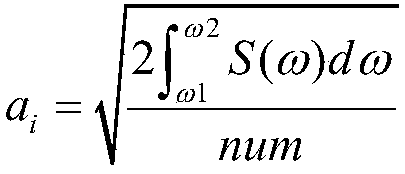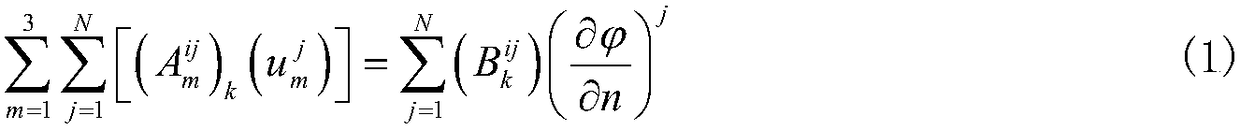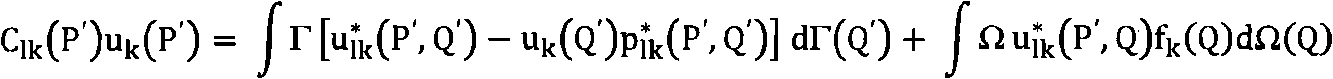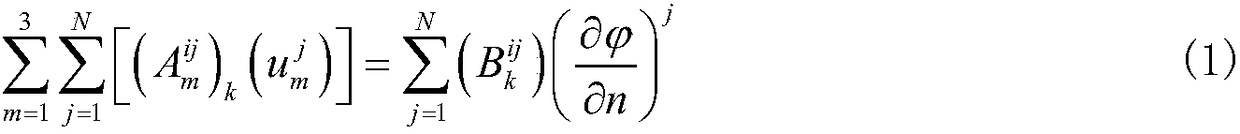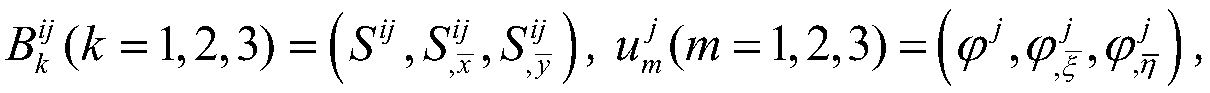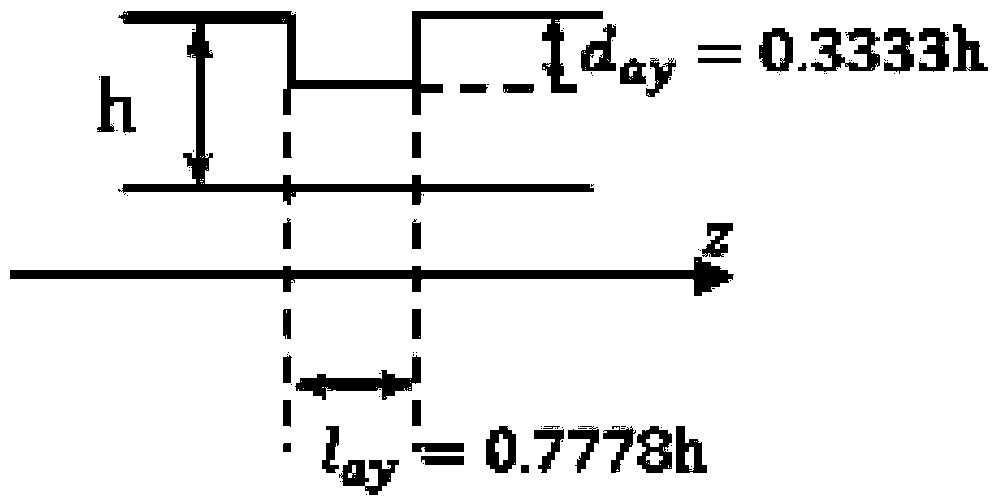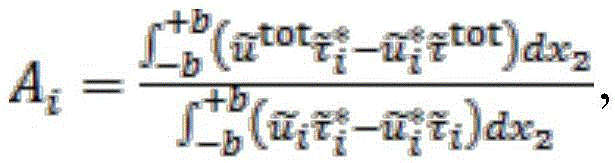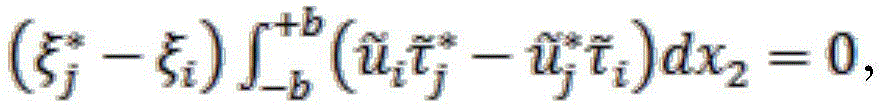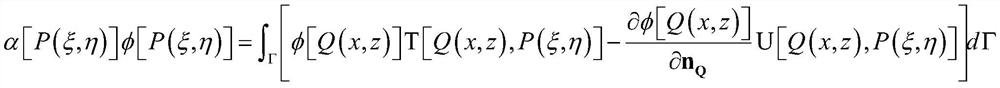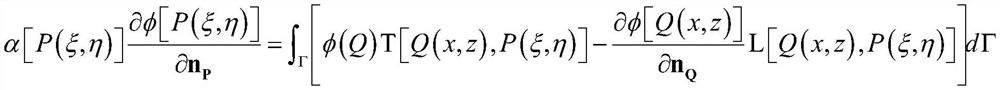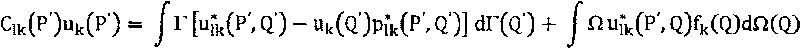Patents
Literature
46 results about "Boundary integral equations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
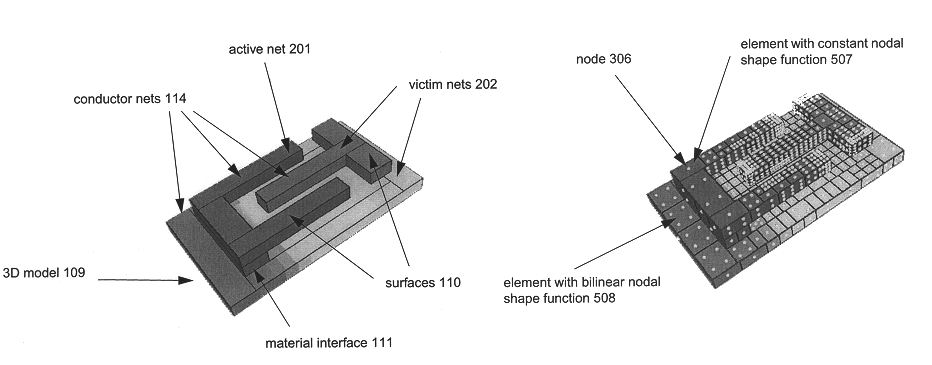
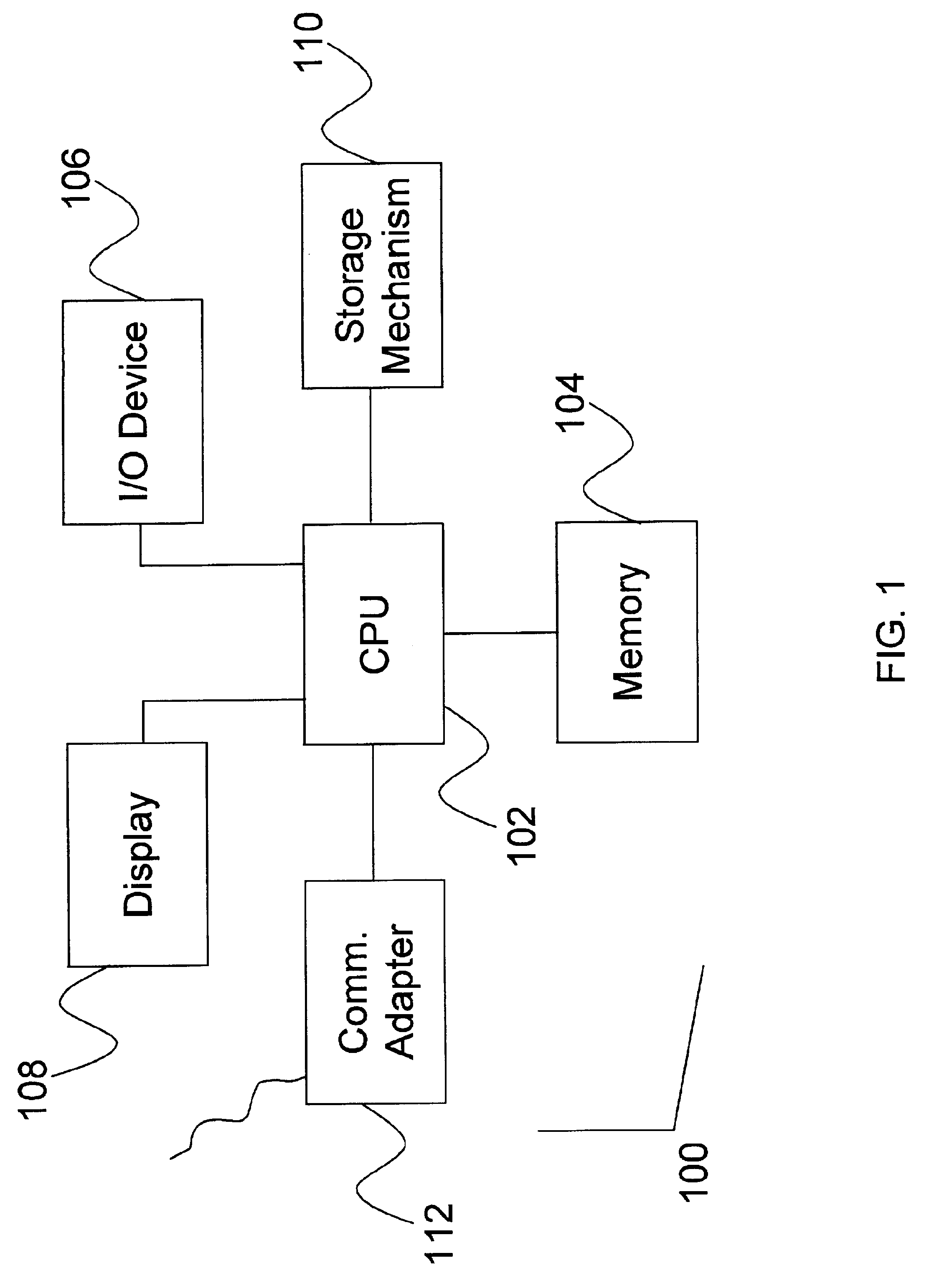
Method and apparatus for three dimensional interconnect analysis
InactiveUS6330704B1Design optimisation/simulationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectrical resistance and conductanceParasitic capacitance
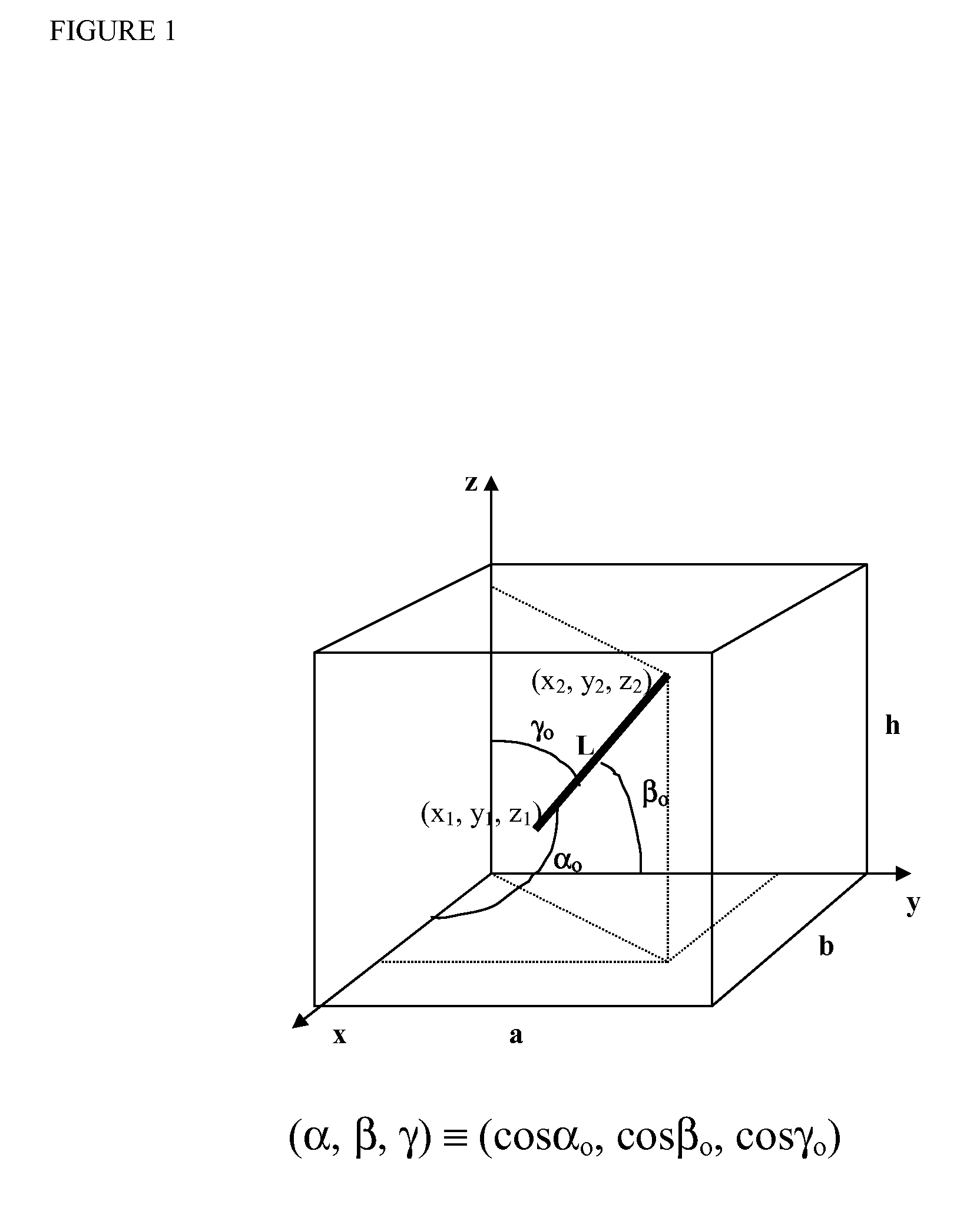
A method for calculating the parasitic capacitance and resistance in a semiconductor device is disclosed. According to the preferred embodiment, a layout file containing the shapes of semiconductor interconnects and a technology file describing the fabrication steps are used to generate a 3D model of the structures. The surfaces of the model are discretized and a double boundary integral equation is solved to compute the field allowing various interconnect parameters to be computed, including resistance, self-capacitance, cross-capacitance, and current density. Further, the preferred embodiment discloses how numerical analysis can be efficiently performed on typical large interconnect and substrate structures.
Owner:SIMPLEX SOLUTIONS INC
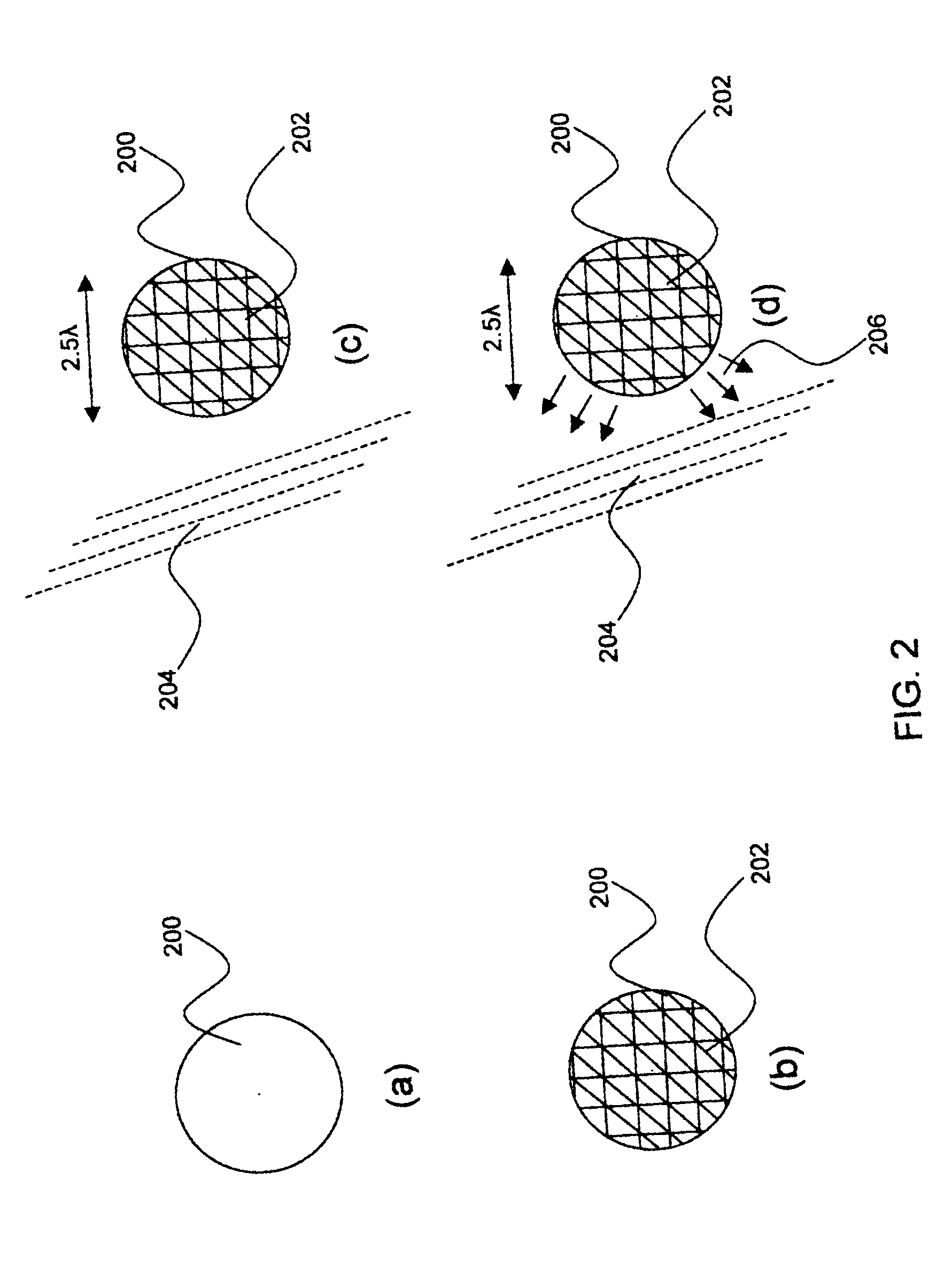
Method for obtaining radar cross section (RCS) of homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object
InactiveCN102508220AUniform Scattering Cross SectionScattered field stabilizationWave based measurement systemsMagnetic sourceRao wilton glisson
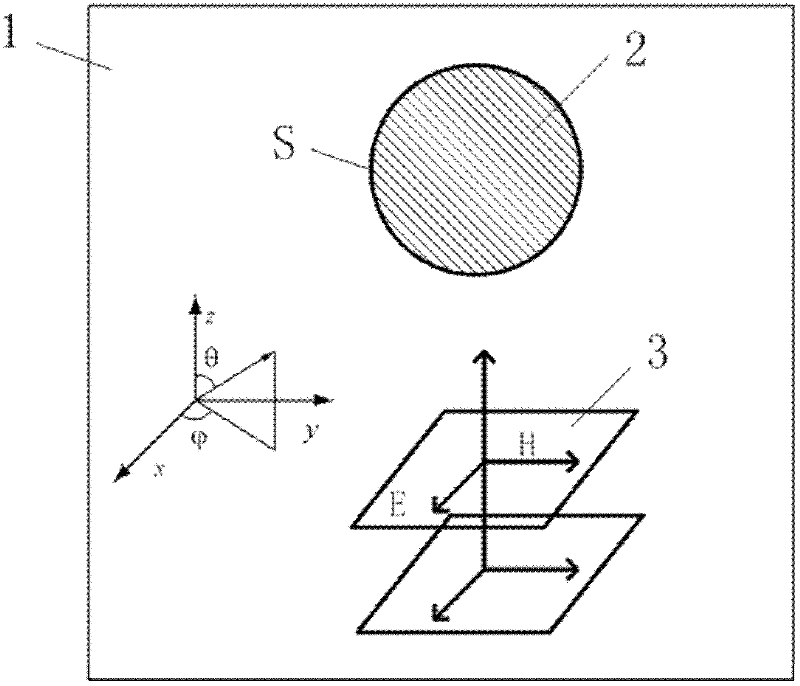
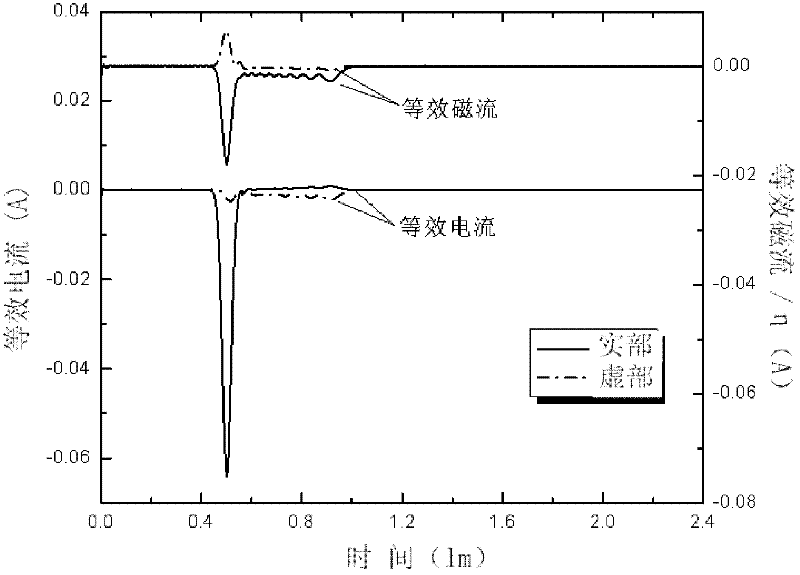
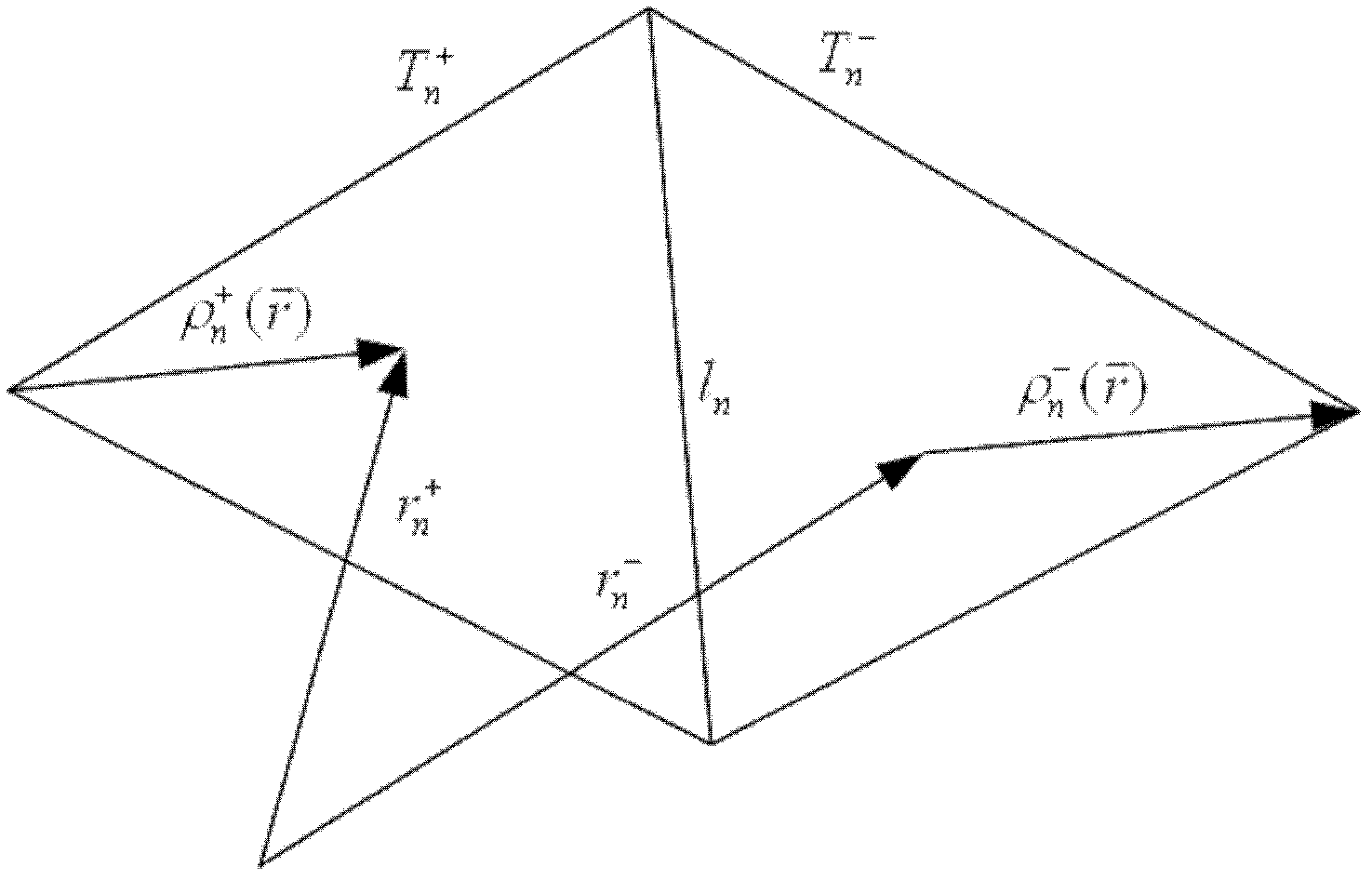
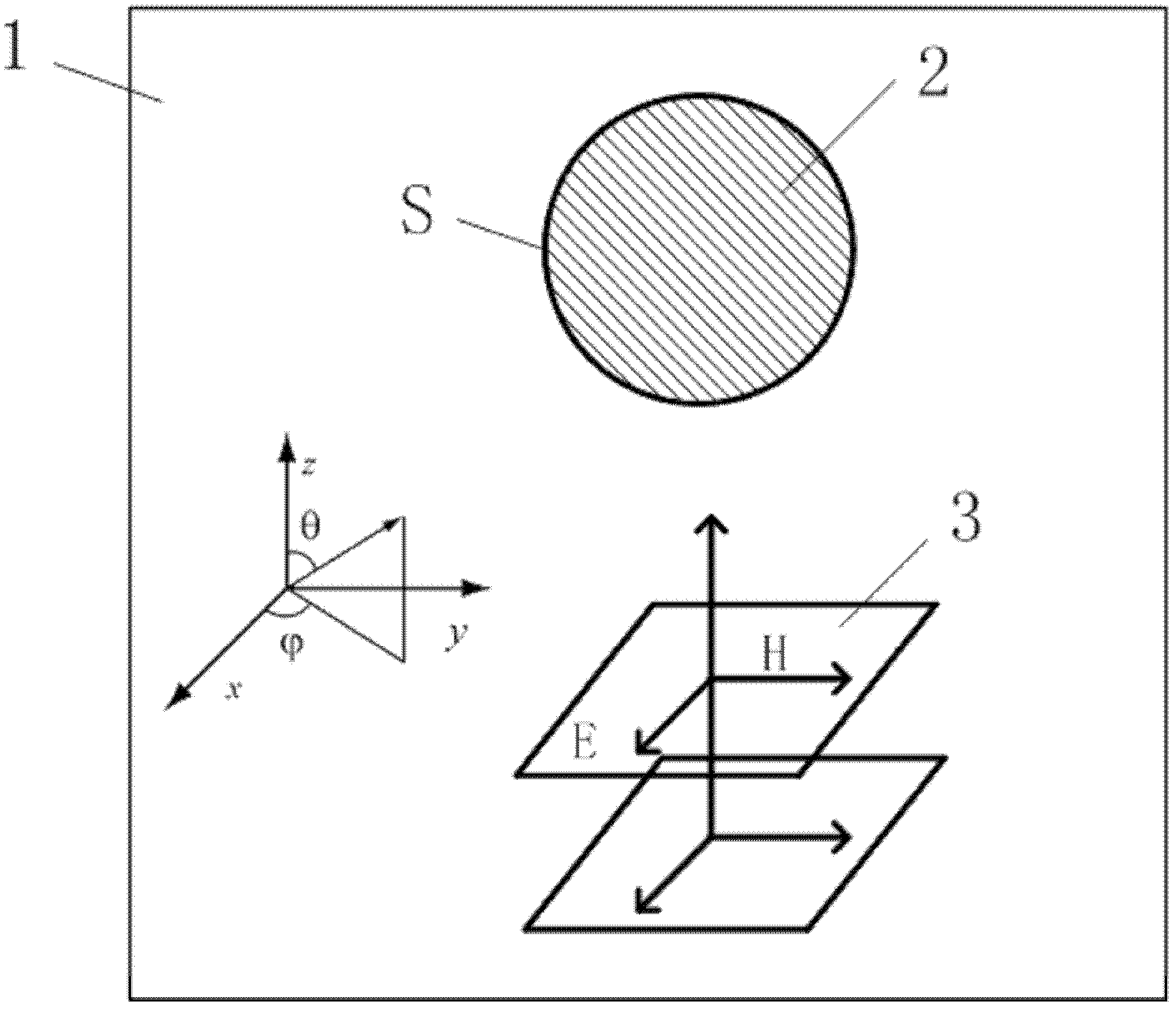
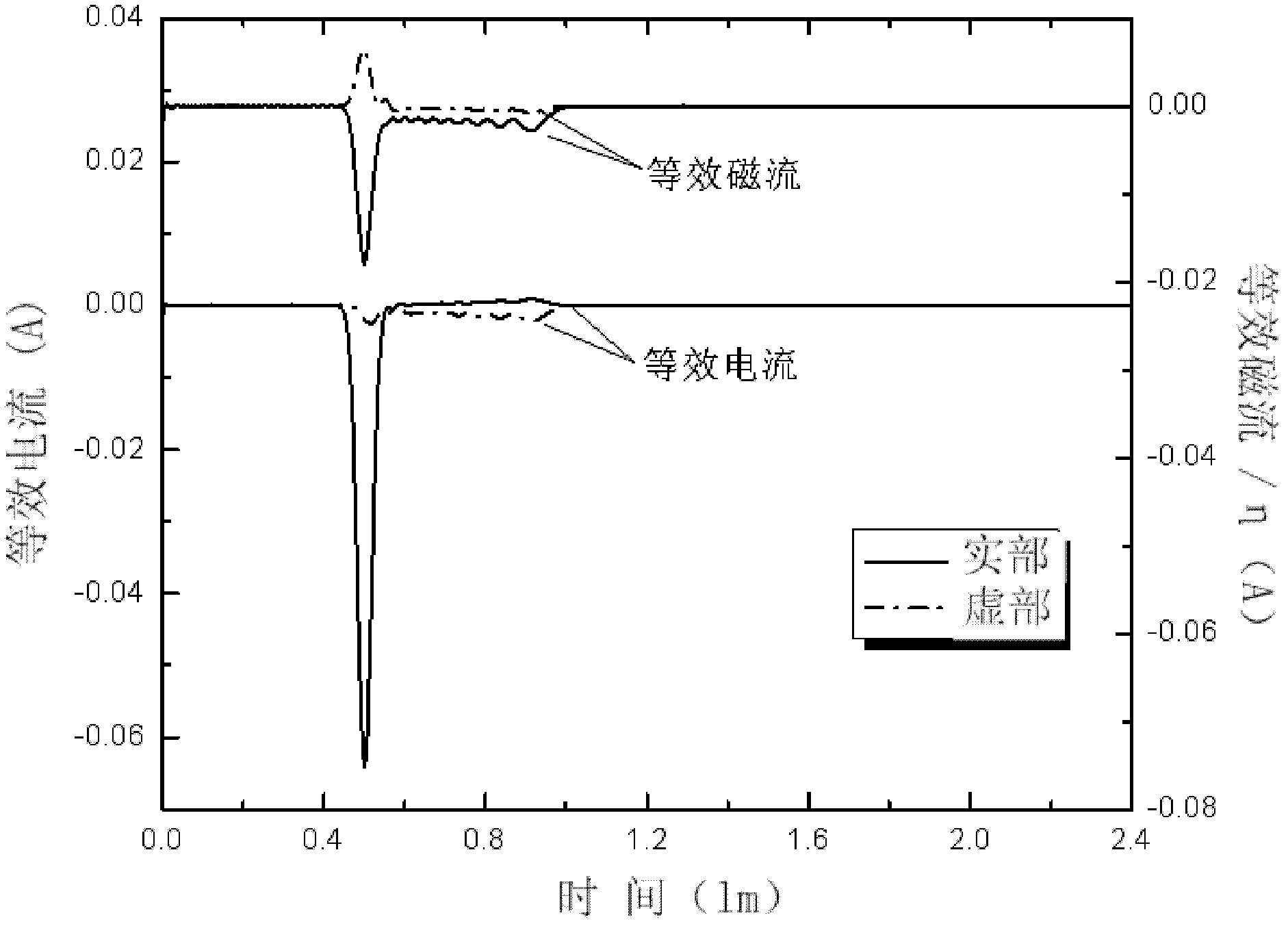
The invention relates to the field of electromagnetic wave and radar monitoring and provides a method for obtaining radar cross section (RCS) of a homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object. The method comprises the following steps of: building a geometrical model of the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object and dividing the surface of the model into a plurality of triangular patches in seamless connection; introducing a planar power source vector function and a planar magnetic source vector function; applying a field decomposition method in the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object; obtaining a boundary integral equation on the surface of a scatterer according to the boundary conditions; applying a moment method to carry out numerical solution on the boundary integral equation, including space test and time test; adopting RWG (Rao-Wilton-Glisson) basis functions as the spatial basis function and test function and adopting Laguerre functions with amplitude factors as the temporal basis function and test function; and obtaining electromagnetic scattering of an observation point according to the equivalence principle and then applying Fourier transform to obtain the RCS. The method has the following advantages that: the obtained scattered field of the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object is stable; and the RCS with wide frequency range can be obtained.
Owner:郑州微纳科技有限公司
Method and system for representing wells in modeling a physical fluid reservoir
InactiveUS20100286917A1Accurate modelingUnprecedented level of accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid removalReservoir modelingFeedback control
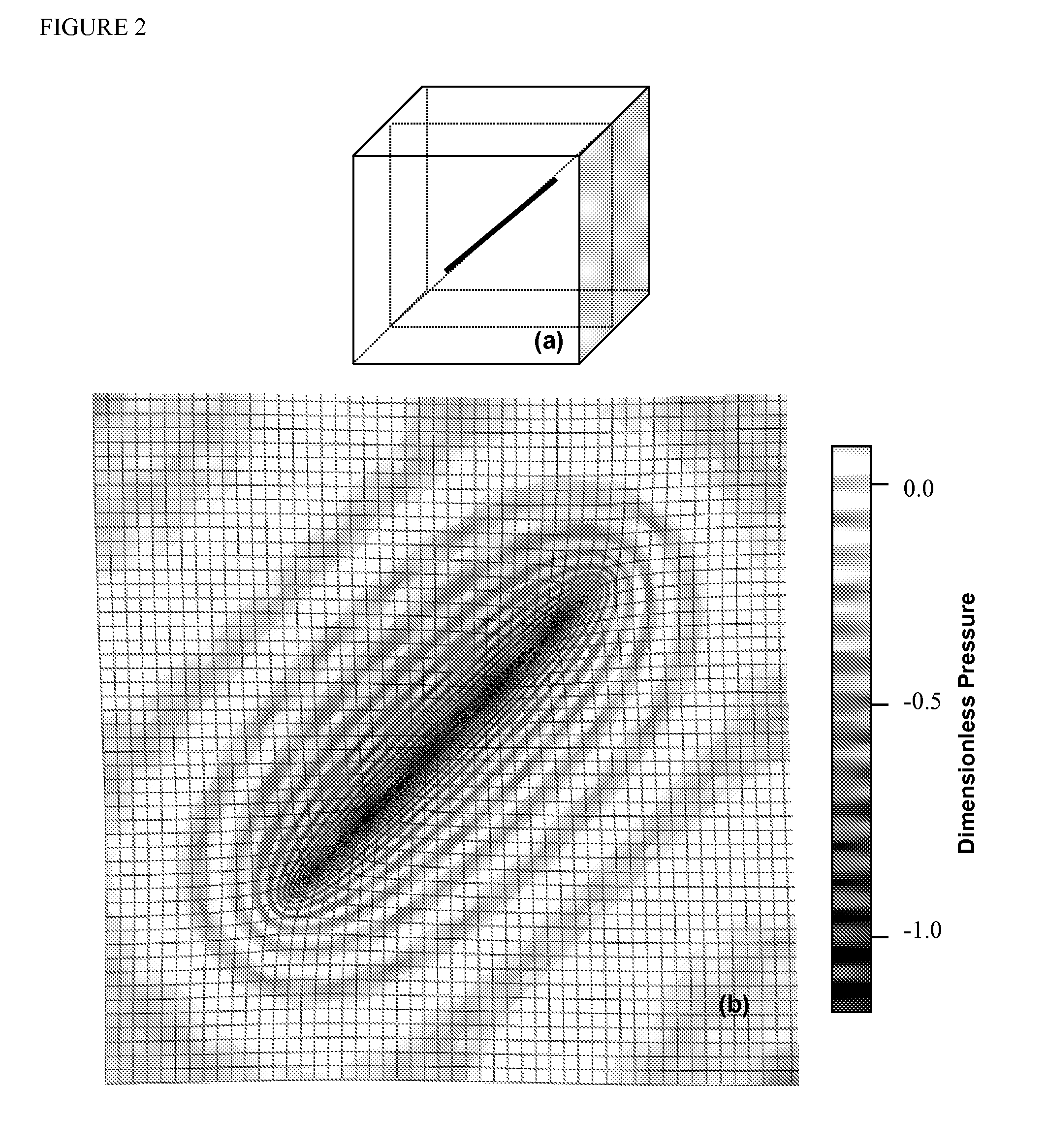
The disclosure is directed to a method of representing fluid flow response to imposed conditions in a physical fluid reservoir through wells. The invention utilizes techniques and formulas of unprecedented accuracy and speed for computations for a fundamental element in analysis of fluid movement through subterranean reservoirs—the calculation of Green's and Neumann functions in finite three-dimensional space. The method includes modeling of pressure and / or flow rate observables at wells in said reservoir using an easily computable, closed-form Green's or Neumann function for a linear well segment in arbitrary orientation within a three dimensional cell of spatially invariant but anisotropic permeability. The method further includes the modeling of fluid flow in the physical fluid reservoir with an assemblage of linear well segments operating in unison with uniform flux density to represent arbitrary well trajectory. The method further includes modeling reservoir flow through one or more linear well segments of non-uniform flux related by a constitutive expression linking pressure distribution and flow rate within the well. The method further includes generalization through integration of easily computable Green's or Neumann functions to represent fractures or fractured wells in modeling fluid flow in a physical reservoir. The system includes modeling fluid flow through a mesh representation of the physical fluid reservoir containing one or more wells represented by easily computable Green's or Neumann functions. The system further includes modeling of flow in the physical reservoir via a numerical method in which the values of pressure and flux assigned to the mesh are related to observables at the well using aforementioned easily computable Green's or Neumann functions. The system further includes the coupling of well and mesh values within the numerical solution method for well observation or feedback control. The system still further includes the localization of the well model to the properties assigned to only those mesh elements penetrated by the well using boundary integral equation methods. The invention also incorporates the addition of transients in fluid flow towards a steady or pseudo-steady state, and use thereof, in the above constructs.
Owner:HAZLETT RANDY DOYLE +1
A three-dimensional numerical simulation method for ship large-scale rolling motion
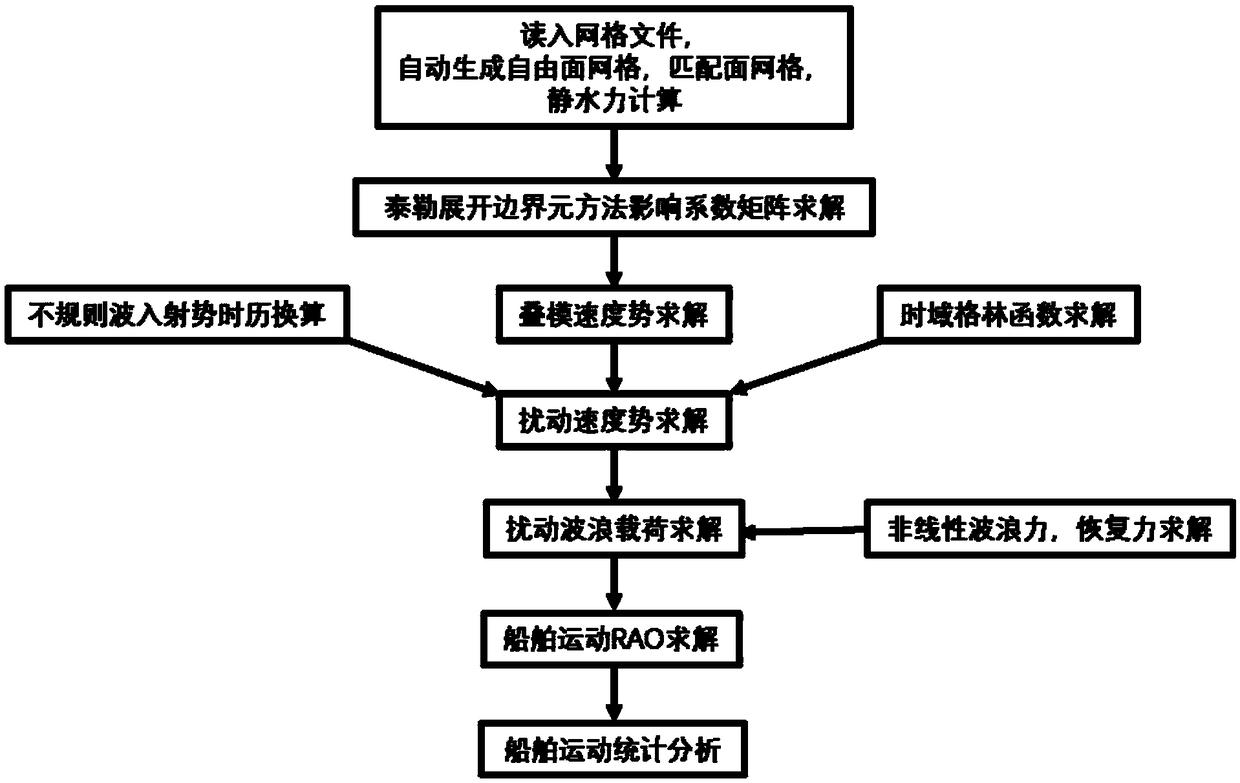
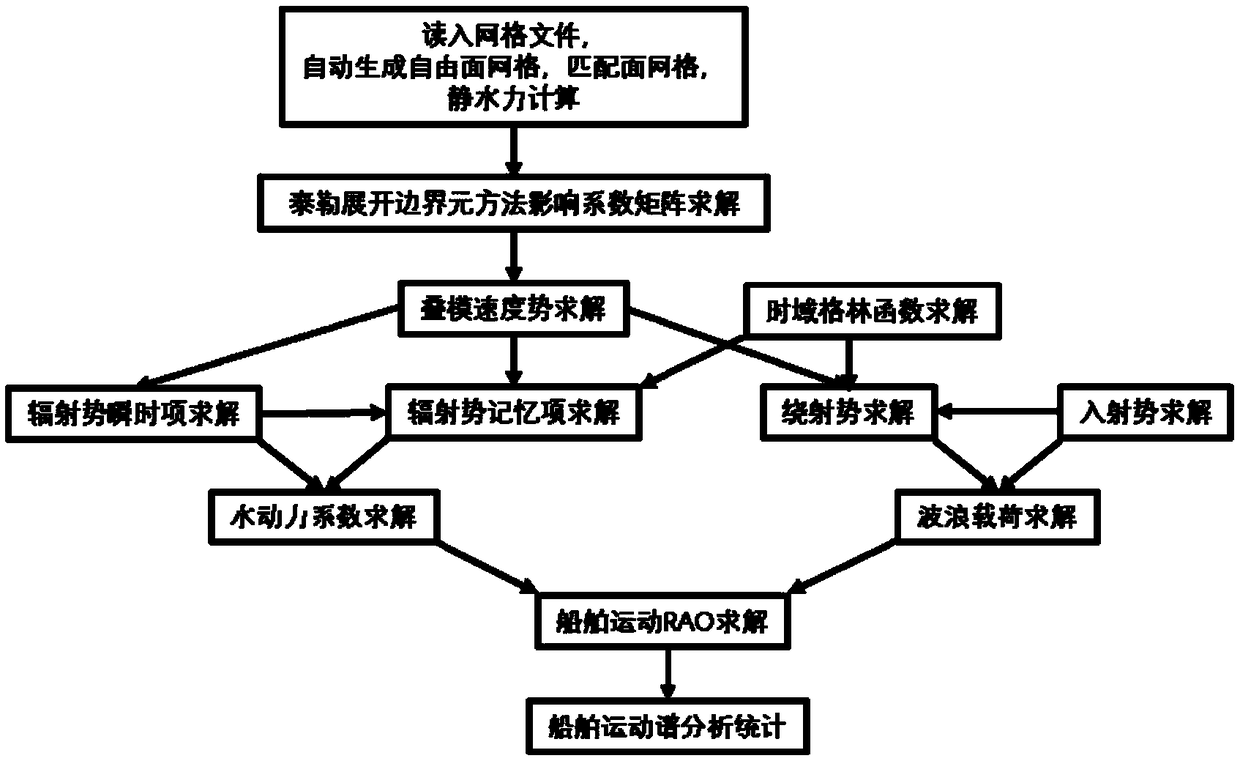
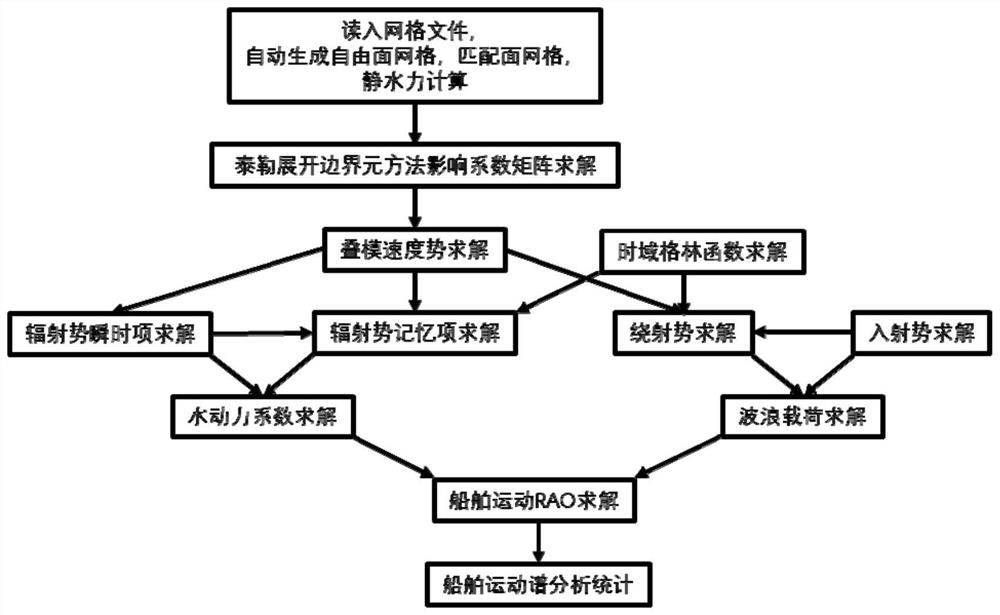
The invention provides a three-dimensional numerical simulation method for ship large-scale rolling motion, which comprises the following steps of reading a grid file to carry out ship hydrostatic calculation; calculating an influence coefficient matrix of boundary integral equation for Taylor expansion boundary element method; solving velocity potential of laminated modes and its spatial first and second derivatives and mj terms; carrying out the green's function in time domain and its spatial derivative solution; calculating a roll damping coefficient; carrying out the irregular wave decomposition, linear superposition into incident wave time calendar; carrying out the direct time-domain disturbance wave force calculation by taylor expansion boundary element method; calculating incidentwave force and hydrostatic recovery force; modeling a large-scale motion forecasting equation; using the fourth-order runge-kutta method to solve the motion equation step by step to evaluate the nonlinear motion of the ship in the top wave or oblique wave; and carrying out the numerical simulation and characteristic statistics of ship large amplitude motion in irregular waves. The method of the invention can predict the large amplitude motion of a container ship in regular waves and irregular waves, and can be used for numerical simulation and characteristic statistics of the large amplitude motion of a ship in irregular waves.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
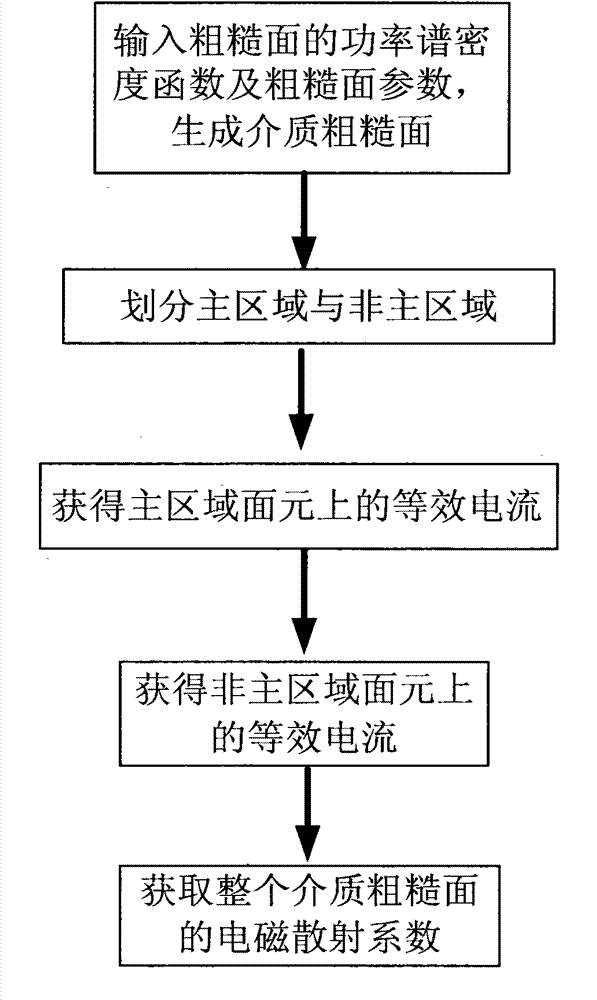
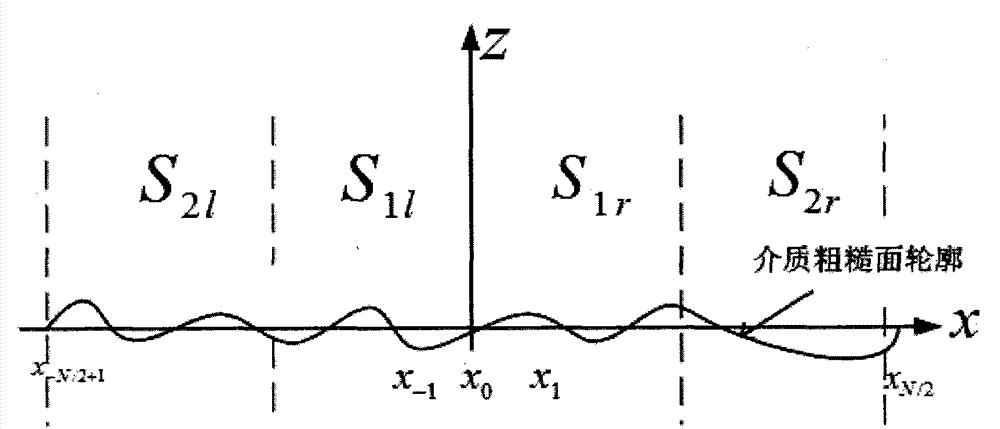
Medium rough surface electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on multi-zone model moment method
InactiveCN103400004AReduce memory requirementsSmall scaleSpecial data processing applicationsRough surfaceRadar
The invention discloses a medium rough surface electromagnetic scattering simulation method based on a multi-zone model moment method. The method includes the steps of inputting a medium rough surface power spectral density function and rough surface parameters, obtaining position coordinates of N scattering surface elements on a rough surface through a Monte Carlo method, dividing the rough surface into a main zone and a non-main zone, obtaining equivalent current on the surface elements of the two zones respectively, obtaining an electromagnetic scattering coefficient of the rough surface, and achieving medium rough surface electromagnetic scattering simulation. According to the method, zone division is performed on the rough surface, a boundary integral equation is built through the moment method in the main zone which has large influences on scattering results, the equivalent current of the main zone is obtained, the equivalent current is obtained approximately in the non-main zone, the number of unknown quantities is lowered under the premise that certain accuracy is guaranteed, internal storage is reduced, calculation efficiency is improved, the technical problem of actual large-zone medium rough surface electromagnetic scattering simulation is solved, and the method is applied to rough surface radar scattering property study in the fields of national defense and civil use.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
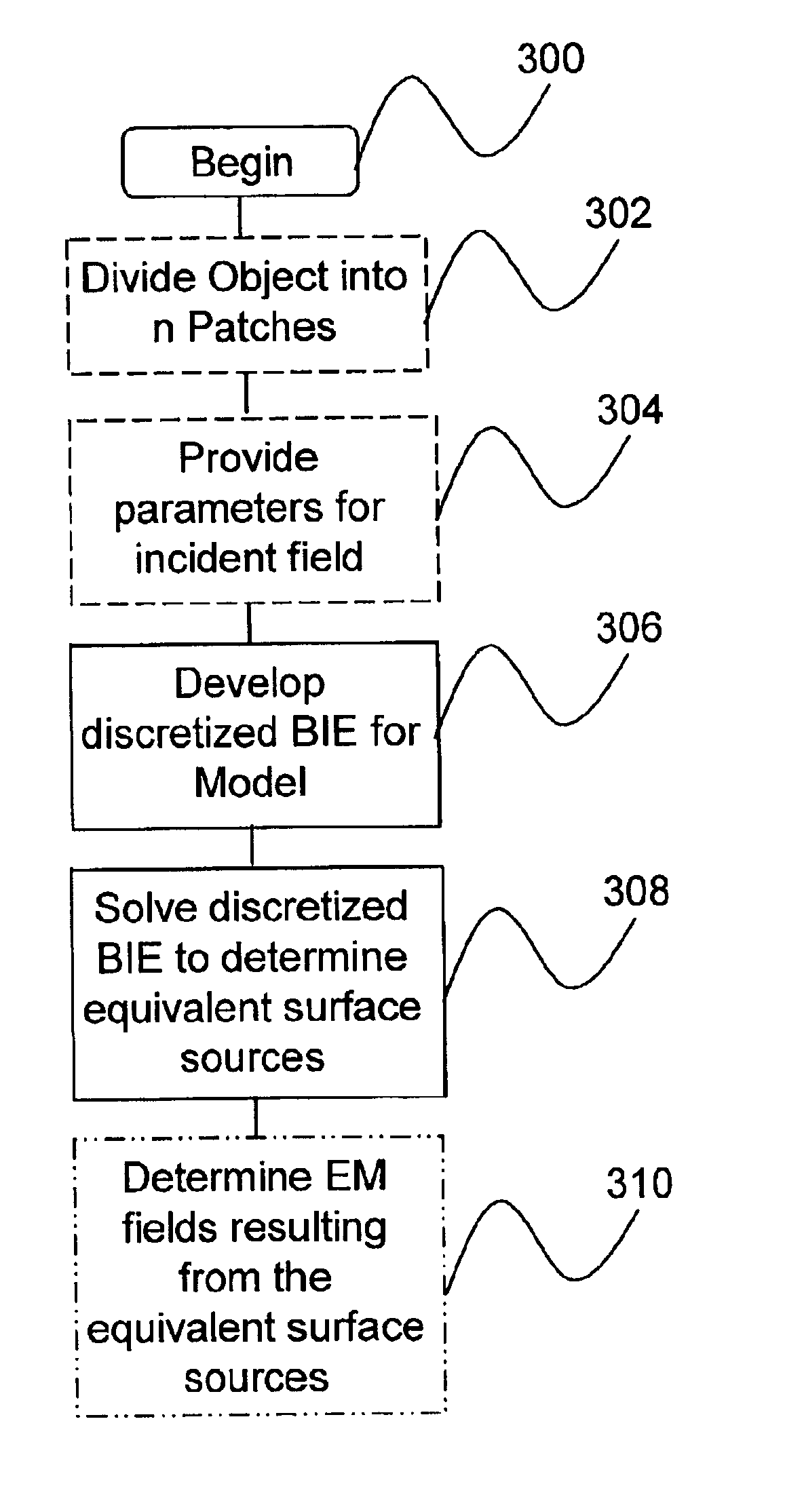
Method and apparatus for modeling three-dimensional electromagnetic scattering from arbitrarily shaped three-dimensional objects
InactiveUS6847925B2High degreeImprove computing efficiencyGeometric CADWave based measurement systemsRadarHarmonic
A computer program product, an apparatus, and a method for modeling equivalent surface sources on a closed, arbitrarily shaped object that result from the imposition of an arbitrary time-harmonic incident field (e.g., a radar wave) are provided. An object divided into by a plurality of patches 302 and parameters for the incident field and the properties of the object 304 are provided to the system. Next, the system produces a discretized representation of a well-conditioned boundary integral equation in the form of a well-conditioned matrix equation, modeling the interaction between the incident field and the object 306. The well-conditioned linear system is solved numerically to determine equivalent surface sources on the object 308. The equivalent sources may then be used to determine electromagnetic fields resulting therefrom 310. The invention provides improved computational efficiency as well as increased modeling accuracy by effectively reducing the numerical precision necessary.
Owner:HRL LAB
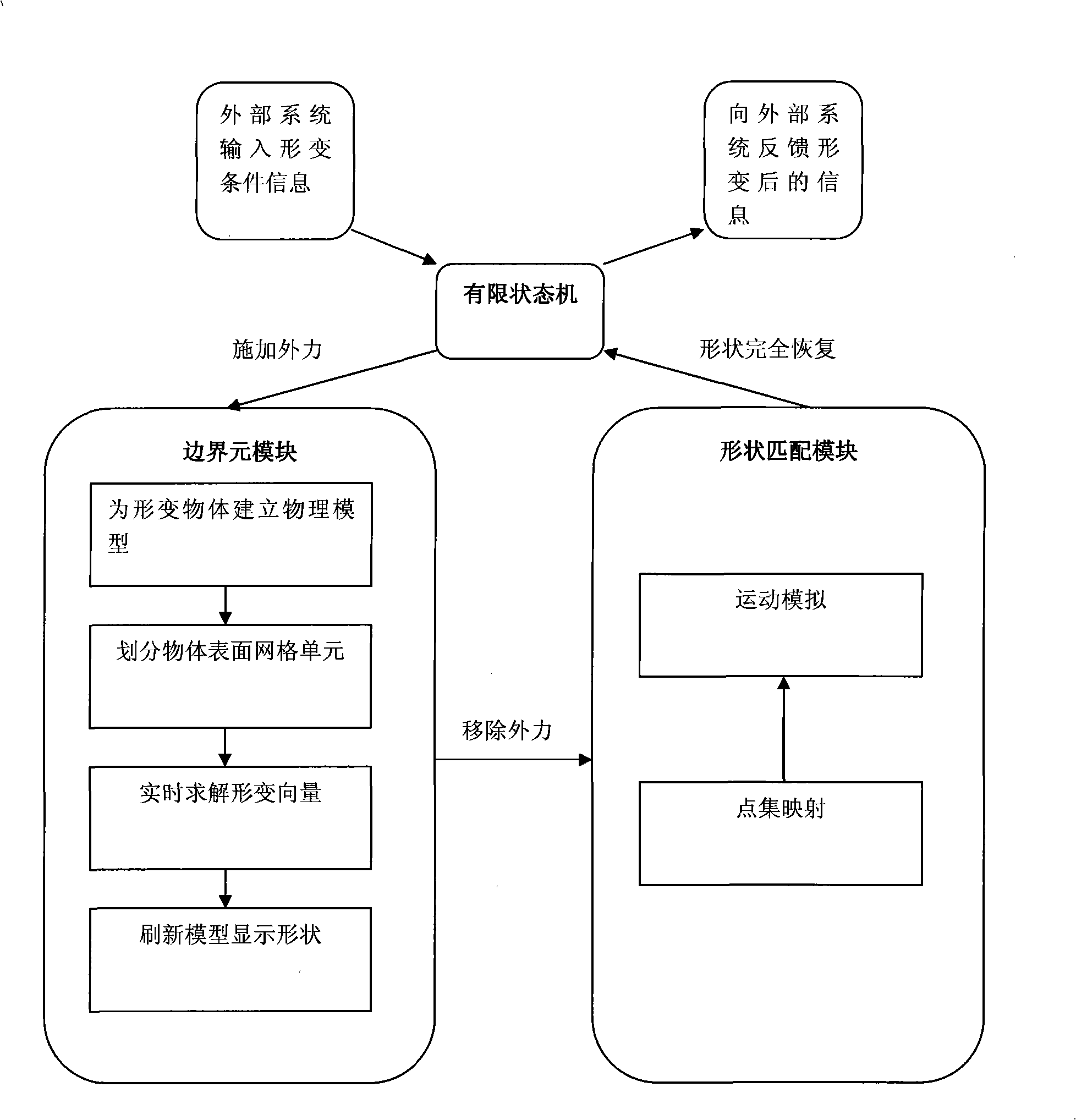
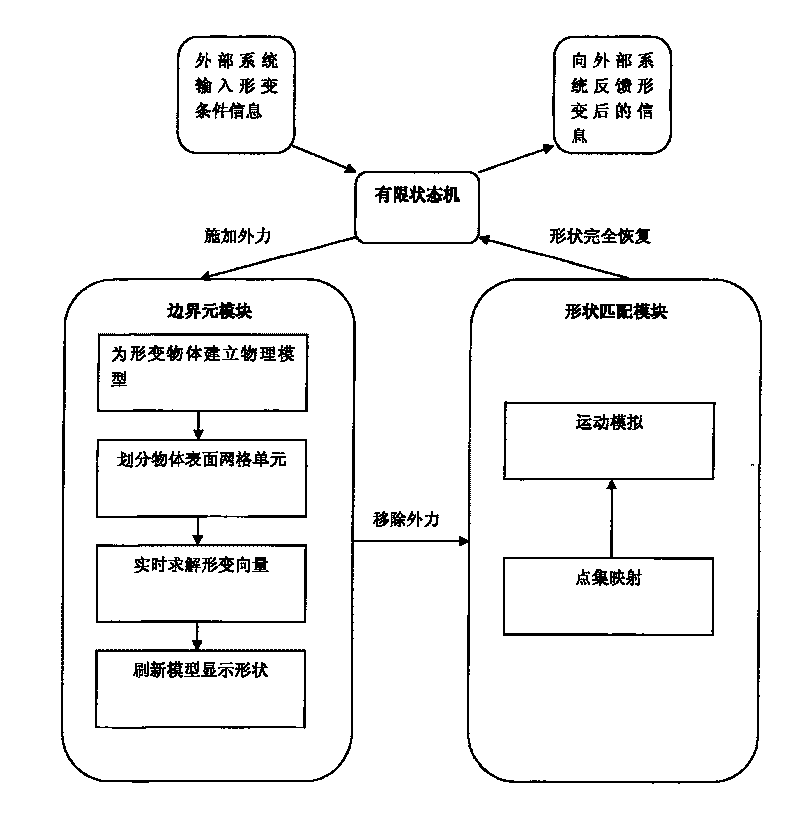
Shape-changing object real-time simulation system of virtual operation system
InactiveCN101295409AImprove interactivityHigh precision2D-image generation3D modellingShape changeKinematics equations
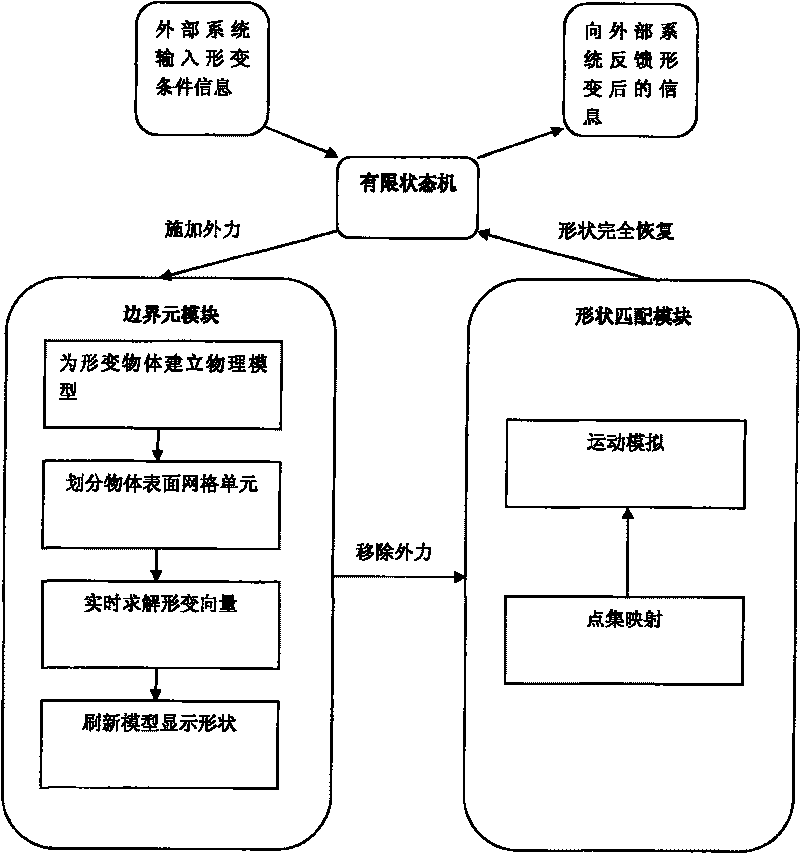
The invention discloses a real-time system for simulating the deformation of soft-issue objects in a surgery simulation system, belonging to the graphic processing technical field, which is characterized in that: a boundary meta-module first establishes a physical model for the deformed object and divides grid units on the surface of the object, carries out discretization for the boundary integral equation and figures out a deformation vector of each grid unit; according to the well-divided grid units, a shape matching module establishes mapping relations between the deformation positions and initial positions of each grid unit; a kinematics equation is established according to the positions of the grid units and the material properties of the object, to calculate the deformation recovery of the object; in the deformation process of the soft-issue object, a finite state machine makes an analysis for the stressing states of the object, and controls a currently-used deformation calculating module through the switching of the basic states. The real-time system for simulating the deformation of soft-issue objects in a surgery simulation system realizes real-time and precisely simulations for the deformation of the soft issues in interactive systems, in particular to renders the interaction between the surgical instruments and the soft issues in the surgery simulation systems are more accurate and quicker.
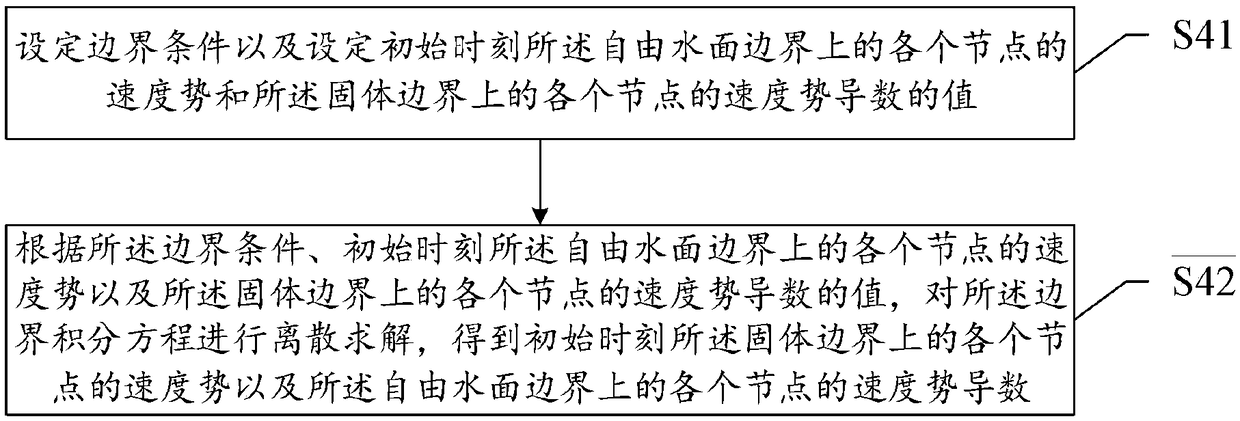
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Ship motion prediction method based on Taylor expansion boundary element method
ActiveCN109446634ARapid Prediction of Hydrodynamic CoefficientsGeometric CADSustainable transportationFull waveVelocity potential
The invention provides a ship motion prediction method based on a Taylor expansion boundary element method. The method comprises the steps of reading the grid file and carrying out hydrostatic calculation; calculating the influence coefficient matrix of a boundary integral equation needed by the taylor expansion boundary element method; solving the velocity potential of laminated modes and its spatial first and second derivatives and Mj terms; solving the green's function in time domain and its spatial derivative; solving the instantaneous terms of radiation velocity potential and their spatial first and second derivatives; solving the radiation velocity potential memory term and its spatial first and second derivatives; solving the impulse response function of added mass, wave-making damping and radiation wave force; solving the impulse response function of whole wave incident velocity potential; diffraction velocity potential and its first and second derivatives in space, solving theimpulse response function of diffraction wave force; solving the ship motion in full wave direction; analyzing and calculating the ship motion spectrum under different sea conditions. The invention can predict the hydrodynamic coefficients of three main ship types, wave loads, six-degree-of-freedom motion of the ship in full wave direction, and ship motion spectrum analysis under various sea conditions.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
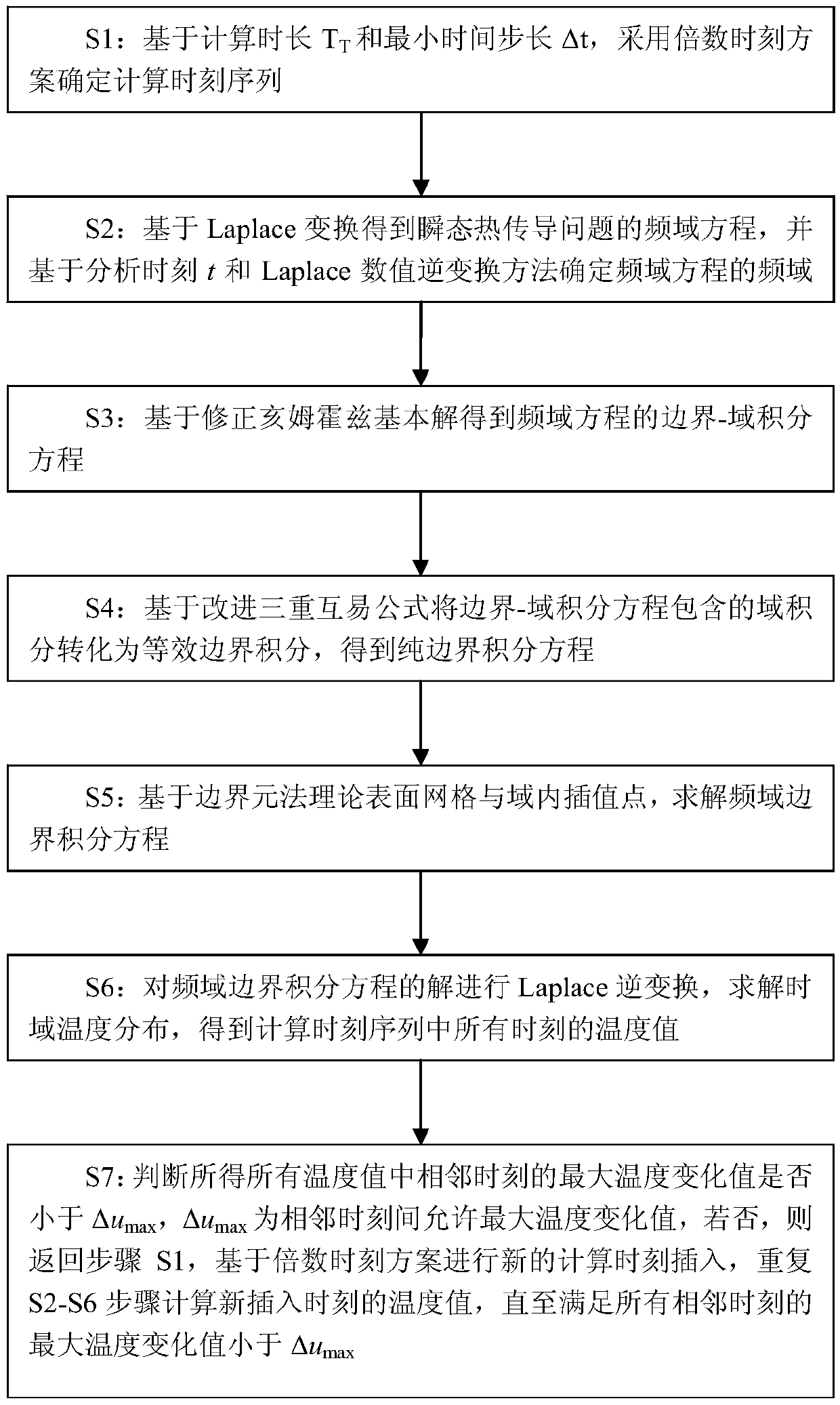
Transient temperature calculation method based on improved triple reciprocal boundary element method
ActiveCN108932392AReduce the number of computing momentsReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsBoundary integral equationsFrequency domain equalization
The invention discloses a transient temperature calculation method based on an improved triple reciprocal boundary element method, comprising the following steps: adopting a multiple time scheme to determine a calculation time sequence; obtaining a frequency domain equation of a transient heat conduction problem based on Laplace transform, and determining frequency domain parameters of the frequency domain equation based on analysis time t and an inverse Laplace transformation method; obtaining a boundary-domain integral equation of the frequency domain equation based on a modified Helmholtz fundamental solution; based on an improved triple reciprocity formula, transforming a domain integral contained in the boundary-domain integral equation to equivalent boundary integral, to obtain a pure boundary integral equation; solving a frequency domain boundary integral equation based on a theoretical surface mesh of a boundary element method and intra-domain interpolation points; performing inverse Laplace transformation on a solution in frequency domain, and solving time domain temperature distribution. The invention provides an improved triple reciprocity method calculation formula withlow degree of freedom expression, thereby greatly reducing calculation time of the triple reciprocity method and saving storage space at the same time.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mechanical noise far field sound pressure prediction method based on inverse boundary element method
ActiveCN105004416AAvoid the inconvenience of multiple measurementsEngineering measurement is convenientSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSpecial data processing applicationsSingular value decompositionSound sources
The invention discloses a mechanical noise far field sound pressure prediction method based on an inverse boundary element method, and belongs to the sound pressure prediction field. A microphone array is arranged in a wavelength of the highest analysis frequency of a target sound source, a test surface is bigger than a positive projection plane of a target sound source. One wavelength contains at least two measuring points. A reference microphone is arranged near the target sound source, and a field point complex sound pressure after cross spectrum of the microphone array and the reference microphone is obtained through measuring. a transmission relation of a field point complex sound pressure and a normal vibration speed is created based on the inverse boundary element method, and a transmission matrix is obtained. The transmission matrix is subjected to singular value decomposition, and a normal vibration speed is obtained. A far field sound pressure py is predicted according to the normal vibration speed. the relation of the far field sound pressure and the normal vibration speed is created according to a boundary integration equation, py=ATMyvn, and ATMy is the transmission matrix corresponding to the far field sound pressure. The prediction method is suitable for a surface with a complex structure and has an advantage of high precision.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Elastic fracture simulation method based on dual boundary element and strain energy optimization analysis
ActiveCN108763841AApplications for Extended FractureSimple calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStrain energyEngineering
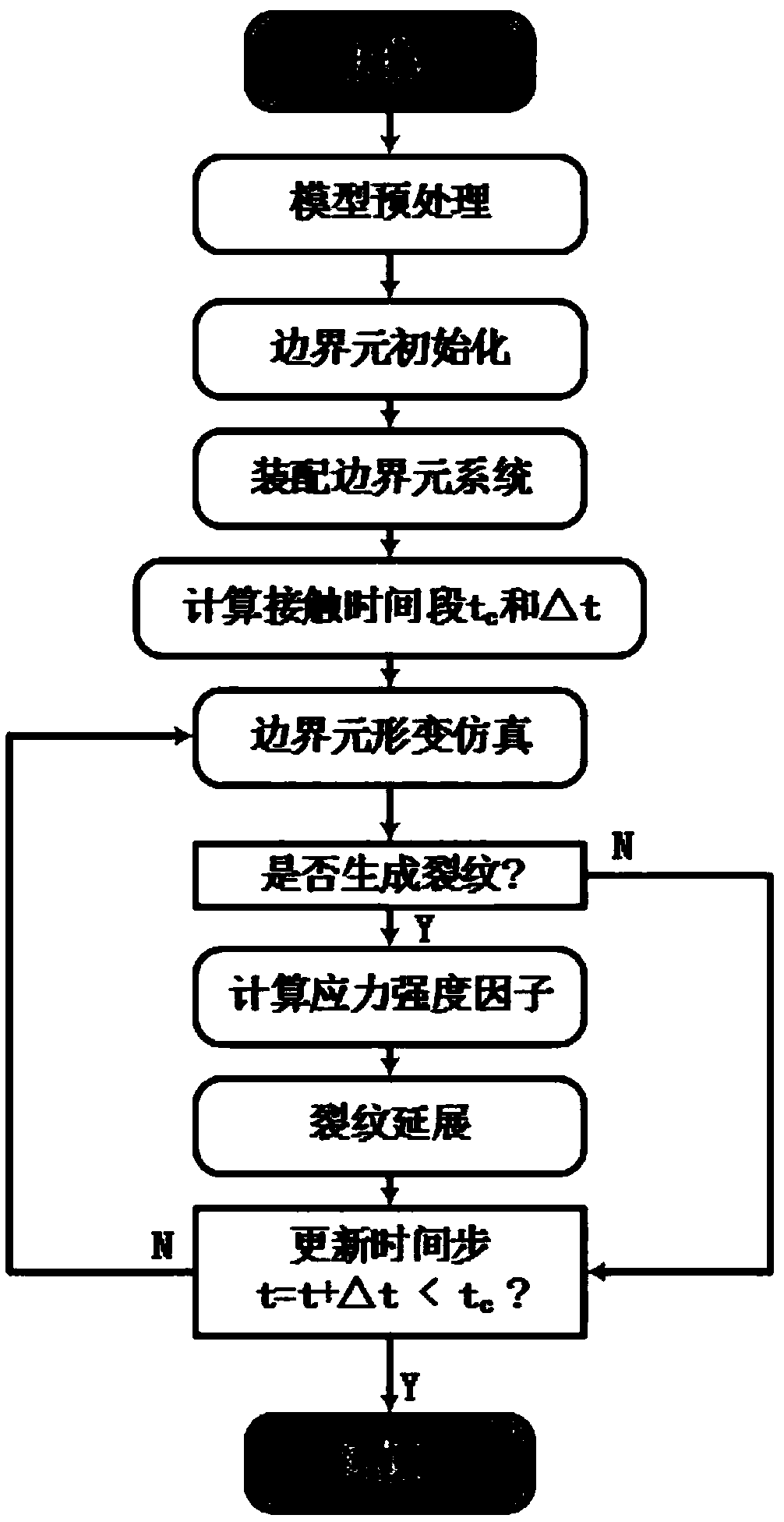
The invention proposes an elastic fracture simulation method based on a dual boundary element and strain energy optimization analysis. The two basic problems related to three-dimensional linear elastic fracture are handled. A model containing an overlapped cleft surface is expressed by using a dual boundary element method, and a super-singular boundary integral equation is solved by using a semi-analytic method. The continuous attribute from the contact load and released by the strain energy at the front end of the crack is represented by introducing a contact force model. A fracture factor ofthe extension distance of the crack is calculated within the fracture duration to perform accurate control on the extension of the cracking end.
Owner:QINGDAO RES INST OF BEIHANG UNIV +1
Seismic migration method for coupled transmission coefficient
ActiveCN102608659AAccurately obtainedAchieving transmission loss compensationSeismic signal processingSeismic migrationWave field
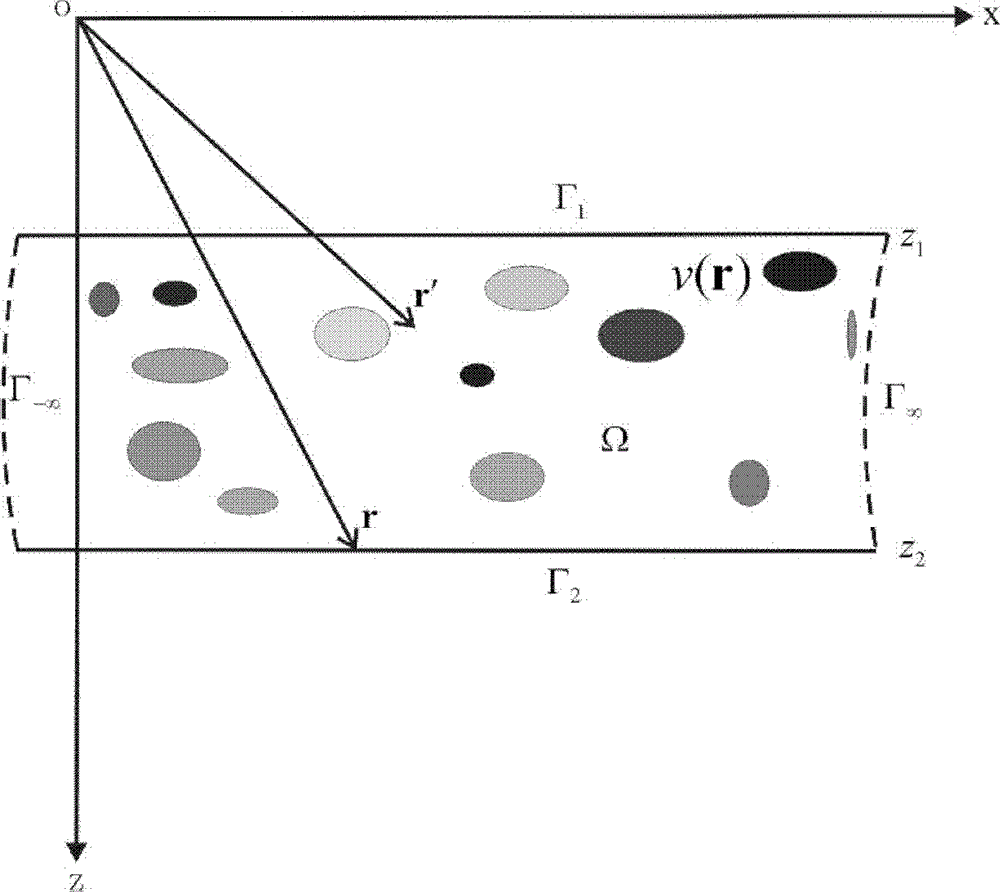
The invention relates to a seismic migration method for a coupled transmission coefficient, which comprises the following steps of: 1) dividing different depth layers by taking the earth surface as an initial point, namely dividing underground media to be explored into different depth layers according to different depth intervals, and assuming the different depth intervals of the underground media to be explored as different horizontal sheets, wherein the thickness of the horizontal sheets is the depth interval of the underground media to be explored; 2)based on a Lippmann-Schwinger integral equation, solving the Lippmann-Schwinger equation by establishing an integral equation of an upper boundary gamma1 and a lower boundary gamma2 of a seismic wave field in in the closed area omega of any horizontal sheet; 3) establishing a boundary integral equation at the lower boundary gamma2 of the closed area omega according to a transmission effect of the lower boundary gamma2 of the horizontal sheet; and 4) solving a seismic migration wave field according to the transmission and reflection effects between the horizontal sheets and of the upper boundaries and lower boundaries of the horizontal sheets. The seismic migration method can be widely applied to a seismic migration technology for imaging a complex oil exploration structure.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
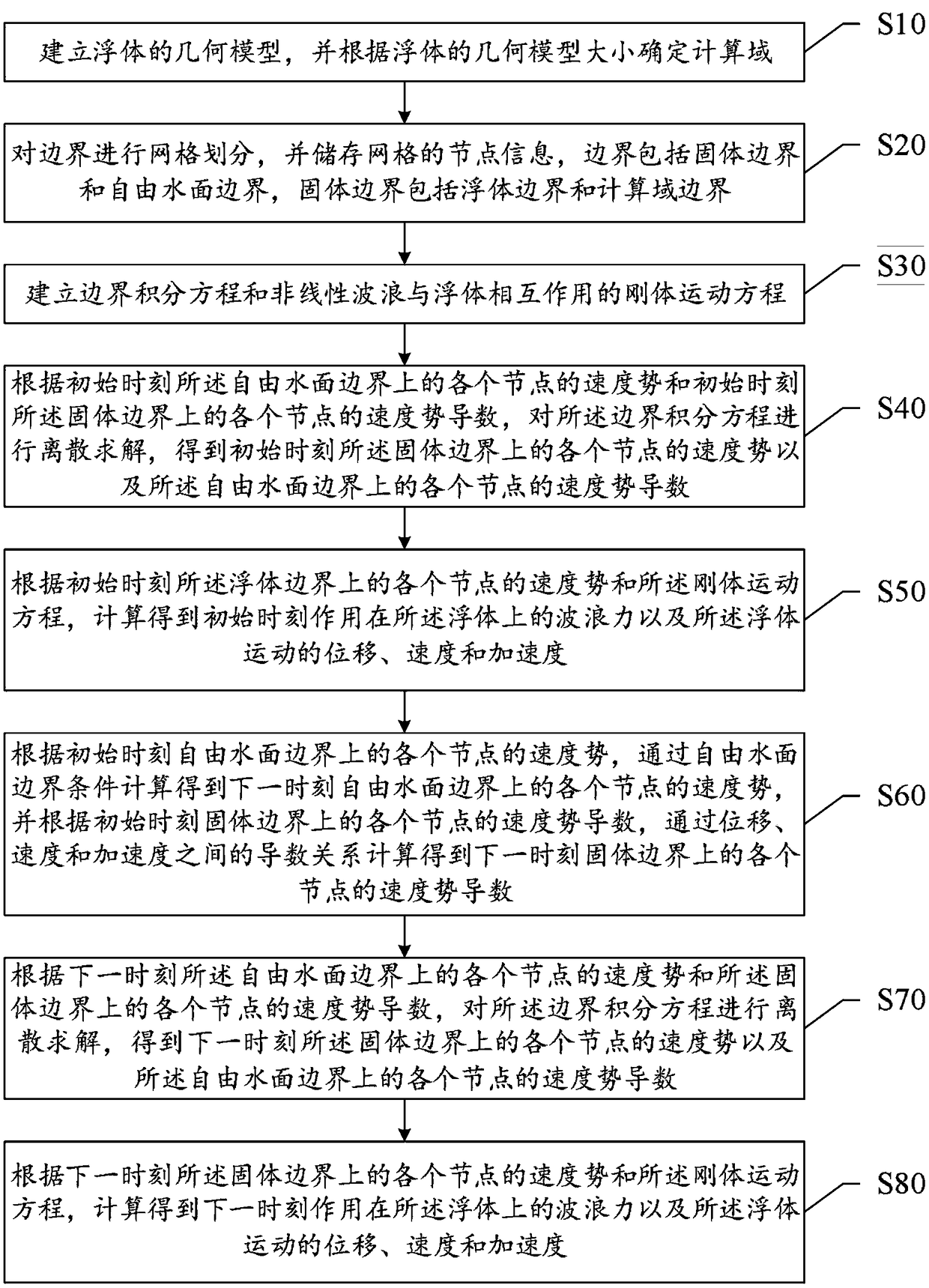
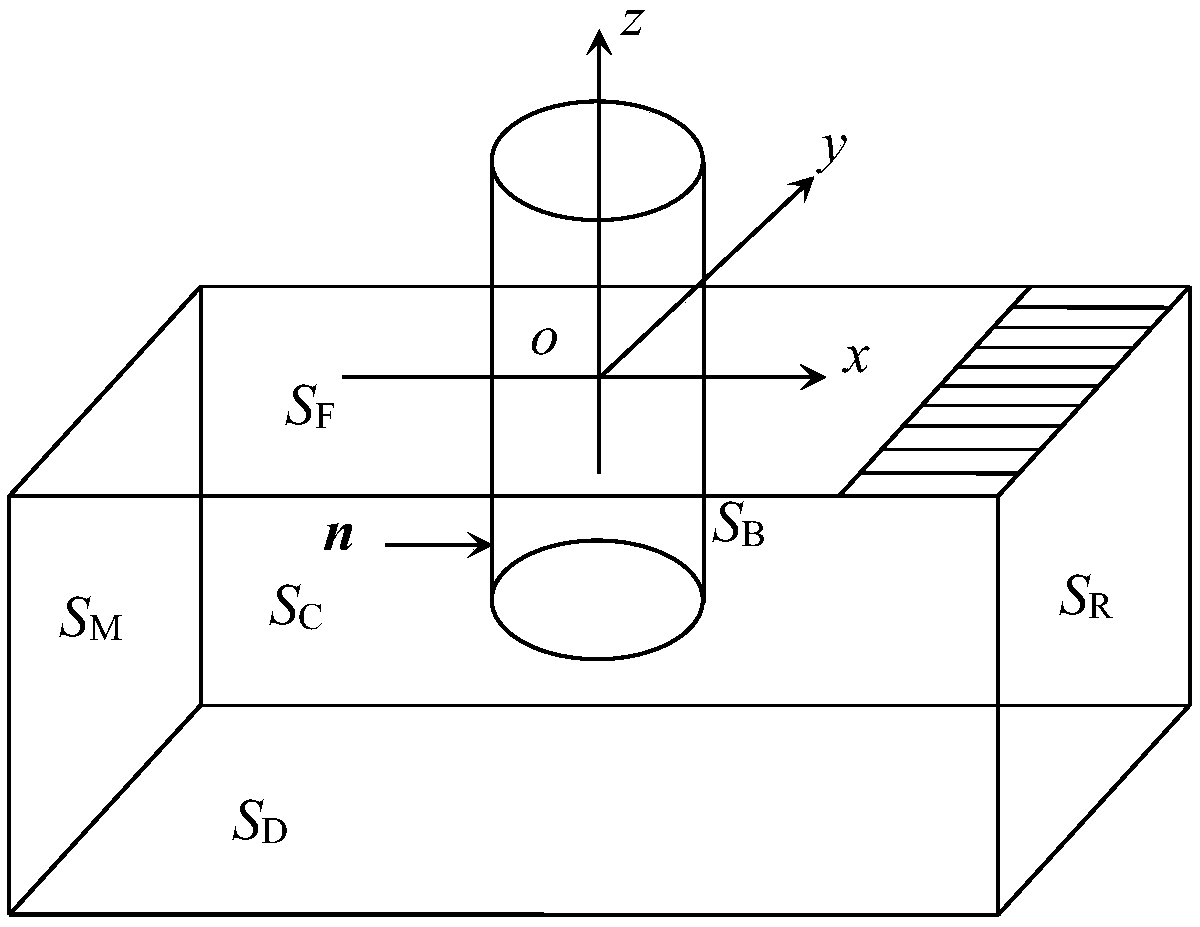
A method and system for measuring hydrodynamic response of a floating body under wave action
ActiveCN109446581ASolve the problem of insufficient consideration of nonlinearityImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADHydrodynamic testingComputer scienceVelocity potential
The invention discloses a method and system for measuring the hydrodynamic response of a floating body under the wave action. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a floating body geometric model and determining a calculation domain; meshing the boundary and storing the node information of the mesh; establishing boundary integral equation and rigid body motion equation; solvingthe boundary integral equation and rigid body motion equation at the initial time, and obtaining the velocity potentials of each node on the solid boundary at the initial time, the velocity potentialderivatives of each node on the free surface boundary, the wave forces on the floating body and the displacement, velocity and acceleration of the floating body motion; according to the parameters ofeach node at the initial time, calculating the velocity potential of each node on the solid boundary at the next time, the velocity potential derivative of each node on the free surface boundary, thewave force on the floating body and the displacement, velocity and acceleration of the floating body motion. The present invention solves the problem of insufficient consideration of nonlinearity in the process of interaction between wave and structure in the prior art, and improves the calculation accuracy.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
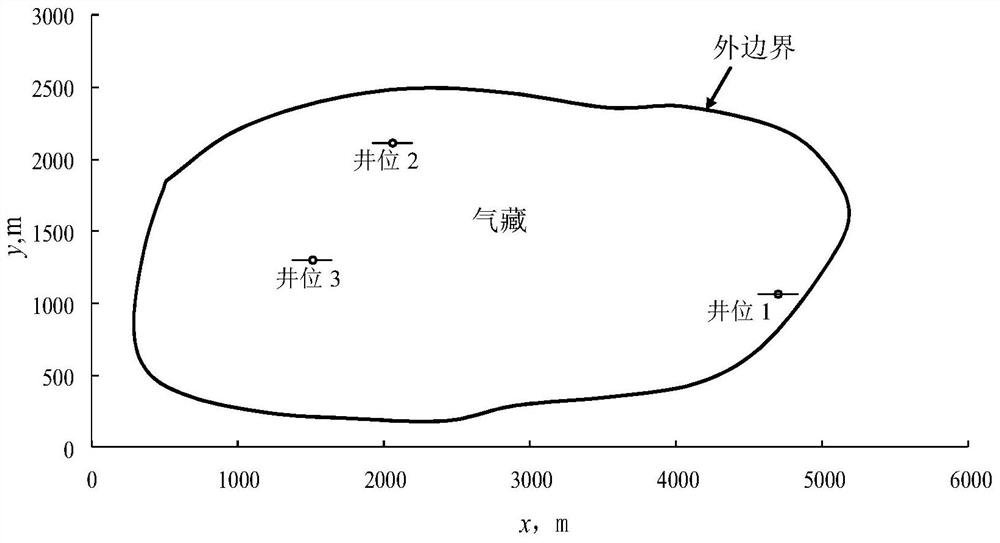
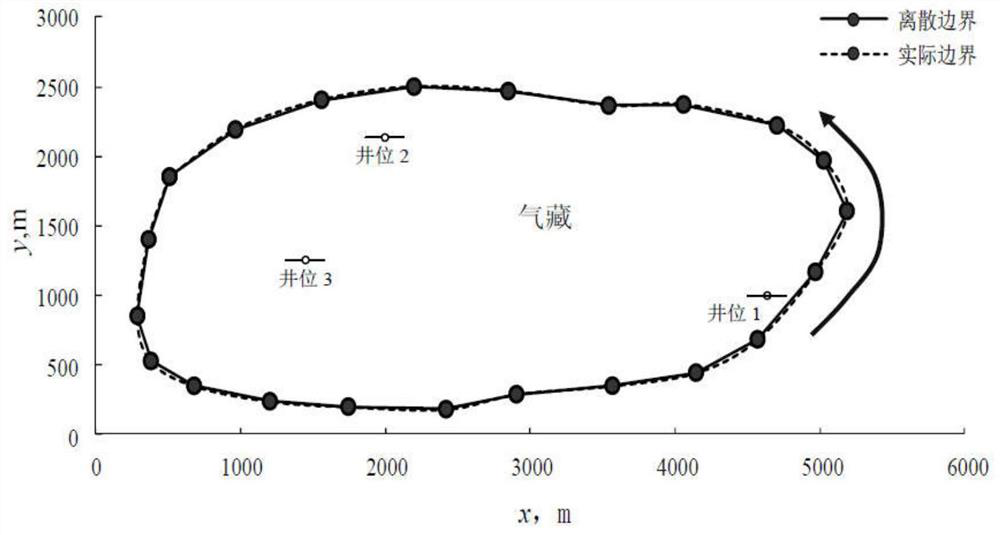
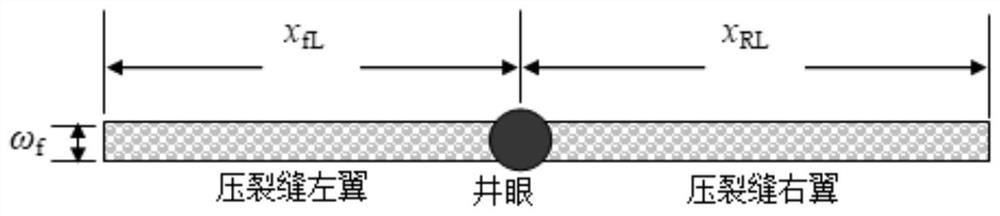
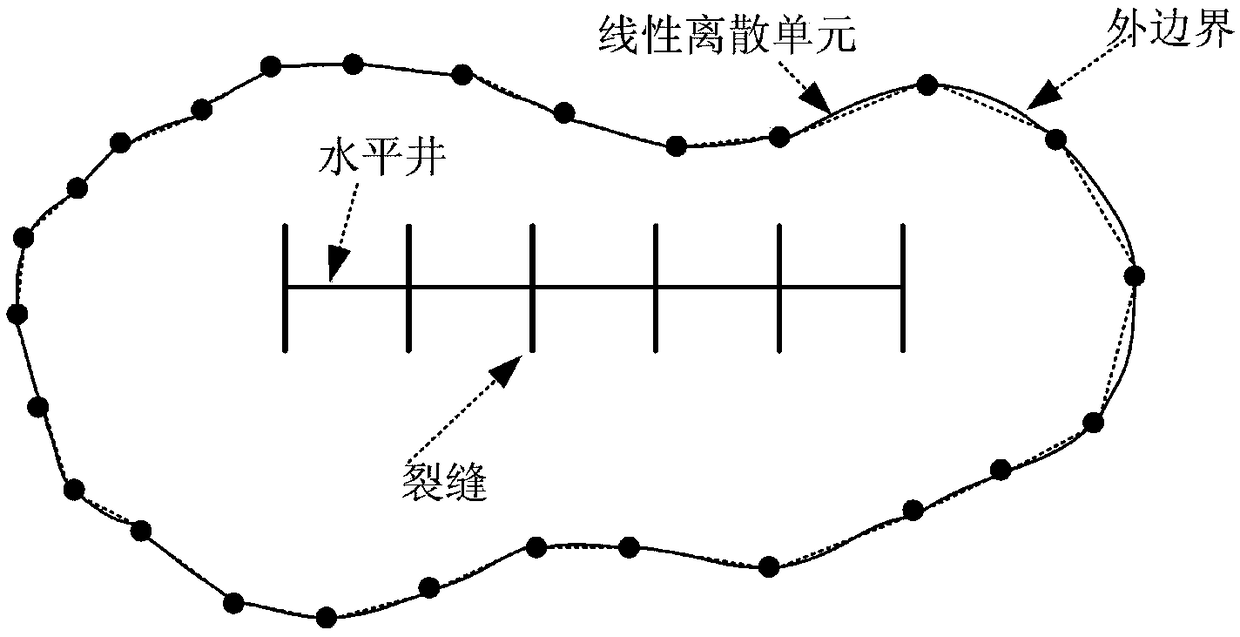
Method for simulating pressure of gas reservoir finite diversion asymmetric fractured well in any shape
InactiveCN111927420AAccurate calculationAccurate portrayalGeometric CADSurveyBottom hole pressureMathematical model
The invention provides a method for simulating the pressure of a gas reservoir finite diversion asymmetric fractured well in any shape. The method comprises the following steps that the boundary condition in a fracturing fracture is coupled to a gas reservoir mass conservation equation, and a seepage differential equation is export; definite solution conditions are wrote, and combine with the seepage differential equation to form a stratum seepage mathematical model without dimensionality; an intra-domain differential equation is converted into an integral equation on the boundary and discretization is carried out, a finite flow guide fracturing fracture seepage mathematical model is established, and integrating and dispersing are carried out; matrixes obtained by the discrete boundary integral equation and the discrete fracturing crack equation is simultaneously solved; and a dimensionless bottom hole pressure curve and a derivative curve are drawn, and the influence of the position,a skin coefficient of the fractured well in the complex-shape gas reservoir, a dimensionless flow conductivity coefficient of a fracturing crack and the asymmetry of fracturing crack two wings on thecurve are analyzed. According to the method, an unstable well testing mathematical model of a gas well is established, a transient state of the bottom hole pressure of the gas well is accurately calculated, which is a theoretical basis for well testing interpretation to obtain important stratum parameters.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
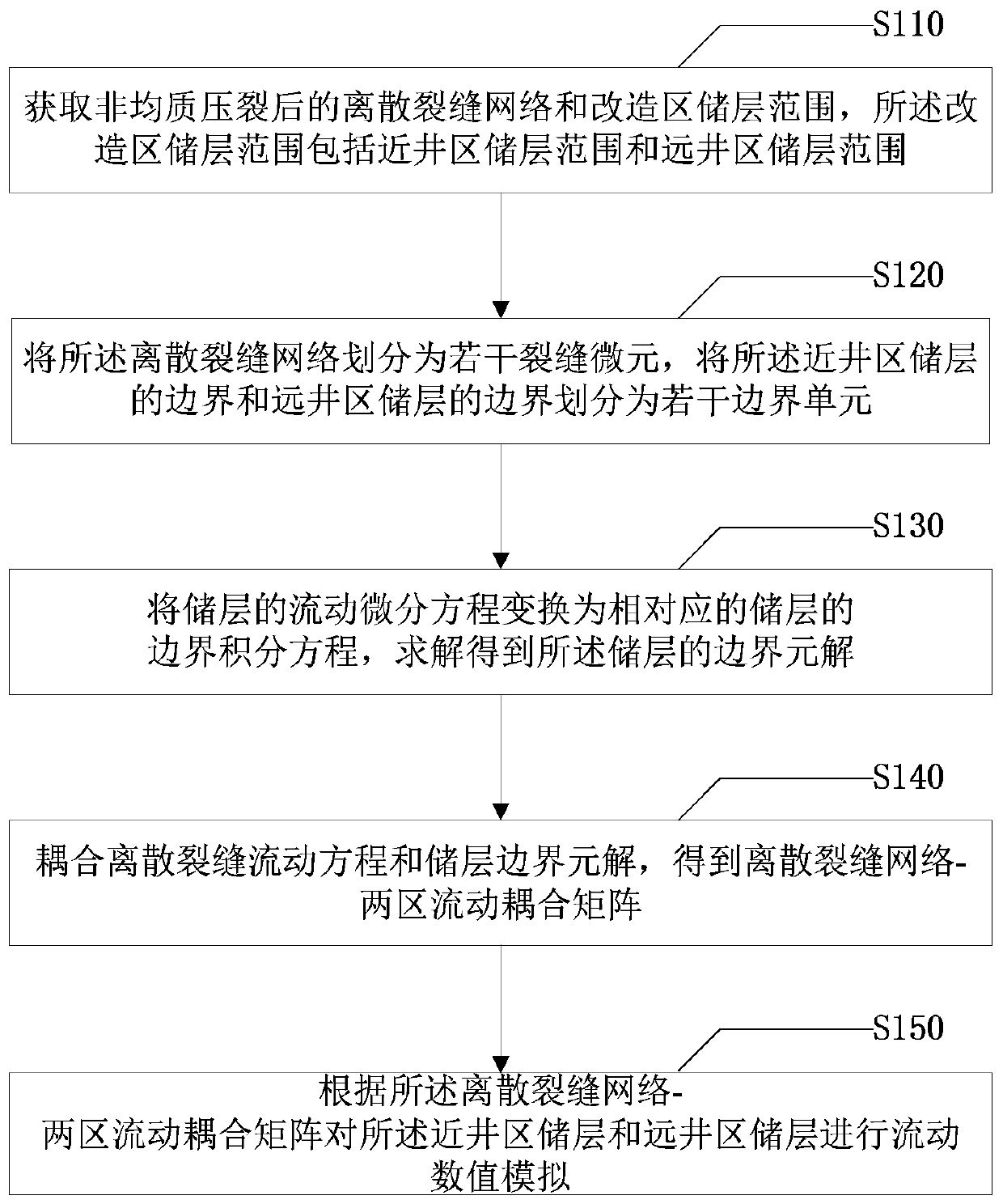
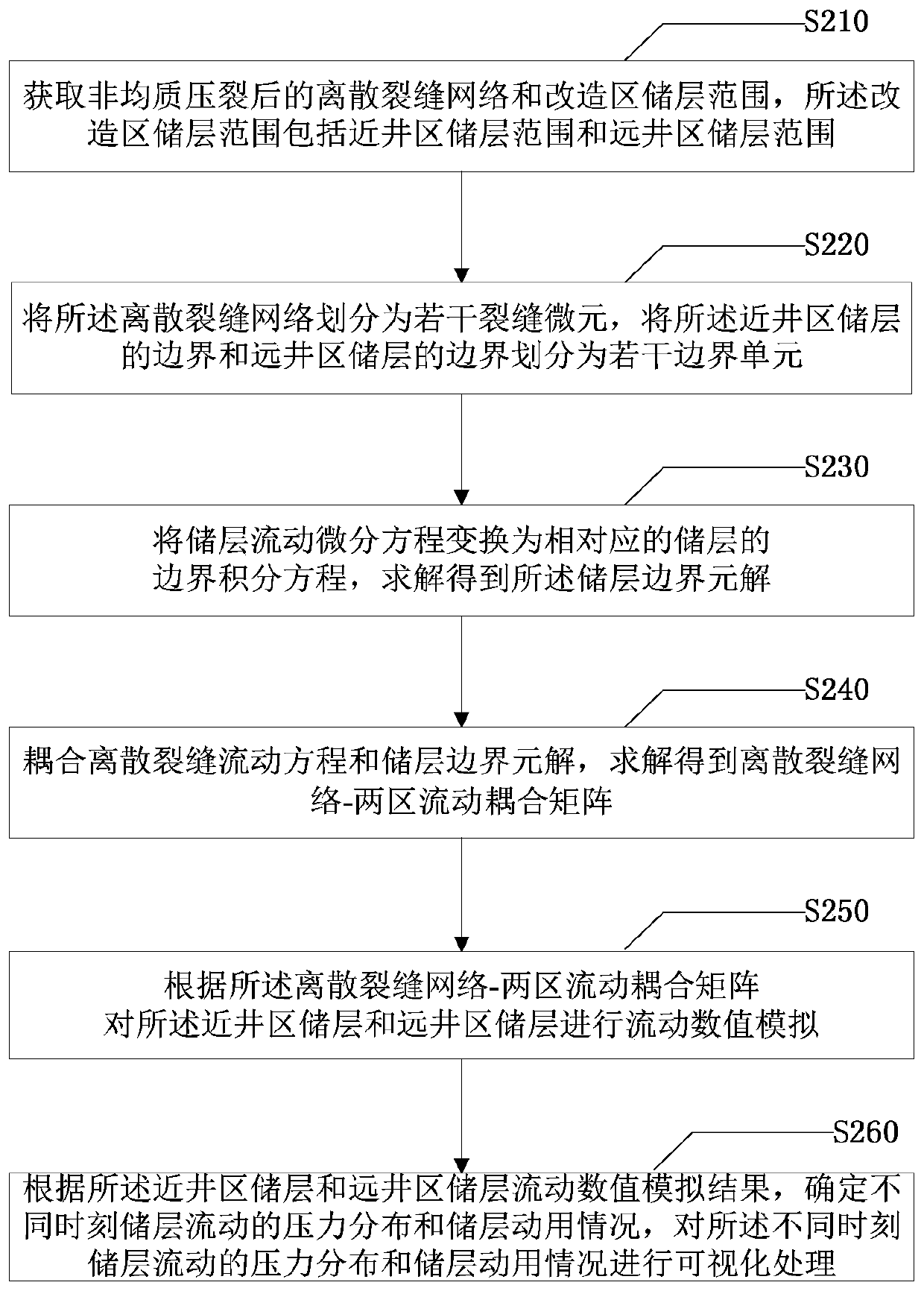
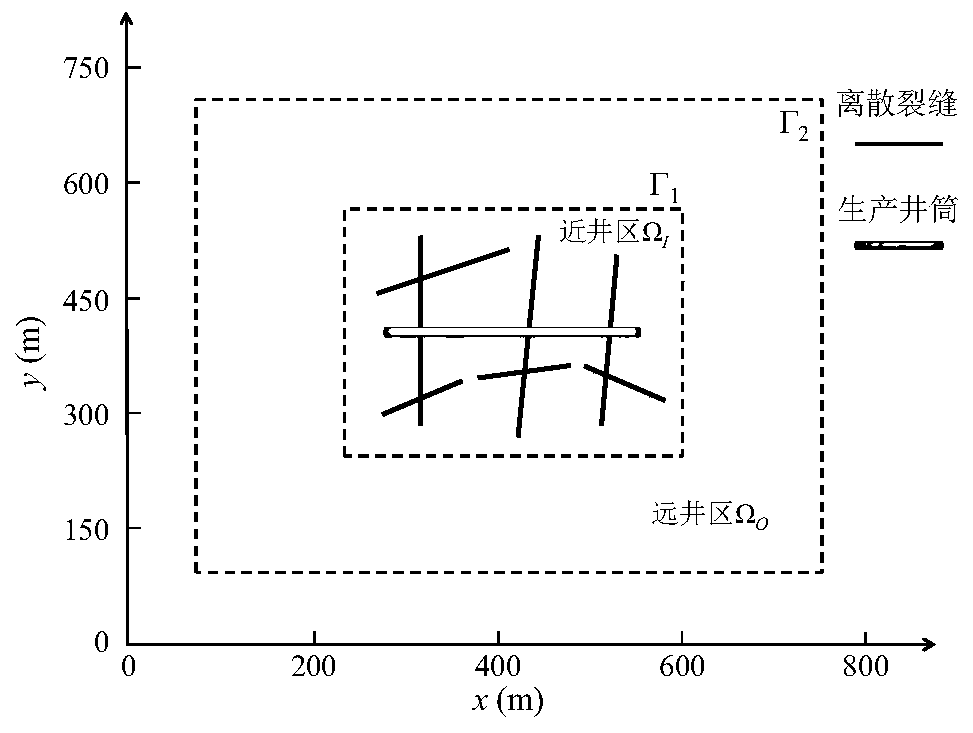
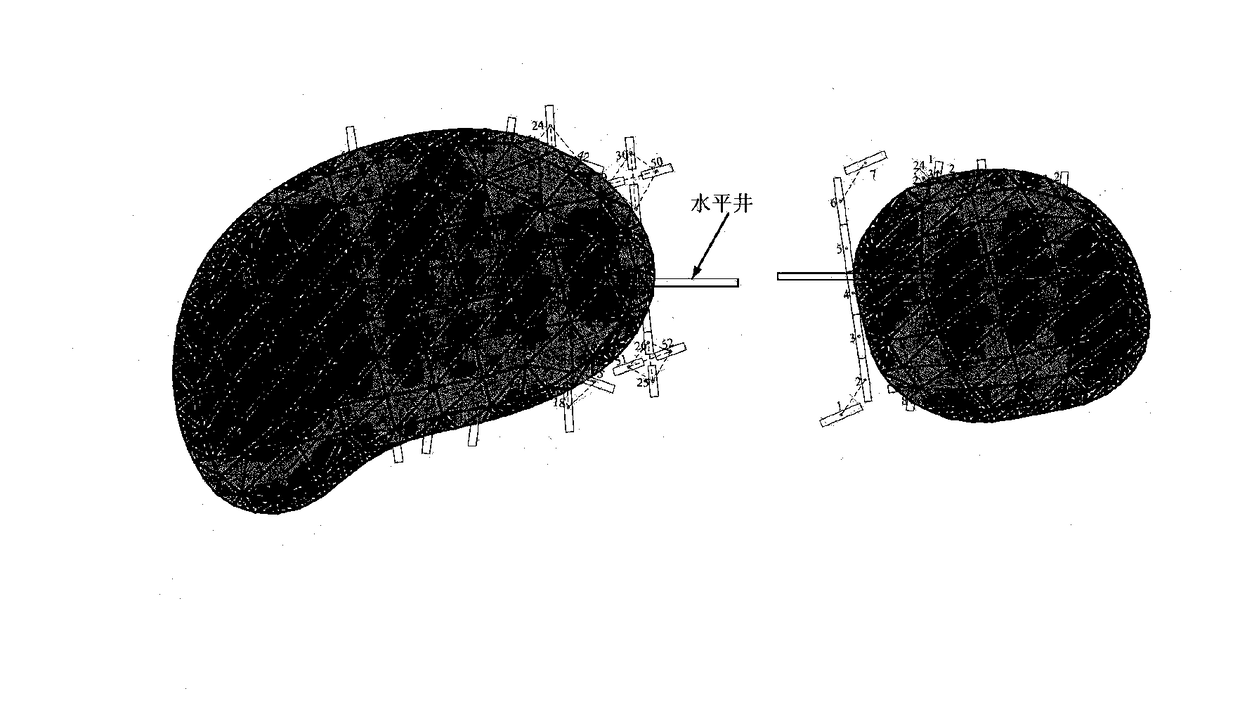
Reservoir flow numerical simulation method and system after heterogeneous fracturing
ActiveCN110334365AAccurately describe flow lawsSimulation is accurateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelConceptual model
The embodiment of the invention provides a reservoir flow numerical simulation method and system after heterogeneous fracturing. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a discrete fracturenetwork after heterogeneous fracturing and a transformation area reservoir range; dividing the boundary of the discrete fracture network and the reservoir into a plurality of fracture micro-elementsand a plurality of boundary units; converting the flowing differential equation of the reservoir into a boundary integral equation of the corresponding reservoir, and solving to obtain a boundary element solution of the reservoir; coupling the discrete fracture flow equation and the reservoir boundary element solution to obtain a discrete fracture network-two-region flow coupling matrix; and performing flow numerical simulation on the reservoir according to the discrete fracture network-two-region flow coupling matrix. From the perspective of seepage mathematical model establishment, a fracturing fracture network formed by artificial fractures, induced fractures and natural fractures is extracted into a discrete fracture network-two-region heterogeneous conceptual model, and the discrete fracture network-two-region heterogeneous conceptual model can be used for simulating flow behaviors under different arbitrary reservoir two-region heterogeneous forms and arbitrary fracture network distribution combinations.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
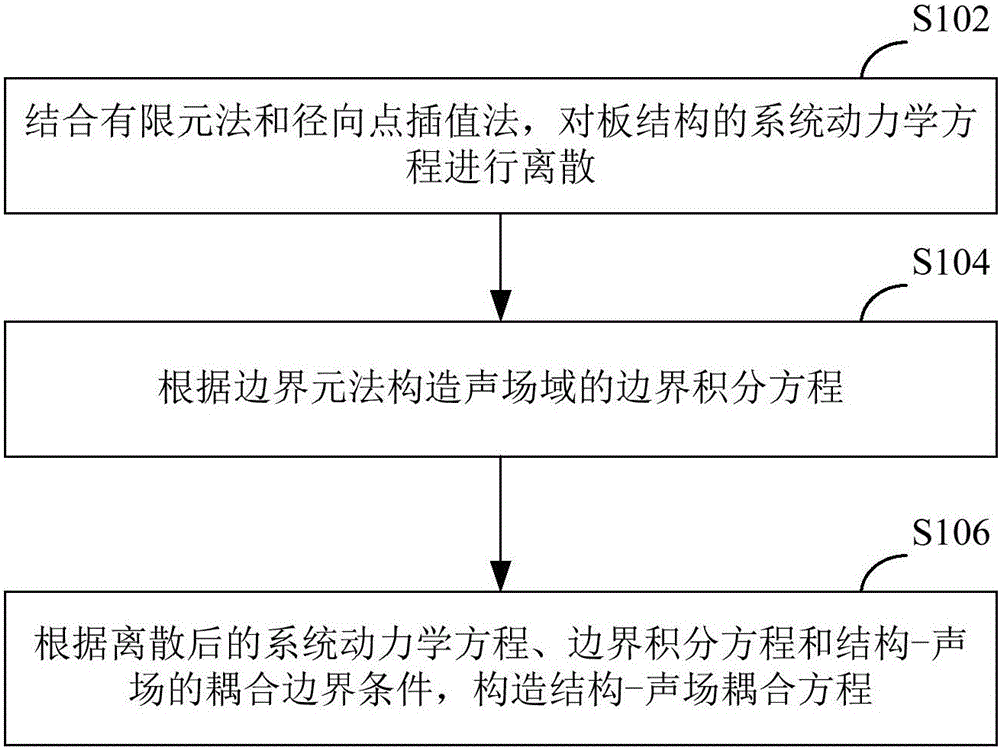
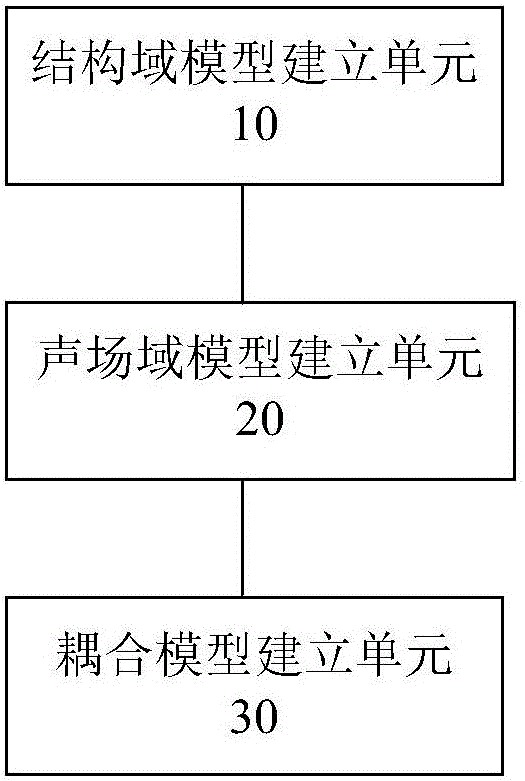
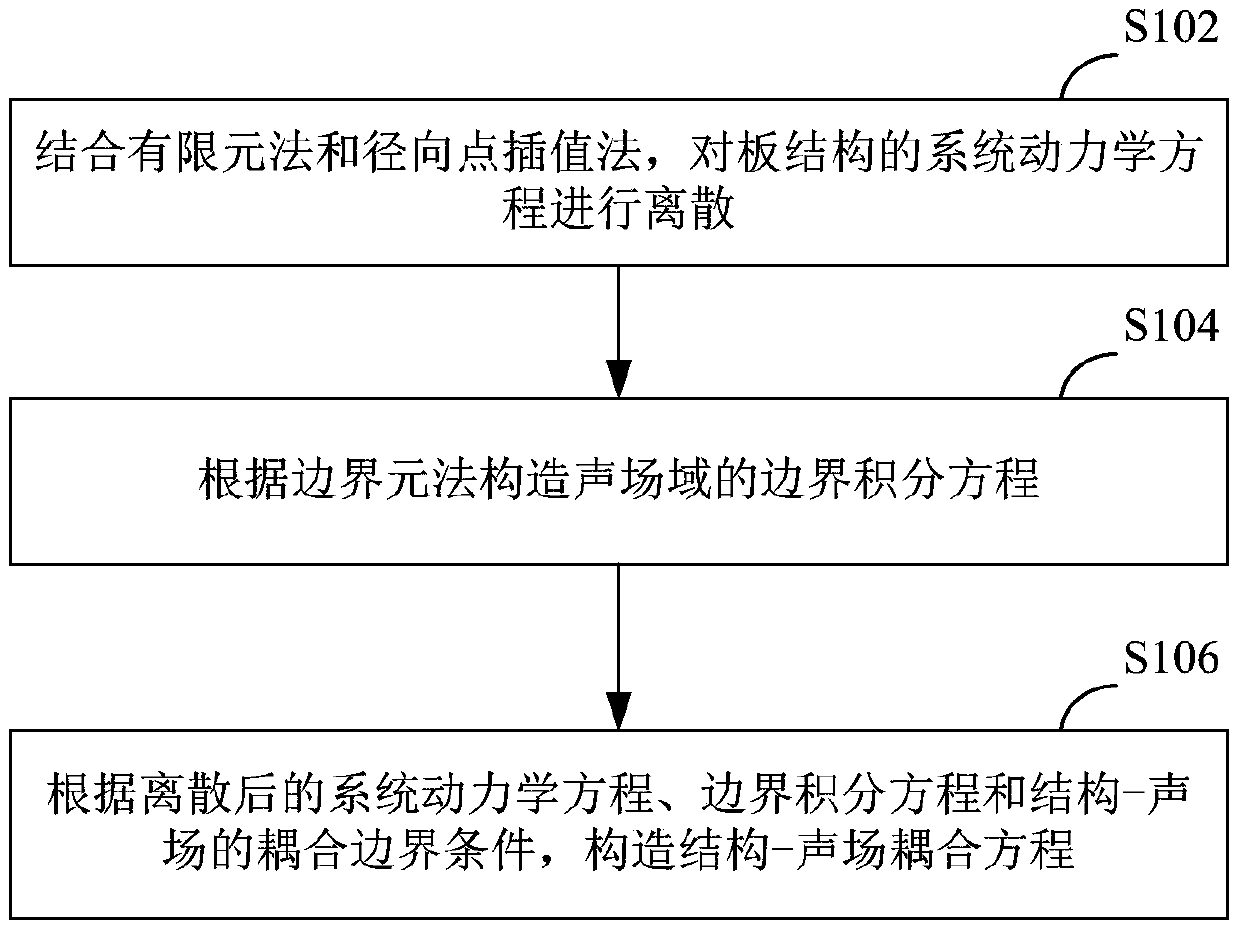
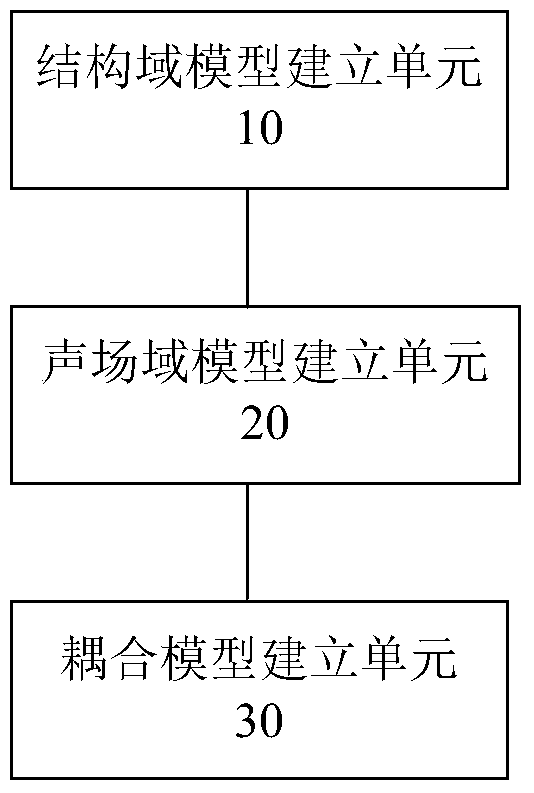
Plate structure-sound field coupling analysis method and device and computing device
ActiveCN104951596AUnit quality requirements are lowReduce roughnessSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringAnalysis method
The invention discloses a plate structure-sound field coupling analysis method. The method includes the steps that a finite element method and a radial point interpolation method are combined, and dispersing is conducted on a system kinetic equation of a plate structure; a boundary integral equation of a sound field domain is established according to a boundary element method; a structure-sound field coupling equation is established according to a dispersed system kinetic equation, the boundary integral equation and the structure-sound field coupling boundary condition. The invention further discloses a plate structure-sound field coupling analysis device corresponding to the plate structure-sound field coupling analysis method and a computing device with the plate structure-sound field coupling analysis device.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
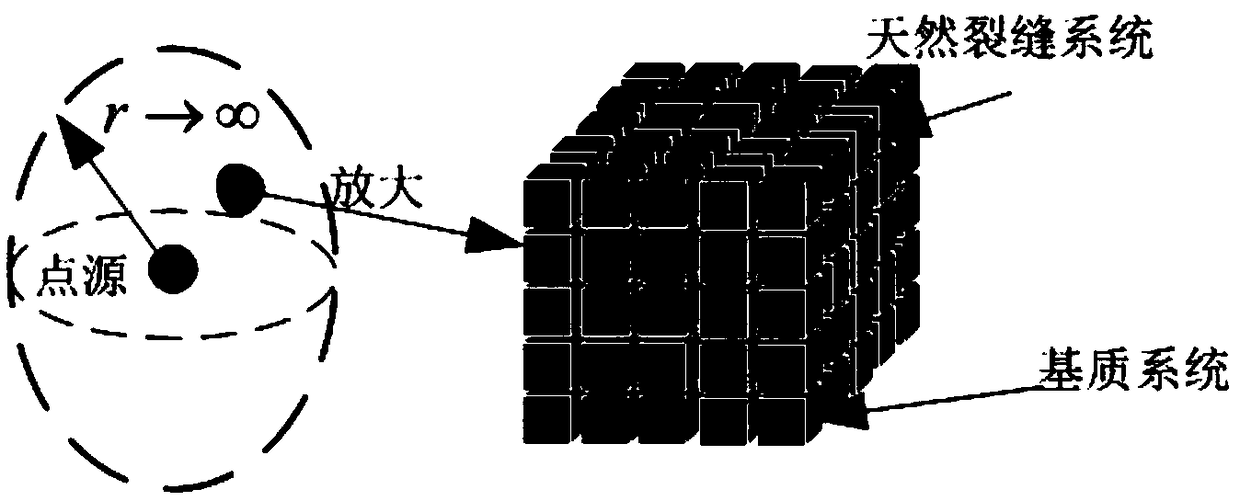
A method for establishing a three-dimensional percolation model of a volume fracturing horizontal well in a tight reservoir
ActiveCN109446649ACalculation speedHigh solution accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelAlgebraic equation
The invention discloses a method for establishing a three-dimensional percolation model of a volume fracturing horizontal well in a tight reservoir, which comprises the following steps of firstly establishing a three-dimensional percolation basic solution based on a boundary element method; establishing a point source physical model of a space of an infinite tight reservoir; establishing the mathematical model corresponding to the physical model of point source, solving the mathematical model to obtain the three-dimensional percolation basic solution; secondly, establishing the seepage model based on the basic solution of three-dimensional seepage; transforming the differential equation of regional seepage into the boundary integral equation; discreting the boundaries into finite-sized boundary elements; discreting the boundary integral equation on the boundary element; and writing the algebraic equation in the form of a matrix equation; depending on whether the boundary stress and flow rate are known, performing the corresponding operation. The invention has the advantages that the three-dimensional seepage flow model is obtained, the influence of the intersection of different fractures and the stress sensitivity of the reservoir is considered, and the influence of the complex fracturing network on the seepage flow can be more truly simulated.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
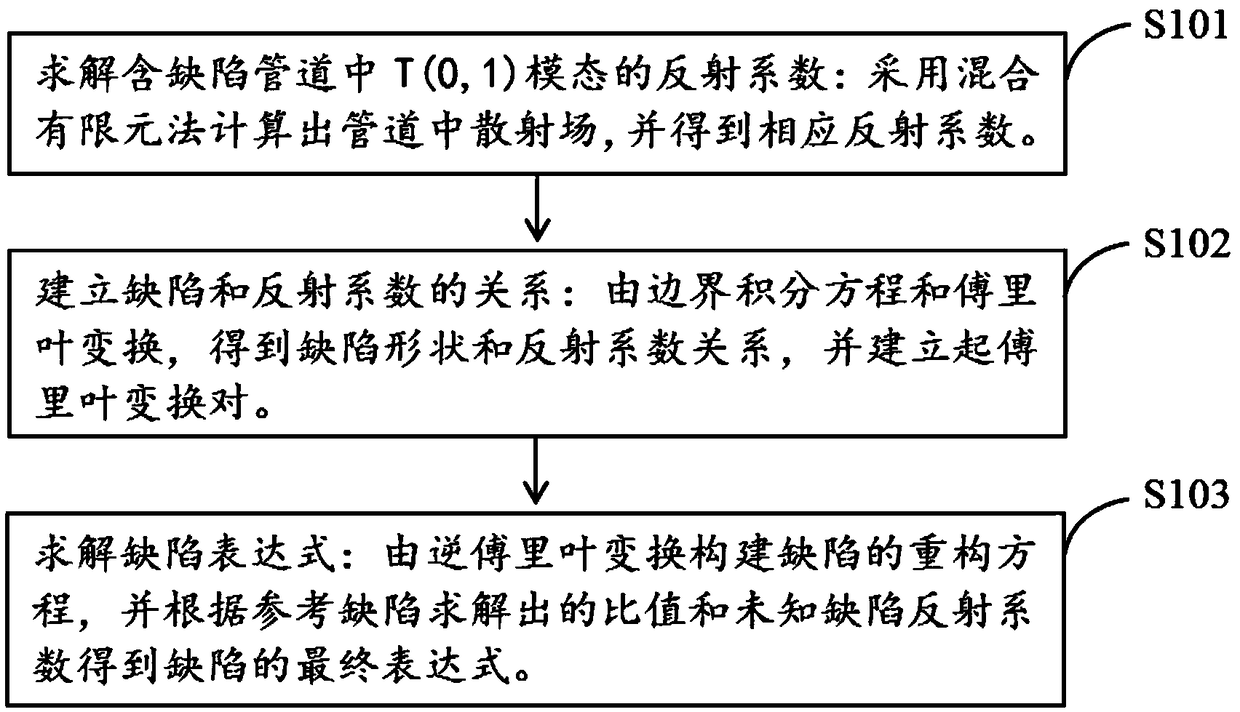
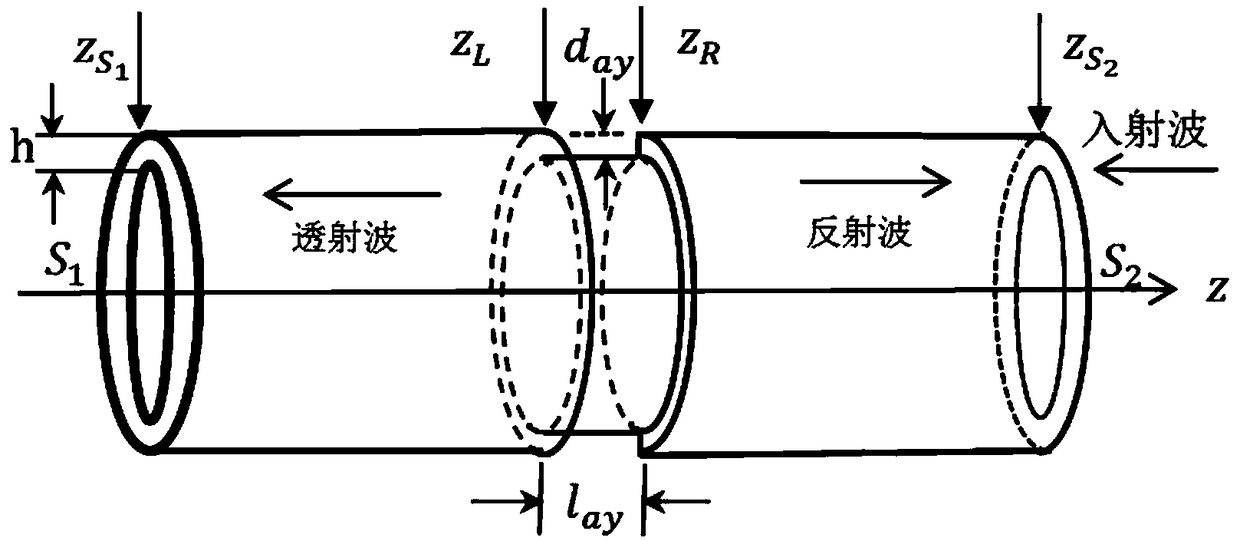
Method of quantitatively detecting pipeline defects based on ultrasonic guided waves
ActiveCN109187769AWeakening the Small Defect AssumptionIncreased sensitivityProcessing detected response signalMixed finite element methodUltrasonic guided wave
The invention discloses a method of quantitatively detecting pipeline defects based on ultrasonic guided waves. The method comprises the following steps of: solving the reflection coefficient of a T (0,1) mode in a pipeline with defects, to be specific, calculating the scattered field in the pipeline by adopting a mixed finite element method and obtaining the corresponding reflection coefficient;establishing the relationship between the defect and the reflection coefficient: to be specific, obtaining the relationship between the defect shape and the reflection coefficient through a boundary integral equation and Fourier transform, and establishing a Fourier transform pair; and solving a defect expression, to be specific, establishing a reconstitution equation of the defect through inverseFourier transform, and obtaining the final expression of the defect according to the ratio solved through the reference detect and the unknown defect reflection coefficient. The method effectively solves the problem that the solving of elementary solution is difficult in the boundary integral equation reconstitution defect method, weakens the restrictive condition in the defect reconstitution, and provides an efficient and easy new method for pipeline detection in practical engineering.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for no-reference quantitative inspection of panel thinning defect based on Lamb wave
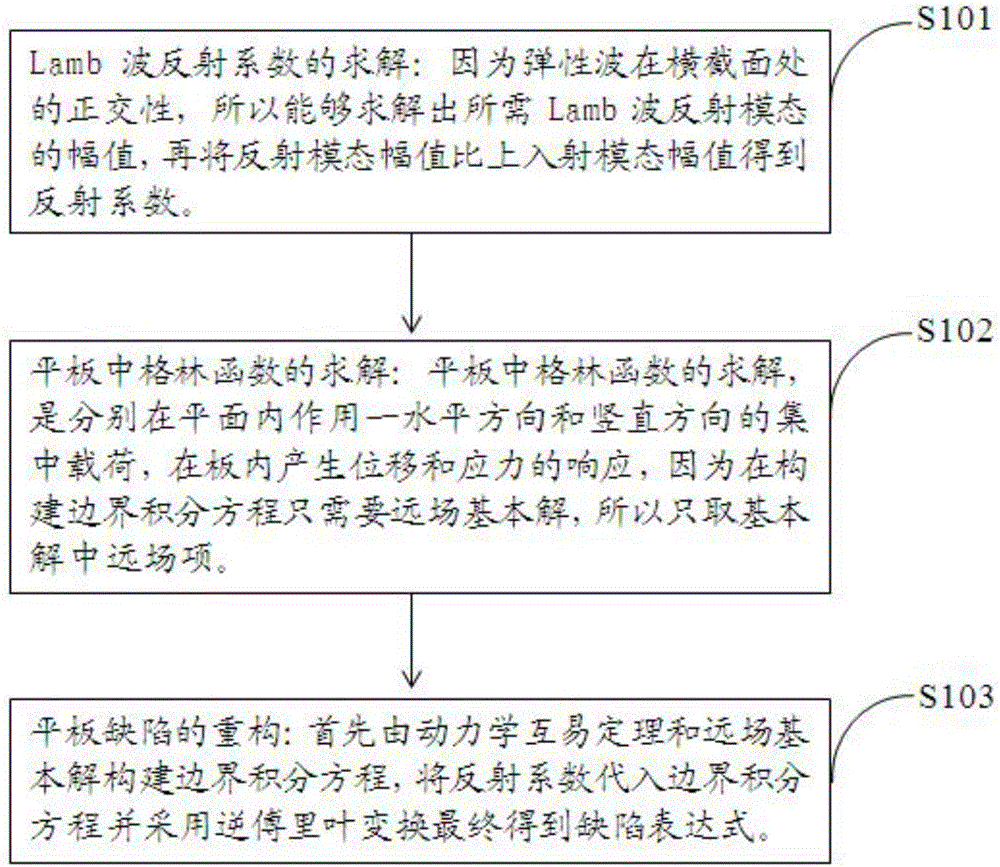
InactiveCN106153724AThe result is accurateAccuracy meetsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalThinningComputer science
The invention discloses a method for no-reference quantitative inspection of panel thinning defect based on Lamb wave. The method comprises the following steps: solving a coefficient of the required Lamb wave reflection modal; solving a green function in a zero-defect panel; constructing a boundary integral equation by use of the dynamics reciprocal theory and far-field basic solution; substituting a reflection coefficient into the boundary integral equation and performing inverse Fourier transform to finally obtain a defect expression; and reconstructing the defect position and shape in the panel. In the invention, the problems of quantitative inspection of panel thinning defect are effectively solved, the panel defect is reconstructed by directly using the reflection information of Lamb wave without referring to any condition in advance, and an efficient and accurate method is provided for engineering quantitative detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
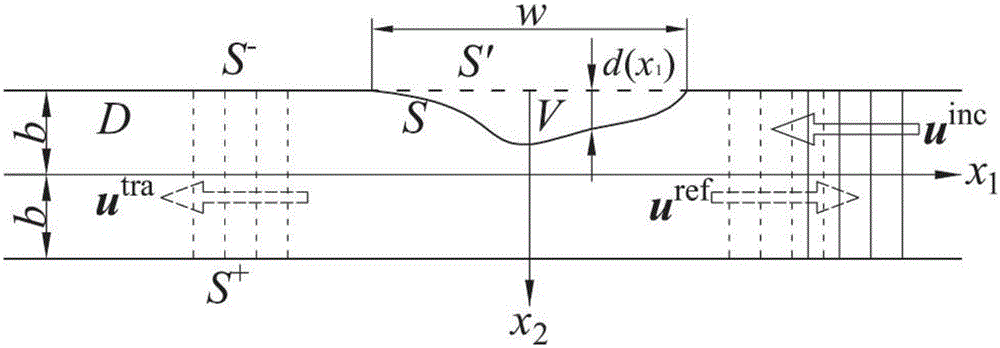
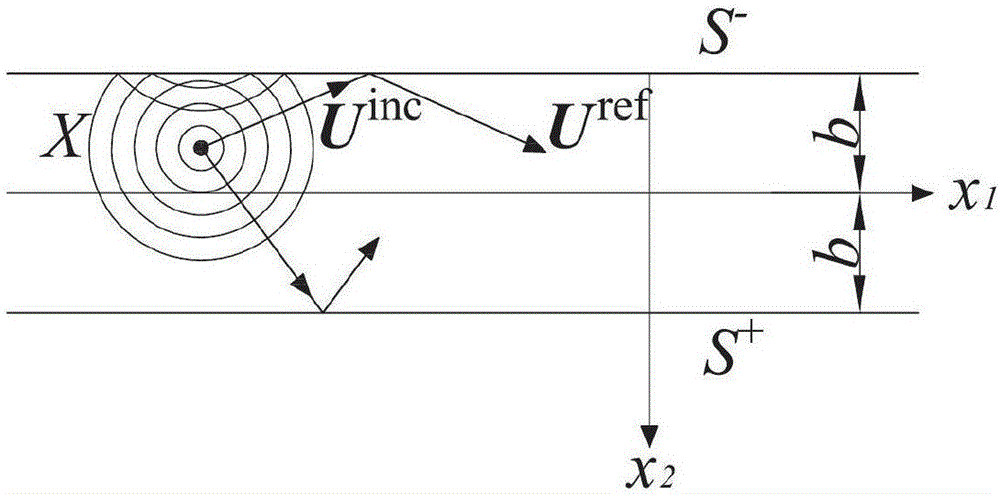
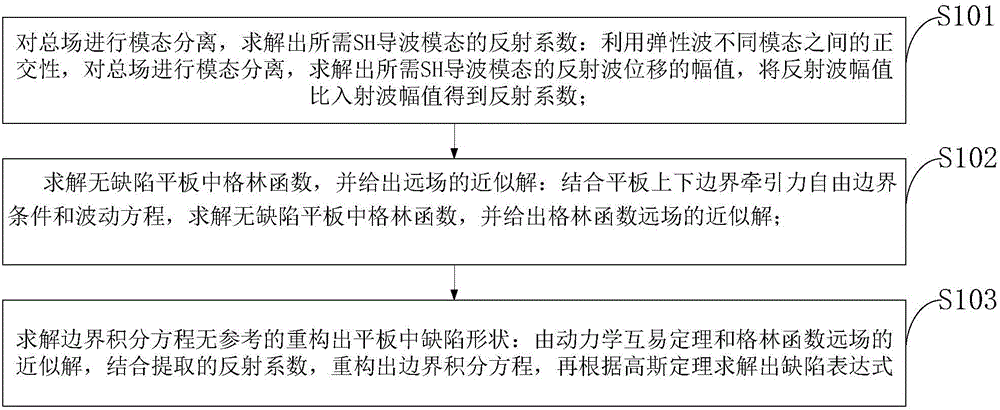
No-reference SH wave guide method used for flat plate thinning defect quantitative detection
InactiveCN106018552AIncreased sensitivityHigh precisionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalEngineeringDefect reconstruction
The invention discloses a no-reference SH wave guide method used for flat plate thinning defect quantitative detection. Defect reconstruction is conducted on a flat plate by means of no-reference SH wave guide, and the specific position and shape of a defect are given. The method includes the steps that mode separation is conducted on a total field, and a reflection coefficient of a required SH wave guide mode is obtained; a green function in the no-defect flat plate is solved, and a approximate solution of a far field is obtained; a boundary integral equation is solved, and the shape of the defect in the flat plate is reconstructed in a no-reference mode. The method relates to a quantitative detection technology, people do not need to refer to the approximate position of the defect in advance, a defect expression is directly induced theoretically, a whole component can be detected at a time, an efficient and precise scheme is provided for ultrasonic wave guide quantitative detection, the method has important application value in engineering, and a whole structure can be detected at a time. Detection can be conducted without removing coating and insulating layers, and complex rotating and walking devices are not needed. Defect sensitivity and precision are high, energy consumption is low, and the method is economical.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for evaluating micro-defect working stress of large casting and forging
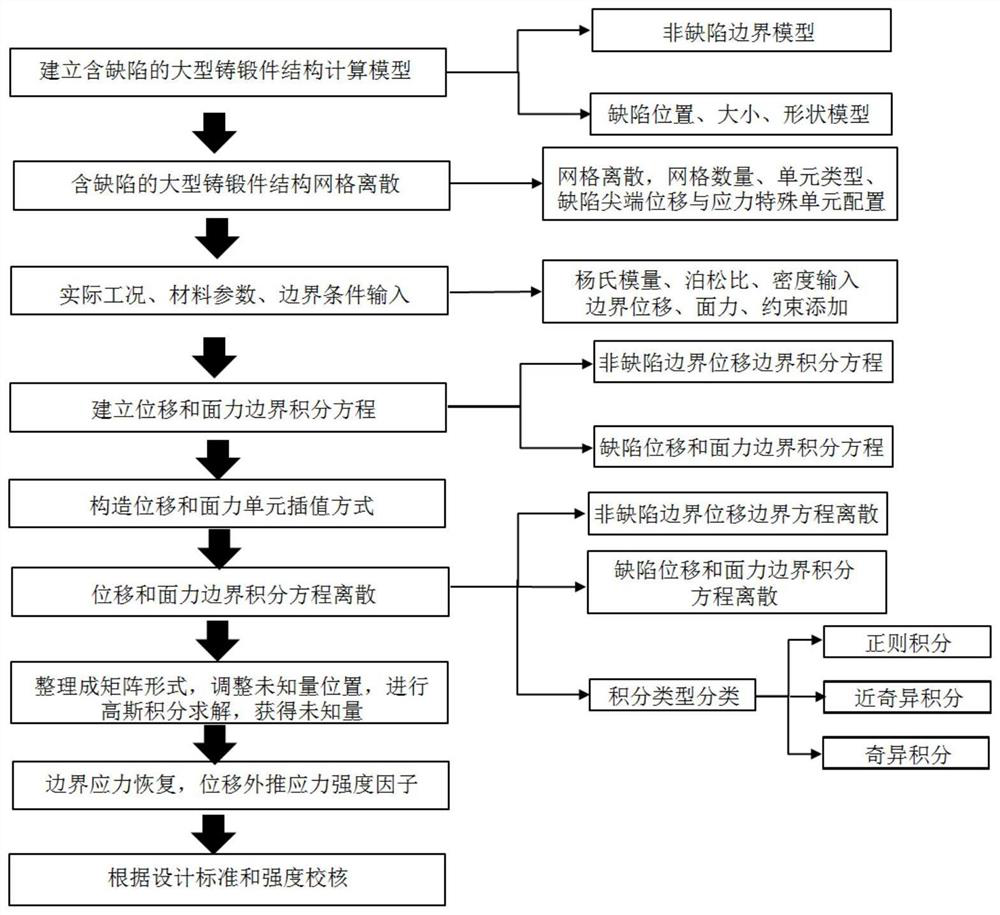
ActiveCN112257197ASimulation is accurateReduce singularityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStress intensity factorEngineering
The invention relates to a method for evaluating micro-defect working stress of a large-scale casting and forging, which comprises the following steps of: obtaining the size, position and shape of a defect in a large-scale casting and forging structure by using an ultrasonic detection technology, establishing a calculation model of the large-scale casting and forging structure with the defect, andcorrecting a dual reciprocal boundary integral equation. The method has the advantage that only one crack surface is discrete in a displacement discontinuity method, and also has the universality advantage of a traditional dual boundary element method. In the application of the large-scale casting and forging structure, corresponding stress and stress intensity factors can be obtained only by inputting the calculation grid model of the large-scale casting and forging structure with defects, corresponding material parameters, boundary conditions, unit types and concerned areas, and display analysis is carried out.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
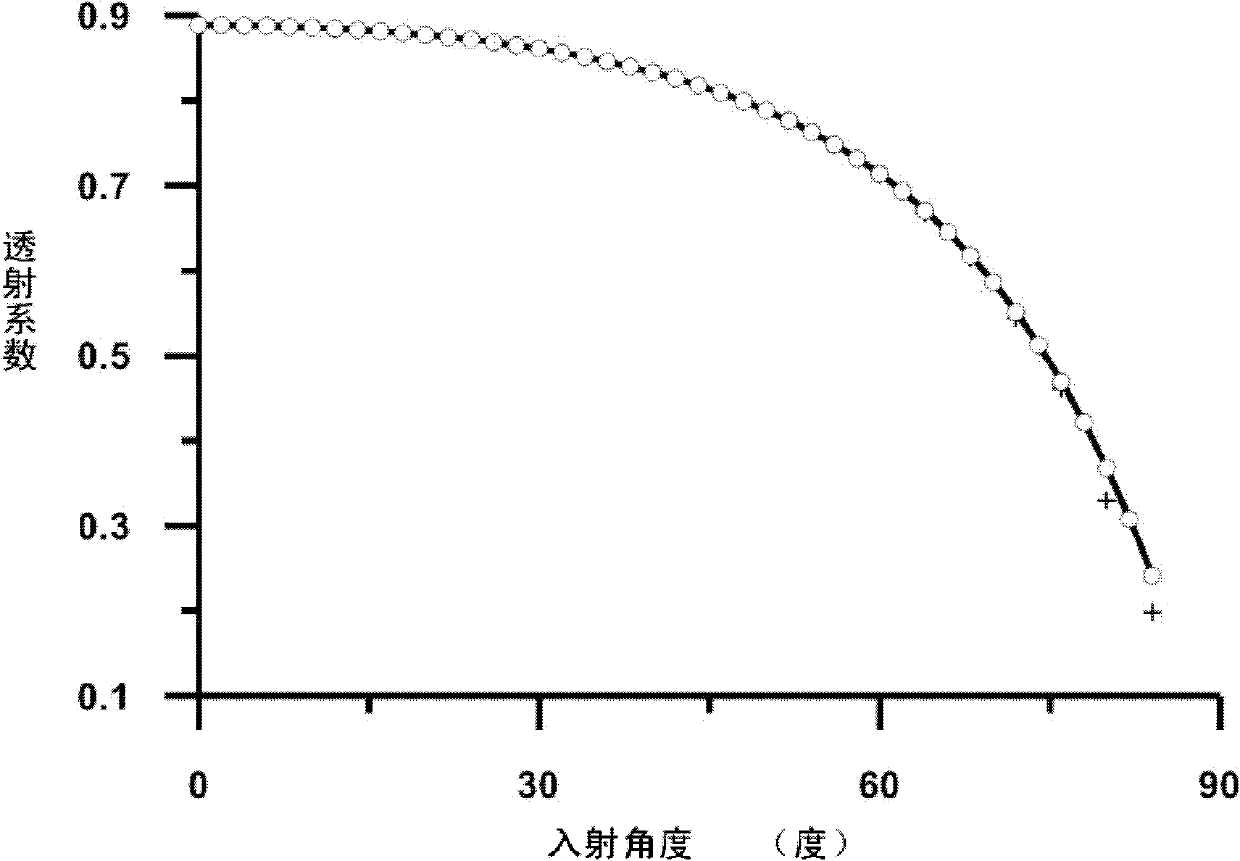
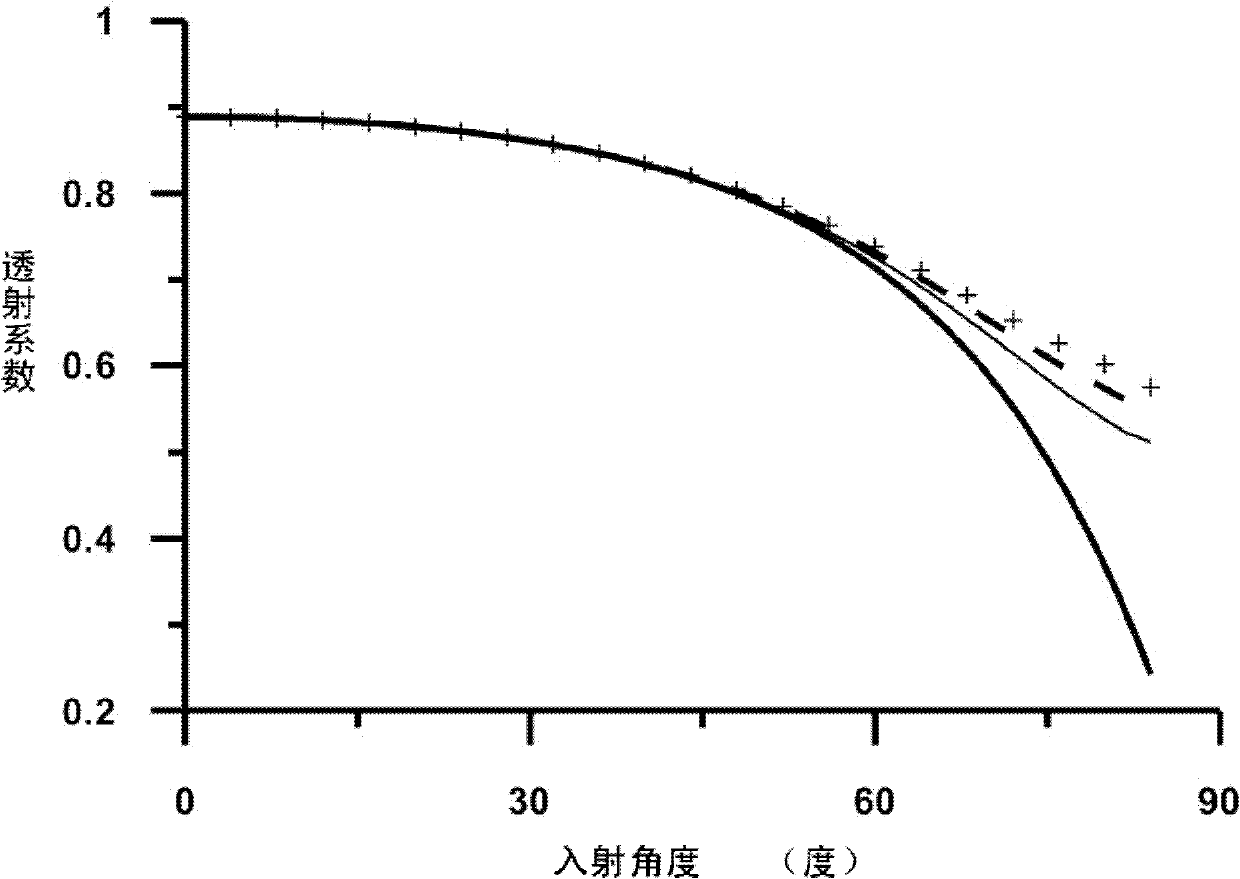
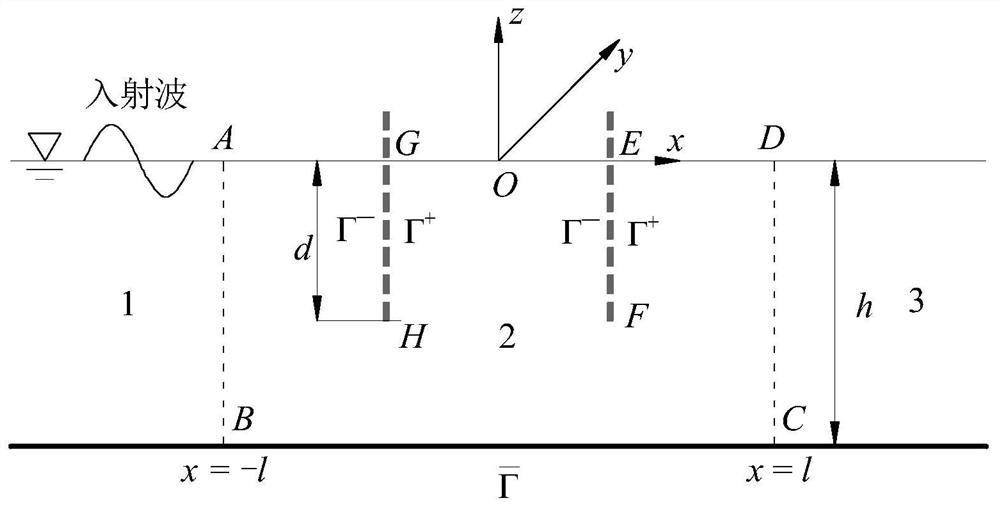
Hydrodynamic analysis method and device for ocean structure with perforated plate by considering wave incident angle
ActiveCN113392598AReduce complexityReduce mesh countDesign optimisation/simulationAngle of incidenceAlgebraic equation
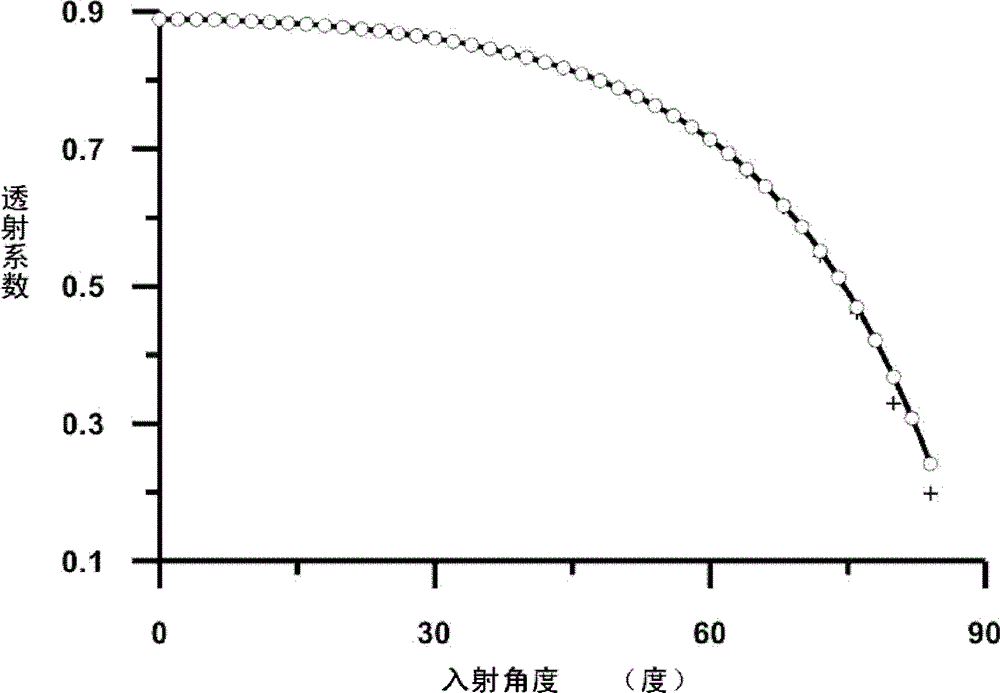
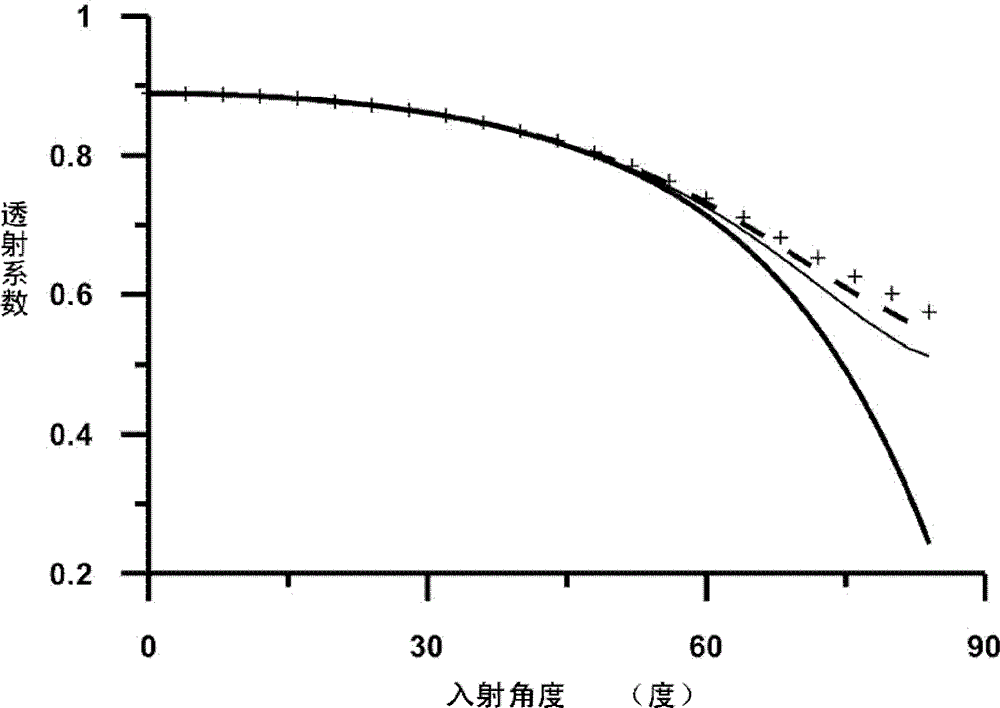
The invention provides a hydrodynamic analysis method and device for an ocean structure with a perforated plate by considering a wave incident angle, and belongs to the technical field of hydrodynamic analysis. A drainage basin where the perforated plate is located is divided into three areas, in the second area, the speed potential of an oblique incident wave and the normal derivative of the speed potential meet a singular boundary integral equation and a super singular boundary integral equation, the boundary of the second area is discretized into N units, an algebraic equation set is established through the discretized boundary integral equation, corresponding boundary conditions are combined, and the algebraic equation set is solved to obtain the velocity potential of each unit after discretization and the velocity potential external normal derivative, and further solving is carried out to obtain the reflection coefficient, the transmission coefficient and the wave force of the ocean structure with the perforated plate. According to the method, the hydrodynamic characteristics of the structure with the perforated plate under the action of the oblique waves can be rapidly and reasonably analyzed, and important reference is provided for actual engineering design.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Boundary element analytic method and a boundary element analytic program
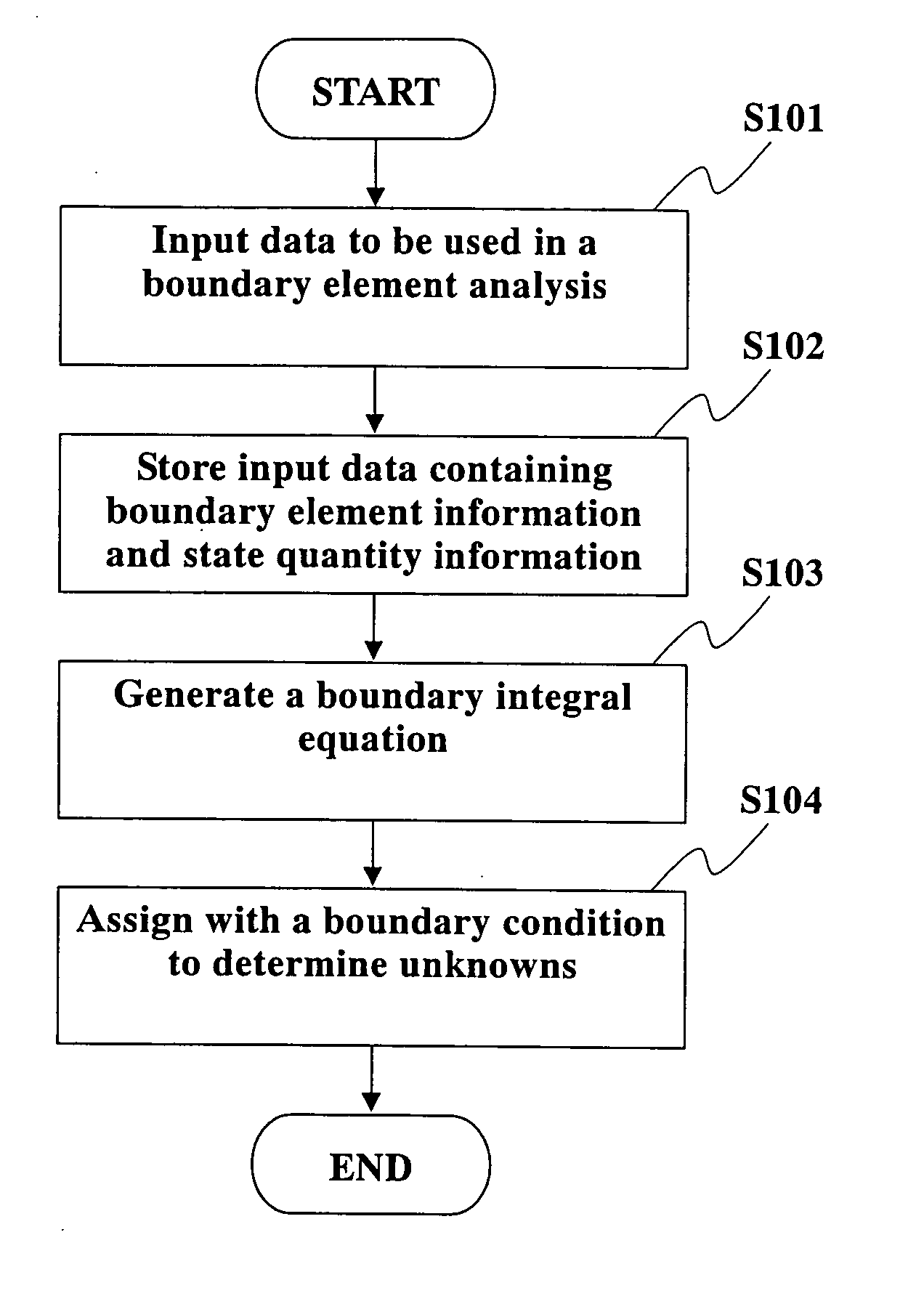
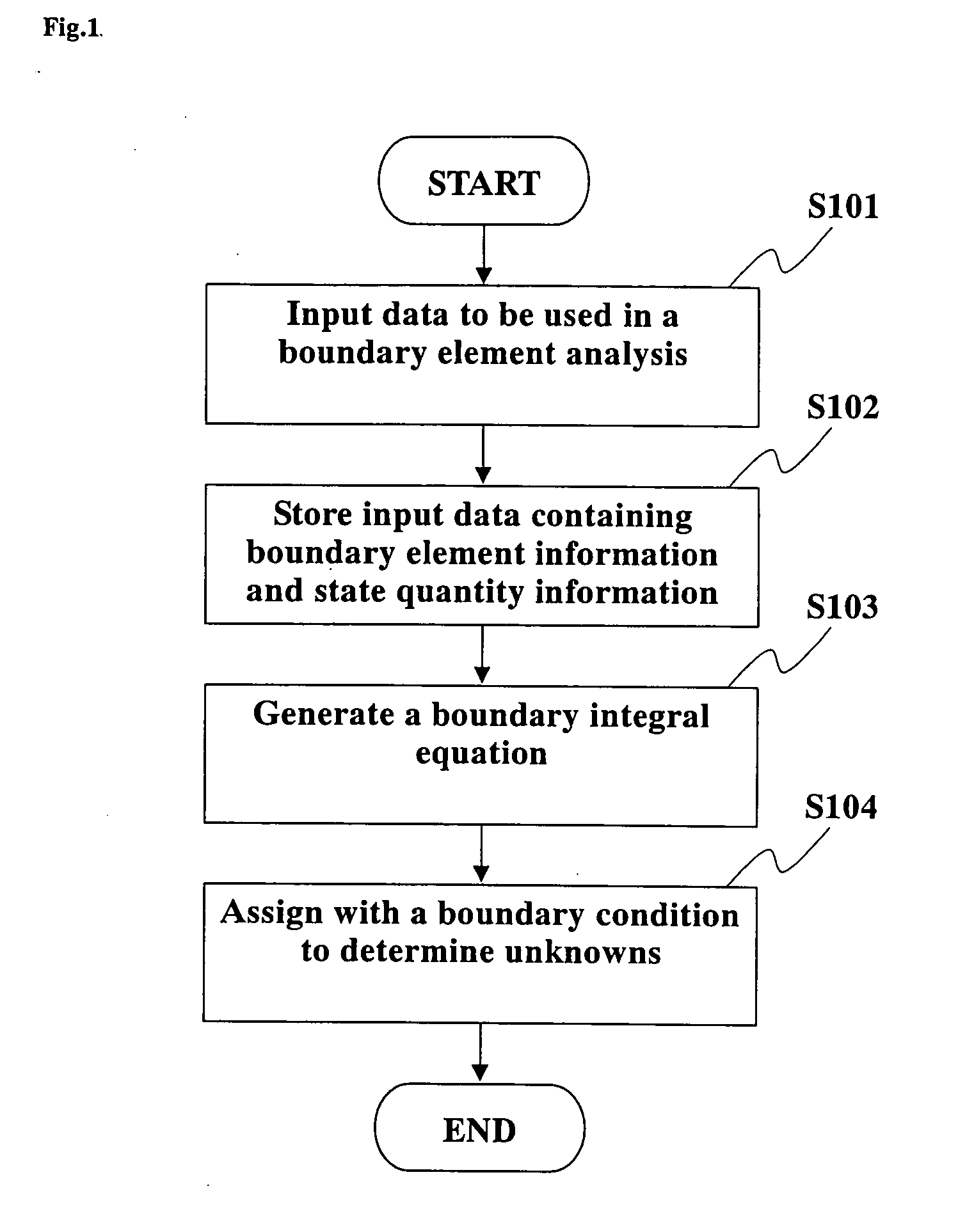
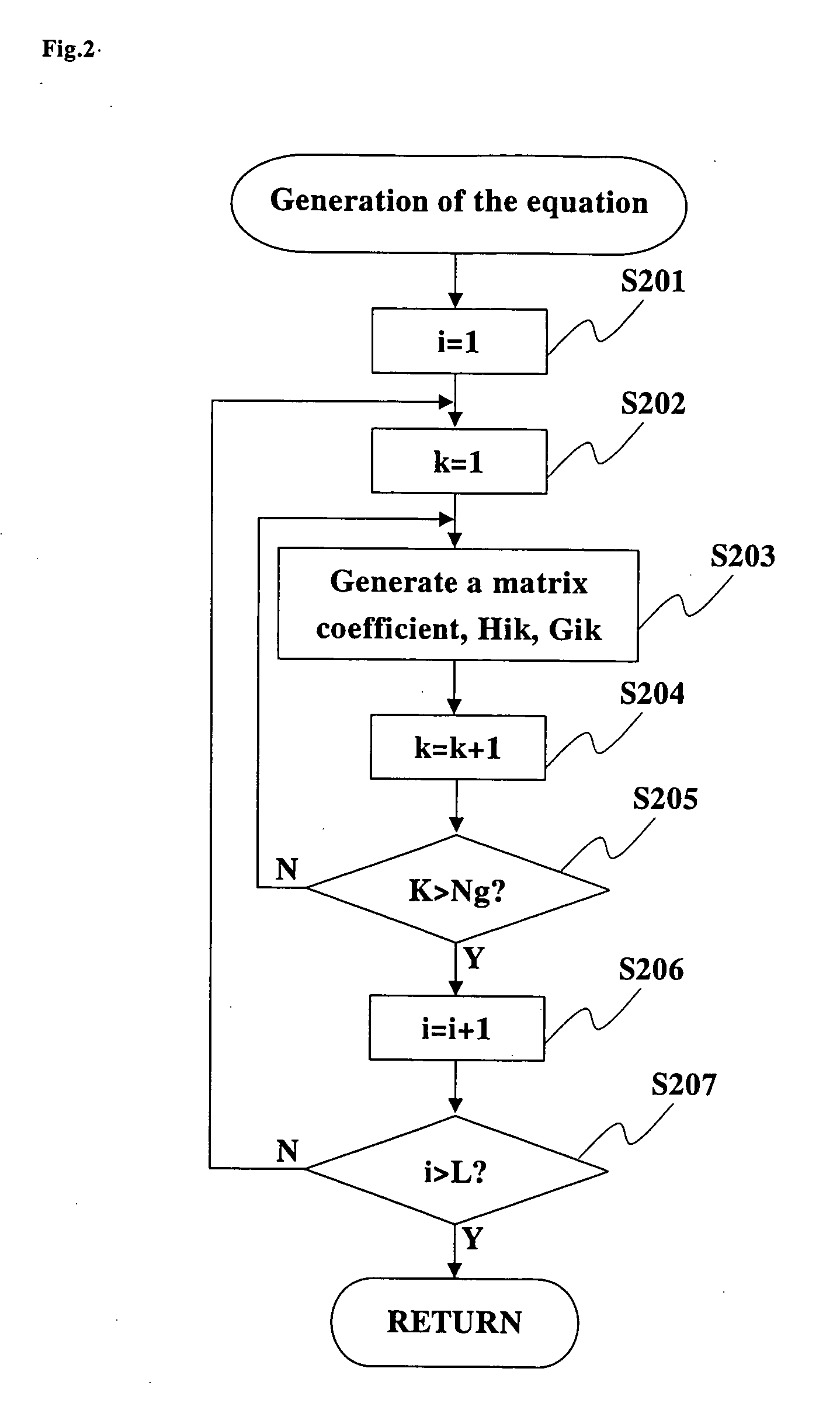
InactiveUS20060004552A1Efficient analysisReduce in quantityComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationBoundary valuesElement analysis
An object of the present invention is to provide a boundary element analytic method and a boundary element analytic program, which are capable of coping with the problem of diversity in symmetric property to be encountered when carrying out an analytic operation by taking advantage of the symmetric property of a subject to be analyzed, and thus providing an efficient analysis. Various types of data for the use in the boundary element analysis, which have been previously input at step S101, are stored at step S102. To carry out this operation, at least boundary element definition information for defining a boundary element in the subject to be analyzed and state quantity information in which boundary element identification information for identifying the defined boundary element is associated with the boundary element for each state quantity thereof. At step 103, the input different types of data are used to generate a digitized boundary integral equation with a boundary value at a point of element on each defined boundary element taken as a variable. Then, at step S104, the generated boundary integral equation is assigned with the input boundary condition to sort out any unknowns, thus obtaining the simultaneous equations. The obtained simultaneous equations are then solved to determine respective values for the unknowns.
Owner:EBARA CORP +1
A Method of Image Boundary Element Processing
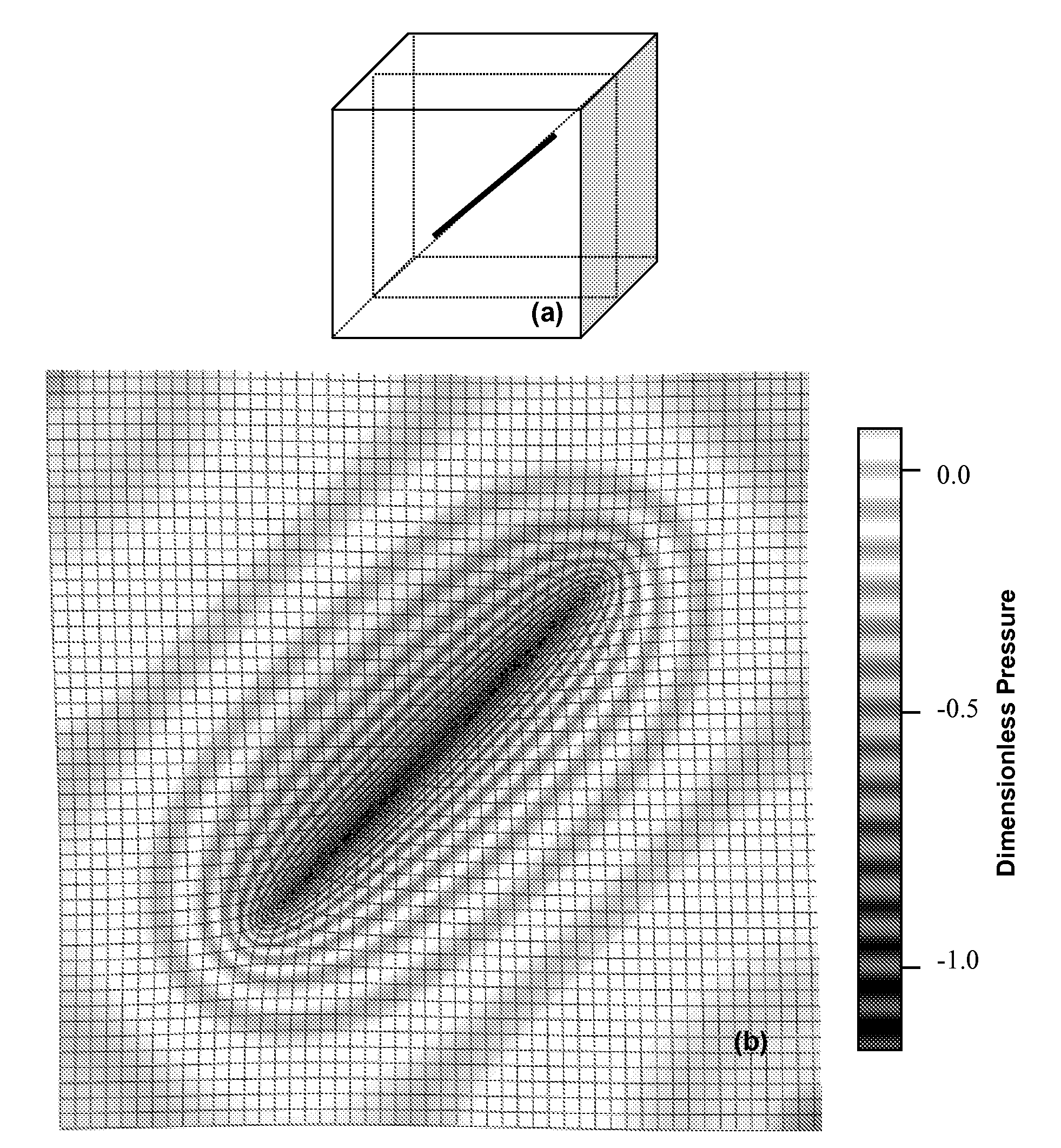
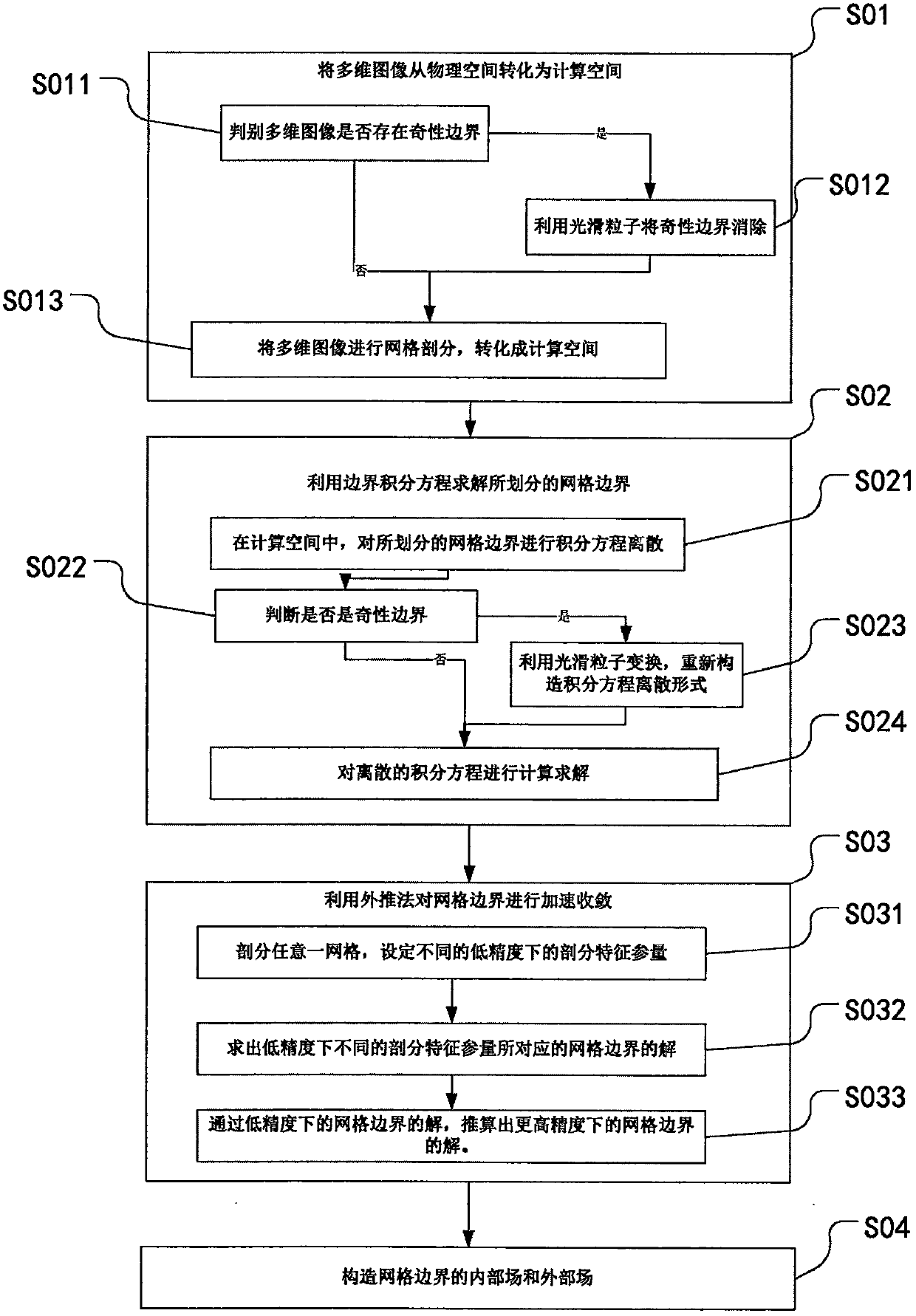
ActiveCN106201995BReduce processingReduce the amount of calculationComplex mathematical operations3D modellingPhysical spaceParticle method
The invention discloses an image boundary element processing method. The image boundary element processing method comprises the following steps of: S01, converting a multi-dimensional image from a physical space to a computing space, wherein the step S01 comprises the following steps of: S011, judging whether the multi-dimensional image has a singularity boundary or not, if so, entering the step S012, and if not, entering the step S013; S012, eliminating the singularity boundary by utilizing a smoothed particle, and entering the step S013; and S013, performing mesh generation of the multi-dimensional image, and converting into the computing space; S02, solving a divided mesh boundary by utilizing a boundary integral equation; S03, performing accelerated convergence of the mesh boundary by utilizing an extrapolation method; and S04, constructing an internal field and an external field of the mesh boundary. According to the image boundary element processing method disclosed by the invention, the physical space of the image is converted into the computing space by utilizing a smoothed particle method; the converted computing space is suitable for the extrapolation method; therefore, the computing precision is increased; and the mesh processing number is reduced.
Owner:苏州中源广科信息科技有限公司
Boundary condition setting method for processing irregular frequency in ship hydrodynamic calculation
ActiveCN112257177ASolve the problem of mutationEliminate irregular frequenciesGeometric CADSustainable transportationClassical mechanicsHydroelasticity
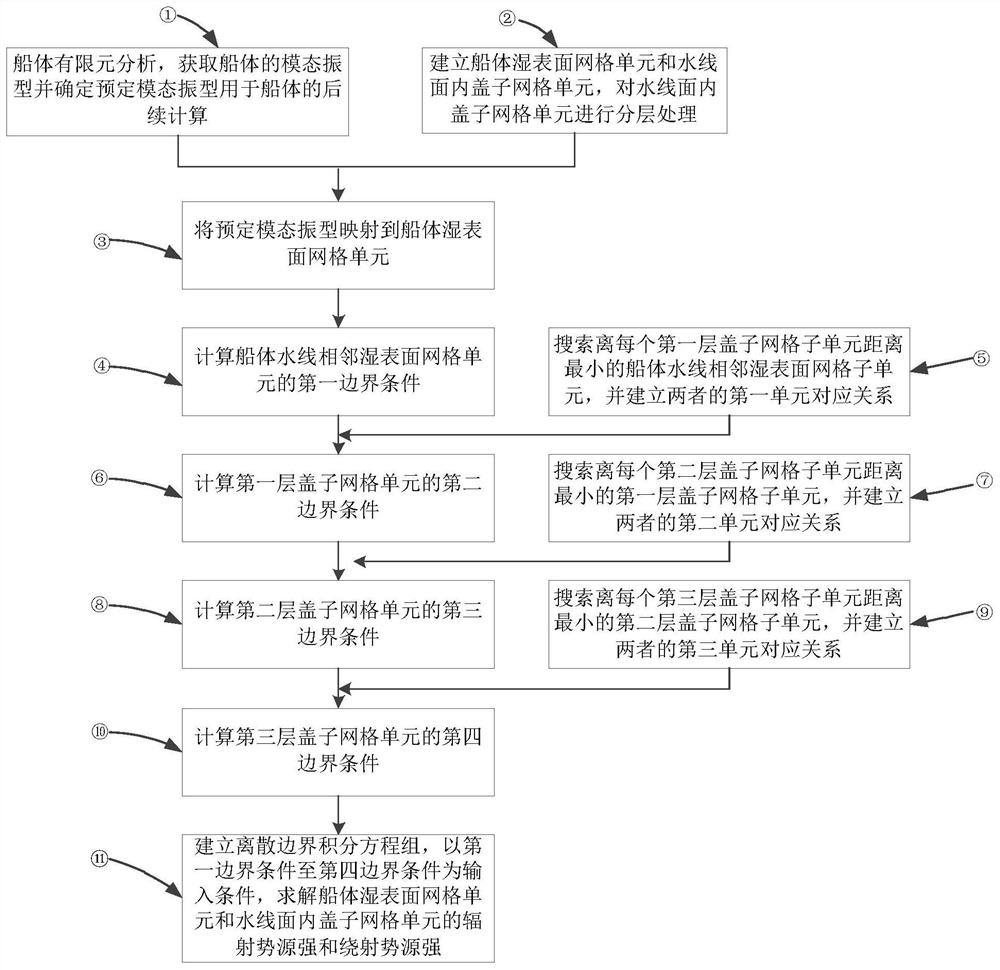
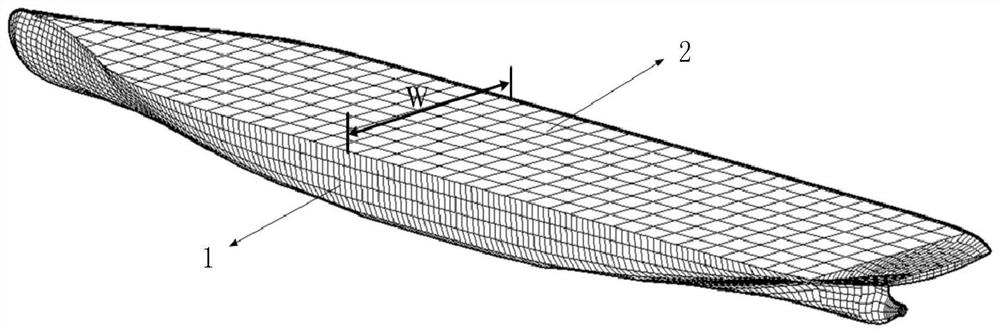
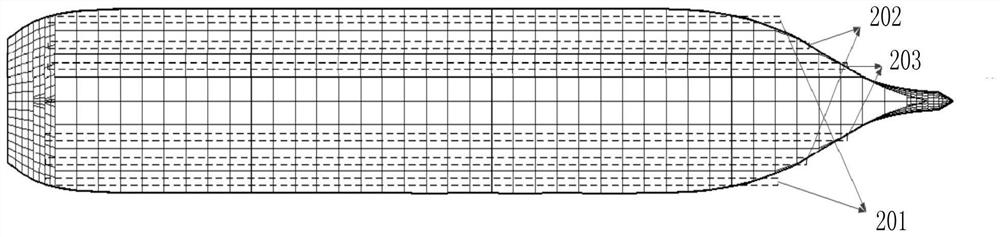
The invention discloses a boundary condition setting method for processing irregular frequency in ship hydrodynamic calculation, and relates to the field of ship hydrodynamic calculation. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring three unit correspondence relationships enabling the distance between every two subunits in a hull wet surface grid unit, a first-layer cover grid unit, a second-layer cover grid unit and a third-layer cover grid unit which are adjacent to a hull waterline to be minimumbased on the three-dimensional hydroelasticity equations of the hull and the three-dimensional boundary element method. expanding a boundary integral equation by adopting a method of scaling and assigning boundary conditions on the layered cover grid units, so so to further solve the radiation potential source intensity and diffraction potential source intensity of the hull wet surface grid units and the cover grid units in the waterline plane. The sudden change problem of boundary conditions of hull wet surface grids and capping grids is solved; the application of the irregular frequency elimination method in ship hydrodynamic force calculation is achieved.
Owner:CHINA SHIP SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH CENTER (THE 702 INSTITUTE OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDUSTRY CORPORATION)
Method for obtaining radar cross section (RCS) of homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object
InactiveCN102508220BUniform Scattering Cross SectionScattered field stabilizationWave based measurement systemsMagnetic sourceRao wilton glisson
The invention relates to the field of electromagnetic wave and radar monitoring and provides a method for obtaining radar cross section (RCS) of a homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object. The method comprises the following steps of: building a geometrical model of the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object and dividing the surface of the model into a plurality of triangular patches in seamless connection; introducing a planar power source vector function and a planar magnetic source vector function; applying a field decomposition method in the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object; obtaining a boundary integral equation on the surface of a scatterer according to the boundary conditions; applying a moment method to carry out numerical solution on the boundary integral equation, including space test and time test; adopting RWG (Rao-Wilton-Glisson) basis functions as the spatial basis function and test function and adopting Laguerre functions with amplitude factors as the temporal basis function and test function; and obtaining electromagnetic scattering of an observation point according to the equivalence principle and then applying Fourier transform to obtain the RCS. The method has the following advantages that: the obtained scattered field of the homogeneous bi-isotropic medium object is stable; and the RCS with wide frequency range can be obtained.
Owner:郑州微纳科技有限公司
Shape-changing object real-time simulation system of virtual operation system
InactiveCN101295409BImprove interactivityHigh precision2D-image generation3D modellingShape changeKinematics equations
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
A plate structure-acoustic field coupling analysis method
ActiveCN104951596BUnit quality requirements are lowReduce roughnessSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringAnalysis method
The invention discloses a plate structure-sound field coupling analysis method. The method includes the steps that a finite element method and a radial point interpolation method are combined, and dispersing is conducted on a system kinetic equation of a plate structure; a boundary integral equation of a sound field domain is established according to a boundary element method; a structure-sound field coupling equation is established according to a dispersed system kinetic equation, the boundary integral equation and the structure-sound field coupling boundary condition. The invention further discloses a plate structure-sound field coupling analysis device corresponding to the plate structure-sound field coupling analysis method and a computing device with the plate structure-sound field coupling analysis device.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Ship motion prediction method based on Taylor expansion boundary element method
ActiveCN109446634BRapid Prediction of Hydrodynamic CoefficientsGeometric CADSustainable transportationClassical mechanicsImpulse response
The invention provides a ship motion prediction method based on the Taylor expansion boundary element method. Read the grid file and perform hydrostatic calculation; calculate the influence coefficient matrix of the boundary integral equation required by the Taylor expansion boundary element method; Its space normal derivative solution; radiation velocity potential instantaneous term and its spatial first and second derivative solutions; radiation velocity potential memory term and its space first and second derivative solutions; additional mass, wave damping, radiation wave force impulse response function Solving; full wave downward incident velocity potential impulse response function solving; diffraction velocity potential and its spatial first and second derivatives, diffraction wave force impulse response function solving; full wave direction ship motion solution; ship motion spectrum under various sea conditions analysis caculate. The invention can predict the hydrodynamic coefficient of the three main ship types, the wave load, the six-degree-of-freedom motion of the ship in the full wave direction, and the analysis of the ship motion spectrum under various sea conditions.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Seismic migration method for coupled transmission coefficient
ActiveCN102608659BAccurately obtainedAchieving transmission loss compensationSeismic signal processingSeismic migrationWave field
The invention relates to a seismic migration method for a coupled transmission coefficient, which comprises the following steps of: 1) dividing different depth layers by taking the earth surface as an initial point, namely dividing underground media to be explored into different depth layers according to different depth intervals, and assuming the different depth intervals of the underground media to be explored as different horizontal sheets, wherein the thickness of the horizontal sheets is the depth interval of the underground media to be explored; 2)based on a Lippmann-Schwinger integral equation, solving the Lippmann-Schwinger equation by establishing an integral equation of an upper boundary gamma1 and a lower boundary gamma2 of a seismic wave field in in the closed area omega of any horizontal sheet; 3) establishing a boundary integral equation at the lower boundary gamma2 of the closed area omega according to a transmission effect of the lower boundary gamma2 of the horizontal sheet; and 4) solving a seismic migration wave field according to the transmission and reflection effects between the horizontal sheets and of the upper boundaries and lower boundaries of the horizontal sheets. The seismic migration method can be widely applied to a seismic migration technology for imaging a complex oil exploration structure.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com