Patents
Literature
201results about "Frequency to amplitude conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
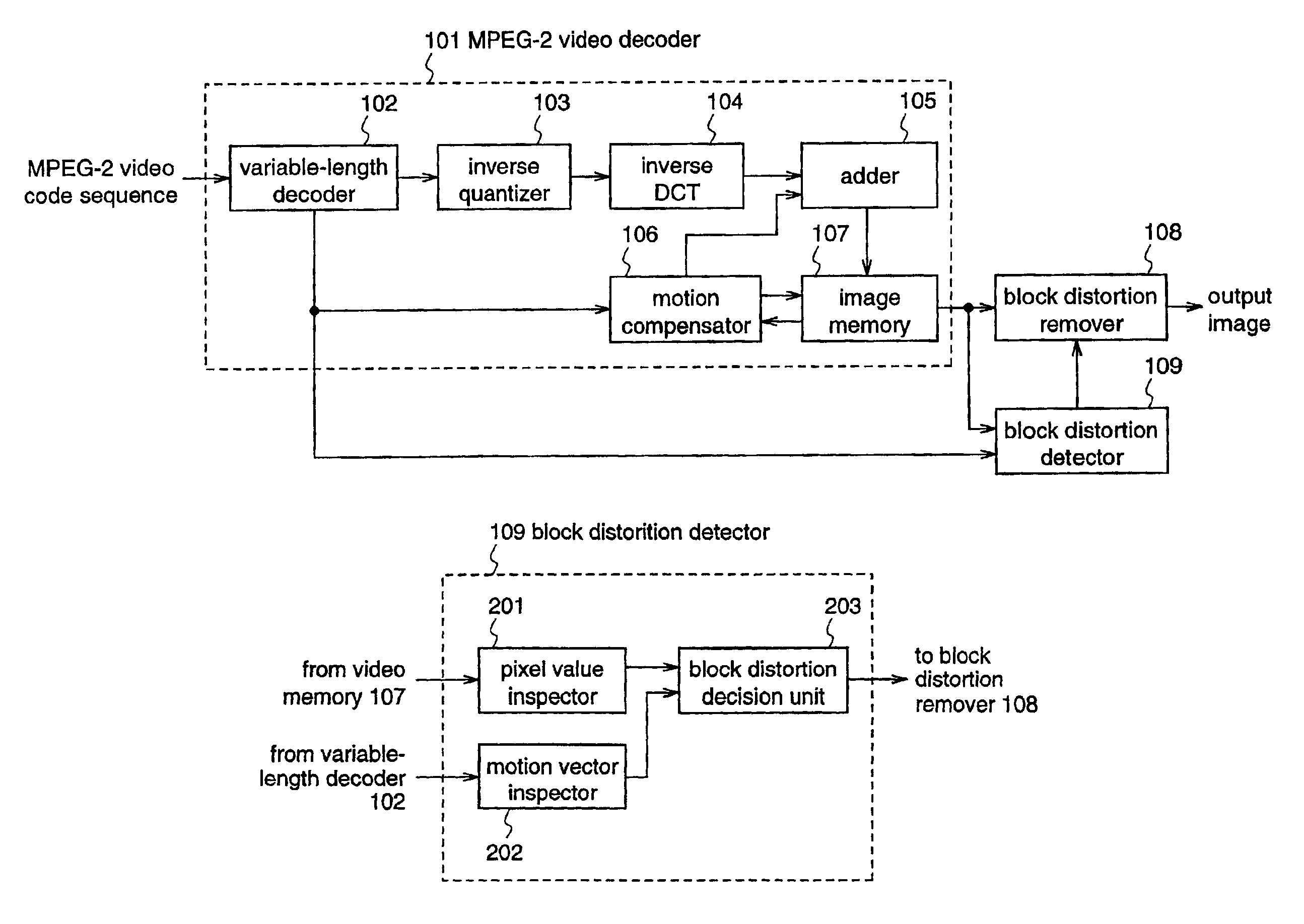
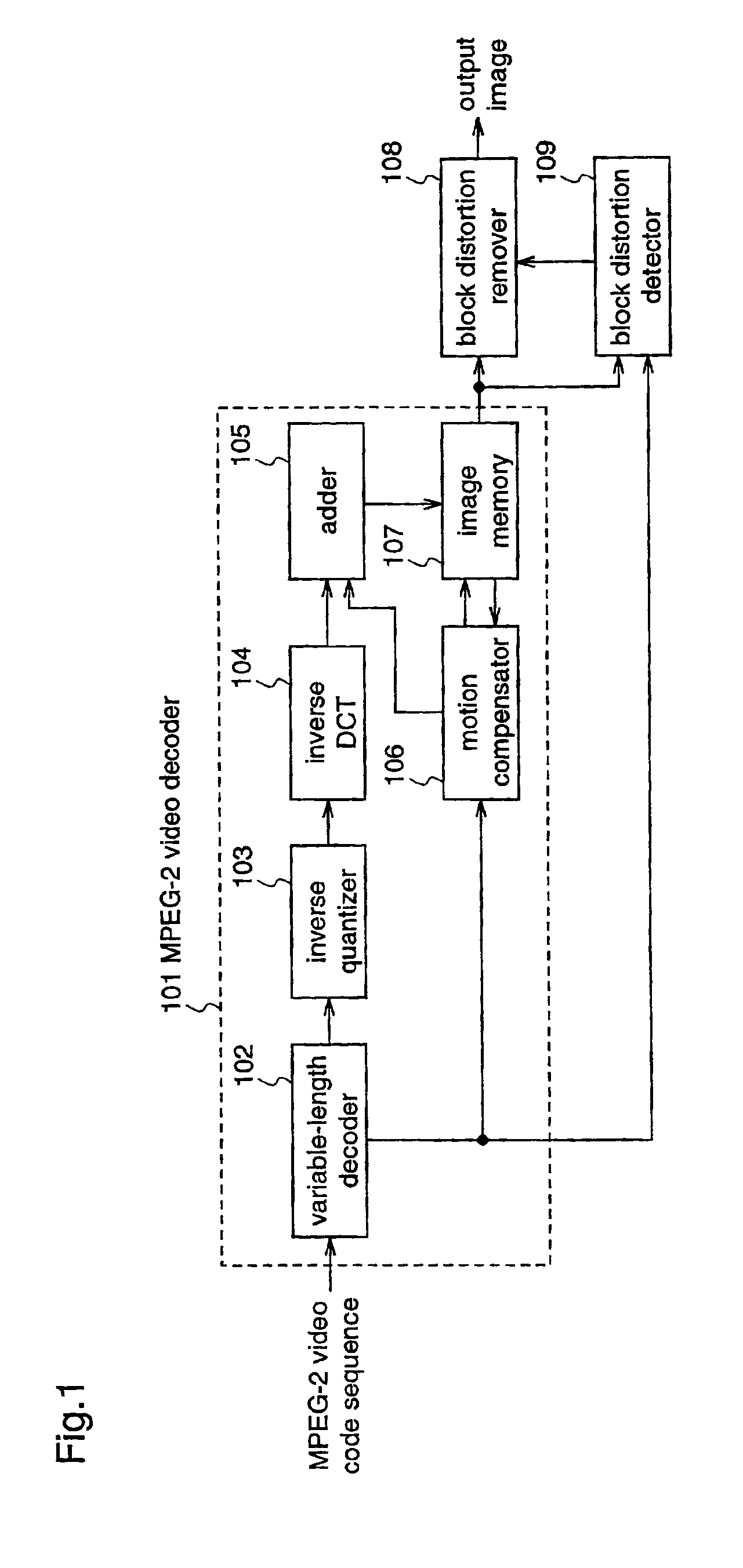
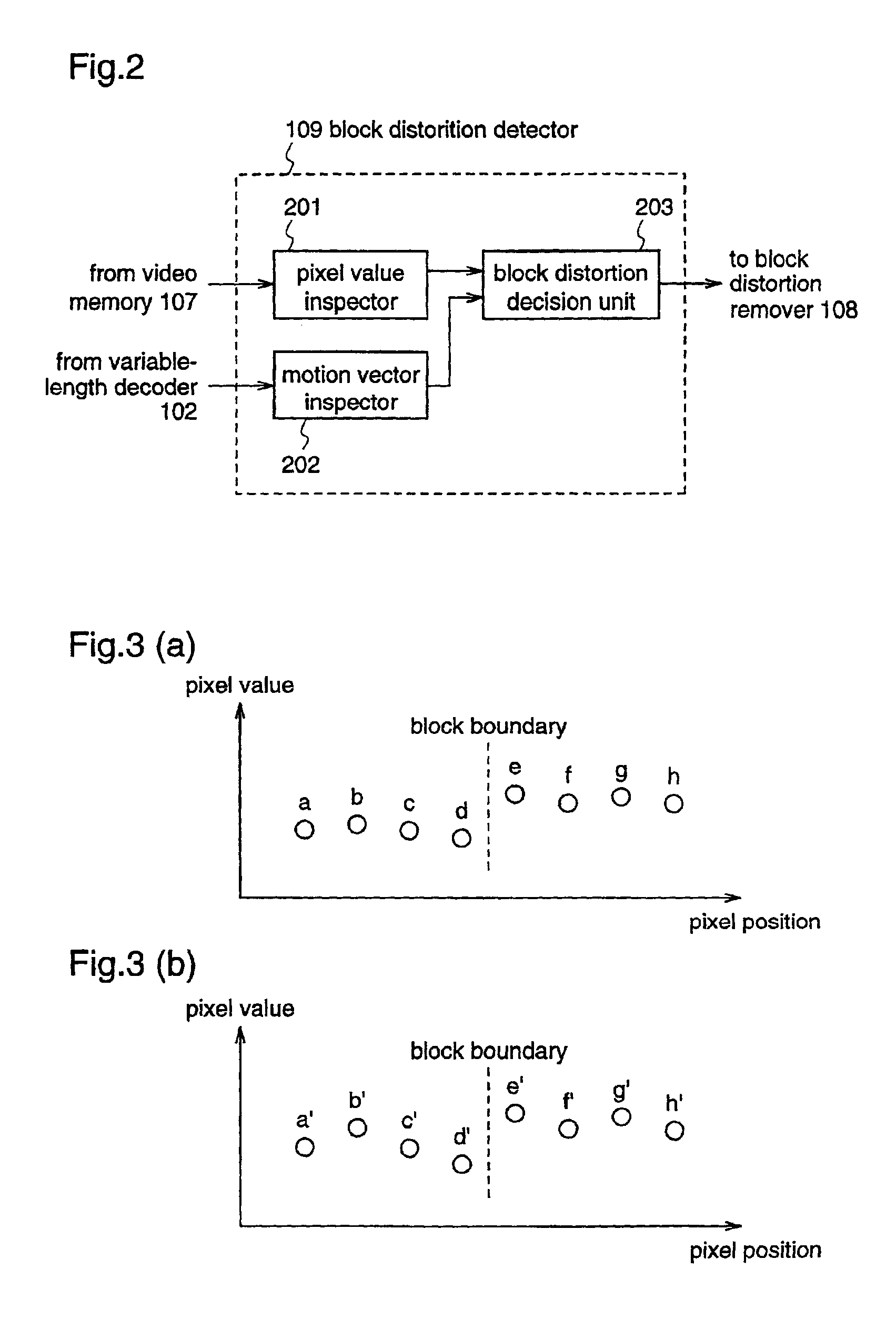
Block distortion detection method, block distortion detection apparatus, block distortion removal method, and block distortion removal apparatus
ActiveUS7031393B2Growth inhibitionIncrease volumeTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionMotion vector
A video decoder is connected with a block distortion detector for specifying the boundary of blocks where block boundary occurs, using decoded image data and information of motion vectors, which are supplied from the video decoder; and a block distortion remover for subjecting pixels in the vicinity of the block boundary of the decoded image to filtering on the basis of the result of detection from the block distortion detector, thereby removing the block distortion. Therefore, block distortion is accurately detected when a compressed and coded image is decoded, and the detected block distortion is removed while minimizing the blurriness of the image.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
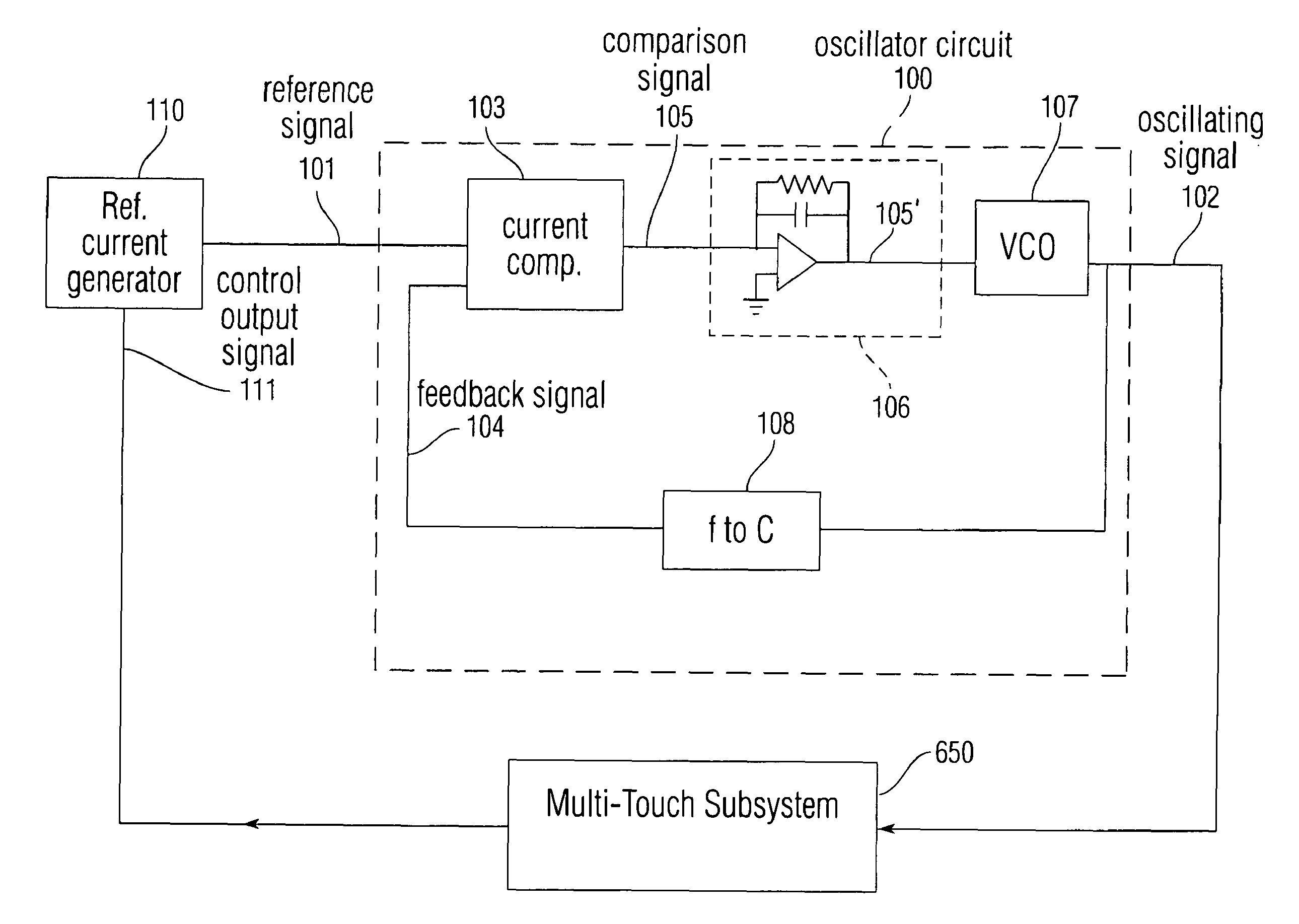
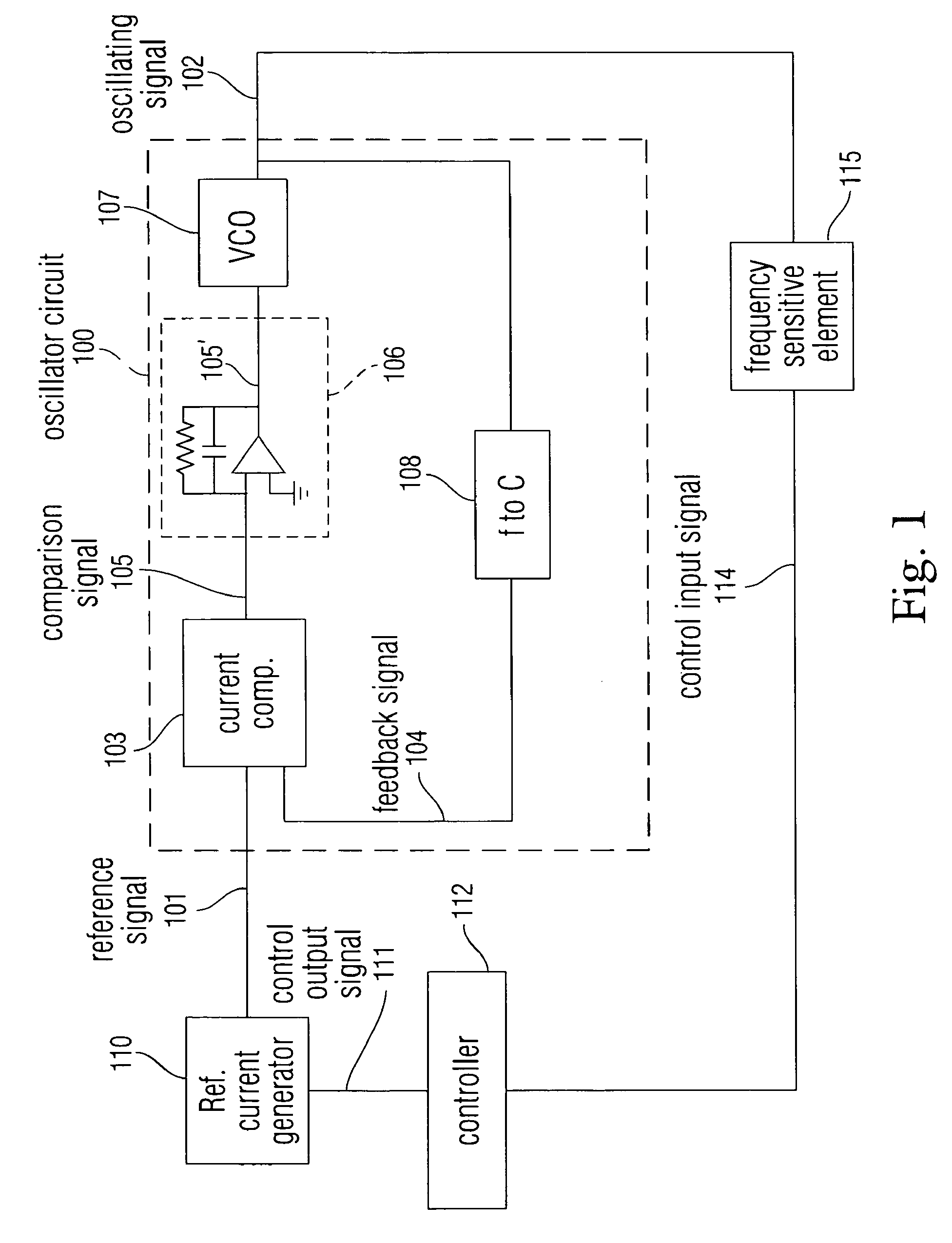
Noise reduction within an electronic device using automatic frequency modulation
Disclosed is a system and method for providing an oscillating signal of relatively precise frequency without using a signal provided by a crystal as a reference. Disclosed is a feedback oscillator circuit configured to output an oscillating signal having a frequency defined by a reference signal. The oscillating signal can be sent to one or more circuits including at least one frequency sensitive element. The frequency sensitive element produces an output signal which depends on the frequency of the oscillating signal. A controller controls the reference signal in order to cause an attribute of the output signal to have a value within a desired range.
Owner:APPLE INC
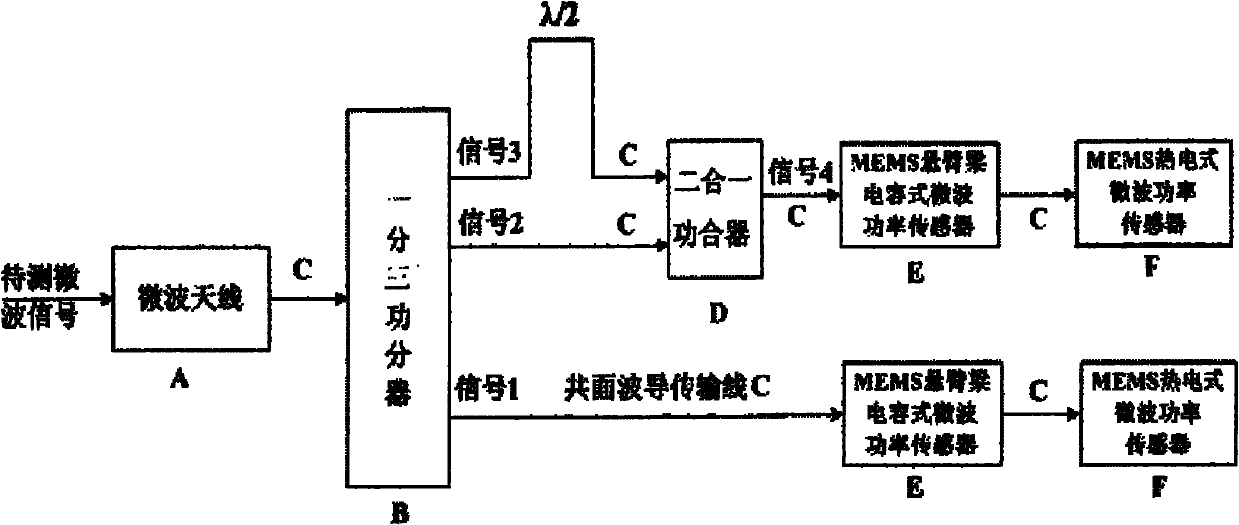
Wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101788605ARealize wireless receptionTo achieve the purpose of wireless detectionTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPower combinerPhase difference
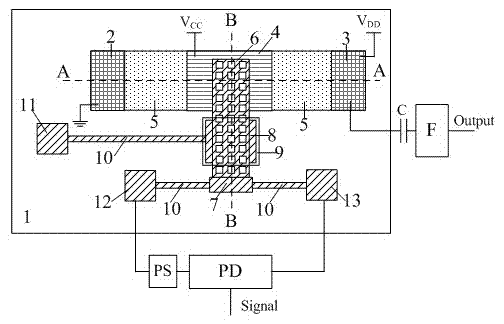
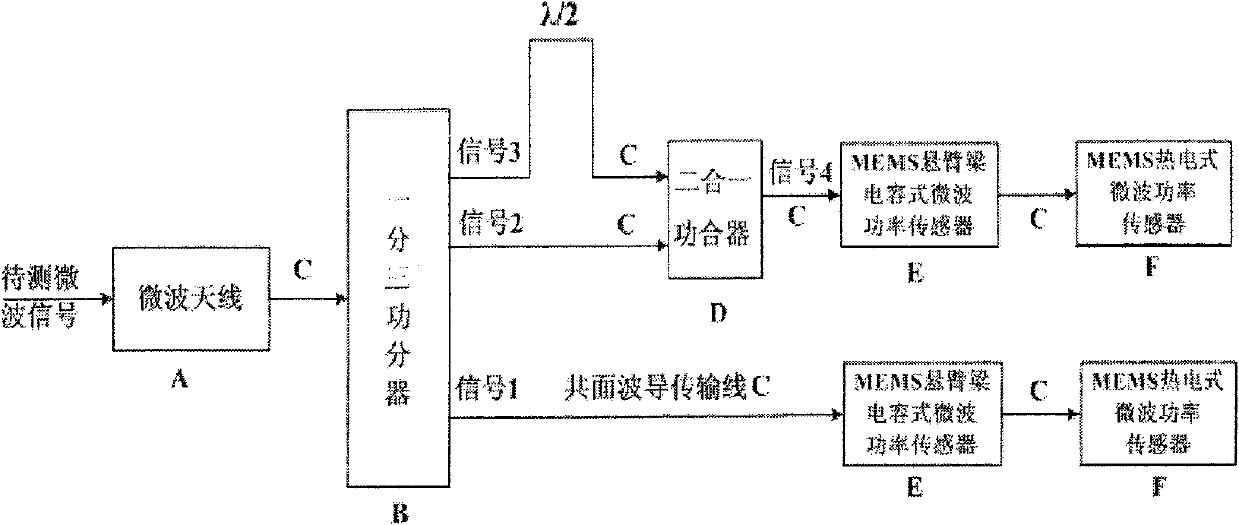
The invention relates to a wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and a preparation method thereof. The wireless-receiving system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency has quite simple structure, large measurement magnitude range, no direct-current power consumption and easy integration. In the system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency, gallium arsenide is used as a substrate, wherein a microwave antenna (A), a one-three power splitter (B), a coplanar waveguide transmission line (C), a two-in-one power combiner (D), an MEMS cantilever capacitive microwave power sensor (E) and an MEMS thermoelectric microwave power sensor (F) are designed on the substrate; and then a phase difference between a signal 3 and a signal 2 after the signal 3 passes through the coplanar waveguide transmission line with the length of lambda / 2 can be determined according to a law of cosines. Because the phase difference corresponds to the frequency of the signal, the frequency of the signal can be measured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Apparatus for Spectrum Sensing and Associated Methods
ActiveUS20120100810A1High resolutionWiden detectable frequency rangeSpectral/fourier analysisMagnetic measurementsFrequency spectrumElectromagnetic radiation
In one embodiment, an apparatus comprises a nano-scale spectrum sensor configured to be electromagnetically excitable at a predetermined frequency based on received ambient electromagnetic radiation. The apparatus is also configured to be able to use this excitation of the nano-scale spectrum sensor to thereby determine ambient electromagnetic radiation spectrum usage.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Communicating with an Implanted Wireless Sensor
The present invention determines the resonant frequency of a sensor by adjusting the phase and frequency of an energizing signal until the frequency of the energizing signal matches the resonant frequency of the sensor. The system energizes the sensor with a low duty cycle, gated burst of RF energy having a predetermined frequency or set of frequencies and a predetermined amplitude. The energizing signal is coupled to the sensor via magnetic coupling and induces a current in the sensor which oscillates at the resonant frequency of the sensor. The system receives the ring down response of the sensor via magnetic coupling and determines the resonant frequency of the sensor, which is used to calculate the measured physical parameter. The system uses a pair of phase locked loops to adjust the phase and the frequency of the energizing signal.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
Communicating with an implanted wireless sensor
ActiveUS7466120B2Increase opportunitiesAvoid breakingEndoradiosondesSensorsLine sensorPhase difference
Aspects of the present invention determine the resonant frequency of a sensor by obtaining sensor signals in response to three energizing signals, measuring the phase of each sensor signal, and using a group phase delay to determine the resonant frequency. The phase difference between the first and second signal is determined as a first group phase delay. The phase difference between the second and third signal is determined as a second group phase delay. The first group phase delay and second group phase delay are compared. Based on the comparison, the system may lock on the resonant frequency of the sensor or adjust a subsequent set of three energizing signals.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
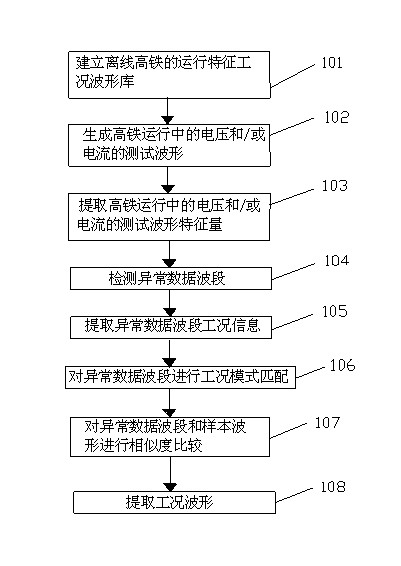
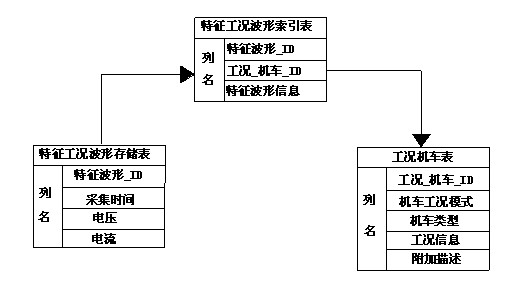
Waveform identification method based on operating-characteristic working condition waveform library of high-speed rail
InactiveCN102542262AOptimization of characteristic parameters of high-speed railGood for running informationCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency to amplitude conversionPattern matchingVoltage
The invention discloses a waveform identification method based on an operating-characteristic working condition waveform library of a high-speed rail, which comprises the following steps of: 101, setting an operating-characteristic working condition waveform library of an off-line high-speed rail; 102, generating a testing waveform of voltage and / or current in operation of the high-speed rail; 103, extracting the testing waveform characteristic quantity of voltage and / or current in operation of the high-speed rail; 104, detecting an abnormal data waveband; 105, extracting the working condition information of the abnormal data waveband; 106, carrying out working condition pattern matching for the abnormal data waveband; 107, comparing the similarity of the abnormal data waveband and a sample waveform; 108, and extracting the working condition waveform. The identification method utilizes the characteristic working condition waveform library of the high-speed rail to carry out the working condition pattern matching for the abnormal waveband existing in the actual operation of the high-speed rail, so that a user can detect the operation of the high-speed rail in real time, and the operation security of the high-speed rail is beneficially ensured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Communicating with an implanted wireless sensor
ActiveUS20070247138A1Avoid breakingIncrease opportunitiesEndoradiosondesSensorsLine sensorPhase difference
Aspects of the present invention determine the resonant frequency of a sensor by obtain sensor signals in response to three energizing signals, measure the phase of each sensor signal, and using a group phase delay to determine the resonant frequency. The phase difference between the first and second signal is determined as a first group phase delay. The phase difference between the second and third signal is determined as a second group phase delay. The first group phase delay and second group phase delay are compared. Based on the comparison, the system may lock on the resonant frequency of the sensor or adjust a subsequent set of three energizing signals.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
Cantilever beam frequency detector and detection method based on micromechanical gallium arsenide
InactiveCN102735928ASmall sizeNovel structureFrequency to amplitude conversionCapacitanceLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a cantilever beam frequency detector and a cantilever beam frequency detection method based on micromechanical gallium arsenide. The frequency detector comprises a power divider (PD), a phase shifter (PS), a low pass filter (F) and a gallium arsenide metal semiconductor field effect transistor (MESFET), wherein the PD is used for receiving a microwave signal to be detected and dividing the microwave signal to be detected into two branch signals with the same amplitude and phase. The detection method comprises the following steps that: when a pull-down electrode (8) is loaded with direct current (DC) offset and a cantilever beam (6) is pulled down and contacted with a gate (4), the gate (4) is loaded with the two paths of microwave signals simultaneously, so that the magnitude of saturation current between a source (2) and a drain (3) is changed; and through a capacitor and a filter, the frequency is measured by detecting the magnitude of the saturation current between the source (2) and the drain (3). By the detector and the method, DC power consumption is low, and the frequency is easy to measure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101788605BRealize wireless receptionTo achieve the purpose of wireless detectionTelevision system detailsImpedence networksPower combinerPhase difference
The invention relates to a wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and a preparation method thereof. The wireless-receiving system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency has quite simple structure, large measurement magnitude range, no direct-current power consumption and easy integration. In the system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency, gallium arsenide is used as a substrate, wherein a microwave antenna (A), a one-three power splitter (B), a coplanar waveguide transmission line (C), a two-in-one power combiner (D), an MEMS cantilever capacitive microwave power sensor (E) and an MEMS thermoelectric microwave power sensor (F) are designed on the substrate; and then a phase difference between a signal 3 and a signal 2 after the signal 3 passes through the coplanar waveguide transmission line with the length of lambda / 2 can be determined according to a law of cosines. Because the phase difference corresponds to the frequency of the signal, the frequency of the signal can be measured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Magnetic device and frequency detector
InactiveUS20090140733A1Small half-value widthCut in halfNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsCurrent limitingMagnetization
A magnetic device includes: a magnetoresistive effect element having a magnetization fixed layer, a magnetization free layer, and a nonmagnetic layer sandwiched between the magnetization fixed layer and the magnetization free layer; an input terminal for feeding an AC signal to the magnetoresistive effect element in its stacking direction; and an output terminal for extracting an output voltage from the magnetoresistive effect element, wherein the nomagnetic layer includes an insulating layer portion comprising an insulating material, and a current-constricting layer portion comprising a conductive material which passes through the insulating layer portion in its film thickness direction.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
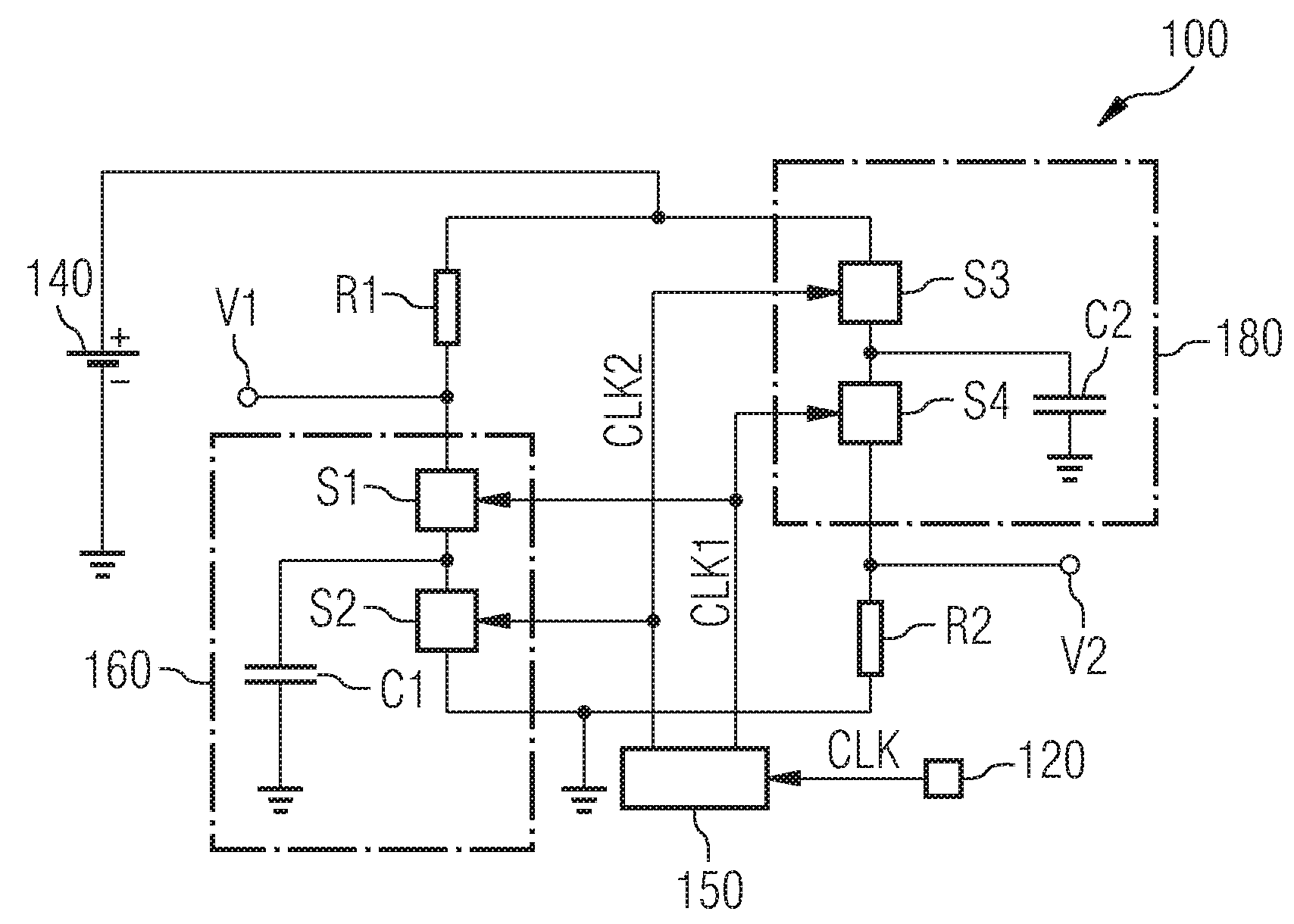
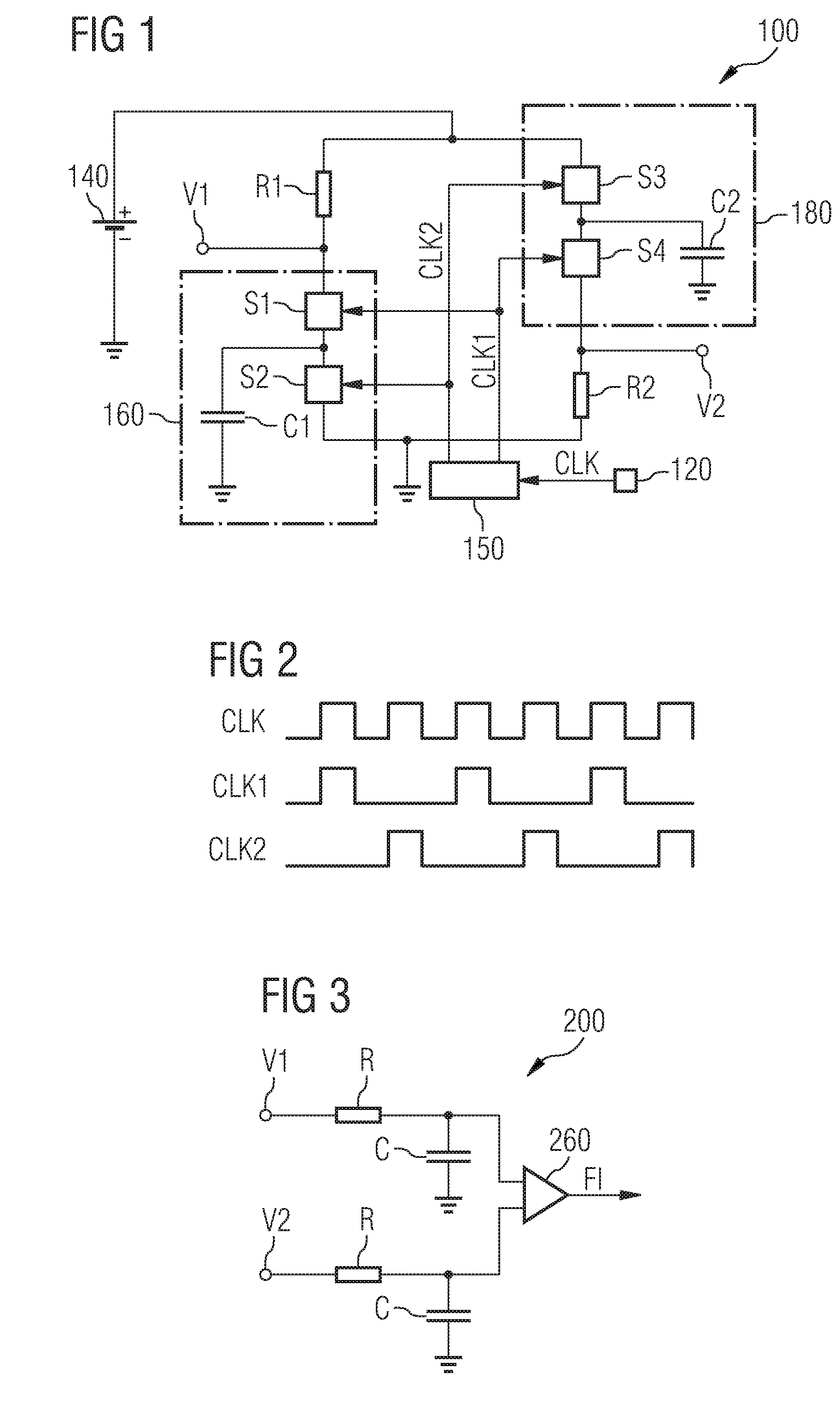
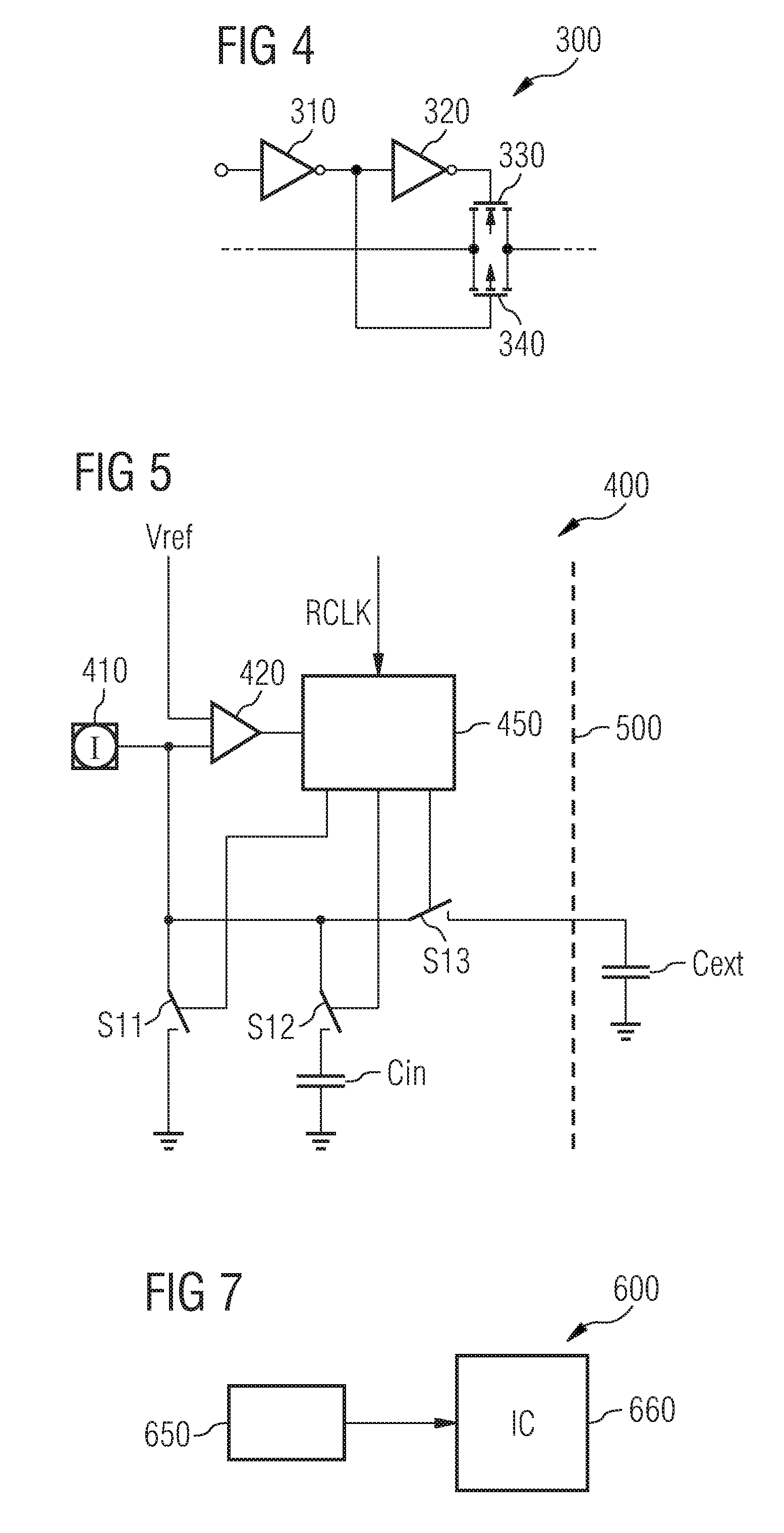
Method of Detecting the Frequency of an Input Clock Signal of an Integrated Circuit and Integrated Circuit
InactiveUS20090058468A1Ac-dc conversionFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationCapacitanceDetector circuits
An integrated circuit includes a first switched capacitor element and a second switched capacitor element, which are coupled to form a bridge circuit, the first switched capacitor element being located in a first branch of the bridge circuit and the second switched capacitor element being located in a second branch of the bridge circuit. A detector circuit is coupled to the first branch and to the second branch of the bridge circuit. Switching signals of the first switched capacitor element and of the second switched capacitor element are generated on the basis of an input clock signal of the integrated circuit.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Frequency rectification system: apparatus and method
InactiveUS7065474B2Spectral/fourier analysisVibration measurement in fluidFrequency spectrumComputer module
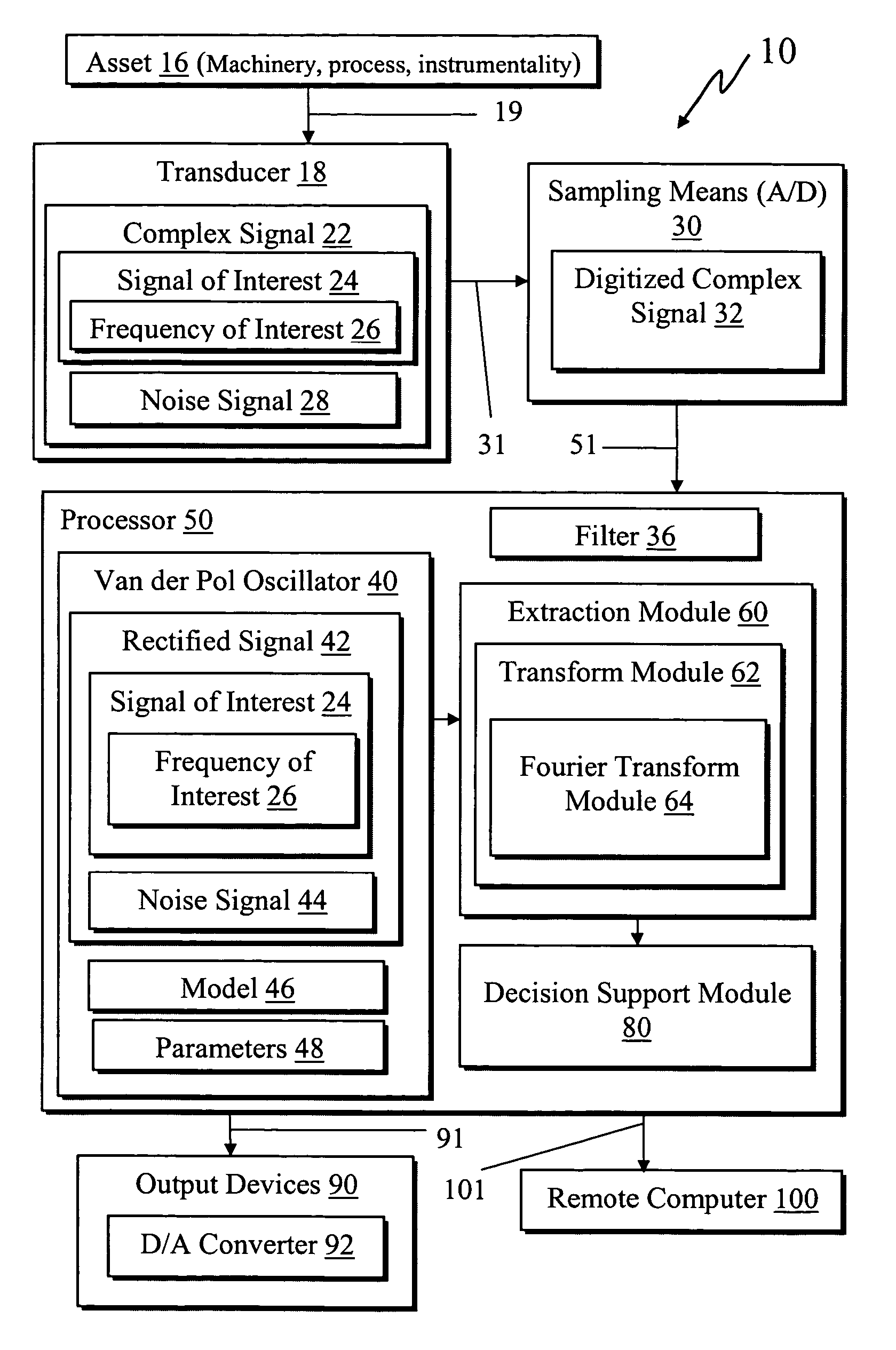
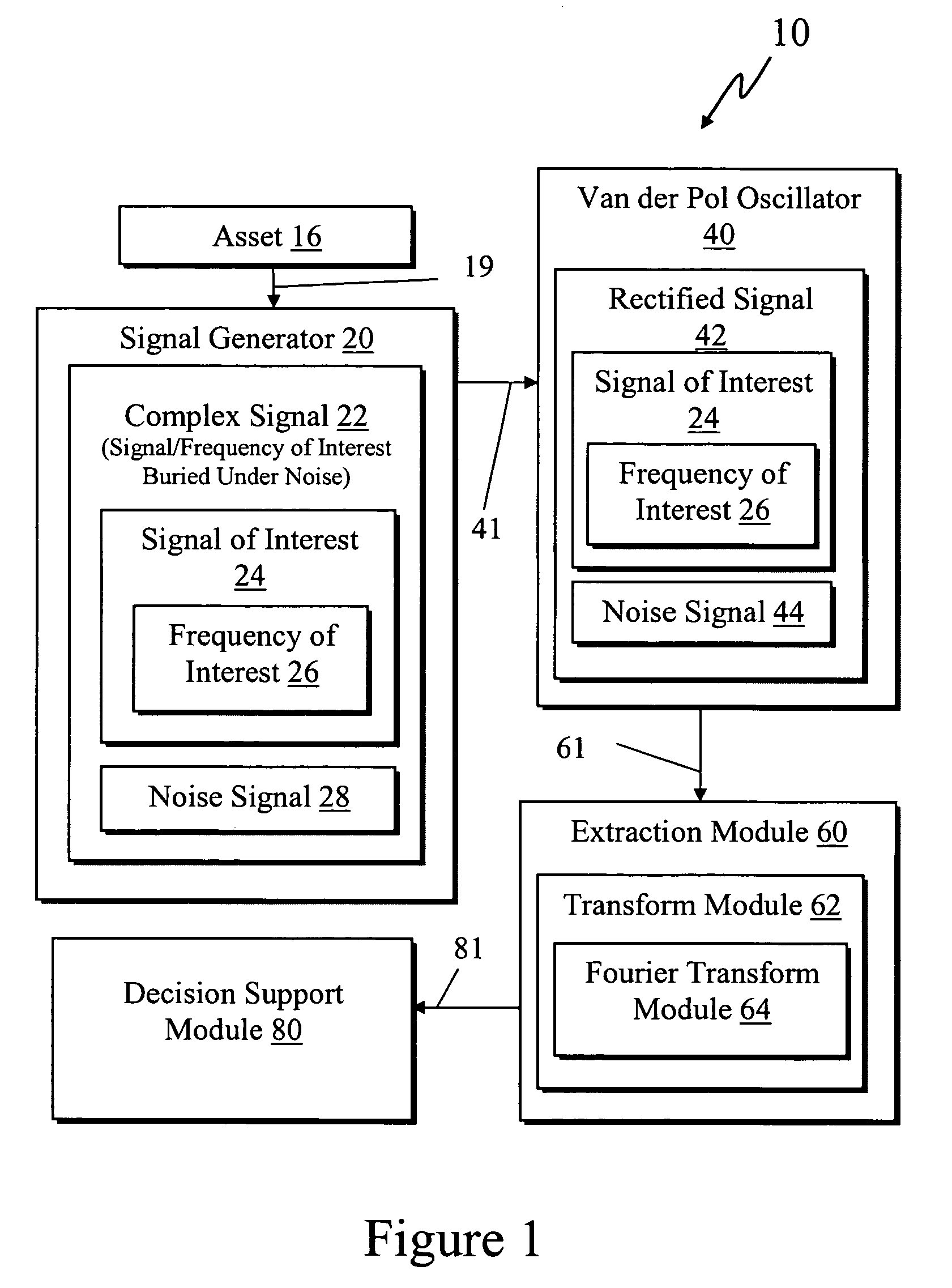
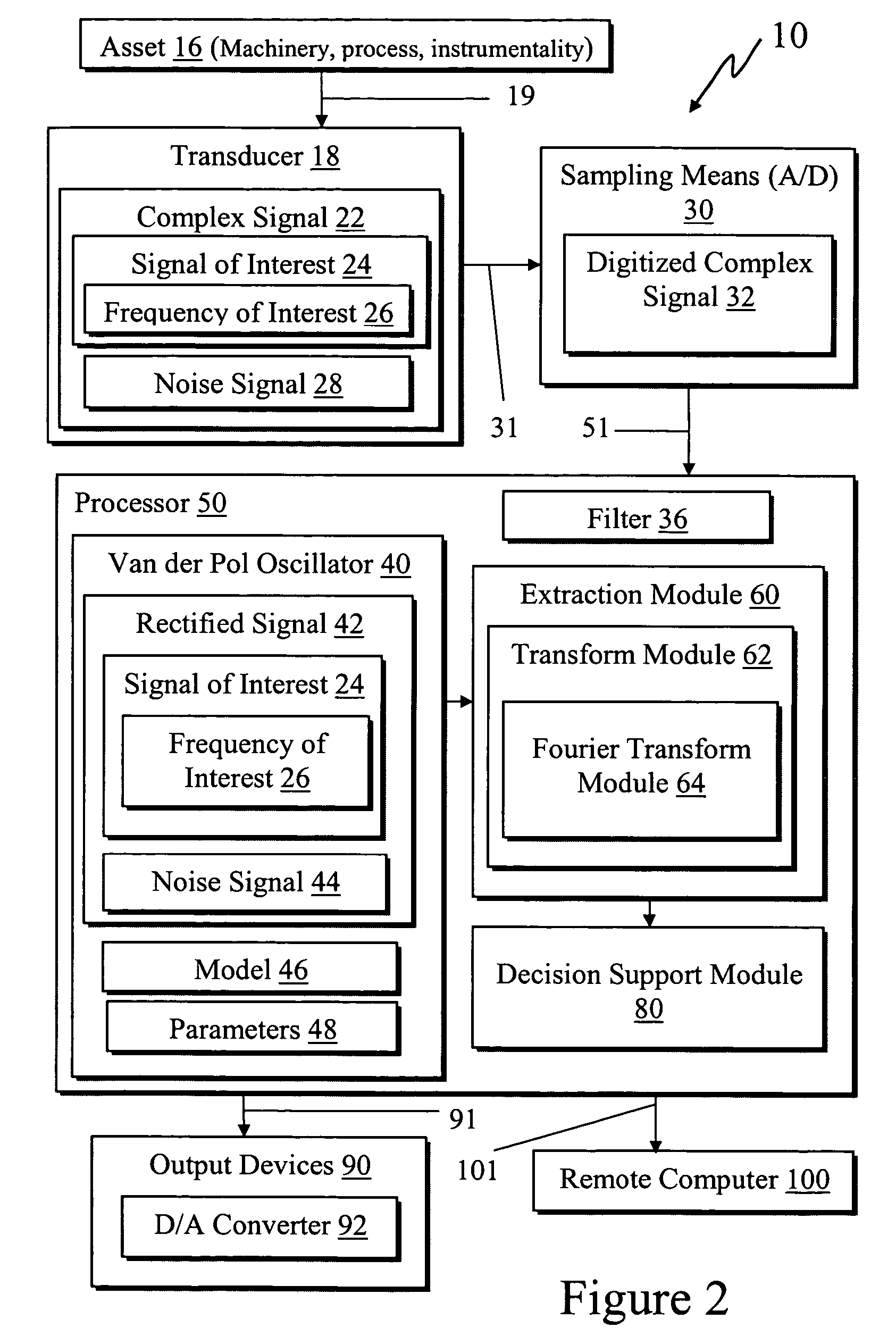
Frequency rectification system using a Van der Pol oscillator for processing an asset signal by obtaining a complex signal from an asset comprised of a noise signal and a signal of interest having a corresponding frequency of interest wherein the complex signal includes a first spectrum having all of its largest spectral peaks corresponding to the noise signal such that the signal of interest is hidden under the noise signal. The system processes the complex signal with the Van der Pol oscillator with selected parameters for rectifying the complex signal into a rectified signal such that the noise signal is abated and the rectified signal is comprised of a second spectrum having a largest spectral peak corresponding to the signal of interest with all other spectral peaks smaller. The system extracts the frequency of interest from the rectified signal with an extraction module for use in providing asset information.
Owner:BENTLY NEVADA INC
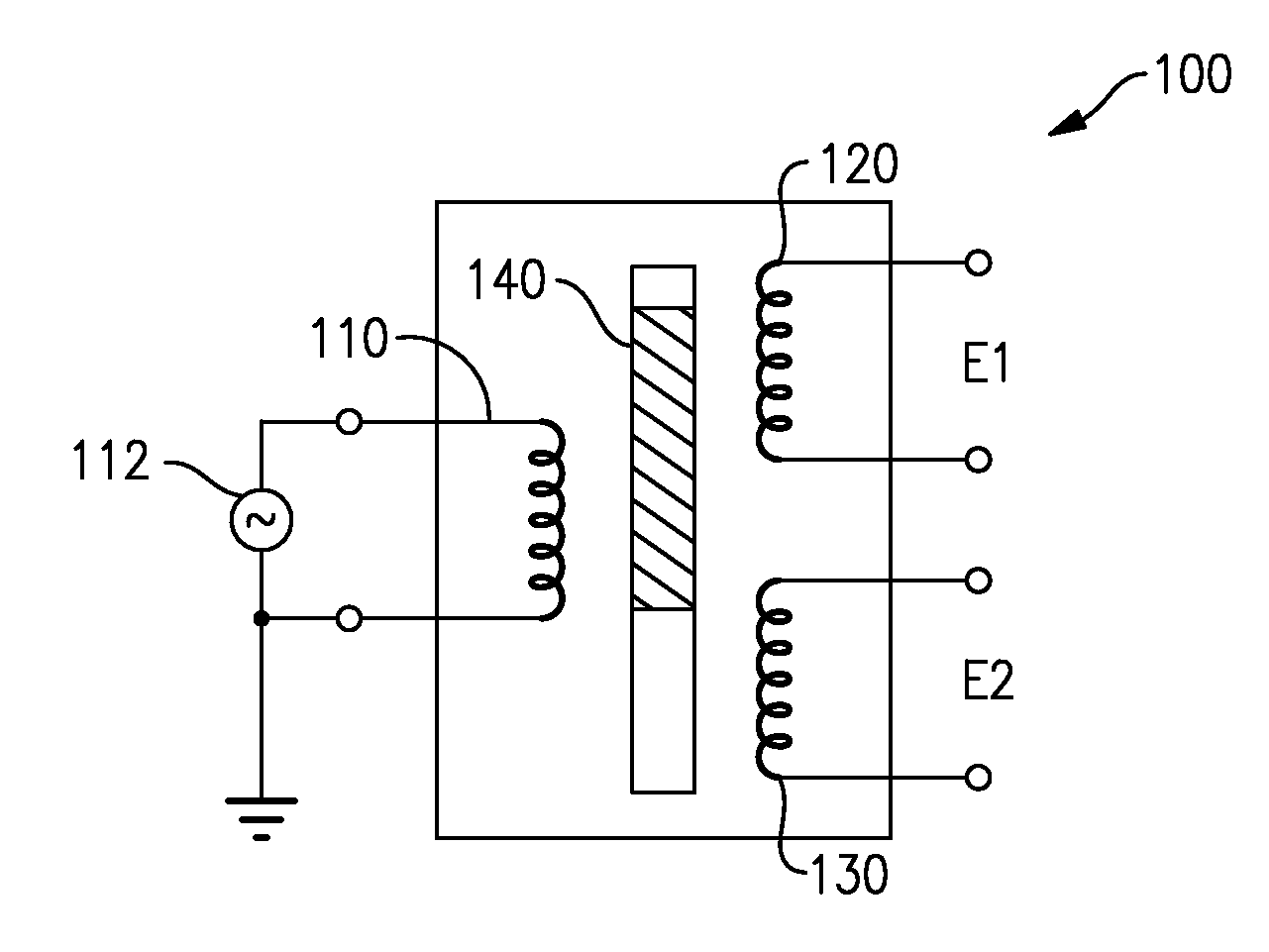
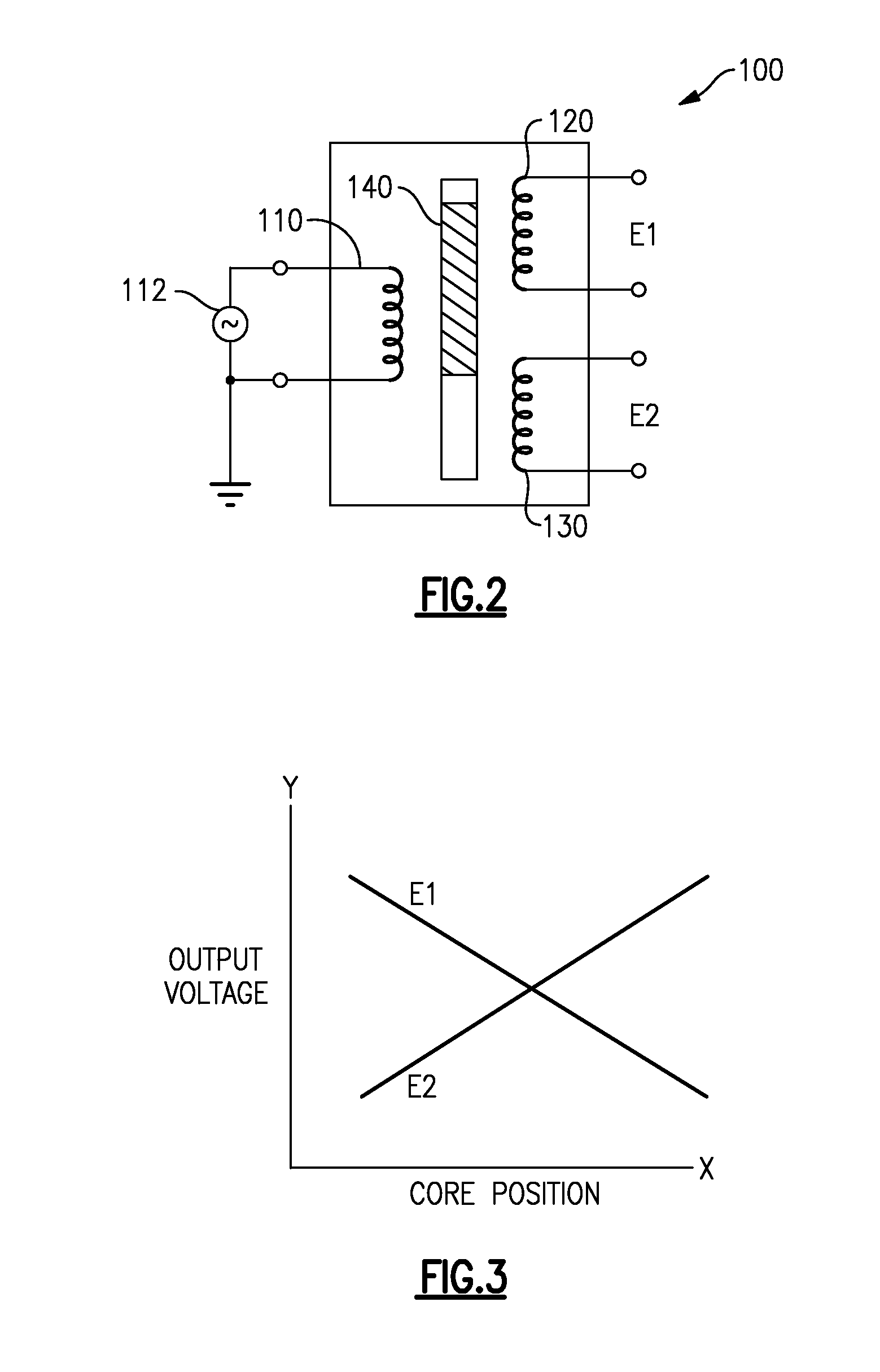
Transformer based sensor arrangement
A position sensor arrangement has a transformer based position sensor and a cable peaking correction apparatus. The cable peaking correction apparatus is coupled to at least one of a transformer based position sensor excitation input and the plurality of outputs from the transformer based position sensor.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Electronic circuit for tuning vibratory transducers
InactiveUS6417659B1Frequency to amplitude conversionTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsSelf-tuningResonance
A method and self-tuning circuit for tuning vibratory transducers, broadly including electroacoustic speakers and specifically including the speakers of common back-up alarms used for safety reasons on commercial vehicles and heavy equipment. The self-tuning circuit is physically coupled to the transducer's input terminals and operates by comparing the rising and falling edges of one period of a test waveform elicited from the transducer by the application of a test signal having a test frequency. Depending on the results of this comparison, the test frequency is adjusted by predetermined increments upward or downward until the transducer's resonance frequency has been tightly bracketed though not exactly pinpointed.
Owner:SYST MATERIAL HANDLING
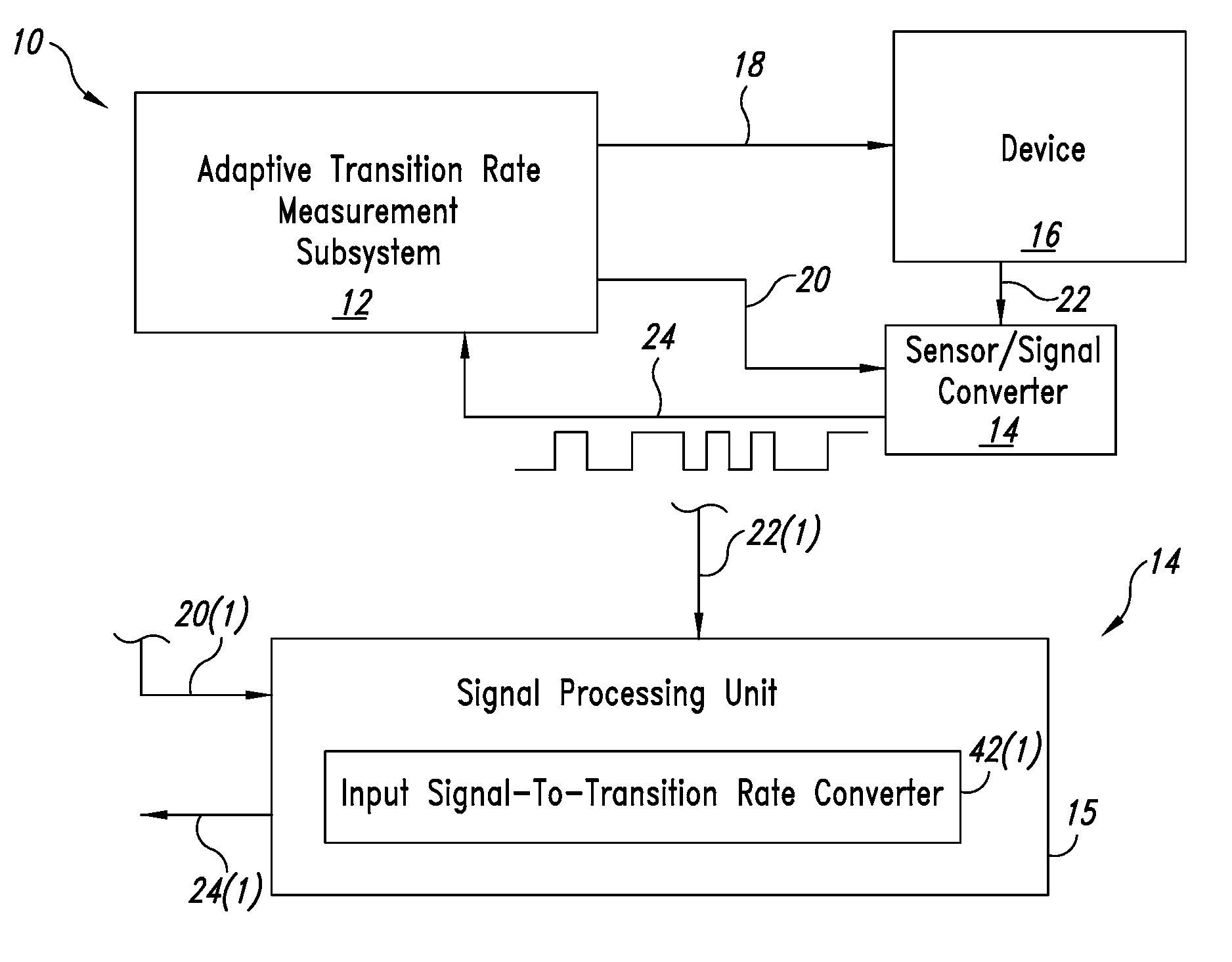
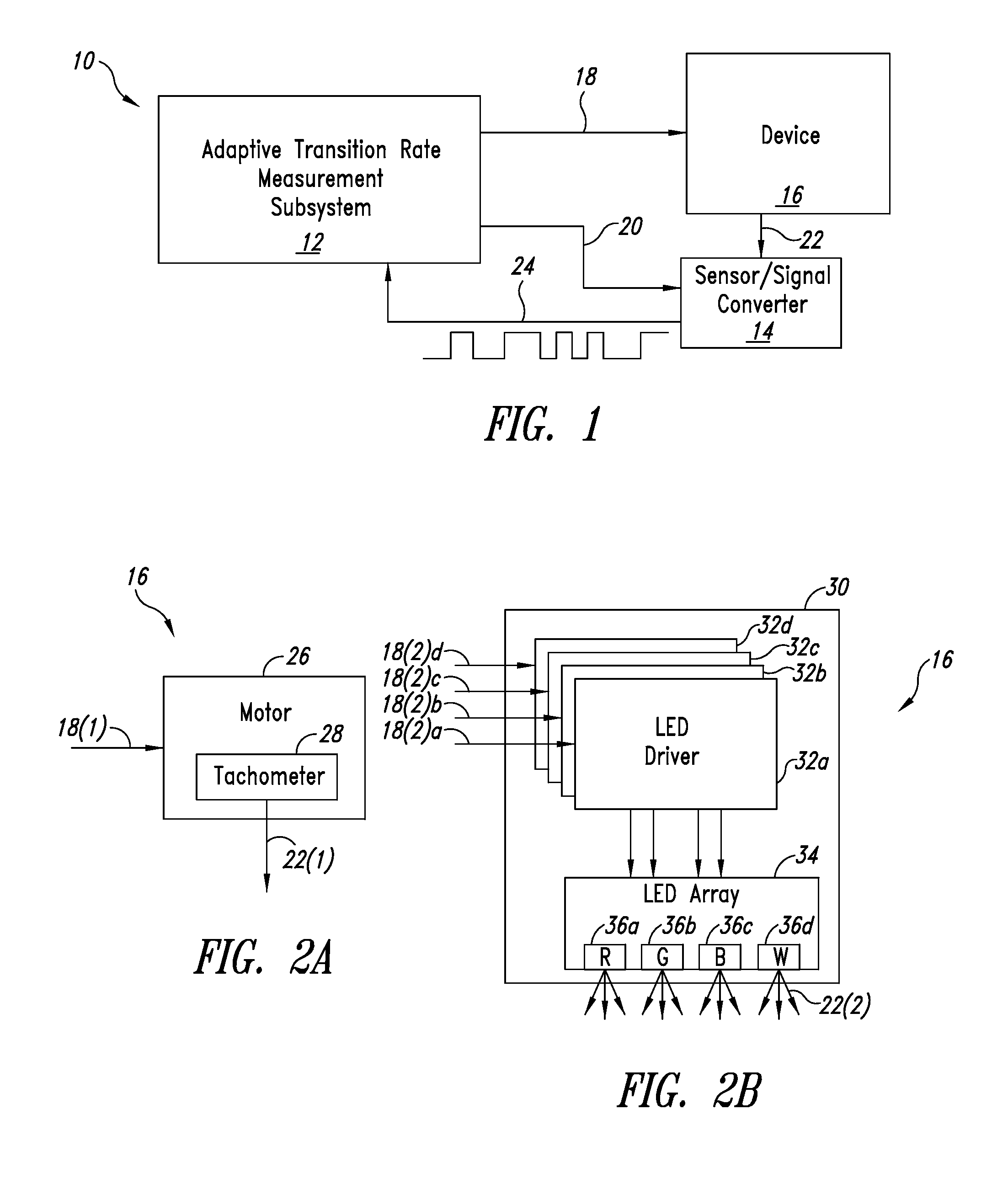
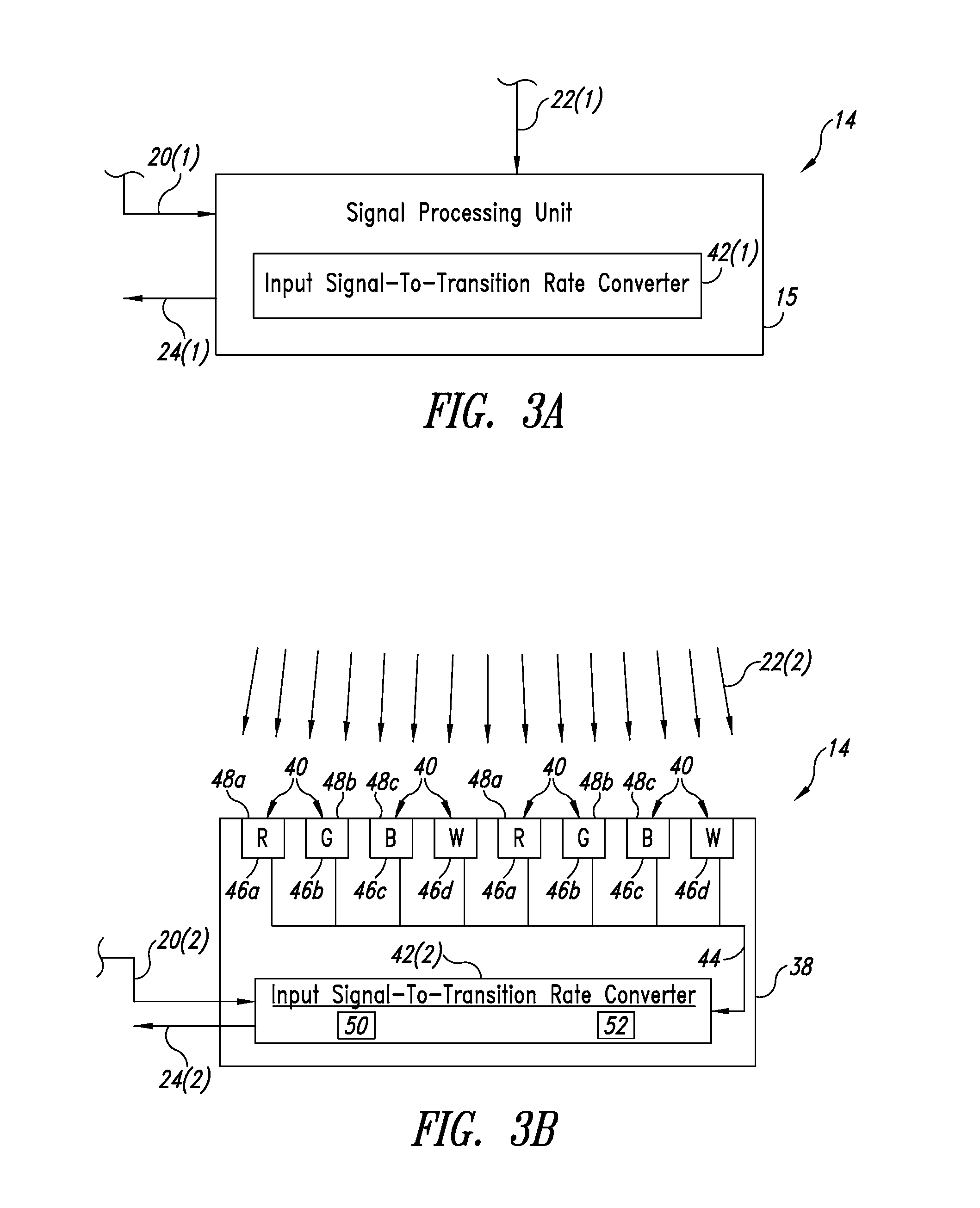
System and method for adaptively determining the transition rate of a quantized signal
An adaptive measurement system measures a transition rate associated with an output of a device. An input signal that is characteristic of the output of the device is received by an input signal-to-frequency converter, which changes state based upon a characteristic of the input signal. The input signal-to-frequency converter provides a second signal, which reflects the state changes of the input signal-to-frequency converter. The second signal is sampled over a sample period and an instance of average transition rate is determined. A control subsystem may use the instance of average transition rate for regulating the device.
Owner:GOLDMAN SACHS BANK USA AS SUCCESSOR COLLATERAL AGENT +1
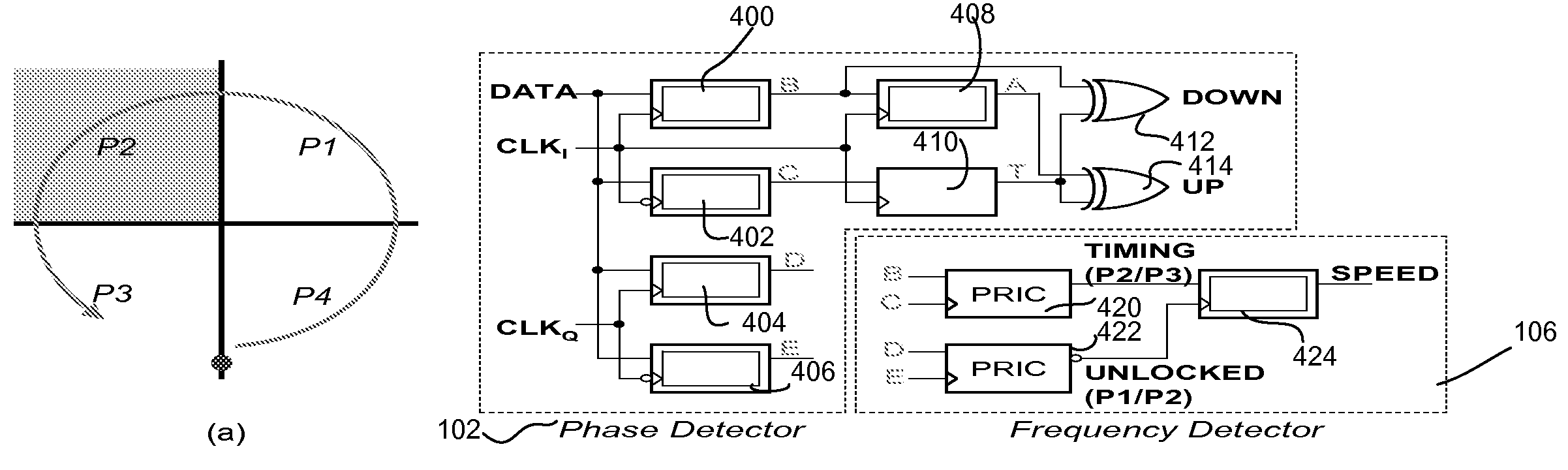
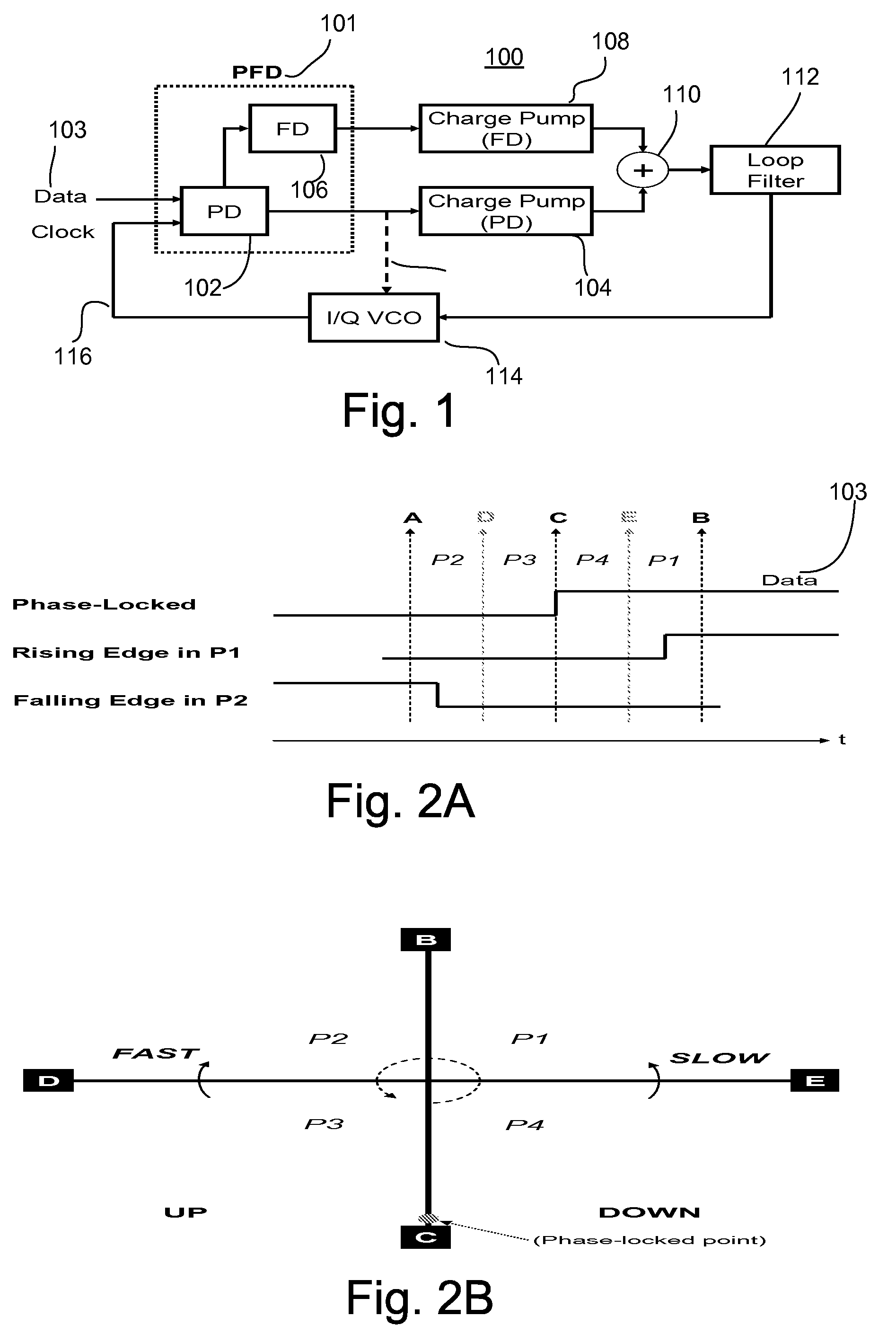
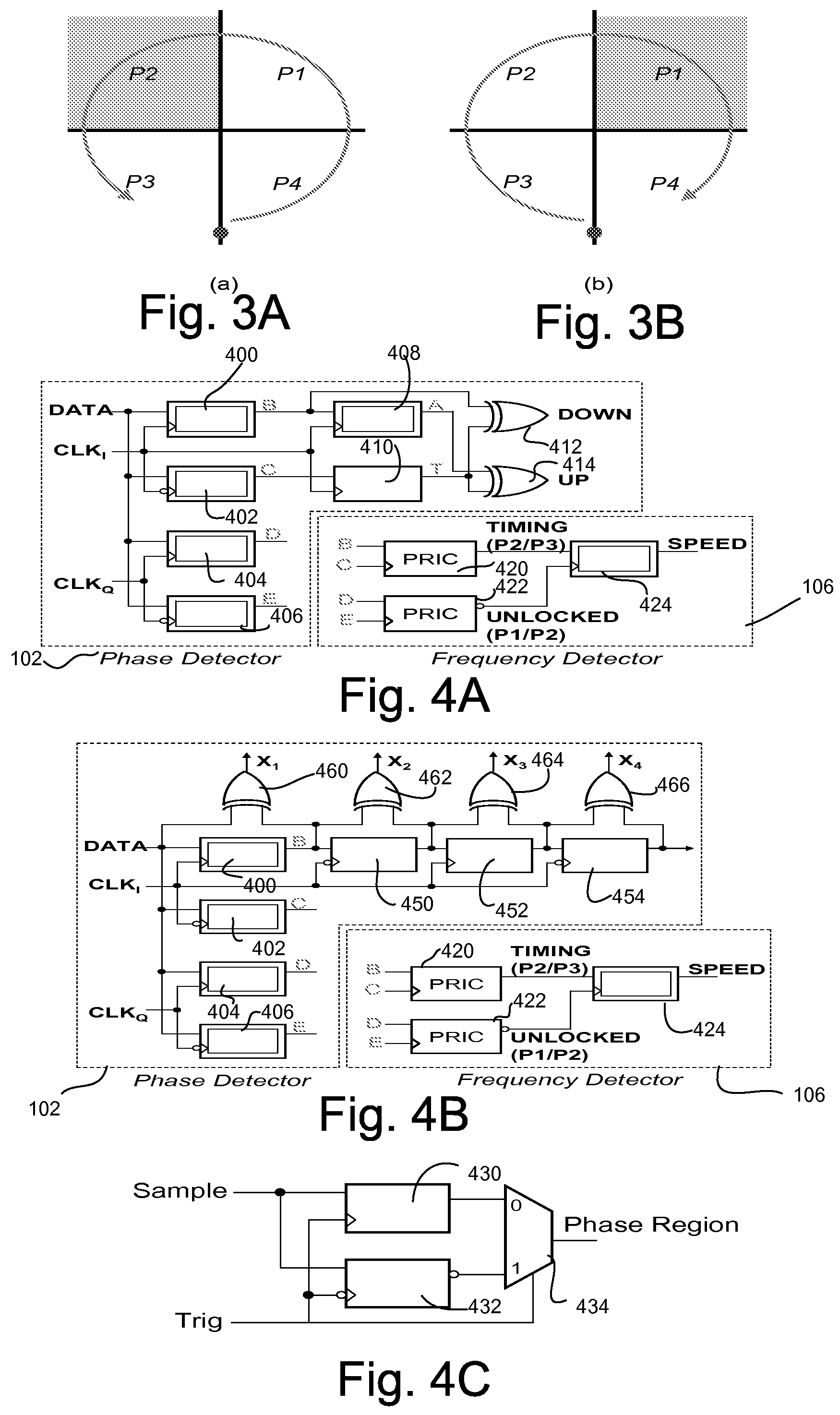
Phase/frequency detector and charge pump architecture for referenceless clock and data recovery (CDR) applications
A stream of data may flow over a fiber or other medium without any accompanying clock signal. The receiving device may then be required to process this data synchronously. Embodiments describe clock and data recovery (CDR) circuits which may sample a data signal at a plurality of sampling points to partition a clock cycle into four phase regions P1, P2, P3, and P4 which may be represented on a phase plane being divided into four quadrants. A relative phase between a data signal transition edge and a clock phase may be represented by a phasor on the phase plane. The clock phase and frequency may be adjusted by determining the instantaneous location of the phasor and the direction of phasor rotation in the phase plane.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for calculating multi-frequency AC signal
ActiveCN104597320ARealize measurementVoltage-current phase angleFrequency to amplitude conversionUtility frequencyComputer science
The invention discloses a method for calculating a multi-frequency AC signal. The method comprises the steps of sampling N points at each cycle of wave according to the power frequency; calculating the real part and an imaginary part for fourier algorithm through discretion fourier transformation; calculating the frequency according to the intervals of position zero crossing points of the imaginary part; calculating each coefficient value through the frequency; adjusting the amplitude and phase of each signal, calculated based on the power frequency to obtain real phasor. Compared with the other methods, the method has the advantage that extra filtering link is saved, frequency tracking is avoided, the signals at a plurality of frequencies can be measured, and therefore, three elements (frequency, amplitude and angle) of the phasor can be completely measured.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD
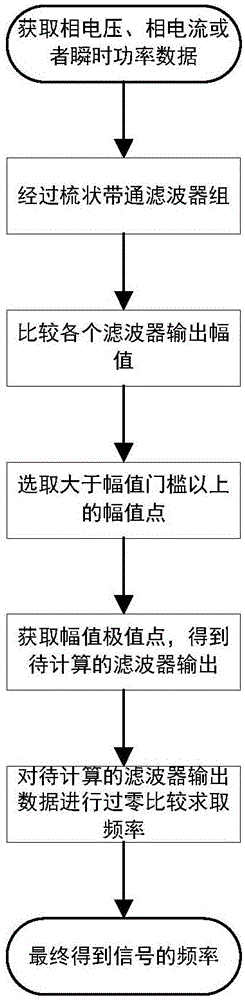
Subsynchronous oscillation inter-harmonic wave extracting method of online adaptive frequency change
The invention discloses a subsynchronous oscillation inter-harmonic wave extracting method of online adaptive frequency change. The method comprises steps of firstly, acquiring original sampling data of phase current and phase voltage of a circuit in real time in an online manner, or through the original sampling data of the phase current and the phase voltage, calculating instantaneous power of the circuit so as to obtain input data to be calculated and extracted; carrying out filtering on the input data through a narrow-band comb-shaped filter group; acquiring real-time output data of each narrow-band filter; comparing output real-time waveform peak values of the narrow-band filters so as to obtain an extreme point of a broadband amplitude value, wherein the central frequency of the filter corresponding to the extreme point is the main oscillation frequency of the oscillation; and carrying out data fitting on the output data of the filters through zero passage comparison, and determining the precise main oscillation frequency. According to the invention, the algorithm can be applied to an online monitoring device of the subsynchronous oscillation monitoring; and online rapid recognition of oscillation signals is achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID XINJIANG ELECTRIC POWER CORP +1
Delay time measurement circuit and delay time measurement method
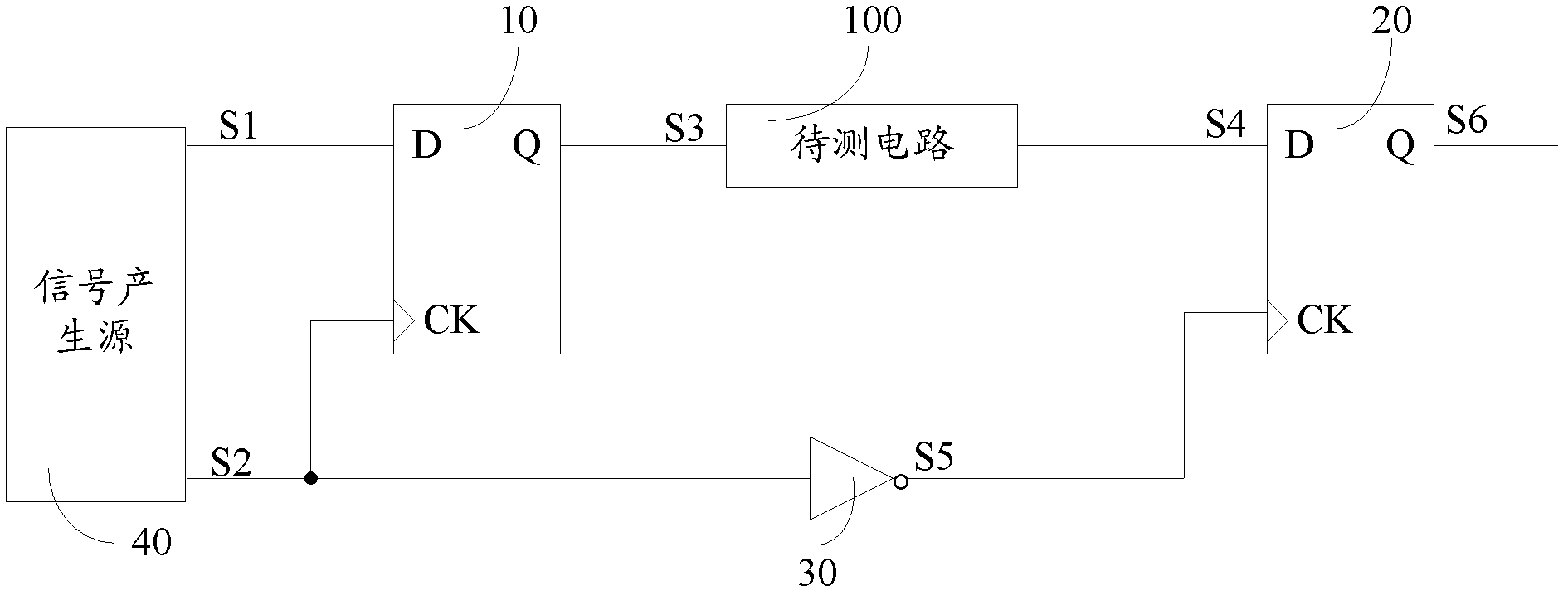
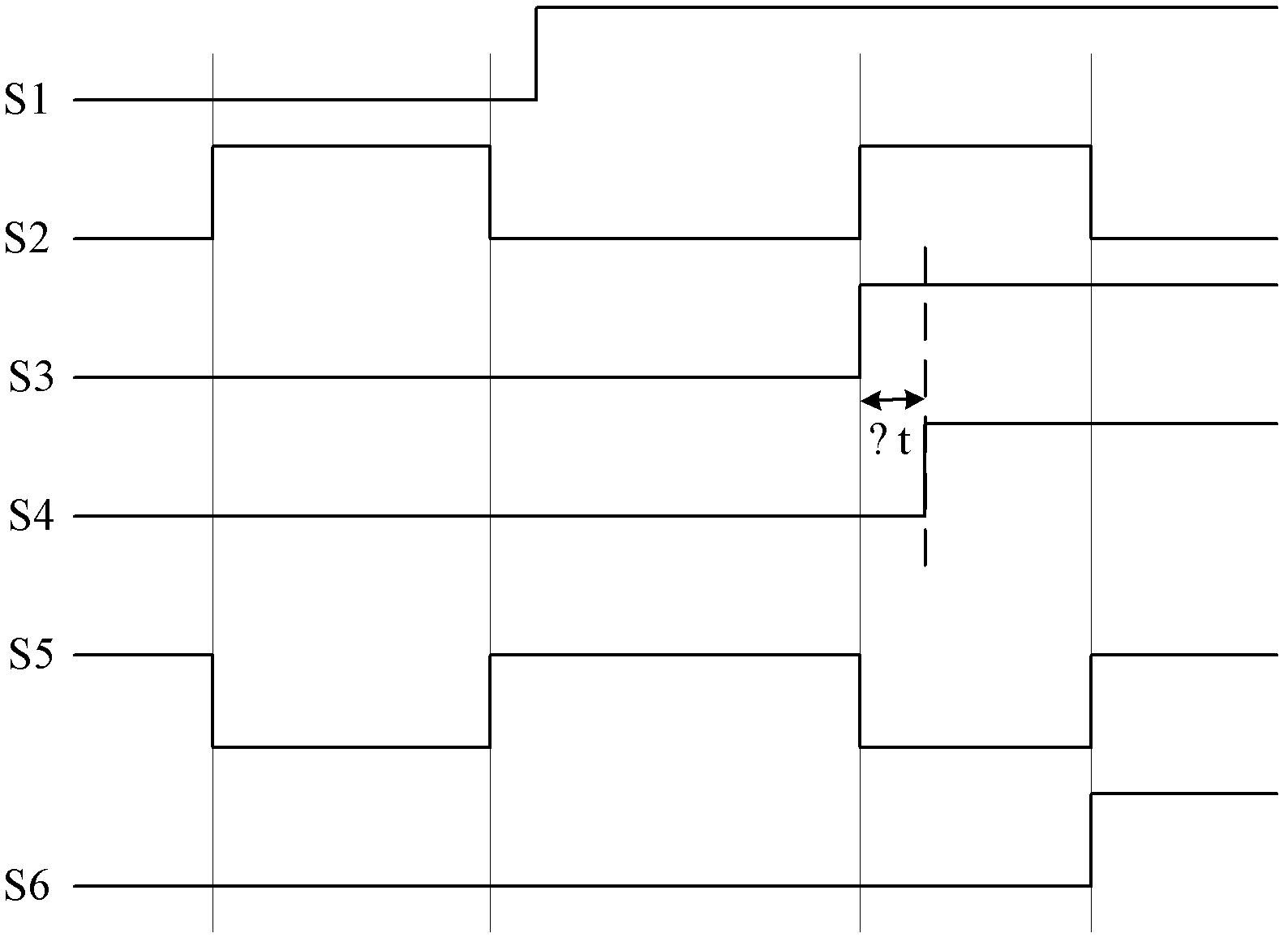
ActiveCN102520338ASimple structureSmall footprintElectronic circuit testingFrequency to amplitude conversionElectricityEngineering
Disclosed are a delay time measurement circuit and a delay time measurement method. The delay time measurement circuit is connected with a to-be-measured circuit and used for measuring delay time of the to-be-measured circuit, and comprises a signal generation source, a D-trigger and an AND gate circuit, wherein a first output end of the signal generation source is connected with a first input end of the AND gate circuit, a second output end of the signal generation source is connected with an input end of the to-be-measured circuit, an output end of the to-be-measured circuit is connected with a first input end of the D-trigger, a third output end of the signal generation source is coupled with a second input end of the D-trigger, and an output end of the D-trigger is connected with a second input end of the AND gate circuit. When the voltage of the output end of the AND gate circuit jumps to low level from high level, the signal time difference between the second output end and the third output end of the signal generation source is the delay time of the to-be-measured circuit. The delay time measurement circuit and the delay time measurement method can measure delay time of the to-be-measured circuit simply and accurately.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
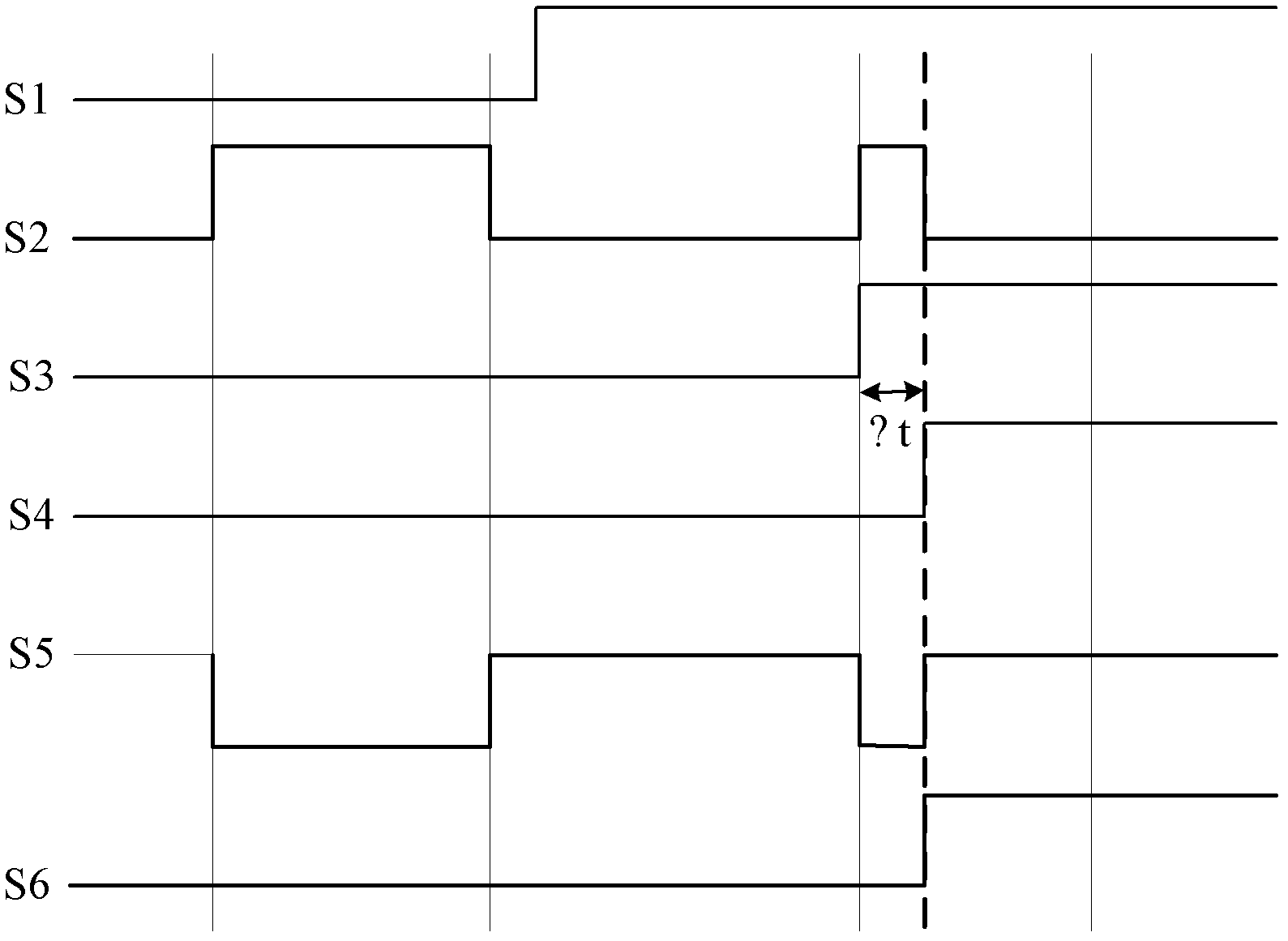
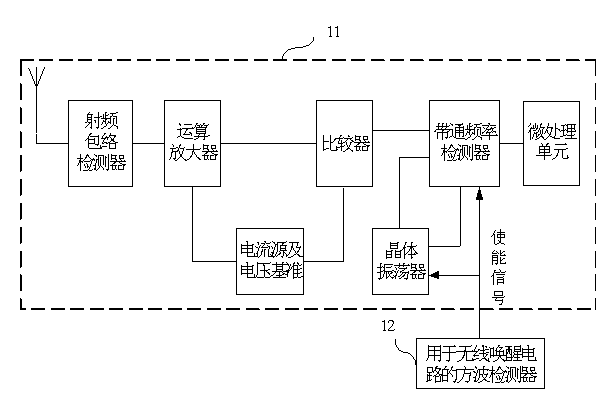
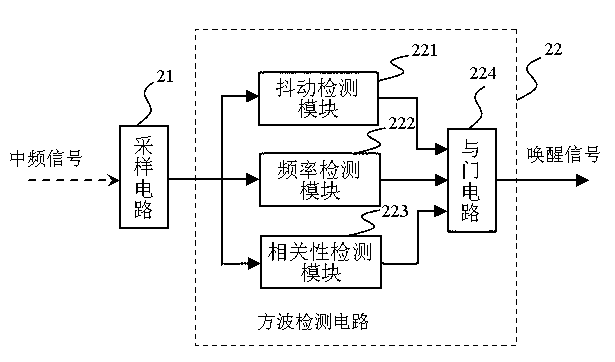
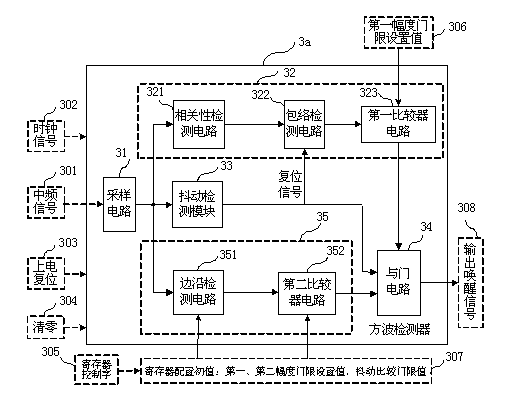
Square wave detector for wireless wake-up circuit
ActiveCN103226169AIncrease the probability of false wake-upImprove accuracyVoltage-current phase angleFrequency to amplitude conversionElectronElectronic toll collection
The invention provides a square wave detector for a wireless wake-up circuit. The frequency of the square wave detector can be configured within the range of 10-200 kHz. The square wave detector comprises a signal acquisition circuit and a square wave detection circuit, wherein the square wave detection circuit comprises a jitter detection module path, a frequency detection module path, a relevant detection module path and an AND circuit which are used for respectively detecting the duty factor, the frequency and the relevance of an input sampling signal; and when outputs of the three detection module paths are high levels respectively, the output of the AND circuit is also high level and the square wave detection circuit outputs a wake-up signal. By detecting the jitter, the frequency and the relevance of the input sampling signal, the accurate judgment and clutter reduction are realized, the mistaken wake-up probability is effectively reduced, the wake-up probability is increased and the wake-up time is remarkably shortened, thereby increasing the work efficiency of a wake-up receiver and reducing the power consumption of the system. The square wave detector provided by the invention is suitable for wake-up receiving circuits of an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) system and an ETC (Electronic Toll Collection) system.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
Method for frequency estimation of non-equilibrium power system
ActiveCN106680583AImprove robustnessFast convergenceFrequency to amplitude conversionVoltage amplitudeComputation complexity
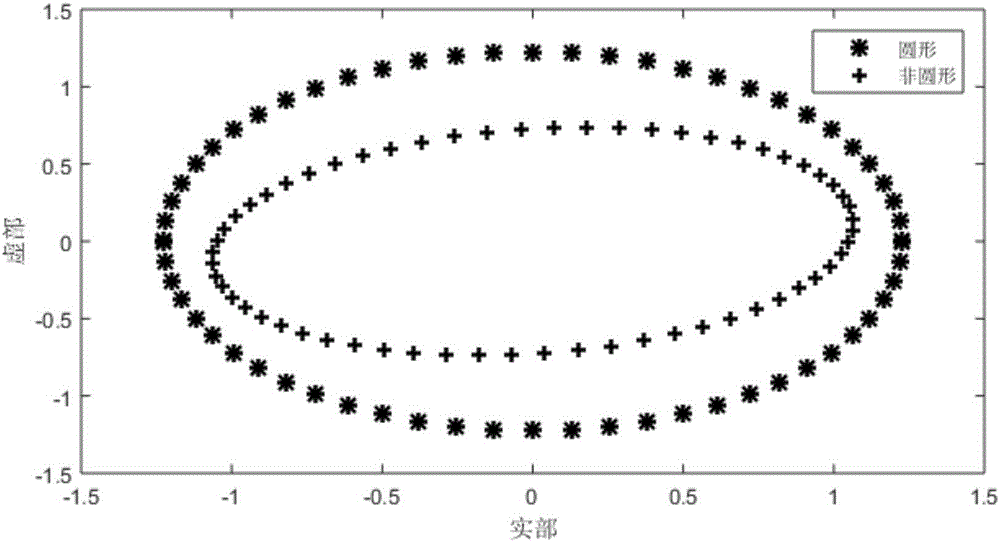
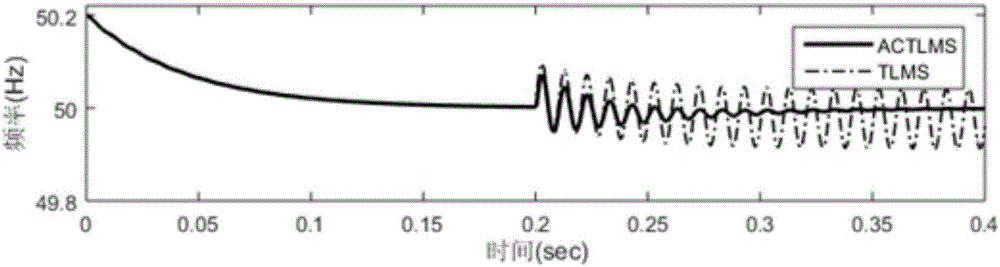
The invention discloses a method for frequency estimation of a non-equilibrium three-phase power system. The method comprises the steps that the frequency of the non-equilibrium three-phase power system is estimated mainly on the basis of a widely-linear total least square self-adaption algorithm model, wherein the widely-linear model sufficiently utilizes three-phase voltage complete two-order information, and the frequency estimation robustness is enhanced. Compared with traditional linear self-adaptation estimation, the method is more applicable to the non-equilibrium system, and unbiased frequency estimation is given. Meanwhile, the model is not sensitive to changes of the three-phase voltage amplitude along with time passage and higher harmonic. The method is more stable and low in computation complexity, and the convergence performance, robust anti-noise performance and stable convergence precision are obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Sine wave parameter measuring method and system in electric power system
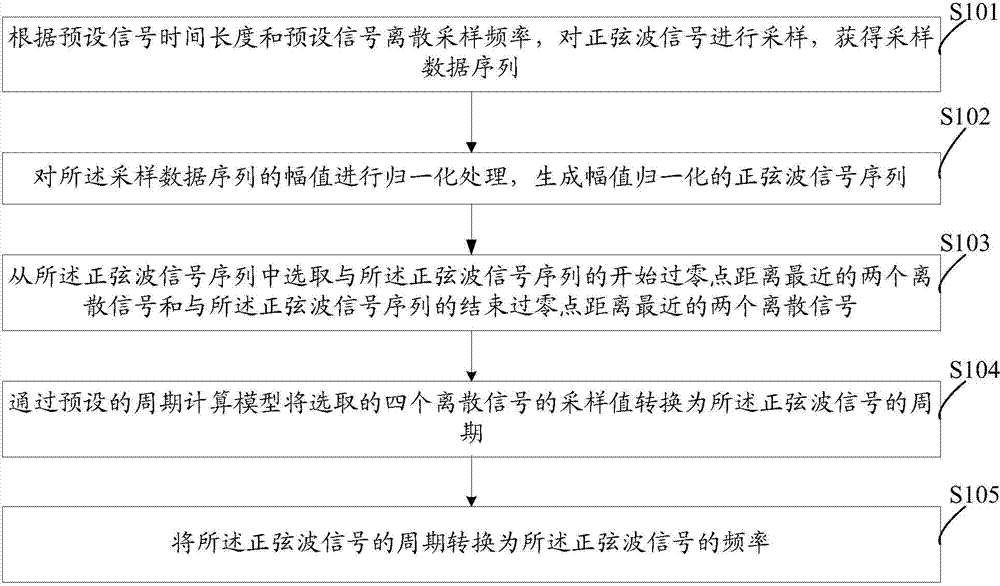
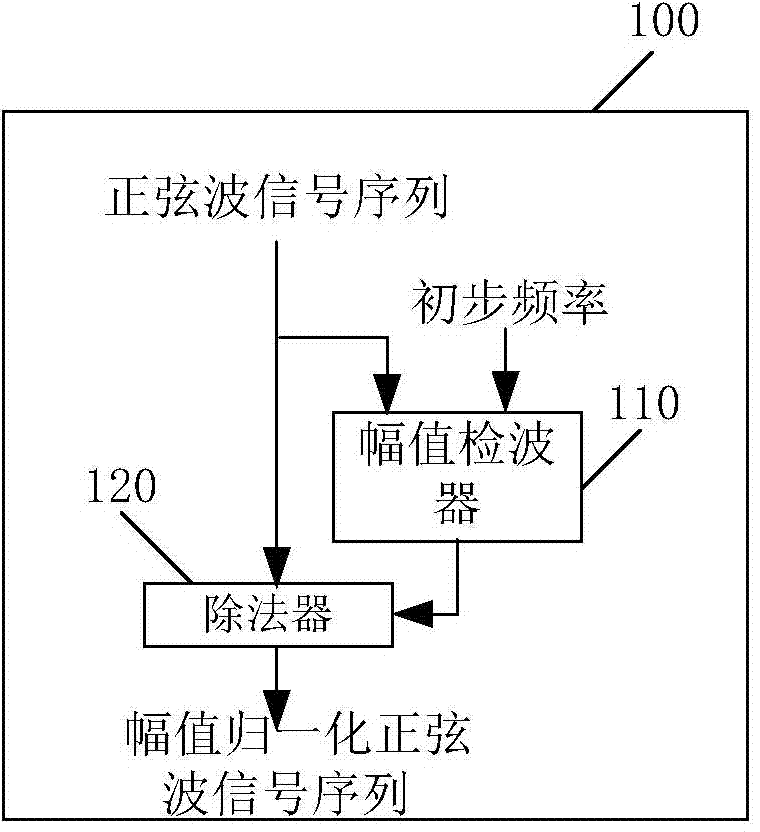
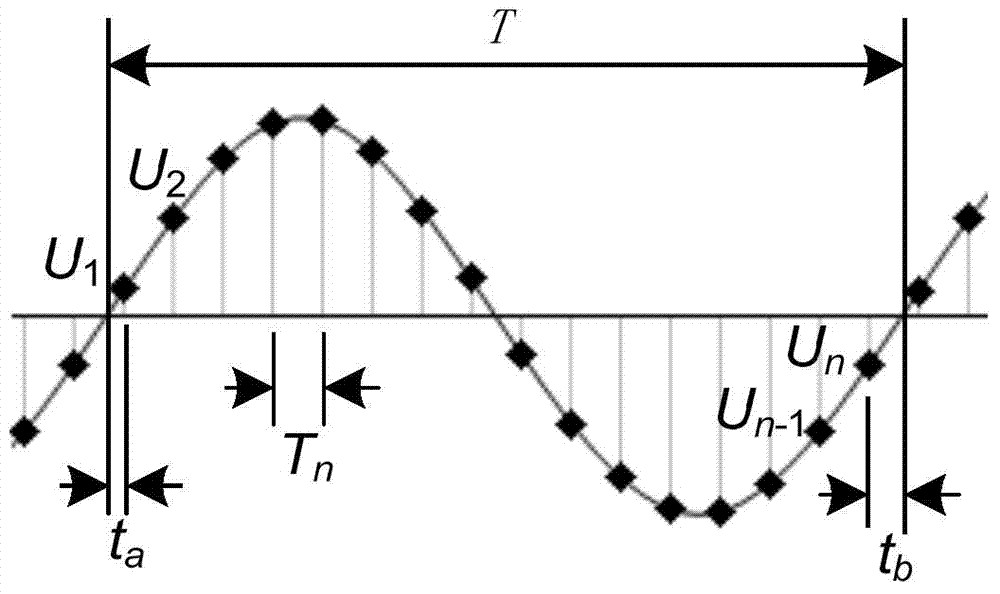
ActiveCN104330623AStable detectionHigh precisionFrequency to amplitude conversionElectric power systemDiscrete-time signal
The invention discloses a sine wave parameter measuring method and system in an electric power system. The sine wave parameter measuring method in the electric power system comprises sampling a sine wave signal and obtaining a sampling data sequence according to the preset signal time duration and a preset signal discrete sampling frequency; normalizing an amplitude of the sampling data sequence and generating into a sine wave signal sequence with the normalized amplitude; selecting two discrete signals being at a nearest starting zero crossing point distance from the sine wave signal sequence and two discrete signals being at a nearest finishing zero crossing point distance from the sine wave signal; converting sampling values of the selected four discrete signals into a period of the sine wave signal through a preset period calculation model; converting the period of the sine wave signal into the sine wave signal frequency. The sine wave parameter measuring method and system in the electric power system can rapidly and stably detect the sine wave signal frequency with high accuracy.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Magnetic device and frequency detector
InactiveUS7825658B2Cut in halfIncrease productionNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsCurrent limitingMagnetization
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
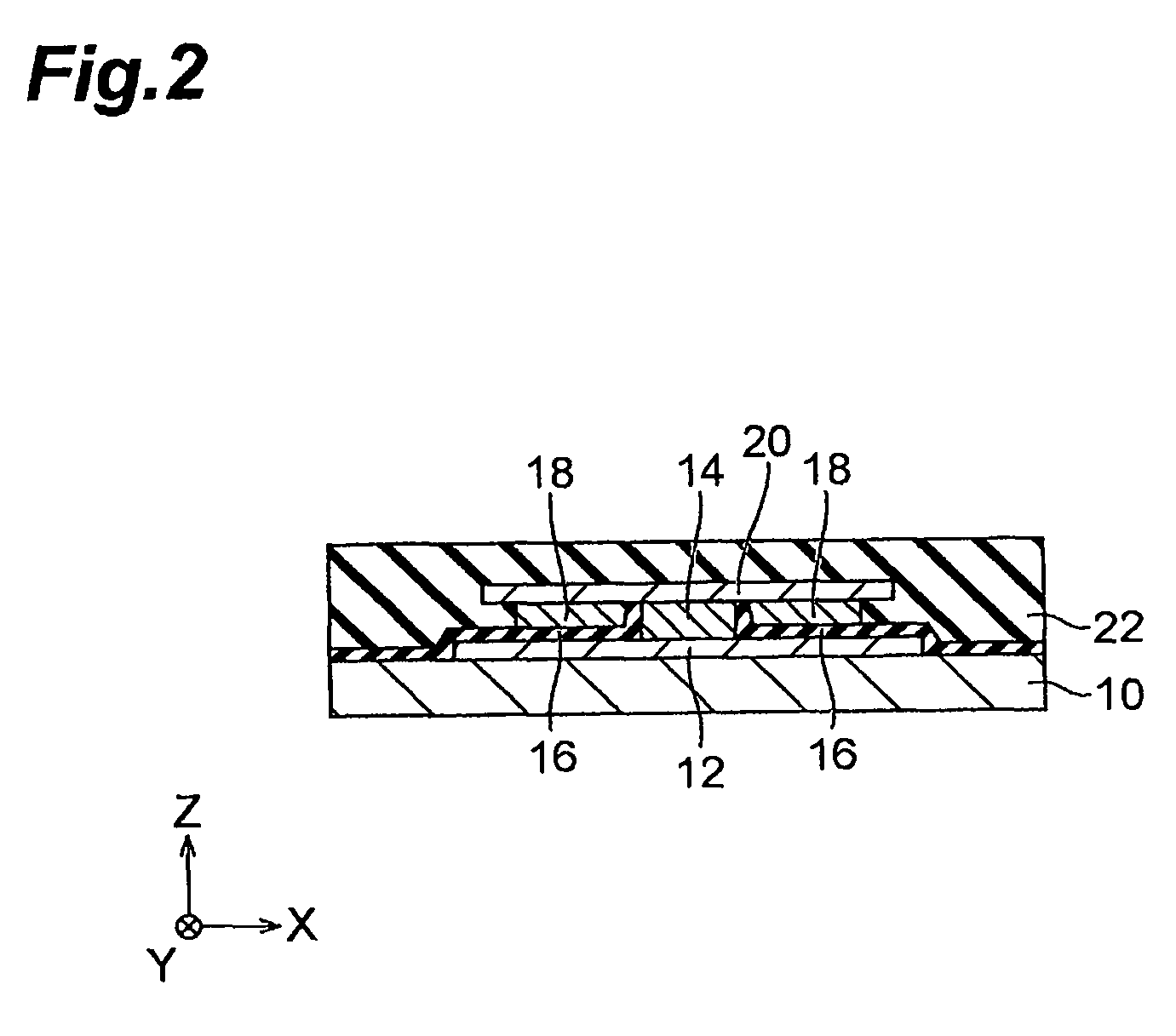
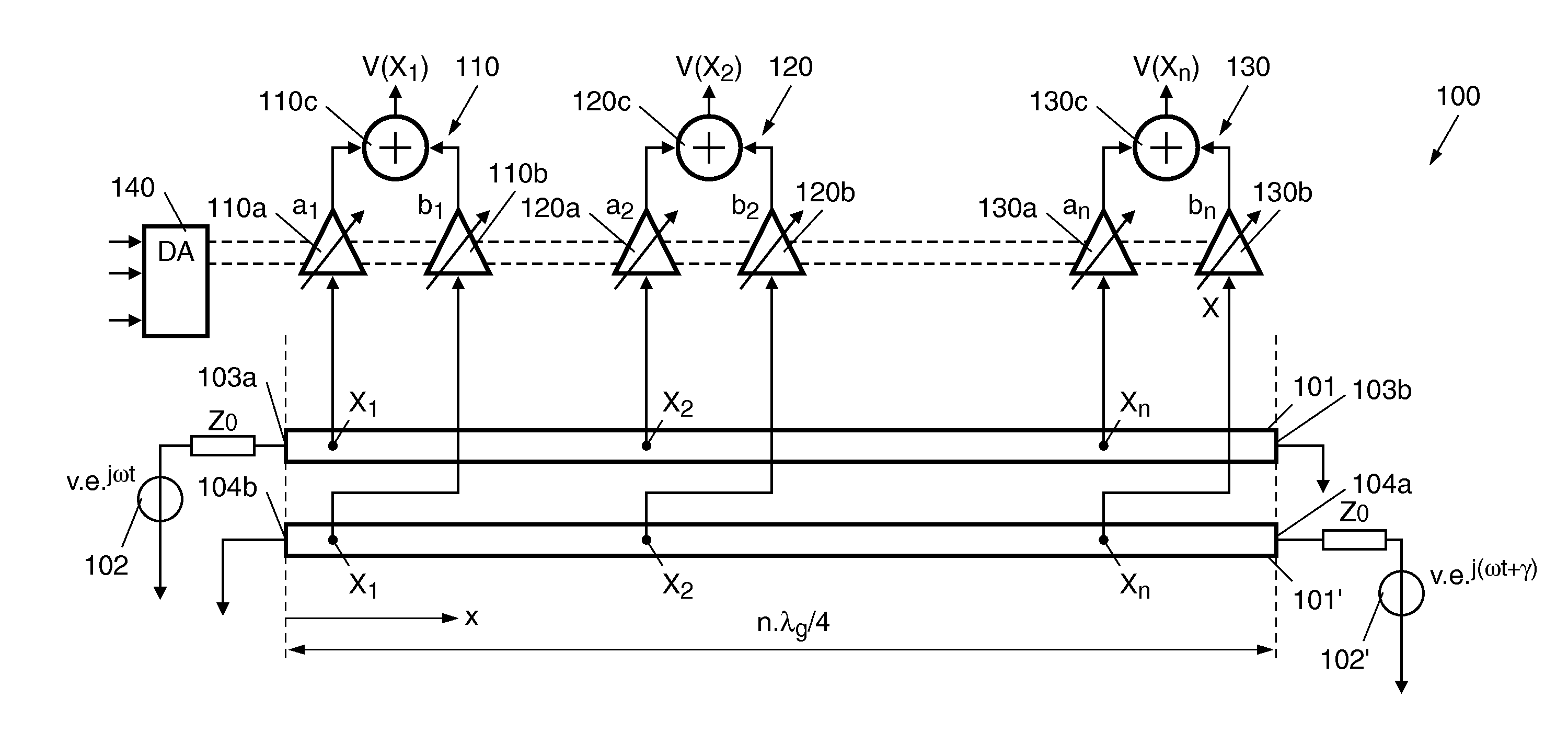
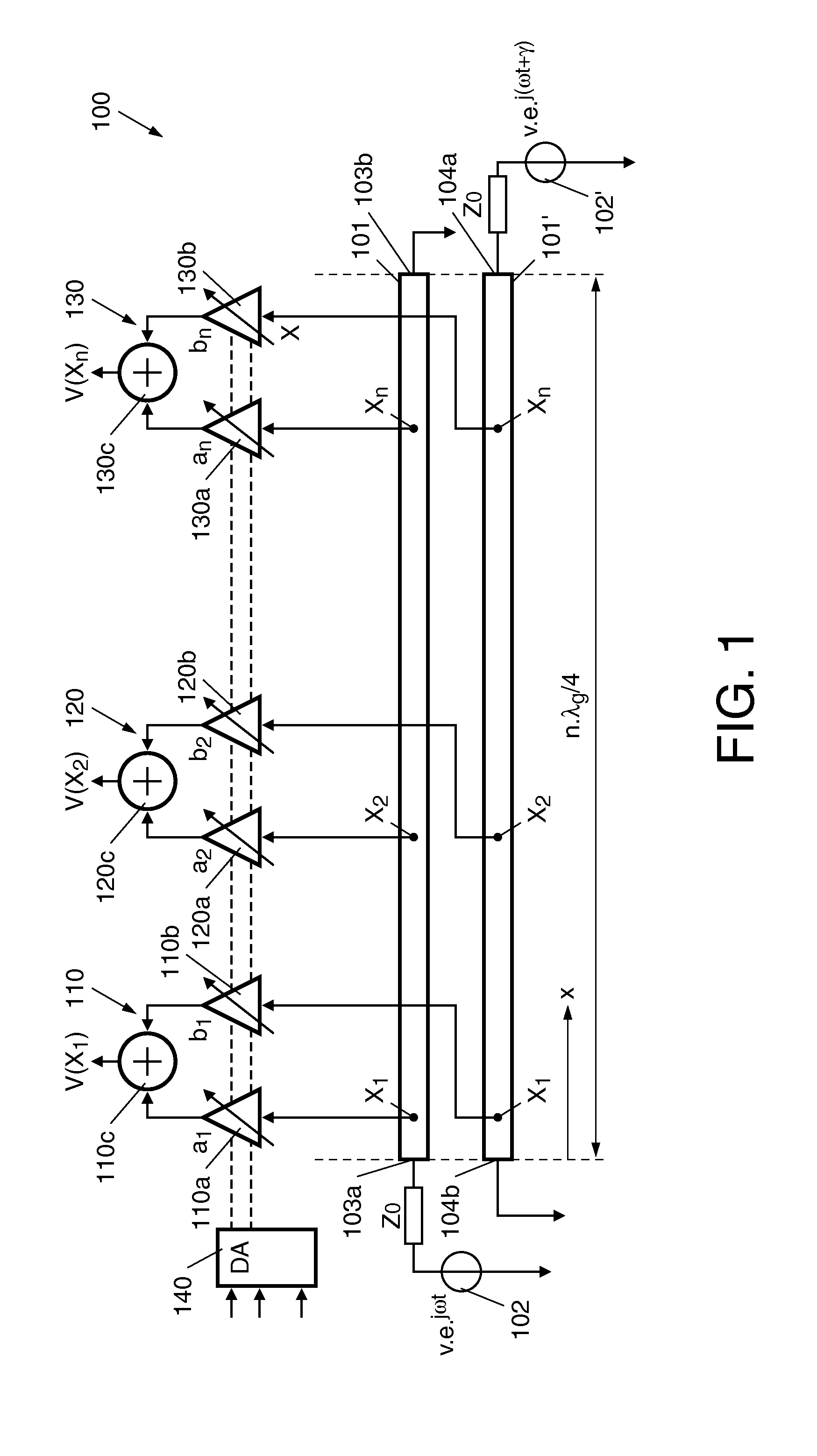
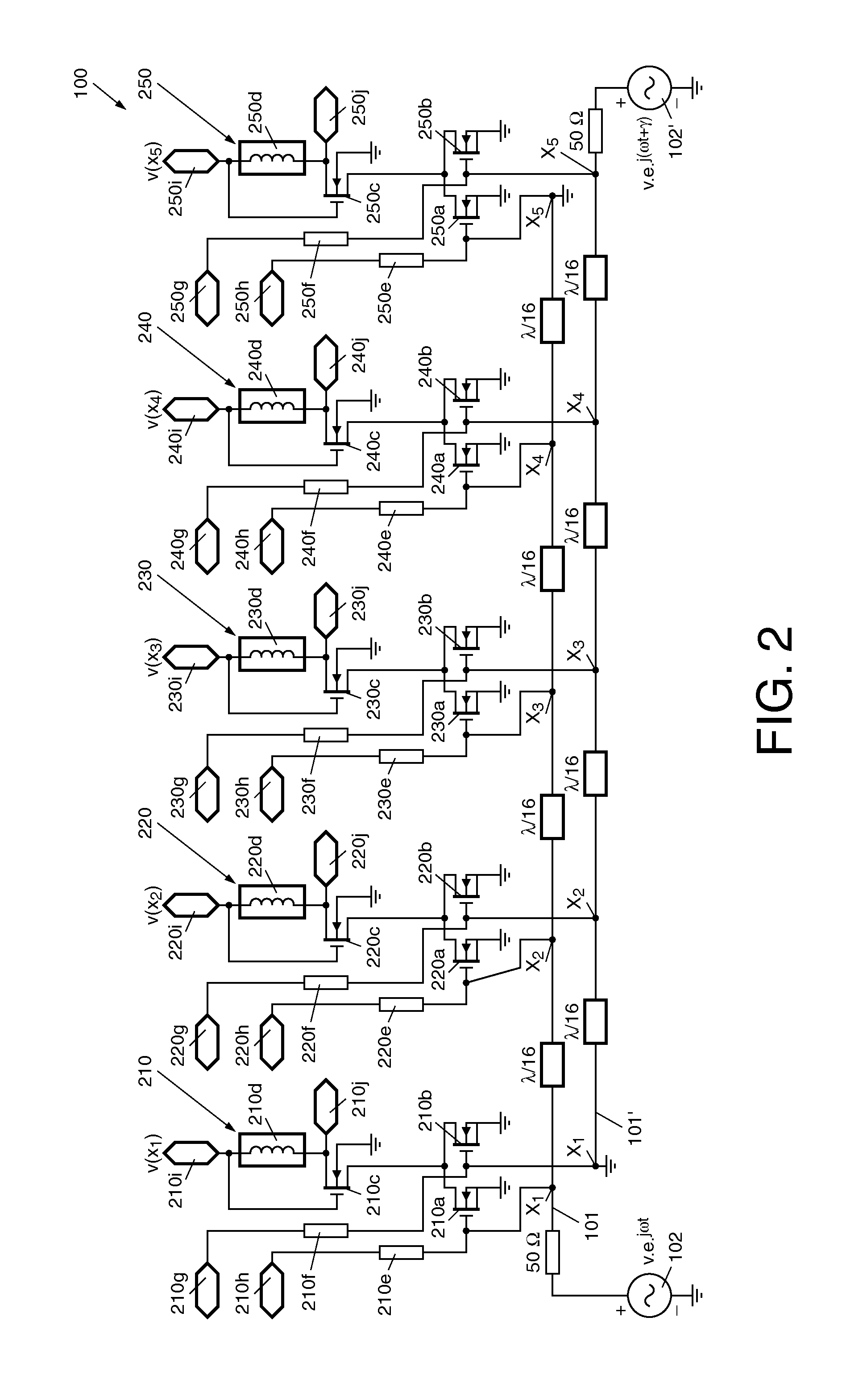
Apparatus for feeding antenna elements and method therefor
ActiveUS20110156694A1MiniaturizationHigh frequencyAntenna arraysFrequency to amplitude conversionWavelengthAntenna element
An apparatus (100) for feeding antenna elements of a phased array antenna, comprises: at least two transmission lines (101, 101) disposed in parallel and operated at a certain frequency as resonators, each of the transmission lines (101, 101) having a predetermined length dimensioned to be at least approximately an electrical quarter-wavelength of the operating frequency, a plurality of measuring positions provided on the transmission lines (101, 101) in spacings along the longitudinal direction (x) of the transmission lines, wherein each measuring position on one of the two transmission lines (101) faces directly a corresponding neighbored measuring position on the other transmission line (101) and such corresponding measuring positions being adjacent to each other in a direction transverse to the longitudinal direction of the transmission lines (101, 101) form a measuring position pair, respectively, wherein each of the circuits (110, 120, 130) detects and amplifies / attenuates the measuring signals from an assigned measuring position pair associated with the transmission lines (101, 101) for a corresponding longitudinal position as a function of a resonant field in the transmission lines at the respective positions, and further adds the measured and processed signals in order to generate output signals for feeding corresponding antenna elements.
Owner:NXP BV
Method and device for measuring the rotational speed of a pulse-activated electric motor based on a frequency of current ripples
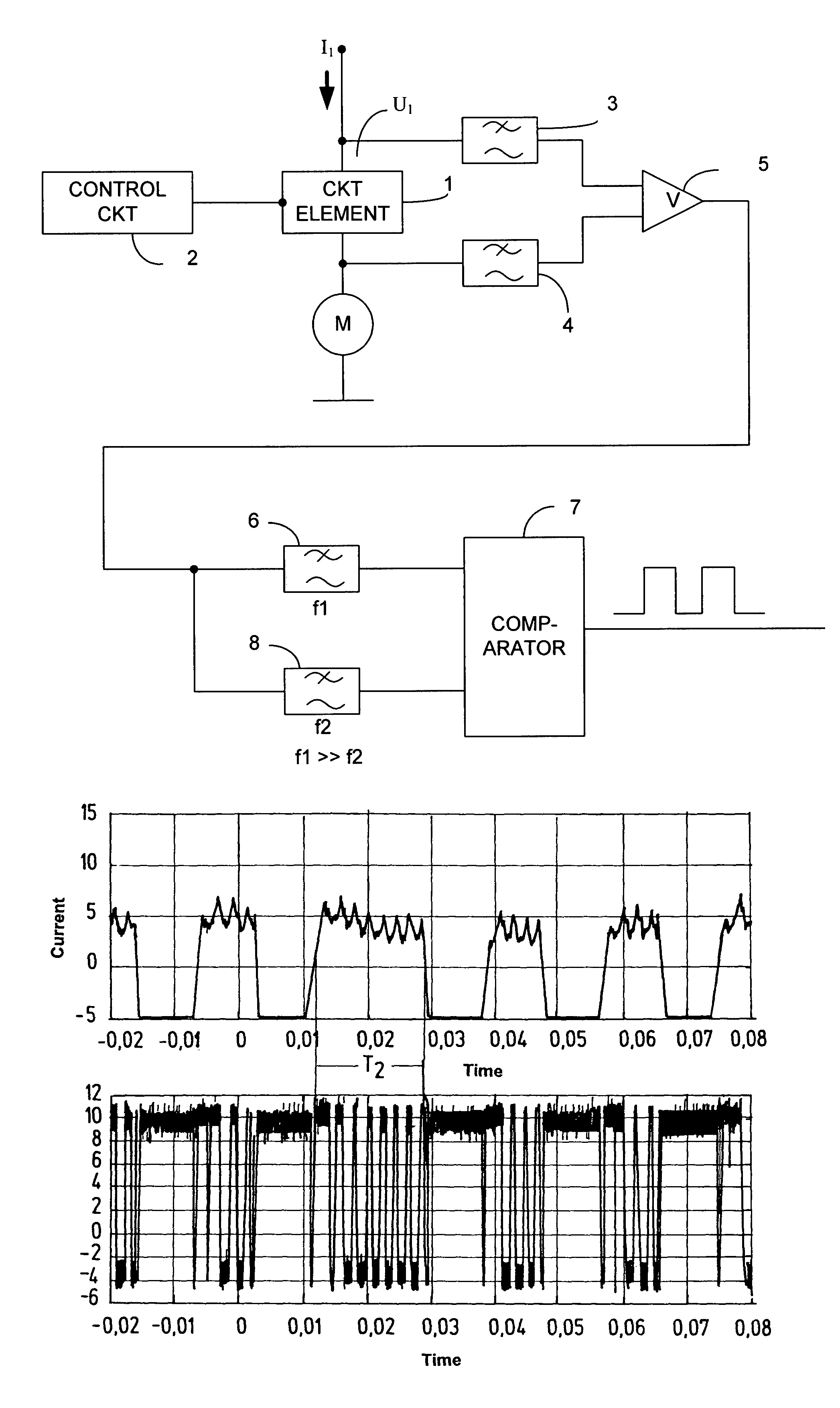
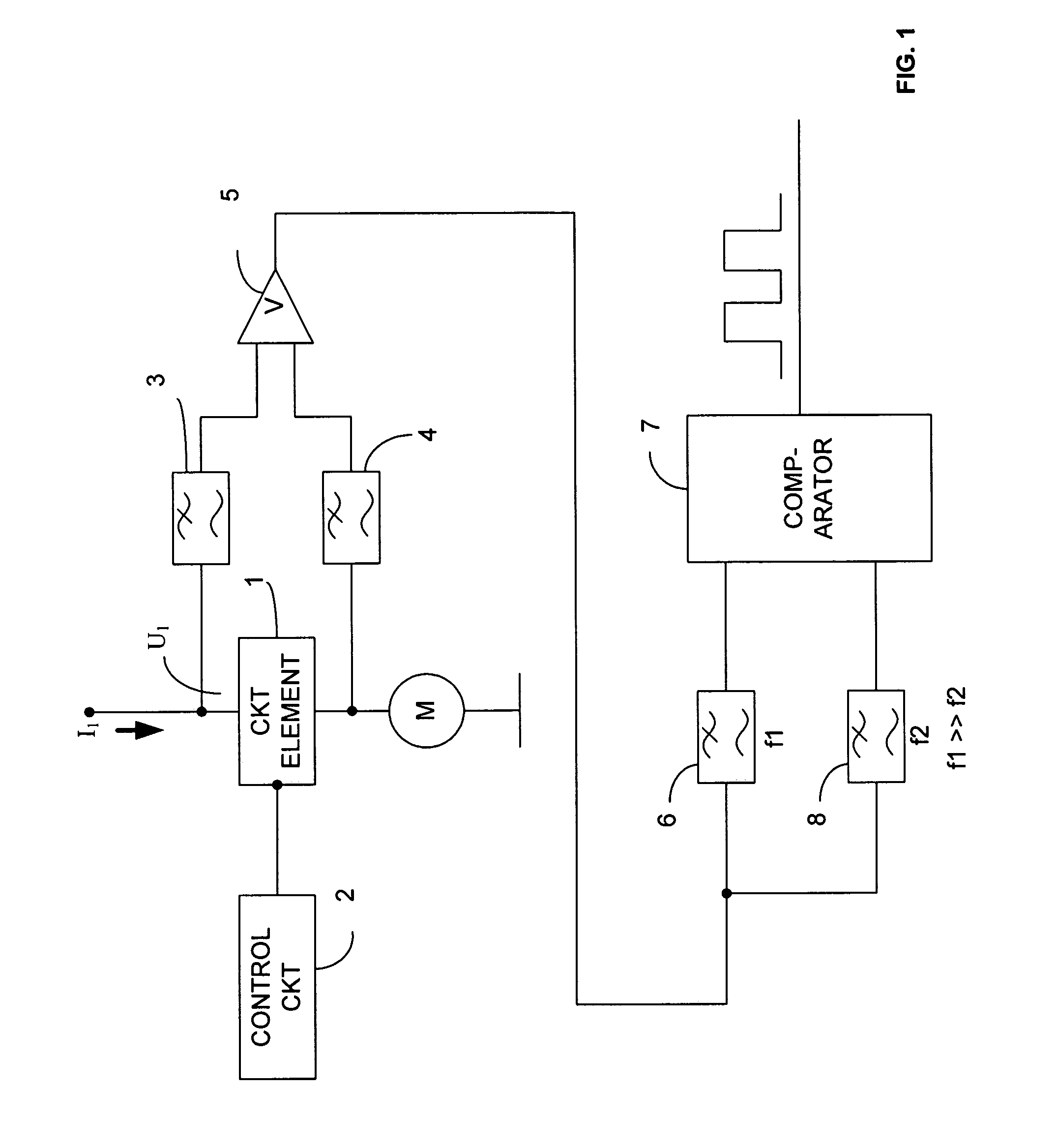
InactiveUS7265538B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersMotor speedAudio power amplifier
A method and a device for measuring the speed of a pulse-activated electric motor are described. According to this method, the motor is fully activated at time intervals to be determined for a defined measuring time by the circuit element provided for timing and, in this time, the frequency of the current ripples, which is proportional to the motor speed, is measured. A current-proportional voltage measuring device is located on the circuit element, on whose load side are located an amplifier, filters, and an evaluation circuit in the form of a comparator for determining the frequency of the current ripples flowing in a measured phase during which the motor is fully activated.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Power system frequency measuring method and device
ActiveCN107064630AAccurate frequencyThe principle is simpleFrequency to amplitude conversionElectric power systemZero crossing
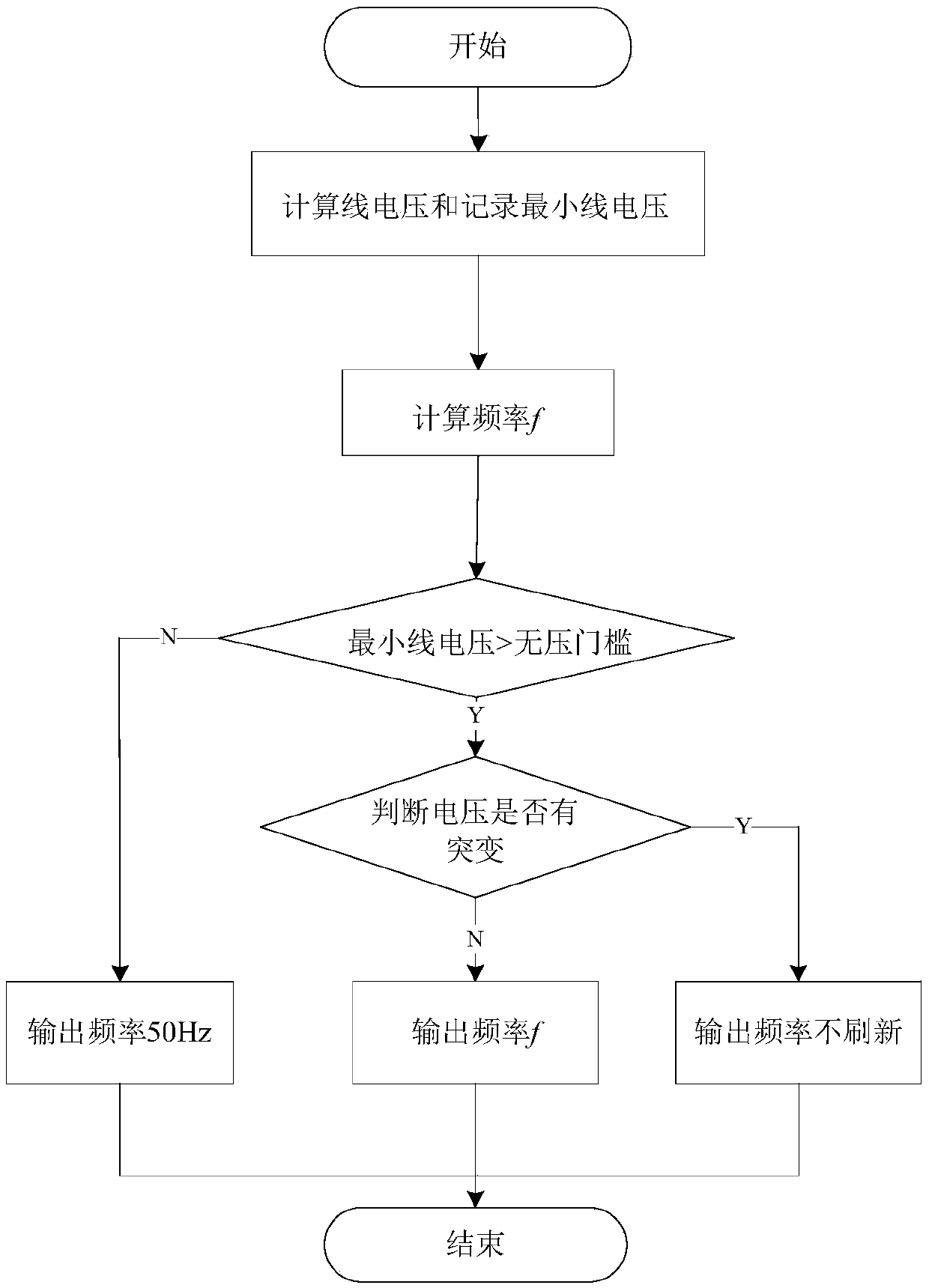
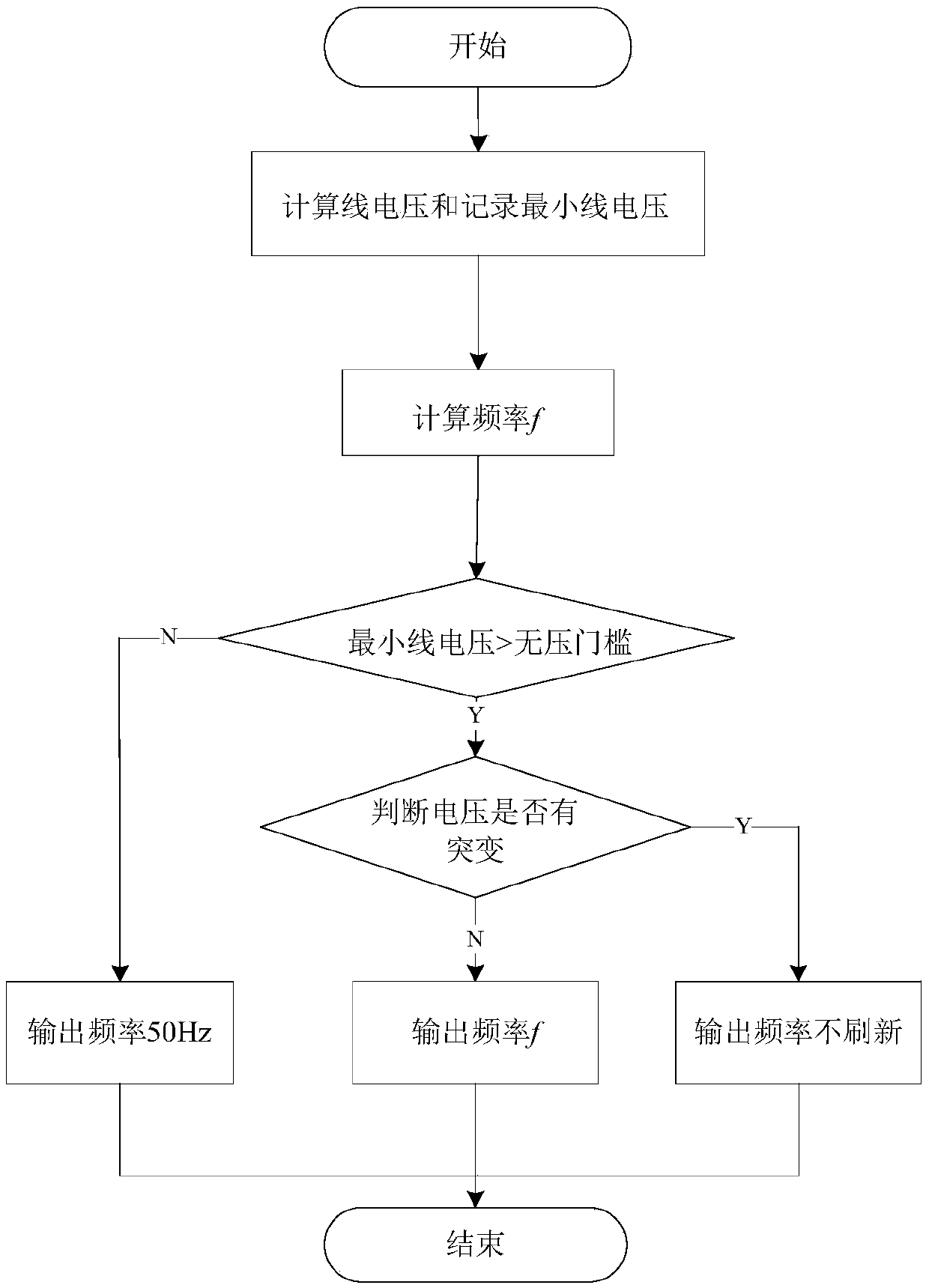
The invention relates to a power system frequency measuring method and a device. The method comprises the steps of calculating the line voltages at three moments with an interval of 1 / P cyclic wave according to a sampling value of bus voltage acquired from a power system, and calculating the current frequency of the system according to the real and imaginary parts of the line voltages at the three moments. The measuring method is based on a simple principle, and is easy to implement. Through the method, the frequency of a power system can be measured accurately without being influenced by the zero crossing point and harmonic wave.
Owner:XUJI GRP +3
Sub-synchronous oscillation parameter identification method for synchronous phasor data based on interpolation DFT
ActiveCN110412349AAccurate identificationSpectral/fourier analysisVoltage-current phase angleDamping factorFrequency spectrum
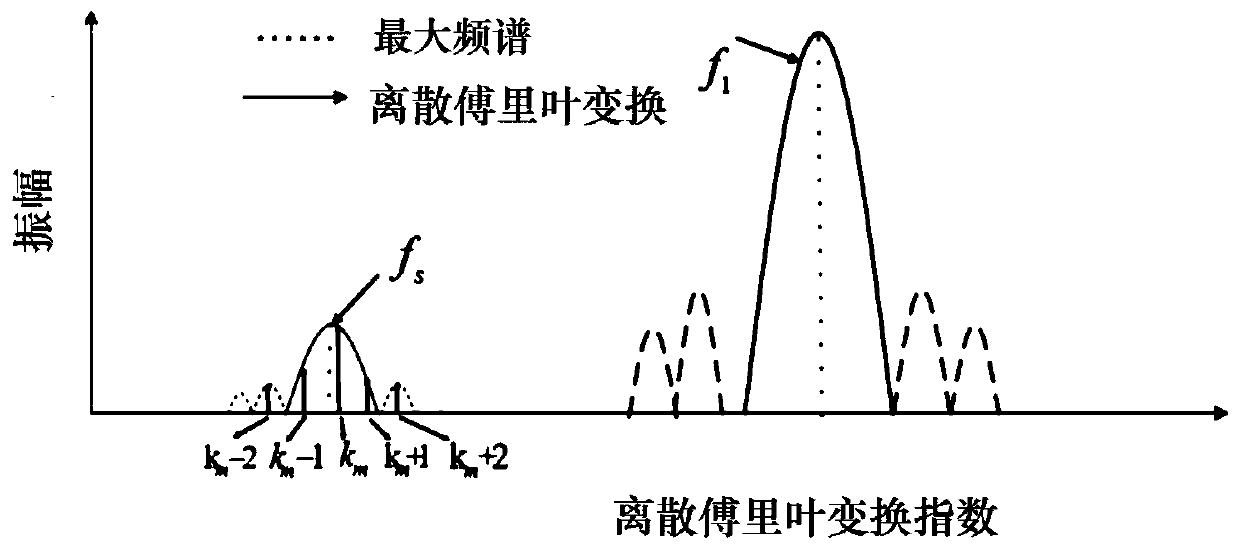
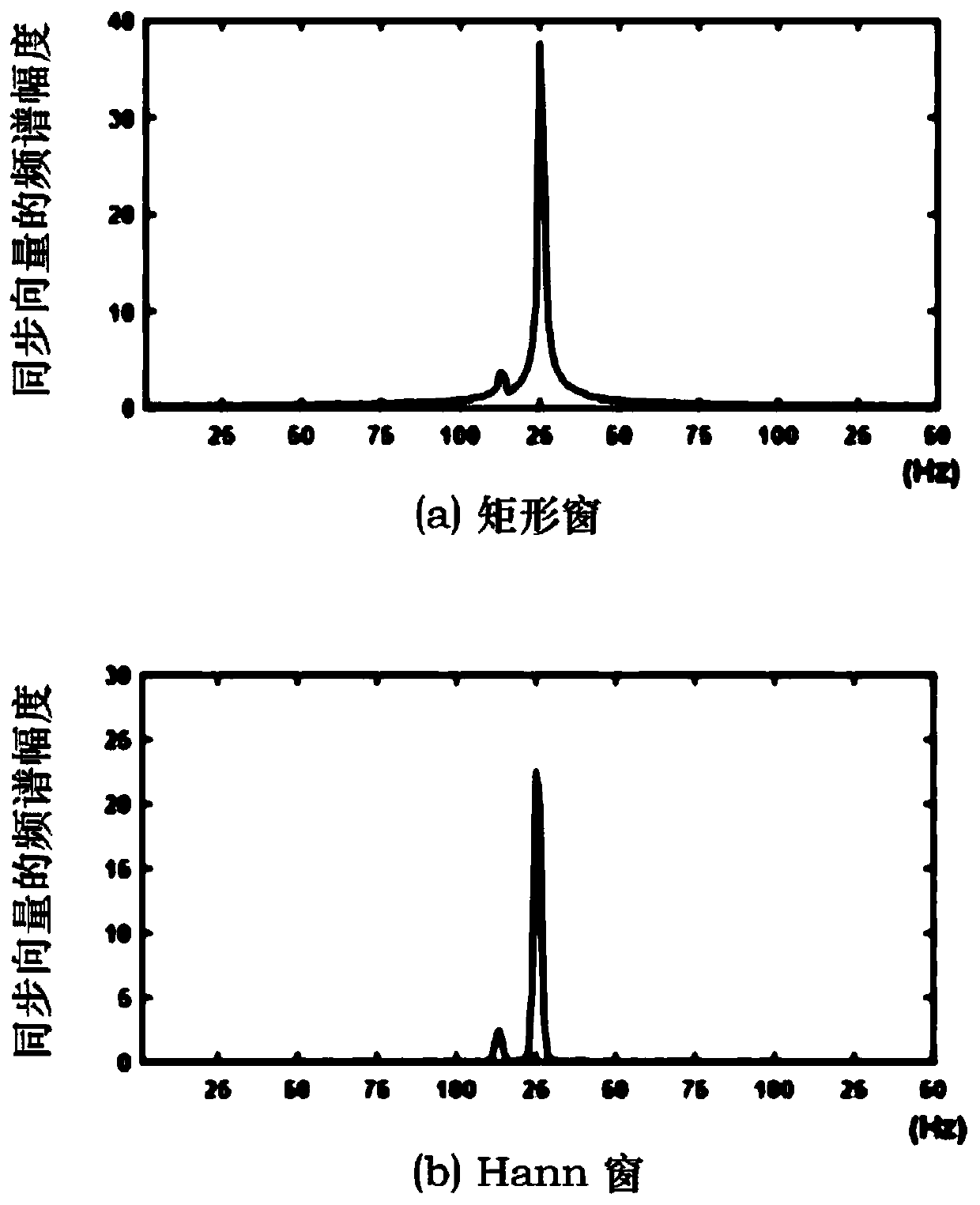
Disclosed is a sub-synchronous oscillation parameter identification method for synchronous phasor data based on interpolation DFT. The method comprises the following steps of 1, acquiring real-time high-resolution waveform data; 2, obtaining a synchronous phasor Xr(m) at a master station; 3, conducting a discrete Fourier transform operation on the synchronous phasor Xr(m) in a rectangular window to obtain a discrete Fourier transform spectrum Fr(k); 4, determining a frequency spectrum line km with the largest sub-synchronous oscillation amplitude; 5, constructing index phasors [k1, k2, k3, k4], introducing a frequency spectrum Frs(ki) of a second-order difference optical spectrum, and obtaining a simplified second-order difference ratio R; 6, calculating the values of a frequency fs and adamping coefficient alphas of sub-synchronous oscillation components; 7, conducting Hann window interception on the synchronous phasor Xr(m), executing the discrete Fourier transform operation, and conducting backstepping to obtain a calculation formula of the amplitude value As of the sub-synchronous oscillation components. By means of the method, the parameters of the sub-synchronous oscillationcomponents can be accurately identified, and the alleviation of the influence of sub-synchronous oscillation on system stability and equipment safety is facilitated.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Frequency detection circuit
InactiveUS20100052732A1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsCurrent/voltage measurementEngineeringFrequency detection
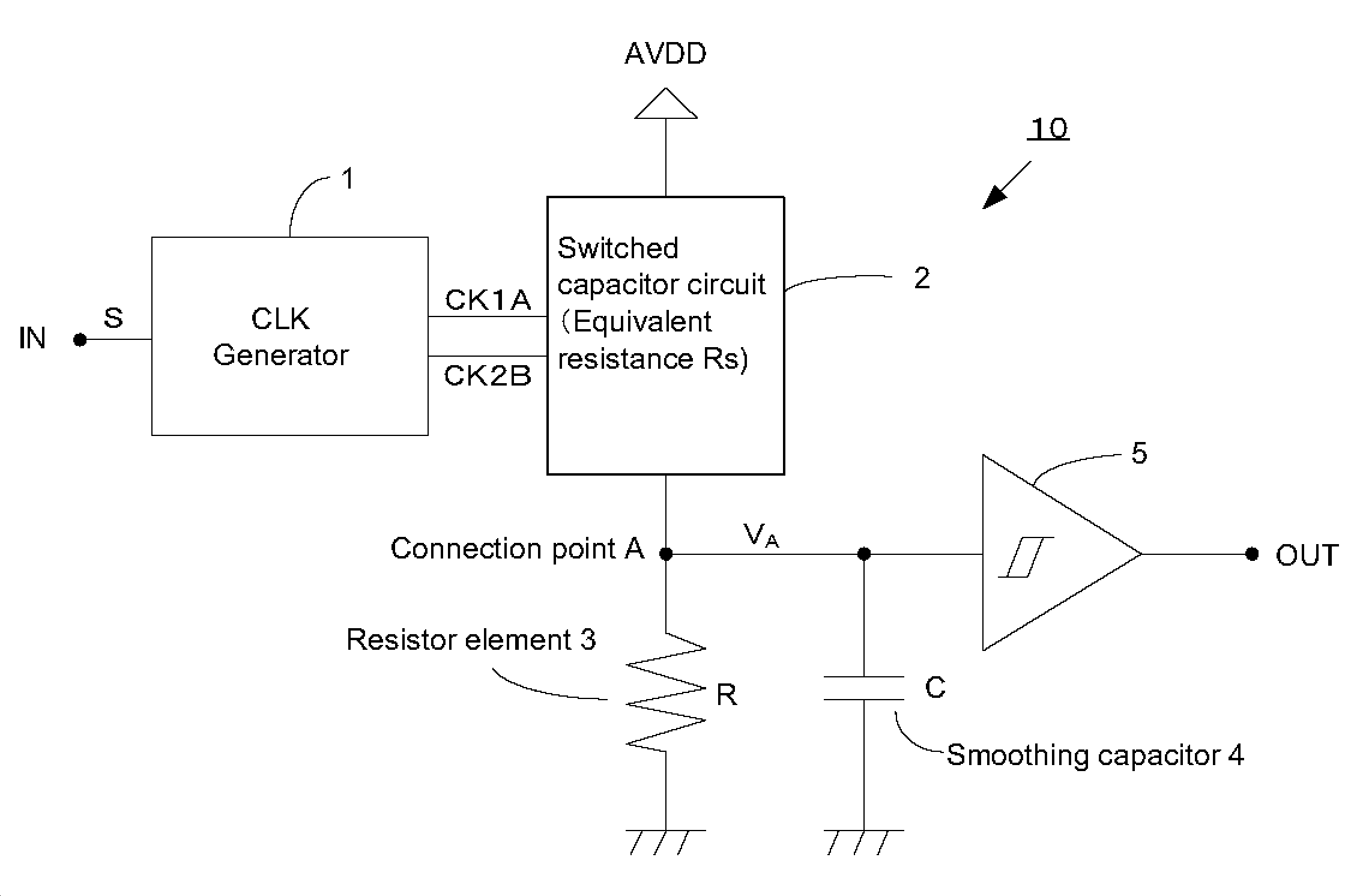
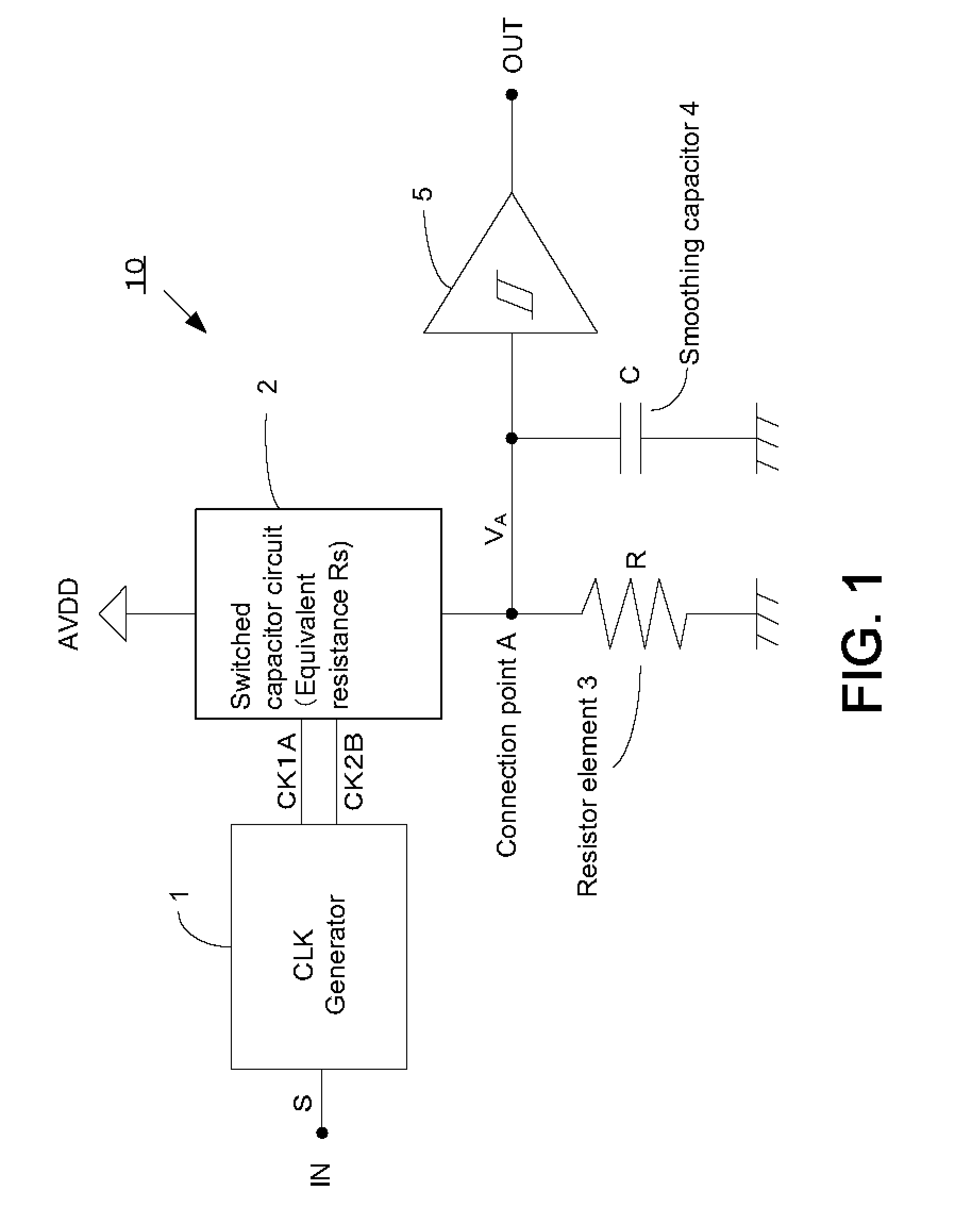
In some preferred embodiments, a switched capacitor circuit configured to change its equivalent resistance depending on the frequency of an input clock signal and a resistor element are connected in series. A power source voltage is divided by the equivalent resistance of the switched capacitor circuit and the resistance of the resistor element, and the divided voltage is inputted to a Schmitt circuit. The Schmitt circuit outputs a high-level signal when the inputted divided voltage is higher than a threshold voltage and a low-level signal when the inputted divided voltage is lower than a threshold voltage. Thus, depending on the frequency of the input clock signal, a high-level signal or a low-level signal is outputted.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Two-stage-FFT-based digital broadband high-precision frequency measuring method and system
InactiveCN108490255AReduce computing pressureImprove frequency measurement accuracyFrequency to amplitude conversionDigital down conversionIntermediate frequency
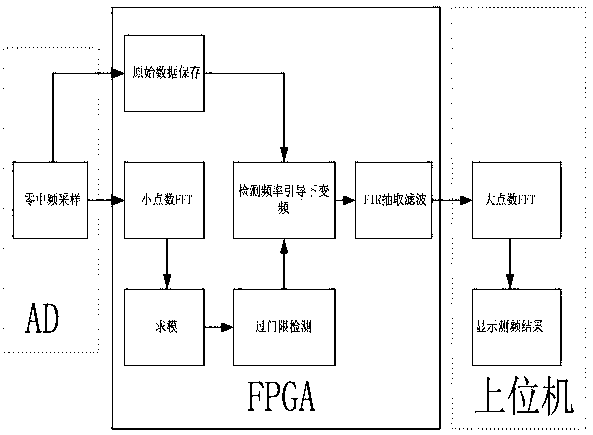
The invention provides a two-stage-FFT-based digital broadband high-precision frequency measuring method and system. Zero-intermediate-frequency AD sampling is carried out on a signal or after sampling, down-conversion is carried out to form a zero-intermediate frequency signal and the processed signal is sent to a signal processing module; the signal processing module receives an original signal,the signal is divided into two paths, and one path of signal is used as original data for storage; the other part of data are used for FFT; modulo calculation is carried out on the result after FFT and over-threshold detection is carried out to detect an over-threshold signal; digital down conversion is carried out on the stored original signal by using the signal obtained by over-threshold detection as guidance, so that the processed signal is transformed to be at a zero-intermediate frequency position; filter extraction is carried out on the signal after frequency conversion; baseband dataafter filter extraction are sent to an upper computer; and the upper computer carries out large-point-number FFT on the baseband data to obtain a high-precision frequency result. Therefore, the high frequency measurement accuracy is kept at a high sampling rate under the circumstance of limited hardware resources.
Owner:SOUTHWEST CHINA RES INST OF ELECTRONICS EQUIP
Popular searches
Picture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanning Picture reproducers using projection devices Picture reproducers using solid-state color display Television signal transmission by single/parallel channels Digital video signal modification Color motion picture films scanning Signal generator with optical-mechanical scanning Color television with pulse code modulation Color signal processing circuits Color television with bandwidth reduction
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com