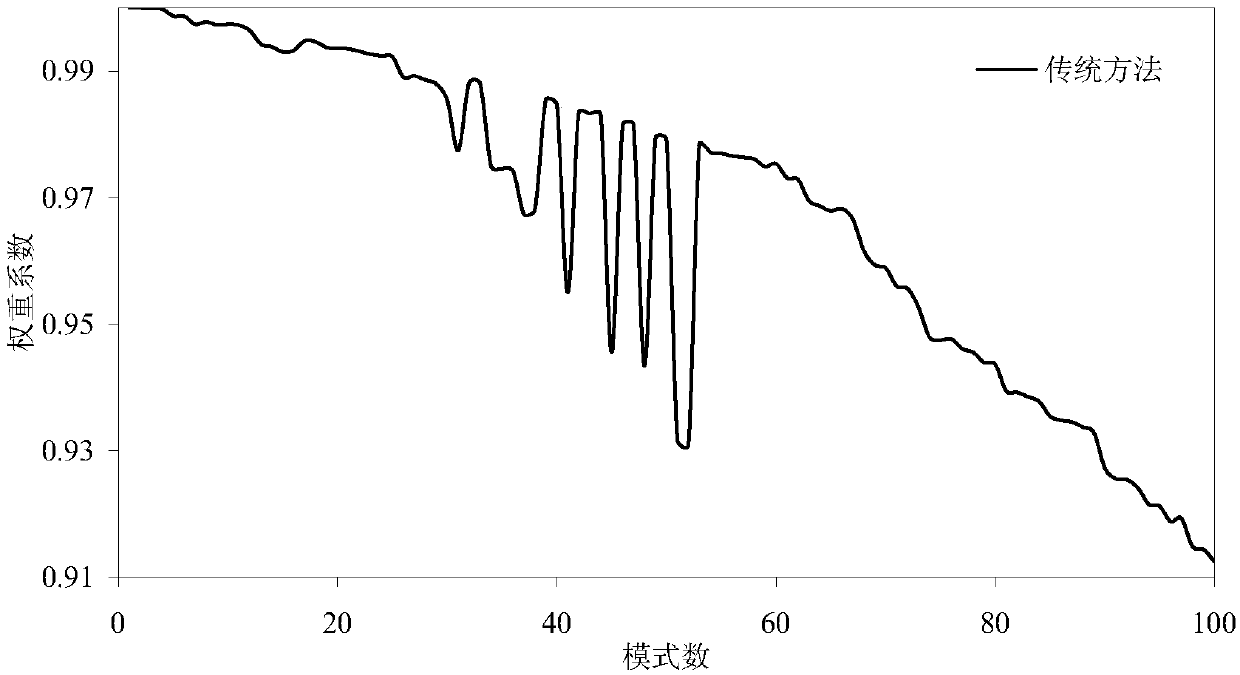
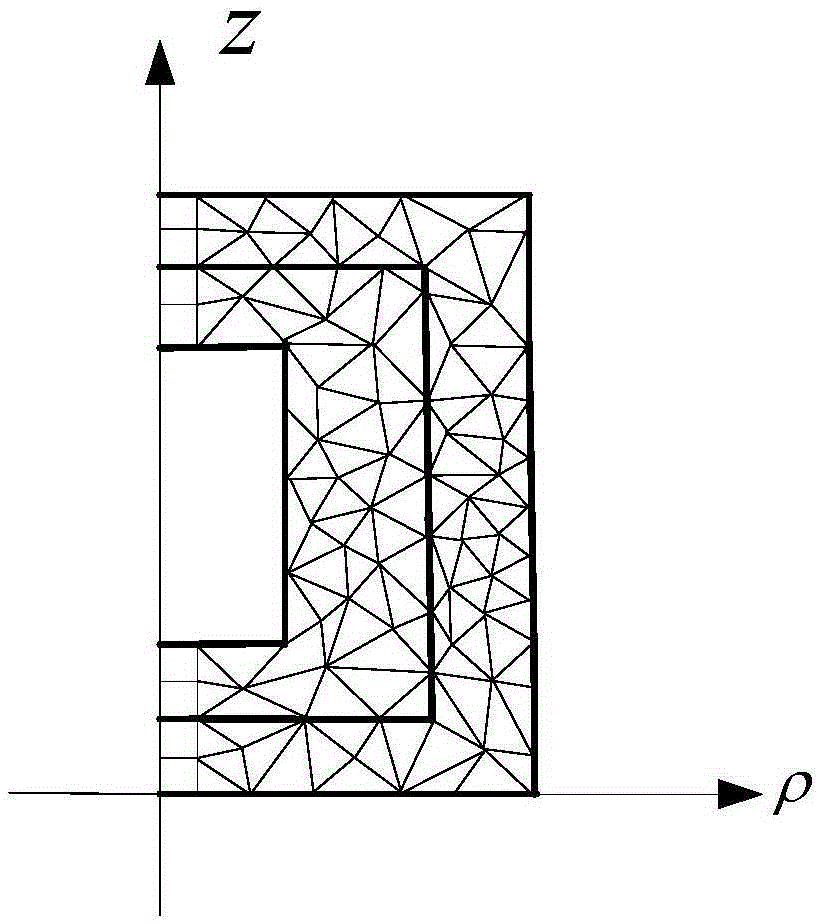
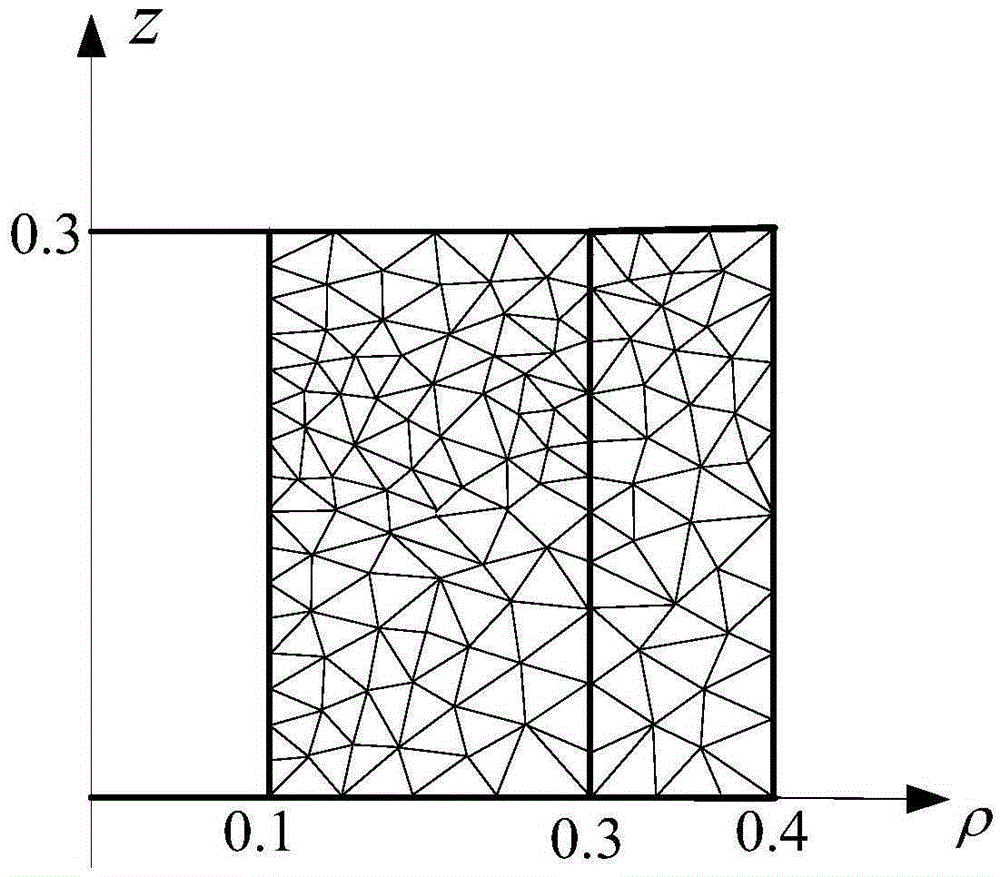
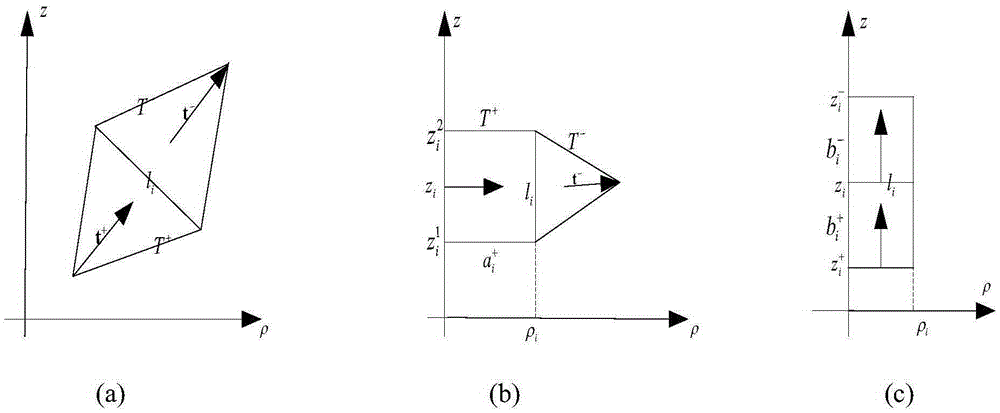
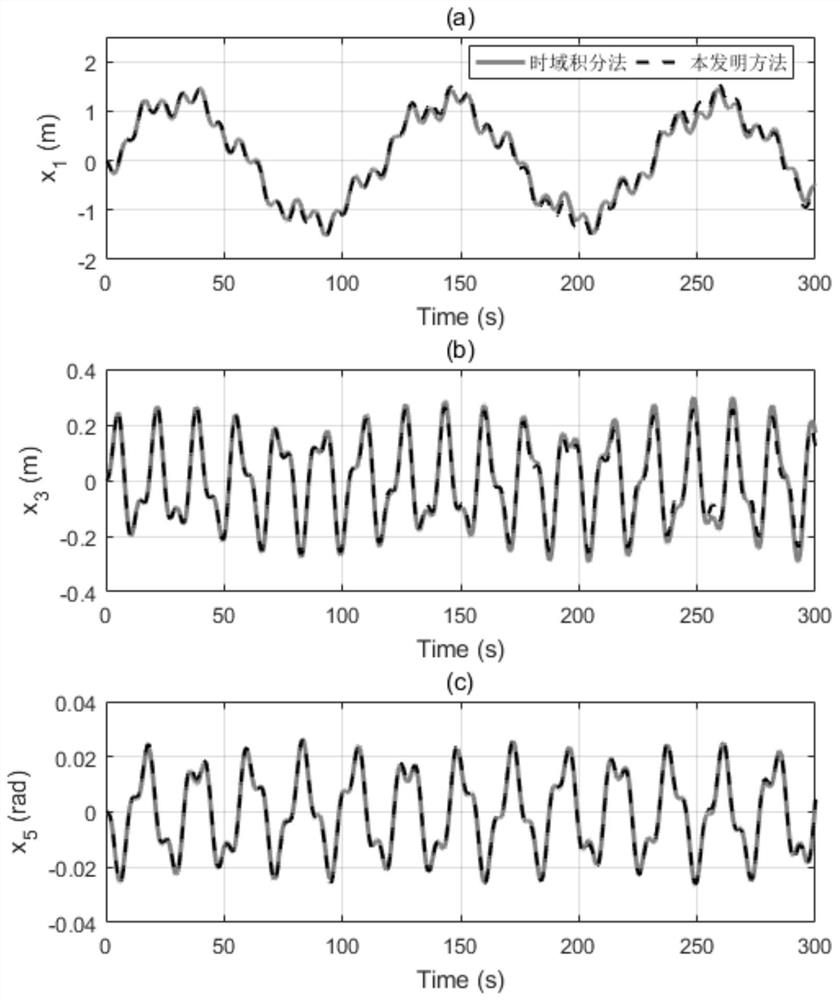
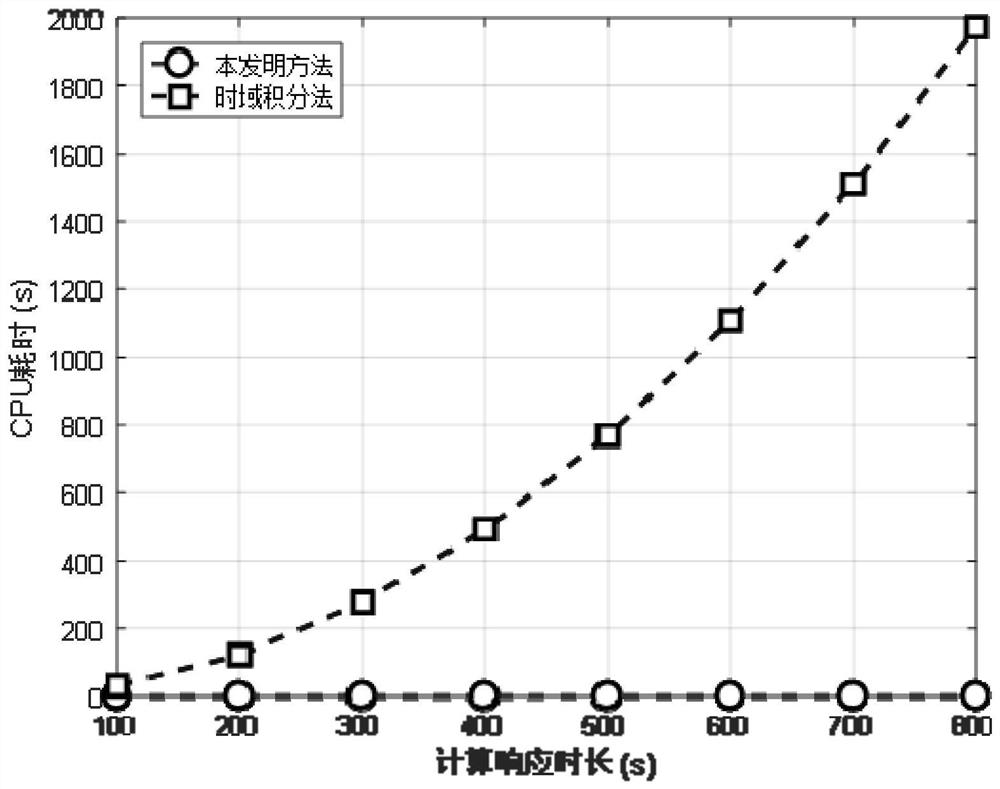
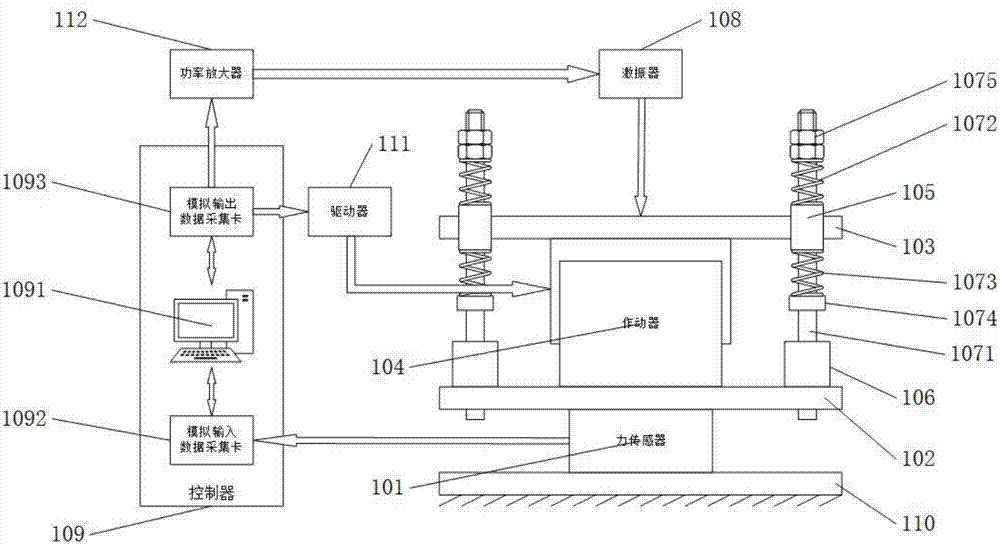
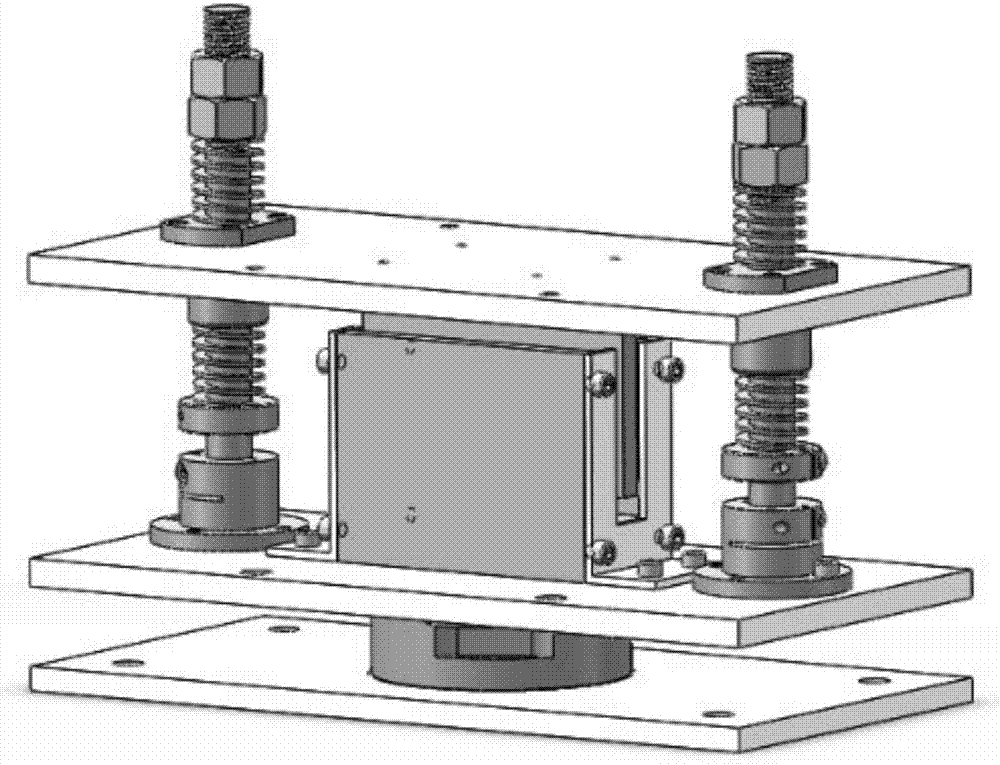
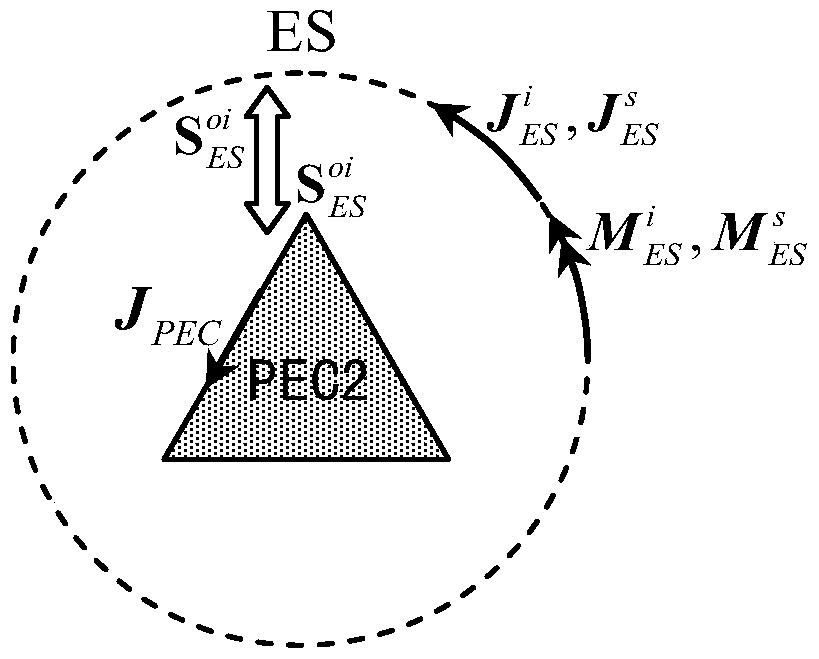
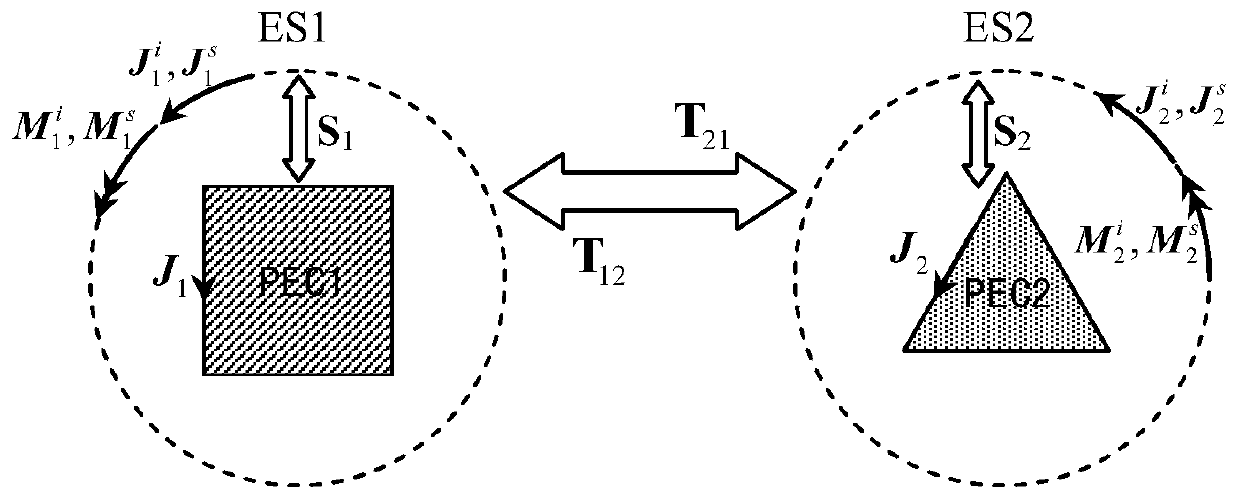
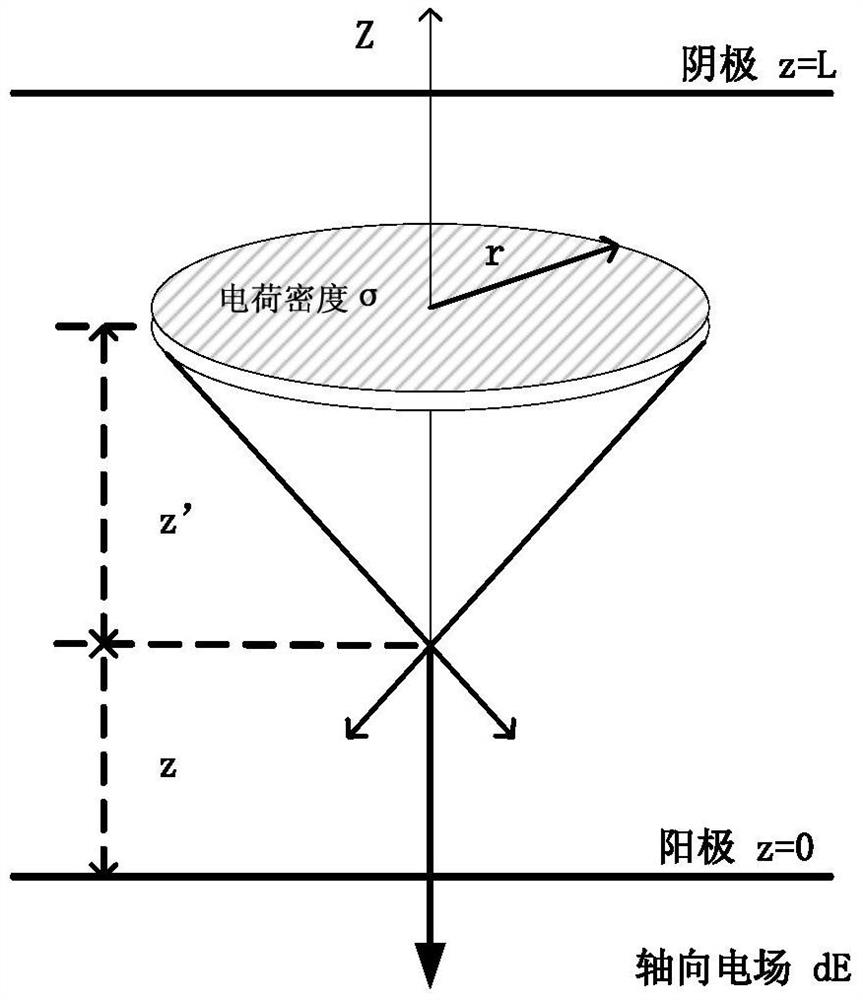
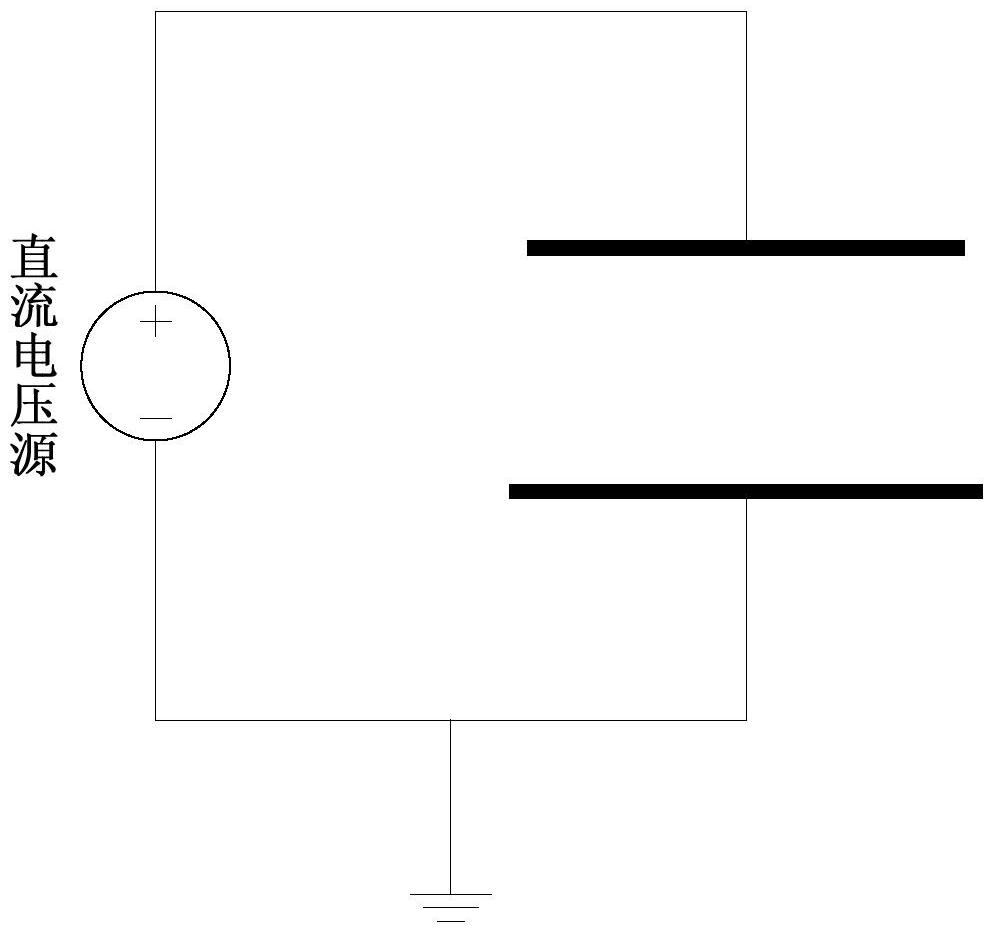
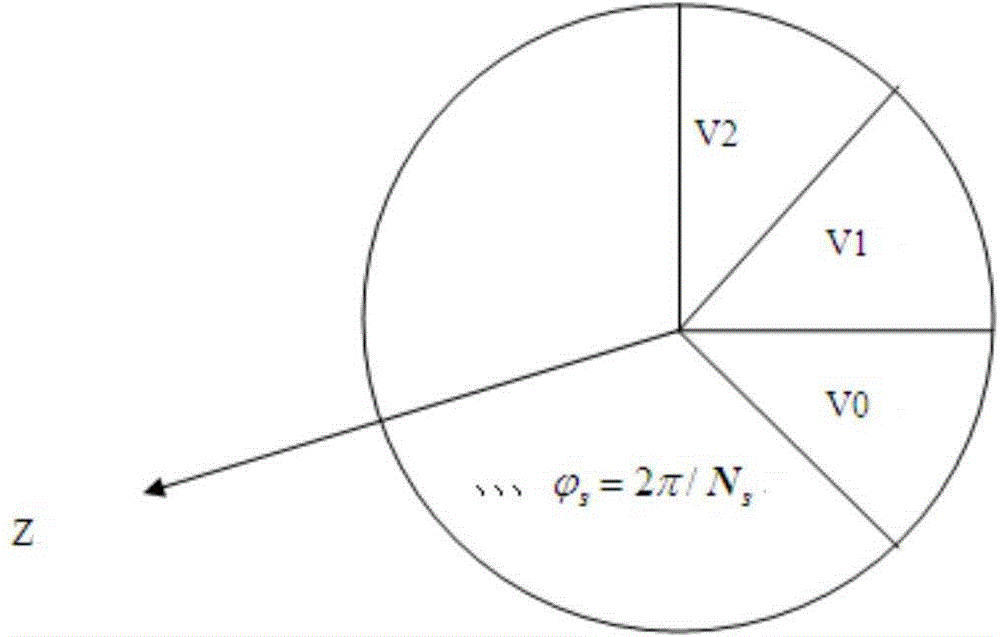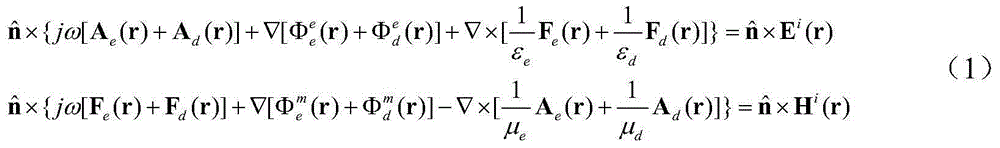Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Little unknown" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
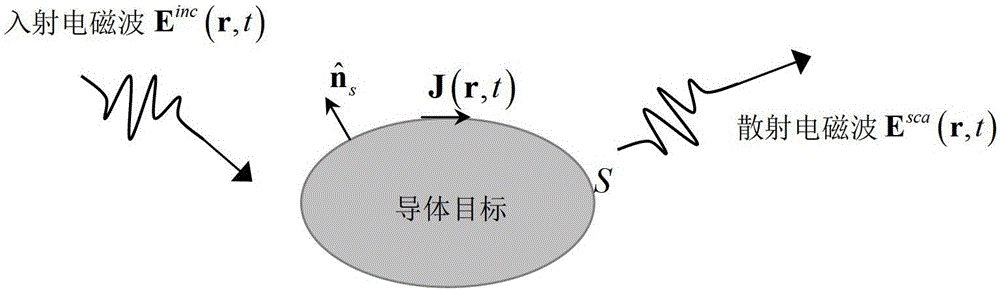
Electromagnetic scattering analyzing method for superspeed flight targets
ActiveCN103198227ALittle unknownFast solutionSpecial data processing applicationsInternal memorySelf adaptive
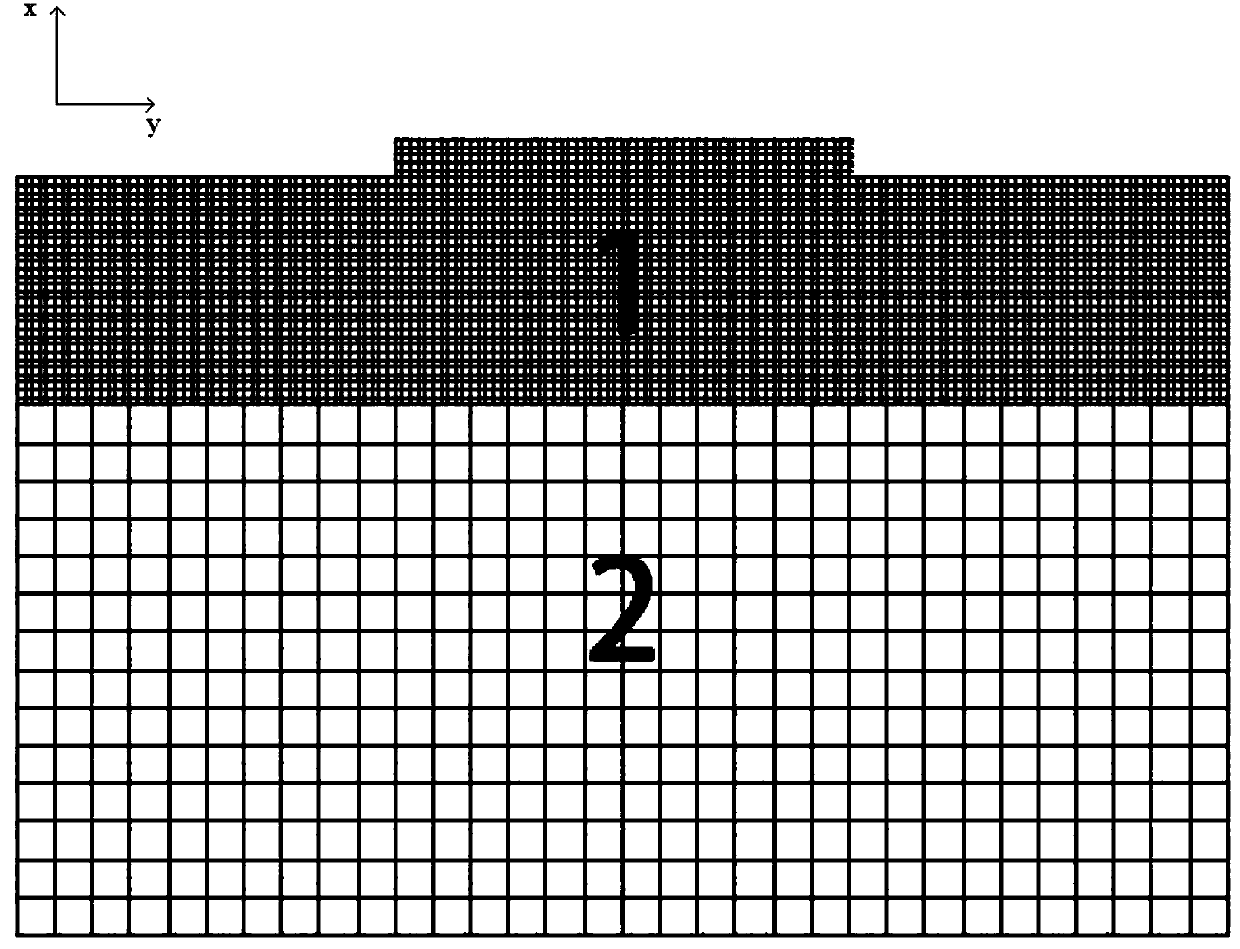
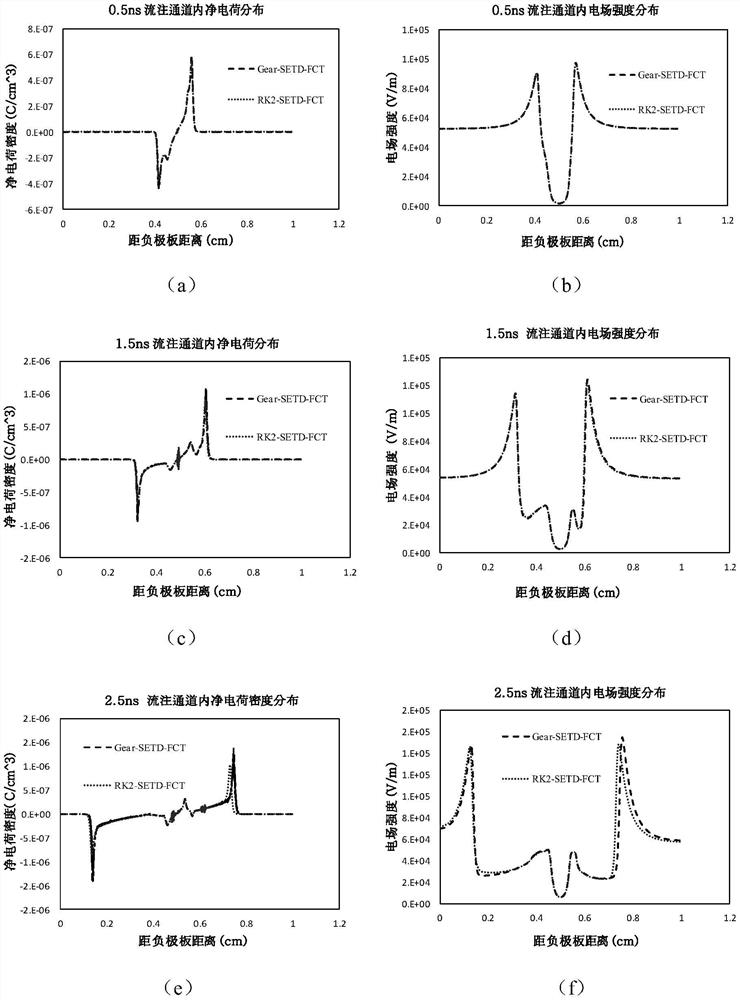
The invention discloses an electromagnetic scattering analyzing method for superspeed flight targets. For non-uniform characteristics of plasmas around the superspeed flight targets, a part of equivalent relative dielectric constant, approximate to one, of the plasmas is used as the air to be processed by analyzing through a volume-surface integer equation, and areas with larger equivalent relative dielectric constant are encrypted by the adaptive network so as to achieve required solving accuracy. By adopting conventional method of uniform grid subdivision plasma casing, the electromagnetic scattering analyzing method can greatly save computing resources, green function adopted in the volume-surface integer equation is green function in vacuum, multilayer speedy multi-step ion technology is used for accelerating solving, so that fewer internal memory and shorter computing time are required for solving the problem of scattering of the superspeed flight targets.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
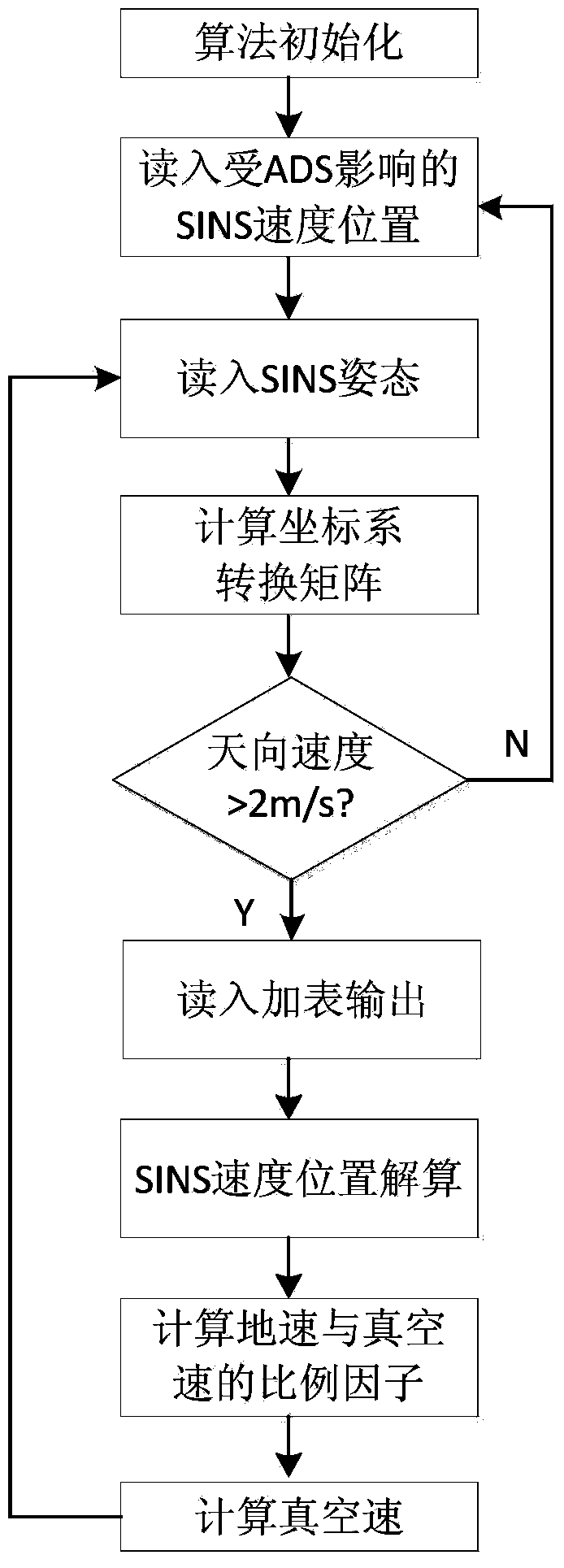
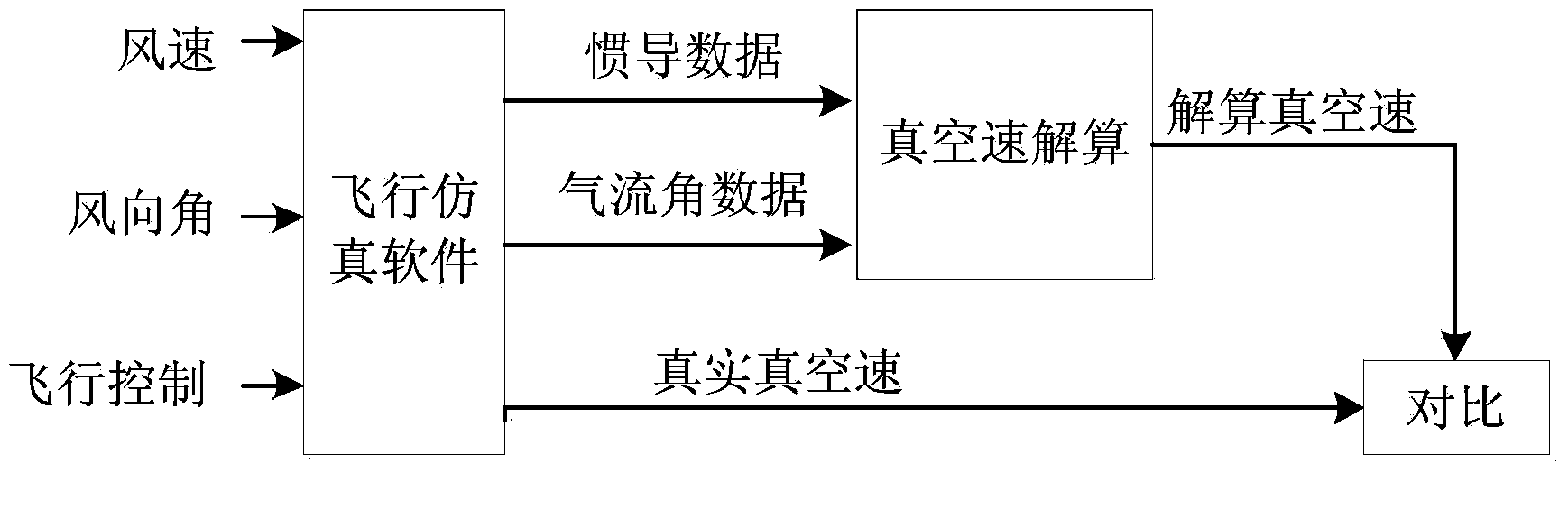
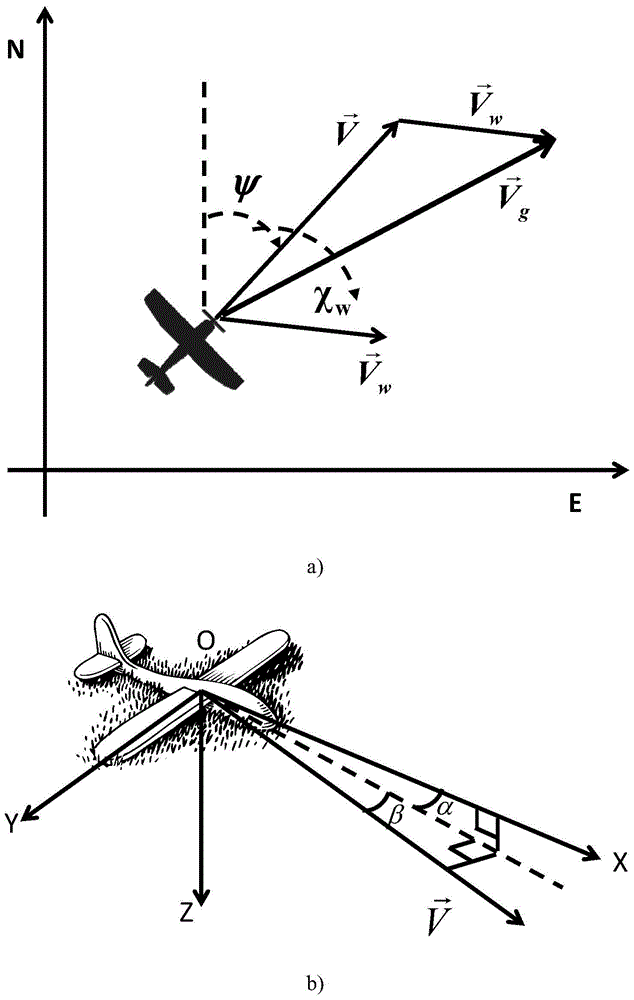
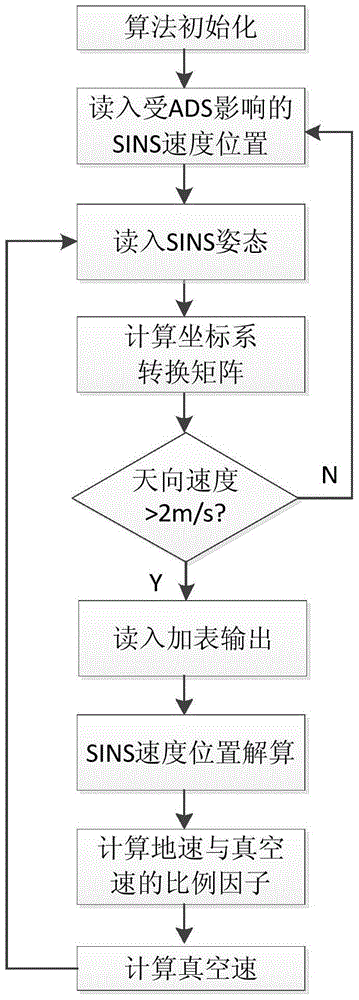
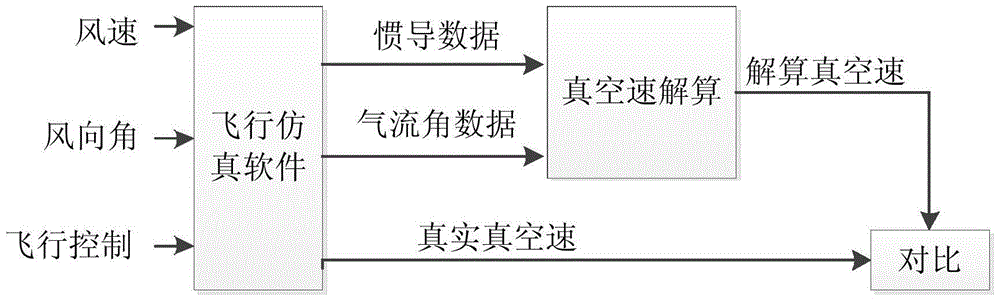
Vacuum speed resolving method for air data/serial inertial navigation combined navigation system
InactiveCN103852081AReduce usageSimplification of calculation method of true air velocityNavigational calculation instrumentsAtmospheric temperatureNavigation system
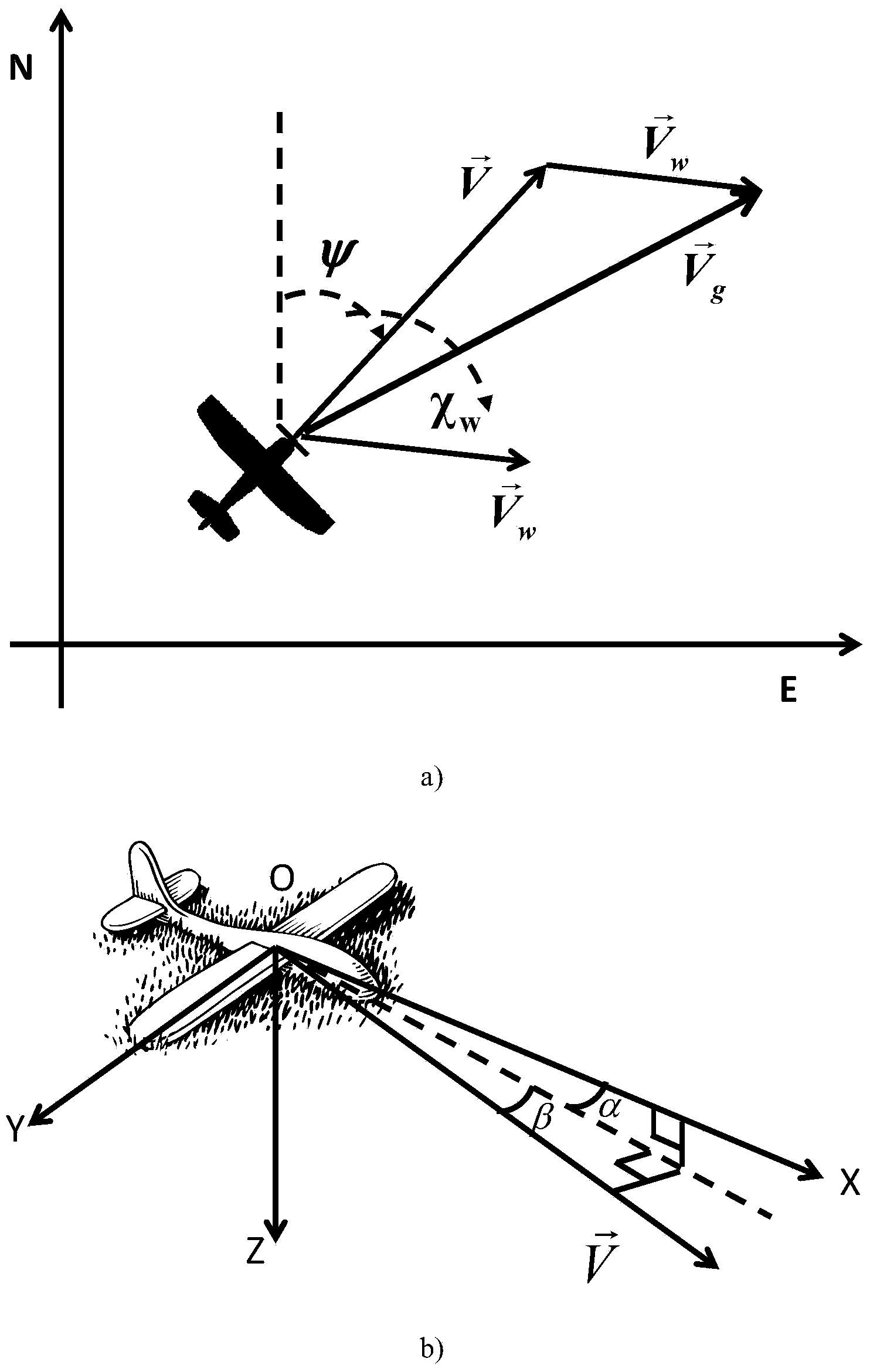
The invention discloses a vacuum speed resolving method for an air data / serial inertial navigation combined navigation system. The method comprises the following steps: calculating a scale factor between the vacuum speed and ground velocity according to a vector relation among the vacuum speed, ground velocity and wind speed based on the characteristic that upper atmosphere is mainly in horizontal flow by utilizing an attack, a sideslip angle and posture of a carrier, and resolving the vacuum speed through numerical calculation. According to the method, the defect that the vacuum speed is severely lagged due to the temperature measurement time constant in a conventional vacuum speed calculation method depending on atmospheric temperature parameters is overcome, and influence of the vacuum speed which is severely influenced by the atmospheric temperature parameters and dependence of uncertain external information of the vacuum speed estimation method on aircraft dynamics parameters are avoided, so that the measuring lag of the vacuum speed and influence on environmental factors are solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
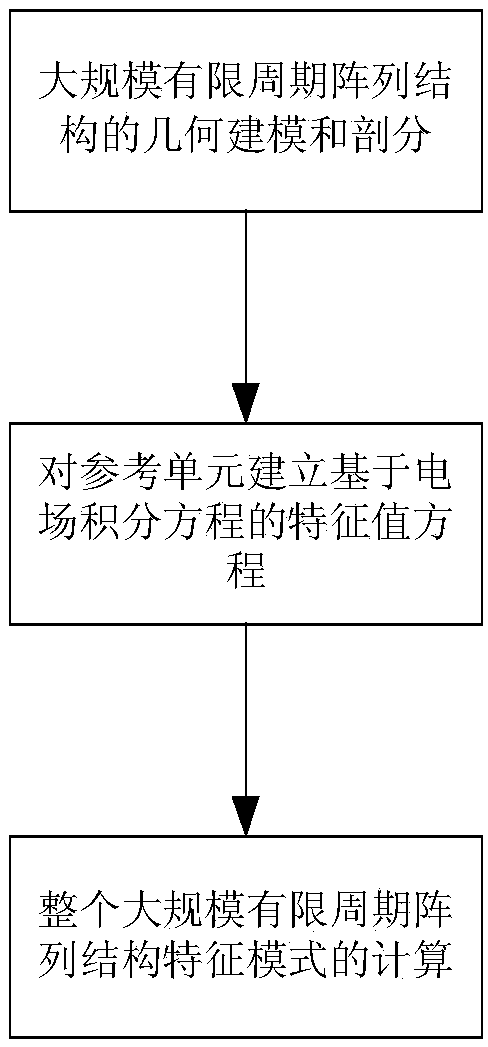
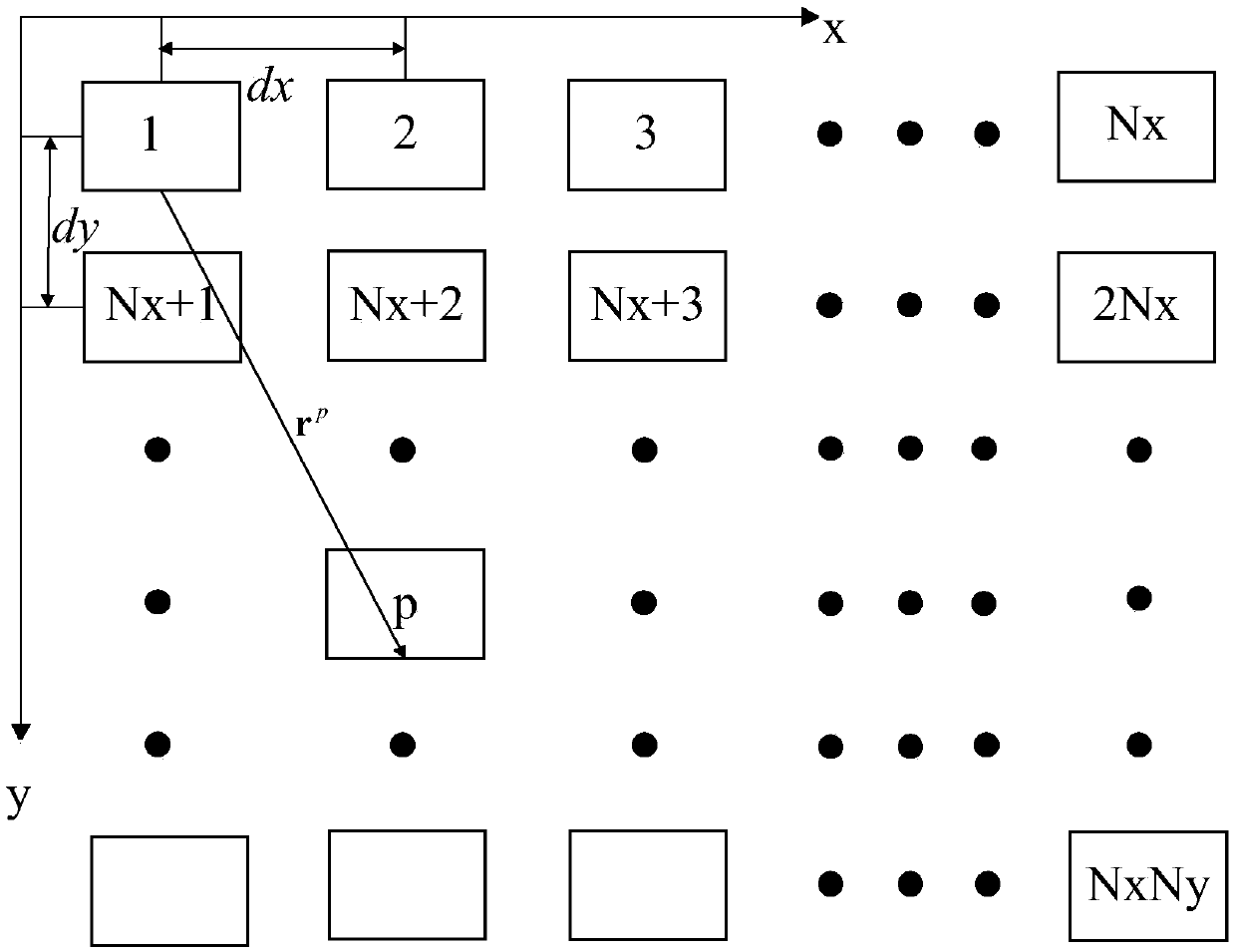
A large-scale finite period array structure characteristic mode analysis method
ActiveCN108959772AReduce the number of unknownsReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsGeometric modelingComputer science
The invention relates to a large-scale finite period array structure characteristic mode analysis method, which solves the defect that the characteristic mode analysis method cannot be applied to thelarge-scale finite period array structure compared with the prior art. The invention comprises the following steps: carrying out geometric modeling and division of a large-scale finite period array structure; establishing an eigenvalue equation based on the electric field integral equation for the reference cell; performing computation of the eigenmodes of a large-scale finite-period array structure. The invention can remarkably reduce the number of unknown quantities of the matrix characteristic equation of the periodic array, and greatly reduce the calculation memory and the calculation timerequired.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Metal target transient electromagnetic scattering analysis method based on delay laguerre polynomials
InactiveCN104915465ALittle unknownSave memorySpecial data processing applicationsTransient electromagneticsReference Document
The invention discloses a metal target transient electromagnetic scattering analysis method based on delay laguerre polynomials. A target is subdivided through curved surface triangle surface elements. Spatial dispersion and time dispersion are carried out on a time domain mixed field integral equation through a CRWG primary function and the delay laguerre polynomials. A test is carried out through a galerkin method. An order-stepped matrix equation is finally formed, and the transient electromagnetic scattering characteristic of the target can be obtained through resolution of the equation and post-processing. As a delay item related to the spatial position of the target is introduced into a time primary function, the time primary function contains the spatial phase information of the target is adopted, and the target can be subdivided with less curved surface triangle surface elements. The unknown calculation amount is greatly reduced, consumption of an inner storage is effectively reduced, the calculation time is shortened, and important reference documents are provided for accurate analysis of the transient electromagnetic scattering characteristic of an electric large-size metal target.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Time domain analysis method for electromagnetic properties of non-uniform rotational symmetric body
ActiveCN106649900AEfficient analysisLittle unknownComplex mathematical operationsDiscretizationRadar cross-section
The invention discloses a time domain analysis method for electromagnetic properties of a non-uniform rotational symmetric body. The method comprises the steps that in a space domain, triangular patch discretization is adopted for an axial section of a target on a dielectric part, rectangular patch discretization is adopted on the part adjoining a rotation axis, and a one-dimensional scalar triangular basis function is adopted on a metal part to perform line segmentation on a generatrix of the target, and a Laguerre polynomial is adopted as a time basis function of a whole time domain to perform discretization; a body surface integral equation of the non-uniform rotational symmetric body is established according to boundary conditions, a source expanded in a Fourier mode after being subjected to space and time discretization is plugged into the body surface integral equation, and a Galerkin test is adopted to obtain a matrix equation under all modes and all orders finally; the matrix equation is solved to obtain dielectric body current coefficients and metal surface current coefficients under different modes and different orders; at last, the bistatic radar scattering sectional area of a target scatterer under a broadband is determined. Through the method, computing resources can be saved, and computing efficiency can be improved, and the method has quite high practical engineering application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electric-heat integrated analysis method for MESFET under action of high-power electromagnetic pulses
ActiveCN106156388AFlexible modelingEasy to divideSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical field strengthCharge carrier mobility
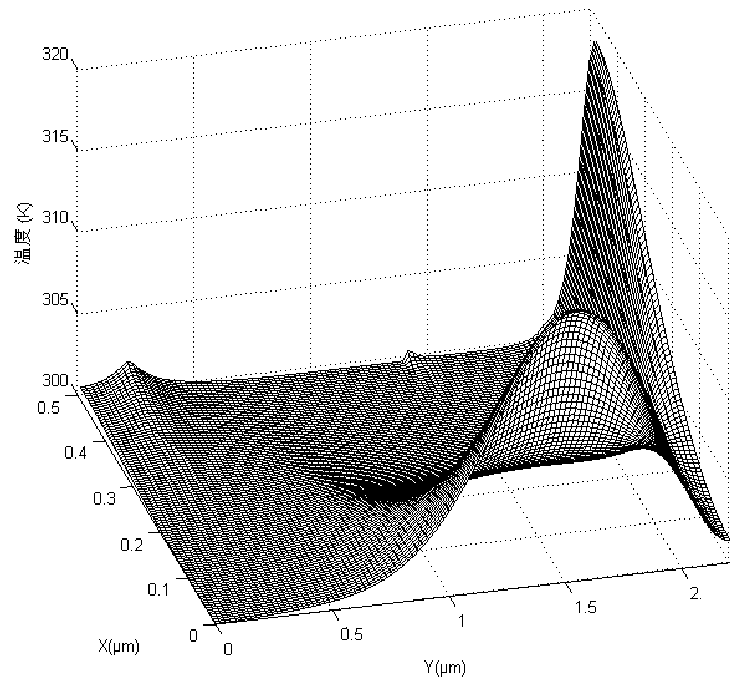
The invention discloses an electric-heat integrated analysis method for a MESFET under the action of high-power electromagnetic pulses. The method comprises the steps that a drifting-diffusing equation set is solved by taking the electronic quasi Fermi potential, the hole quasi Fermi potential and the electric potential as variables and adopting a time domain spectral-element method to solve the instaneous quasi Fermi potential and electric potential of the metal-semiconductor field effect tube (MESFET) under the action of the high-power pulses, and then the electric field intensity and the current density at the moment are obtained; temperature distribution of all positions at the moment can be obtained under the action of a joule heat source by considering the influences of ambient environment temperature and heat convection; the carrier mobility and the generation-recombination rate are updated according to temperature changes, electric field distribution is recalculated, the steps are repeatedly conducted until the drifting-diffusing equation set meets the convergence precision, and electric field distribution and heat distribution at the moment are to-be-solved electric-heat distribution inside the MESFET at the moment. The method is achieved on the basis of a MESFET physical model, and the distribution conditions, changing along with time, of an electric field and the temperature in a device under the action of the high-power electromagnetic pulses can be clearly obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
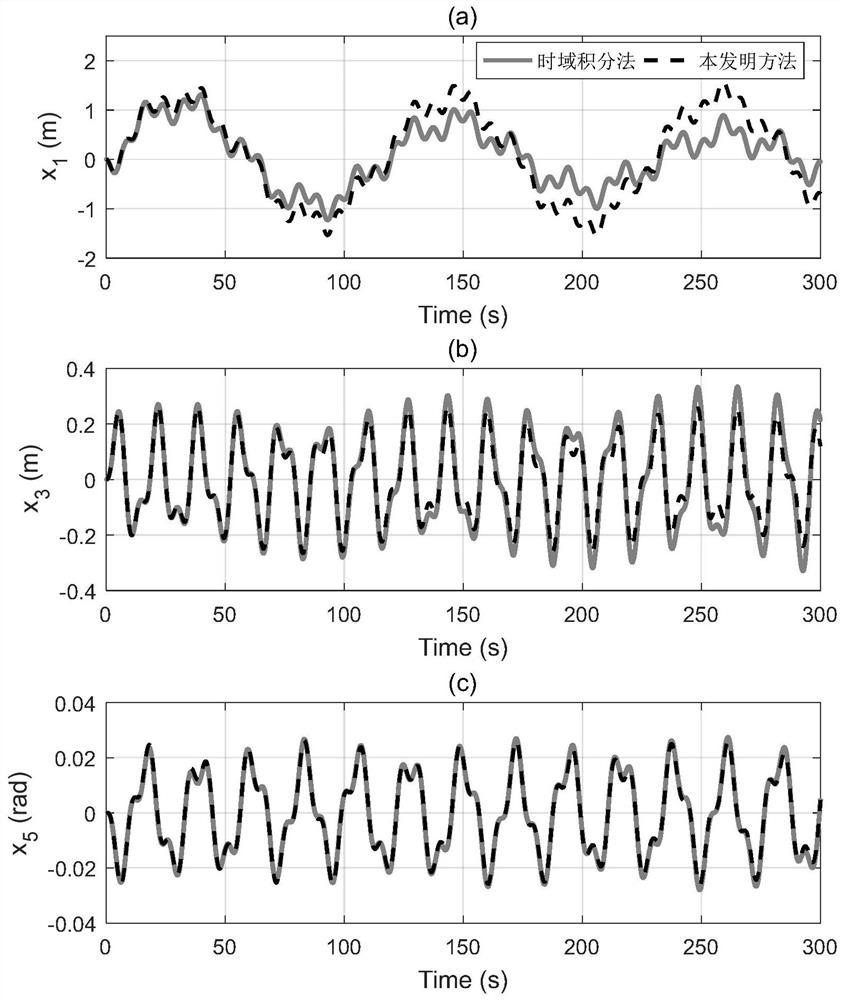
Dynamic response solving method suitable for ocean floating structure
ActiveCN113673076AAvoid complex solutionsSimplify the solution processDesign optimisation/simulationWind energy generationTime domainState space
The invention belongs to the technical field of ocean engineering dynamic calculation, and provides a dynamic response solving method suitable for an ocean floating structure. The method comprises the following steps: S10, establishing a state space model corresponding to a floating structure motion equation, and constructing state space model parameters; S20, based on the floating structure motion equation, constructing a transfer function and a rational score form thereof, and establishing a relationship between the state space model parameters and transfer function coefficients; S30, linearly solving transfer function coefficients in a rational fraction form; S40, according to the solved transfer function coefficients, solving the state space model parameters in a time domain; S50, based on the state space model, substituting the solved state space model parameters, and calculating and forecasting a dynamic response of each freedom degree of of the floating structure. According to the method, high-efficiency calculation and forecasting can be realized, and the forecasting accuracy can be ensured.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Experimental platform used for verifying vibration isolation effect of active control methods
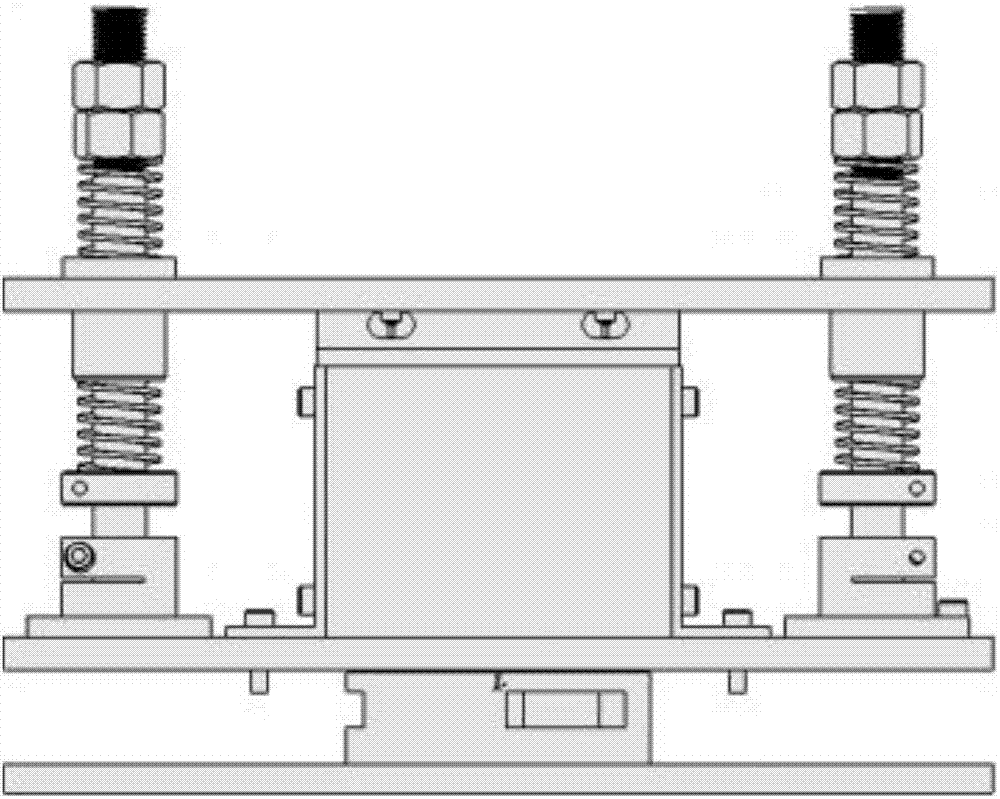
InactiveCN107422721AVersatileEasy to promote and applyElectric testing/monitoringEngineeringForce sensor
The invention discloses an experimental platform used for verifying vibration isolation effect of active control methods. The experimental platform comprises a force sensor, a bearing plate, a floating plate, an actuator, a linear bearing, shaft supporting bases, a rigidity component, a vibration exciter, and a controller. The rigidity component comprises vertical shafts, a first spring, a second spring, a baffle ring, and nuts. The lower surface of the bearing plate is provided with the force sensor, and the upper surface of the bearing plate is provided with the actuator and the two shaft supporting bases. The actuator is provided with the floating plate, and the vibration exciter is corresponding to the floating plate. The floating plate is provided with the linear bearing, and the various vertical shafts pass through the first spring, the linear bearing, the second spring, the baffle ring, and the shaft supporting bases sequentially, and then are connected with the bearing plate, and in addition, the nuts are in a screwed connection with the vertical shafts, and therefore the two springs are in a compressed state. The controller is connected with the force sensor and the actuator, and according to residual force detected by the force sensor, a compensation signal is determined, and according to the compensation signal, actuating force output by the actuator is adjusted. The experimental platform is used for the experimental verification of the vibration isolation effect of the different active control methods.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
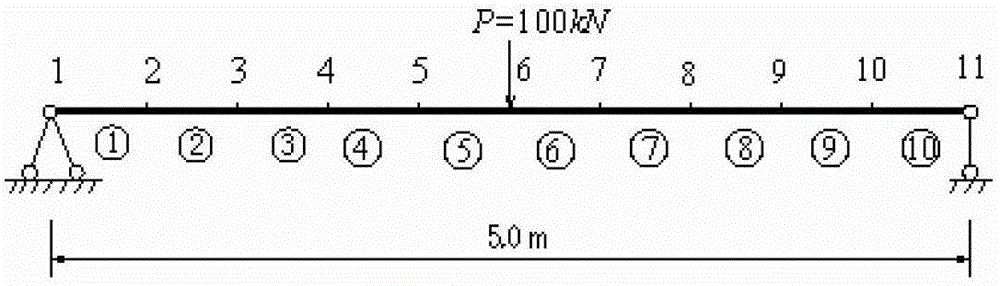
Damage Identification Method for Stochastic Structures Based on Genetic Algorithm and Static Measurement Data
ActiveCN103164627BLittle unknownReduce misjudgmentGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsGenetic algorithmGoverning equation
The invention relates to an identification method of random structural damage based on genetic algorithm and static force measurement data. The identification method of the random structural damage based on the genetic algorithm and the static force measurement data comprises the following steps: (1) preliminarily obtaining statistical properties of random structural damage indexes; (2) defining the probability of unit damage as the random rigidity before occurrence of the damage or the probability that an elastic modulus Kai is larger than Kdi; (3) introducing damage probability indexes, determining several units of the damage probability indexes as non-damage units, and conducting corresponding adjustment on the statistical properties of the damage indexes; (5) going back to the governing equation of the initial damage identification in the step (1), and obtaining the objective function of the structural damage indexes after rearranging; and (6) solving the minimum value of the objective function in the step (5) by means of the genetic algorithm, and obtaining the statistical properties of the damage indexes. The identification method of the random structural damage based on the genetic algorithm and the static force measurement data has the advantages that multiple damage identification of different damage degrees can be carried out due to the fact that the genetic optimized algorithm has little limit on the type, the quantity and the size of the parameter.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Electromagnetic scattering analysis method for ultra-high-speed flying targets
ActiveCN103198227BLittle unknownFast solutionSpecial data processing applicationsUltra high speedAdaptive mesh refinement
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
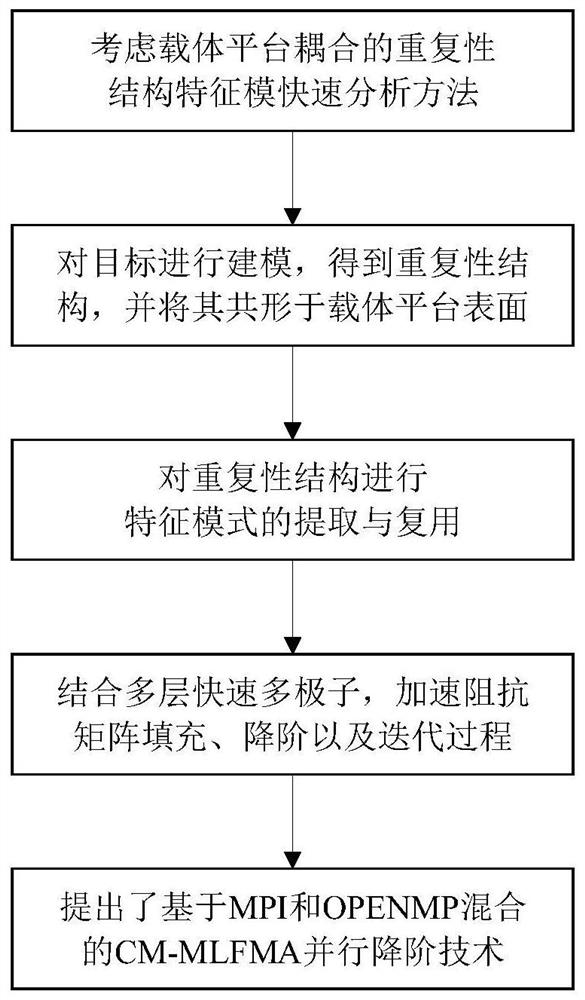
Rapid analysis method for electromagnetic property characteristic model of repetitive structure considering carrier platform coupling
ActiveCN112329204ALittle unknownReduce computational complexitySustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationComputational physicsOrder reduction
The invention discloses a rapid analysis method for an electromagnetic property characteristic model of a repetitive structure considering carrier platform coupling. The method comprises the followingsteps: firstly, integrally modeling the repetitive structure conformal on the surface of a carrier platform; then, for the integrated structure, fully utilizing repetitive characteristics in the structure, introducing a characteristic mode global basis function method to reduce the impedance matrix dimension of the repetitive structure part, and greatly reducing the number of unknown quantities to be solved; then, fusing the multi-layer fast multipole with a feature mode, accelerating a reduced-order impedance matrix filling process and an iteration process, and improving the efficiency; andfinally, using a parallel order reduction technology based on MPI (Message Passing Interface) and OPENMP mixing to reduce the memory consumption and shorten the calculation time. An efficient and accurate analysis tool is provided for numerical optimization and design of a conformal repetitive structure and carrier platform integrated target.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
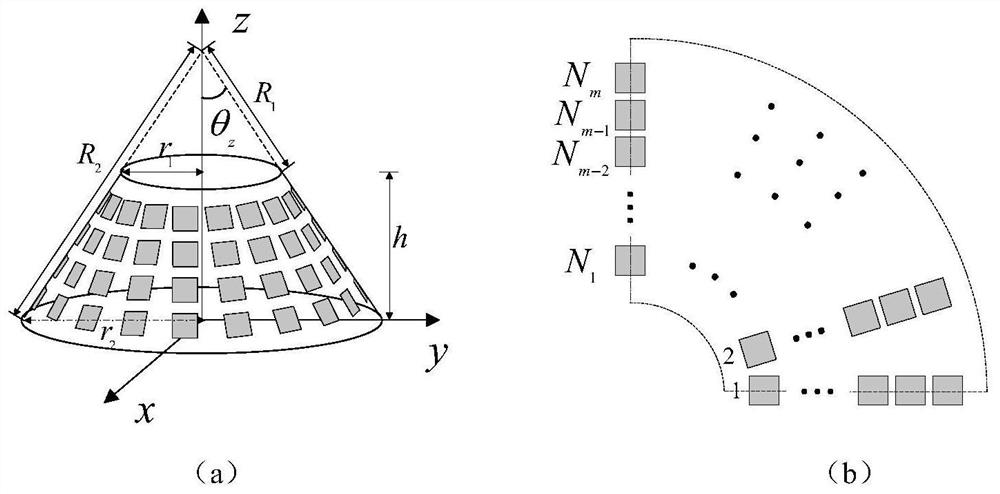
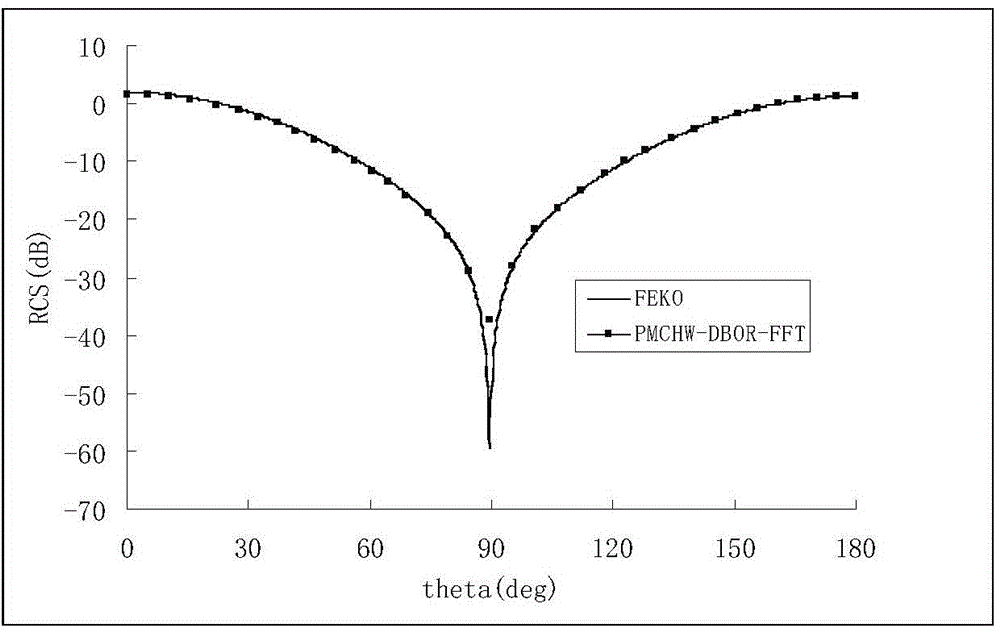
Frequency-domain electromagnetic scattering characteristic analysis method for dielectric object with cylindrical periodic characteristics
InactiveCN105095541AAvoid the build processSimple modelSpecial data processing applicationsClassical mechanicsAnalysis method
The invention discloses a frequency-domain electromagnetic scattering characteristic analysis method for a dielectric object with cylindrical periodic characteristics. When the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of the dielectric object with a cylindrical periodic structure is calculated by adopting a surface area integral equation (PMCHW), the whole object with the periodic structure needs to be subjected to electromagnetic modeling, and a modeling mode is relatively cumbersome especially for a complicated structure with more cycles. For the object with the cylindrical periodic characteristics, the object can be calculated with a discrete rotational symmetric method (DBOR) and only one complete periodic region in the periodic structure needs to be modeled, so that the establishment of a complicated model is avoided, the unknown quantity of subdivision is reduced, the matrix filling time is greatly shortened, and a memory is saved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
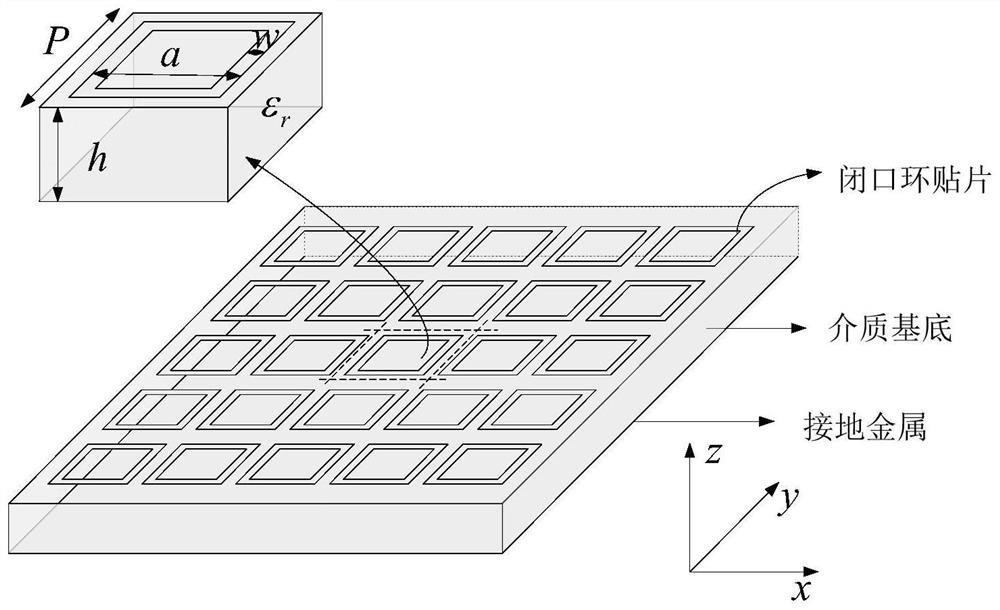
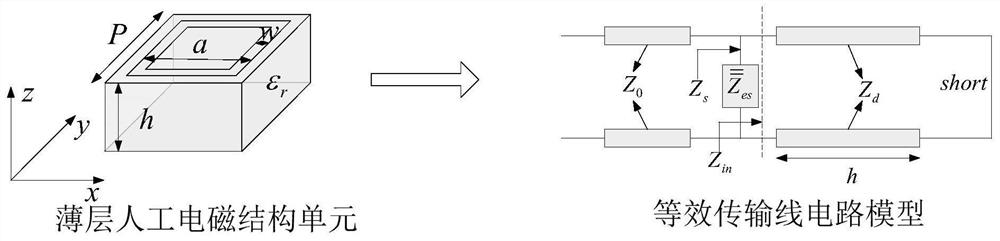
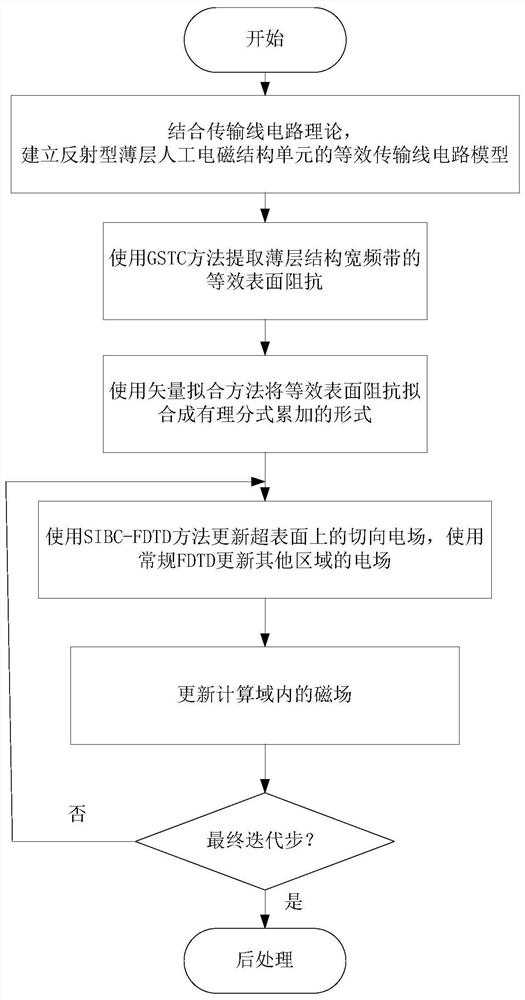
Time domain analysis method of thin-layer electromagnetic structure based on surface impedance boundary
ActiveCN112380737AEffective simulationSimulation is accurateDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsModel extractionFull wave
The invention discloses a time domain analysis method of a thin-layer electromagnetic structure based on a surface impedance boundary. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an equivalent transmission line circuit model of a thin-layer artificial electromagnetic structure unit by applying an equivalent transmission line circuit theory; extracting equivalent surface impedance of thethin-layer artificial electromagnetic structure unit, and fitting the equivalent surface impedance of the broadband into a rational fraction accumulation form by adopting a vector fitting method; carrying out full-wave simulation on the structure by using a time domain finite difference method based on a surface impedance boundary condition, wherein the surface impedance boundary condition is used for replacing a thin-layer artificial electromagnetic structure unit in the simulation process; and carrying out post-processing on the electromagnetic field obtained by the full-wave simulation. According to the method, for calculating the thin-layer artificial electromagnetic structure, the longitudinal and transverse calculation unknown quantities of the thin-layer structure are remarkably reduced, the operation time and memory are saved, and high flexibility and effectiveness are achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
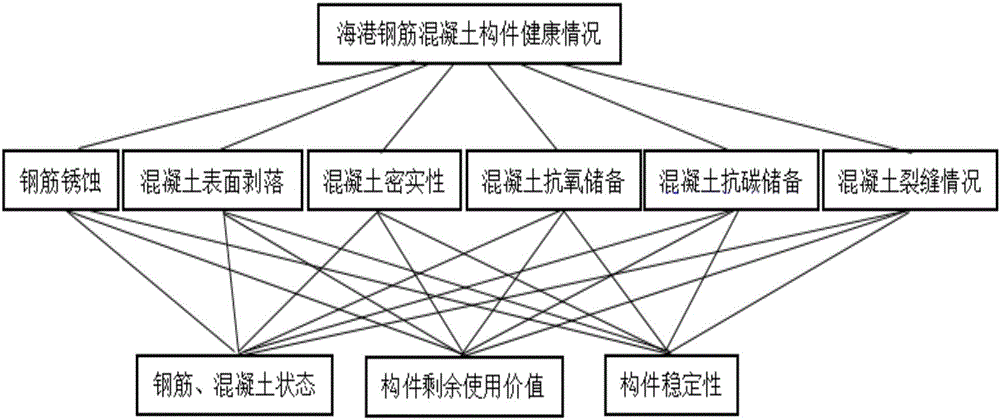
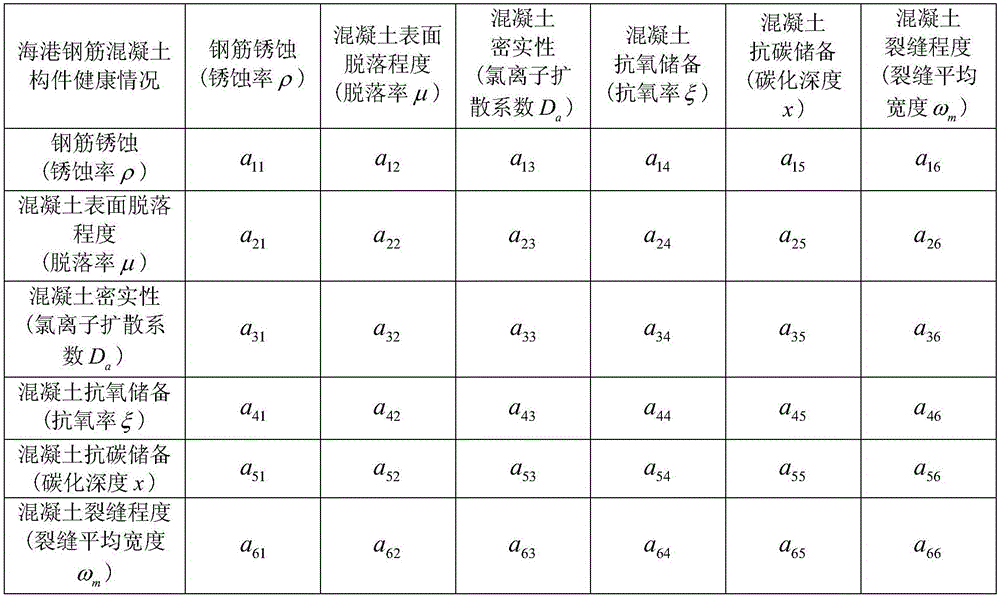
Method for evaluating health indexes of harbor concrete member based on analytic hierarchy process
InactiveCN106599363AEvaluate health indicators specificallyObjective health indicatorsGeometric CADData processing applicationsHealth indexWeight coefficient
The invention provides a method for evaluating the health indexes of a harbor concrete member based on the analytic hierarchy process. The method for evaluating the health indexes of a harbor concrete member based on the analytic hierarchy process comprises the following steps: confirming the target layer, the criterion layer and the decision layer and structuring a judgment matrix; calculating the weight coefficients of the six variables of the criterion layer assigned on the basis of the target layer; and calculating the score of the target layer according to the consistency weight distribution equation to measure the health status of concrete. By means of the analytic hierarchy process provided by the invention to evaluate the health indexes of a harbor concrete member, the working performances of the harbor concrete members can be monitored accurately, and the defects that the calculation amount is large, the calculation time is long and the calculation is difficult to use in routine conditions in the evaluation of concrete health indexes in engineering practice can be solved effectively, and the method for evaluating the health indexes of a harbor concrete member based on the analytic hierarchy process has the advantages of less unknown quantity, small calculation scale, high accuracy and convenient application.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
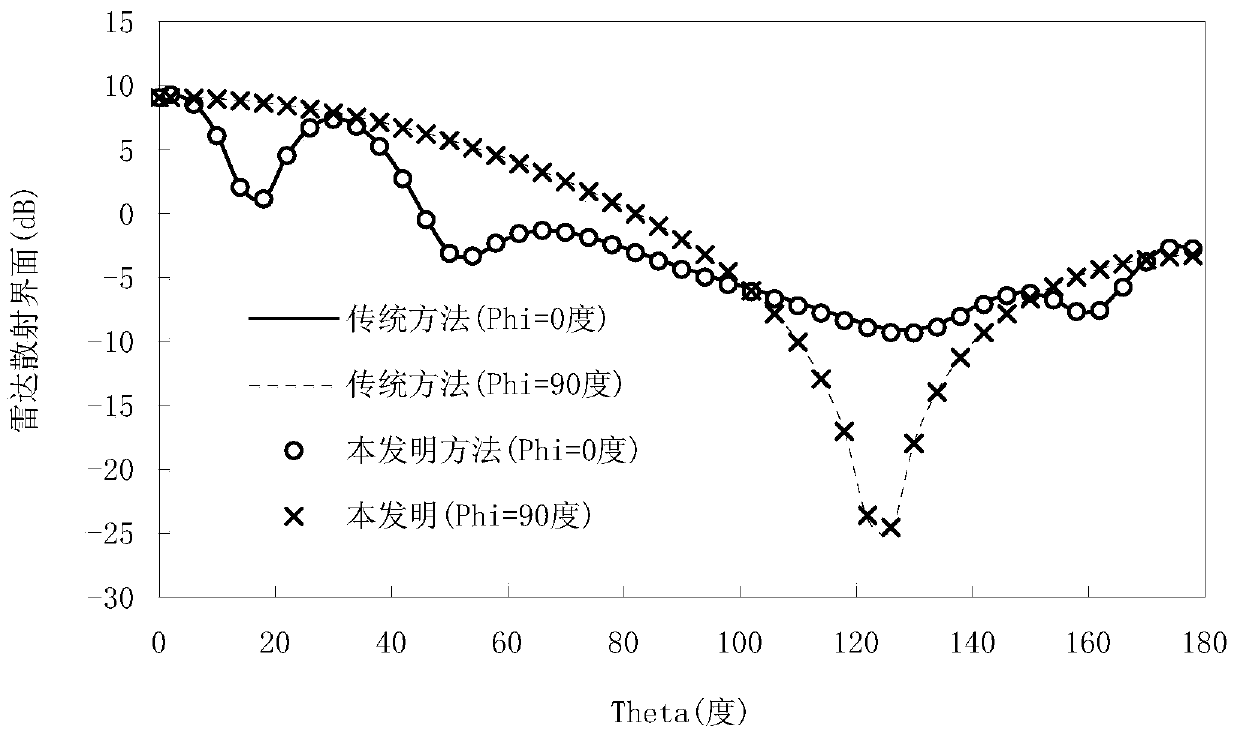
Simulation Method of Broadband Electromagnetic Scattering Characteristics of Conductive Targets
ActiveCN103279601BAccurate descriptionExact discrete fitSpecial data processing applicationsElectrical conductorTime delays
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
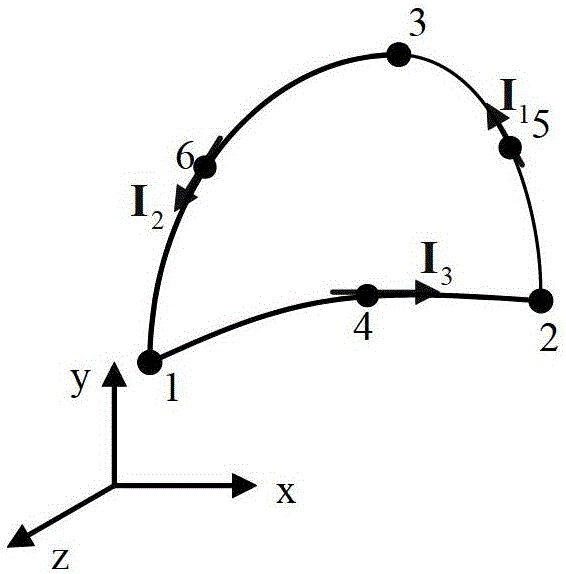
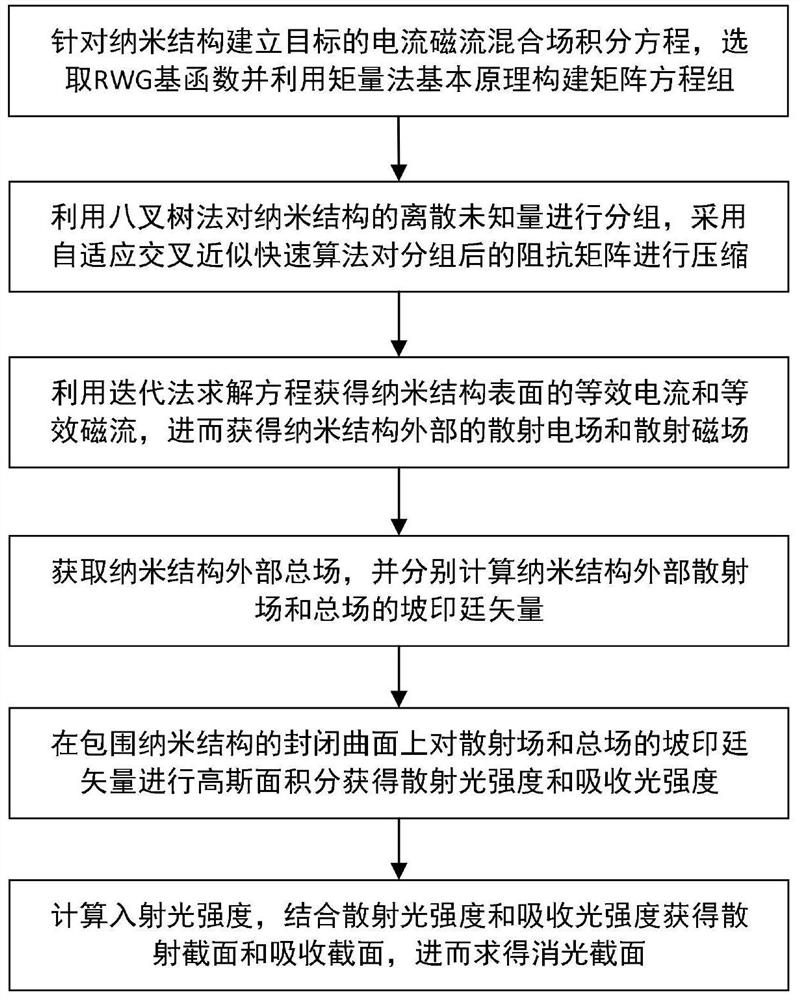
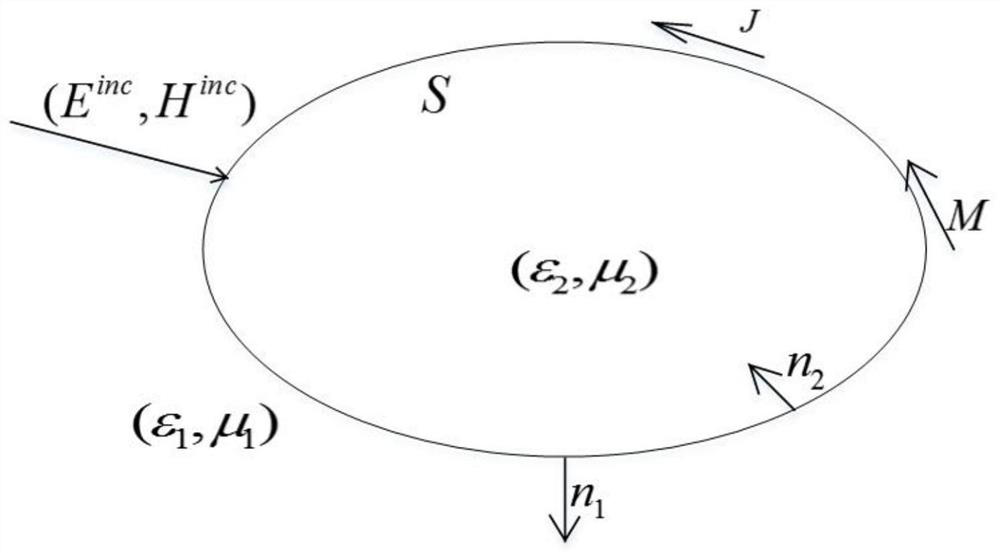
Nanostructure extinction characteristic simulation method based on moment method in combination with adaptive cross approximation fast algorithm
InactiveCN112711856AHigh precisionLittle unknownDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingNumerical methodologyFast algorithm
The invention discloses a nanostructure extinction characteristic simulation method based on a moment method in combination with an adaptive cross approximation fast algorithm. According to the method, a moment method in an integral equation method is adopted for solving, and compared with a traditional numerical method such as a finite element method based on a differential equation method, dispersion errors do not exist, and the accuracy is high. According to the method, the extinction characteristic of the large-scale nanostructure can be solved by combining the adaptive cross approximation fast algorithm on the basis of the moment method, transplantation can be conveniently carried out under different background media, and the application range is wide.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Identification method of random structural damage based on genetic algorithm and static force measurement data
ActiveCN103164627ALittle unknownReduce misjudgmentGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsElastic modulusStatic force
The invention relates to an identification method of random structural damage based on genetic algorithm and static force measurement data. The identification method of the random structural damage based on the genetic algorithm and the static force measurement data comprises the following steps: (1) preliminarily obtaining statistical properties of random structural damage indexes; (2) defining the probability of unit damage as the random rigidity before occurrence of the damage or the probability that an elastic modulus Kai is larger than Kdi; (3) introducing damage probability indexes, determining several units of the damage probability indexes as non-damage units, and conducting corresponding adjustment on the statistical properties of the damage indexes; (5) going back to the governing equation of the initial damage identification in the step (1), and obtaining the objective function of the structural damage indexes after rearranging; and (6) solving the minimum value of the objective function in the step (5) by means of the genetic algorithm, and obtaining the statistical properties of the damage indexes. The identification method of the random structural damage based on the genetic algorithm and the static force measurement data has the advantages that multiple damage identification of different damage degrees can be carried out due to the fact that the genetic optimized algorithm has little limit on the type, the quantity and the size of the parameter.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
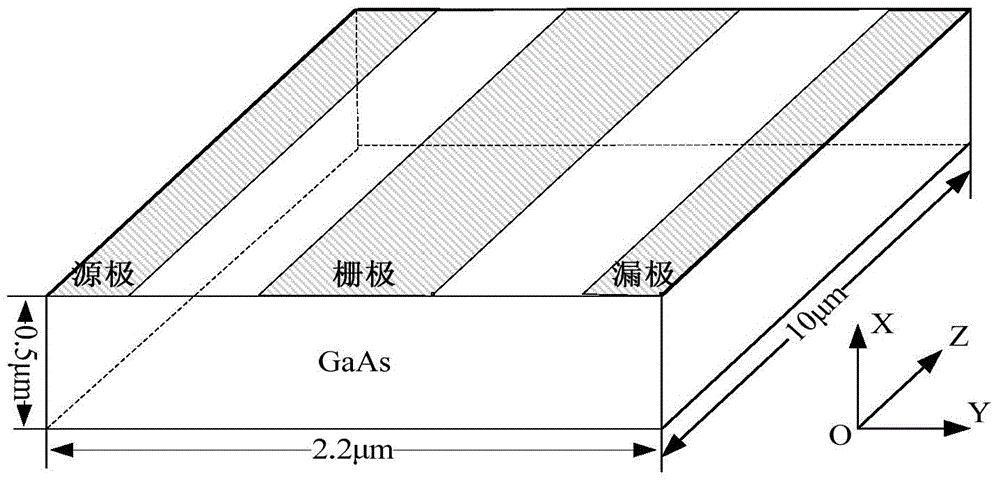
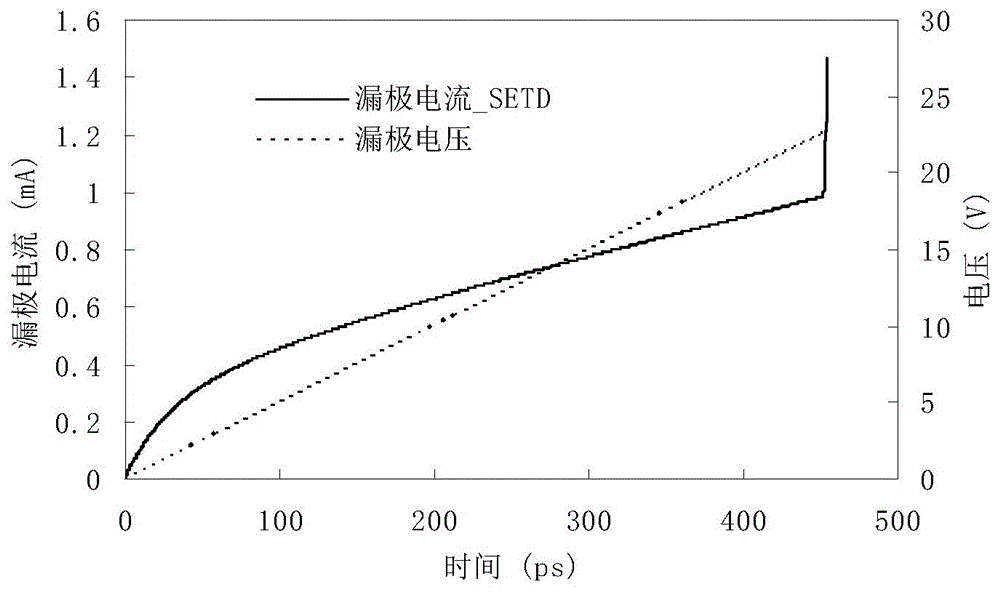
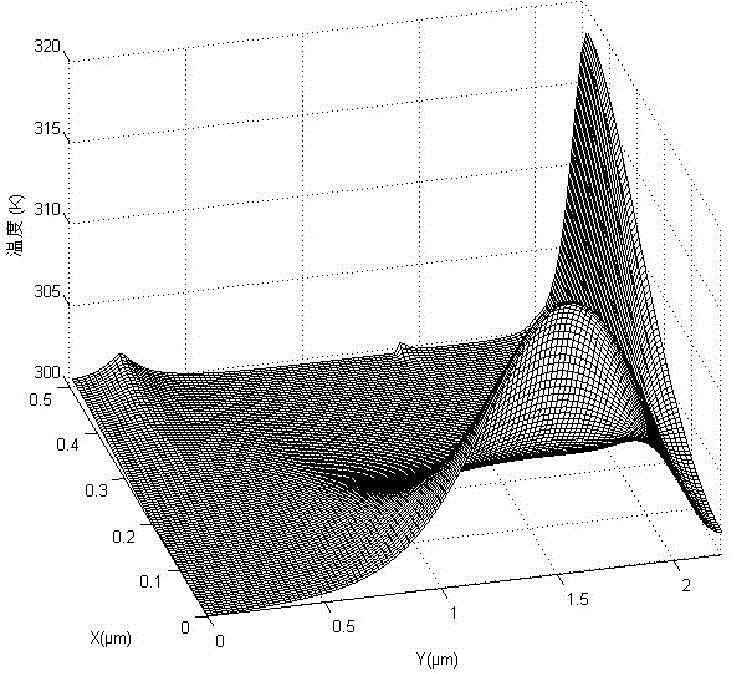
Electric field analysis method of electromagnetic pulse nano-semiconductor device
ActiveCN109543205ASolve problems of different sizesFlexible modelingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDevice materialElectromagnetic pulse
The invention discloses an electric field analysis method of an electromagnetic pulse nano semiconductor device. The steps of the method are as follows: in the first step, the solution model of MOSFETis established, and the model is divided by using the curved hexahedrons to obtain the structural information of the model, including the element information and node information of the hexahedron; in the second step, starting from the carrier current continuity equation, Poisson equation and carrier quantum correction equation, the backward Euler time difference is used firstly, then the discontinuous Galerkin method is used to test the equation, and the electric field boundary condition is imposed to obtain the electric field and current distribution of each node. On the premise of the samecalculation amount, Under the action of electromagnetic pulse and voltage, the distribution of the internal electric field with time can be obtained more clearly, which can reduce the computational load when the convergence accuracy is the same. In addition, the method has the advantages of flexible modeling and convenient dissection, and the formed matrix has good sparsity and high efficiency ofsolution.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
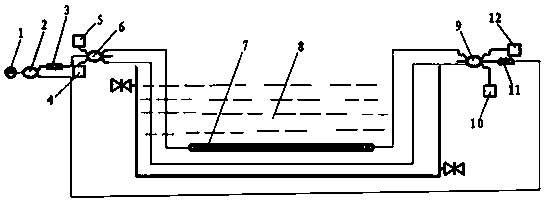
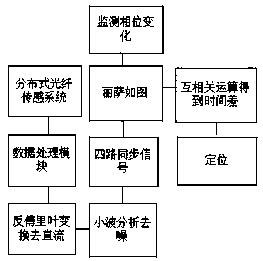
Submarine natural gas pipeline leakage monitoring experimental platform and data processing method thereof
PendingCN108131569AReduce the number of applicationsReduce lossPipeline systemsDesign optimisation/simulationOcean bottomEngineering
The invention discloses a submarine natural gas pipeline leakage monitoring experimental platform and a data processing method thereof. The submarine natural gas pipeline leakage monitoring experimental platform comprises an optical path system, a photoelectric detection system, a signal processing system and a scene simulation system. The optical path system is provided with a first optical fiberset and a second optical fiber set in a connected mode. The first optical fiber set enters the scene simulation system in the clockwise direction and penetrates out of the scene simulation system, and the second optical fiber set enters the scene simulation system in the counterclockwise direction and penetrates out of the scene simulation system. The first optical fiber set and the second optical fiber set penetrate out of the scene simulation system and then are connected with the photoelectric detection system, and the photoelectric detection system is in circuit connection with the signalprocessing system. The submarine natural gas pipeline leakage monitoring experimental platform and the data processing method thereof have the beneficial effects that by adopting the experimental platform, the application number of optical instruments is greatly decreased, the loss of optical power on an optical path and unnecessary interference are greatly reduced, setting-up of the optical pathof the experimental platform is easy, and meanwhile, the experimental cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
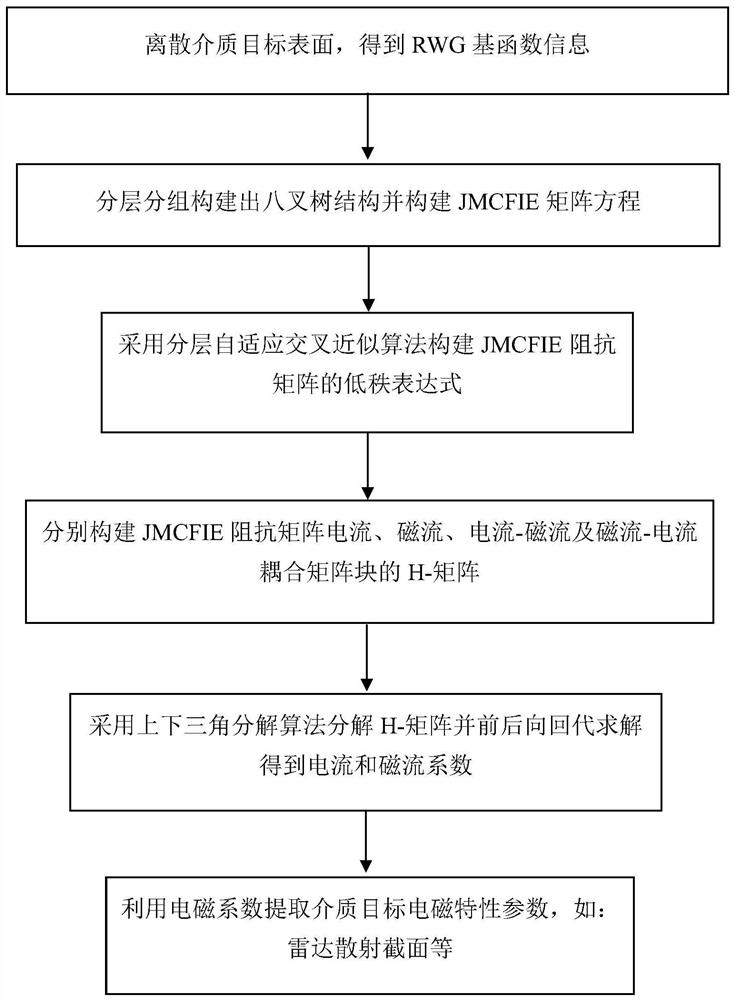
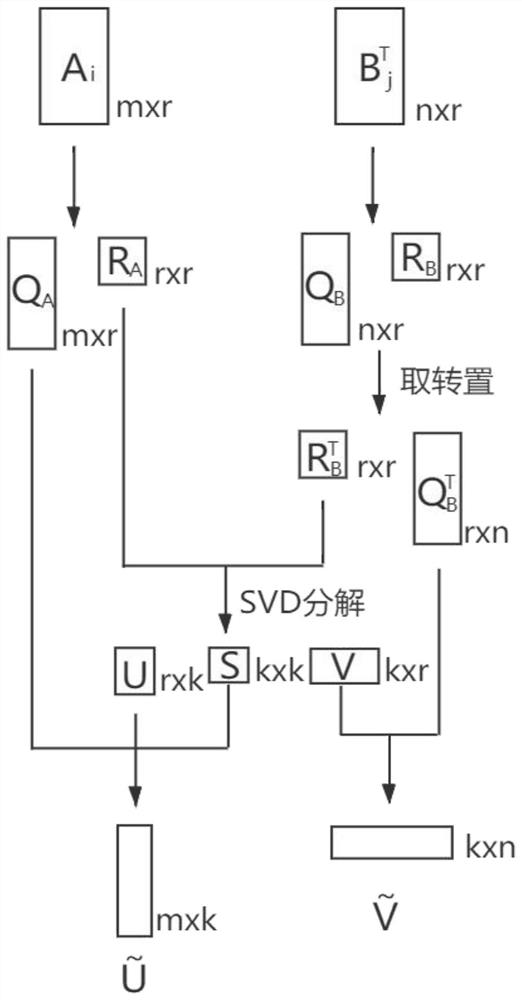
Integral equation direct solving method for analyzing electromagnetic characteristics of medium target
InactiveCN113158409AWide range of applicationsThe solution process is stableDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsComputational physicsSingular value decomposition
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Electrothermal integration analysis method of mesfet under the action of high power electromagnetic pulse
ActiveCN106156388BFlexible modelingEasy to divideDesign optimisation/simulationElectrical field strengthCharge carrier mobility
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Manifold Mapping Algorithm Based on High and Low Order Time Domain Spectral Element Method
ActiveCN107818201BSimple and fast operationEasy and flexible operationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationTime domainMicrowave
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
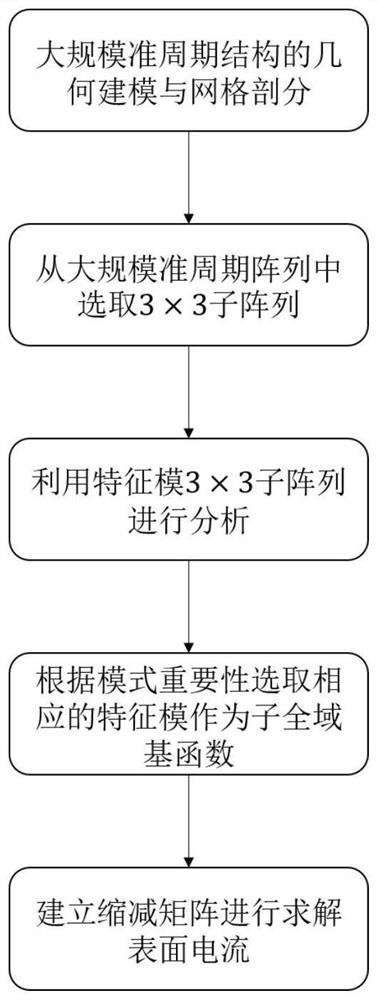
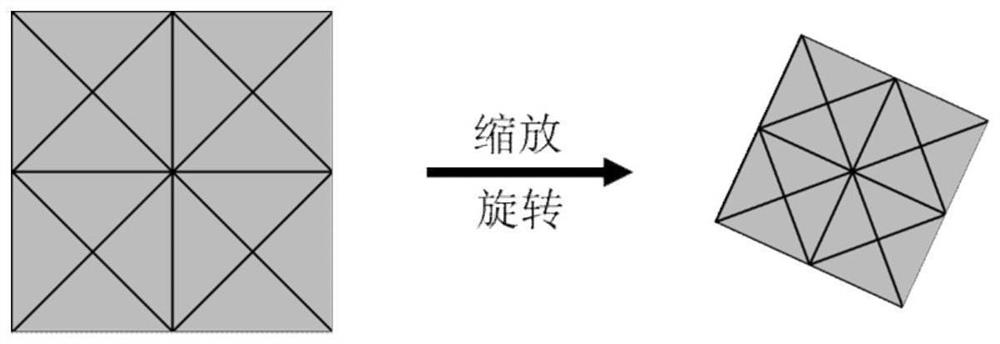
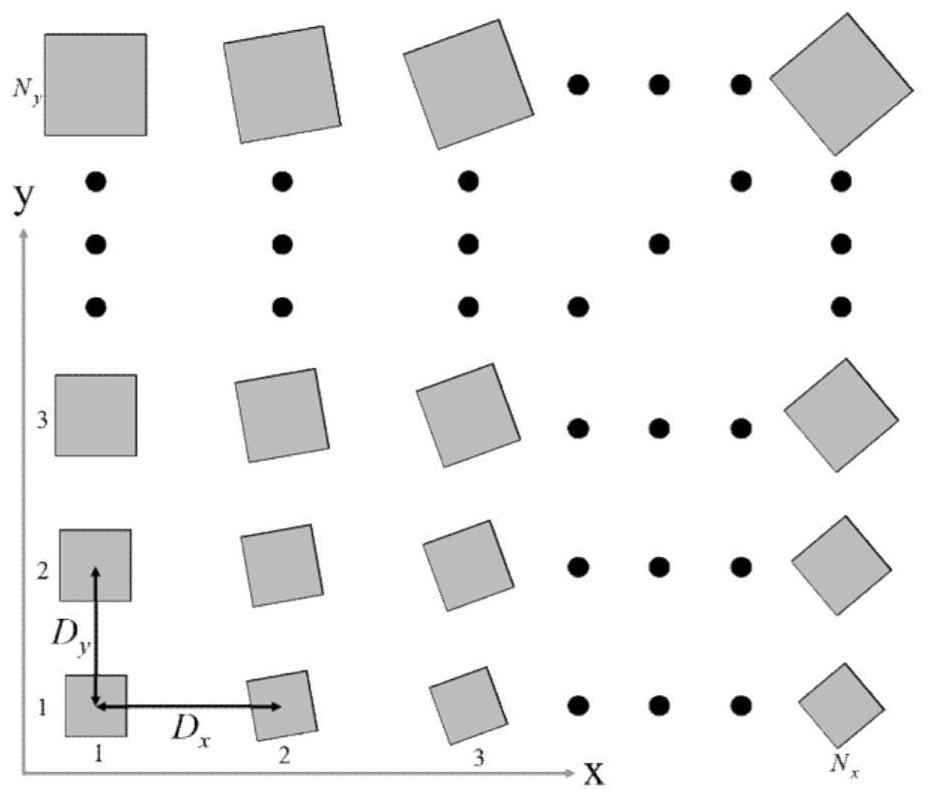
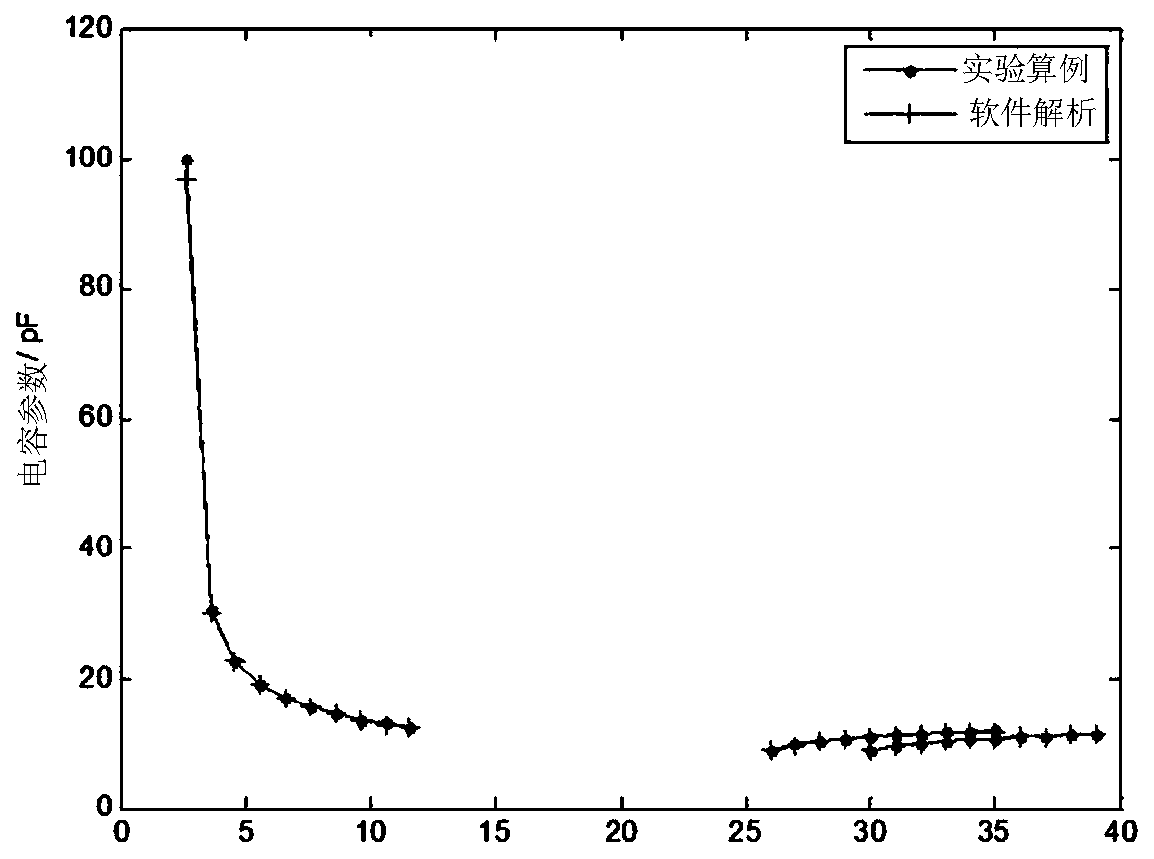
Large-scale quasi-periodic structure electromagnetic scattering characteristic analysis method based on sub-global basis function method
ActiveCN111832157ALittle unknownSimple modelDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsComputational physicsBasis function
The invention discloses a large-scale quasi-periodic structure electromagnetic scattering characteristic analysis method based on a sub-global basis function method. The method makes full use of the physical characteristics of a quasi-periodic structure and extracts a main characteristic current mode as a sub-global basis function through a characteristic model, thereby greatly reducing the complexity of solution and improving the calculation efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Complex cable bundle distribution parameter modeling method based on moment method
ActiveCN110909481ABreak through the constraintsLittle unknownDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingCapacitanceElectrical conductor
The invention provides a complex cable bundle distribution parameter modeling method based on a moment method. By combining a Maxwell equation set with the physical characteristics of a cable bundle,the complex cable bundle distribution parameter modeling method solves the charge distribution on the surface of a cable so as to obtain the potential distribution of charges and the voltage distribution among cables in the cable bundle, obtains the distributed capacitance parameter of the cable bundle based on the relationship among the capacitance C, the voltage and the charges, and then acquires other distribution parameters of the complex cable bundle according to the relationship among the capacitance C, the inductor L and the conductance G. The complex cable bundle distribution parametermodeling method based on the moment method has the advantages of being high in universality and capable of accurately extracting the distribution parameters of the multi-conductor transmission cablebundle.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS & COMPUTATIONAL MATHEMATICS
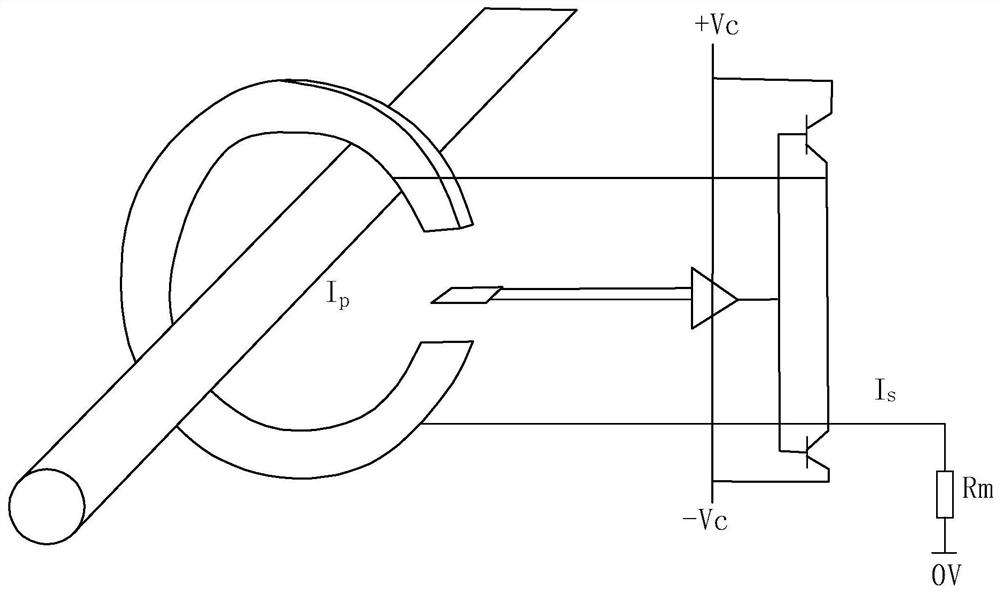
A Simulation Method of Closed-loop Hall Effect Current Sensor
The invention relates to a closed loop Hall effect current sensor simulation method. The correlated matrix coefficients of closed-loop Hall-effect sensors such as structure matrixes C, K, D and a gradient matrix G are calculated, magnetic core circuit models of the closed-loop Hall-effect current sensors are established, core network table files of the closed-loop Hall-effect current sensors are obtained, circuit network table files of closed-loop Hall effect current sensors are generated through line network table converters, the core network table files and circuit network table files of closed-loop Hall effect current sensors are input into HSPICE software, and the closed-loop Hall effect current sensors are subjected to simulated analysis. The closed loop Hall effect current sensor simulation method can more accurately reflect the influence of factors such as magnetic core structures and air gap positions, the unknown quantity is little, and the simulation process is easily converged.
Owner:NINGBO CRRC TIMES TRANSDUCER TECH CO LTD
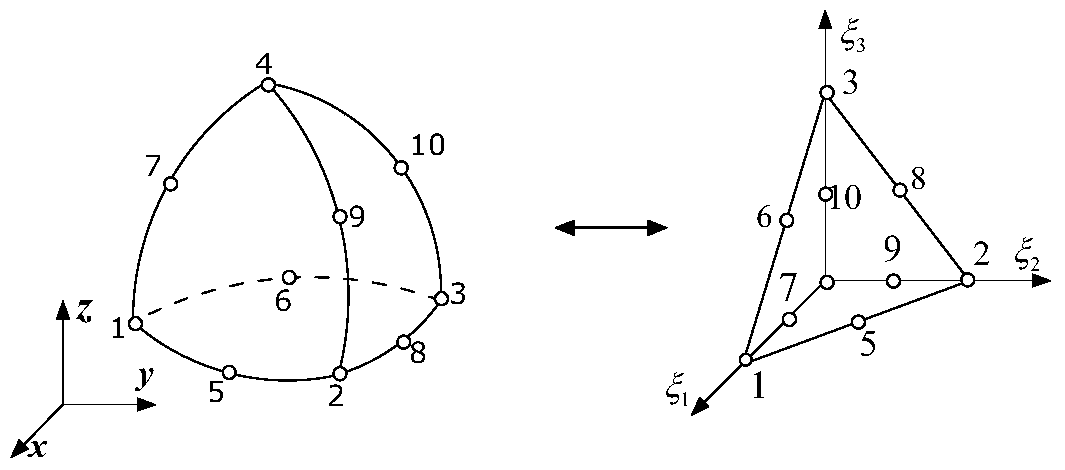
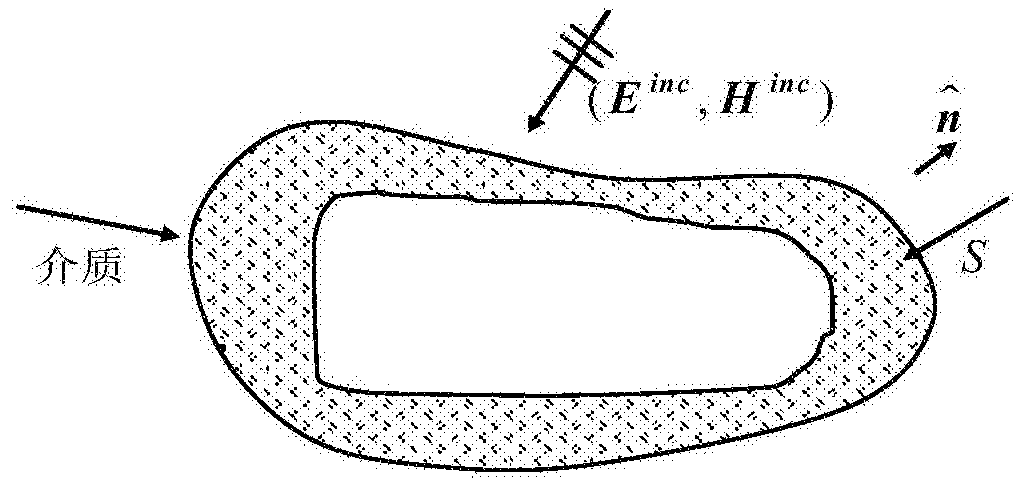
Volume Integral Nystrom Analysis Method of Electromagnetic Scattering in Inhomogeneous Media Targets
ActiveCN104778293BNo current continuity requirementLittle unknownSpecial data processing applicationsElectromagnetic shieldingAnalysis method
The invention discloses a volume integral Nystrom analysis method of inhomogeneous medium target electromagnetic scattering. A high-order curved tetrahedron unit is taken as a partition unit for simulating the shape of an object; a Lagrange interpolation polynomial in each tetrahedron is taken as a current expansion equation; and a Gauss integral point is taken as a Lagrange interpolation point to guarantee that a volume current expression form has high-order precision. A high-order primary function still can be adopted for analysis by aiming at the inhomogeneous characteristics of the object. The high-order primary function is used to enable the method to consume lower computation memory and shorter computation time relative to a traditional method based on a SWG primary function.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
True Air Speed Calculation Method for Air Data/SINS Integrated Navigation System
InactiveCN103852081BReduce usageSimplification of calculation method of true air velocityNavigational calculation instrumentsAtmospheric temperatureNavigation system
The invention discloses a vacuum speed resolving method for an air data / serial inertial navigation combined navigation system. The method comprises the following steps: calculating a scale factor between the vacuum speed and ground velocity according to a vector relation among the vacuum speed, ground velocity and wind speed based on the characteristic that upper atmosphere is mainly in horizontal flow by utilizing an attack, a sideslip angle and posture of a carrier, and resolving the vacuum speed through numerical calculation. According to the method, the defect that the vacuum speed is severely lagged due to the temperature measurement time constant in a conventional vacuum speed calculation method depending on atmospheric temperature parameters is overcome, and influence of the vacuum speed which is severely influenced by the atmospheric temperature parameters and dependence of uncertain external information of the vacuum speed estimation method on aircraft dynamics parameters are avoided, so that the measuring lag of the vacuum speed and influence on environmental factors are solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Time-domain order step-by-step analysis method for transient electromagnetic characteristics of aircraft formation
ActiveCN105277927BReduce consumptionIncrease condition numberWave based measurement systemsDomain analysisElectromagnetic pulse
The invention discloses a time-domain order stepping analysis method for the transient electromagnetic property of an aircraft fleet. According to the method, broadband time-domain electromagnetic pulses serve as excitation to establish a time-domain analysis model of the aircraft fleet; each aircraft is set as a solving sub area, and scattering current of the sub area reaches the equivalent surface surrounding the sub area in an equivalent manner; the equivalent surfaces couples each other to update the equivalent scattering electromagnetic flows at the surfaces continuously till the flows are stable; and the sectional radar scattering area is solved via the final equivalent scattering electromagnetic flows of the equivalent surfaces. Multiple objects can be simulated rapidly in the electromagnetic manner, the method can be used to analyze the transient electromagnetic property of the objects, expansion of an incident field, interaction of the equivalent surfaces and calculation of the sectional radar scattering surfaces all utilize a rotary symmetric moment method, the calculation speed is improved, consumption of memory is greatly reduced, the time-domain order stepping analysis method is post-time stable, and the application value of practical engineering is very high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Numerical Simulation Method of Short Gap Gas Discharge Based on Time Domain Spectral Element Method
ActiveCN107729608BIncrease time stepReduced simulation timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainIon density
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Estimation method of electromagnetic distribution in carbon fiber material flying target under lightning pulse
ActiveCN104732050BFast filling speedImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsFiberFrequency spectrum
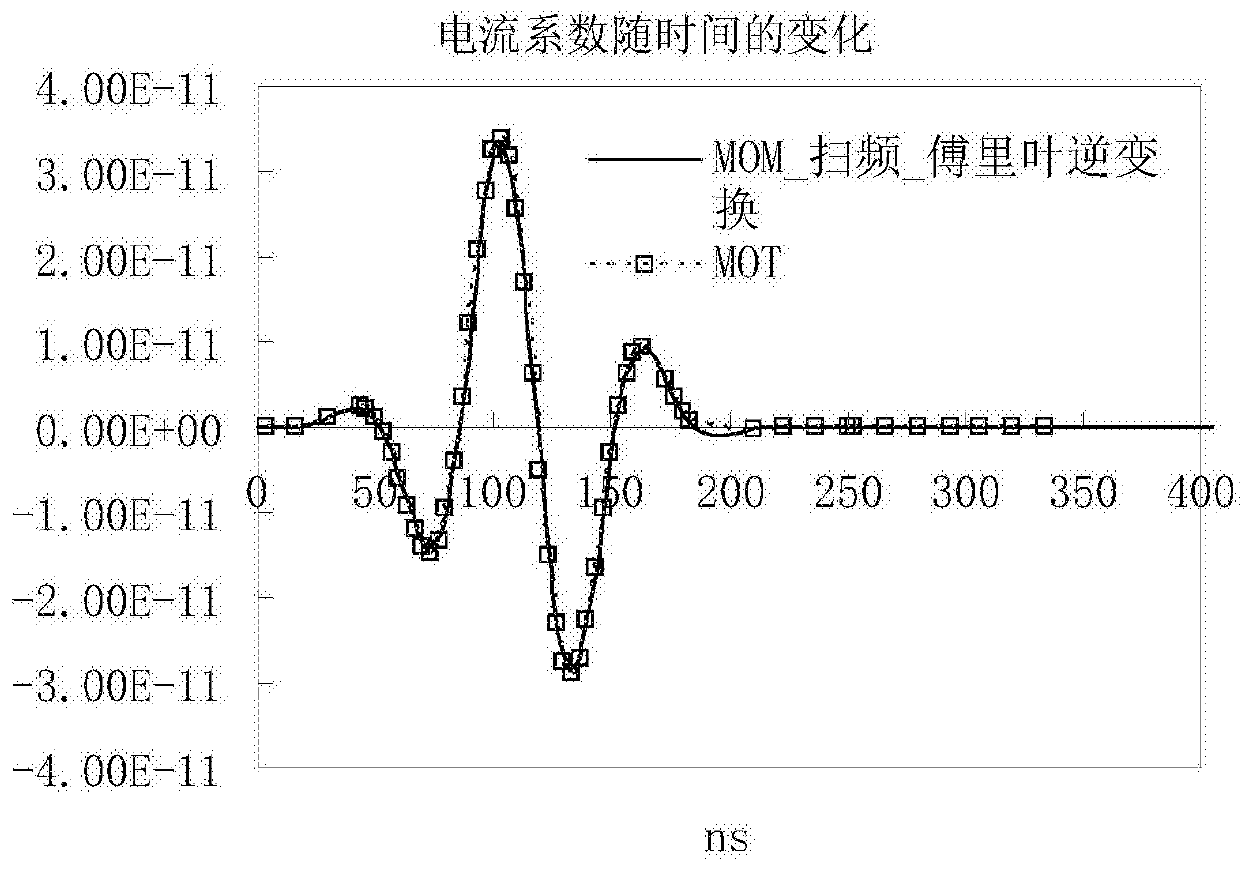
The invention discloses a method for estimating electromagnetic distribution in a carbon fiber material flying target under lightning pulse. In this method, the lightning pulse with extremely wide spectrum range is simulated by the plane wave in time domain, and the time domain analysis model of the carbon fiber material flying target under the lightning pulse is established. Use the time-domain plane wave algorithm PWTD to realize efficient calculation of the transient far field, apply the equivalent electric dipole model, quickly calculate the time-step time-domain volume integral equation MOT impedance matrix, solve the time-domain matrix equation and extract the electromagnetic characteristics in a wide frequency band . The invention only discretizes the flying target of carbon fiber material, uses the free space Green's function, the equation is simple, can analyze the non-uniform target, has high calculation accuracy and the unknown quantity is small; at the same time, because the time domain method is used to solve the problem, the invention can calculate once The electromagnetic characteristics of all frequency points in a frequency band, compared with the frequency domain method that requires frequency sweep operation, the time consumed for solving is greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com