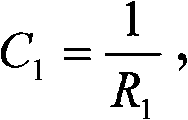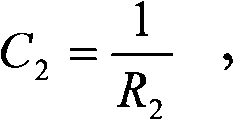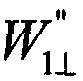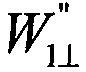Patents
Literature
42 results about "Symmetric property" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Measuring overlay and profile asymmetry using symmetric and anti-symmetric scatterometry signals
Systems and methods are disclosed for using ellipsometer configurations to measure the partial Mueller matrix and the complete Jones matrix of a system that may be isotropic or anisotropic. In one embodiment two or more signals, which do not necessarily satisfy any symmetry assumptions individually, are combined into a composite signal which satisfies a symmetry assumption. The individual signals are collected at two or more analyzer angles. Symmetry properties of the composite signals allow easy extraction of overlay information for any relative orientation of the incident light beam with respect to a 1D grating target, as well as for targets comprising general 2D gratings. Signals of a certain symmetry property also allow measurement of profile asymmetry in a very efficient manner. In another embodiment a measurement methodology is defined to measure only signals which satisfy a symmetry assumption. An optional embodiment comprises a single polarization element serving as polarizer and analyzer. Another optional embodiment uses an analyzing prism to simultaneously collect two polarization components of reflected light.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
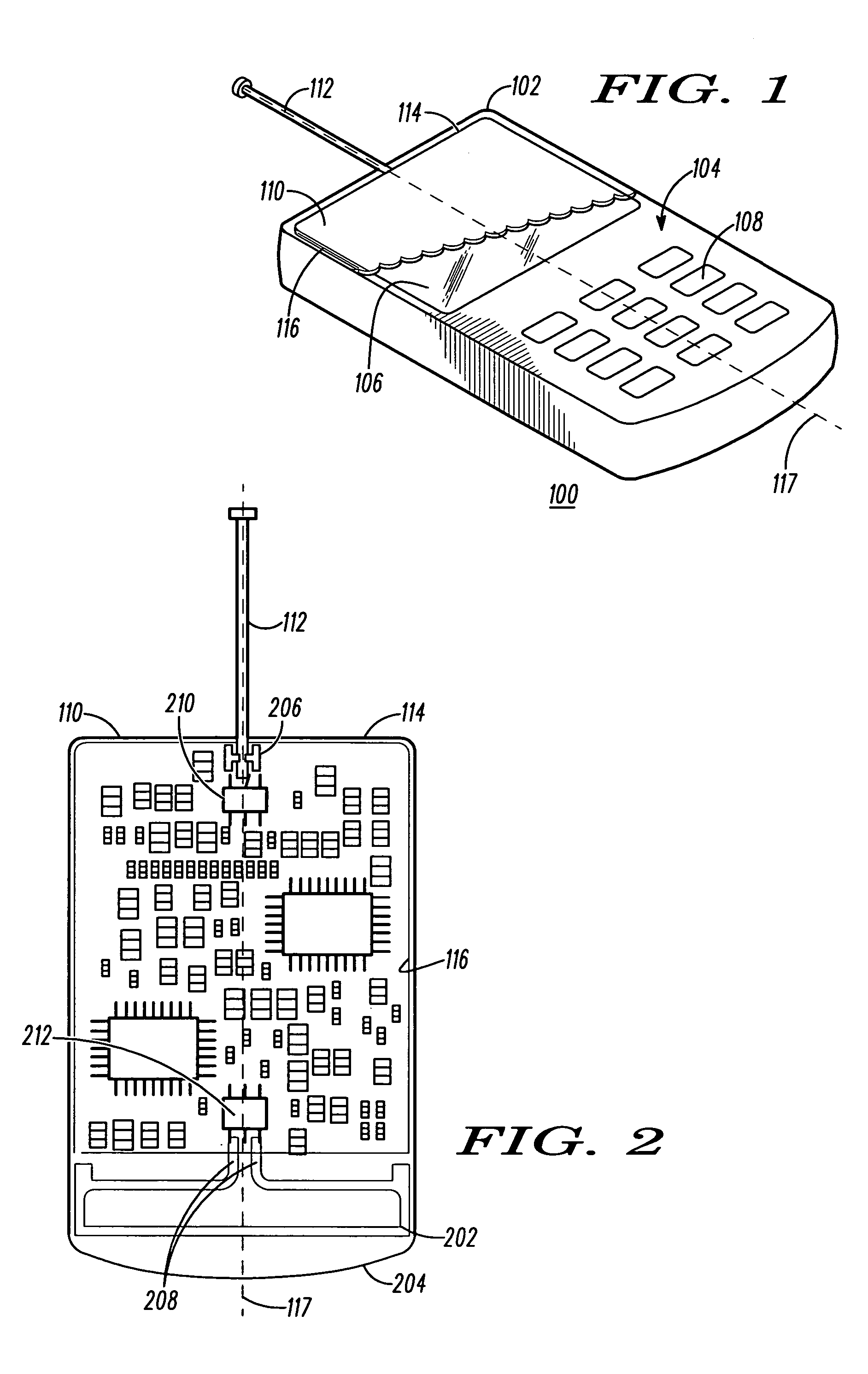
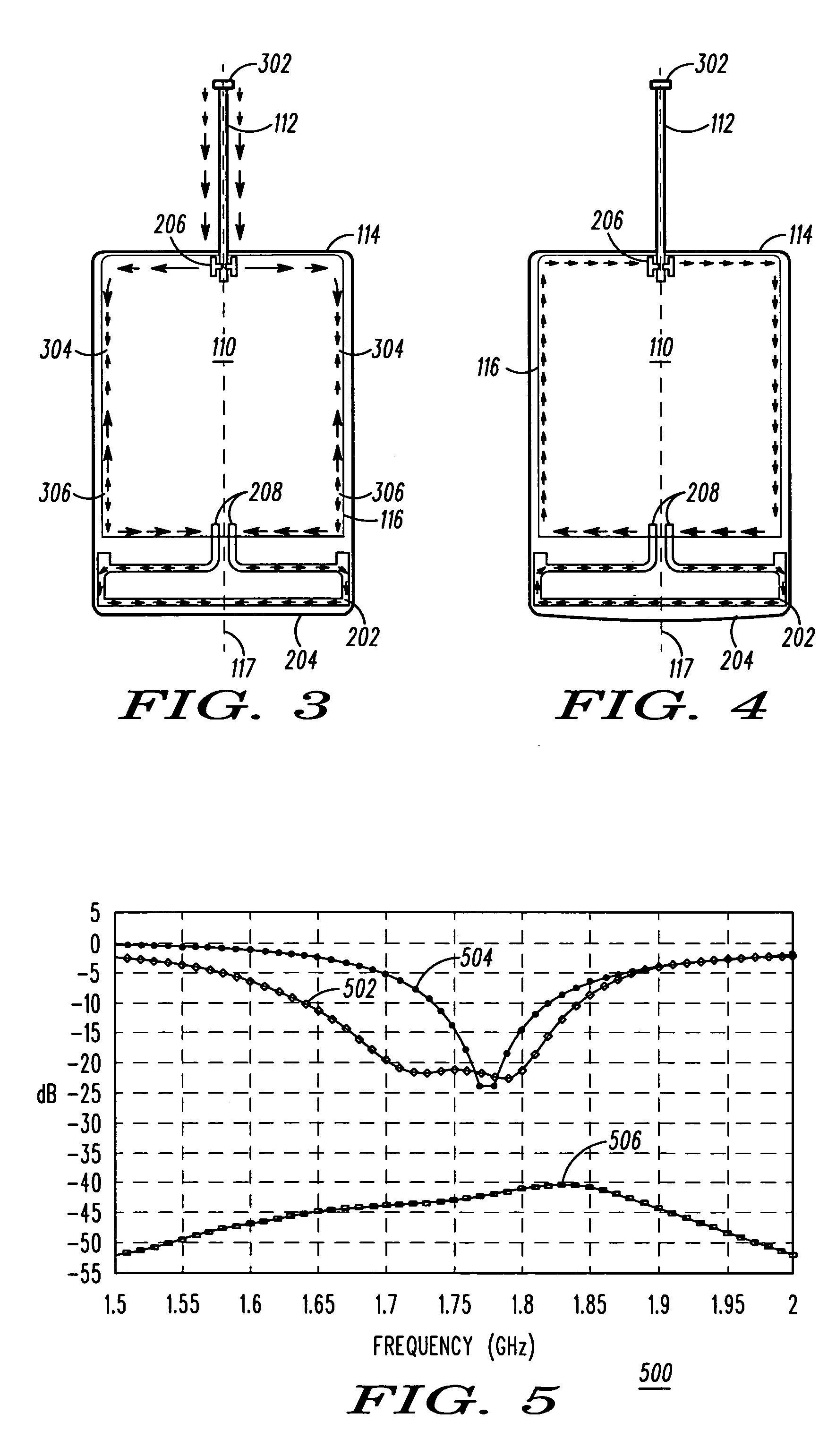
Multi-antenna handheld wireless communication device
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
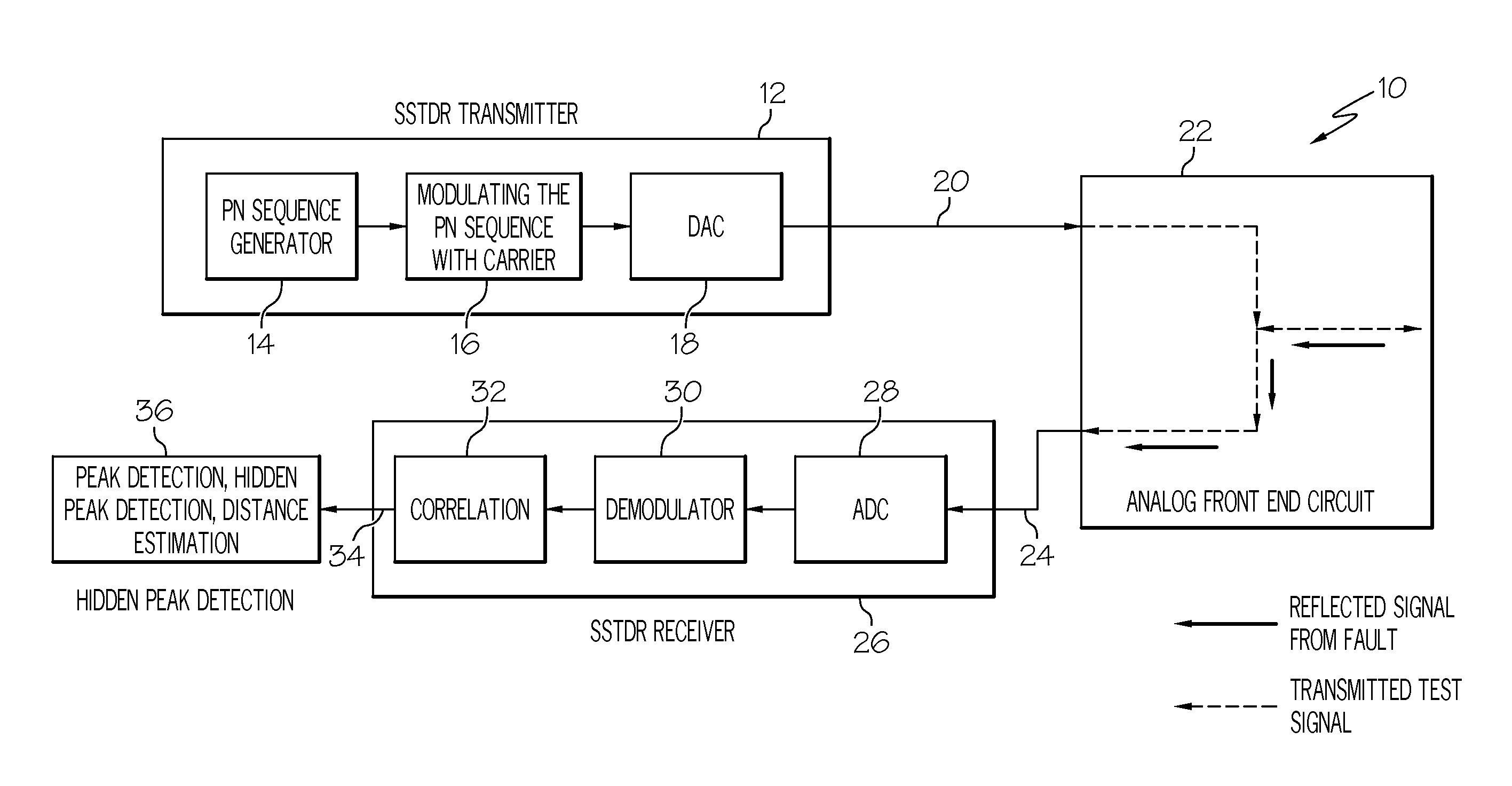
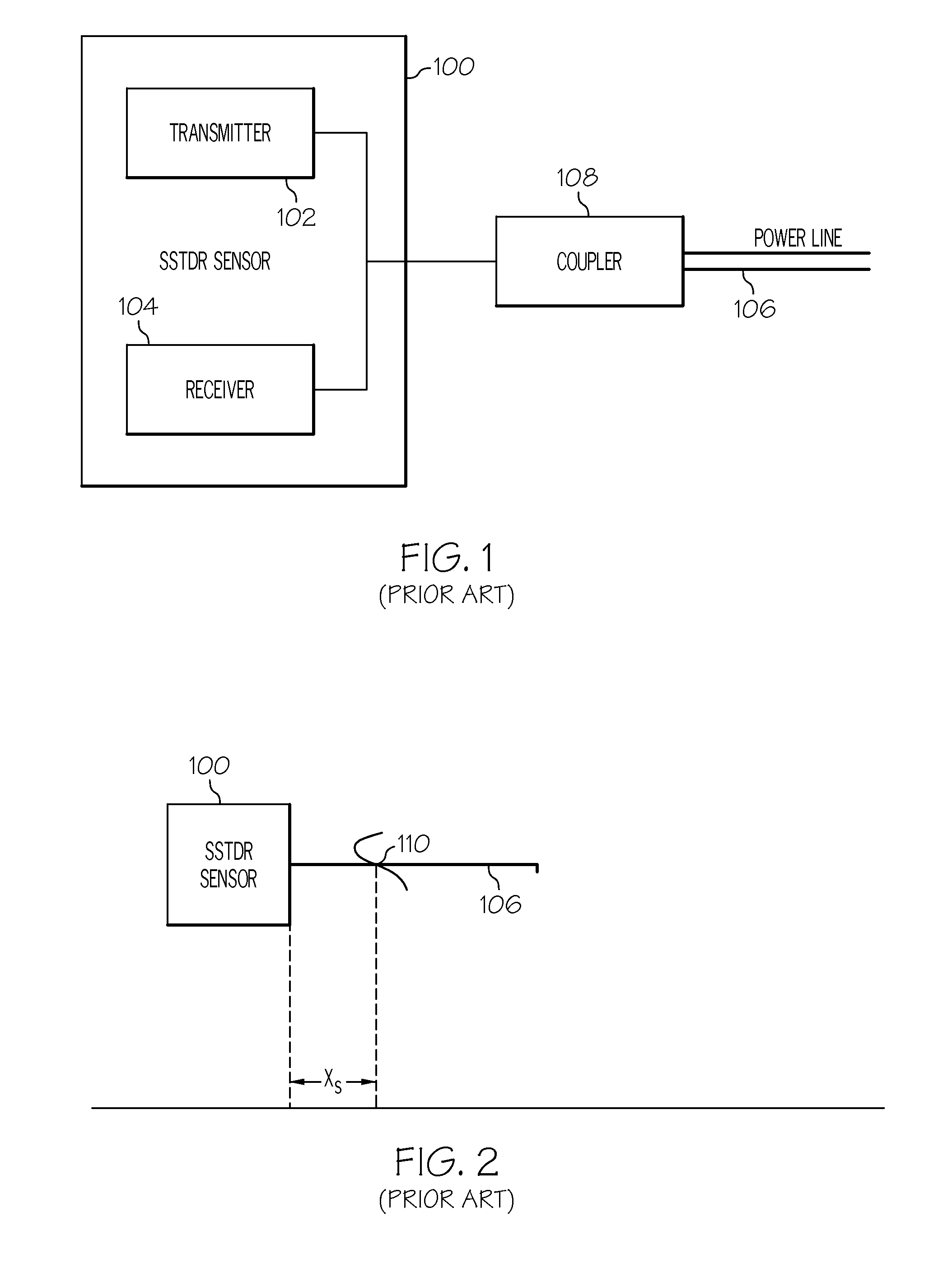
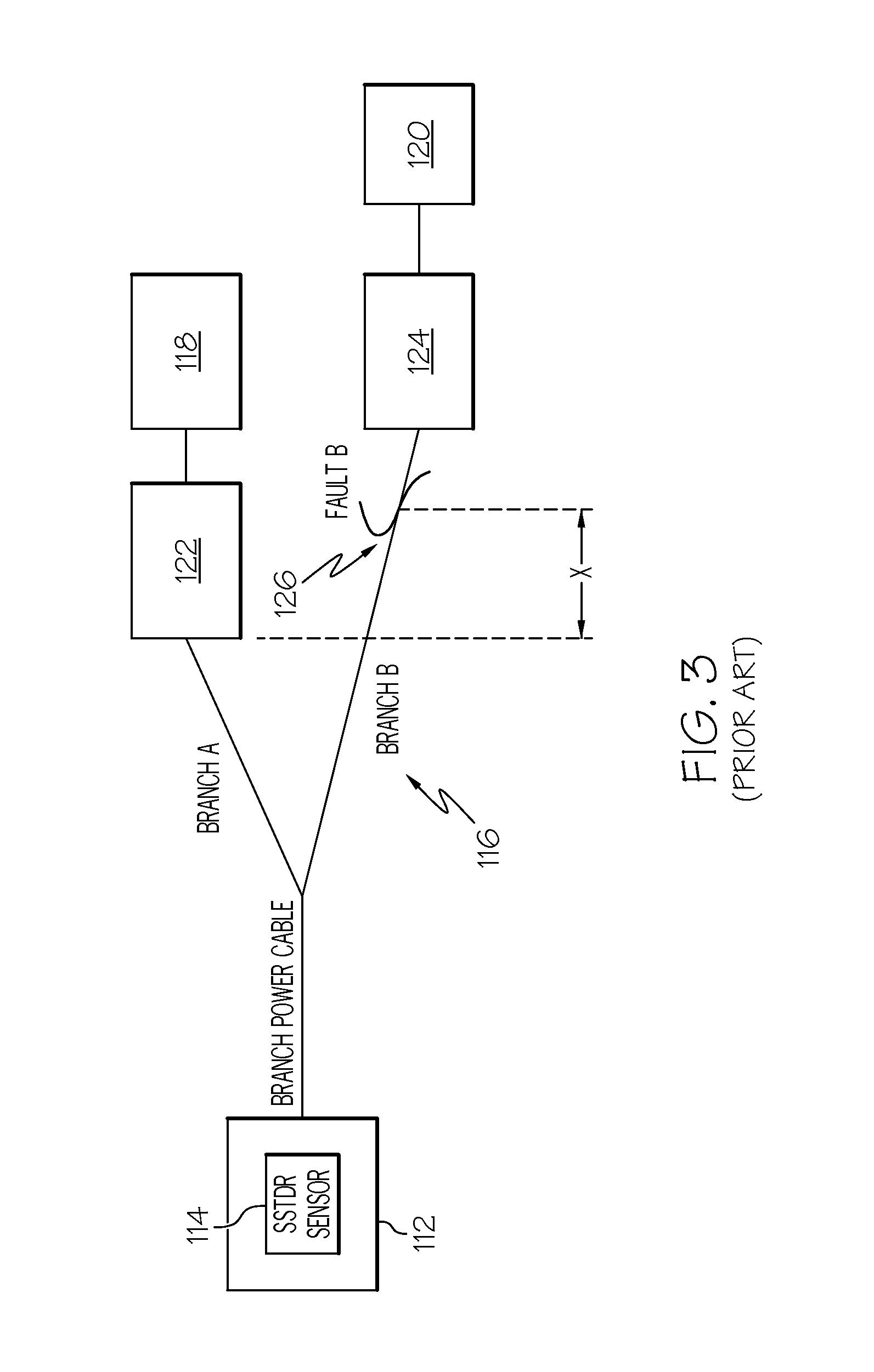
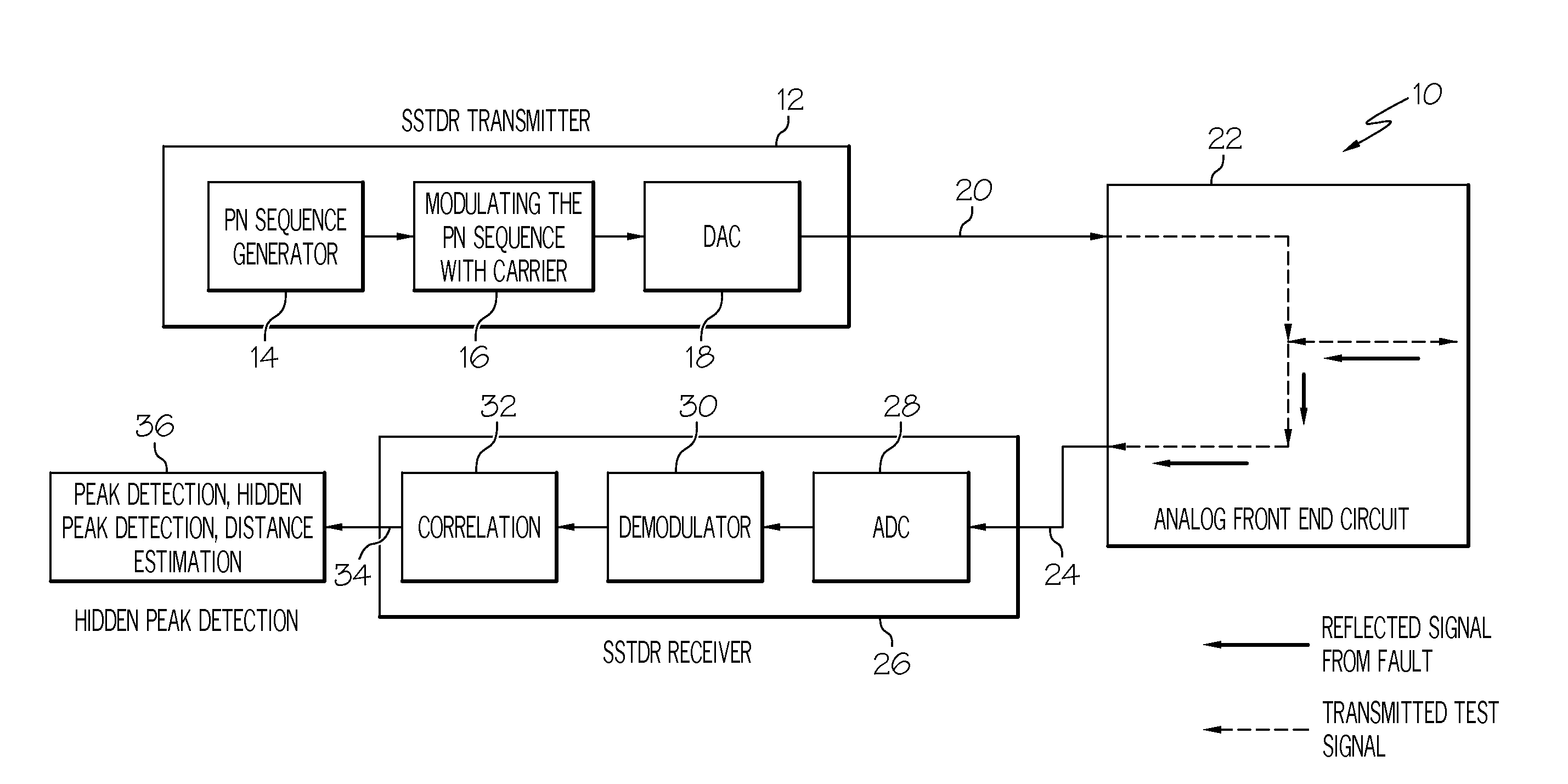
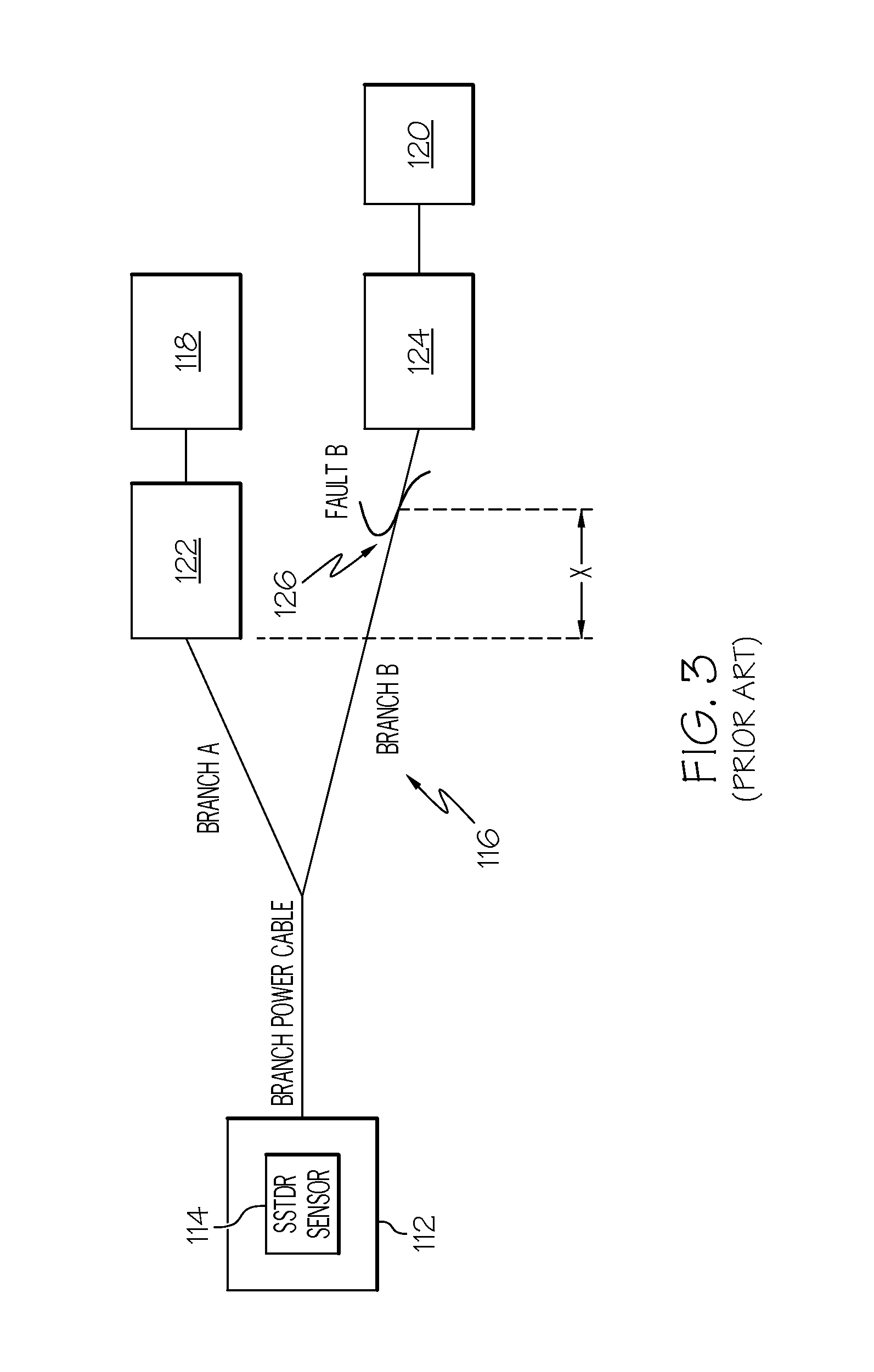
Methods for detecting a hidden peak in wire fault location applications - improving the distance range resolution
InactiveUS20110227582A1Testing electric installations on transportFault location by pulse reflection methodsImage resolutionEngineering
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
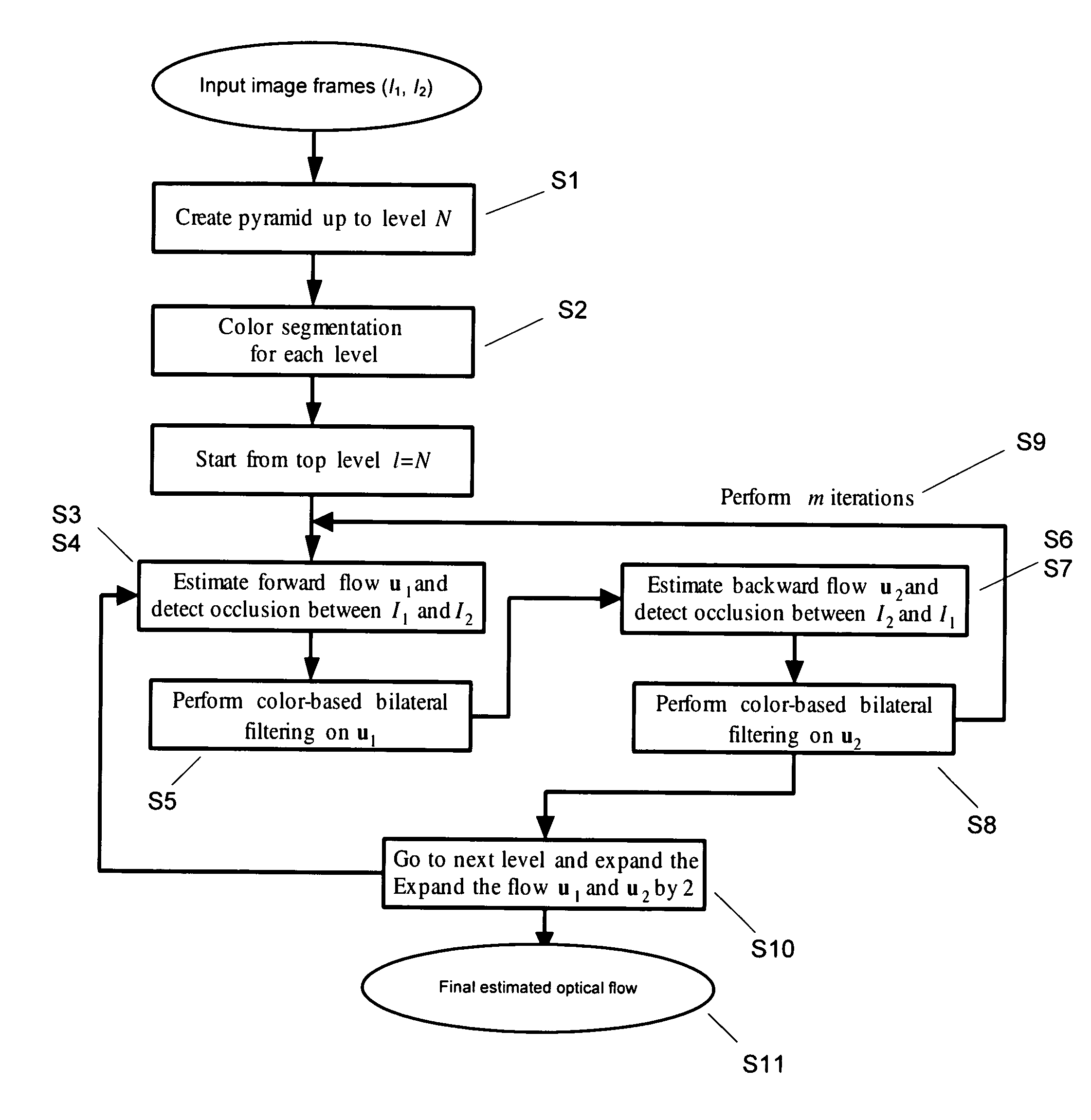
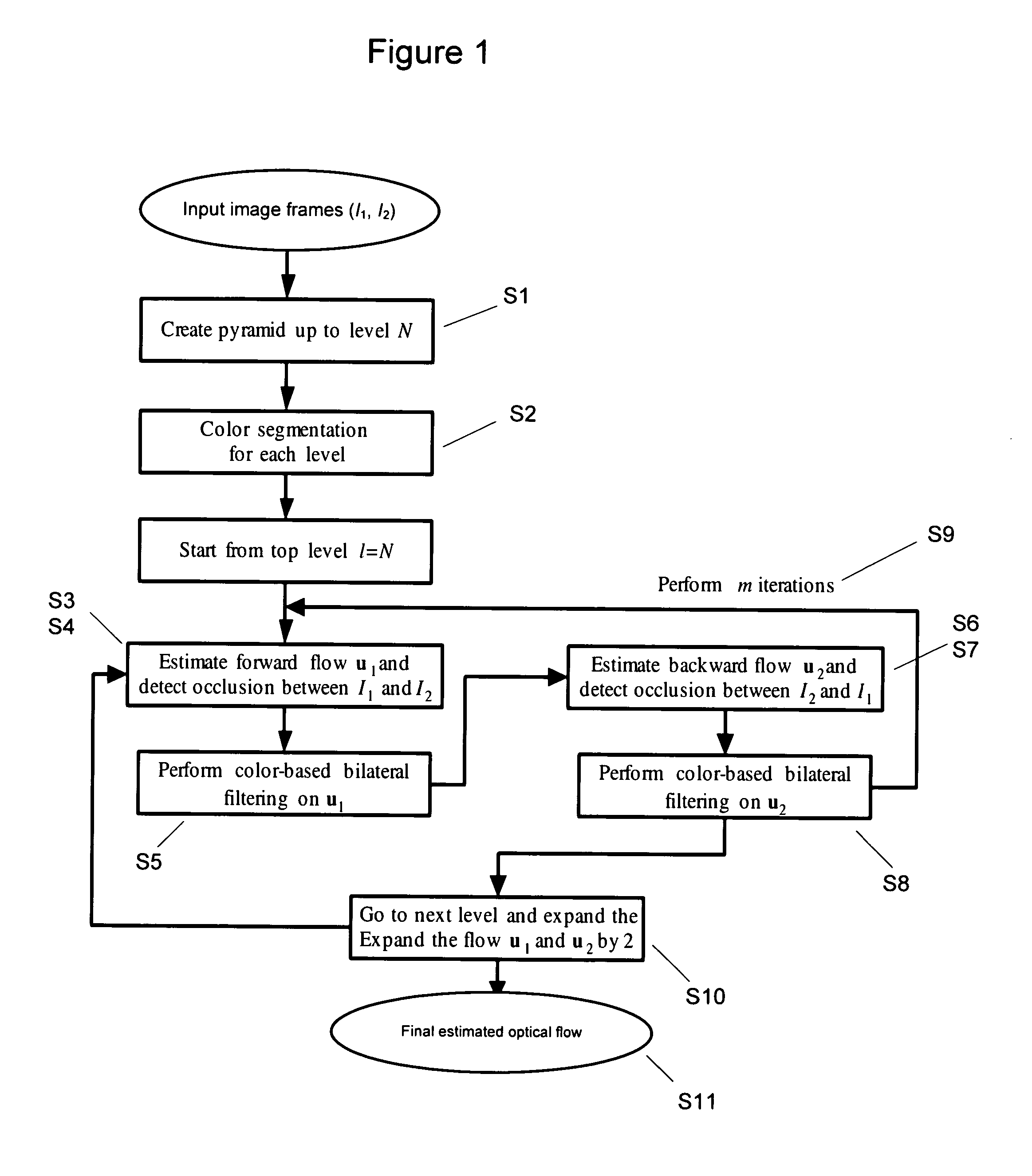
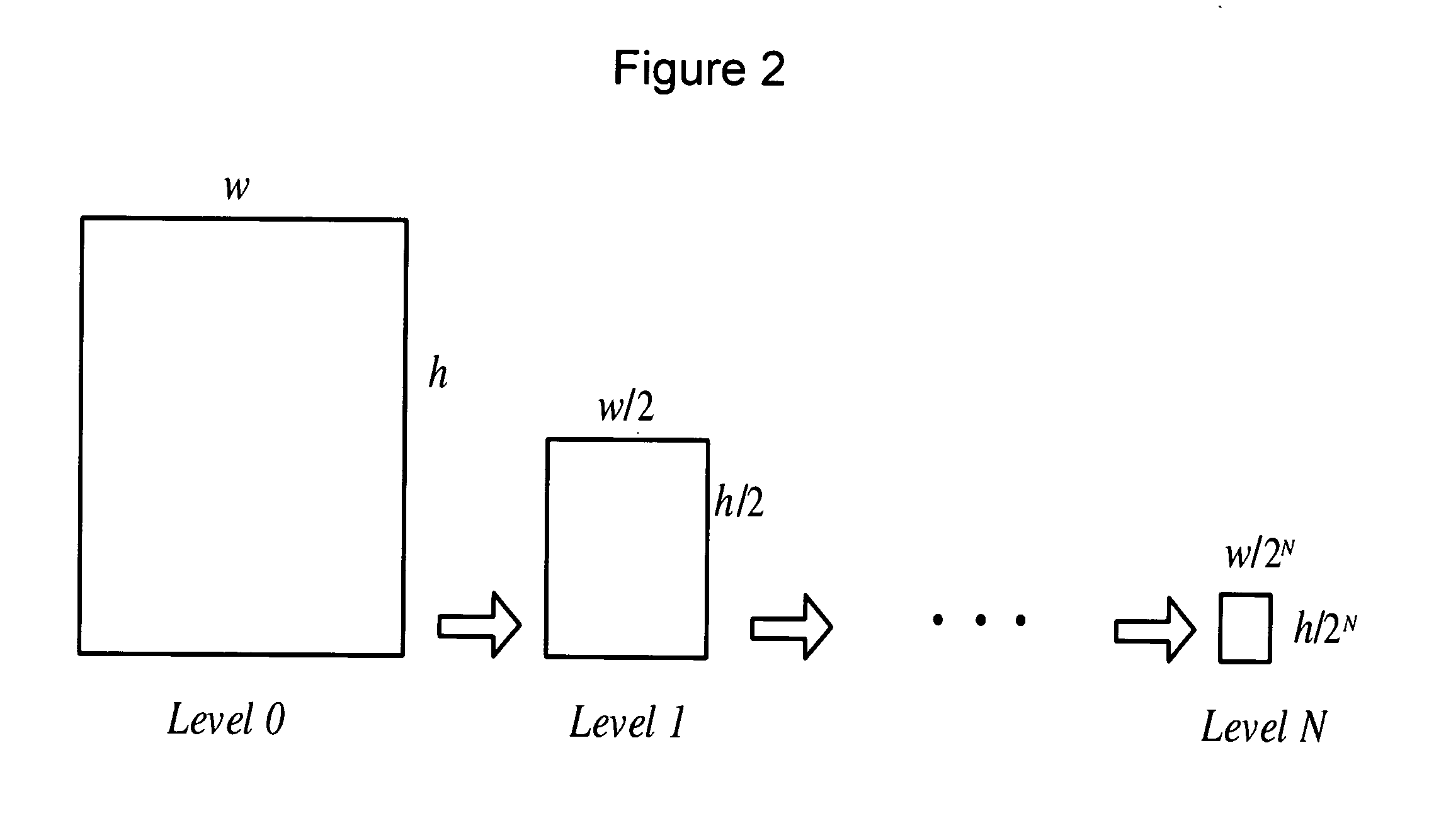
Method and system for segment-based optical flow estimation
InactiveUS20070092122A1Reduce transmissionEfficiently breaks the spatial coherence over the motion boundariesTelevision system detailsImage analysisOcclusion detectionPyramid
The methods and systems of the present invention enable the estimation of optical flow by performing color segmentation and adaptive bilateral filtering to regularize the flow field to achieve a more accurate flow field estimation. After creating pyramid models for two input image frames, color segmentation is performed. Next, starting from a top level of the pyramid, additive flow vectors are iteratively estimated between the reference frames by a process including occlusion detection, wherein the symmetric property of backward and forward flow is enforced for the non-occluded regions. Next, a final estimated optical flow field is generated by expanding the current pyramid level to the next lower level and the repeating the process until the lowest level is reached. This approach not only generates efficient spatial-coherent flow fields, but also accurately locates flow discontinuities along the motion boundaries.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
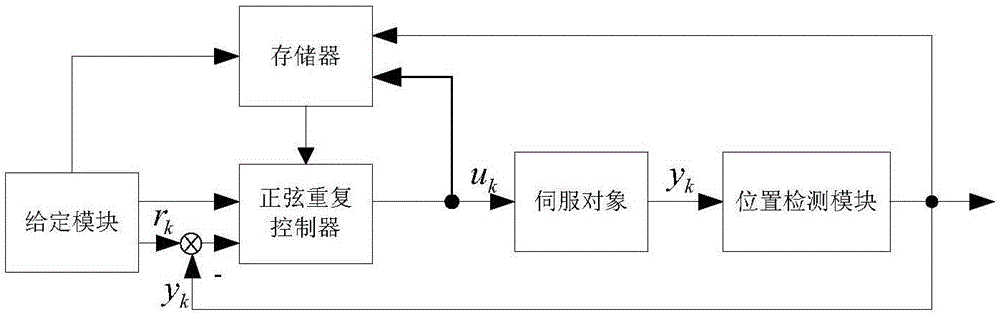
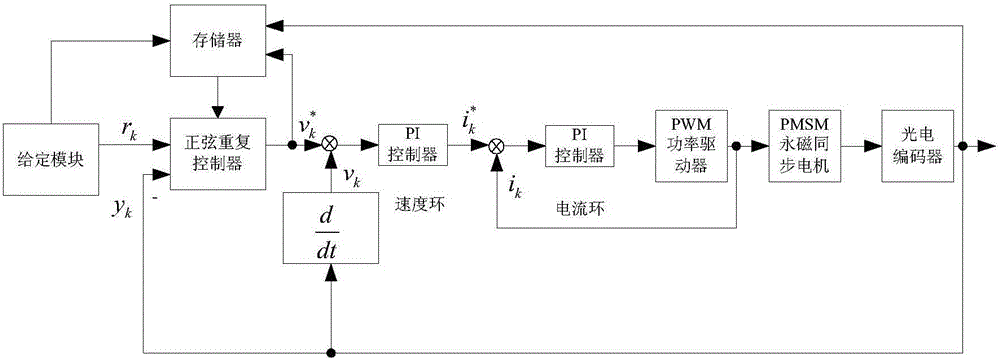
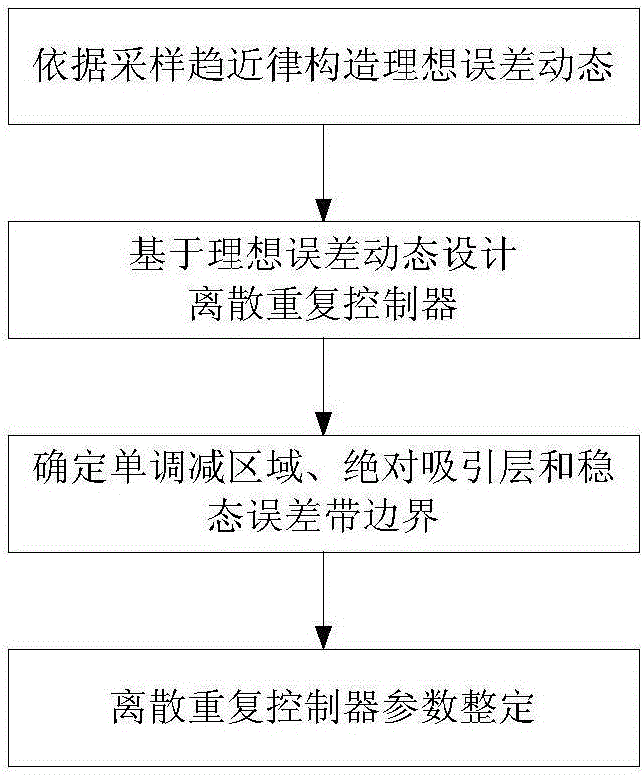
Sliding mode repetitive controller for motor servo system
ActiveCN106444372AFast Track Error ConvergenceHigh control precisionAdaptive controlTime domainFinite time
The invention provides a sliding mode repetitive controller for motor servo system. Introduced repetitive control is based on an idea of tracking a periodic signal and inhibiting a periodic interference signal, according to the cyclic symmetric property of the interference signal in a time domain, the sampling sliding mode repetitive controller is designed based on a sine saturation function reaching law, the design is a time domaindesign method. By adopting a finite time reaching law, the discrete repetitive controller is designed based on the finite time reaching law, and the repetitive control technology not only can track a given periodic reference signal, but also can achieve the complete suppression of the periodic interference signal.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving synchronization and information transmission in a communication system
ActiveUS20080310567A1Improve performanceReduce the amount of solutionTransmission path divisionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemInformation transmission
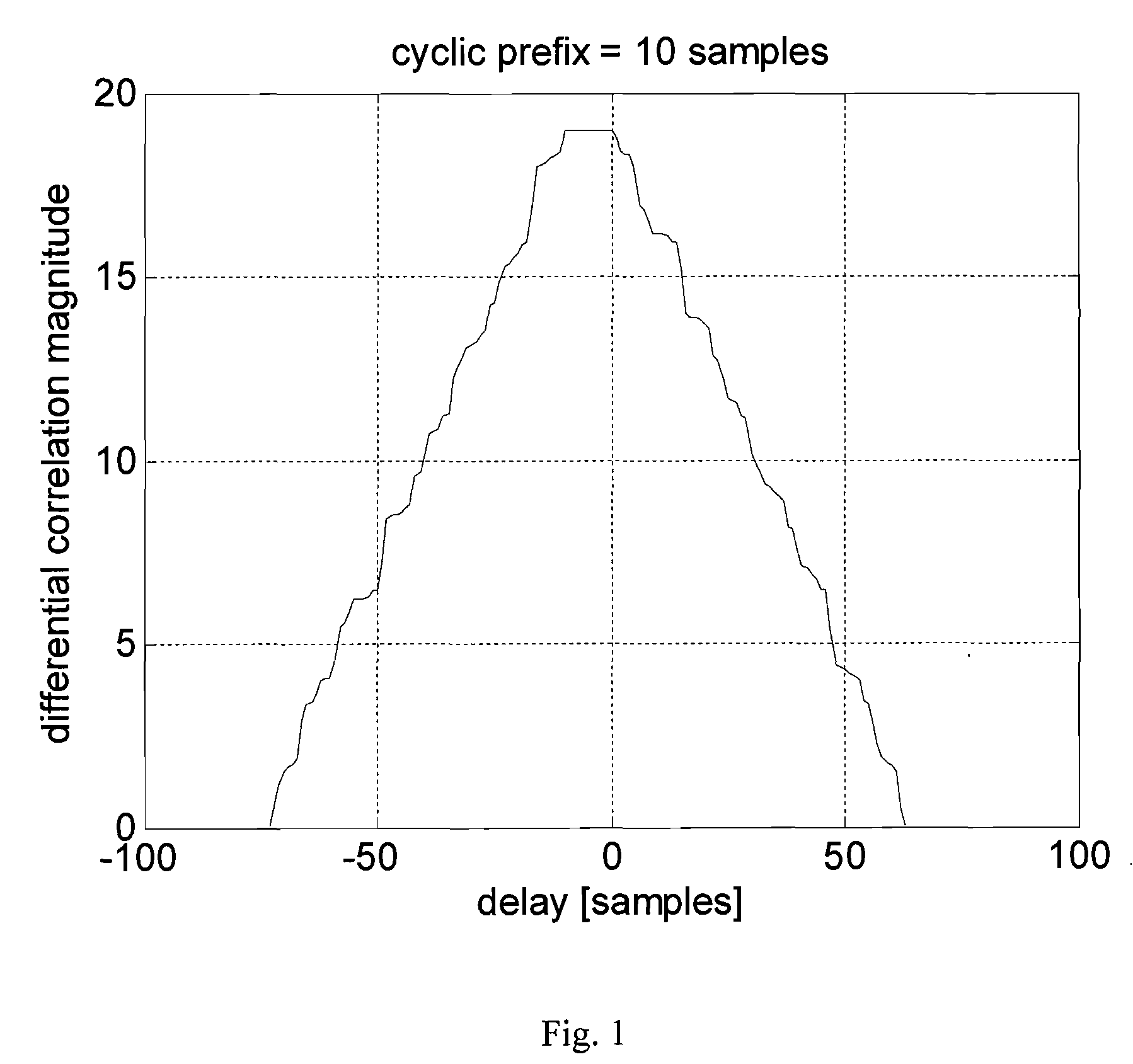
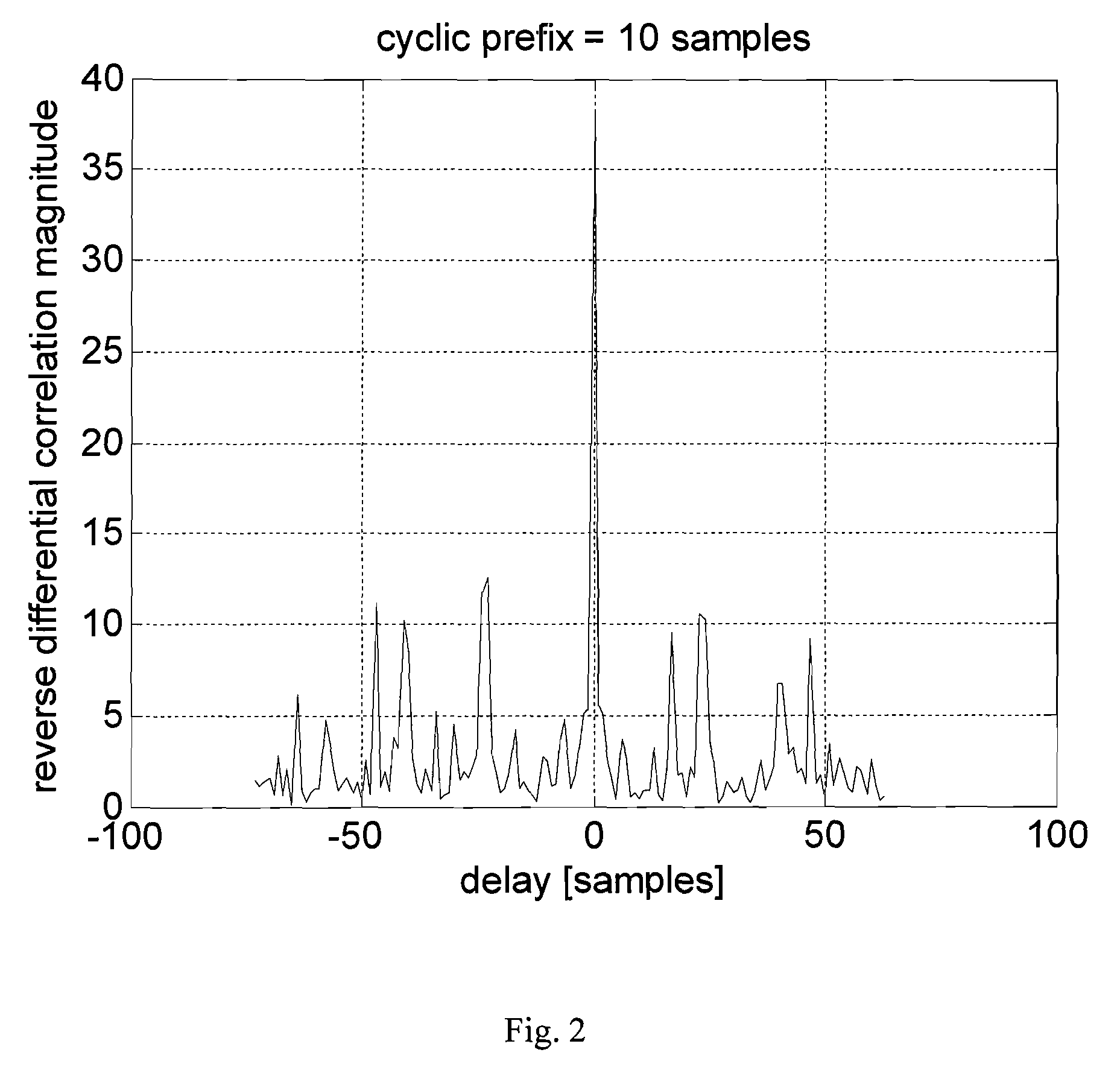
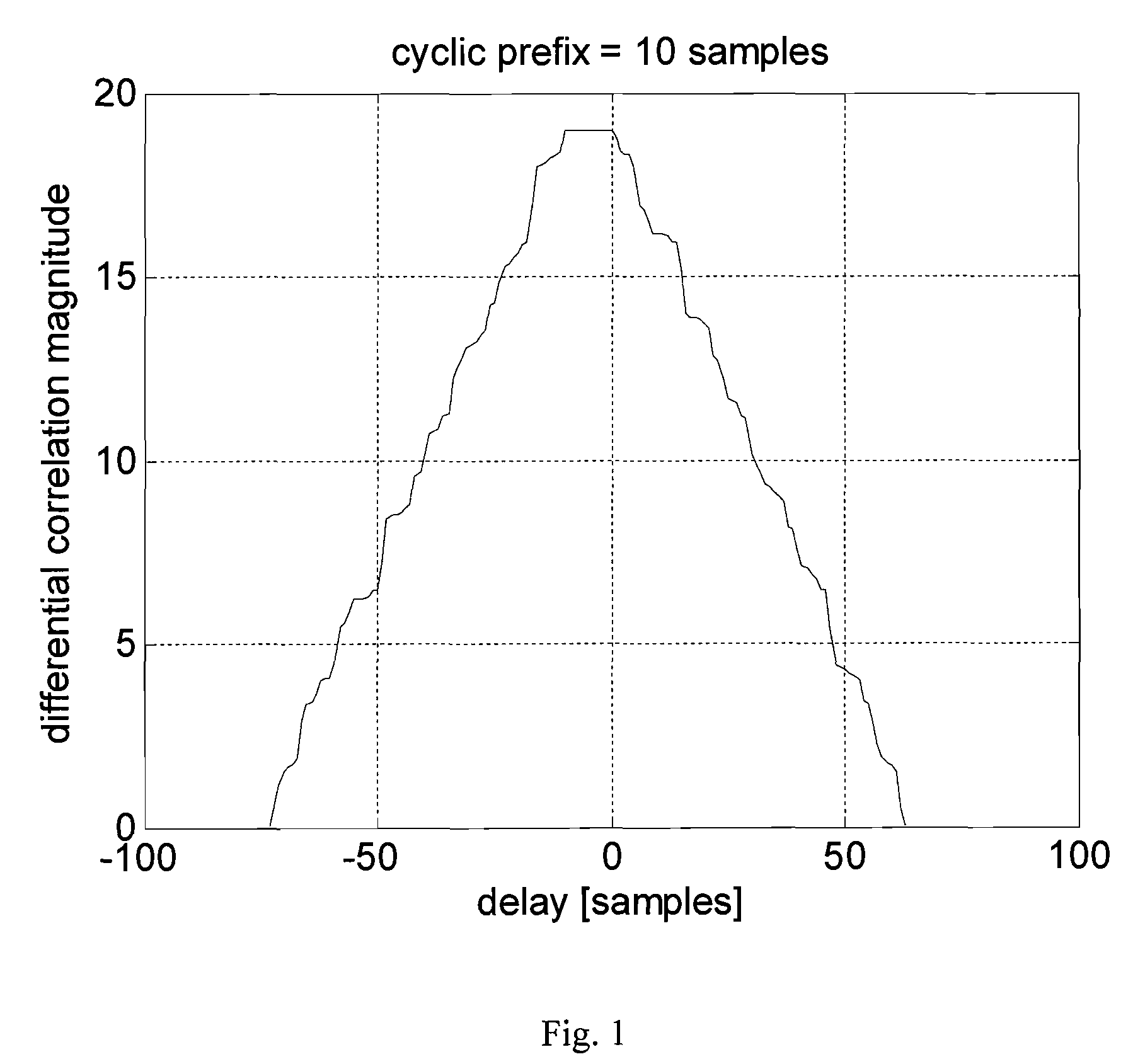
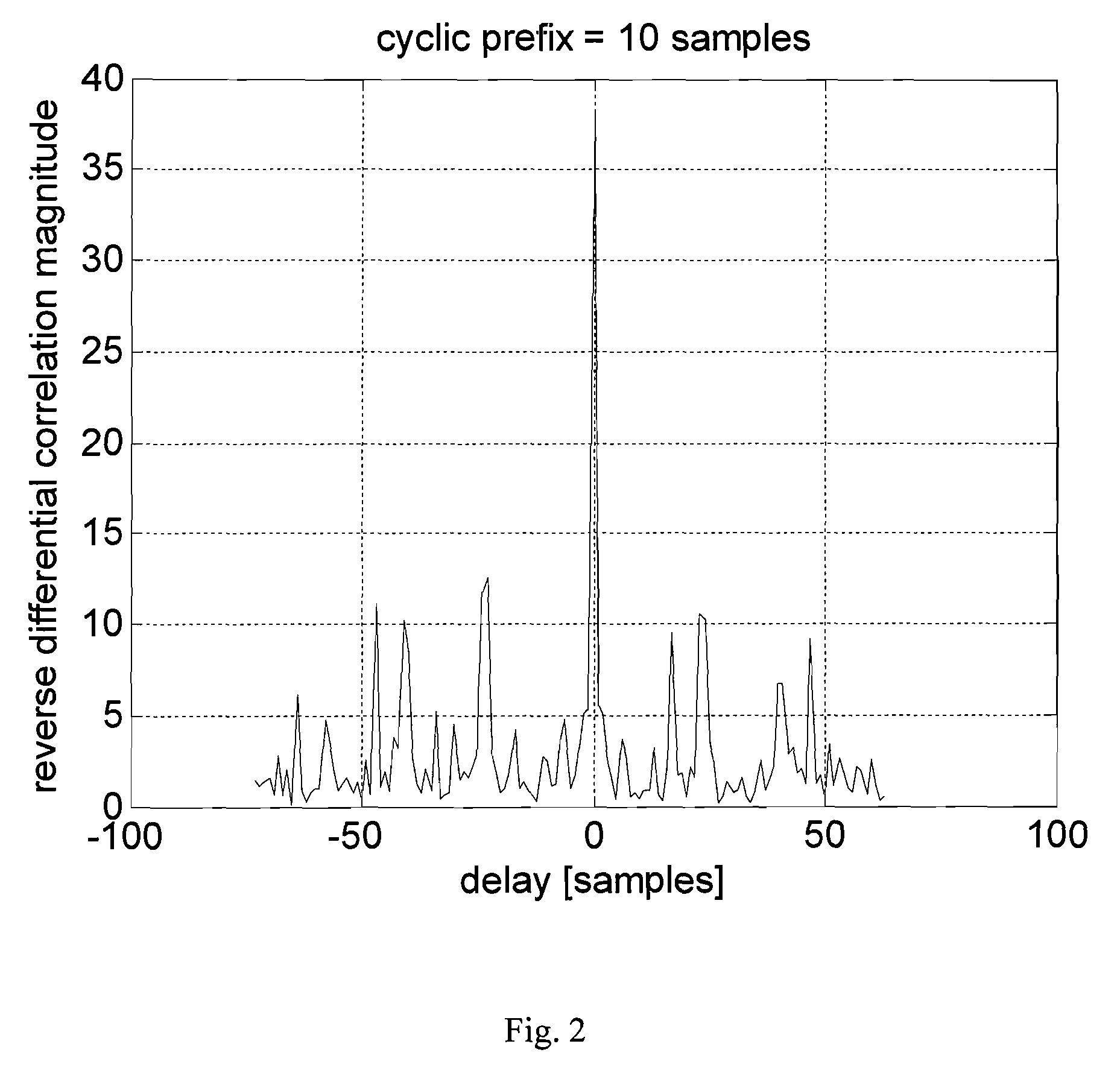
The present invention relates to a method for improving synchronization and information transmission in a communication system, including: generating a signal with a time symmetric property based on a uniquely identifiable sequence c(l) from a set of sequences, sending the signal over a communication channel, receiving the signal, calculating and storing a correlation, finding the delay that result in a maximum correlation magnitude, detecting the unique sequence c(l) from the set of sequences. The method is distinguished by: generating the signal with a centrally symmetric part, s(k), the centrally symmetric part s(k) being symmetric in the shape of the absolute value thereof, storing the reverse differential correlation D(p) from a block of N received signal samples r(k), k=0, 1, . . . , N−1. The present invention also relates to a transmitter unit and a receiver unit of a communication system, and a radio communication system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for improving synchronization and information transmission in a communication system
ActiveUS8139663B2Improve performanceReduce the amount of solutionTransmission path divisionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemInformation transmission
The present invention relates to a method for improving synchronization and information transmission in a communication system, including: generating a signal with a time symmetric property based on a uniquely identifiable sequence c(l) from a set of sequences, sending the signal over a communication channel, receiving the signal, calculating and storing a correlation, finding the delay that result in a maximum correlation magnitude, detecting the unique sequence c(l) from the set of sequences. The method is distinguished by: generating the signal with a centrally symmetric part, s(k), the centrally symmetric part s(k) being symmetric in the shape of the absolute value thereof, storing the reverse differential correlation D(p) from a block of N received signal samples r(k), k=0, 1, . . . , N−1. The present invention also relates to a transmitter unit and a receiver unit of a communication system, and a radio communication system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
On-line detection device of wave aberration of projection lens of lithography machine with precision calibration function
ActiveCN101813894ASimple structureImprove accuracyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGratingBeam splitting
The invention relates to an on-line detection device of wave aberration of a projection lens of a lithography machine with precision calibration function, which belongs to the field of optical detection. The on-line detection device additionally introduces a grating and two circular holes in a PSPDI by utilizing the property that the system error of the PSPDI rotates along with the beam splitting direction of the grating, the two gratings and the three circular holes are taken as measurement precision calibration elements together, and the system error during the calibration of the measurement precision of the PSPDI is separated according to the orthogonal property and the odd-even symmetry property of a Zernike polynomial in the unit circular region, thereby obtaining the wave surface error of a spherical reference wave produced by diffraction of the circular holes for calibration and characterization of the measurement precision of the PSPDI and leading the on-line detection device of the projection lens of the lithography machine to have the capability of realizing the on-line detection of the wave aberration and also have the measurement precision calibration function.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Aspheric myopia eyeglass
The invention discloses an aspheric myopia eyeglass, comprising a back surface and a front surface. Curved surfaces of the back surface and the front surface are all aspheric even number aspheric refracting surfaces. The even number aspheric refracting surface is determined by a function as below; optimized variables are increased by times, so as to reach higher imaging quality and larger thinning amount. In addition, the even number aspheric refracting surface guarantees holosymmetry of the eyeglass and is beneficial for processing and manufacture; detection is same as a general spherical eyeglass, and measurement of degrees of eyeglass will not be influnced. The front surface and the back surface employ completely opposite aspheric design, so that various design errors and processing errors can compensate mutually. The eyeglass has excellent stability, and will not cause uncomfortableness to first time wearer due to various errors. Therefore, the aspheric myopia eyeglass has advantages of thin thickness, light weight, good imaging quality and facility for processing, etc.
Owner:SUZHOU MASON OPTICAL CO LTD +1
Method of quickly calculating far-field radiation field of large-scale MIMO array based on symmetric property
ActiveCN105912742AAvoid calculationCalculation speedDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsClassical mechanicsArray element
The invention belongs to the field of electromagnetic numerical calculation, and specifically relates to a precise and quick calculation method of calculating the far-field radiation field of a large-scale MIMO array antenna based on the symmetric property of arrays. The method comprises the following steps: S1, determining the structure and parameters of an M*N planar array antenna; S2, determining the size and extraction mode of the sub-matrixes in a large array; S3, approximately calculating out the active unit pattern of each array element of the large array based on an extracted sub-matrix active unit pattern and by making use of the symmetric property of a homogeneous planar array; and S4, calculating the properties of the radiation field of the large array through superimposed calculation. The method of the invention is based on extension of a small array to a large array, and is of high calculation speed. By using the superposition principle of field, the method is flexible in calculation, and has a wide scope of application. The method can be applied to both homogeneous linear and planar arrays. Through superimposed calculation, a large amount of matrix operation is avoided, the amount of calculation is reduced, and the calculation speed is improved.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
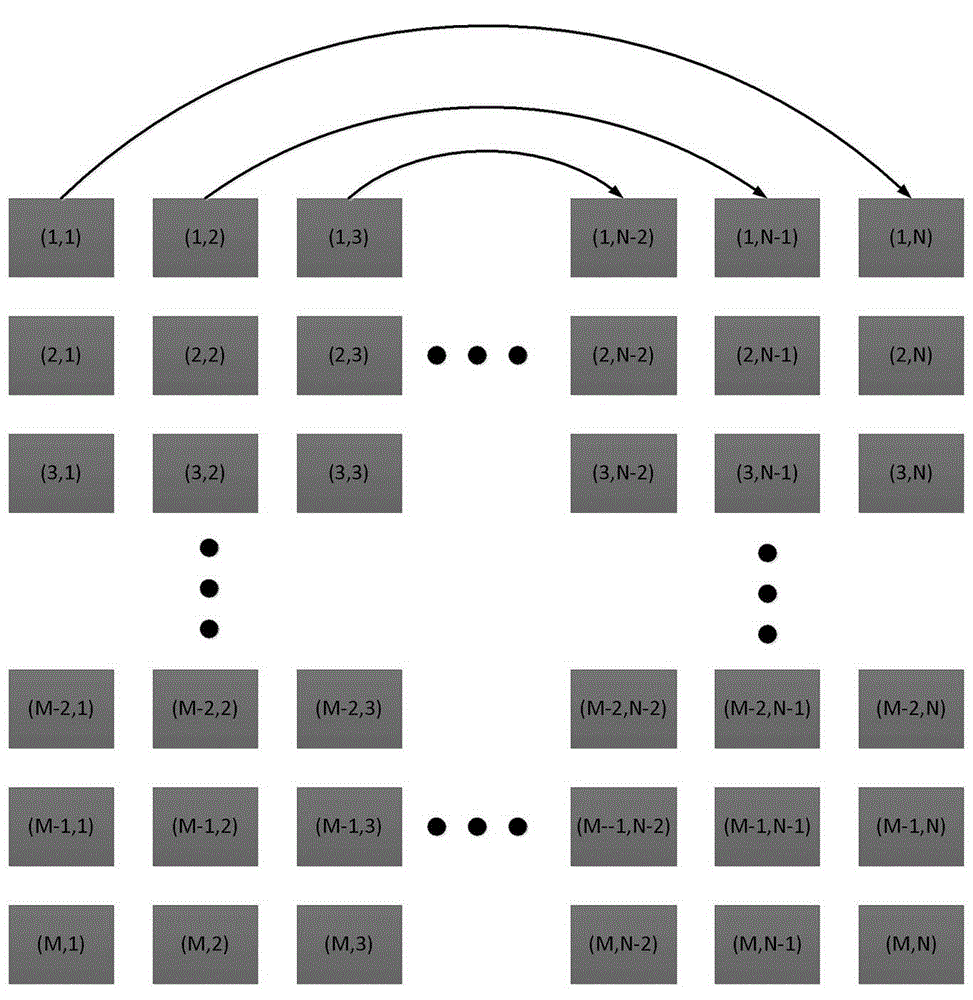
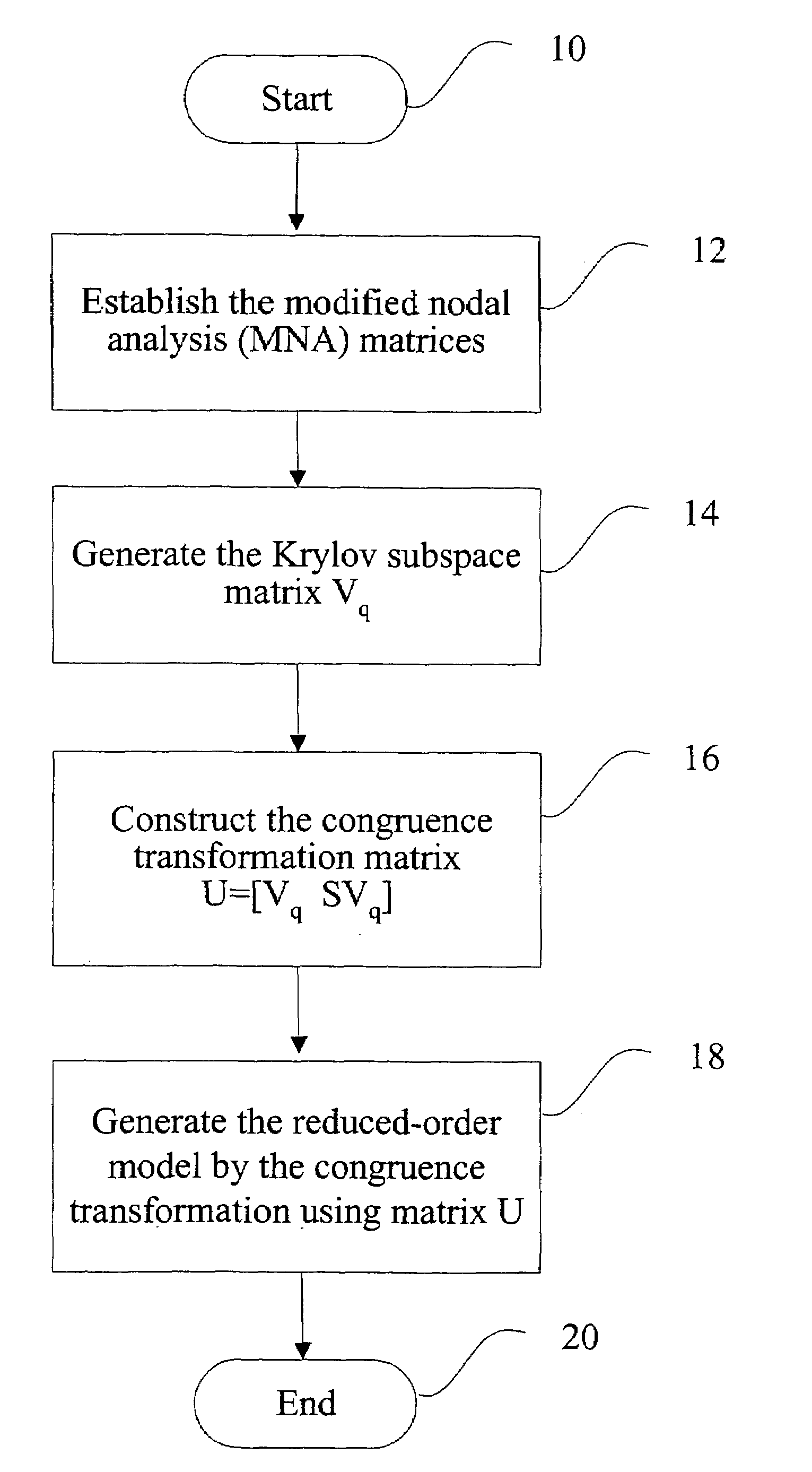
Method and apparatus for model-order reduction and sensitivity analysis
InactiveUS7216309B2Reduce computing costLow costDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationVlsi interconnectAlgorithm
Computer time for modeling VLSI interconnection circuits is reduced by using symmetric properties of modified nodal analysis formulation. The modeling uses modified nodal analysis matrices then applies a Krylov subspace matrix to construct a congruence transformation matrix to generate the reduced order model of the VLSI.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Method for judging movability of symmetric rod system structure based on group theory
InactiveCN102508978AImprove computing efficiencyAvoid Duplicate Decision CalculationsSpecial data processing applicationsSpatial structureIrreducible representation
The invention discloses a method for judging the movability of a symmetric rod system structure based on a group theory, belonging to the field of building structure designs and space structural designs. The method is particularly suitable for the initial design of a deployable structure. According to the method, a degree of freedom formula of the symmetric rod system structure is simplified to various types of symmetric linear expressions based on inherent irreduable representations and characteristic standard values of a symmetric group; and the symmetric property of a mechanism displacement mode and a self-stress mode is obtained, so that the movability of the symmetric structure can be directly judged. Compared with the conventional movability judgment method in which the symmetric property of the structure is not used fully and the analysis calculation for large structures is complicated, the method has the advantages that: the movability of most symmetric rod systems can be judged by only carrying out simple vector calculation and simplification, and a structure designer can popularize and apply the method conveniently.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
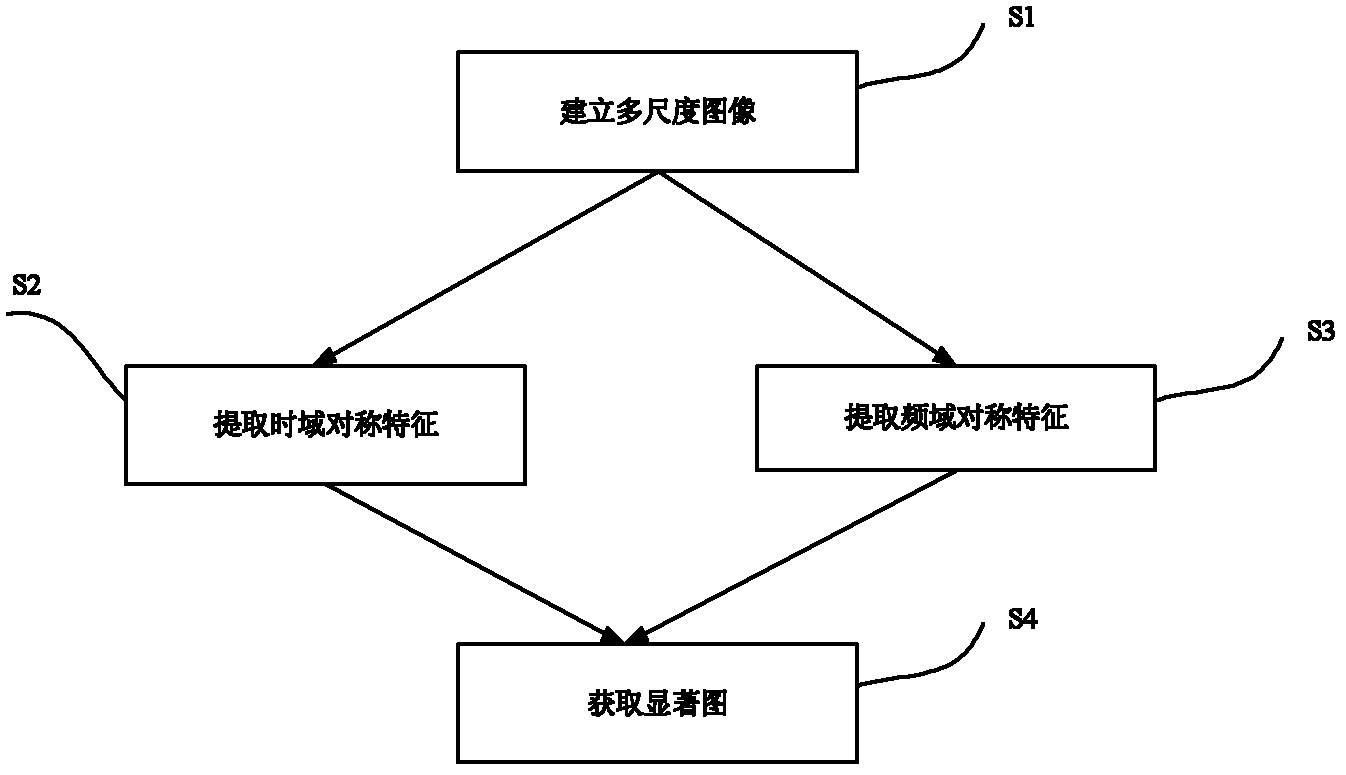
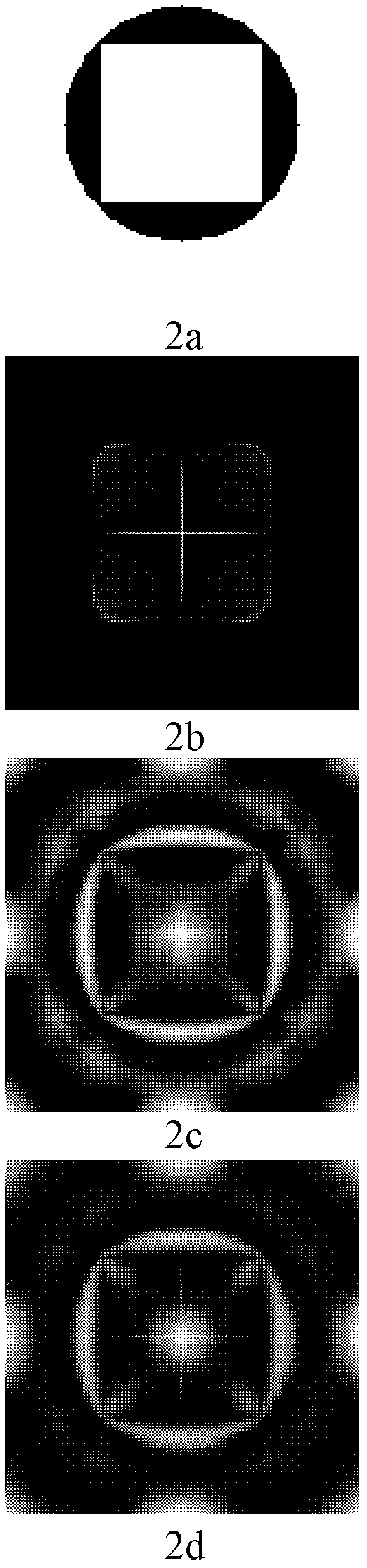
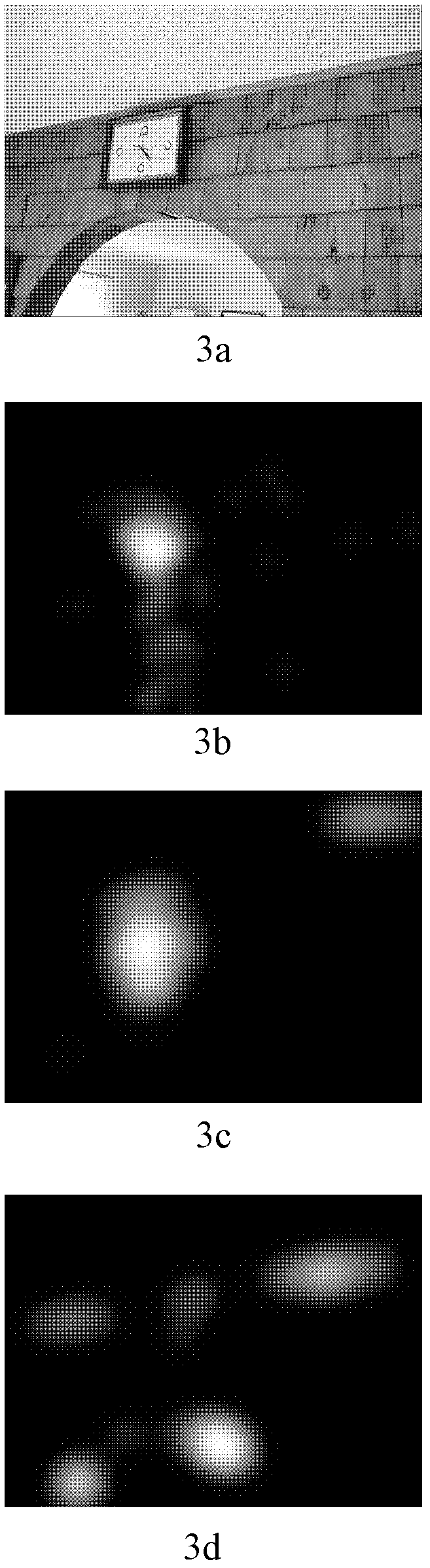
Symmetry property-based method for detecting salient regions of images
ActiveCN102222324AResults in line with human gazeImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainSaliency map
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer vision, and discloses a symmetry property-based method for detecting salient regions of images, aiming at solving the problem of salient regions during the existing Itti model detection. The method comprises the following steps of processing target images to obtain images with different dimensions, respectively extracting frequency domain symmetric properties and time domain symmetric properties of the images with the different dimensions, and merging the images to obtain a time frequency characteristic image so as to obtain a final saliency map. The method combines the time domain symmetric properties with the frequency domain properties to accomplish the detection of the salient regions of the images. The detection method can more completely detect salient targets by utilizing the function of the symmetry properties, which is played in the process of eye fixation, so that the detected salient regions of the images are more in line with the result of the eye fixation.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
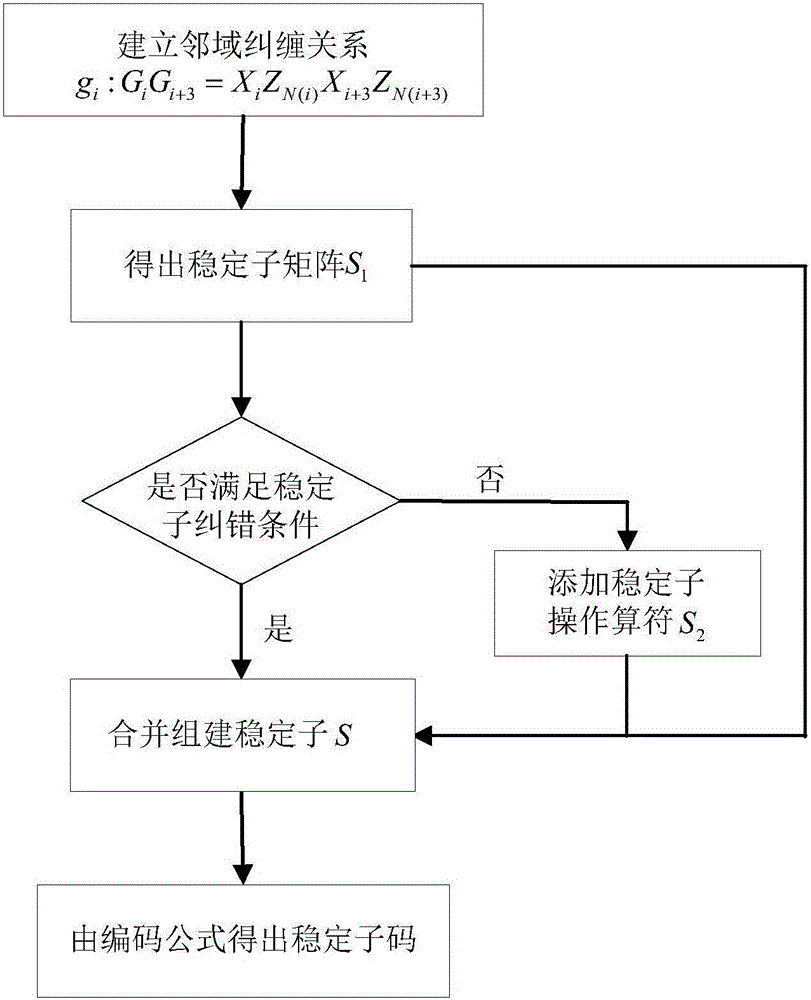
Graph state-based link chain structure quantum stabilizer subcode construction method
ActiveCN106100642AIncreased complexityGet rid of the bondageKey distribution for secure communicationError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsGraphicsChain structure
The invention discloses a graph state-based link chain structure quantum stabilizer subcode construction method which is different from a current popular method for constructing a stabilizer subcode through a graph state in ideas. According to the method, specific rotation symmetry of a structure of a graph state of quantum bit subcodes arranged in a link chain manner is adopted, a main part of a stabilizer is analytically constructed by establishing an entanglement relation of neighborhoods, then through calculating and analyzing, a missing part which does not meet an error correction condition is supplemented, and an error correction capability of the stabilizer is ensured by adding a stabilizer sub-operation operator, so that a complete stabilizer subcode is acquired. According to the method for constructing the quantum error-correcting code by establishing the entanglement relation of the neighborhoods through a topological structure and the specific symmetric property of the graph state, excellent promotion significance and application prospects are realized on two aspects of extending a higher dimensional quantum error-correcting code and exploring a new type of quantum error-correcting code.
Owner:易迅通科技有限公司
Semiconductor device having a pseudo power supply wiring
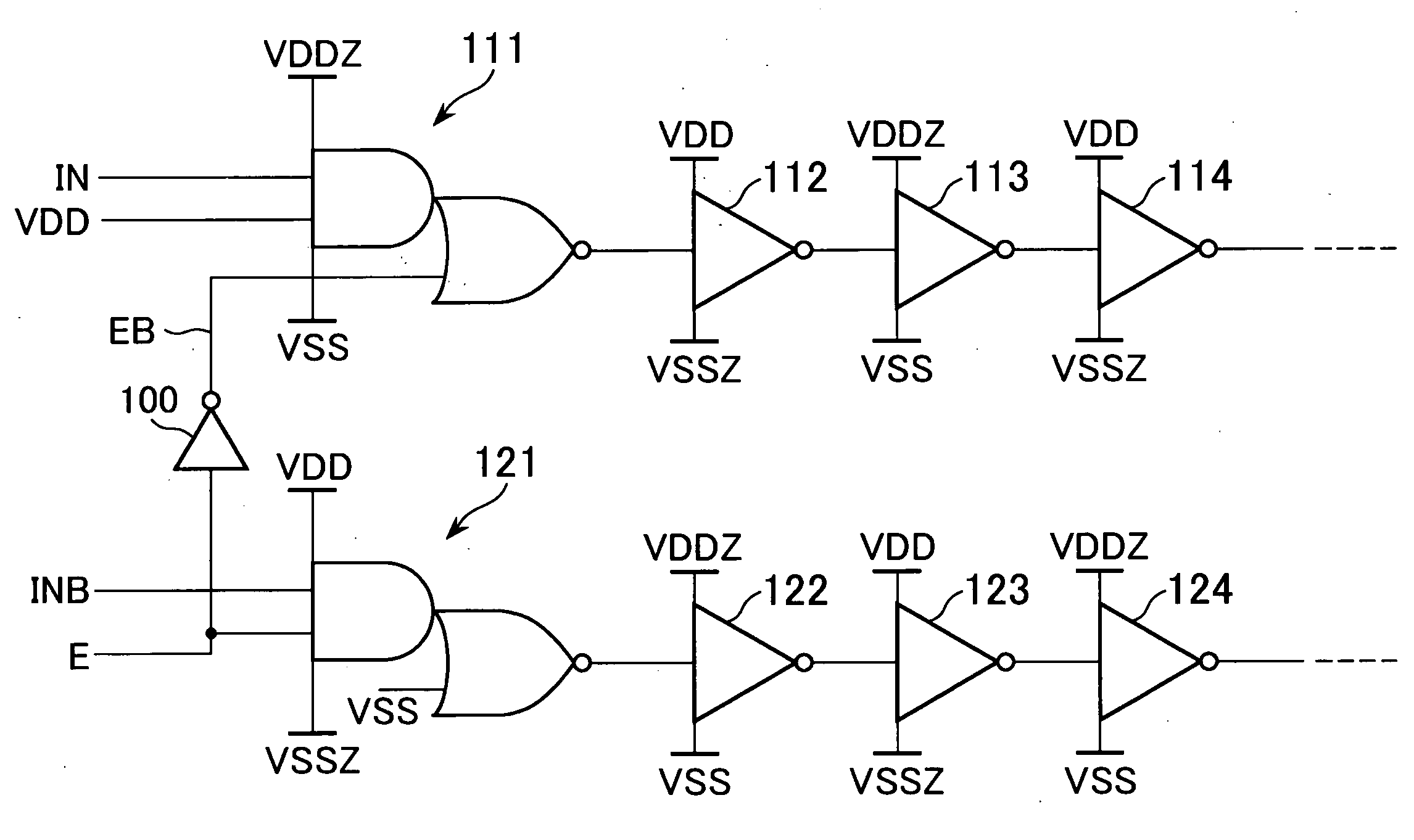
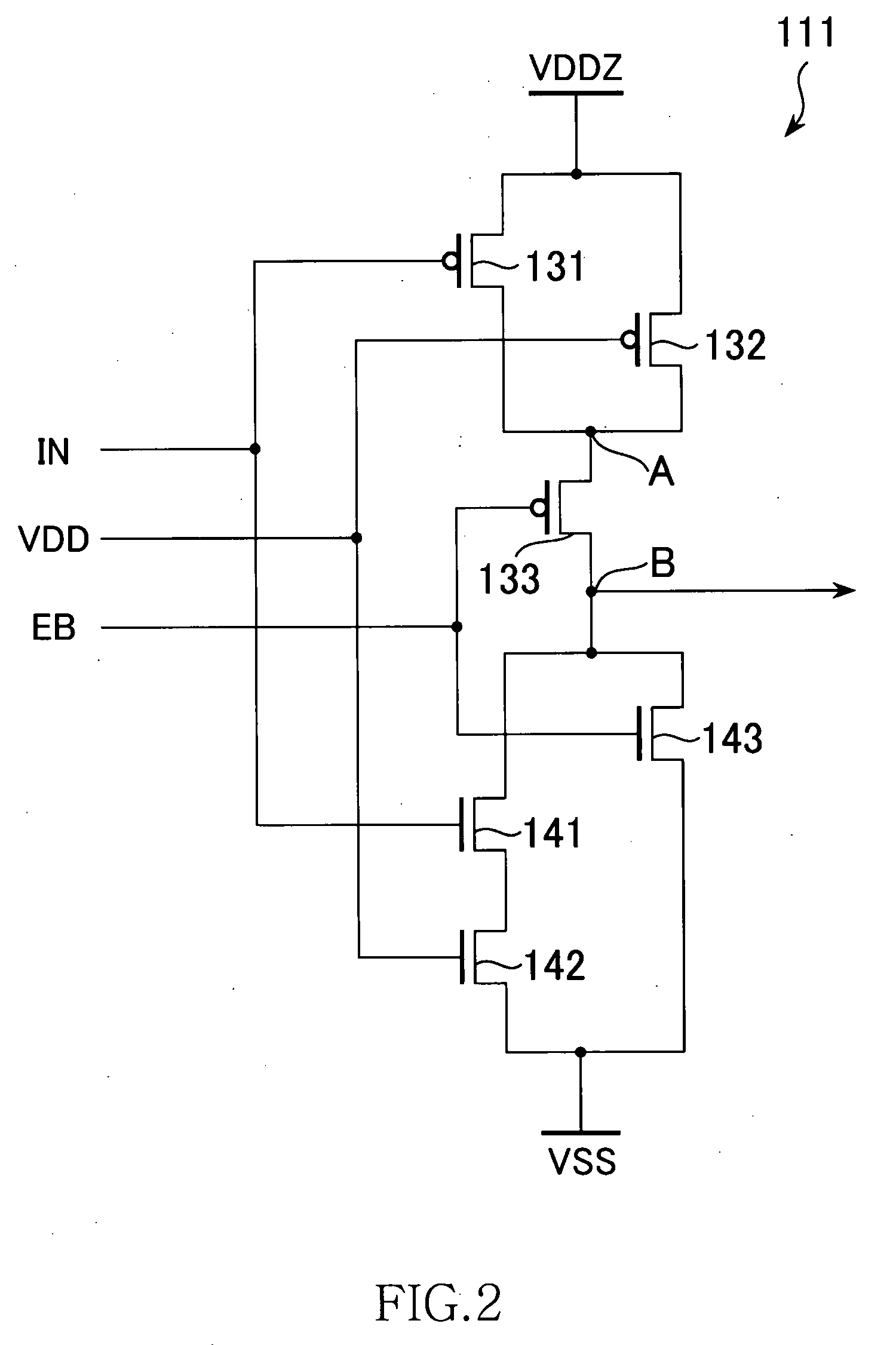
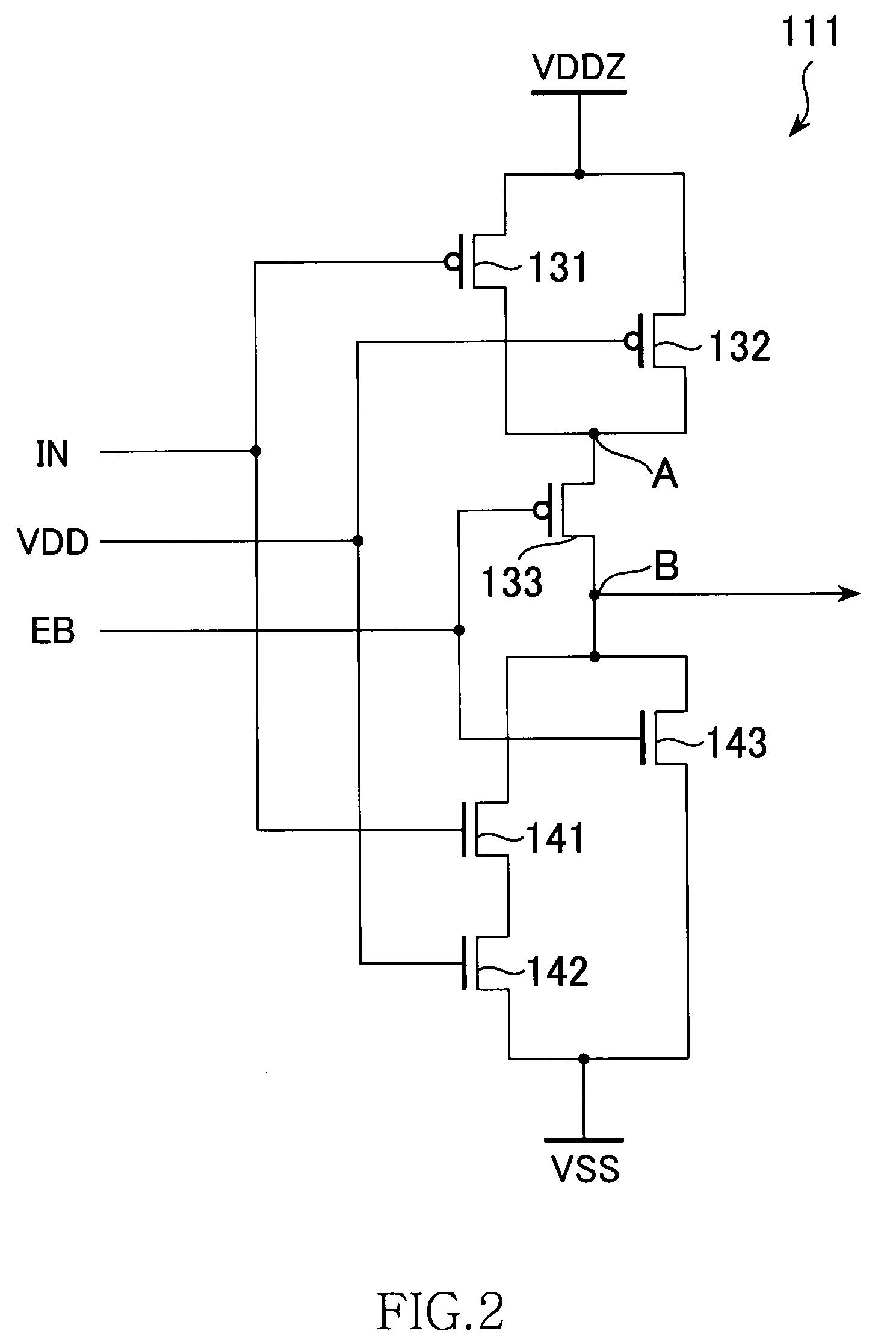
ActiveUS20080169840A1Inhibit currentPower reduction in field effect transistorsReliability increasing modificationsSub thresholdEngineering
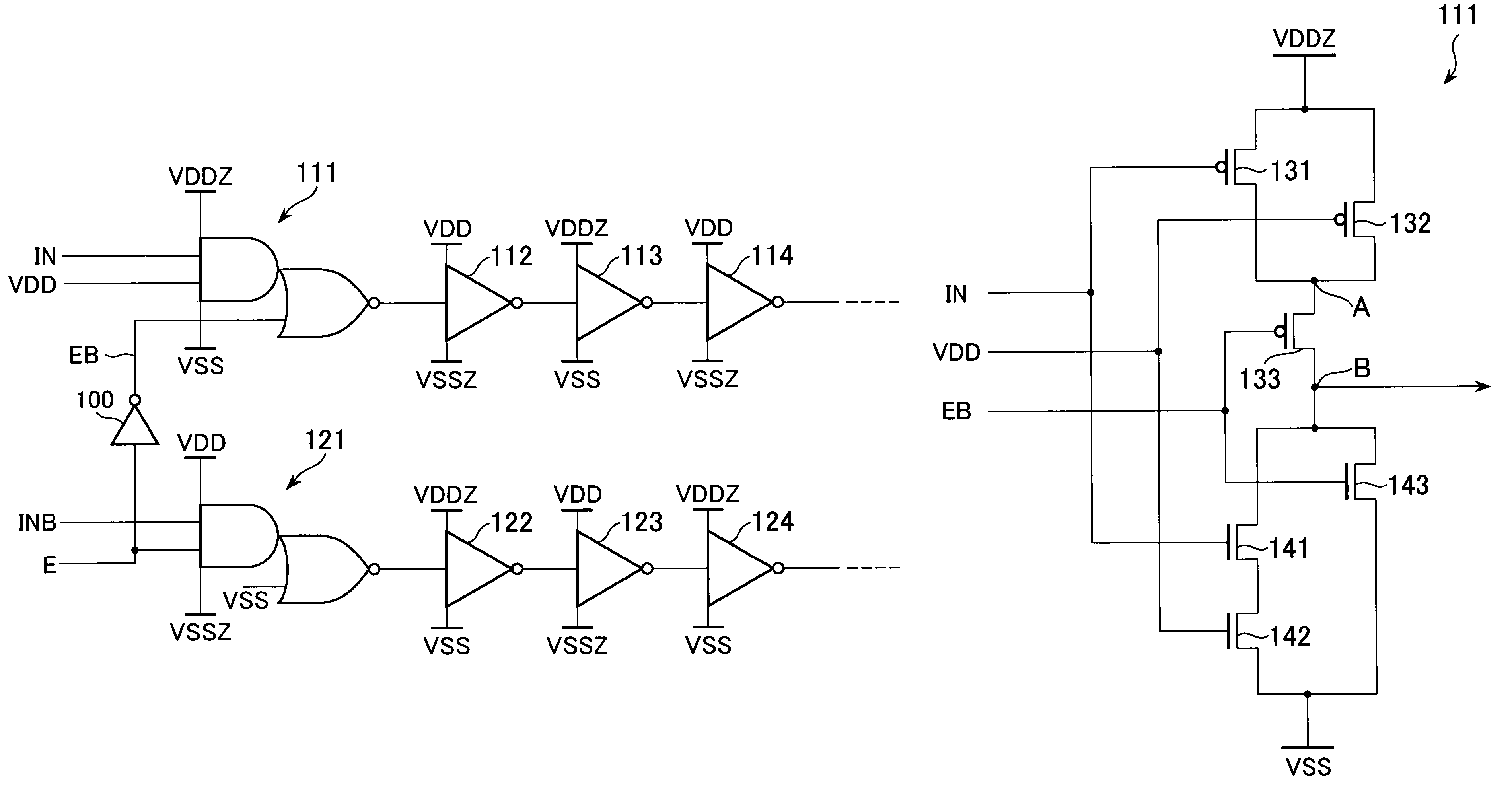
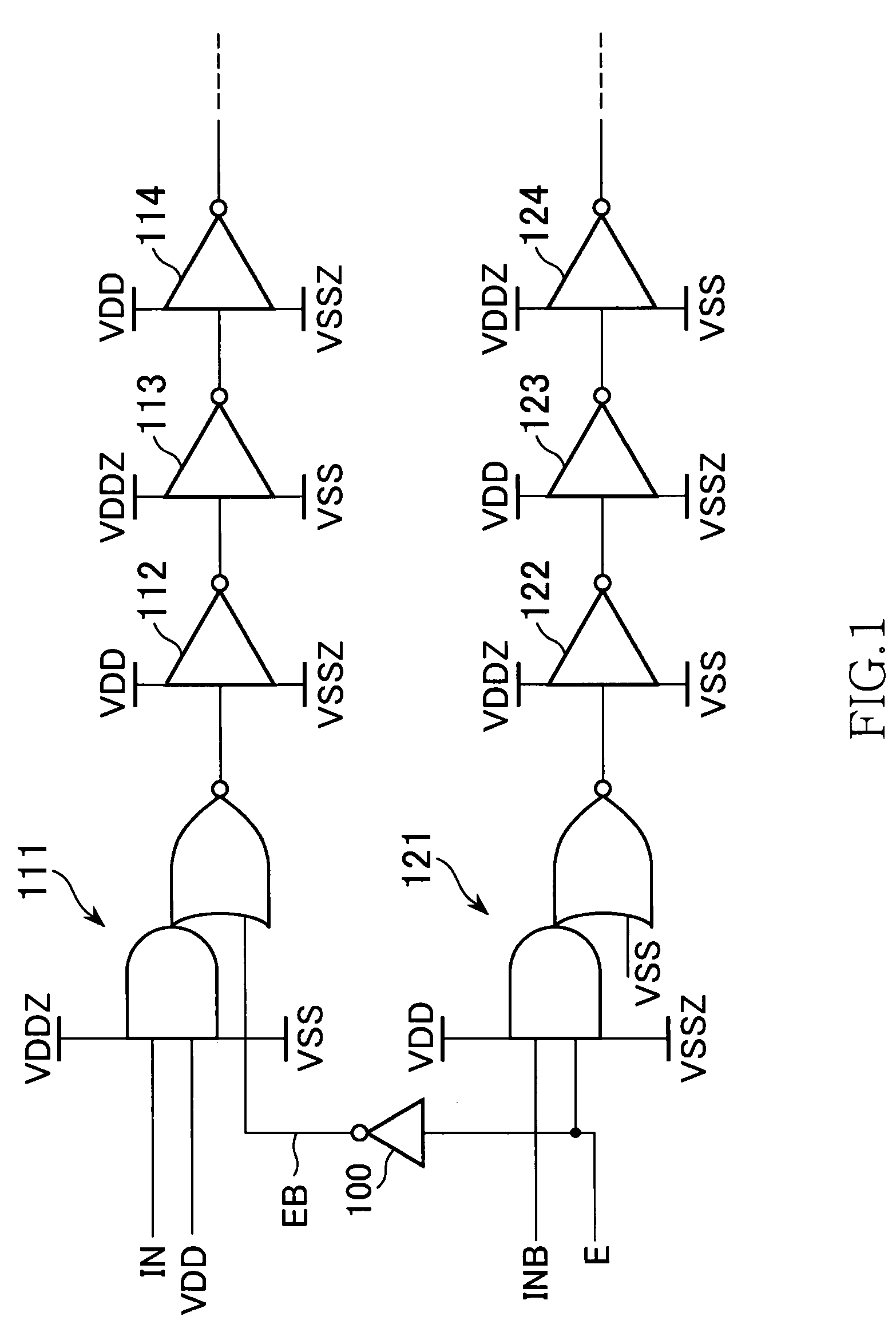
A semiconductor device including an AND-NOR composite gate of which AND unit is supplied with input signals IN and VDD and NOR unit is supplied with an inverted signal EB of an enable signal E, and an AND-NOR composite gate of which AND unit is supplied with an input signal INB and an enable signal E and NOR unit is supplied with VSS. These gates are inserted into a path to which the input signals IN and INB are supplied. Thereby, a symmetric property of a complimentary signal can be retained. Further, outputs of the AND-NOR composite gates are fixed irrespective of a logical level of the enable signal E. Thus, a sub-threshold current also is inhibited.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Integrated half-beam profile measurement and polar profile for circular radiation field symmetry assessment
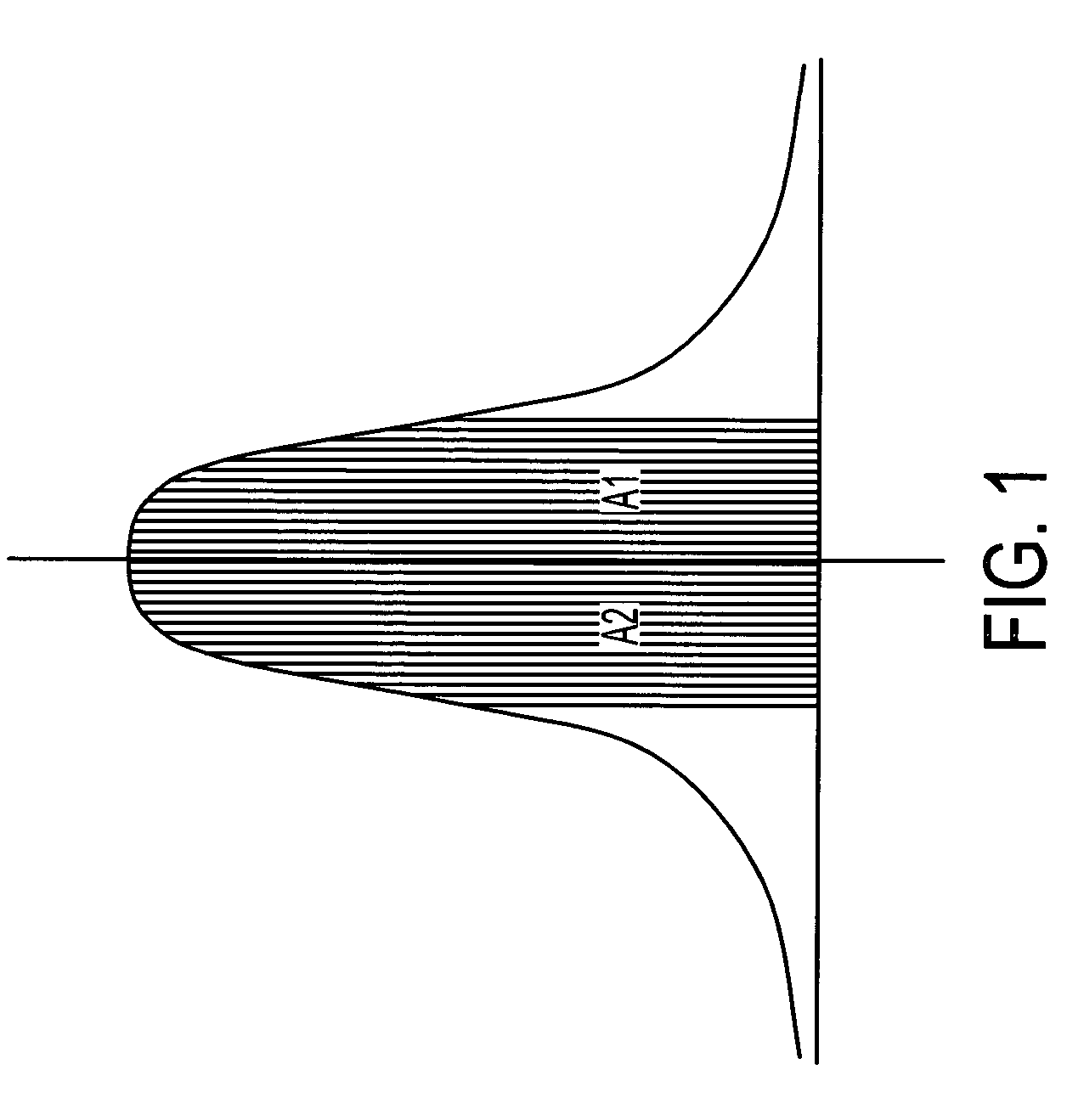
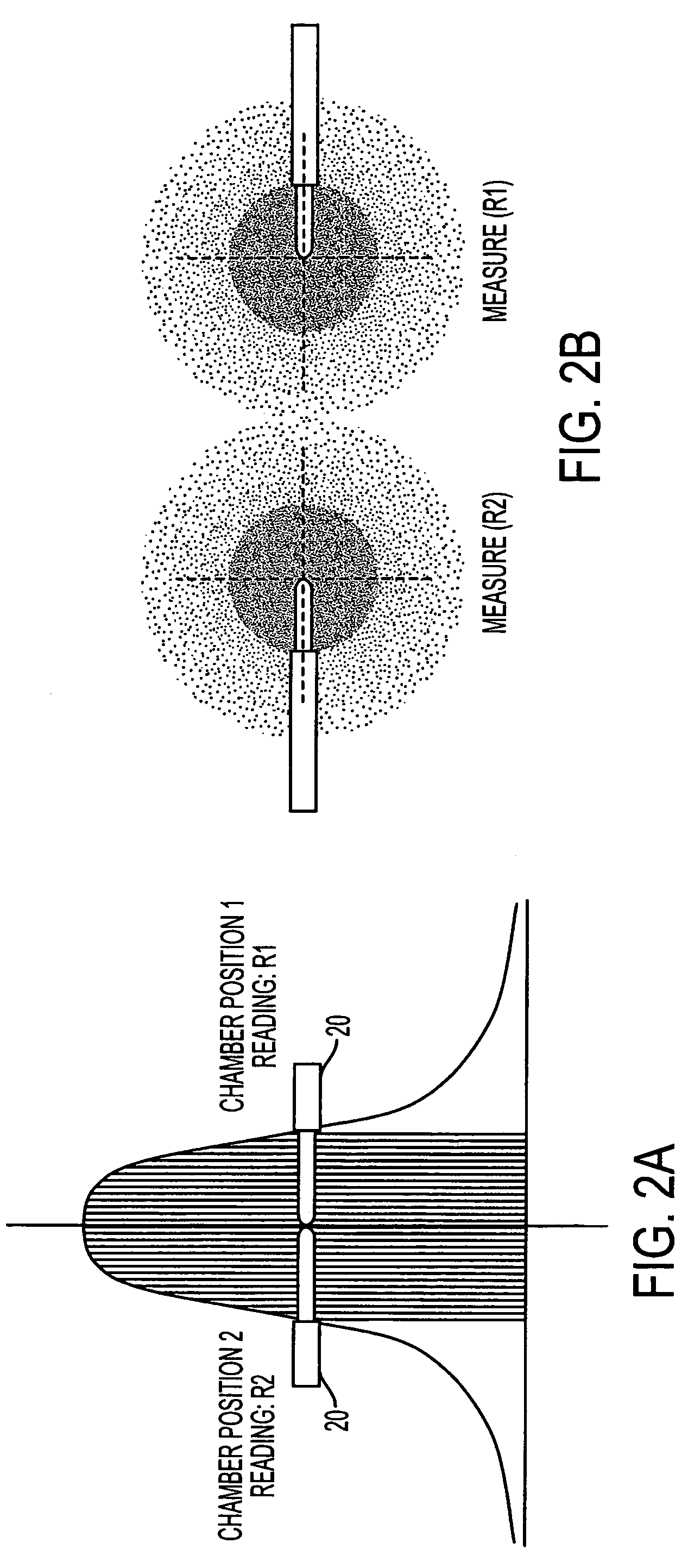
InactiveUS7531810B2Simplify QA processOptical radiation measurementElectrotherapyRadiosurgeryQuality assurance
A method for routine monitoring and quality assurance of field asymmetry of high energy circular radiation beam producing equipment. The quality assurance process of field symmetry for devices such as stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) systems is simplified by directly measuring the integration of the half-beam profile. The method of the invention provides that the field symmetry is obtained by positioning the tip of an ion chamber, with a collecting length approximately half the diameter of the beam, at the central axis of the beam, and rotating the ion chamber at varying angular positions, acquiring and comparing readings at desired angular positions. Each pair of readings from positions 180 degrees opposed from each other, are plugged into the equation, Asymmetry=2(R1−R2) / (R1+R2) to compute asymmetry.
Owner:SCHWADE JAMES G
Electromagnetic-force-balancing-type electronic balance
InactiveUS20070075810A1Improve adjustabilityHigh process yieldWeighing apparatus using electromagnetic balancingMagnetic materialsHysteresisMagnetic reluctance
Disclosed is an electromagnetic-force-balancing-type electronic balance having a magnetic circuit which includes a yoke 4, a first permanent magnet 1, a pole piece 3, a second permanent magnet 2 and a cover 5. A connection member 7 made of a magnetic material is disposed in an air-gap region included in the magnetic circuit. The connection member 7 may be disposed between the second permanent magnet 2 and the cover 5 or between the cover 5 and the yoke 4 to facilitate assembling operations. Alternatively, first and second gap-defining members 8, 9 made of a non-magnetic material may be disposed, respectively, between the first permanent magnet 1 and the yoke 4 and between the second permanent magnet 2 and the cover 5, to provide symmetric properties in magnetic sub-circuits so as to counteract an imbalance in hysteresis characteristic. The present invention can suppress adverse influences of a magnetic resistance caused by an air gap existing in the magnetic circuit of the electronic balance.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
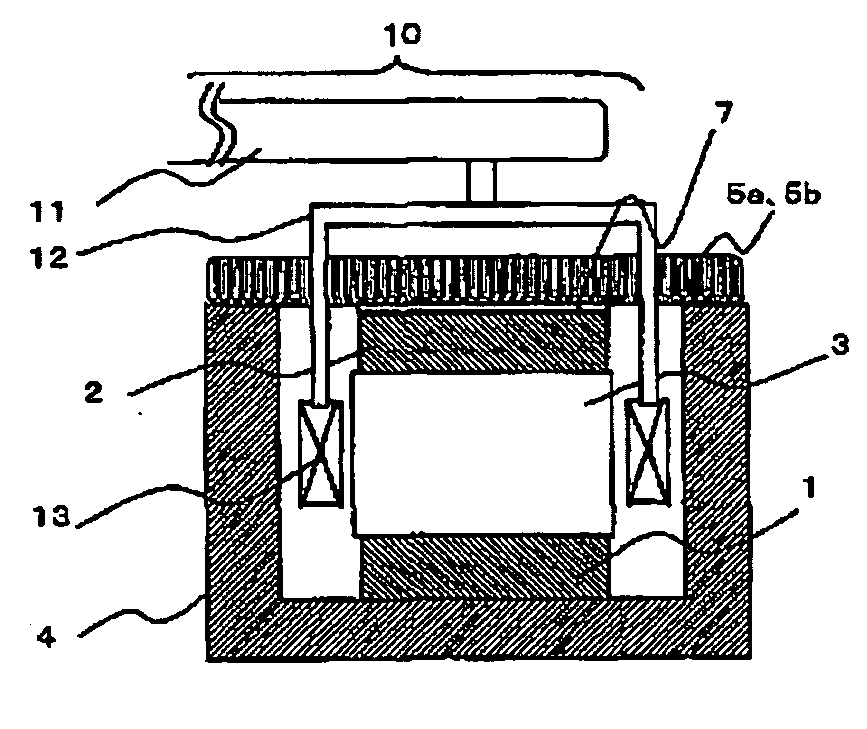
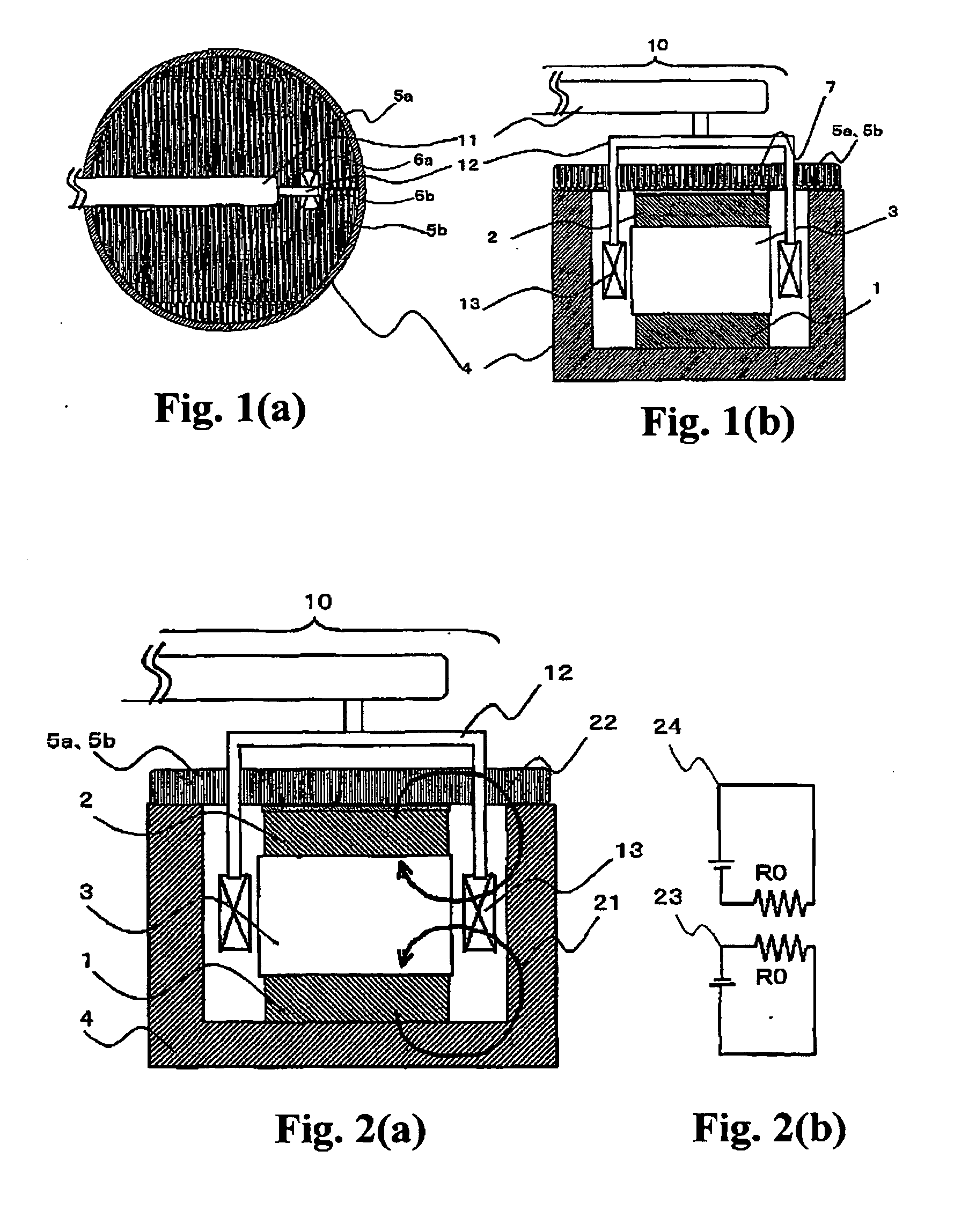
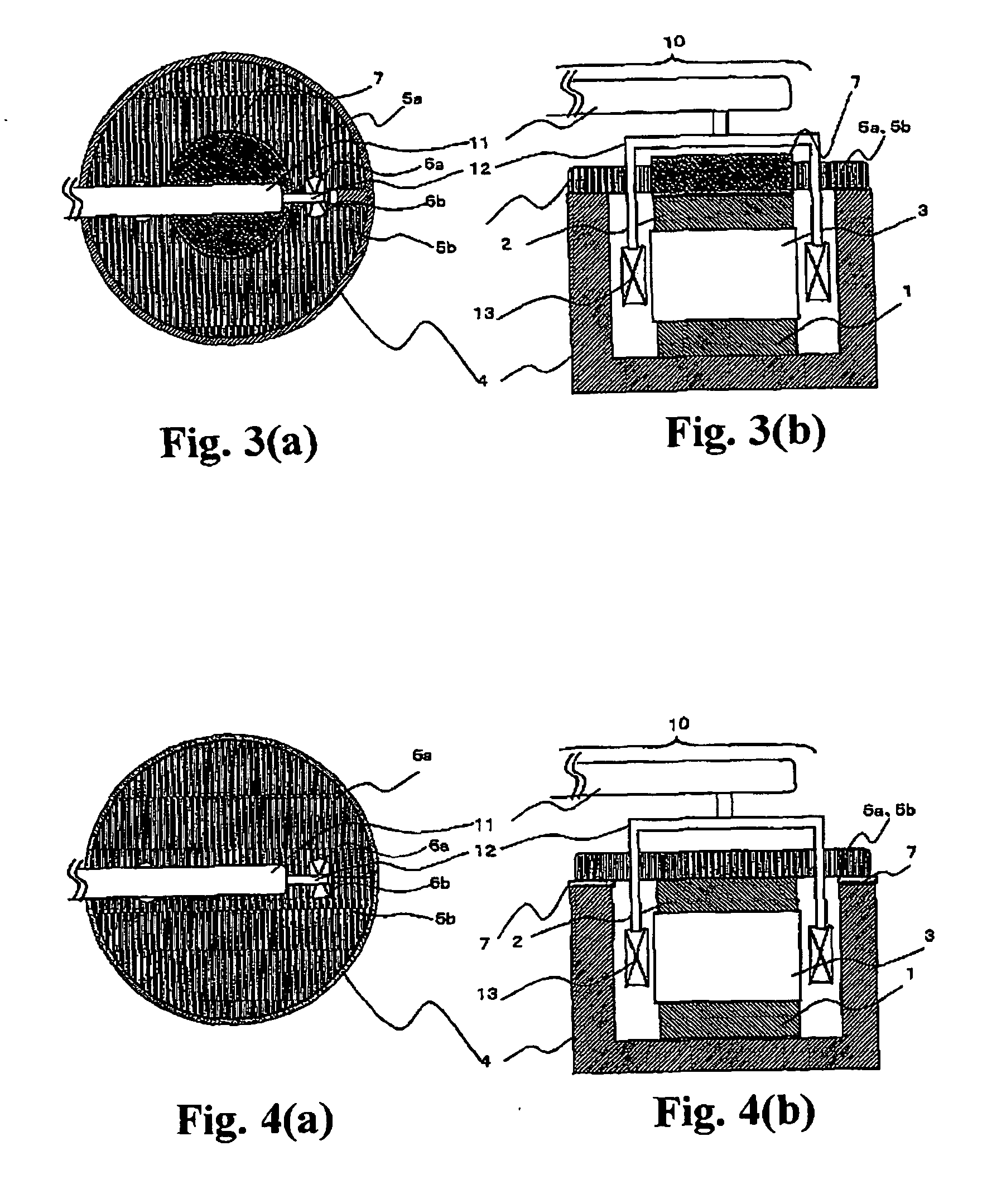
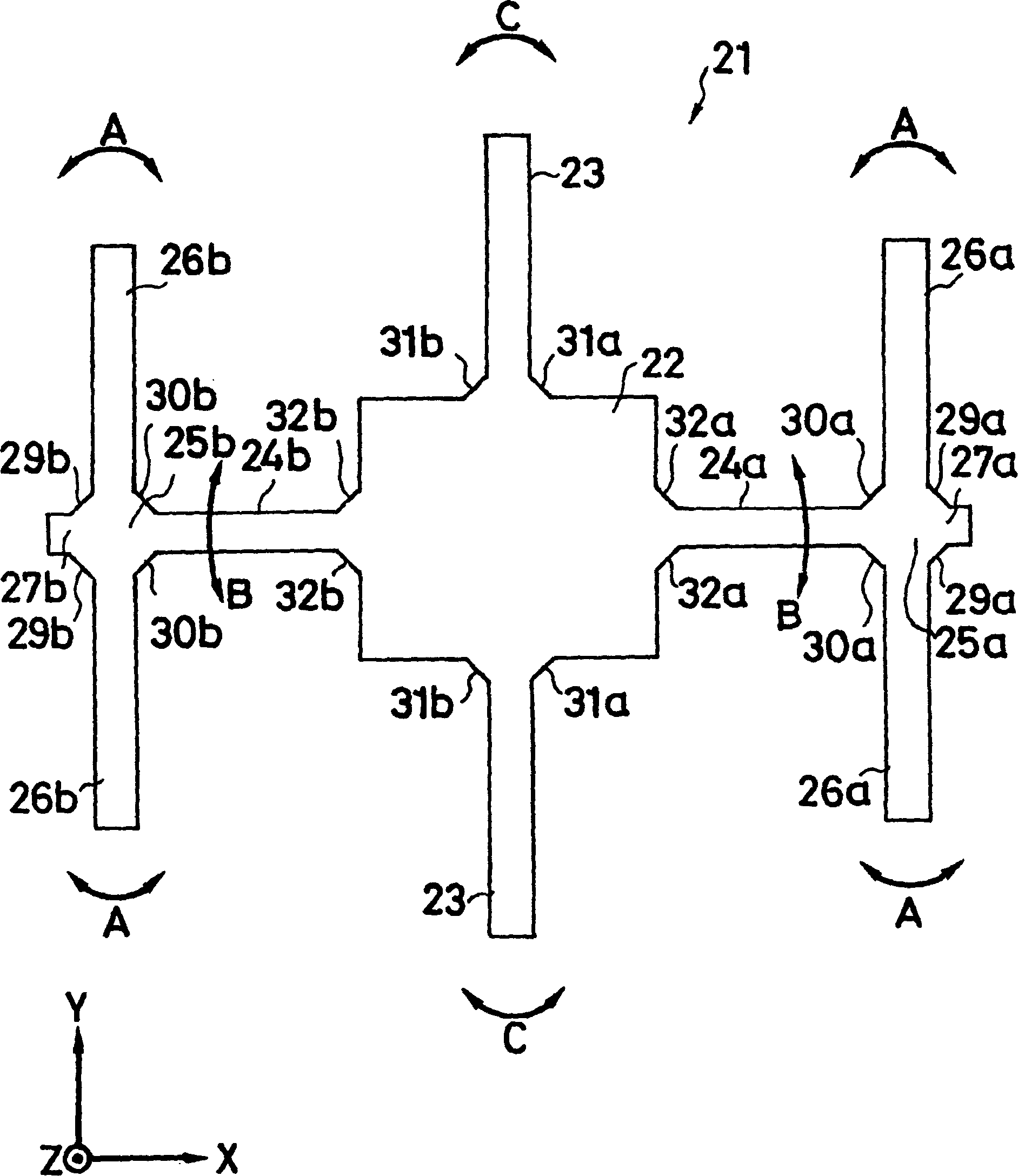
Piezoelectric vibration gyro element, method for manufacturing the same, and piezoelectric vibration gyro sensor
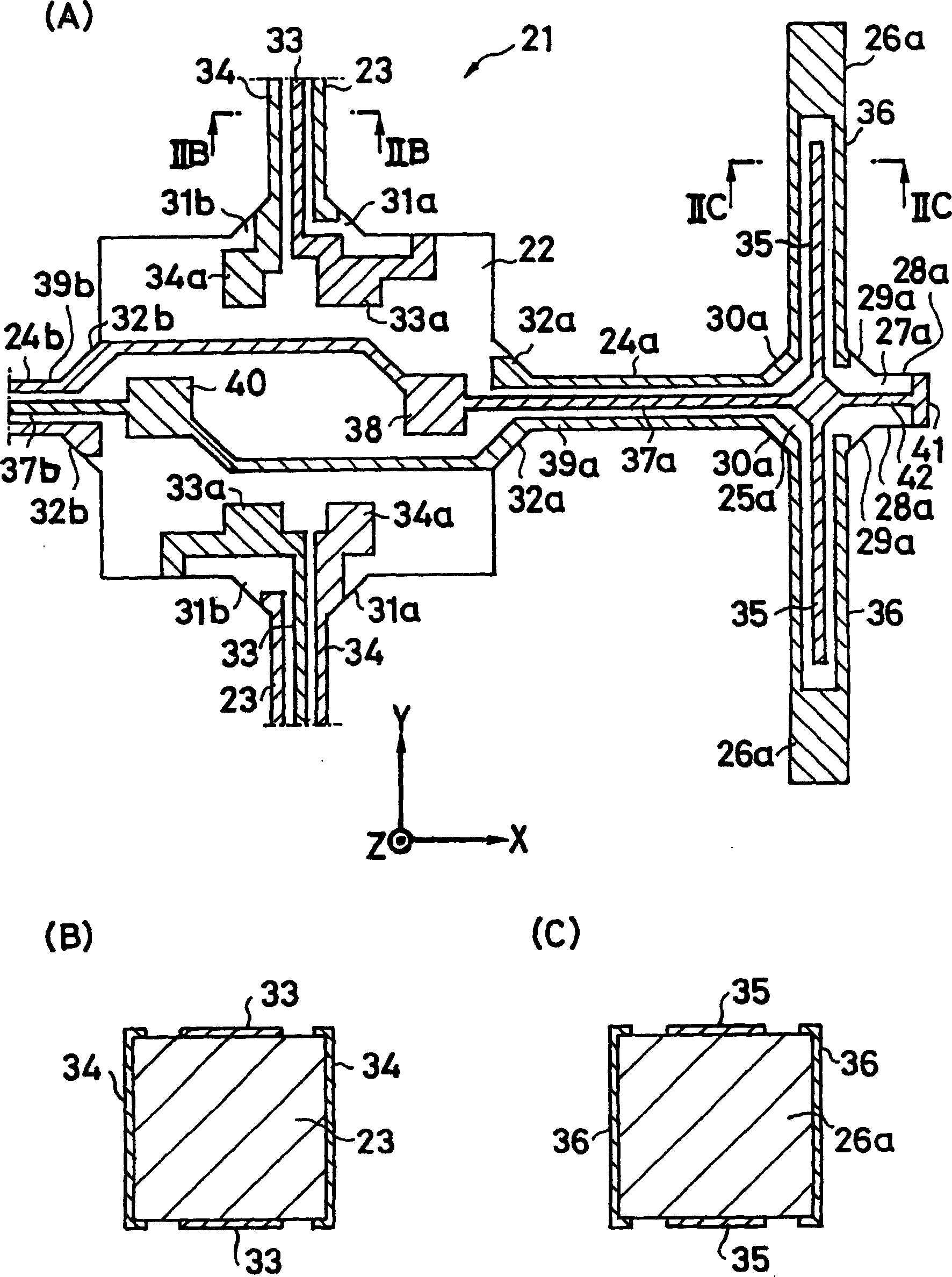
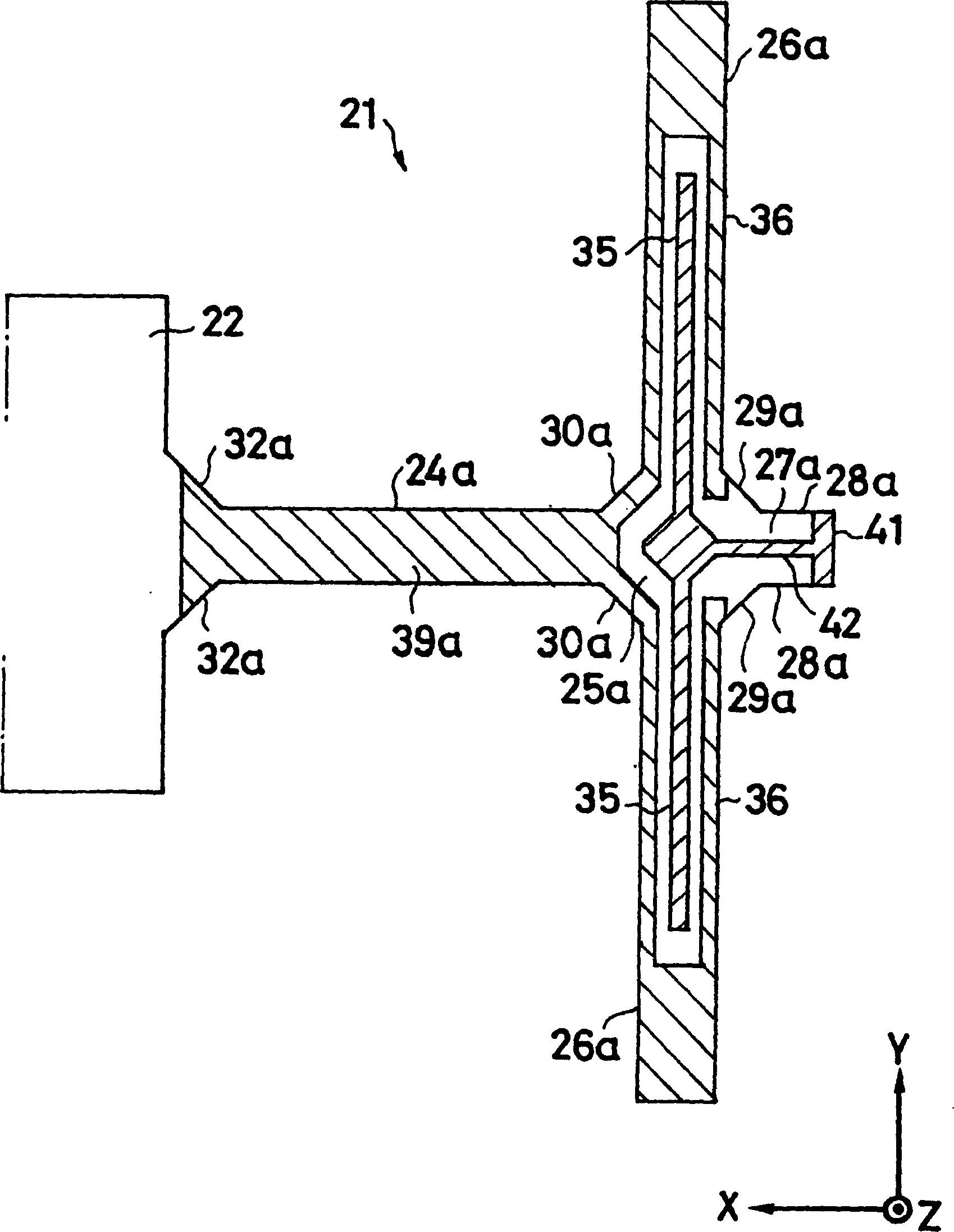
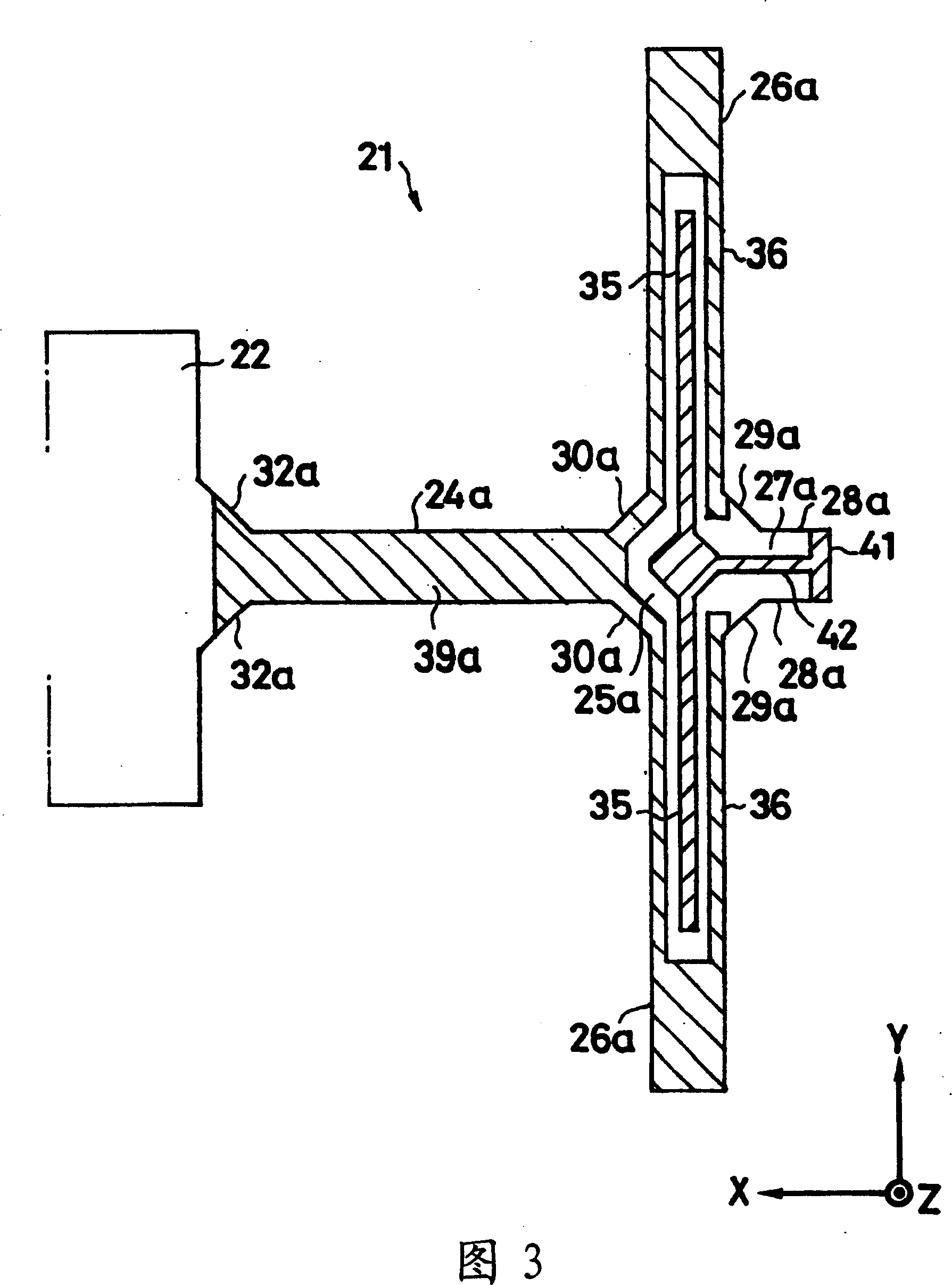
InactiveCN1573290AGuaranteed symmetryEliminate electrical shortsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyMechanical apparatusGyroscopeClassical mechanics
To ensure a symmetric property of bending vibrations for vibrating arms, and to accurately and easily divide electrodes, in a piezoelectric vibrating gyroscope element provided with a pair of vibrating arms for detection at the center thereof and connecting arms on both sides thereof, and a pair of vibrating arms for drive at their tip parts. Planar parts 28a and 28b, oriented perpendicular to the direction of extension of the vibrating arms 26a and 26b for drive, are provided to both sides of the side surfaces of extension parts 27a and 27b extending further along the direction of extension of the tip parts of the connecting arms 24a and 24b from them. Wiring 42 is formed, in such a way, as to traverse the tip faces of the extension parts in the direction of their thickness and connect the tip parts of the connecting arms to the main front and back surfaces of the extension parts. First electrodes 35 and 35 in the main front and back surfaces of the vibrating arms for drive are electrically connected to each other. In an exposure process for dividing electrodes, the main surfaces and the side surfaces are simultaneously exposed obliquely from above perpendicular to the plane parts of the extension parts and at some angle from the perpendicular direction with respect to the main surfaces of the vibrating arms for driving.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Methods for detecting a hidden peak in wire fault location applications—improving the distance range resolution
InactiveUS8324906B2Testing electric installations on transportFault location by pulse reflection methodsImage resolutionPeak value
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Constant width beam forming method based on FIR filter
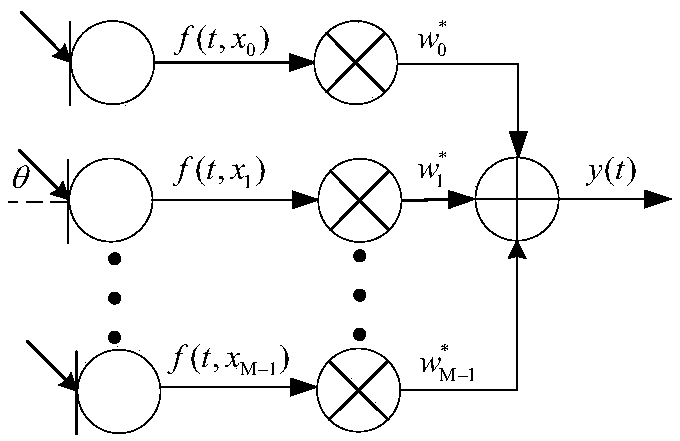
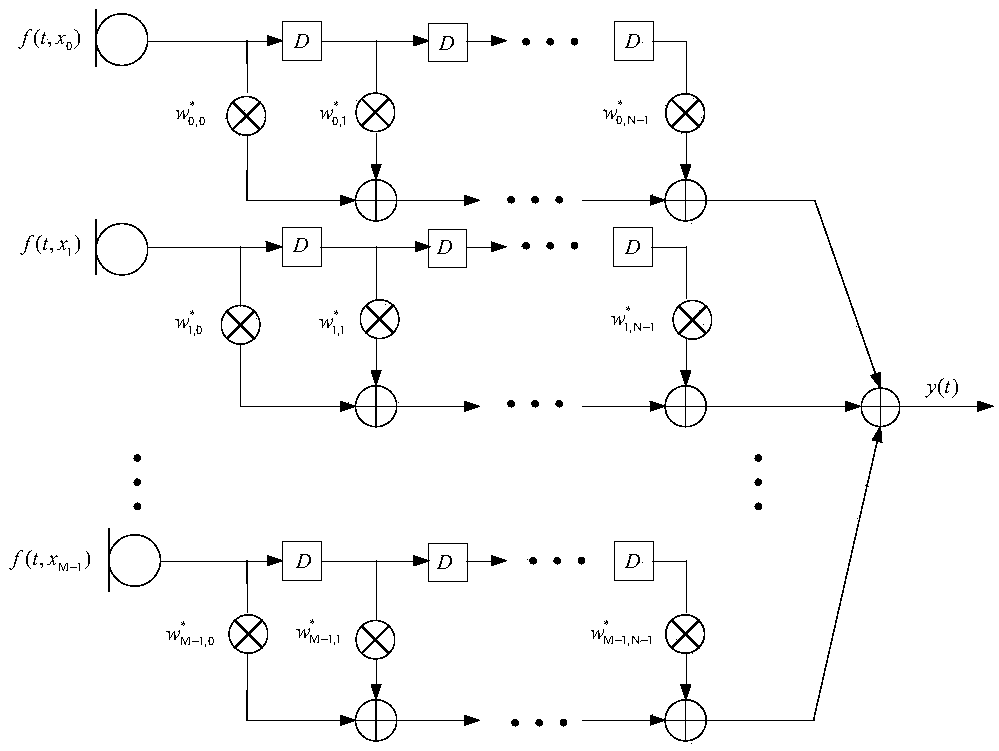
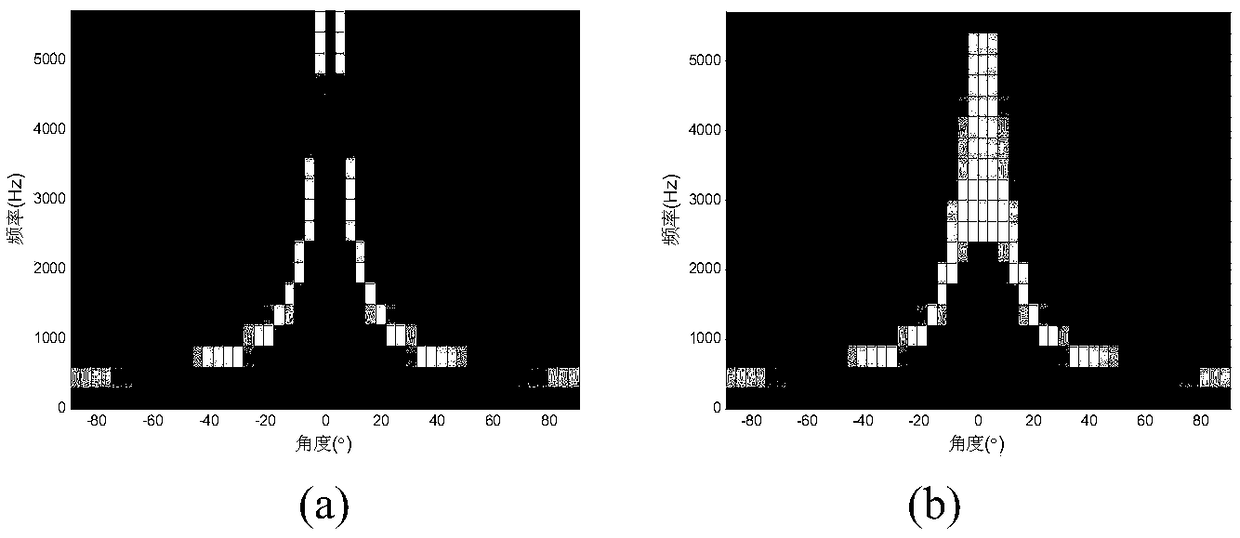
InactiveCN109493844AAchieving frequency invarianceUniform gainSound producing devicesSide lobeArray element
The invention discloses a constant width beam forming method based on an FIR filter, wherein a received signal f (t, x) =[f(t, x0), ..., f(t, xm), ..., f(t, xM-1)] T of a microphone array is processedthrough a beam forming method to obtain an output signal which is shown in the description, wherein f (t, x) represents a sampled signal of the microphone array at a t time position of x, () T represents a matrix transpose, m represents a microphone index, wherein m=0,1,... M-1, M represents the number of microphone array elements, xm represents the array element positions corresponding to the mth microphone, and x=[x0, ... ,xm,... ,xM-1); N represents the order of the FIR filter followed by each microphone, the description represents the coefficient of the n-order FIR filter followed by themth microphone, the superscript * represents the conjugate, and Ts represents the delay between adjacent filters. The method can enable the array to have the same spatial response to input signals with different frequencies within the main lobe width, and the beam forming device with approximately constant beam width and low side lobe array response is designed by utilizing the symmetric properties of the FIR filter array and microphone uniform linear array.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
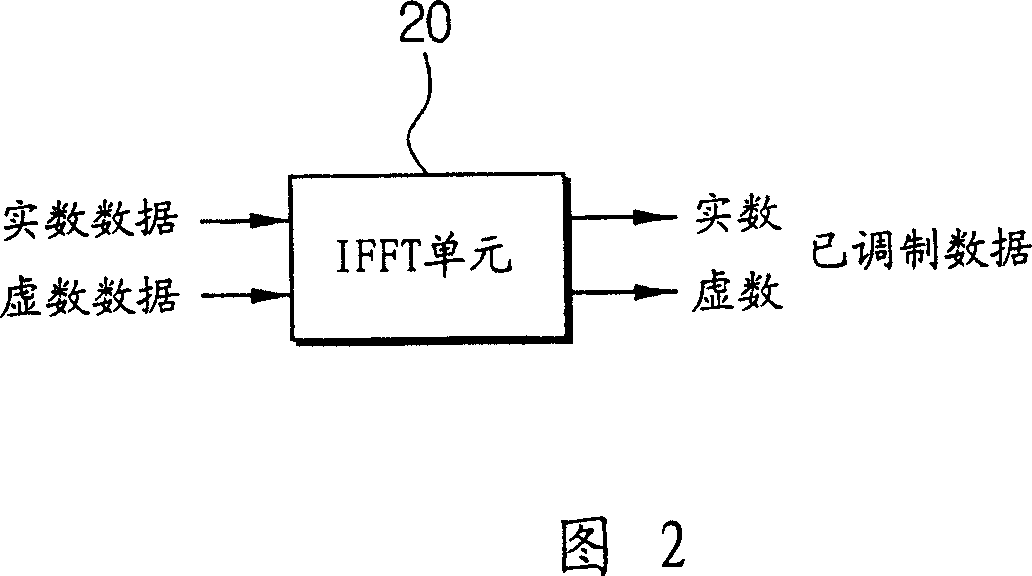
Time-recursive lattice structure for IFFT in DMT application
InactiveUS6985919B2Reduce the number of iterationsReduce power consumptionDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsComputer scienceData sequences
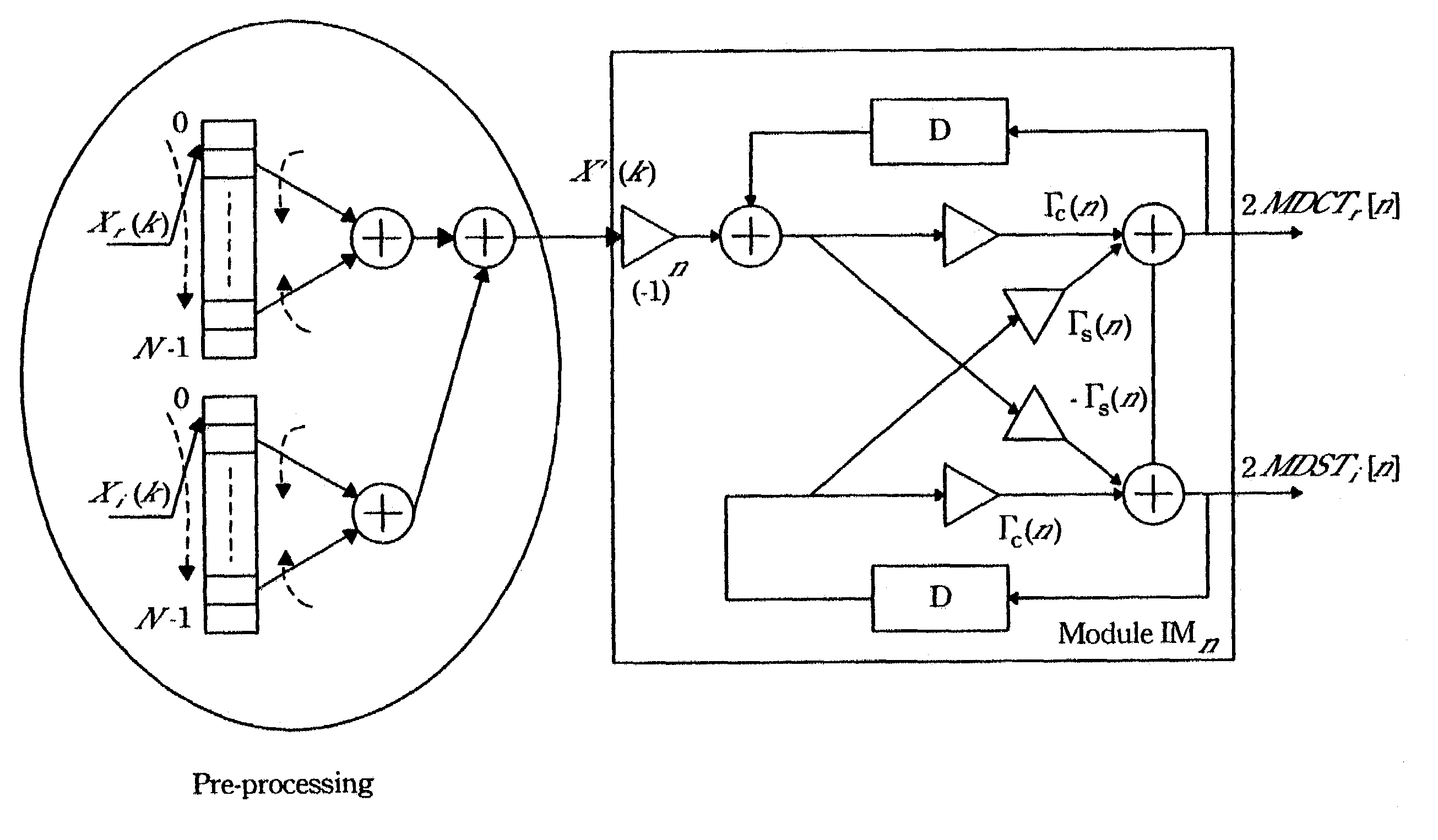
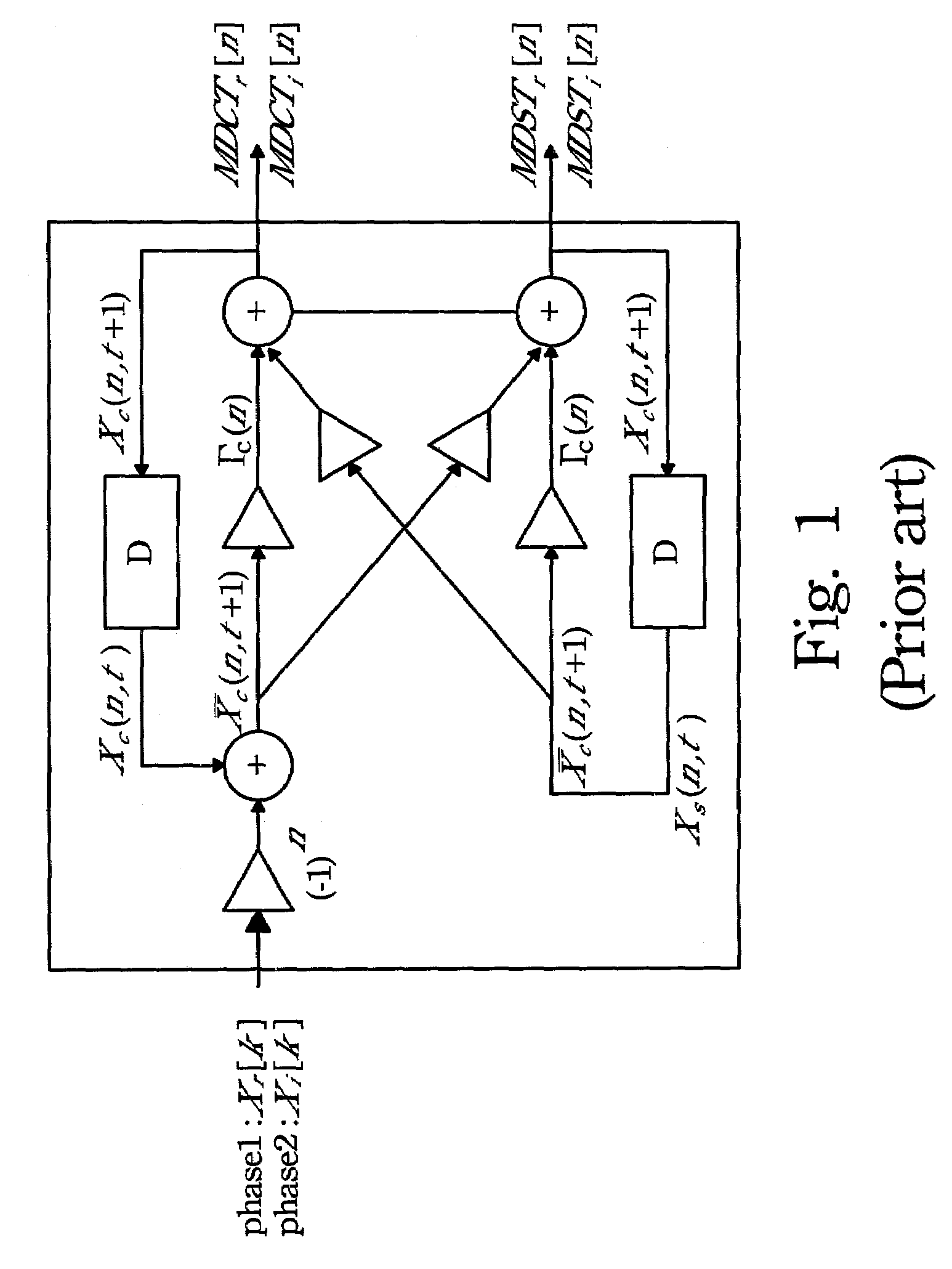
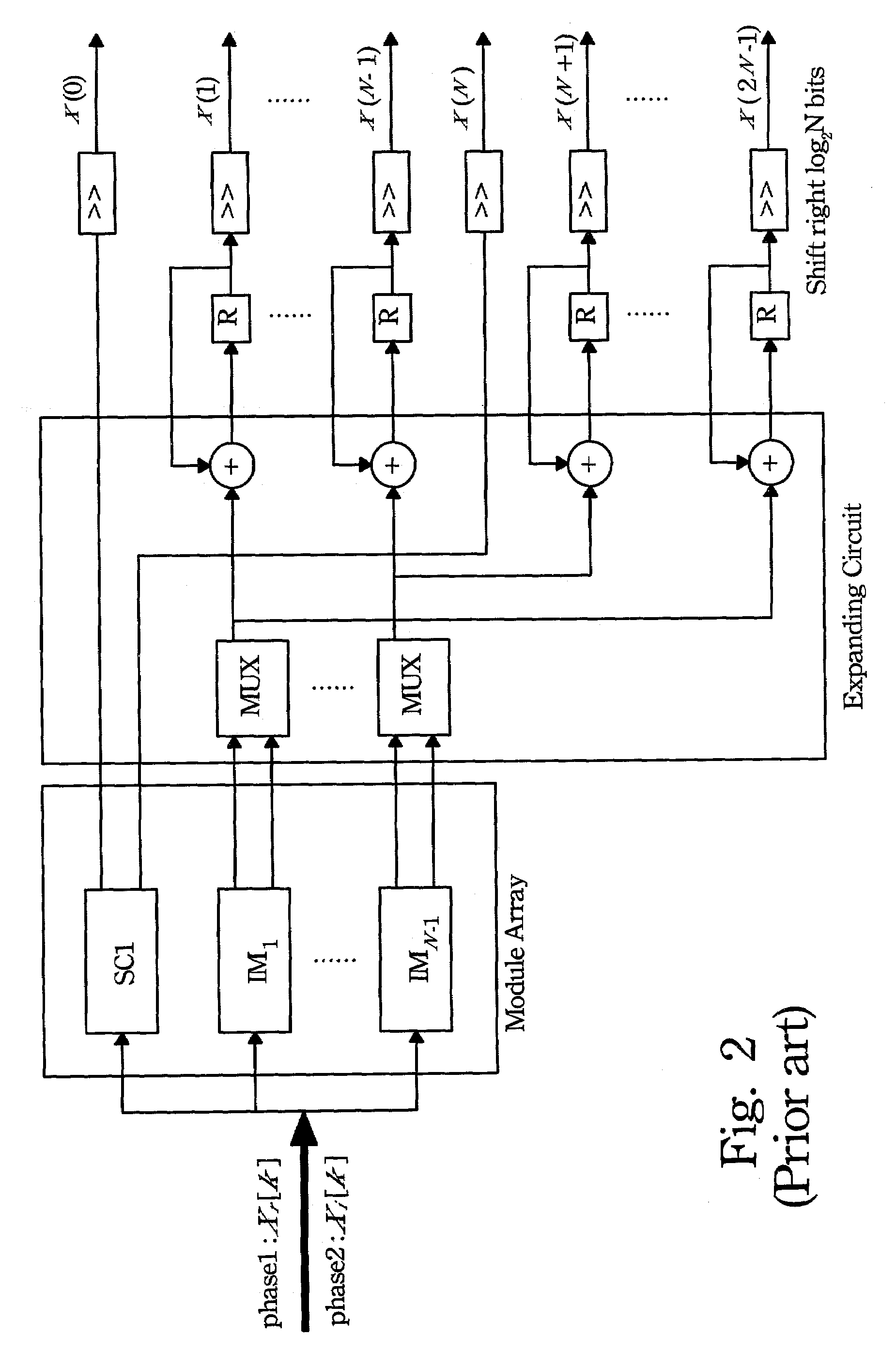
The present invention may significantly reduce the number of iteration of the time recursive IFFT structure. First, the real and imaginary part of the input signal are modified based on the symmetric and anti-symmetric. Then, they are mixed together by an adder and fed into the lattice module. Next, an IFFT is performed on the modified input data sequence to generate a transformed sequence. Through the symmetric and anti-symmetric properties, the redundant terms may be eliminated.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
On-line detection device with function of calibrating systematic error for wave aberration of projection objective of photoetching machine
ActiveCN101655670BHigh measurement accuracyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusAs elementMeasurement device
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Semiconductor device having a pseudo power supply wiring
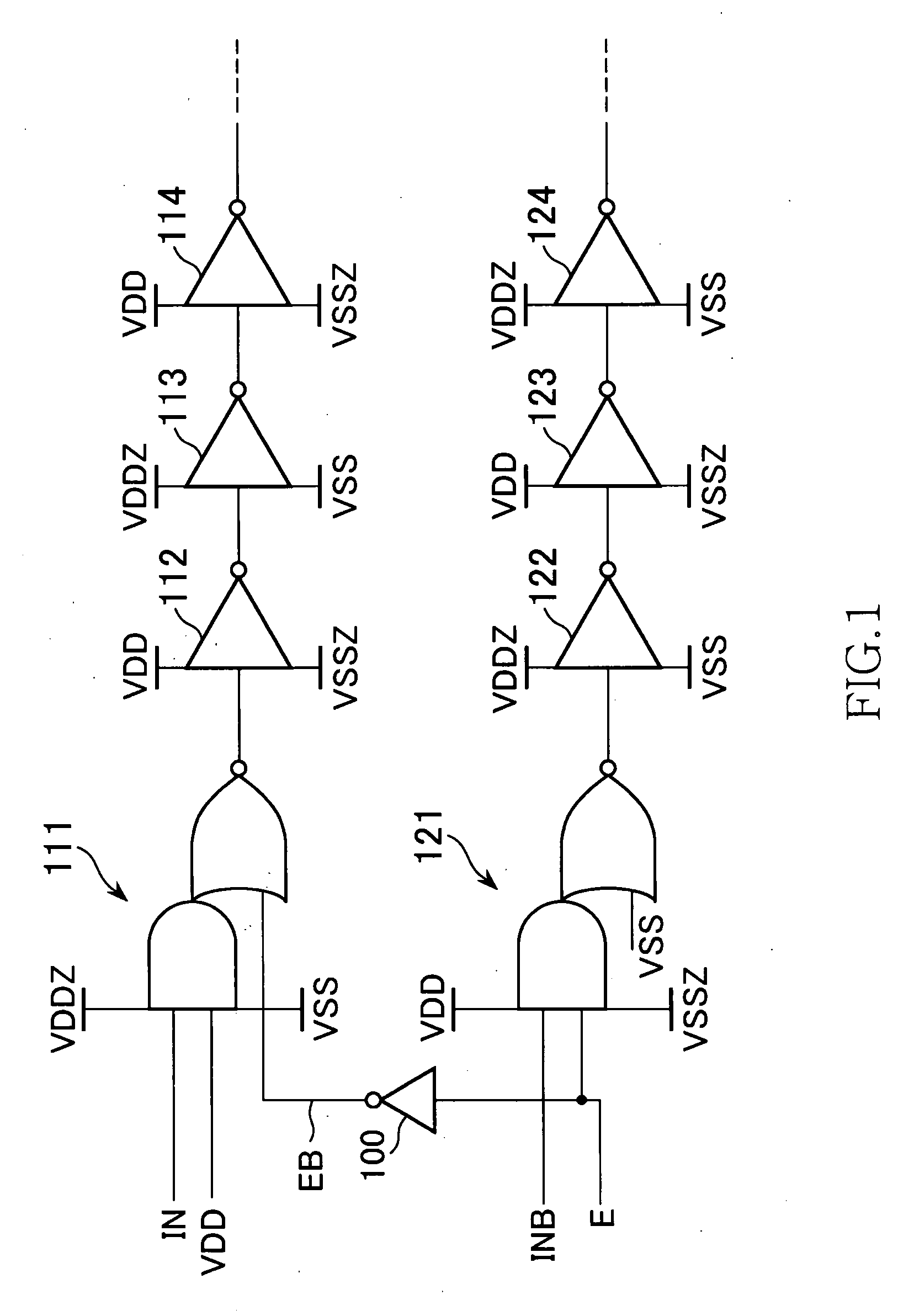
ActiveUS7541839B2Power reduction in field effect transistorsReliability increasing modificationsSub thresholdEngineering
A semiconductor device including an AND-NOR composite gate of which AND unit is supplied with input signals IN and VDD and NOR unit is supplied with an inverted signal EB of an enable signal E, and an AND-NOR composite gate of which AND unit is supplied with an input signal INB and an enable signal E and NOR unit is supplied with VSS. These gates are inserted into a path to which the input signals IN and INB are supplied. Thereby, a symmetric property of a complimentary signal can be retained. Further, outputs of the AND-NOR composite gates are fixed irrespective of a logical level of the enable signal E. Thus, a sub-threshold current also is inhibited.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
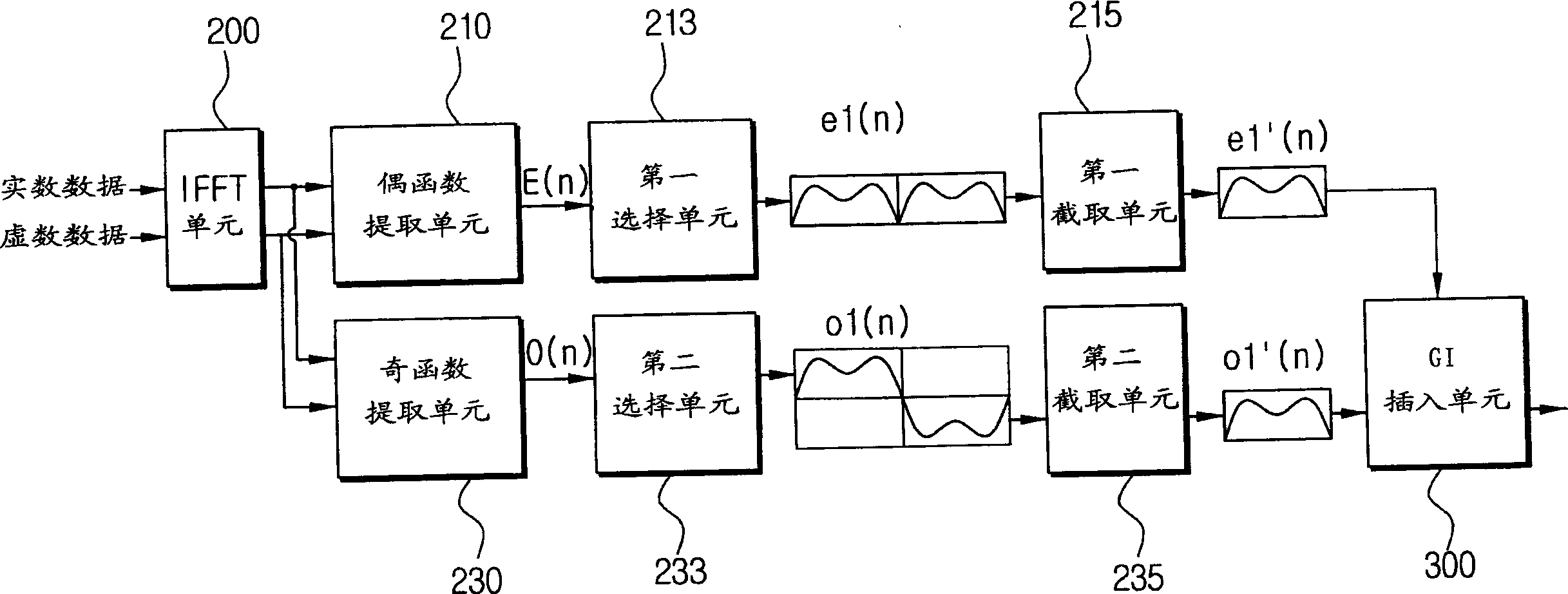
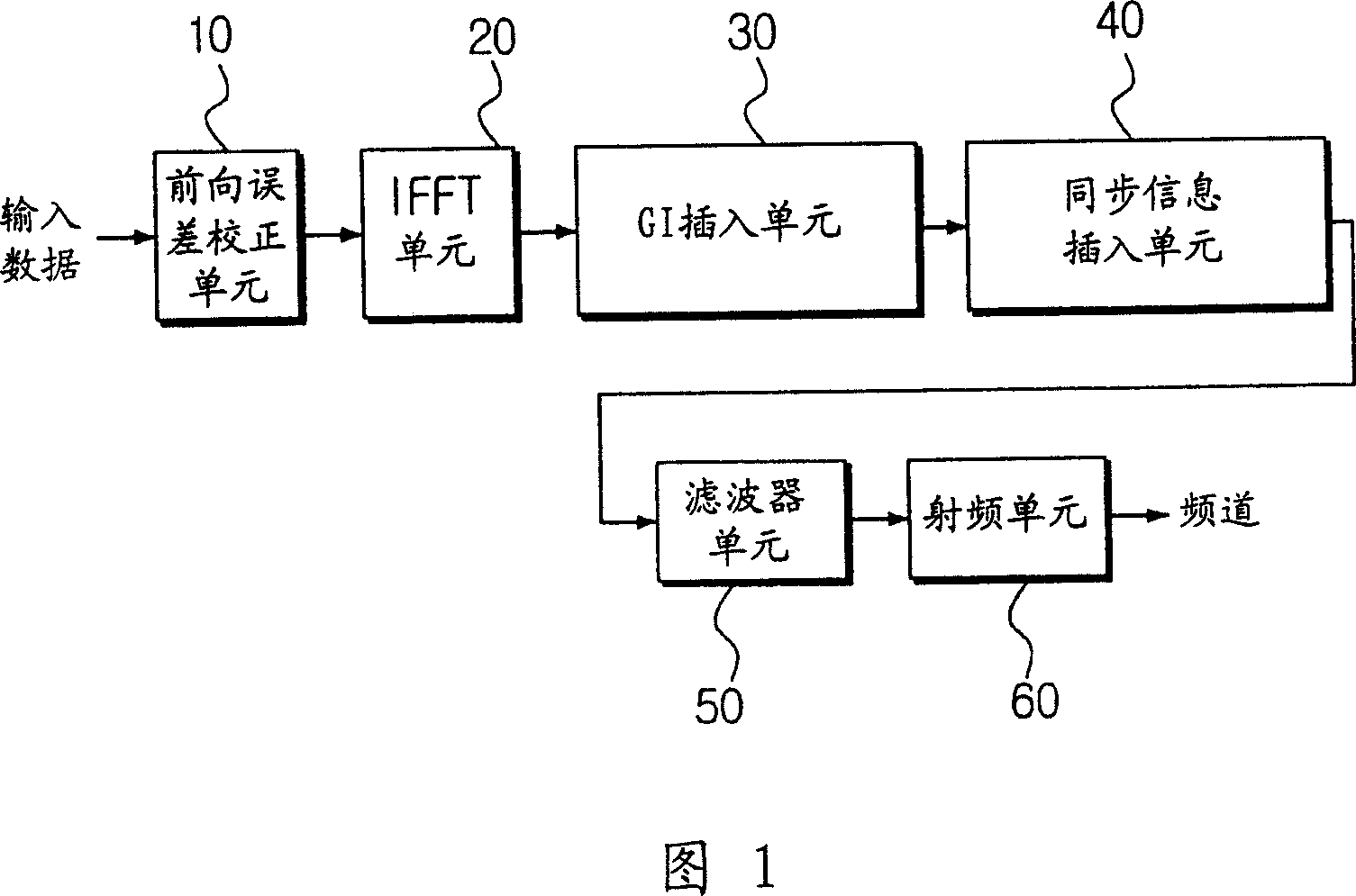
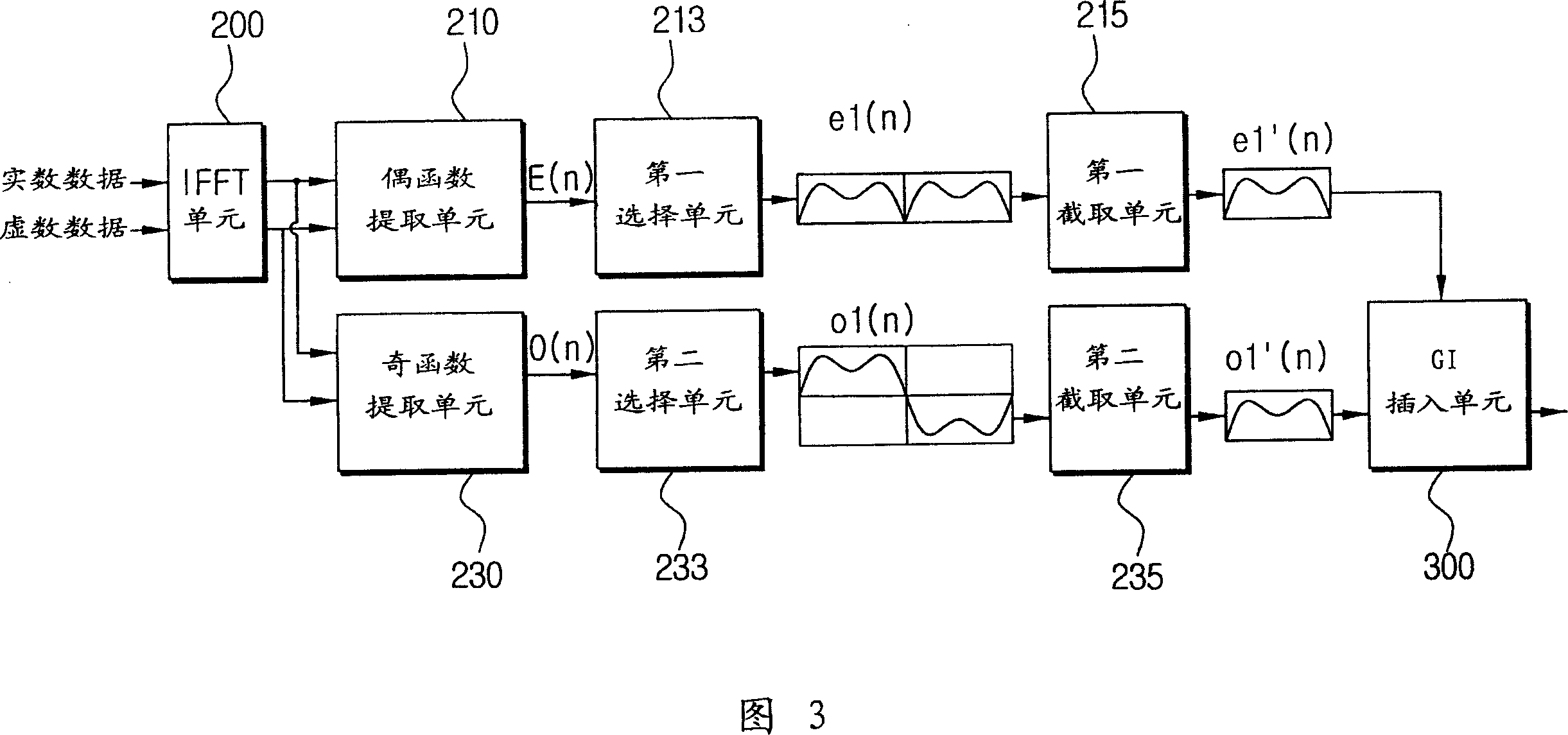
OFDM transmitter for raising transfer rate and signal compressing method
InactiveCN1466291AIncrease data rateCode division multiplexFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTime domainOfdm transmitter
An OFDM transmitter capable of improving a transmission rate of OFDM signals and a method for compressing signals thereof are provided to increase a transmission rate of whole data by reducing the length of one OFDM symbol. An inverse fourier transform unit(200) transforms OFDM(Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) signals of a frequency domain into OFDM signals of a time domain through inverse fourier transform. An even function extracting unit(210) extracts an even function signal symmetrical to a y axis from the OFDM signals of the time domain. An odd function extracting unit(230) extracts an odd function signal symmetrical to the origin from the OFDM signals of the time domain. The even function signal is formed of the sum of a first even function signal and a second even function signal. A first selecting unit(213) selects anyone of the first even function signal and the second even function signal. The odd function signal is formed of the sum of a first odd function signal and a second odd function signal. A second selecting unit(233) selects anyone of the first odd function signal and the second odd function signal. A first cutting unit(215) takes one half signal of the selected even function signal. A second cutting unit(235) takes one half signal of the selected odd function signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Spin-stabilized magnetic levitation without vertical axis of rotation
The symmetry properties of a magnetic levitation arrangement are exploited to produce spin-stabilized magnetic levitation without aligning the rotational axis of the rotor with the direction of the force of gravity. The rotation of the rotor stabilizes perturbations directed parallel to the rotational axis.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Piezoelectric vibration gyro element, method for manufacturing the same, and piezoelectric vibration gyro sensor
InactiveCN100351609CGuaranteed symmetryEliminate electrical shortsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyMechanical apparatusGyroscopeClassical mechanics
To ensure a symmetric property of bending vibrations for vibrating arms, and to accurately and easily divide electrodes, in a piezoelectric vibrating gyroscope element provided with a pair of vibrating arms for detection at the center thereof and connecting arms on both sides thereof, and a pair of vibrating arms for drive at their tip parts. Planar parts 28a and 28b, oriented perpendicular to the direction of extension of the vibrating arms 26a and 26b for drive, are provided to both sides of the side surfaces of extension parts 27a and 27b extending further along the direction of extension of the tip parts of the connecting arms 24a and 24b from them. Wiring 42 is formed, in such a way, as to traverse the tip faces of the extension parts in the direction of their thickness and connect the tip parts of the connecting arms to the main front and back surfaces of the extension parts. First electrodes 35 and 35 in the main front and back surfaces of the vibrating arms for drive are electrically connected to each other. In an exposure process for dividing electrodes, the main surfaces and the side surfaces are simultaneously exposed obliquely from above perpendicular to the plane parts of the extension parts and at some angle from the perpendicular direction with respect to the main surfaces of the vibrating arms for driving.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Boundary element analytic method and a boundary element analytic program
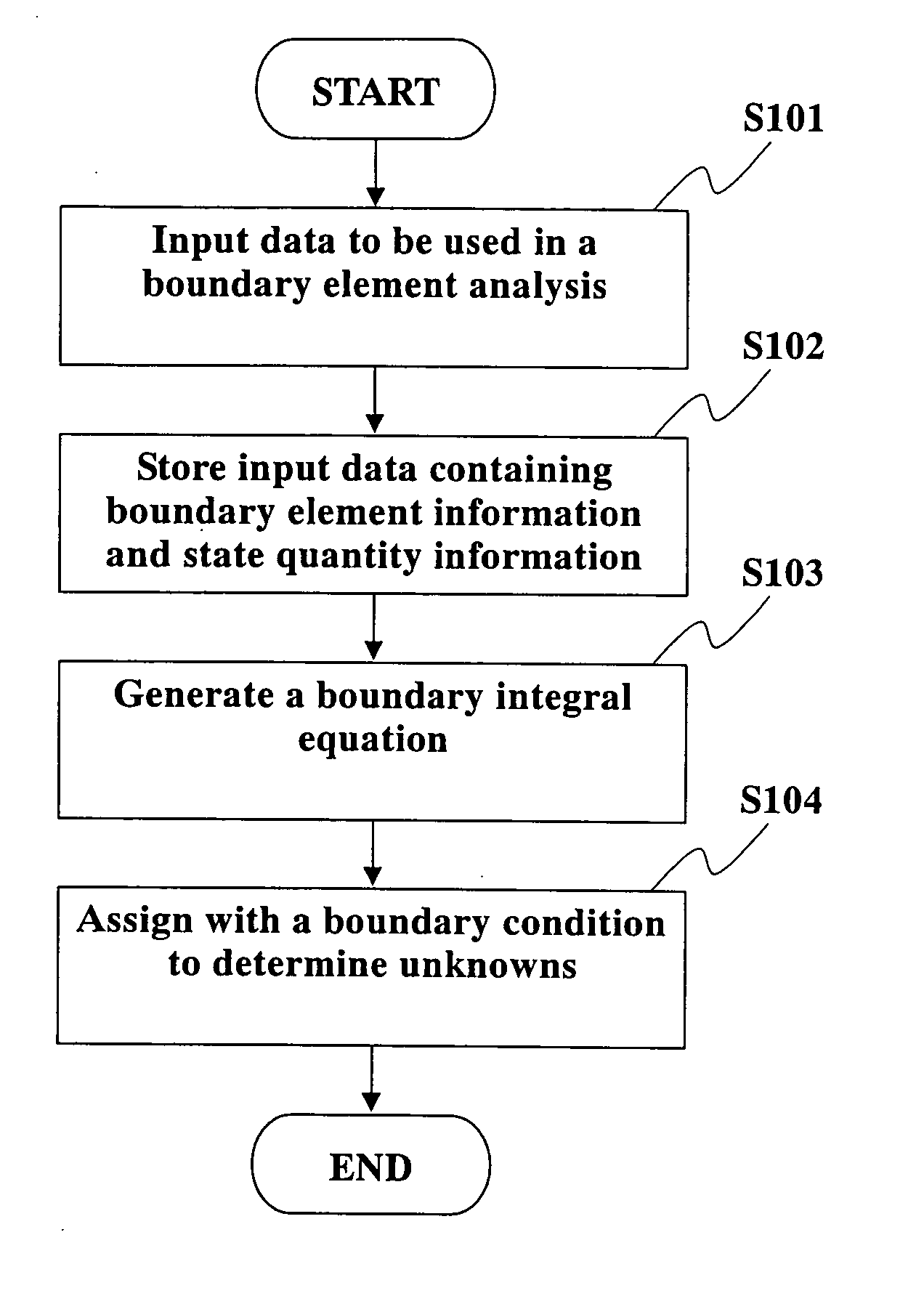
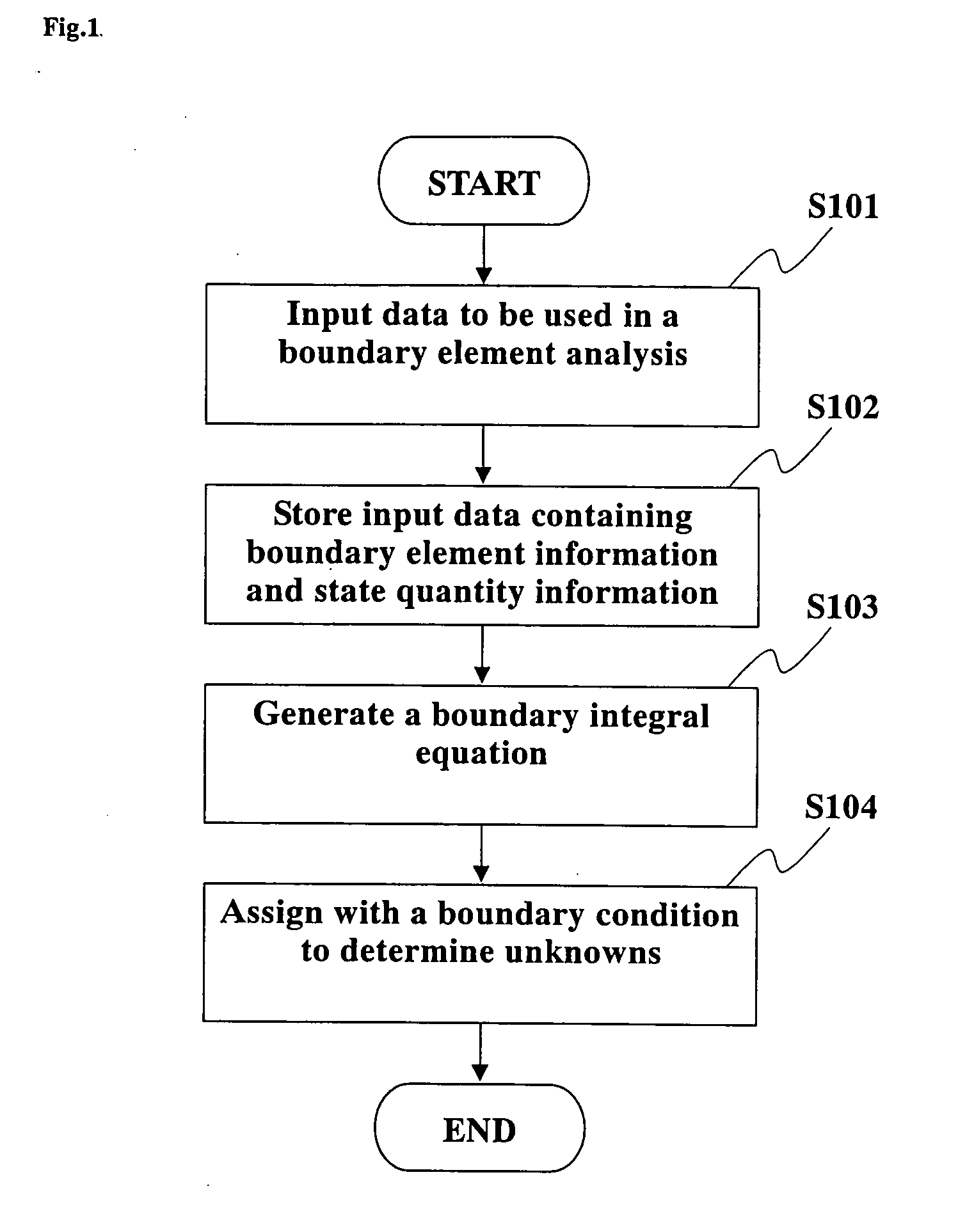
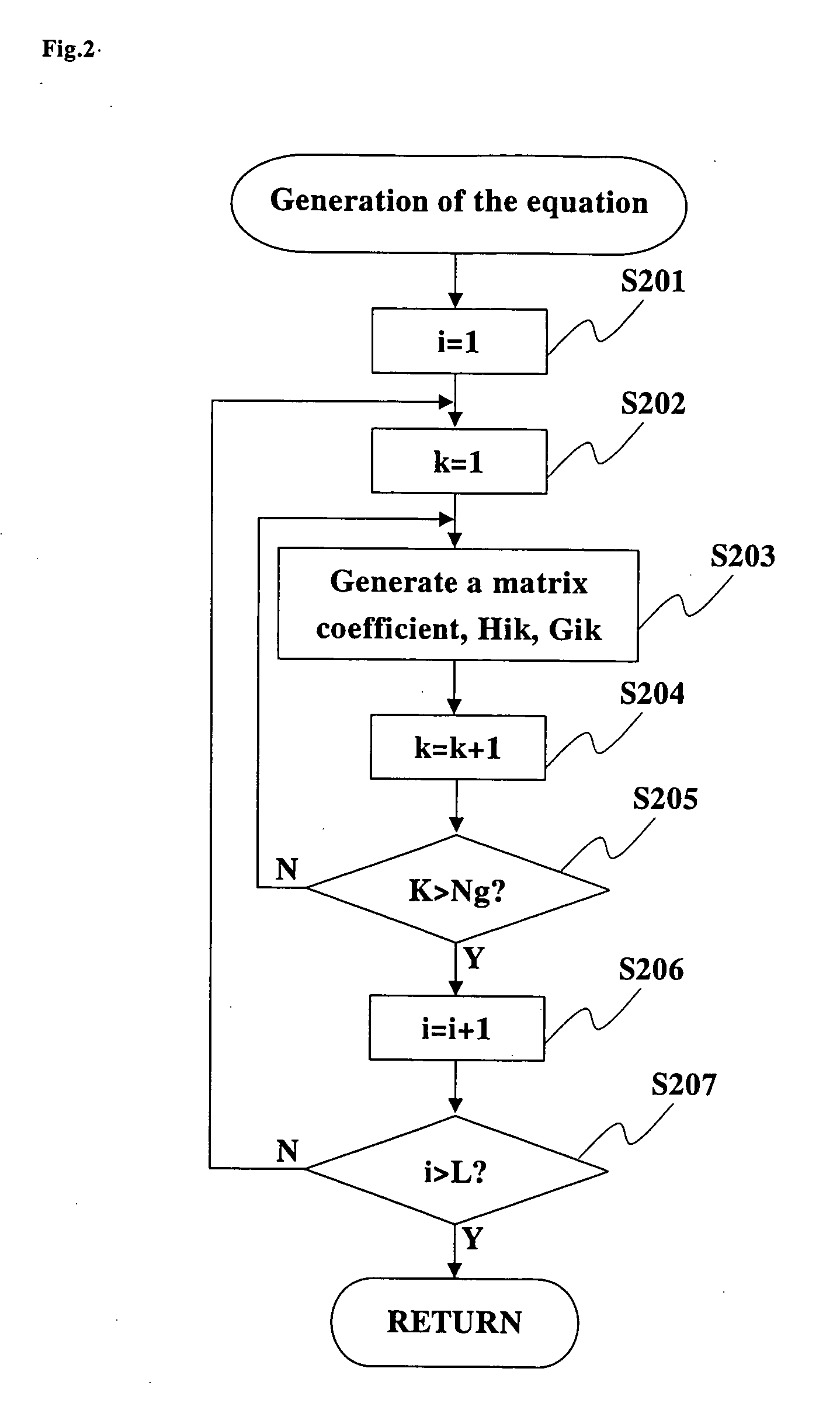
InactiveUS20060004552A1Efficient analysisReduce in quantityComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationBoundary valuesElement analysis
An object of the present invention is to provide a boundary element analytic method and a boundary element analytic program, which are capable of coping with the problem of diversity in symmetric property to be encountered when carrying out an analytic operation by taking advantage of the symmetric property of a subject to be analyzed, and thus providing an efficient analysis. Various types of data for the use in the boundary element analysis, which have been previously input at step S101, are stored at step S102. To carry out this operation, at least boundary element definition information for defining a boundary element in the subject to be analyzed and state quantity information in which boundary element identification information for identifying the defined boundary element is associated with the boundary element for each state quantity thereof. At step 103, the input different types of data are used to generate a digitized boundary integral equation with a boundary value at a point of element on each defined boundary element taken as a variable. Then, at step S104, the generated boundary integral equation is assigned with the input boundary condition to sort out any unknowns, thus obtaining the simultaneous equations. The obtained simultaneous equations are then solved to determine respective values for the unknowns.
Owner:EBARA CORP +1
OFDM transmitter for raising transfer rate and signal compressing method
InactiveCN1317839CIncrease data rateCode division multiplexFrequency-modulated carrier systemsTime domainOfdm transmitter
An OFDM transmitter capable of improving a transmission rate of OFDM signals and a method for compressing signals thereof are provided to increase a transmission rate of whole data by reducing the length of one OFDM symbol. An inverse fourier transform unit(200) transforms OFDM(Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) signals of a frequency domain into OFDM signals of a time domain through inverse fourier transform. An even function extracting unit(210) extracts an even function signal symmetrical to a y axis from the OFDM signals of the time domain. An odd function extracting unit(230) extracts an odd function signal symmetrical to the origin from the OFDM signals of the time domain. The even function signal is formed of the sum of a first even function signal and a second even function signal. A first selecting unit(213) selects anyone of the first even function signal and the second even function signal. The odd function signal is formed of the sum of a first odd function signal and a second odd function signal. A second selecting unit(233) selects anyone of the first odd function signal and the second odd function signal. A first cutting unit(215) takes one half signal of the selected even function signal. A second cutting unit(235) takes one half signal of the selected odd function signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
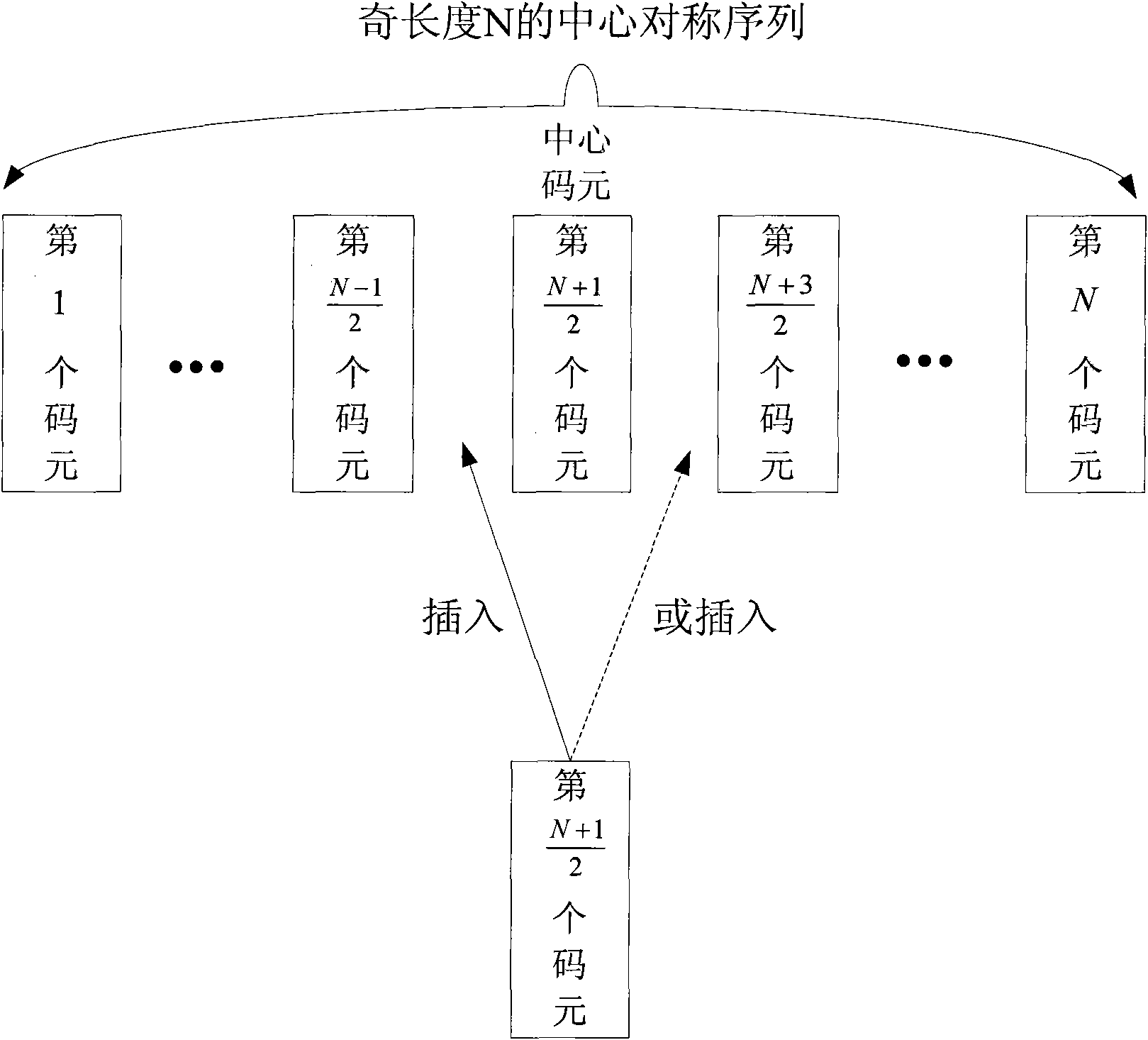
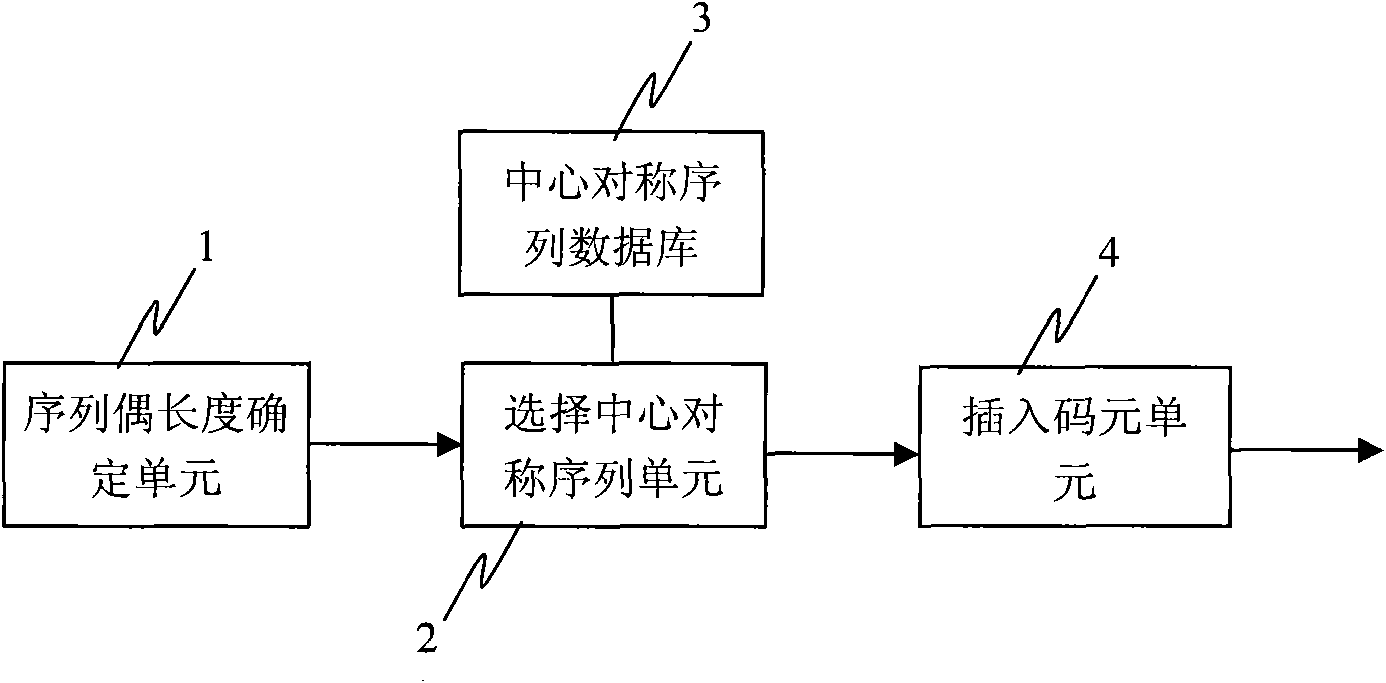
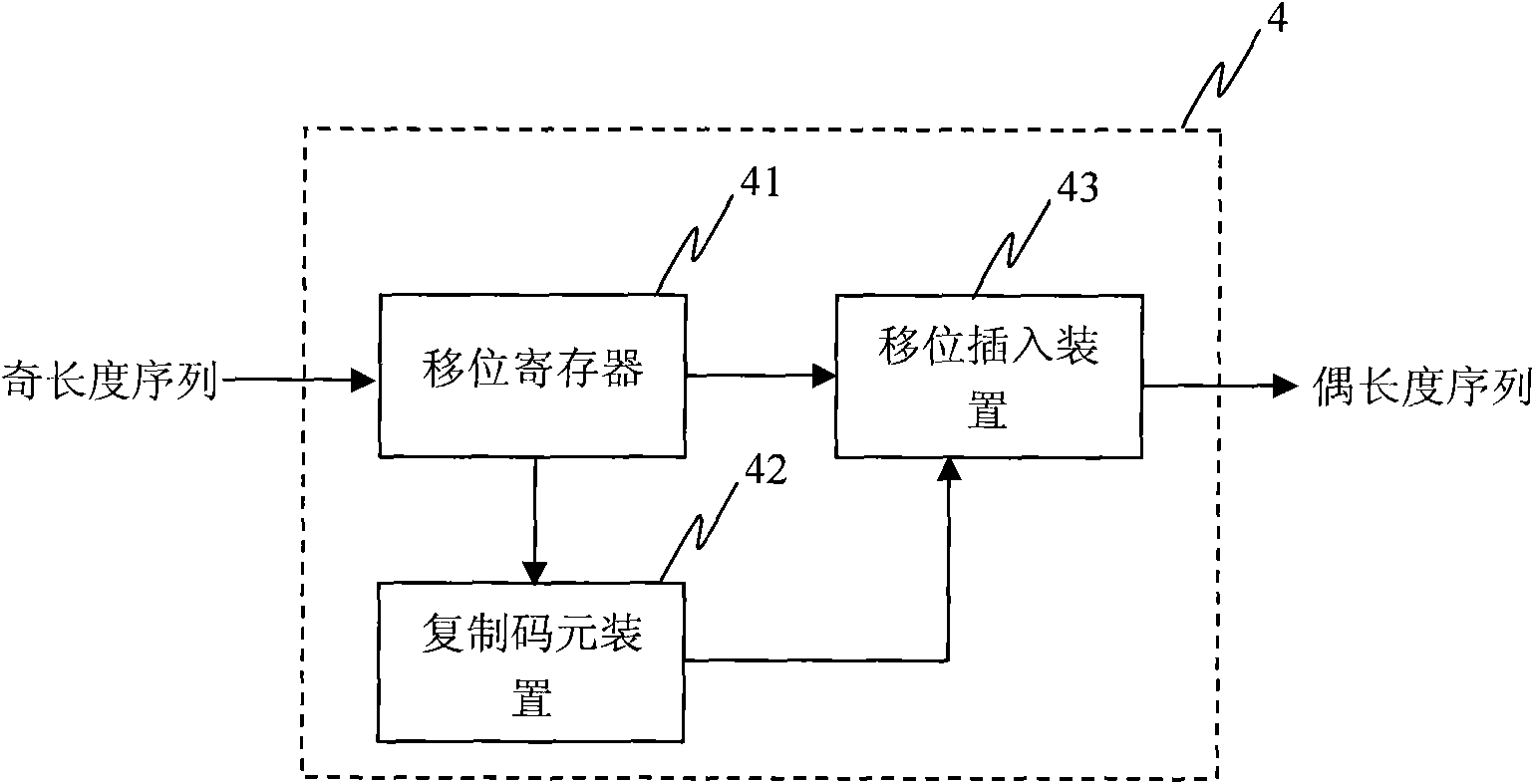
Method and device for generating even-length mirror symmetric sequence
InactiveCN102088308BImprove featuresGood anti-frequency offset characteristicsRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemCoded element
Owner:CHONGQING WIRELESS OASIS COMM TECHCO
Method and electron microscope for measuring the similarity of two-dimensional images
ActiveUS8351710B2The process is fast and accurateHigh resolutionElectric discharge tubesCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionElectron microscope
Disclosed is a method for measuring the similarity of two-dimensional images, at least one image exhibiting an additional signal, the location dependence or symmetry properties of which are known at least approximately. The images are partitioned into mutually identical subimages such that the extension of at least one subimage in the direction of the gradient of the additional signal is smaller than the extension of this subimage in the direction perpendicular thereto. The subimages are compared separately, and the results of all comparisons are combined to form the measurement result for similarity. As a result, the method becomes insensitive to variations in the additional signal. The method is particularly suited for the determination of defocusing and astigmatism of an electron-microscopic image. For this purpose, it is important to compare the similarity of an experimentally measured image to simulated images, which were generated using defined defocusing and astigmatism values.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com