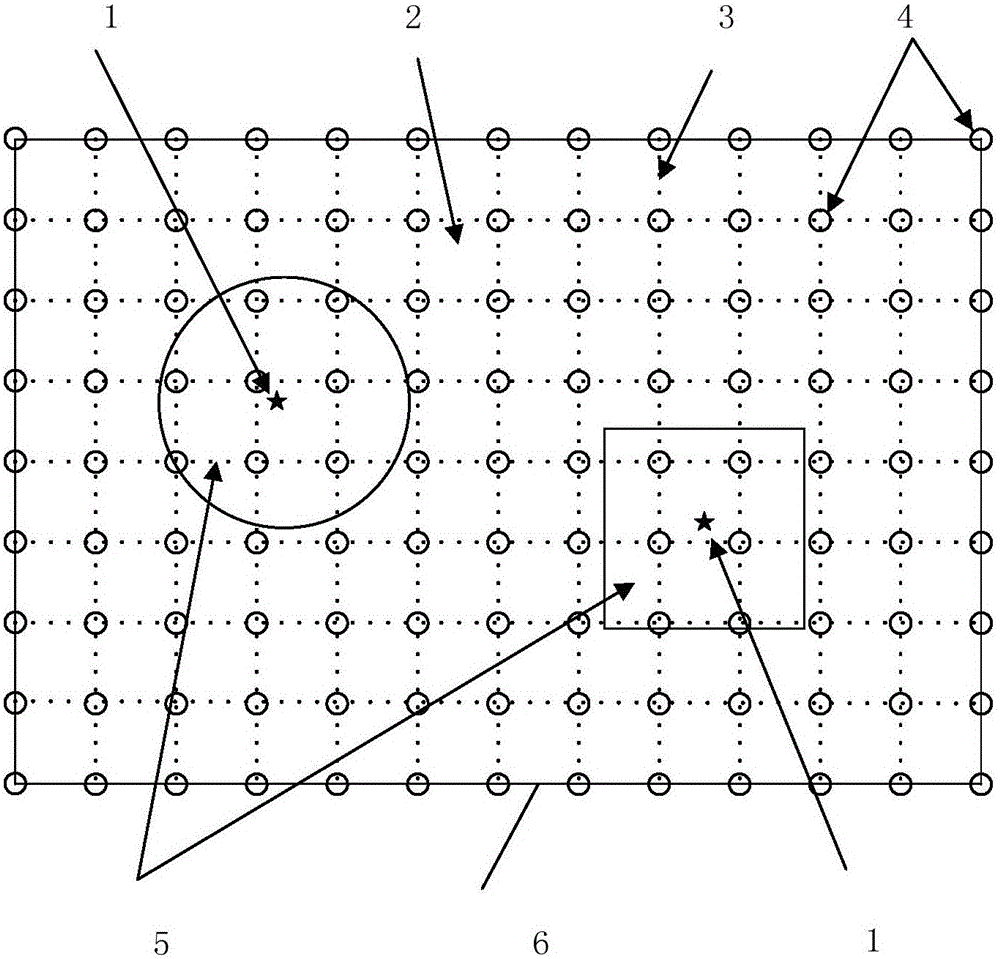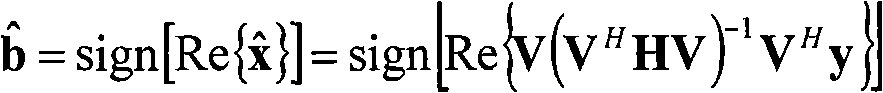Patents
Literature
59 results about "Krylov subspace" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In linear algebra, the order-r Krylov subspace generated by an n-by-n matrix A and a vector b of dimension n is the linear subspace spanned by the images of b under the first r powers of A (starting from A⁰=I), that is, Kᵣ(A,b)=span {b,Ab,A²b,…,Aʳ⁻¹b}.
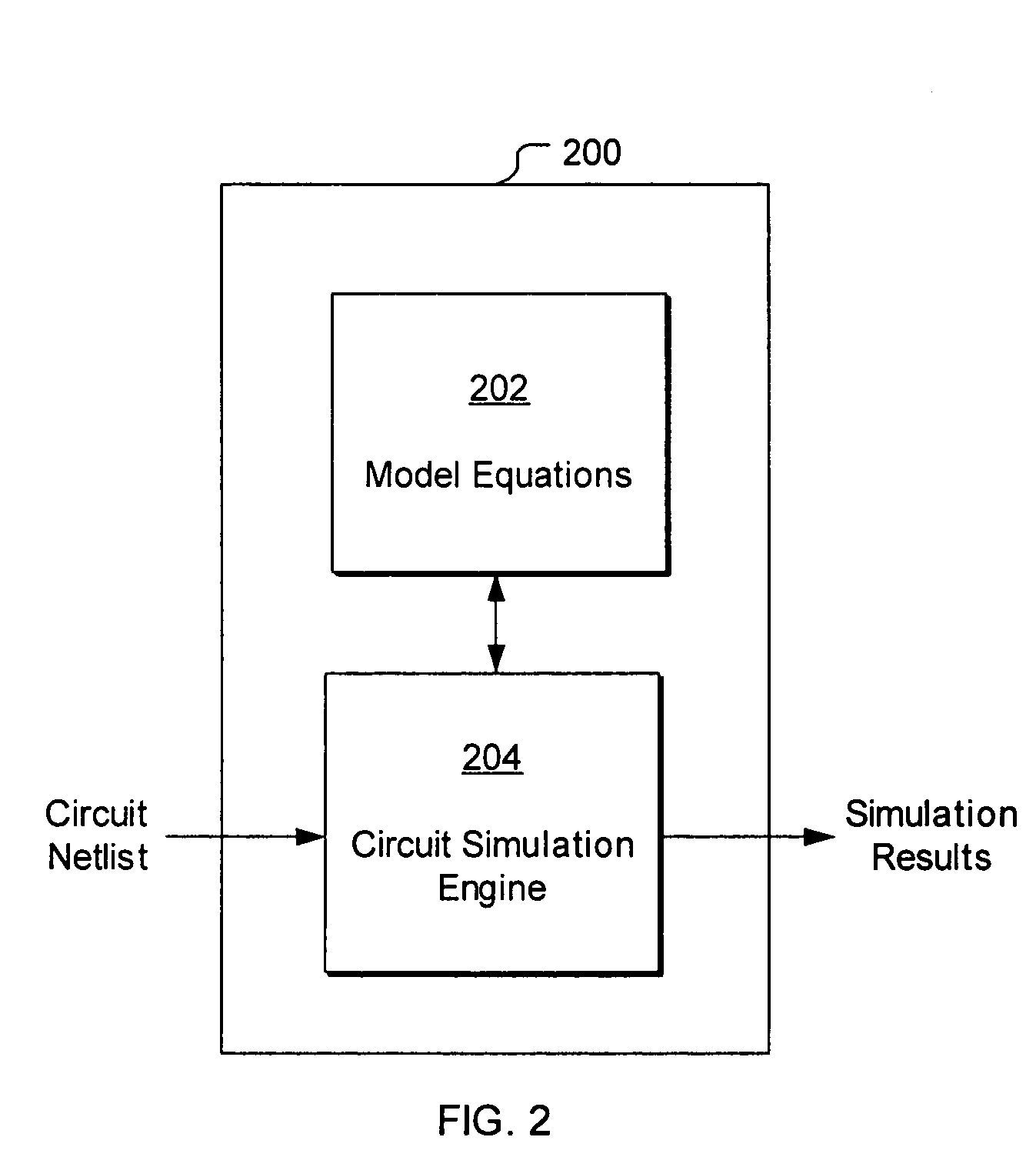
Methods, systems, and computer program products for modeling nonlinear systems
InactiveUS20050021319A1Computation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designEngineeringSeries expansion
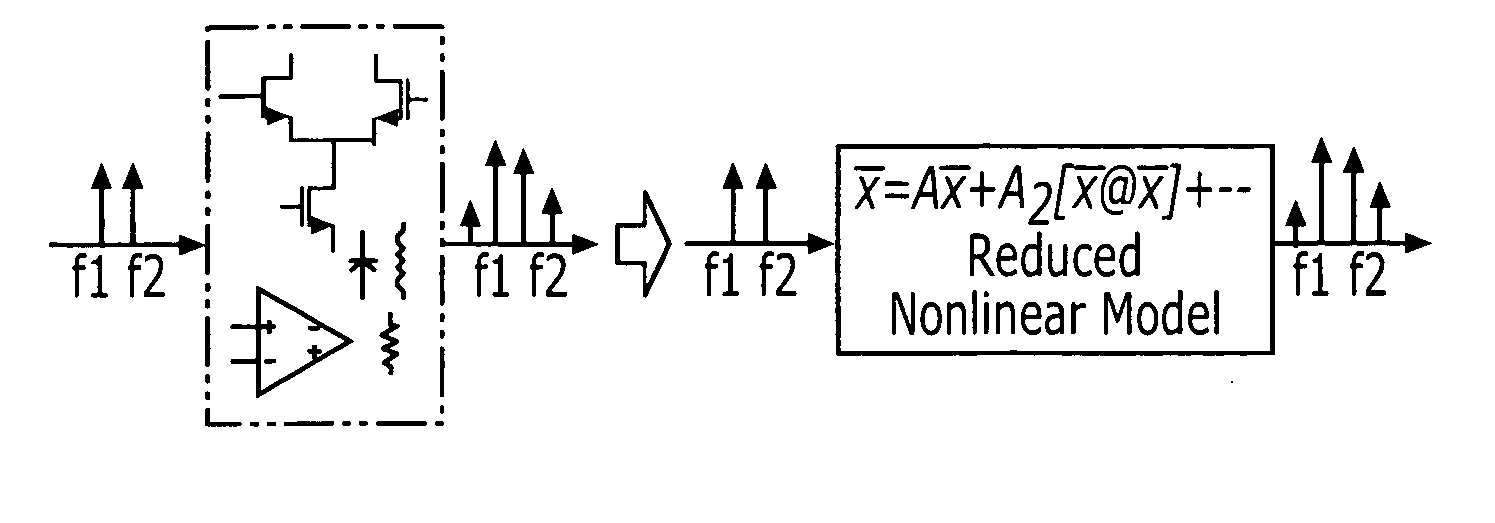
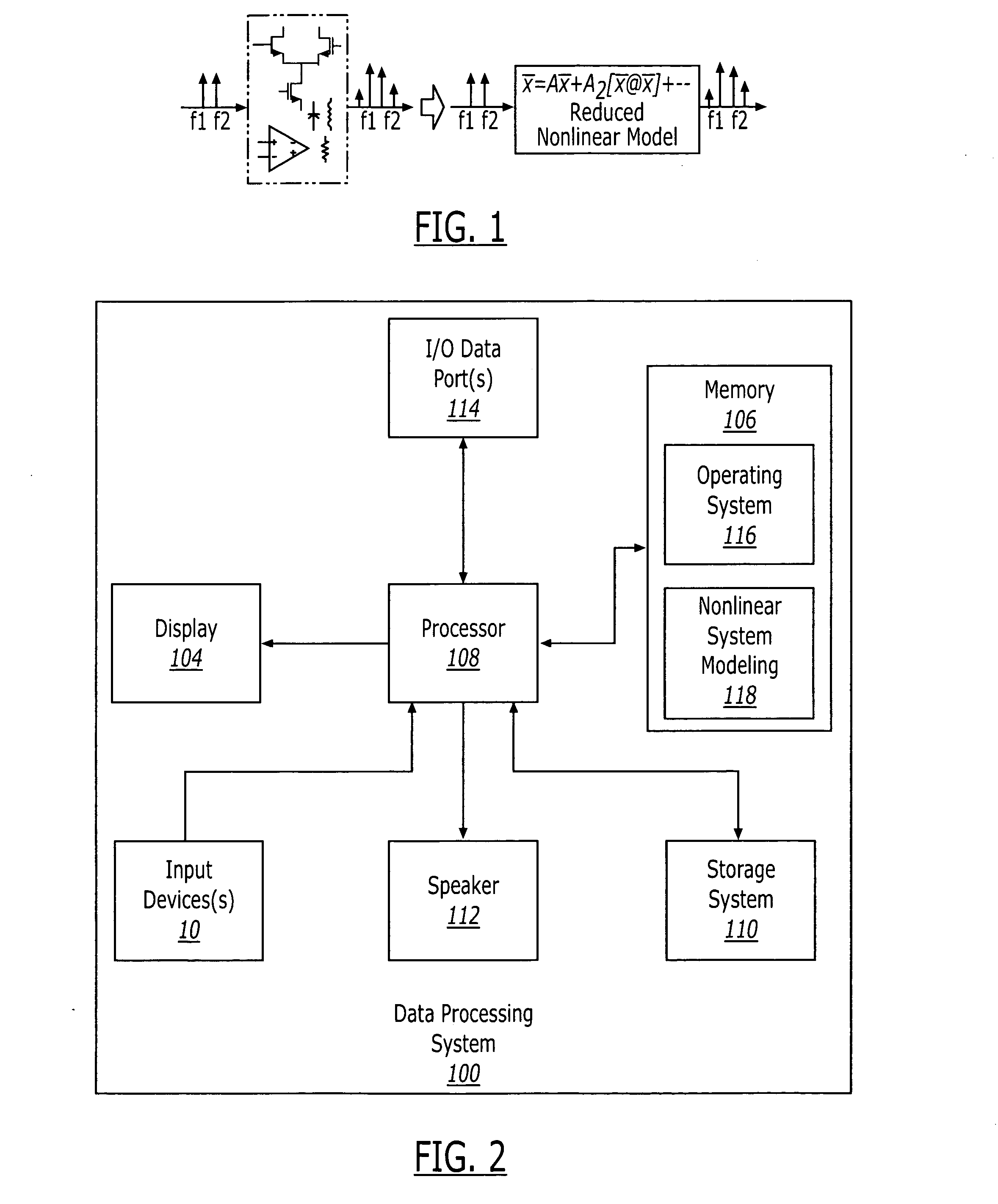
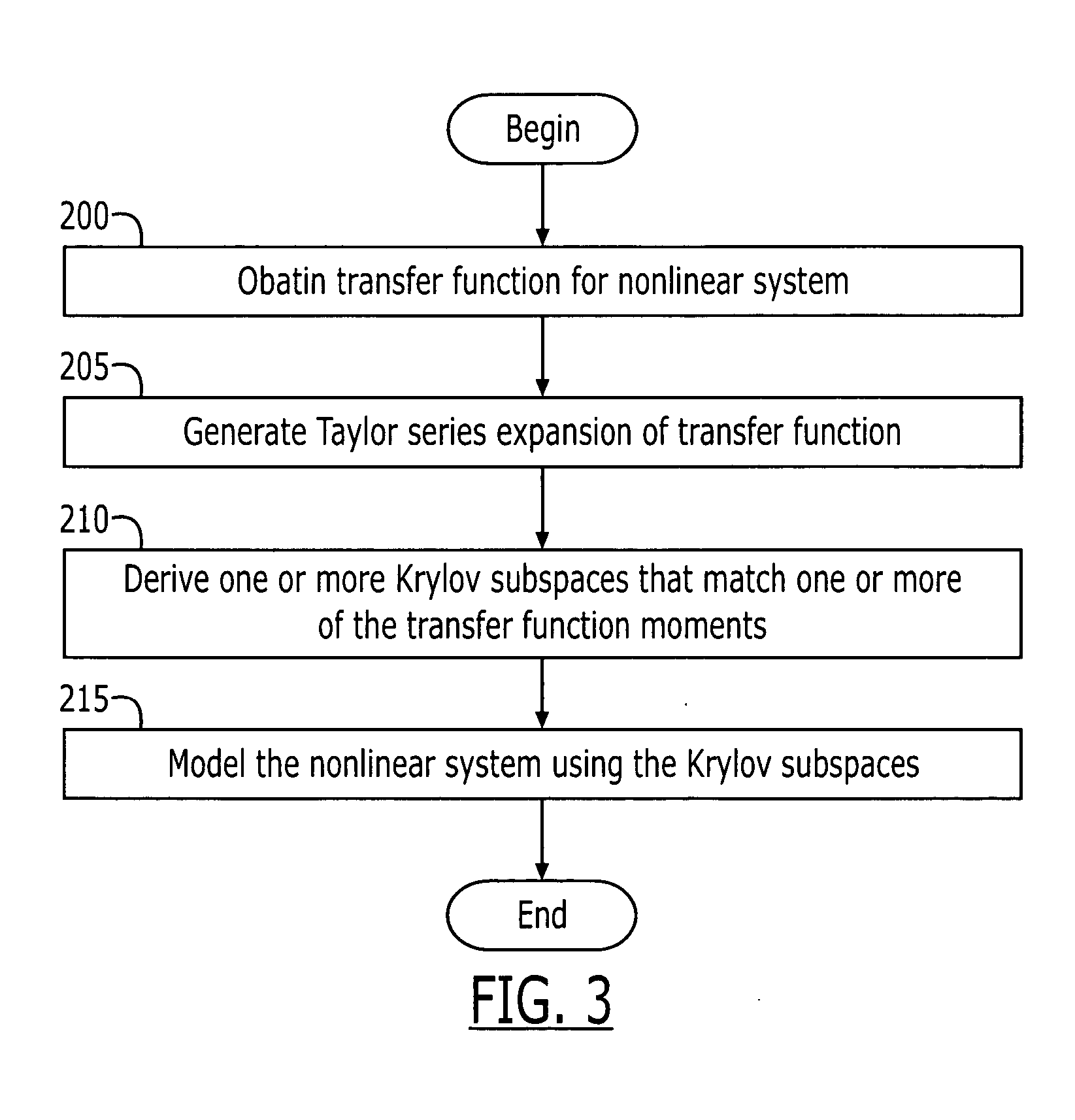
According to some embodiments of the present invention, a nonlinear system may be modeled by obtaining a transfer function for the nonlinear system and generating a Taylor series expansion of the transfer function. The Taylor series expansion includes a plurality of moments respectively corresponding to a plurality of coefficients of the Taylor series terms. At least one Krylov subspace is derived that matches at least one of the plurality of moments. The nonlinear system is modeled using the at least one Krylov subspace.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Driving Techniques for Phased-Array Systems
ActiveUS20180166063A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical vibrations separationPhased arrayComputer science
Various techniques for driving phased array systems are described, specifically intended for acoustic phased arrays with applications to mid-air haptics, parametric audio, acoustic levitation and acoustic imaging, including a system: 1) that is capable of mitigating the effect of the changes in the air to provide a consistent haptic experience; 2) that produces trap points in air; 3) that defines phased-array optimization in terms of vectors for the production of more consistent haptic effects; 4) that defines one or more control points or regions in space via a controlled acoustic field; 5) that uses a reduced representation method for the construction of acoustic basis functions; 6) that performs efficient evaluation of complex-valued functions for a large quantity of throughput; 7) that generates a Krylov sub-space of a matrix; and 8) that maximizes an objective described by different control points and / or regions to those used to create the acoustic basis functions.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
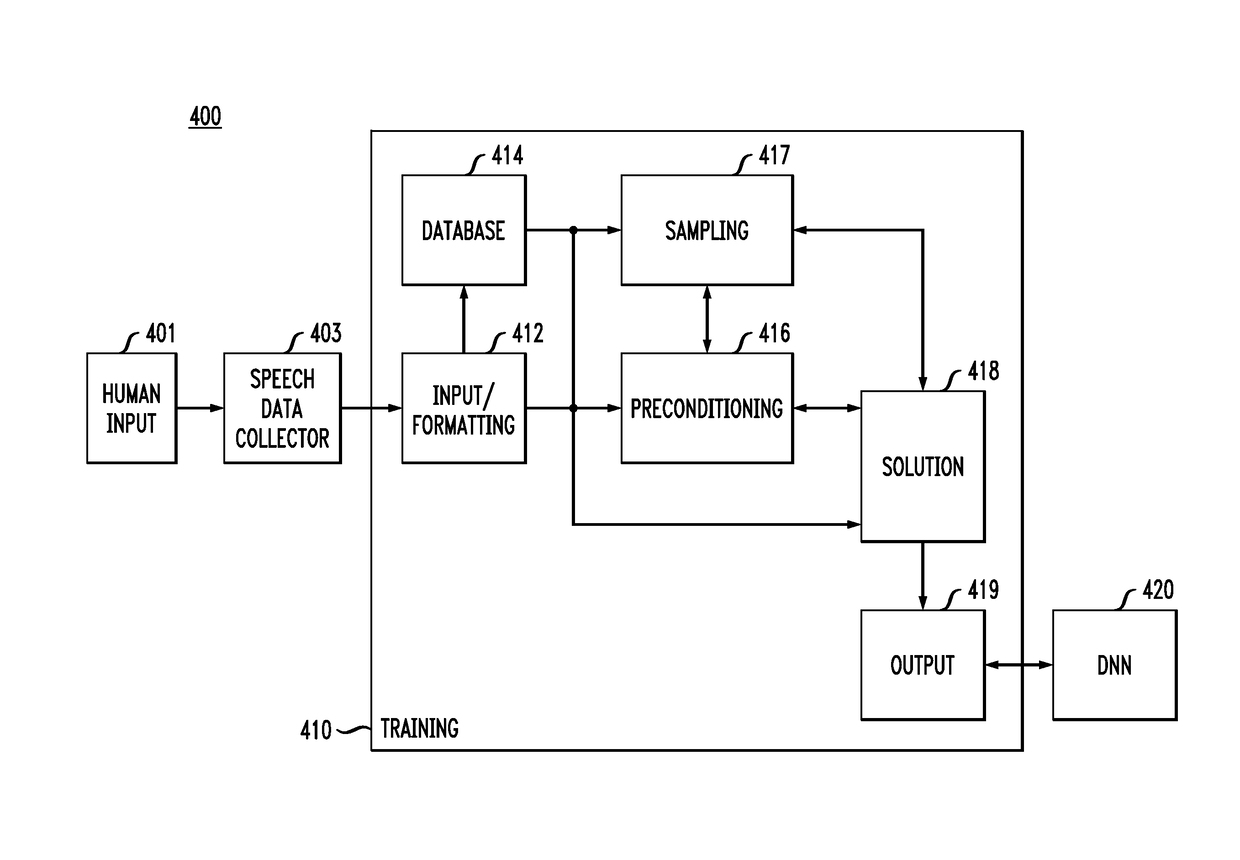
Systems and methods for accelerating hessian-free optimization for deep neural networks by implicit preconditioning and sampling
A method for training a deep neural network, comprises receiving and formatting speech data for the training, preconditioning a system of equations to be used for analyzing the speech data in connection with the training by using a non-fixed point quasi-Newton preconditioning scheme, and employing flexible Krylov subspace solvers in response to variations in the preconditioning scheme for different iterations of the training.
Owner:IBM CORP
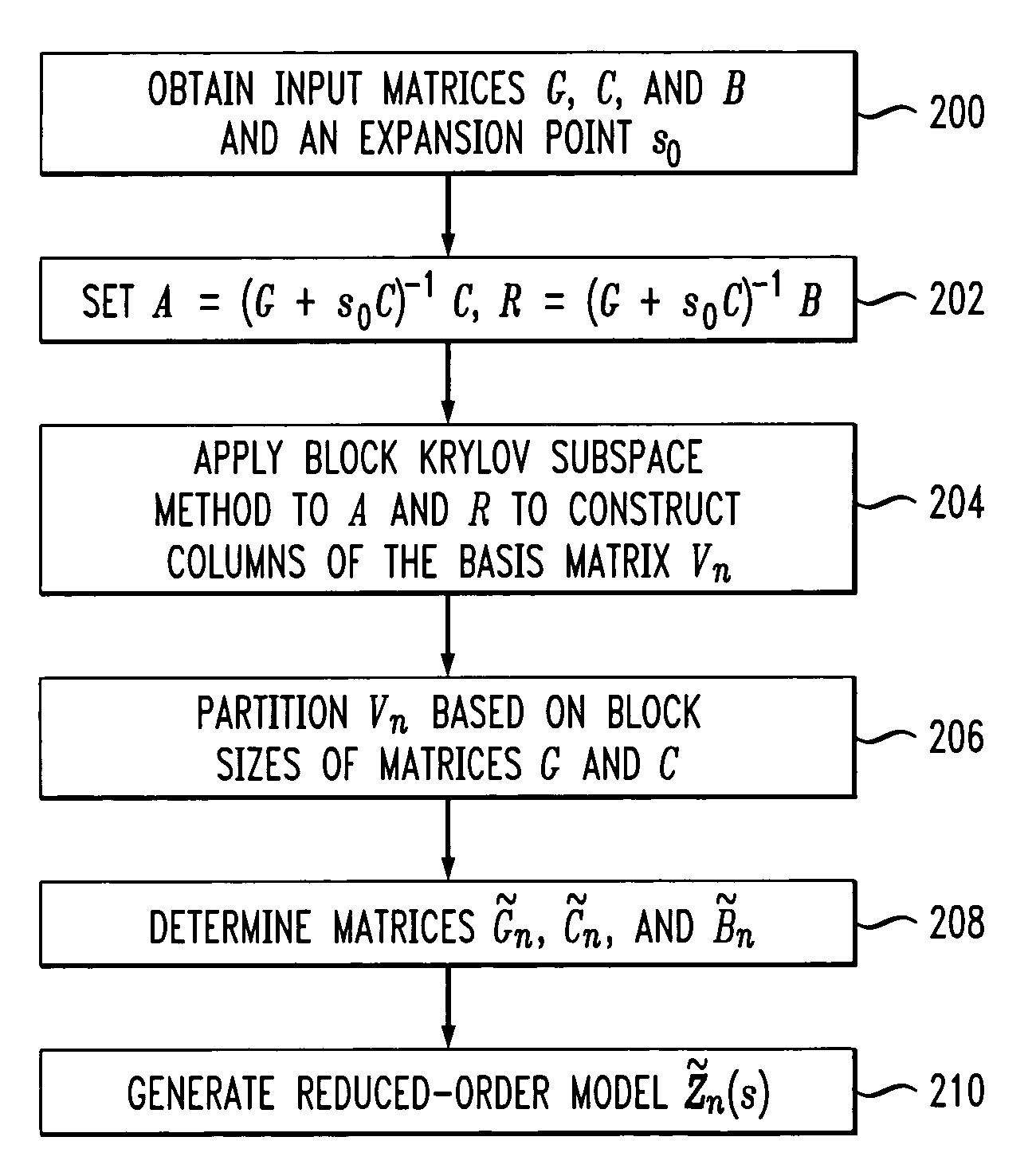
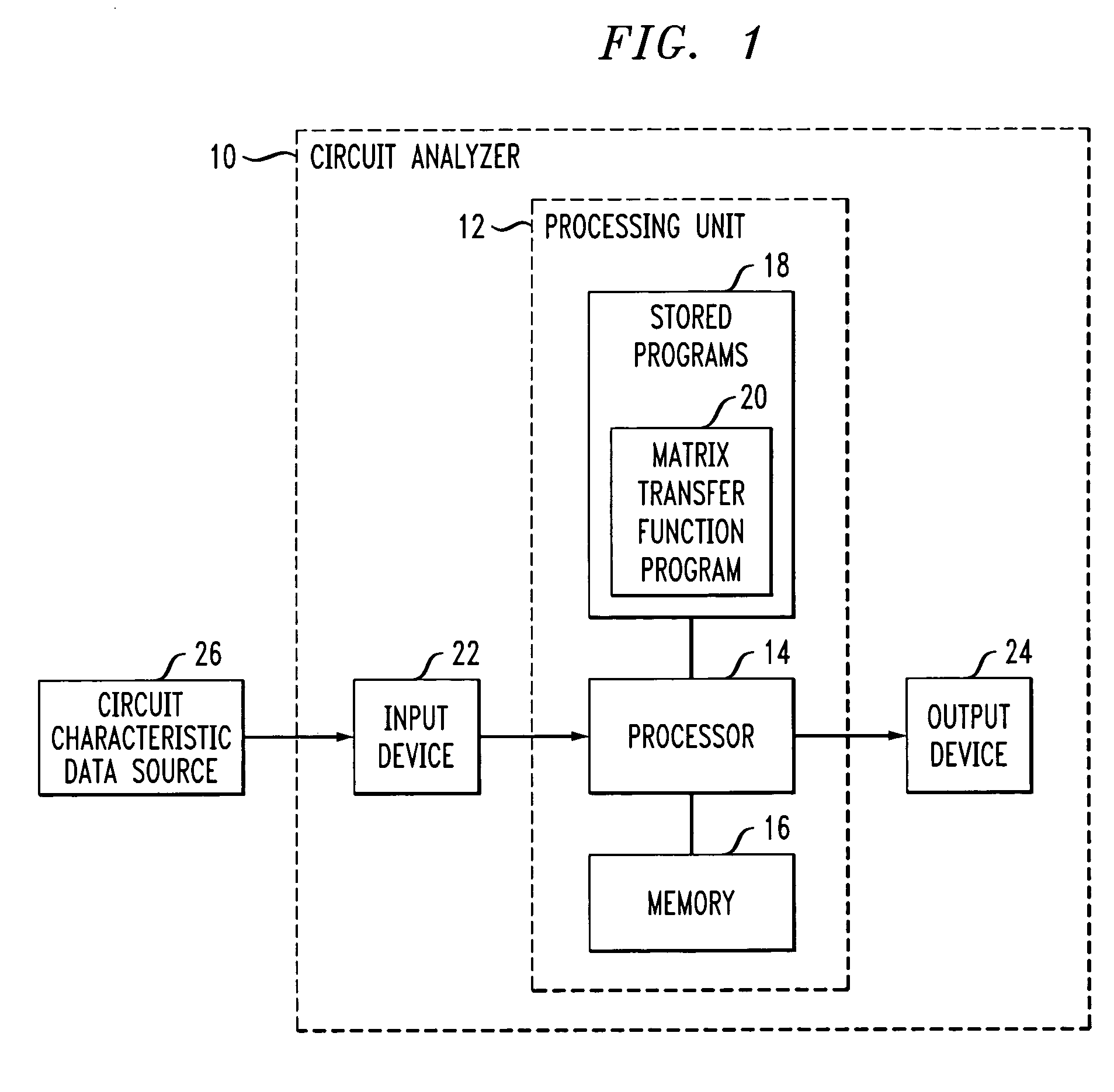
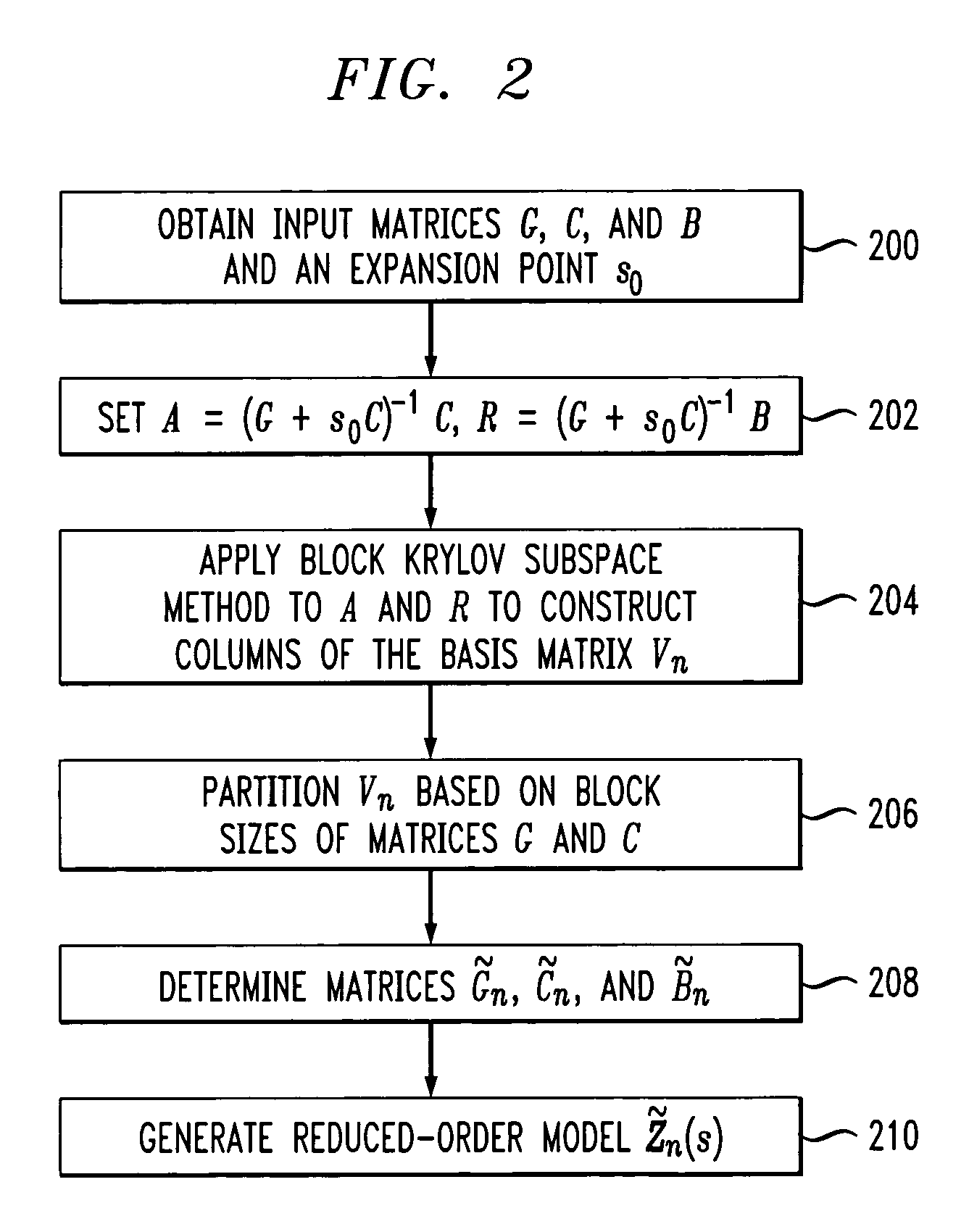
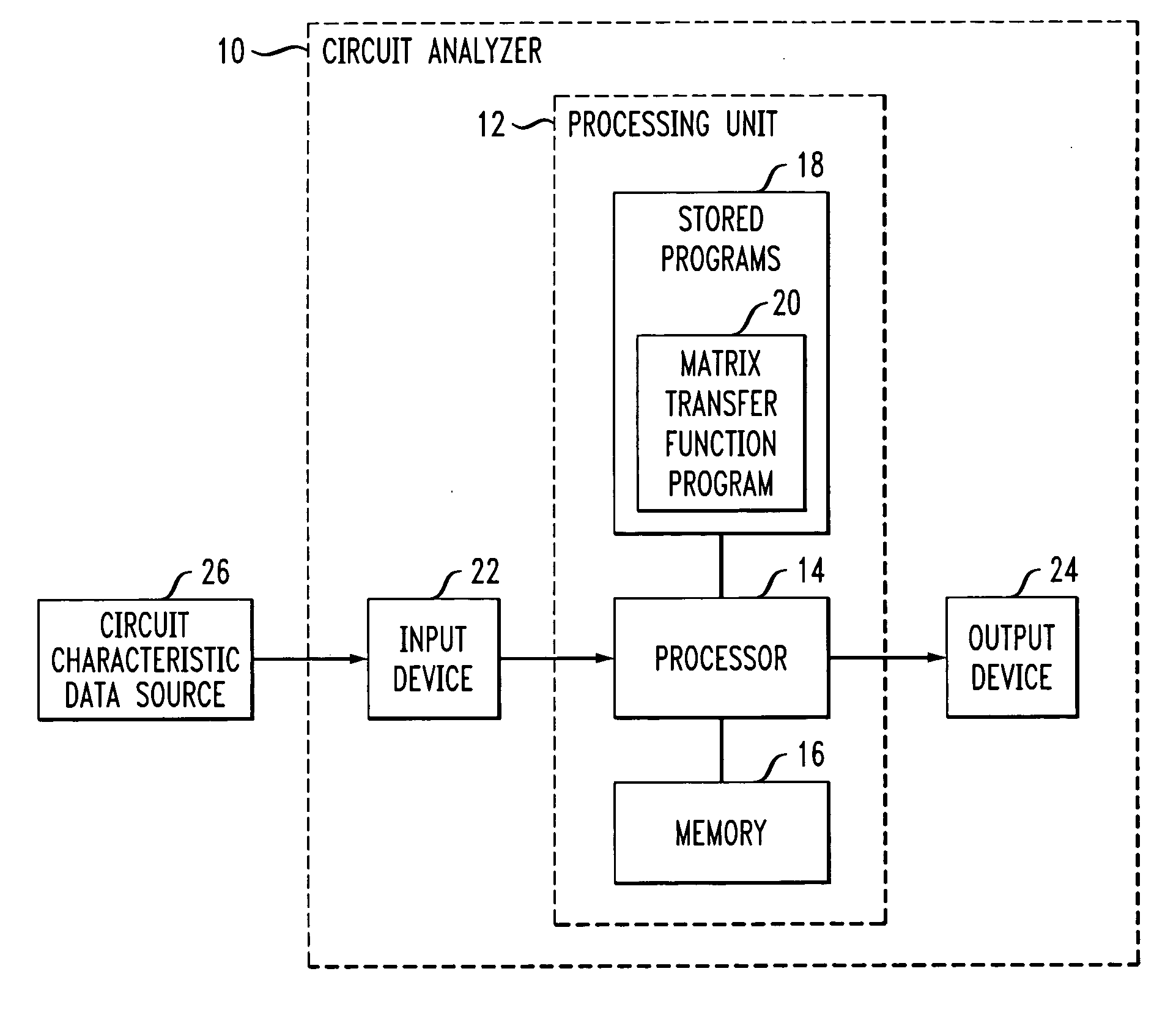
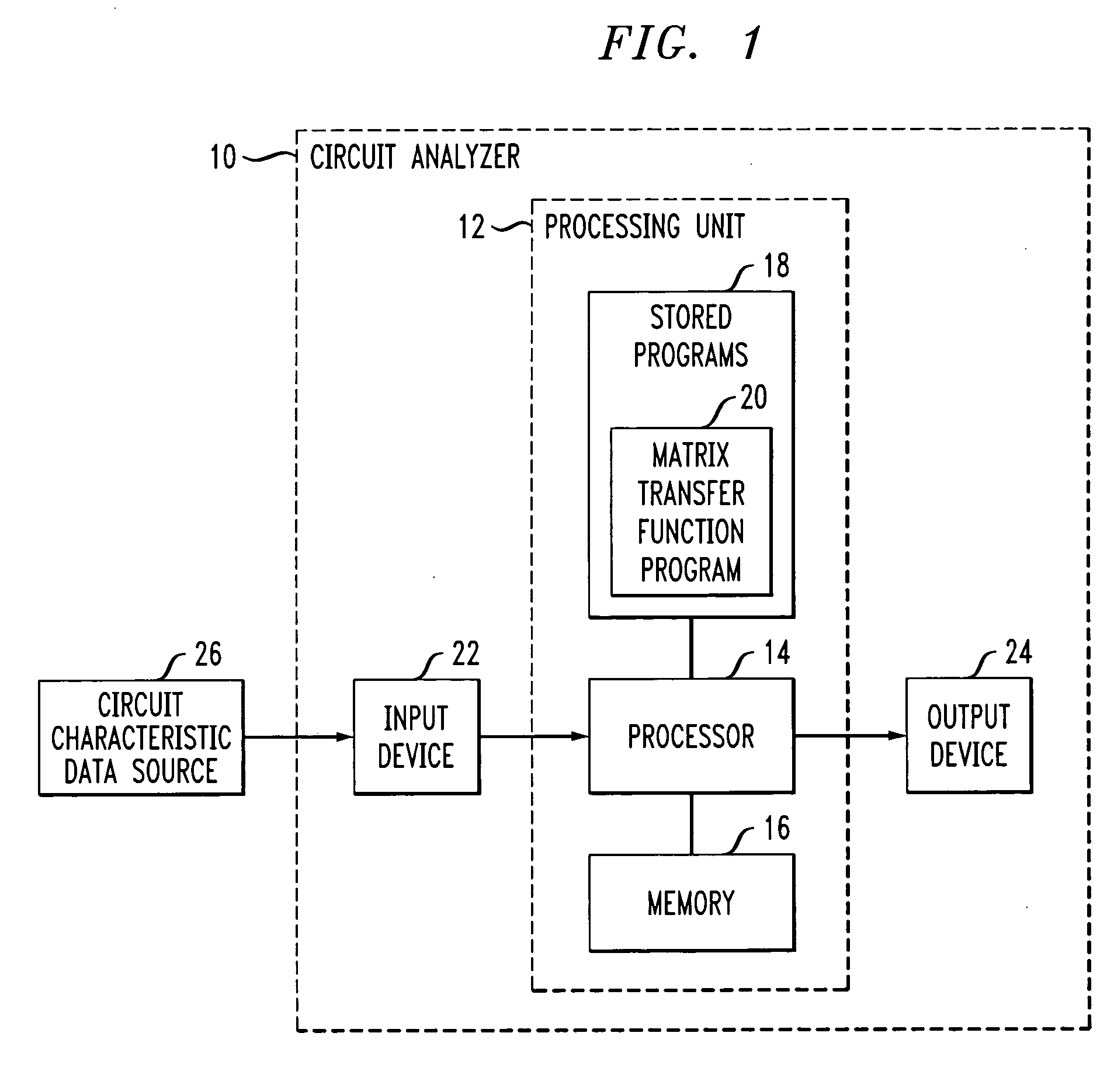
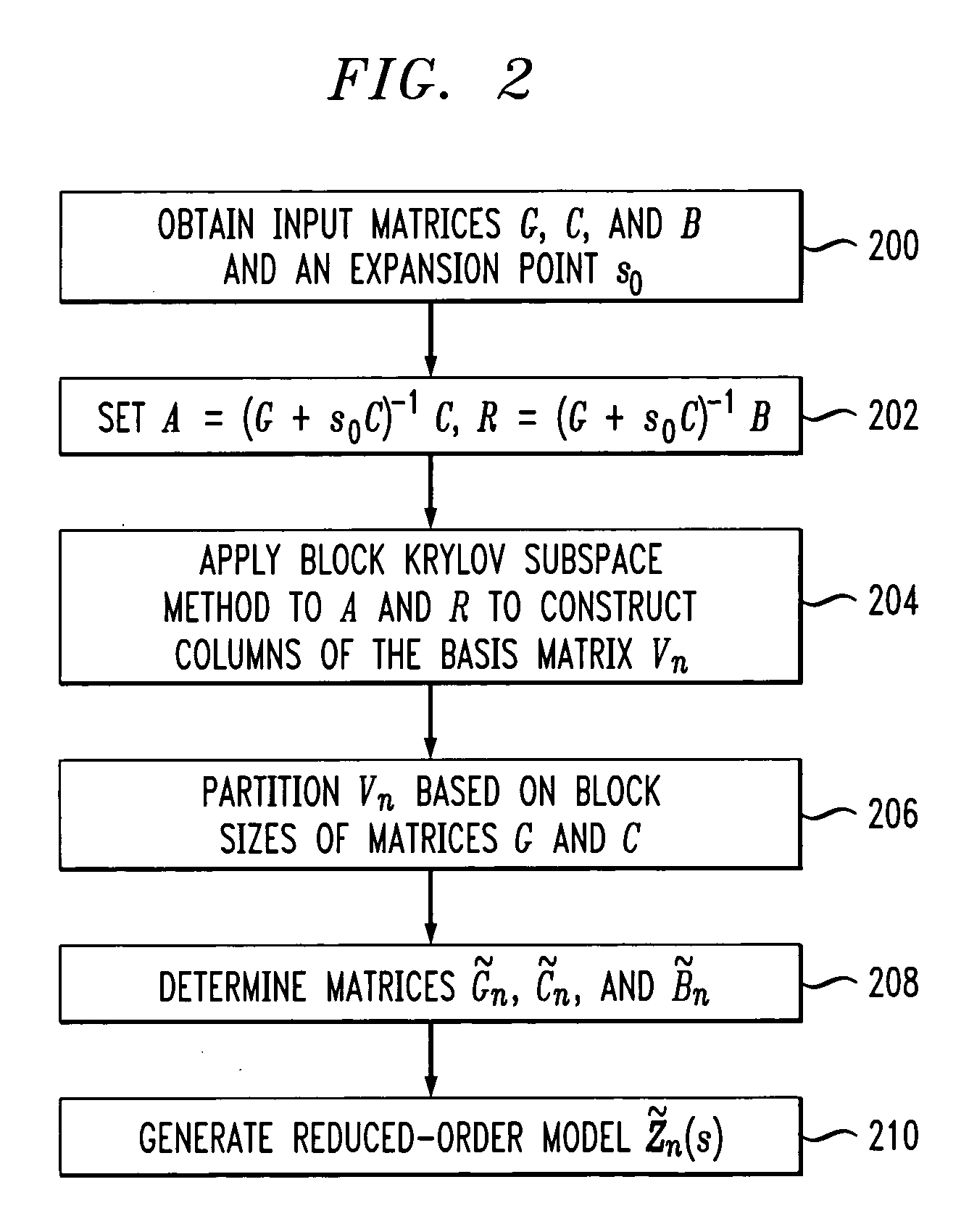
Method and apparatus for structure-preserving reduced-order modeling
InactiveUS7228259B2Improve approximationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationAlgorithmProcessing element
A processing unit of an analysis system comprises a processor coupled to a memory, and is configured to generate a structure-preserving reduced-order model of a circuit, device or system. The reduced-order model in one embodiment is generated by projection of input matrices characterizing the circuit, device or system onto at least one block Krylov subspace, the block Krylov subspace having a corresponding basis matrix. The projection utilizes at least one matrix that has a column range which includes a corresponding portion of the block Krylov subspace but is not itself the basis matrix of the block Krylov subspace. The processing unit generates a frequency response or other signal characterizing the circuit, device or system, based at least in part on the reduced-order model, and an associated output unit presents the generated signal in a user-perceptible format.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
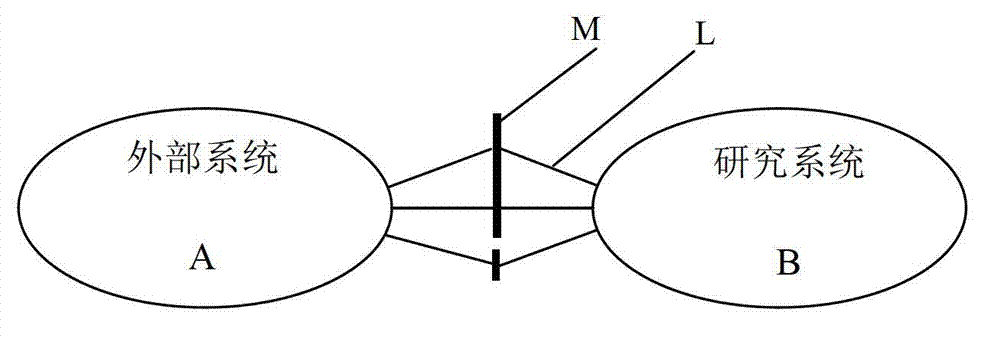
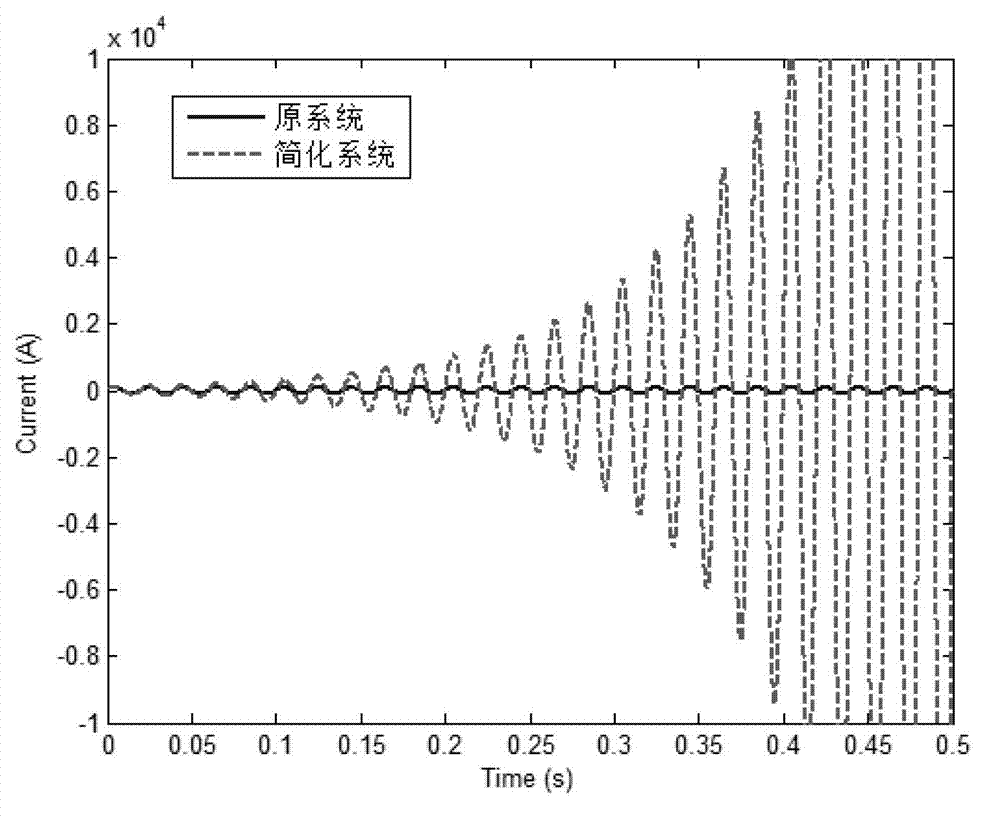
Method for simplifying passive electromagnetic transient-state simulation model of large-scale power distribution network
ActiveCN103049617AReduce orderHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsTransient stateDistribution power system
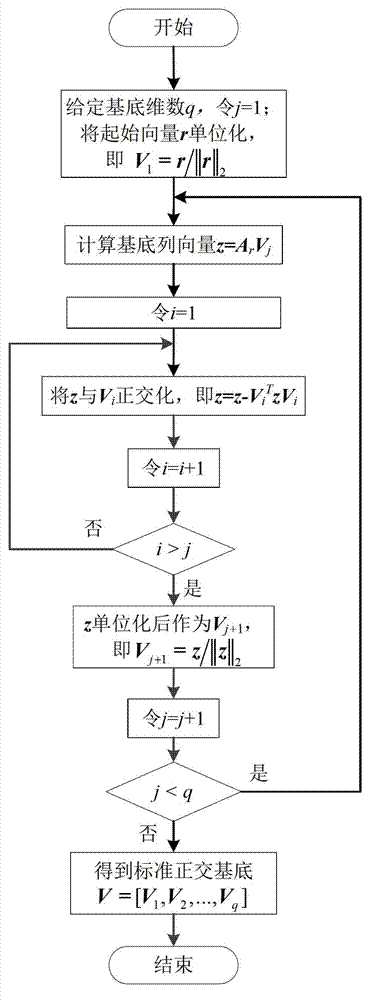
A method for simplifying a passive electromagnetic transient-state simulation model of the large-scale power distribution network includes steps of dividing a large-scale intelligent power distribution system into an external system and a research system which are connected; respectively establishing an electromagnetic transient-state simulation model of the external system and the research system; setting a low-dimension system model order q; calculating A=-G<-1>C, R=G<-1>B according to a state-output equation model of the external system; selecting a corresponding basis calculating method according to the number of input quantity of the external system, solving a standard orthogonal basis V of Kq(A, R, q) of a krylov subspace of the q dimension; calculating Cq=V<T>CV, Gq=V<T>GV, Bq=V<T>B, Lq=V<T>L to obtain a low-dimension simplified system model shown in the description, utilizing a simplified reduced-order model y=Lq<T>xq of the external system to substitute for an original external system model, and simultaneously subjecting a detailed model of the research system to simulation calculation to obtain an internal detailed transient process of the research system. The method for simplifying the passive electromagnetic transient-state simulation model of the large-scale power distribution network has the advantages of high accuracy, good stability, simplicity in algorithm and proneness to realizing.
Owner:南京首风智慧电力研究院有限公司
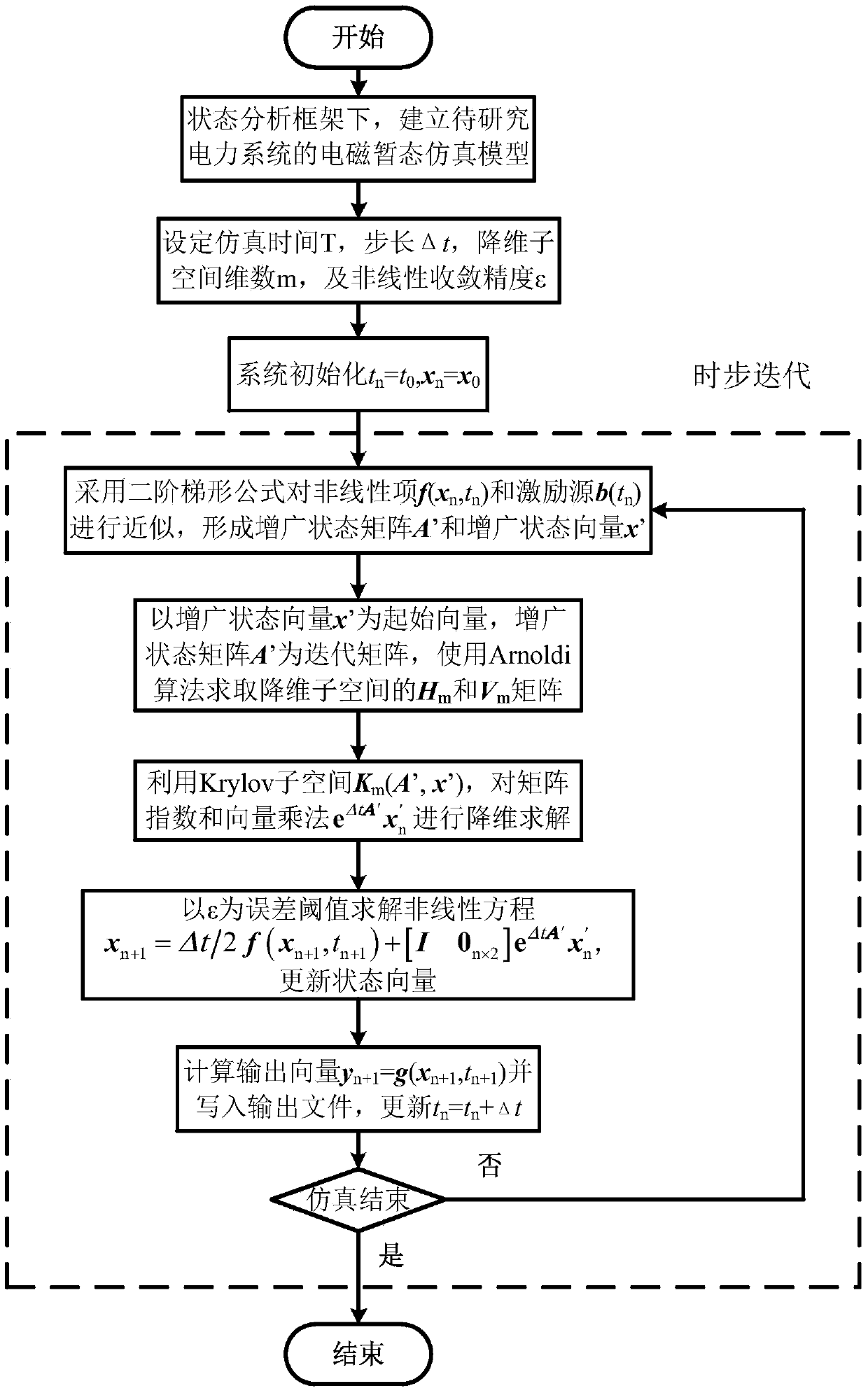
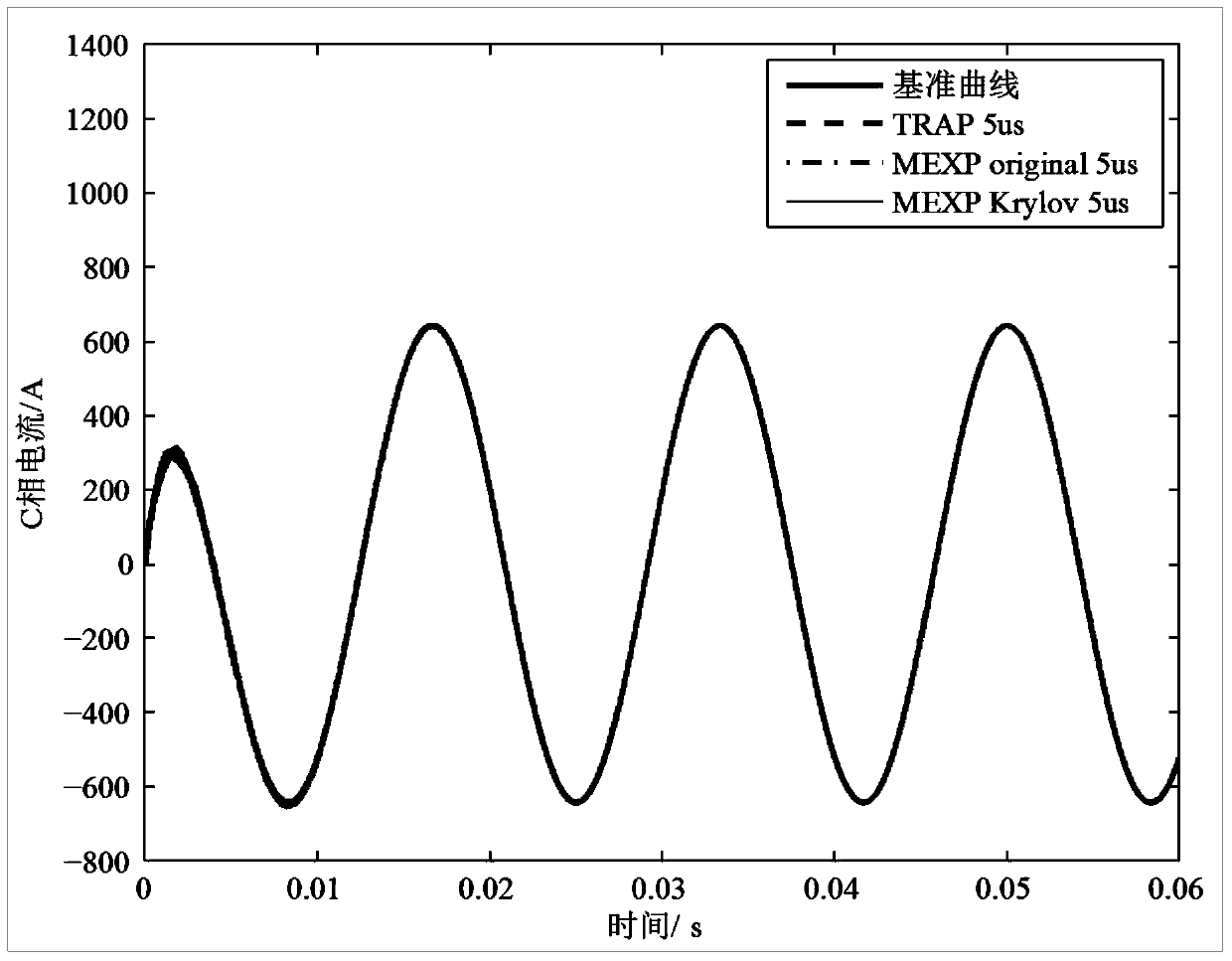
Electromagnetic transient implicit reduced order simulation method based on matrix index
ActiveCN104217074ASolving Electromagnetic Transient Simulation ProblemsEasy error controlSpecial data processing applicationsTransient stateElectric power system
The invention discloses an electromagnetic transient implicit reduced order simulation method based on a matrix index. The electromagnetic transient implicit reduced order simulation method comprises the steps of constructing a high-dimensional nonlinear electromagnetic transient simulation model of a power system to be researched under a state analysis framework; setting simulation parameters such as a dimension number m of a dimension reduction sub space, and initializing and starting a simulation program; generating an augmentation state matrix and a state vector within each simulation step length, and generating an orthogonal basis of the dimension reduction Krylov sub space by an Arnoldi algorithm; approximating a high-dimension matrix index of an original system by a low-dimension matrix index according to a Krylov sub space approximating formula of the matrix index, calculating a nonlinear equation to obtain a state variable at the current moment, and boosting one step length for simulation; performing iteration in sequence until simulation is ended. According to the electromagnetic transient implicit reduced order simulation method, high value precision and high rigid processing performance of a matrix index integration method are kept, and general purpose modeling simulation capacity is realized on the nonlinear characteristic of the power system; by the implicit reduced order method, the application range of the matrix index integration method in the field of large-scale power system electromagnetic transient simulation is expanded.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +2
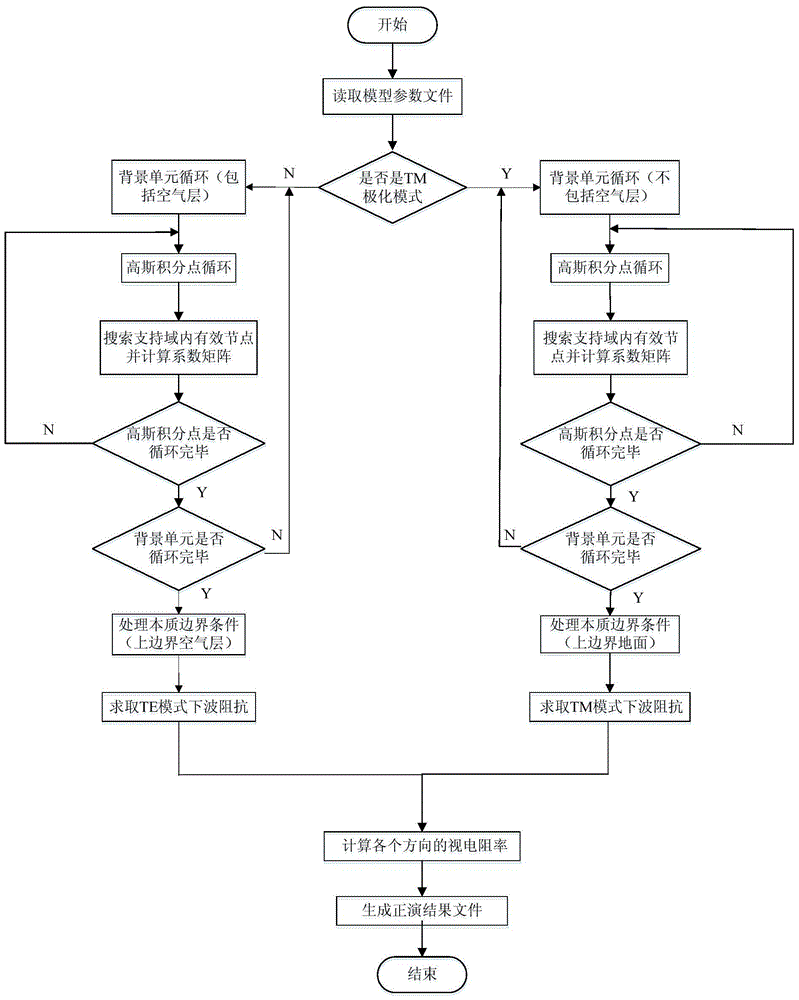
Anisotropy medium magnetotelluric meshless value simulation method
InactiveCN105717547AAvoid singularity problemsHigh precisionElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationConductivity tensorShape function
The invention brings forward a magnetotelluric meshless value simulation method for constructing a shape function on the basis of discrete nodes, for solving the problem of anisotropy widely existing in underground space media. It is assumed that one of electrical main shafts of an anisotropy medium is vertical to a bedding plane aspect and the other is parallel to a bedding plane direction, and thus a conductivity tensor model of an anisotropy medium model is constructed. For the purpose of solving an anisotropy magnetotelluric boundary value problem, an equivalent linear equation group corresponding to a meshless radical point interception method is derived, the shape function is constructed by compounding a multiquadric radial basis function (MQ-RBF) two times, and a large-scale sparse linear equation group is efficiently and accurately solved through QR preprocessing in a Krylov subspace and a quasi-minimal residual method (QMR). According to the invention, the constructed shape function is smooth and stable, complex distribution of physical property parameters of an electromagnetic method can be realized, and high-precision self-adaptive value simulation is realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
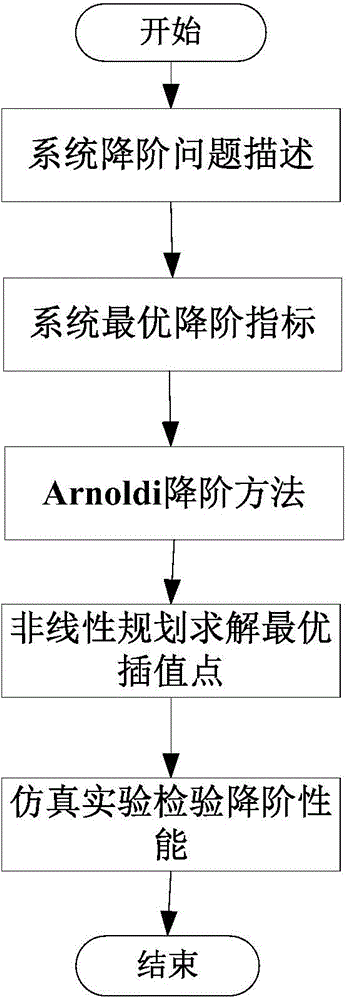
Nonlinear programming based optimal reduction method of high-order system
InactiveCN104614985AOvercome the disadvantage of only finding a single interpolation pointReduce numerical simulationAdaptive controlAlgorithmOrder system
The invention provides a nonlinear programming based optimal reduction method of a high-order system. The method comprises six major steps of 1, describing the reduction problem; 2, determining the optimal reduction indexes of the system; 3, graining the Arnoldi reduction method; 4, solving an optimal interpolation point by nonlinear programming; 5, inspecting the reduction performance by simulation experiment; 6, finishing the design; the first step is to determine the high-order linear system reduction purchase and perform mathematical description; the second step is to determine error norm index of the system reduction so as to prepare for the proposing of the optimal reduction method; the third step is to gain the Arnoldi reduction method based on the krylov subspace; the fourth step is to propose the optimal interpolation point solution method based on the nonlinear programming to obtain the optimal reduction model; the fifth step is to perform simulation experiment for the designed system optimal reduction method; after the steps above are done, the design is finished. The method is used for processing the high-order linear system, and the control rule design is simplified.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
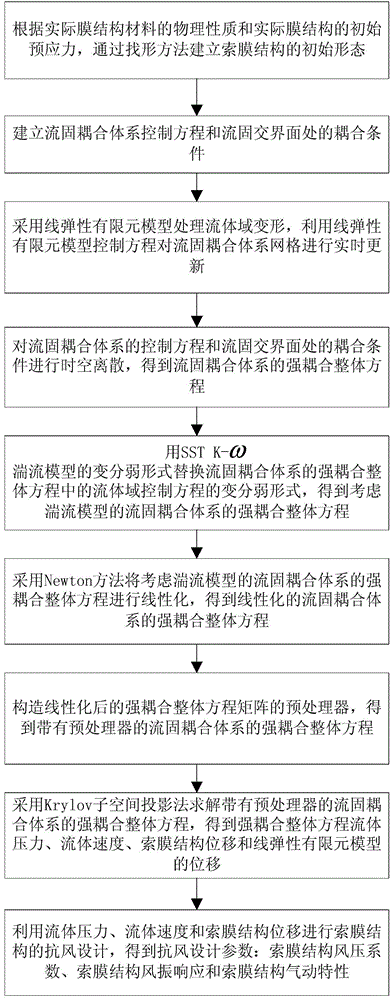
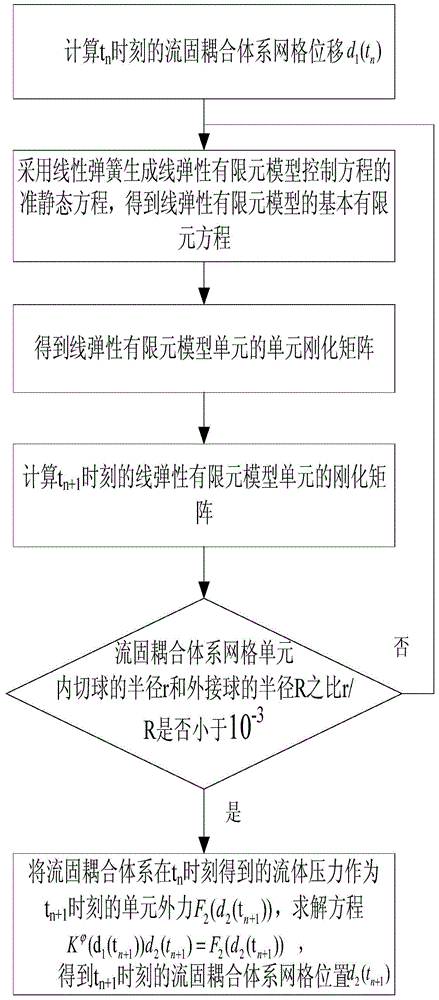
Strong-coupled overall technology-based wind-resistant design method of cable-membrane structure
ActiveCN104573269ASolve the problem of data exchange transmissionSolving Convergence ProblemsSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEngineering
The invention relates to a strong-couple overall technology-based wind-resistant design method of a cable-membrane structure. The strong-couple overall technology-based wind-resistant design method includes establishing an initial form of the cable-membrane structure; establishing and subjecting a fluid-structure interaction system control equation and a coupling condition on a fluid-structure interface to space-time dispersing, and a strong-coupled overall equation of the fluid-structure interaction system is obtained; employing an SSTK-Omega turbulence model to simulate turbulence to obtain a strong-coupled overall equation matrix with the turbulence model considered of the fluid-structure interaction system, and subjecting the strong-coupled overall equation matrix to linearization in the Newton way; building a preprocessor of the strong-coupled overall equation matrix linearized to obtain a strong-coupled overall equation with the preprocessor of the fluid-structure interaction system, and employing the Krylov subspace projection method to solve the strong-coupled overall equation with the preprocessor so as to obtain strong-coupled overall equation fluid pressure and speed, cable-membrane structure displacement and displacement of linear elastic finite element model; the wind-resistant design of the cable-membrane structure is performed to obtain wind-resistant design parameters.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for structure-preserving reduced-order modeling
InactiveUS20060004551A1Improve approximationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationAlgorithmProcessing element
A processing unit of an analysis system comprises a processor coupled to a memory, and is configured to generate a structure-preserving reduced-order model of a circuit, device or system. The reduced-order model in one embodiment is generated by projection of input matrices characterizing the circuit, device or system onto at least one block Krylov subspace, the block Krylov subspace having a corresponding basis matrix. The projection utilizes at least one matrix that has a column range which includes a corresponding portion of the block Krylov subspace but is not itself the basis matrix of the block Krylov subspace. The processing unit generates a frequency response or other signal characterizing the circuit, device or system, based at least in part on the reduced-order model, and an associated output unit presents the generated signal in a user-perceptible format.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
A new order reduction method for dynamic heat transfer model of building envelope
ActiveCN109214113AReduce running timeSimple methodGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationData setBalanced truncation
The invention discloses a new model reduction solution method for building envelope dynamic heat transfer. Aiming at building dynamic heat transfer problem, based on heat balance principle, a controlequation for building envelope dynamic heat transfer is established. According to the indoor and outdoor meteorological parameters and the thermal performance parameters of the envelope, the characteristics of the partial differential equation are analyzed, and the boundary conditions and initial conditions are established. By using the robust discretization method, the discretized state space form of the original system of the partial differential equation is obtained. Based on Laguerre orthogonal polynomials, a new model reduction method is proposed for the original system. Finally, the solution of the reduced order system is restored to the solution of the original system. Compared with the Krylov subspace model reduction method, the new method is more intuitive and simpler in time domain. Compared with the balanced truncation model, the computational resource consumption is reduced. The eigenorthogonal decomposition (POD) model reduction method is avoided to obtain the data set ofthe system state in advance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
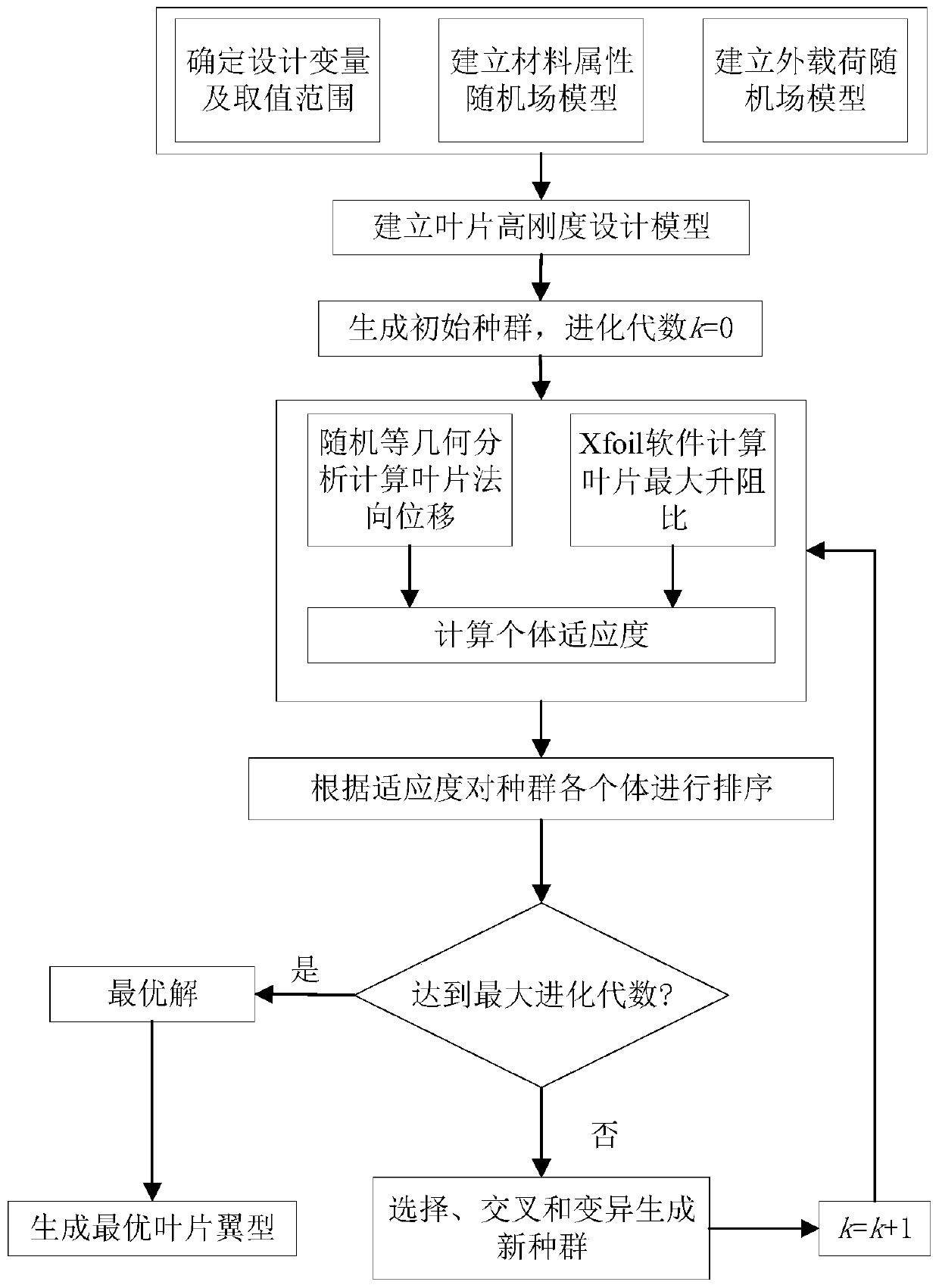
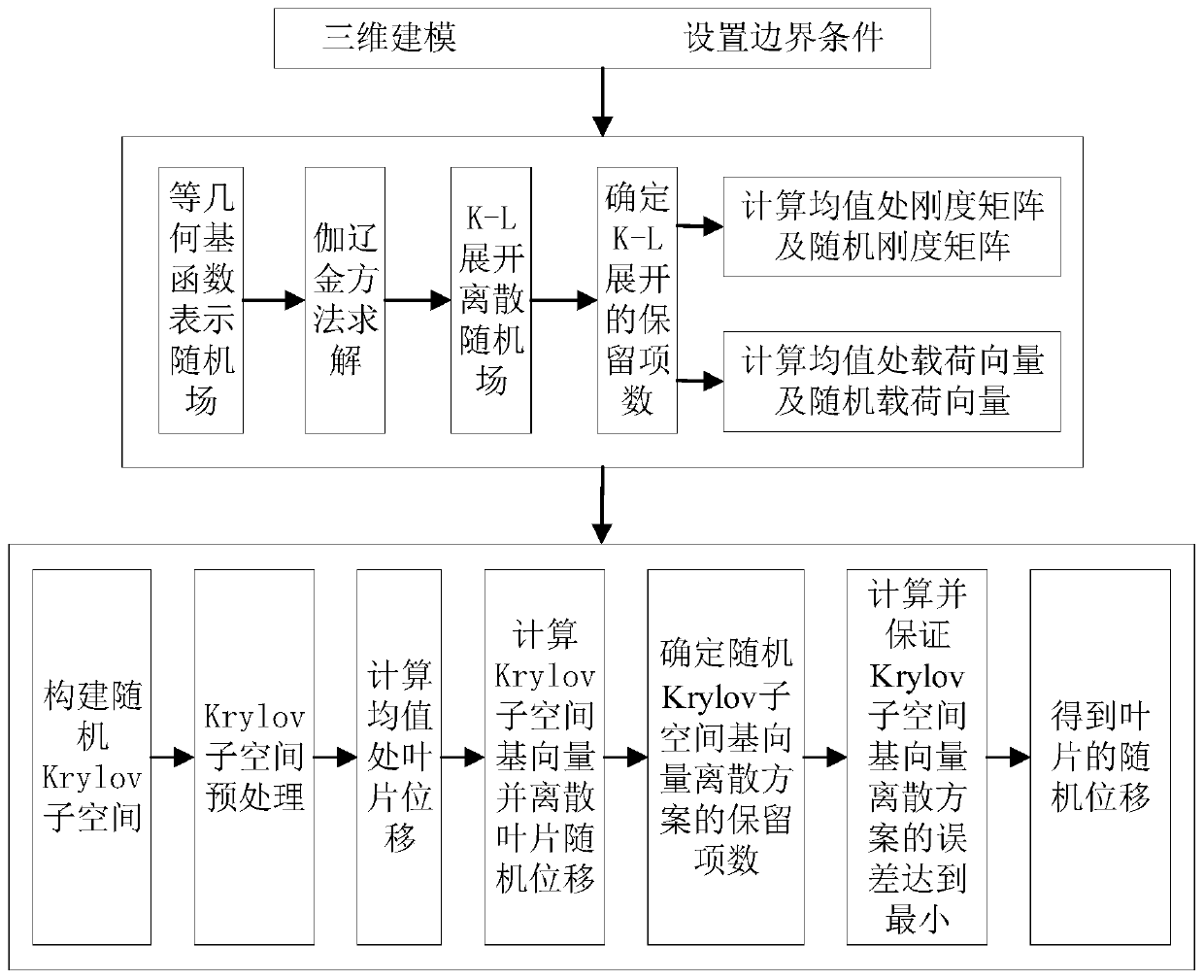
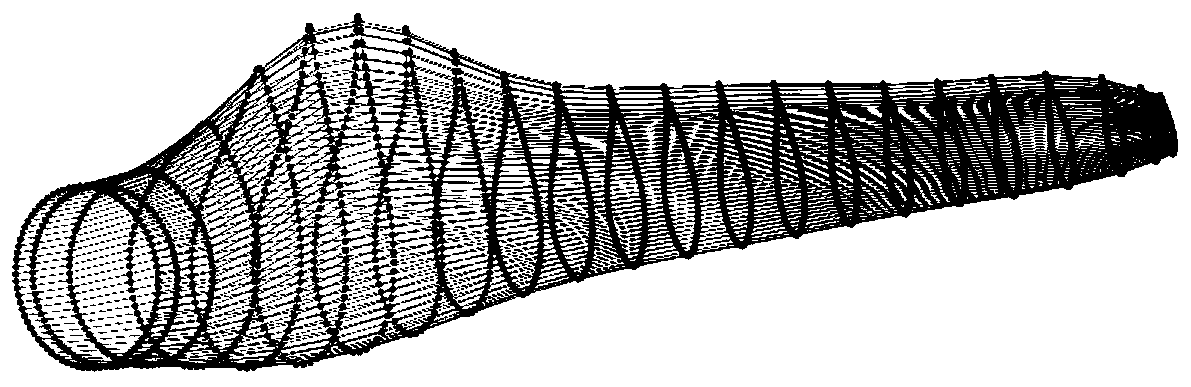
A blade high-rigidity design method based on random isogeometric analysis
ActiveCN109766604AIncrease stiffnessGuaranteed hydrodynamic performanceGeometric CADFinal product manufactureComputer scienceOptimal design
The invention discloses a blade high-rigidity design method based on random isogeometric analysis. According to the method, firstly, a random field model of the material attribute and the external load is established according to the manufacturing condition and the service environment of the blade, on the basis, an optimal design model is established according to the high-rigidity design requirement and the lift-drag ratio constraint condition of the blade, and the model is solved. During the solving process, a random isogeometric analysis method is adopted for calculating the random displacement of the blade under the influence of the material attribute and the external load randomness, meanwhile, the maximum lift-drag ratio of the blade wing section is calculated, then the fitness of theindividual of the current population is calculated, and therefore high-rigidity design of the blade on the premise that the lift-drag ratio is guaranteed is achieved. According to the blade high-rigidity design method, the randomness of blade material attributes and external loads is comprehensively considered, a random isogeometric analysis method based on a random Krylov subspace base vector discrete scheme is adopted for calculating the random displacement of the blade, and the high-precision blade random displacement can be efficiently obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
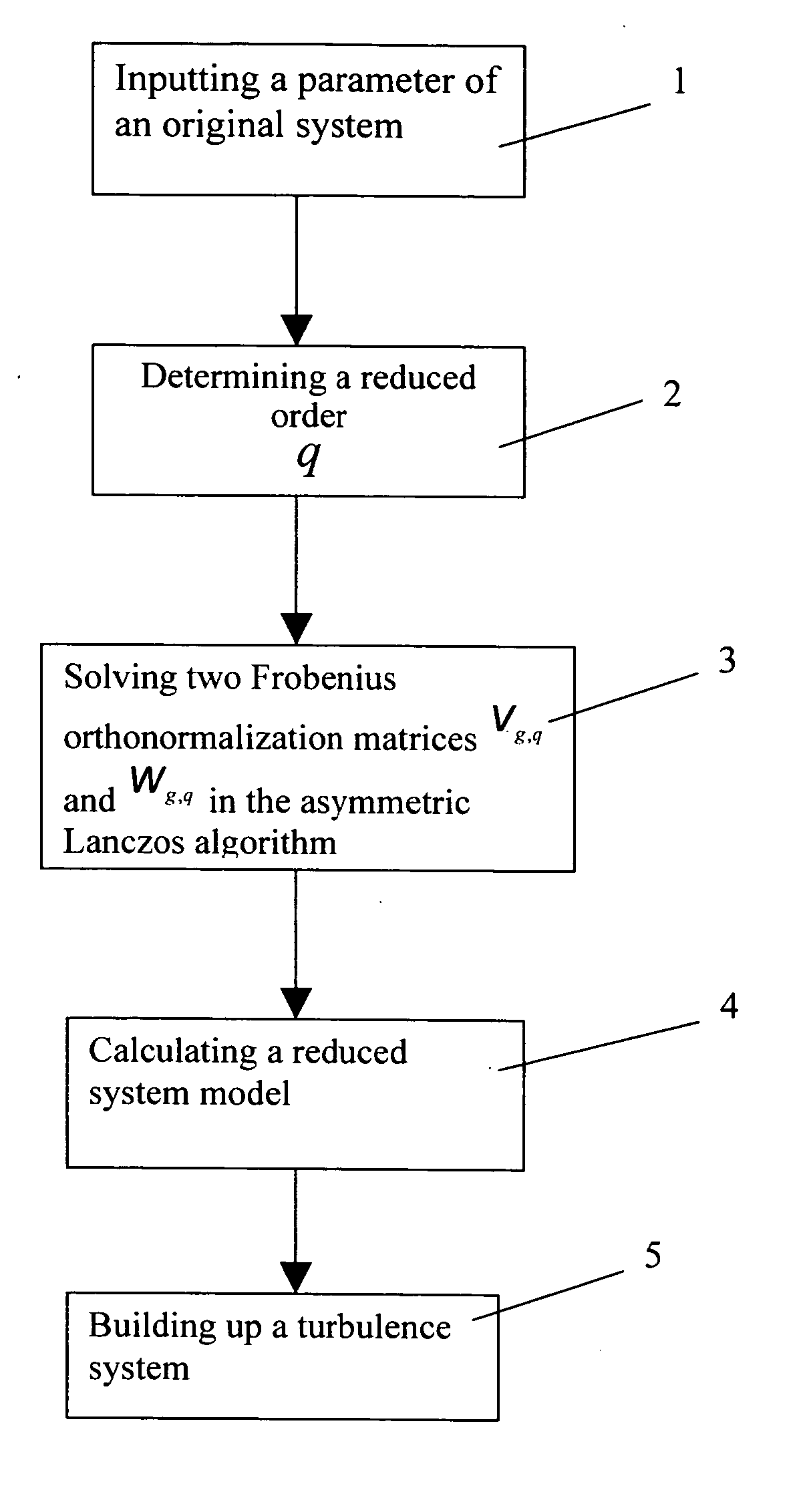
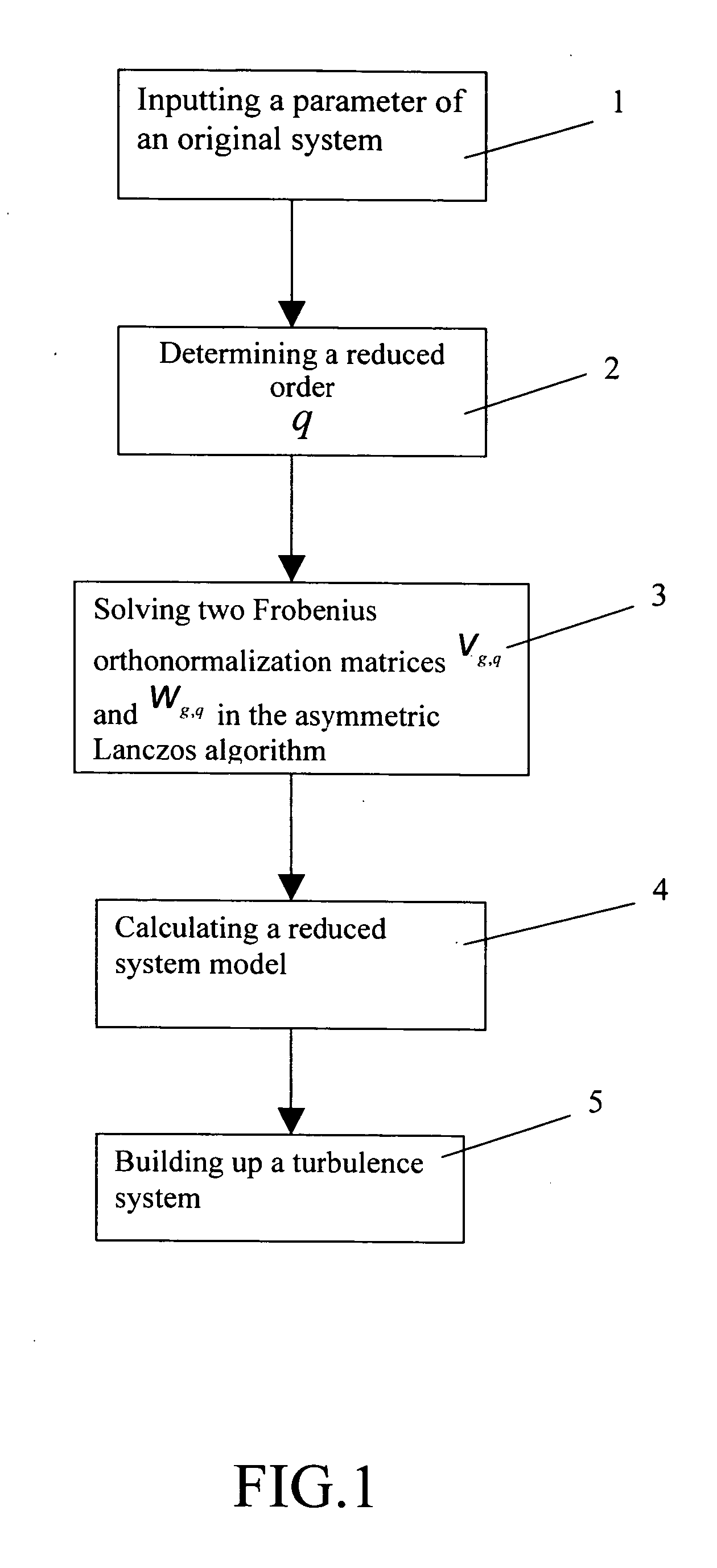
Method of reducing a multiple-inputs multiple-outputs (MIMO) interconnect circuit system in a global lanczos algorithm
InactiveUS20080126028A1Promote resultsUnstable valueComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designHat matrixReduced model
A method of reducing a MIMO interconnect circuit system in a global Lanczos algorithm is used for estimation of the error margin between the original model and the reduced model of MIMO circuit system. In the algorithm, a projection matrix and then a circuit of declining order system are given. A turbulence system being added to the original system, the transfer function union is completely identical to the reduced system union given in the algorithm. It proves that the union of preceding 2q order of the transfer function of reduced system may be surely corresponding to that of original system. It is deduced from the turbulence system added to the original system that the union of preceding 2q order is equal to that of reduced system. In this invention, the algorithm is the basis of determination of the reduced circuit order in a model reduction algorithm a Krylov subspace.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
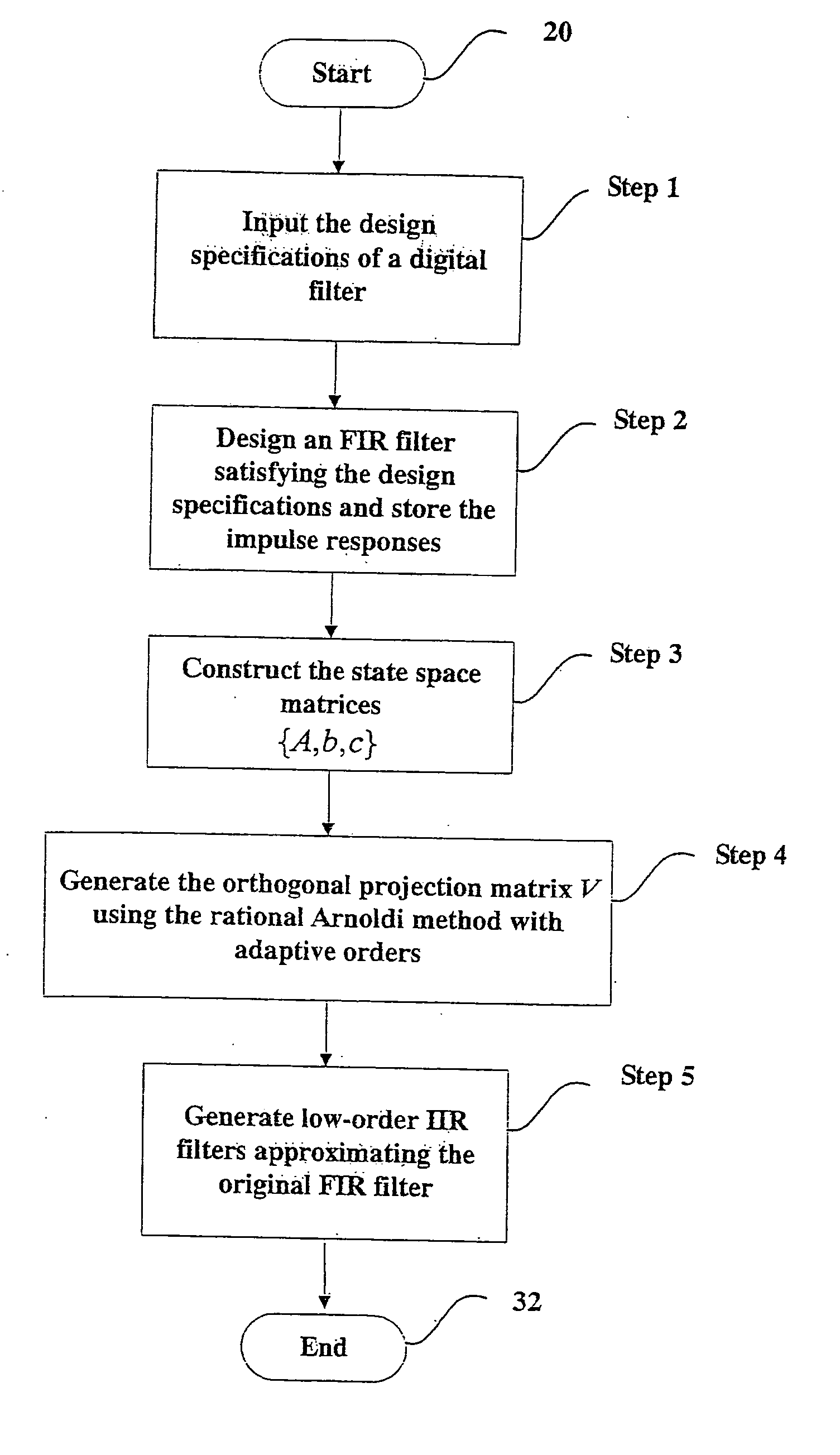
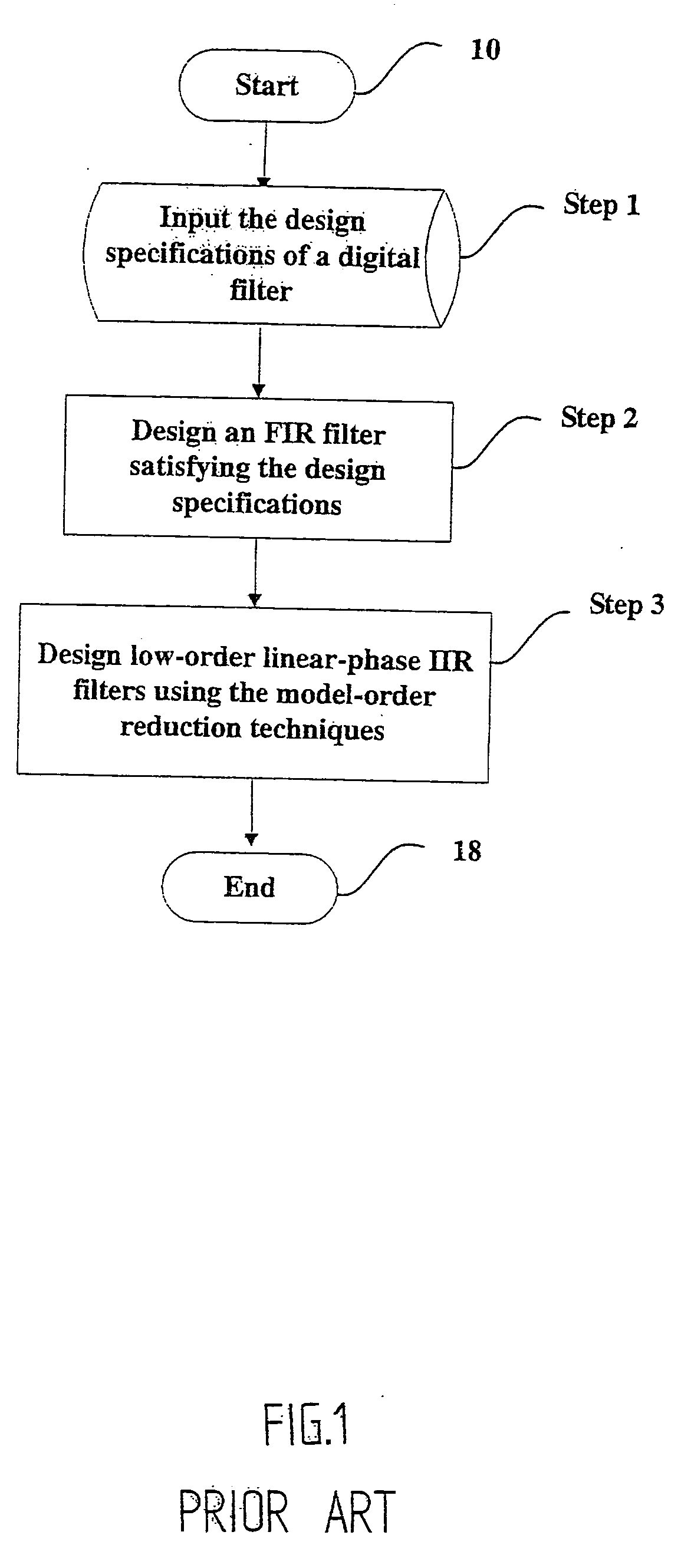
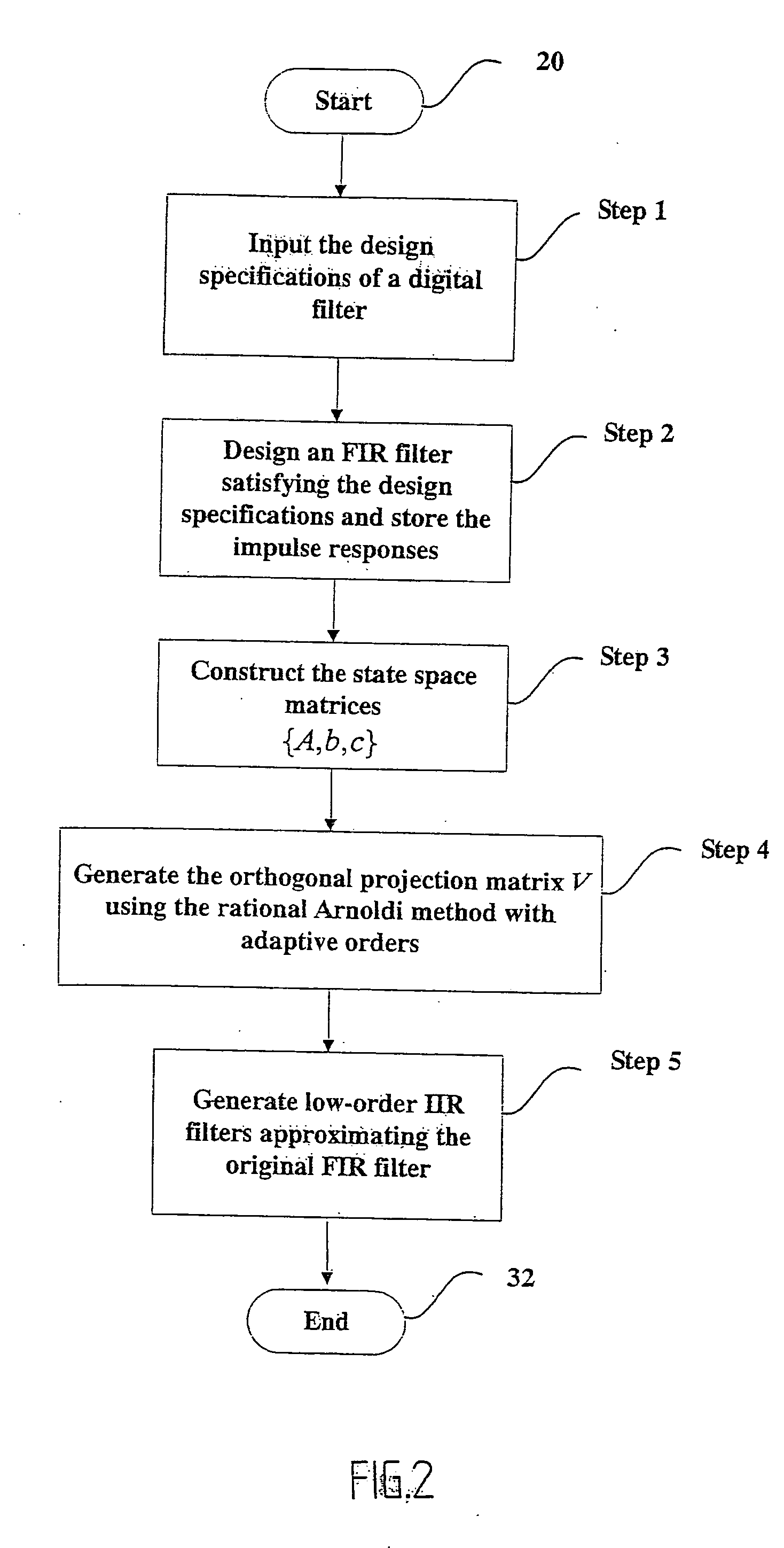
Efficient digital filter design tool for approximating an FIR filter with a low-order linear-phase IIR filter
InactiveUS20050235023A1Avoid failureEfficiently keeps water out of the pull chain switchDigital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsIir filteringComputation complexity
A method and apparatus for designing low-order linear-phase IIR filters is disclosed. Given an FIR filter, the method utilizes a new Krylov subspace projection method, called the rational Arnoldi method with adaptive orders, to synthesize an approximated IIR filter with small orders. The method is efficient in terms of computational complexity. The synthesized IIR filter can truly reflect essential dynamical features of the original FIR filter and indeed satisfies the design specifications. In particular, the linear-phase property is stilled remained in the passband.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
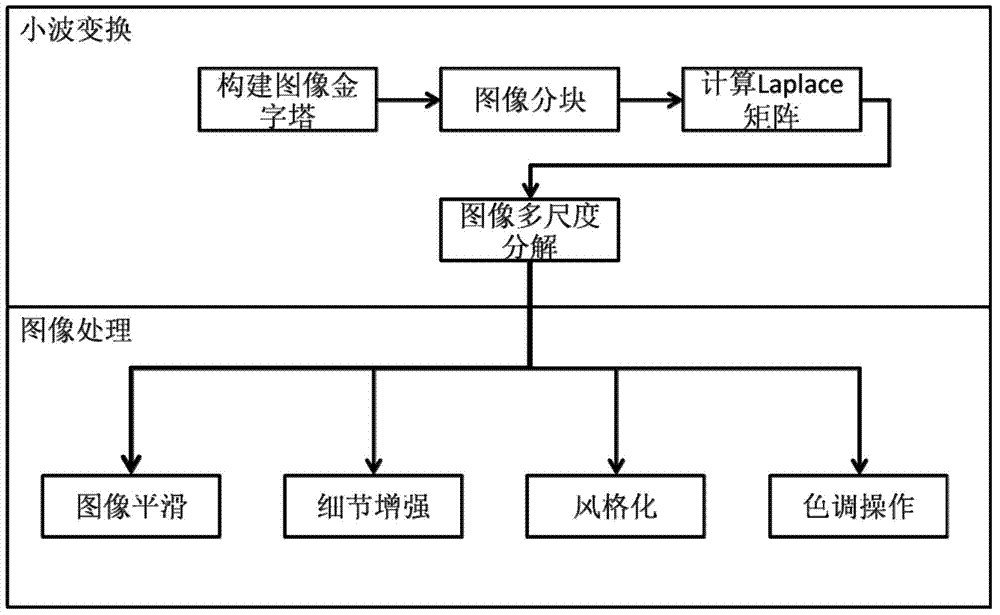
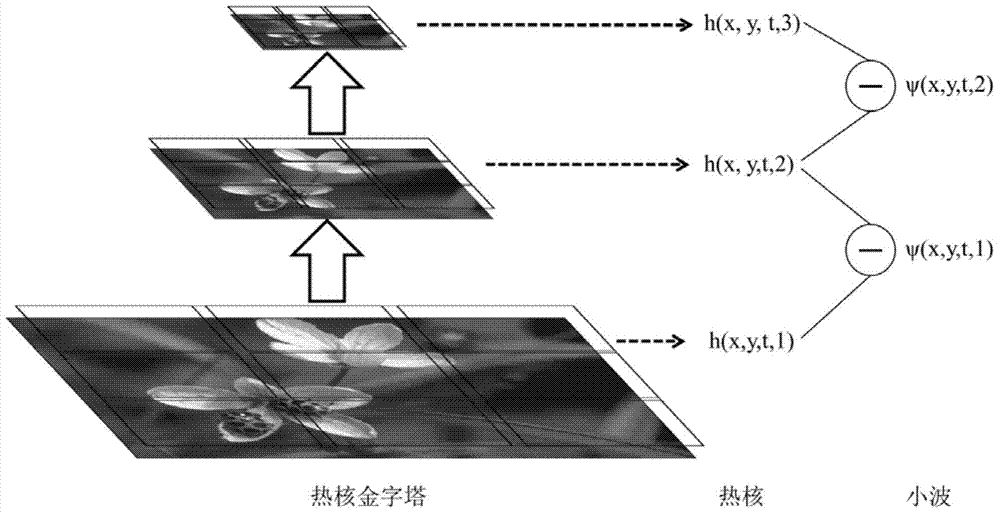
Anisotropism wavelet image processing method based on thermonuclear pyramid
InactiveCN103700064AImage smoothingMulti-scale conceptImage enhancementMultiscale decompositionPartial differential equation
The invention provides an anisotropism wavelet image processing method based on a thermonuclear pyramid. According to the method, at the theoretical part, wavelets are obtained through thermonuclear difference between adjacent layers of an image pyramid, and are equal to negative one order derivation of a thermal diffusion partial differential equation, relative to time; at an implementation part that: 1), mapping images to be a weight undirected graph, coding structural characteristics into a Laplacian matrix, and achieving anisotropism thermal diffusion; 2), dividing the images into image subblocks with overlaps, calculating wavelets of all image blocks in a parallel mode, reducing calculated amount by using a block overlapping method and effectively eliminating blocking effects after recombination; 3), adopting Krylov subspace technology to accelerate image block wavelet transform calculation, and avoiding time-consuming matrix spectral factorization. At the application part, the method is applied to image processing with structural protecting function. The data related anisotropism wavelet system provided by the invention achieves structure protection multiscale decomposition for the images, and shows excellent performance in various image processing applications.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
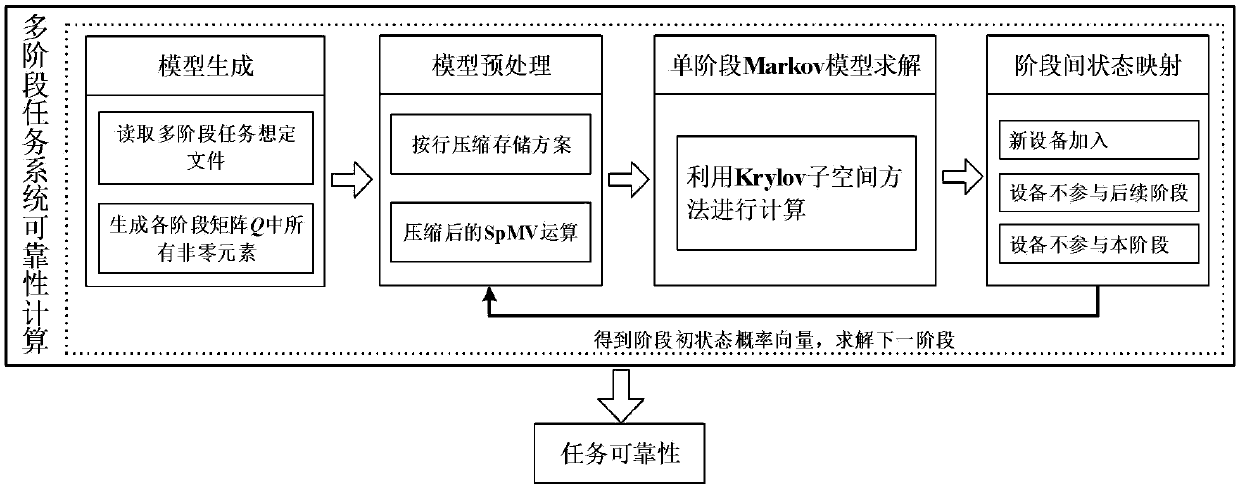
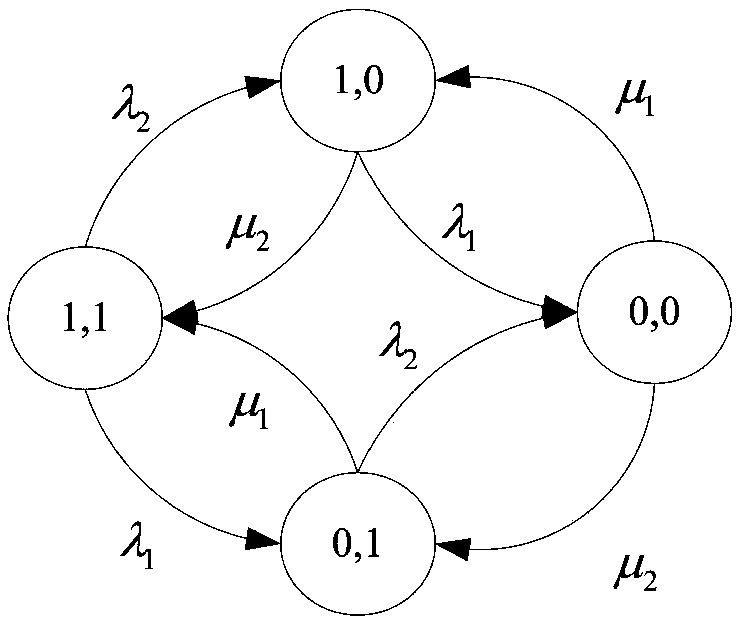
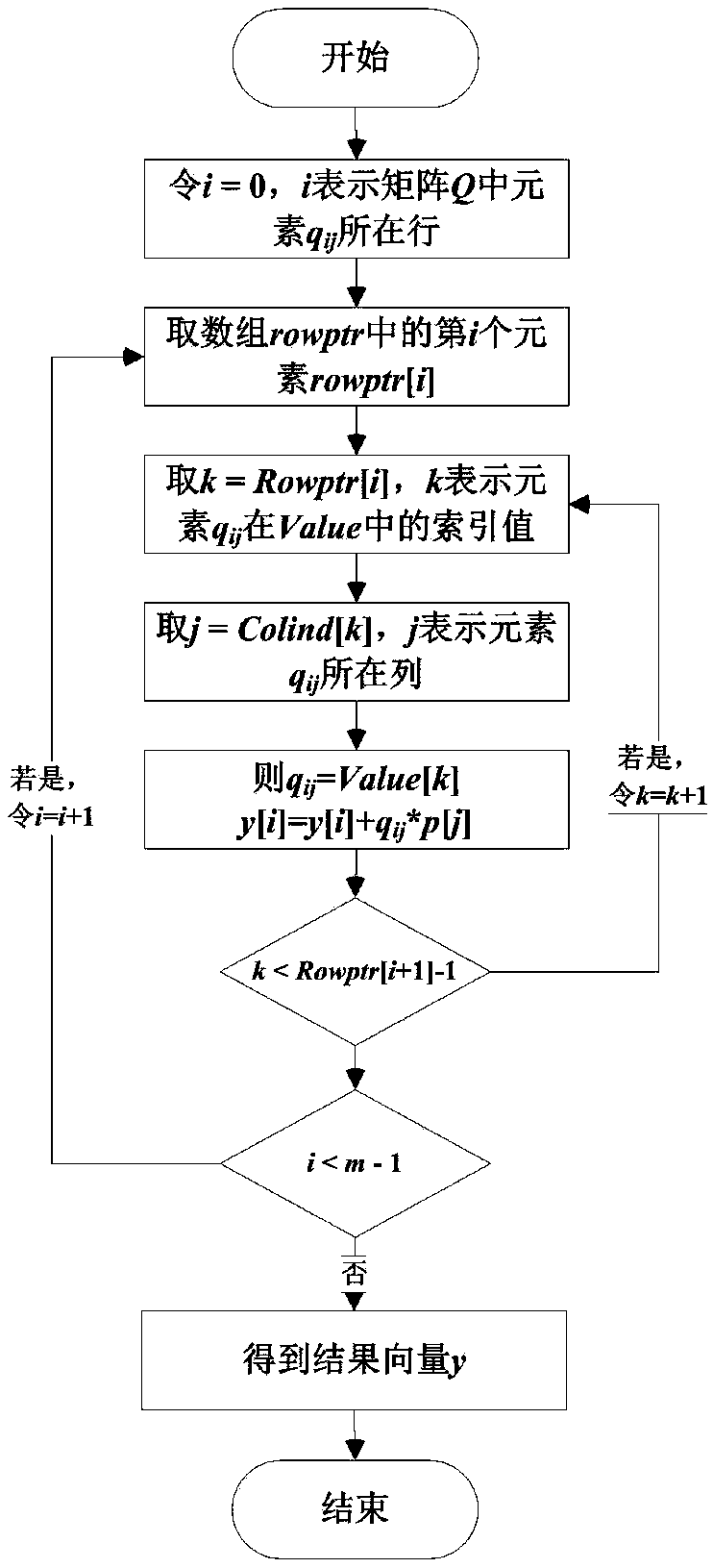
Method for reliability model and analysis of multi-phase mission system
PendingCN109063264AHigh speedHigh precisionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMarkov chainReliability model
The invention belongs to the technical field of system reliability. A reliability modeling and analysis method for multi-phase mission system is disclosed. Based on continuous-time Markov chain, a single-phase reliability model of multi-phase mission system is generated and solved. The reliability of the last phase is the reliability of the whole mission. The sparse matrix compression storage method is used to preprocess the single-stage Markov model. The generated Markov reliability model is solved based on the Krylov subspace computation method. By using the state mapping mechanism between stages, the single-stage model can be solved step by step. The idea of phase-by-phase modeling is adopted to avoid the problem of large scale caused by unified modeling. At that same time, compress storage based on sparse matrix and Krylov subspace method can effectively improve the spatial storage efficiency and computational efficiency of the model.
Owner:LOGISTICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF PLA
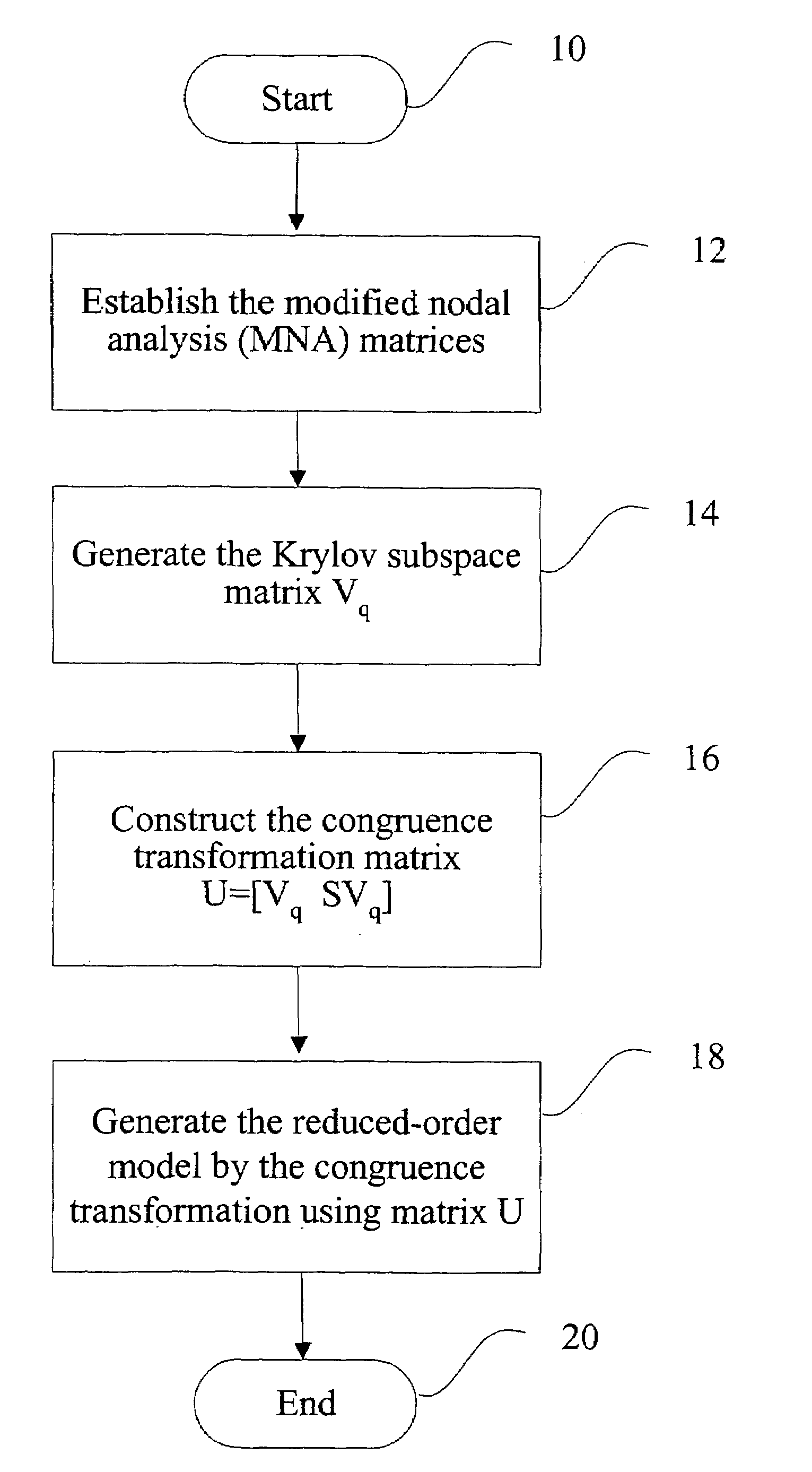
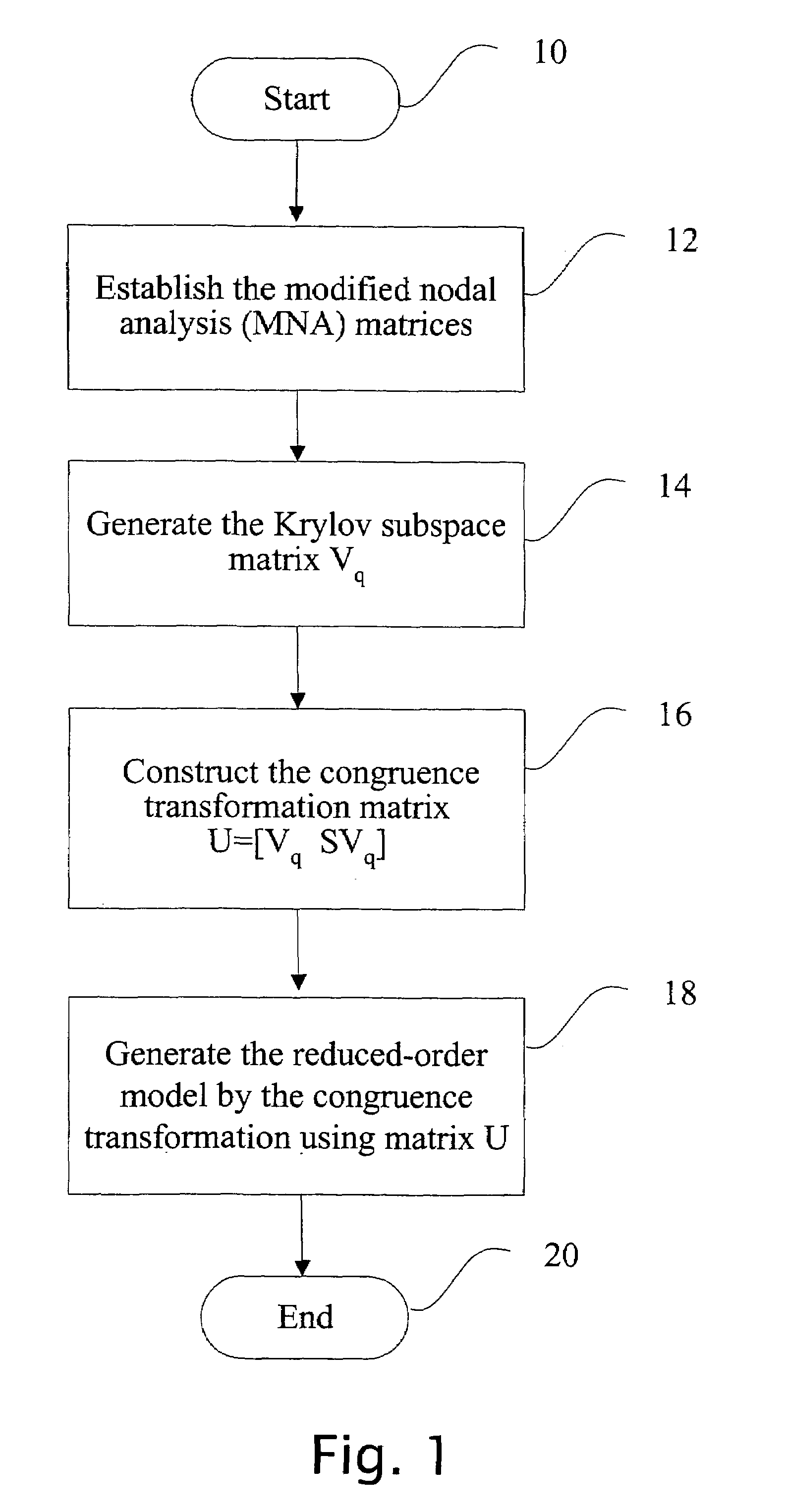
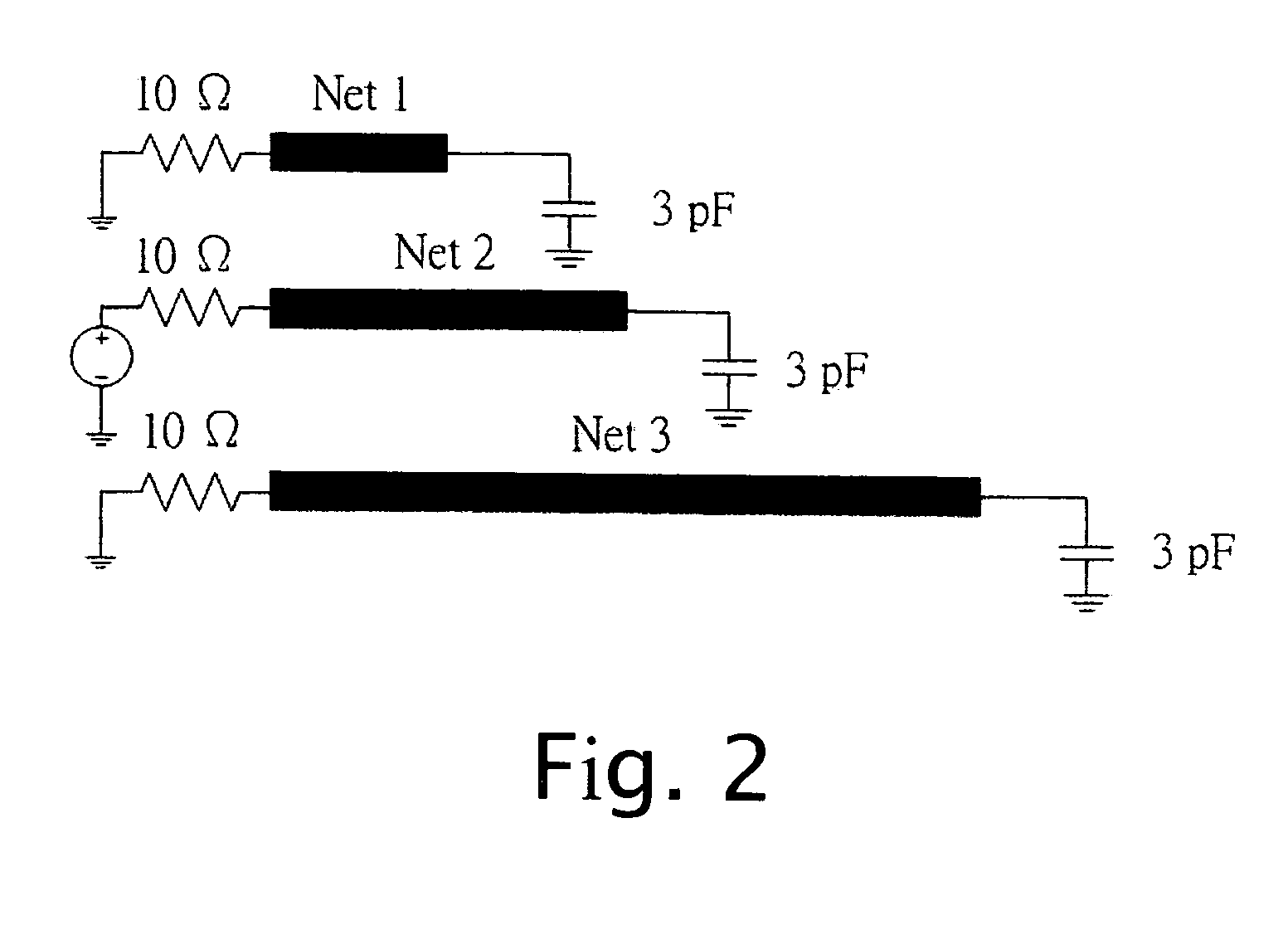
Method and apparatus for model-order reduction and sensitivity analysis
InactiveUS7216309B2Reduce computing costLow costDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationVlsi interconnectAlgorithm
Computer time for modeling VLSI interconnection circuits is reduced by using symmetric properties of modified nodal analysis formulation. The modeling uses modified nodal analysis matrices then applies a Krylov subspace matrix to construct a congruence transformation matrix to generate the reduced order model of the VLSI.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
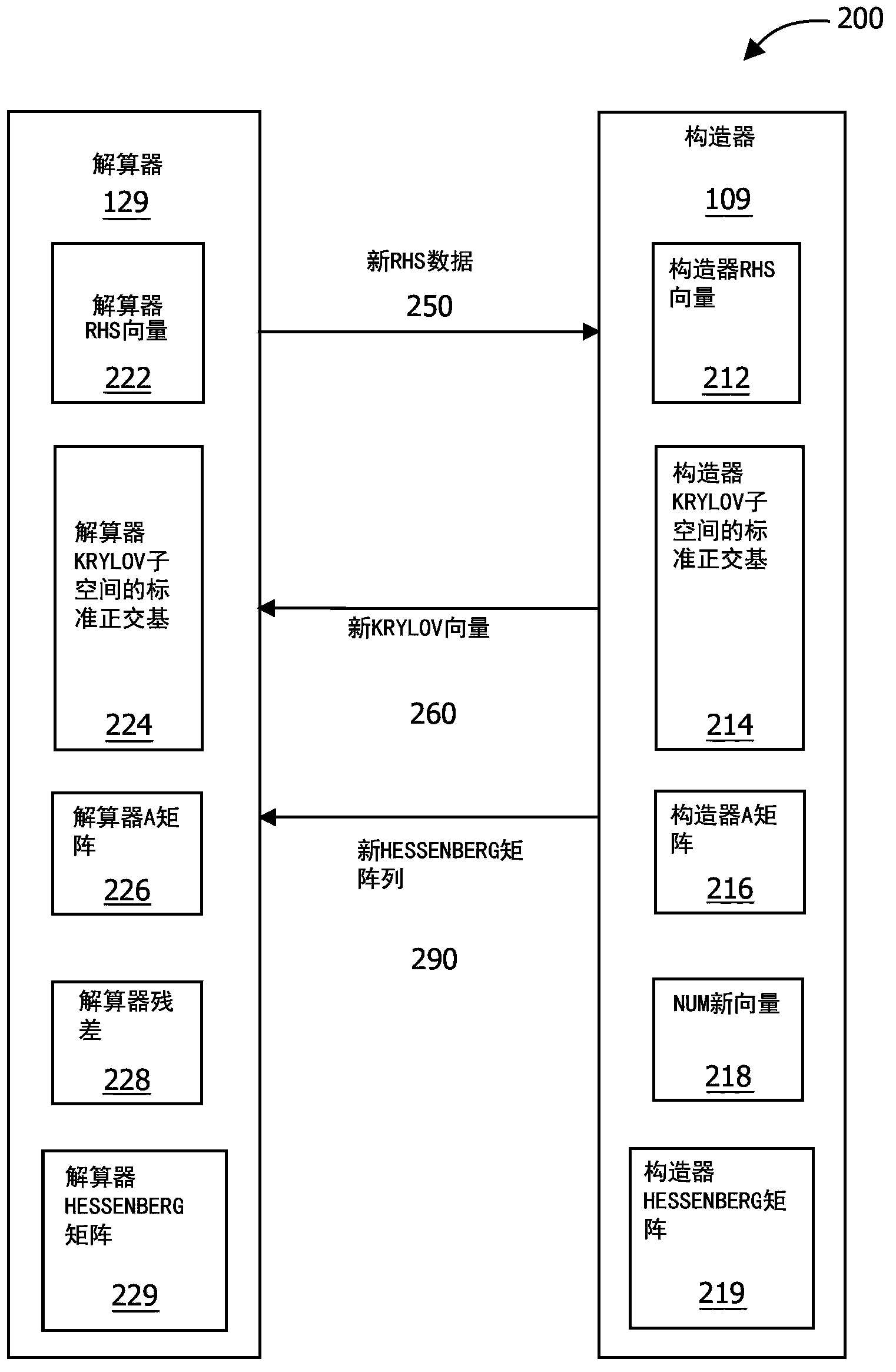
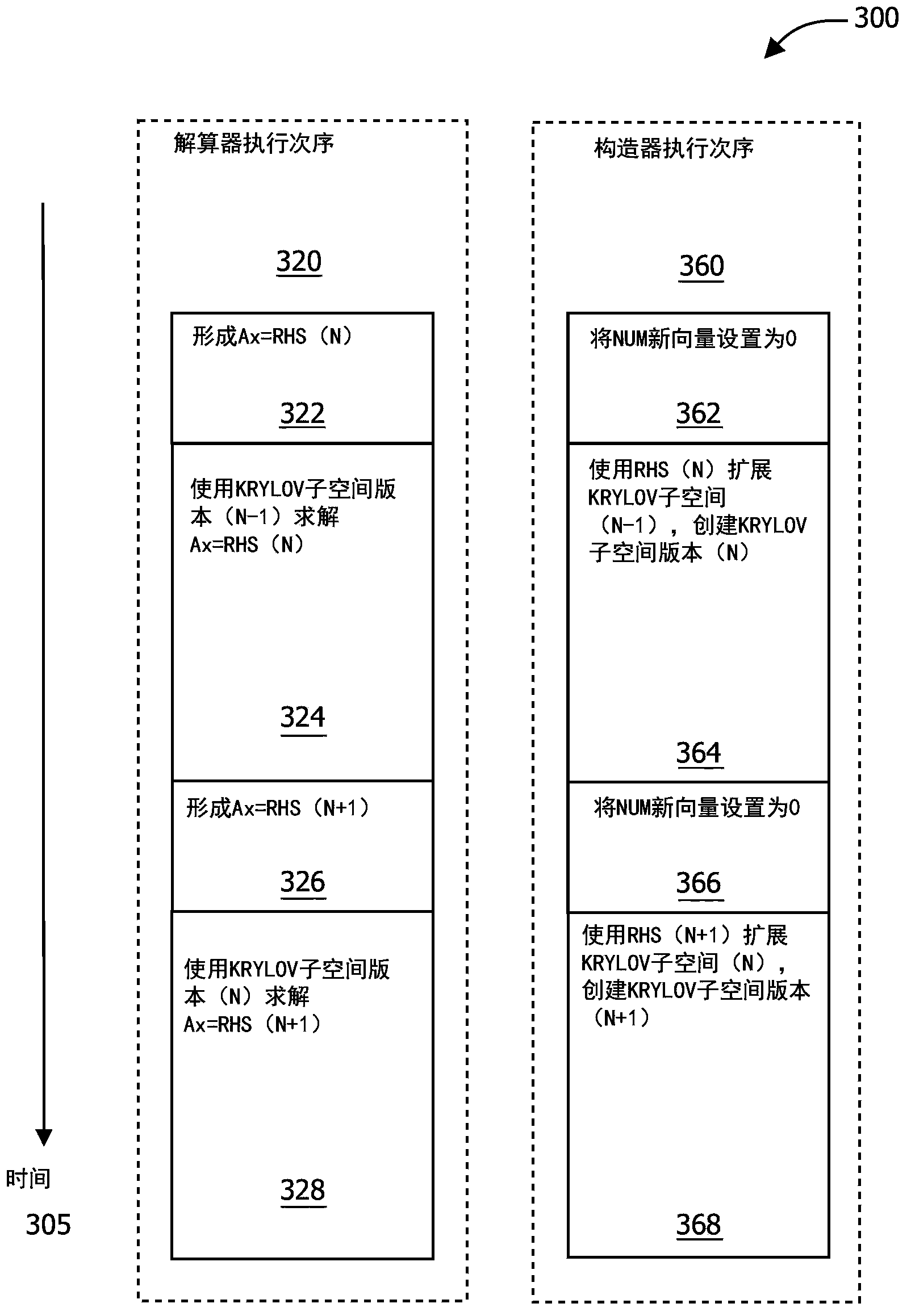
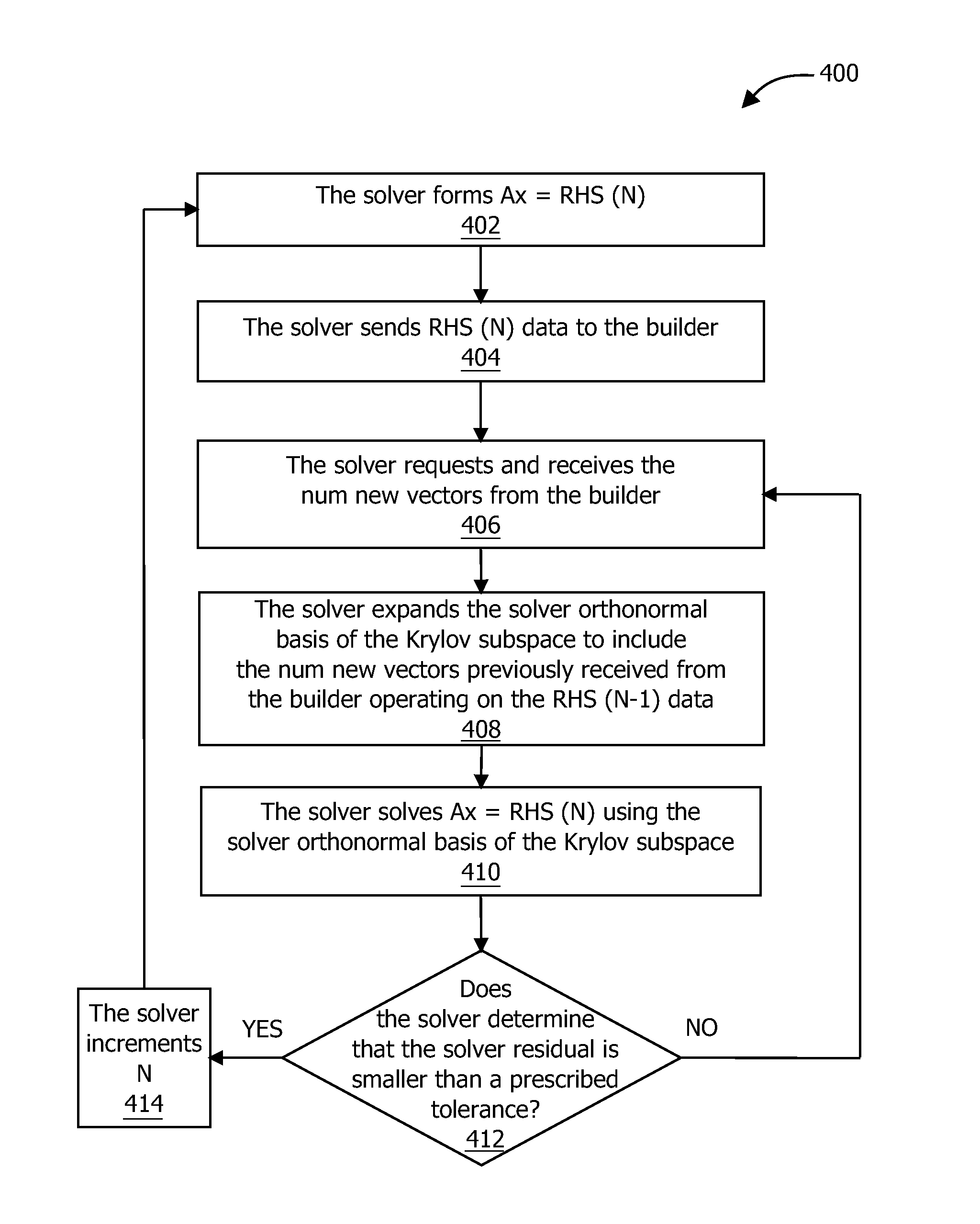
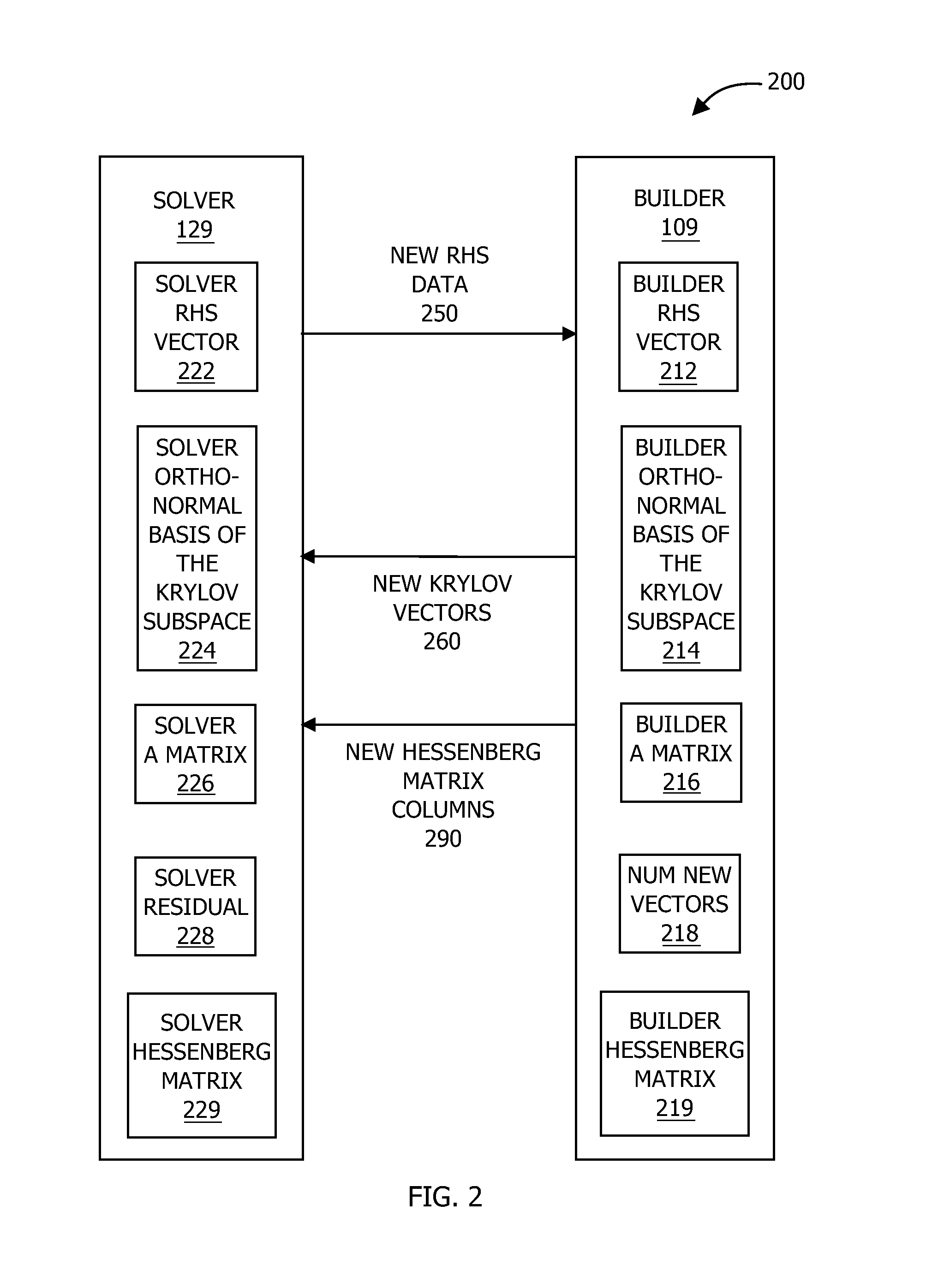
Technique for solving linear equation systems with multiple right hand sides by KRYLOV subspace expansion
InactiveCN103577385AImprove performanceShorten the timeComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmEuclidean vector
One embodiment sets forth a method for solving linear equation systems that include the same matrix A coupled with multiple right-hand-side vectors. For each new right-hand-side vector, a solver expands an existing Krylov subspace based on the Krylov subspace and data associated with the previous right-hand-side vector. The solver then uses the expanded Krylov subspace to approximately solve the linear equation system for the new right-hand-side vector. By expanding the Krylov subspace for each new right-hand-side vector, the solver continually leverages the information from the preceding right-hand-side vectors. Advantageously, expanding the Krylov subspace is typically computationally quicker than prior art-techniques, such as creating a new Krylov subspace or transforming an existing Krylov subspace. Consequently, by implementing the disclosed techniques, the likelihood of exceeding time constraints associated with algorithms that include solving certain classes of linear equation systems may be decreased.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
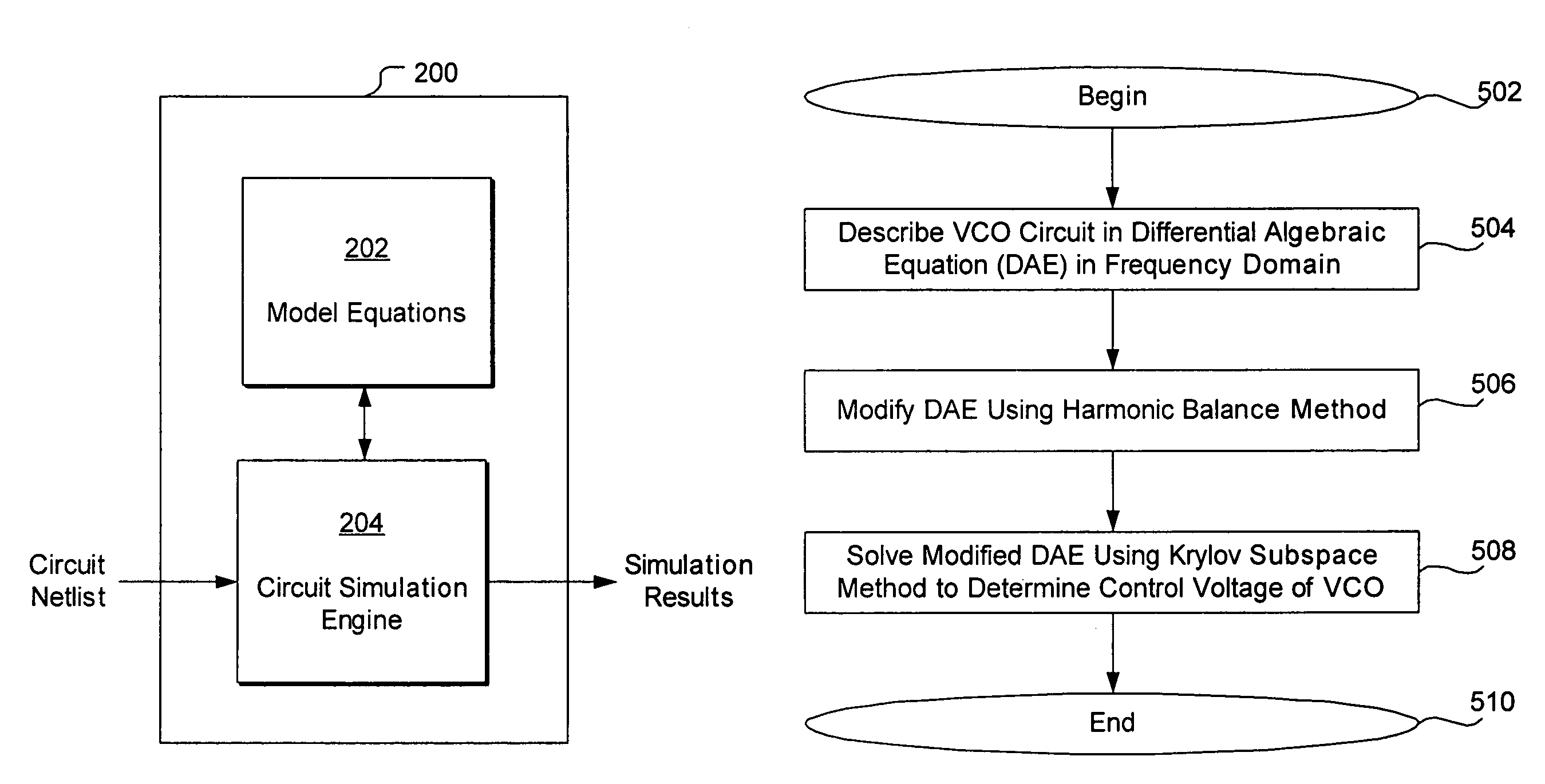
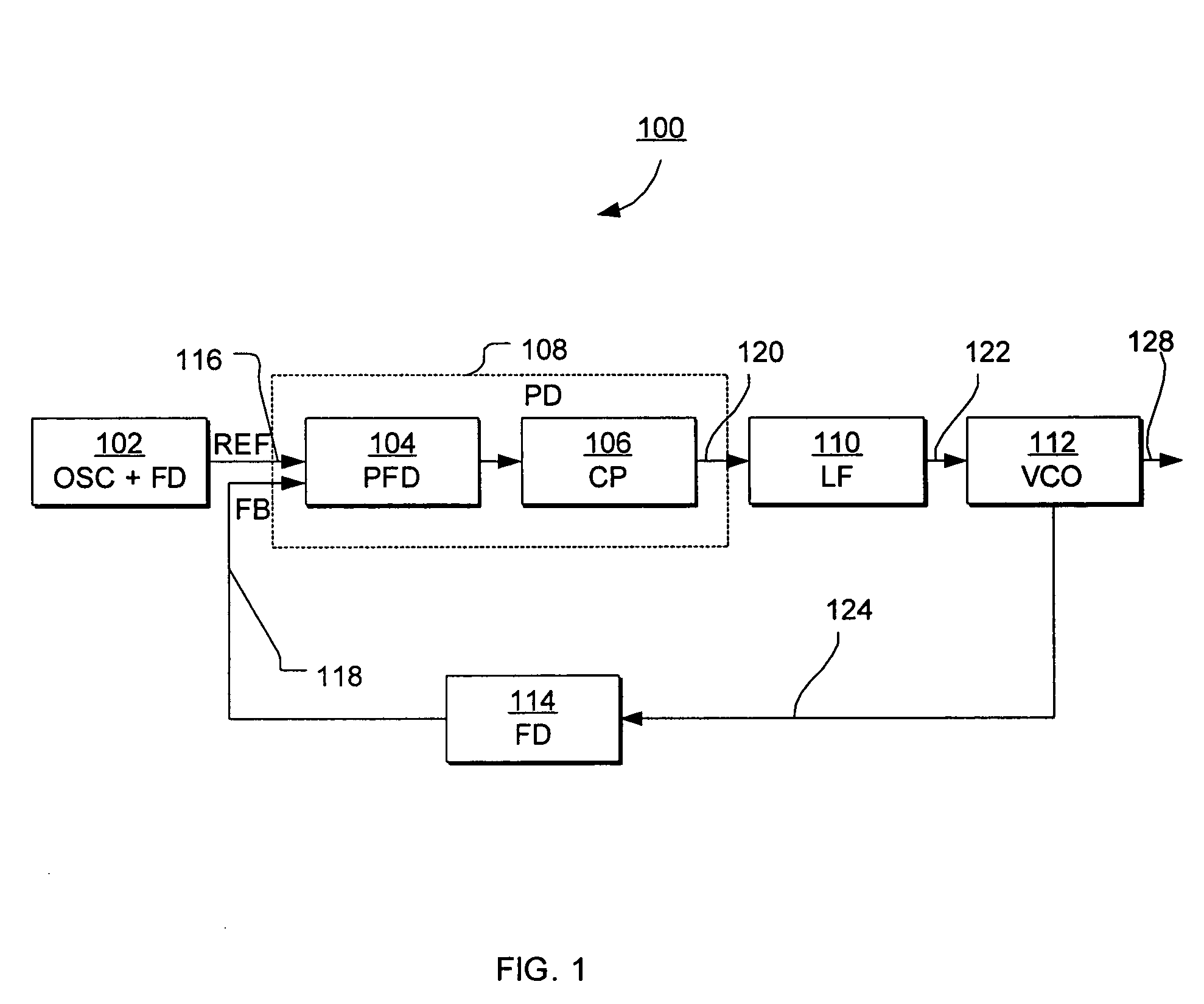
Method and apparatus for steady state analysis of a voltage controlled oscillator
ActiveUS7332974B1Computationally efficientShort runtimeFrequency to amplitude conversionComputer aided designDifferential algebraic equationHarmonic
A computer-implemented method computes the steady-state and control voltage of a voltage controlled oscillator, given a known frequency or a known period of oscillation of the voltage controlled oscillator. Differential algebraic equations representative of the voltage controlled oscillator are generated, where the differential algebraic equations includes a known period or frequency of oscillation and an unknown control voltage of the voltage controlled oscillator. The differential algebraic equations are modified using a finite difference method, a shooting method, or a harmonic balance method, to obtain a set of matrix equations corresponding to the differential algebraic equations. A solution to the matrix equations is obtained using a Krylov subspace method, using a preconditioner for the Krylov subspace method that is derived from a Jacobian matrix corresponding to the matrix equations, where the solution includes the control voltage of the voltage controlled oscillator in steady state.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Calculation method of internal scattering characteristic of complicated cavity
InactiveCN106649197AReduce designLittle unknownComplex mathematical operationsClassical mechanicsElectromagnetic field
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Single input single output RCS interconnection circuit degradation method
InactiveCN1604092AHigh order reduction accuracyImprove numerical stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsNumerical stabilityInterconnection
This invention belongs to electron technique field, which is in detail single input and output RCS connection circuit based on second order Arnoldi process. The method comprises the following steps: to form second order system, system frequency shift, system linearization, getting orthogonal matrix Q o f Krylov sub-space; finally to get N order deduction system. This invention is characterized by the following: it has high accuracy and ensures the data stability of the order deduction and has low computation and storage and ensures the passivity of the order deduction system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Electrical tomography hybrid method
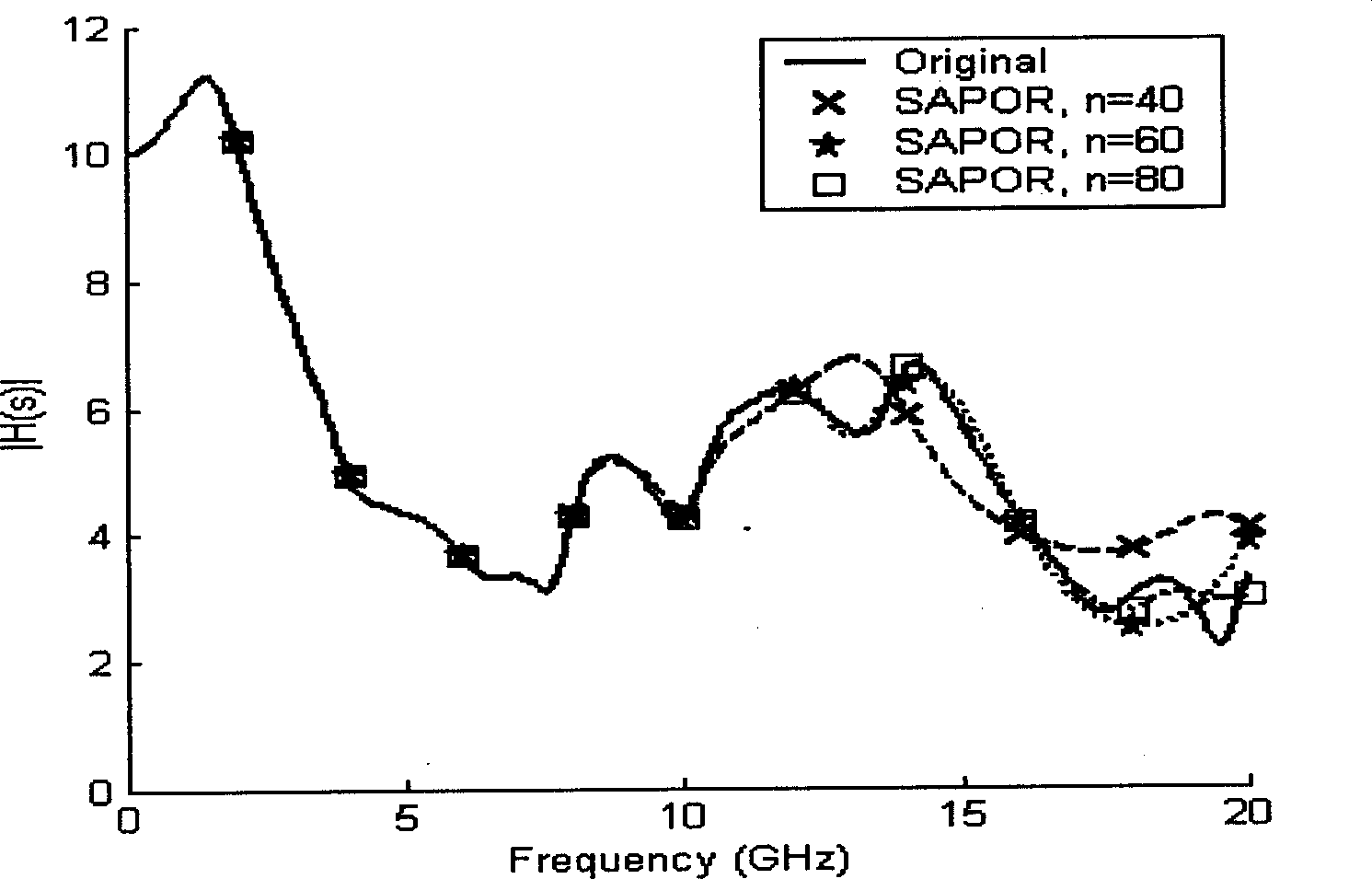
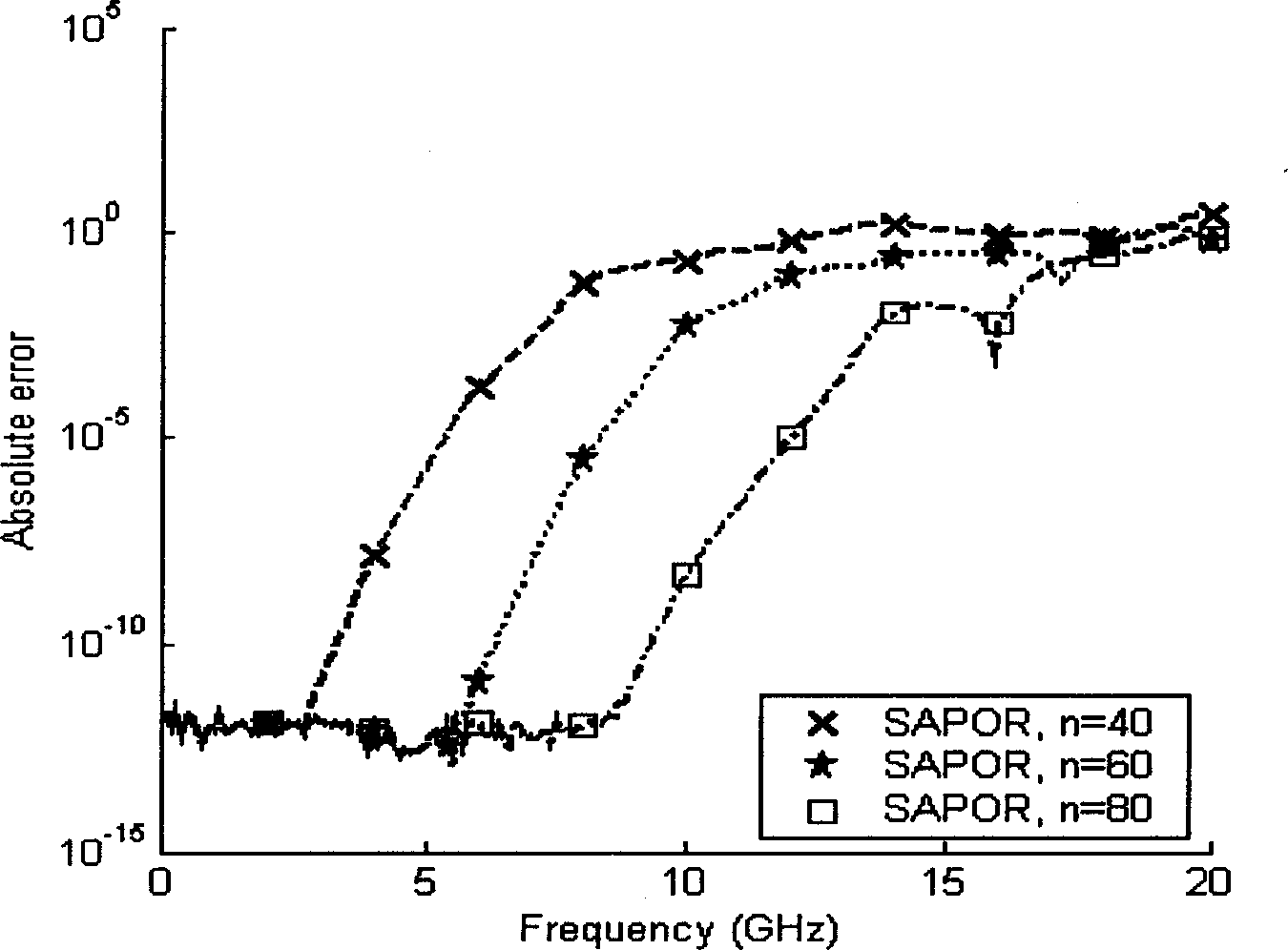
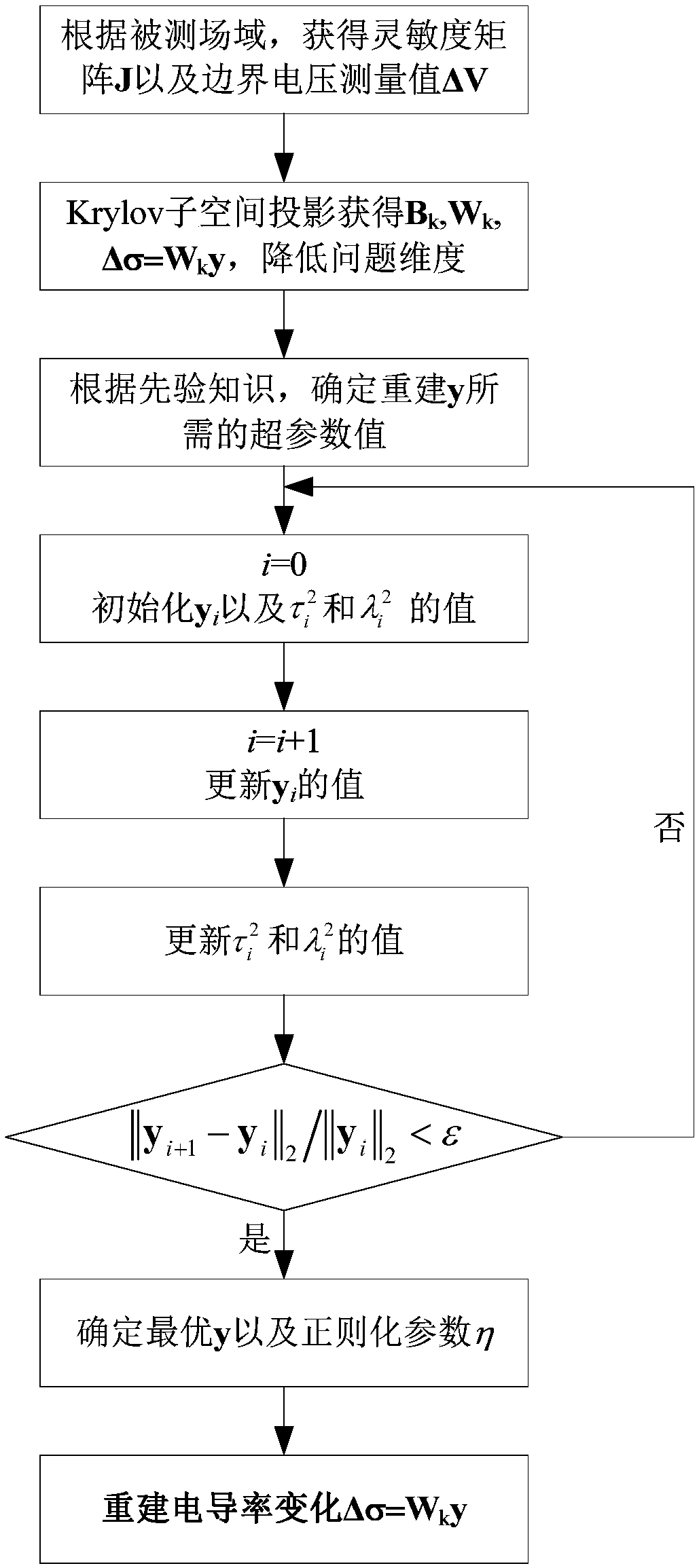
ActiveCN107845119AReduce dimensionalityImproving the exact solve processReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomographyImaging technique
The embodiment of the invention discloses an electrical tomography hybrid method and relates to the field of electrical tomography technology. Through the method, the calculation amount in the processof determining regularization parameters can be lowered. The method comprises the steps that before and after changing of internal conductivity of a target object, voltage data of a boundary of the target object is measured; according to the collected voltage data, a Krylov subspace projection method is adopted to perform dimension reduction analysis, and an analysis result is obtained; and a Bayesian regularization method is adopted to acquire a change value of the internal conductivity of the target object. The method is applicable to electrical tomography.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
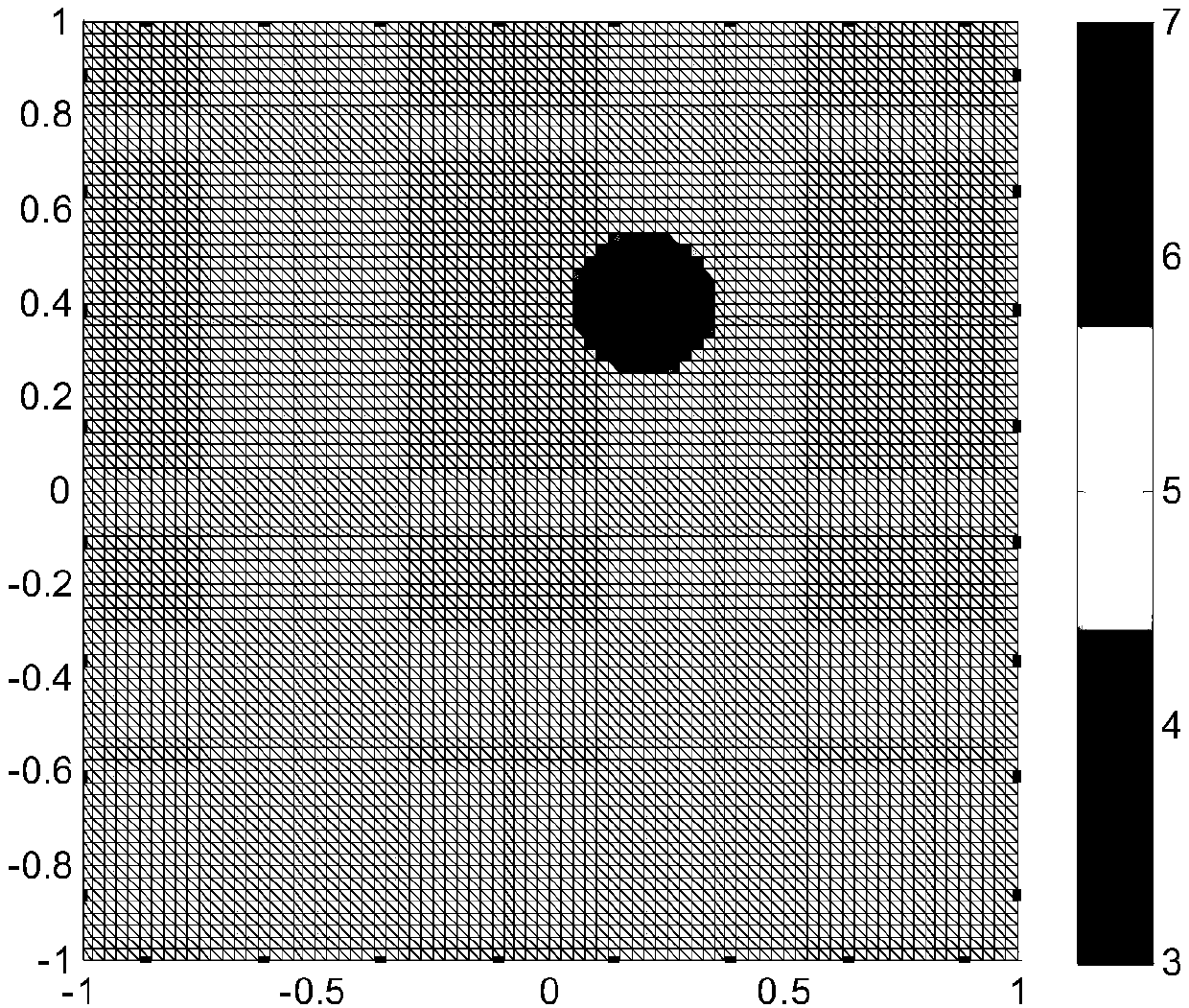
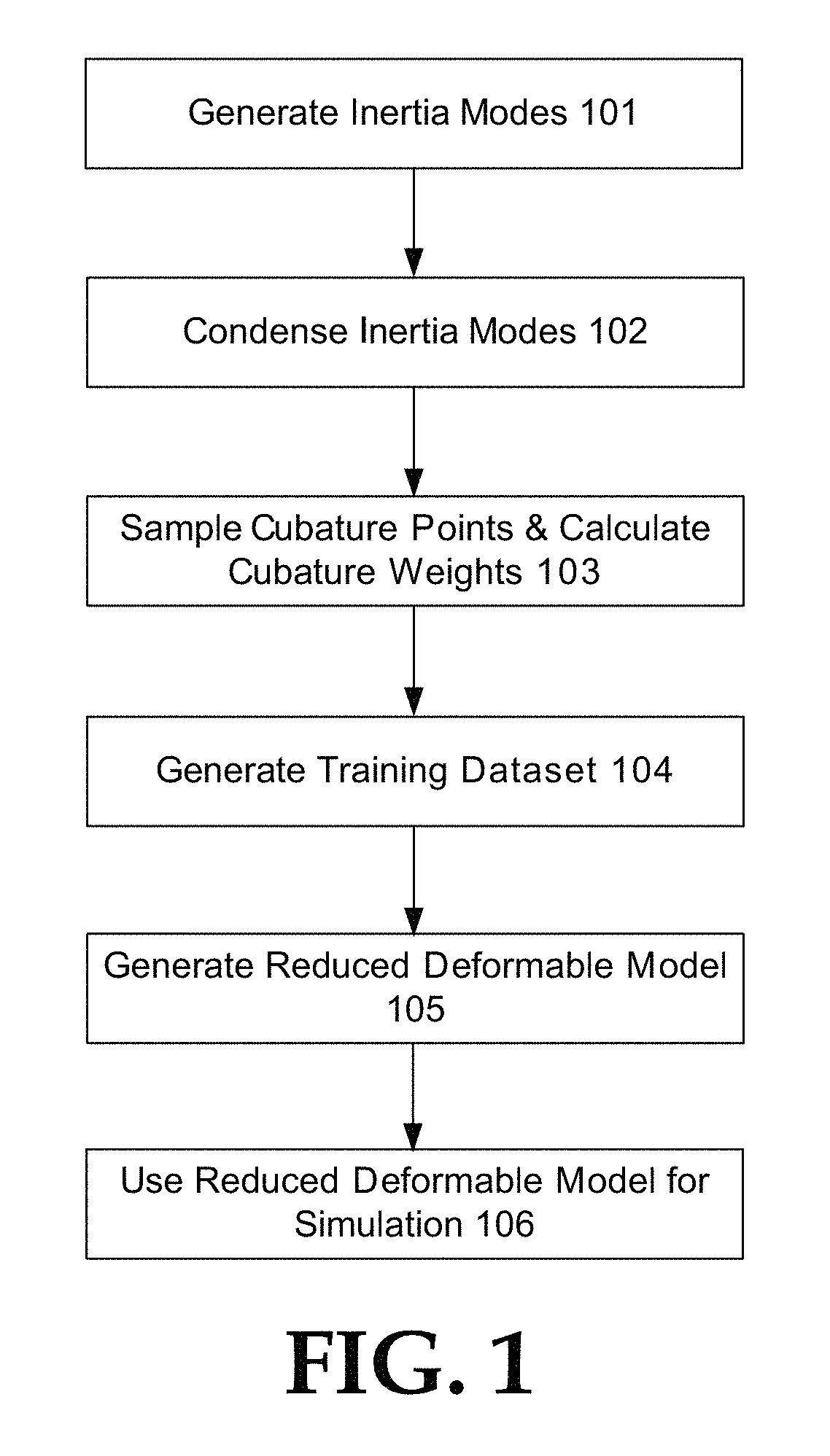
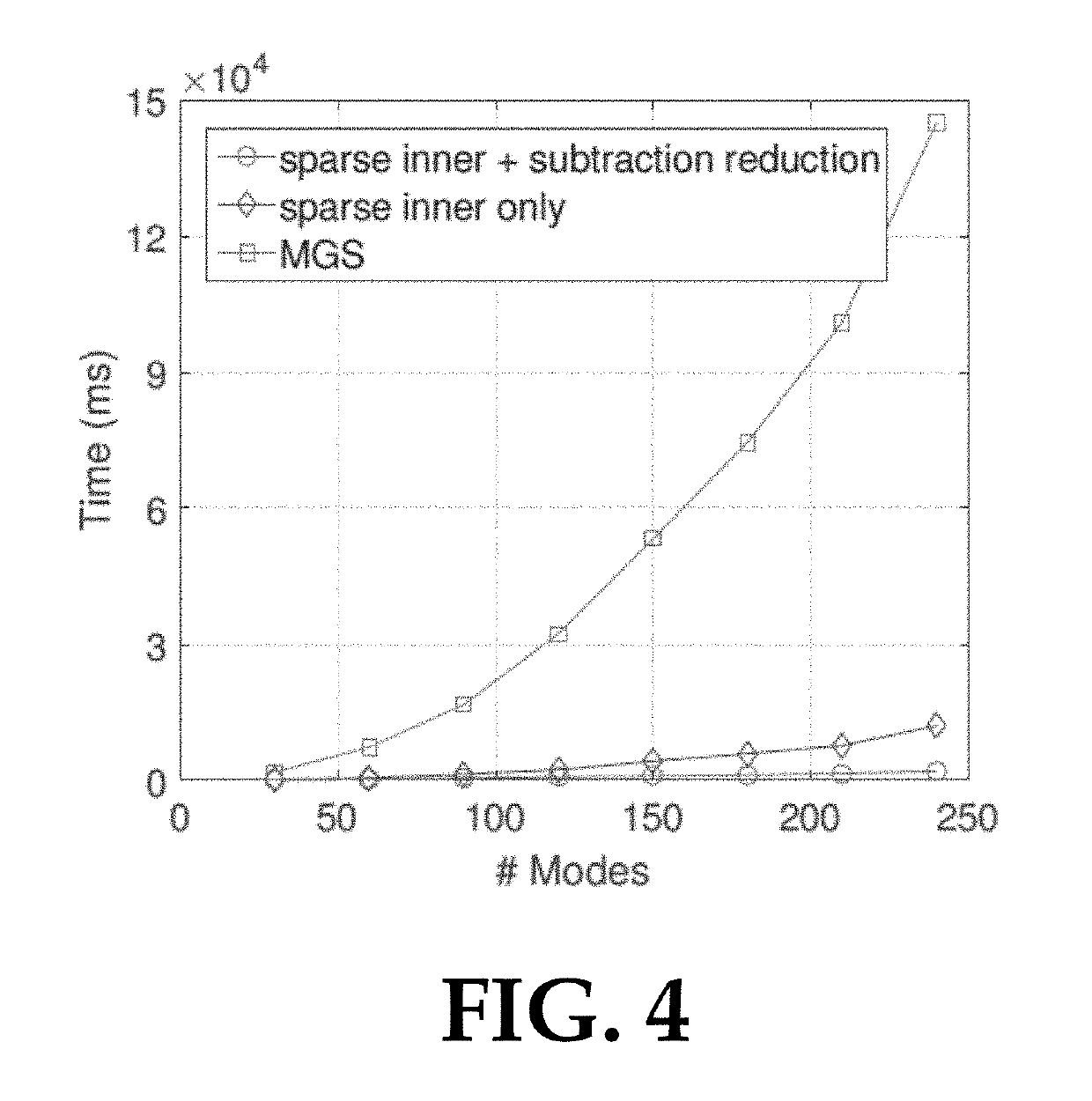
Accelerated precomputation of reduced deformable models
Technologies are disclosed for precomputation of reduced deformable models. In such precomputation, a Krylov subspace iteration may be used to construct a series of inertia modes for an input mesh. The inertia modes may be condensed into a mode matrix. A set of cubature points may be sampled from the input mesh, and cubature weights of the set of cubature points may be calculated for each of the inertia modes in the mode matrix. A training dataset may be generated by iteratively adding training samples to the training dataset until a training error metric converges, wherein each training sample is generated from an inertia mode in the mode matrix and corresponding cubature weights. The reduced deformable model may be generated, including inertia modes in the training dataset and corresponding cubature weights.
Owner:STC UNM
Solving linear equation systems with multiple right hand sides by krylov subspace expansion
InactiveUS20140025720A1Shorten the timeImprove performanceComplex mathematical operationsComputation using denominational number representationAlgorithmEuclidean vector
One embodiment sets forth a method for solving linear equation systems that include the same matrix A coupled with multiple right-hand-side vectors. For each new right-hand-side vector, a solver expands an existing Krylov subspace based on the Krylov subspace and data associated with the previous right-hand-side vector. The solver then uses the expanded Krylov subspace to approximately solve the linear equation system for the new right-hand-side vector. By expanding the Krylov subspace for each new right-hand-side vector, the solver continually leverages the information from the preceding right-hand-side vectors. Advantageously, expanding the Krylov subspace is typically computationally quicker than prior art-techniques, such as creating a new Krylov subspace or transforming an existing Krylov subspace. Consequently, by implementing the disclosed techniques, the likelihood of exceeding time constraints associated with algorithms that include solving certain classes of linear equation systems may be decreased.
Owner:JPL INVESTMENTS +1
Method for accelerating nuclear reactor core channel computing
ActiveCN106126931AAvoid generatingSave memoryInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsNuclear reactor coreNon symmetric
The invention discloses a method for accelerating nuclear reactor core channel computing. The method includes: 1, performing linearization on a sub-channel mass, energy and momentum conservation nonlinear equation system; and 2, solving a linearized sub-channel equation through a Krylov subspace method, and storing an equation coefficient matrix through a compression line non-zero storage technique and restarting a GMRES algorithm to solve a linear equation system. The method can accelerate reactor core channel computing and decrease memory consumption at the same time; and the method can solve the large-scale non-symmetric linear equation system including an energy equation, an axial momentum equation, and a pressure correction equation through the Krylov subspace method, and has high computing efficiency.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Deep stratum heat conductivity coefficient three-dimensional prediction method and device based on Krylov subspace
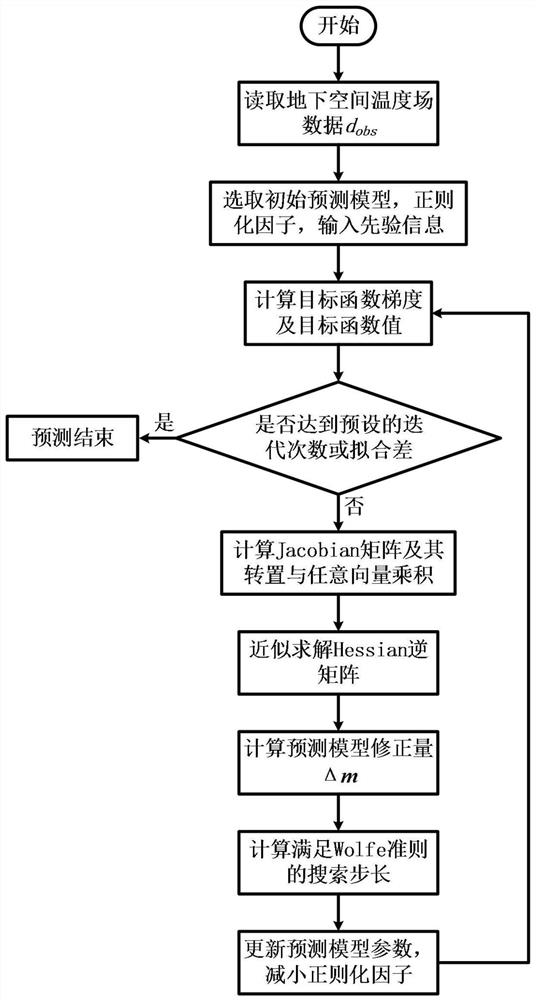
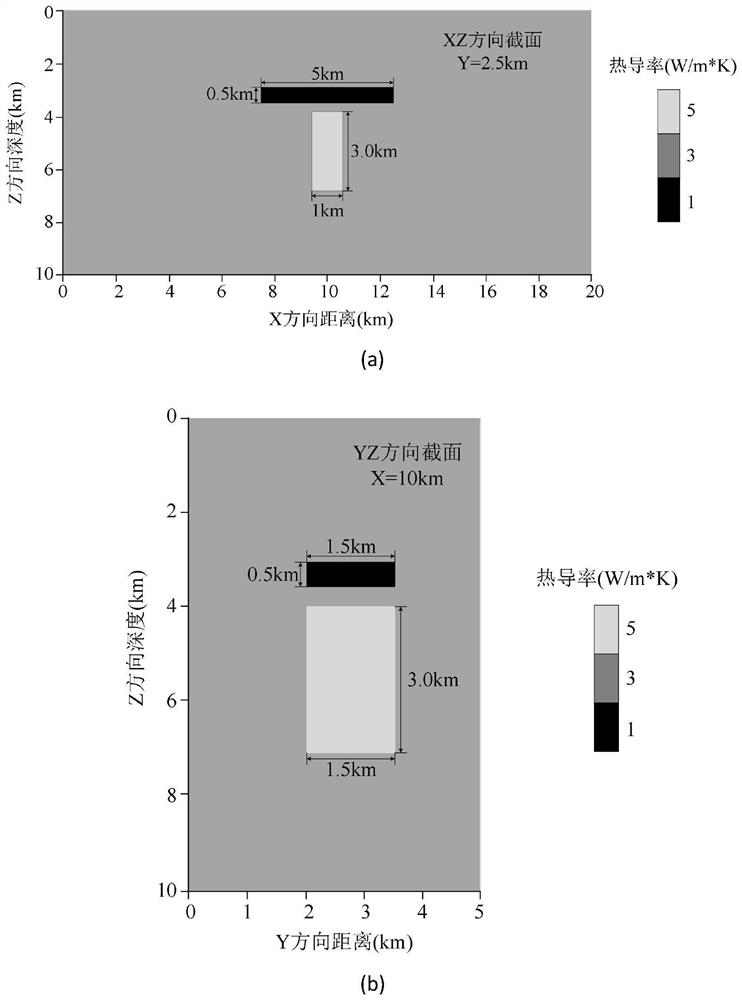
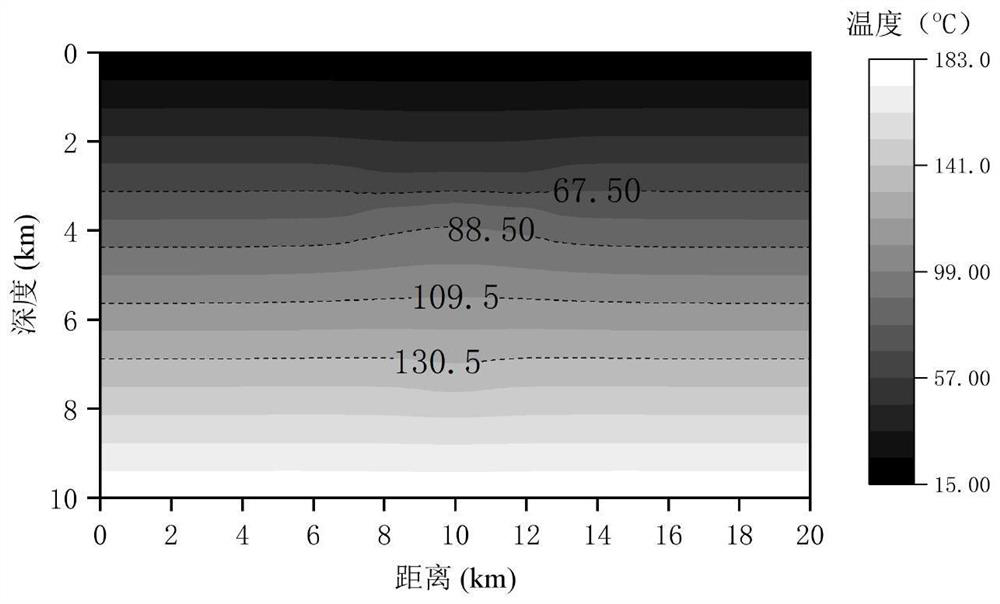
PendingCN114707385AAccurate predictionReduce the amount of calculationGeothermal energy generationForecastingComputational physicsModel parameters
The invention provides a deep stratum heat conductivity coefficient three-dimensional prediction method and device based on a Krylov subspace, and the method comprises the following steps: constructing a heat conductivity coefficient abnormal body in a uniform half-space research region, setting the boundary condition of the research region, carrying out the finite element temperature numerical simulation, and obtaining an underground space three-dimensional temperature field dobs; the method comprises the following steps: constructing an initial prediction model and a regularization objective function, and solving a product of a Jacobian matrix and any vector by adopting a Jacobian-freeKrylov subspace technology in a prediction process to avoid solving and storage of a large dense Jacobian matrix; a Gaussian-Newton algorithm and an L-BFGS algorithm are utilized to construct a Hessian matrix and approximately solve an inverse matrix of the Hessian matrix to reduce storage requirements and calculation amount and obtain a model correction amount delta m, a model step length is searched based on a Wolfe criterion to update model parameters, a fitting difference between actually measured data and simulated data is enabled to be smaller than a preset value through cyclic prediction, and an optimal prediction result is output. The method can quantitatively characterize the distribution characteristics of the heat conductivity coefficient of the deep medium, and is high in prediction precision, wide in range and high in practicability.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Calculation device and calculation method for deriving solutions of system of linear equations and program that is applied to the same
ActiveUS20150293883A1Easy to useLittle timeComplex mathematical operationsComputation using denominational number representationDiagonal matrixEuclidean vector
A calculation device for deriving solutions of a system of linear equations, which realizes a solution of the system of linear equations using an iterative method belonging to a Krylov subspace method, includes a plurality of arithmetic units. In the calculation device, a vector sequence xk (k is a natural number containing 0) approximating to the solutions of the system of linear equations is formed by a plurality of components in accordance with an order of the vector sequence xk, and when the vector sequence xk is divided into a plurality of different regions corresponding to the plurality of components and the respective arithmetic units are caused to execute arithmetic processings corresponding to the plurality of different regions in parallel in iterative computation of causing the vector sequence xk to approximate to the solutions, a preconditioned matrix that is used in the iterative computation is a diagonal matrix.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Dimension reduction recognition method for large-scale process control in process industry
ActiveCN111025898AImprove recognition accuracySmall amount of calculationAdaptive controlAlgorithmDimensionality reduction
According to the dimension reduction recognition method for large-scale process control of the process industry, manual participation is not needed in the calculation process, and parameter recognition of a high-order system can be achieved with a very low calculation amount on the basis that the calculation precision is ensured. According to the technical scheme, in the system parameter recognition process, the to-be-identified 2n-dimensional parameters are used for constructing the Krylov subspace through the Arnoldi method, the 2n-dimensional parameters are reduced to the k-dimensional parameters, and the calculated amount of the system is reduced; then solving the parameter optimization step length through a Givens transformation method, and ensuring that the calculation method is convergent; through a preset threshold value and an iteration method, the recognition precision of system parameters is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Detecting method and apparatus for multiple transmitted signal
ActiveCN101286805AReduce operational complexityDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTransmission monitoringRound complexityComputer science
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for detecting multiple emission signals, which are is applied to solving the problems of high computational complexity or relatively large storage space is required when detecting multiple emission signals. The method comprises the steps that: signals which comprising multiple emission signals, channel alluvial response and white noise are received; the signals received are carried out space time matched filtering treatment to obtain sufficient statistics y of the signals received and a channel correlation matrix H is obtained according to the sufficient statistics y and a channel model; with respect to the y, H is in Krylov subspace to calculate multi emission signals. The embodiment of the invention can reduce computational complexity by calculating in the Krylov subspace.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com