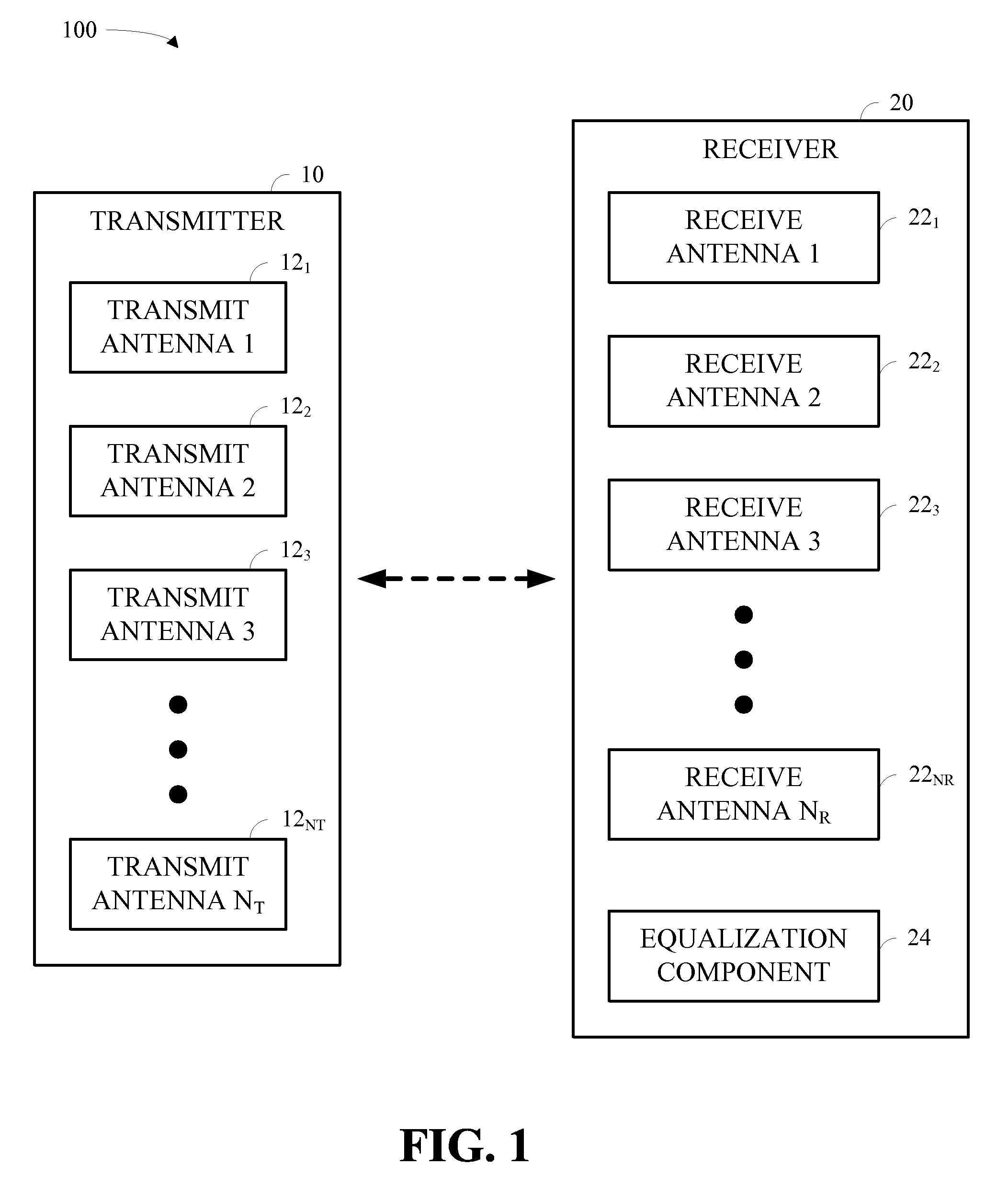
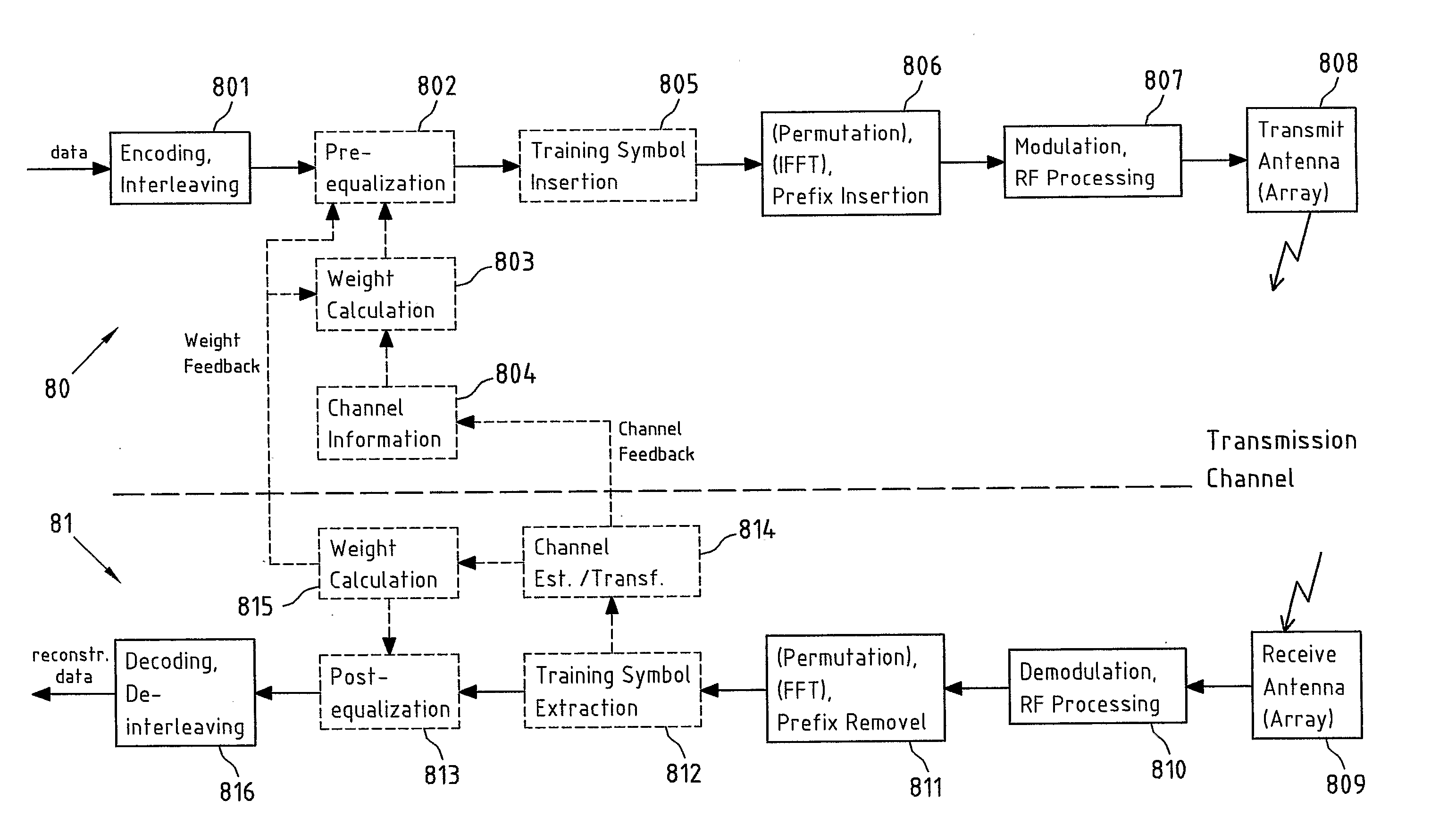
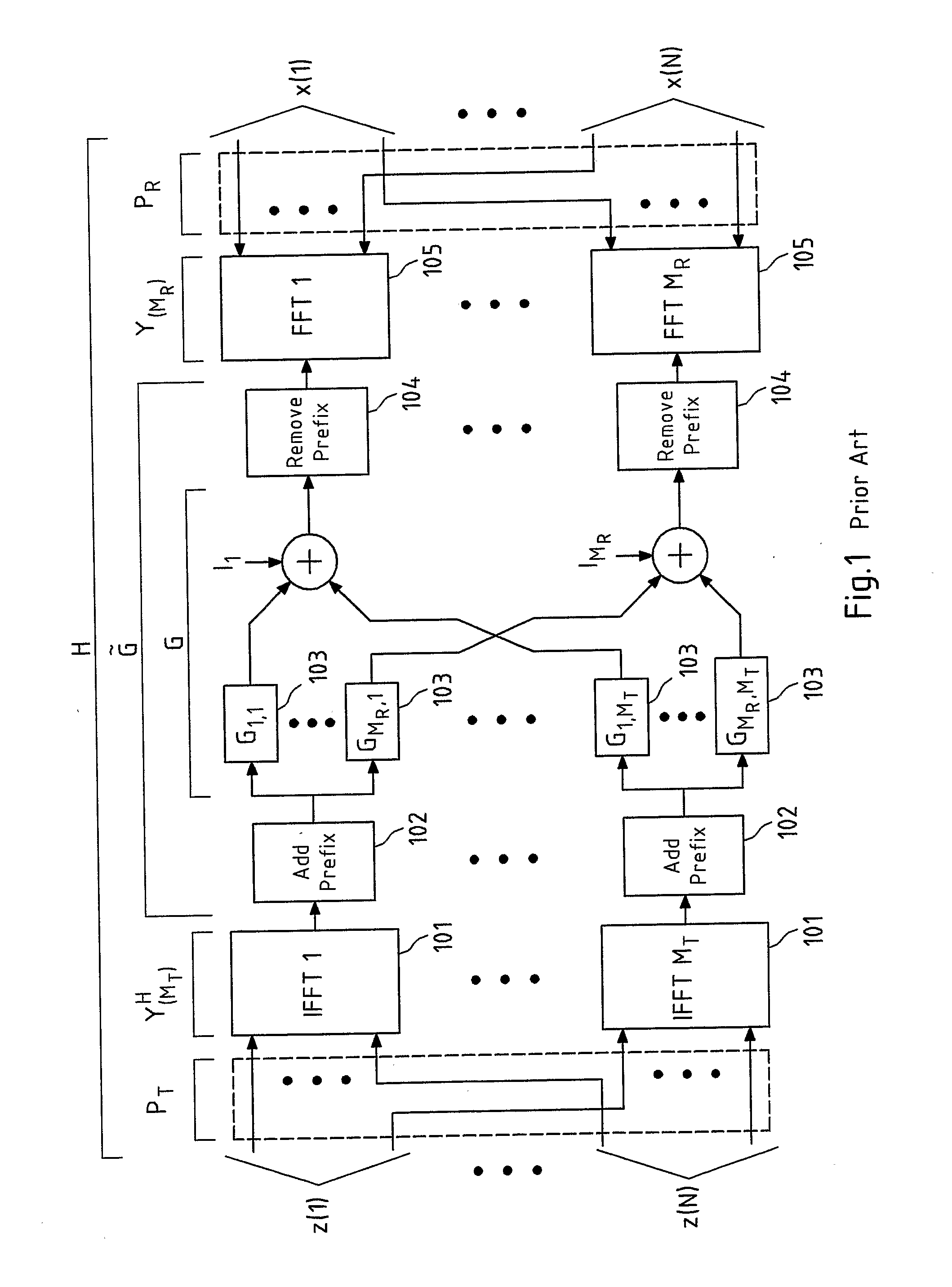
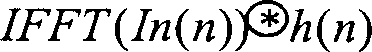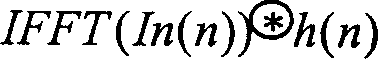Patents
Literature
652 results about "Frequency domain equalization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
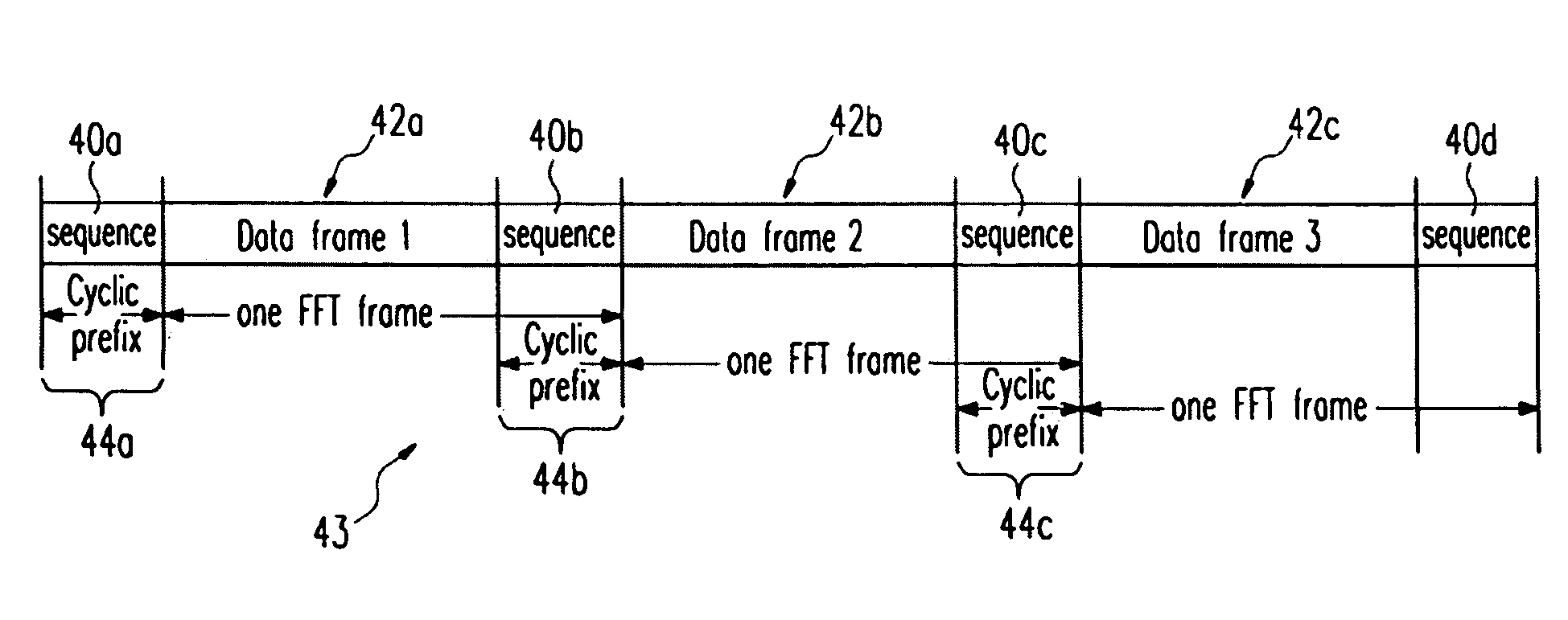
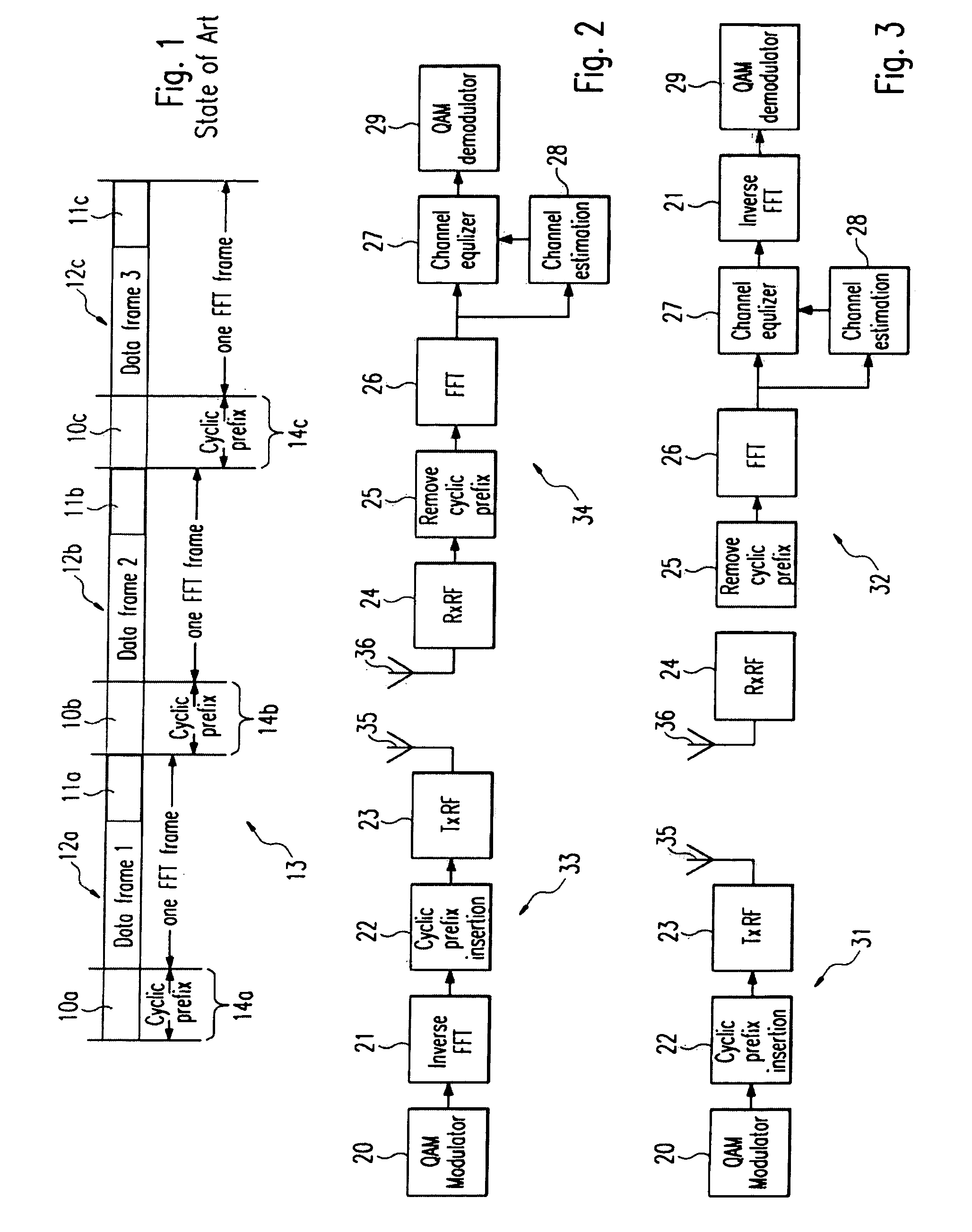
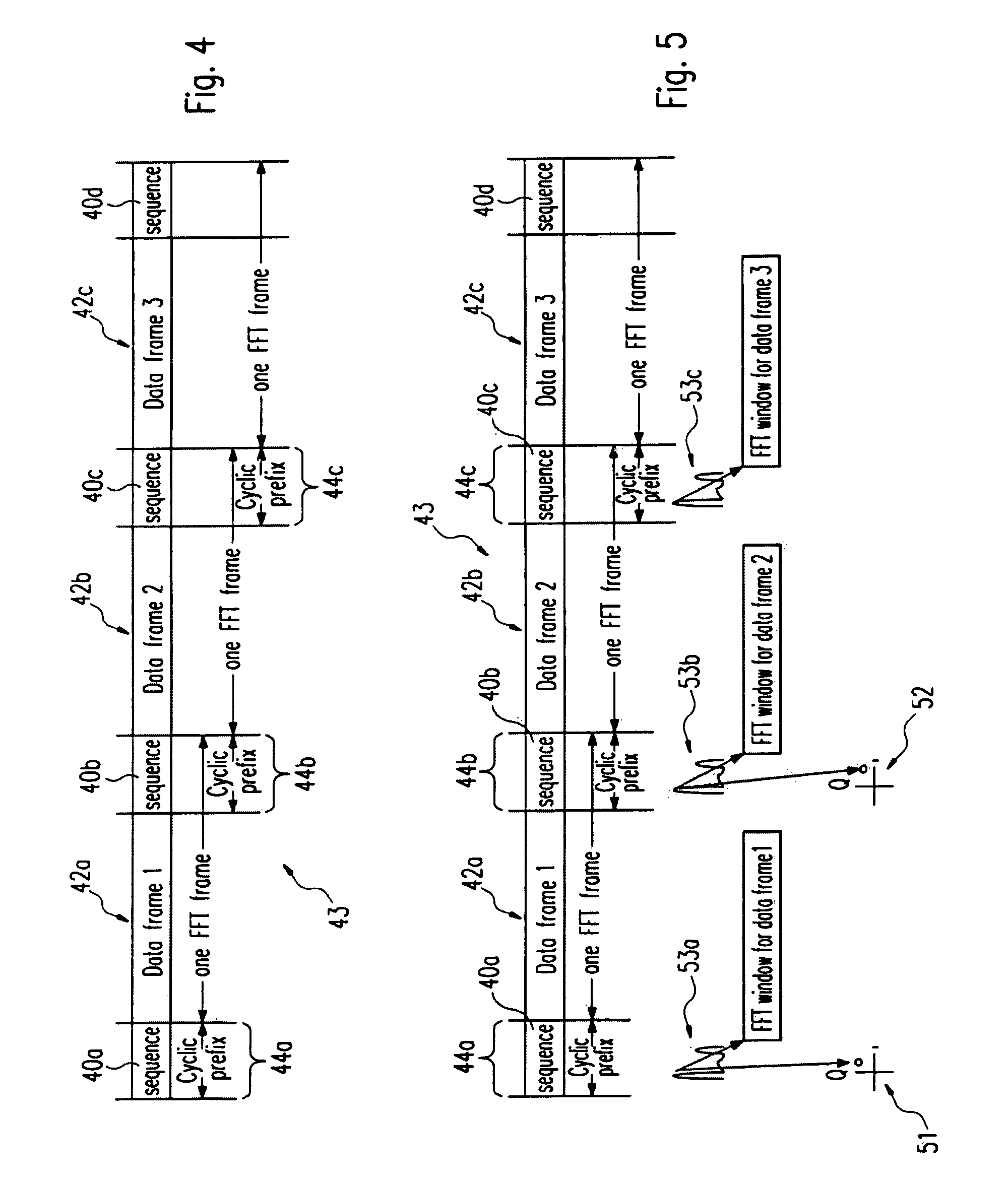
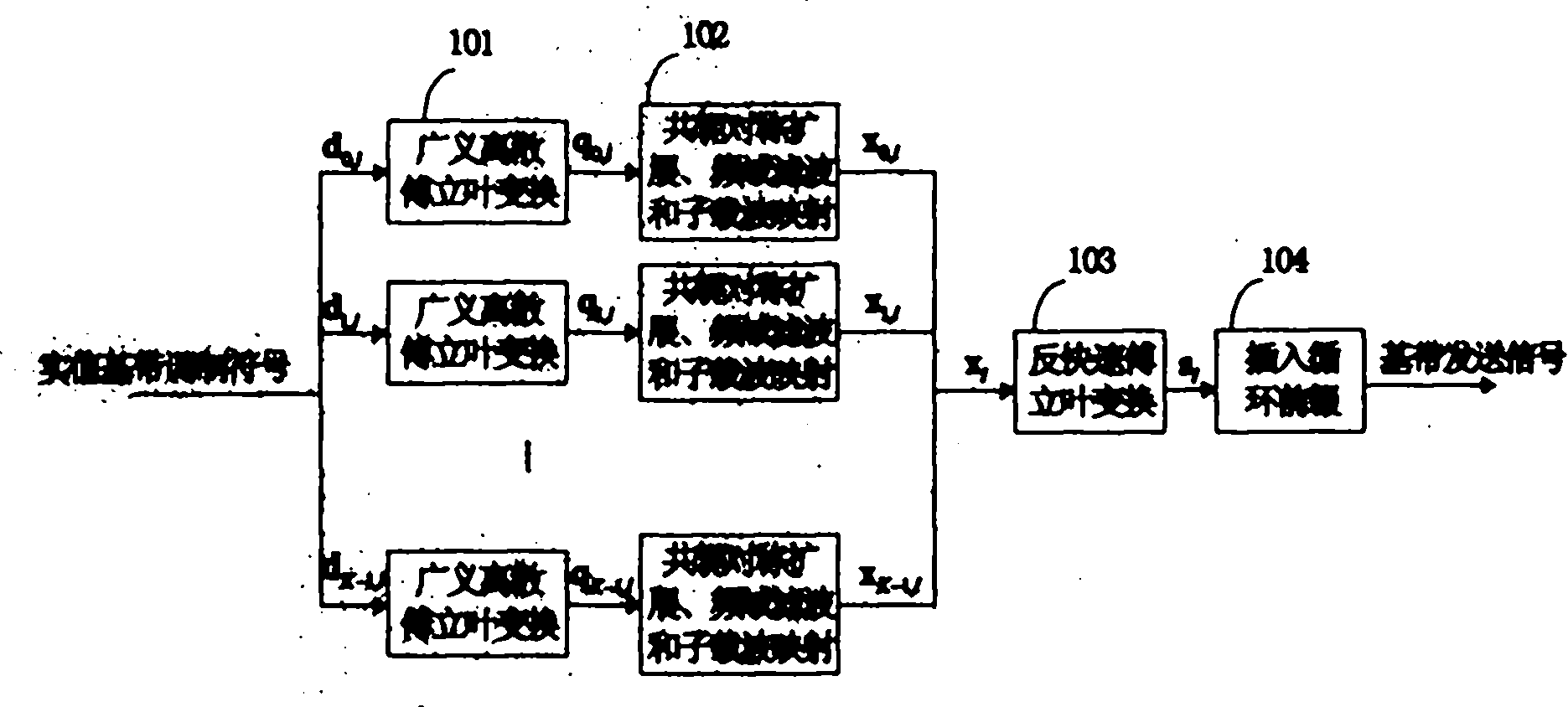
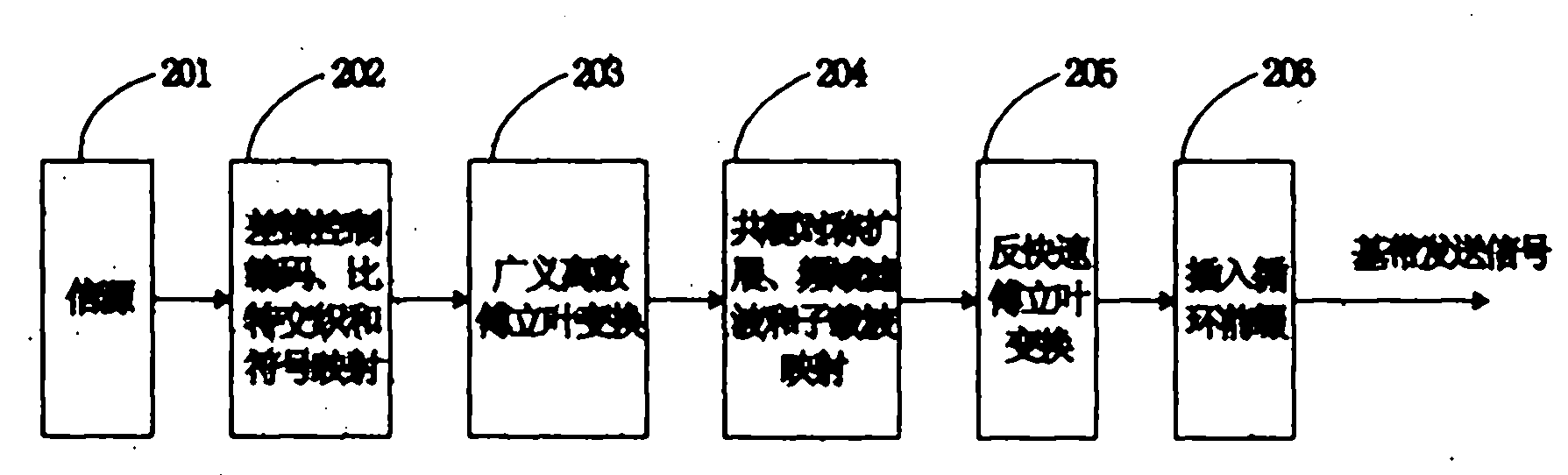
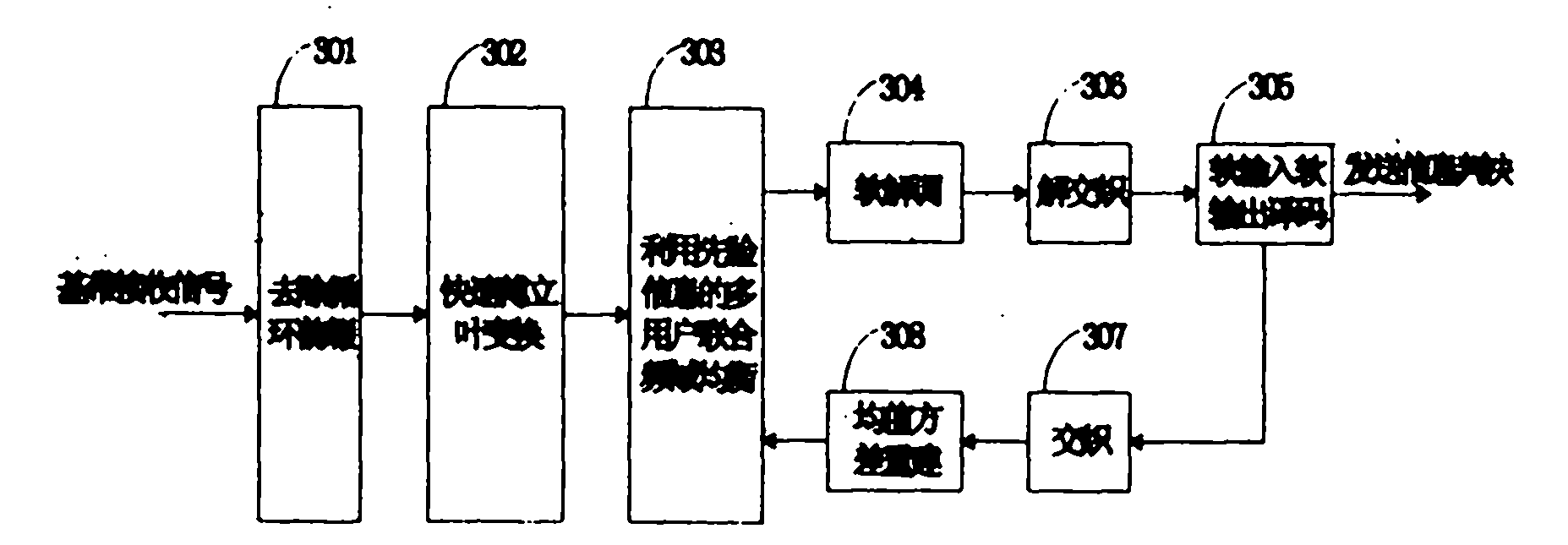
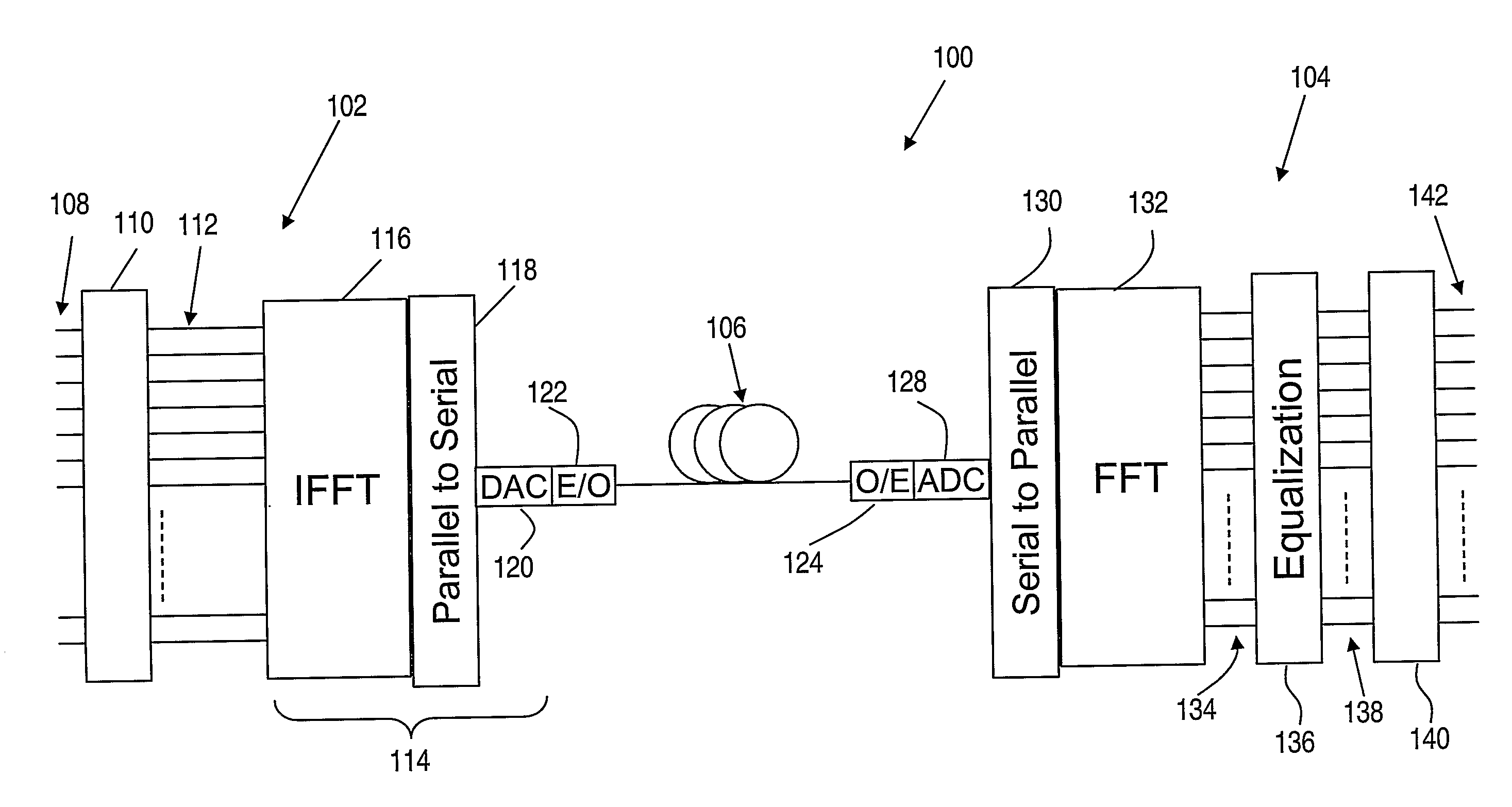
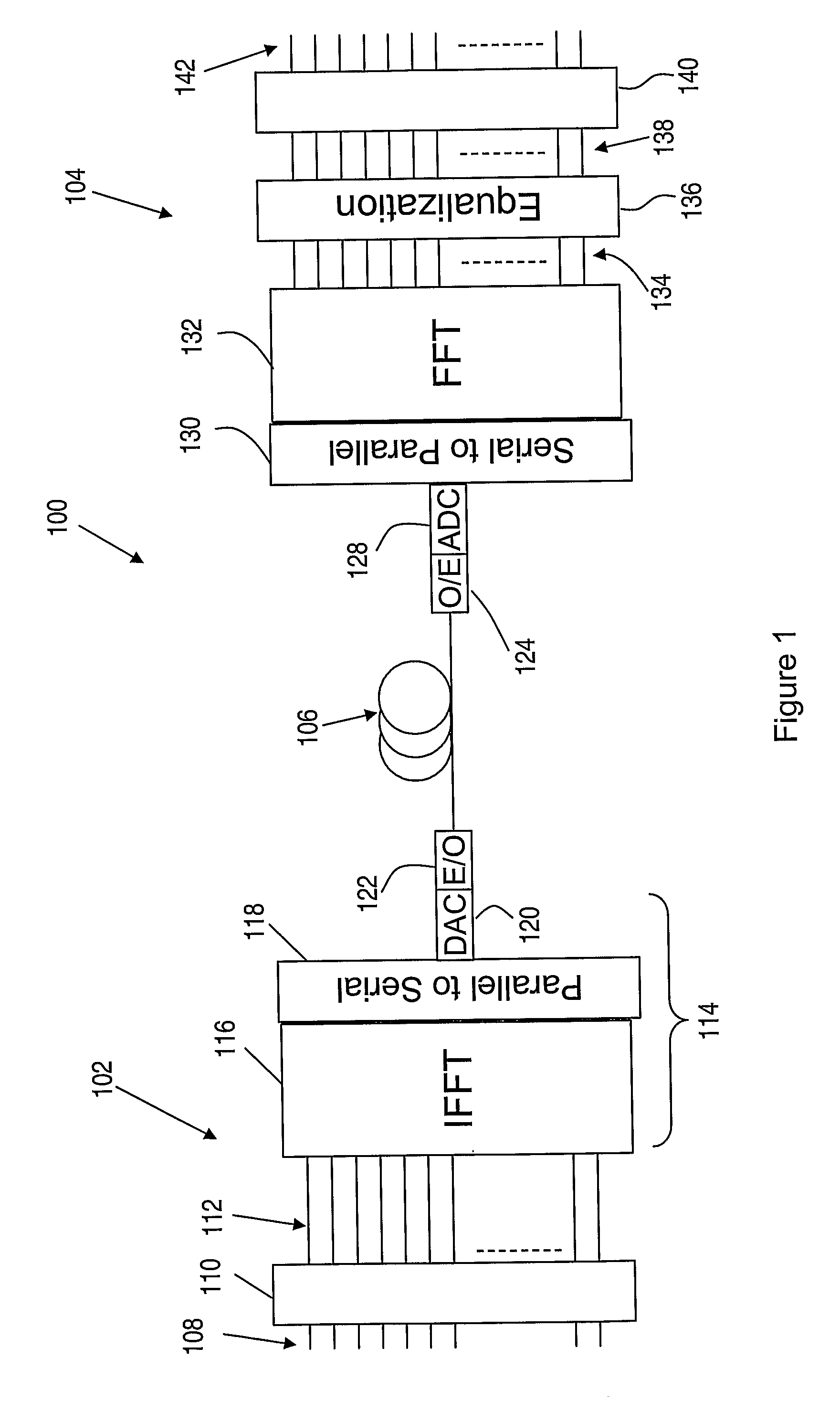
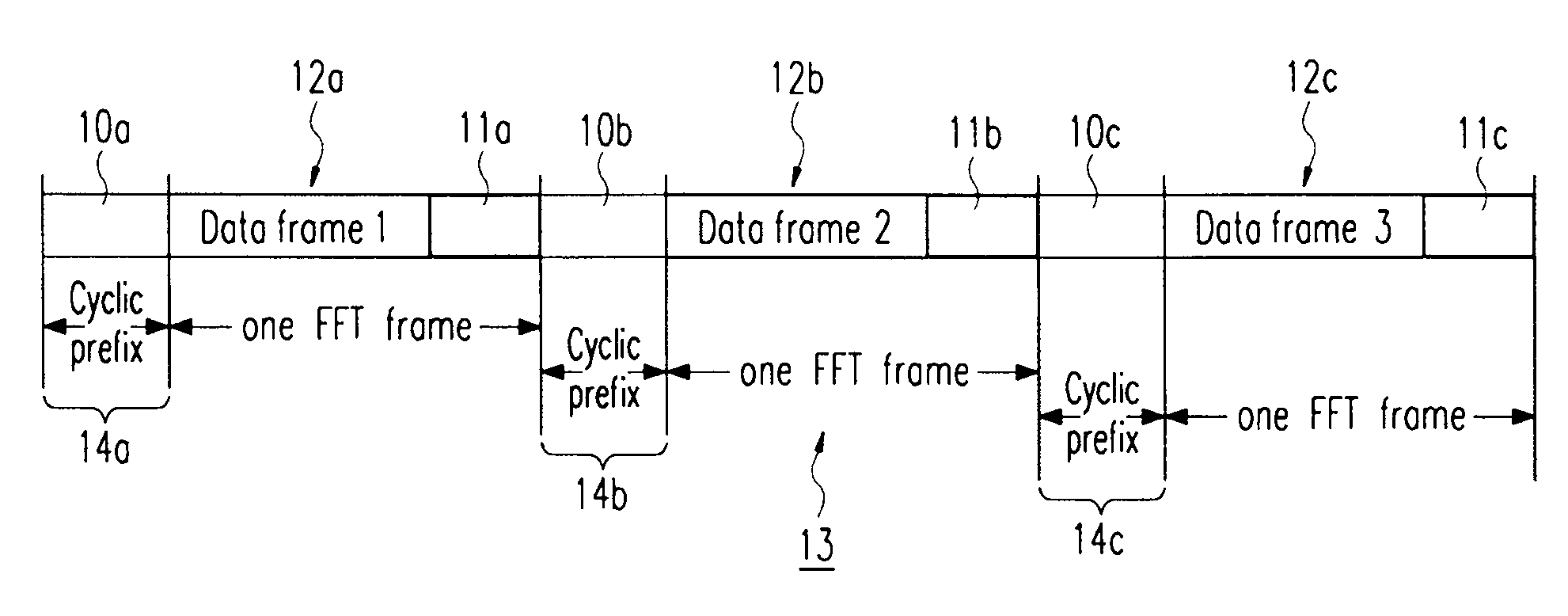
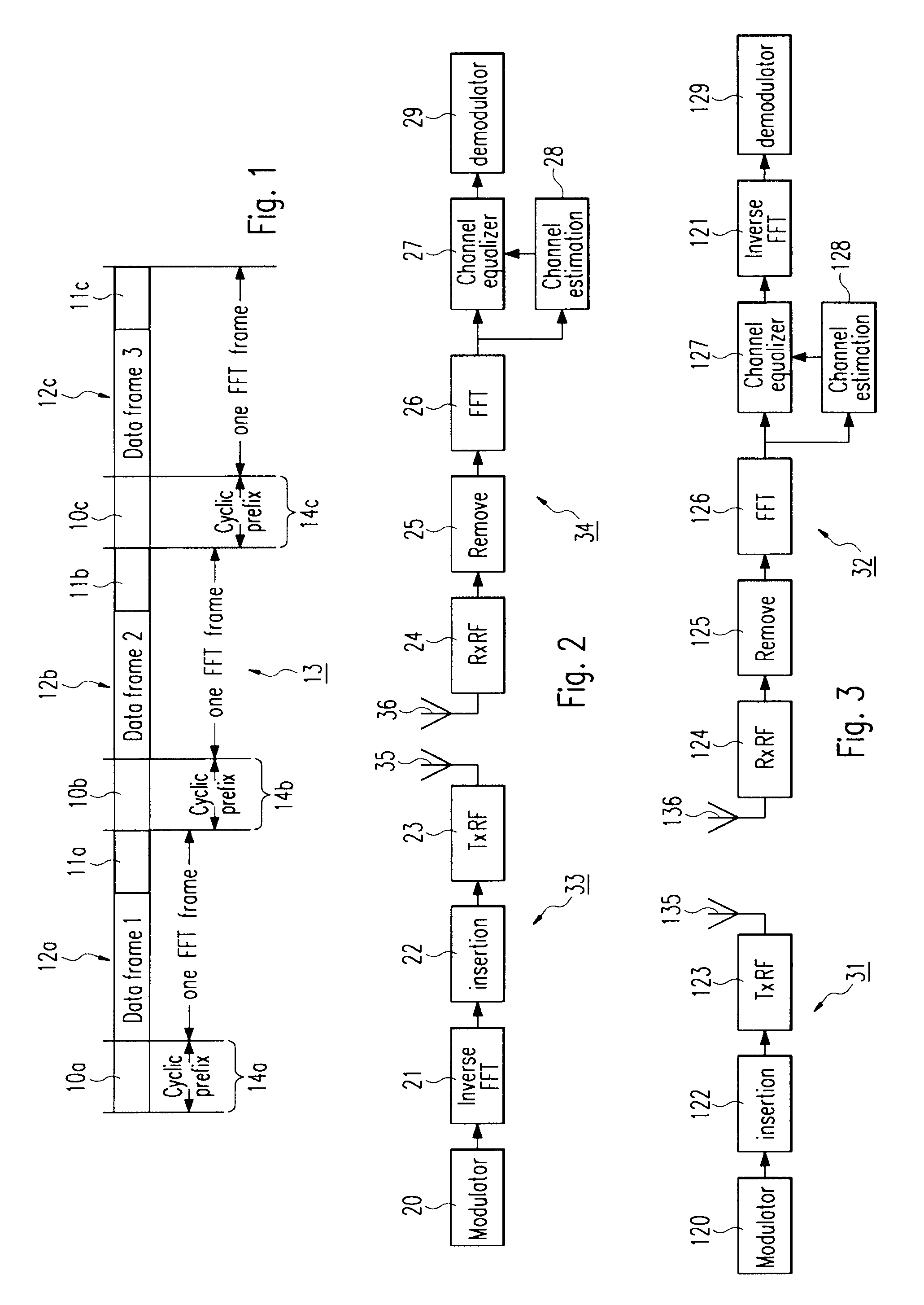
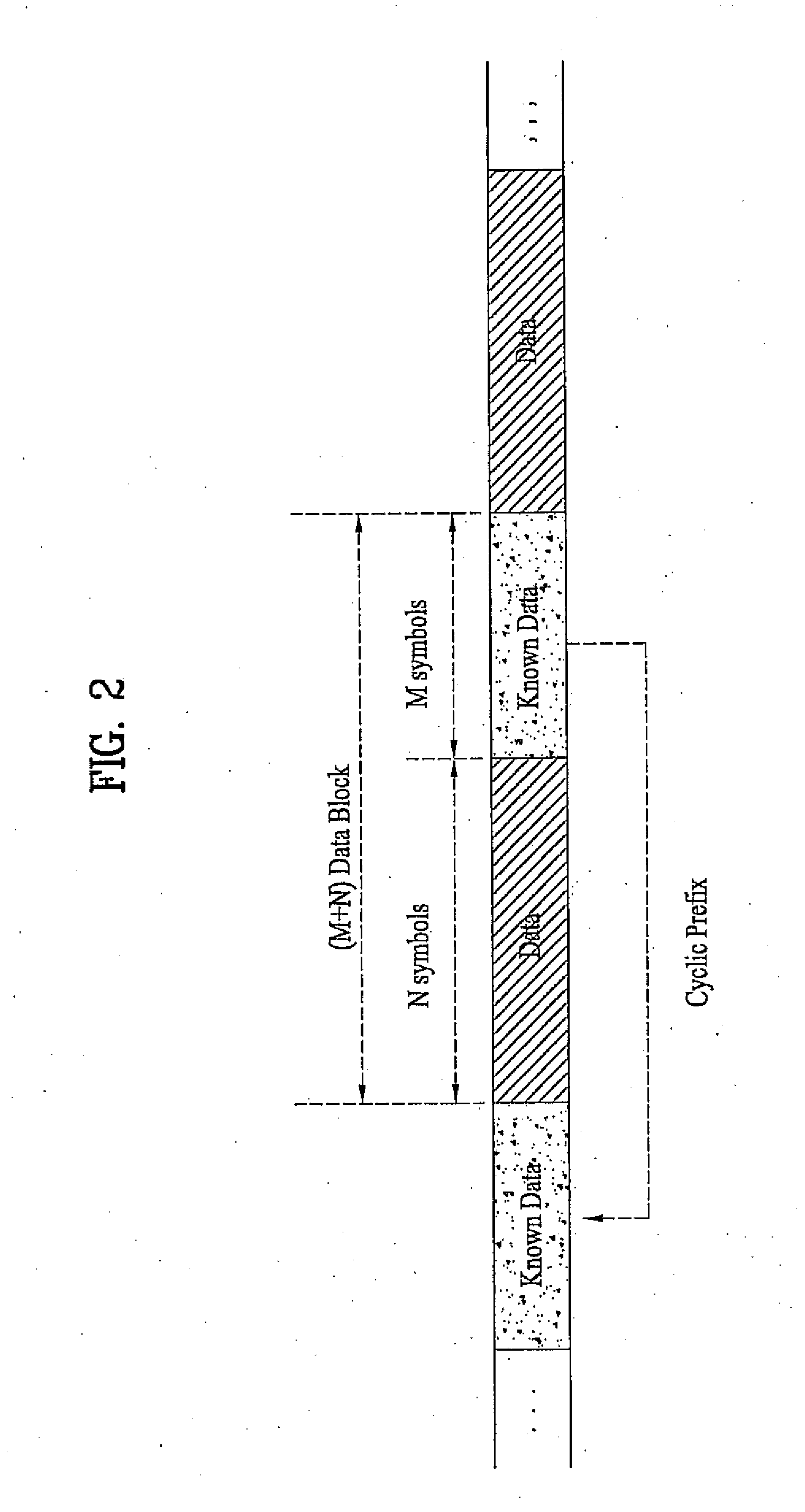
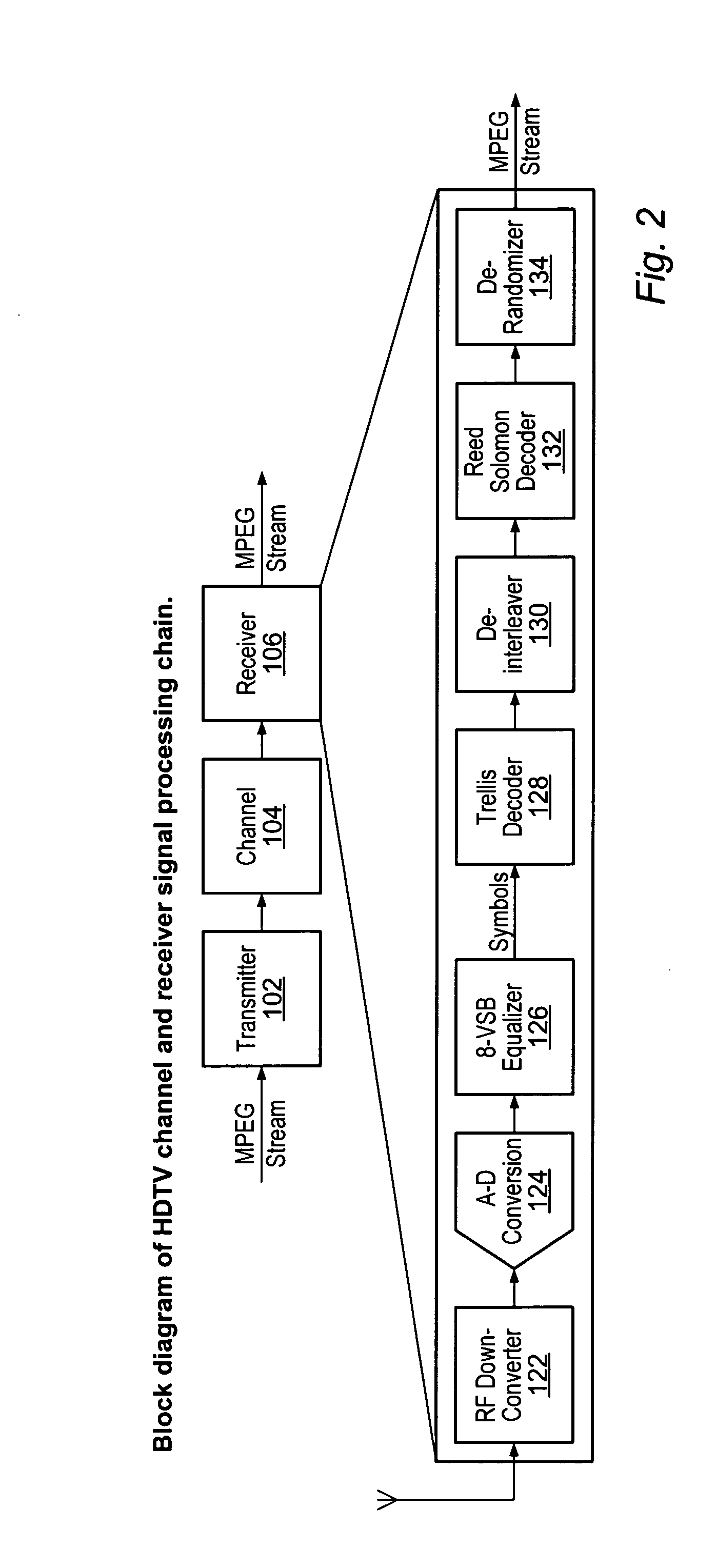
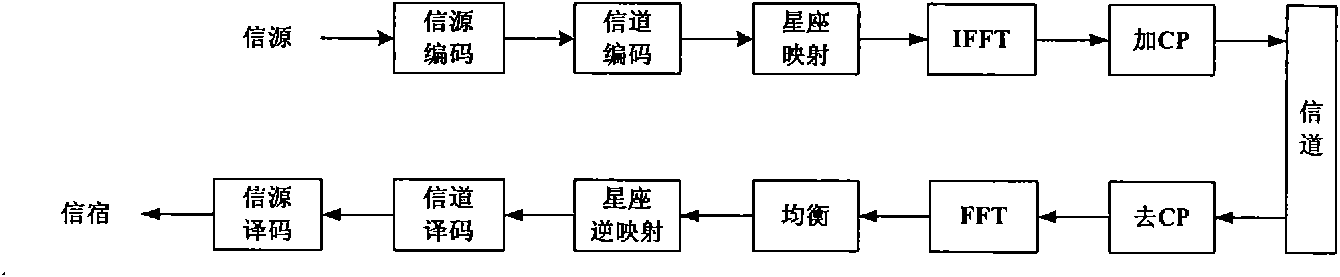
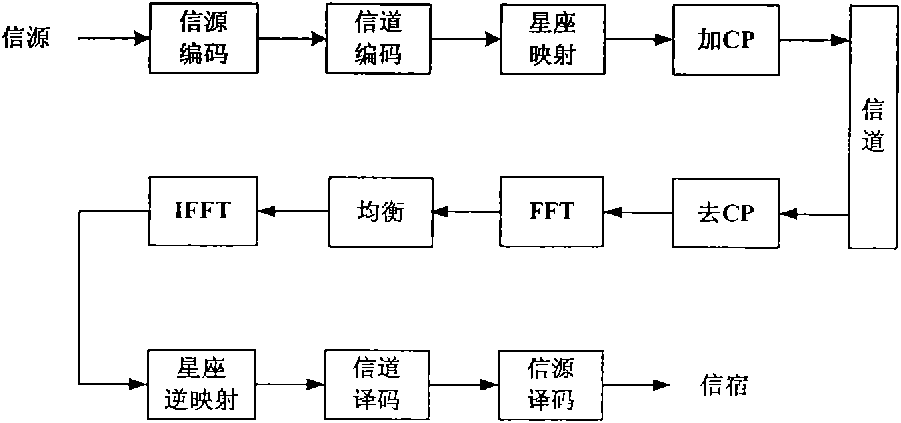
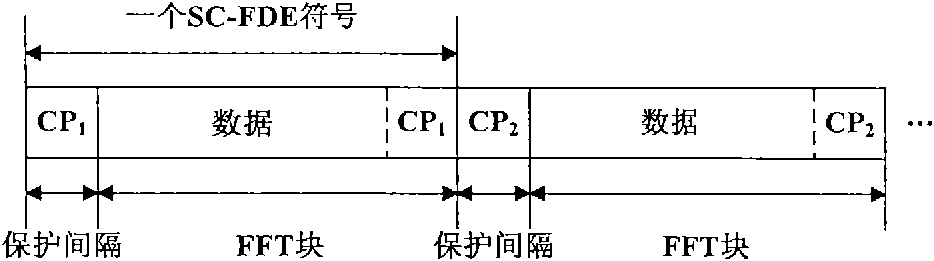
Frequency domain equalization requires a certain block structure to be efficient. In OFDM, adding a cyclic prefix to the transmitted block, and using IDFT at the transmitter and DFT at the receiver allows the use of one-tap frequency equalizer.
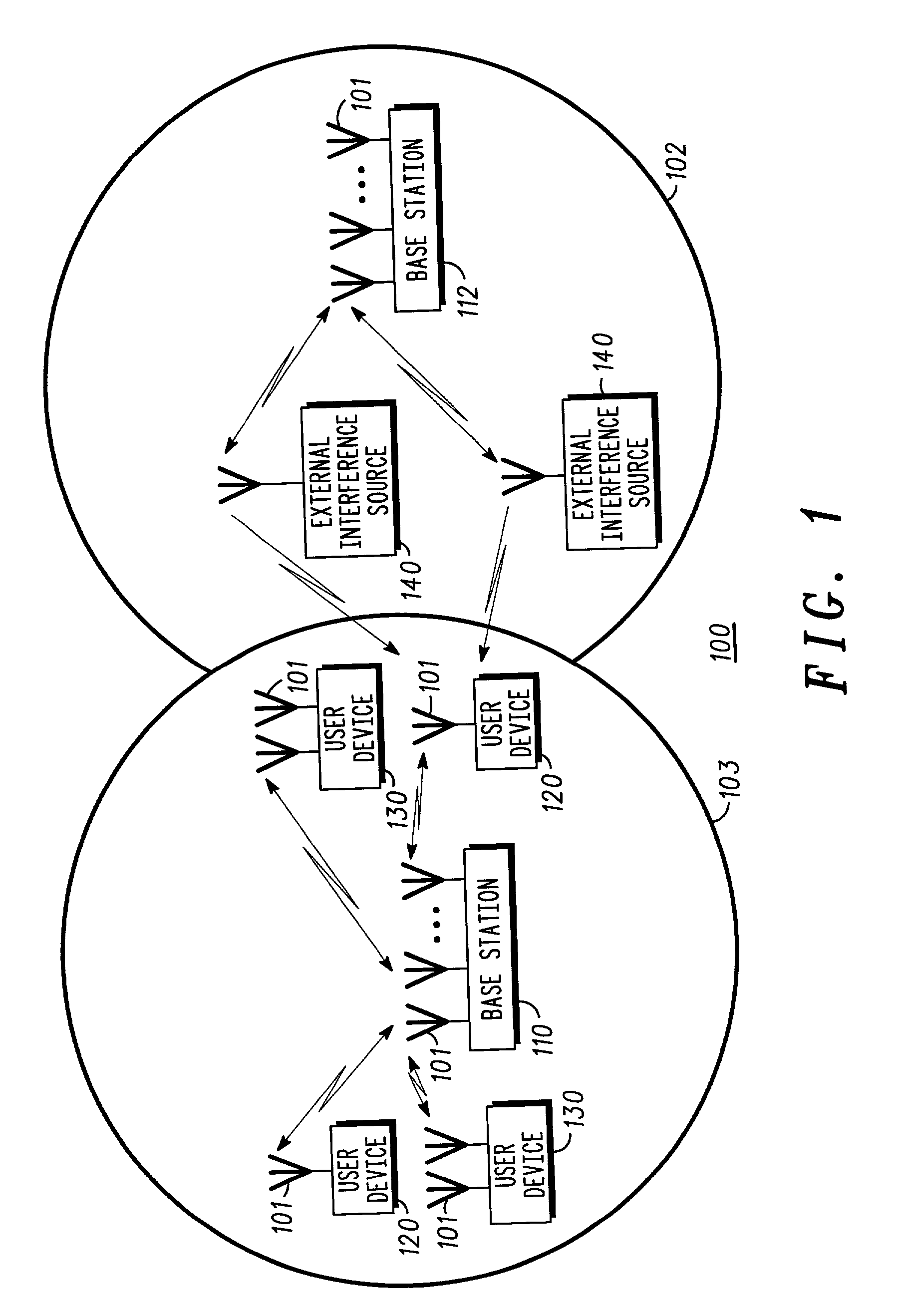
Single carrier high rate wireless system
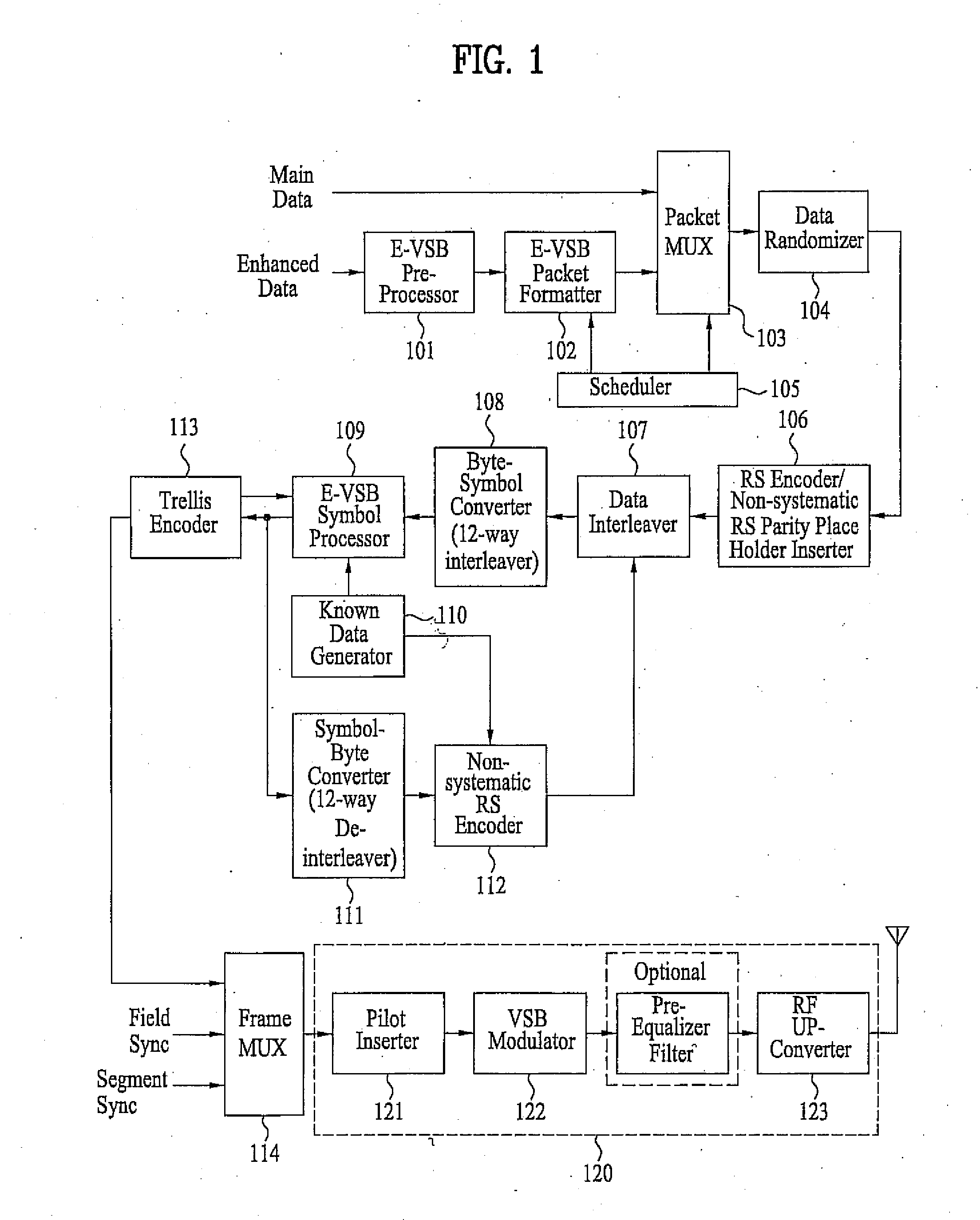
ActiveUS20080240307A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationElectrical and Electronics engineeringCyclic prefix
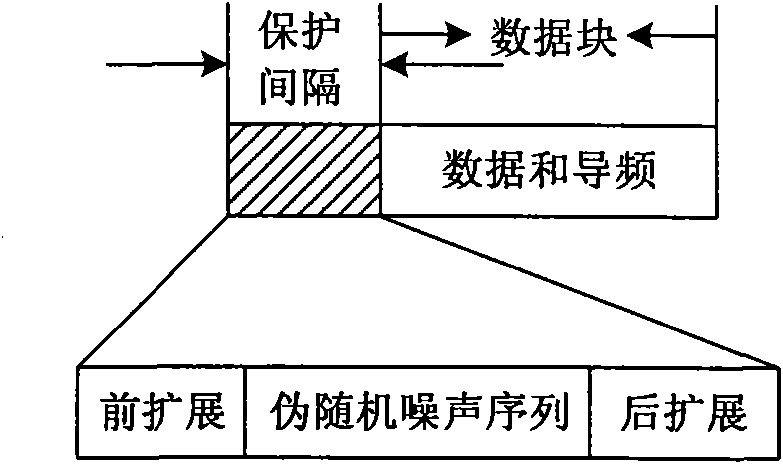
The present invention relates to a signal generator and signal processor for single carrier wireless communication systems with frequency domain equalizer, which are operable to use pseudorandom-noise sequences for cyclic prefix. The different arrangements and examples of said pseudorandom-noise sequences could be used for coarse timing synchronization, channel estimation, carrier synchronization, signal-noise-ration estimation and channel equalization.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
Hybrid time-frequency domain equalization over broadband multi-input multi-output channels
InactiveUS20080304558A1Good flexibilityMore reliabilityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMulti inputData stream
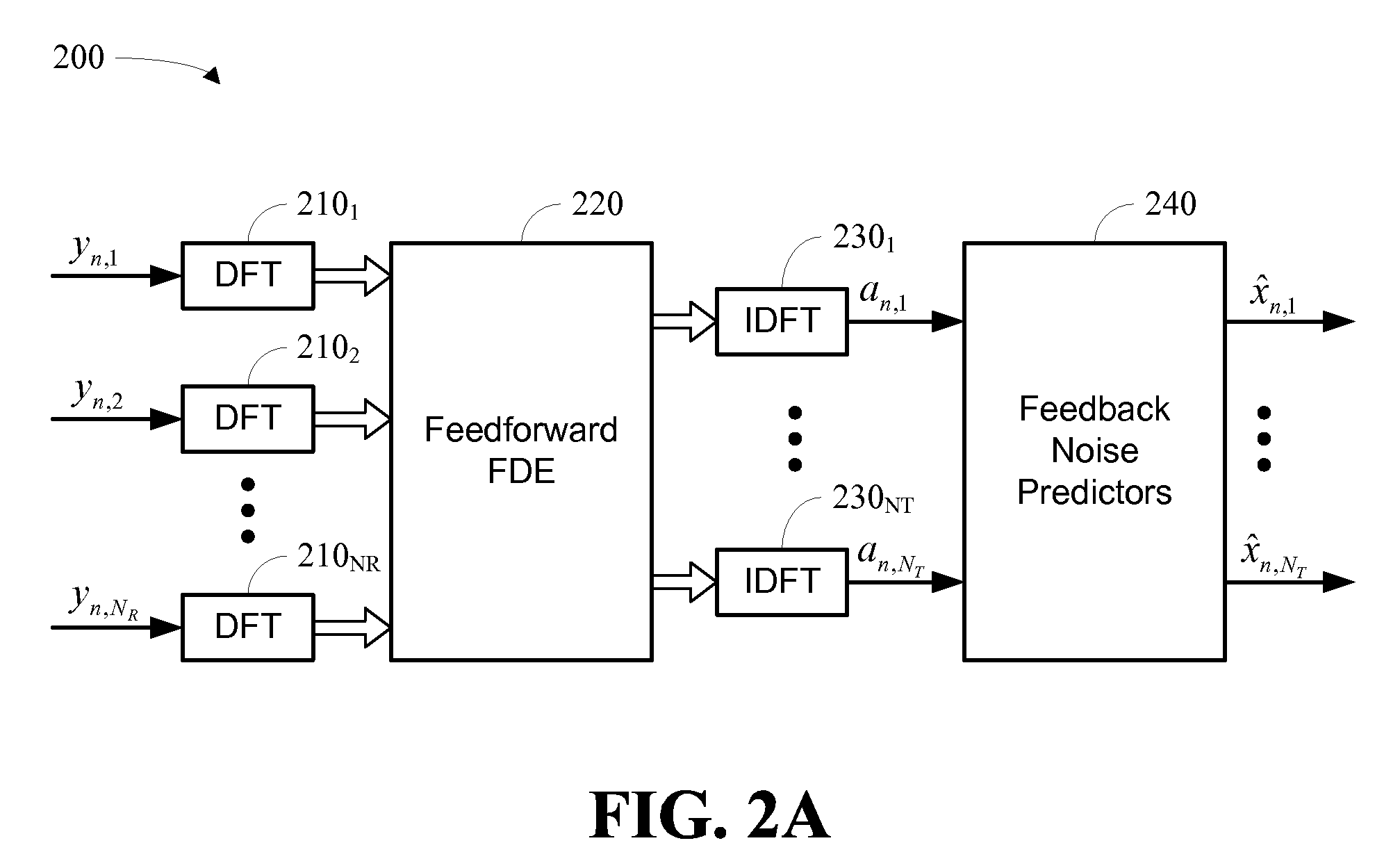
A system and methodology for channel equalization are provided. According to one aspect, a receiver structure for a MIMO system is provided that employs frequency domain equalization (FDE) with noise prediction (FDE-NP). The FDE-NP structure may include a feedforward linear frequency domain equalizer and a group of time domain noise predictors (NPs), which may operate by predicting a distortion corresponding to a given linearly equalized data stream based on previous distortions of all linearly equalized data streams. According to another aspect, a receiver structure for a MIMO system is provided that employs FDE-NP with successive interference cancellation (FDE-NP-SIC), which can extend the functionality of FDE-NP by ordering all linearly equalized data streams according to their minimum mean square errors (MMSEs) and detecting those streams which have a low MMSE first, thereby allowing current decisions of lower-indexed streams to be considered along with previous decisions for all data streams for noise prediction. According to a third aspect, a method for analyzing the performance of a MIMO system with equalization is provided. Pursuant to the method, a general expression of MMSE may first be derived. The MMSE expression may then be related to an error bound by applying the modified Chernoff bounding methodology in a general MIMO system. The parameters in the result may then be varied for applicability to single-input single-output (SISO), multiple-input single-output (MISO), and single-input multiple-output (SIMO) systems with receiver equalization technology.
Owner:YIM TU INVESTMENTS
Reduced Complexity Frequency Domain Equalization of Multiple Input Multiple Output Channels
InactiveUS20070253476A1Expensive partReduce complexityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCarrier signalTransmission channel
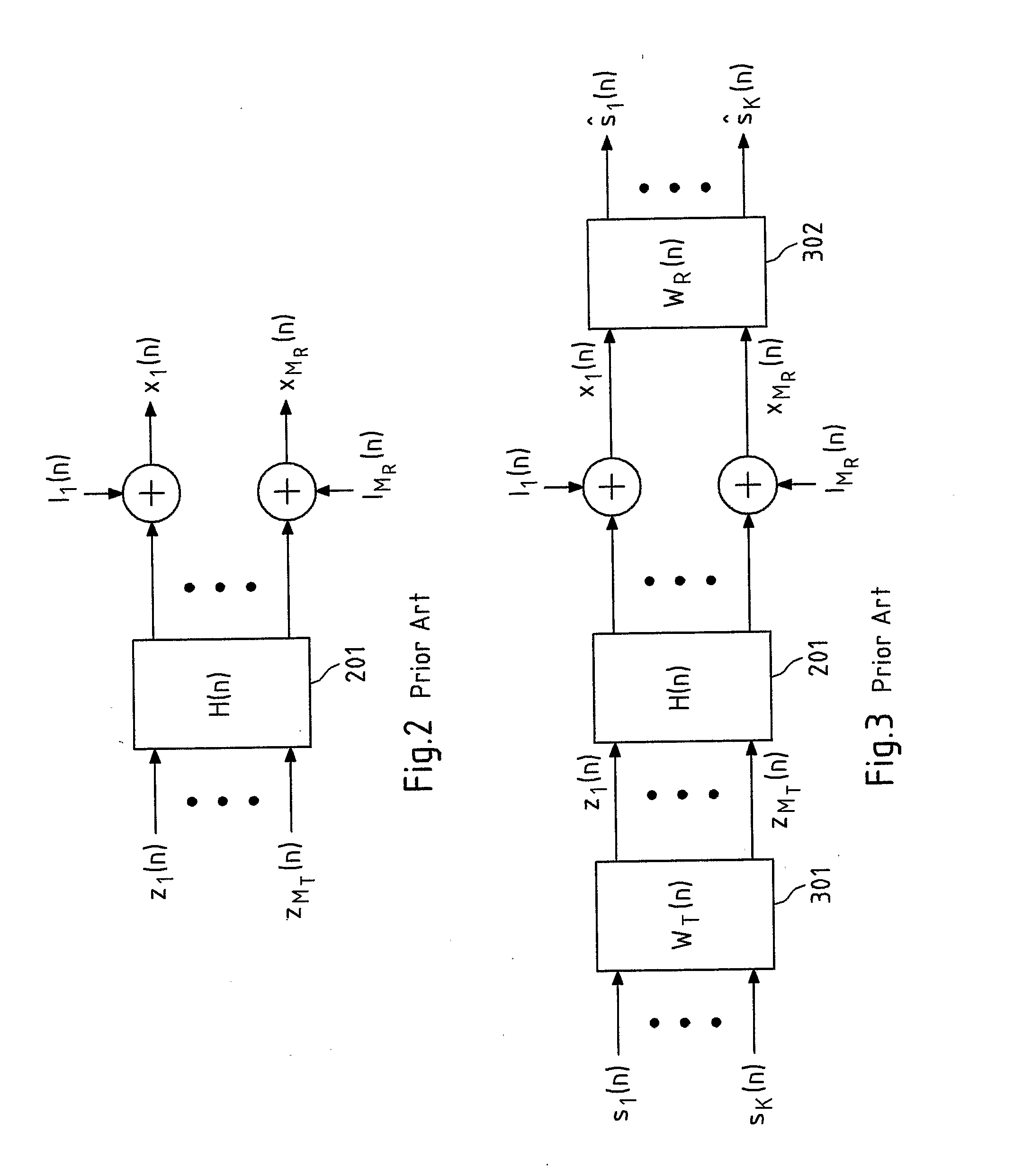
A method for equalizing a frequency-selective transmission channel (103) with N inputs and MR outputs is shown, the transmission channel representable in a transformation domain based on N orthogonal sub-carriers, and wherein the transmission characteristics from the MT inputs to the MR outputs for each of the N respective orthogonal sub-carriers are represented by N respective sub-carrier channels (201), the method using (904) equalization filters (301, 302) for at least two of the N sub-carrier channels, wherein at least one set (501) of sub-carrier channels comprising at least two of the N sub-carrier channels is formed (901), wherein for at least one sub-carrier channel, a first-type equalization filter is used that is determined (902) based on a representation of at least one sub-carrier channel, and wherein for at least one sub-carrier channel, a second-type equalization filter is used that is derived (903) at least partially from the first-type equalization filter.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Efficient method for multi-path resistant carrier and timing frequency offset detection
InactiveUS7245677B1Reduce the impactReduce impactAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsChannel estimationModem deviceCarrier signal
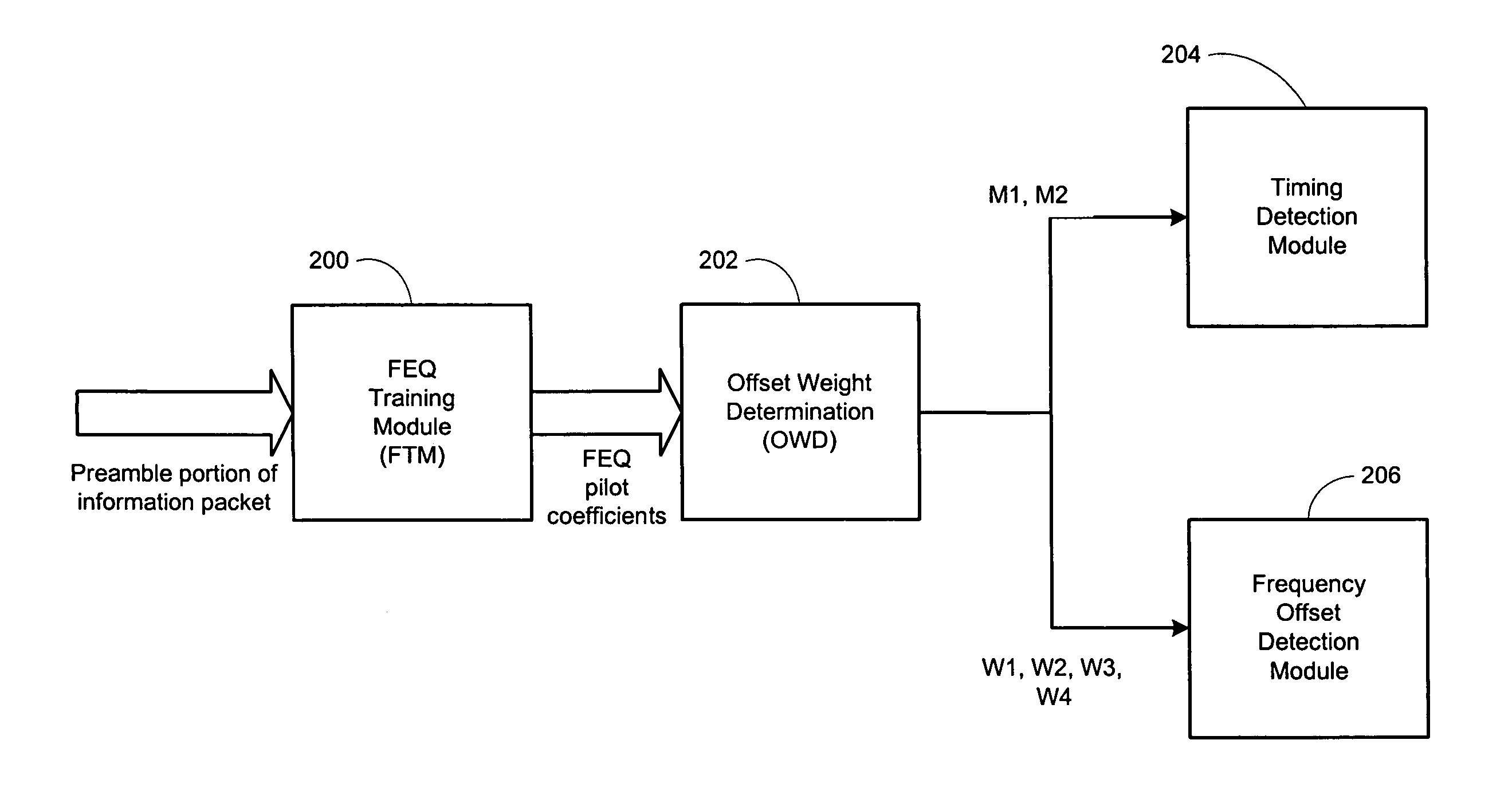
A modem receiver for receiving signals having a frequency domain equalizer training module (FTM) being responsive to a frequency channel response for processing the same to generate one or more frequency domain equalizer (FEQ) coefficients, said modem receiver being responsive to an input signal for processing the same to generate said frequency channel response, said input signal being generated from transmission of a transmitted signal, said frequency channel response for including one or more pilot tones, said FEQ coefficients for including one or more pilot tone FEQ coefficients, in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. The modem receiver further includes an offset weight determination (OWD) module being responsive to said pilot tone FEQ coefficients for processing the same to generate one or more carrier weights, said modem receiver for using said carrier weights to generate a carrier offset, said OWD module for using said pilot tone FEQ coefficients to generate one or more timing weights, said modem receiver for using said timing weights to generate a timing offset, said modem receiver for reducing the effects of faded pilot tones on determination of said timing offset and said carrier offset between said transmitted signal and said input signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method and apparatus for equalization and decoding in a wireless communications system including plural receiver antennae
ActiveUS7065146B1Amplified equalizationSimplify complexityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsChannel state informationCommunications system
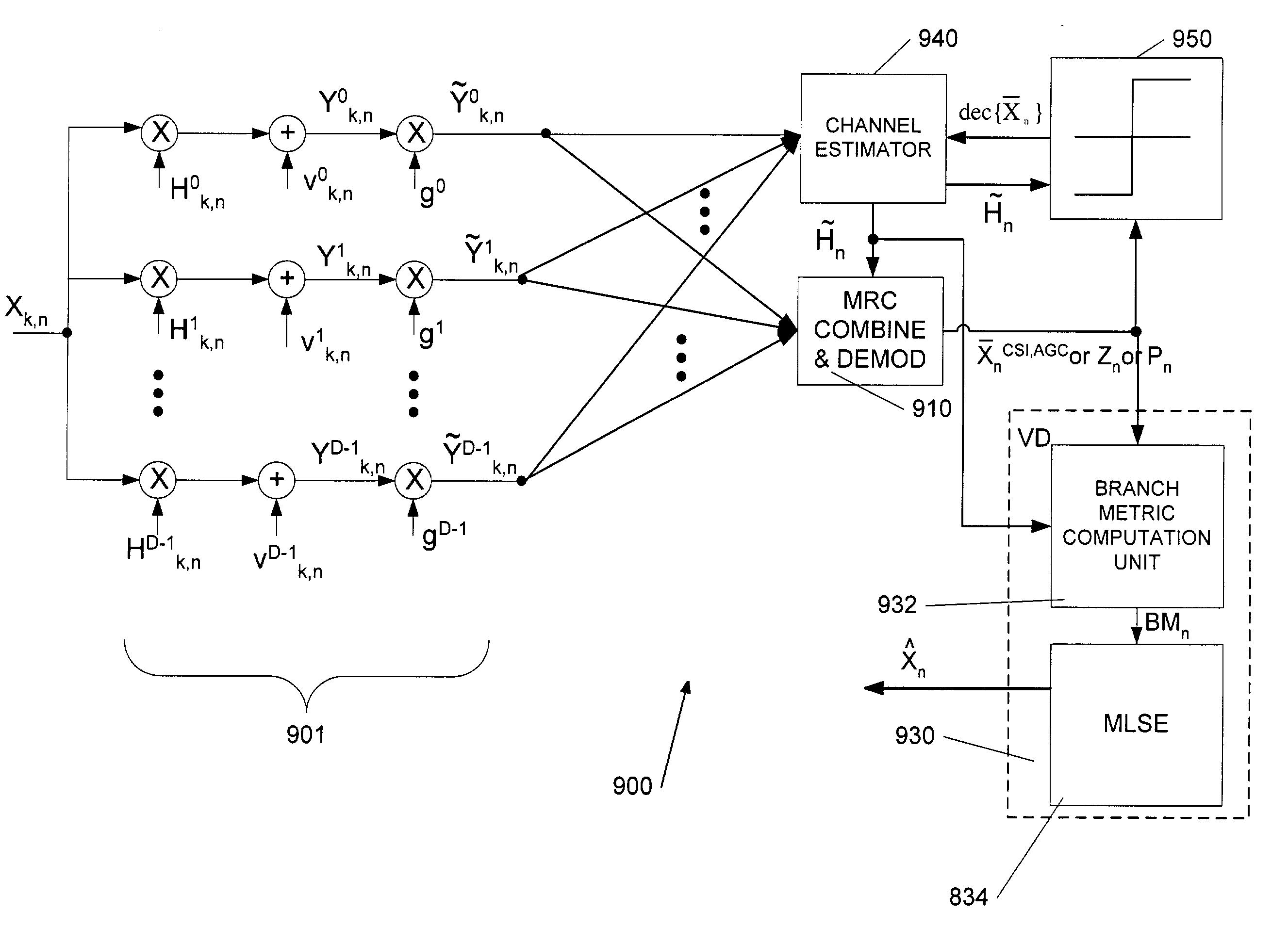
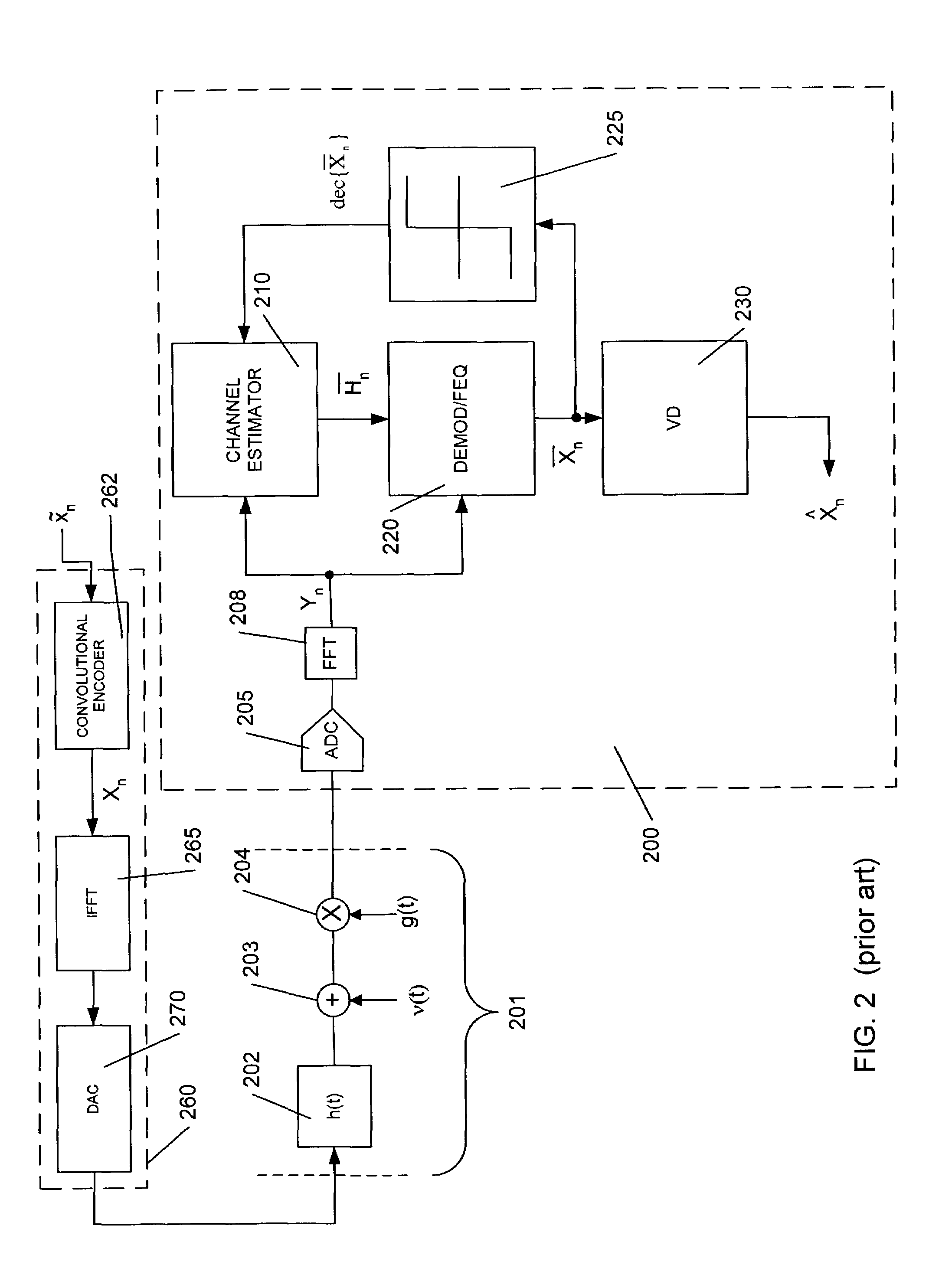
Joint equalization and decoding techniques to eliminate the division operations in the Frequency domain Equalizer (FEQ) of an Orthogonal Frequency Division Modulation (OFDM) receiver by incorporating the magnitude of the channel impulse response estimates into the decision metrics in the decoder. This includes methods for both hard-decision symbol-by-symbol detection and soft-decision decoding using the Viterbi algorithm. Further, Channel State Information (CSI) is incorporated to improve the performance of the receiver. The disclosure also introduces a computationally efficient bit-by-bit piecewise approximation technique incorporating CSI to implement decoder decision metrics. Finally, an efficient implementation technique for multiple receiver antennae using Maximum Ratio Combining (MRC) and Viterbi decoding with CSI is disclosed.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
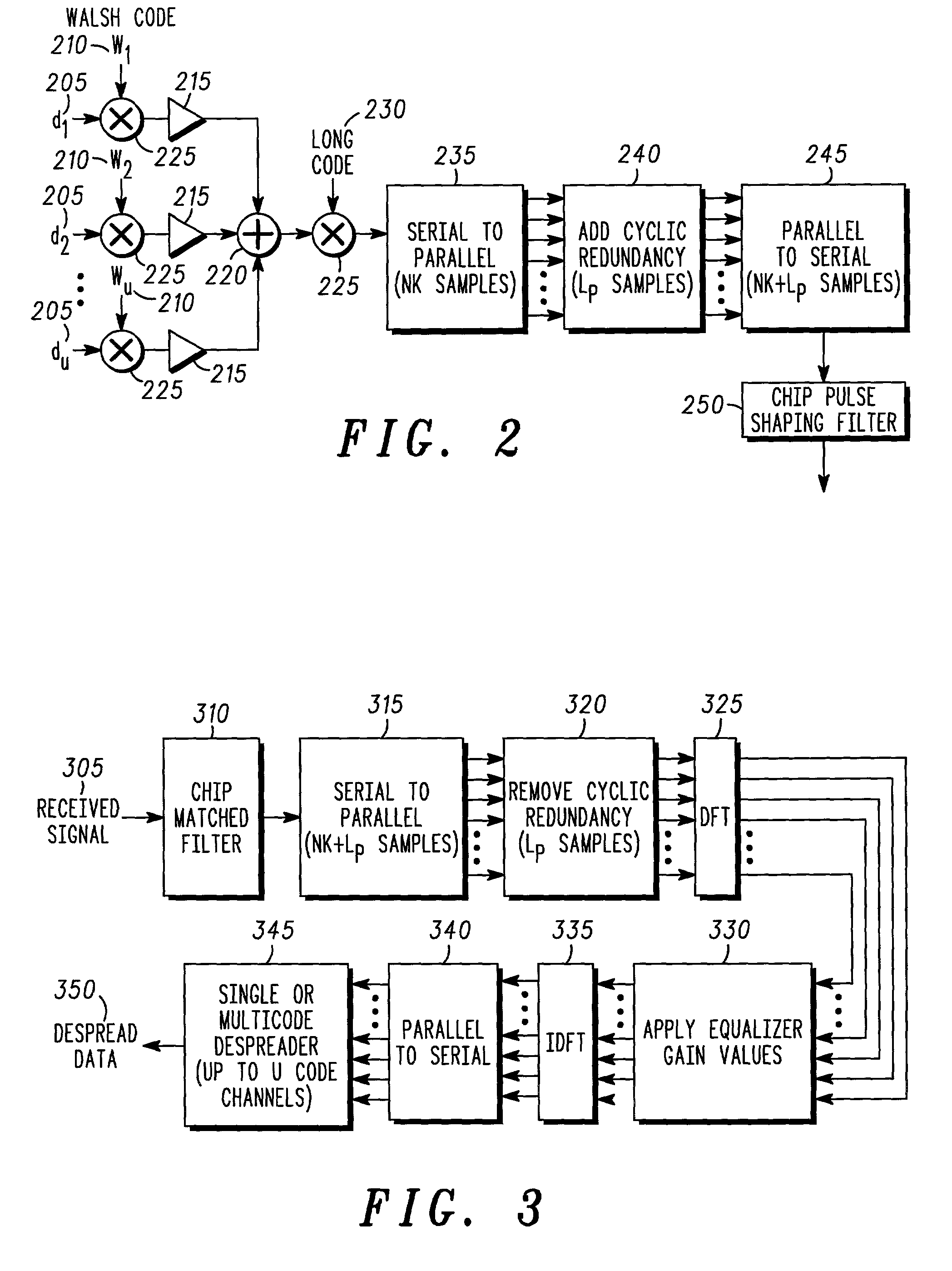
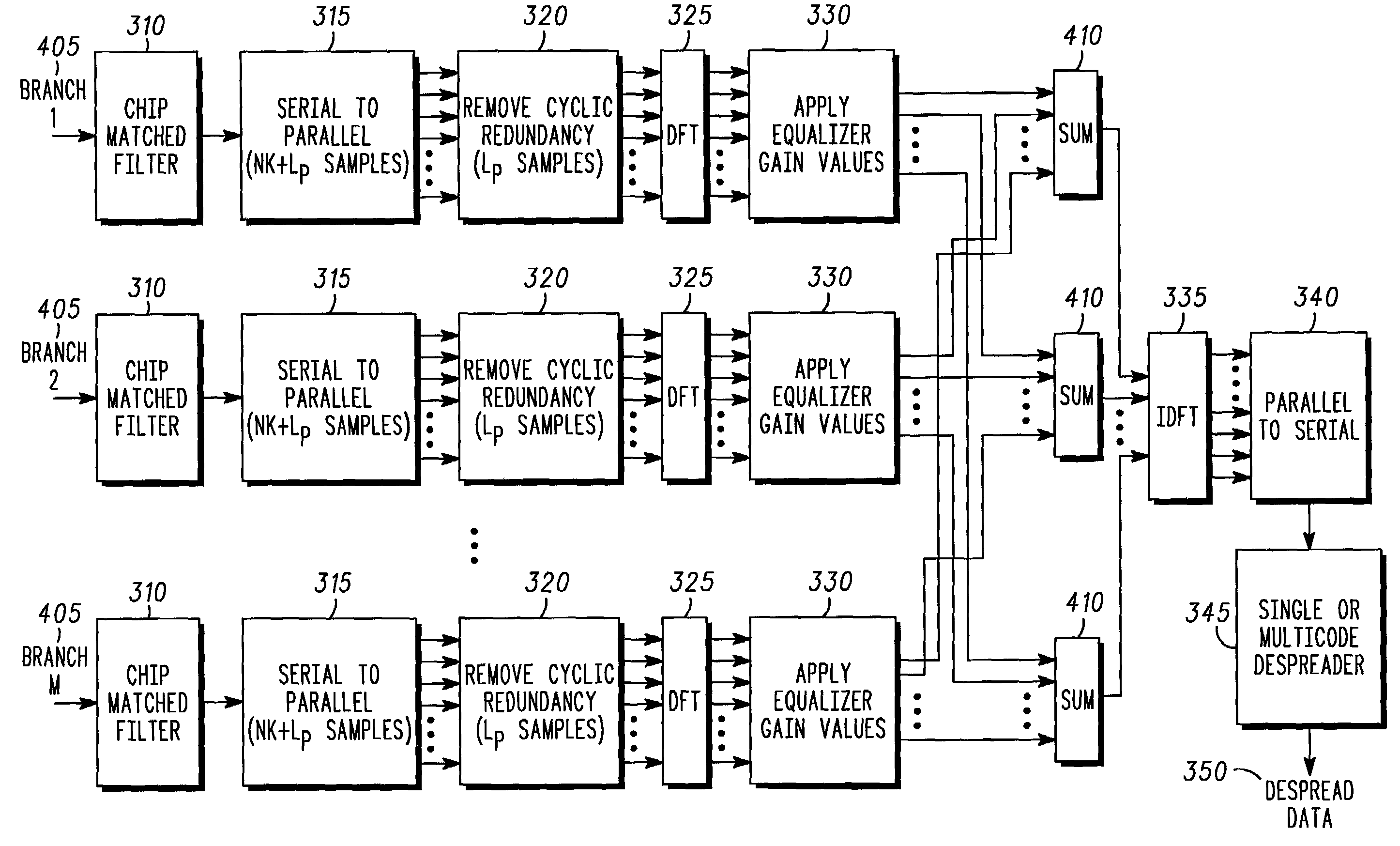
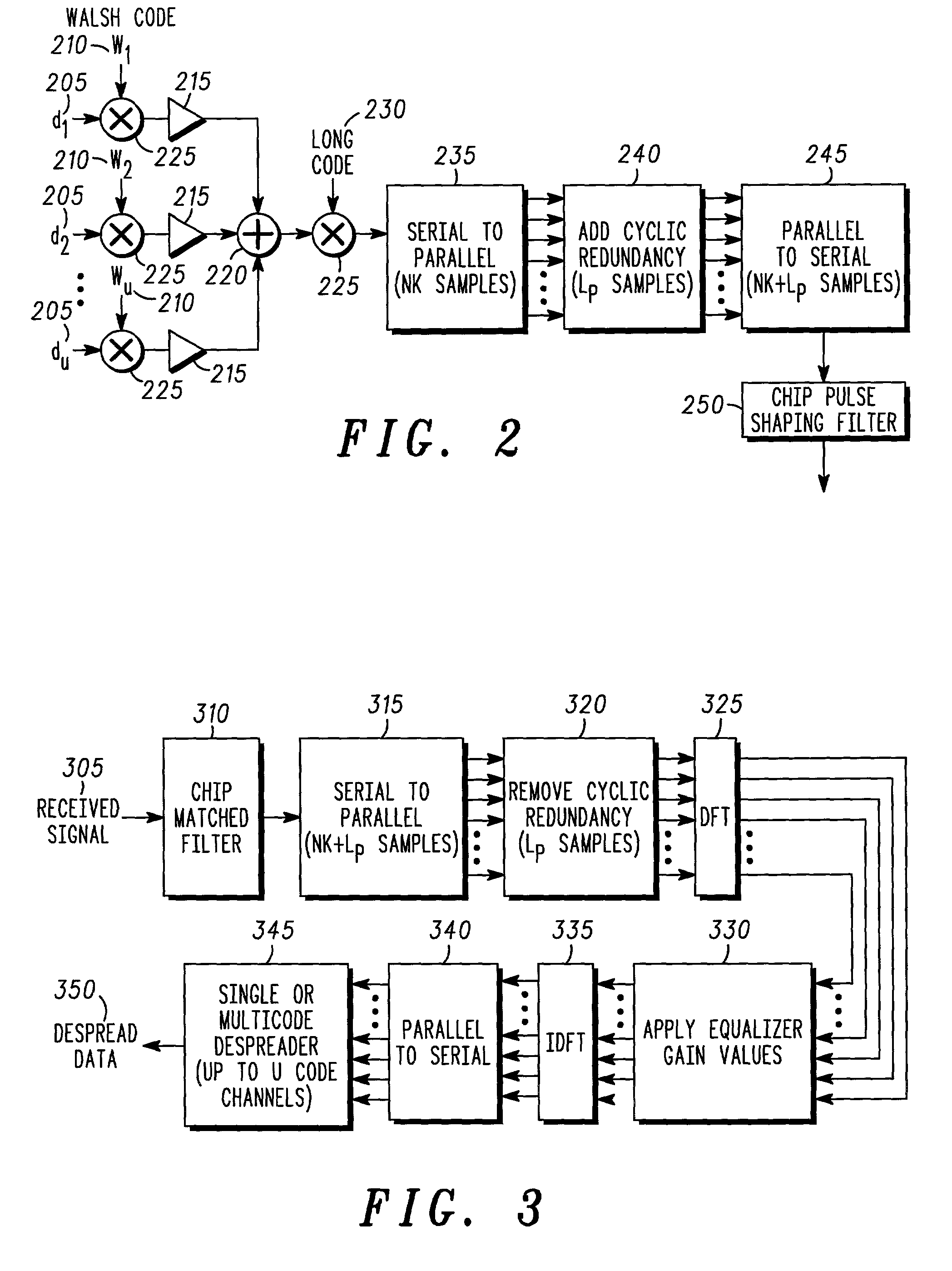
Method and system for transmission and frequency domain equalization for wideband CDMA system
The invention provides a method and system for transmission and frequency domain equalization for wideband CDMA communications by providing at least one spread sequence portion, and inserting a cyclic redundancy to the spread sequence to form a transmitted baseband sequence. The invention further provides a method and system for converting a plurality of receive samples from at least one spread sequence portion into a plurality of frequency domain samples, determining a plurality of frequency domain equalization weights for the frequency domain samples, and determining a time domain signal estimate based on the frequency domain equalization weights and frequency domain samples.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
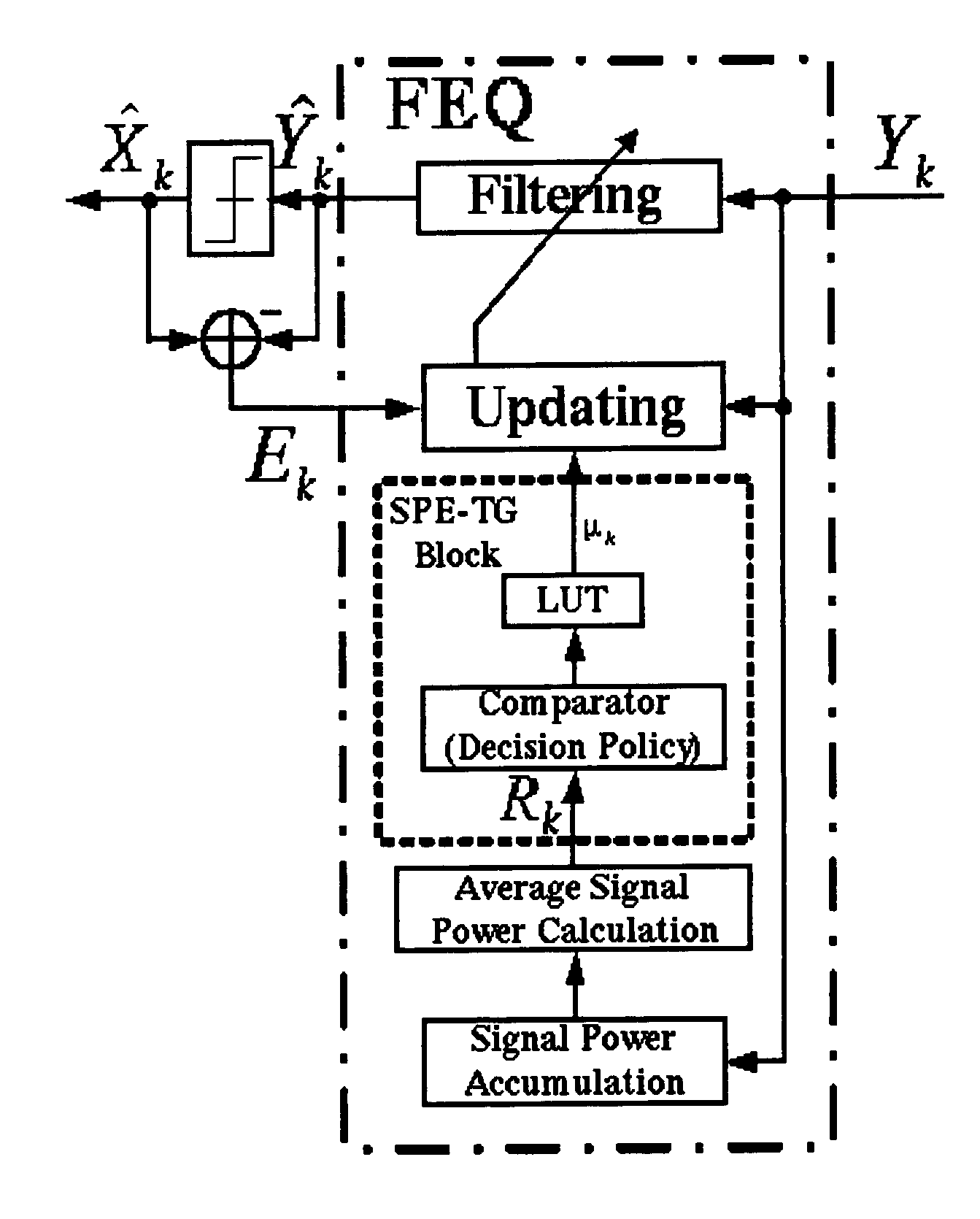
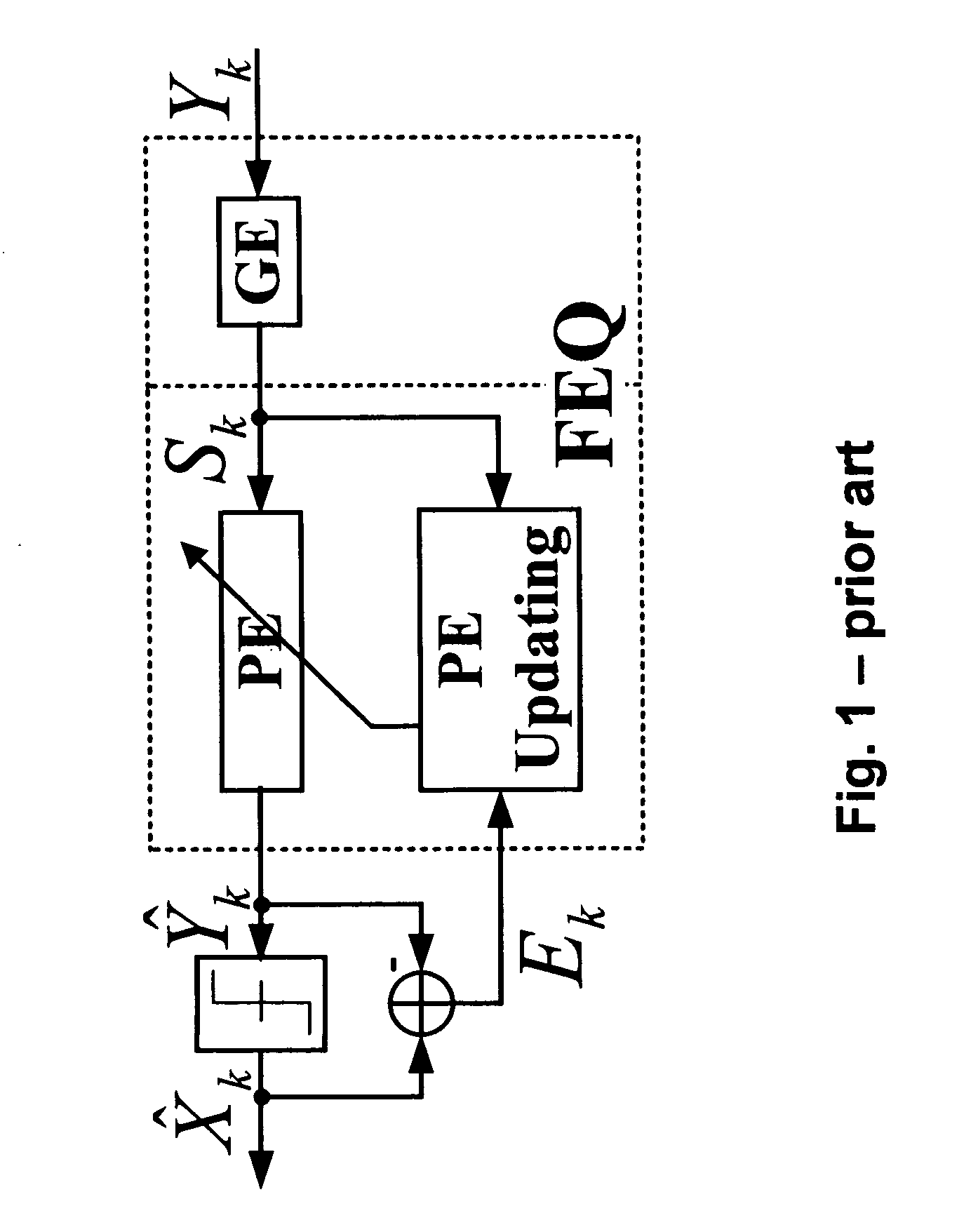
On-line step-size calculation using signal power estimation and tone grouping of the frequency-domain equalizer for DMT-based transceiver
InactiveUS20070127563A1Reduce complexityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCommunications systemTransceiver
An efficient method for calculating the step-sizes for a frequency-domain equalizer of a discrete-multitone communications system using signal power estimation and tone grouping (SPE-TG) while on-line. The SPE-TG method is used to calculate a plurality of subchannel step-sizes which are then stored in a lookup table. When on-line, the method uses signal power estimation to select step sizes for each tone, and uses these step sizes for frequency domain equalization. The SPE-TG method simplifies the calculations necessary for frequency domain equalization, thereby saving significant hardware and / or processing resources. The SPE-TG method is reliable and robust, and does not depend upon assumptions about the line, location, or channel.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Frequency-domain equalizer for terrestrial digital TV reception
InactiveUS6912258B2Few computational resourceImproving integrated circuit cost-effectiveness of the multi-standard demodulatorTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksCost effectivenessSelf adaptive
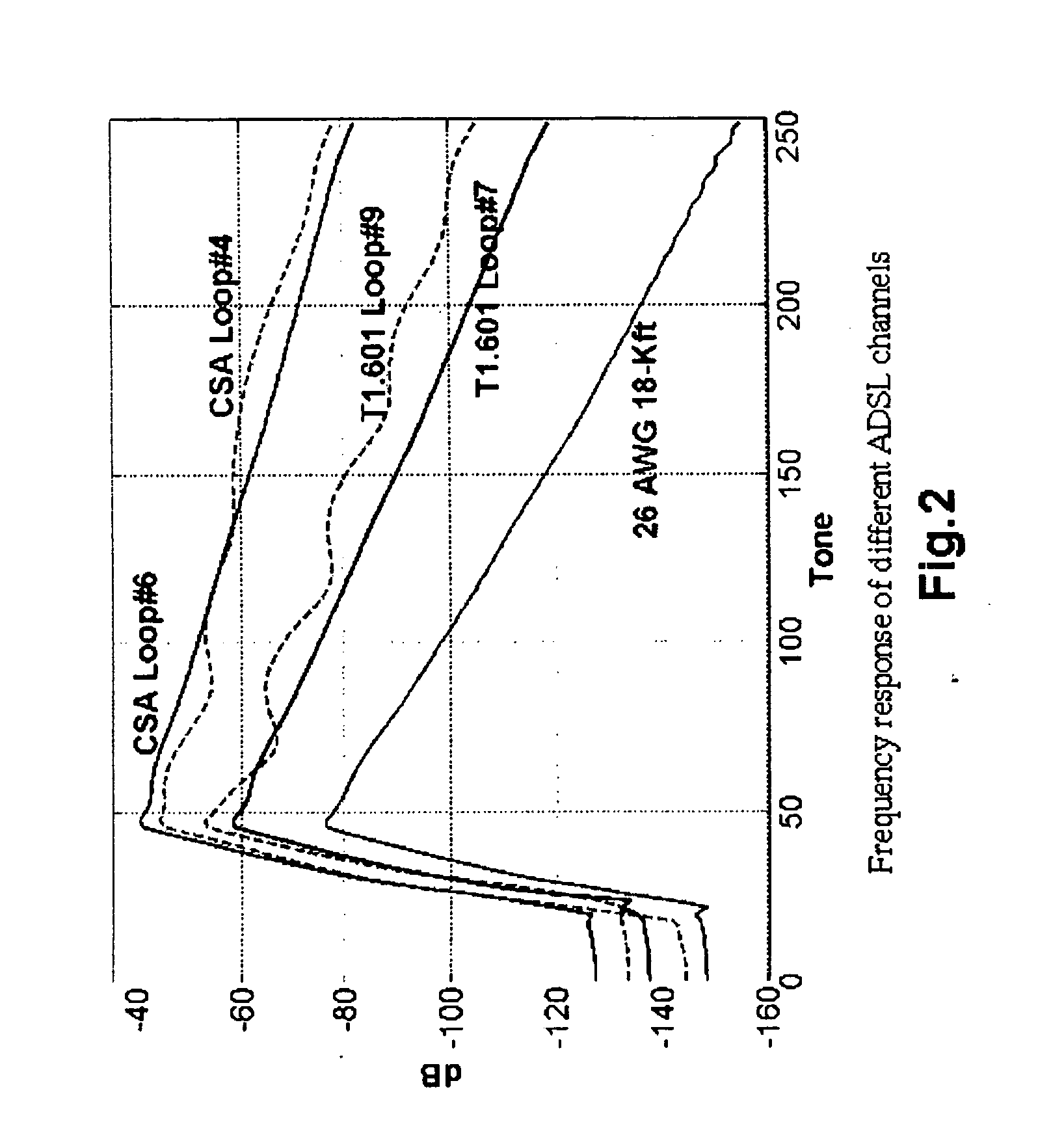
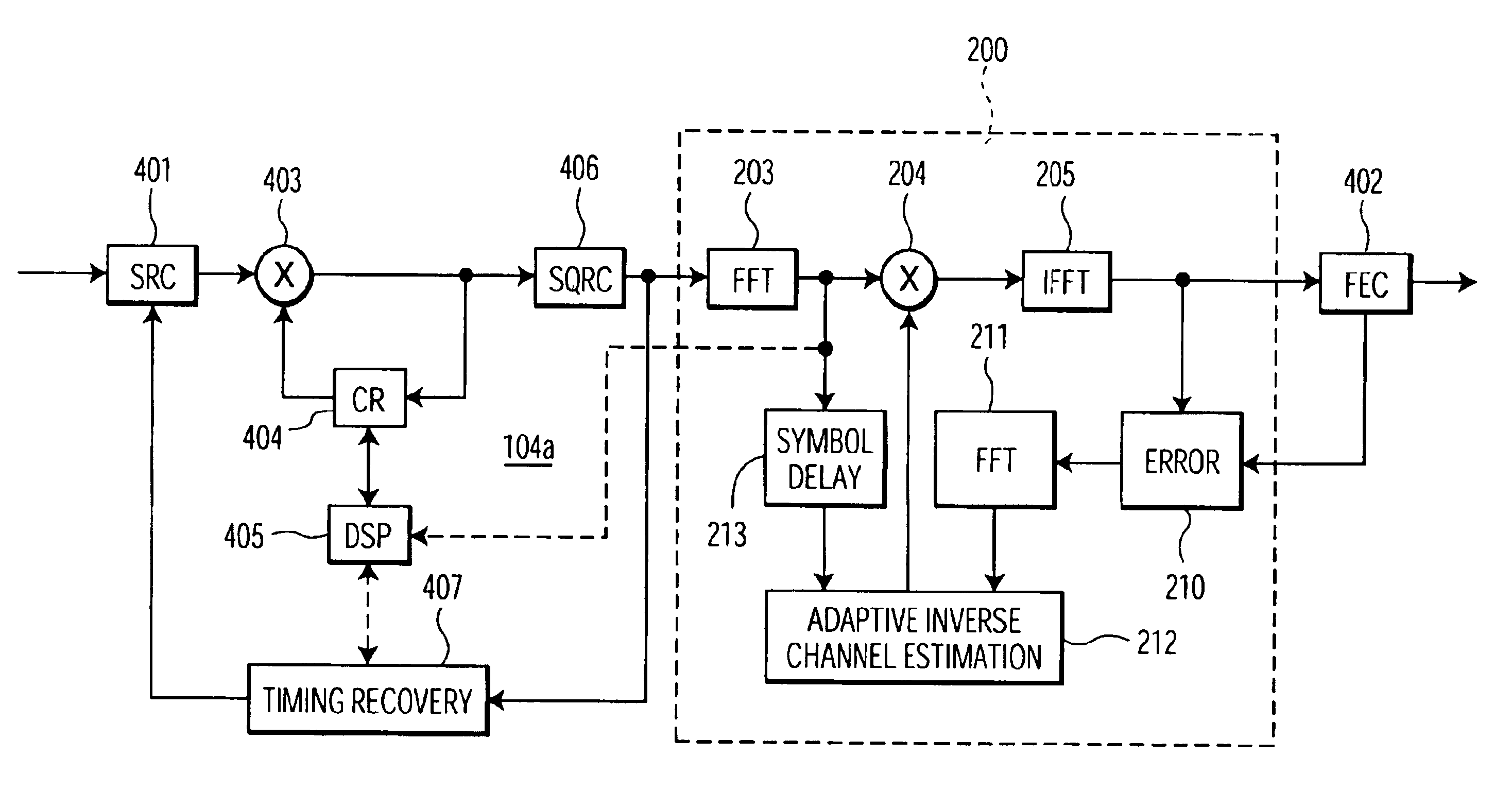
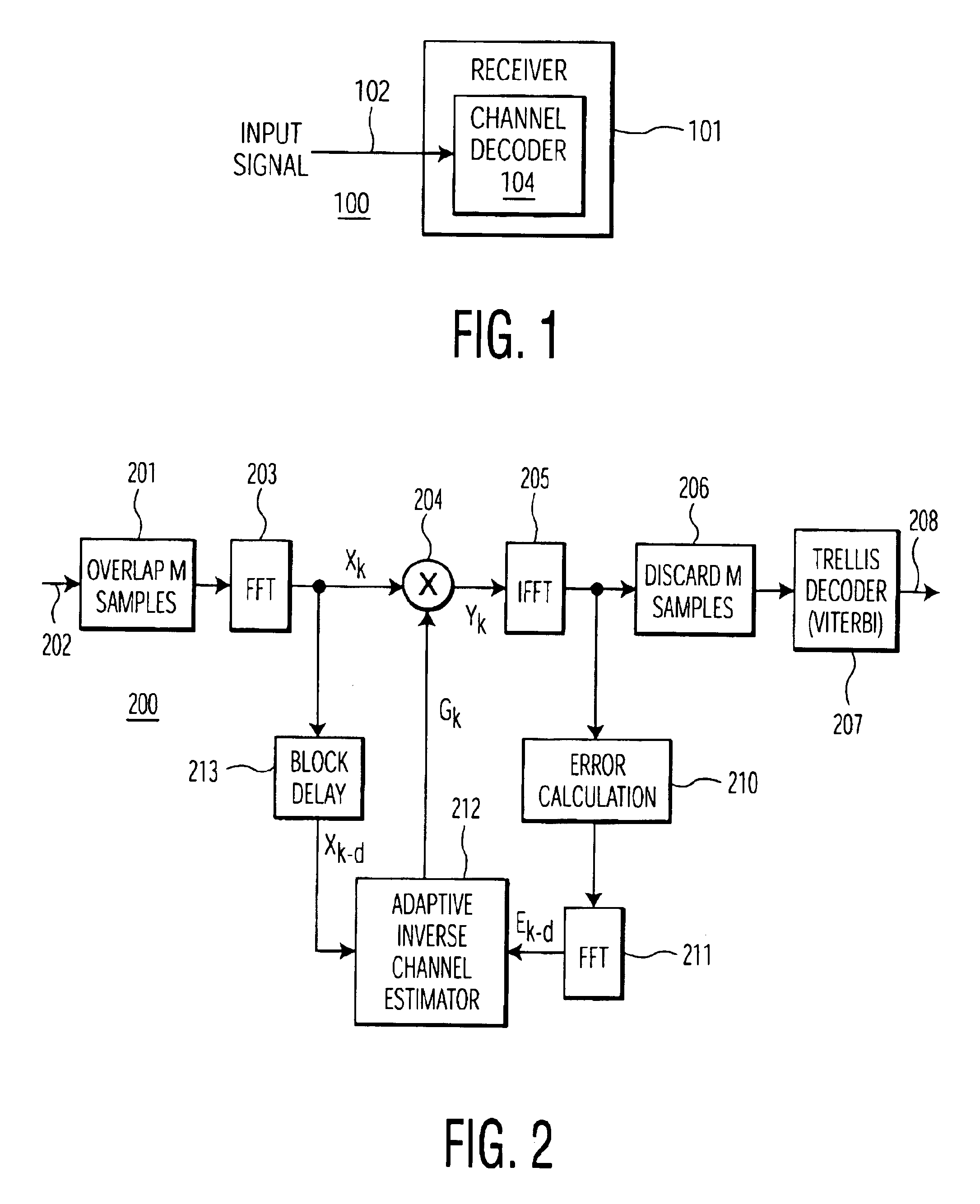
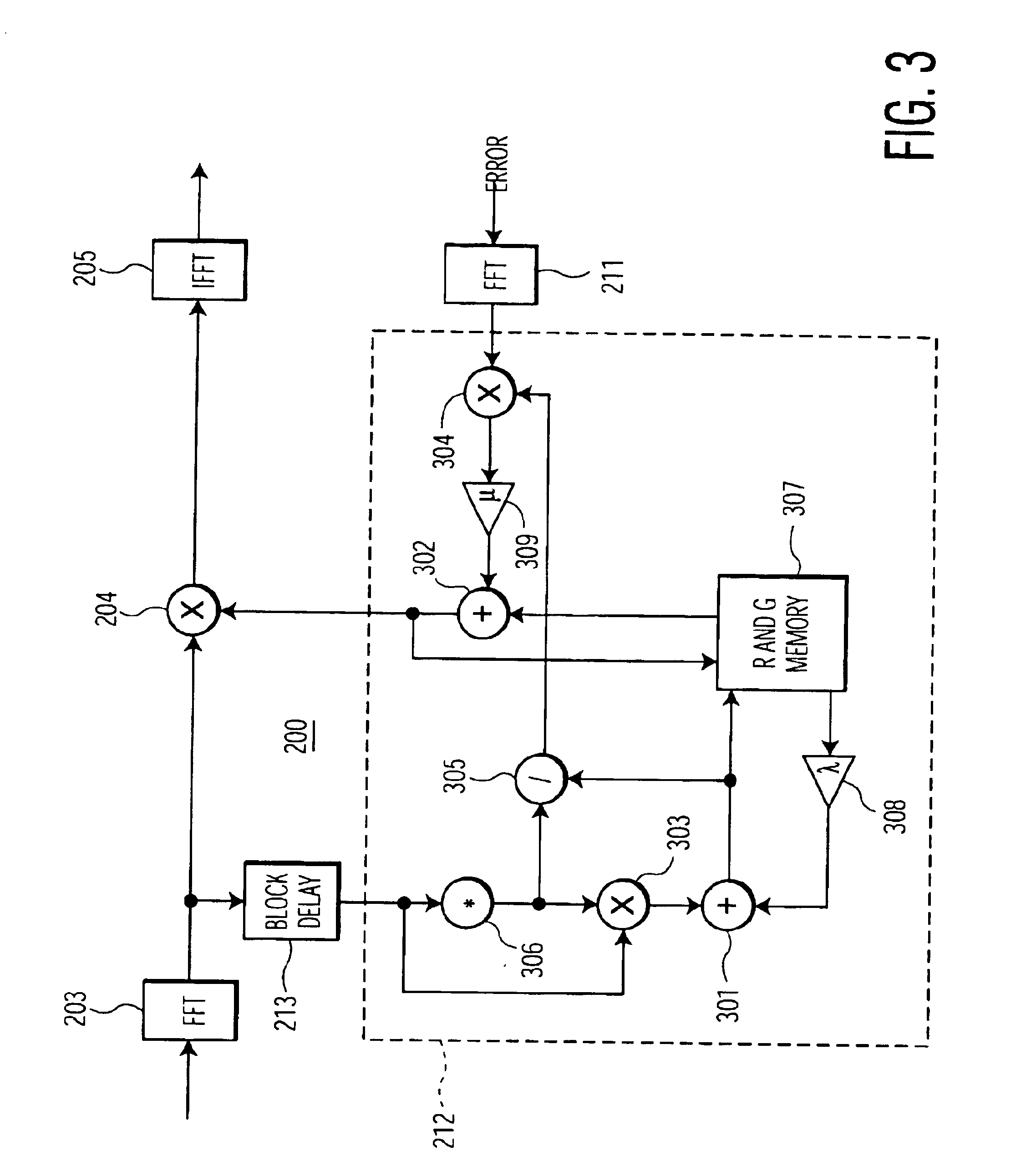
A single integrated circuit multi-standard demodulator includes an adaptive inverse channel estimator for frequency domain equalization which employs a recursive least square cost function in estimating the inverse channel from the received signal and an error estimate. Utilizing a diagonal correlation matrix, the solution to may be determined utilizing fewer computational resources than required by conventional frequency domain equalizers, shifting from a computational intensive to memory intensive implementation. The memory requirement is fully satisfied by memory available within conventional OFDM decoders, and the necessary computational resources may be readily mapped to the resources available within such decoders, improving integrated circuit cost-effectiveness of the multi-standard demodulator.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for offset-modulation orthogonal frequency division multiplexing transmission with cyclic prefix
ActiveCN101795257ALow signal envelope fluctuation performanceReduce complexityMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Frequency domain estimation of IQ imbalance in a wireless OFDM direct conversion receiver using loopback connection
ActiveUS7184714B1Accurate estimateAccurate amplitudeModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationLocal oscillator signalPhase imbalance
An OFDM transceiver has a transmitter, a receiver, and a loopback switch. The loopback switch configured is for selectively establishing a physical connection between an output terminal of the transmitter and an input terminal of the receiver. The transmitter is configured for outputting to the output terminal an OFDM signal generated based on a local oscillator signal. The receiver is configured for demodulating the OFDM signal, received via the physical connection, using the local oscillator signal and determining amplitude and phase imbalance parameters based on performing frequency-domain estimation of amplitude and phase imbalances. Hence, the receiver is configured for performing imbalance compensation on a received wireless OFDM signal based on the determined amplitude and phase imbalance parameters. Hence, amplitude and phase imbalances can be estimated accurately despite channel fading and frequency variations encountered between the transmitter of the wireless OFDM signal and the receiver.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Receiver for discrete multitone modulated signals having window function
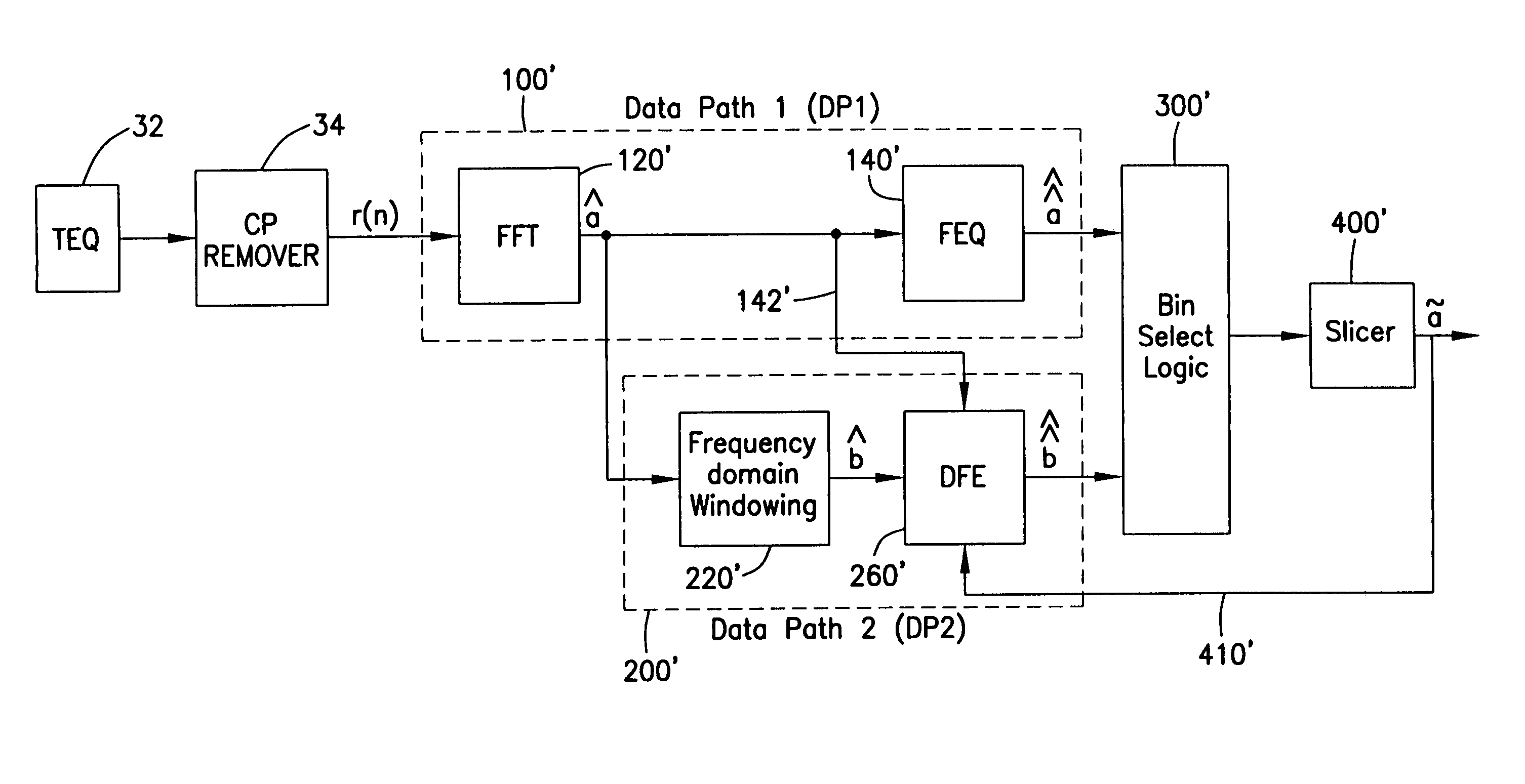
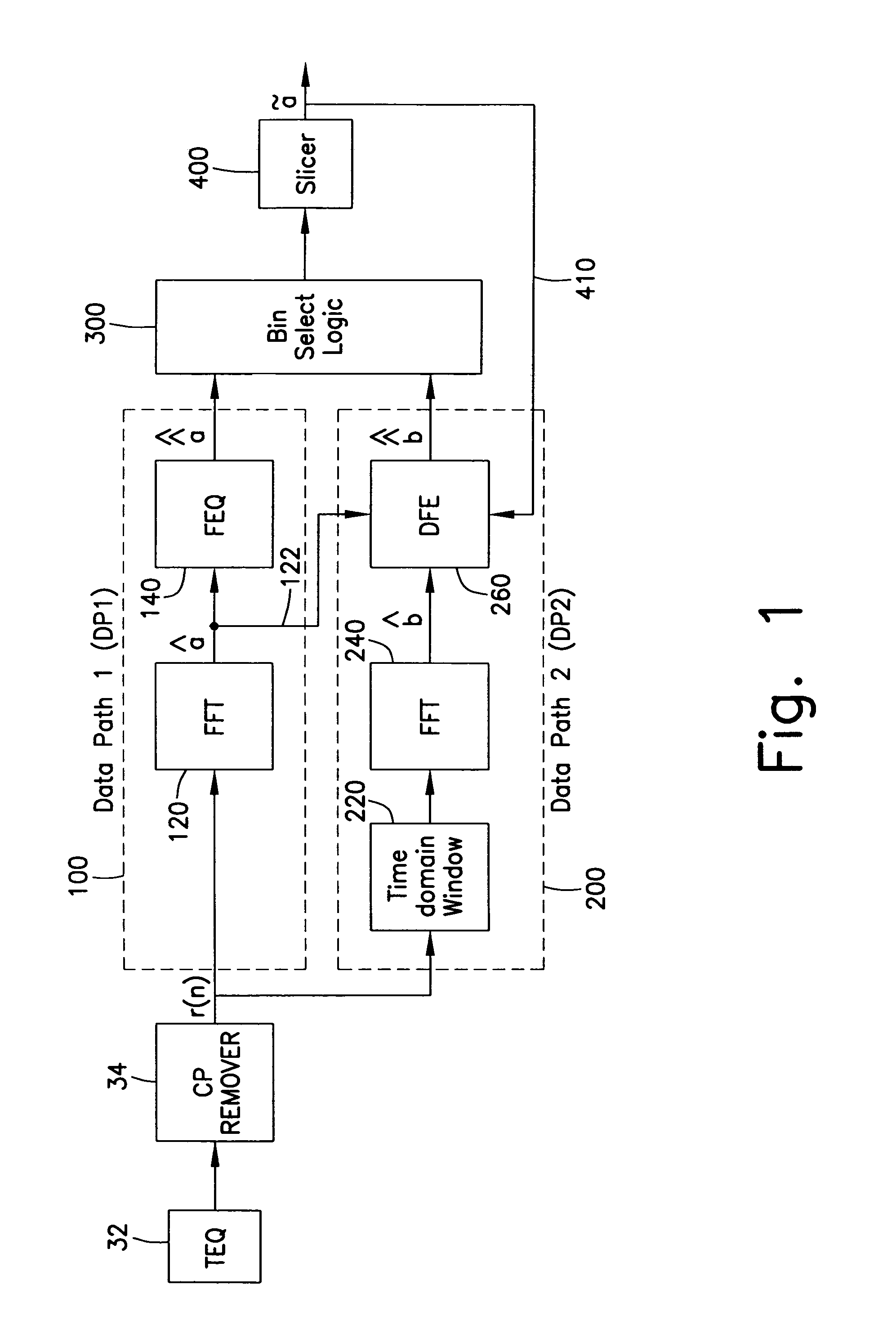
InactiveUS7023938B1Reduce threat of error propagationEasy to implementMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationTime domainModem device
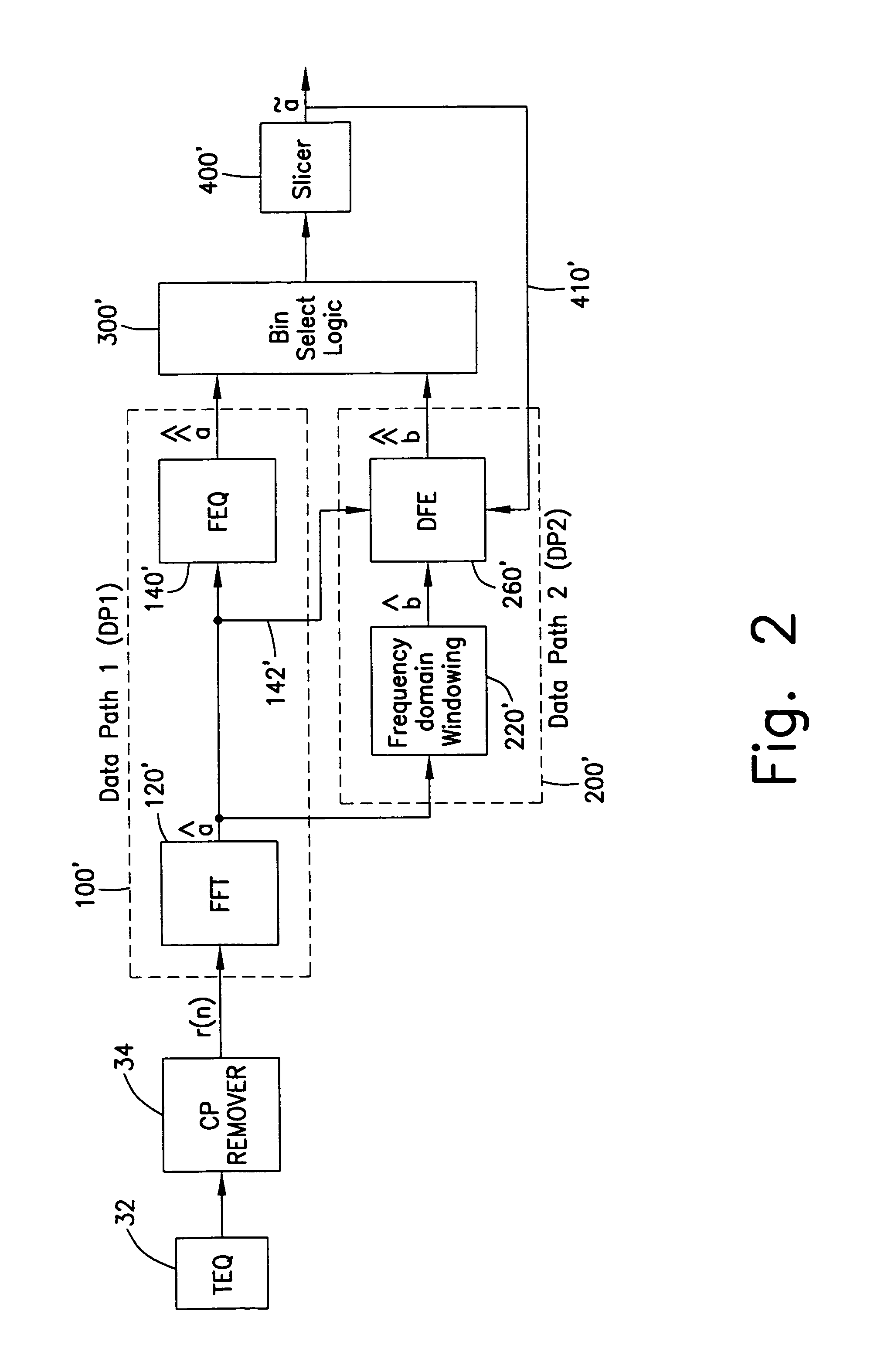
A receiver for improving the performance of conventional Discrete Multitone Modulation (DMT) based Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) modems, in the presence of noise and / or interference. A demodulator having an FFT followed by a single-tap-per-bin frequency-domain equalizer is augmented by an additional data-path utilizing windowing or pulse shaping. Windowing is done independently for each symbol over the orthogonality interval and efficiently in the time domain or frequency domain. A decision feedback equalizer at the output of the windowed data-path cancels inter-bin-interference created by windowing.
Owner:NEC CORP
Hybrid domain block equalizer
The invention provides a method and device for iterative hybrid time-frequency domain block equalization of signals received via a communication channel subject to multipath interference. The equalization method includes frequency-domain equalization of blocks of received signals in a forward path, and time-domain inter-block echo correction and intra-block cyclic echo addition in the feedback path. The invention can be used for equalizing signals transmitted without cyclic prefix and subjected to multi-path interference with long delay spread.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
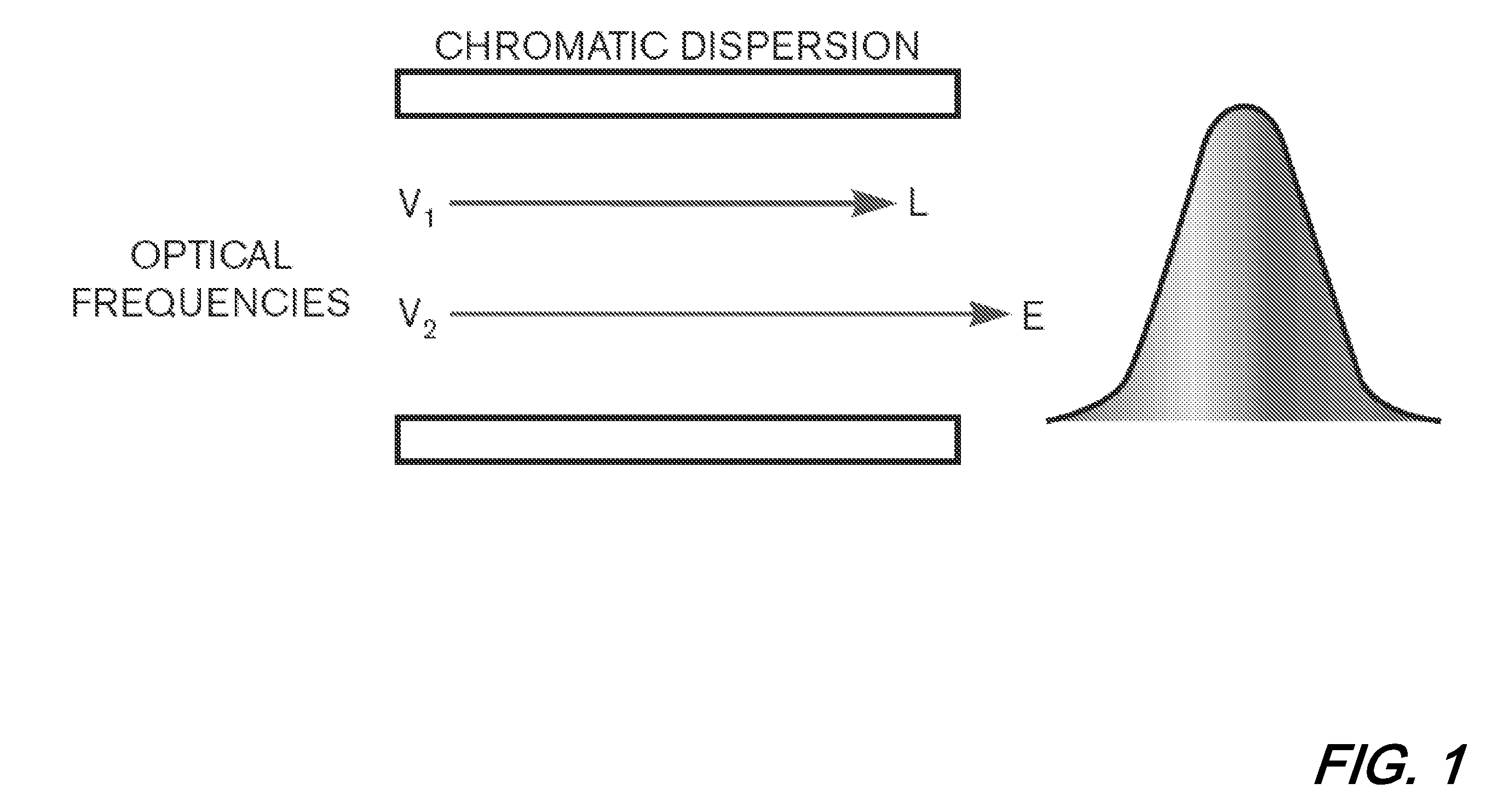
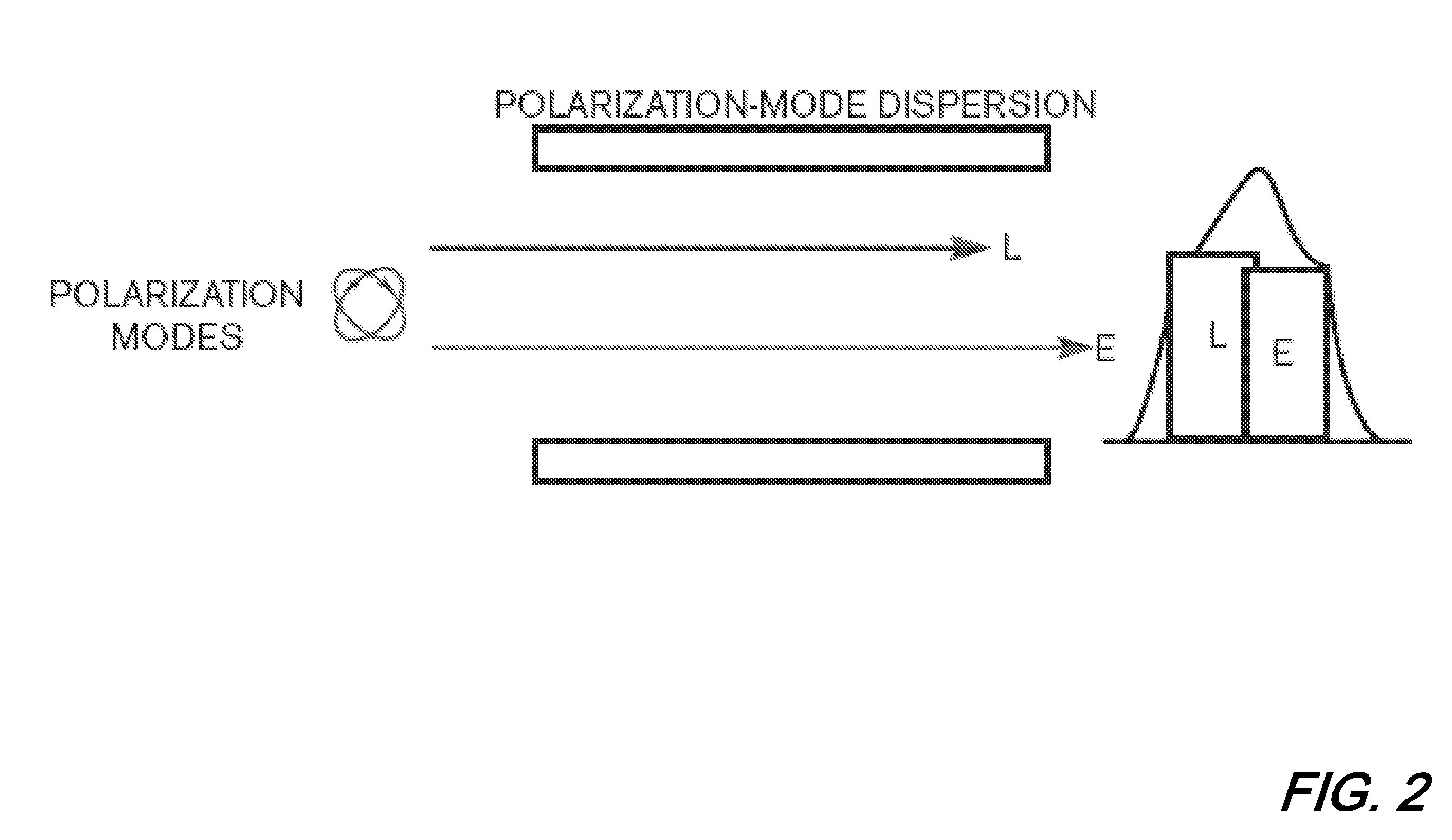
Methods and apparatus for optical transmission of digital signals
ActiveUS20090220239A1High levelImprove power efficiencyWavelength-division multiplex systemsFibre transmissionBipolar signalOptical data transmission
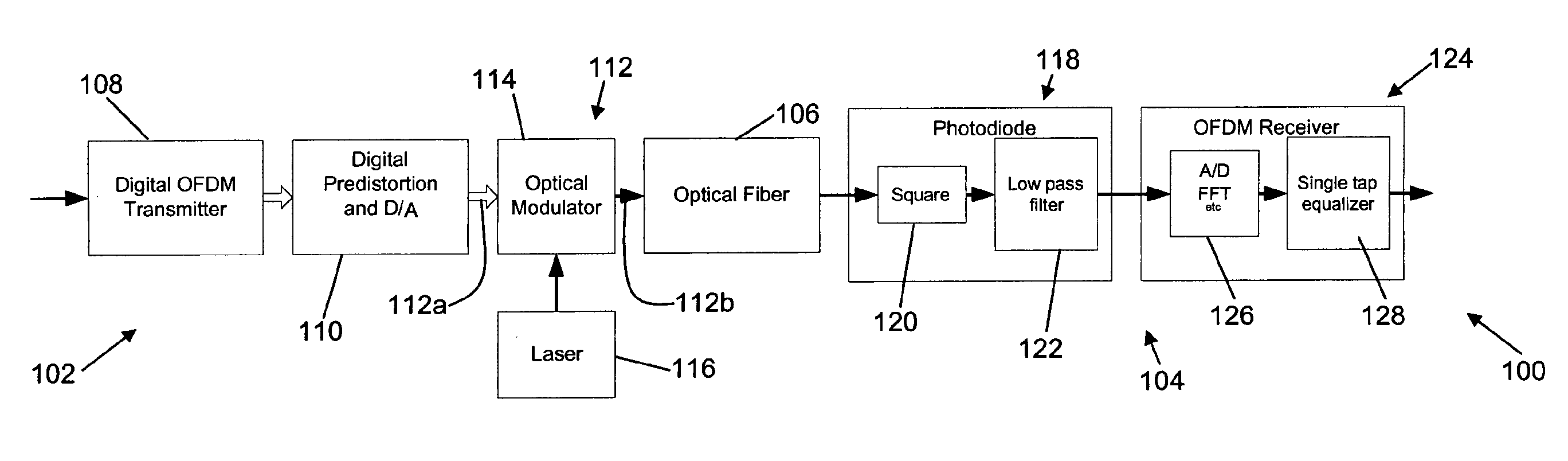
A method of communicating digital information over a dispersive optical channel includes encoding the digital information into a plurality of data blocks, each of which includes a number of bits of the information. A time-varying electrical signal is generated which corresponds with each of said data blocks. The time-varying electrical signal is applied to an optical transmitter (122) to generate an optical signal which includes an asymmetrically amplitude limited transmitted signal modulated onto an optical carrier. The optical signal is then transmitted over the dispersive optical channel (106). At a receiving apparatus (104) the optical signal is detected to produce an electrical signal which corresponds with the asymmetrically amplitude limited transmitted signal. A frequency domain equalisation of the electrical signal mitigates the effect of dispersion of the optical channel (106) on the transmitted optical signal, and the equalised signal is decoded to recover the encoded data blocks and the corresponding transmitted digital information. The method enables bipolar signals to be transmitted over a dispersive unipolar optical channel, and reduces or eliminates the need to apply a high optical bias level at the transmitter, thereby improving optical power efficiency and enabling output power levels to be maintained below applicable safe levels, while simultaneously enabling the effects of channel dispersion to be substantially mitigated.
Owner:MONASH UNIV
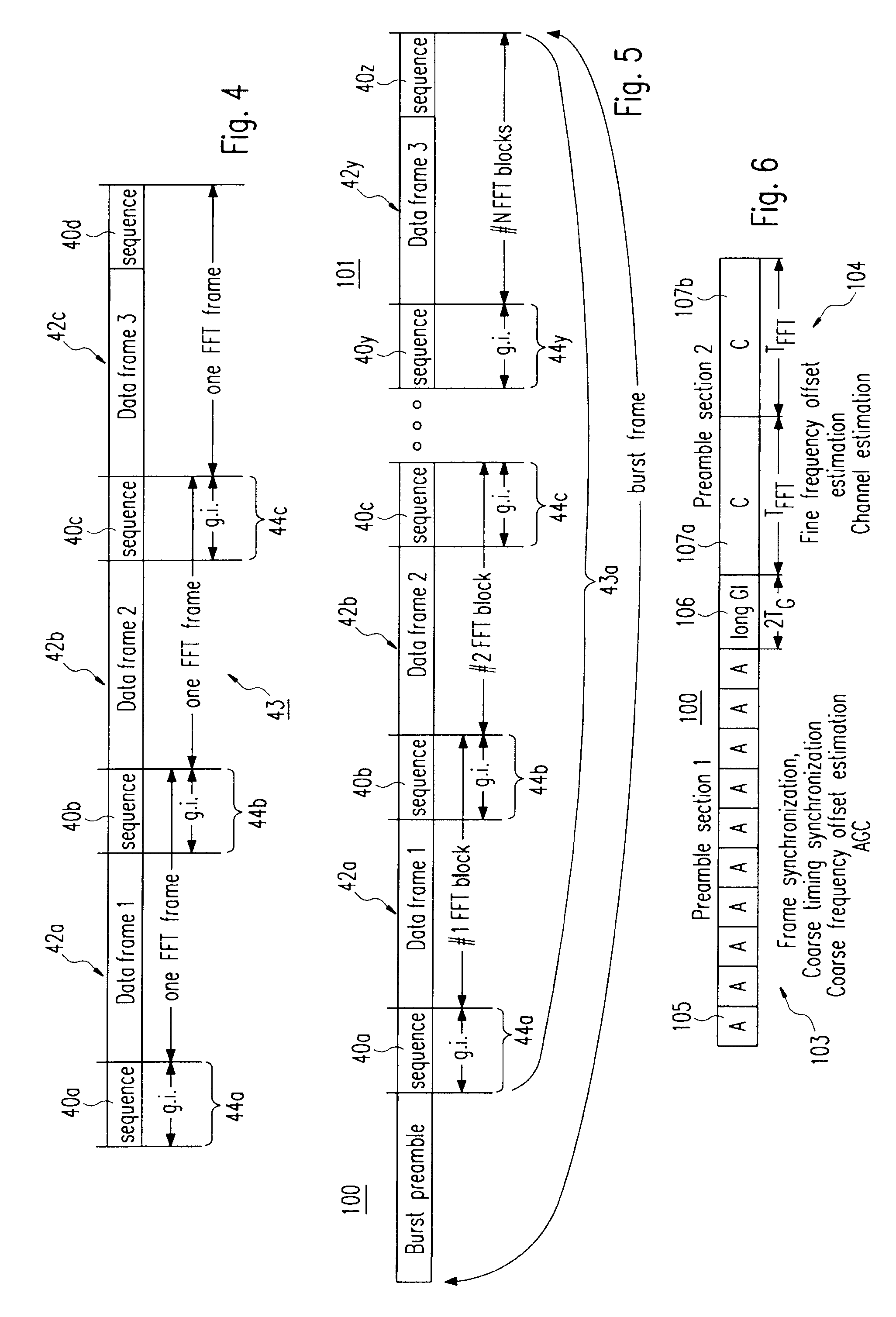
Wireless system using a new type of preamble for a burst frame
InactiveUS20090225741A1Easy to identifyModulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexCyclic prefixCarrier signal
The present invention relates to a signal generator and signal processor for single carrier wireless communication systems with frequency domain equalizer, which are operable to use pseudorandom-noise sequences as part of a preamble and possibly as cyclic prefix. The different arrangements and examples of said pseudorandom-noise sequences could be used for coarse timing synchronization, channel estimation, carrier synchronization, signal-noise-ratio estimation and channel equalization.
Owner:SONY CORP
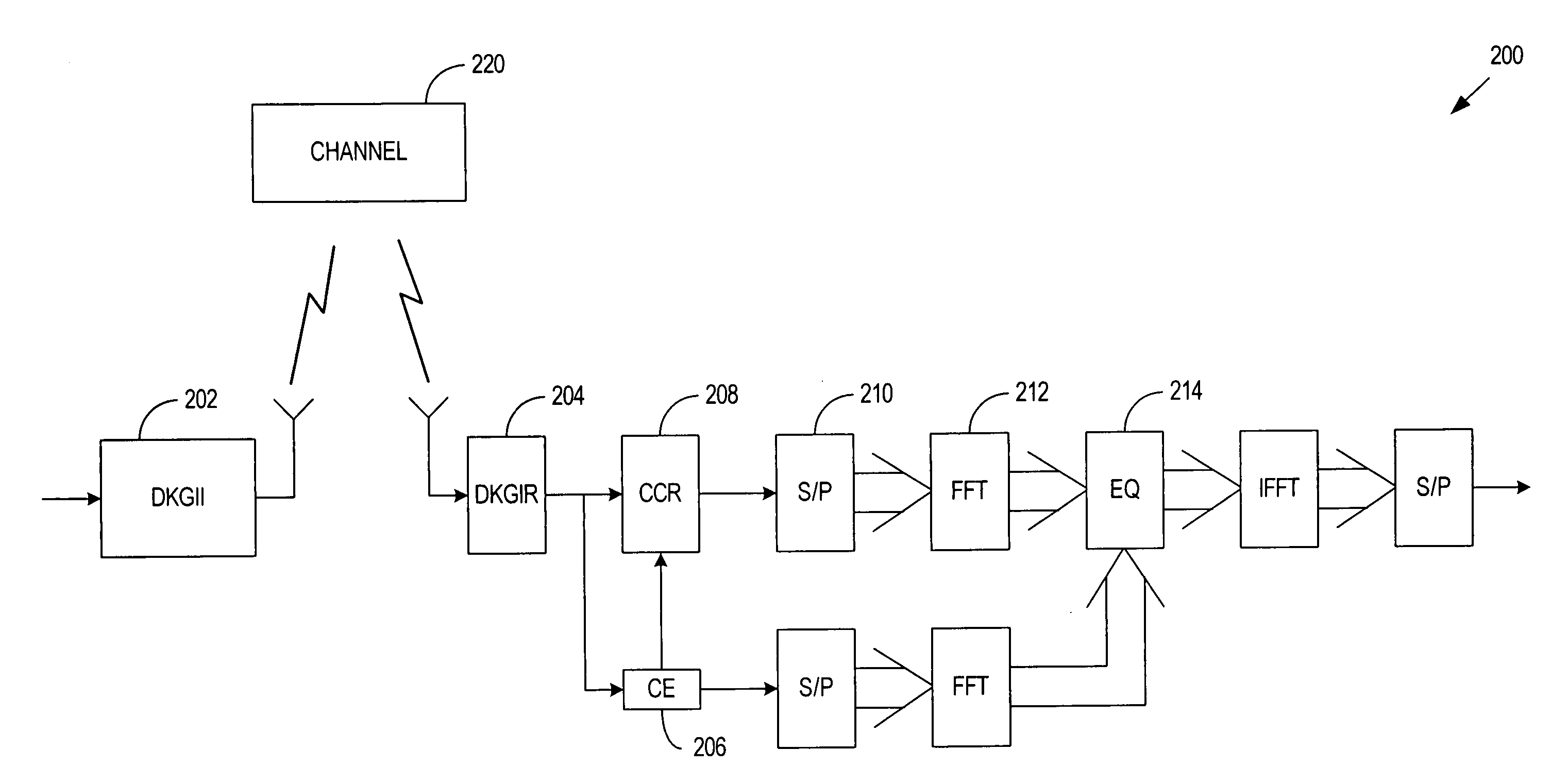
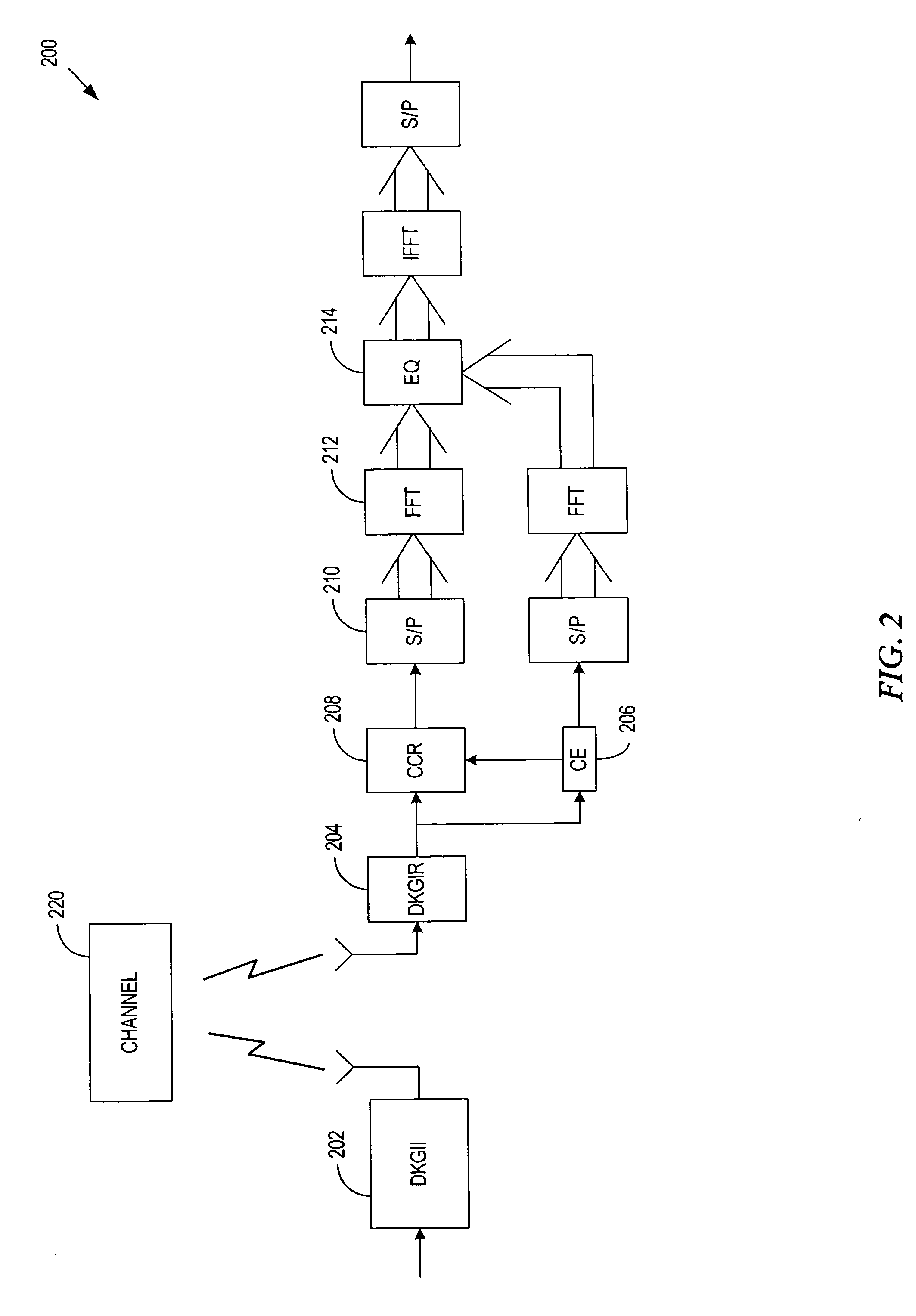
System and method for utilizing different known guard intervals in single/multiple carrier communication systems
InactiveUS20060159187A1Facilitates FFT transformationEliminates pilot signal overheadSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTransceiverEqualization
A system and method for a transceiver structure, where Different Known Guard Intervals (DKGI) are appended to multiple, consecutive data blocks and are then used in combination with Channel State Information (CSI) to restore cyclic convolution in the time domain. Once restored, the CSI and cyclic convolution are transformed into the frequency domain by FFT processing to facilitate equalization of the channel through Frequency Domain Equalization (FDE). Through performance of time domain channel estimation, there is no need for pilot signals and related overhead, thus channel capacity is enhanced.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
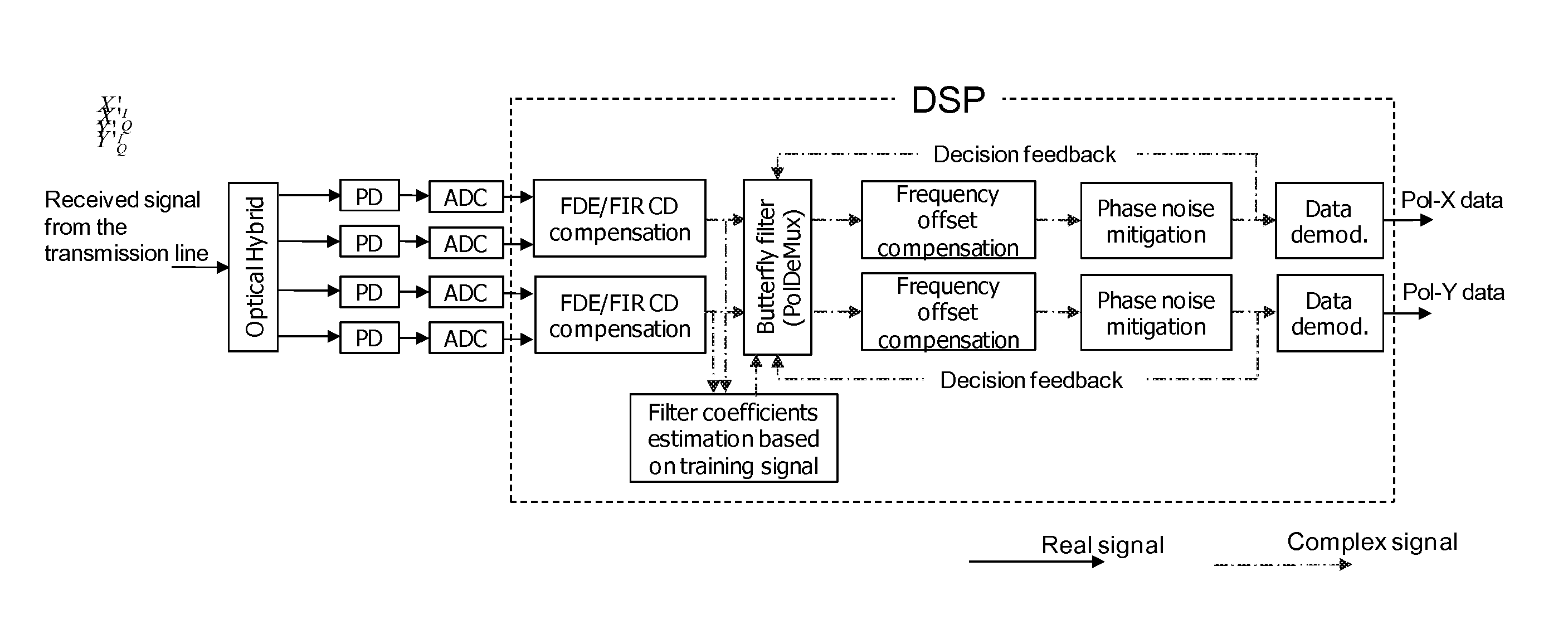
Adaptive crossing frequency domain equalization (FDE) in digital polmux coherent systems
ActiveUS20100142952A1Efficient use ofSimple multiplicationPolarisation multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingPolarization multiplexedSelf adaptive
A method for the polarization independent frequency domain equalization (FDE) on polarization multiplexing (POLMUX) coherent systems employing an adaptive crossing FDE which advantageously produces CD compensation, PMD compensation and PolDeMux within one functional block of a digital signal processor (DSP).
Owner:NEC CORP
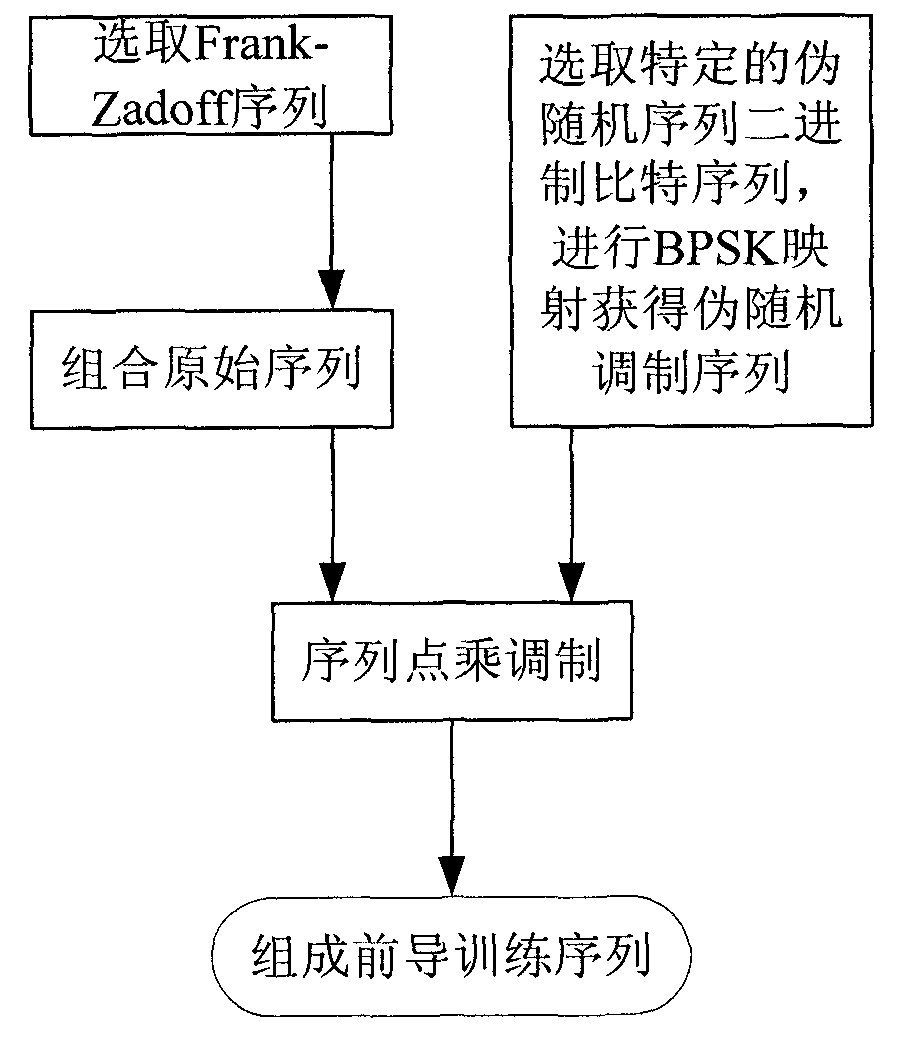
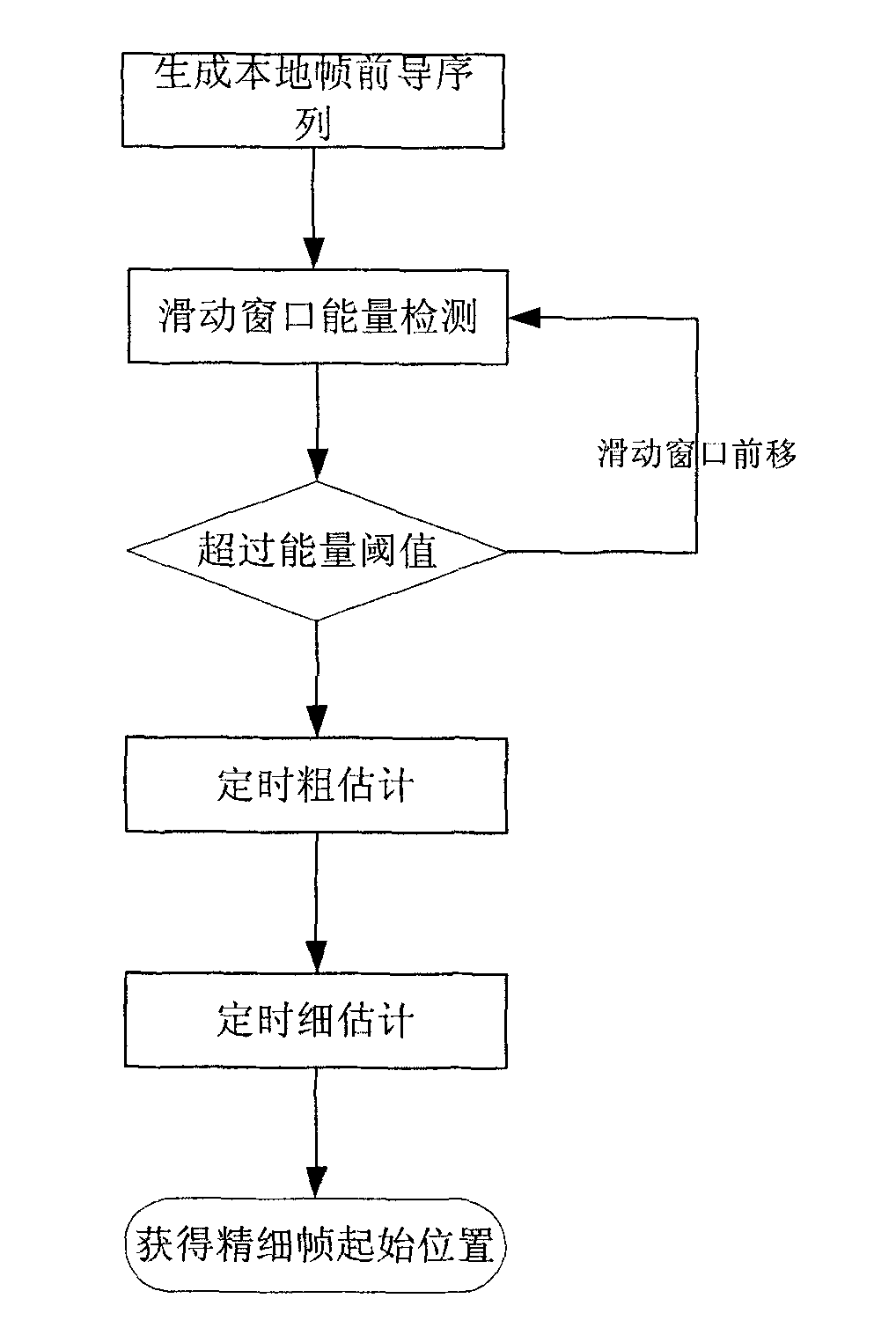
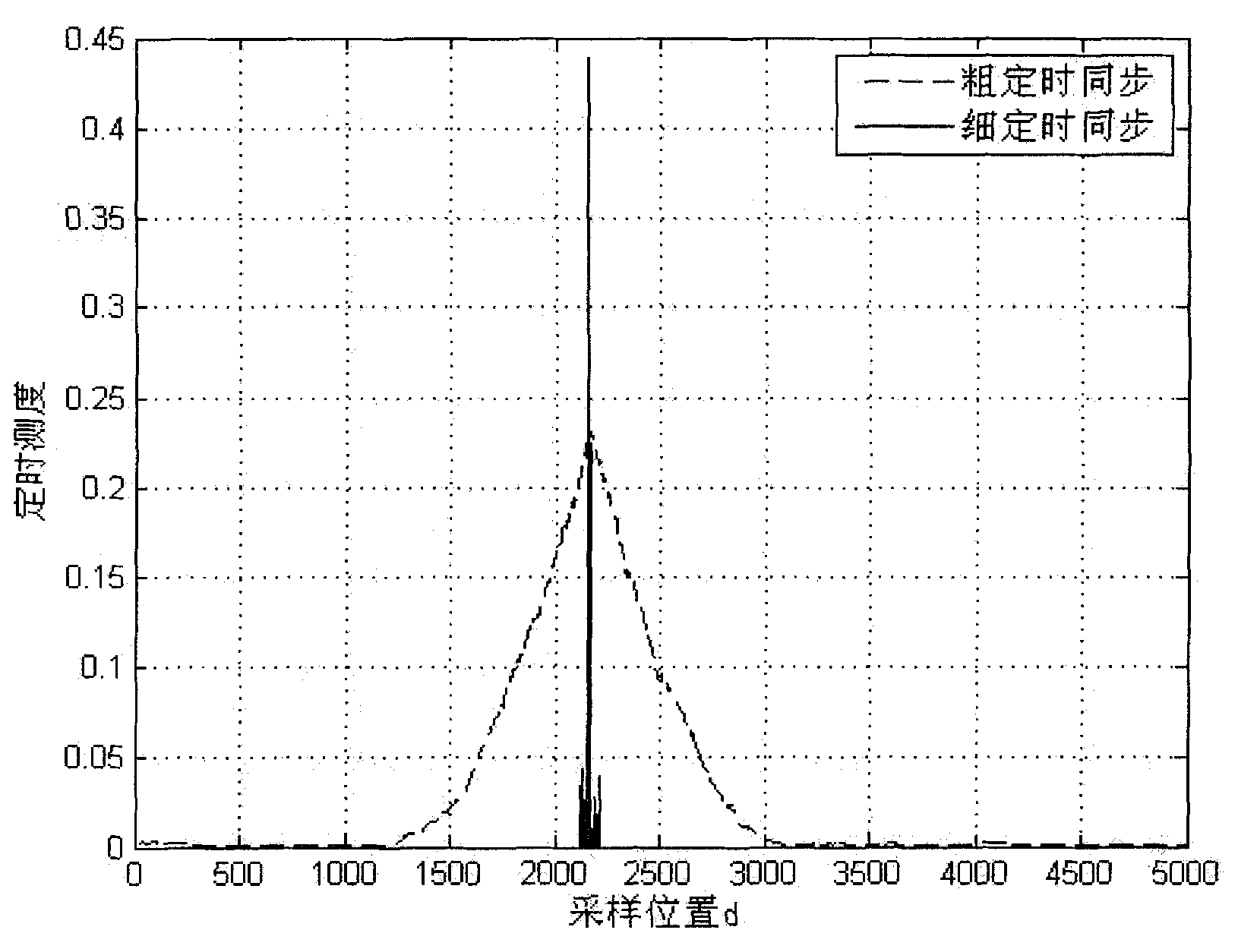
Training sequence frame timing synchronized method based on pseudo-random sequence modulation based
InactiveCN101778088AImprove featuresSharp peakMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier signalSelf correlation
The invention discloses a training sequence frame timing synchronized method based on pseudo-random sequence modulation, which can be applied in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system or a single carrier frequency domain equalization system, and comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out an energy detection by using the relevance of the front part and the back part of a training sequence at a receiving terminal; (2) taking the certain range around the peak position of the energy detection as a rough synchronization timing range; (3) in the rough synchronization timing range, using a local frame leading sequence generated by the receiving terminal to carry out the cross-correlation with a receiving sequence, according to the peak position of the cross-correlation, determining the position of the local frame accurate synchronization timing, wherein the first half part of the leading training sequence is gained by modulation of cascade sequence of self-correlation of a plurality of constant amplitude zero values by adopting the pseudo-random modulation sequence, and the second half part thereof is inverse operation of the first half part. The method can gain higher timing accuracy by using the pseudo-random modulation sequence to carry out the complex fine synchronization.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method based on slide window for estimating and equalizing channels of block signals containing pilot
InactiveCN1398118AAccurate demodulationReliable receptionEqualisersHigh-definition television systemsMain channelCarrier signal
Channel estimation of block signals containing pilot frequency and balanced method characterizes in containing side channels of force and after of a main channel component in a movable window to determine to get a correct channel estimation interval again to get channel impulse response estimation with the length of N, M or M+2XN, then to take position of home and end of the said window as the positioning information needed by circular convolution of the signal and channel inputs response structure and process the data block via channel transmission as the one after channel distortion via frequency domain balance offset or make time-domain over-sampling channel estimation in the sliding window interval to inerase time-domain resolution of channel estimation. The data block can be IDFT of OFDM or modulated by single carrier.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
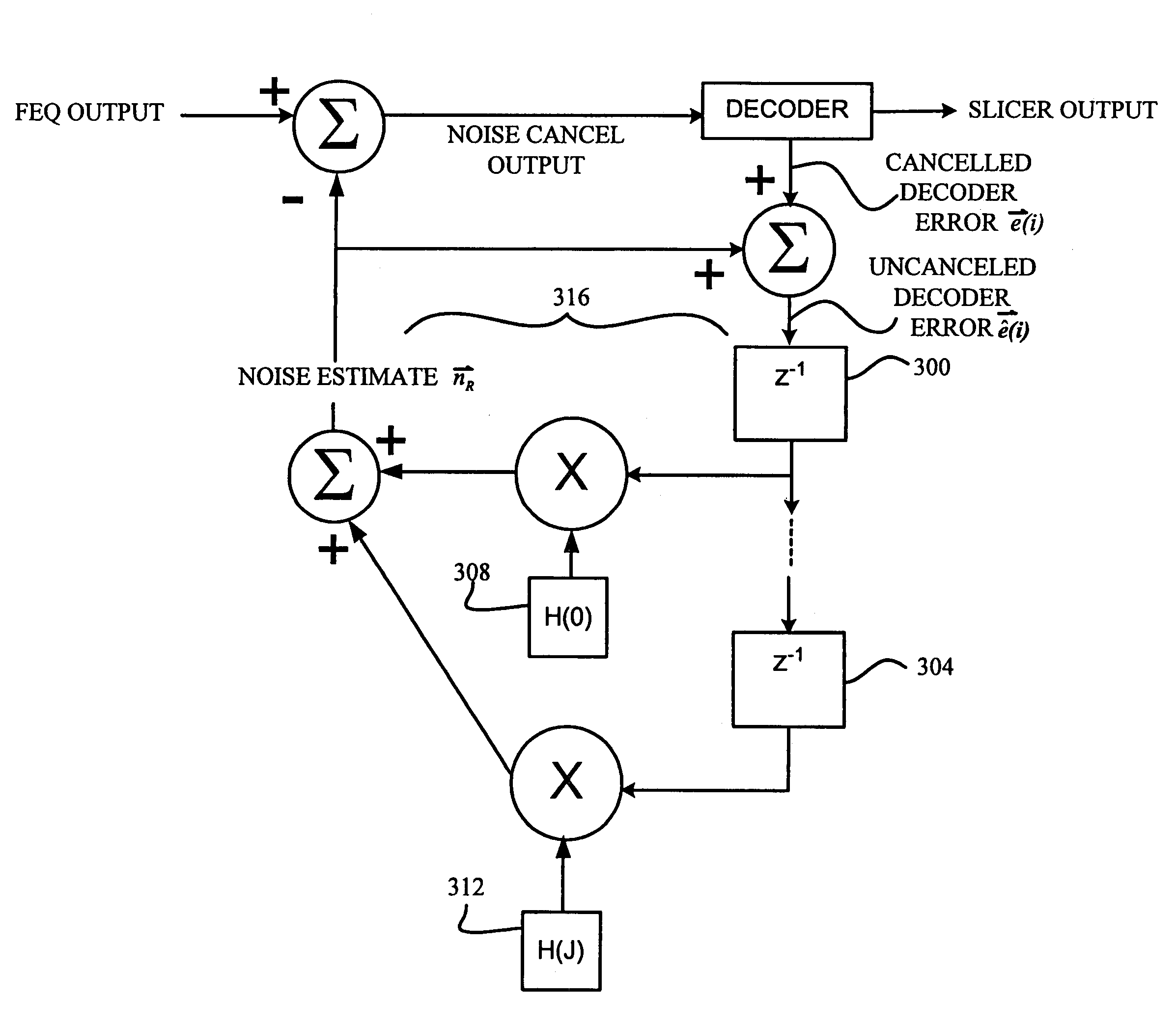
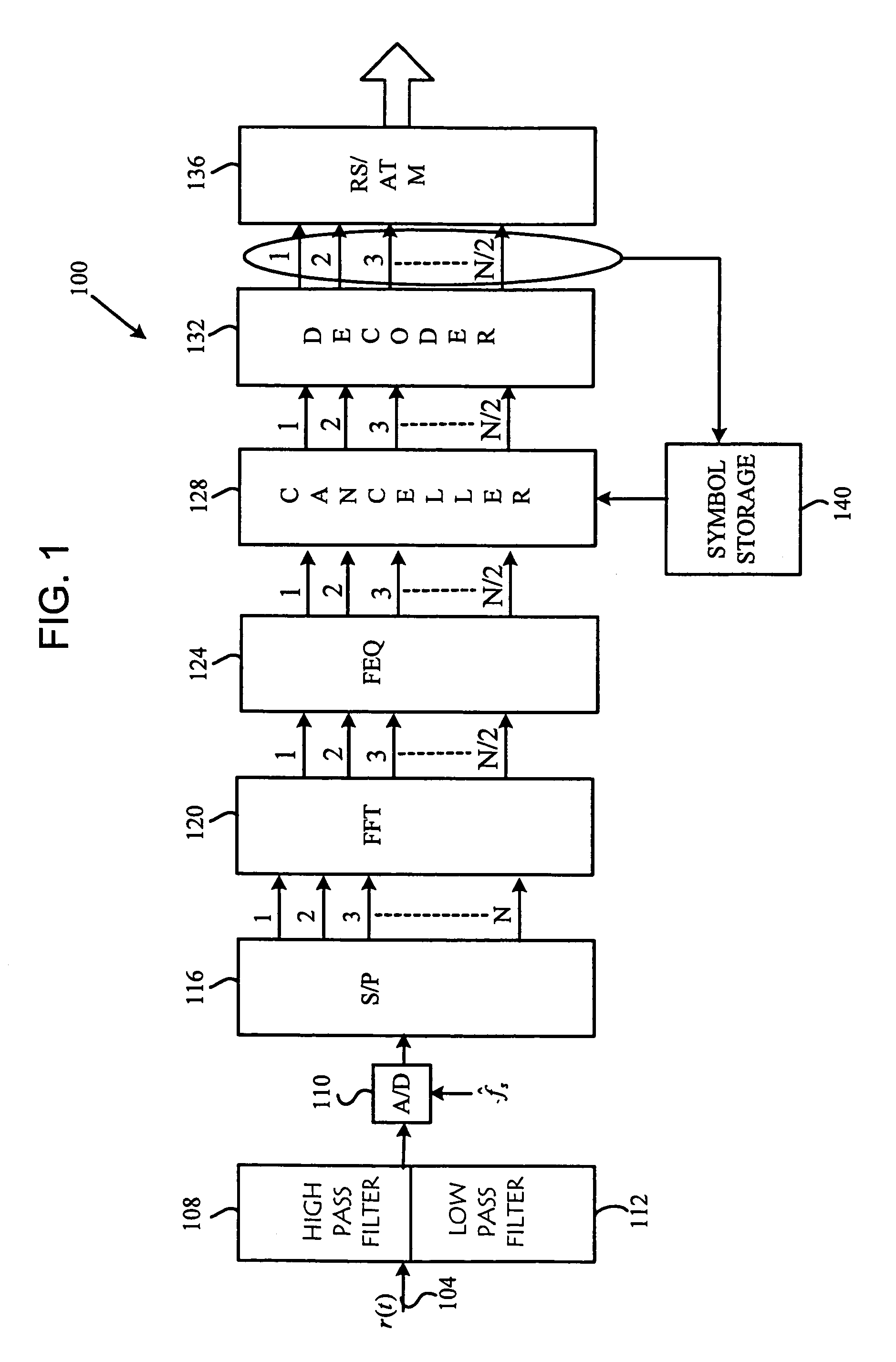
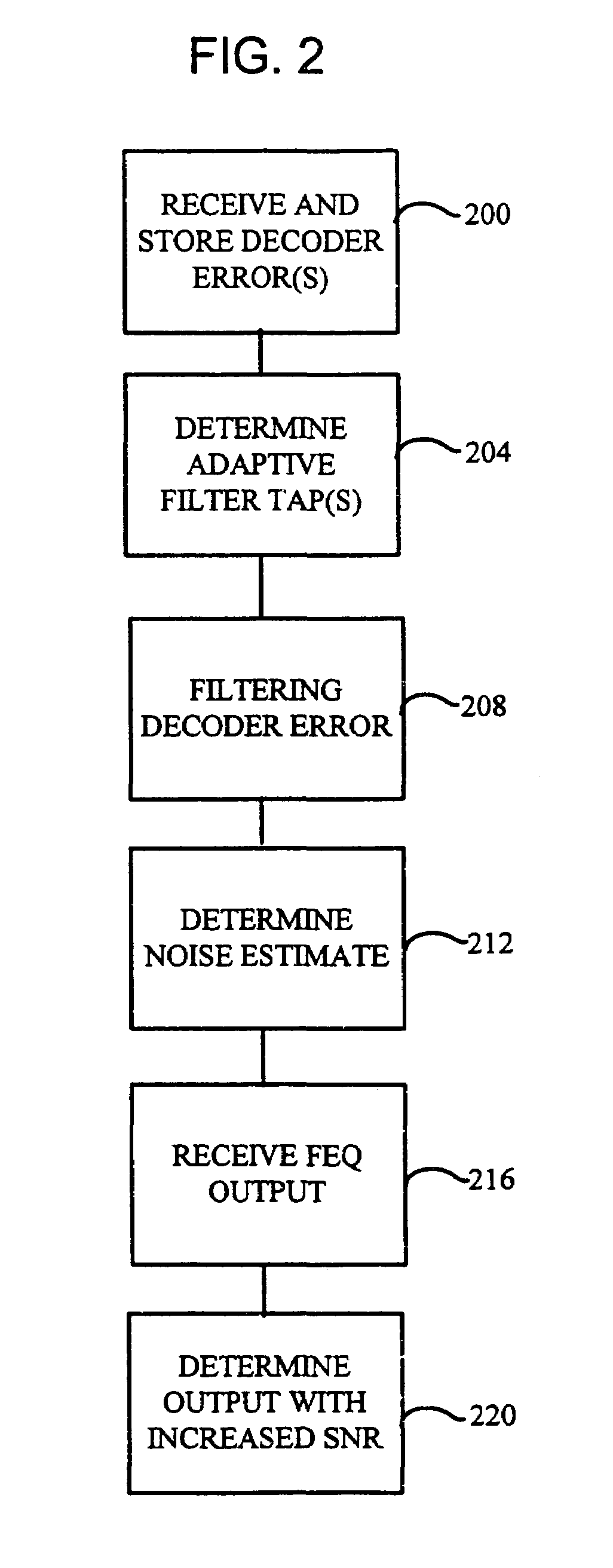
Method and system for a multiple dimensional adaptive frequency domain noise canceler for DMT transceivers
InactiveUS7020212B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduction of narrowband interferenceSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTransceiverFrequency spectrum
The system and method of the preferred embodiments may be directed to improving the signal-to-noise ratio in frequency spectrum regions where narrowband interference may be present. The system and method of the preferred embodiments includes reducing the narrowband interference by determining a noise estimate. In accordance with the noise estimate and output of a frequency domain equalizer, a noise-cancelled output may be obtained.
Owner:MEIZU TECH CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for generation and transmission of optical signals
InactiveUS20100034542A1Remove distortionAvoid the needAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePulse generatorSignal qualityOptical field
Methods and apparatus (100) for composing, generating and transmitting information-bearing optical signals are provided. An information-bearing electrical signal is composed (108) having desirable spectral properties, preferably configured to ensure that undesired interference between electrical spectral components generated in a square-law direct detection process (120) at a corresponding optical receiver (104) is substantially avoided. Predistortion (110) is advantageously applied to transmitted signals, in order to account for a nonlinear relationship arising in a modulation process (114) between electrical signal amplitude and corresponding optical field amplitude. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) techniques may be applied to composed signals having the desired characteristics, and additionally may facilitate the application of frequency domain equalisation (128) in order to mitigate transmission impairments, including dispersion. Improvements in received signal quality, and / or transmission distance, may thereby be achieved, along with simplification of receiver configuration and operation.
Owner:OFIDIUM PTY LTD
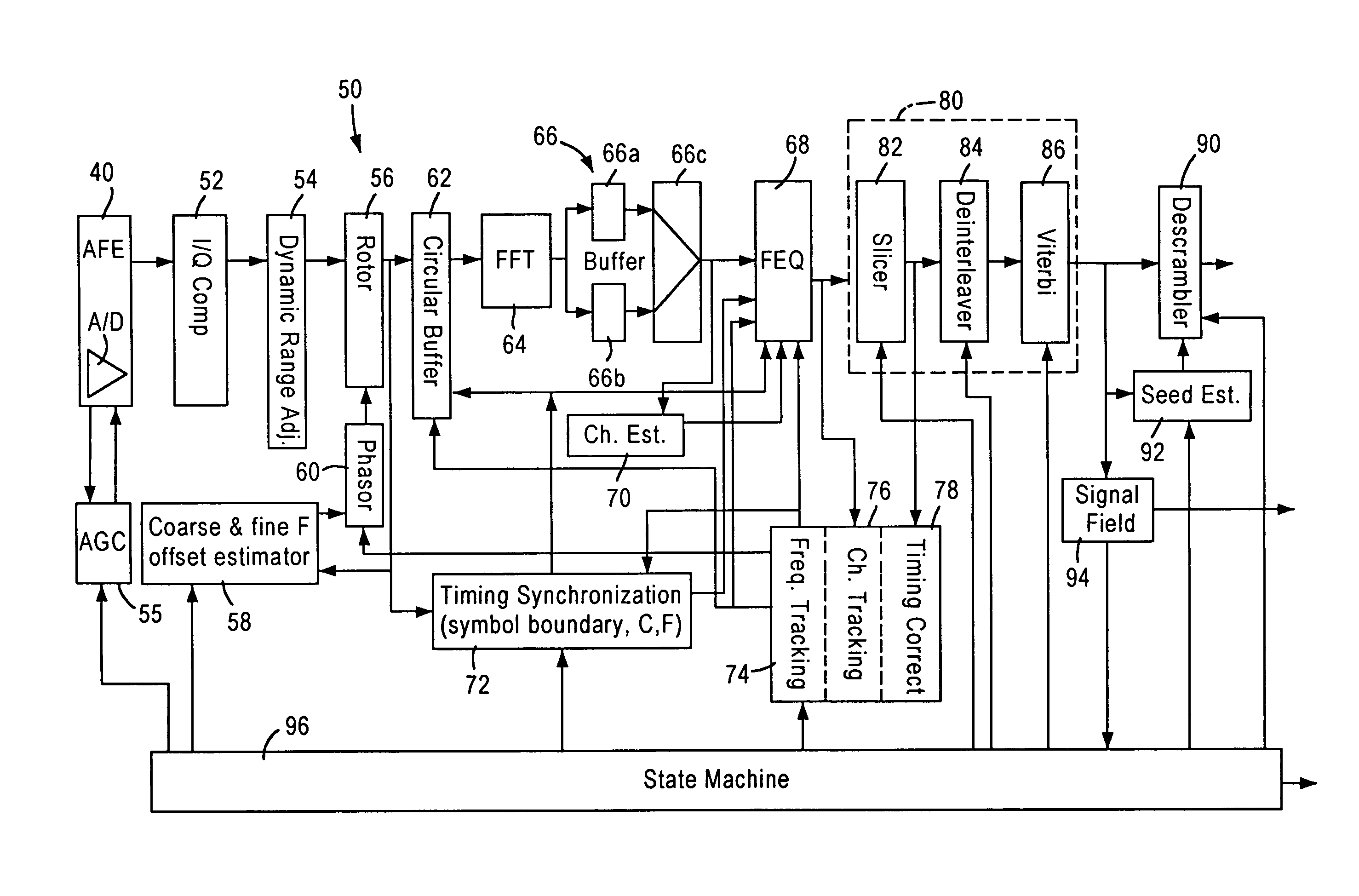
DTV receiver and method of processing broadcast signal in DTV receiver
ActiveUS20070153888A1Improve reception performanceEnhance channel equalization performanceTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksTime domainDTV receiver
A DTV receiver includes a tuner, a demodulator, a known sequence detector, and a frequency domain equalizer. The tuner initially receives a broadcast signal including valid data in which a known data sequence is periodically repeated. The demodulator demodulates the broadcast signal, and the known sequence detector detects the known data sequence from the demodulated signal. The frequency domain equalizer compensates channel distortion of the demodulated broadcast signal in a frequency domain using the detected known data sequence. In addition, the DTV receiver may further include a time domain equalizer which compensates channel distortion of the time domain signal, or a noise canceller which removes a predicted noise from the time domain signal.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
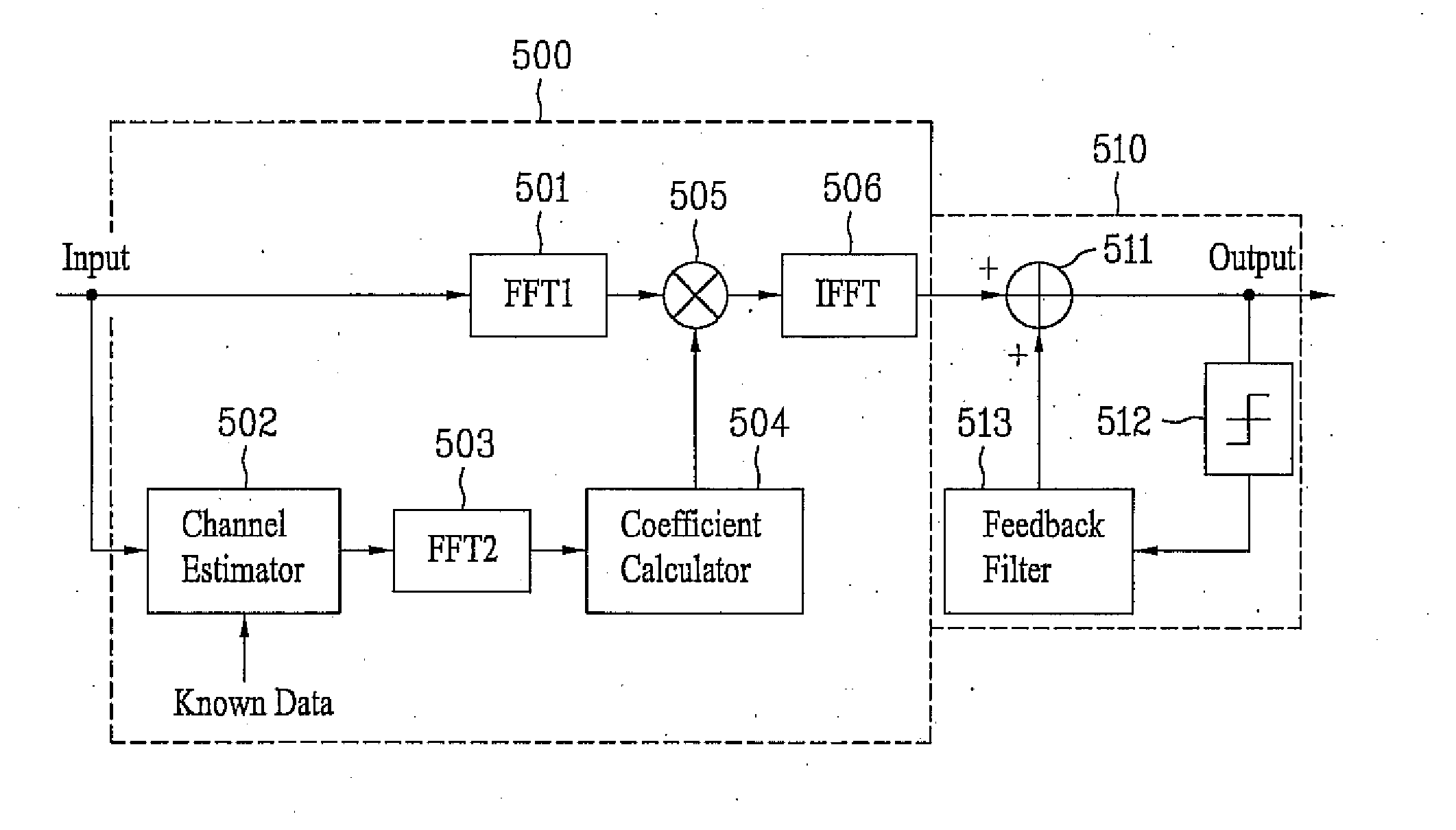
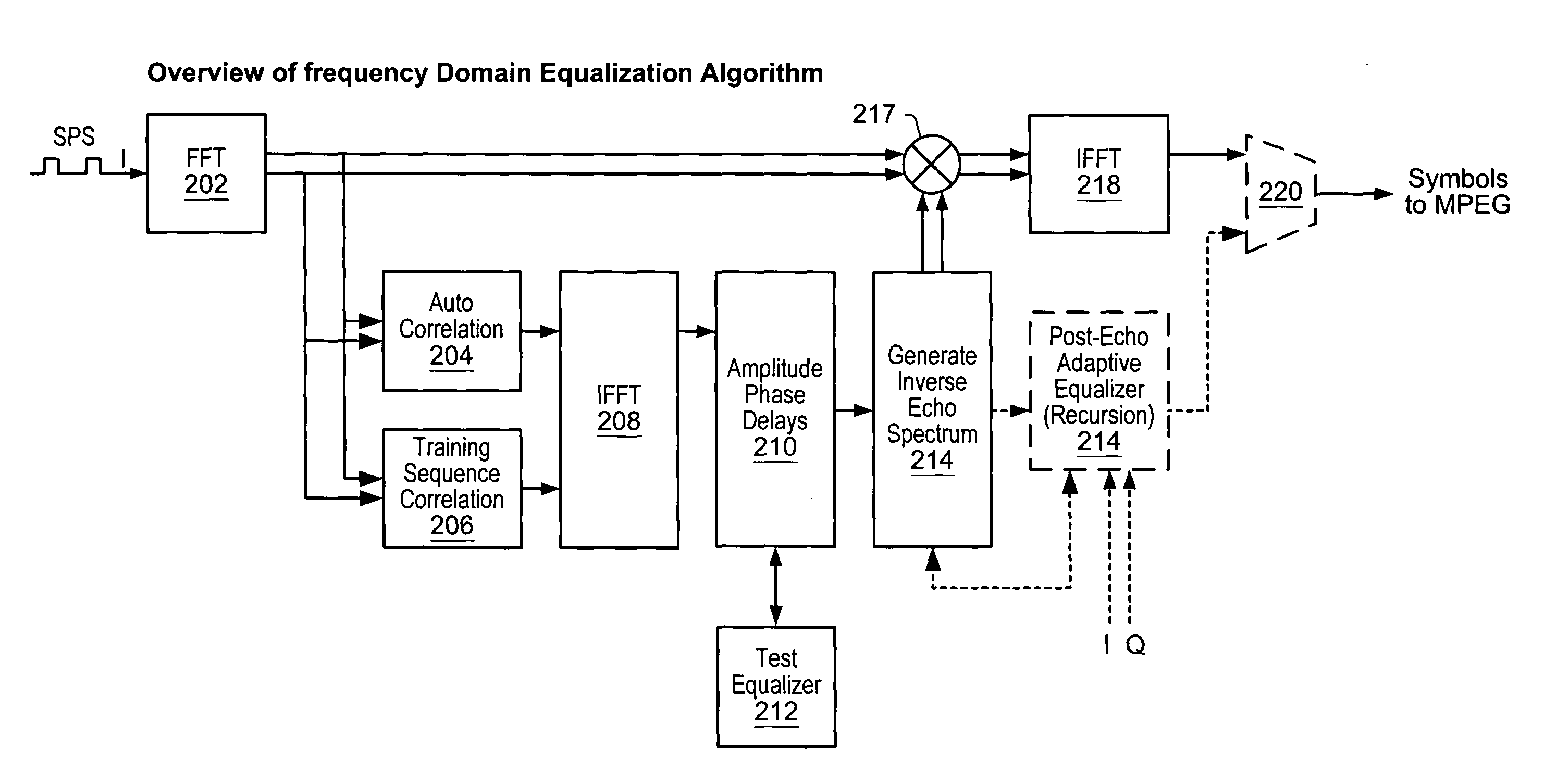
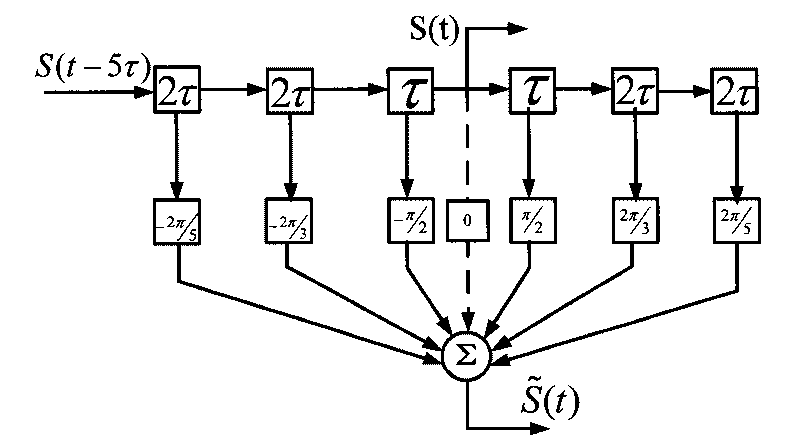
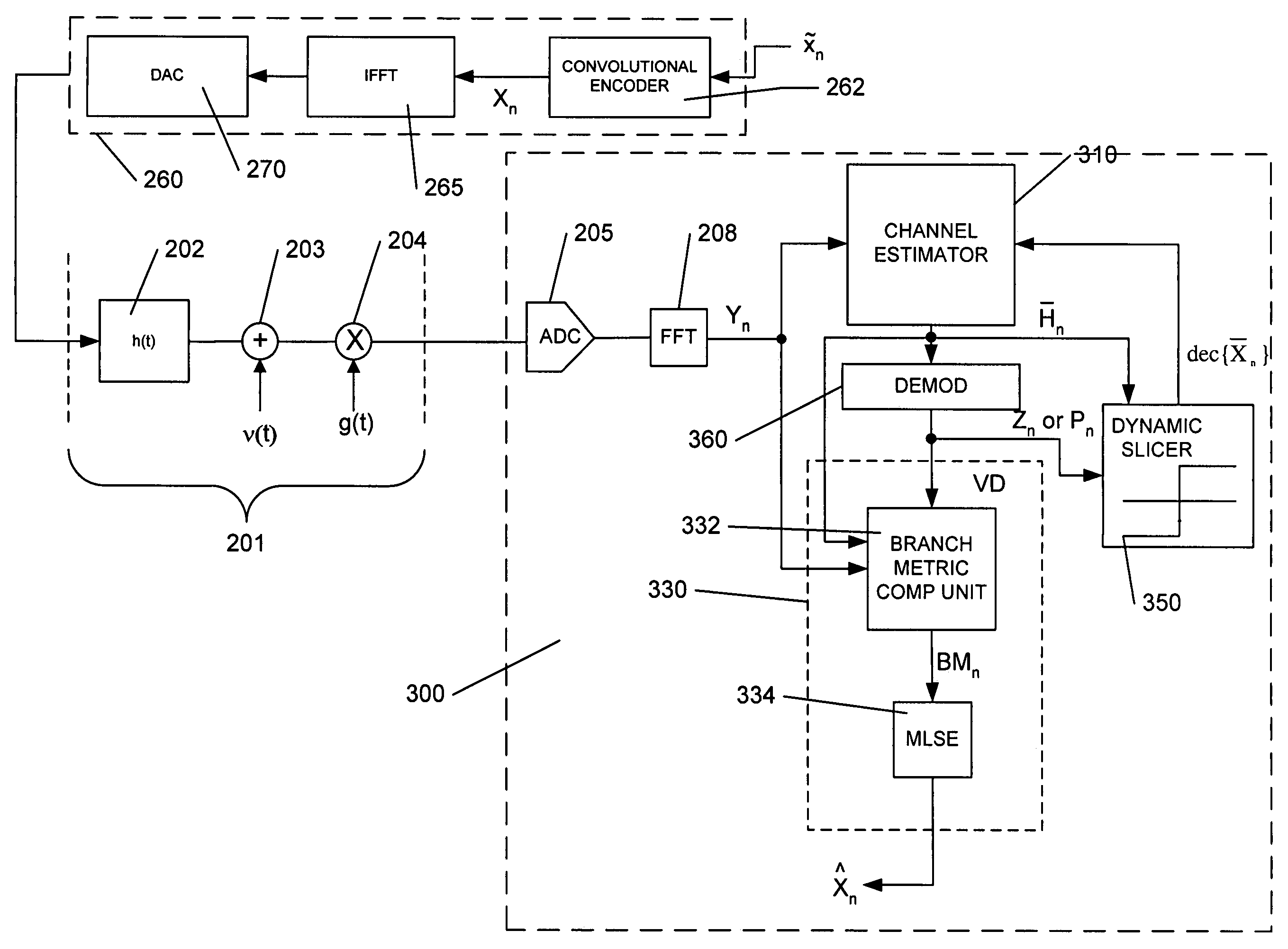
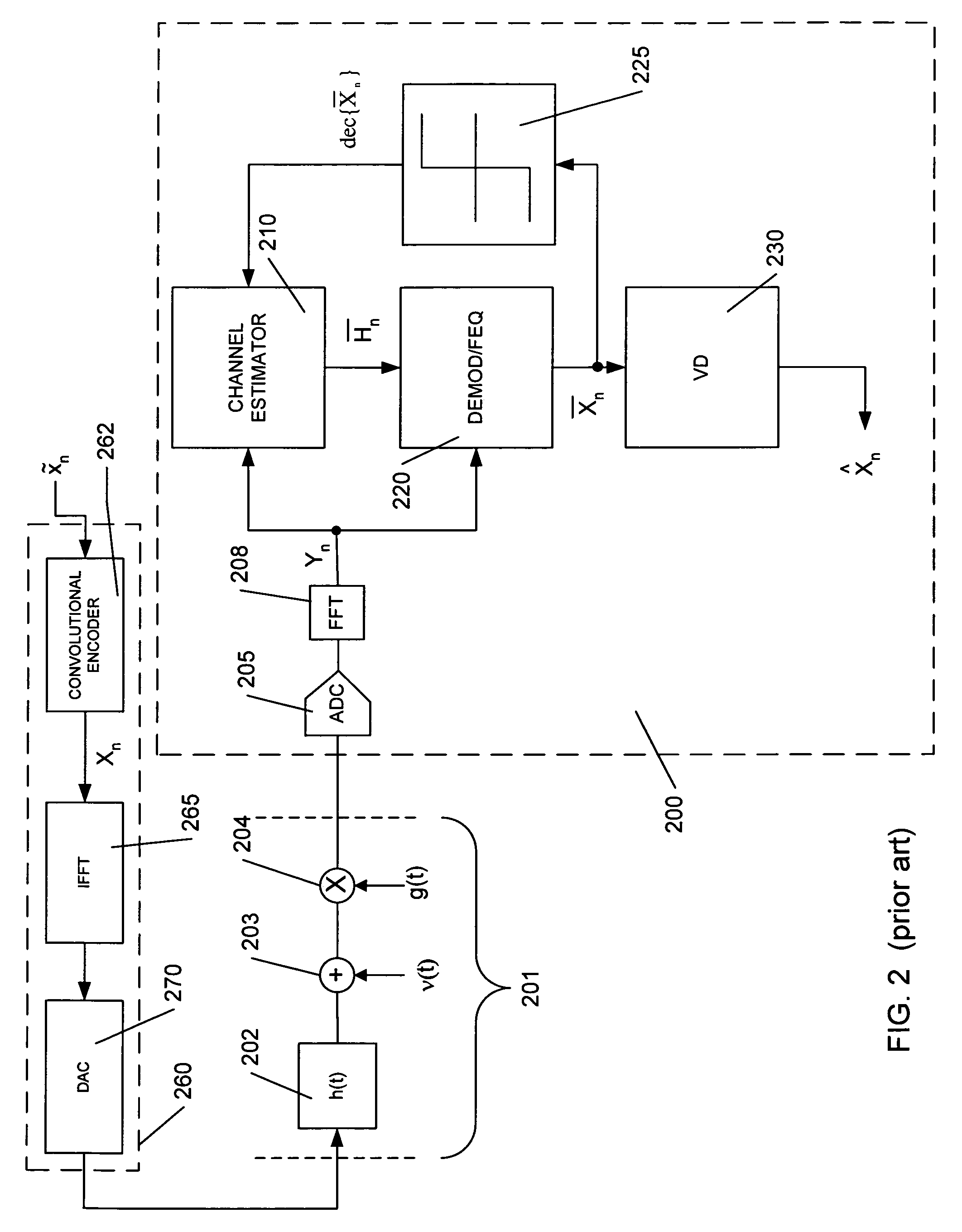
Frequency domain equalization of communication signals
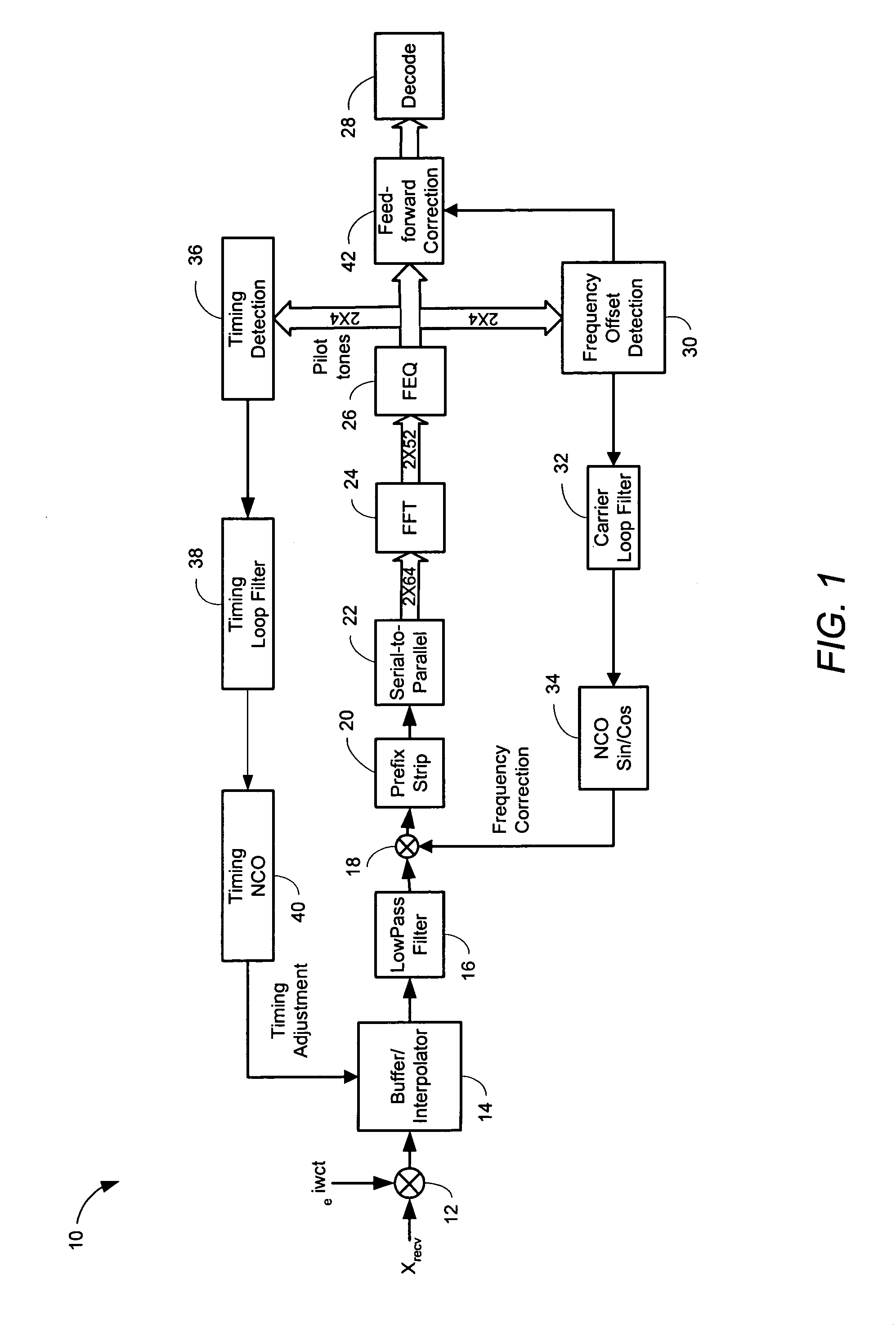
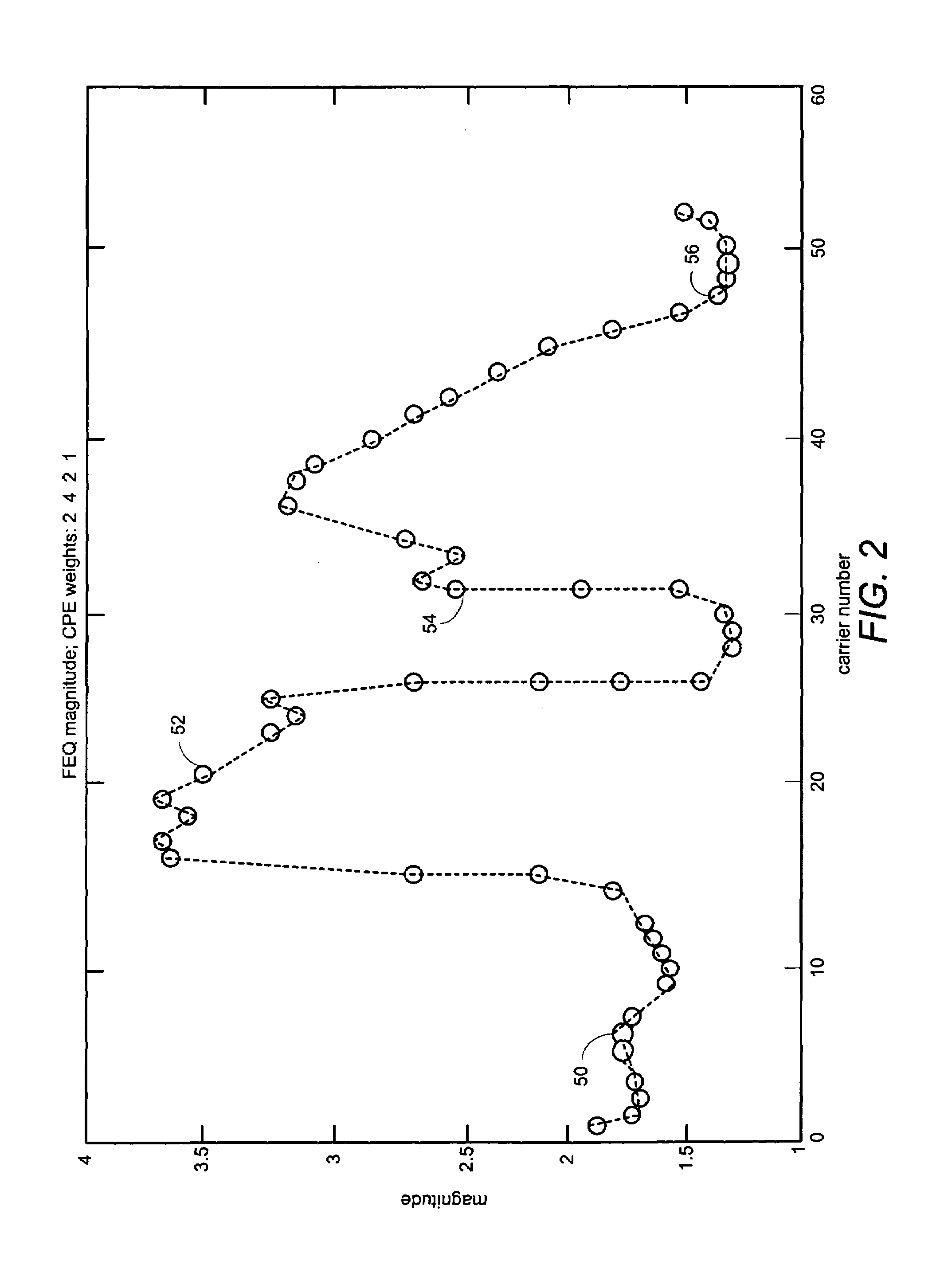
ActiveUS20050259767A1Great time separationFast convergenceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsTransmission control/equalisingFrequency spectrumFrequency domain equalization
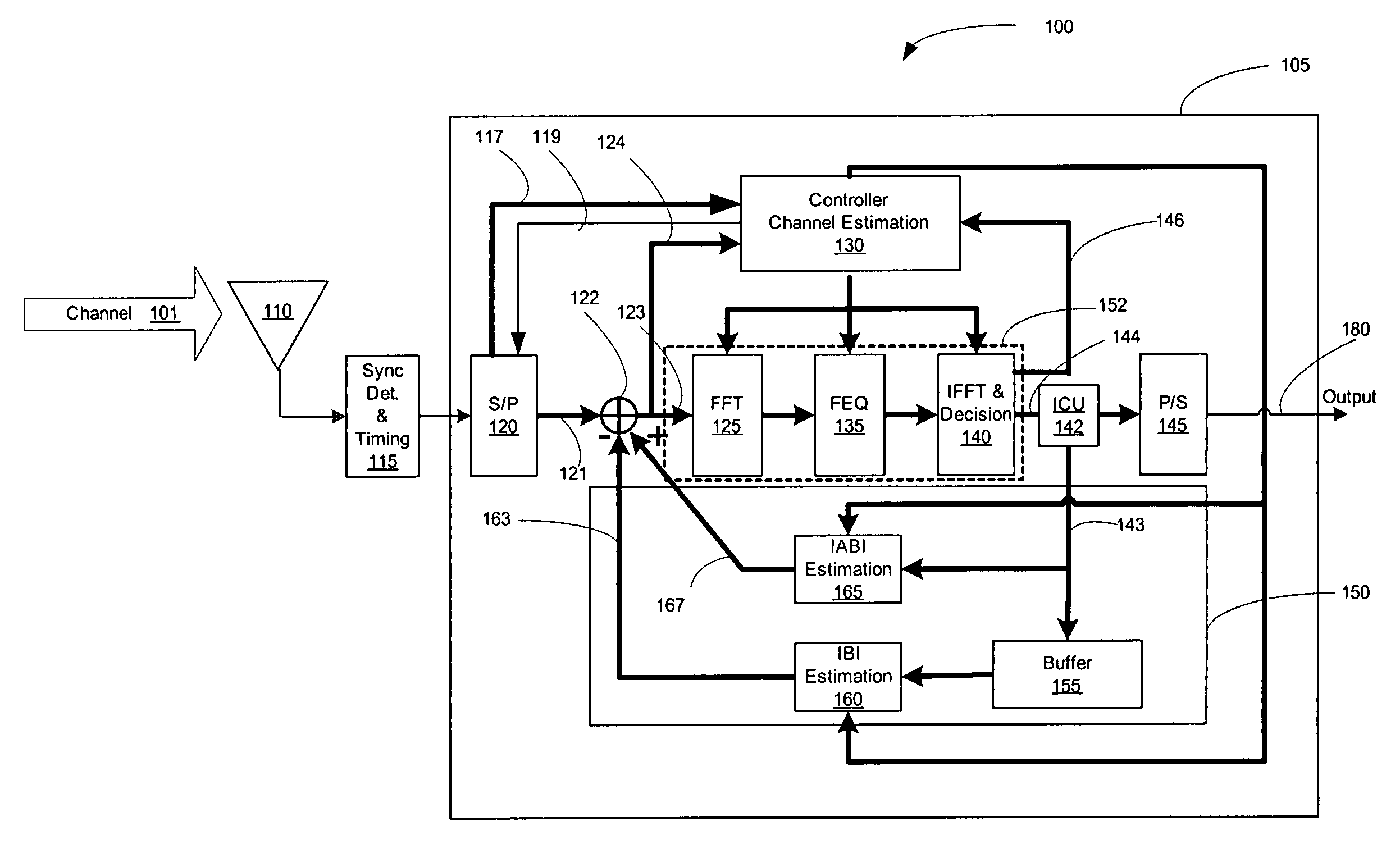
A system and method for estimating a channel spectrum. The method includes: (a) receiving an input signal from a channel, where the input signal includes one or more major echoes and zero or more minor echoes introduced by the channel; (b) identifying the one or more major echoes present in the input signal; (c) identifying the minor echoes from a filtered autocorrelation function of the input signal in response to a determination that there is only one major echo; (d) identifying the minor echoes from a filtered power spectrum of the input signal in response to a determination that there is more than one major echo; (e) computing a channel spectrum estimate from the major echoes and minor echoes; where the channel spectrum estimate is usable to remove at least a portion of the one or more major echoes and one or more minor echoes from the input signal.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
Method and device for the baseband process of the space-time/space -frequency/spatial diversity transmitter
ActiveUS20090303866A1Efficient spatial diversityReduce PAPRError preventionInter user/terminal allocationData setDiversity scheme
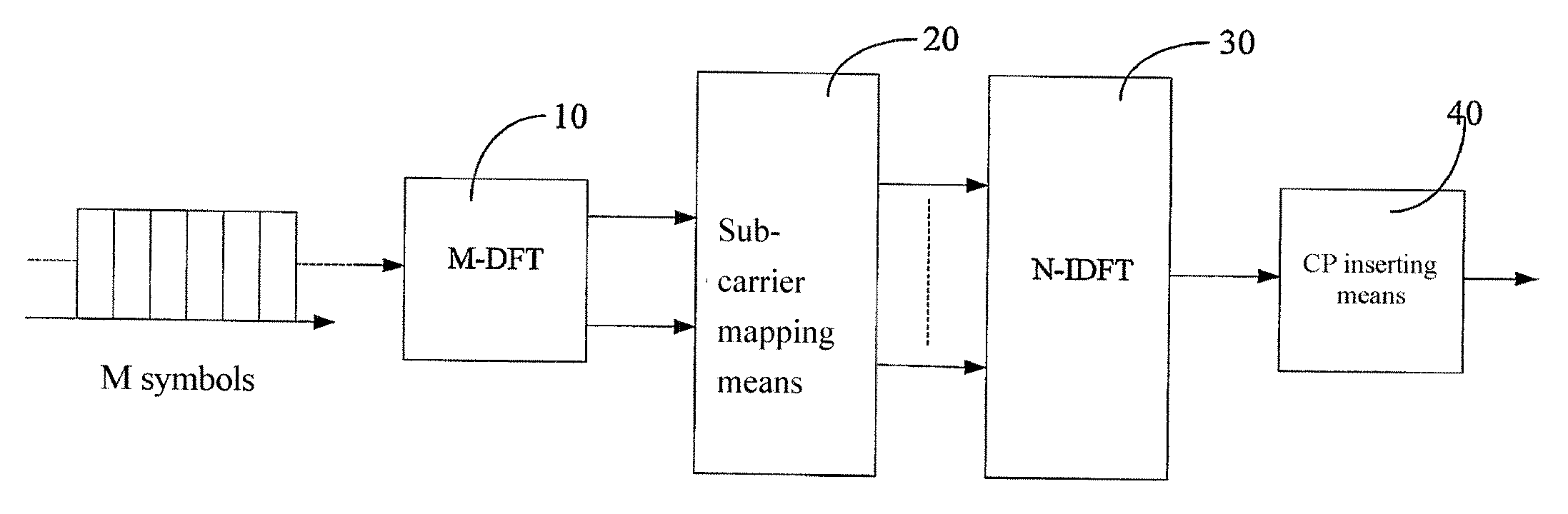
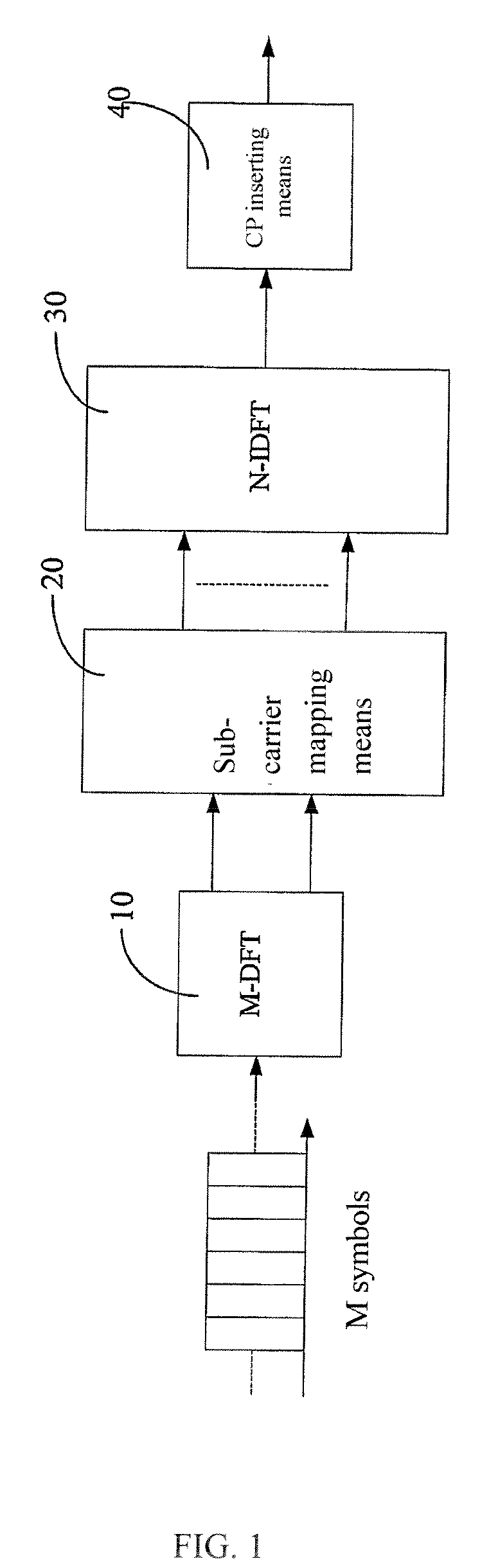
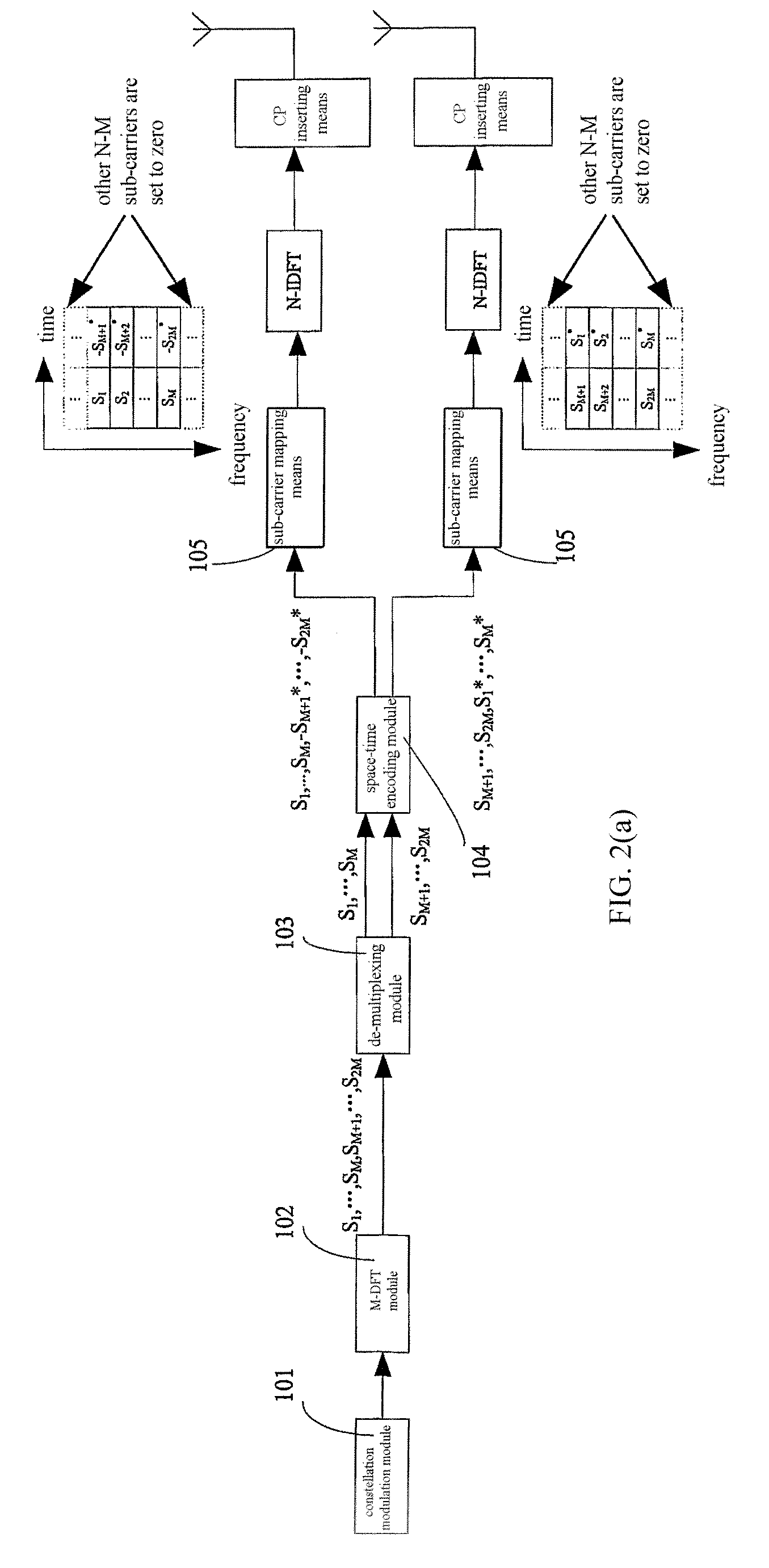
A method and device for the baseband process of space-time / space-frequency / spatial diversity transmitter in the SC-FDMA system, the device is characterized in that: 1) an encoding means is connected to the output end of the M-point DFT module; 2) a space-time encoding means, for encoding the corresponding symbol of at least two adjacent symbol sets, and outputting at least two data sets; each sub-carrier mapping means maps respectively each data set to the corresponding antenna, so that the mapped data satisfy the requirements: The symbols mapped on each antenna keep the same sequence as the M symbols outputted by the M-point DFT module; the mapped symbols keep the same sub-carrier interval; the M data of each mapped SC-FDMA symbol are the M outputted data of the DFT module, or the inverse of the M outputted data, or the complex conjugate of the M outputted data, or the inverse complex conjugate of the M outputted data. The present invention implements effective space diversity, reduces PAPR, and makes frequency domain equalization feasible.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) block transmission method based on time-frequency two-dimension training information
ActiveCN102158459AImprove performanceAvoid Iterative Interference Cancellation AlgorithmsMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDynamic channelFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an OFDM block transmission method based on time-frequency two-dimension training information, relating to the wireless transmission in digital communication. The method comprises the following steps of: A, the training information simultaneously existing in time domain training sequence and frequency domain grouping pilot frequency; B, estimating the multi-path time delay information of the channel by directly using the time domain training sequence with interference, and estimating the coefficient of each path through the frequency domain grouping pilot frequency estimating channel so as to finish the channel estimation of time-frequency joint; C, finishing the cycle performance reconfiguration of OFDM data block by the using of the result of channel estimation, and eliminating the sub-carrier interference under the dynamic channel, and then performing the frequency domain balance again. The method has very high frequency spectrum efficiency and also obtains better transmission performance under the dynamic channel.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
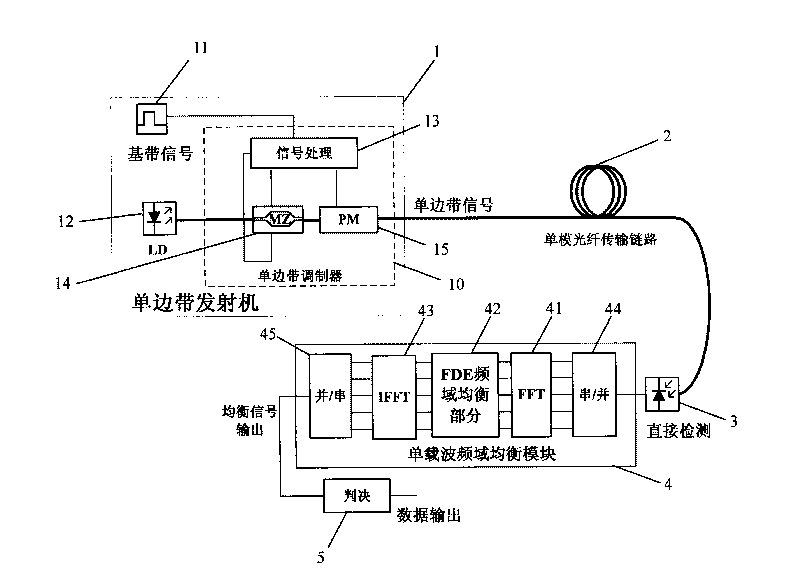
Single-sideband modulated single carrier frequency-domain equalization technology-based fiber communication system
InactiveCN101692628AImprove transmission qualityTransmission power is halvedDistortion/dispersion eliminationDigital signal processingTransport system
The invention belongs to the technical field of fiber communication and optical network transmission signal equalization treatment, and particularly discloses a single-sideband modulated single carrier frequency-domain equalization technology-based fiber communication system. In a transmission system of fiber communication, by using a DSP equal high-speed digital signal processing mode, single-sideband modulated electrical signals received by direct detection are transformed to a frequency domain from a time domain by adopting FFT transformation, an equalization module designed aiming at a transmission link is adopted for performing equalization compensation in the frequency domain, and finally the signals processed by the equalization module are transformed to the time domain from the frequency domain through IFFT to acquire the final equalization signal. The fiber communication system can improve the transmission quality of the signals, and has the signal equalization compensation capacity of the self-adaptive fiber transmission link.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method and system for transmission and frequency domain equalization for wideband CDMA system
The invention provides a method and system for transmission and frequency domain equalization for wideband CDMA communications by providing at least one spread sequence portion, and inserting a cyclic redundancy to the spread sequence to form a transmitted baseband sequence. The invention further provides a method and system for converting a plurality of receive samples from at least one spread sequence portion into a plurality of frequency domain samples, determining a plurality of frequency domain equalization weights for the frequency domain samples, and determining a time domain signal estimate based on the frequency domain equalization weights and frequency domain samples.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Divisionless baseband equalization in symbol modulated communications
ActiveUS7133473B1Reduce complexityEliminate operationError preventionCode conversionChannel state informationChannel impulse response
Joint equalization and decoding techniques to eliminate the division operations in the Frequency domain Equalizer (FEQ) of an Orthogonal Frequency Division Modulation (OFDM) receiver by incorporating the magnitude of the channel impulse response estimates into the decision metrics in the decoder. This includes methods for both hard-decision symbol-by-symbol detection and soft-decision decoding using the Viterbi algorithm. Further, Channel State Information (CSI) is incorporated to improve the performance of the receiver. The disclosure also introduces a computationally efficient bit-by-bit piecewise approximation technique incorporating CSI to implement decoder decision metrics. Finally, an efficient implementation technique for multiple receiver antennae using Maximum Ratio Combining (MRC) and Viterbi decoding with CSI is disclosed.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
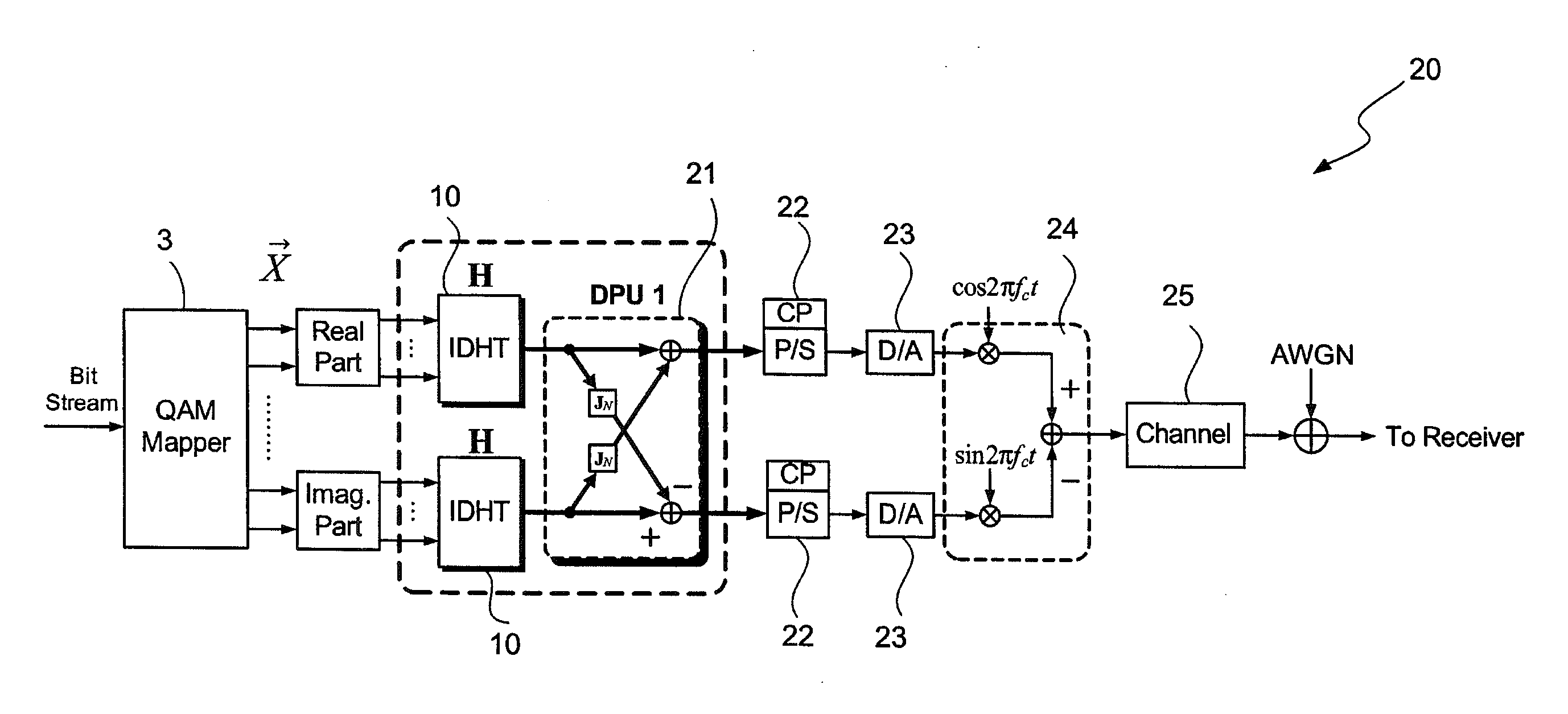
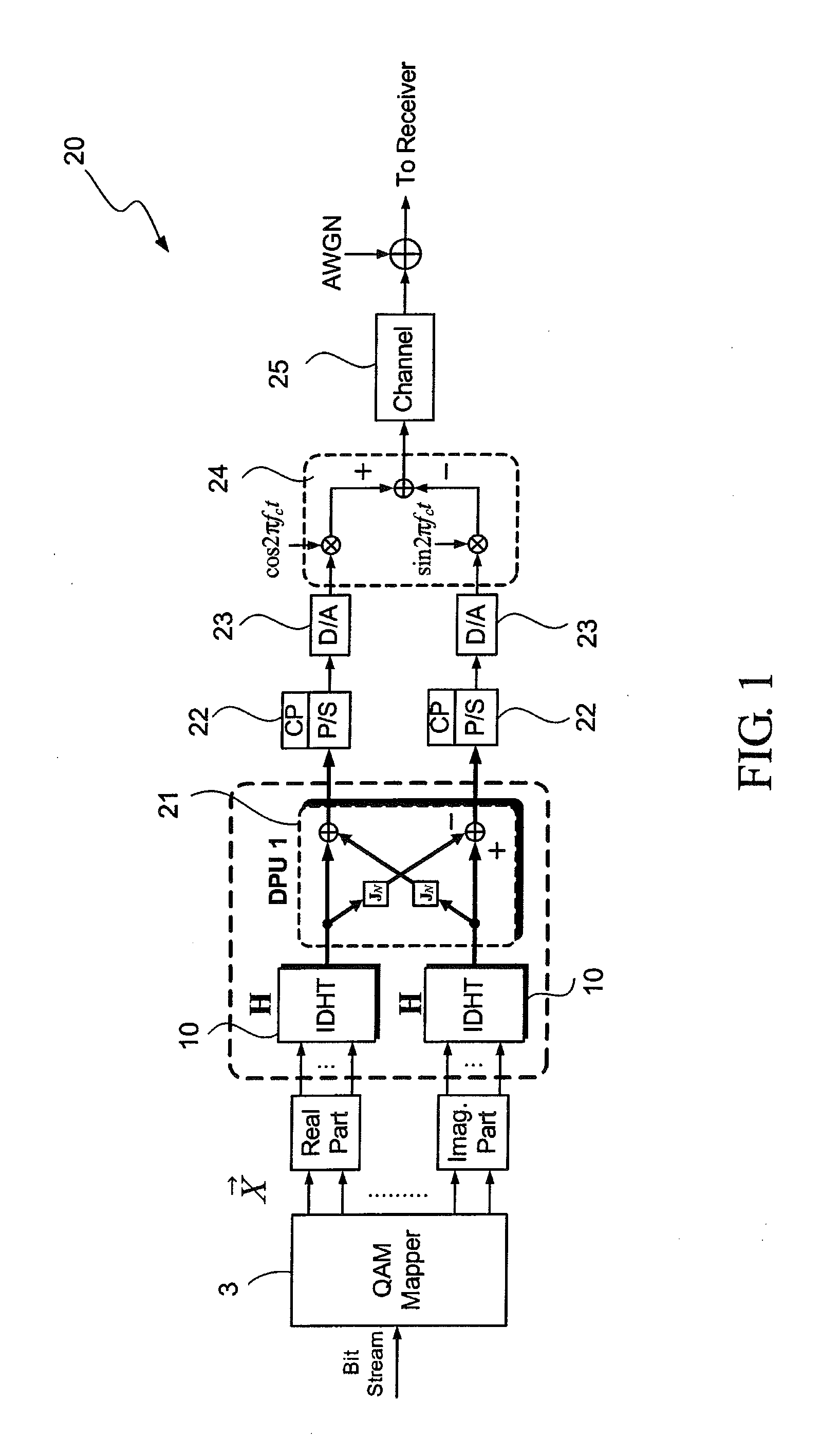
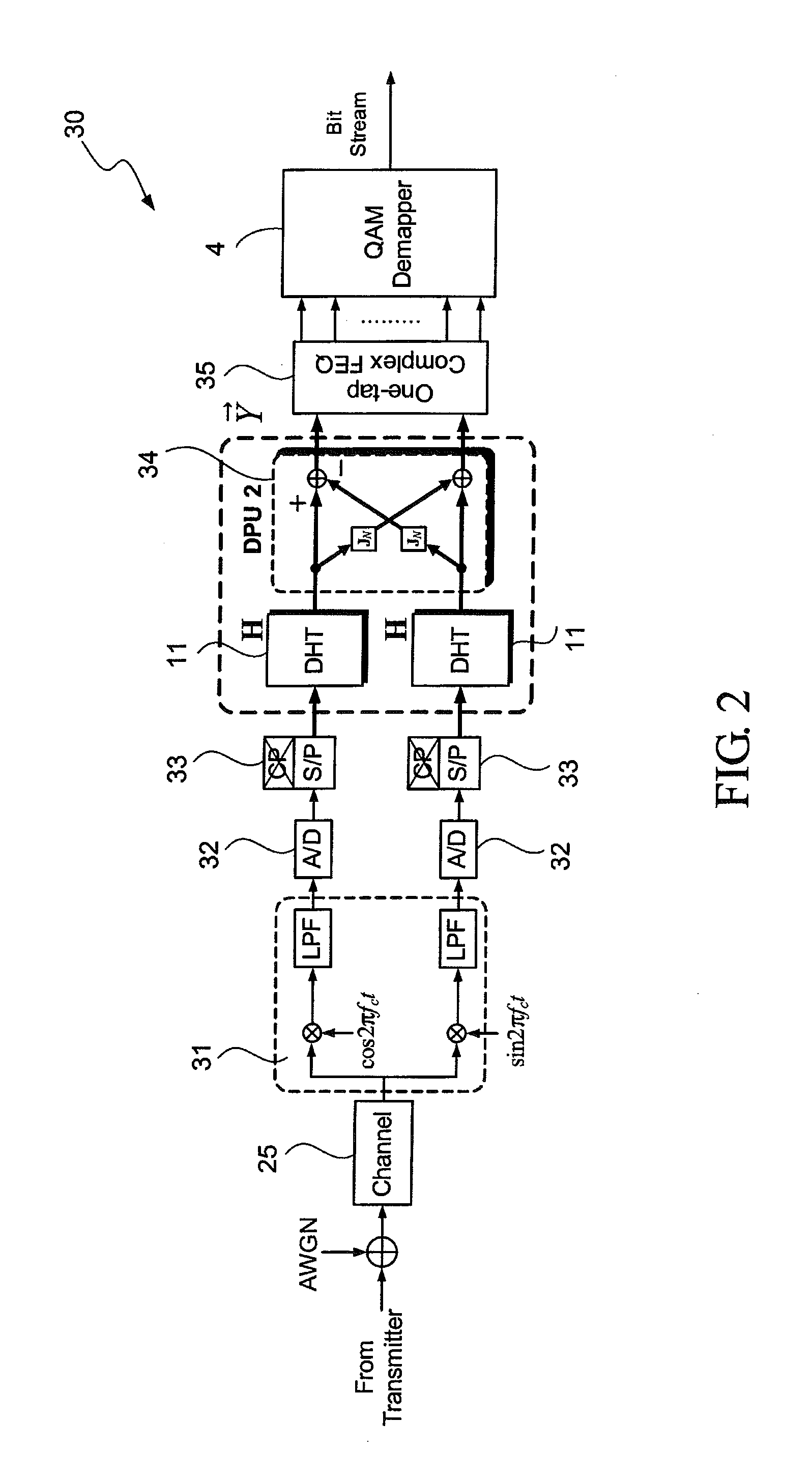
DHT-Based OFDM Transmitter and Receiver
InactiveUS20110249709A1Improve bandwidth efficiencyAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsMultiple carrier systemsOfdm transmitterDiscrete Hartley transform
A DHT-based OFDM transmitter and receiver use discrete Hartley transform to implement multicarrier transmission. A transmission terminal (or a receiving terminal) of a transmitter and receiver comprises two IDHT (or DHT) processors and a diagonal processing device. The two IDHT processors make the DHT-OFDM system transmit the 2D modulation signal to increase the bandwidth efficiency. The diagonal processing device is used to diagonalize the circulant channel matrix into discrete memoryless subchannels, and thus only one-tap frequency domain equalizer can compensate the channel effects. Besides, the proposed DHT-OFDM transmitter and receiver are also compatible with a conventional DFT-OFDM system, and they can flexibly works with the conventional DFT-OFDM transmitter and receiver.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Time- and frequency-domain unified single carrier modulation signal transmission method
InactiveCN101986631AAccurate estimateReduce complexityModulated-carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksCarrier signalLow complexity
The invention relates to a time- and frequency-domain unified single carrier modulation (TFU-SCM) signal transmission method, and belongs to the technical field of digital information transmission. The method comprises that: information generated by a sending end is subjected to source coding, channel coding and constellation mapping in turn to form mapped information; the mapped information is subjected to time- and frequency-domain unified single carrier modulation FU-SCM modulation, and a plurality of modulated symbols form a frame signal to be sent; the received frame signal is split into a TFU-SCM modulation symbols in a corresponding composition mode; and the modulation symbols are subjected to TFU-SCM demodulation to form serial data, and the serial data is subjected to constellation inverse mapping, channel decoding and source decoding in turn to form the original information. The method maintains the advantage of low complexity of the sending end of the single carrier frequency domain equalization (SC-FDE) technology, the number of UW in the pilot frequency can be flexibly selected according to requirement on system performance, operation such as synchronization, channel estimation, balance and the like can be convenient to carry out at a receiving end by operating the pilot frequency in the frequency domain, the processing efficiency of the system is improved, and the method is more suitable for a broadband wireless mobile communication system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Time division duplex transmission method for broadband wireless communication system
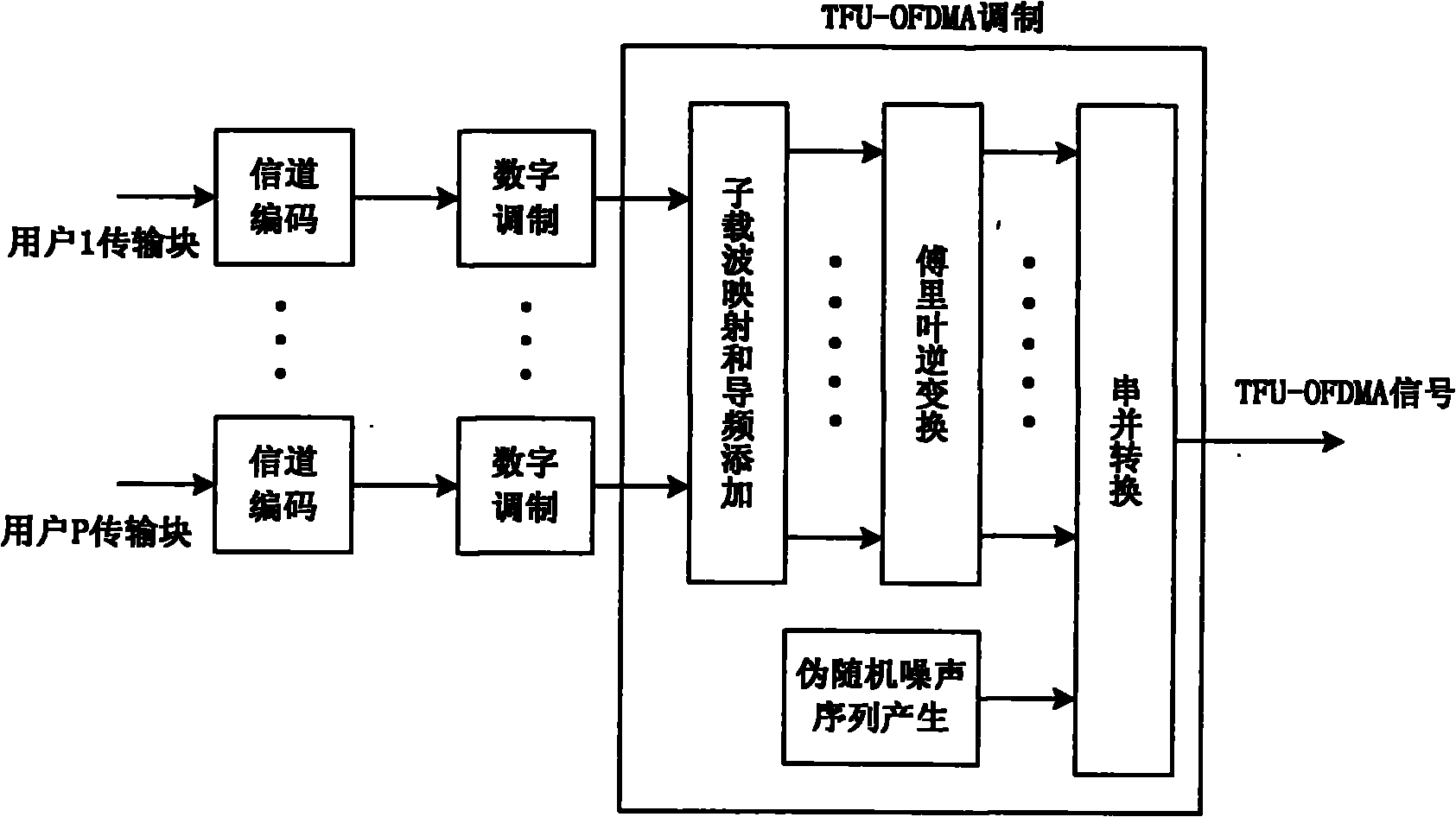
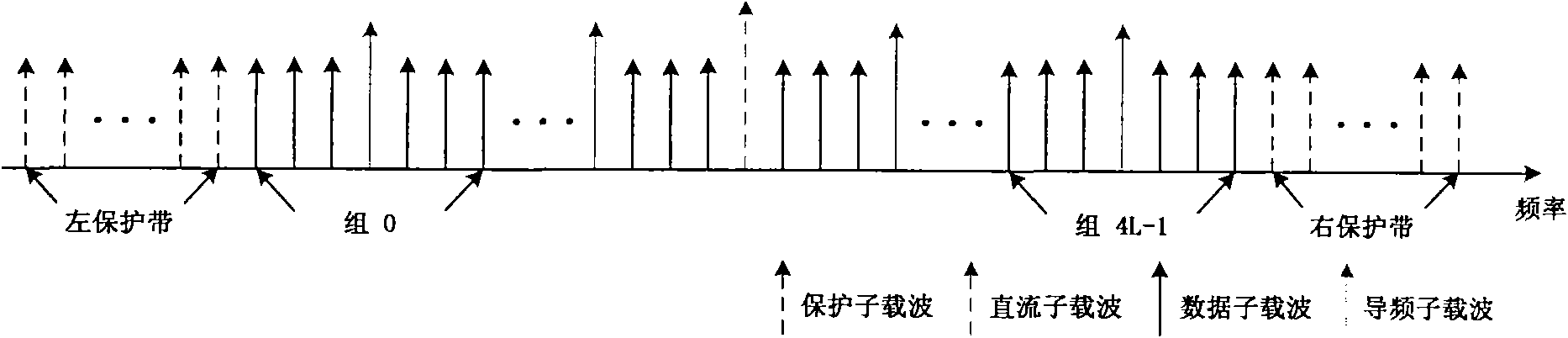
InactiveCN102035786AFlexible allocationAddress multiple accessMulti-frequency code systemsDuplex signal operationCarrier signalUser equipment
The invention relates to a time division duplex transmission method for a broadband wireless communication system, belonging to the technical field of digital information transmission. The method comprises the following steps: using a time / frequency-domain unified orthogonal frequency division multiple access (TFU-OFDMA) technology to carry out downlink multiple access so as to obtain downlink signals at a transmitting end of a base station; using a time / frequency-domain unified single carrier multiple access (TFU-SCMA) technology to carry out uplink multiple access so as to obtain uplink signals at a transmitting end of user equipment; and using a time division duplex frame structure to carry out duplex transmission on the downlink signals and the uplink signals. The TFU-OFDMA technology provided by the invention solves the multiple access problems in the TFU-OFDM (Time / Frequency-domain Unified Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) modulation process, can flexibly allocate wireless resources and can effectively overcome deep fade, narrow-band interference and the like. The TFU-SCMA technology provided by the invention solves the multiple access problems in the improved SC-FDE (Single Carrier Frequency Domain Equalization) modulation process, reserves the advantages of low complexity of the transmitting end in the SC-FDE technology, low peak-to-average power ratio and the like, and enables the receiving end to be subject to synchronization and channel estimation better.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com