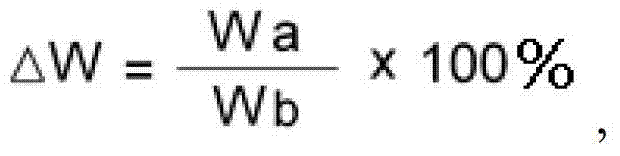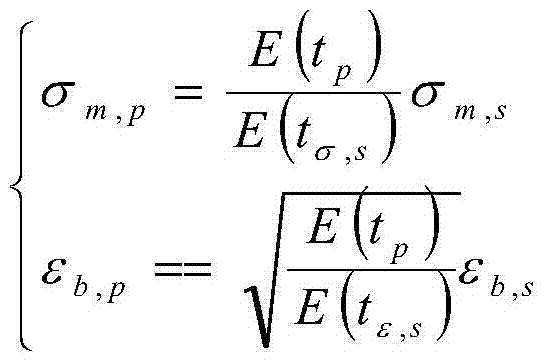Patents
Literature
60 results about "Relaxation modulus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
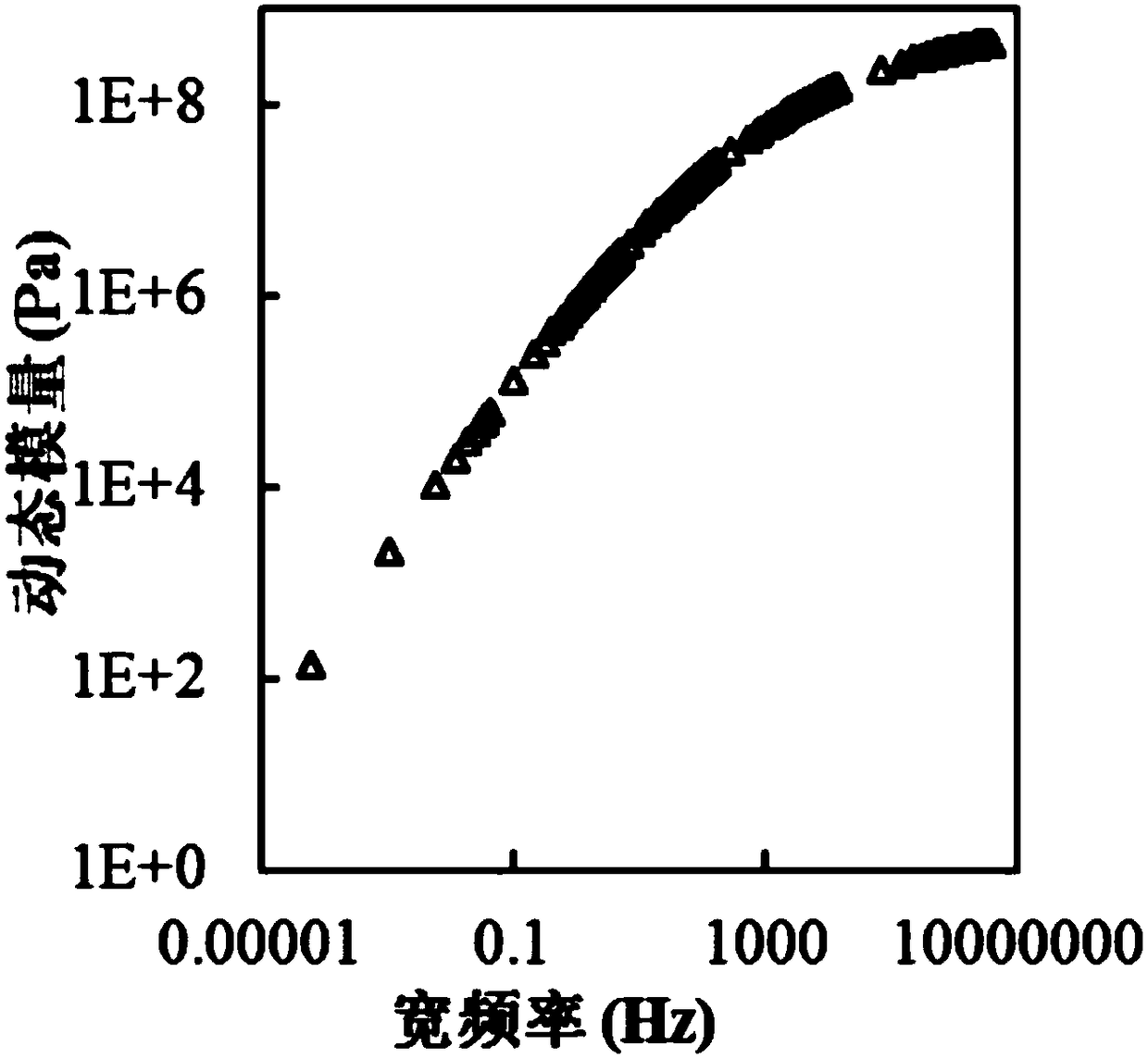
Relaxation modulus. Relaxation modulus - short version. For viscoelastic polymers, the time-dependent modulus of elasticity. It is determined from stress relaxation measurements as the ratio of stress (taken at some time after the load application-normally 10 s) to strain.
Colored optical fiber, optical fiber ribbon, and optical fiber cable
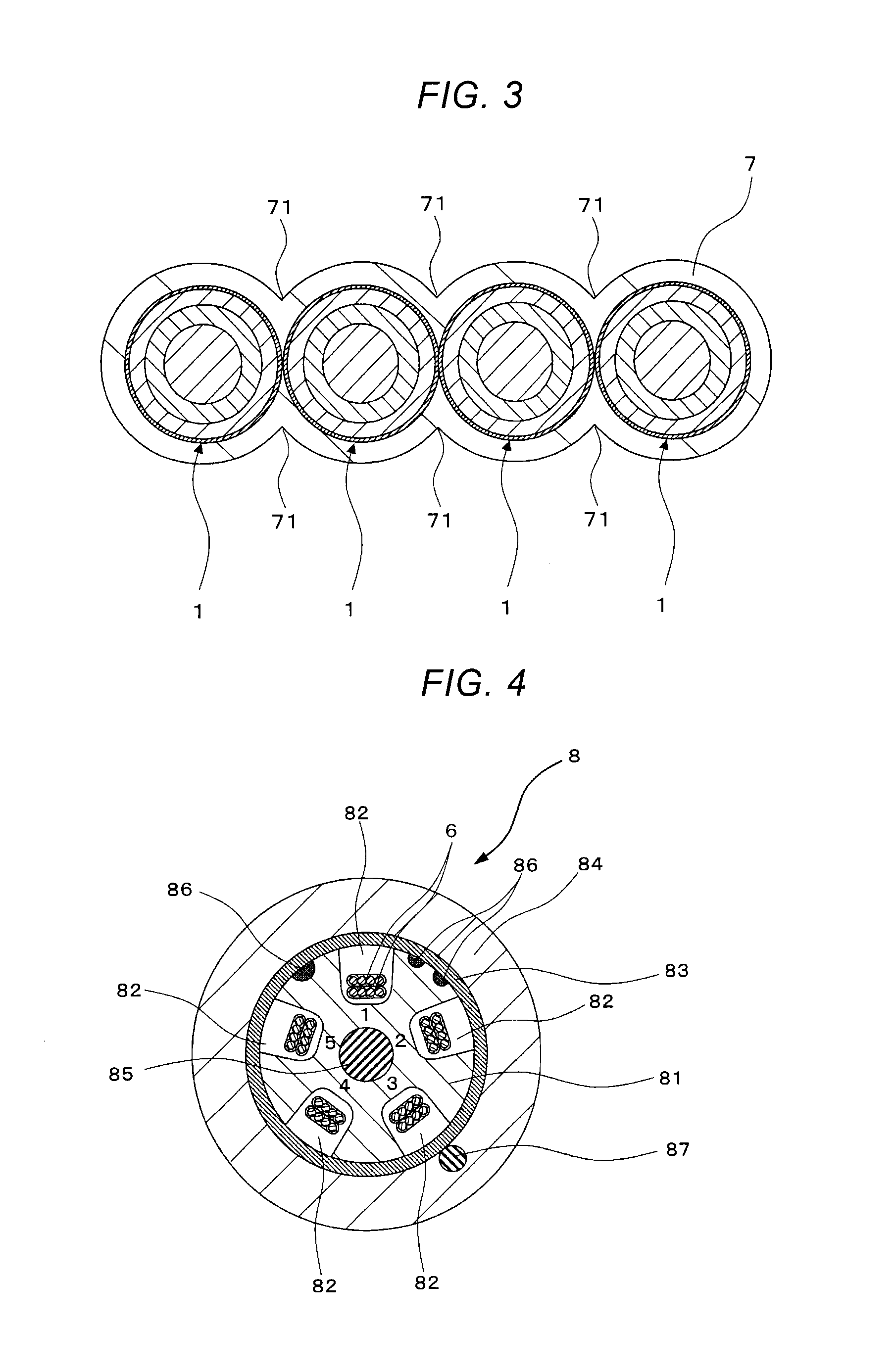
InactiveUS20140226941A1Good anti-microbend propertyIncreased transmission lossGlass optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresRelaxation modulusOptical fiber cable
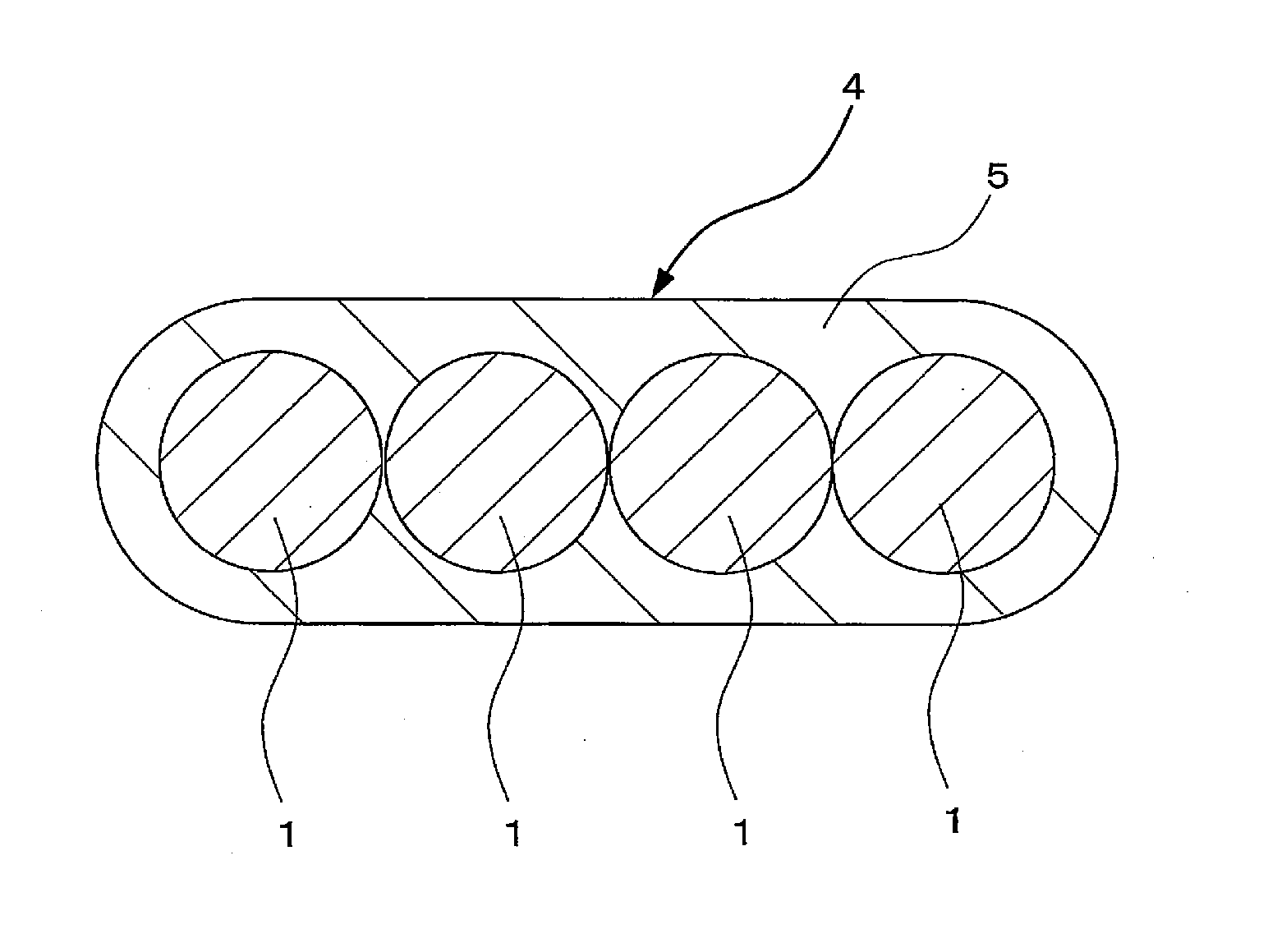
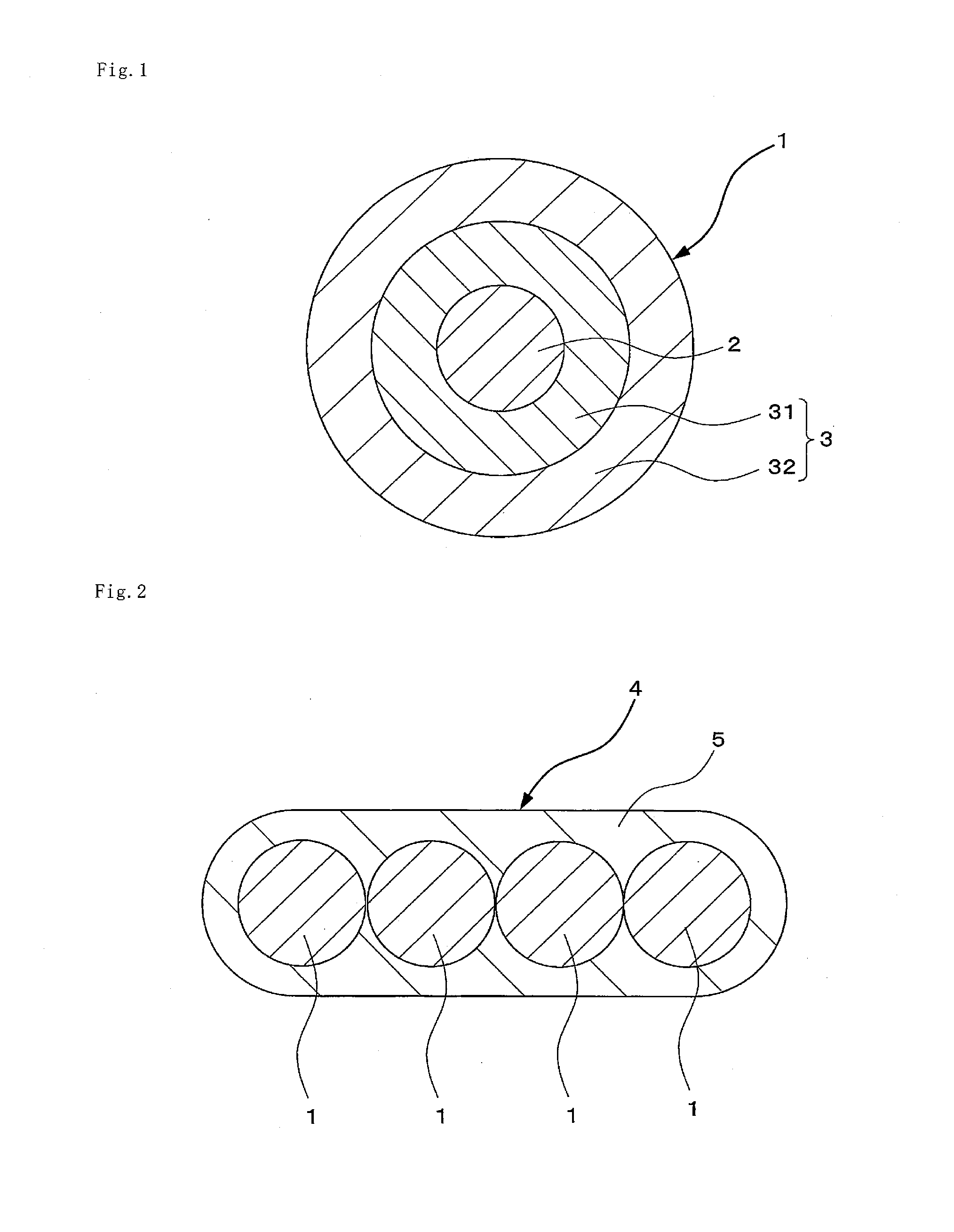
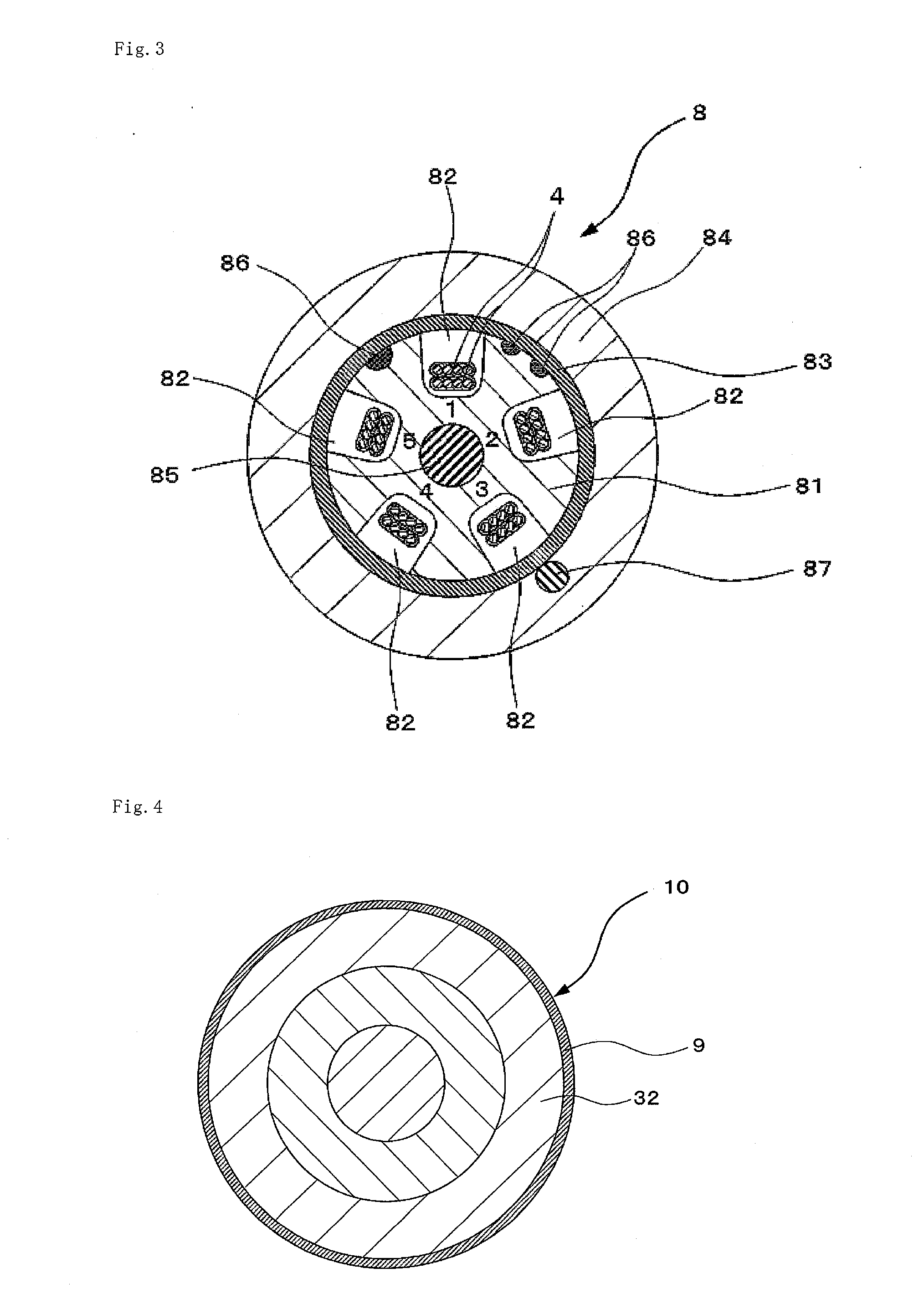
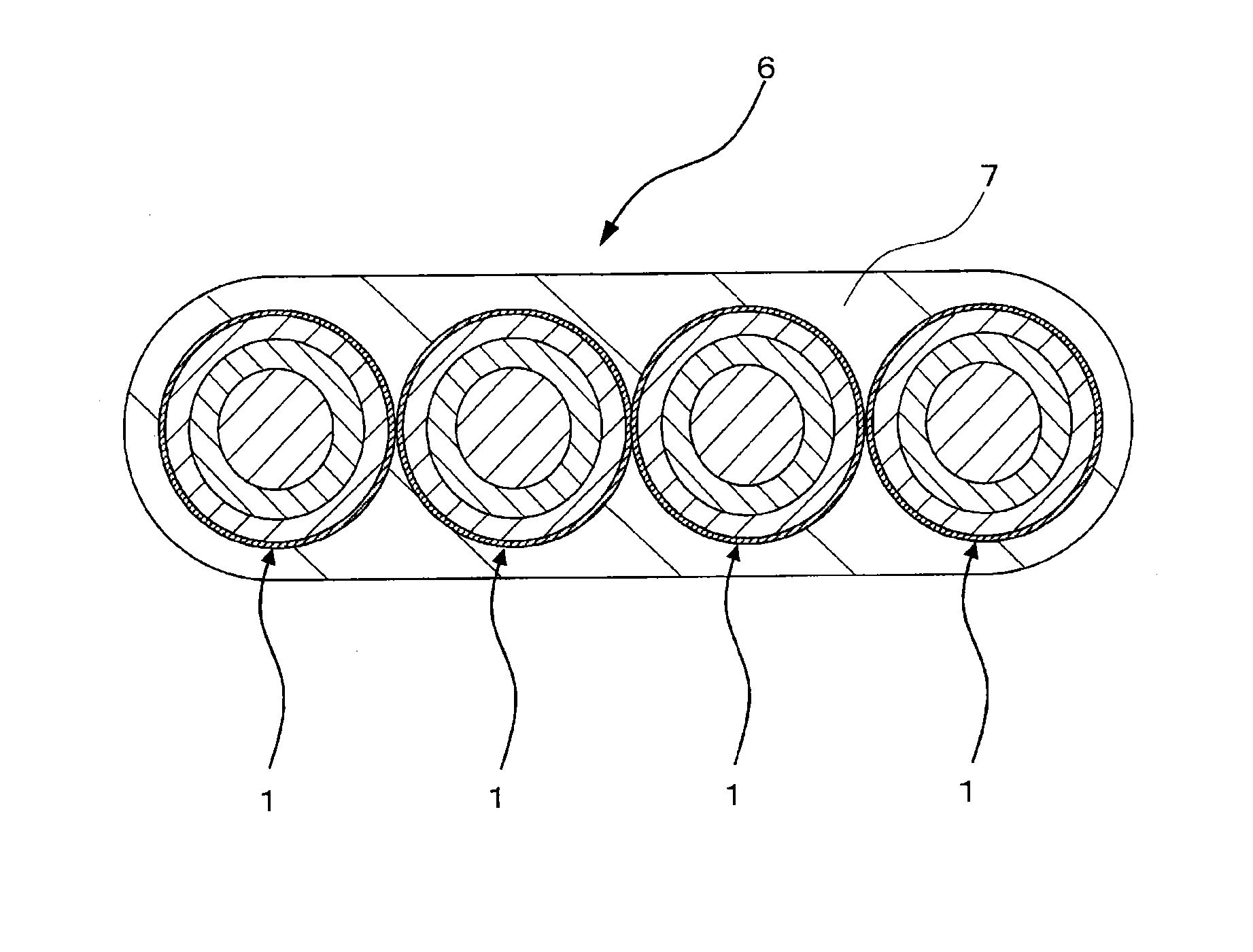
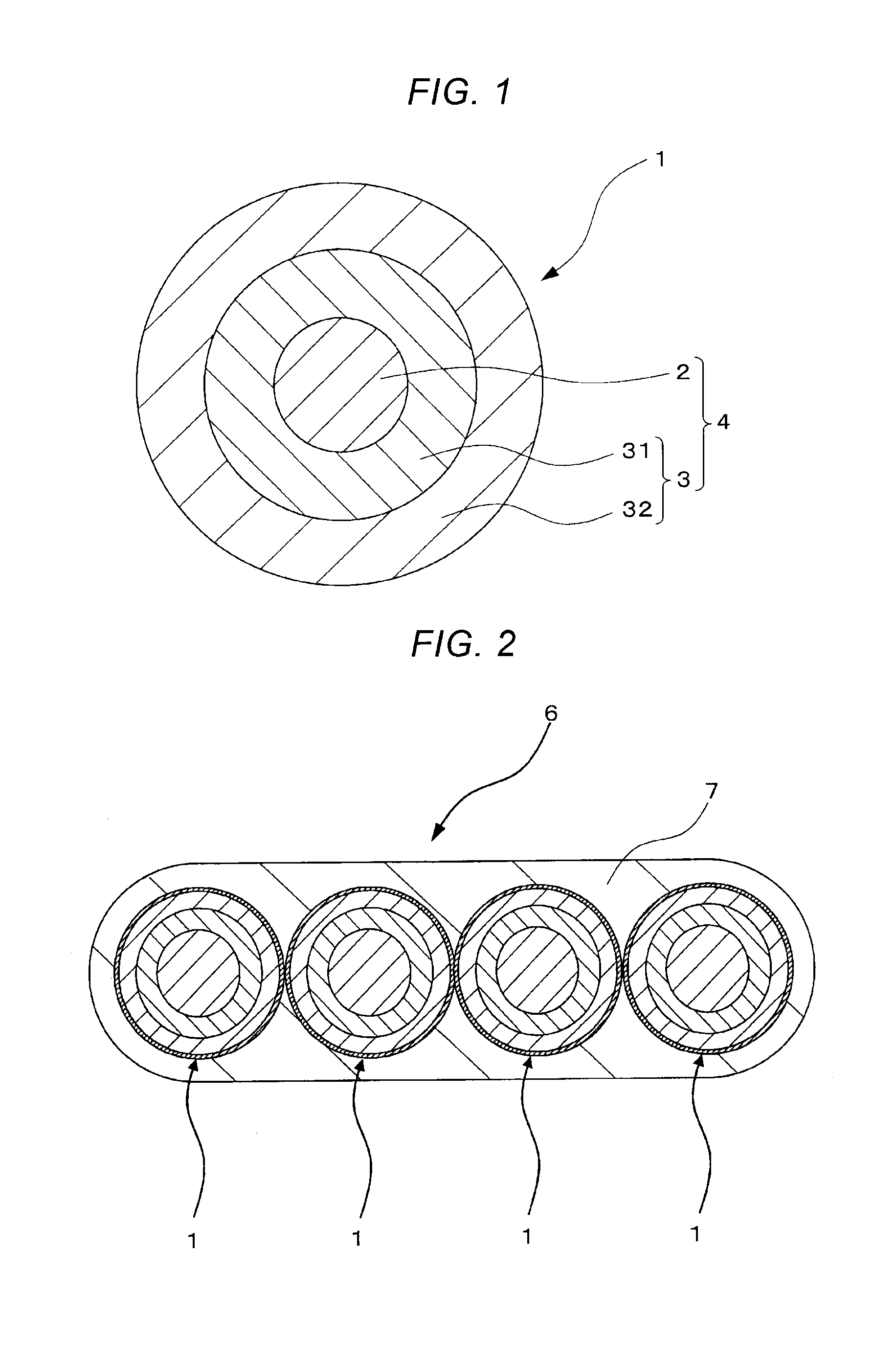
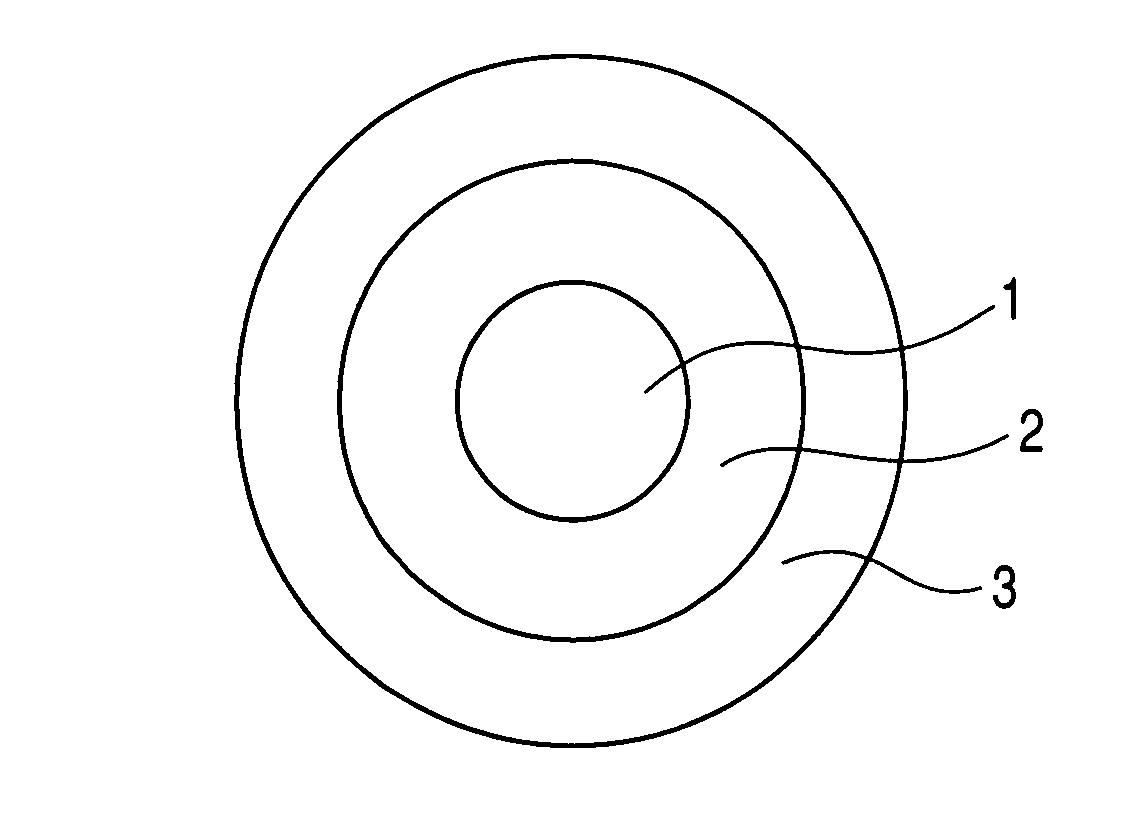
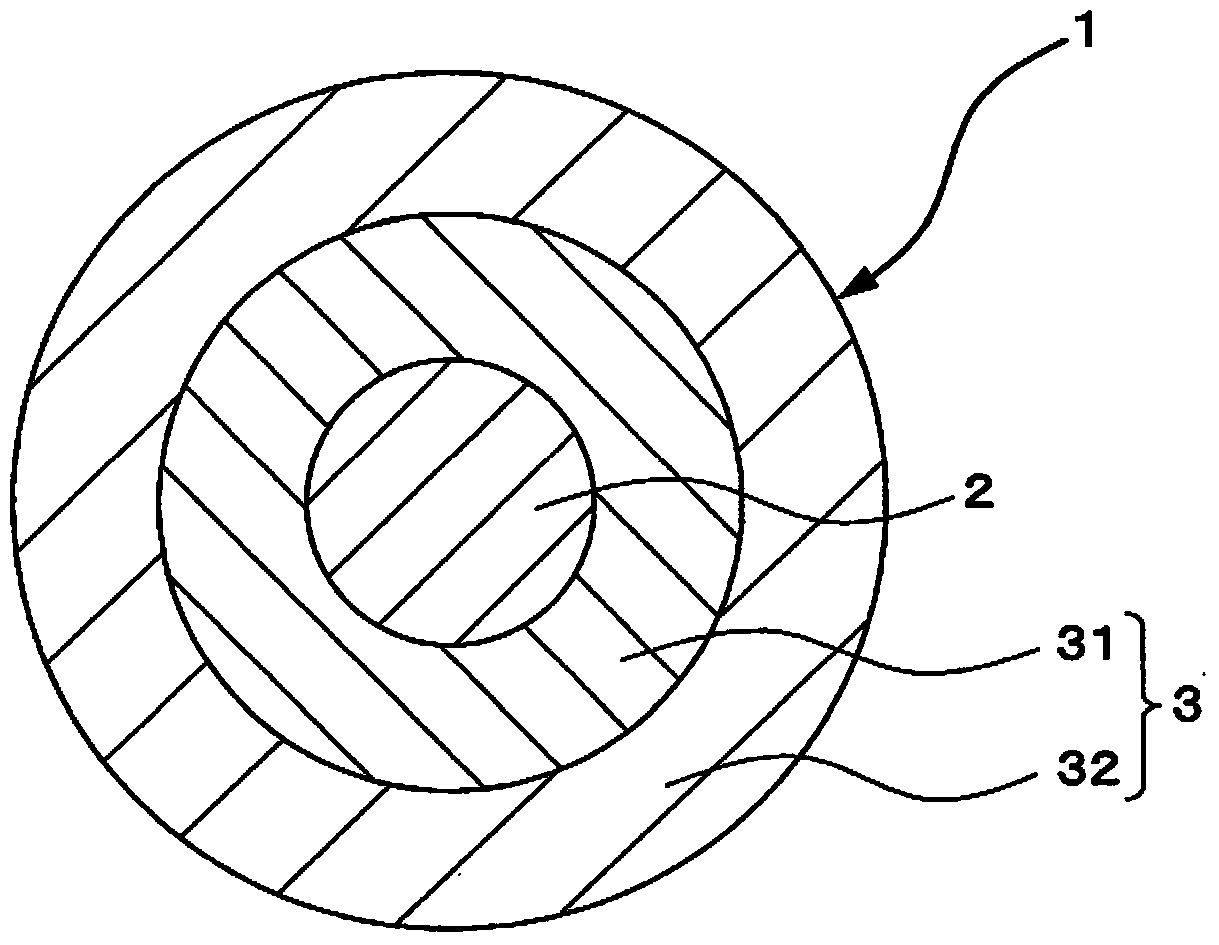
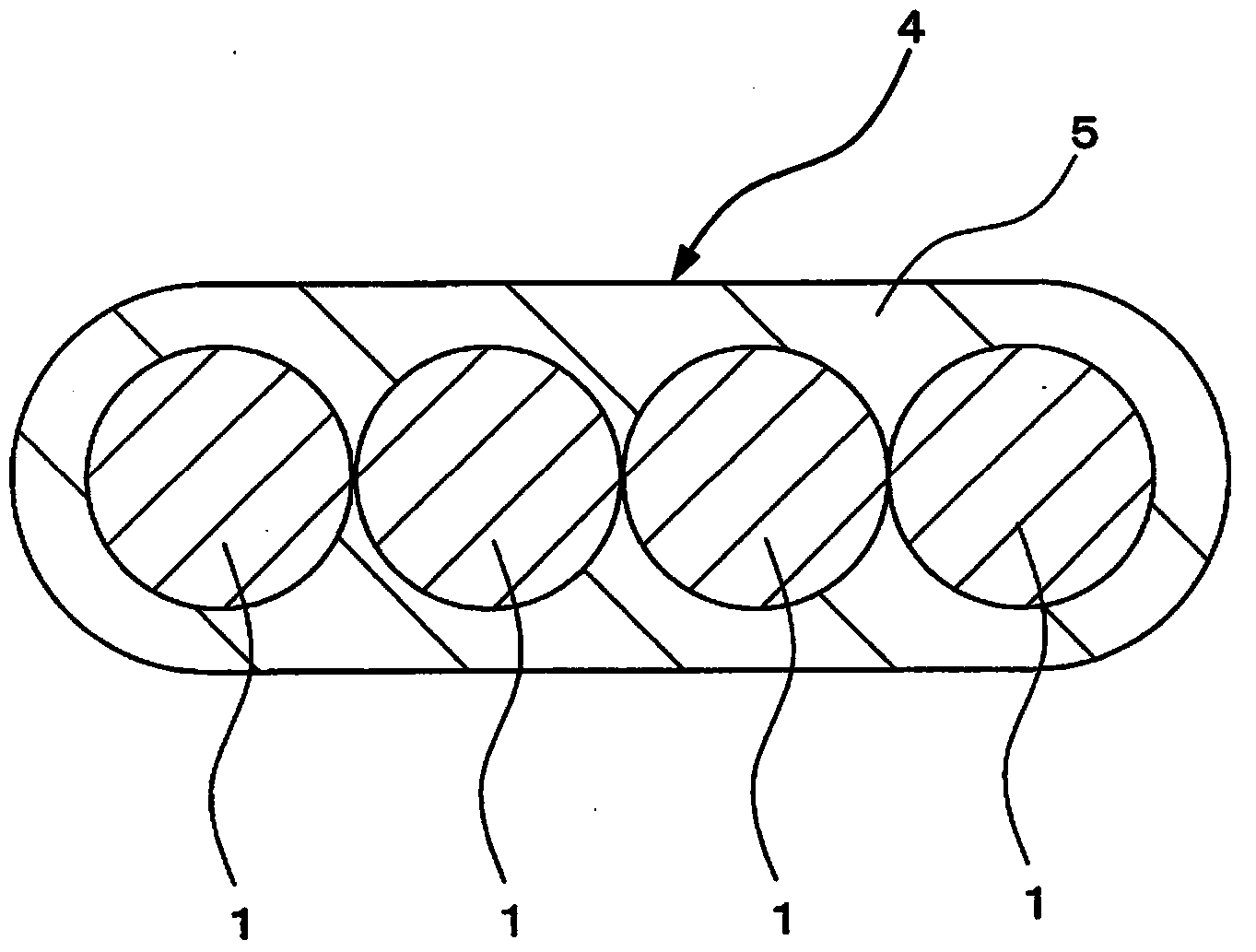
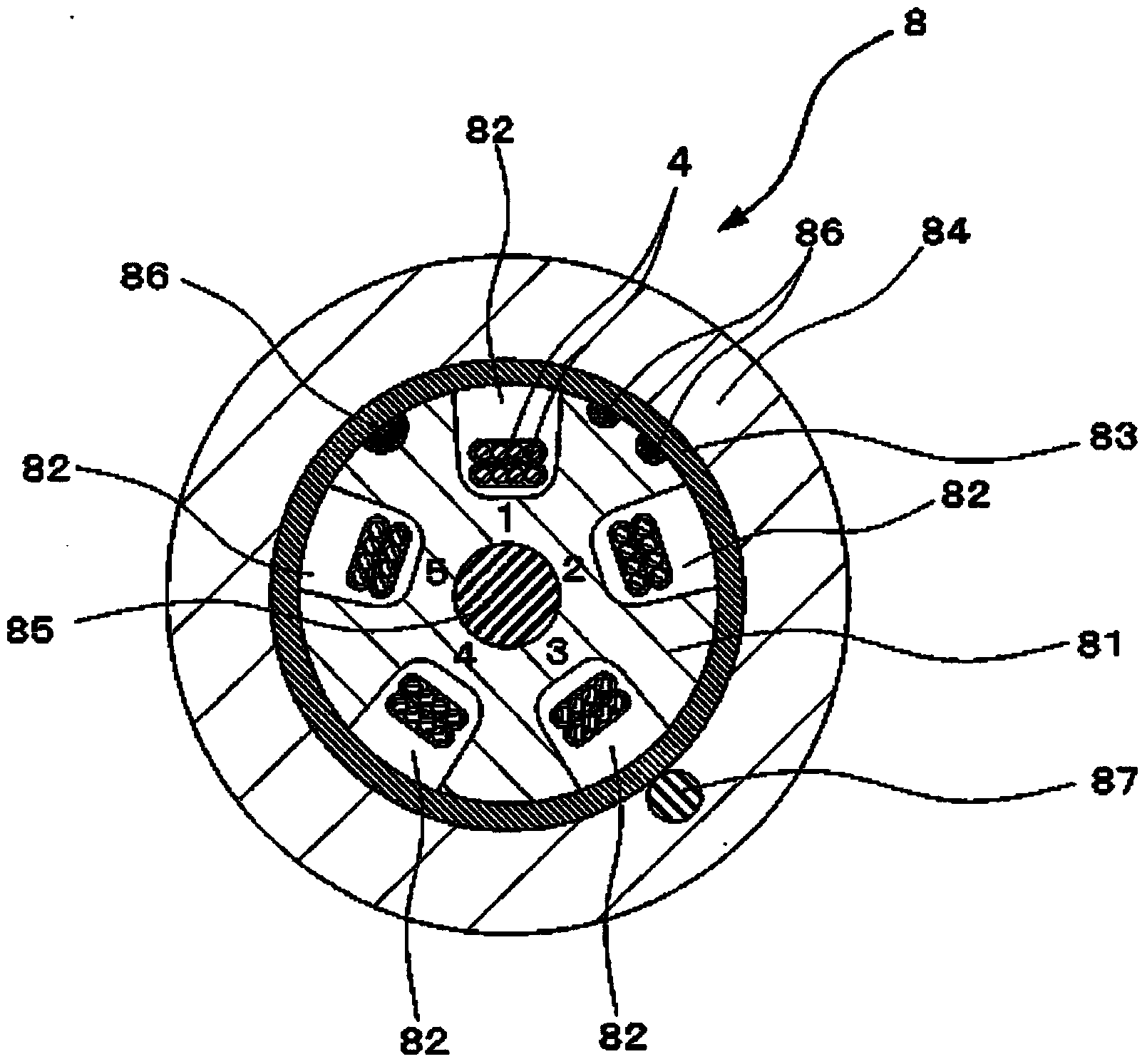
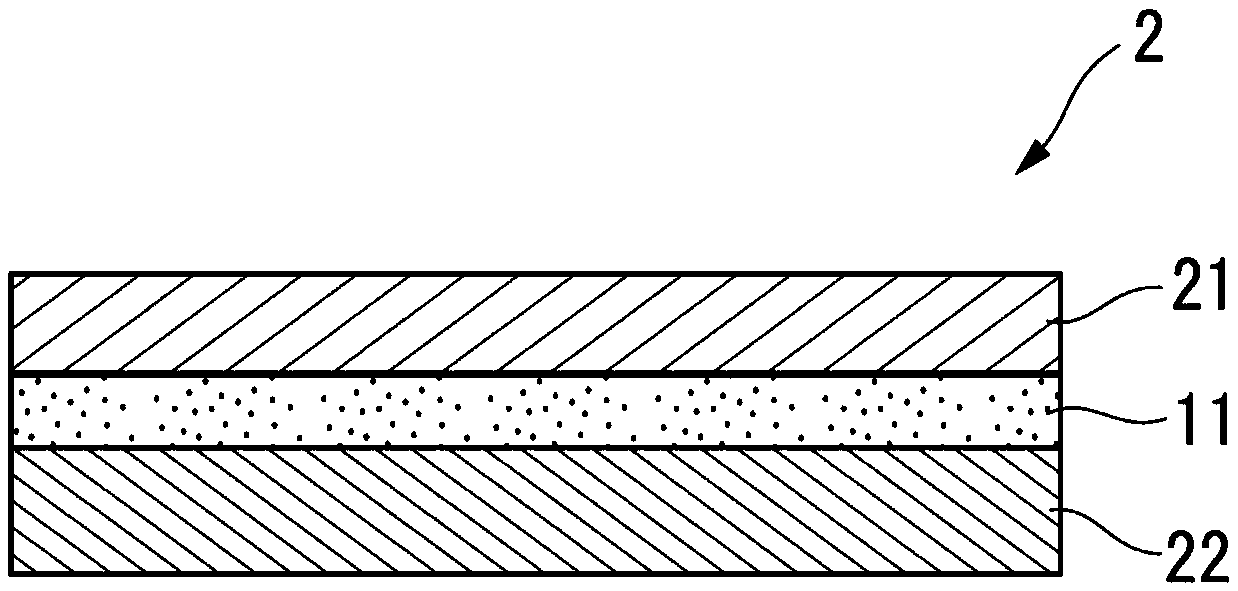
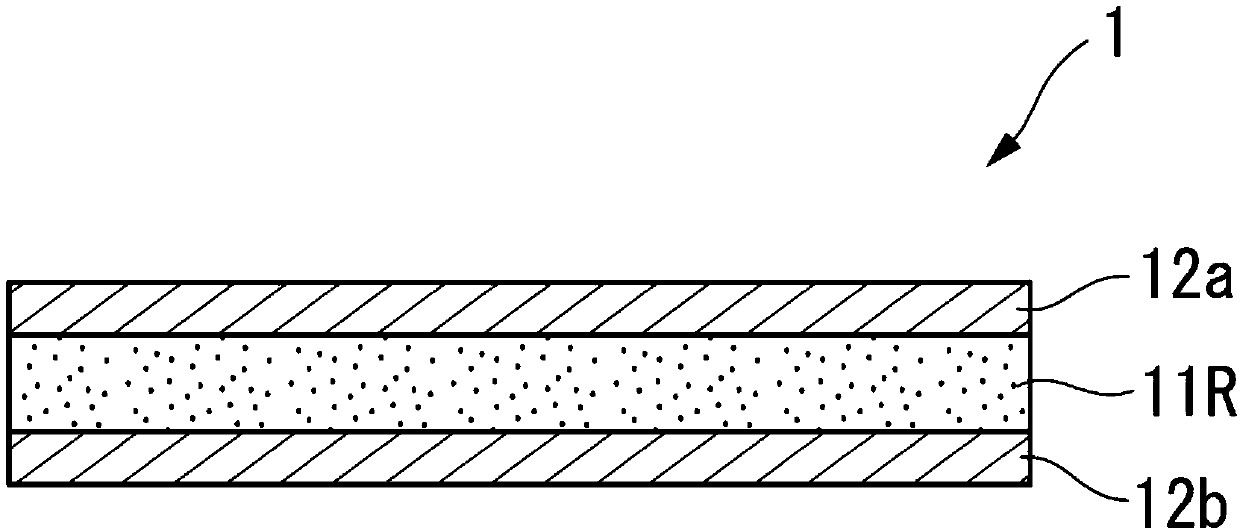
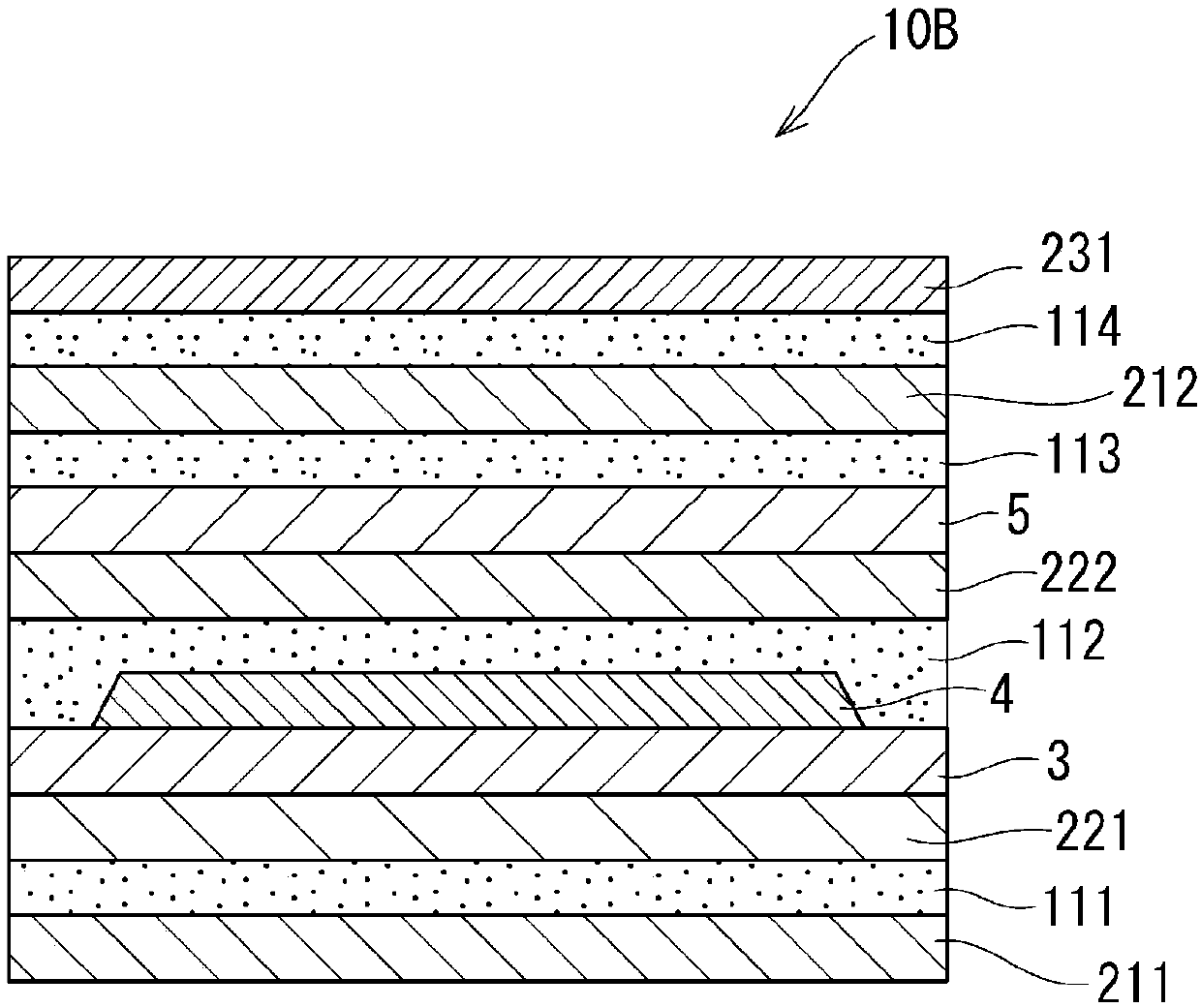
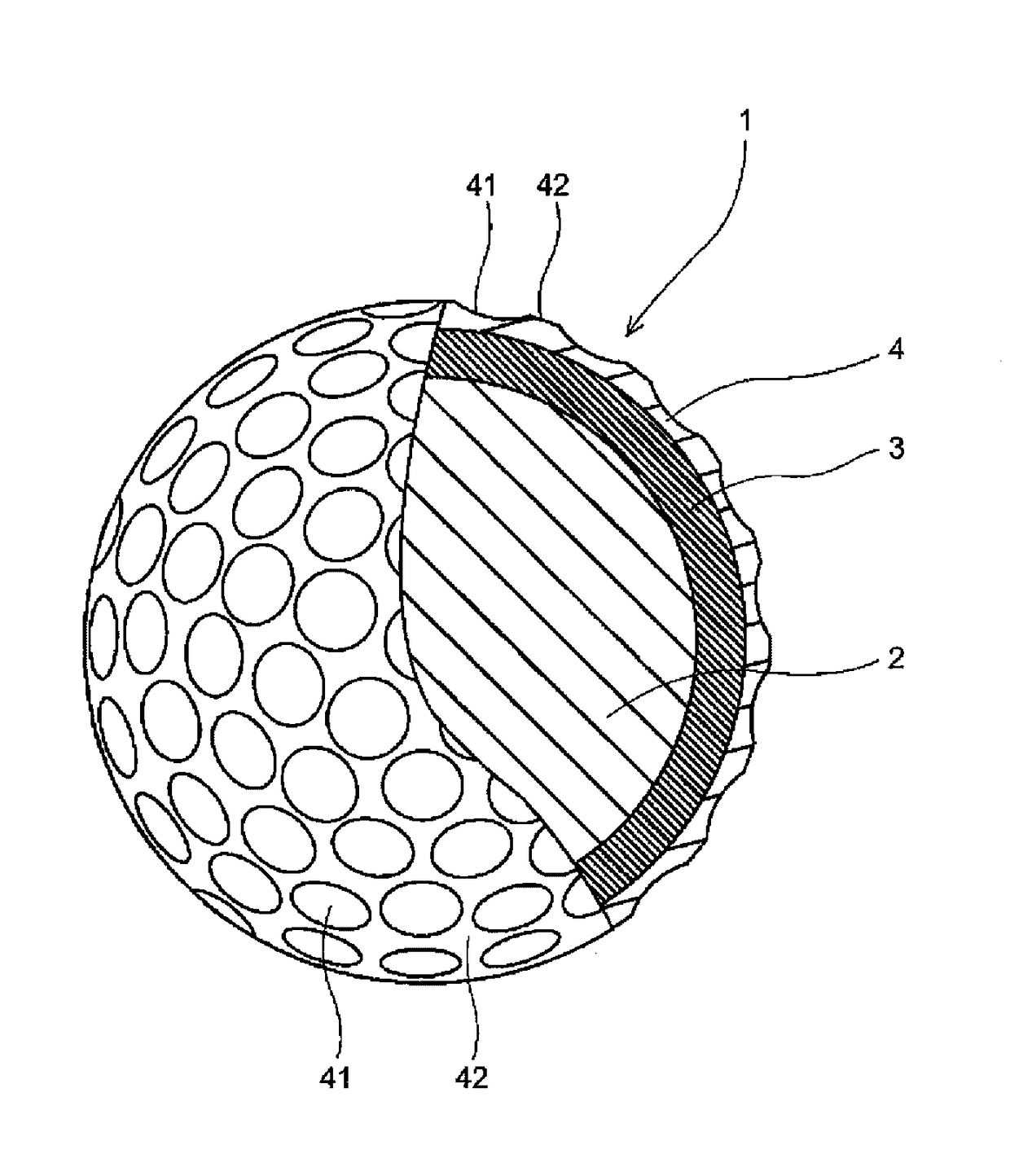
The present invention provides a colored optical fiber that shows anti-microbend property and hot-water resistance, an optical fiber ribbon that utilizes the same, and an optical fiber cable.It is a colored optical fiber 1, which comprises two coating layers of a primary coating layer 31 and a secondary coating layer 32, wherein either one of the primary coating layer 31 or the secondary coating layer 32 is colored, both coating layers have equilibrium elastic moduli of 60 MPa or less, and the secondary coating layer 32 has a relaxation modulus of 410 MPa or more, an optical fiber ribbon 4 that utilizes it, and an optical fiber cable 8.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Parameter identification method of asphalt viscoelastic model based on comprehensive data optimization criterion
InactiveCN108846143AReflect viscoelastic propertiesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic shear rheometerSynthetic data
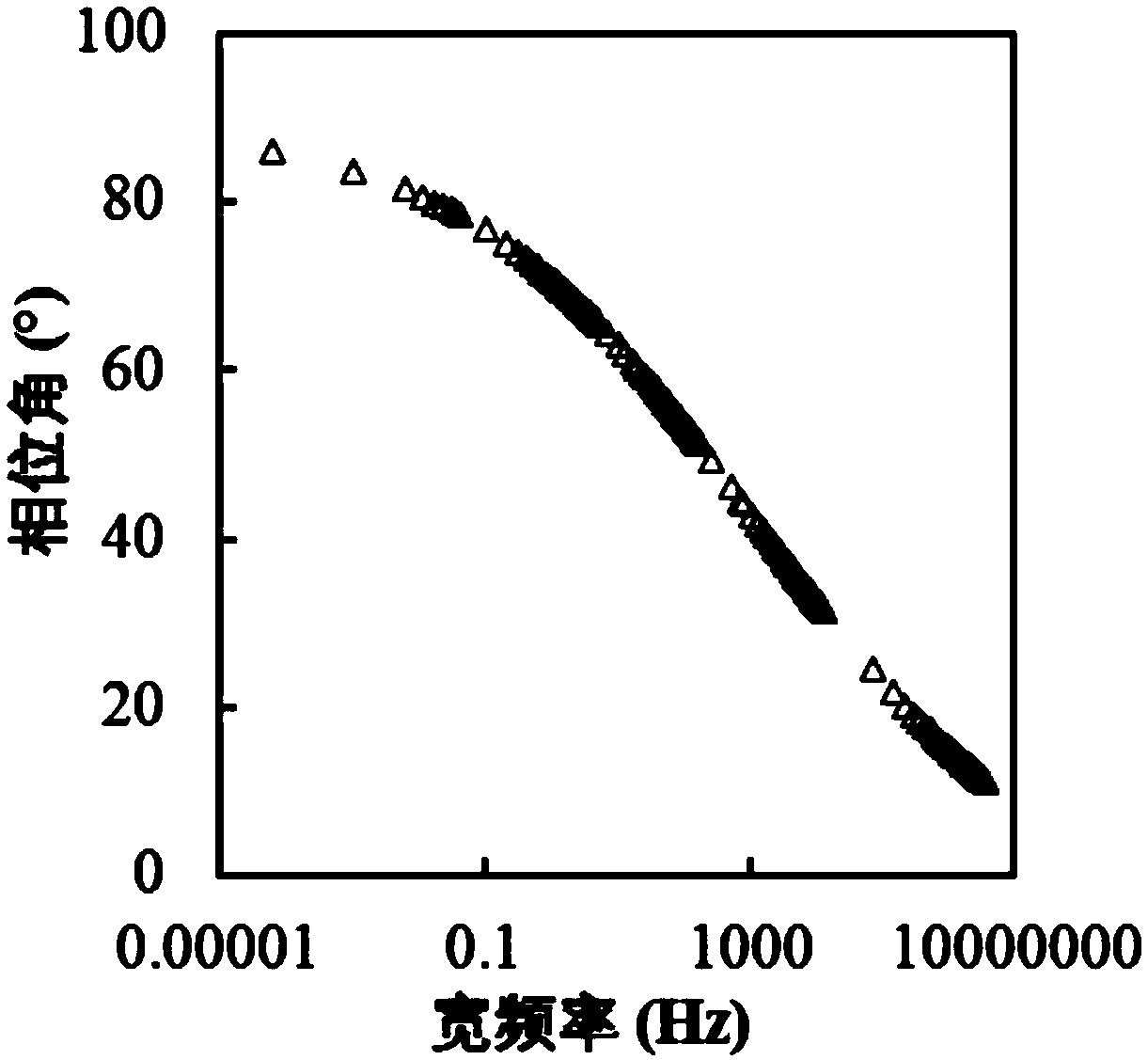
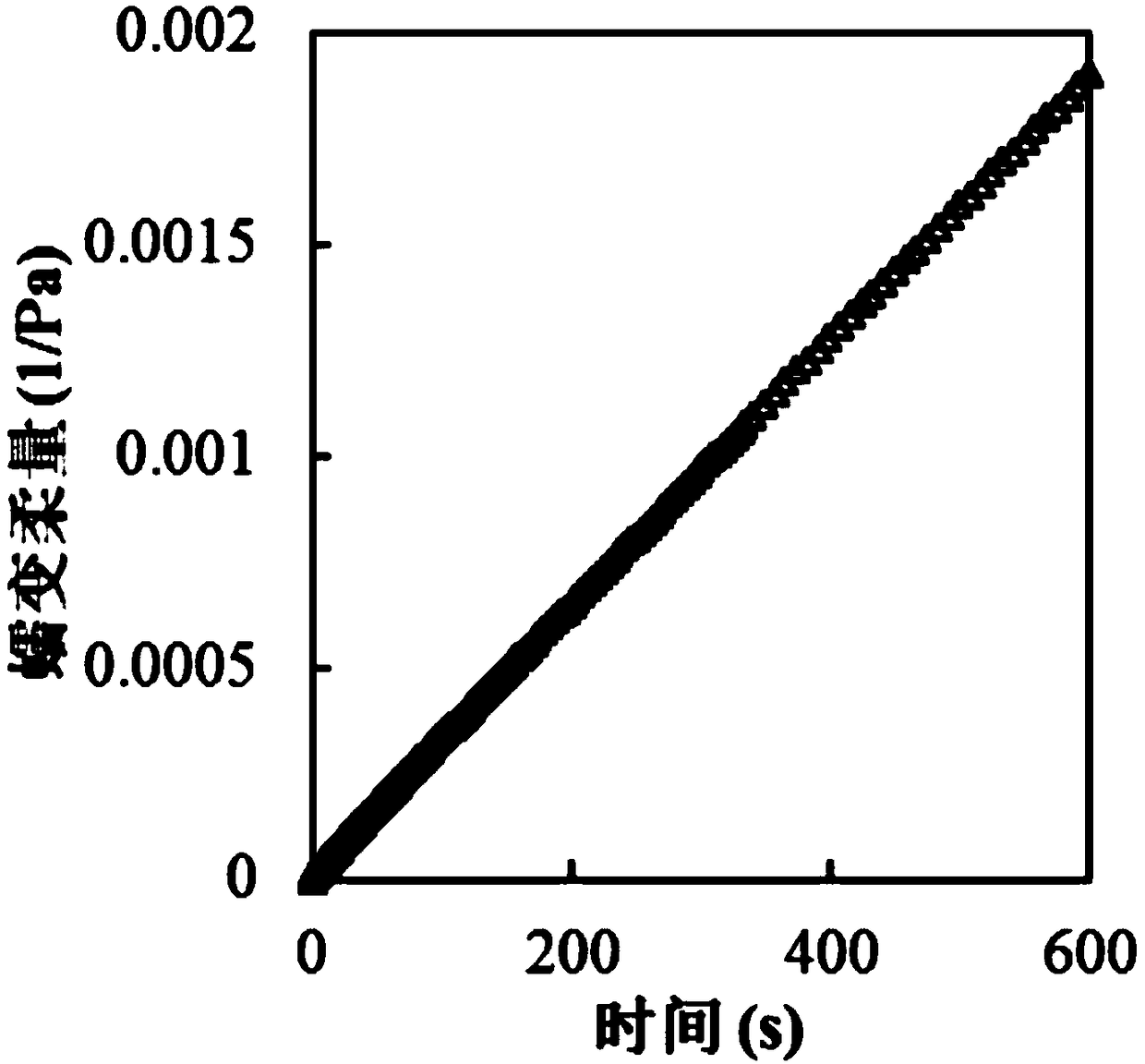
The invention provides a parameter identification method of an asphalt viscoelastic model based on a comprehensive data optimization criterion and belongs to the technical field of a parameter identification method of an asphalt viscoelastic model. The method comprises a step of carrying out a dynamic frequency scanning test, a static creep test and a stress relaxation test on asphalt by using a dynamic shear rheometer, establishing a dynamic modulus main curve and a phase angle main curve based on the test data, and drawing a creep compliance-time curve and a relaxation modulus-time curve, astep of establishing the asphalt viscoelastic model and deriving an expression of each viscoelastic parameter, which is a fitting value of the model, and a step of identifying model parameters according to the comprehensive data optimization criterion, thus modifying the model parameters, and taking a set of parameters corresponding to a smallest sum-of-squared differences to be parameter values in a final model. According to the method, the dynamic and static viscoelastic properties of the asphalt are comprehensively considered, and the method has important significance for the comprehensivecharacterization of the viscoelastic performance of an asphalt material by the model and the design and maintenance of an asphalt pavement.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Colored optical fiber, optical fiber ribbon and optical fiber cable
InactiveUS20140301704A1Glass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRelaxation modulusPlastic optical fiber
A colored optical fiber including a glass optical fiber; a primary coating layer that covers the glass optical fiber; a secondary coating layer that covers the primary coating layer; and a colored layer that coats the secondary coating layer. The relaxation modulus after 24 hours at 60° C. of of the layers coated is 140 MPa or less.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Relaxation modulus sensor, structure incorporating same, and method for use of same
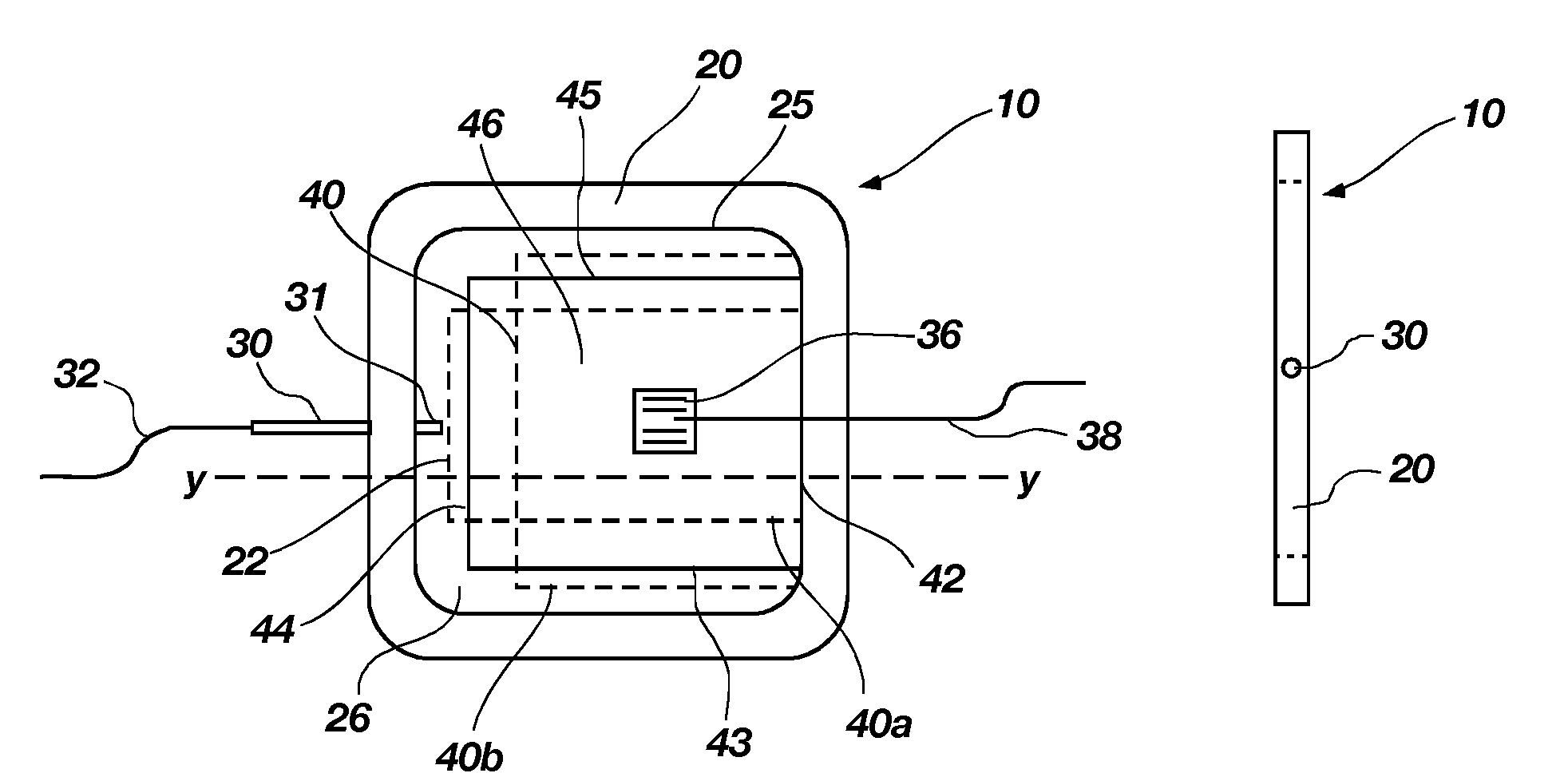
A sensor for measuring material properties such as the relaxation modulus of a material in situ and a method of measuring material properties of a material are disclosed. The sensor may be substantially embedded in the material, and includes a deformable driver. When actuated, the deformable driver may create a stress in the adjacent material. The movement or deformation of the driver may be measured with a sensing device, for example a strain gage mounted on a surface thereof. The stress in the adjacent material may be measured with a second sensing device, for example a pressure sensor. The measured movement and stress over a predetermined period of time may he used to determine the relaxation modulus of the material.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Optical fiber provided with reliable coating layers
ActiveUS7729564B2Transmission line is highImprove transmission lossGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRelaxation modulusPlastic optical fiber
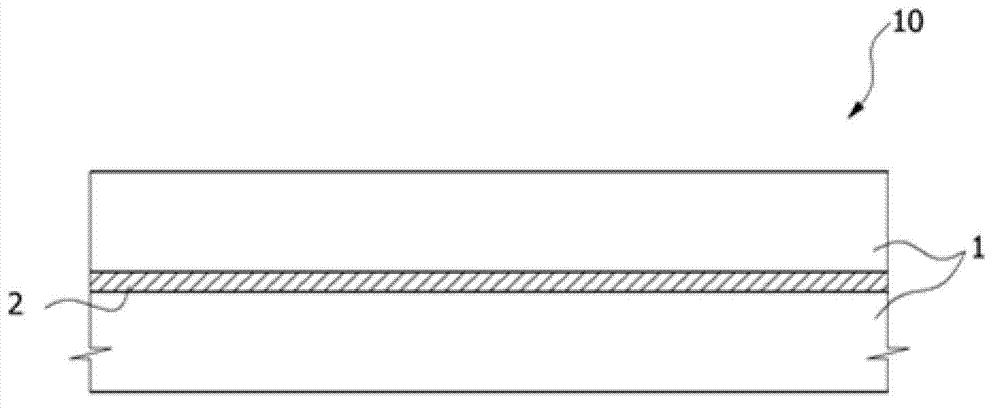
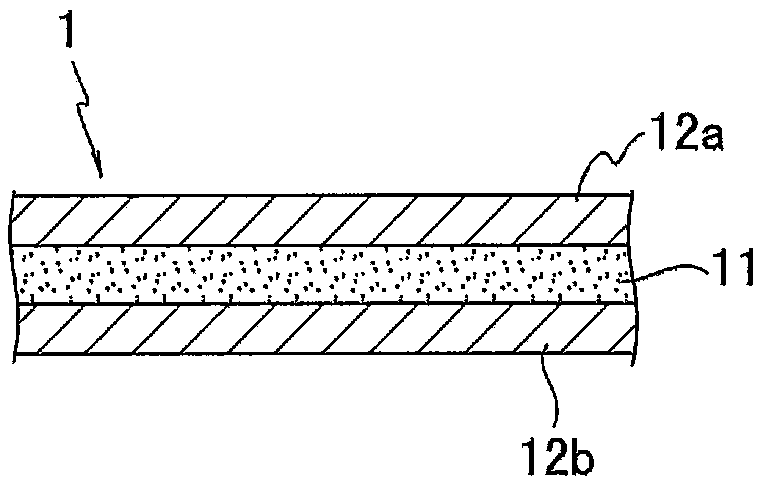
An optical fiber is provided, which is unlikely to cause interlayer delamination between a glass optical fiber and a primary coating layer even when it is immersed in water. The optical fiber of the present invention includes a glass optical fiber 1 consisting of a core and a cladding, a primary coating layer 2 overlaid on the glass optical fiber, and a secondary coating layer 3 overlaid on the primary coating layer, wherein the relaxation modulus of the secondary coating layer is set at 400 MPa or less.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Thermoplastic resin composition and injection-molded article thereof
A thermoplastic resin composition comprising: (A) polypropylene-based resin selected from the group consisting of a propylene homopolymer, an ethylene-propylene block copolymer composed of a propylene homopolymer portion and ethylene-propylene random copolymer portion having an intrinsic viscosity measured in tetralin at 135° C. of 1.0 or more and less than 8.0 dl / g and a mixture thereof, of 35 to 85 wt %; (B) elastomer of 10 to 35 wt %; (C) inorganic filler of 2 to 30 wt %; and (D) resin of 0.1 wt % or more and less than 5 wt %, wherein (1) the melt tension of (D) at 190° C. and a winding rate of 15.7 m / min. is 0.1 N or more, (2) the swelling ratio of (D) at 220° C., an L / D ratio of an orifice of 40 and a shear rate of 1.2x103 sec-1 is 1.8 or more, and (3) the time required until the ratio (G(t) / G(0.02)) of the relaxation modulus G(t) at 210° C. to that G(0.02) in a time of 0.02 sec. reaches 0.01, of (D) is 10 sec. or more.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
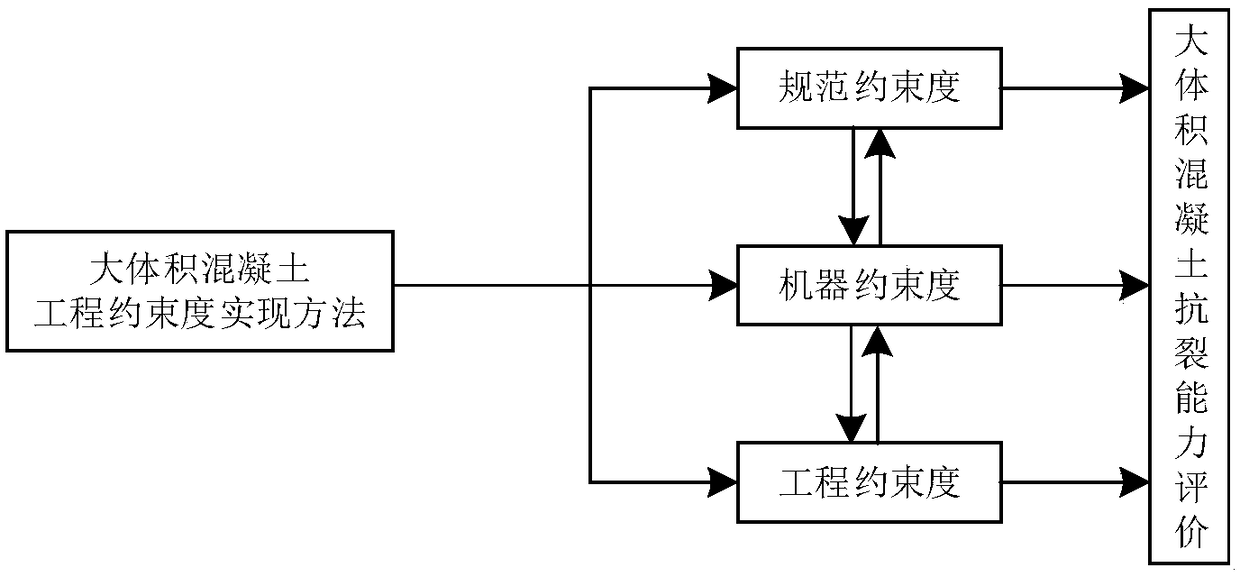
Large-size concrete engineering constraint realizing method
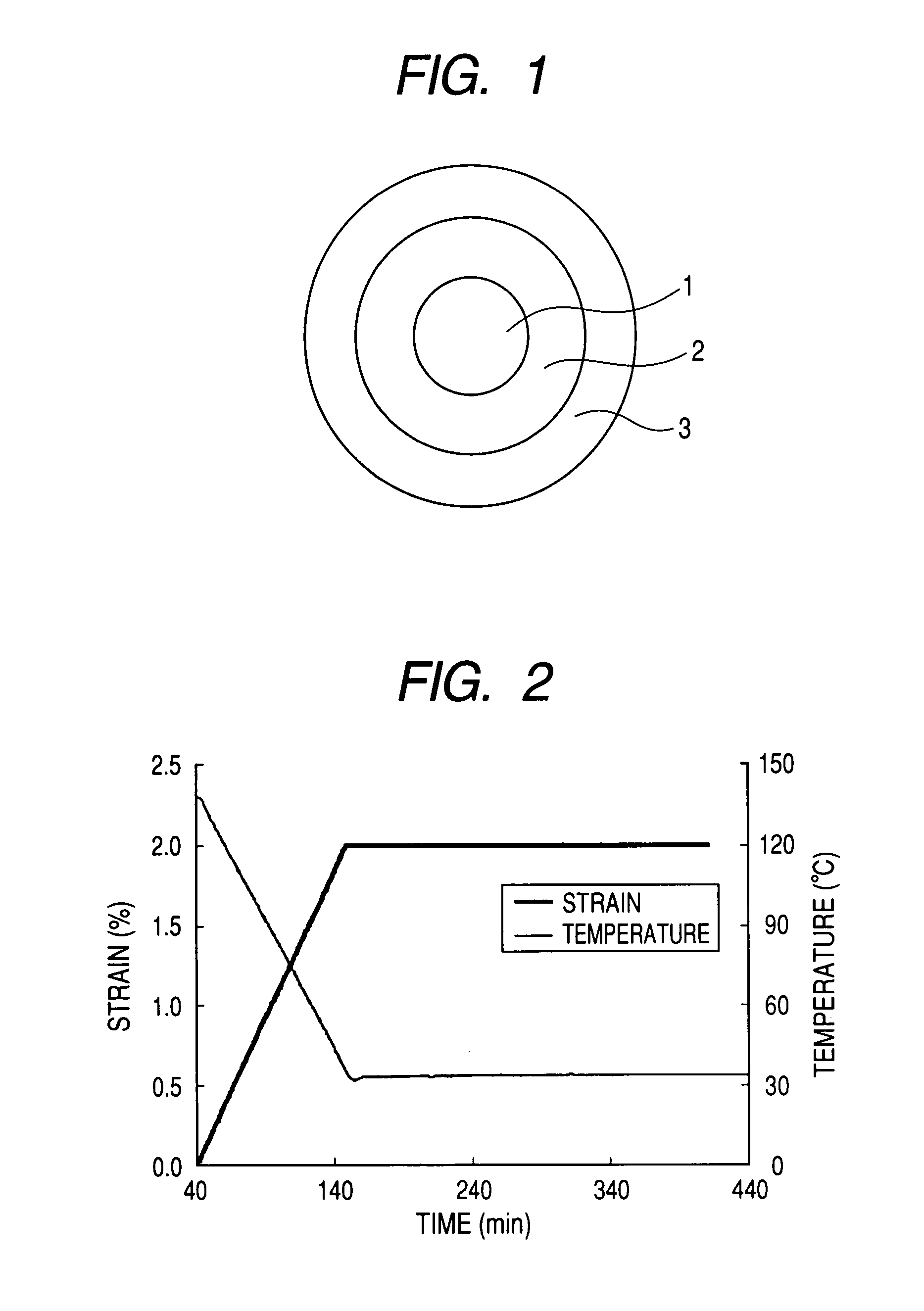
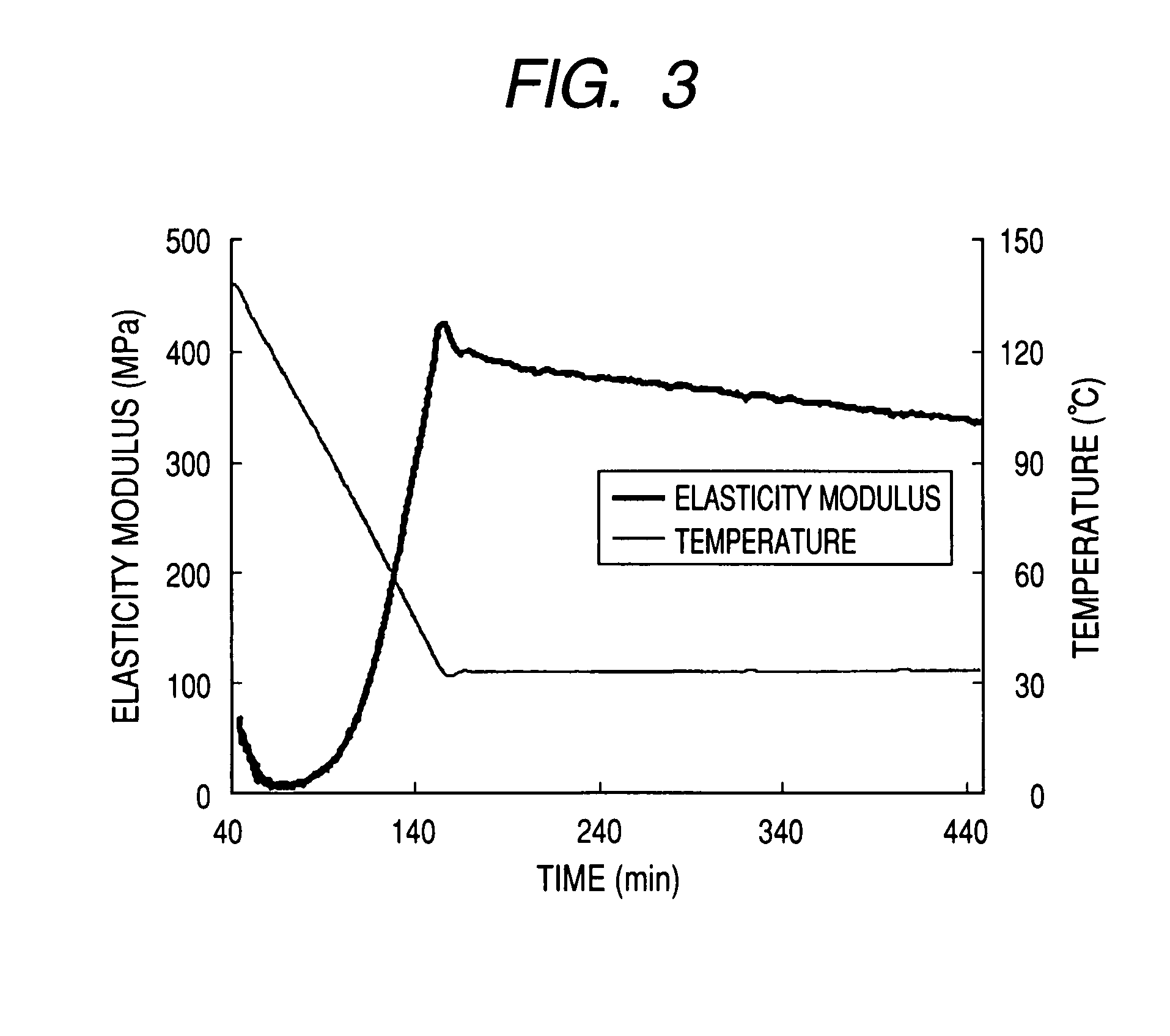
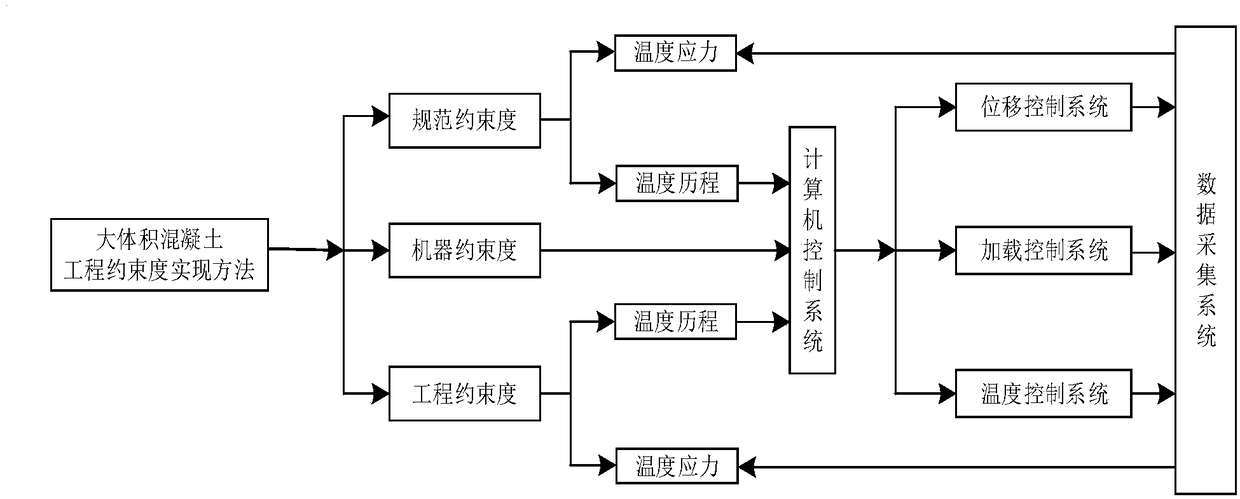
The invention discloses a large-size concrete engineering constraint realizing method. The method mainly includes following steps: (1), calculating standard constraint degree: according to actual engineering concrete block size, combining with elastic modulus of newly-cast concrete and old concrete to calculate constraint degree at a corresponding position of large-size concrete; (2), calculatingengineering constraint degree: calculating the constraint degree at the corresponding position of the large-size concrete according to on-site measured relaxation modulus and free deformation; (3), combining with on-site construction to measure time-temperature curve and time-deformation curve of the large-size concrete; (4), inputting the measured time-temperature curve and the time-deformation curve into a computer system for experimenting; (5), according identical temperature process and deformation process, realizing conversion between engineering constraint degree and machine constraint degree of the large-size concrete, and evaluating crack resistance of the concrete according to measured parameters like stress and strain and cracking process to formulate more accurate standard constraint degree.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +2
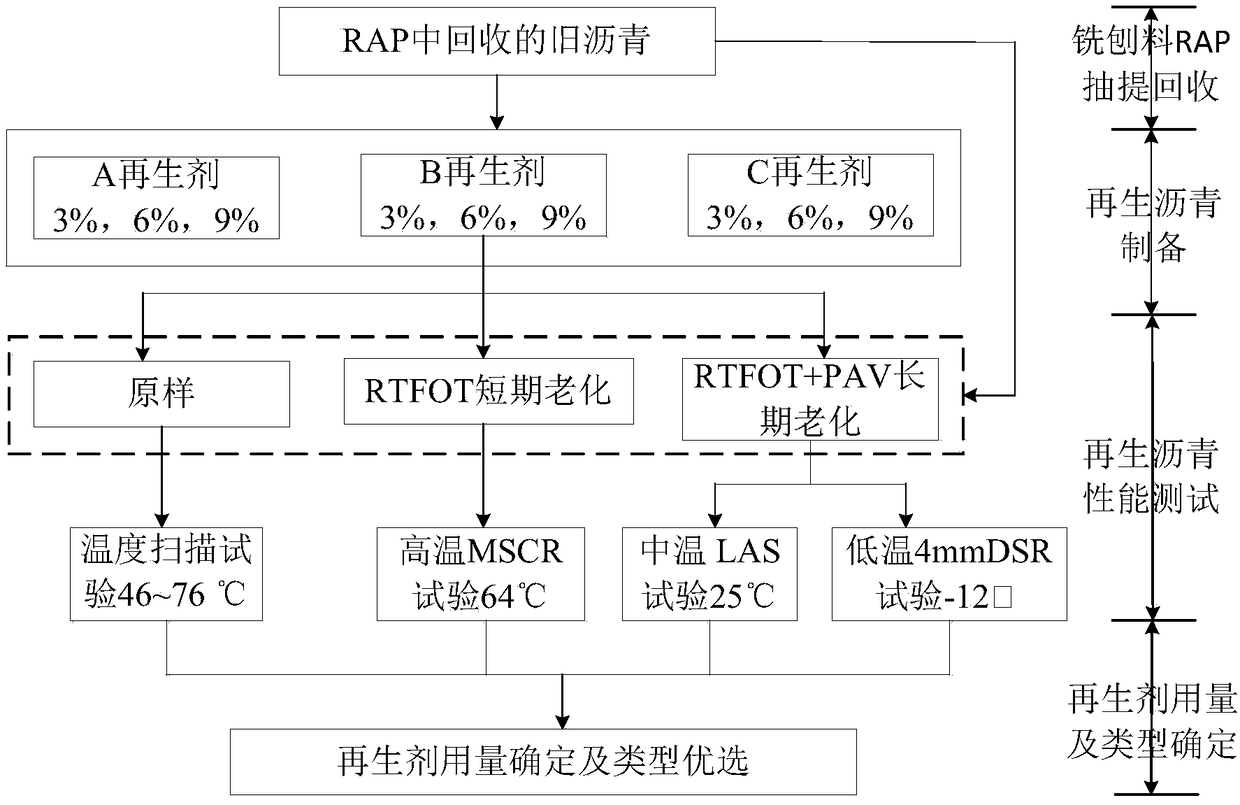
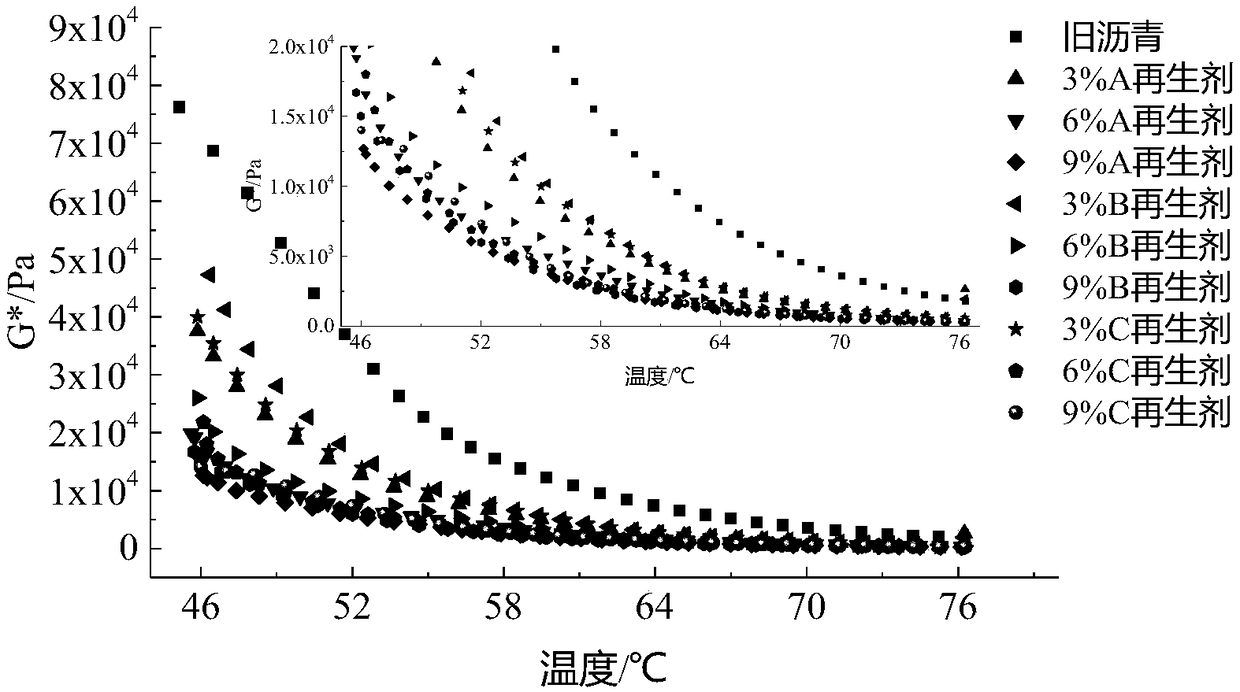
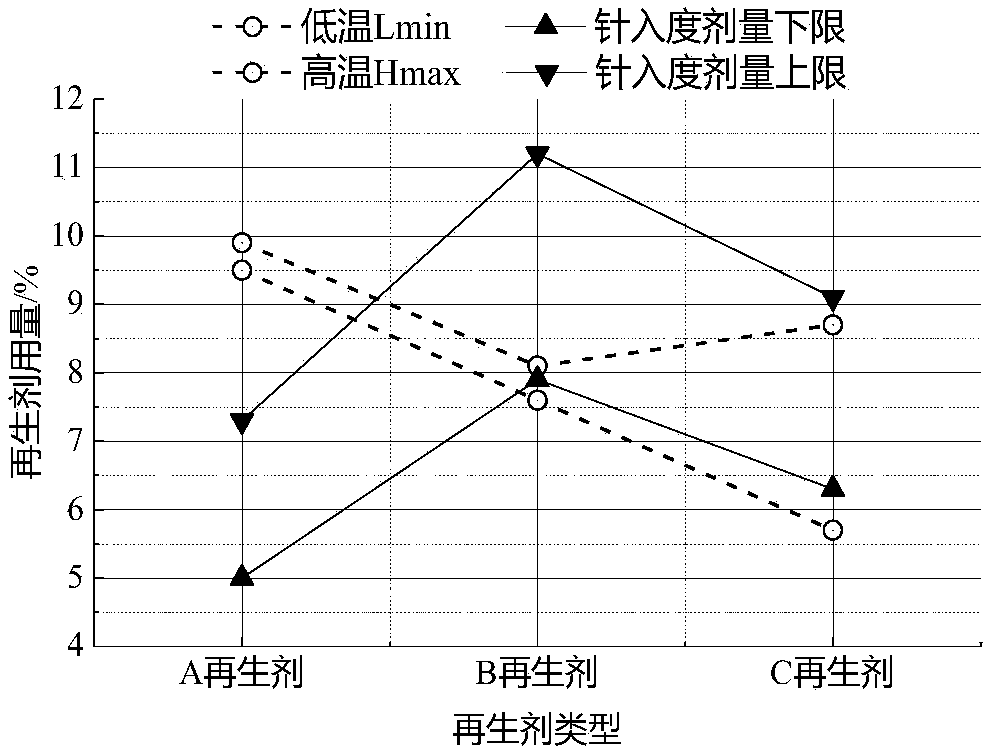
Asphalt regenerant consumption determining method based on rheological performance balance design
InactiveCN109142694AImprove permeabilityImprove diffusivityMaterial testing goodsShear modulusRelaxation modulus
The invention discloses an asphalt regenerant consumption determining method based on rheological performance balance design. The method includes steps: 1), recycling used asphalt from a milling and planing material RAP; 2), preparing regenerated asphalt samples for different regenerant consumptions; 3), testing composite shear modulus G*, high-temperature unrecoverable creep compliance Jnr-3.2, fatigue failure life Nf, low-temperature relaxation modulus G (t) and relaxation rate mr (t); 4), determining optimal regenerant consumption and type. Through the above mode, optimal regenerant consumption and type can be determined during used asphalt regeneration by starting from rheological performance reflecting regenerated asphalt material nature to enable pavement performance of a regeneratedasphalt mixture to meet requirements.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method for fast conversion of asphalt mixture material parameters by Laplace transformation
ActiveCN109470553AQuick conversionDerivation is simpleStrength propertiesTime domainRelaxation modulus
Method for fast conversion of asphalt mixture material parameters by Laplace transformation. The invention belongs to the field of asphalt mixture material parameter conversion, and aims to solve theproblems that the precision of an existing method for calculating a relaxation modulus of an asphalt mixture is difficult to ensure and the algorithm is complex. The parameter conversion method comprises: 1, calculating creep compliance of an asphalt mixture, and adopting a Prony series model to fit the creep compliance of the asphalt mixture; 2, applying Laplace positive transformation to the Prony series model of the asphalt mixture, and calculating a Laplace domain relaxation modulus through a conversion relation (as described in the specification) between relaxation modulus and creep compliance in a viscoelastic material; and 3, applying Laplace inverse transformation by adopting an FT method to solve a relaxation modulus time domain solution of the asphalt mixture. According to the method provided by the invention, a relaxation modulus value can be quickly and accurately obtained, and a relaxation modulus at any time can be solved through Laplace integral inverse transformation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Composition for anisotropic pigmented film, anisotropic pigmented film, and polarizing element
InactiveUS20090166583A1High dichroismImprove uniformityLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsProduction rateRelaxation modulus
An anisotropic dye film that exhibits a high dichroism and a high uniformity in a coating film is formed at a high level of productivity. In the composition for an anisotropic dye film containing a dye and being capable of forming a lyotropic liquid crystal phase, the time until the relaxation modulus G measured 0.01 seconds after the application of strain drops to 1 / 10 is equal to or shorter than 0.1 seconds at a temperature of 5° C. The composition contains a cation and a strongly acidic anion that respectively account for contents in the range of 0.9 to 0.99 equivalence and in the range of 0.02 to 0.1 equivalence relative to the content of the acidic groups of the dye. An anisotropic dye film is formed using this composition for an anisotropic dye film. A polarizing element is formed using this anisotropic dye film.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Thermoplastic resin composition and injection-molded article thereof
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Method for measuring crosslinking density of molded article of crosslinked thermoplastic polymer foam and molded article of crosslinked foam
ActiveCN103068893ASolesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesPolymer scienceRelaxation modulus
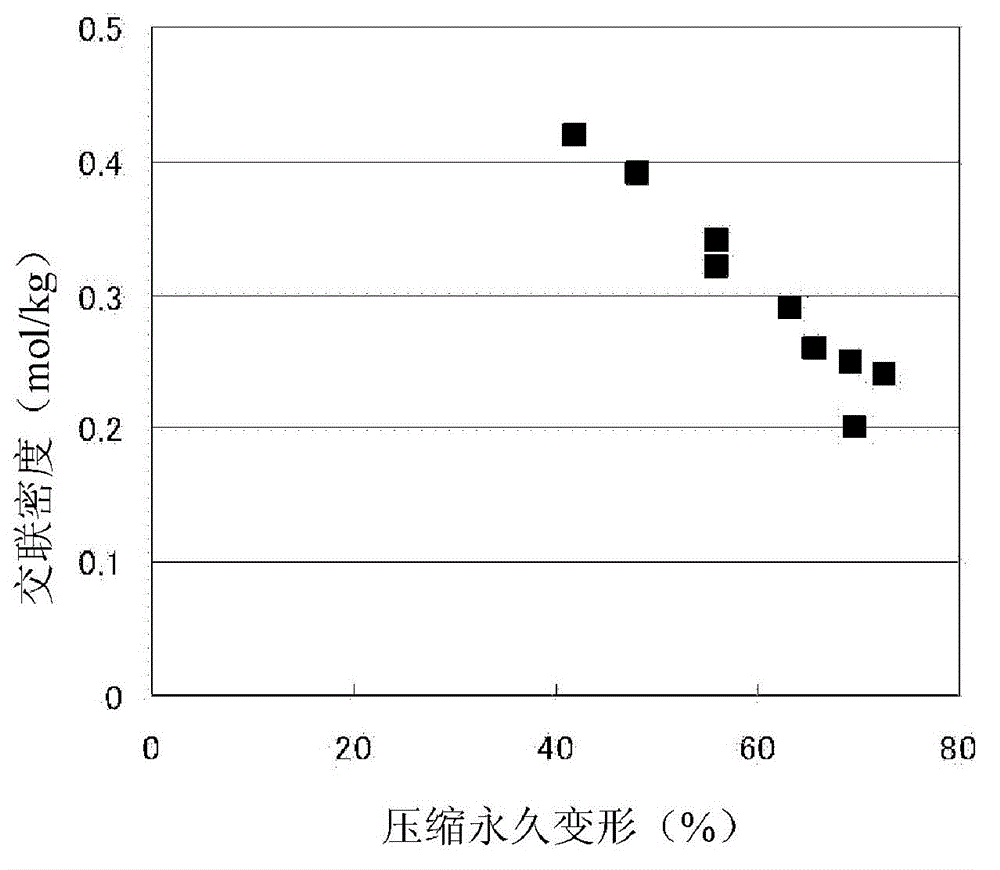
The present invention relates to a molded article of a crosslinked ethylenic polymer foam. The molded article of a crosslinked ethylenic polymer foam has a crosslinking density of 0.30 mol / kg or higher as determined using a relaxation modulus based on a stress relaxation measurement obtained by measuring the stress relaxation of the molded article of the crosslinked foam when the molded article of the crosslinked foam is subjected to compressive deformation under conditions of a measurement temperature of 60 C, compressive strain of 50%, and a measurement time of 1,800 seconds. The present invention also relates to a method for measuring the crosslinking density of a molded article of a crosslinked thermoplastic polymer foam, the method comprising: a step for heating the molded article of the crosslinked thermoplastic polymer foam to a predetermined temperature; a step for applying pressure to the molded article of the crosslinked thermoplastic polymer foam, which is maintained at the predetermined temperature, in order to induce compressive deformation of the molded article of the crosslinked foam, and for measuring the stress relaxation of the molded article of the crosslinked foam while the compressive strain of the molded article of the crosslinked foam is maintained at a constant level; a step for determining a relaxation modulus (Gc) from the stress relaxation; and a step for calculating the crosslinking density of the crosslinked thermoplastic polymer foam from Gc using the following formula in which Gc is the elastic modulus when the stress of the molded article of the crosslinked foam is at a constant level: n = Gc / RT (n: crosslinking density, R: gas constant, T: measurement temperature).
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Simulation method for macromolecular material
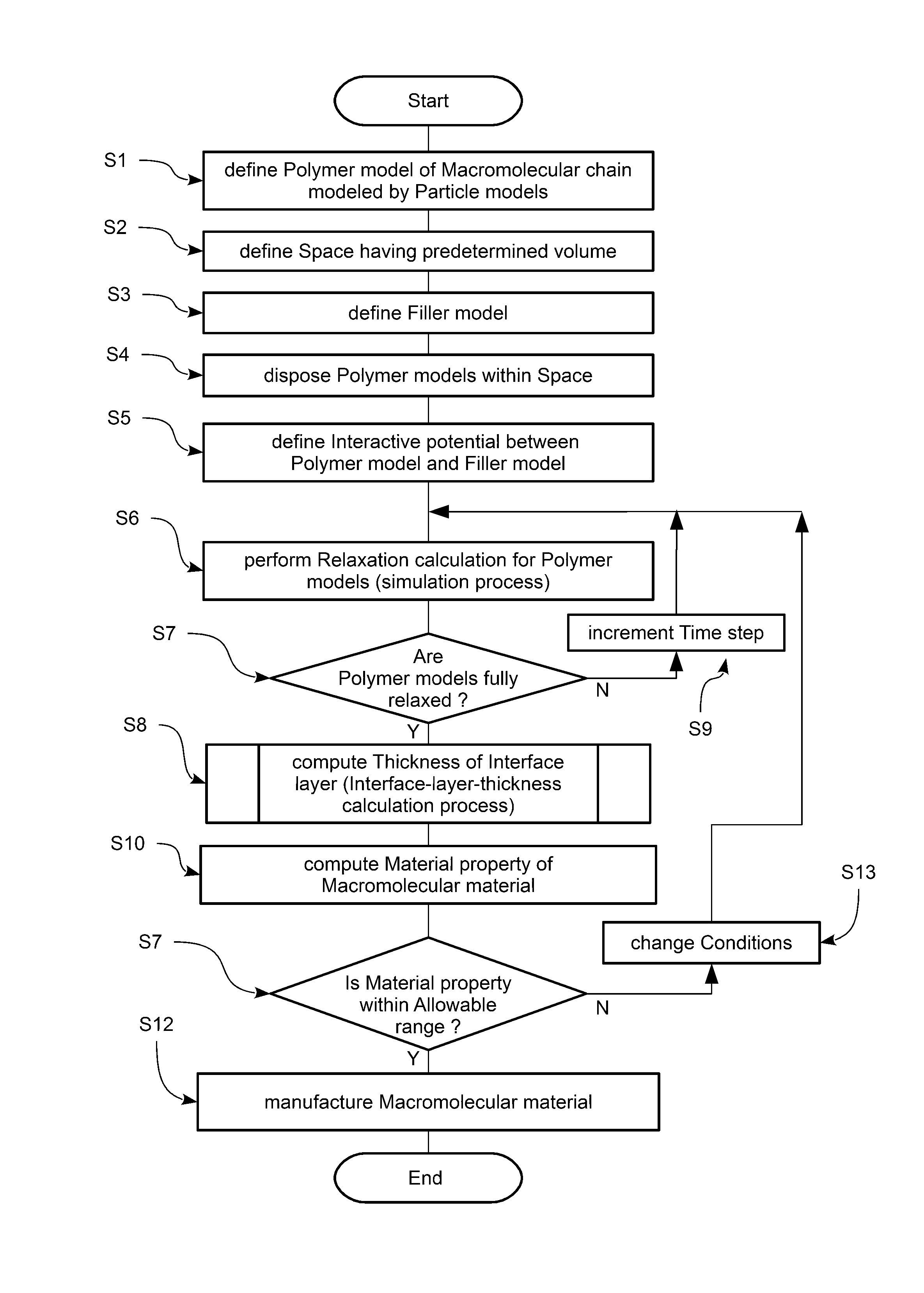
ActiveUS20140303945A1Repulsive force increaseGeometric CADChemical property predictionRelaxation modulusInterface layer
A computer simulation method for a macromolecular material and filler is disclosed, wherein a polymer model of a macromolecular chain of the macromolecular material and a filler model of the filler are defined; and a molecular dynamics calculation is performed using the filler model and the polymer models disposed in a space in order to compute the thickness of an interface layer between the filler and the macromolecular material. To compute the thickness, the space is partitioned into domains bounded by boundary surfaces; relaxation moduli of the domains are computed; and based on a variation of the relaxation moduli of the domains, the thickness of the interface layer is computed.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Composition for anisotropic pigmented film, anisotropic pigmented film, and polarizing element
An anisotropic dye film that exhibits a high dichroism and a high uniformity in a coating film is formed at a high level of productivity. In the composition for an anisotropic dye film containing a dye and being capable of forming a lyotropic liquid crystal phase, the time until the relaxation modulus G measured 0.01 seconds after the application of strain drops to 1 / 10 is equal to or shorter than 0.1 seconds at a temperature of 5°C. The composition contains a cation and a strongly acidic anion that respectively account for contents in the range of 0.9 to 0.99 equivalence and in the range of 0.02 to 0.1 equivalence relative to the content of the acidic groups of the dye. An anisotropic dye film is formed using this composition for an anisotropic dye film. A polarizing element is formed using this anisotropic dye film.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Organic light emitting display apparatus including viscoelastic layer and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9203051B2Reducing visually recognizable bubblesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRelaxation modulusStress measures
Disclosed is an organic light emitting display (OLED) apparatus that includes a substrate; an organic light emitting element on the substrate, the organic light emitting element including a first electrode, an organic light emitting layer and a second electrode; a viscoelastic layer on the organic light emitting element, wherein an elastic portion of the viscoelastic layer is about 30% or more, the elastic portion being defined by <Equation 1>: Elastic portion (Ep) (%)=(σ / σ0)×100, wherein σ0 is an initial stress generated when a strain of about 50% is applied to the viscoelastic layer and σ is a final stress measured after the strain is continuously applied thereto for about 180 seconds, with the initial stress σ0 and the final stress σ being measured at about 80° C. through a relaxation modulus test.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Optical fiber provided with reliable coating layers
ActiveUS20090269015A1Improve long-term reliabilityImprove adhesionGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRelaxation modulusPlastic optical fiber
An optical fiber is provided, which is unlikely to cause interlayer delamination between a glass optical fiber and a primary coating layer even when it is immersed in water. The optical fiber of the present invention includes a glass optical fiber 1 consisting of a core and a cladding, a primary coating layer 2 overlaid on the glass optical fiber, and a secondary coating layer 3 overlaid on the primary coating layer, wherein the relaxation modulus of the secondary coating layer is set at 400 MPa or less.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Composite sheet, method for preparing the same and display substrate including the same
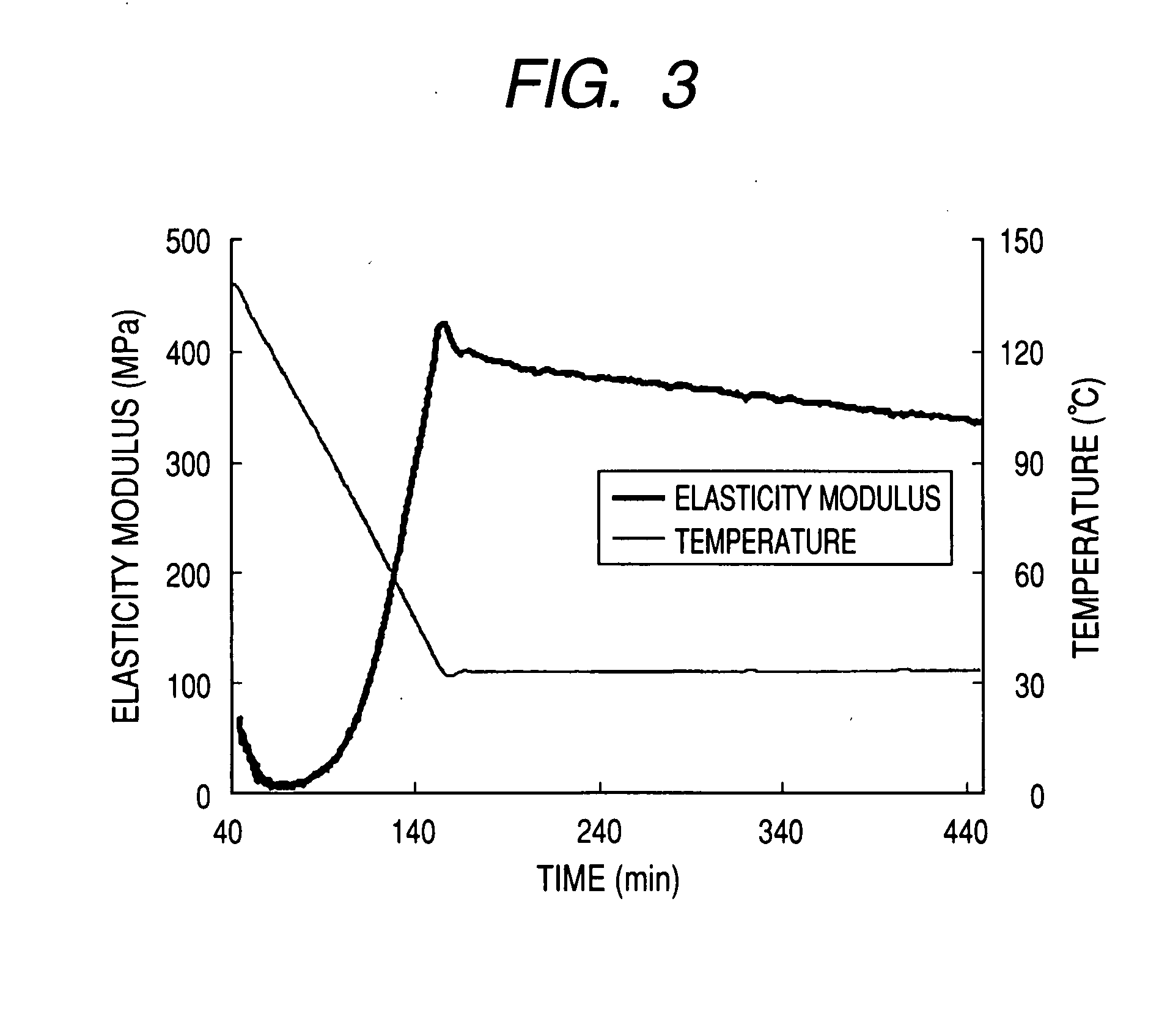
Disclosed herein is a composite sheet including a matrix and a reinforcing material impregnated in the matrix. The composite sheet has a weight variation (”W) of 98% or more at 350°C and a relaxation modulus of 1000 MPa or less under a load of 100 µN. The composite sheet suppresses the formation of a ring structure and thermal decomposition at temperatures of 350°C or more, thereby preventing a failure of the materials at high temperatures in the manufacture of a substrate.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Optical fiber colored core, optical fiber tape core and optical fiber cable
ActiveCN103765272AGood anti-microbending propertiesTransmission loss is not easy to increaseGlass optical fibreFibre mechanical structuresRelaxation modulusWarm water
The present invention provides an optical fiber colored core which has superior microbend-resistant characteristics and warm-water resistance, as well as an optical fiber tape core and optical fiber cable using the same. Provided is an optical fiber colored core (1) which has two layers of cladding layers, which are a primary cladding layer (31) and a secondary cladding layer (32), wherein either the primary cladding layer (31) or the secondary cladding layer (32) is colored, the equilibrium modulus of either layer is less than or equal to 60 MPa, and the relaxation modulus of the secondary cladding layer (32) is greater than or equal to 410 MPa. Also provided are an optical fiber tape core (4) using the same, and an optical fiber cable (8).
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Adhesive for repeatedly foldable device, adhesive sheet, repeatedly foldable laminate member and repeatedly foldable device
PendingCN109929491AReduce the impactNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesEster polymer adhesivesRelaxation modulusAdhesive
The invention provides an adhesive for a repeatedly foldable device and an adhesive sheet, which can inhibit the deformation of an adhesive layer and alleviate the influence caused by the repeated folding and the folding state of the repeatedly foldable device after the folding state is released when the adhesive is suitable for the repeatedly foldable device and is repeatedly bent and placed in the long-term folding state. The adhesive is used for bonding one folding member and the other folding member which form the repeatedly foldable device. Wherein the JIS K7244-1 is taken as a reference,and the JIS K7244-1 is taken as a reference; the maximum relaxation modulus value measured when the adhesive is deformed by 10% is set as the maximum relaxation modulus G(t)max (MPa). The adhesive iscontinuously deformed by 10% from the measurement of the maximum relaxation modulus G(t)max to 3757 seconds later, the minimum relaxation modulus value measured during this period is set to be the minimum relaxation modulus G(t)min (MPa), and the relaxation modulus variation value logG(t) calculated by formula (I) is 0.85 or less. Delta(logG(t)) = logG(t) max-logG(t) min...(I).
Owner:LINTEC CORP
Repeated bending device, manufacturing method therefor, and suppressing method for bending traces
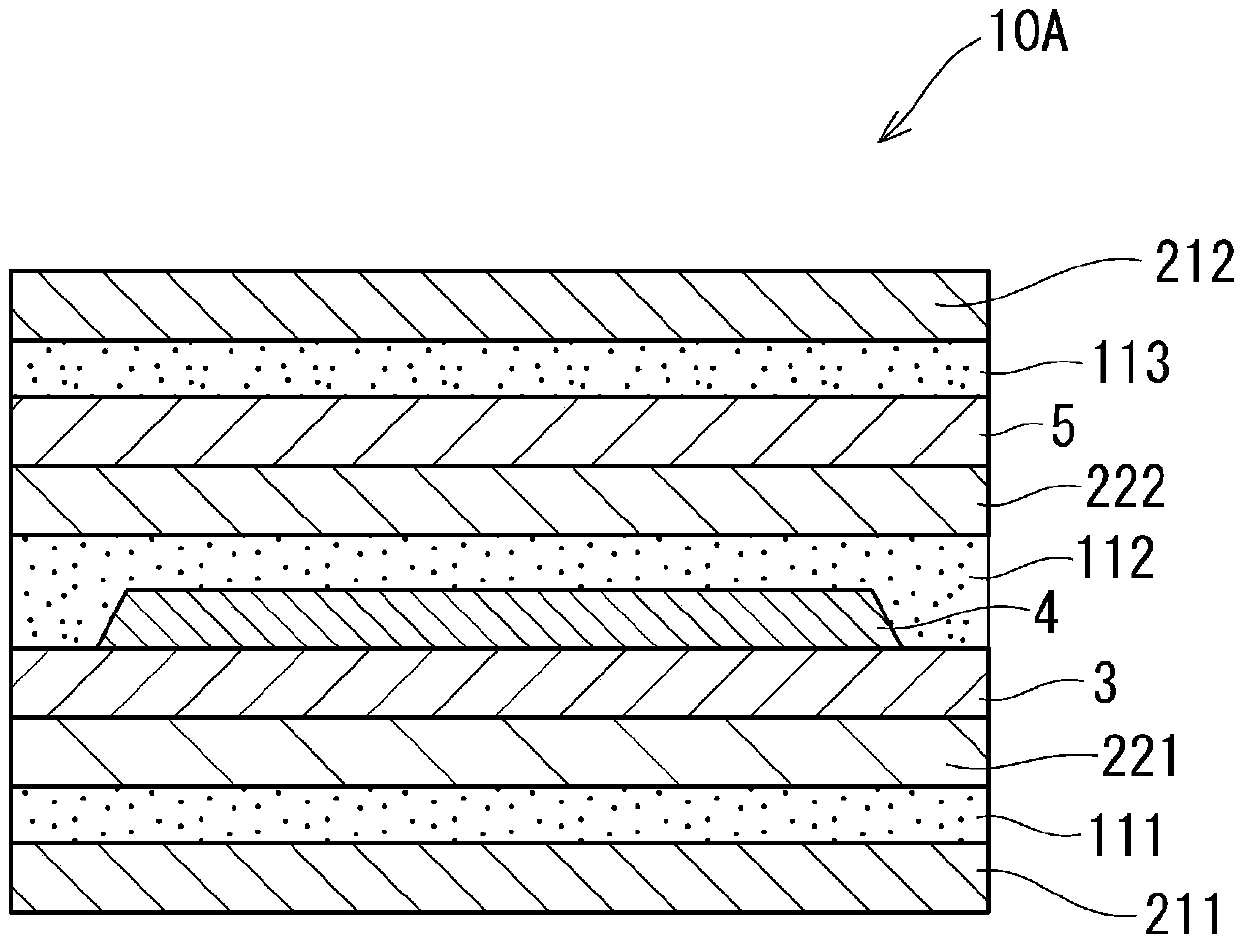
ActiveCN109929480ALess prone to bending marksBend mark suppressionAdhesive processesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesRelaxation modulusEngineering
The invention provides a repeated bending device, which is not easy to generate bending traces after the bending state is released when the repeated bending is carried out or the repeated bending device is placed in a long-term bending state. Namely, a repeated bending device (10A) is provided. The pressure-sensitive adhesive tape is provided with one or more adhesive layers (111), (112), and (113). At least one layer of the adhesive layer is composed of the following adhesives: an adhesive; the maximum relaxation modulus value measured when the adhesive is deformed by 10% is set as the maximum relaxation modulus G(t)max(MPa). Continuously deforming the adhesive by 10% from the measurement of the maximum relaxation modulus G(t)max to 3,757 seconds later, wherein the minimum relaxation modulus value measured during this period is set as the minimum relaxation modulus G(t)min(MPa), and the relaxation modulus variation value logG(t) calculated from the following formula (I) is 1.20 or less. Delta(logG(t))=logG(t)max-logG(t) min... (I).
Owner:LINTEC CORP
Relaxation modulus sensor, structure incorporating same, and method for use of same
A sensor for measuring material properties such as the relaxation modulus of a material in situ and a method of measuring material properties of a material are disclosed. The sensor may be substantially embedded in the material, and includes a deformable driver. When actuated, the deformable driver may create a stress in the adjacent material. The movement or deformation of the driver may be measured with a sensing device, for example a strain gage mounted on a surface thereof. The stress in the adjacent material may be measured with a second sensing device, for example a pressure sensor. The measured movement and stress over a predetermined period of time may he used to determine the relaxation modulus of the material.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method for detecting high-temperature viscoelastic parameters of glass material
PendingCN112881196AOvercome the defect of easy breakageEffective and reliable measurementMaterial strength using steady bending forcesTime domainRelaxation modulus
A method for detecting high-temperature viscoelastic parameters of a glass material comprises the following steps: A, heating a glass test piece to a test temperature, applying force to the glass test piece for a preset time, and recording a curve of bending deformation of the glass test piece along with time; B, processing the measured data to obtain a curve of the creep compliance of the glass test piece along with time, and fitting the creep compliance of the glass test piece; C, performing Laplace transformation on the creep compliance obtained by fitting, obtaining Laplace transformation of the relaxation modulus according to a conversion relation between the creep compliance and the relaxation modulus, and then performing inverse Laplace transformation to obtain an expression equation of the relaxation modulus in a time domain; and D, judging whether the expression equation of the relaxation modulus is a Prony series expression form of the relaxation modulus or not, if yes, taking the expression equation as a detection result, otherwise, fitting the expression equation by using the Prony series, and taking the expression equation as a high-temperature viscoelastic parameter detection result. According to the invention, the defects of temperature limitation and easy breakage of the glass test piece can be overcome, and the viscoelastic parameters of the glass material in a high-temperature state can be effectively and reliably measured.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
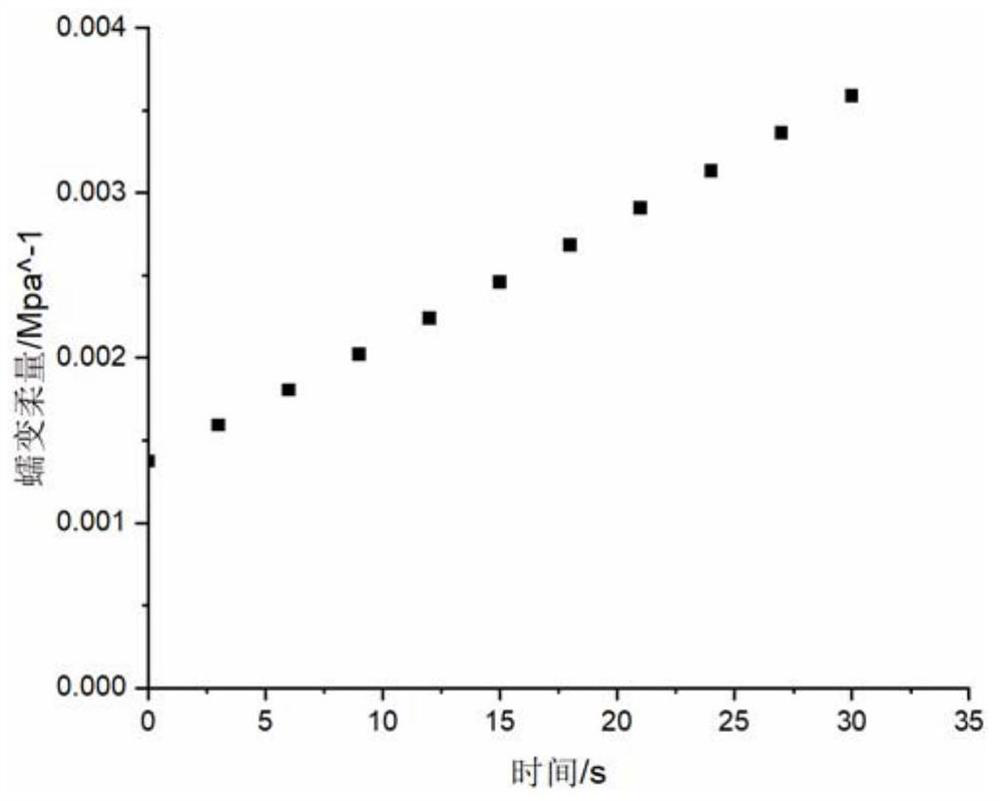
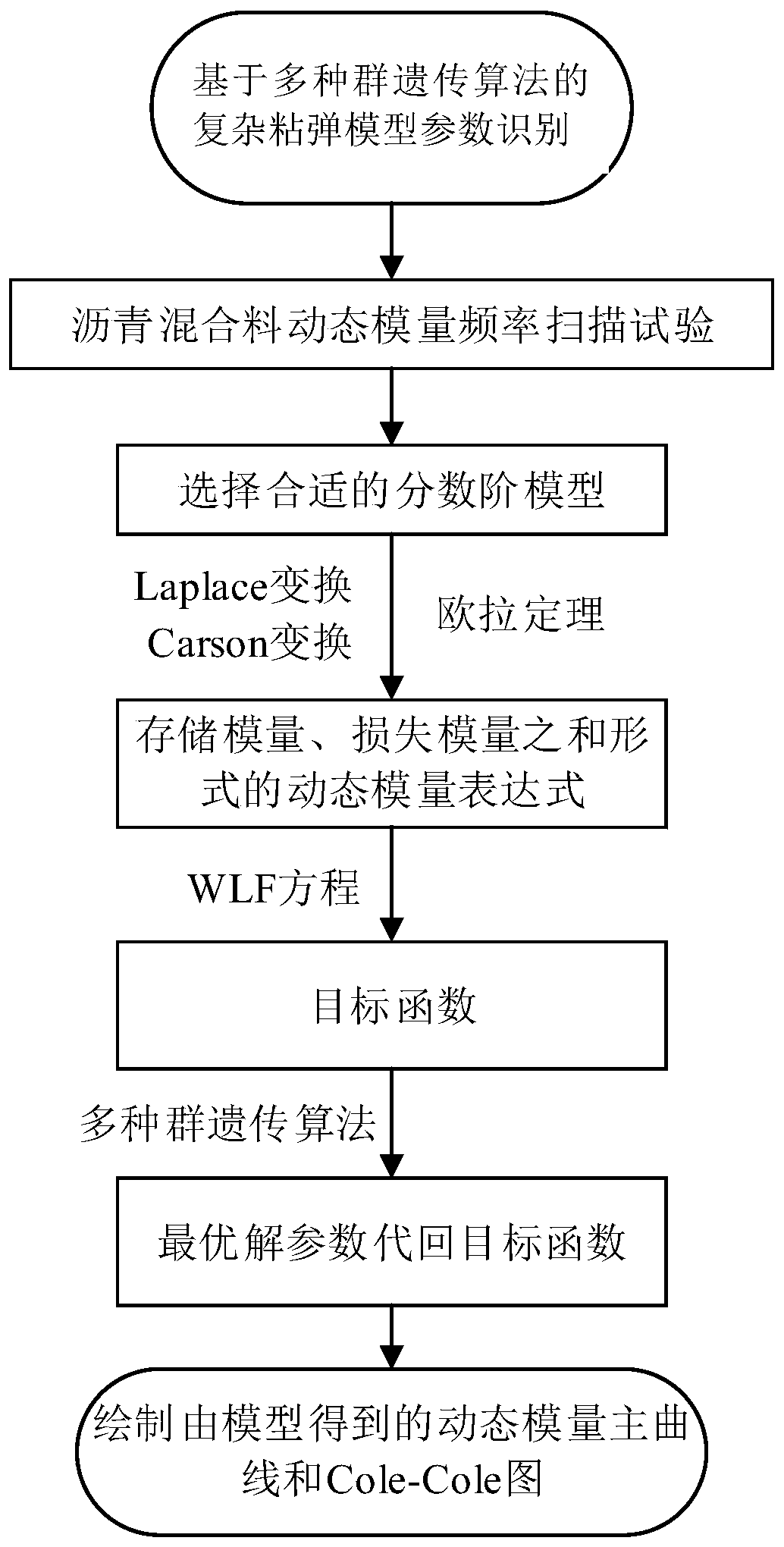
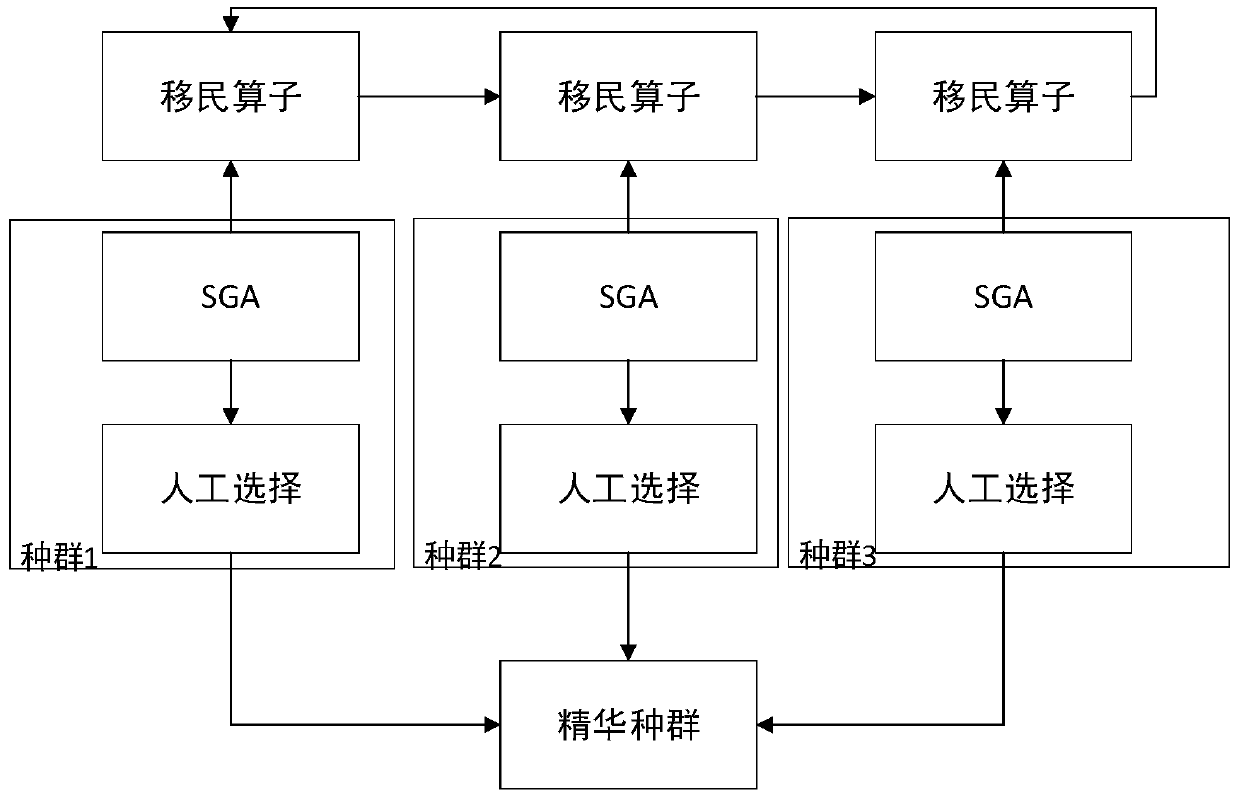
Method for identifying fractional order viscoelastic model parameters based on multi-population genetic algorithm
ActiveCN110031611AOvercome the inability to identify all parameter values in the modelMaterial testing goodsRelaxation modulusAlgorithm
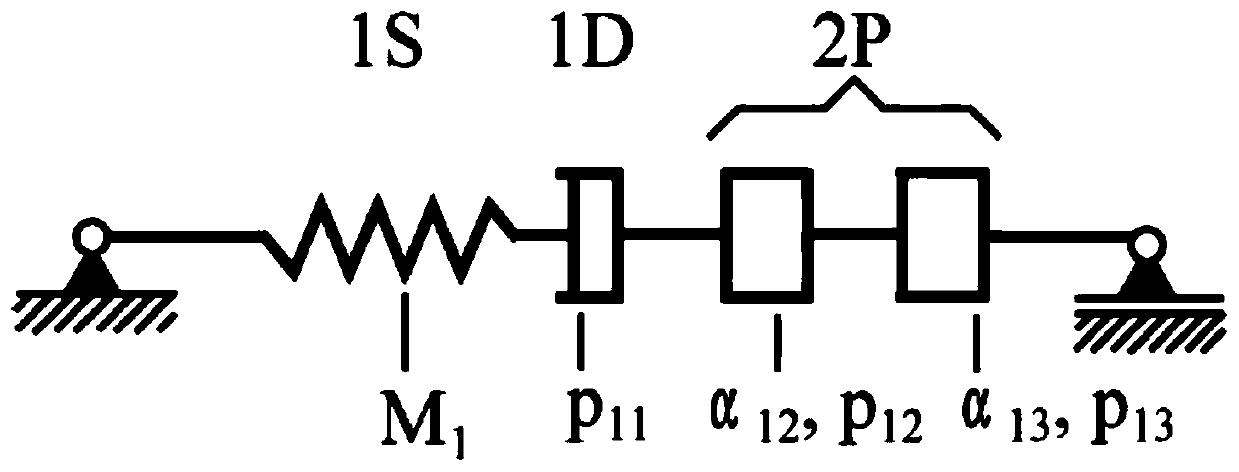
The invention provides a method for identifying fractional order viscoelastic model parameters based on a multi-population genetic algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of constitutive behavior studies of bituminous mixtures. The problem that as for an existing method, all parameter values in a model cannot be identified during mutual transformation among the creep compliance, the relaxation modulus and the dynamic modulus is solved. According to the dynamic modulus value, the appropriate 1S2P1D model is selected, and through Laplace conversion, the stress-strain relationship of the 1S2P1D model is converted into the stress-strain relationship of the 1S2P1D model within the Laplace domain; then 1S2P1D model parameters considering the temperature effect are obtained; and finally, all the parameter values in the model are automatically obtained at a time based on the multi-population genetic algorithm, and thus the problem that as for the existing method, all the parameter valuesin the model cannot be identified during mutual transformation among the creep compliance, the relaxation modulus and the dynamic modulus is solved. The method can be applied to the technical field of the constitutive behavior studies of the bituminous mixtures.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Thermoplastic resin composition and its injection shaped products
Disclosed is a thermoplastic resin composition comprising specific amounts of (A) a polypropylene resin, (B) an elastomer, (C) inorganic filler, (D) a resin having a melt tension of 0.1 N or more and a swelling ratio of 1.8 or more and being characterized by that the time required for the resin until the ratio (G(t) / G(0.02)) of a relaxation modulus G(t) measured at 210 DEG C. to a relaxation modulus G(0.02) at a time of 0.02 sec reaches 0.01 is 10 sec or more, and (E) a resin characterized by that, with respect to a swelling ratio measured at 220 DEG C. at an L / D of an orifice of 40, the ratio of a swelling ratio (SR10<3>) at a shear rate of 2.4x10<3 >sec<-1 >to a swelling ratio. (SR10<2>) at a shear rate of 1.2x10<2 >sec<-1>, SR10<3> / SR10<2>, is from 1.0 to 1.1.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Method of producing film
ActiveUS20160325477A1Reduce the numberExcellent designOptical articlesFlat articlesPolymer scienceRelaxation modulus
Disclosed herein is a method of producing a film, the method being capable of suppressing formation of die lines in melt extrusion molding using a T die. A thermoplastic resin composition having a relaxation modulus of not less than 100 Pa and not more than 2,000 Pa is melted and kneaded, the relaxation modulus being measured under conditions of a temperature of 260° C., distortion of 1%, and a relaxation time of 1 second, and extrusion molding of the thermoplastic resin composition using the T die is performed to form the film. The thermoplastic resin composition may contain an acrylic resin and a rubber particle.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
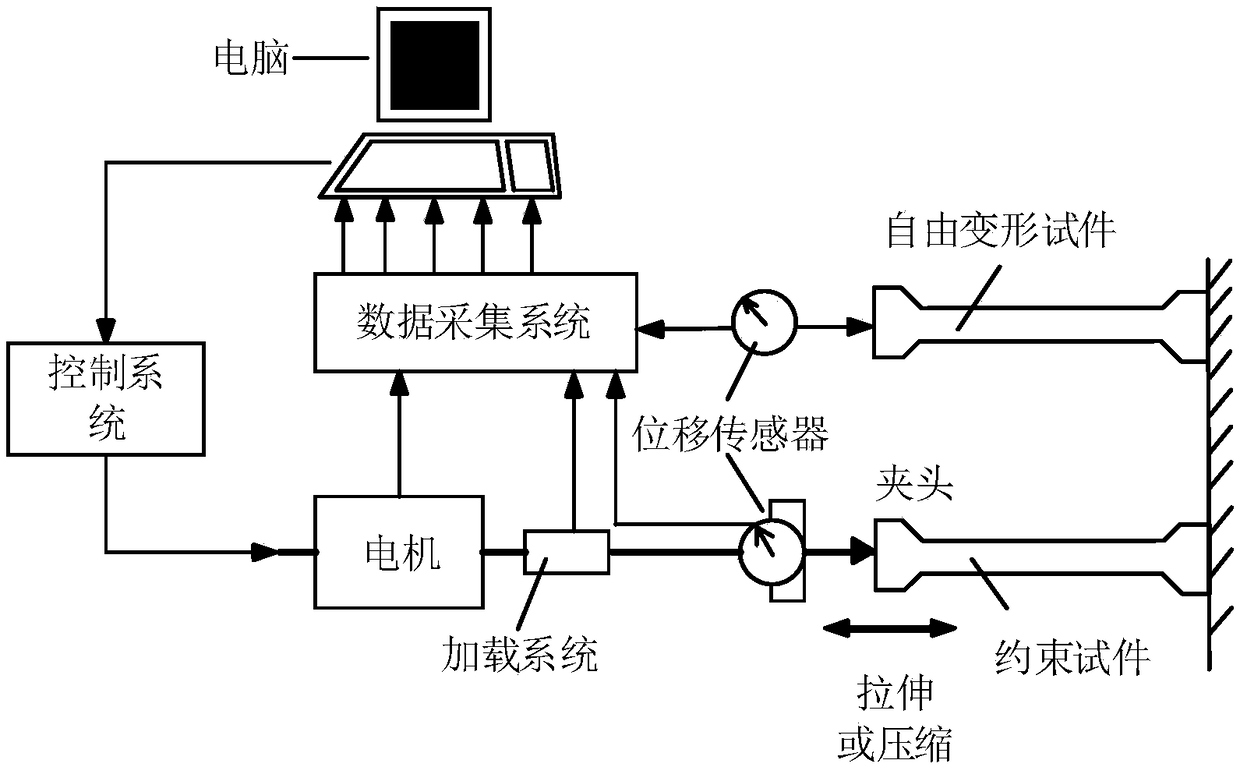
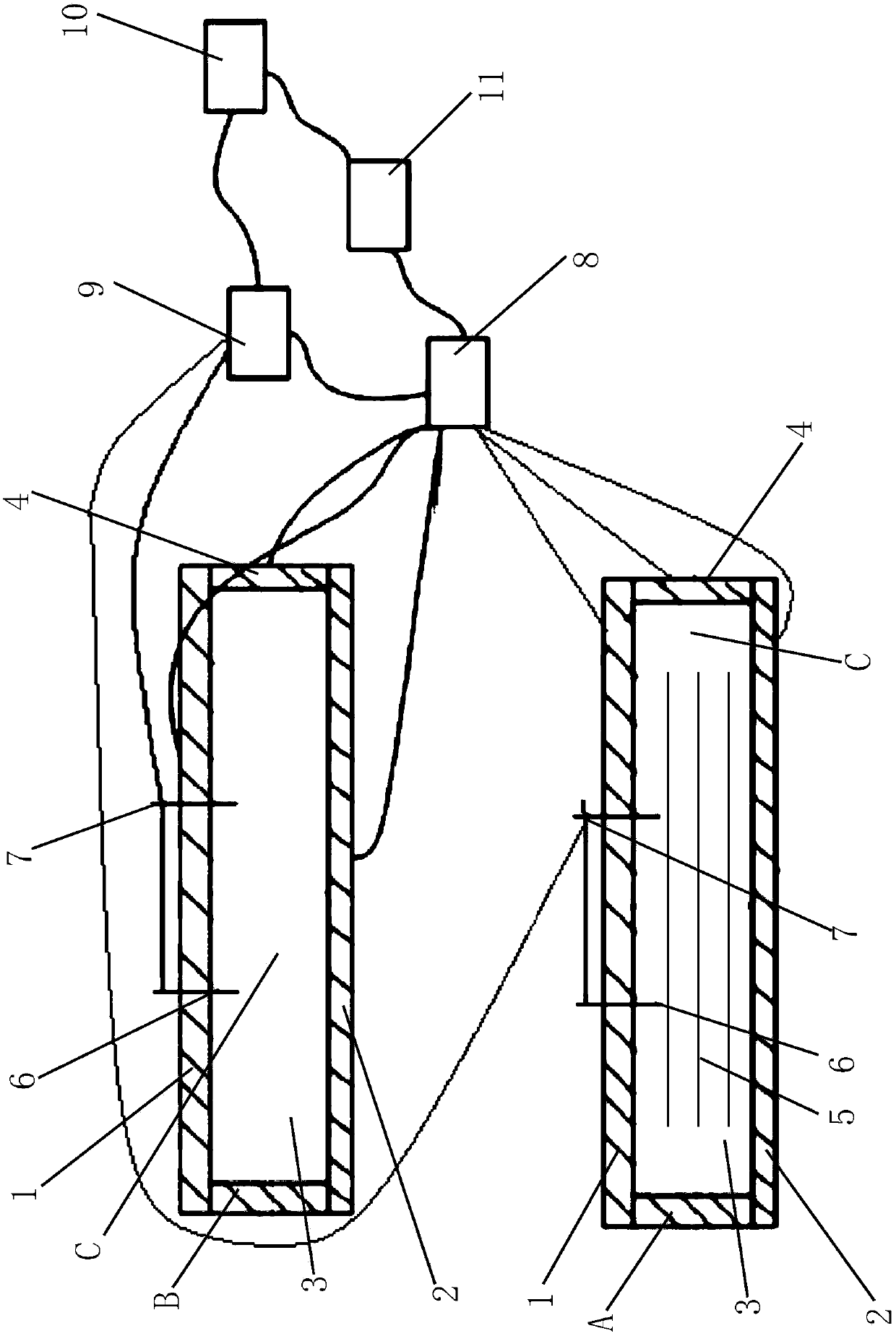
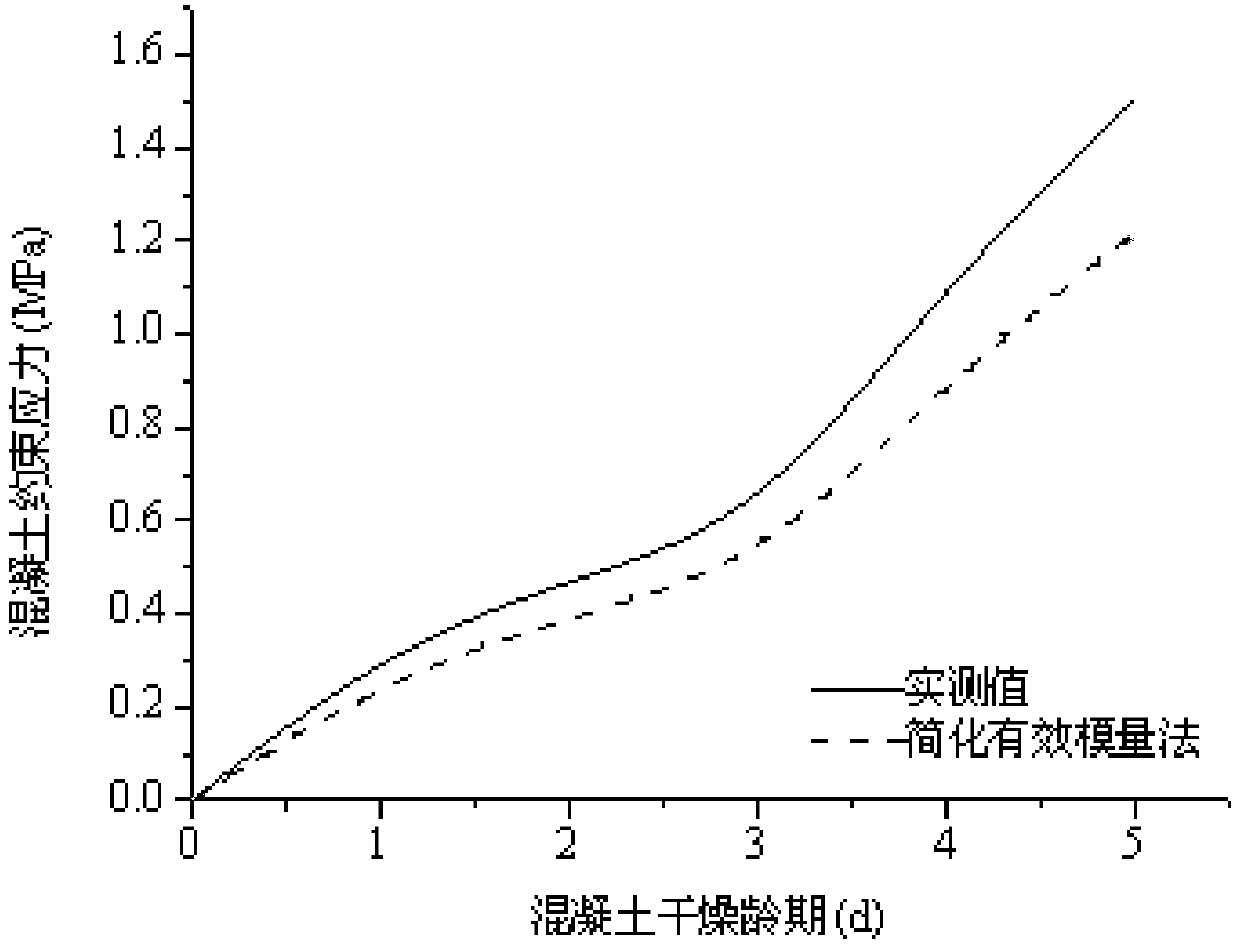
Device and method for evaluating relaxation modulus of concrete under different curing conditions
ActiveCN108254537AThe relaxation modulus is determined directlyAccurate measurementMaterial testing goodsTemperature controlRelaxation modulus
A device and a method for evaluating a relaxation modulus of concrete under different curing conditions are disclosed. The device comprises a template system, a temperature system, an acquisition system, a control system and a computer system; the template system comprises an experimental template and a control template, the experimental template and the control template both includes an upper template with a temperature control channel, a lower template and two symmetrical side templates, the upper template is provided with two quartz rods in a penetration manner, and a displacement sensor isarranged between the two quartz rods; the upper template, the lower template, the side templates, an end template and the center of a pouring space are provided with first temperature sensors respectively, the temperature system includes a water tank with a water pump, the water tank is internally provided with a temperature control device and a second temperature sensor; the input end of the acquisition system is connected with the displacement sensor, the first temperature sensor and the second temperature sensor, the output end of the acquisition system is connected with the input end of the computer system; the input end of the control system is connected with the output end of the computer system, and the output end of the control system is connected with the temperature control device and the water pump.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
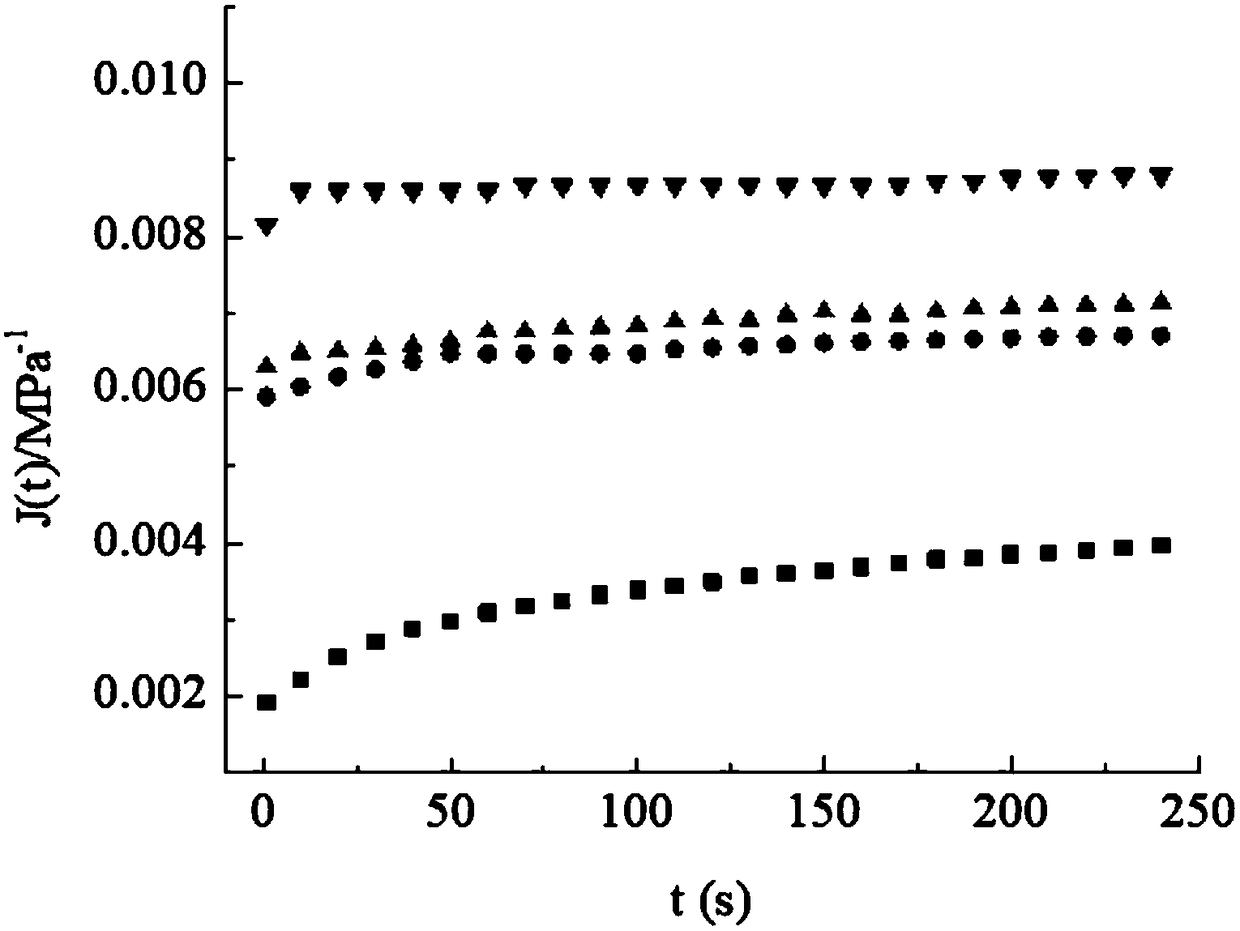
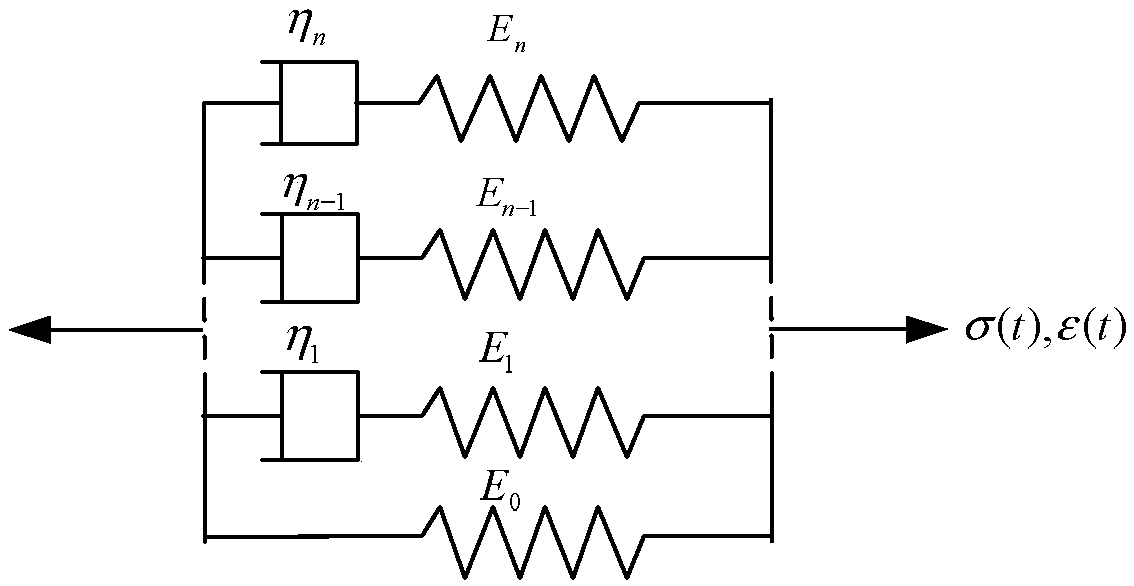
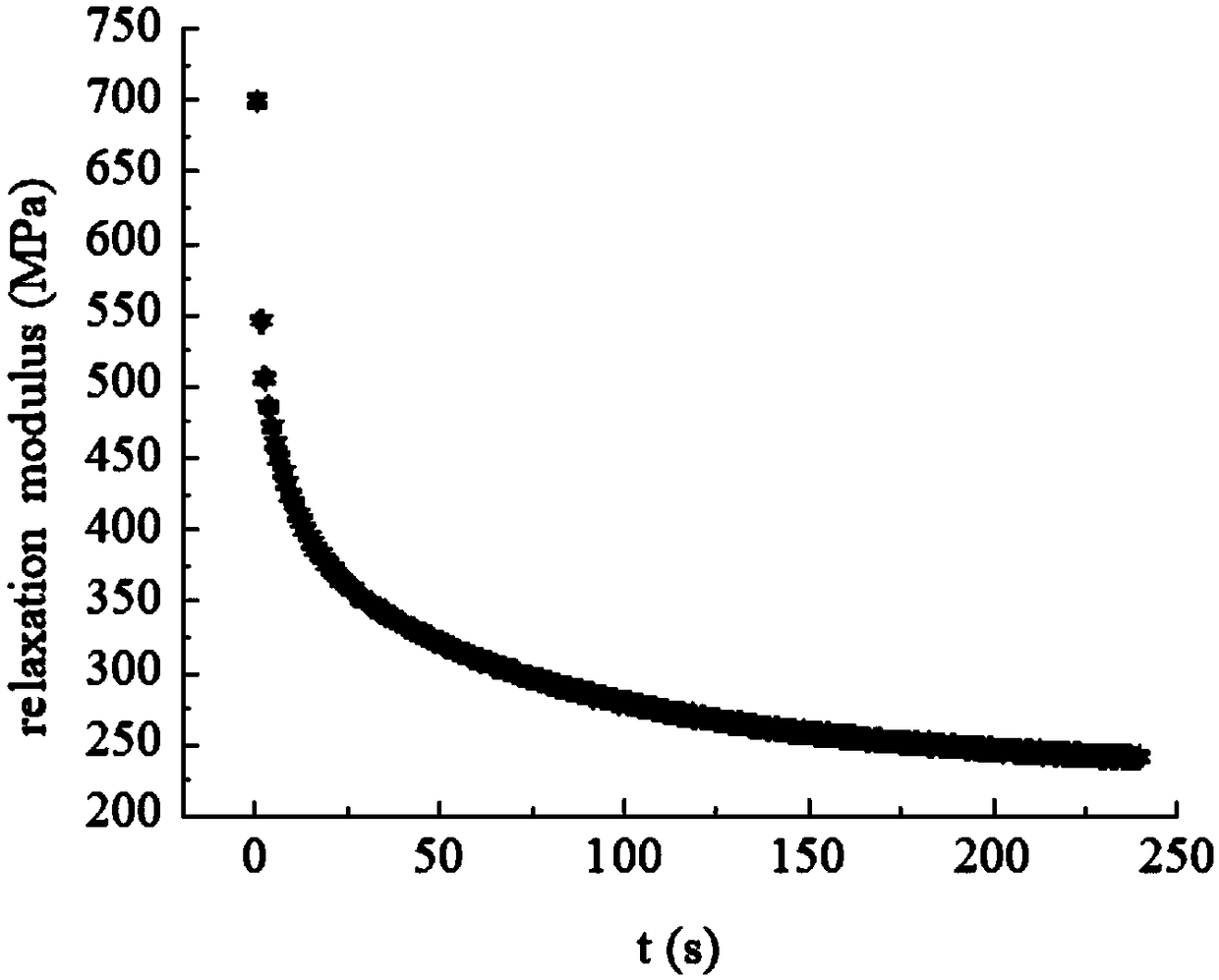
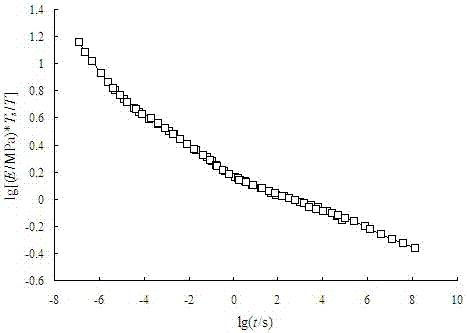
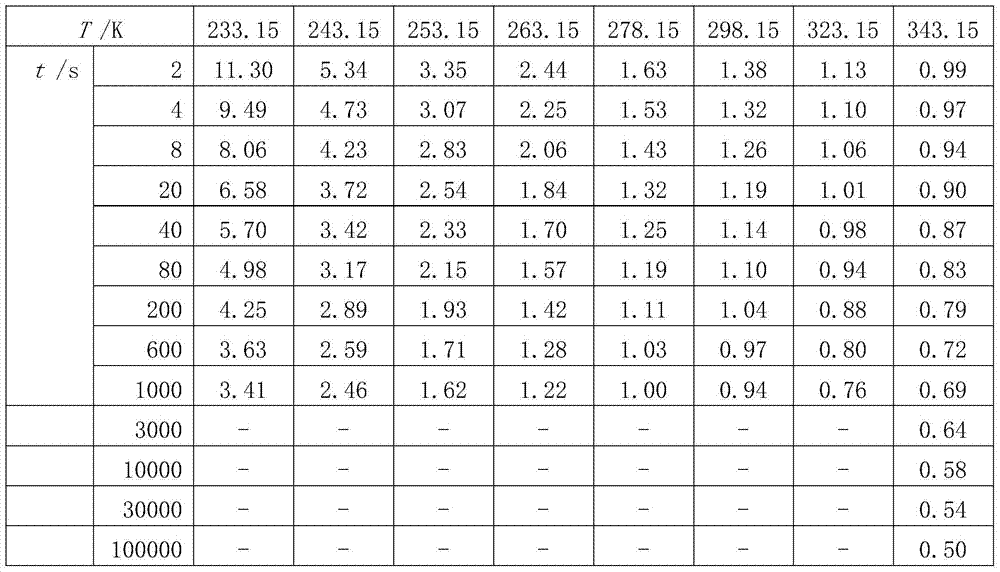
A Prediction Method of Durable and Instantaneous Limit Mechanical Properties of Polymers
ActiveCN104568602BSave materialWide time scaleMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesPredictive methodsTest failure
The invention is a method for predicting the permanent and instantaneous limit mechanical properties of polymers for the performance evaluation of viscoelastic materials. Including the following steps: condition selection and sample preparation, mechanical test, curve preparation and data prediction. In the selection of conditions and sample preparation, the target is all viscoelastic materials. During the mechanical test, perform stress relaxation test, creep failure test and stress relaxation failure test at a series of temperatures to obtain data such as relaxation modulus and failure time; in the curve preparation and data prediction stage, according to the mechanical test results and prediction goals, make The relaxation modulus-time curve and the relaxation modulus master curve at a series of temperatures can be used to determine the relationship between a set of ultimate mechanical properties and action time, and obtain the predicted value of the permanent and instantaneous fracture strain or fracture strength of the polymer. The invention has the advantages that the method is simple and effective, the data is accurate and reliable, the test operation is convenient, the test process is simplified, and the test conditions are reasonable.
Owner:HUBEI INST OF AEROSPACE CHEMOTECHNOLOGY
Golf ball resin composition and golf ball
ActiveUS20180171127A1Increased durabilityEnhance resilienceGolf ballsSolid ballsPolymer scienceRelaxation modulus
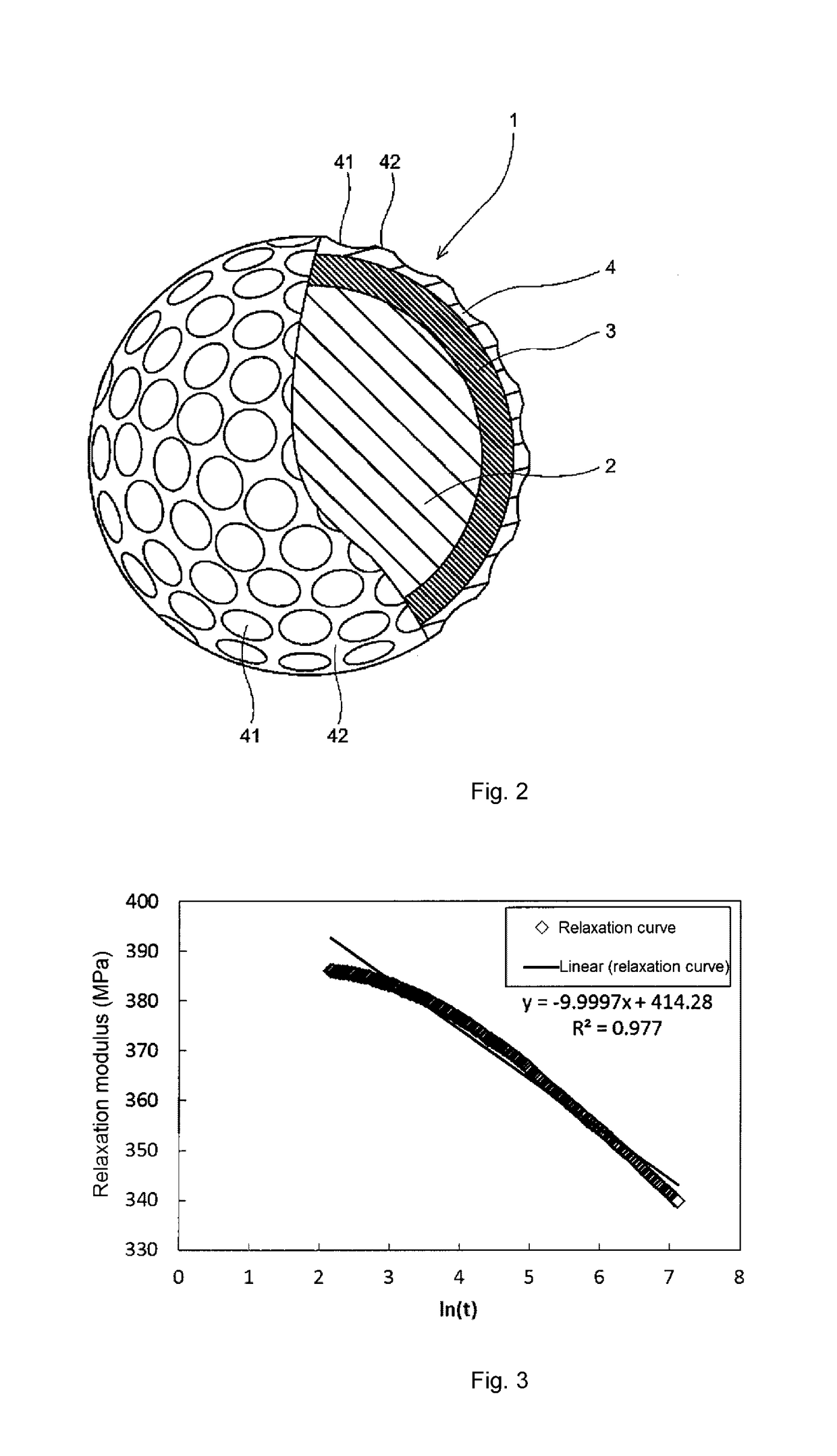
An object of the present invention is to provide a golf ball resin composition having improved rebound resilience performance. The present invention provides a golf ball resin composition containing: (A) a thermoplastic resin having an infrared absorption peak in a region from 3200 cm−1 to 3600 cm−1, and (B) at least one resin component selected from the group consisting of (b-1) a binary copolymer composed of an olefin and an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms, (b-2) a metal ion-neutralized product of a binary copolymer composed of an olefin and an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms, (b-3) a ternary copolymer composed of an olefin, an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms and an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid ester, and (b-4) a metal ion-neutralized product of a ternary copolymer composed of an olefin, an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid having 3 to 8 carbon atoms and an α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid ester, wherein when a relaxation modulus Er (−20° C., 9%) of the golf ball resin composition is measured under conditions of −20° C. and a strain of 9%, a relaxation curve is plotted with the relaxation modulus (MPa) as the vertical axis and a logarithm (ln(t)) of time (sec) as the horizontal axis, and the relaxation curve is linearly approximated to obtain a linear approximation curve, the linear approximation curve has a slope in an absolute value of 7 or more.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Propellant vertical storage and turnover performance evaluation method
PendingCN114840967AImprove R&D efficiencySolve engineering problems related to storage fieldSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationRelaxation modulusEngineering
The invention discloses a propellant vertical storage and turnover performance evaluation method, which comprises the following steps of: obtaining a relaxation modulus main curve and a time-temperature translation factor of a propellant to be evaluated through a stress-strain curve so as to obtain a propellant related failure criterion; obtaining a propellant relaxation modulus main curve according to the stress-strain curve, and establishing a viscoelastic constitutive equation for describing the mechanical properties of the propellant to be evaluated; performing numerical simulation calculation according to the propellant charging structure and the constitutive equation, and evaluating the creep and tensile response characteristics of the propellant to be evaluated in combination with the numerical calculation result and the failure criterion; according to the result, the limit and the optimal overturning time of propellant vertical storage under the current grain structure are obtained, and the related safety coefficient is calculated according to the limit and the optimal overturning time; on the basis, grain structure parameters are adjusted, standing storage time ranges under different parameters are repeatedly obtained, the improvement direction of the charging structure is defined, and then the research and development efficiency of the propellant charging structure meeting the standing storage requirement is improved.
Owner:XIAN AEROSPACE PROPULSION TECH INST
Adhesive composition for polarizing plate
ActiveUS10487248B2Improving thermal-shock durabilityImproved thermal-shock durabilityLayered productsPolarising elementsRelaxation modulusMedicine
An adhesive composition for a polarizing plate is adapted to exhibit a variation in relaxation modulus of an adhesive layer in a range of 75% to 95% before and after leaving the same at a temperature of −20° C. to 0° C. for 4 hours, such that it is possible to remarkably improve thermal-shock durability of the polarizing plate, and suppress a damage of the polarizing plate in a thermal-shock durability test, while maintaining excellent adhesiveness.
Owner:DONGWOO FINE CHEM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com