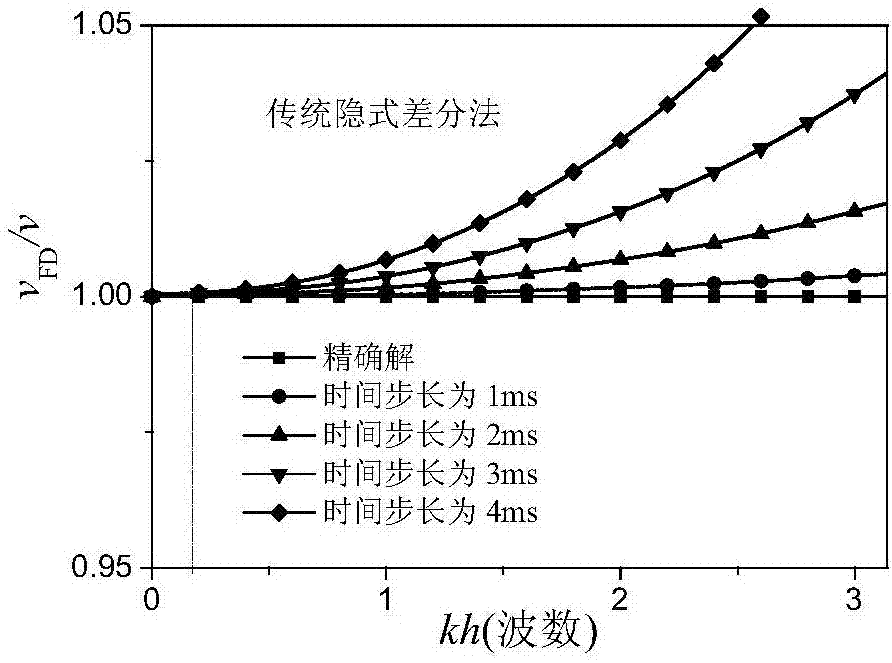
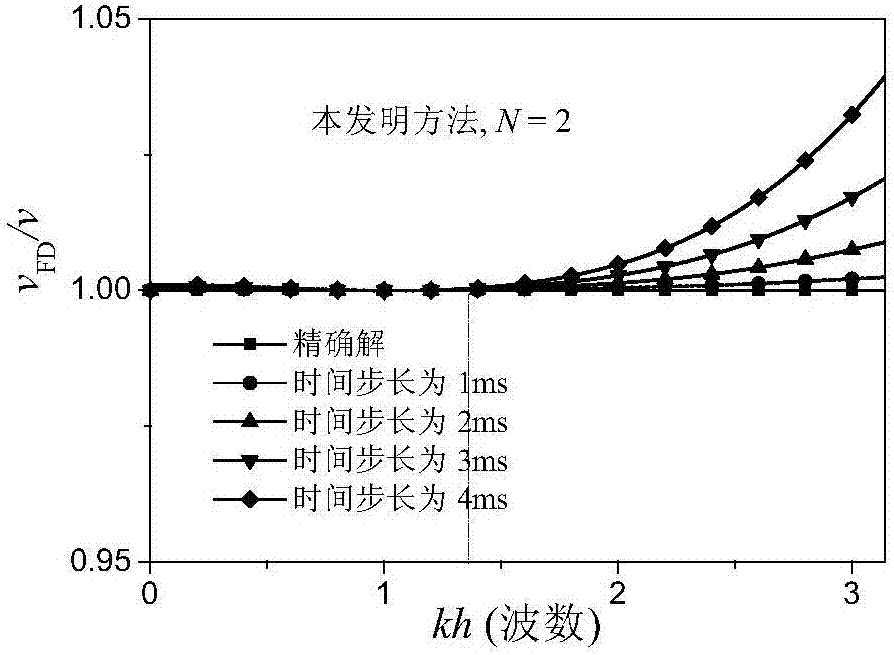
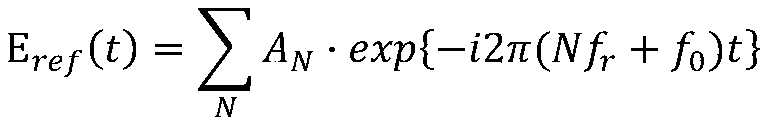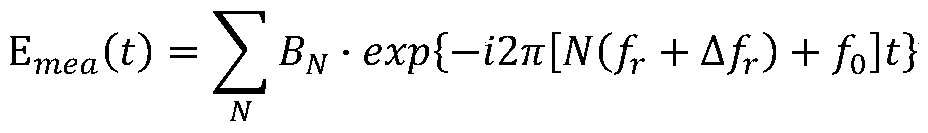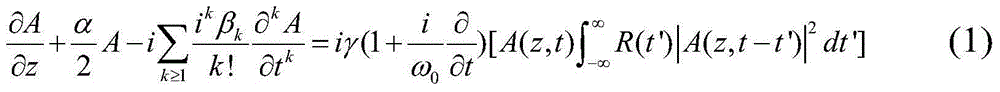Patents
Literature
99 results about "Spatial dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the physics of continuous media, spatial dispersion is a phenomenon where material parameters such as permittivity or conductivity have dependence on wavevector. Normally, such a dependence is assumed to be absent for simplicity, however spatial dispersion exists to varying degrees in all materials.
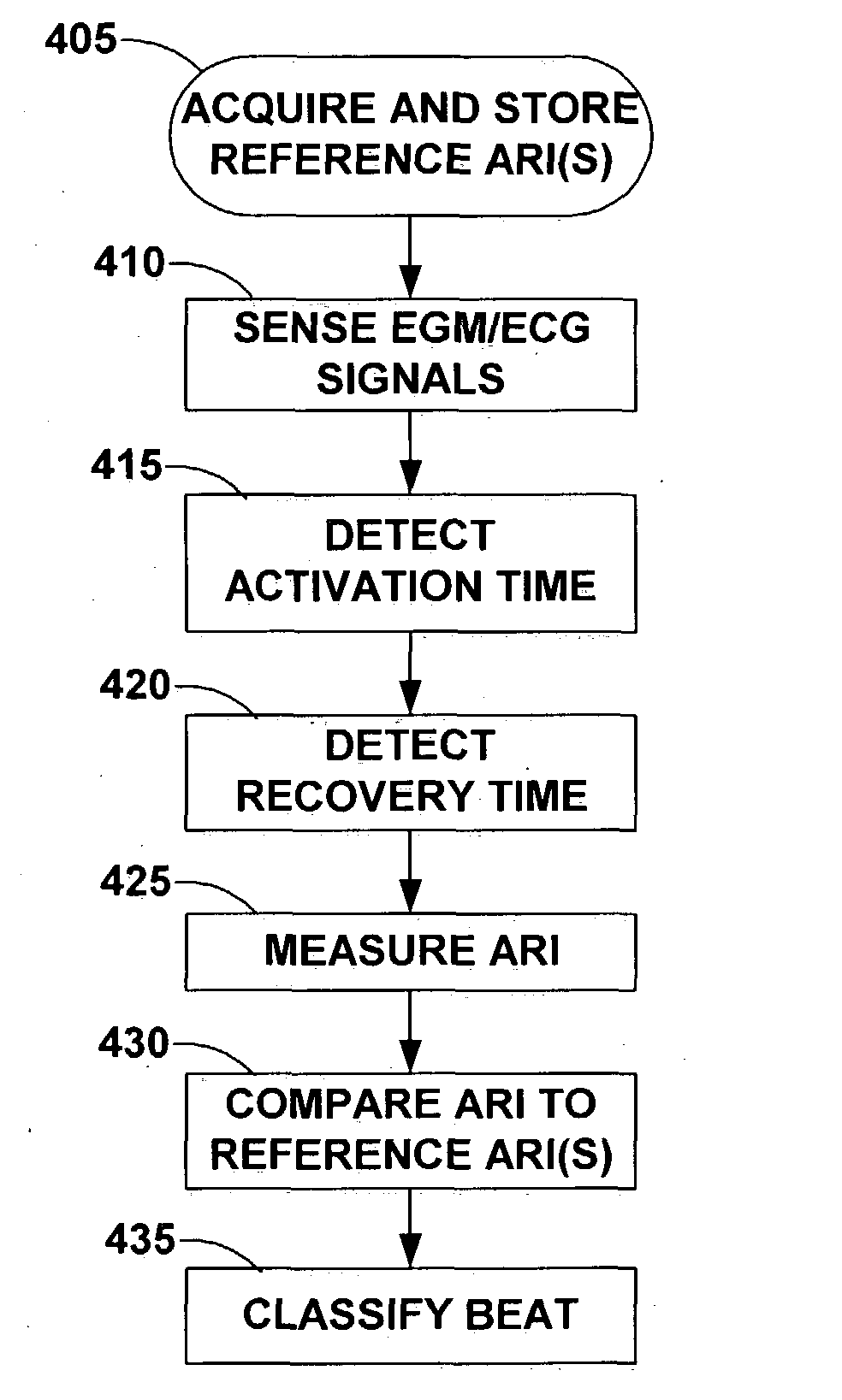
Activation recovery interval for classification of cardiac beats in an implanted device
The present invention provides a system and method for classifying cardiac beats based on activation-recovery intervals (ARIs) or an ARI-related parameter such as the spatial dispersion of activation, recovery or ARIs. The beat classification method may be used in monitoring and detecting cardiac rhythms and / or for controlling a cardiac stimulation therapy. The beat classification method includes acquiring a reference ARI for one or more known types of cardiac beats; measuring the activation-recovery interval of an unknown cardiac beat during cardiac activity monitoring; comparing the measured activation-recovery interval to the stored reference ARI(s); and classifying the cardiac beat based on the comparison between the measured ARI and the reference ARI(s).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
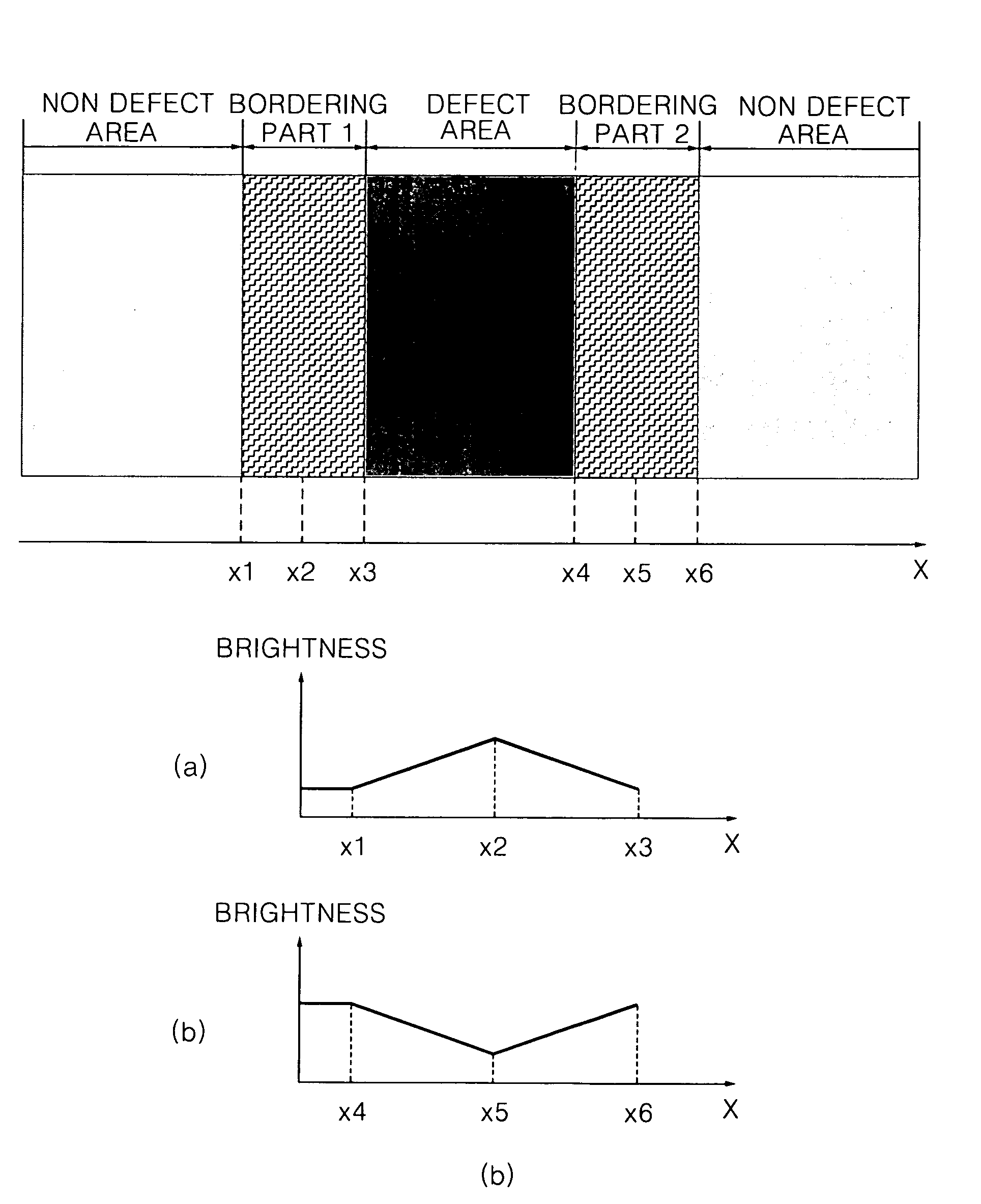
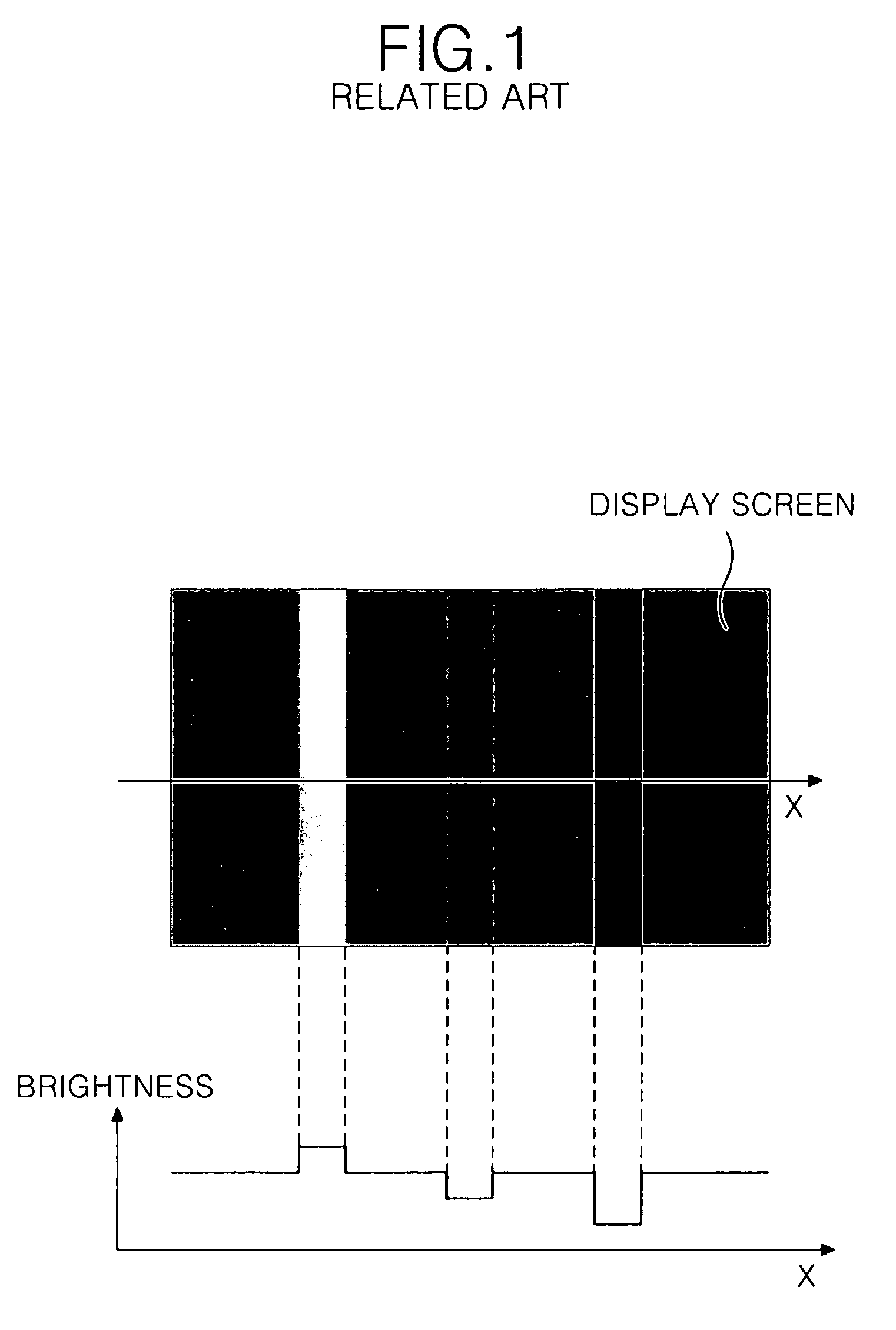
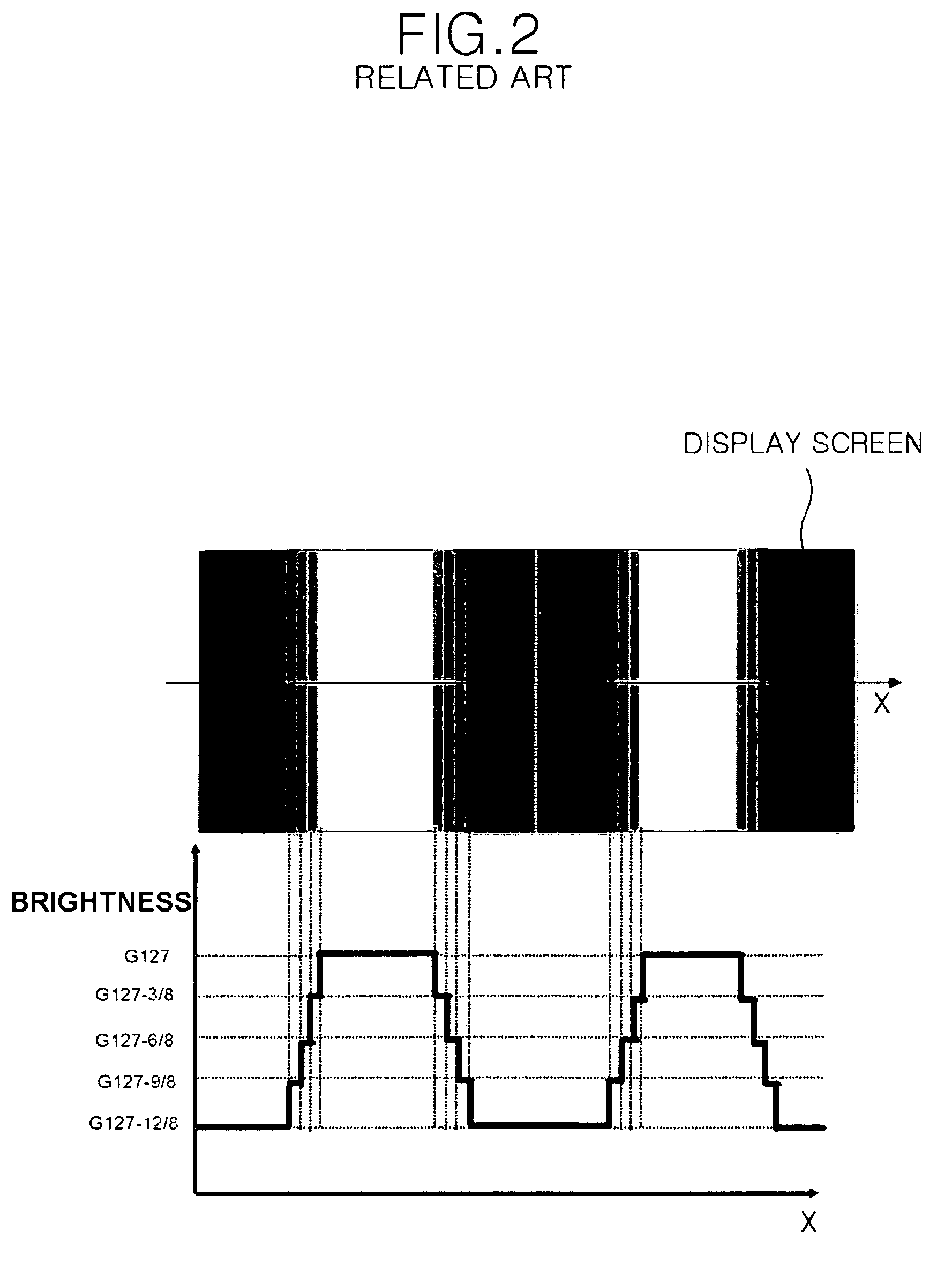
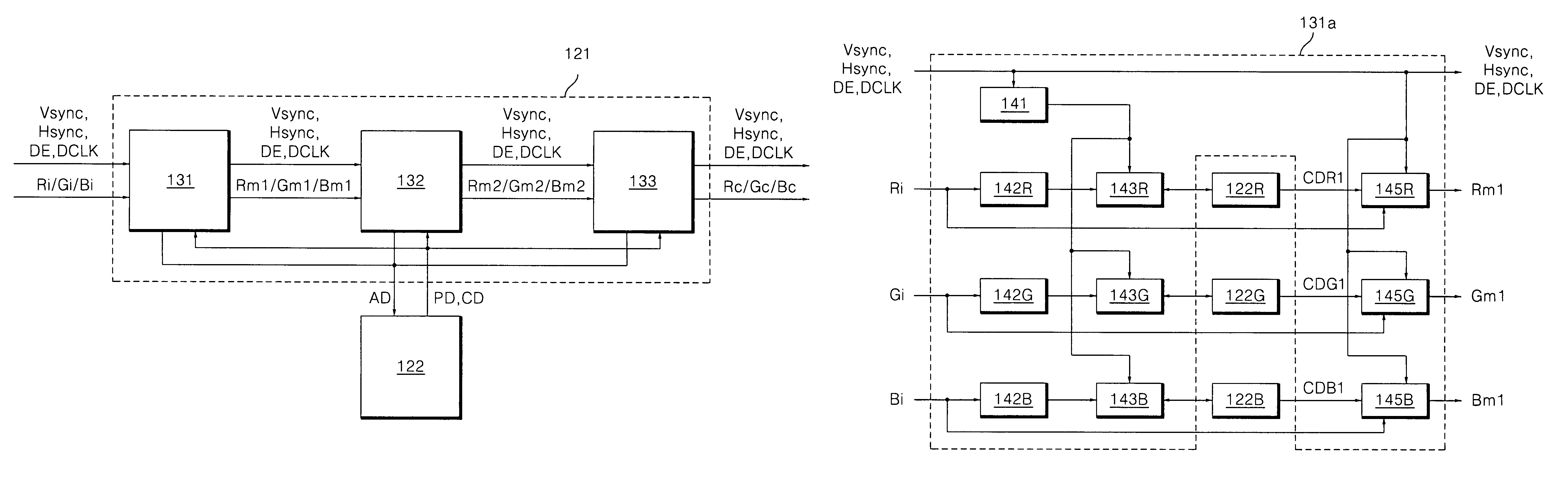
Flat panel display and method of controlling picture quality thereof
ActiveUS20080001869A1Fix bugsCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsFlat panel displayComputer science
A flat panel display device includes a display panel having at least one link pixel which has a non-defect area and a panel defect area and where adjacent pixels are linked to each other; a memory which stores a first compensation data for compensating the data which are to be displayed in the panel defect area, a second compensation data for compensating the data of a bordering part between the panel defect area and the non-defect area, and a third compensation data for compensating the data which are to be displayed in the link pixel. The first compensation data is adjusted through at spatial dispersion or temporal dispersion; the data that are to be displayed in a fixed area inclusive of the boundary are adjusted by dispersing the second compensation data to the fixed area inclusive of the boundary; the data that are to be displayed in the link pixel are adjusted to the third compensation data.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
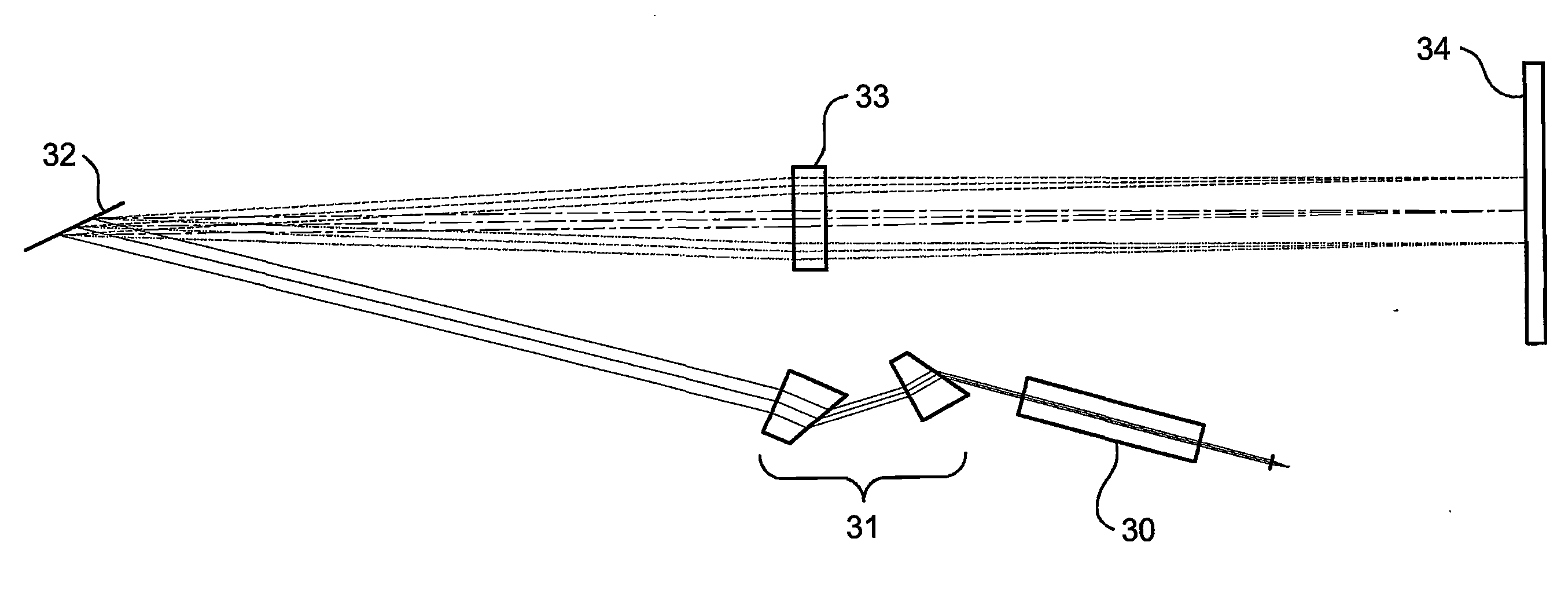
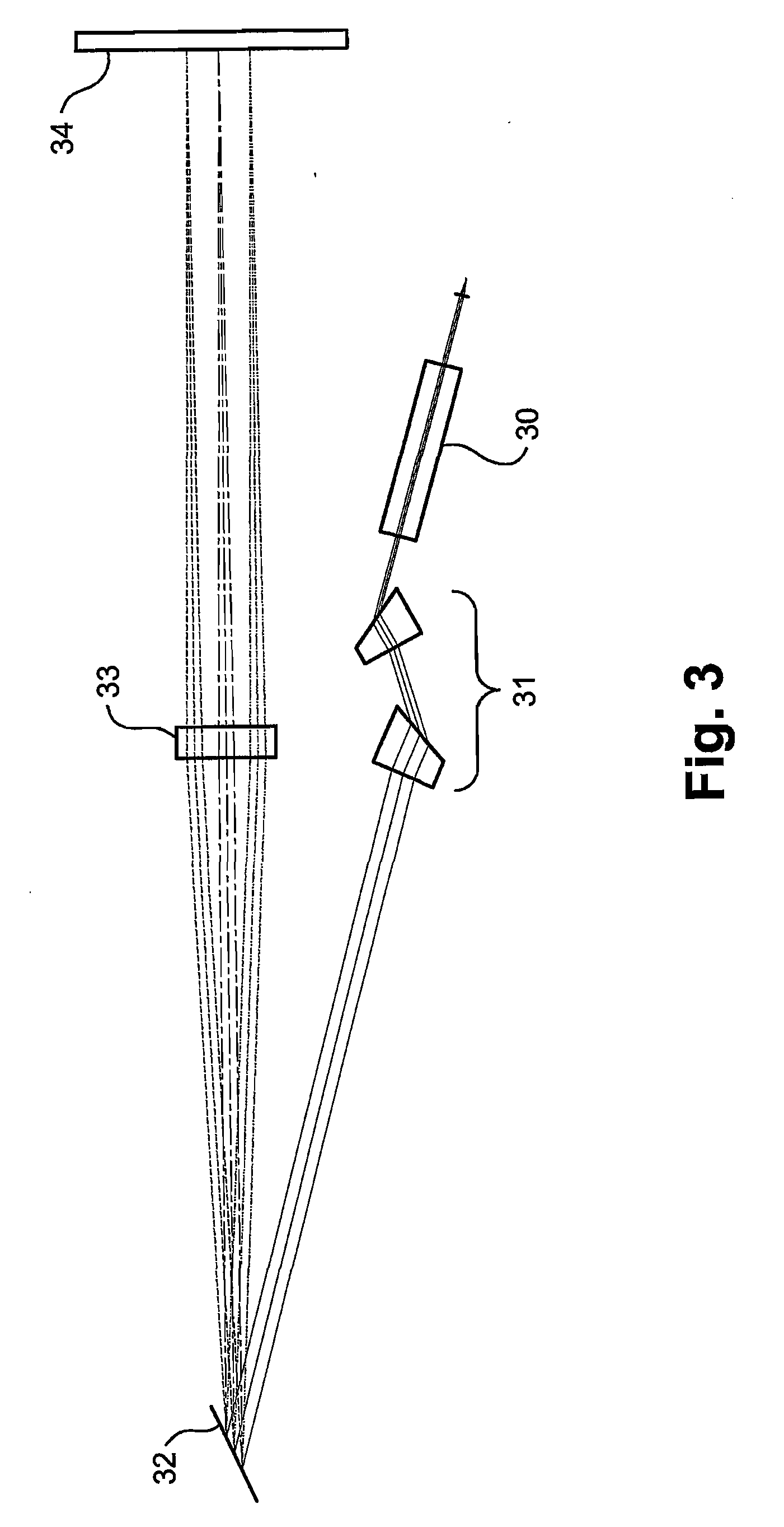
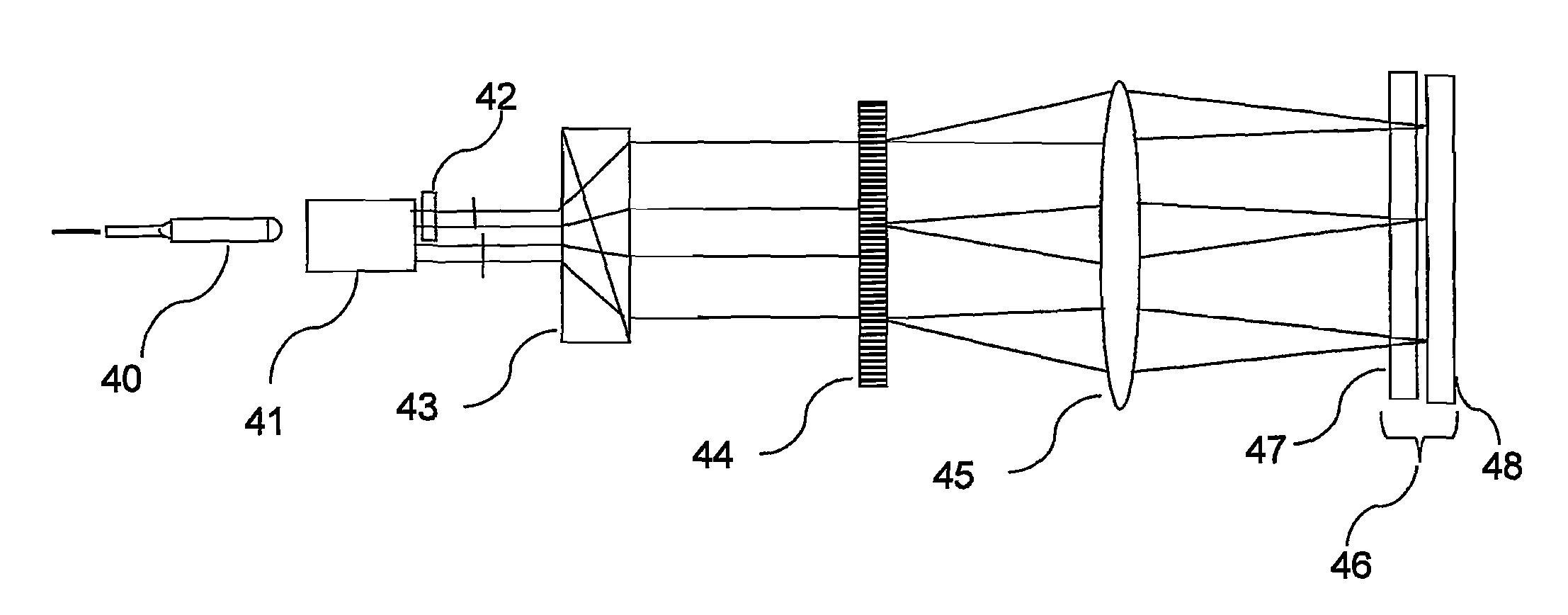
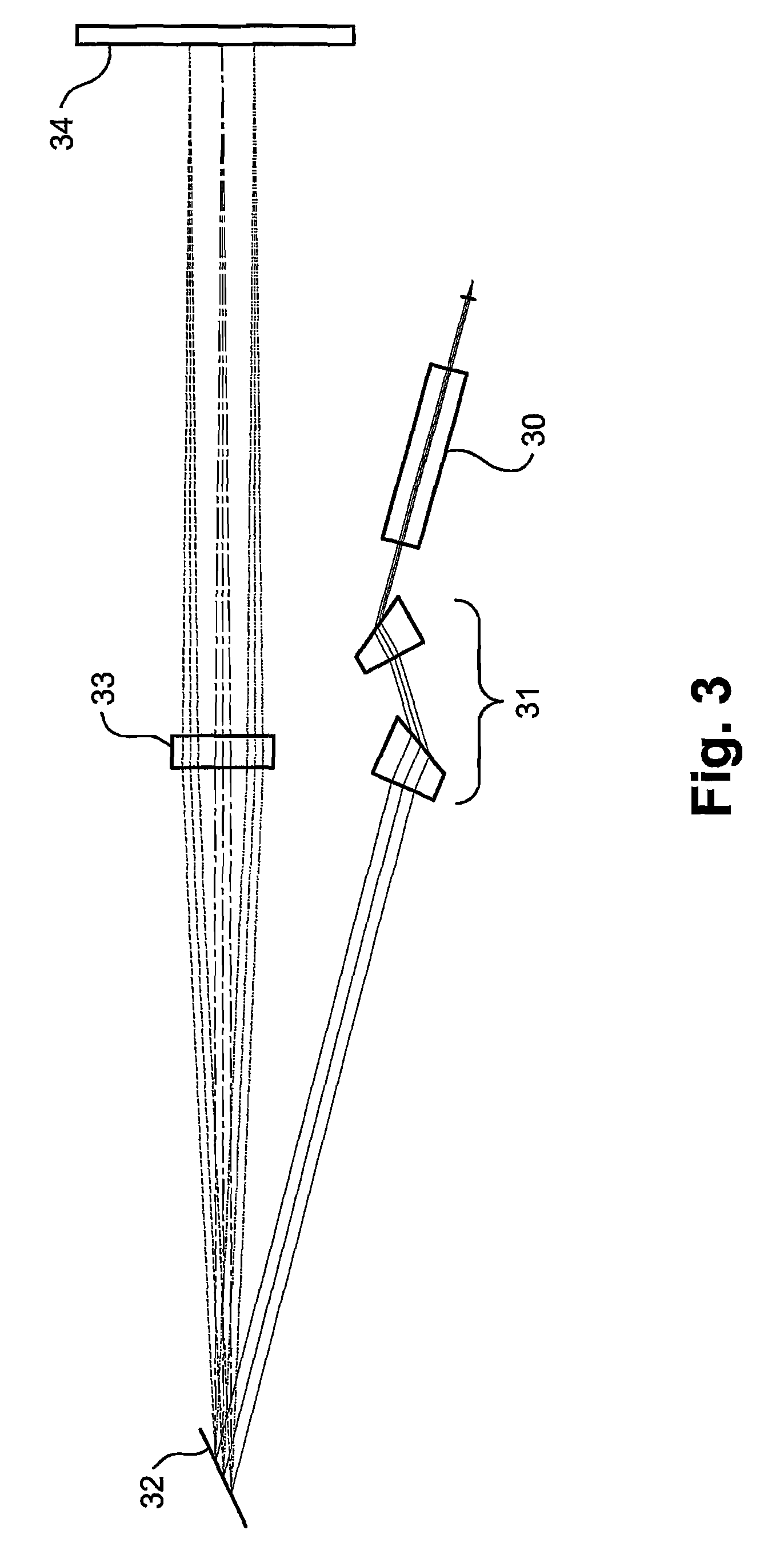
Optical Wavelength Selective Router
ActiveUS20080316585A1Economically constructedEasy constructionMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesLight beamBeam steering
A fiber-optical, wavelength selective switch, especially for channel routing with equalization and blocking applications. The input signals are converted to light beams having predefined polarizations (41). The beams are then laterally expanded (43), and then undergo spatial dispersion in the beam expansion plane. The different wavelength components are directed through a polarization rotation device, pixilated along the wavelength dispersion direction such that each pixel operates on a separate wavelength. Each beam is passed into a pixilated beam steering array (48), for directing each wavelength to a desired output port. The beam steering devices can be MEMS-based or Liquid crystal-based, or an LCOS array. When the appropriate voltage is applied to a pixel and its associated beam steering element, the polarization of the light passing through the pixel is rotated and the beam steered to couple to the selected output port.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Optical wavelength selective router
ActiveUS7822303B2Easy constructionAvoid couplingMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesLight beamBeam steering
A fiber-optical, wavelength selective switch, especially for channel routing with equalization and blocking applications. The input signals are converted to light beams having predefined polarizations (41). The beams are then laterally expanded (43), and then undergo spatial dispersion in the beam expansion plane. The different wavelength components are directed through a polarization rotation device, pixilated along the wavelength dispersion direction such that each pixel operates on a separate wavelength. Each beam is passed into a pixilated beam steering array (48), for directing each wavelength to a desired output port. The beam steering devices can be MEMS-based or Liquid crystal-based, or an LCOS array. When the appropriate voltage is applied to a pixel and its associated beam steering element, the polarization of the light passing through the pixel is rotated and the beam steered to couple to the selected output port.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Oil and gas reservoir numerical simulation calculation method
InactiveCN103246820AGood calculation stabilityImprove stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsFluid phaseGas phase
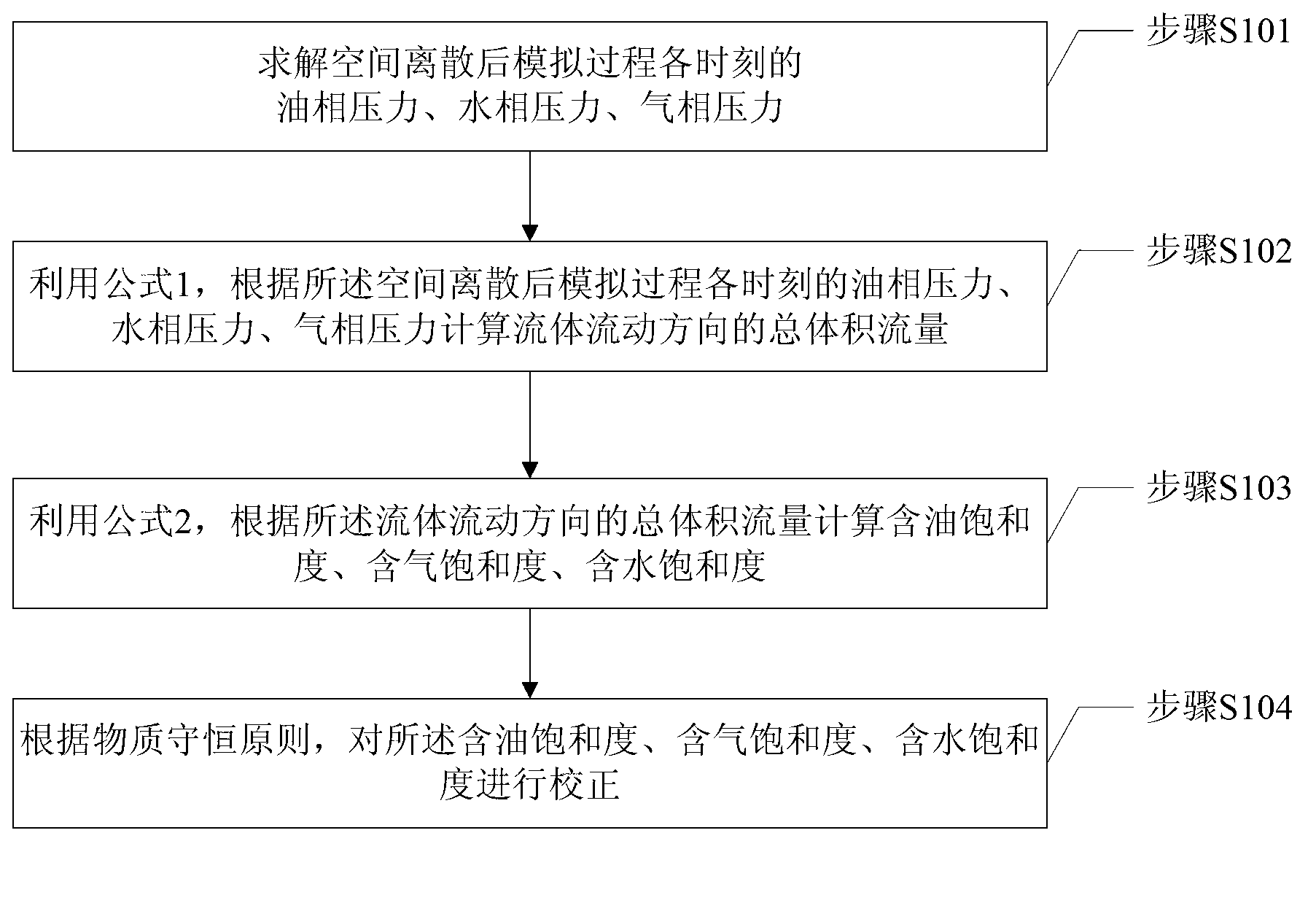
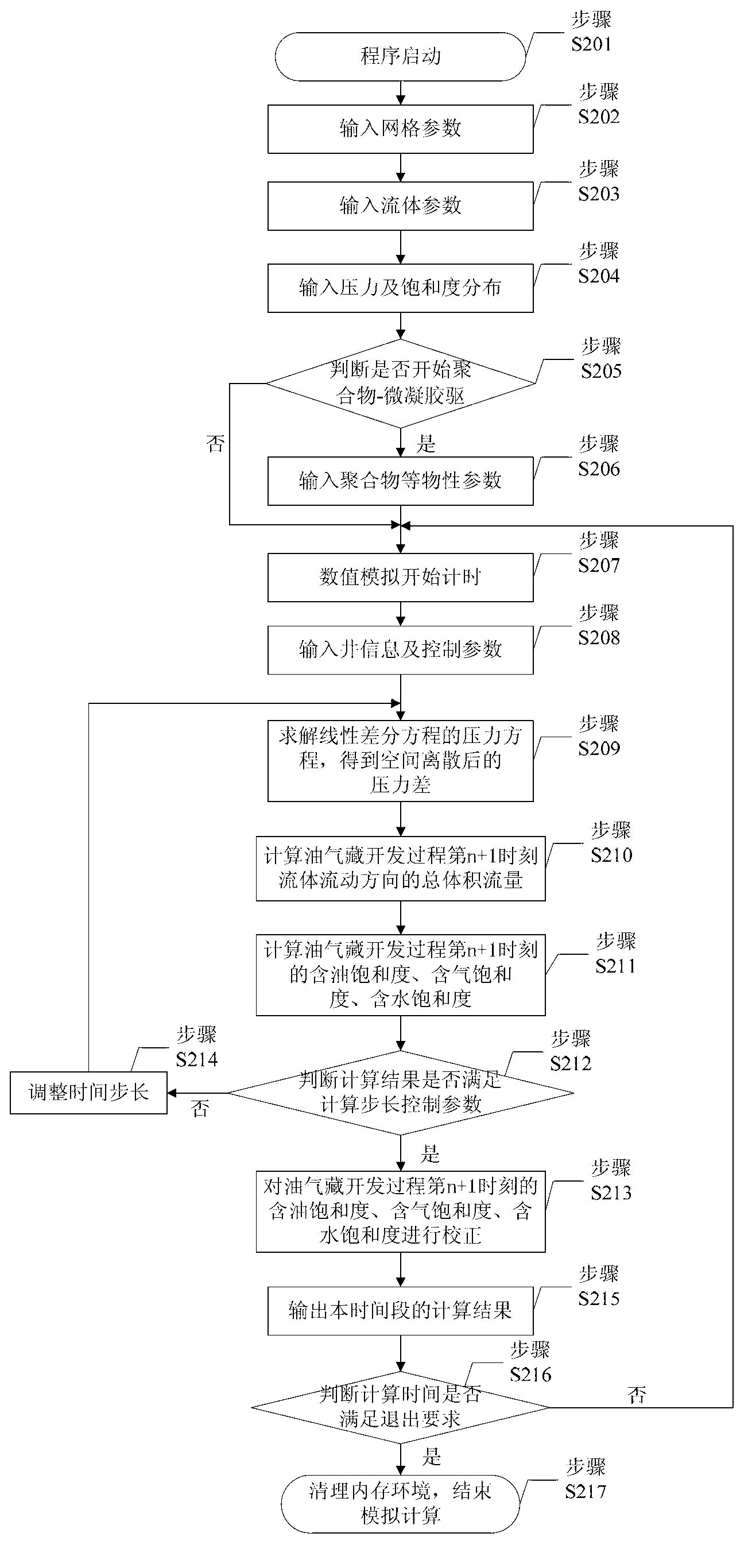
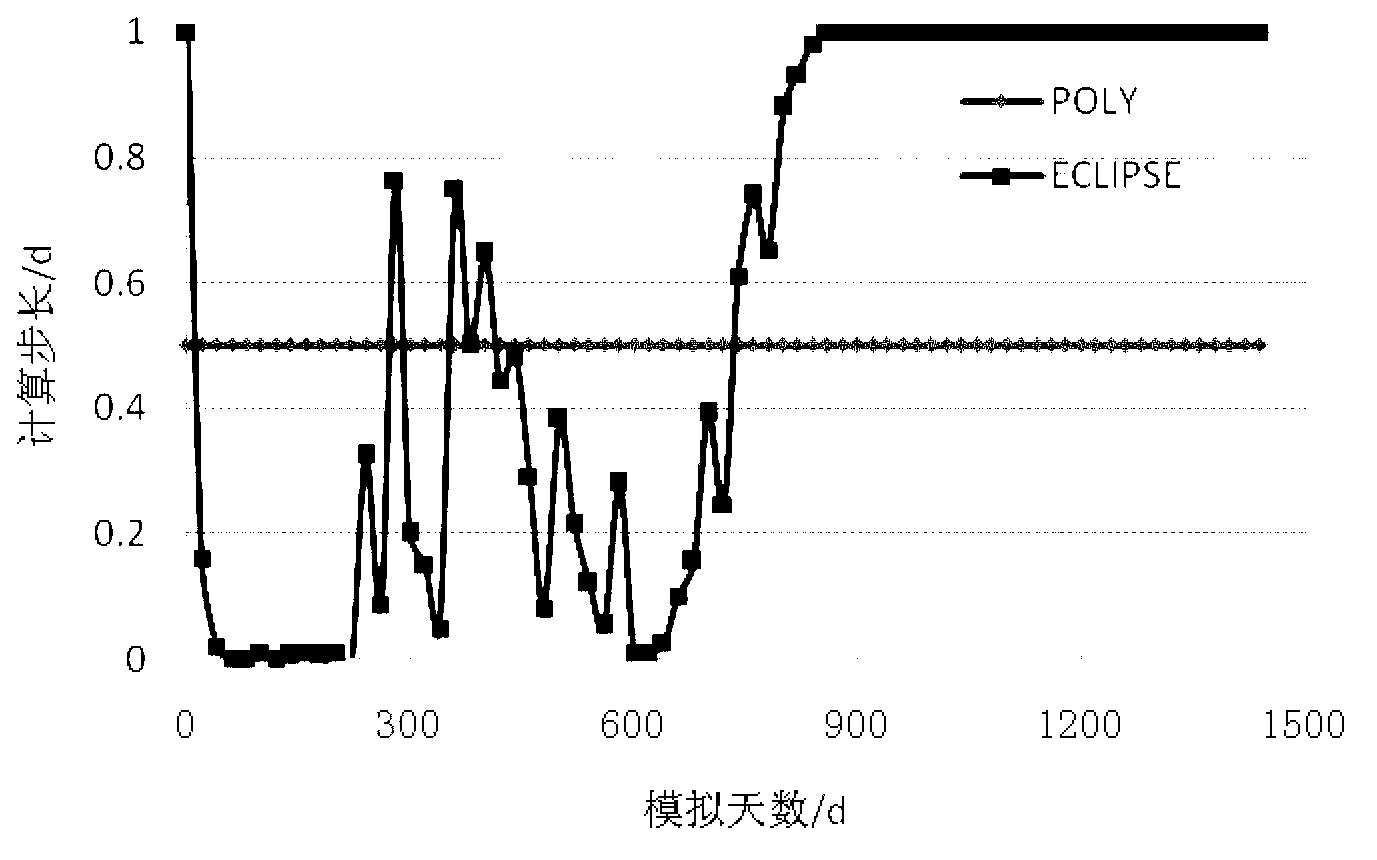
The invention provides an oil and gas reservoir numerical simulation calculation method. The method includes calculating oil phase pressure, water phase pressure and gas phase pressure of a spatial dispersion post simulation process at any moment, calculating total volume flow of fluid in the flowing direction according to the oil phase pressure, water phase pressure and gas phase pressure of the spatial dispersion post simulation process at any moment, calculating oil saturation, gas saturation and water saturation according to the total volume flow of the fluid in the flowing direction and correcting the oil saturation, the gas saturation and the water saturation according to the substance conservation principle. In the method, the pressure is calculated in one step, the speed is calculated in one step, and branch flow and saturation are calculated in multiple steps, velocity item calculation is introduced, and calculation misconvergence caused by factors such as anisotropy, fluid phase change and unreasonable production systems is avoided. The numerical simulation stability is better, the convergence condition is easy to judge, and the method is suitable to be applied when a common oil and gas reservoir numerical simulation method sinks into misconvergence.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Hypersonic aerocraft leading edge fluid-heat-solid integrated calculation method
InactiveCN107832494AImprove stabilityImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADSustainable transportationPhysical fieldEngineering
The invention discloses a hypersonic aerocraft leading edge fluid-heat-solid integrated calculation method, and belongs to the field of aerocraft pneumatic calculation. For solving the problem of complex coupling of structure heat transfer and hypersonic speed flow aerodynamic heating, the method avoids the complex data exchange and calculation amount caused by flow field and structure coupling alternate iteration calculation performed within a time domain through a traditional aerodynamic heating / structure heat transfer coupling solving method, the flow field and the structure are adopted asa physical field, and a uniform control equation is adopted. Physical parameters of a fluid and solid interface are defined again, a finite volume method is performed on a full physical field for spatial dispersion, and hidden time iteration is adopted for time stepping. Compared with a coupling algorithm, the method needs no extra data exchange or coupling strategy, the calculation result and anexperiment value are closer, the calculation amount and the grid dependency are smaller, and the better stability and calculation precision are achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
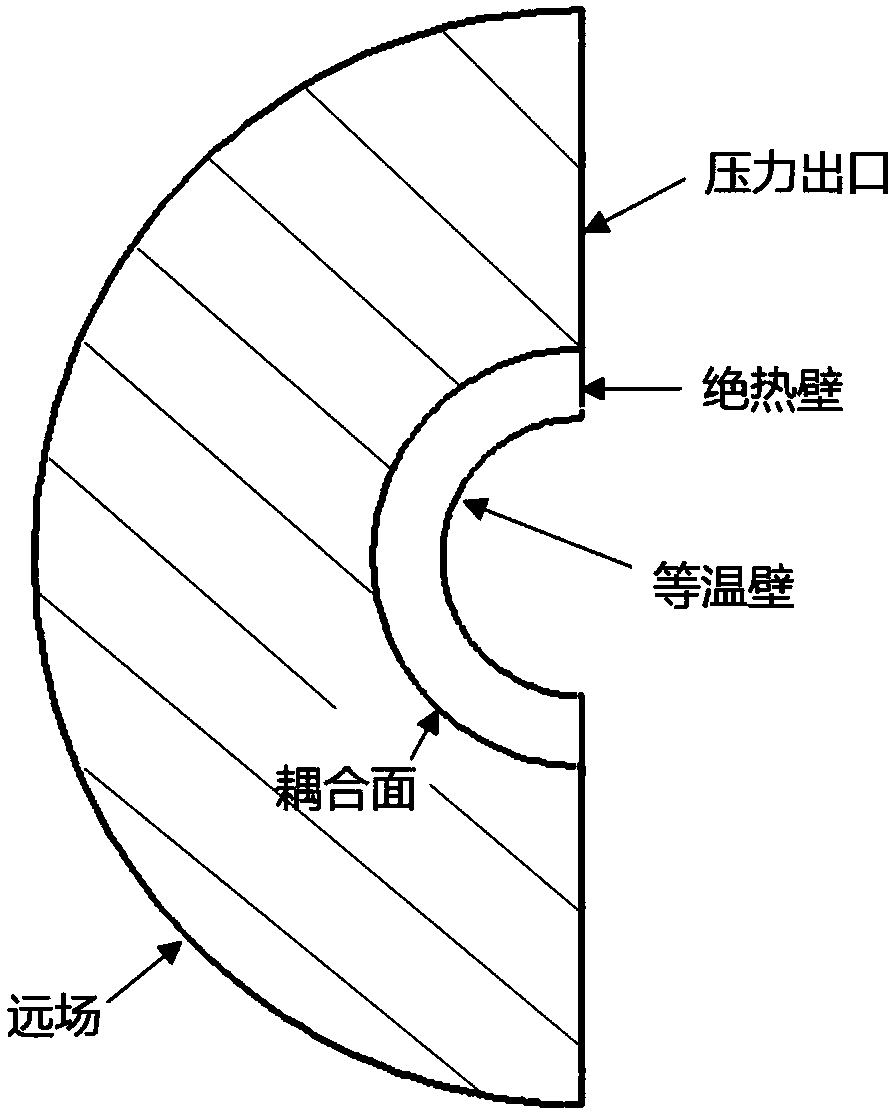
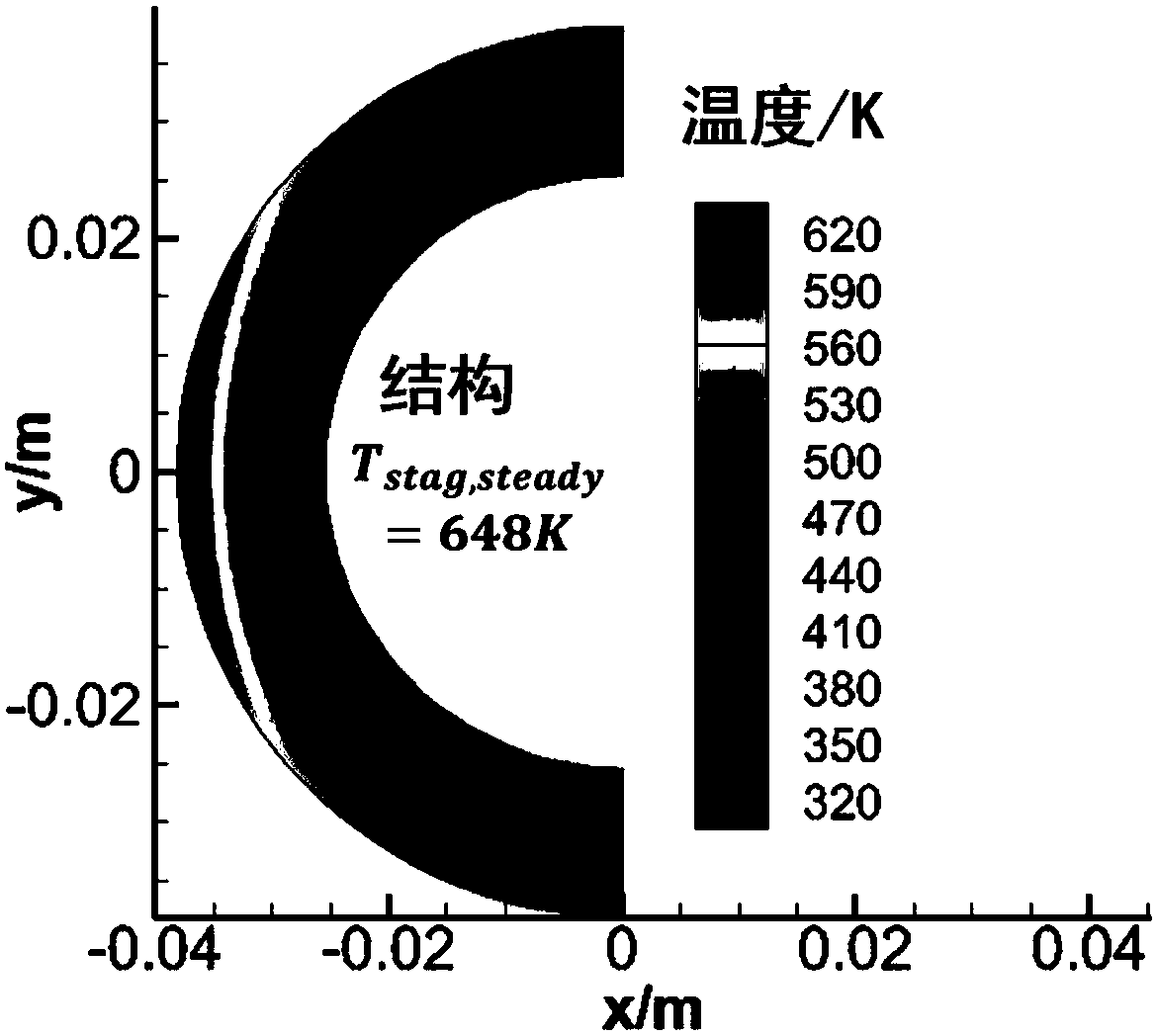
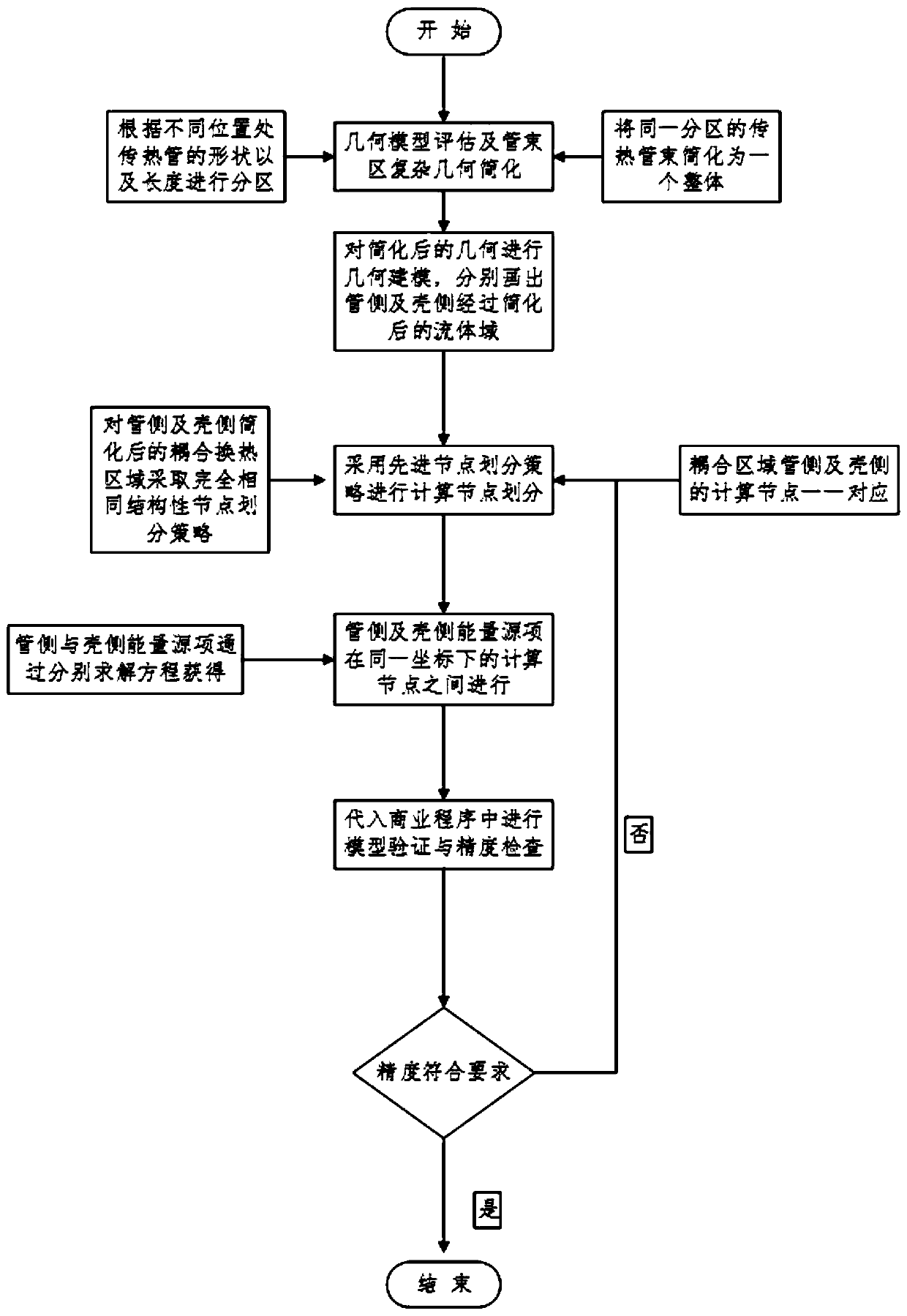
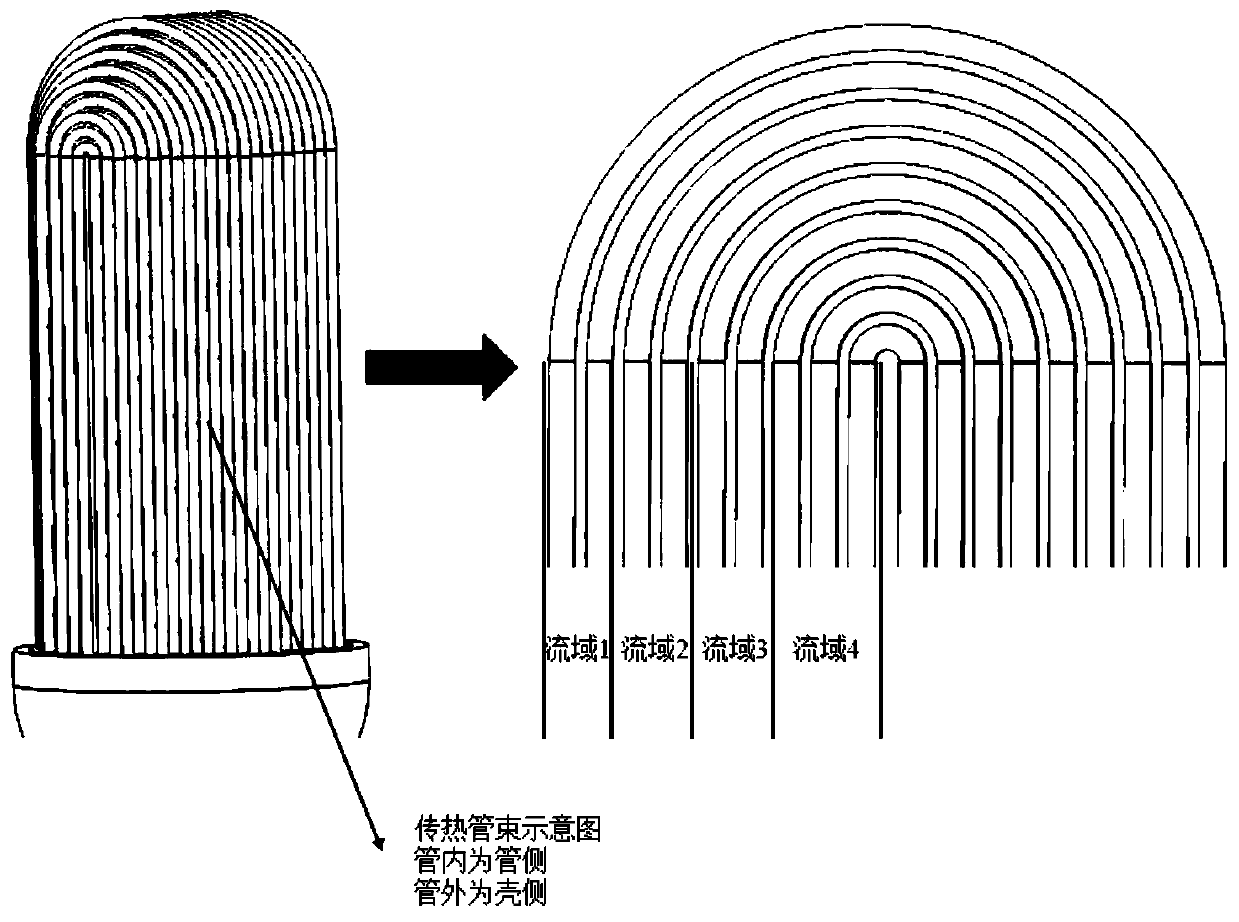
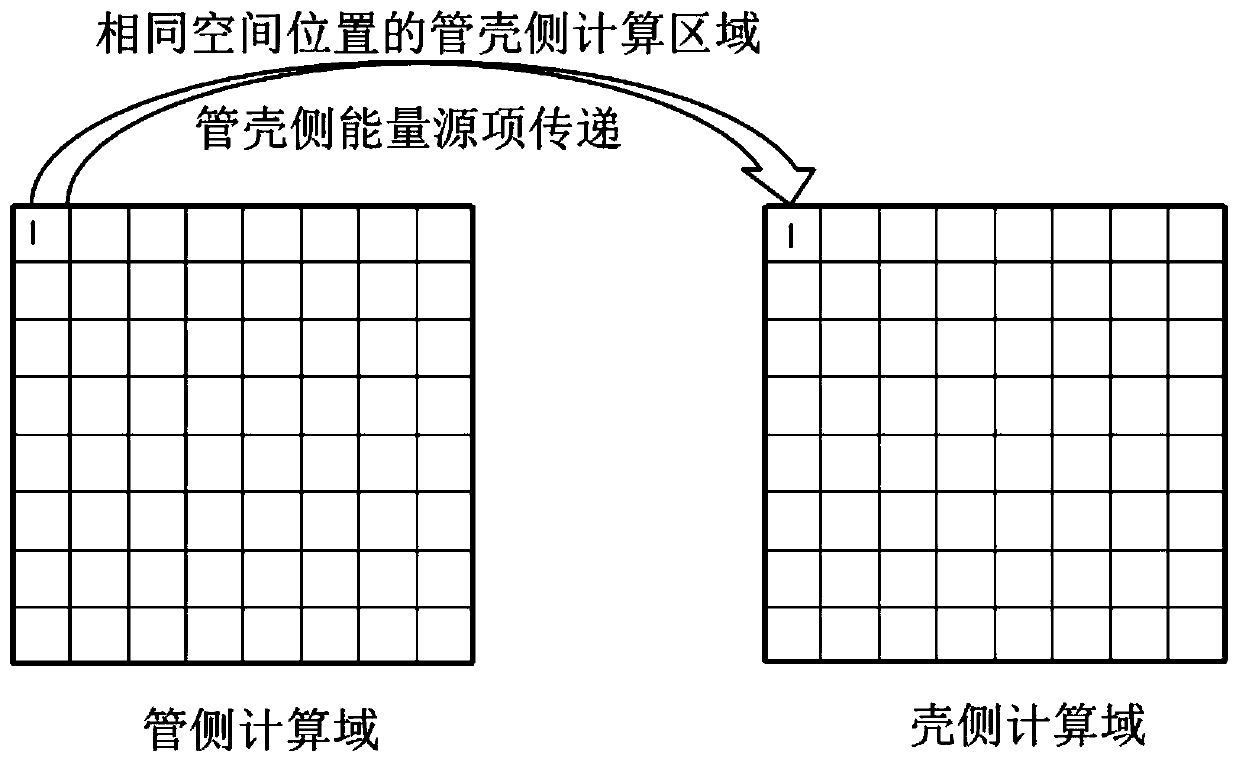
Method for establishing full three-dimensional coupling model of reactor U-shaped tubular steam generator
ActiveCN110020476AAchieve couplingHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsShell and tube heat exchangerCoupling
The invention discloses a method for establishing a full three-dimensional coupling model of a reactor U-shaped tubular steam generator, which is suitable for all systems related to energy conversionby adopting a shell-and-tube heat exchanger in the field of energy. The coupling method mainly comprises the following steps: 1, simplifying a geometric model of the steam generator; 2, establishing aprimary and secondary side geometric model; 3, carrying out primary and secondary side three-dimensional computing node division; 4, performing spatial dispersion on a pipe side (primary side) energysource item; 5, performing spatial discretization on a shell side (secondary side) energy source item; 6, coupling primary and secondary side energy source items at the same coordinate node; and 7, performing data transmission between the primary side and the secondary side and on internal nodes of each side, and performing iteration to obtain a convergence solution. Geometric model simplification is mainly used for simplifying the workload caused by the number of a large number of heat transfer pipes to model establishment and numerical calculation. Primary and secondary side computing nodedivision adopts a completely identical division strategy; each side energy source item is obtained through a discrete flow heat transfer equation; and the data exchange of the energy source items on the two sides is carried out between the corresponding primary and secondary side computing nodes under the same coordinate.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
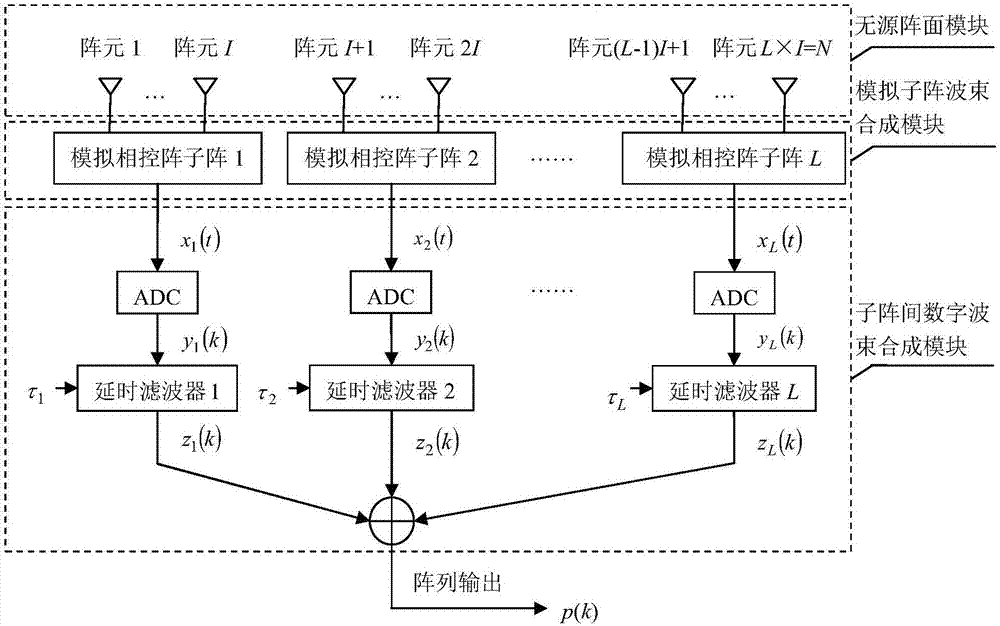
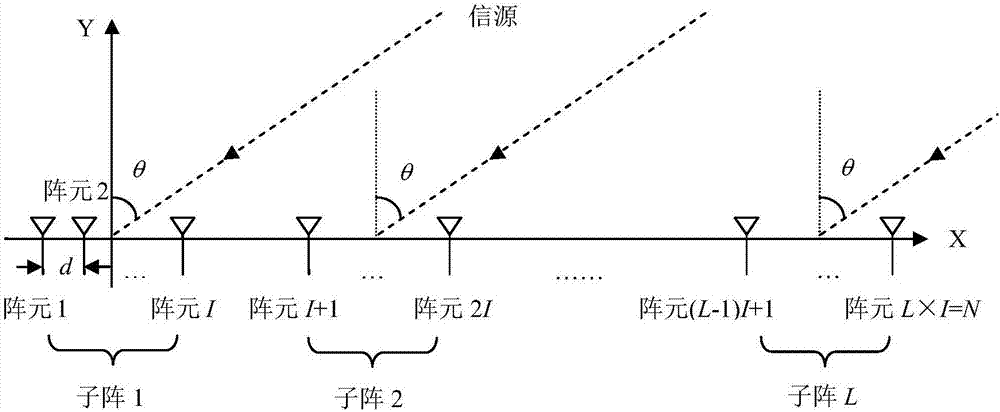
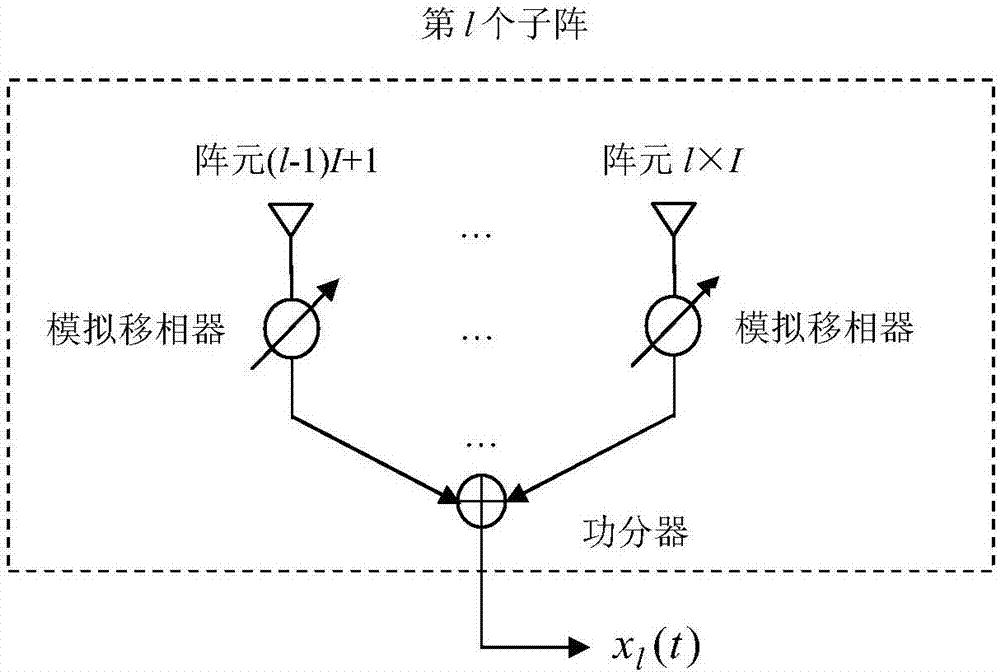
Large-diameter wideband reception phased-array antenna
InactiveCN106935975AGuaranteed correctnessOvercome spaceAntenna arraysAntennas earthing switches associationRadarArray element
A large-diameter wideband reception phased-array antenna is characterized in that (1) the reception phased-array antenna employs a sub-array structure, N array elements are divided into L sub-arrays, each sub-array is an independent simulation narrowband phased-array antenna, an output signal of each sub-array is x(t), and I is 1, 2 until L; (2) the output signal of a first sub-array is converted to a digital signal y(k) by an analog-digital converter (ADC), y(k) passes through a digital delay filter, a filter coefficient vector c=[c<I1> until c<IJ>], J is filter order, the realization function of a first digital delay filter is in a way that an input signal is delayed by time span being Tau, and the output signal is z(k); (3) the digital delay filter corresponding to each sub-array employs a Farrow filter structure, namely, a coefficient is shown as specification, and the coefficient Zeta(j) is calculated by a frequency domain weighting method; and (4) the final output p(k) of the phased-array antenna is sum of outputs of all digital delay filters, namely, p(k) is shown as specification. By the large-diameter wideband reception phased-array antenna, the problems of spatial dispersion and time dispersion of the phased-array antenna are solved, and the phased-array antenna can be applied to the field of the large-diameter wideband phased-array antenna for radar and communication.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
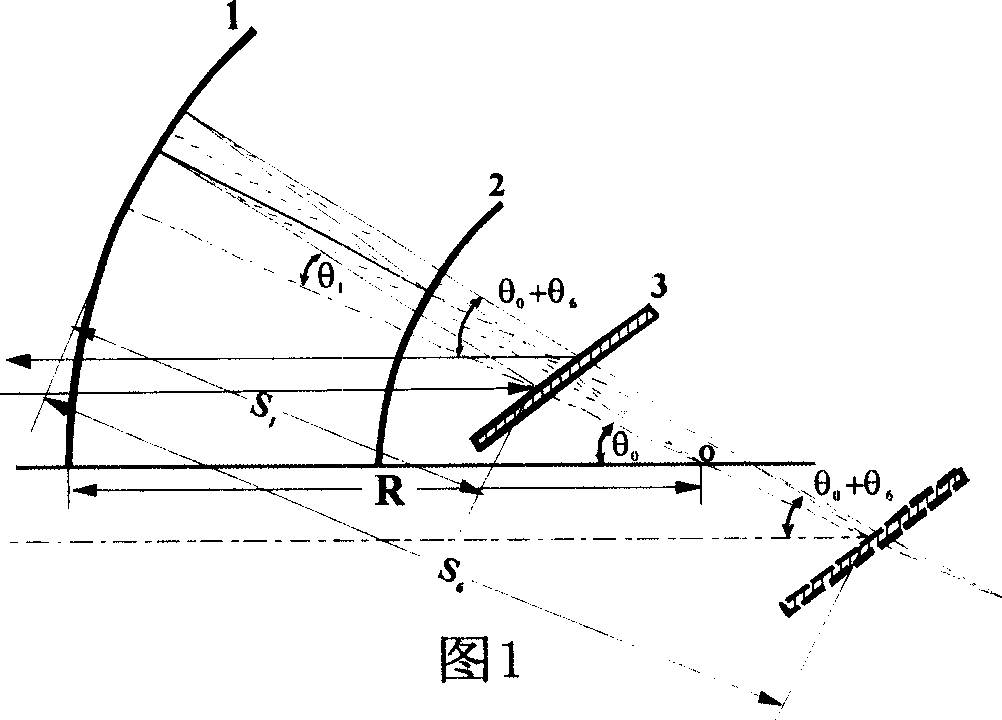
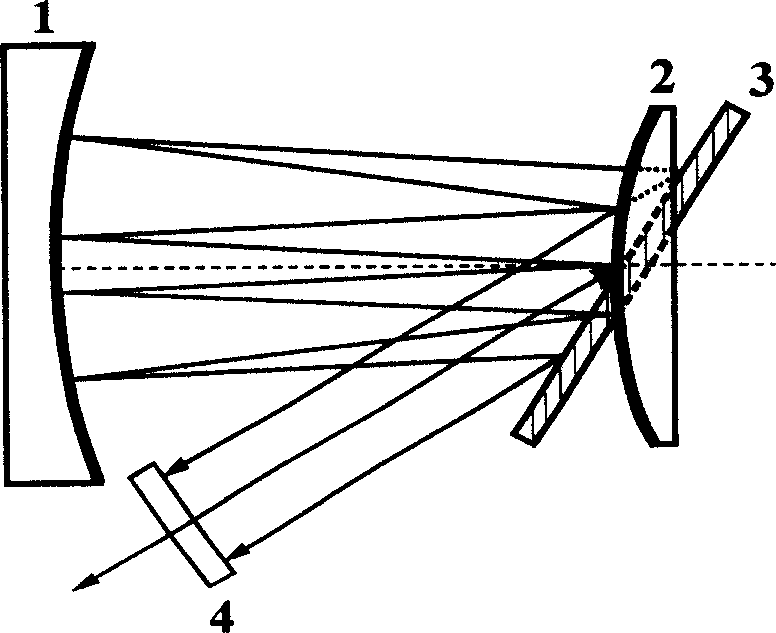
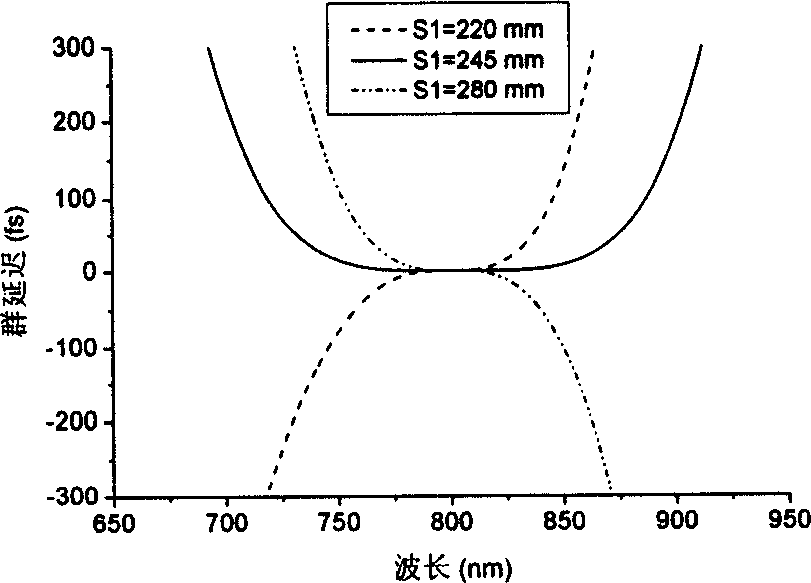
Miniaturization pulse stretcher design method for compensating high material dispersion of regenerative amplifier
InactiveCN1595272AGood collimationSmall spatial dispersionNon-linear opticsGratingAudio power amplifier
This invention discloses a design method for small femtosecond laser impulse stretcher used in regenerative amplifier high-dispersion material compensation, which belongs to the femtosecond impulse amplify technique. This method adopts concave spherical lens, convex spherical lens, grating and plane lens to design structure according to the phase Phi and grating position S1 of the stretcher. This method is characterized by the following: If the curvature radius of spherical lens is R, the distance between the grating and the concave spherical lens varies between zero to R; the convex spherical lens overlapped with the grating; if the stretching spectrum of the incidence light is larger than the lens width of the concave spherical lens, then it needs to reduce with equal proportion the curvature radium of the concave spherical lens and convex spherical lens and reduces the spectrum stretching width and keeps the original stretching degree.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Quadrupole mass spectrometer with spatial dispersion
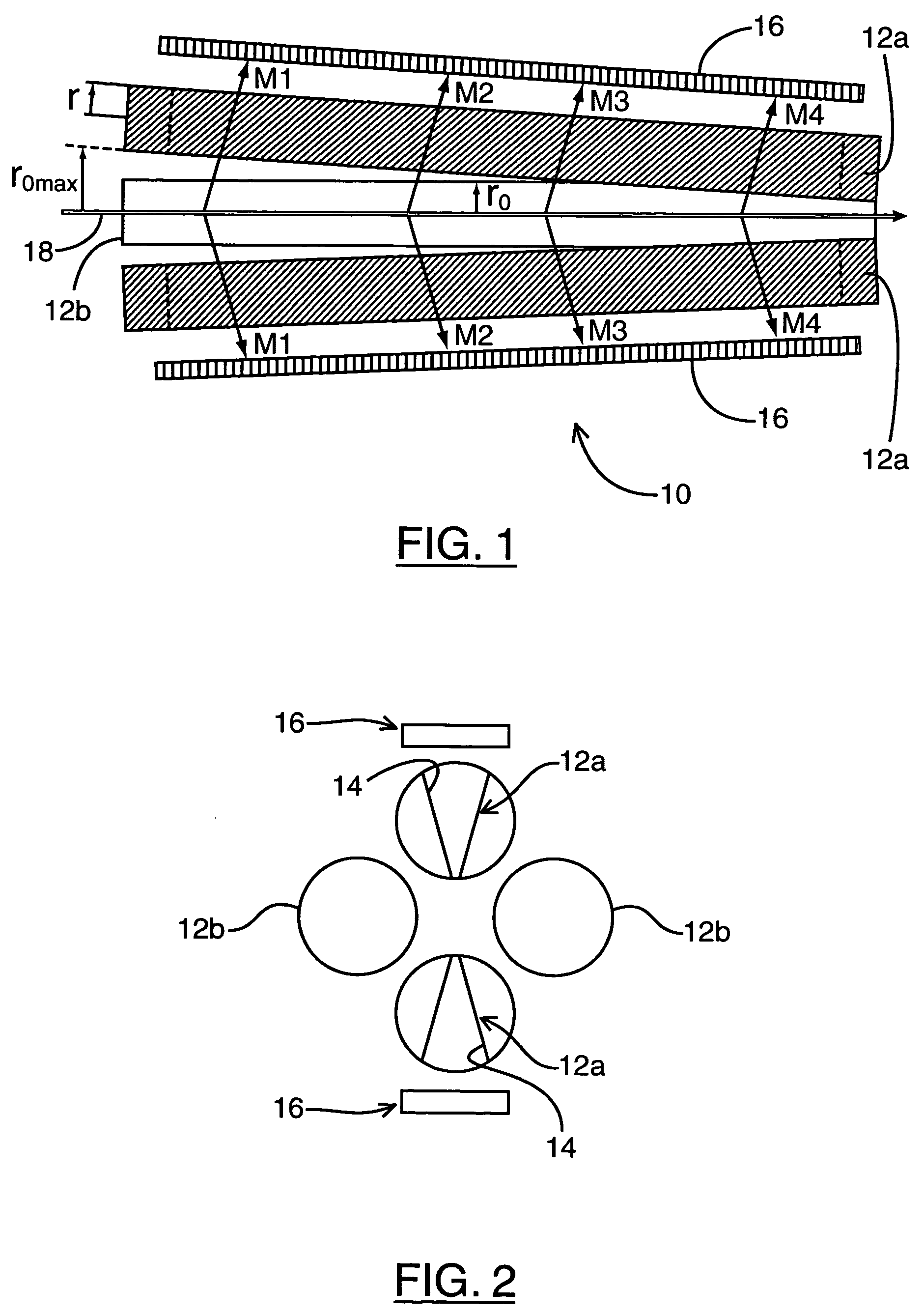
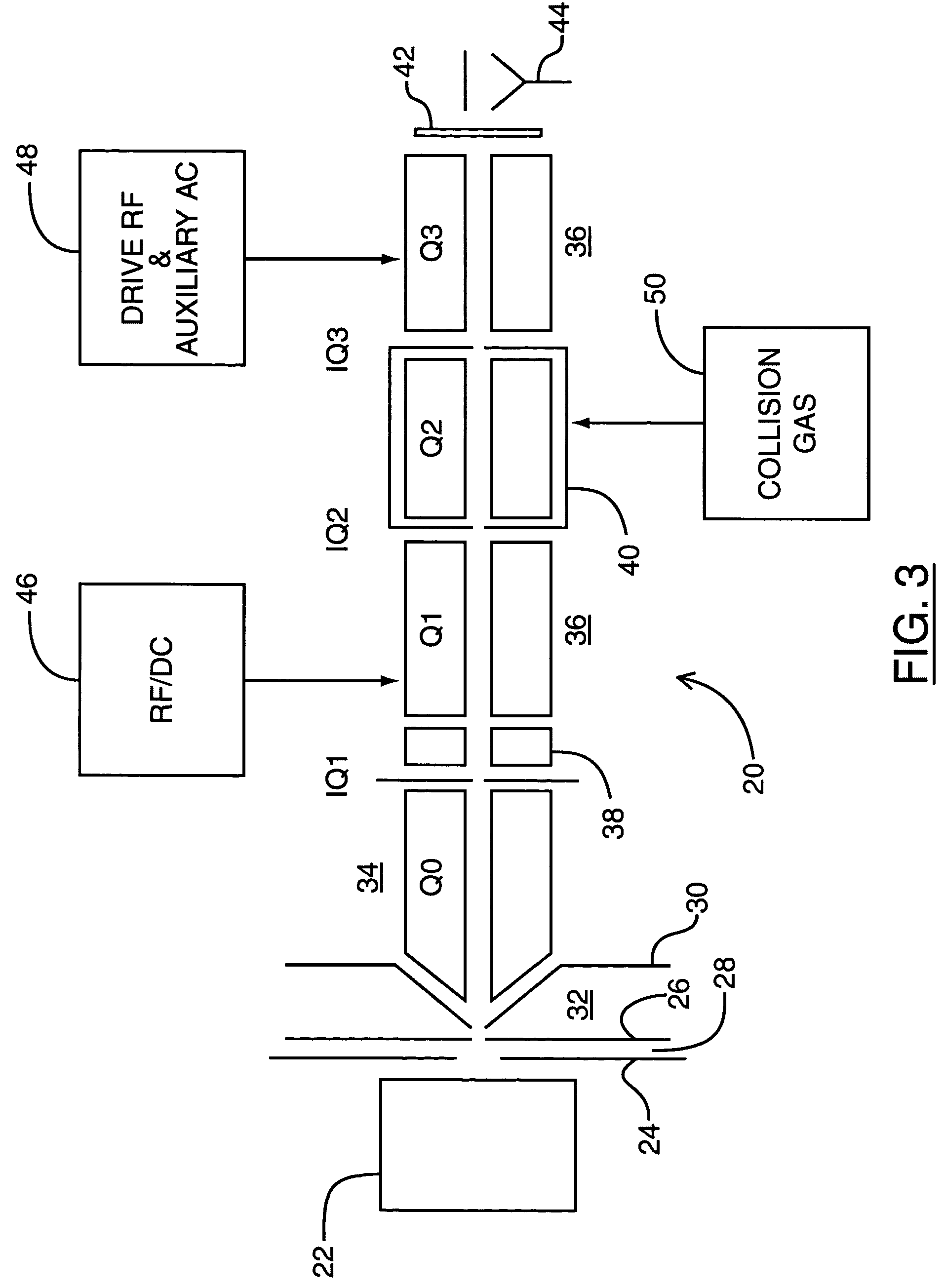
ActiveUS7196327B2Stability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
A mass analyzer for use in a mass spectrometry system comprises an elongate rod set. The rod set has first and second ends and an inscribed circle within the rod set. The radius of the rod set varies from one end of the rod set to the other, so that ions of different mass to charge ratios will become unstable at different locations along the rod set. This characteristic can then be used to cause ejection of ions at different locations along the rod set, in a mass dependent manner. Detectors placed linearly along the rod set can then be used to detect ions and determine the mass of the ions from their ejection locations.
Owner:MDS CO LTD +2
Real-time phase measurement system and method based on double-optical-comb beat frequency
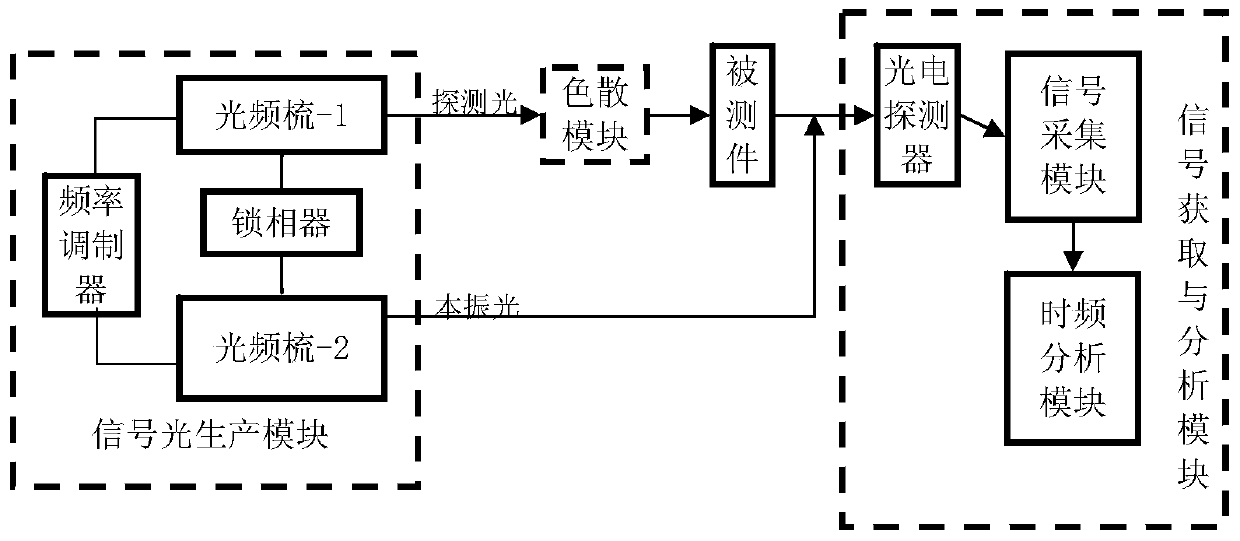
ActiveCN111289223AImprove spatial resolutionHigh speedTesting optical propertiesEngineeringOptical communication
The invention discloses a real-time phase measurement system and method based on double-optical-comb beat frequency. Two optical frequency comb lasers precisely controlled in a time-frequency domain are adopted to form a double-optical-path test system; and a real-time phase measurement method is designed and used for achieving real-time measurement of phase distortion of all channels of a liquidcrystal optical phased array antenna. A dispersion module performs spatial dispersion on test light, and real-time high-resolution detection of wavefront phase distortion of each channel of the liquidcrystal optical phased array antenna is realized by using the wide spectrum characteristic of an optical frequency comb light source. The tiny repetition frequency difference existing in the repetition frequency of the two optical frequency combs is utilized; the optical signal is down-sampled, and real-time high-resolution phase distortion detection is realized through high-precision time-frequency analysis. Therefore, a reliable basis is provided for realizing high-precision real-time phase compensation of phase distortion of the liquid crystal optical phased array, but also a foundation islaid for realizing application of a non-mechanical light beam deflection technology in space optical communication.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
A dynamic time history analysis method for a super high-rise structure
ActiveCN109409006AHigh precisionPreserve the banded sparsity propertyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelHigh rise
The invention relates to a dynamic analysis numerical simulation method for a super high-rise structure. The unconditionally stable dynamic time history analysis method for the super high-rise structure with the high-order precision comprises the following steps that 1, spatial finite element dispersion is conducted on the super high-rise structure, a finite element model dispersion system of thesuper high-rise structure is established, and a motion equation set of the dispersion system is exported according to the Hamilton principle; 2, calculating an equivalent dynamic load; 3, selecting atime step length; 4, calculating time step by step, and calculating the displacement, speed and acceleration of each time step at the end moment; Compared with a traditional second-order dynamic time-history analysis method such as a Newmark method, the dynamic time-history analysis method has the advantages of being high in precision order, high in calculation efficiency and the like, false high-frequency modes caused by spatial dispersion can be filtered out, operation steps are simple, implementation is easy, and high engineering application value is achieved.
Owner:INST OF ENG MECHANICS CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTRATION
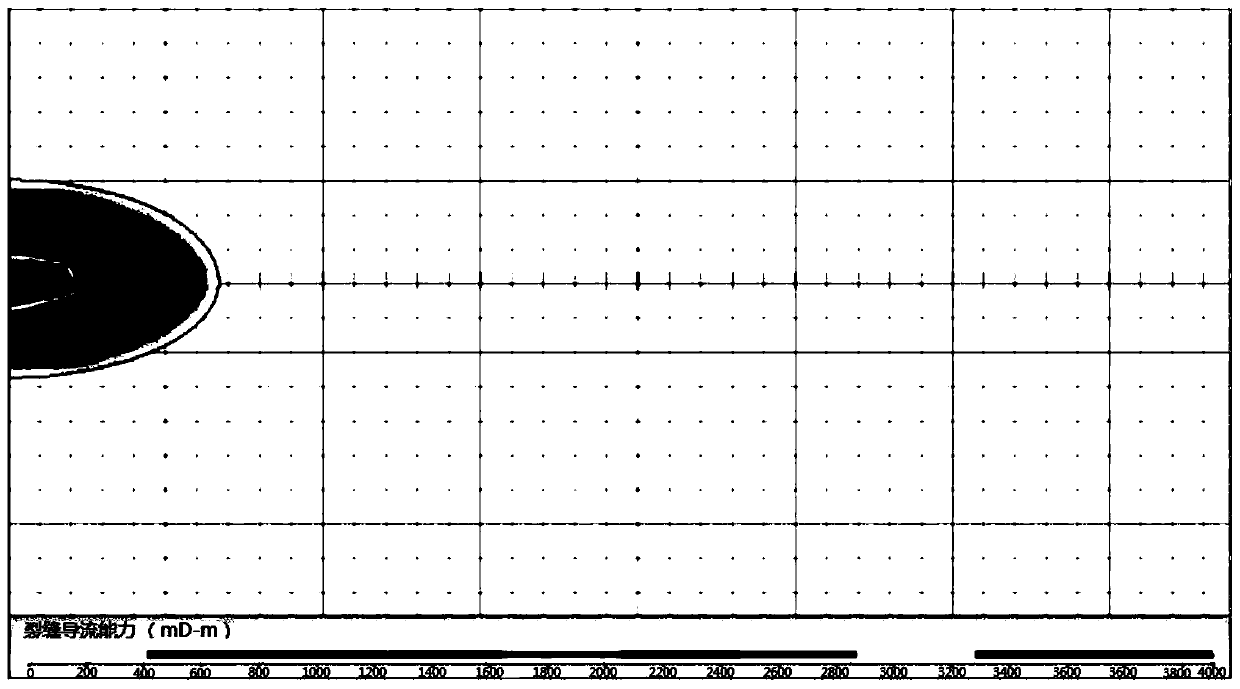
Prediction method for variable space-time diversion capacity of fractures of coal-bed gas well
ActiveCN110410054ARealize dynamic predictionAvoid method flaws of combining simple multiplicationFluid removalSpecial data processing applicationsCapacity valueCoal
The invention discloses a prediction method for a variable space-time diversion capacity of fractures of a coal-bed gas well. The prediction method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting related parameters of reservoir rock of the target coal-bed gas well; S2, calibrating spatial distribution of a global diversion capacity of a prop fracture at an initial moment after fracturing; S3, establishing a mechanism expression about the influence of pulverized coal deposit, proppant embedding and time on diversion capacity of the fracture filled with a proppant; S4, performing spatial dispersion on the global diversion capacity calibrated in the step S2 according to a built diversion capacity change mechanism model to obtain diversion capacity values of each discrete unit at different moments; S5, repeating the steps S3-S4 until the global diversion capacity is completely computed on the basis of computing results of the step S4 as a starting point. According to the prediction method, the defects of diversion capacity prediction by existing indoor experiments are overcome, damage to the diversion capacity by pulverized coal deposit and proppant embedding are taken into account afterthe coal-bed gas well is fractured, and the global variable space-time diversion capacity of the fracture filled with the proppant can be effectively predicted.
Owner:CHINA UNITED COALBED METHANE +2
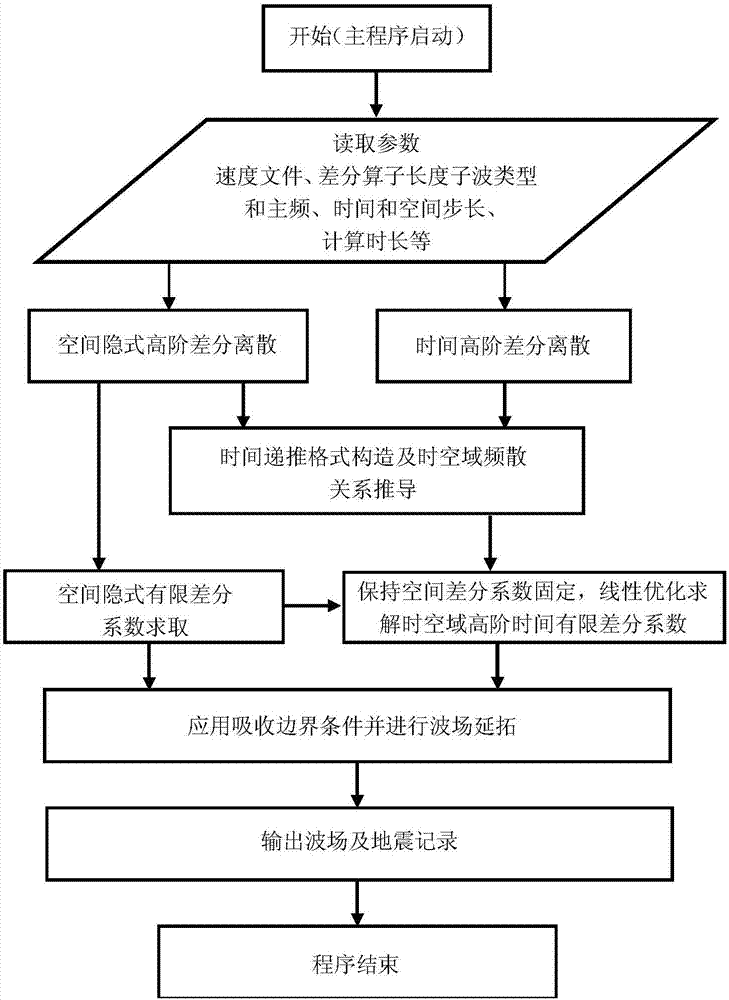
Linear optimization implicit time-space domain finite difference numerical simulation method based on acoustic wave equation
ActiveCN107976710AHigh precisionHigh time accuracySeismic signal processingDifferential coefficientWave equation
The invention discloses a linear optimization implicit time-space domain finite difference numerical simulation method based on an acoustic wave equation, including the following steps: (1) reading parameters; (2) obtaining the time high-order discrete format of a time derivative based on a diamond difference operator and second-order time central difference; (3) solving a second-order spatial derivative by using a spatially implicit discrete format, and solving an implicit differential coefficient based on a spatial dispersion relation and an optimization method; (4) obtaining the time-spacedomain dispersion relation based on the time high-order discrete format and the spatial implicit discrete format; (5) solving the differential coefficient in the time high-order discrete format by using a linear optimization algorithm; (6) absorbing the boundary reflection by using a mixed absorption boundary condition and the obtained differential coefficient, performing recursion according to the wave equation to obtain the wave field at any time and an entire seismic record; and (7) recording a wave field snapshot, outputting the seismic record and ending the process. The finite differencenumerical simulation method has high accuracy, good stability and low dispersion errors.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
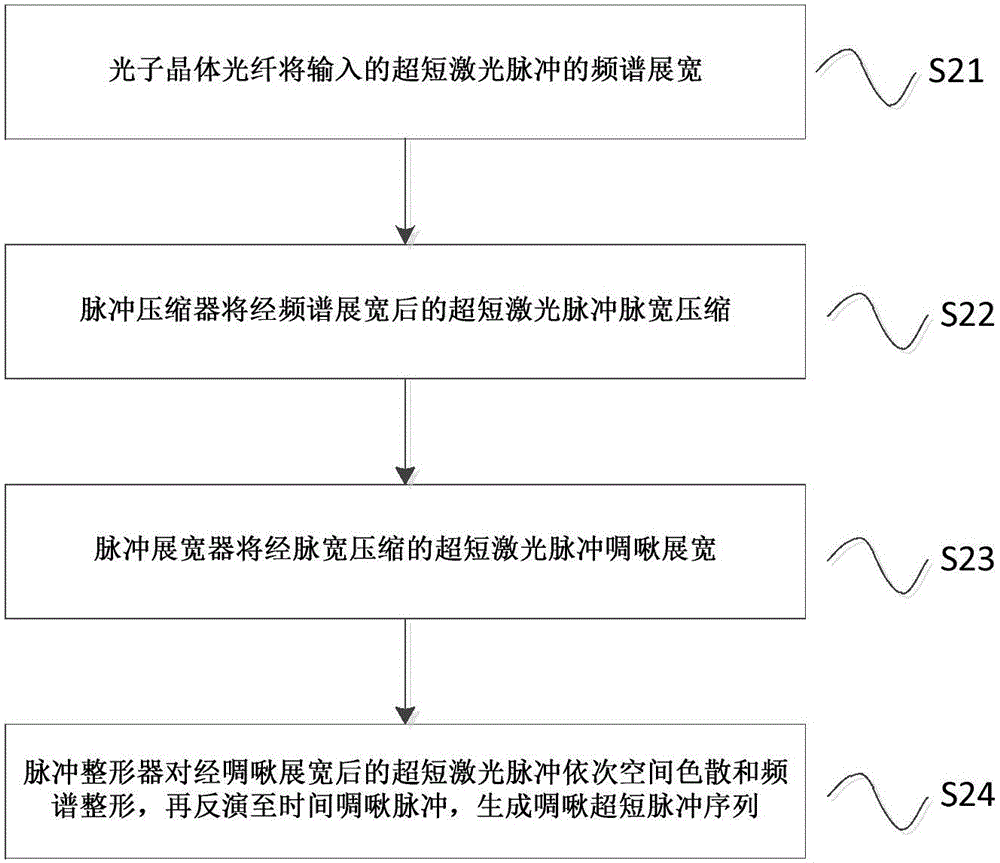
Imaging device and ultra-short pulse sequence generation method
InactiveCN104868346AStrong nonlinear effectActive medium shape and constructionNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumOptoelectronics
The invention discloses an imaging device and an ultra-short pulse sequence generation method. A photonic crystal fiber receives ultra-short laser pulses emitted by a laser, and the spectrum of the inputted ultra-short laser pulses is stretched; a pulse compressor compressed the pulse width of the ultra-short laser pulses outputted by an ultra-continuous spectrum generator after spectrum stretching; a pulse stretcher carries out chirped stretching on ultra-short laser pulses outputted by the pulse compressor after pulse width compression; and a pulse shaper carries out spatial dispersion and spectrum shaping on the ultra-short laser pulses outputted by the pulse stretcher after chirped stretching, the ultra-short laser pulses after spectrum shaping are inverted to time chirped pulses, and a chirped ultra-short pulse sequence is generated. According to the imaging device and the ultra-short pulse sequence generation method disclosed by the invention, the spectrum width of the ultra-short laser pulse source can be effectively increased, the ultra-short pulse sequence whose sub pulse width is smaller than hundred femtosecond is generated, and ultra-fast resolution imaging can be realized.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
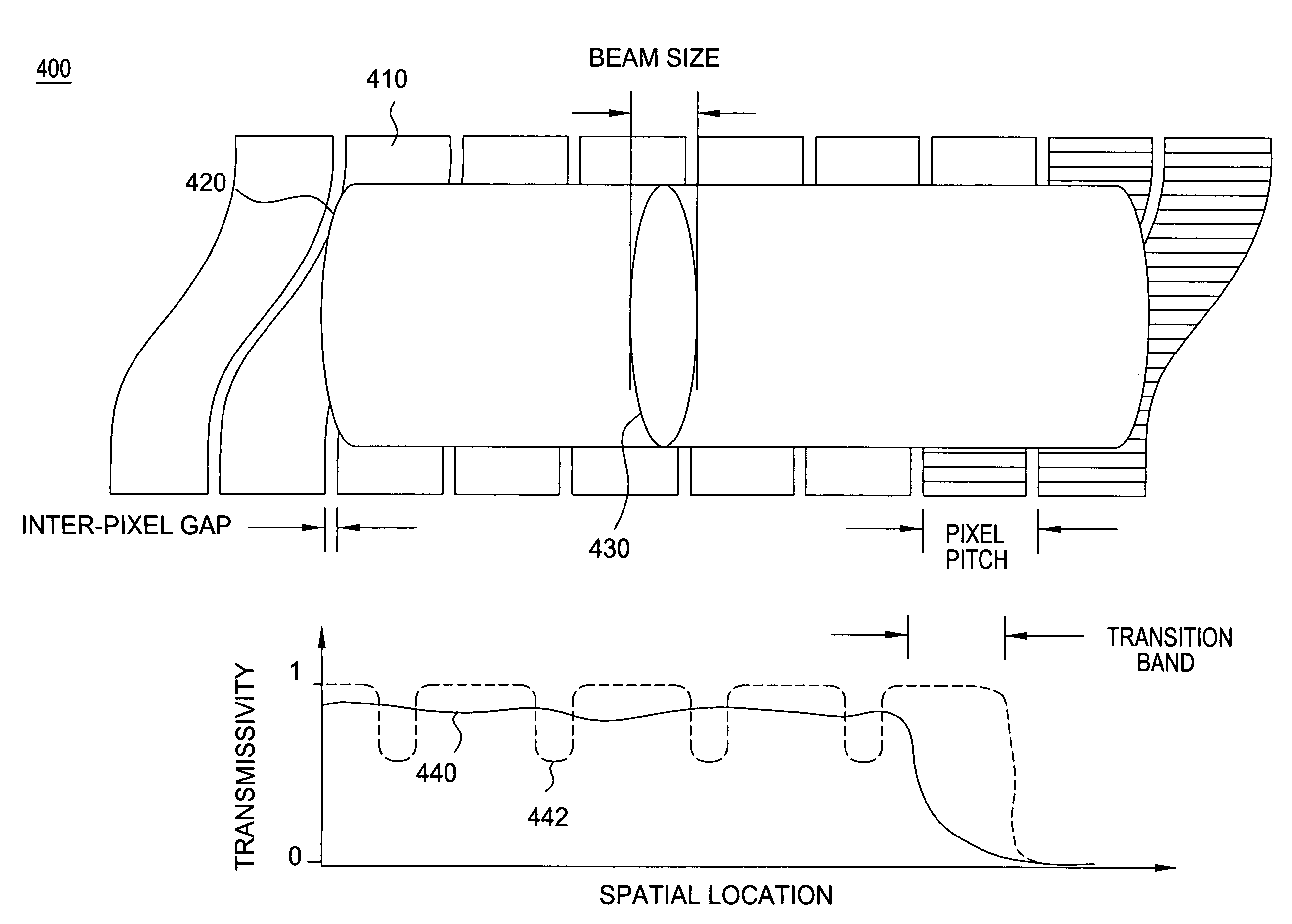
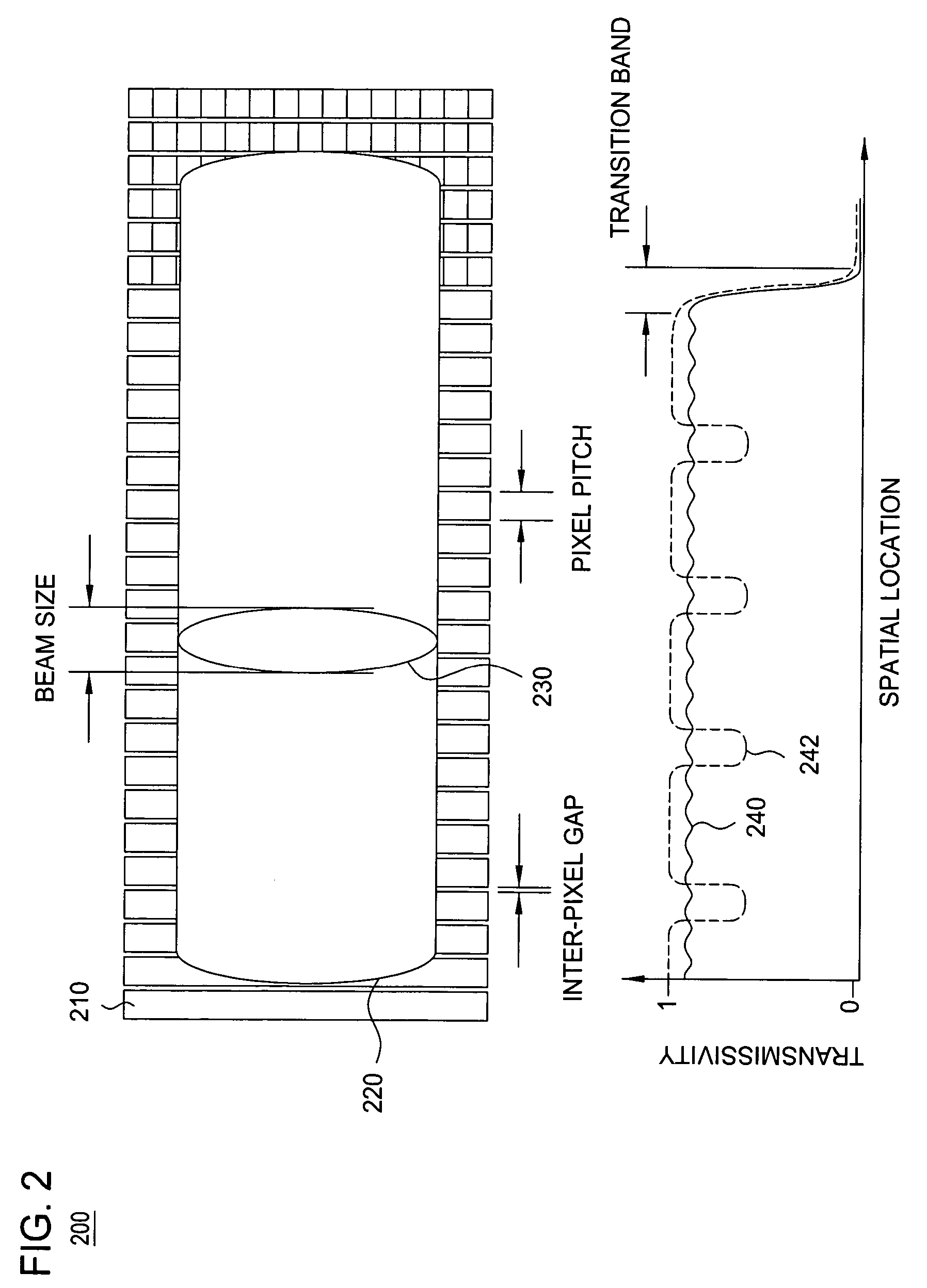
Apparatus for reducing drops in a transmission spectrum due to inter-pixel gaps
ActiveUS7372607B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsDiffraction gratingsFrequency spectrumBeam size
Owner:RPX CORP +1
A long-span bridge seismic response time history analysis method
PendingCN109446715AHigh precisionPreserve the banded sparsity propertyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEngineering
The invention relates to a long-span bridge seismic response time history analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of performing THE spatial finite element discretization on a bridgestructure; establishing a finite element model of a bridge structure, wherein a main beam, a skew tower, a stay cable, a main cable and other components all adopt Euler beam units, adopting a Rayleighdamping matrix, deriving a motion equation set of a discrete system according to the Hamilton principle, and calculating the equivalent inertia force according to input acceleration; 2 selecting a time step length, wherein the time step length is n times of an acceleration recording time interval; 3 calculating time step by step, and calculating displacement, speed and acceleration of each time step. The dynamic time history analysis method has the advantages of high-order precision, high calculation efficiency and the like, false high-frequency oscillation caused by spatial dispersion can becompletely filtered out, and the dynamic time history analysis method is very suitable for solving the rigidity problem of a long-span bridge.
Owner:李鲁
Fingertip detection method based on three-dimensional K curvature
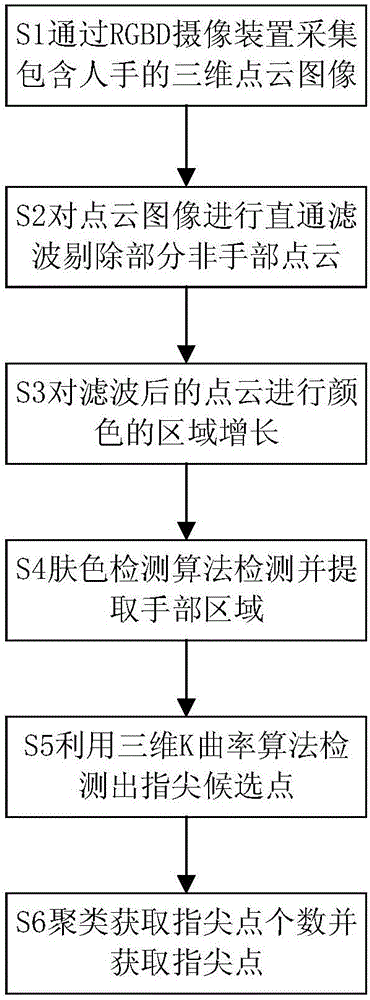
ActiveCN106650628AEasy to detectReduce distance errorCharacter and pattern recognitionFingertip detectionPoint cloud
The invention discloses a fingertip detection method based on three-dimensional K curvature. The method comprises two steps; in the first step, a hand region is extracted based on point cloud color region growing, wherein first, point cloud data acquired by an RGB-D sensor is filtered, then color region growing partitioning is performed on the filtered point cloud data, and finally a skin color detection algorithm is adopted to acquire the point cloud data in the hand region; in the second step, fingertip points are extracted based on a three-dimensional K curvature algorithm, wherein hand point cloud is filtered to remove some spatial dispersion points after the hand region is acquired, then the thought of the K curvature algorithm is utilized to process the point cloud data, fingertip candidate points are determined and clustered, and the fingertip points are obtained. Through the method, the fingertip points can be well detected at different positions, and under different backgrounds and different light environments under a plurality of common gestures such as gestures of representing the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5. According to the method, the distance error between the obtained fingertip points and actual fingertip points is only about 5mm, and therefore good precision and robustness are achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Metal target transient electromagnetic scattering analysis method based on delay laguerre polynomials
InactiveCN104915465ALittle unknownSave memorySpecial data processing applicationsTransient electromagneticsReference Document
The invention discloses a metal target transient electromagnetic scattering analysis method based on delay laguerre polynomials. A target is subdivided through curved surface triangle surface elements. Spatial dispersion and time dispersion are carried out on a time domain mixed field integral equation through a CRWG primary function and the delay laguerre polynomials. A test is carried out through a galerkin method. An order-stepped matrix equation is finally formed, and the transient electromagnetic scattering characteristic of the target can be obtained through resolution of the equation and post-processing. As a delay item related to the spatial position of the target is introduced into a time primary function, the time primary function contains the spatial phase information of the target is adopted, and the target can be subdivided with less curved surface triangle surface elements. The unknown calculation amount is greatly reduced, consumption of an inner storage is effectively reduced, the calculation time is shortened, and important reference documents are provided for accurate analysis of the transient electromagnetic scattering characteristic of an electric large-size metal target.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ensemble learning method based on self-adaptive sample expansion
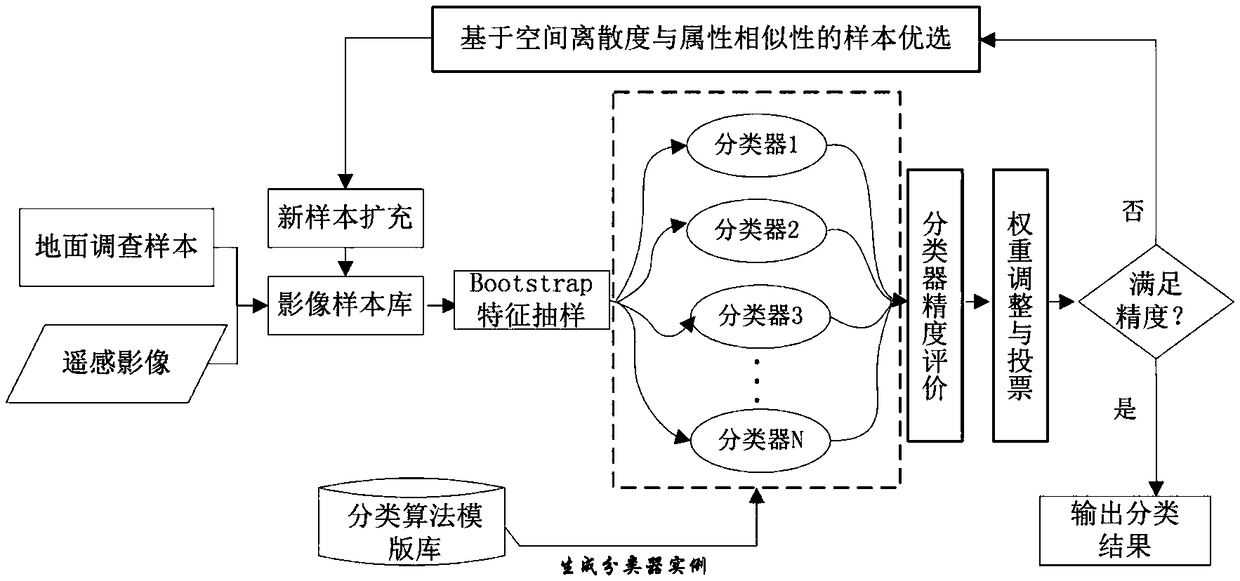
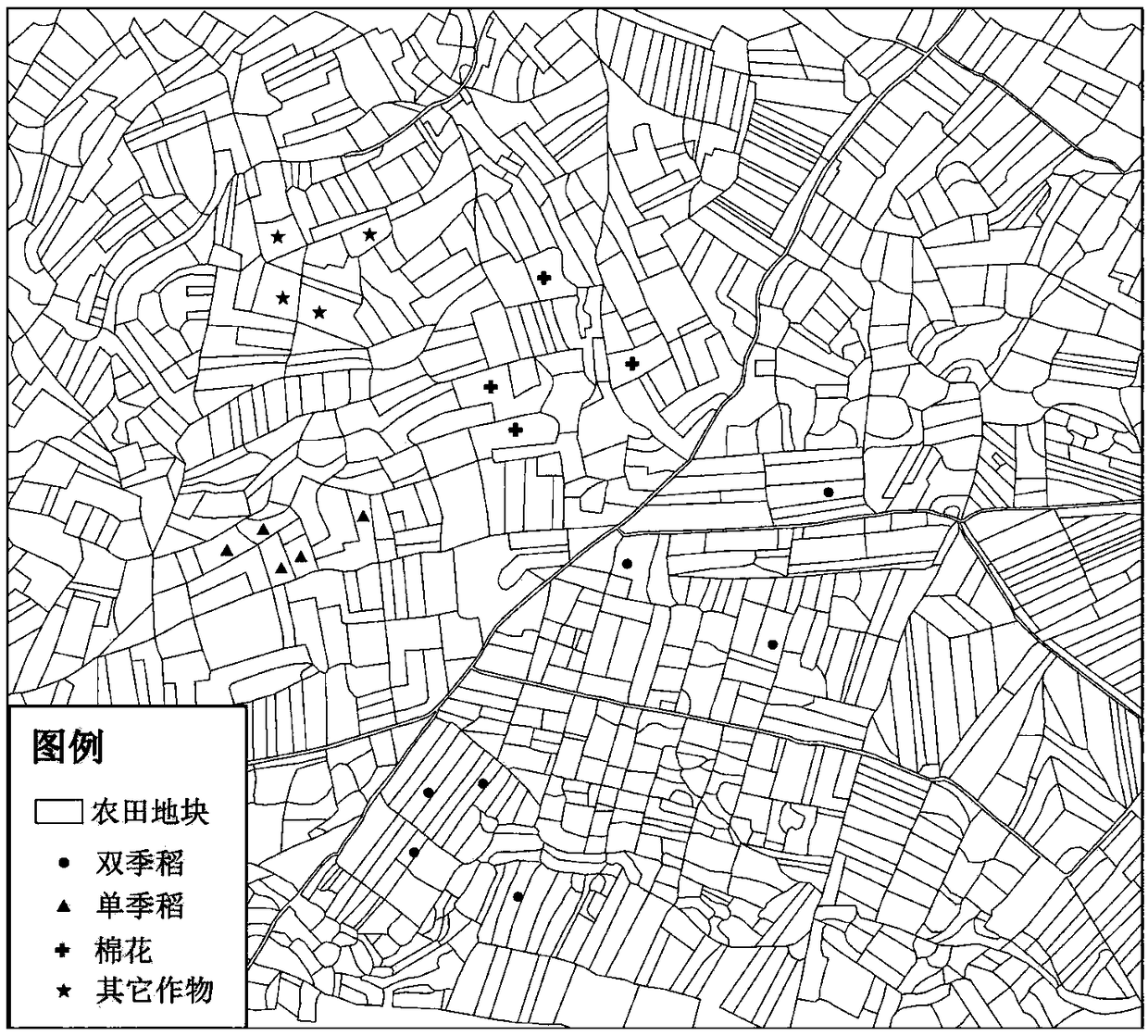
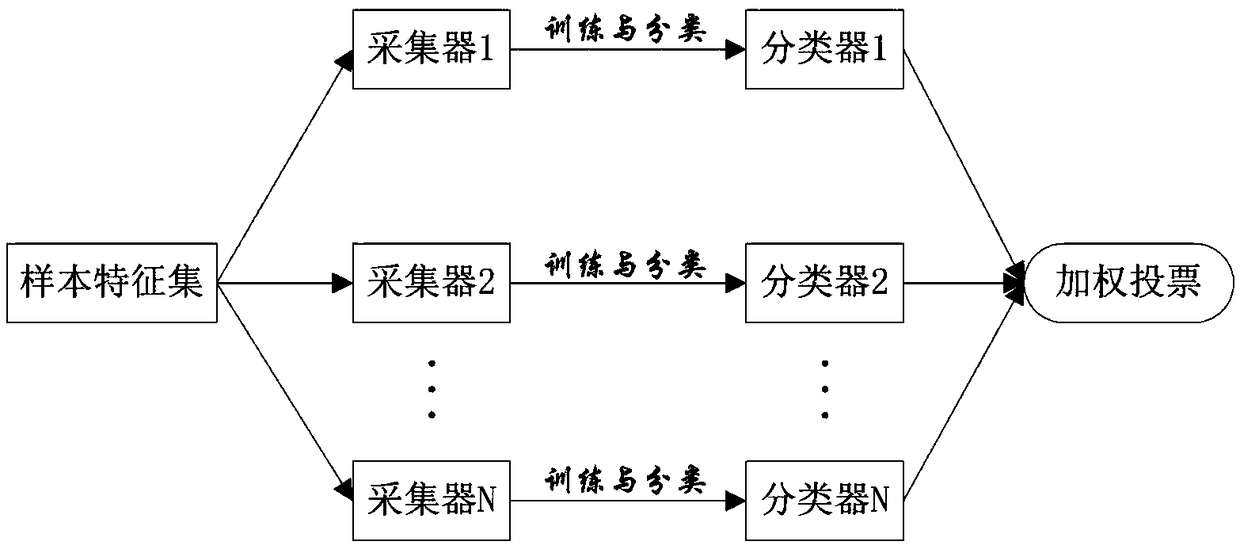
ActiveCN108830312AAdaptive extension implementationSolve problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionInsufficient SampleStudy methods
The invention discloses an ensemble learning method based on self-adaptive sample expansion. On the one hand, multiple weak classifiers are integrated through adopting a manner of bootstrap feature sampling and dynamic weighted voting, and the advantages of high classification accuracy and good repeatability of the ensemble learning method are inherited; and on the other hand, the method can realize self-adaptive expansion of samples through iteration classification and sample screening based on spatial dispersion and attribute similarity on the basis of a small number of ground survey samples, and the model under-learning problem caused by small / medium-sized samples in classification is solved. The ensemble learning method to which the scheme relates adopts a manner of self-adaptive sample expansion, can effectively solve the problem of insufficient samples in a remote-sensing classification process, and reduces manpower and time spent by researchers for obtaining samples at the sametime.
Owner:SUZHOU ZHONGKE IMAGE SKY REMOTE SENSING TECH CO LTD +2
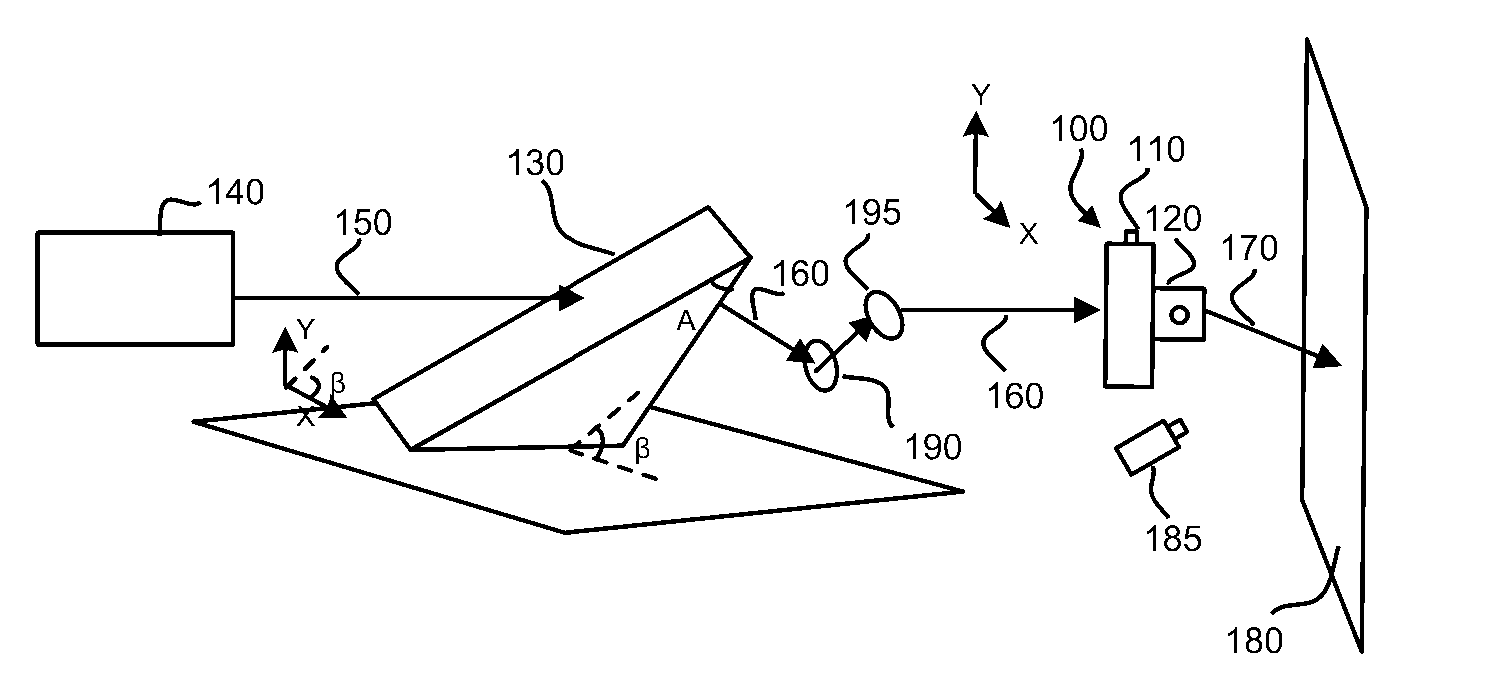
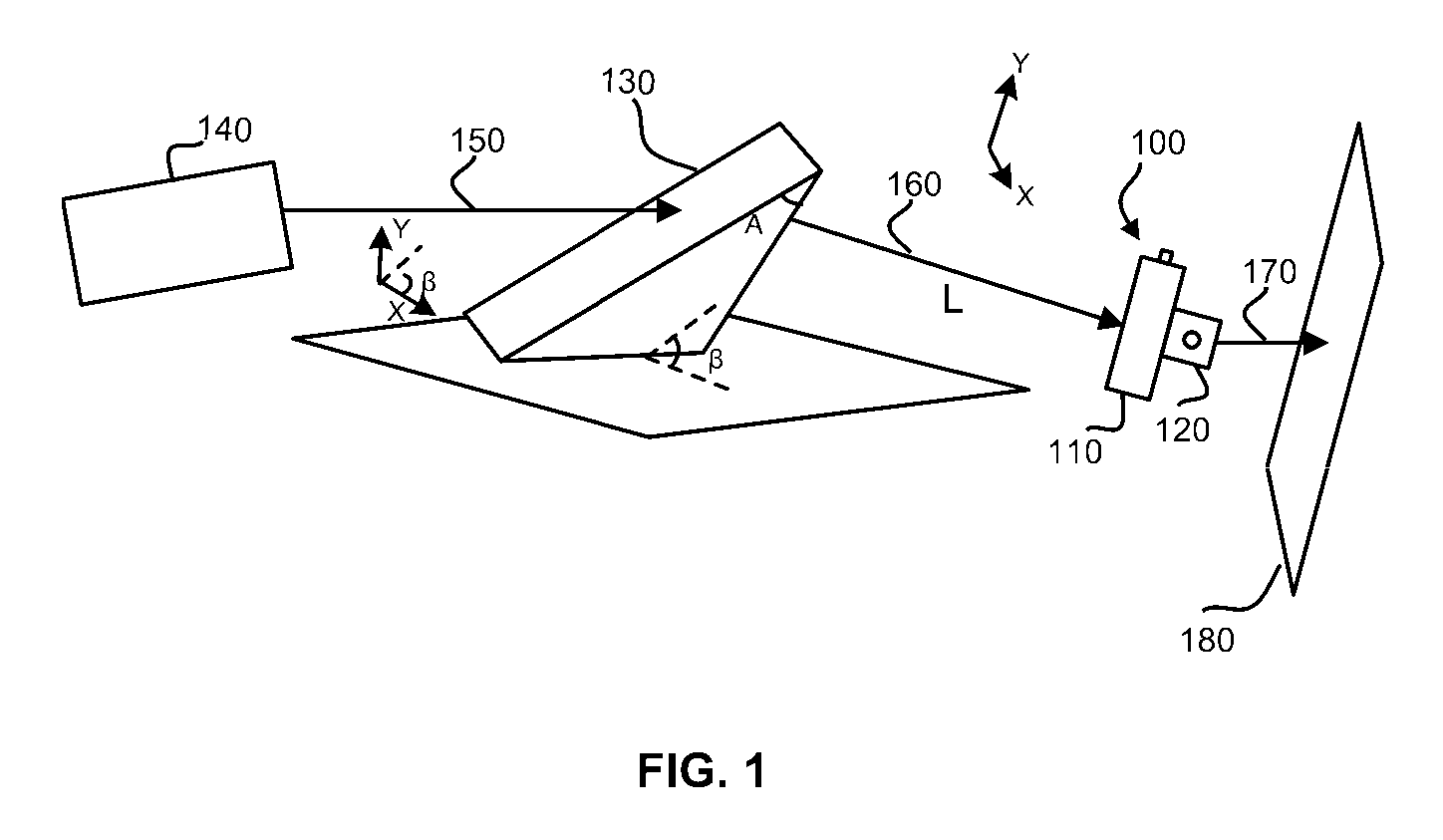
Light pulse positioning with dispersion compensation
InactiveUS20070019276A1High refreshing rate scanningHigh resolutionPrismsNon-linear opticsAcousto optic deflectorOptoelectronics
A light pulse positioning apparatus with dispersion compensation includes an acousto-optical device and a dispersive element optically coupled thereto. The dispersive element is placed and oriented in relation to the acousto-optical device to spatially and temporally disperse the light pulse and thus compensate, respectively, a spatial dispersion and a temporal dispersion caused by the acousto-optical device. The acousto-optical device can include one or more acousto-optical deflectors for one-dimensional or two-dimensional laser pulse positioning. The dispersive element can be a prism placed in front of the acousto-optical device. In a two-dimensional configuration, a single prism, if properly oriented, is sufficient for dispersion compensation of both acousto-optical deflectors.
Owner:ZENG SHAOQUN +3
Method and system for determining an error in the estimation of the time taken to cross the ionosphere
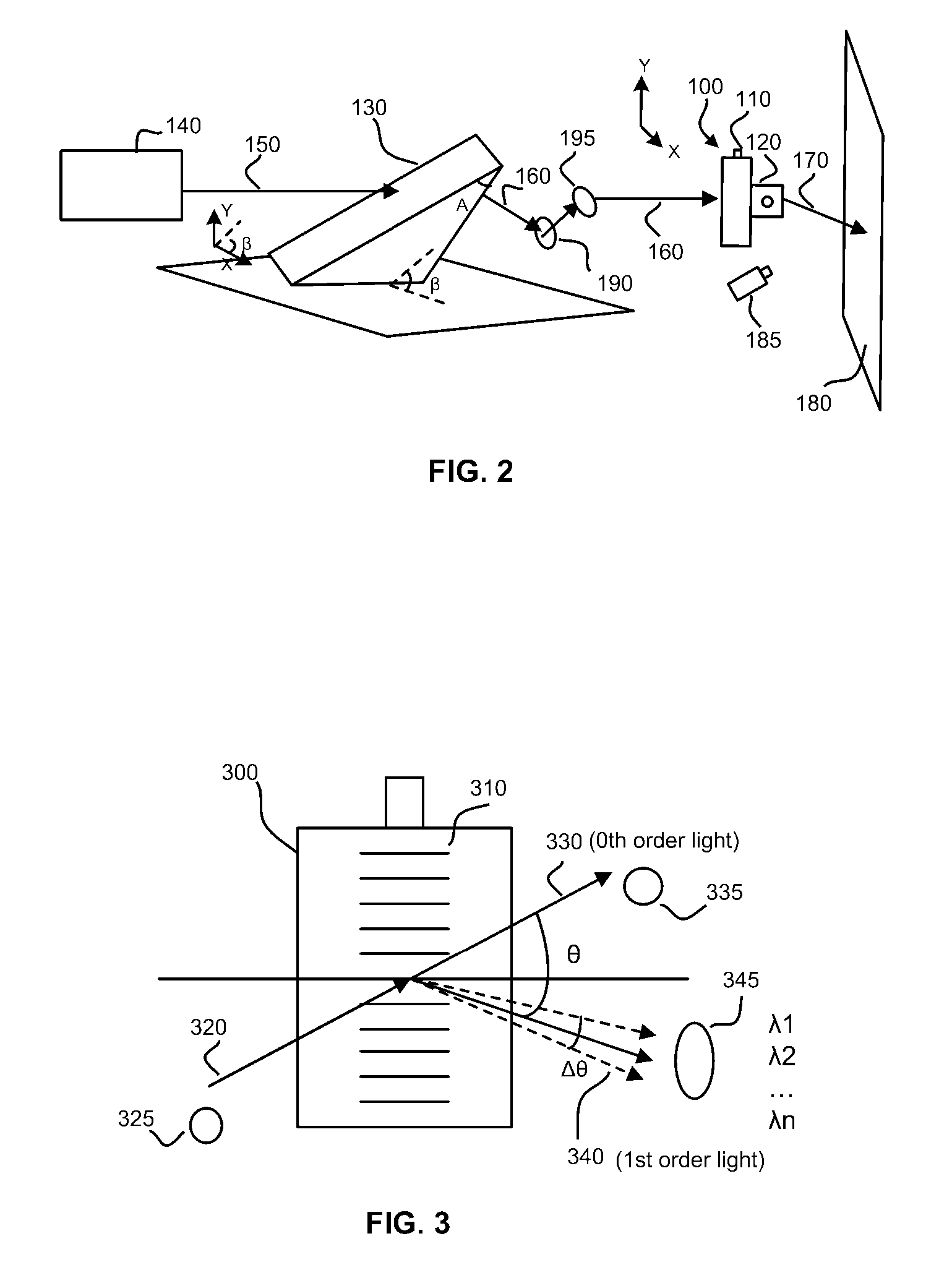
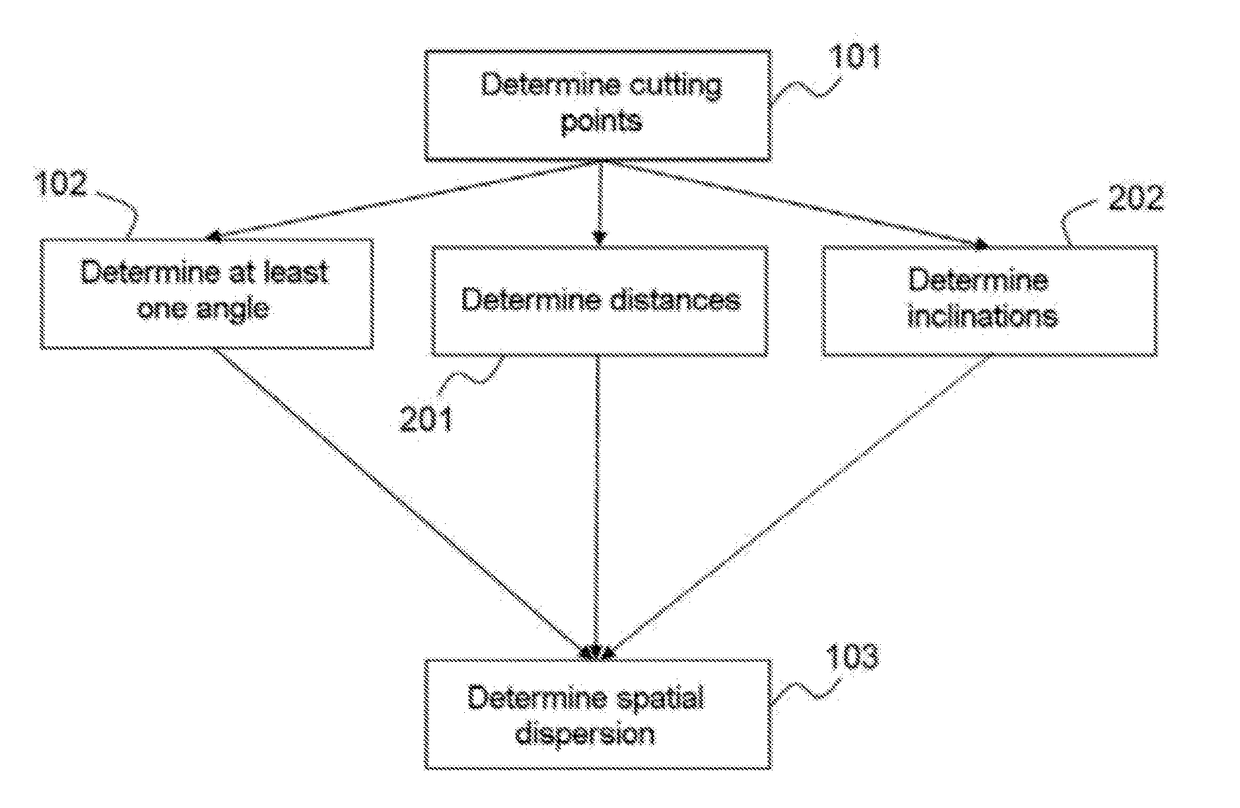
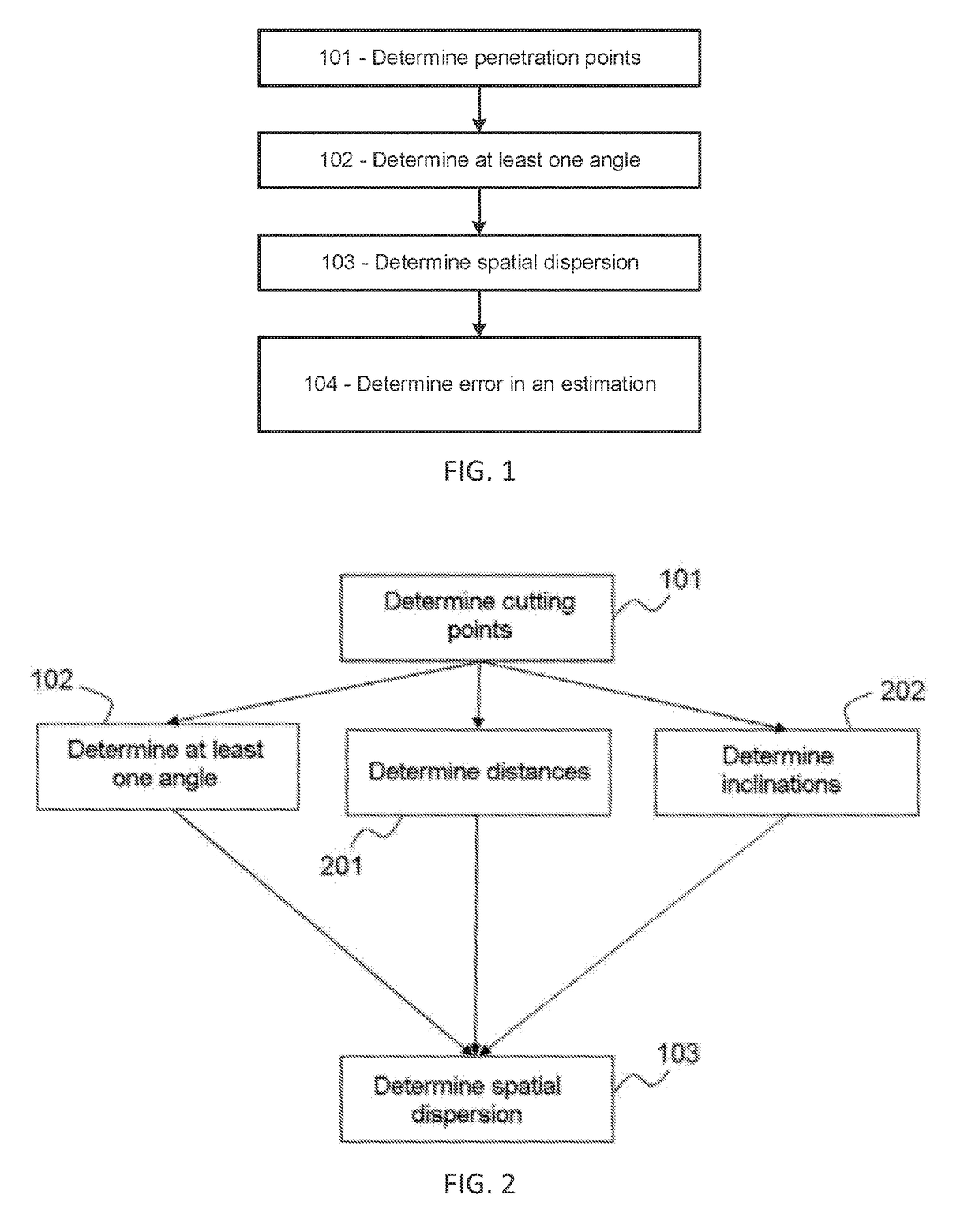
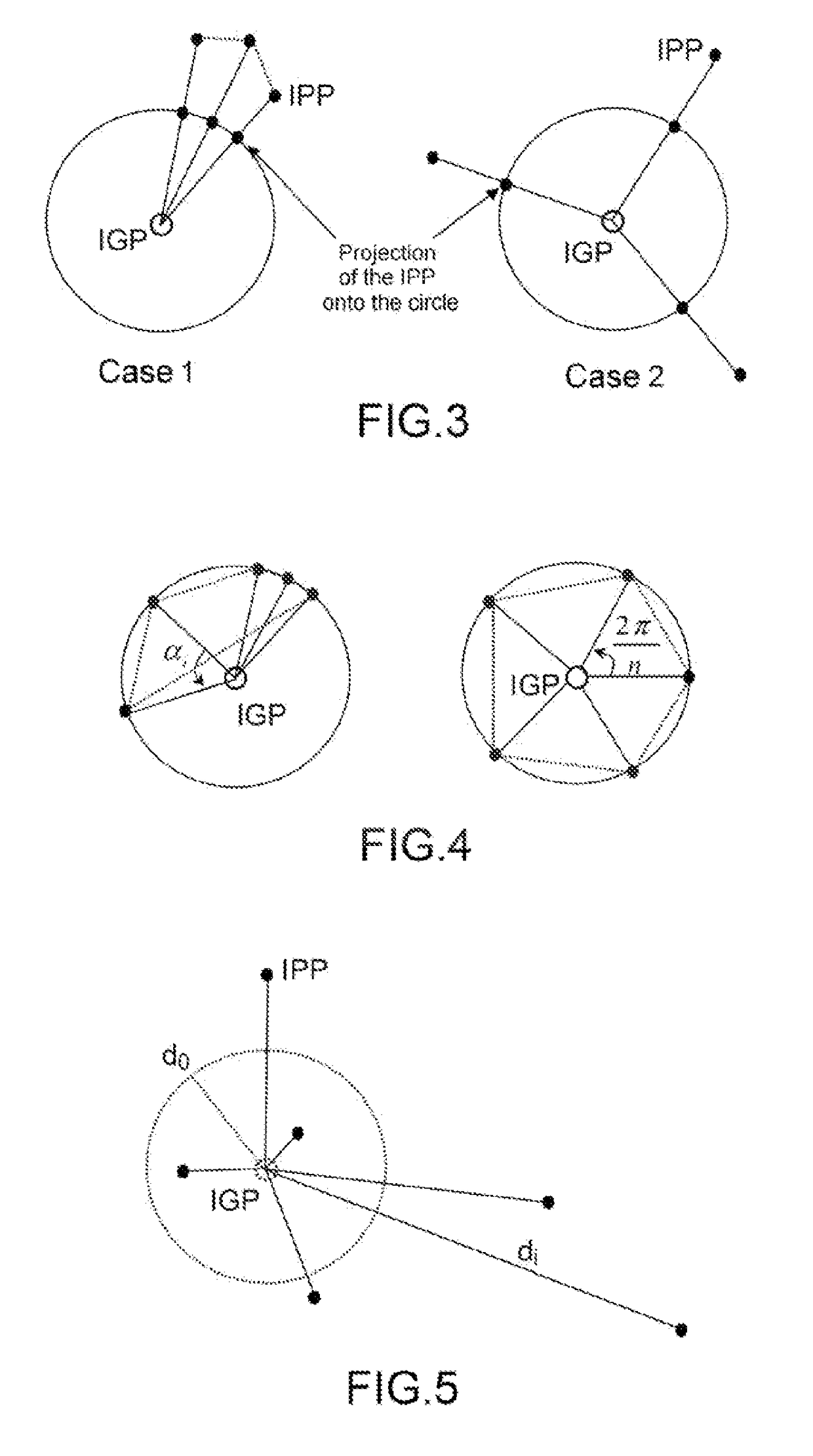
ActiveUS9651668B2Maximize availabilityEstimate the impreciseness in the propagation delaySatellite radio beaconingGeomorphologyIonosphere
A method for determining an error in the estimation of time taken to cross the ionosphere by a signal along a vertical sight axis associated with a receiver, the vertical sight axis cutting the ionosphere at a point of interest, the vertical sight axis being an axis passing through the receiver and a satellite of interest, comprises: determining at least two points of cutting of the ionosphere by two sight axes between a satellite and at least two ground stations; determining at least one angle formed by segments going from the point of interest to two of the cutting points; and determining the spatial dispersion of the cutting points with respect to the point of interest on the basis of the angle, by finding the difference with a predetermined angle and taking the average of the difference or differences.
Owner:THALES SA
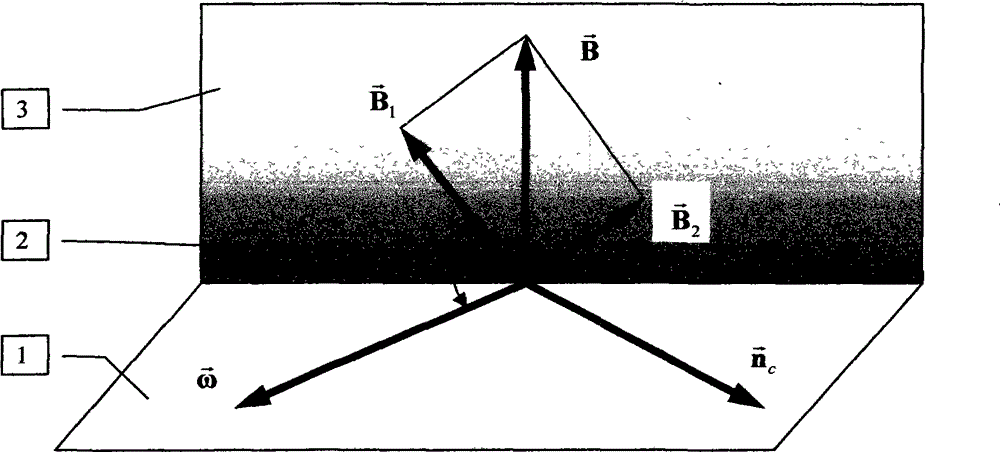
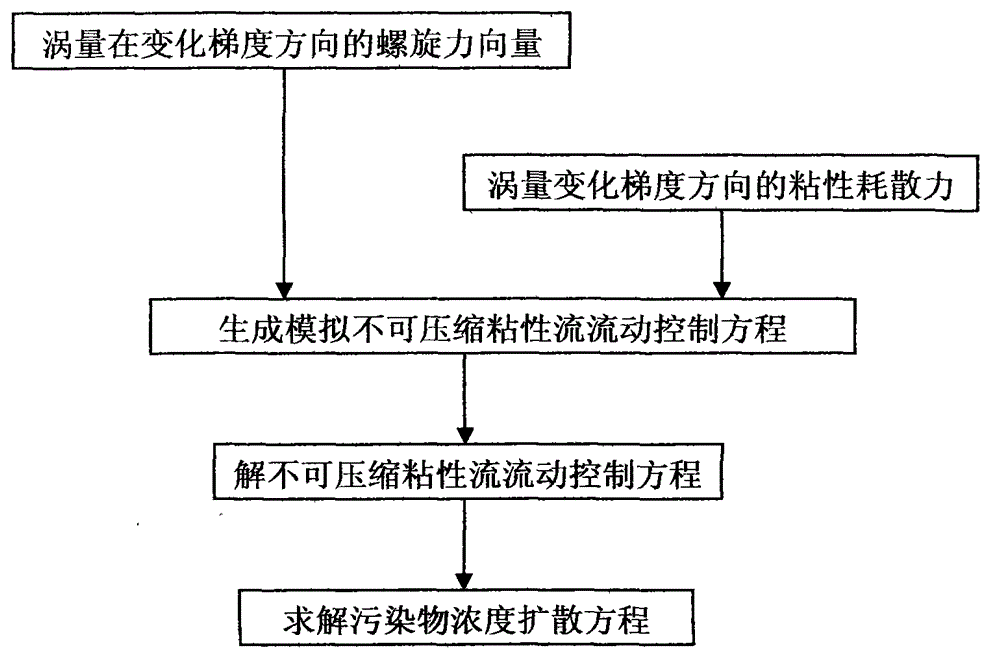
Numerical method for simulating pollutant dispersion in swirling flow field
InactiveCN103064996AHigh precisionFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumViscous dissipation
The invention provides a numerical method for simulating pollutant dispersion in a swirling flow field. According to characteristics of incompressible flows, two forms of force are added in a momentum equation to improve numerical simulation accuracy of the vortical-motion-oriented flow field. The two forms of force are respectively vortical force and viscous dissipation force of a vorticity in the changing gradient direction. The numerical method enables integral calculation of the vortical force of the vorticity in a computational grid in the changing gradient direction to be converted into flux calculation of force on a boundary of the computational grid and can enable spatial dispersion to have a high-order accuracy form. In addition, the viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the changing gradient direction is retained by a source item of the momentum equation so as to improve convergence and stability of a numerical solution. The two forms of force adopt different amplification coefficients, the accuracy of the vorticity can be further kept, and pollutant dispersion movement in the swirling flow field can be accurately simulated.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
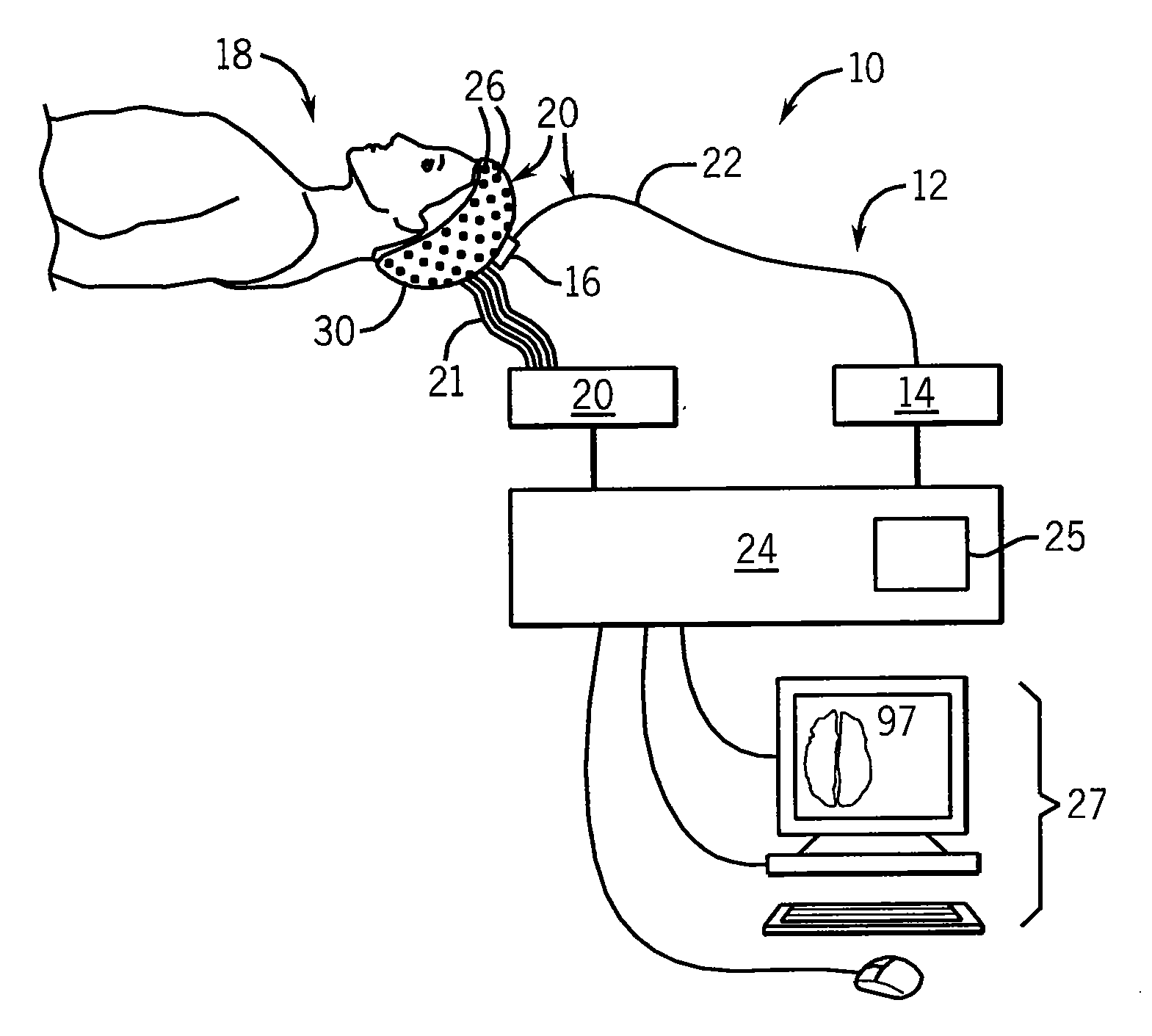
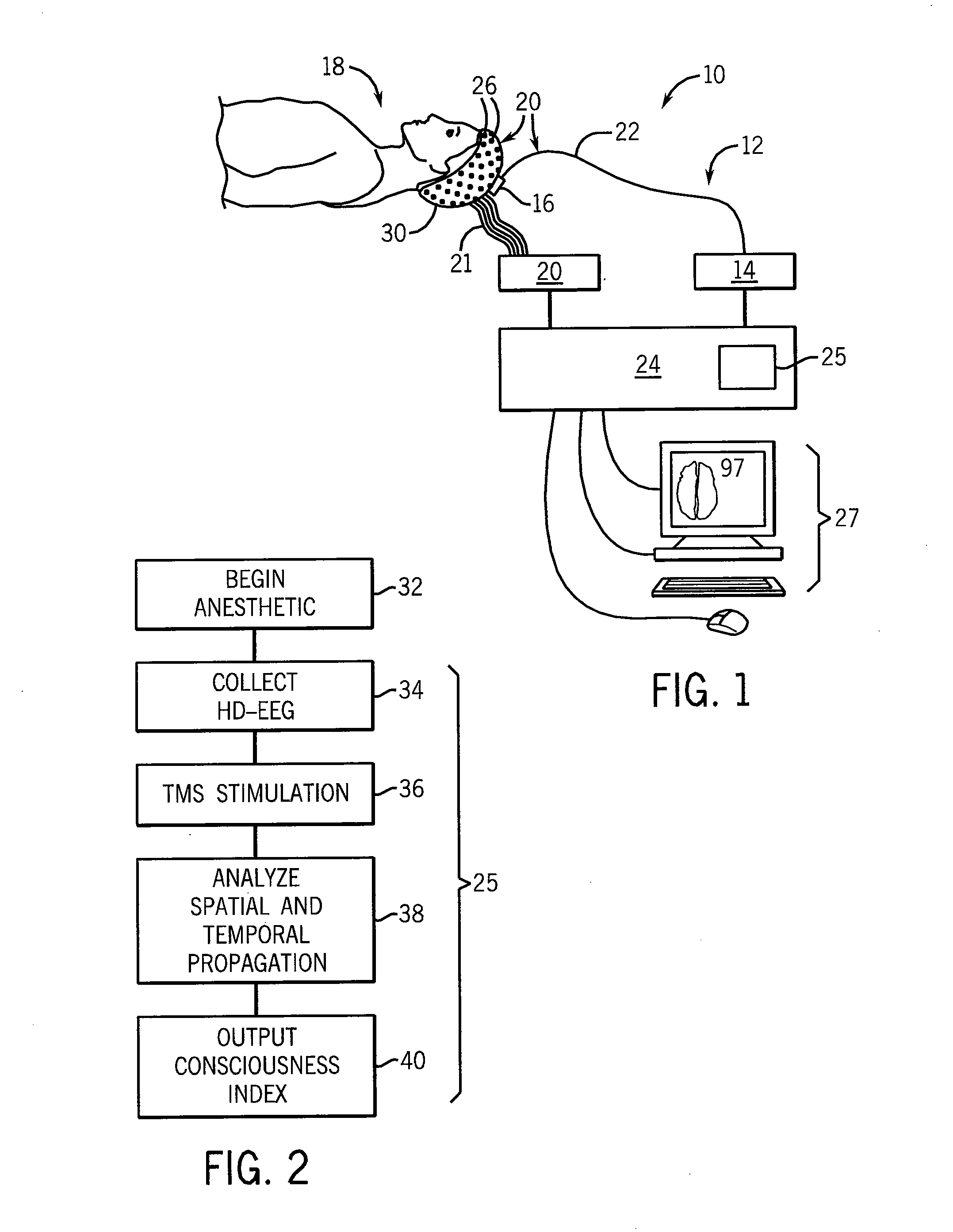
Method for assessing anesthetization
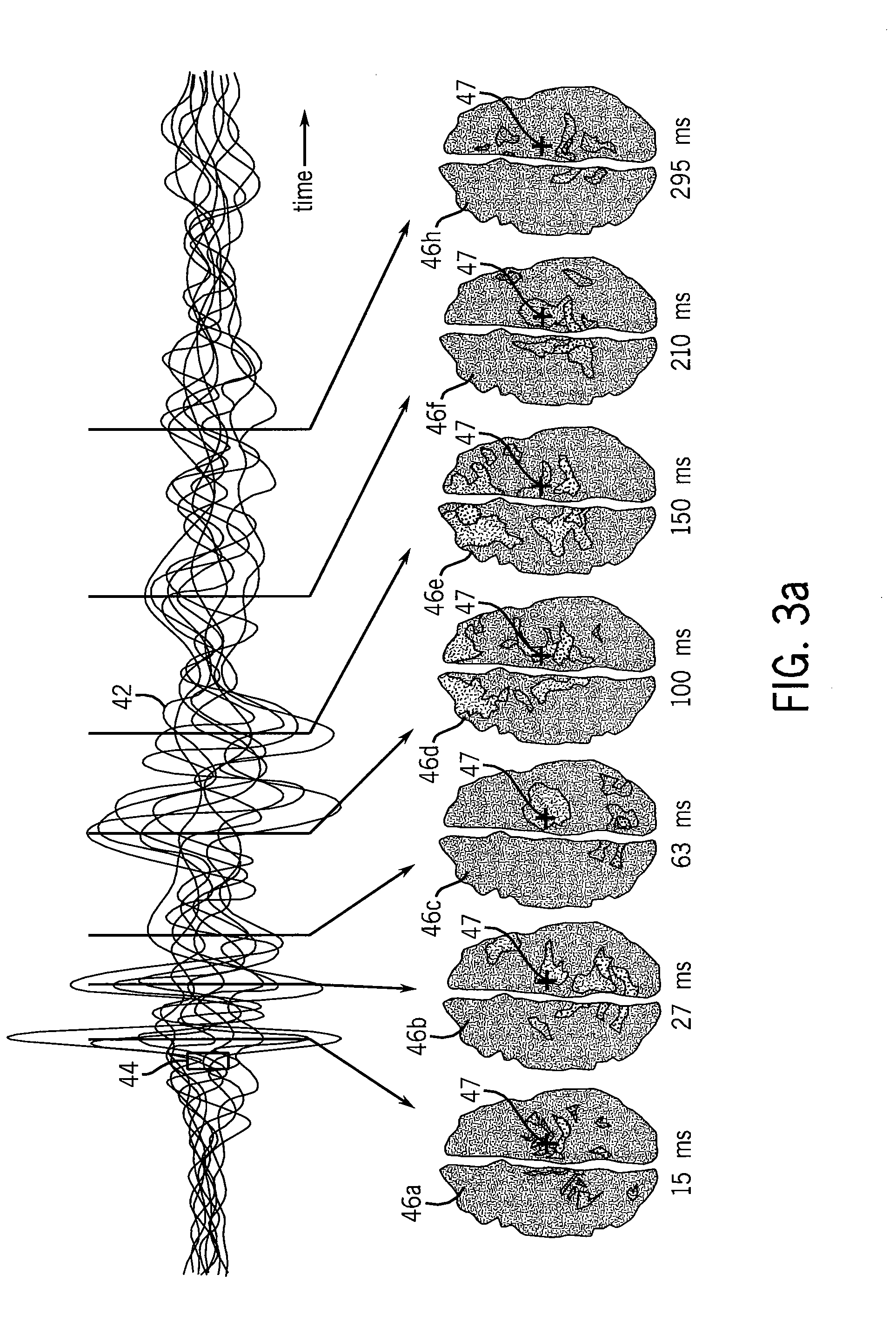
An evaluation of consciousness during the application of anesthetic evaluates causal propagation of neural activity in response to a localized stimulus, for example, by transcranial magnetic stimulation. A longer duration of invoked activity and a greater spatial dispersion of the invoked activity or greater complexity are matched to greater wakefulness comporting with a theory of consciousness as cortical integration of information moderated by intraneural communication.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Numerical method for simulating wingtip vortex flow of aircraft
InactiveCN102930134AHigh precisionFast convergenceAerodynamics improvementSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumEngineering
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
Coarse mesh rapid time domain finite difference method
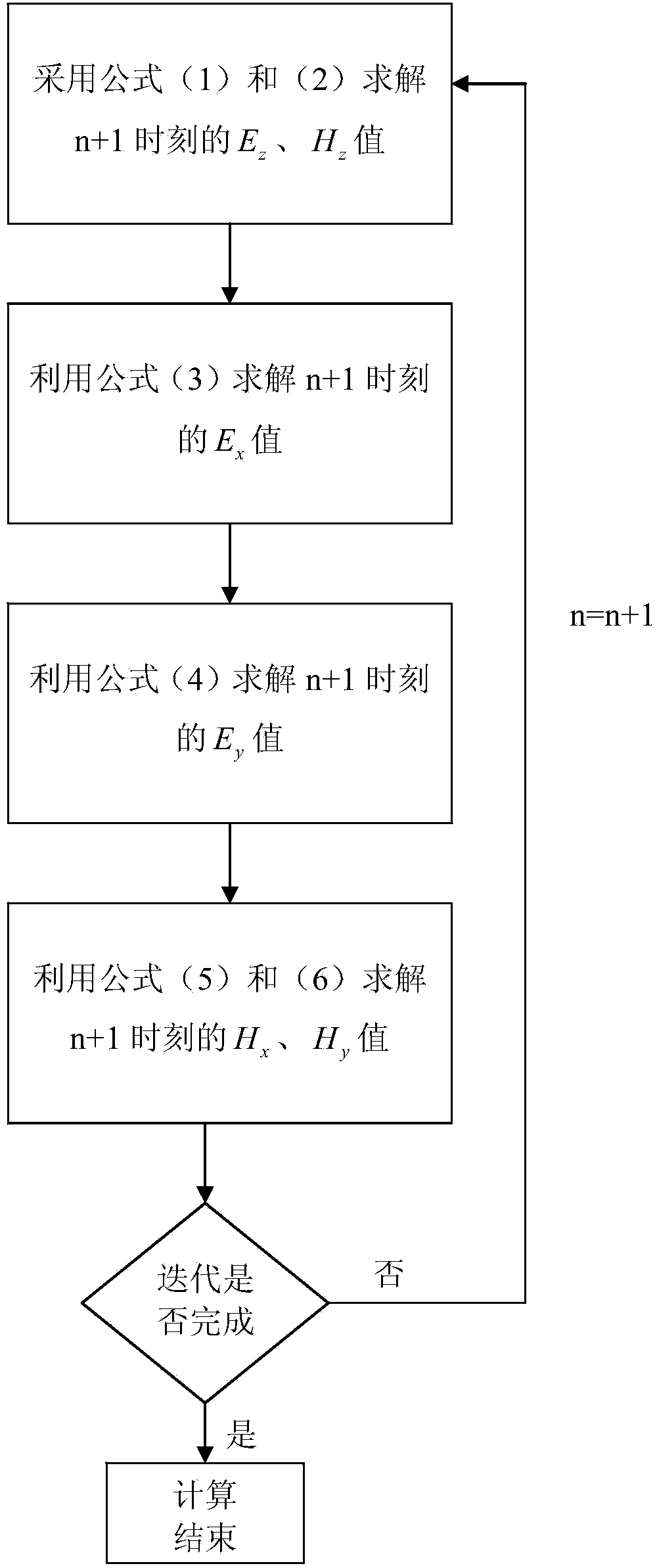
InactiveCN103514143AEasy to limitTemporal Stability Conditions ReducedComplex mathematical operationsFine structureInternal memory
The invention relates to a coarse mesh rapid time domain finite difference method and belongs to the field of electromagnetic field value calculating. A time step length delta t is not related to a spatial mesh length delta z and a spatial mesh length delta x just needs to be smaller than or equal to half the minimal wavelength of a simulation frequency segment. Two major limitation conditions of a traditional time domain finite difference method can be solved at the same time, wherein the two major limitation conditions are a Courant-Friedrich-Levy time stability condition and a spatial dispersion isolation limitation condition. With the method, the time stability condition is lowered and at the same time, limitation of wavelength on the spatial mesh length is perfected. The coarse mesh rapid time domain finite difference method is applicable to simulation of a complicated target with a fine structure and an electrically large structure. Compared with the traditional time domain finite difference method, the coarse mesh rapid time domain finite difference method has two major advantages of being high in calculating efficiency and little in internal memory needed by calculating.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
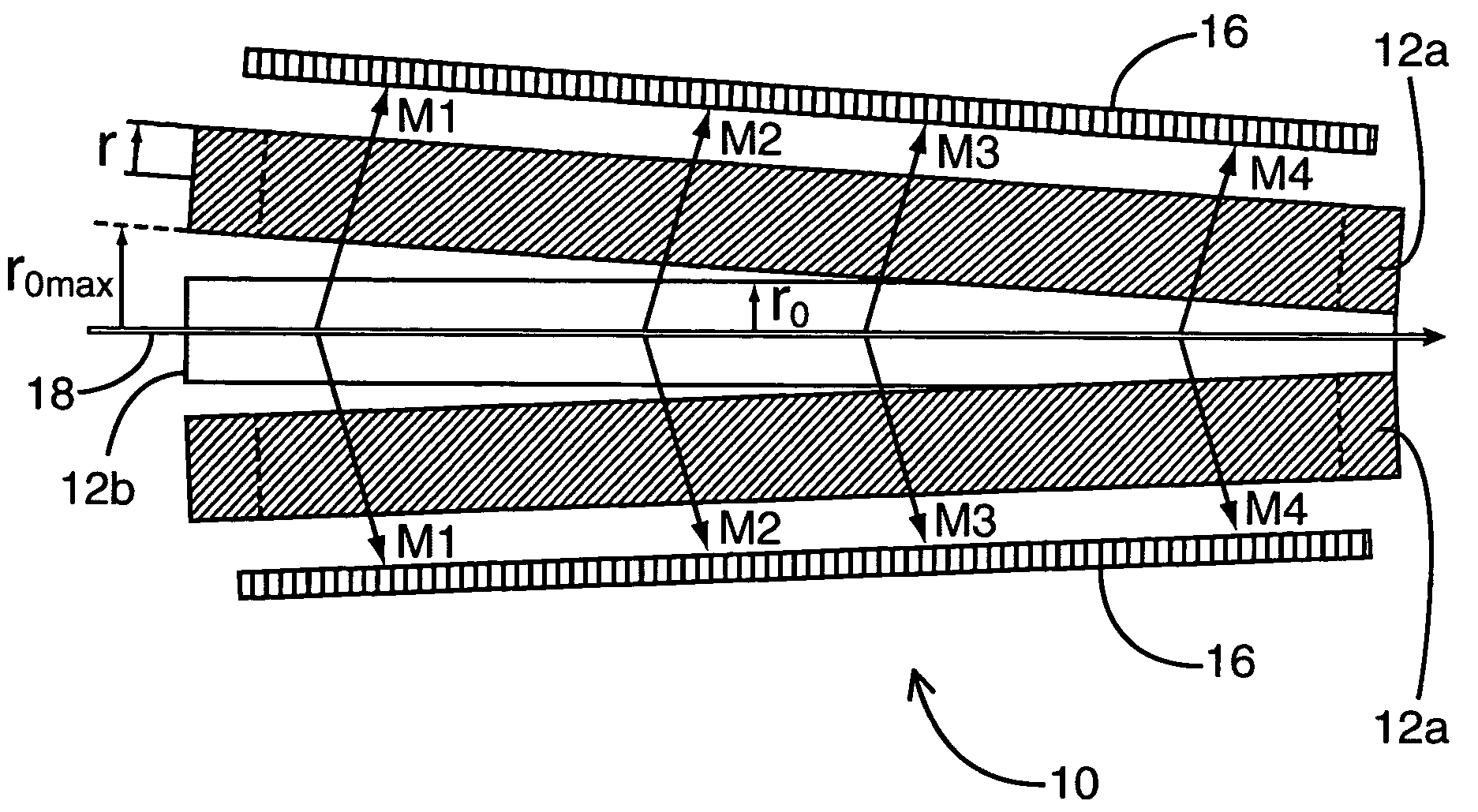
Multi-way pulse compressor and using method thereof
The invention discloses a multi-way pulse compressor and a using method thereof. The main body of the compressor comprises two end mirrors, the concave spherical surfaces of which are relatively coaxially placed; rotating rings are arranged on the end mirrors; and concave spherical reflectors are arranged in the rotating rings. Dispersion compensation film series are plated on the concave spherical surfaces of the concave spherical reflectors, and through grooves are processed on the reflectors. When the compressor is used, closed annular light spot tracks can be obtained on the concave spherical surfaces by setting and repeatedly adjusting the two end mirrors, and then discrete adjustment is implemented by rotating the compression of the rotating rings on the pulse. The compressor and the using method have the advantages that: the compressor has low loss, a compact structure and no spatial dispersion light path; the concave spherical surfaces can effectively counteract the beam broadening caused by the diffraction effect of beams so as to effectively overcome the defects of the conventional grating pair technology, prism pair technology and plane mirror-based dispersion mirror compensation technology; and the using and adjusting method is simple and convenient.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Equivalent characterization method for reservoir stratum cause unit interface
InactiveCN103617291ASeepage effect is obviousGood effectGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceSpatial dispersion
The invention discloses an equivalent characterization method for a reservoir stratum cause unit interface. The equivalent characterization method comprises the specific step of tracking a three-dimensional geologic model sand body cause unit interface based on three-well-point data constraint: combining well-point explanation data to smooth sedimentary microfacies data in a three-dimensional geologic model by adopting a low-pass filtering algorithm, tracking cause units, namely the spatial position of each microfacies interface on the basis, and forming three-dimensional spatial dispersion data of an architecture interface. According to the equivalent characterization method, the influence of the grid conductivity equivalent characterization low-seepage architecture interface between the reservoir stratum cause units on the seepage effect is utilized, and the grid conductivity between the reservoir stratum cause units is adjusted, so that the aim that the low-seepage architecture interface is set in numerical reservoir simulation is achieved, the value of the conductivity equivalently characterizes the influence of the architecture interface on the seepage effect, and the obvious effects are achieved for oil field efficient development and remaining oil prediction.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Flat panel display device and method of controlling picture quality of flat panel display device
ActiveUS8164604B2Fix bugsCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsFlat panel displayComputer science
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Light pulse positioning with dispersion compensation
InactiveUS7821698B2Increase refresh rateHigh resolutionPrismsNon-linear opticsAcousto optic deflectorOptoelectronics
A light pulse positioning apparatus with dispersion compensation includes an acousto-optical device and a dispersive element optically coupled thereto. The dispersive element is placed and oriented in relation to the acousto-optical device to spatially and temporally disperse the light pulse and thus compensate, respectively, a spatial dispersion and a temporal dispersion caused by the acousto-optical device. The acousto-optical device can include one or more acousto-optical deflectors for one-dimensional or two-dimensional laser pulse positioning. The dispersive element can be a prism placed in front of the acousto-optical device. In a two-dimensional configuration, a single prism, if properly oriented, is sufficient for dispersion compensation of both acousto-optical deflectors.
Owner:ZENG SHAOQUN +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com