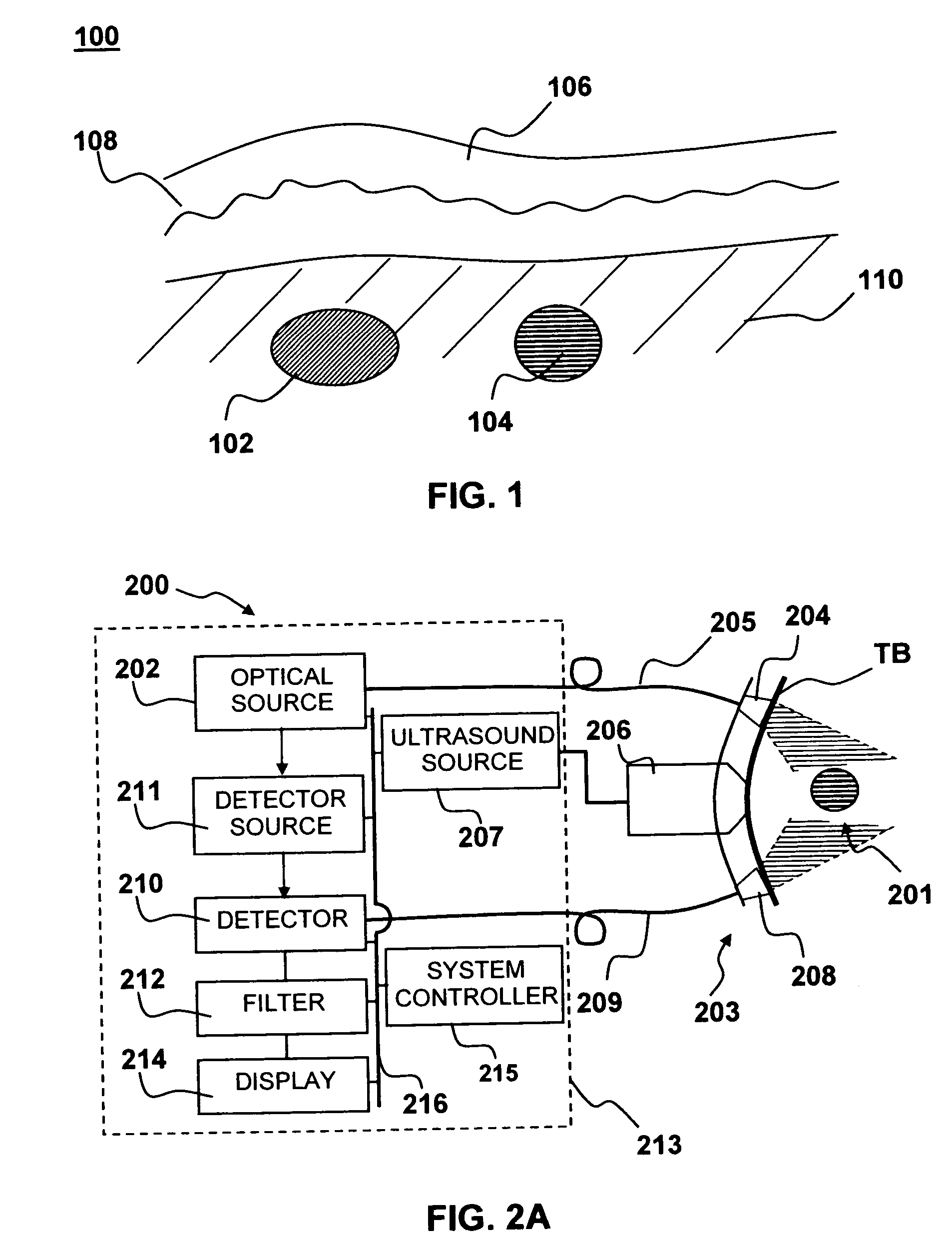
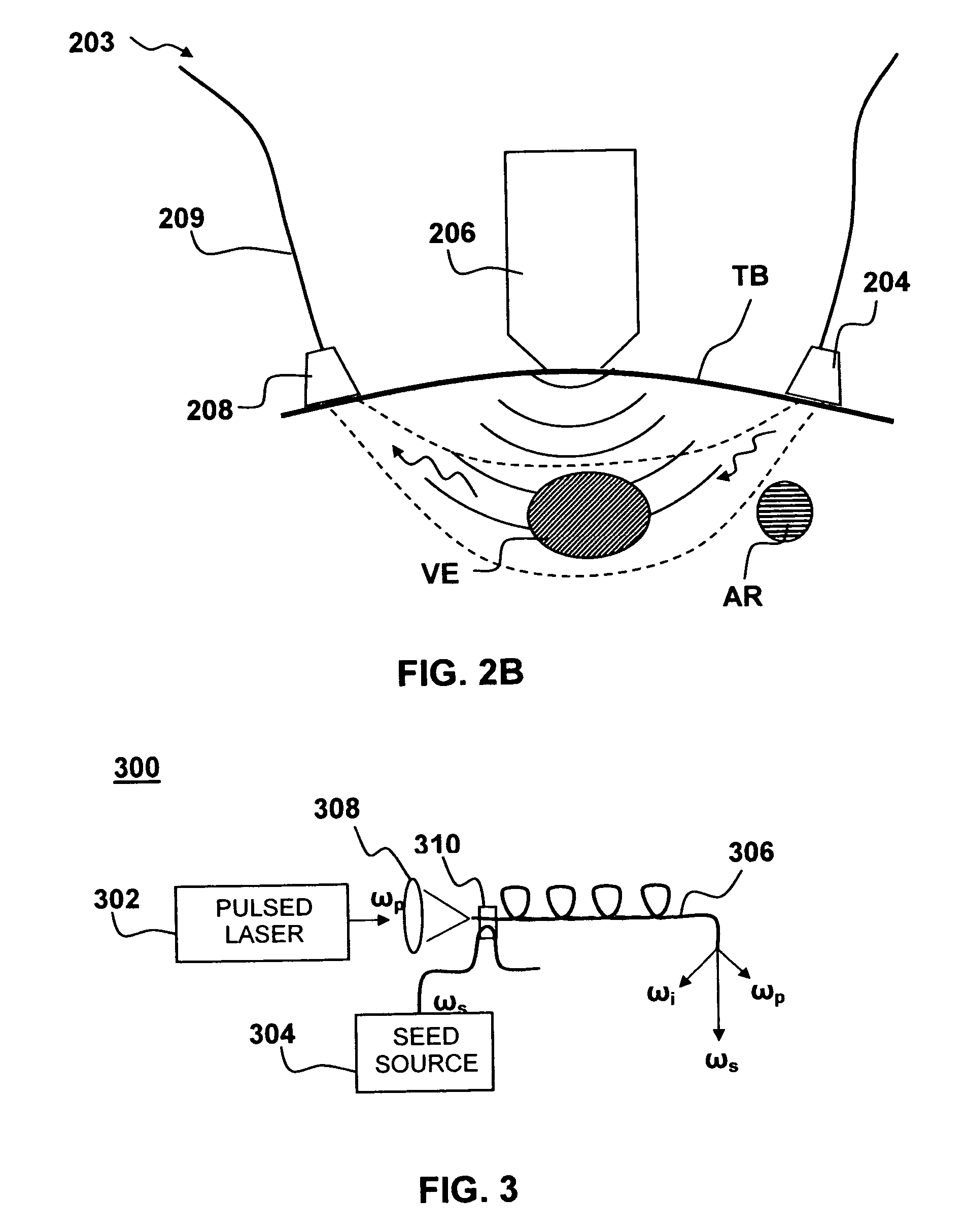
Medical diagnostic apparatus and methods are disclosed. Ultrasound radiation pressure selectively modulates a target area within a body. One or more pulses of radiation containing temporally correlated groups of photons are generated. The photons are characterized by two or more different wavelengths that are selected to have specific interaction with a target chromophore. The two or more different wavelengths are also selected to have substantially similar scattering cross-sections and anisotropy parameters in the target and its surroundings. The pulses of radiation are injected into the body proximate the target area being modulated by the radiation pressure field. Photon groups at each of the different wavelengths that are backscattered from the target area are detected in temporal coincidence. Time-gated background-free amplification of the return signal is used to exclude photons which could not by virtue of their arrival time have interacted with the radiation-pressure-modulated target. Photon groups are selected with a modulation component at the modulation frequency of the radiation pressure modulation field, or at a harmonic of the modulation frequency. From the arrival rate of the detected temporally correlated photon pairs or multiplets, chemical information about the target area, such as an oxygenation or pH level can be inferred. Cardiac output may be computed from measurements of venous and / or arterial oxygenation using this technique.
Owner:SKYLINE BIOMEDICAL
Optical waveguide grating coupler with varying scatter cross sections
ActiveUS7260293B1Reduce scatter cross-sectionCoupling light guidesScattering cross-sectionCurve shape
Various configurations of elongate scattering elements in an optical waveguide grating coupler for coupling light between a planar waveguide and an optical element such as an optical fiber, where the light may have a Gaussian intensity distribution. The elongate scattering elements are preferably curved, and in some embodiments, the scattering elements have elliptically curved shape. One or more of the elongate scattering elements may be segmented into various geometrical shapes, such as rectangular, square, circular and elliptical. The elongate scattering elements have at least one characteristic selected from the group consisting of grating width, height, spacing, depth and index of refraction forming the elongate scattering elements, where the magnitude of the at least one characteristic varies irregularly with position along the guiding portion of the optical waveguide grating coupler.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for color matching paints
InactiveUS6166814AScattering properties measurementsColor matchingScattering cross-sectionLight beam
A method for characterizing a coating comprising a pigment and metallic flakes, said method by directing beams of light toward a coating; measuring the reflectance of light from the coating at the specular angle; measuring the reflectance of light from the coating at one or moren on-specular angles; analyzing said measured light at the specular and non-specular angles as a function of wavelength; and determining the K / S of the pigment and the volume fraction of said metal flakes within the coating from the measurements of the specular and non-specular reflectance; wherein K is the absorption cross-section of the pigment multiplied by its volume concentration; and S is the scattering cross-section of the pigment multiplied by its volume concentration.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Electrically Large complex target and rugged face background composite electromagnetic scattering numerical value emulation method
InactiveCN101216556AElectromagnetic wave reradiation3D modellingScattering cross-sectionClassical mechanics
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar target monitor, in particular to a numerical simulation method of composite electromagnetic scattering of electric-large complex body target and coarse land-sea surface background. The method comprises the following steps of : respectively dividing a body target and a surface target into polygonal planar elements; respectively tracing the front incident direction and the inverse scattering direction with rays and recording rays of each order irradiating the scattering elements; constructing the tracing path by an arbitrary pair of front and back rays meeting at the same planar element or edge to form a scattering item by adopting the resolution of body target scattering element, or the edge physic-optics scattering or physical diffracting as well as the coarse surface element scattering and through the surface-body target scattering and interaction described by scattering ray tracing; and accumulating the scattering items of all planar elements to obtain the composite electromagnetic scattering of the body target and the surface target. The method can numerically simulate composite electromagnetic scattering or radar scattering cross section of a coarse land-sea surface background with complex shape, electric-large size and a three-dimensional body target at high speed and high efficiency.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome
InactiveCN102882002AReduce processing difficultyDoes not affect normal work scanningRadiating element housingsWaveguide type devicesScattering cross-sectionMicrowave
The invention discloses a composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome and relates to the technical field of microwaves. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome solves the problems that an existing radome is streamline in shape and cannot be spread to a plane, random preparation of an FFS (frequency selective surface) on the radome is difficult in process implementation, and FFS passband transmittance is low as incident angles of electromagnetic waves on the FFS are large. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome is prepared by embedding an inner Y-ring-unit frequency-selective-surface conical cover into an outer radome by the aid of special laminating equipment. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome has a band-pass filtering characteristic within a specific radar frequency range and good passband characteristics, is capable of efficiently transmitting through the working frequency range electromagnetic waves, reflects the out-of-band detection electromagnetic waves to a vast space according to the radome shape and reduces backward radar cross section so that invisibility of the radome is achieved. The composite frequency-selective-surface invisible radome can be used for invisibility of radomes of guided missiles and airplanes.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antenna for reducing radar scattering cross section
InactiveCN102176537ASimple structureEasy to processRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsCapacitanceScattering cross-section
The invention discloses an antenna for reducing a radar scattering cross section, aiming to solve the problem of large radar scattering cross section of the traditional microstrip antenna. The antenna comprises a dielectric slab (1), a microstrip radiating unit (2) and an earth plate (3), wherein the microstrip radiating unit is arranged at the upper surface of the dielectric slab, and the earth plate is arranged at the lower surface of the dielectric slab; both sides of the microstrip radiating unit are provided with a high impedance surface array (4) respectively; each high impedance surface array is formed by arranging a plurality of metal chips into a rectangle, a gap is arranged between the adjacent metal chips to form a capacitor C; the center of each metal chip is provided with a metal via hole which penetrates through the dielectric slab; a current path connected by the via holes can form an inductor L, and the capacitor and the inductor form an LC resonant circuit; the frequency of the resonant circuit can be adjusted to be coincident with the working frequency of the antenna, thus realizing scattered field compensation of the high impedance surface array and the antenna. The invention has stable performance of reducing radar scattering cross section within and outside the frequency band of the antenna, and also has no effect on the size, weight and cost of the antenna.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Array antenna used for reducing radar scattering cross section
InactiveCN102227040ASimple structureEasy to processWave based measurement systemsAntenna arraysCapacitanceMicrostrip array antenna
The invention discloses an array antenna used for reducing radar scattering cross section, and mainly solves a problem of large scattering cross section of a present microstrip array antenna radar. The array antenna in the invention comprises a medium plate, a ground plate and n microstrip radiation units (2). The n microstrip radiation units (2) are on the upper surface of the medium plate (1). The ground plate (3) is on the lower surface of the medium plate (1). Structural type absorbing material arrays (4) are provided between each two adjacent microstrip radiation units, and N*M square metal pasters (5) are arranged as rectangular. The metal pasters (5) form inductances L. Connection resistors (7) connect adjacent metal pasters to form resistors R. Gap (6) between adjacent metal pasters (5) form capacitors C. The capacitors C, the inductances L and the resistors R form RLC resonance circuits. By adjusting resonance circuits frequency to superpose the resonance circuits frequency with antenna work frequency, absorption of vertical incident surface wave is realized. The array antenna used for reducing radar scattering cross section in the invention has the advantages of stable performance of reducing in-band and outband radar scattering cross sections of antenna and no influence on antenna volume, weight and cost.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Radiation and scattering integrated information metamaterial surface and application thereof
PendingCN110504550AReduced Scattering Cross SectionAddress limitationsWave based measurement systemsAntenna arraysPhysical spaceScattering cross-section
The invention discloses a radiation and scattering integrated information metamaterial surface. The information metamaterial surface is composed of periodically or non-periodically arranged artificialelectromagnetic structural units, and has the ability of radiation electromagnetic field / wave regulation and scattering electromagnetic field / wave regulation, the unit constituting the information metamaterial surface has at least 1-bit unit code element, and the information metamaterial surface can be regulated within at least one electromagnetic physical domain. The information metamaterial surface solves the limitation that traditional metasurfaces are only used in the field of scattering or radiation, meanwhile has the ability to regulate and control electromagnetic waves in time-space-frequency-polarization and other multidimensional electromagnetic physical spaces in real time, that is, has more powerful comprehensive control capability, and has broad application prospects in high-performance antennas, smart antennas, new-system radars, new-system communication systems, and reduction of radar scattering cross sections, etc.
Owner:JIANGSU EMETASPACE TECH CO LTD
Digital programmable super surface
ActiveCN104078771AFlexible designCoding is real-time controllableAntenna arraysScattering cross-sectionRadar
The invention discloses a digital programmable super surface. The digital programmable super surface is composed of a digital control unit and a controlled artificial electromagnetic surface, wherein the artificial electromagnetic surface is formed by artificial unit structures periodically arrayed, a switching diode is integrated in each artificial unit structure, the artificial unit structures can present two different electromagnetic characteristics under two different bias voltages, and namely each unit structure can be switched between two electromagnetic states in real time. The switching is realized through the bias voltages provided by the digital control part, the different bias voltages can be provided for the different unit structures, the artificial surface can achieve different electromagnetic functions, and each function corresponds to a set of control codes of the digital control unit. The digital programmable super surface has the advantages of being simple in design process, flexible, easy and convenient to use, and easy to machine and has important application prospects in high-performance antennas and the aspect of reducing a radar scattering cross section.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Sequencing single molecules using surface-enhanced Raman scattering
InactiveUS20080239307A1Simple designRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansScattering cross-sectionElectric field
A surface-enhanced Raman scattering method and apparatus to sequence polymeric biomolecules such as DNA, RNA, or proteins is introduced. The method uses metallic nanostructures such as, for example, spherical or cylindrical Au or Ag nanoparticles having characteristic lengths of 10-100 nm which when illuminated with light of the appropriate wavelength produce resonant oscillations of the conduction electrons (plasmon resonance). Electric field enhancements of 30-1000 near the particle surface resulting from such oscillations increase Raman scattering cross-sections by about 106-1015 due to the E4 dependence of the Raman scattering, wherein the largest enhancements occur in the gap / junction between novel closely spaced structures as disclosed herein.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
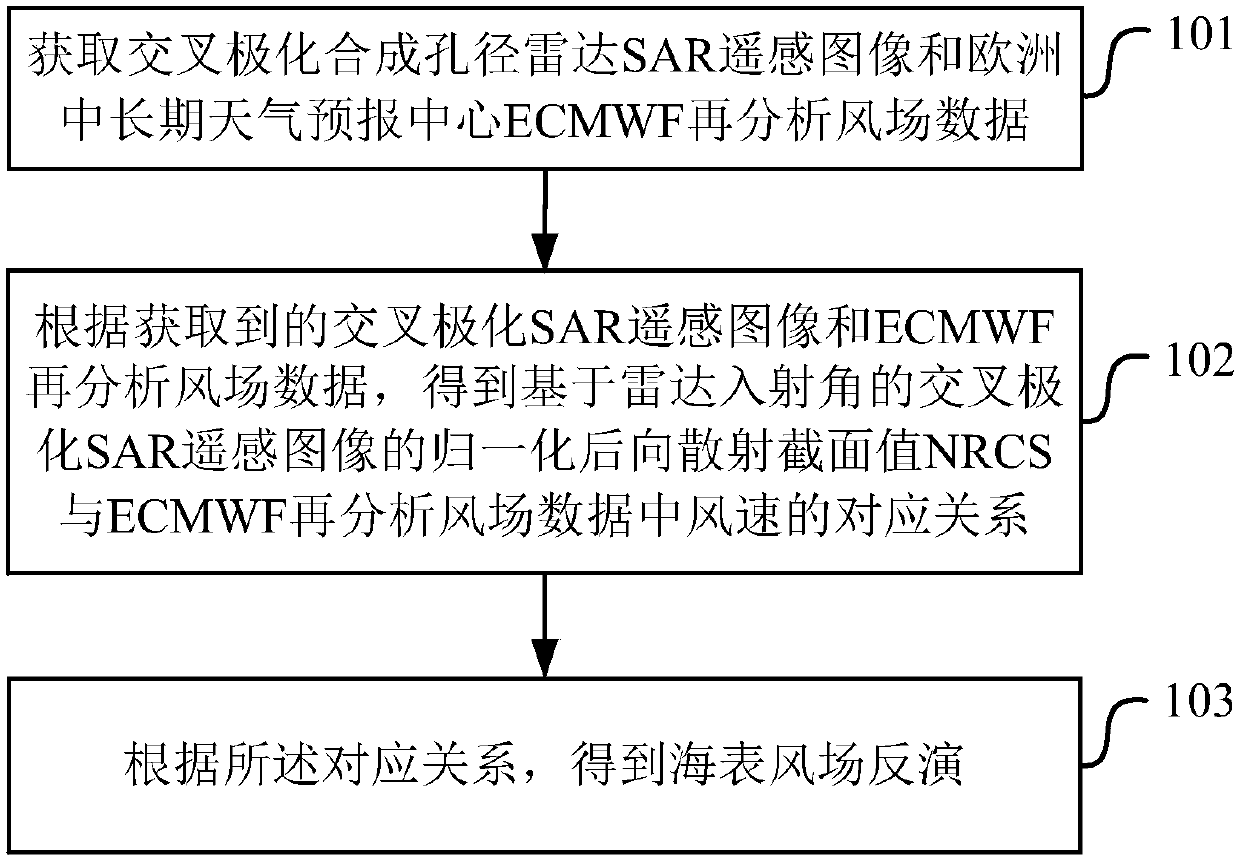
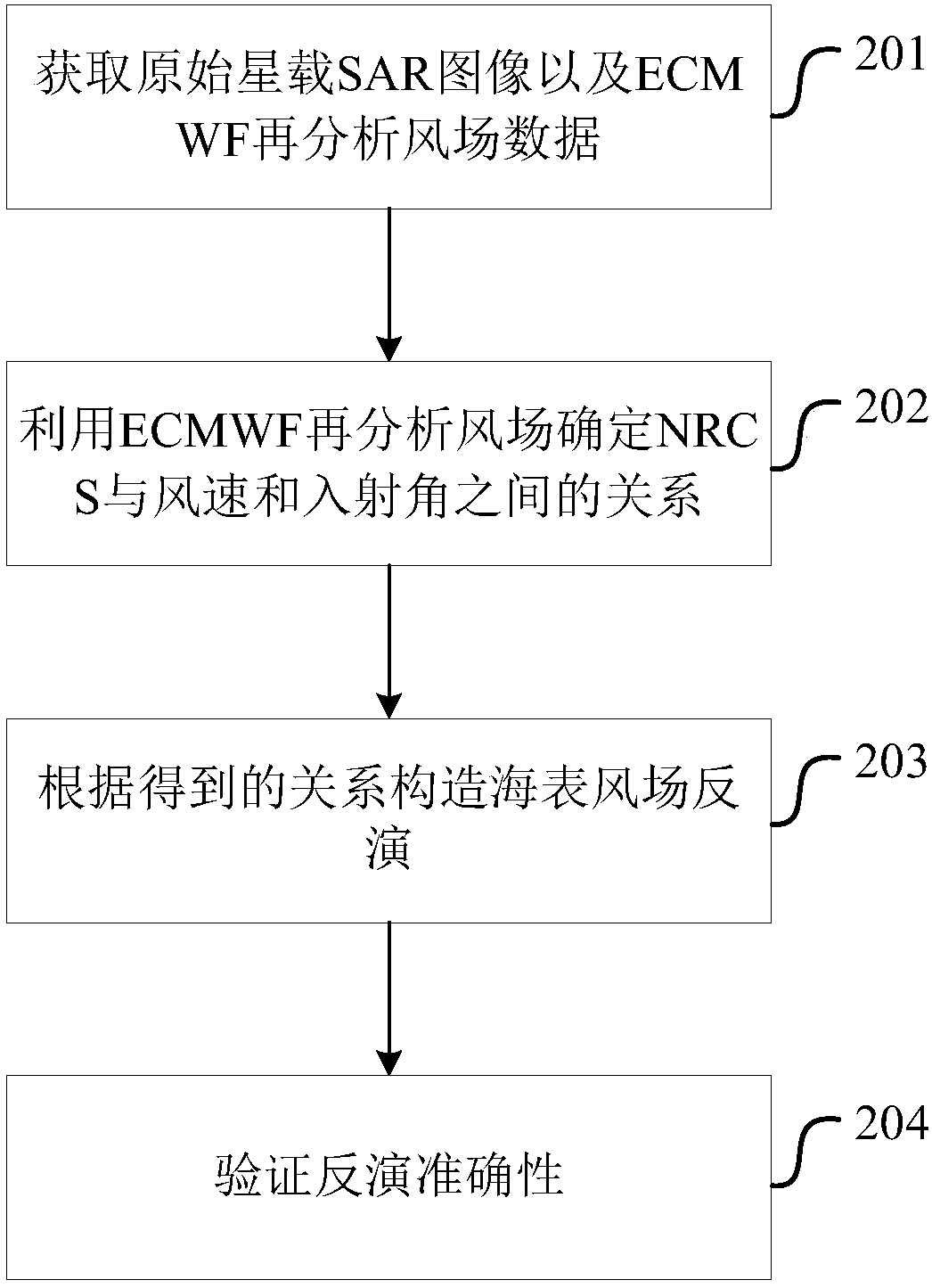
Sea surface wind field inversion method and device
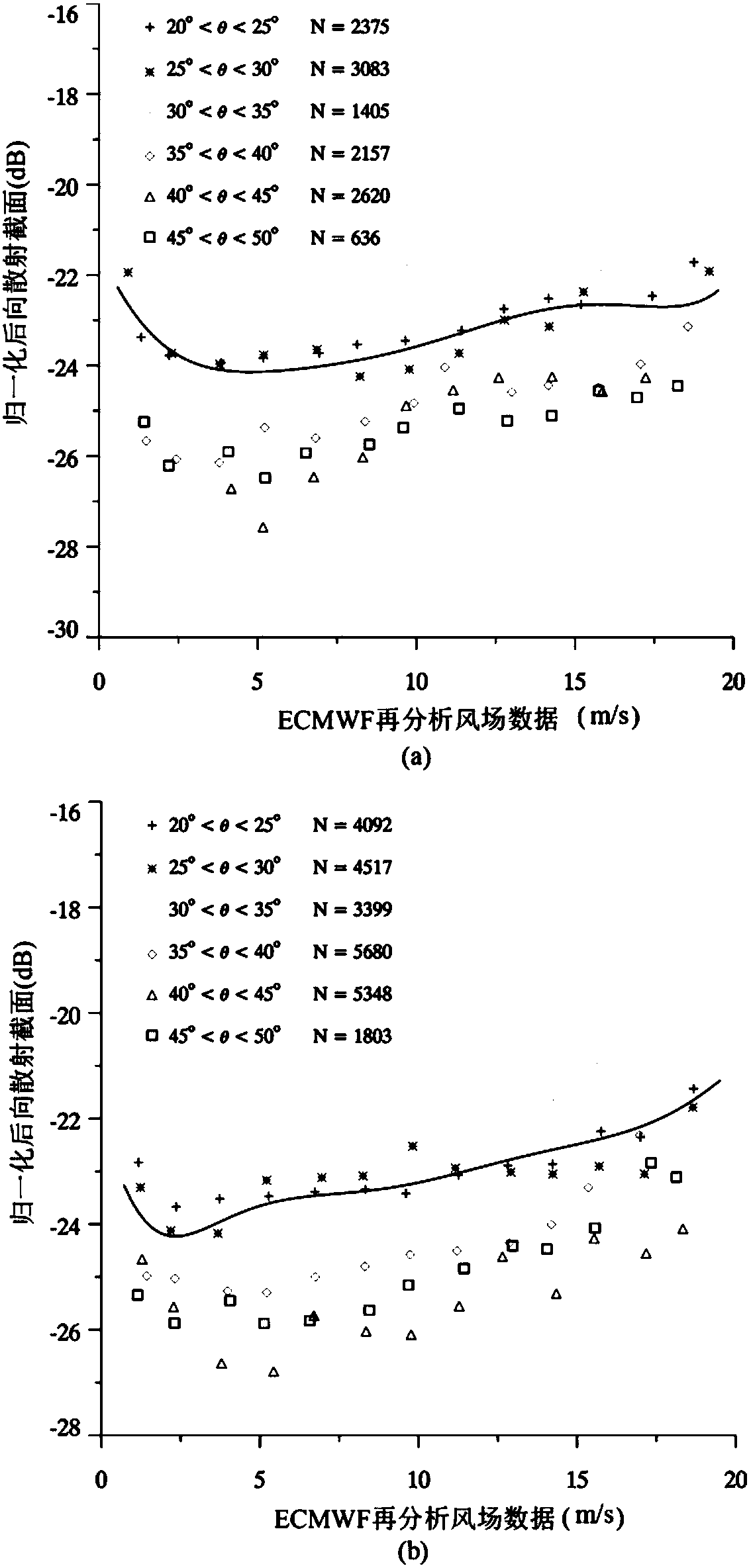
InactiveCN107748360ARadio wave reradiation/reflectionScattering cross-sectionSynthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a sea surface wind field inversion method and device and belongs to the technical field of a synthetic aperture radar. The method comprises steps that a cross polarization synthetic aperture radar (SAR) remote sensing image and European medium and long term weather forecast center (ECNWF) re-analysis wind field data are acquired; according to the acquired cross polarizationSAR remote sensing image and the ECNWF re-analysis wind field data, the corresponding relationship between a normalization backward scattering cross section value NRCS of the cross polarization SAR remote sensing image based on a radar incidence angle and the wind speed of the ECNWF re-analysis wind field data is acquired; sea surface wind field inversion is acquired according to the correspondingrelationship. The method is advantaged in that sea surface wind field inversion can be carried out without the auxiliary wind direction information, and sea surface wind field inversion of the synthetic aperture radar remote sensing image based on the cross polarization mode is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Optical waveguide grating coupler with varying scatter cross sections
ActiveUS7260289B1Reduce scatter cross-sectionCoupling light guidesScattering cross-sectionCurve shape
Various configurations of elongate scattering elements in an optical waveguide grating coupler for coupling light between a planar waveguide and an optical element such as an optical fiber, where the light may have a Gaussian intensity distribution. The elongate scattering elements are preferably curved, and in some embodiments, the scattering elements have elliptically curved shape. One or more of the elongate scattering elements may be segmented into various geometrical shapes, such as rectangular, square, circular and elliptical. The elongate scattering elements have at least one characteristic selected from the group consisting of grating width, height, spacing, depth and index of refraction forming the elongate scattering elements, where the magnitude of the at least one characteristic varies irregularly with position along the guiding portion of the optical waveguide grating coupler.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
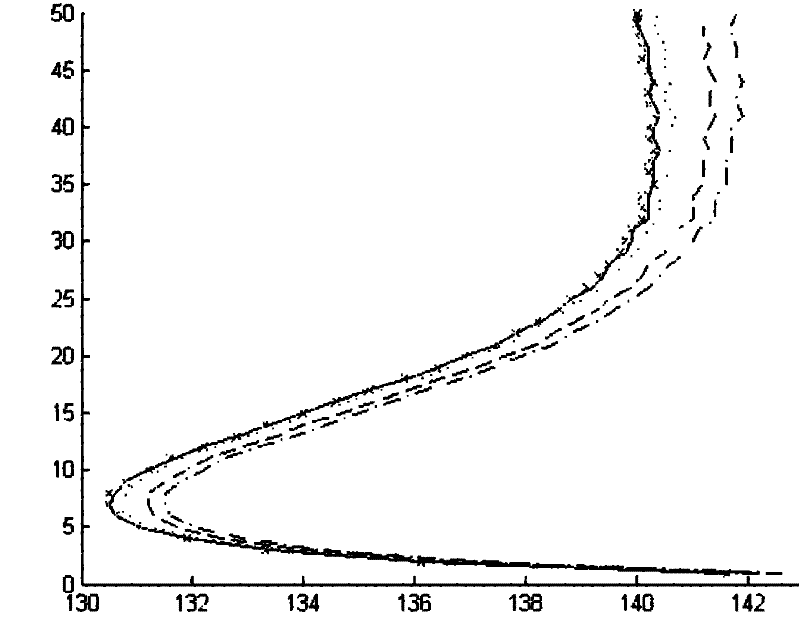
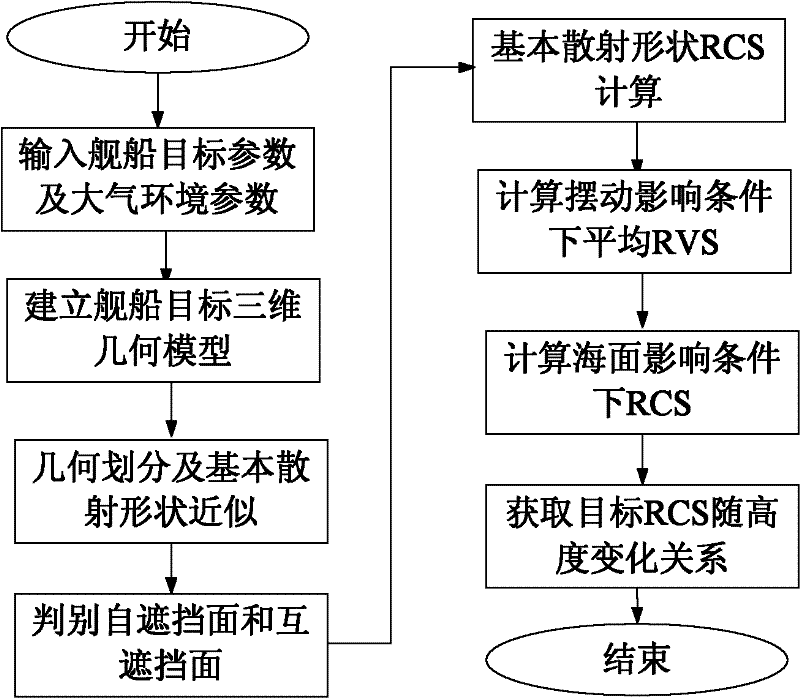
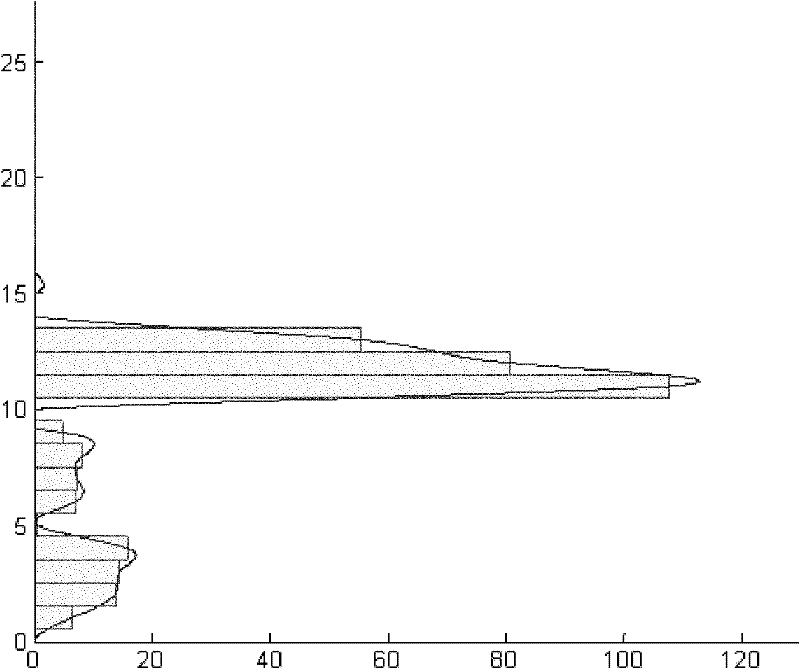
Radar cross-section layered calculation method of ship target within atmospheric duct range
InactiveCN102226840ALower requirementSmall amount of calculationWave based measurement systemsHorizonScattering cross-section
The invention discloses a radar cross-section (RCS) layered calculation method of a ship target within an atmospheric duct range. According to the invention, after partition of a three-dimensional geometric model of a ship target, most similar basic geometrical shapes of the all partitioned parts of the three-dimensional geometric model are selected and are approximated as basic scatterers; geometric information of all basic scatterers are extracted and RCSs of the all basic scatterers are calculated; Change relations of RCS values of all parts of the ship target at different heights are calculated by combining heights of all parts of the ship target; and scattering power intensity of the ship target is calculated according to a transmission factor of an electromagnetic wave of an atmospheric duct. According to the RCS calculation method of the ship target within the atmospheric duct range provided in the invention, computational complexity and requirements for computing equipment canbe substantially reduced and real-time calculation is allowed. Besides, an influence of up-and-down sea surface on transmission of an electromagnetic wave is fully considered, and a calculation result is more reasonable and effective. The method provided in the invention has important military significances for technological development, equipment update, and operational application of microwave beyond-the-horizon radar.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
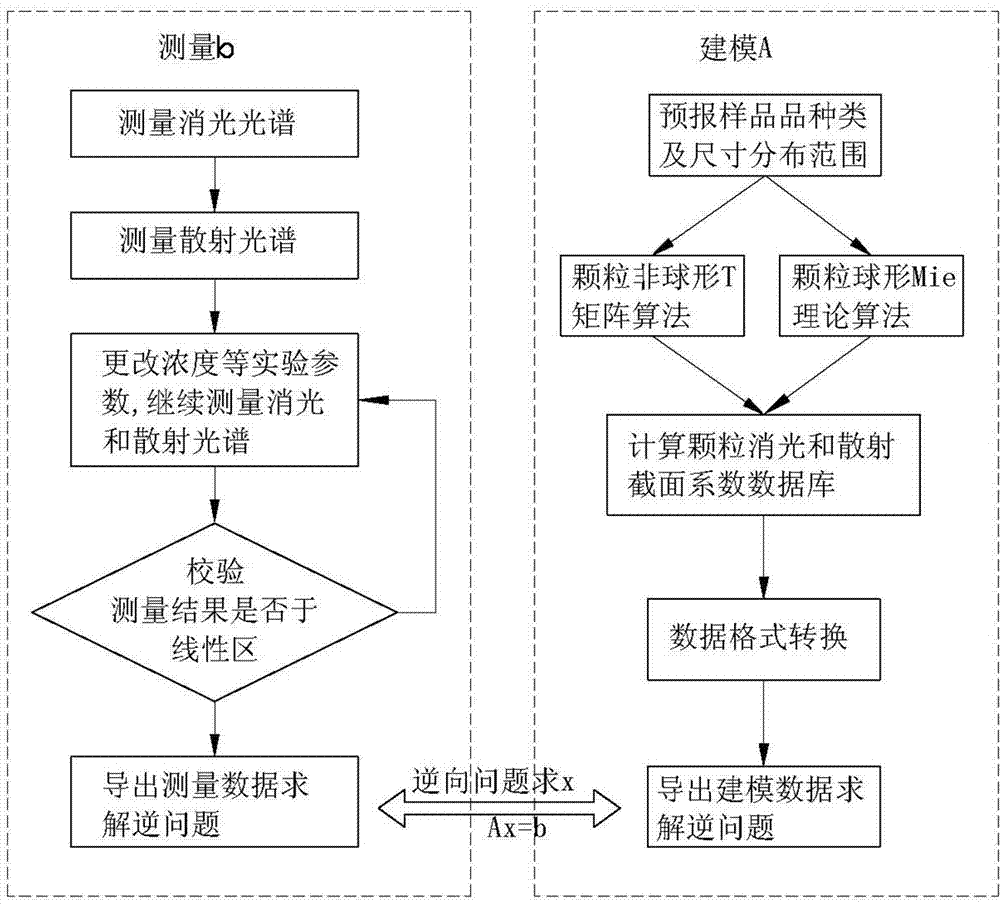
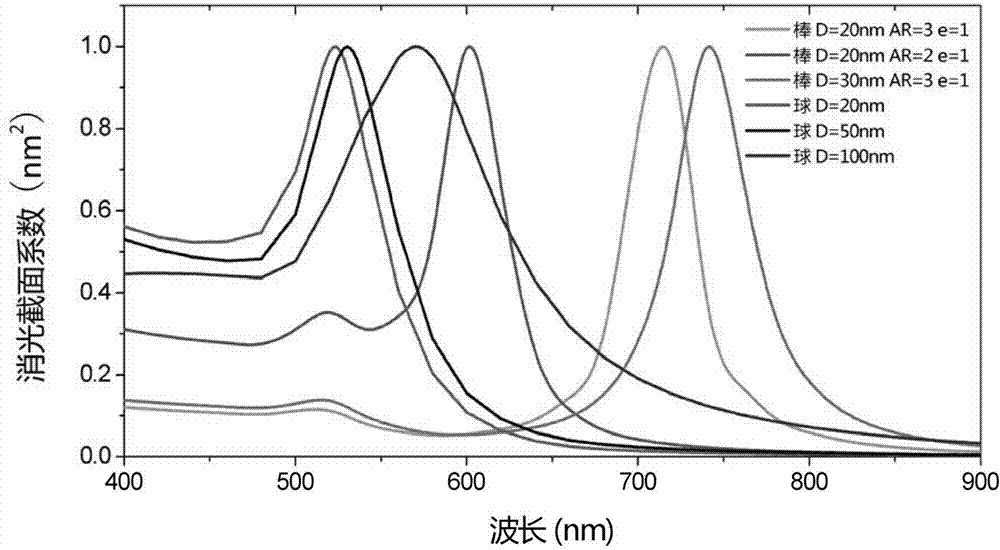
Method for measuring key geometrical characteristics of nanometer particles
ActiveCN103499521AQuick measurementAccurate and stable measurementParticle size analysisScattering cross-sectionNanoparticle
A provided method for measuring key geometrical characteristics of nanometer particles comprises the following steps: loading the nanometer particles on a sample pool to obtain an extinction spectrum of the nanometer particles; arranging a mixed solution containing the nanometer particles in a referential sample pool and the sample pool for measuring to obtain a scattered spectrum of the nanometer particles; changing the concentration and the optical path length of metal nanometer particles, repeating the above steps, exporting measured data according with a linear response zone; pre-estimating the kinds of the key geometrical characteristics contained by the nanometer particles and the geometrical scale distribution scope; establishing databases of the relationship about the key geometrical characteristics with the extinction section coefficient and with the scattering cross-section coefficient; respectively converting the databases of the relationship about the key geometrical characteristics with the extinction cross-section coefficient and with the scattering section coefficient into matrixes, and converting the inverse problem into a linear equation group; and solving according to the databases of the extinction spectrum, the scattered spectrum and the extinction cross-section coefficient and the database of the scattering cross-section coefficient, to obtain the key geometrical characteristics of the nanometer particles.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Light Guide Member, Planar Lighting Device Using the Same, and Rod-Type Lighting Device
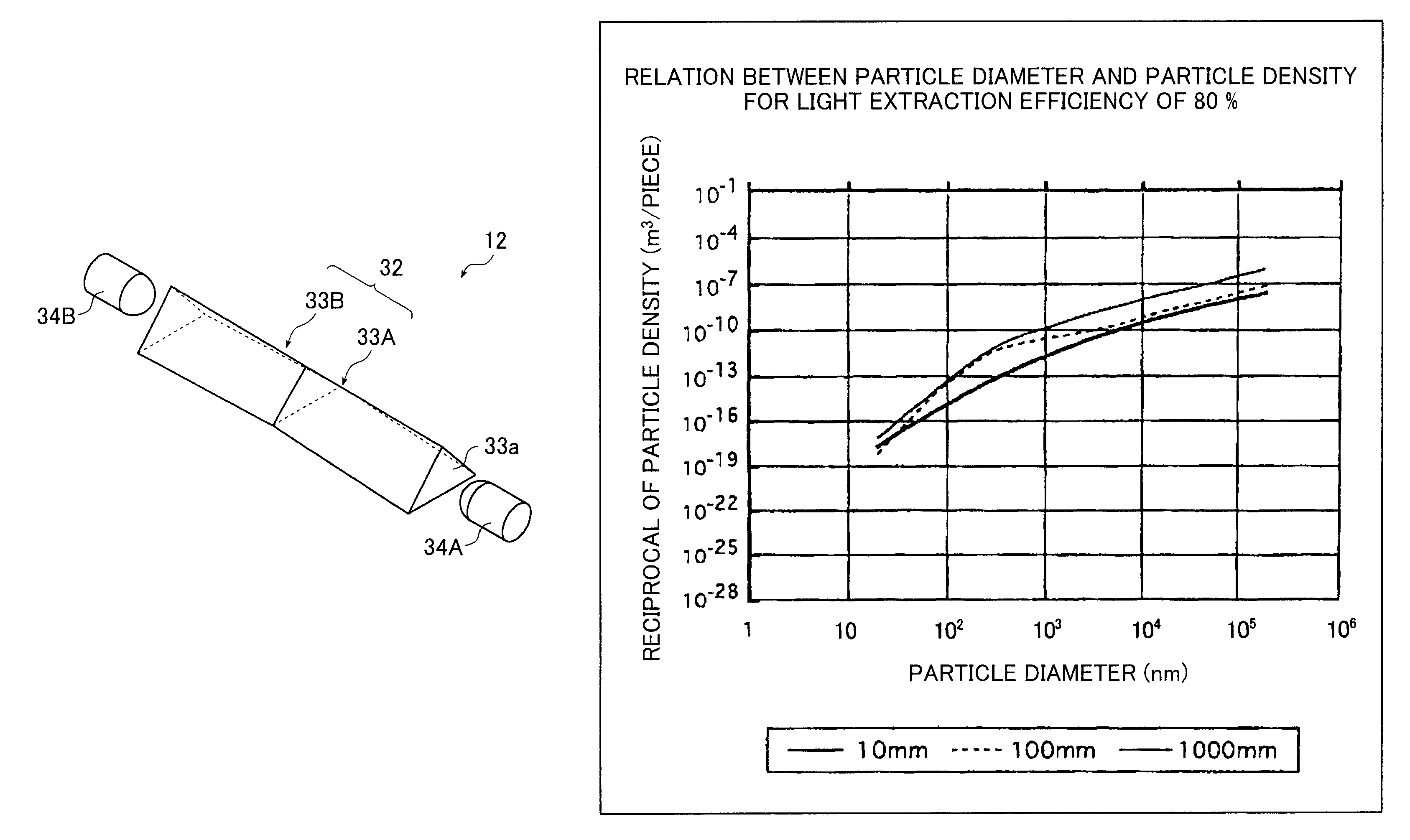
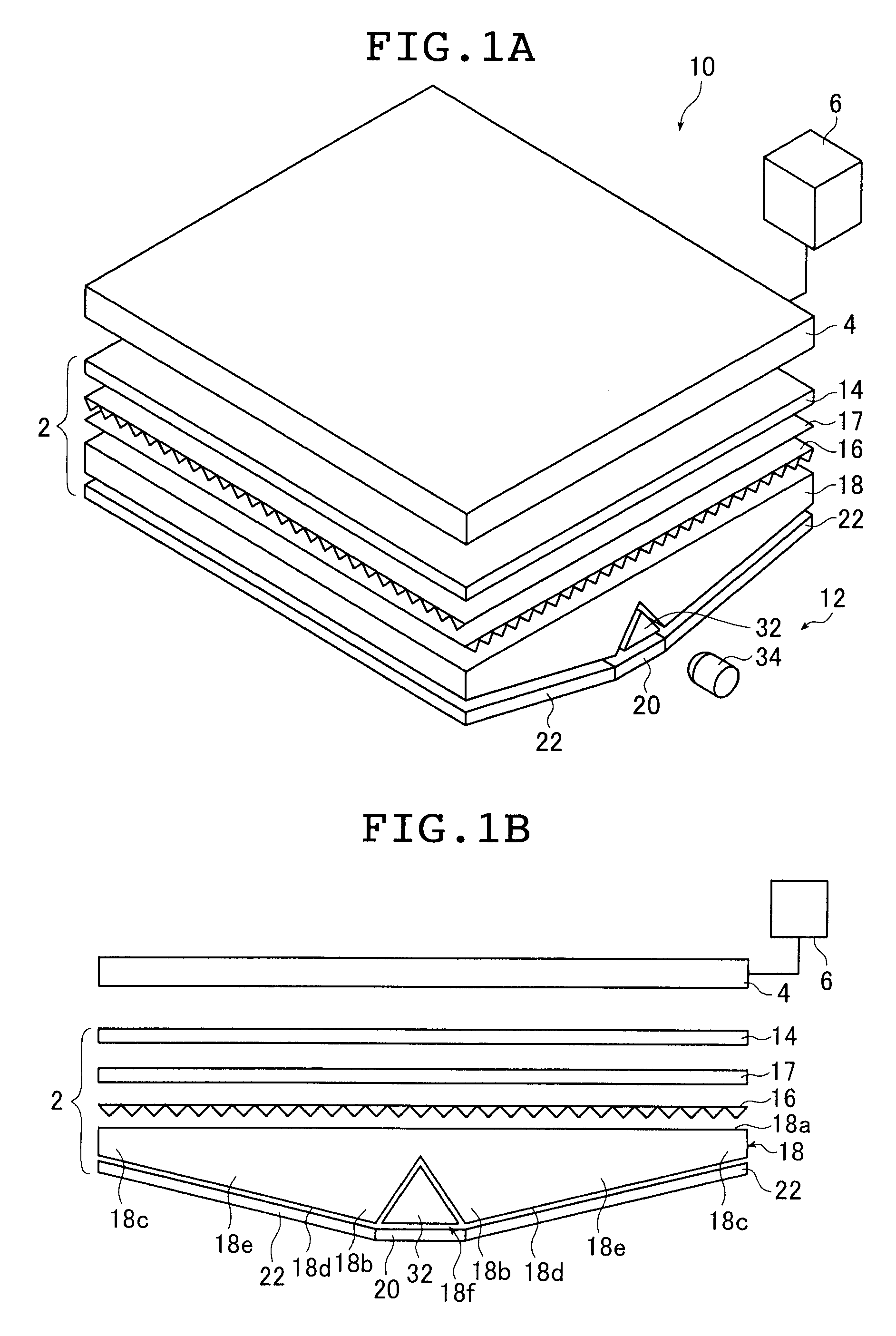
ActiveUS20090147537A1Reduce designSolve the thickerMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesScattering cross-sectionLight guide
A transparent light guide member comprising a first light guide unit in the form of a transparent plate having a rectangular light emitting plane and a parallel groove formed on a rear surface located opposite from the rectangular light emitting plane and parallel to one side of the rectangular light emitting plane; and a second light guide unit, which is transparent, having a columnar external shape to be accommodated in the parallel groove and containing light-scattering particles. Let Φ be the scattering cross section of the particles, LG the length of the light guide unit 32 in the direction in which light propagates, Np the particle density, and KC a compensation coefficient, then a value Φ·LG·Np·KC the light guide member assumes is not smaller than 1.1 and not greater than 8.2, and the compensation coefficient KC is not smaller than 0.005 and not greater than 0.1.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
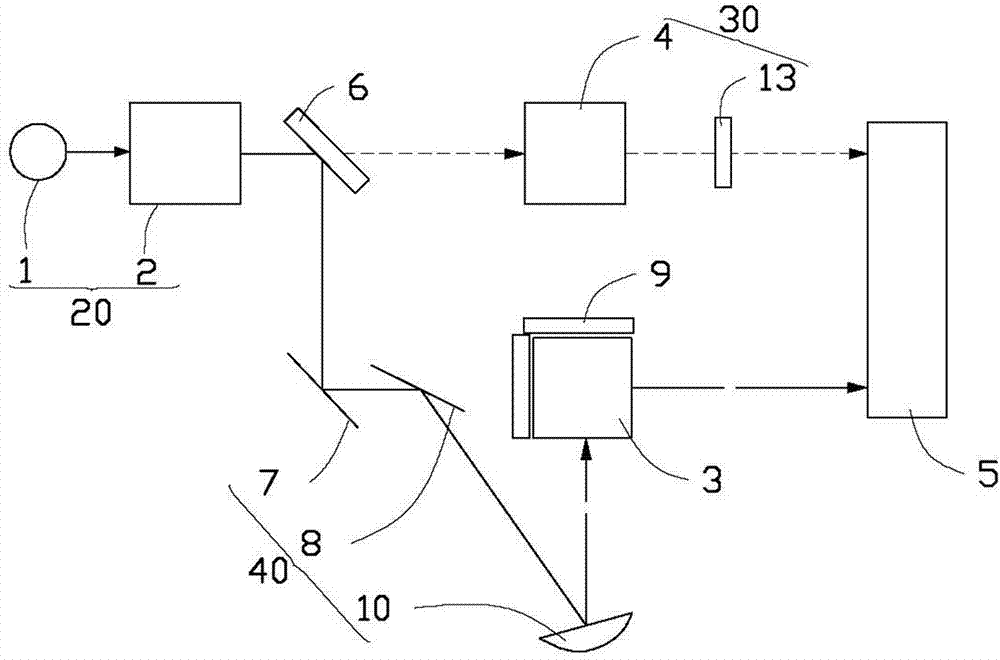
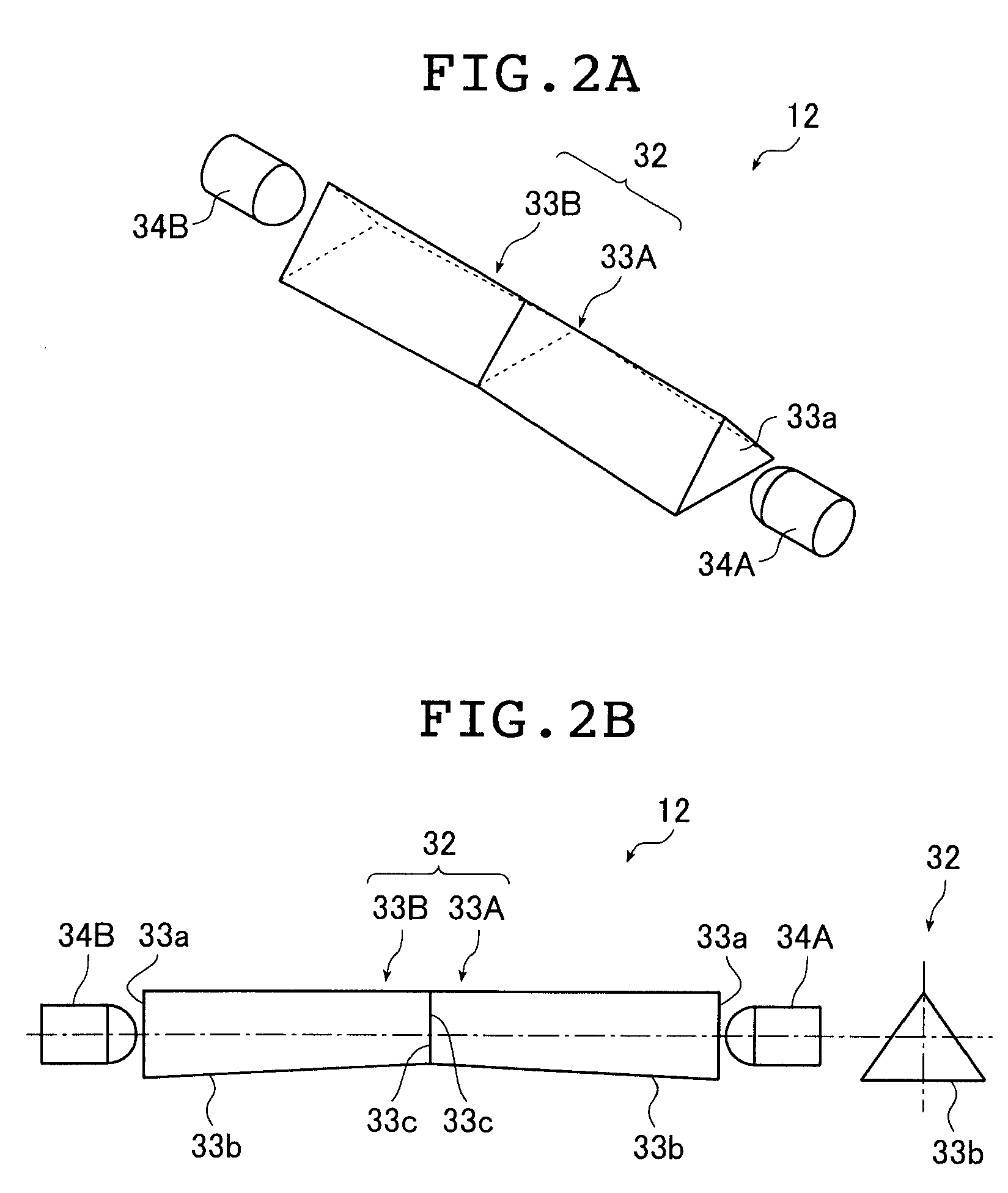
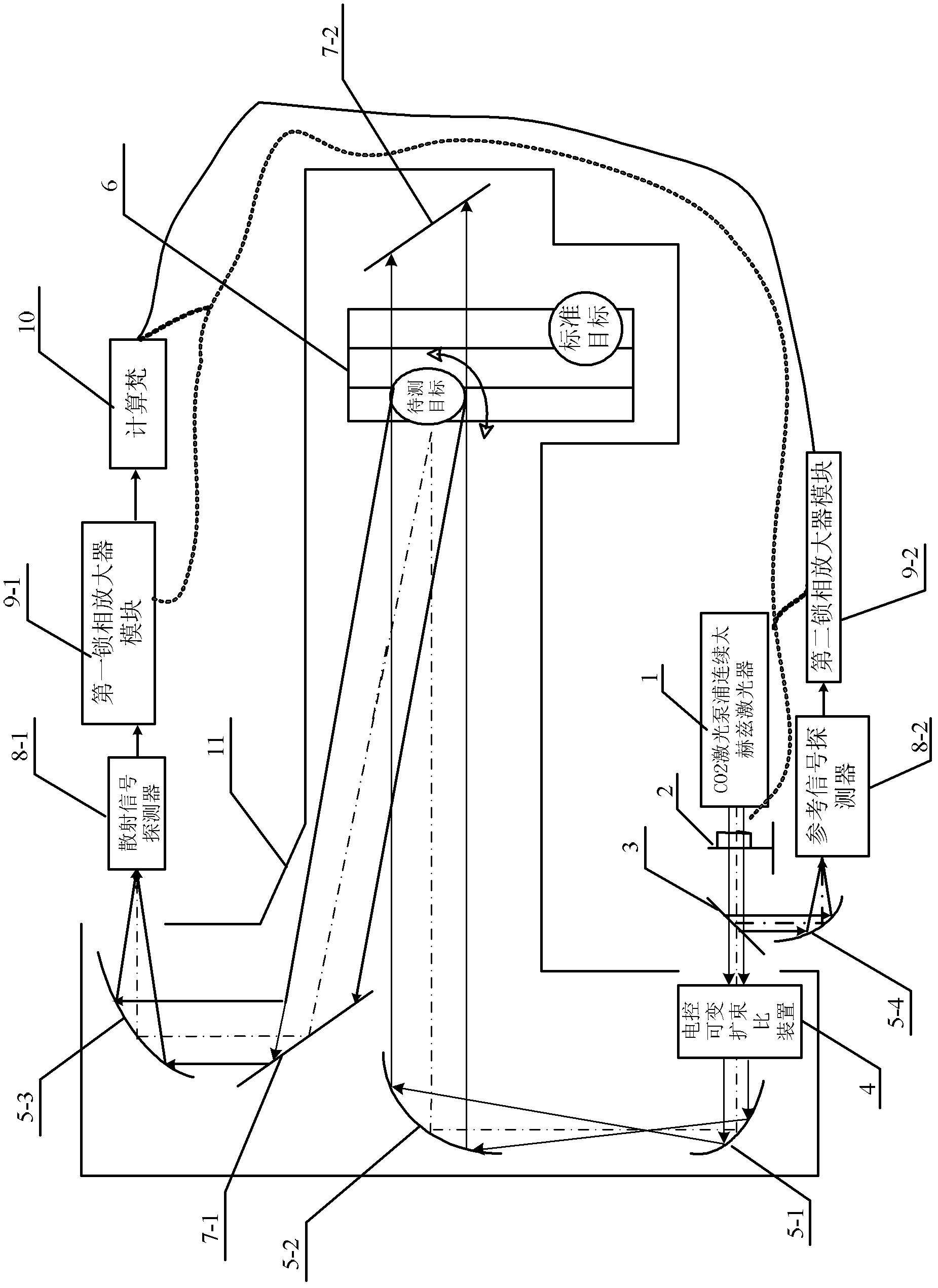
RCS (radar cross section) measurement device based on single continuous terahertz laser source
ActiveCN102435987ARelatively smallSimple structureWave based measurement systemsBeam splitterMeasurement device
The invention relates to an RCS (radar cross section) measurement device based on a single continuous terahertz laser source and belongs to the technical field of terahertz RCS measurement. The RCS measurement device can be used for solving the problem in measuring the RCS of target radars of different sizes in a 2.52THz waveband. The RCS measurement device comprises a CO2 laser pumping continuous terahertz laser, a chopper, a beam splitter, an electrical control variable expansion ratio device, a P3 off-axis parabolic mirror, a P2 off-axis parabolic mirror, a precise movement platform, an M1total reflector, a P1 off-axis parabolic mirror, a scattered signal detector, a first lock-in amplifier module, a computer and a chopper driver. The RCS measurement device is suitable for RCS measurement on the target radars of different sizes.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and system for extracting radar scattering feature data based on plasma near-field testing
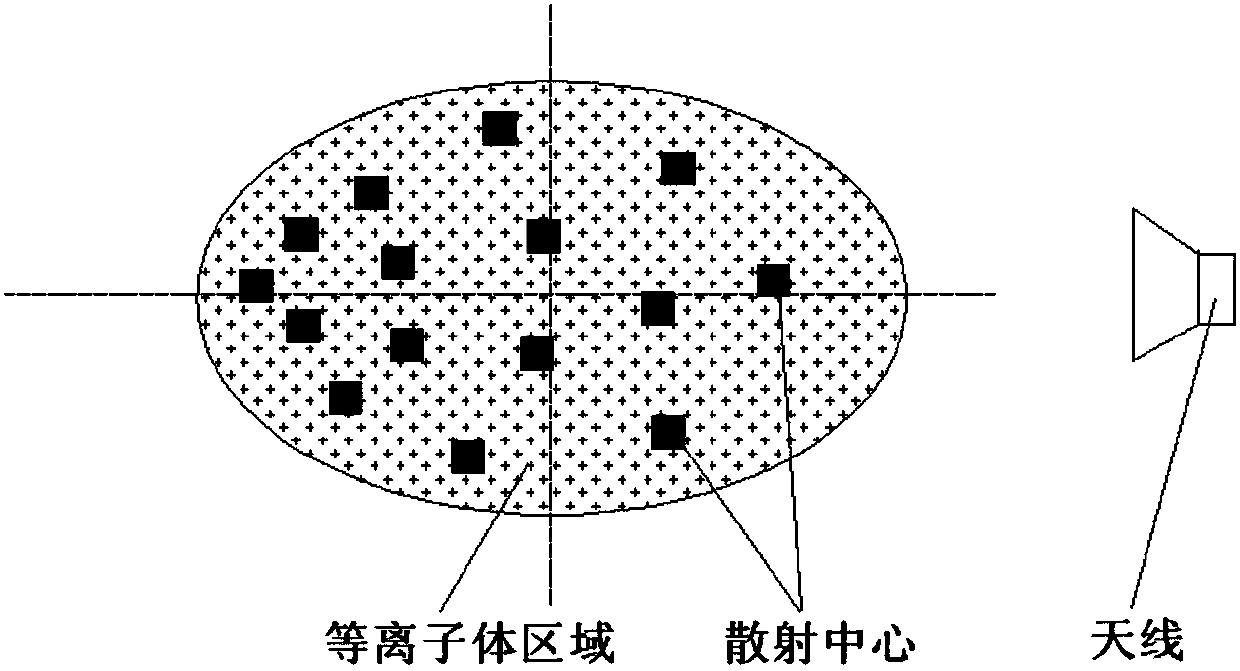
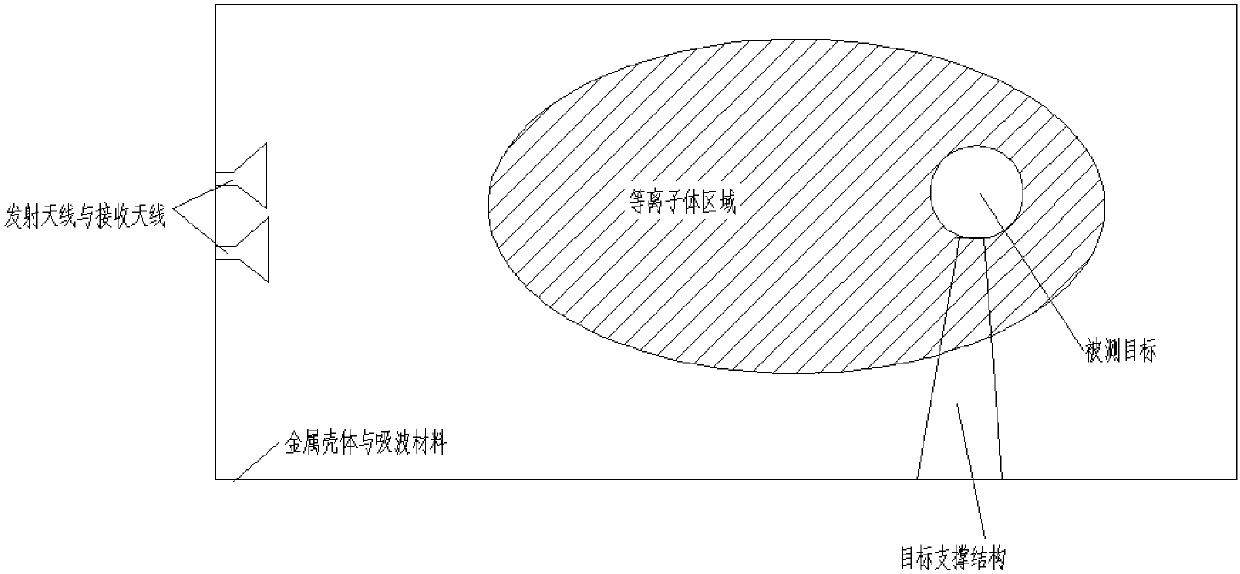
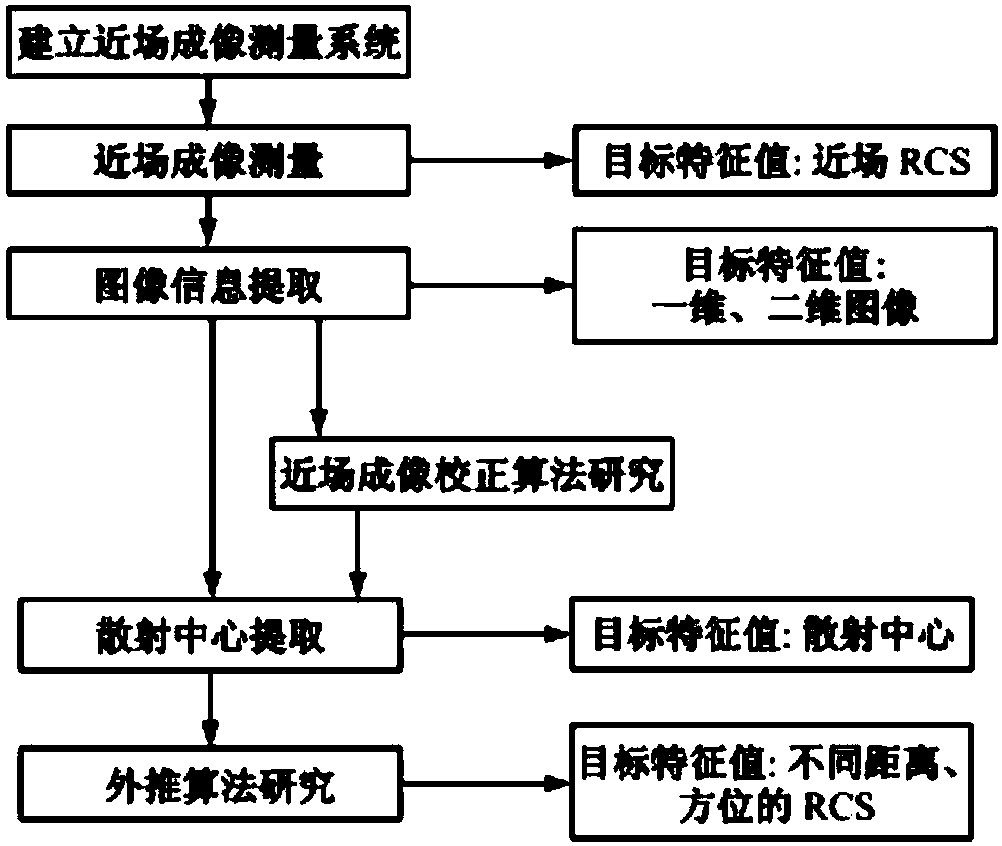
ActiveCN107942330ARealize generationImplementing Scattering Cross Section Performance TestingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionScattering cross-sectionTechnology research
A method and system for extracting radar scattering feature data based on plasma near-field testing are disclosed. An ISAR imaging principle is adopted in a microwave anechoic chamber simulating vacuum environment, and a one-dimensional scanning near-field test method is employed to test scattering performance of a tested target. A near-field scattering 2D image of the tested target is obtained, and near-field correction techniques are used to correct errors of influence error exerted by spherical waves on RCS performance tests. A scattering center is adopted to achieve far-field RCS extrapolation of the tested target, and radar scattering cross section far field data of the test target is obtained. Via the test and the data extraction method, overall target radar cross section data of a plasma-coated aircraft can be provided for a special environment that generates plasma clouds and for peculiar diffusion and ionization characteristics of plasma. A test angle covers a wide angle rangeof -30 degrees to 30 degrees, test accuracy is higher than 2dB, and therefore a test method is provided for plasma stealth technology research and stealth performance evaluation.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE INST OF THE LONG MARCH VEHICLE +1
Ultra-wideband full polarization full-angle rotating parabolic gradient electromagnetic stealth super-surface and design method thereof
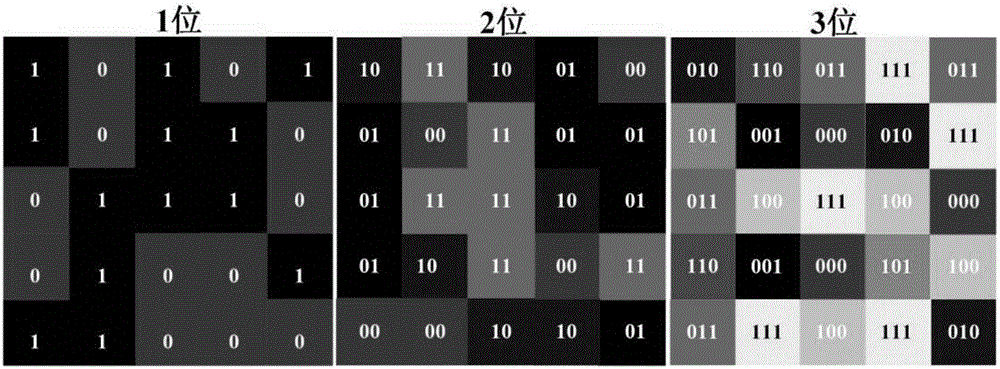
ActiveCN106410425ASolve the problem of full-angle electromagnetic stealthImprove robustnessAntennasUltra-widebandScattering cross-section
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar scattering cross section shrinkage stealth, and in particular relates to an ultra-wideband full polarization full-angle rotating parabolic gradient electromagnetic stealth super-surface and a design method thereof. According to the invention, the electromagnetic stealth device is a rotational parabolic gradient digital super-surface of a finite size, and consists of L*M parabolic gradient modules (subarrays) with the same cycle but different phases, wherein the modules are arranged according to a random sequence; a 1-bit digital super-surface, a 2-bit digital super-surface and a 3-bit digital super-surface are comprised; and the modules consist of basic units. The design method comprises the steps of the design of the topology and phase distribution of each module in the multi-bit rotational parabolic gradient digital super-surface, the design of the ultra-wideband unit structure of the multi-bit rotational parabolic gradient digital super-surface, and the modeling of the multi-bit rotational parabolic gradient digital super-surface. The electromagnetic stealth super-surface provided by the invention has the excellent characteristics of good robustness, super-wide working bandwidth, thin thickness, easy processing and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Light guide member, planar lighting device using the same, and rod-type lighting device
ActiveUS7614775B2Reduce designSimple structurePlanar/plate-like light guidesOptical waveguide light guideScattering cross-sectionLight guide
A transparent light guide member comprising a first light guide unit in the form of a transparent plate having a rectangular light emitting plane and a parallel groove formed on a rear surface located opposite from the rectangular light emitting plane and parallel to one side of the rectangular light emitting plane; and a second light guide unit, which is transparent, having a columnar external shape to be accommodated in the parallel groove and containing light-scattering particles. Let Φ be the scattering cross section of the particles, LG the length of the light guide unit 32 in the direction in which light propagates, Np the particle density, and KC a compensation coefficient, then a value Φ·LG·Np·KC the light guide member assumes is not smaller than 1.1 and not greater than 8.2, and the compensation coefficient KC is not smaller than 0.005 and not greater than 0.1.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Light diffusing body and a transmission type screen
ActiveUS20070190291A1Reduce relative shiftLow costPrismsDiffusing elementsScattering cross-sectionRefractive index
A light diffusing body and transmission type screen, which can reduce the shift of the color tone of the light source light seen through the light diffusing body and prevent the phenomenon that the white light source seen through the light diffusing body looks colored, is provide.The light diffusing body 1 of the present invention comprises a transparent resin and spherical micro-particles having a different refractive index from that of the said transparent resin, wherein the relation between the maximum value (Emax) and the minimum value (Emax) of the effective scattering efficiency values (E) obtained for each center wavelength in the wavelength ranges of blue, green and red by dividing the sum of scattering cross-sections of all spherical micro-particles contained in the unit area of the aforementioned light diffusing body 1 by the sum of geometrical cross-sections of all these spherical micro-particles satisfies Emin / Emax≧0.90.
Owner:KIMOTO CO LTD
Target-body radar scattering cross section obtaining method and device based on darkroom frequency sweep
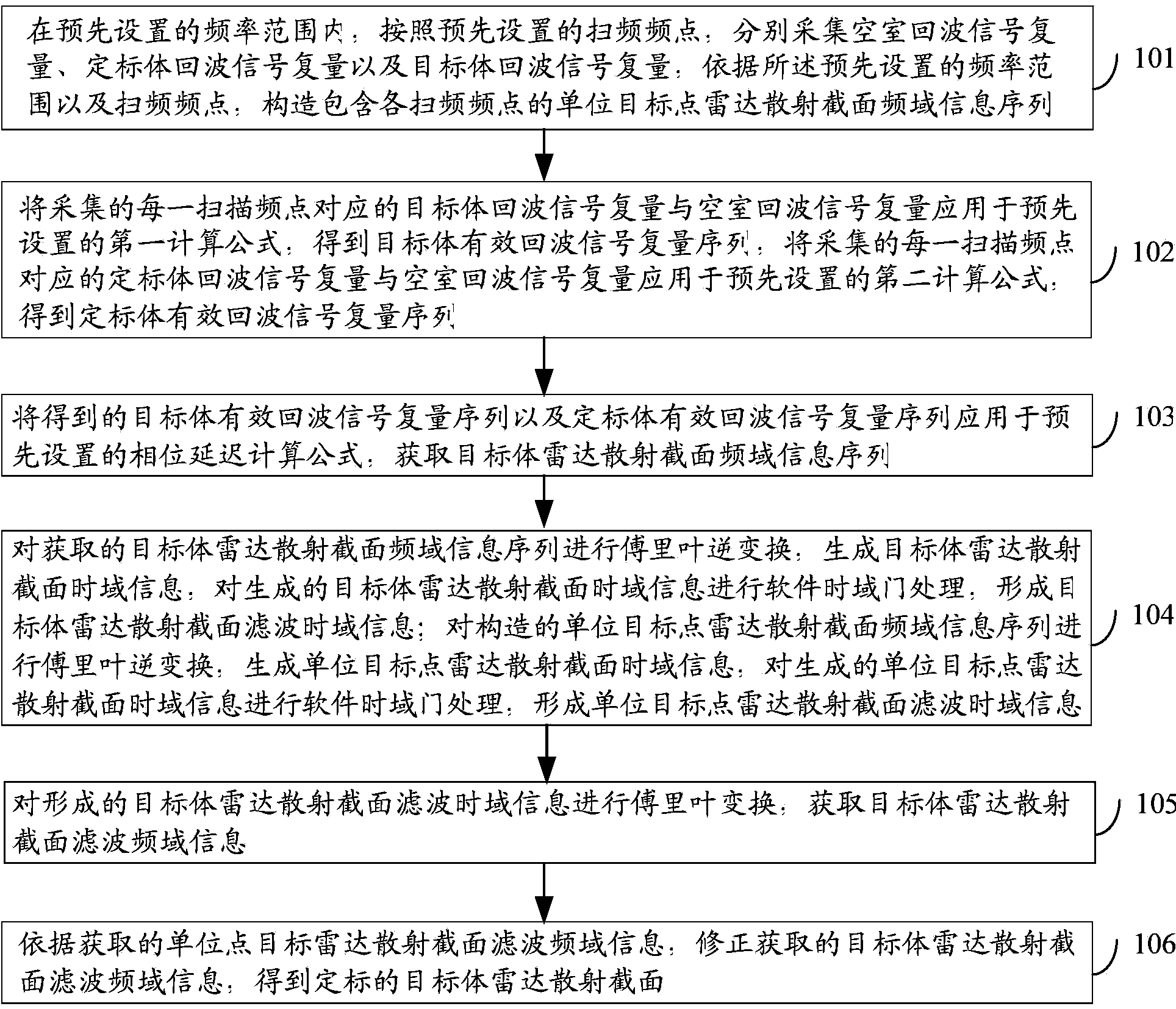
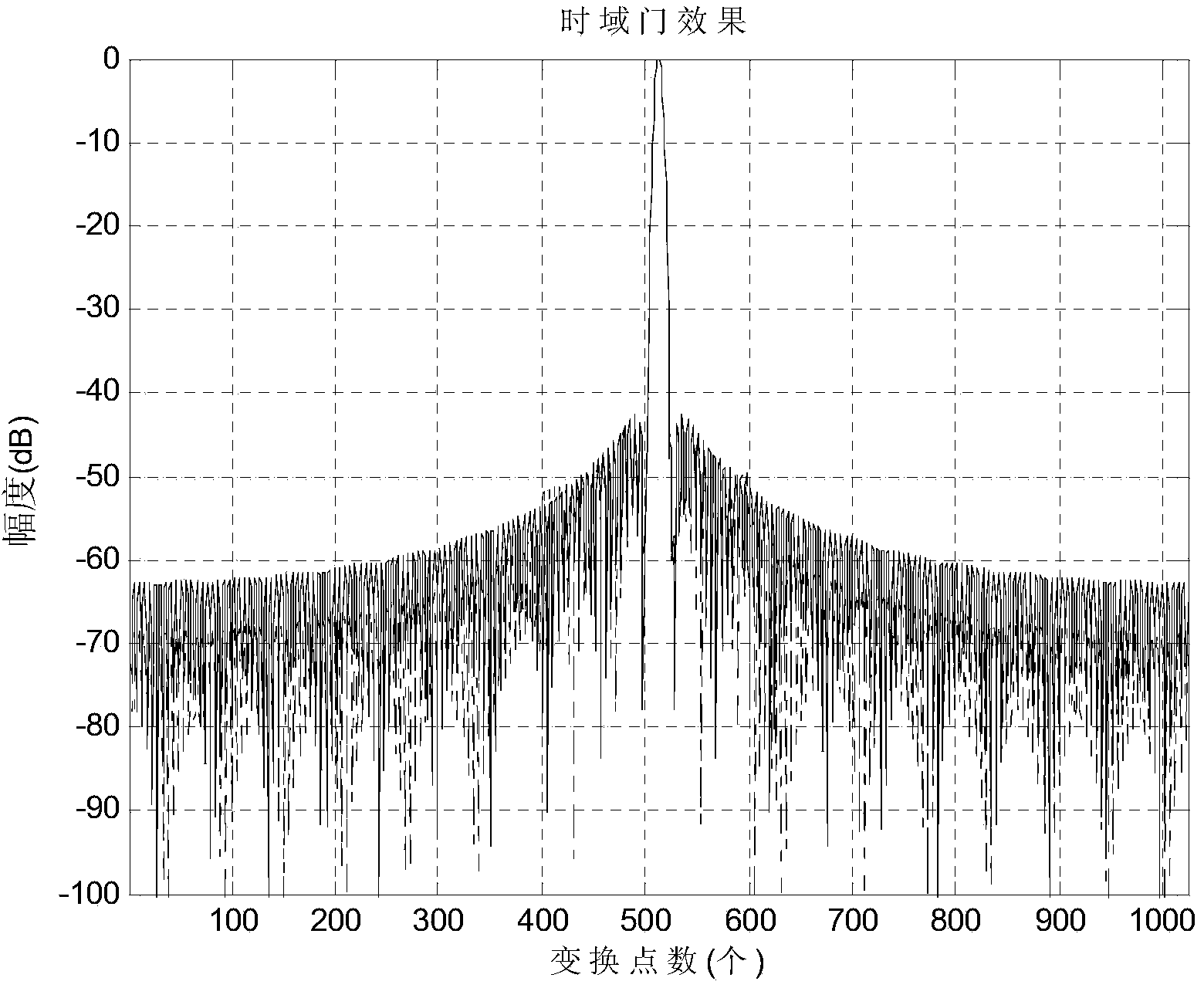
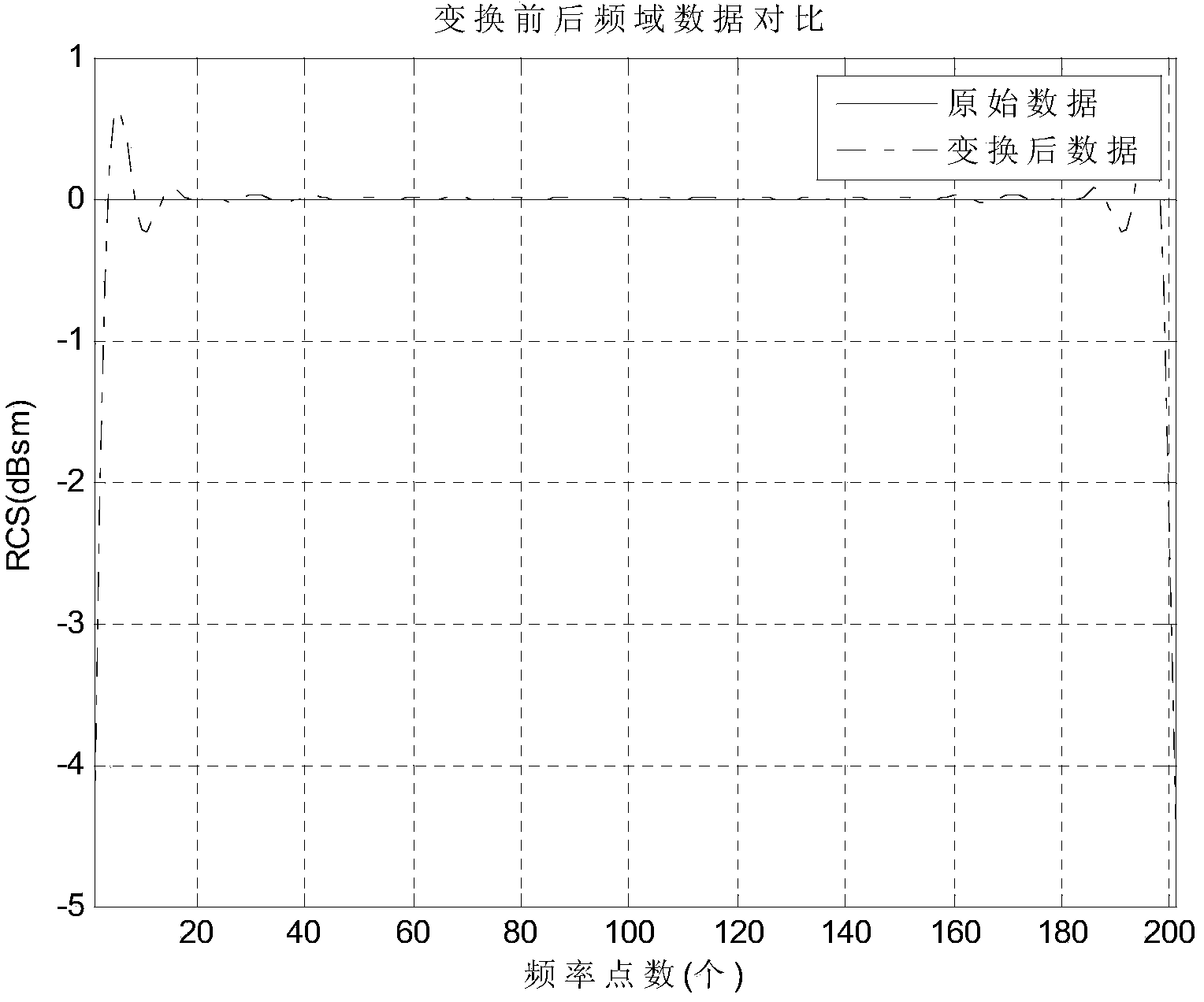
ActiveCN103777185AReduce the amount of resourcesGood time domain resolutionWave based measurement systemsTime domainScattering cross-section
The invention discloses a target-body radar scattering cross section obtaining method and device based on darkroom frequency sweep. In the method and device, in a preset frequency range, according to preset frequency-sweep frequency points, a unit target point radar scattering cross section frequency domain information frequency which contains the different frequency-sweep frequency points is constructed and Fourier inversion is performed, so that unit target point radar scattering cross section time domain information is generated and software time domain gate processing is performed so that unit target point radar scattering cross section filtering time domain information is formed; Fourier inversion is performed on the formed unit target point radar scattering cross section filtering time domain information and unit target point radar scattering cross section filtering frequency domain information is obtained; and according to the obtained unit target point radar scattering cross section filtering frequency domain information, pre-obtained target-body radar scattering cross section filtering frequency domain information is corrected and a calibrated target-body radar scattering cross section is obtained. Through application of the target-body radar scattering cross section obtaining method and device, resource cost needed calibration and time needed in the calibration can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
Micro-motion target characteristic extraction method and system based on wavelet multi-scale analysis
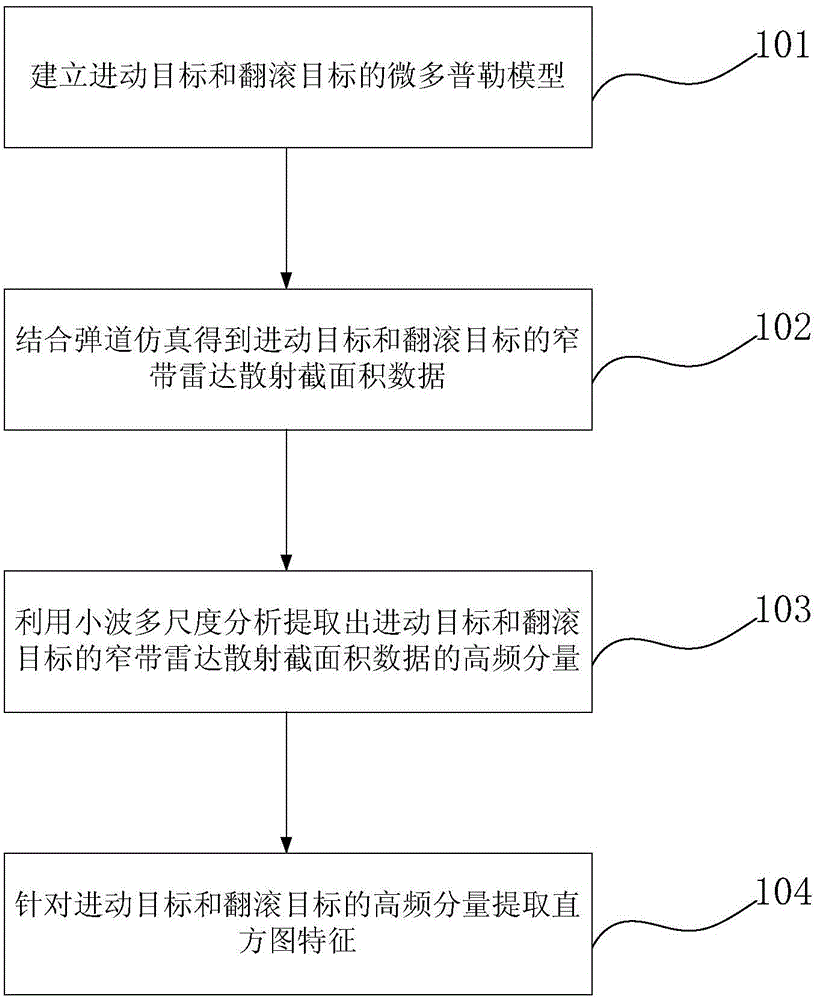
ActiveCN104459662AImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsSpecial data processing applicationsScattering cross-sectionFeature extraction
The invention provides a micro-motion target characteristic extraction method and system based on wavelet multi-scale analysis. The micro-motion target characteristic extraction method based on wavelet multi-scale analysis comprises the steps that a micro Doppler model of a precessional motion target and a micro Doppler model of a rolling target are established, narrow-band radar scattering cross section data of the precessional motion target and narrow-band radar scattering cross section data of the rolling target are obtained based on ballistic trajectory simulation, the high-frequency component of the narrow-band radar scattering cross section data of the precessional motion target and the high-frequency component of the narrow-band radar scattering cross section data of the rolling target are extracted by means of wavelet multi-scale analysis, and column diagram characteristics are extracted aiming at the high-frequency component of the precessional motion target and the high-frequency component of the rolling target. According to the micro-motion target characteristic extraction method based on wavelet multi-scale analysis, the micro Doppler high-frequency components of the targets in different micro-motion forms are separated out by means of wavelet multi-scale analysis, new characteristics are extracted for recognizing the truth of targets, and the recognition accuracy of precessional motion targets and rolling targets is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
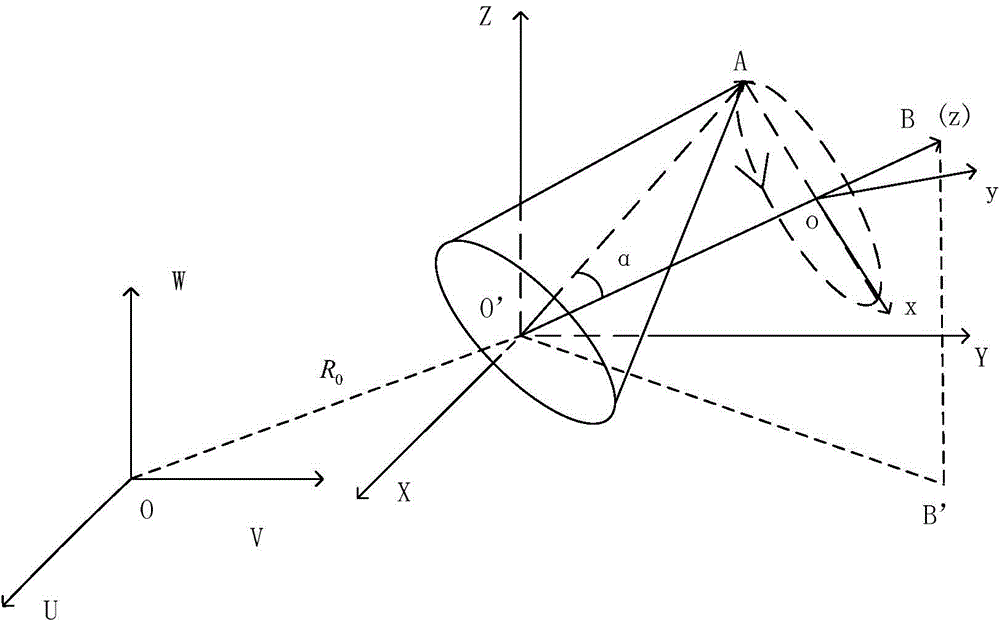
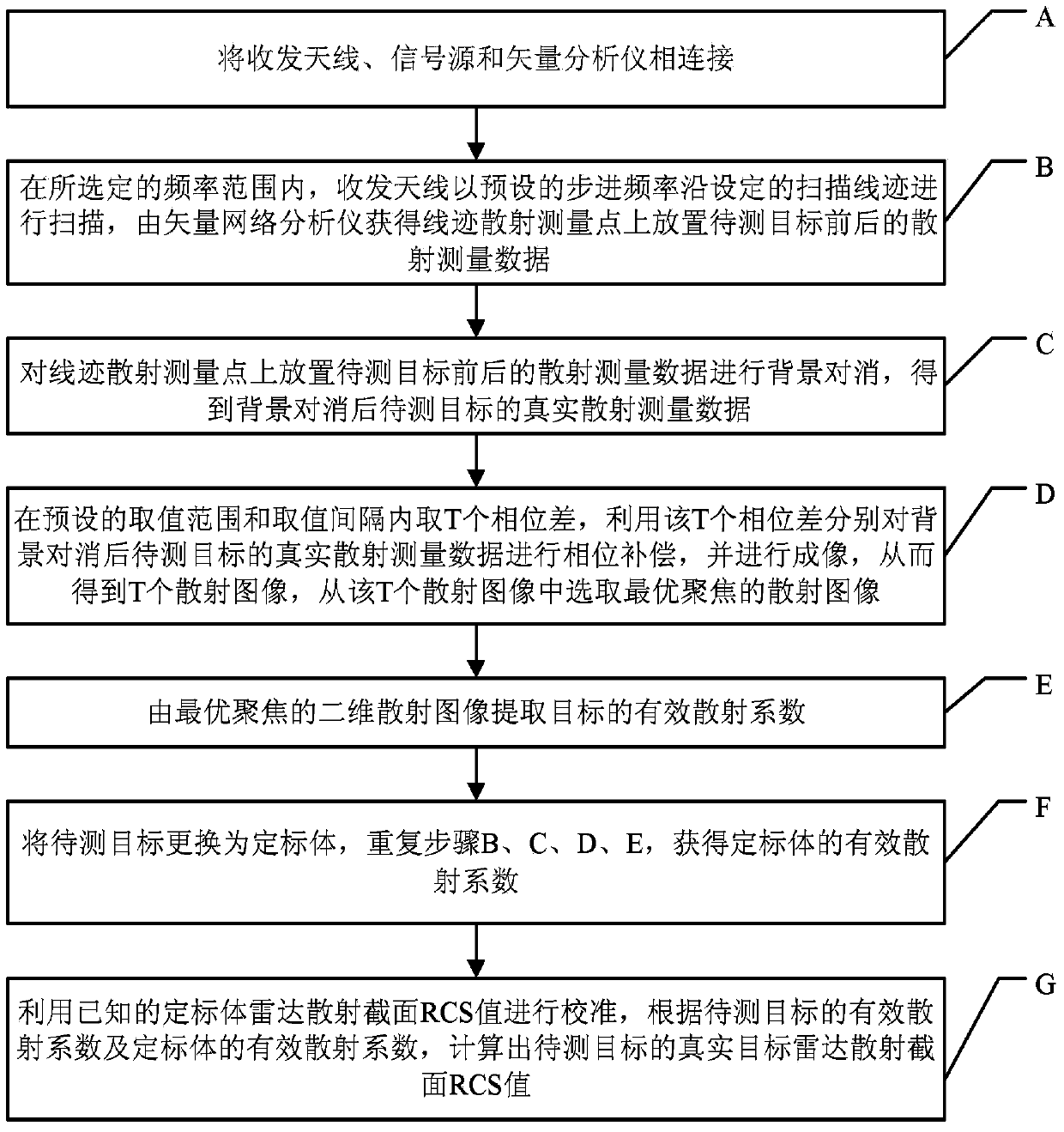
Backscattering cross section measuring method based on trace scanning two-dimensional near field imaging
ActiveCN104199026AImprove space utilizationImprove confidentialitySpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionScattering cross-sectionTransceiver
The invention provides a backscattering cross section measuring method based on trace scanning two-dimensional near field imaging. The backscattering cross section measuring method comprises the following steps: a transceiver antenna scans along a set scanning trace at a predetermined step frequency within a selected frequency range and a vector network analyzer obtains scattering measurement data before and after a target to be measured is placed in a trace scattering measurement point; background cancellation is performed on the scattering measurement data before and after a target to be measured is placed in a trace scattering measurement point; the optimally focused scattering image P is selected; the effective scattering coefficient as shown in the description of the target is extracted from the optimally focused two-dimensional scattering image P; the target to be measured is replaced by a calibration object and the effective scattering coefficient as shown in the description of the calibration object is obtained, and then the real target radar scattering cross-section (RCS) value of the target to be measured is calculated. The backscattering cross section measuring method based on trace scanning two-dimensional near field imaging is capable of obtaining either the scattering image of the target or the RCS value of the target, and further is capable of obtaining the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of the target more clearly, more specifically and more comprehensively.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Array antenna radar cross section reduction method based on space mapping
InactiveCN103246781AGuaranteed accuracyReduce optimization timeSpecial data processing applicationsScattering cross-sectionFull wave analysis
The invention discloses an array antenna radar cross section reduction method based on space mapping. The array antenna radar cross section reduction method based on the space mapping comprises the steps of establishing an array antenna model, enabling unit amplitude uniform plane wave to illuminate on an array antenna, and determining a total scattering field of the array antenna; deducing a radar cross section formula of the array antenna according to a pattern multiplication, establishing a space mapping rough model of the array antenna, optimizing the rough model and determining an optimum design parameter of the rough model; utilizing a method of moments of a full-wave analysis in a fine model; enabling the response of the rough model to approach that of the fine model through parameter extraction, and establishing a mapping relation of a rough model parameter and a fine model parameter; and utilizing the optimum design parameter of the rough model and the inverse mapping of the established mapping relation to obtain a prediction parameter of the fine model, and if the prediction parameter of the fine model does not meet a design requirement, subjecting the mapping relation to iteration updating until the prediction parameter of the fine model meets the design requirement. The array antenna radar cross section reduction method based on the space mapping subjects the design parameter to a global optimization and saves time under the premise of guaranteeing the accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
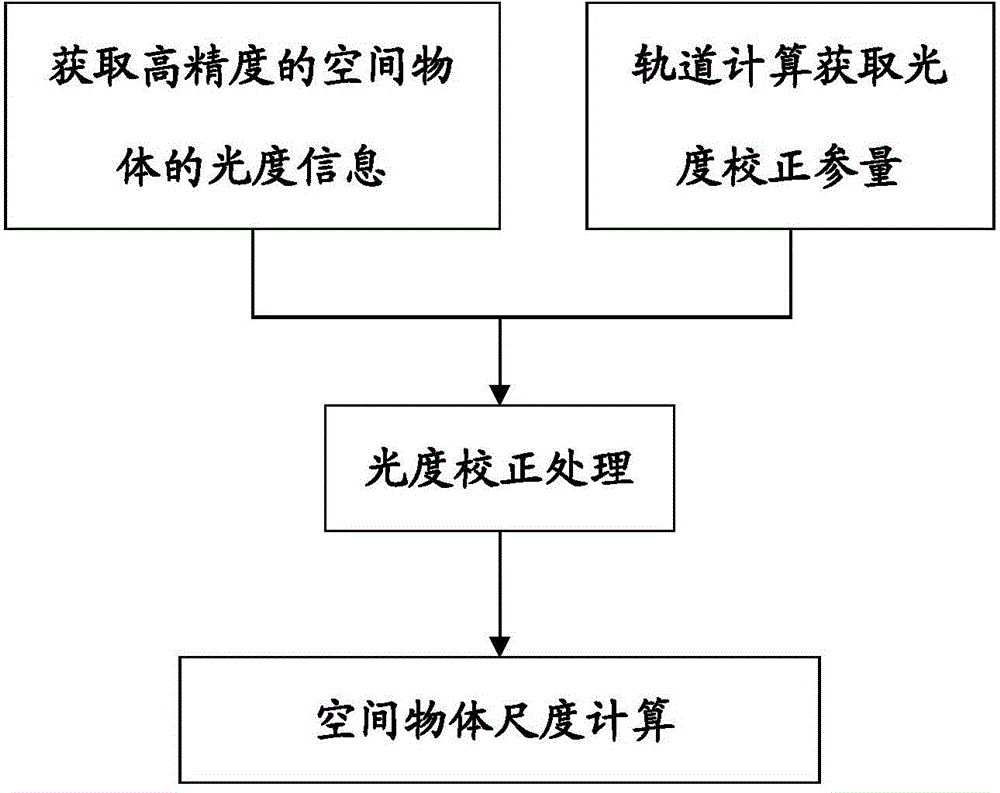
Space object dimension acquisition method based on photoelectric observation
ActiveCN104101297AHas passive passive reception characteristicsProbing behavior is not easy to detectUsing optical meansElectricityScattering cross-section
The invention belongs to the field of foundation photoelectric observation and discloses a space object dimension acquisition method based on photoelectric observation. The method includes the steps of obtaining high-precision photometric information of a space object through observation; obtaining photometric calibration parameters through orbital calculation; performing photometric correction on the space object; calculating the dimension of the space object. The space object dimension acquisition method based on photoelectric observation overcomes the lack of observational capability on middle-orbit and high-orbit space objects in a radar method and is a method for acquiring the optical dimension of the middle-orbit and high-orbit space objects with an optical telescope system by obtaining the parameters of the optical scattering cross section indicating the dimension of the space object. Compared with a wireless method, the space object dimension acquisition method based on photoelectric observation can accurately obtain the dimension of the space object due to the fact that an optical band is longer than a radio band and not sensitive to edges and corners. The space object dimension acquisition method based on photoelectric observation can be rapidly popularized and applied to existing foundation photoelectric detection devices in China without hardware modification to form a certain capability of determining the dimension of the space object.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
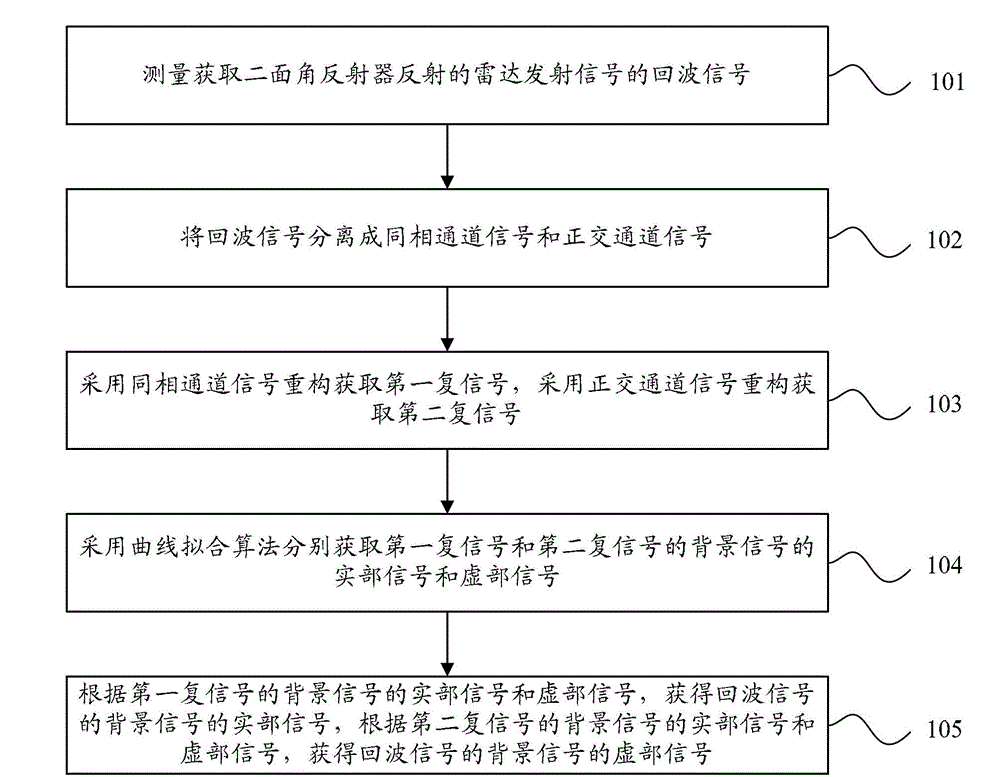
Background signal extraction method in radar scattering cross section measurement
ActiveCN103064072AImplement extractionImprove robustnessWave based measurement systemsScattering cross-sectionAcoustics
The invention provides a background signal extraction method in radar scattering cross section measurement. The method includes measuring echo signals used for obtaining radar transmission signals reflected by a dihedral angle reflector, isolating the echo signals into in-phase channel signals and orthogonal channel signals, obtaining first complex signals through reconstruction of the in-phase channel signals, obtaining second complex signals through the orthogonal channel signals, respectively obtaining real part signals and imaginary part signals of the first complex signals and the second complex signals by means of a curve fitting algorithm, obtaining the real part signals of background signals according to the real part signals and the imaginary part signals of the first complex signals, and obtaining the imaginary part signals of background signals according to the real part signals and the imaginary part signals of the second complex signals. Due to the fact that the background signals are extracted through the curve fitting algorithm in high precision, the background signal extraction method in the radar scattering cross section measurement solves the problem that robustness is poor in practical engineering application.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Device for multiple calibration and background extraction in target RCS measurement and signal processing method thereof
ActiveCN105866759AEliminate inherent disadvantagesEasy extractionWave based measurement systemsScattering cross-sectionRadar
The invention discloses a device for multiple calibration and background extraction in target radar scattering cross section (RCS) measurement and a signal processing method thereof. The invention provides a new calibration member appearance design. By means of a designed novel calibration member (SCAM), just through one 360-DEG direction rotation measurement, data required for background auxiliary measurement, extracting and counteracting processing, and RCS multiple calibration measurement and processing can be simultaneously obtained. The novel calibration member (SCAM) provided by the invention realizes an improvement on the appearance of an existing CAM calibration member and furthermore eliminates inherent defects in background extraction auxiliary measurement and RCS calibration processing by an international universal traditional cylindrical calibration member and a CAM calibration member.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and device for detecting nano particle sizes based on dual-wavelength optical fiber interference method
InactiveCN103424344AReduce noiseEasy to identifyParticle size analysisScattering cross-sectionDifferential measurement
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting nano particle sizes based on a dual-wavelength optical fiber interference method. According to the method, an arc tangent PGC (phase generated carrier) demodulation method is adopted to detect phase shifts when particles pass through, meanwhile, an optical fiber double-interference instrument in wavelength division multiplexing is introduced, two light beams with different wave lengths in one optical fiber are extracted by a split reflector and then are focused to form two closed focused circular cone detection light beams, therefore, two independent phase position detection signals are obtained, difference measurement can be accurately achieved in one optical path to recognize time pulses when nano particles pass through a boundary, the pulse width is relevant to the particle size, accuracy in scattering cross section equivalent diameter measurement on the nano particles can be effectively improved combining with the phase shifts, and single particles with the size as small as 20-40 nanometers can be detected. The method and device for detecting the nano particle sizes based on the dual-wavelength optical fiber interference method have the advantages of being low in noise, high in recognition and analysis accuracy, and strong in crosstalk inhibiting ability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Light-stream control system based on gold-nanoparticle modified carbon nanotube array surface enhanced Raman scattering
ActiveCN103149193ALarge specific surface areaPromote enhancementRaman scatteringScattering cross-sectionCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a light-stream control system based on gold-nanoparticle modified carbon nanotube array surface enhanced Raman scattering and used for molecule detection. According to the system, a carbon nanotube array is used as a nanometal structure carrier, and gold nanoparticles are deposited on the carbon nanotube array carrier, thus a substrate with the three-dimensional surface enhanced Raman scattering activity is formed, wherein the substrate serves as the detection zone of a microchannle in the system; a laser source is introduced into the substrate through an optical fiber and scatters light on the substrate; the scattering light is educed on a spectrometer through an optical fiber to test a spectrum; and a pressure regulating device ensures the smooth flowing of a molecule under test in the microchannle. The substrate with the three-dimensional surface enhanced Raman scattering activity is simple in manufacturing process and low in cost and is free from toxin and pollution. The carbon nanotube array has a large surface area, thus the gold nanoparticle filling effect is improved effectively, the Raman scattering cross section is increased, and the strength of a Raman scattering signal is enhanced. By introducing in the laser through the optical fiber and collecting the Raman scattering light, the traditional micrographic focusing and aligning is omitted. The system is small in volume and low in cost and facilitates the online molecule detection.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Ultra-wideband-radar-based scattering-cross-section-reducing chessboard structure and ultra-wideband radar
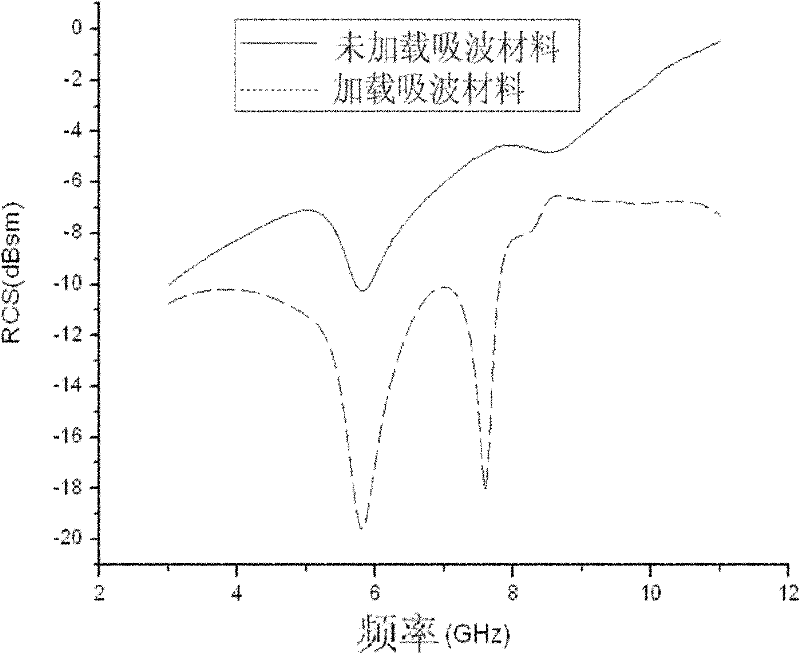
ActiveCN108957429ALow reverse RCS valueLow dual station RCS valueRadio wave reradiation/reflectionScattering cross-sectionDielectric plate
The invention provides an ultra-wideband-radar-based scattering-cross-section-reducing chessboard structure and an ultra-wideband radar. The chessboard structure comprises a metal floor and M*N finiteaperiodic tile units fixed on the metal floor. The finite aperiodic tile units consist of dielectric plates and metal pasters arranged on the dielectric plates; and the metal pasters include metal ring pasters distributed in an array manner.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com