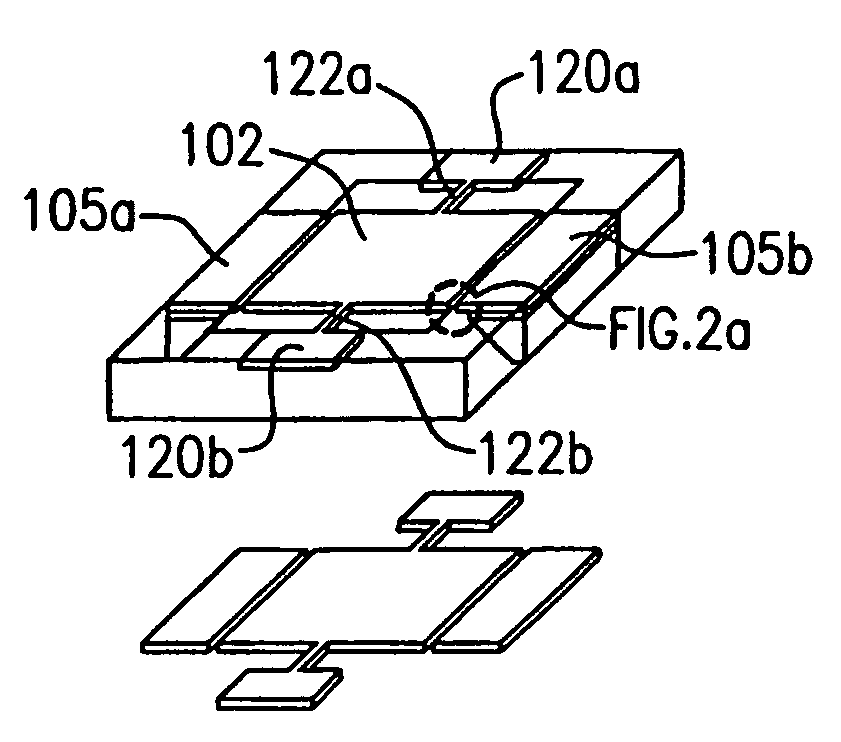
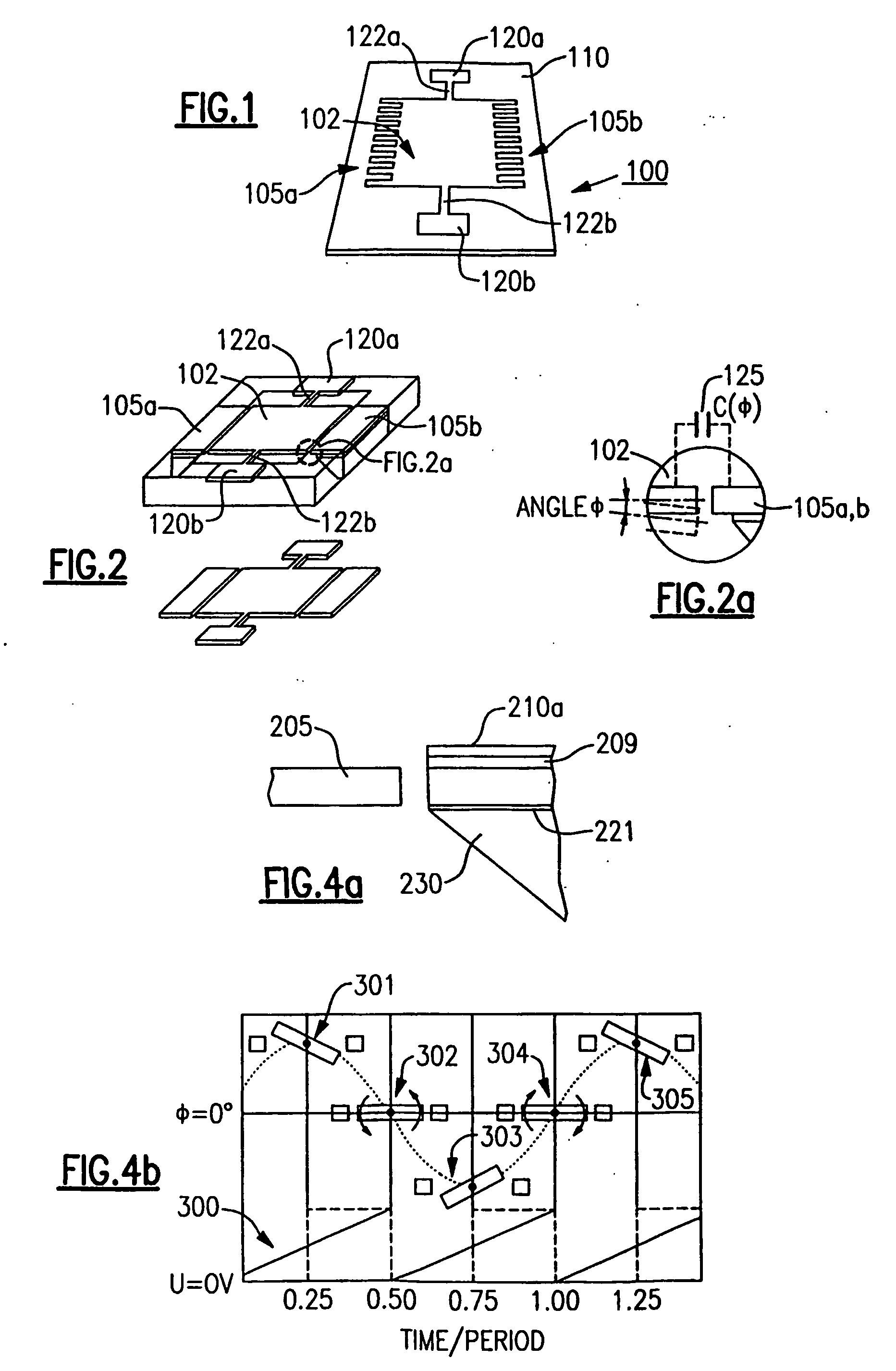
Patents
Literature
150 results about "Acousto optic deflector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
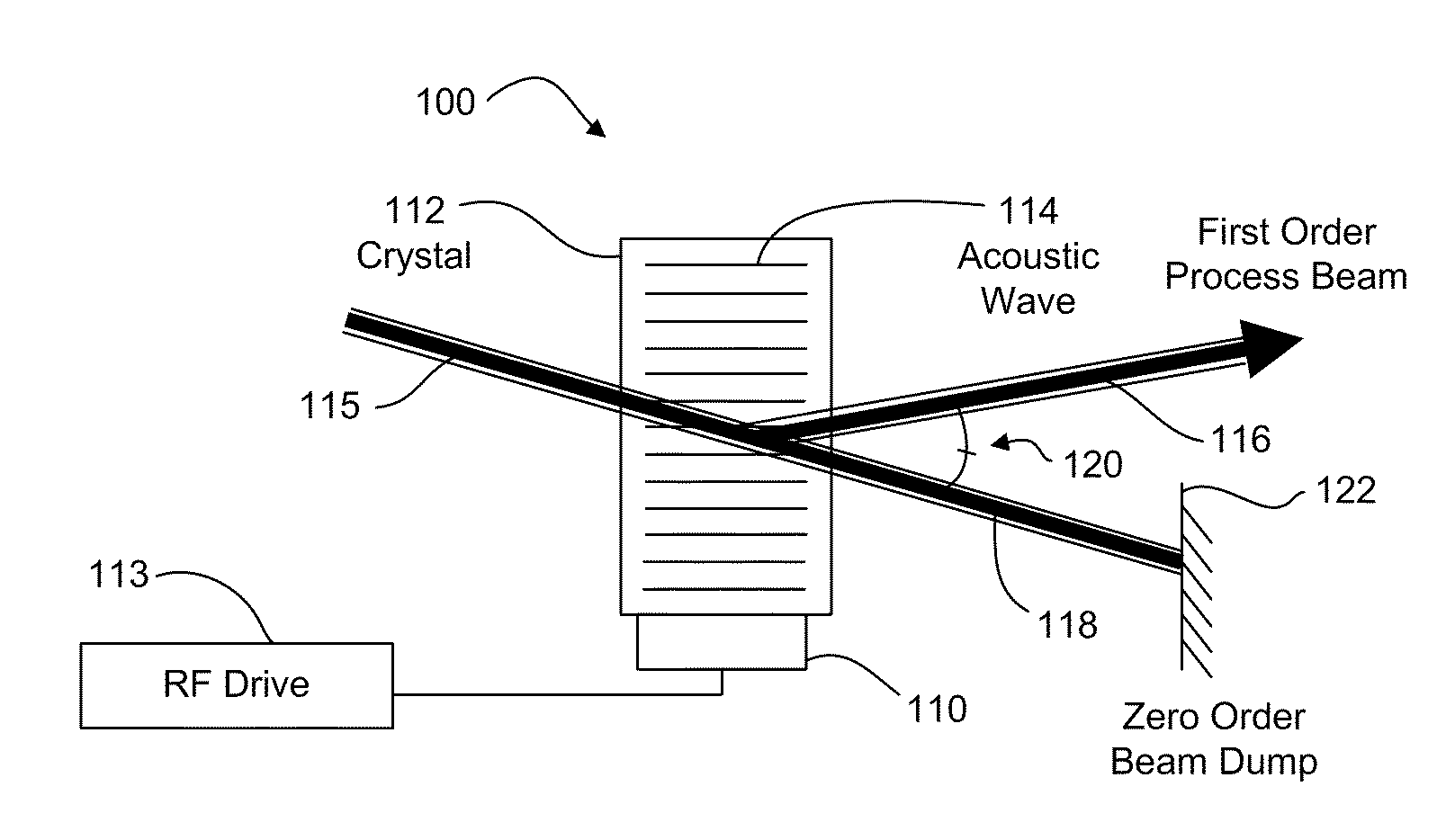
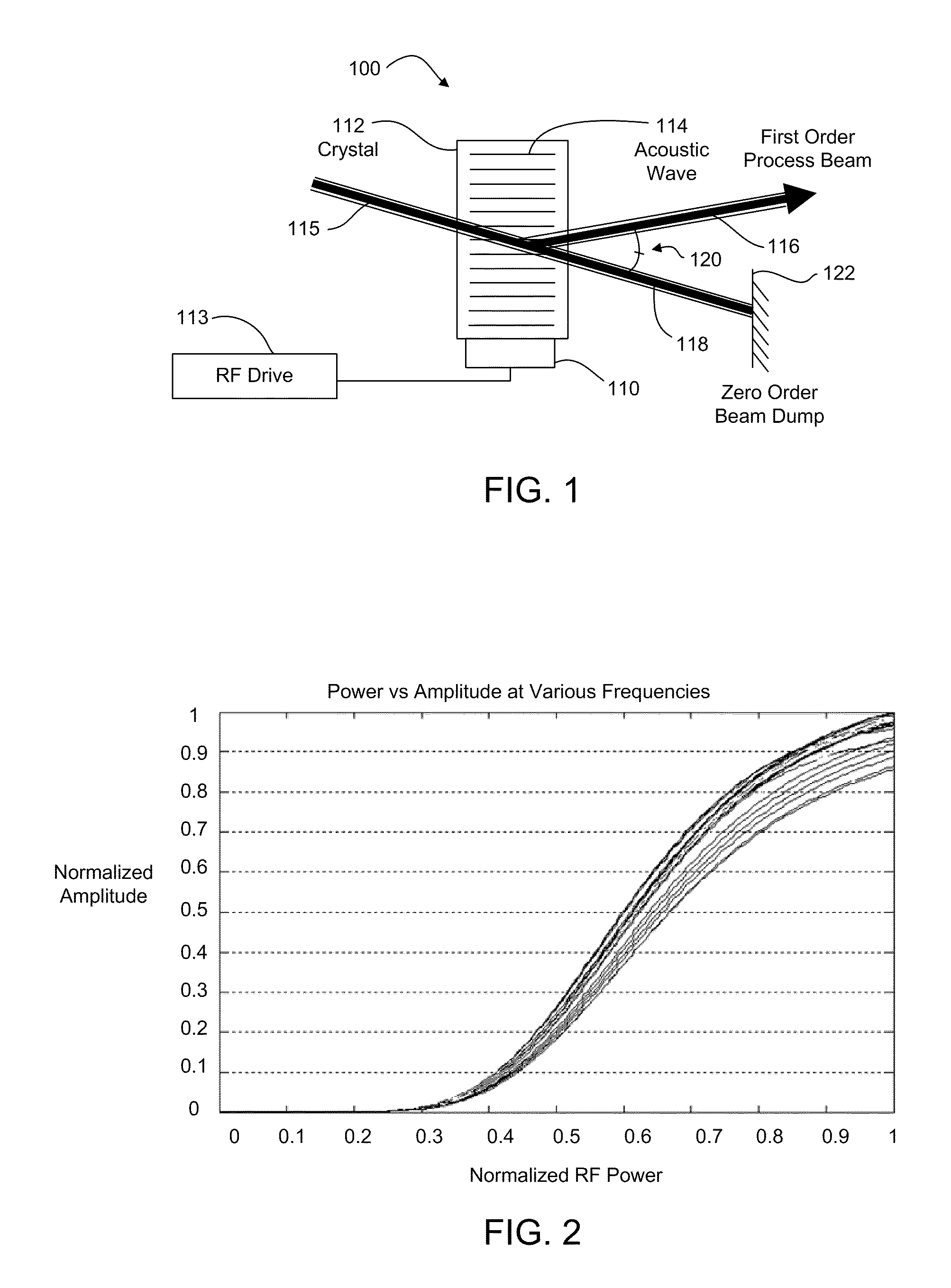
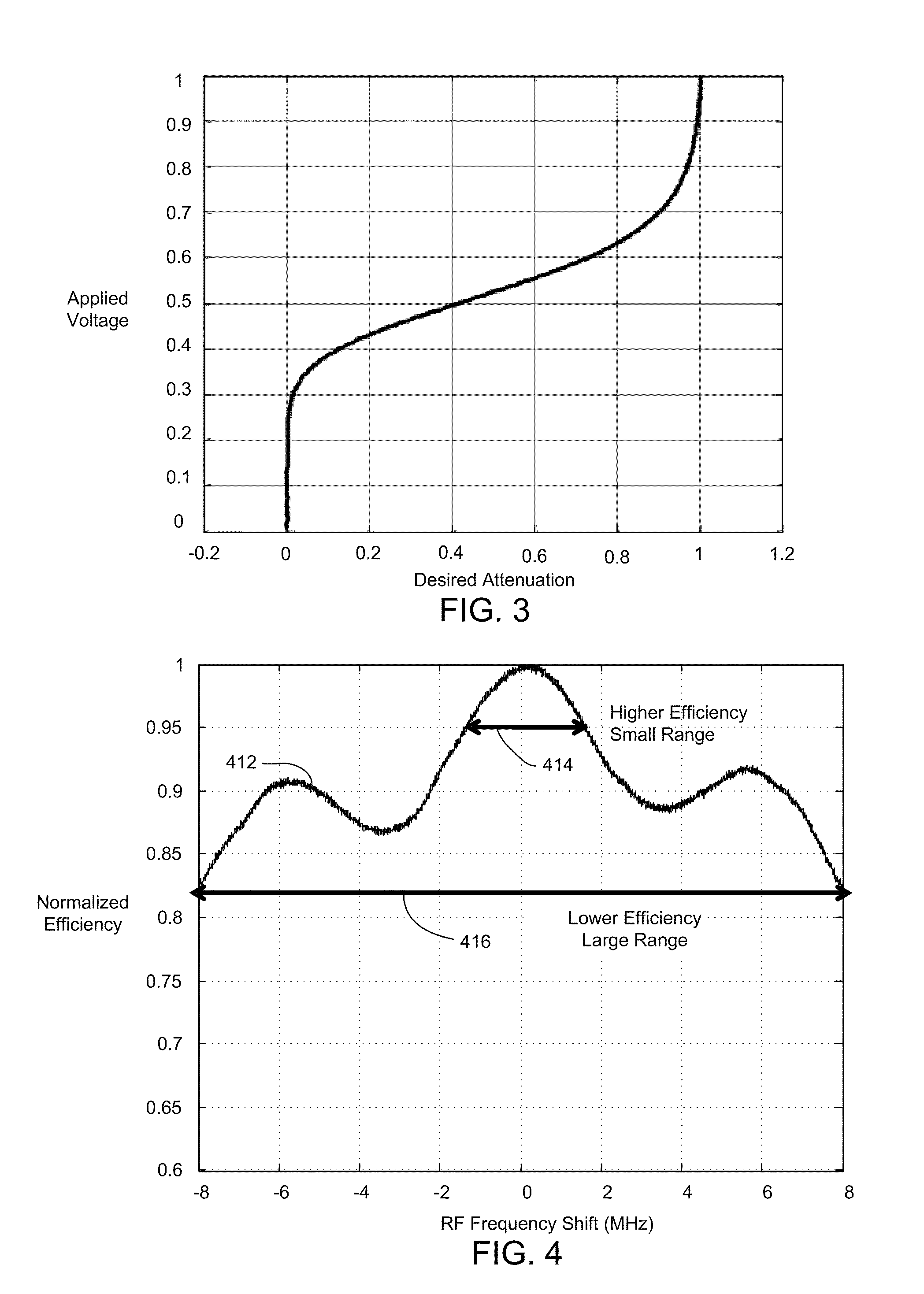
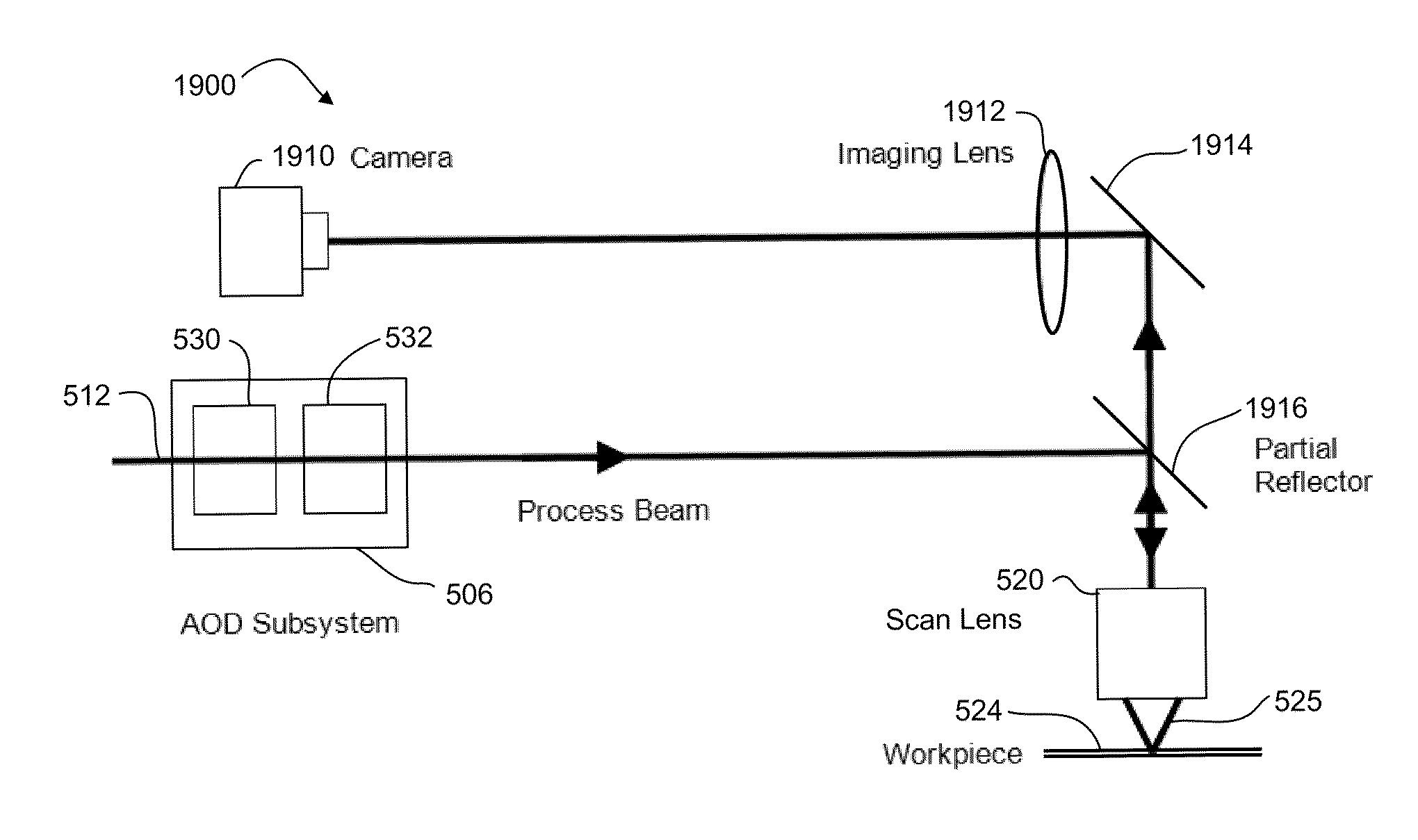
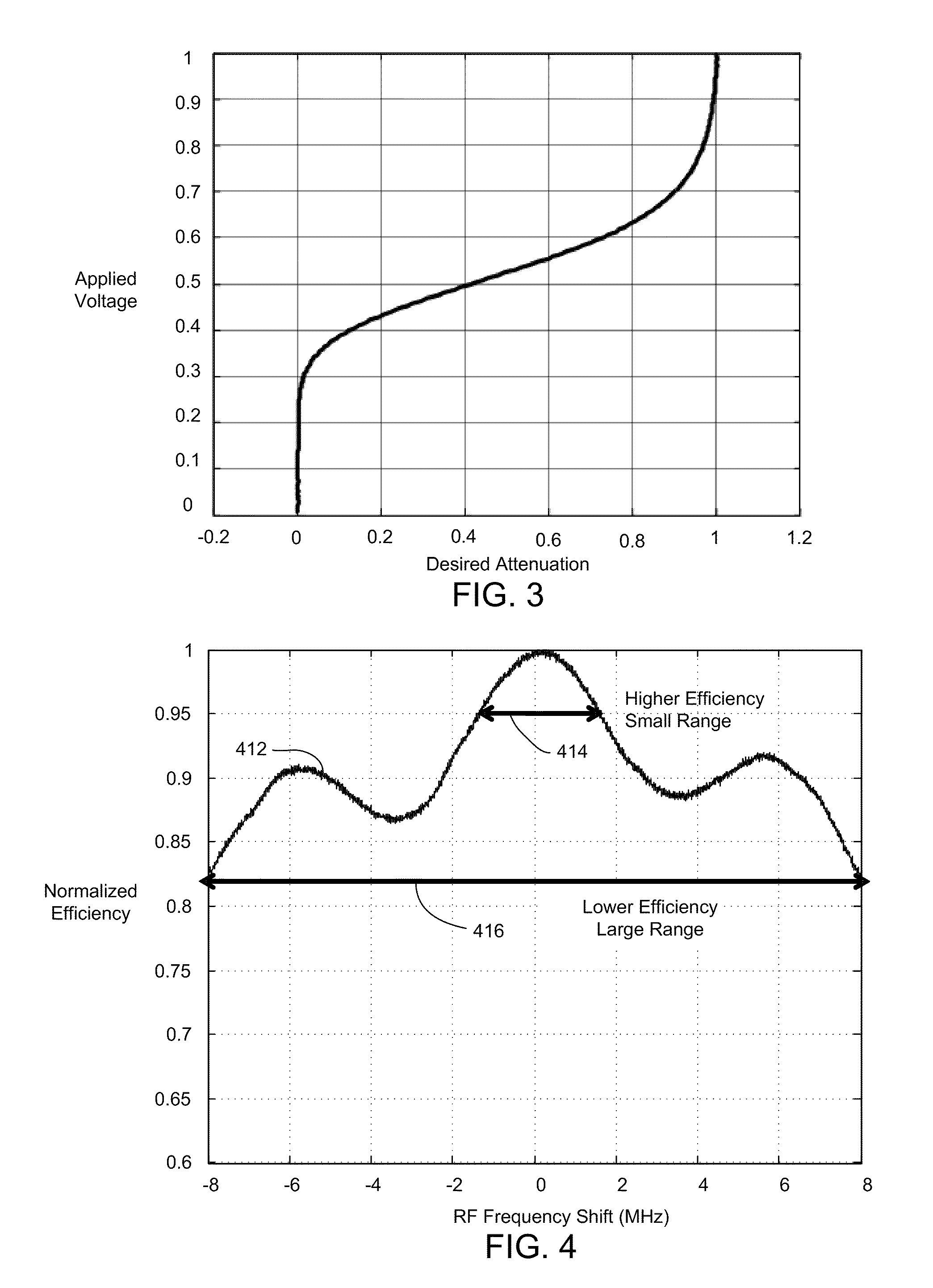
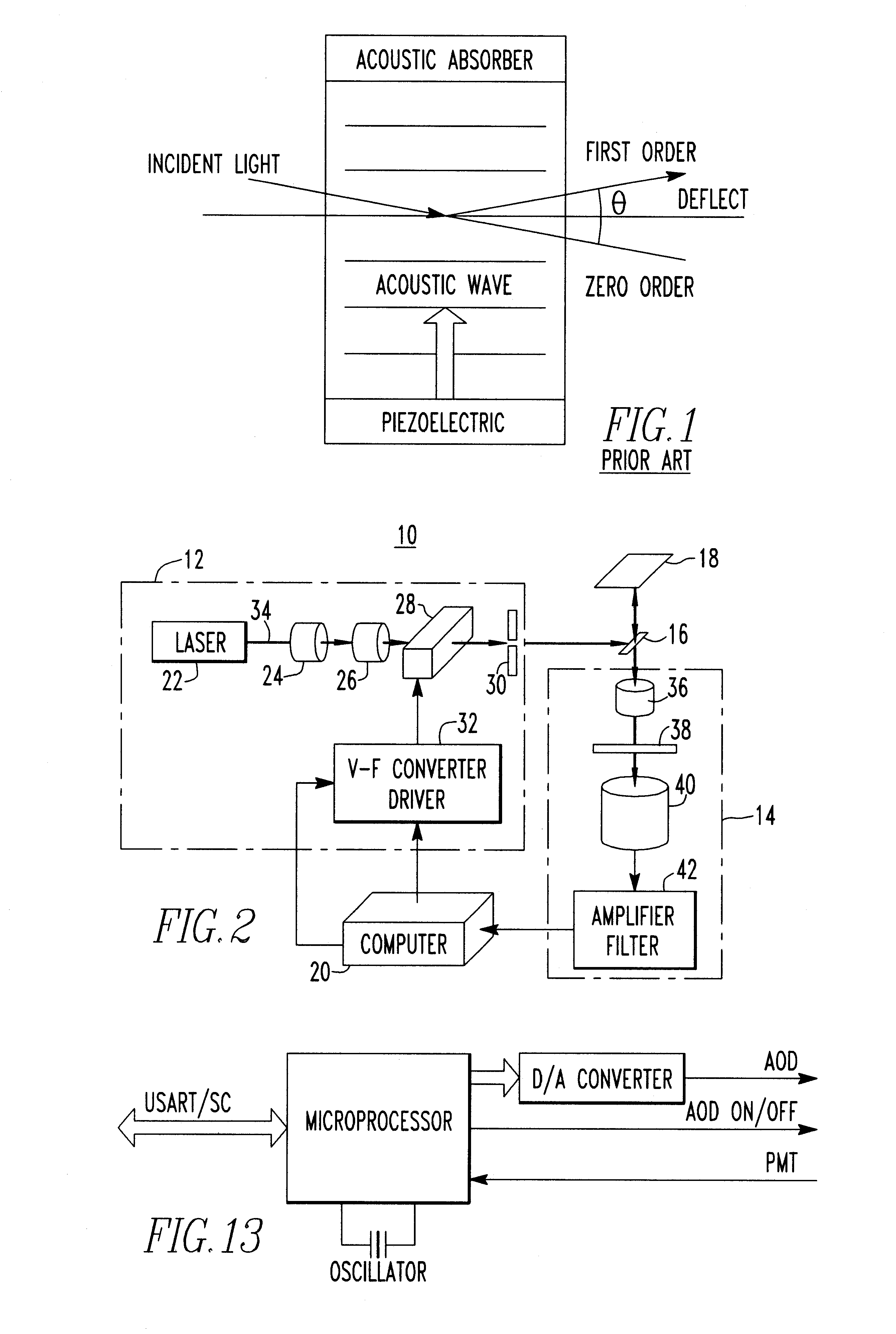
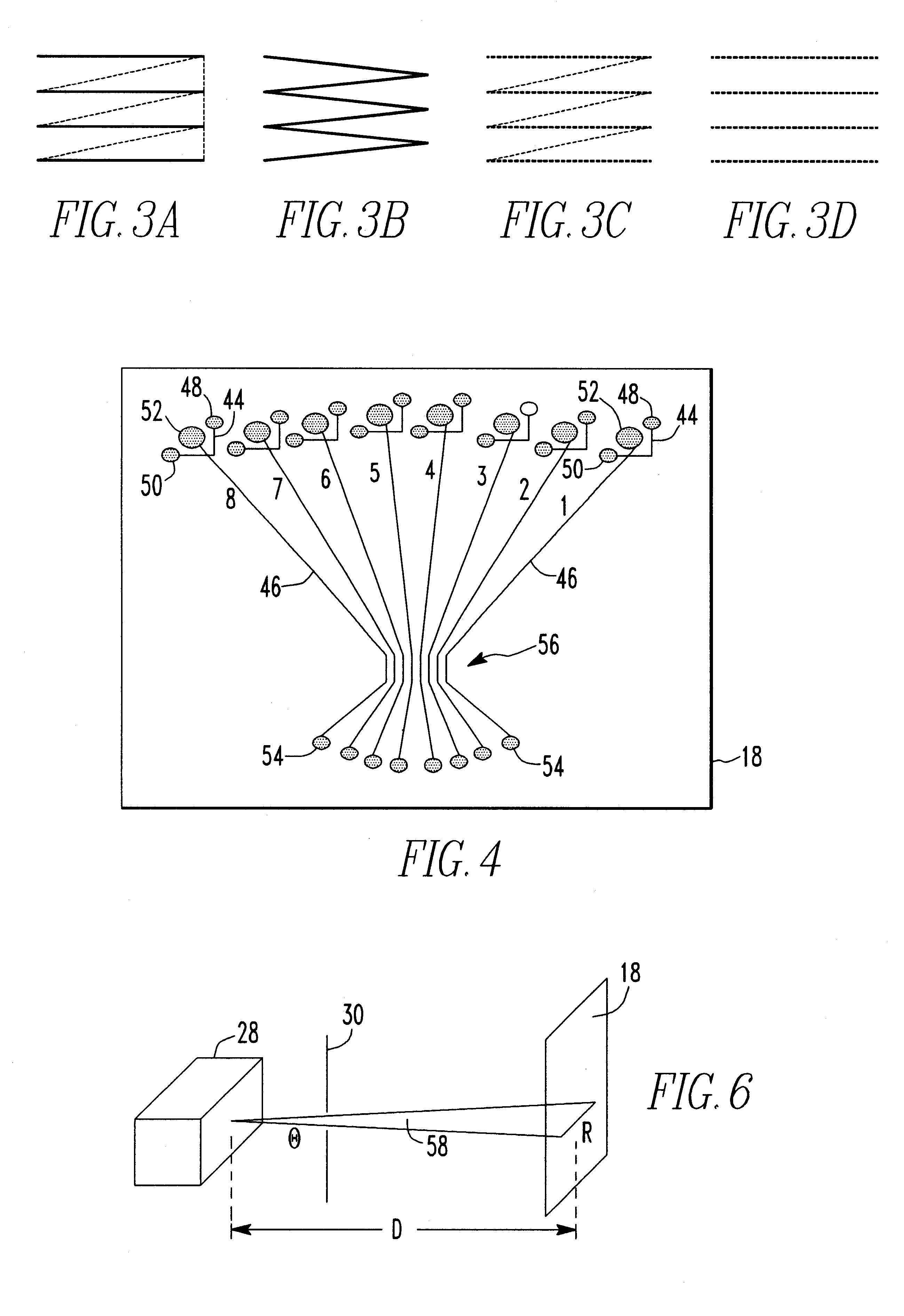
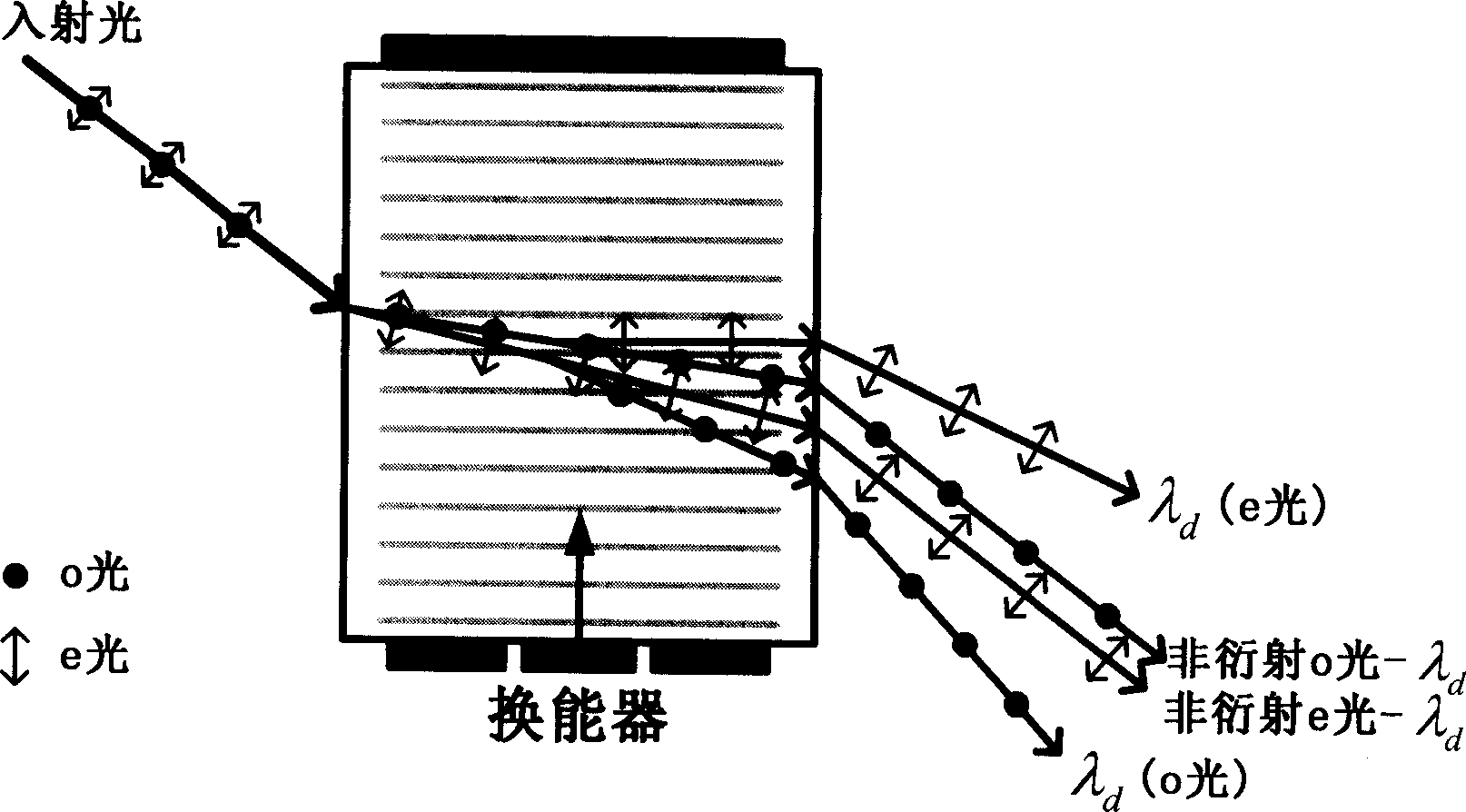
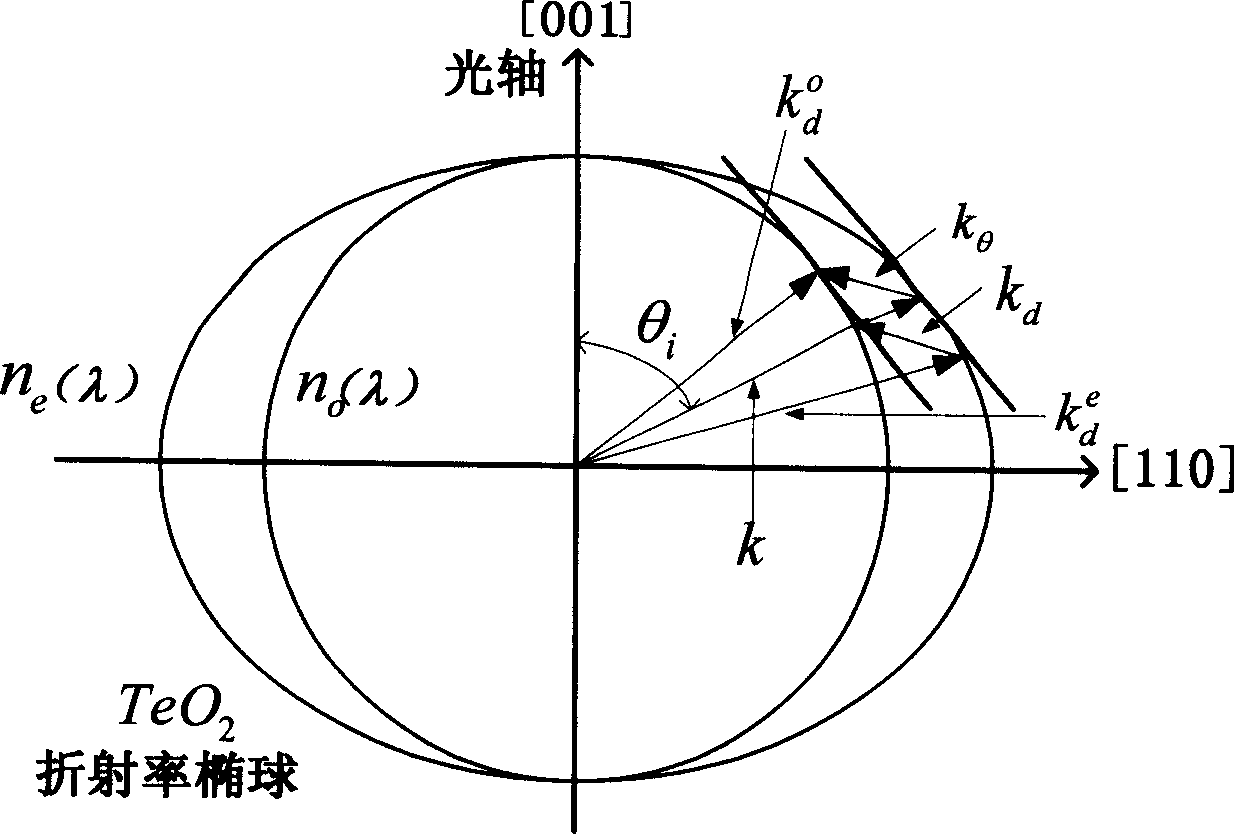
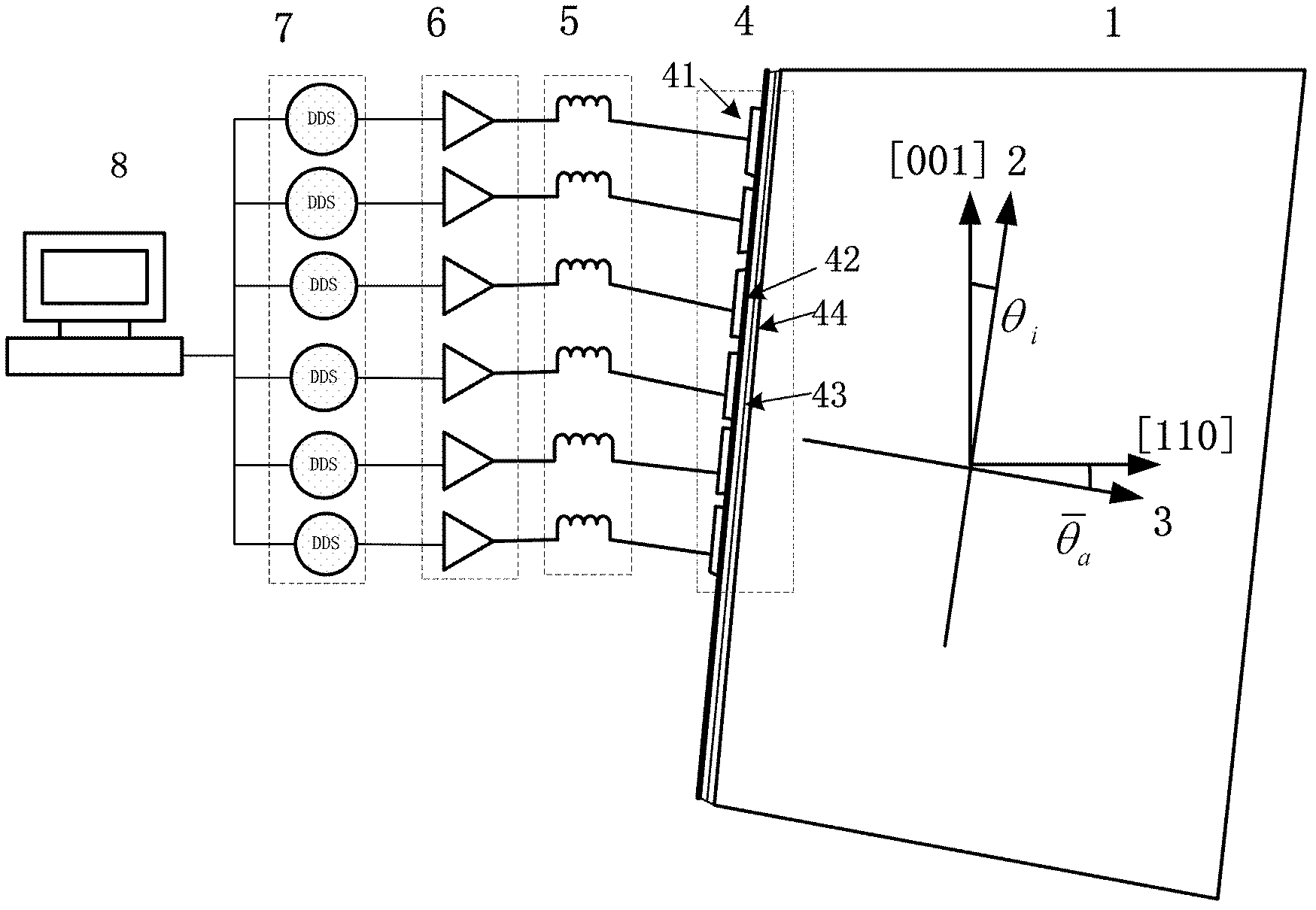
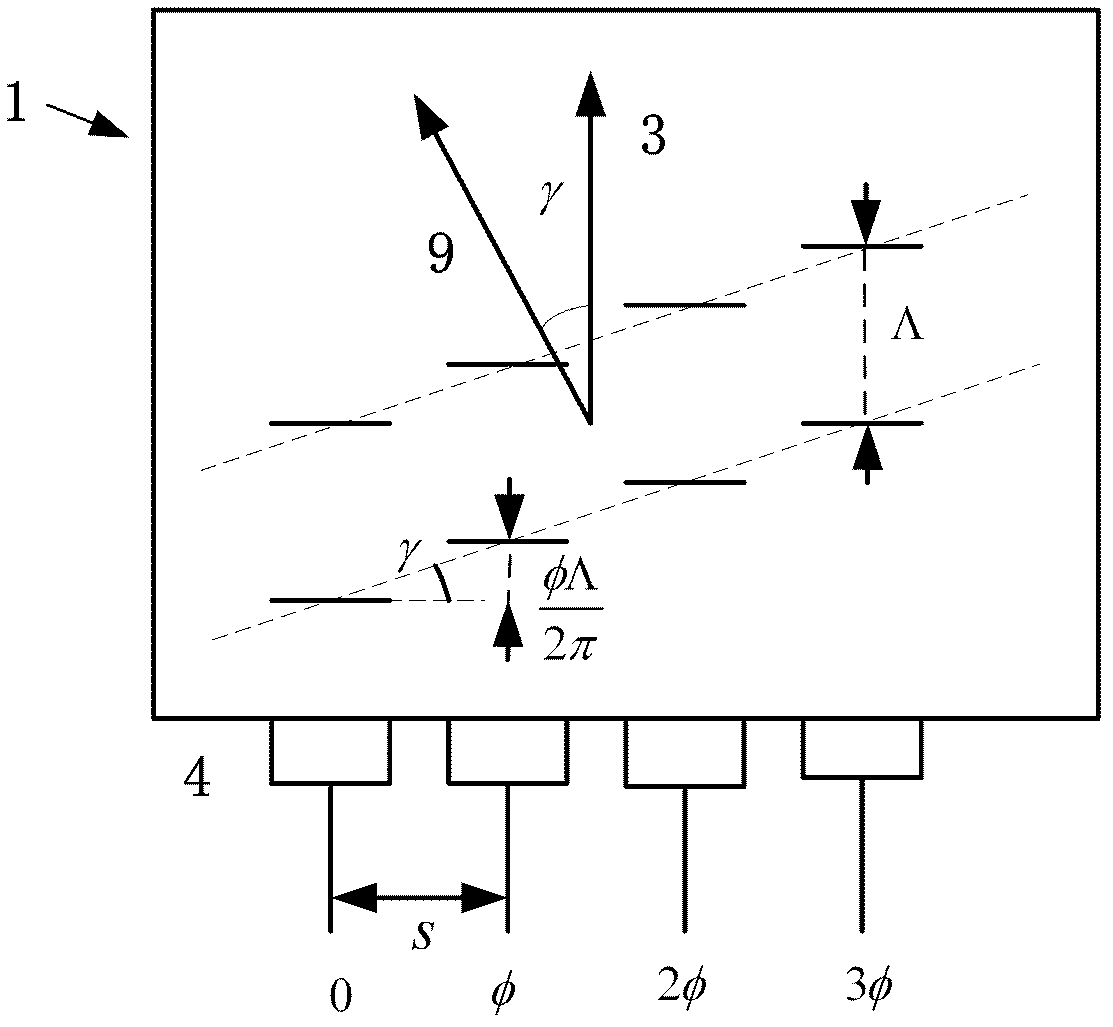
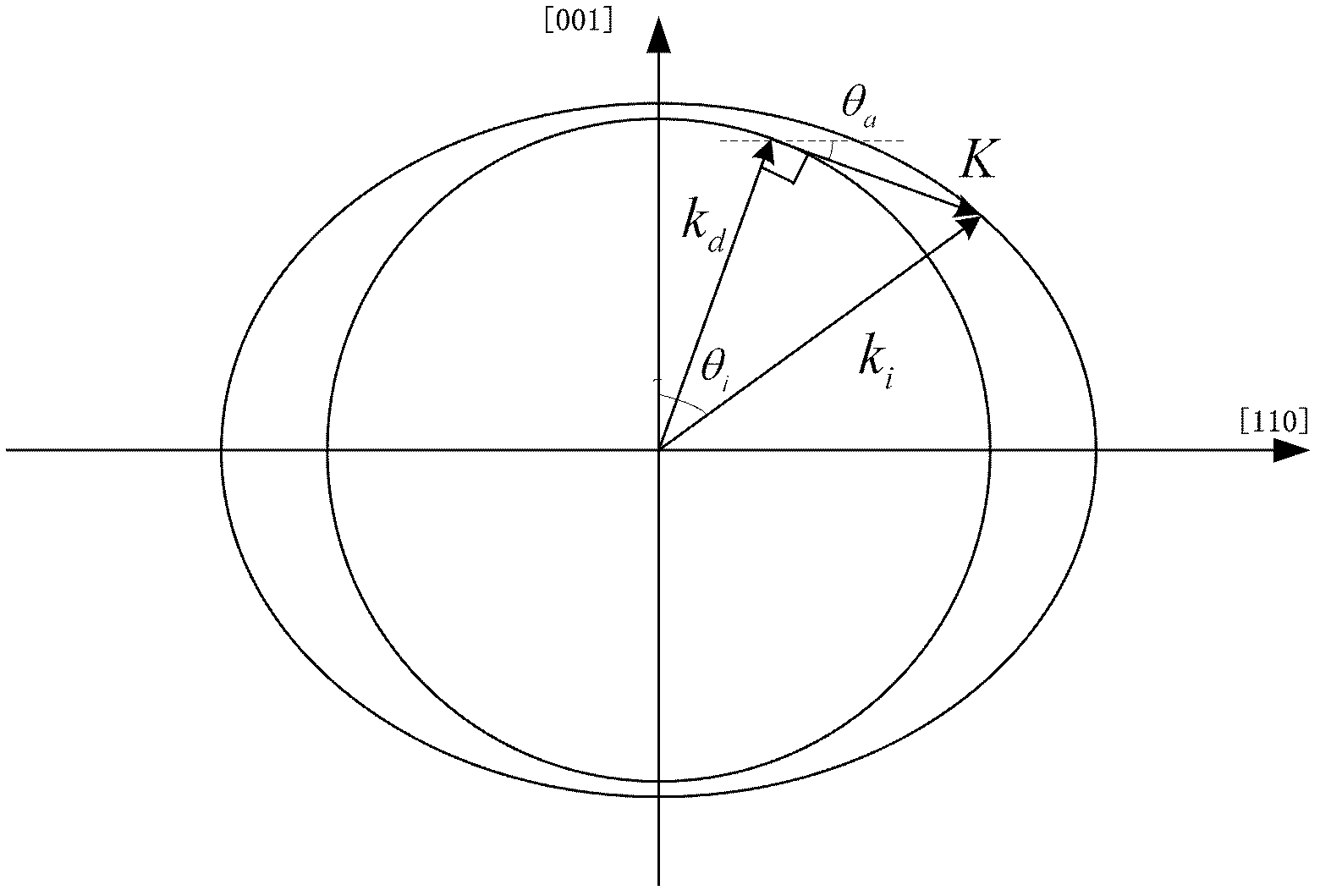
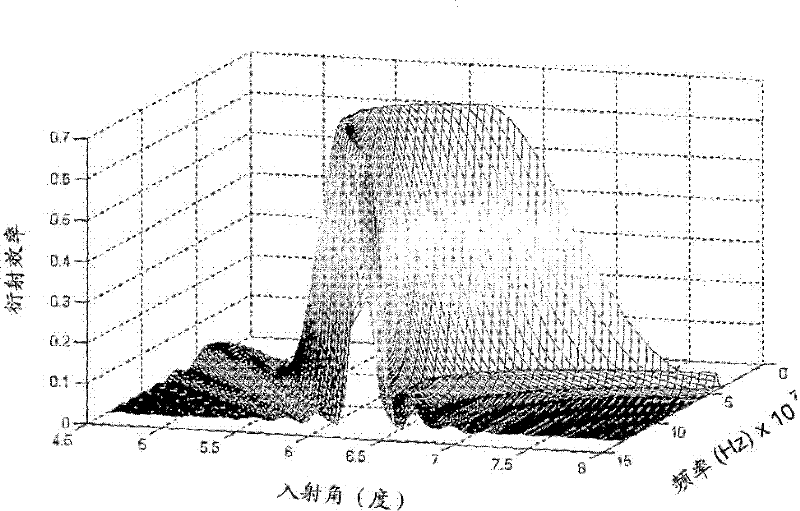
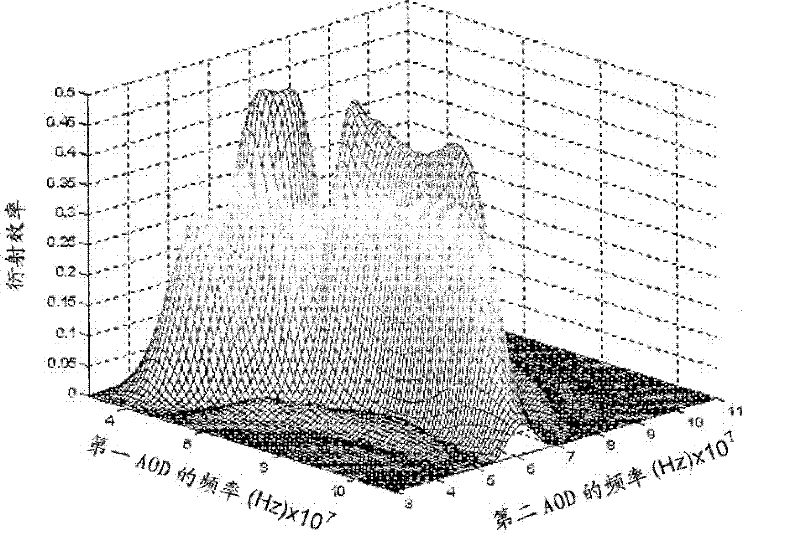
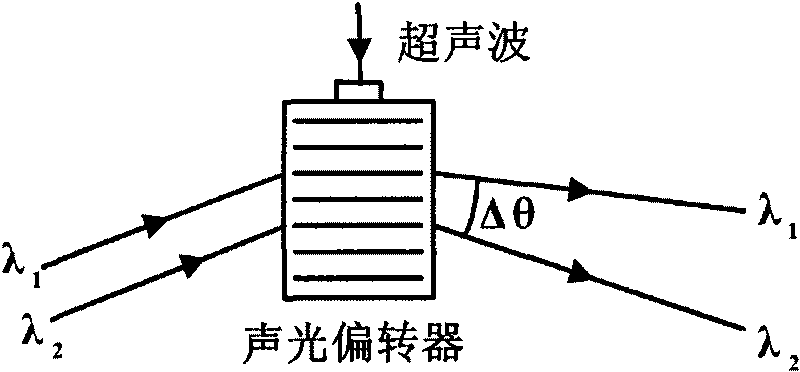
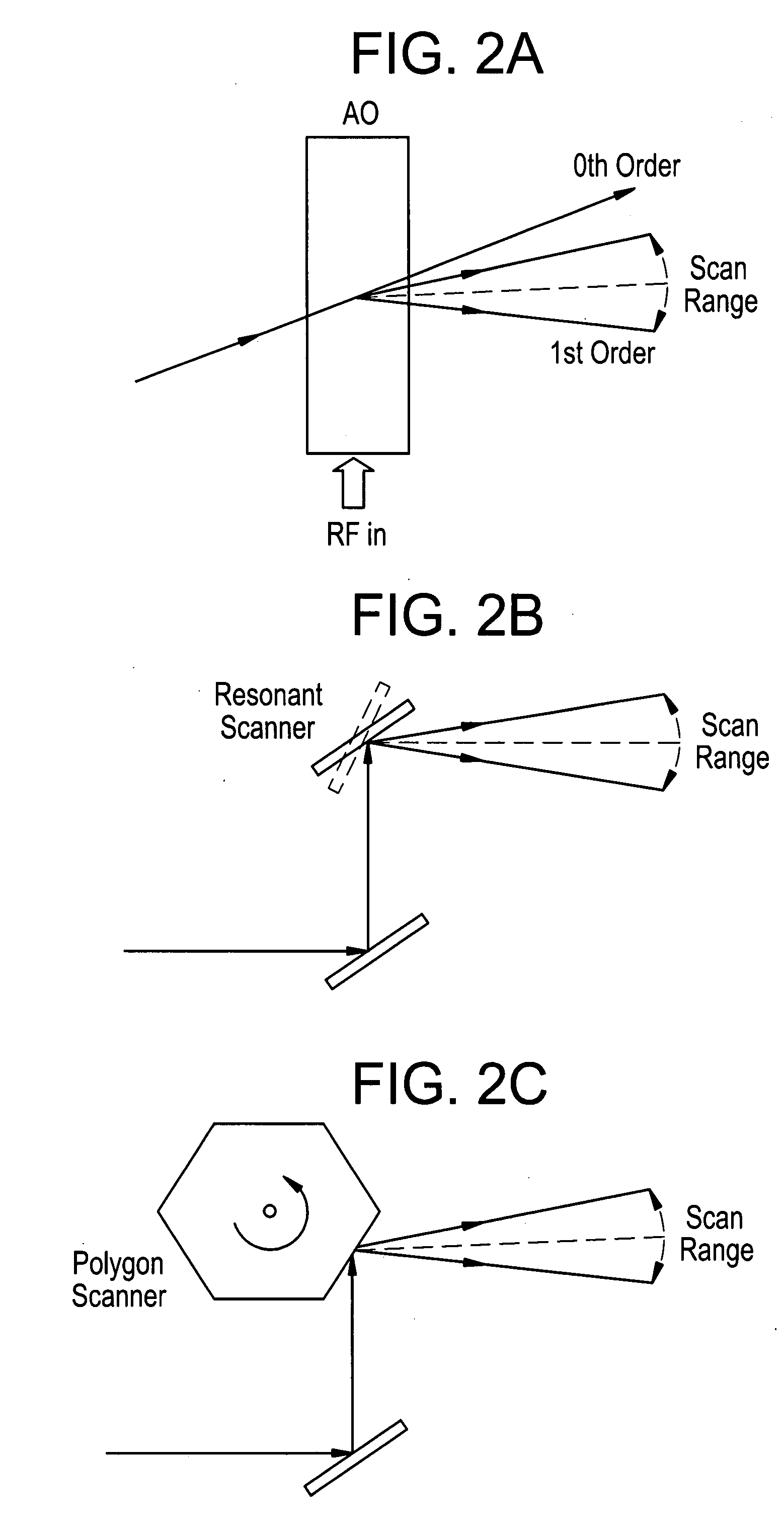
An acousto-optic deflector (AOD) spatially controls the optical beam. In the operation of an acousto-optic deflector the power driving the acoustic transducer is kept on, at a constant level, while the acoustic frequency is varied to deflect the beam to different angular positions. The acousto-optic deflector makes use of the acoustic frequency dependent diffraction angle, where a change in the angle Δθd as a function of the change in frequency Δf given as, (12) Δθd=λ/νΔf where λ is the optical wavelength and ν is the velocity of the acoustic wave.
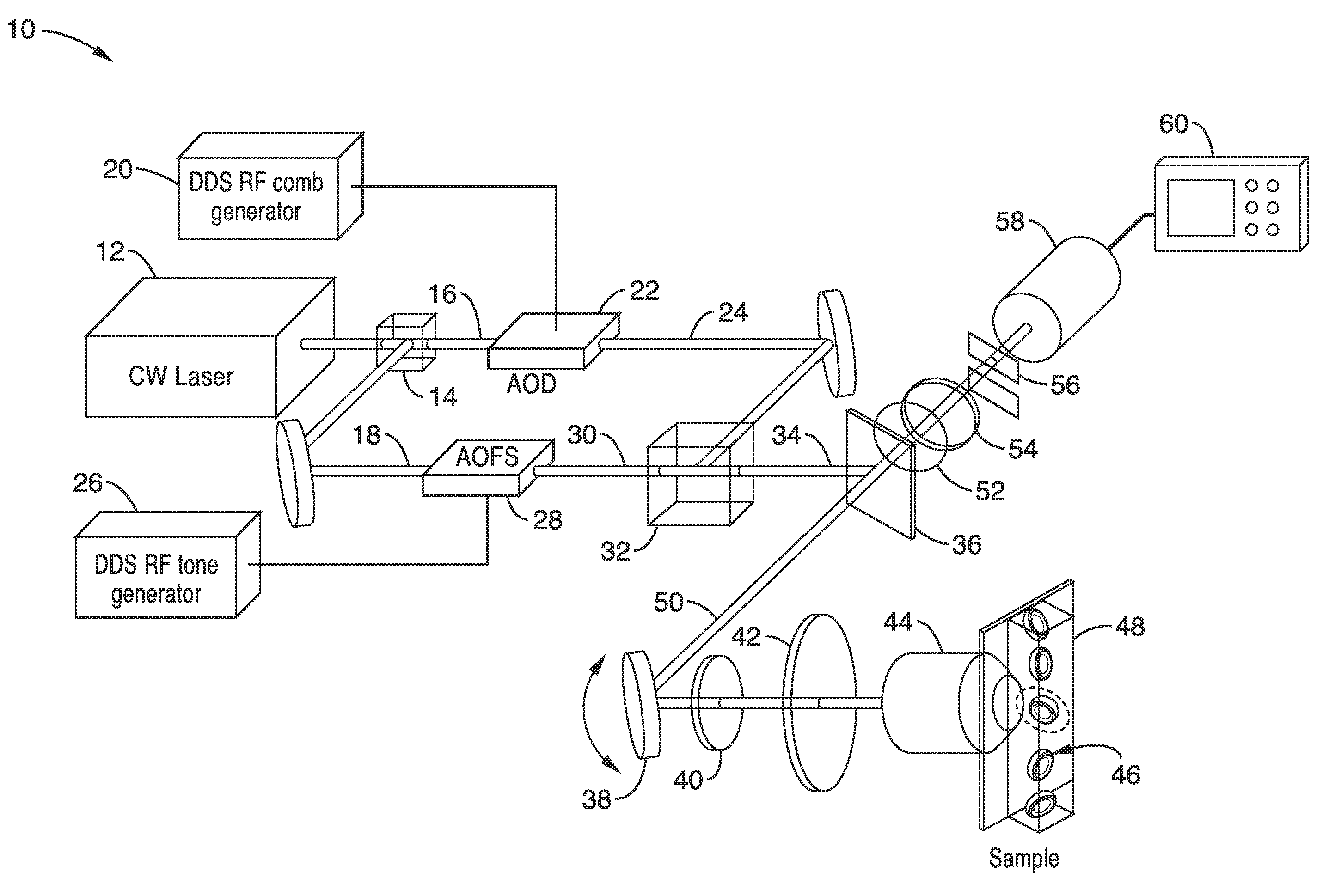
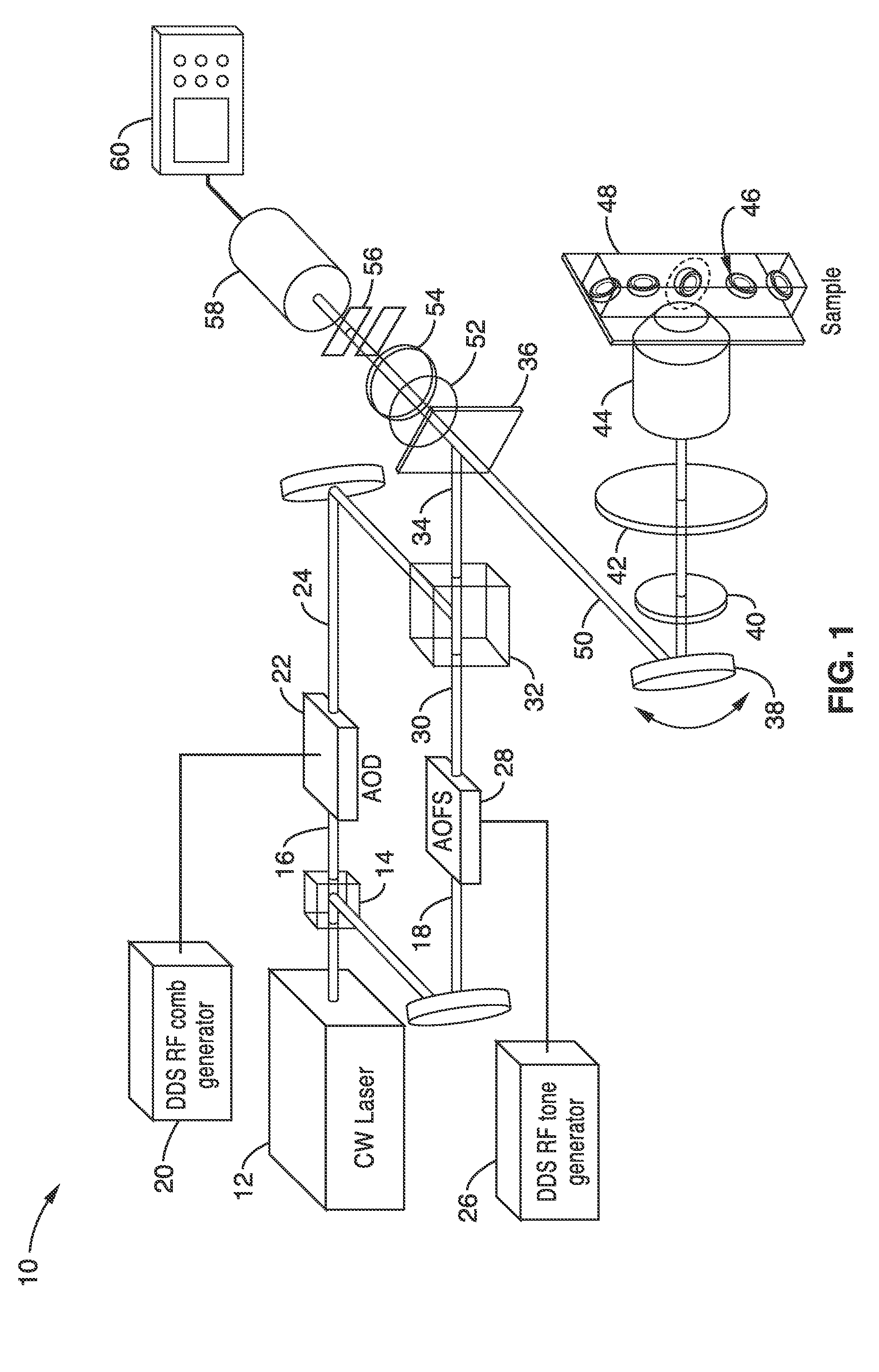
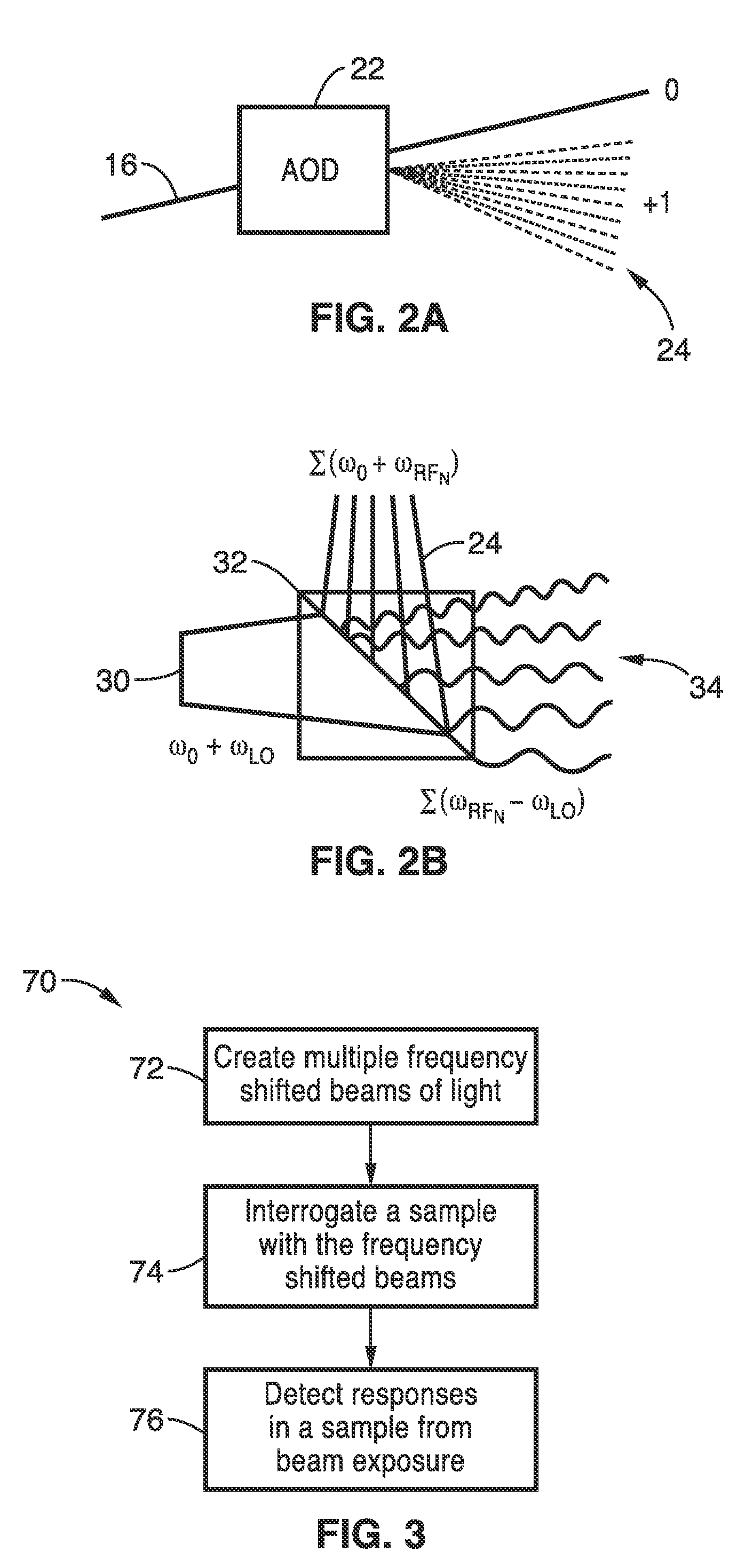
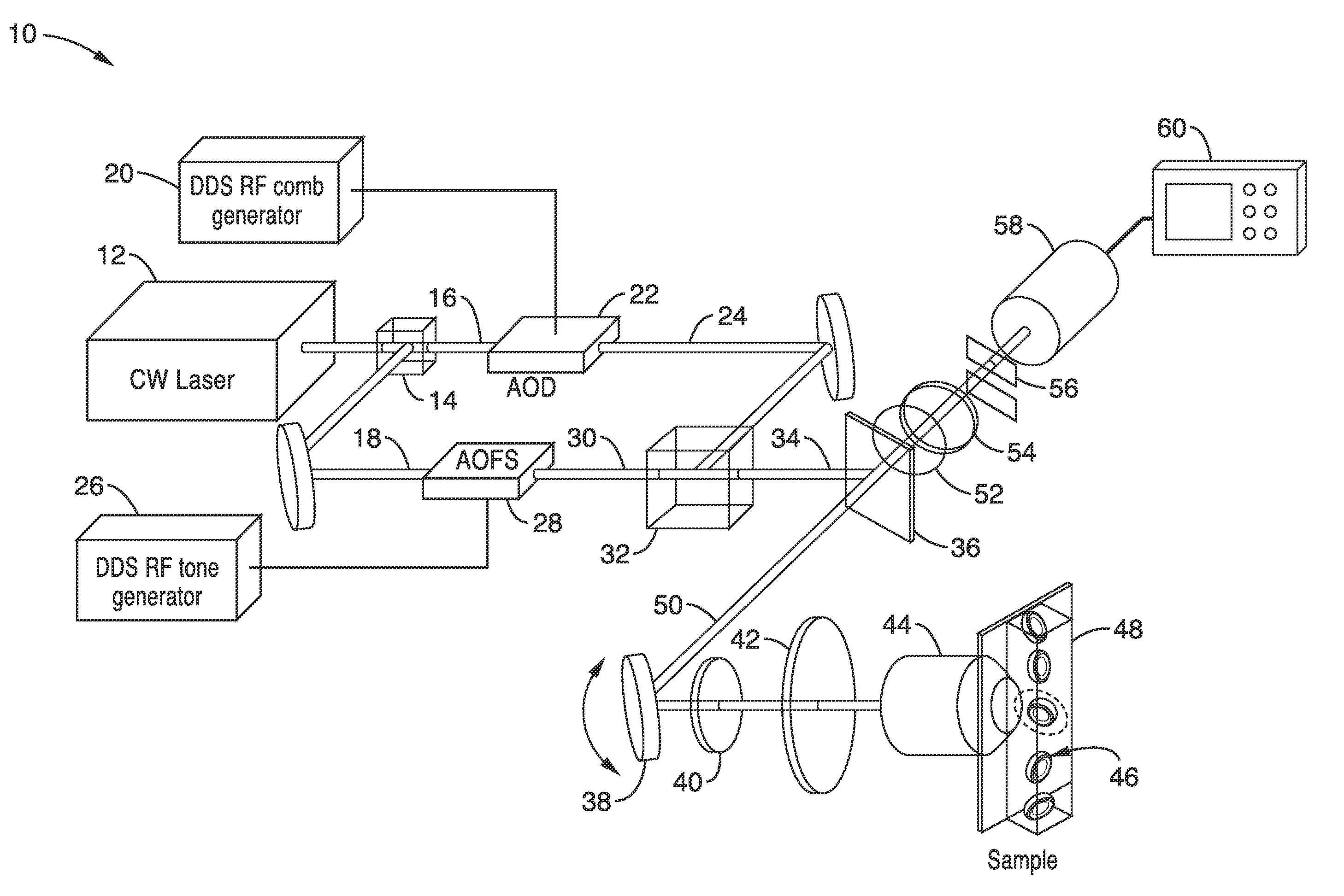
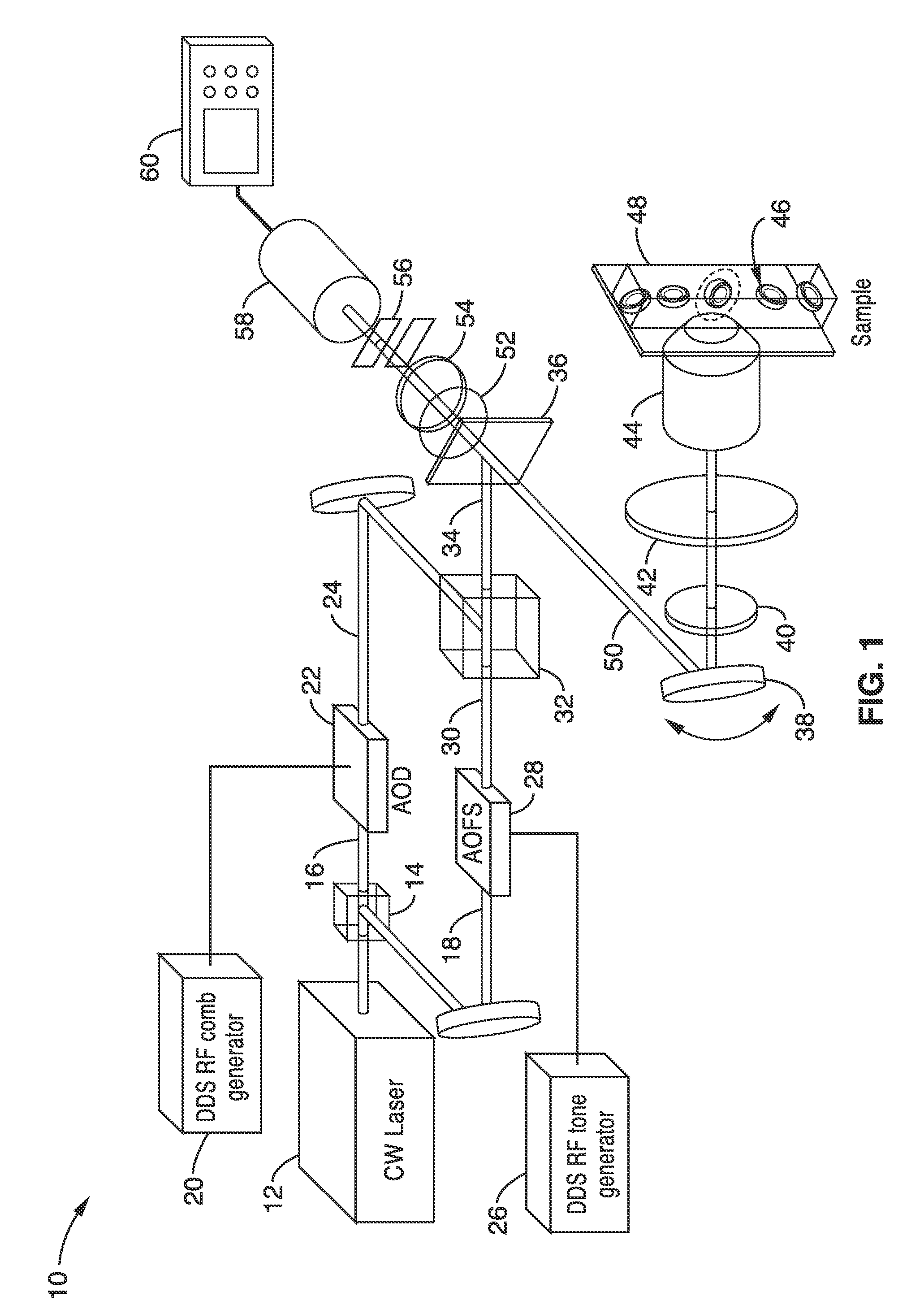
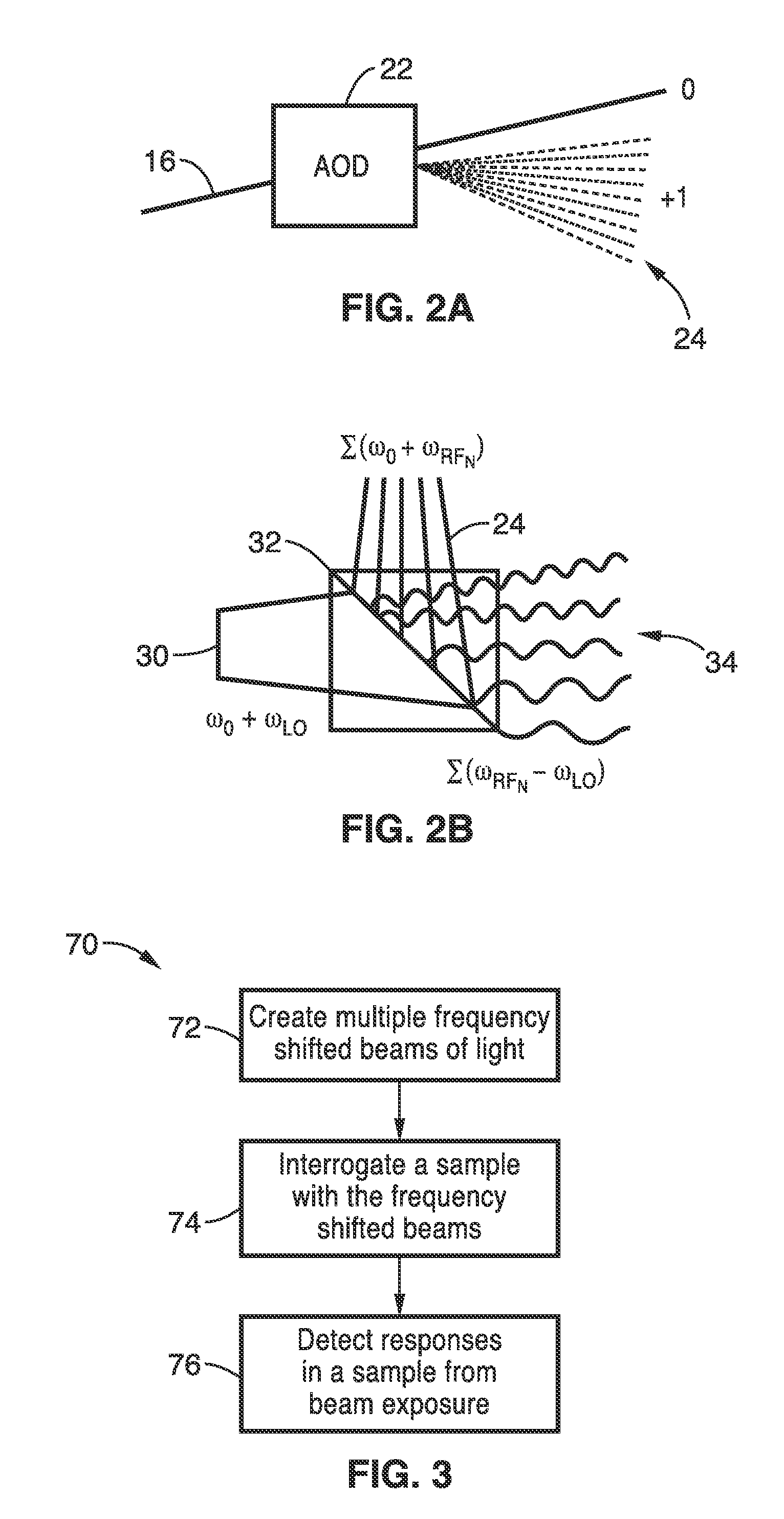
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency-multiplexed excitation
ActiveUS9423353B2Reduce image noiseScalable approachMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceBeam splitterLaser scanning microscope
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency multiplexed excitation. One apparatus splits an excitation laser beam into two arms of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. The light in the first beam is frequency shifted by an acousto-optic deflector, which is driven by a phase-engineered radiofrequency comb designed to minimize peak-to-average power ratio. This RF comb generates multiple deflected optical beams possessing a range of output angles and frequency shifts. The second beam is shifted in frequency using an acousto-optic frequency shifter. After combining at a second beam splitter, the two beams are focused to a line on the sample using a conventional laser scanning microscope lens system. The acousto-optic deflectors frequency-encode the simultaneous excitation of an entire row of pixels, which enables detection and de-multiplexing of fluorescence images using a single photomultiplier tube and digital phase-coherent signal recovery techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Acousto-optic deflector applications in laser processing of dielectric or other materials
ActiveUS20100301023A1Effective expansionIncrease speedWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPower modulationAcousto optic deflector
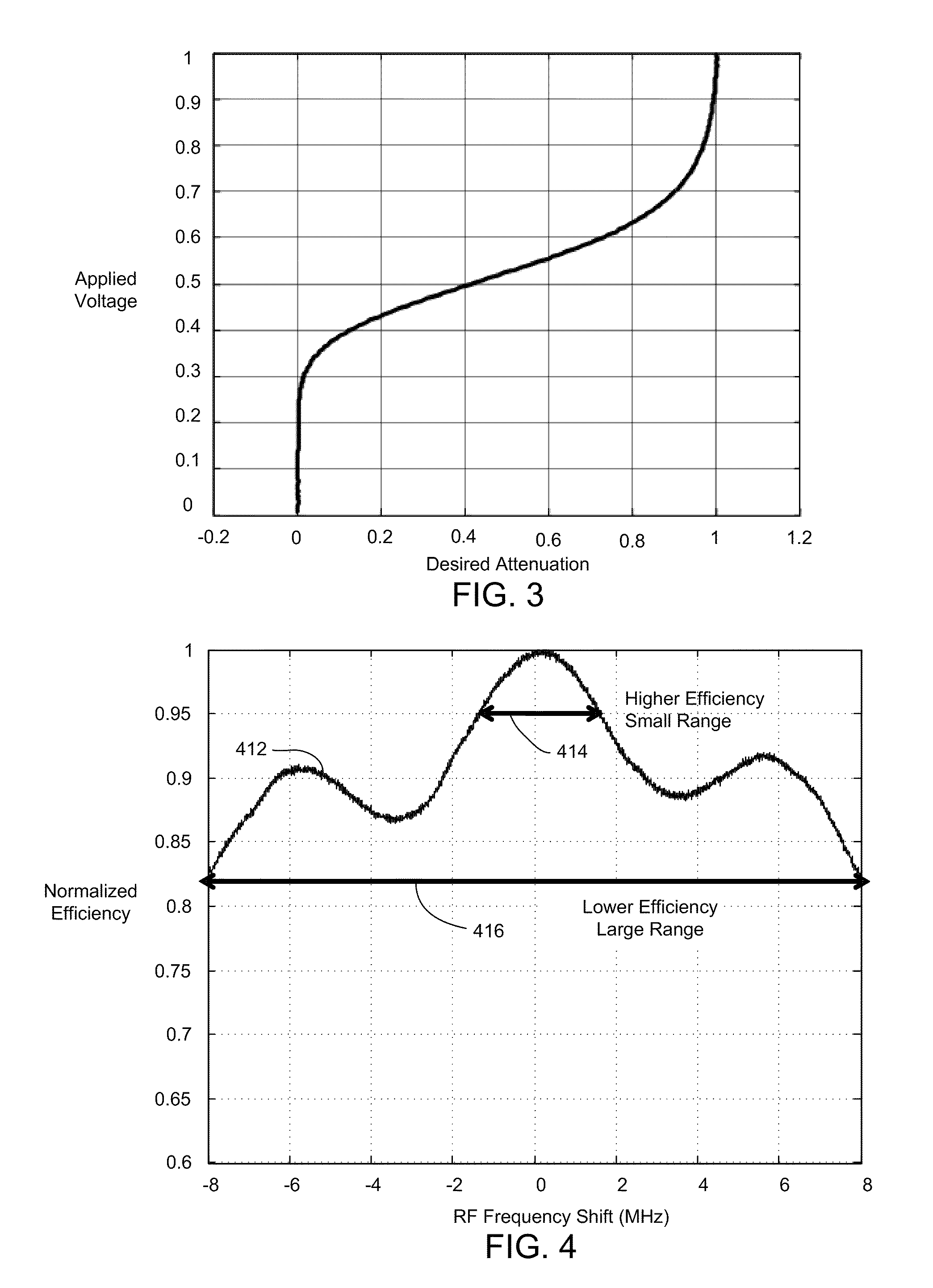
A laser processing system for micromachining a workpiece includes a laser source to generate laser pulses for processing a feature in a workpiece, a galvanometer-driven (galvo) subsystem to impart a first relative movement of a laser beam spot position along a processing trajectory with respect to the surface of the workpiece, and an acousto-optic deflector (AOD) subsystem to effectively widen a laser beam spot along a direction perpendicular to the processing trajectory. The AOD subsystem may include a combination of AODs and electro-optic deflectors. The AOD subsystem may vary an intensity profile of laser pulses as a function of deflection position along a dither direction to selectively shape the feature in the dither direction. The shaping may be used to intersect features on the workpiece. The AOD subsystem may also provide rastering, galvo error position correction, power modulation, and / or through-the-lens viewing of and alignment to the workpiece.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Laser processing systems using through-the-lens alignment of a laser beam with a target feature
ActiveUS20100301024A1Welding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusAcousto optic deflectorLaser processing
A laser processing system for micromachining a workpiece includes a laser source to generate laser pulses for processing a feature in a workpiece, a galvanometer-driven (galvo) subsystem to impart a first relative movement of a laser beam spot position along a processing trajectory with respect to the surface of the workpiece, and an acousto-optic deflector (AOD) subsystem. The AOD subsystem may include a combination of AODs and electro-optic deflectors. The AOD subsystem may vary an intensity profile of laser pulses as a function of deflection position along a dither direction. The AOD subsystem may be used for aligning a processing laser beam to workpiece features.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Laser processing systems using through-the-lens alignment of a laser beam with a target feature
ActiveUS8288679B2Welding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusAcousto optic deflectorLaser processing
A laser processing system for micromachining a workpiece includes a laser source to generate laser pulses for processing a feature in a workpiece, a galvanometer-driven (galvo) subsystem to impart a first relative movement of a laser beam spot position along a processing trajectory with respect to the surface of the workpiece, and an acousto-optic deflector (AOD) subsystem. The AOD subsystem may include a combination of AODs and electro-optic deflectors. The AOD subsystem may vary an intensity profile of laser pulses as a function of deflection position along a dither direction. The AOD subsystem may be used for aligning a processing laser beam to workpiece features.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
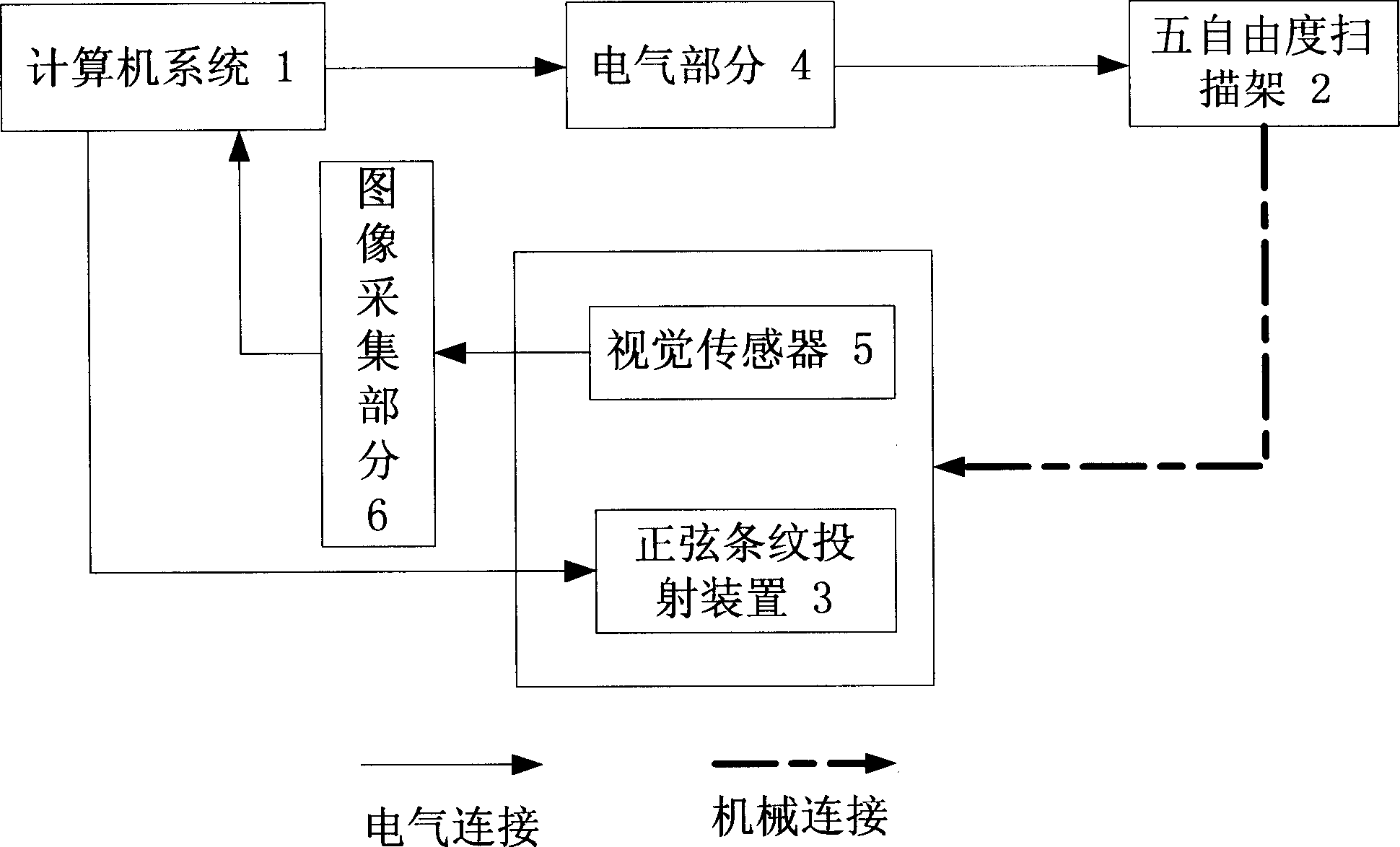
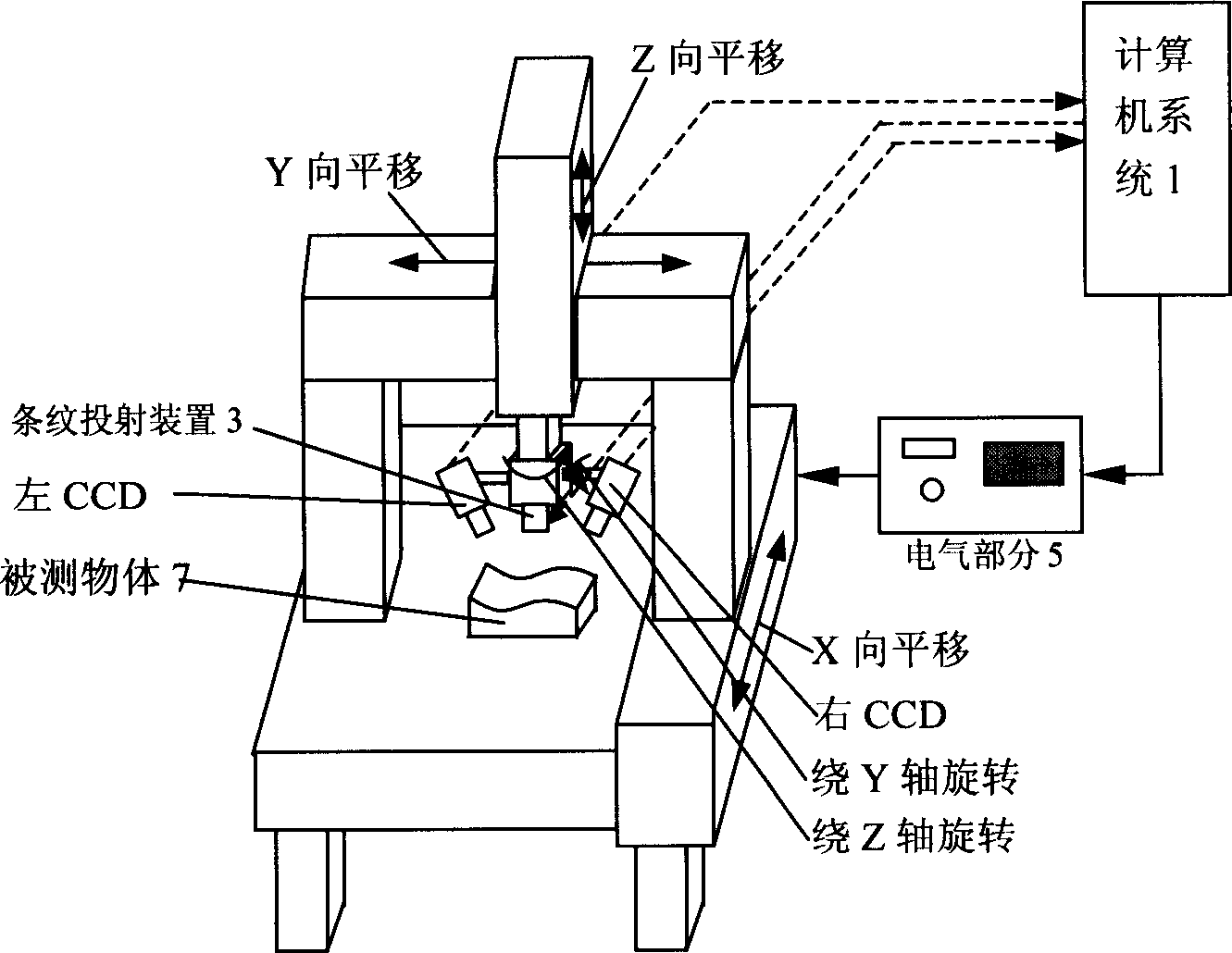
Stereo vision detection system based on adaptive sine streak projection
A stereoscopic visional detecting system based on the adaptive sine fringe projection is composed of computer system, 5D scanning frame, sine fringe projector based on acousto-optic deflector, electric unit, visional sensor and image acquisition unit. When multiple sine rasters are projected onto surface of object, a series of images with different phases is captured by image sensor, then sent to image acquisition unit, and finally processed by computer to obtain the phase diagram about the 3D information of object.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency-multiplexed excitation
ActiveUS20160003741A1Reduce image noiseScalable approachPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersBeam splitterLaser scanning microscope
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency multiplexed excitation. One apparatus splits an excitation laser beam into two arms of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. The light in the first beam is frequency shifted by an acousto-optic deflector, which is driven by a phase-engineered radiofrequency comb designed to minimize peak-to-average power ratio. This RF comb generates multiple deflected optical beams possessing a range of output angles and frequency shifts. The second beam is shifted in frequency using an acousto-optic frequency shifter. After combining at a second beam splitter, the two beams are focused to a line on the sample using a conventional laser scanning microscope lens system. The acousto-optic deflectors frequency-encode the simultaneous excitation of an entire row of pixels, which enables detection and de-multiplexing of fluorescence images using a single photomultiplier tube and digital phase-coherent signal recovery techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
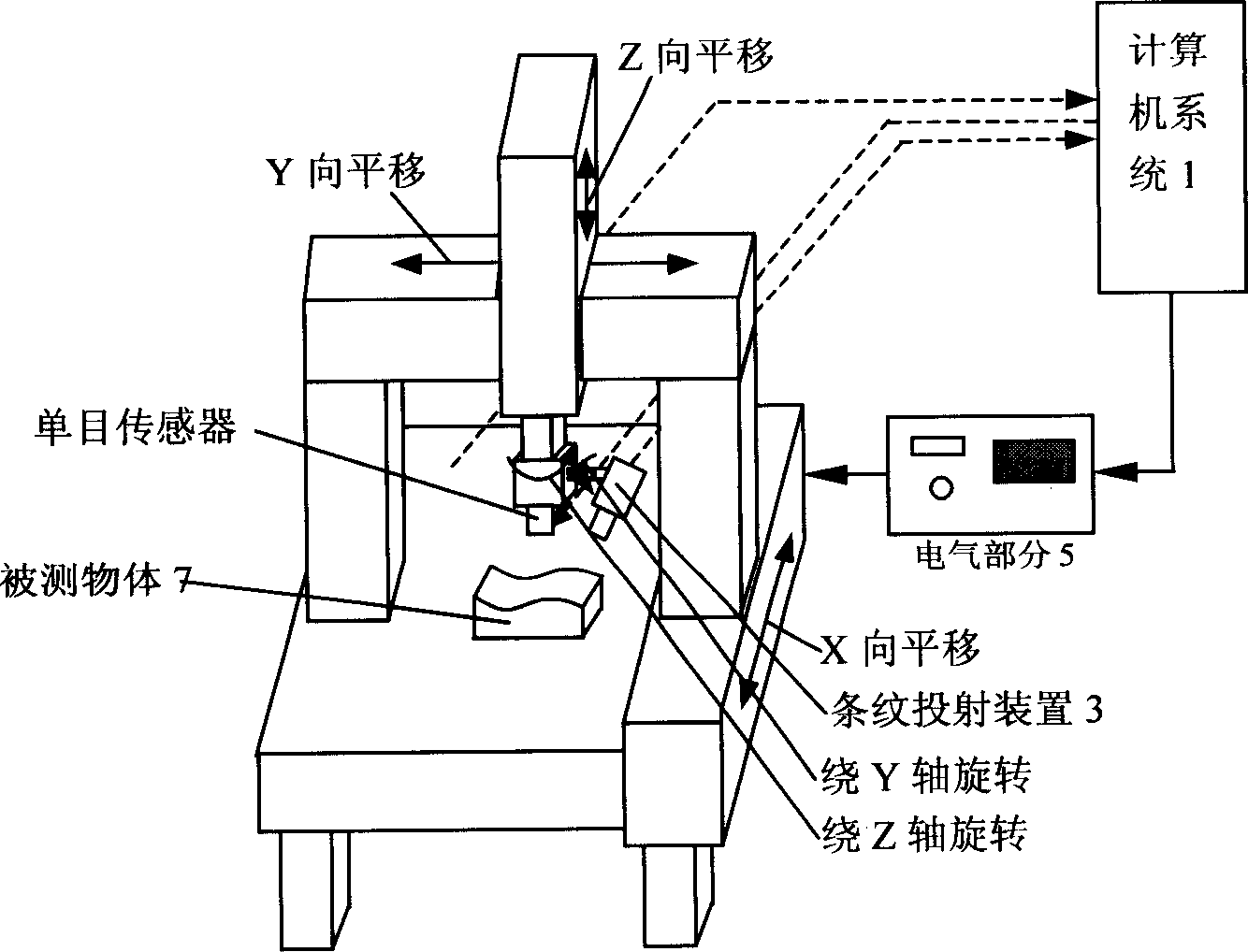
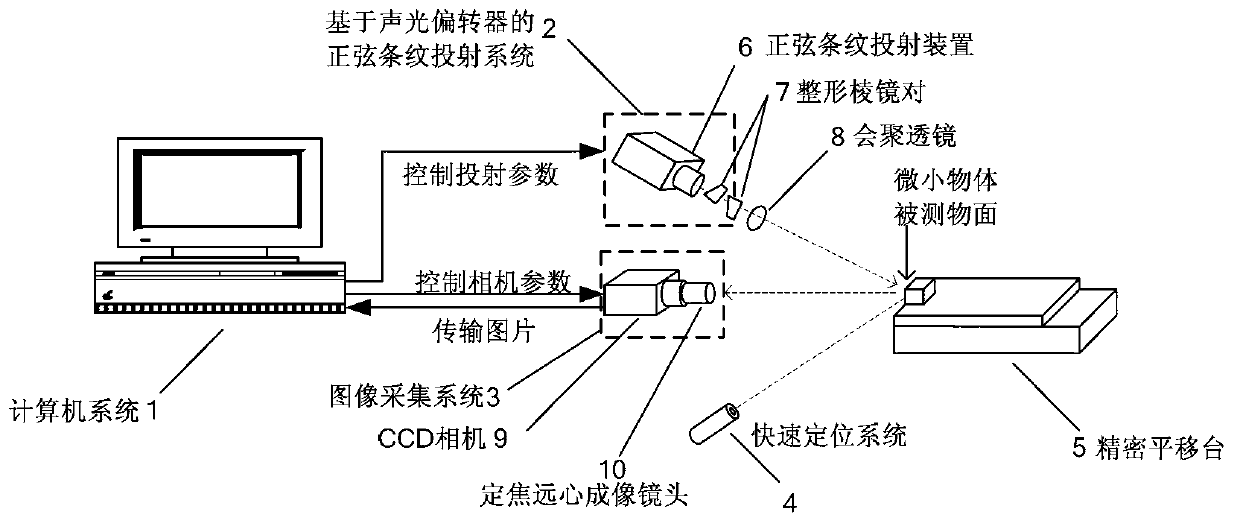
Three-dimensional mirror object shape measurement system based on sinusoidal stripe projection
InactiveCN102721378AMove preciselyChange frequencyUsing optical meansProjection systemPositioning system
A three-dimensional mirror object shape measurement system based on sinusoidal stripe projection mainly comprises a computer system, a sinusoidal stripe projection system based on an acousto-optic deflector, an image acquisition system, a quick positioning system and a precise translation stage. A computer controls the sinusoidal stripe projection system to project a plurality of sinusoidal stripes to a directly measured surface of a mirror object, the phase, the frequency and the brightness of each projected sinusoidal stripe are adjustable, then the image acquisition system acquires corresponding image information and transmits the image information to the computer system, the computer system processes the image information, accordingly, a phase image containing three-dimensional information of the object is obtained, and finally, three-dimensional information of the measured surface of the mirror object is obtained according to a phase and height mapping relation. The three-dimensional mirror object shape measurement system is mainly applied to three-dimensionally measuring shapes of micro-sized mirror objects, the measurement range is about 4.5mmX3mm, the resolution is superior to 5 micrometers, and three-dimensional point cloud space is 3.75 micrometers.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High speed microscope with three-dimensional laser beam scanning
InactiveUS20060071143A1Removes time dependenceFast scanningBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansAcousto optic deflectorLight beam
A system and method for independently controlling the collimation and lateral positioning of a light beam comprises at least one acousto-optic deflector and a pair of counter propagating acoustic waves with offset frequencies. While the frequency offset controls the lateral positioning of the light beam, a frequency gradient across the acousto-optic deflectors controls the collimation of the light beam.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Surface inspection by amplitude modulated specular light detection
ActiveUS7623427B2Combination recordingMaterial analysis by optical meansAcousto optic deflectorVisual inspection
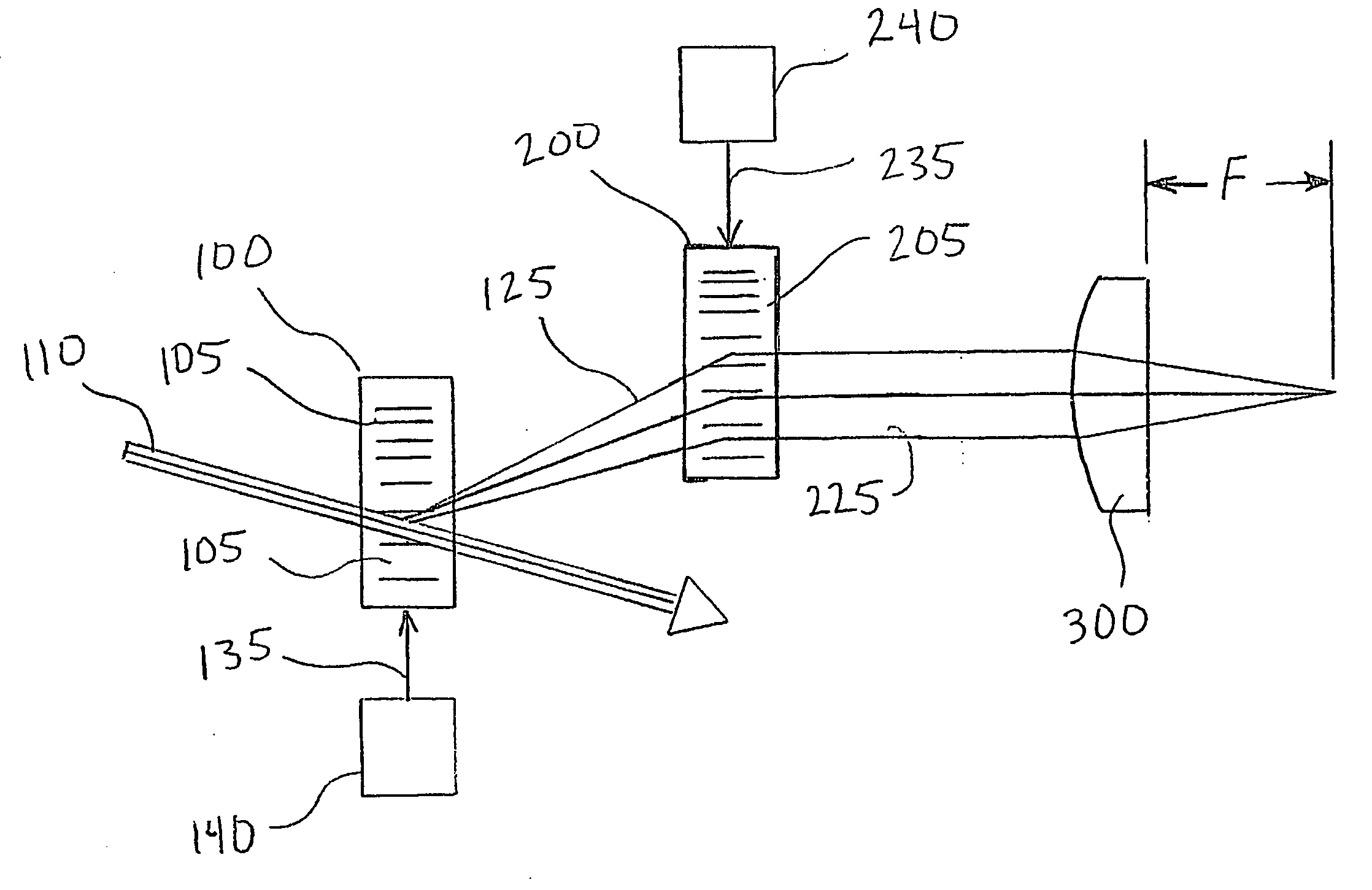
An apparatus for detecting defects on a disk surface includes a light source that generates a light beam and a beamsplitter that splits the light beam into a first light beam portion and a second light beam portion. The first light beam portion illuminates the surface of the disk and produces a reflected light beam. An acoustic-optic deflector deflects the reflected light beam and the second light beam portion producing a deflected output beam having a deflection angle. A detector detects an incident beam translation signal corresponding to reflected light beam angular deflection and acoustic-optic deflector beam angular deflection from the deflected output beam.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method and system for high-speed, high-resolution, 3-D imaging of an object at a vision station
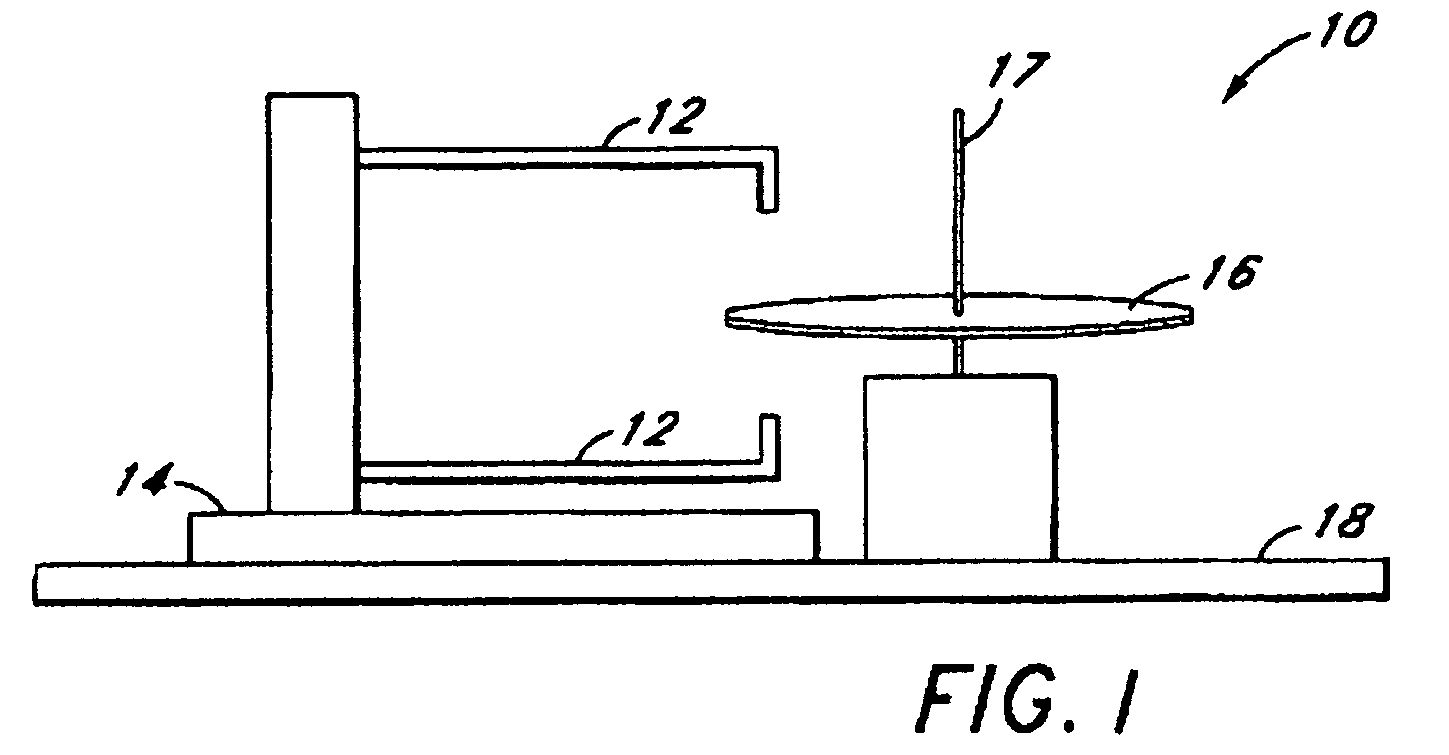
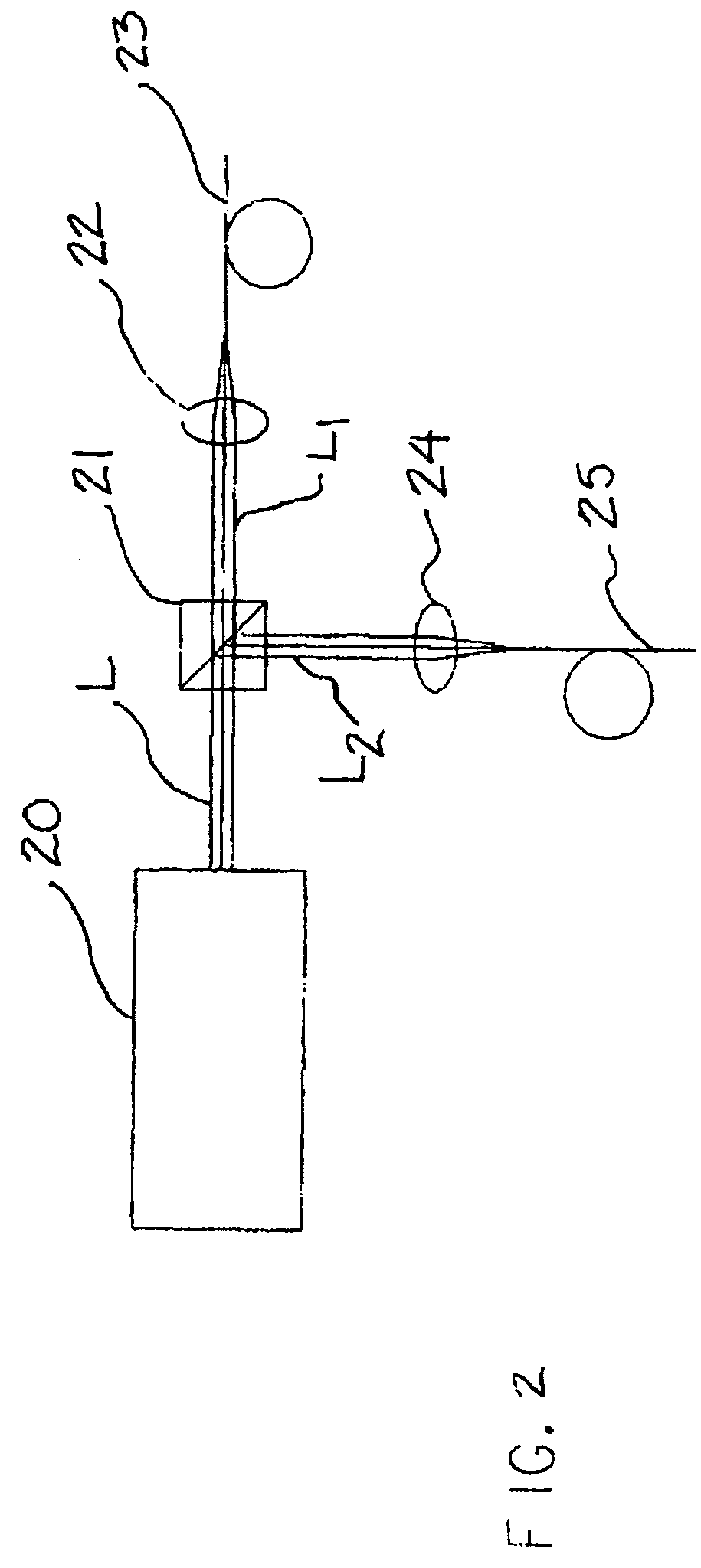
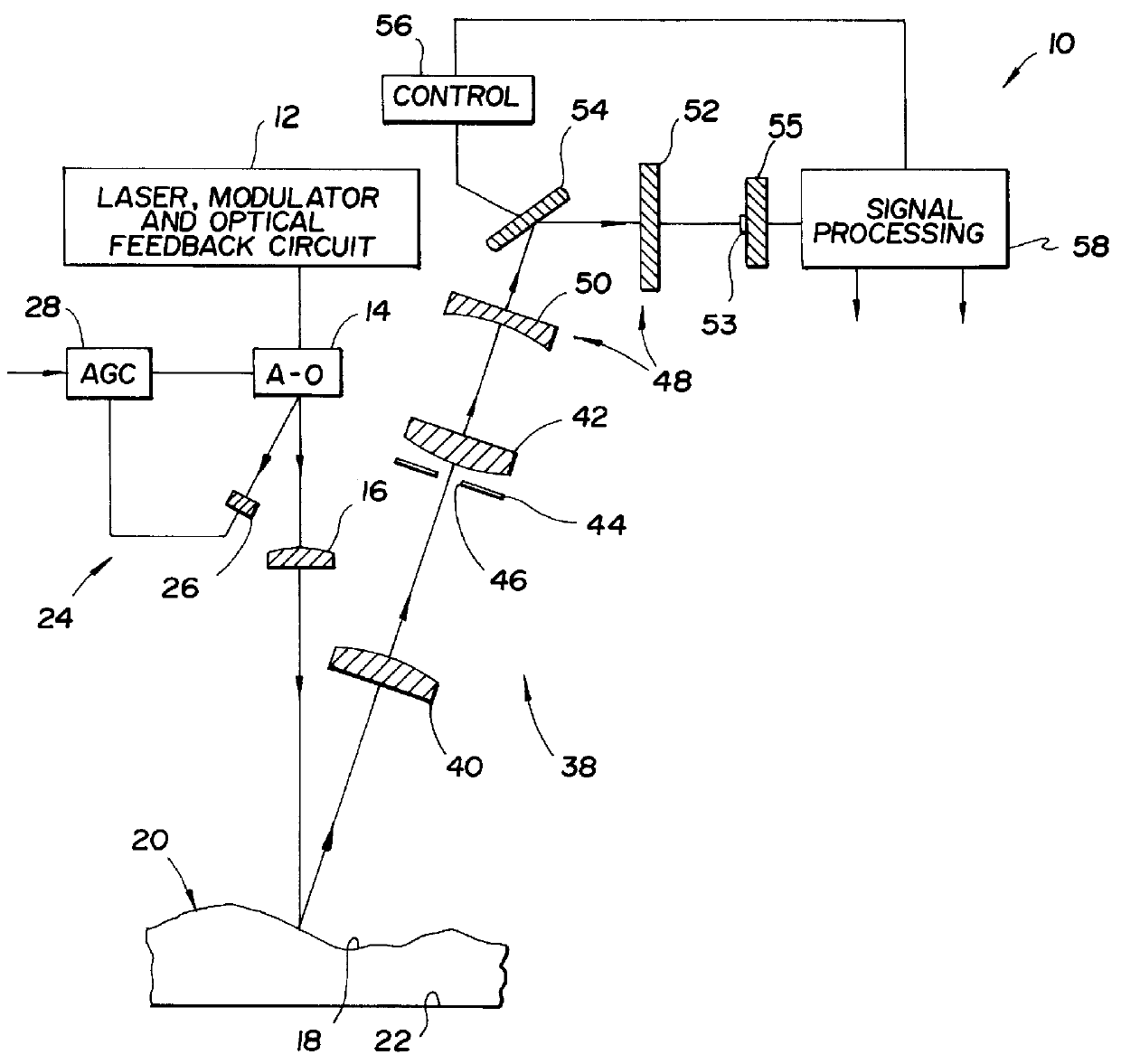
InactiveUSRE36560E1High sensitivityIncrease speedUsing optical meansSignal processing circuitsPhotodetector
A method and system for high-speed, high-resolution, 3-D imaging of an object including an anamorphic magnification and field lens system to deliver the light reflected from the object to a small area position detector having a position-sensing direction. Preferably, an acousto-optic deflector together with associated lens elements scans a beam of modulated laser light across the object to produce a telecentric, flat field scan. The deflector has a feedback loop to enable uniform illumination of the object. The light scattered from the object is collected by a telecentric receiver lens. A combined spatial and polarization filtering plane preferably in the form of a programmable mask is provided to control the polarization and acceptance angles of the collected light. A reduction or focusing lens is positioned immediately behind the filtering plane and is utilized as a telescope objective. The lens system includes a negative cylinder lens having a relatively large focal length and a field lens having a relatively small focal length. The cylinder lens and the reduction lens magnify the image in the position sensing direction of the detector and the field lens delivers the magnified light to the detector. The detector is a photodetector such as a lateral effect photodiode or a rectangular lateral effect detector. A pre-amplifier provides a pair of electrical signals which are utilized by signal processing circuitry to compute the centroid of the light spot.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
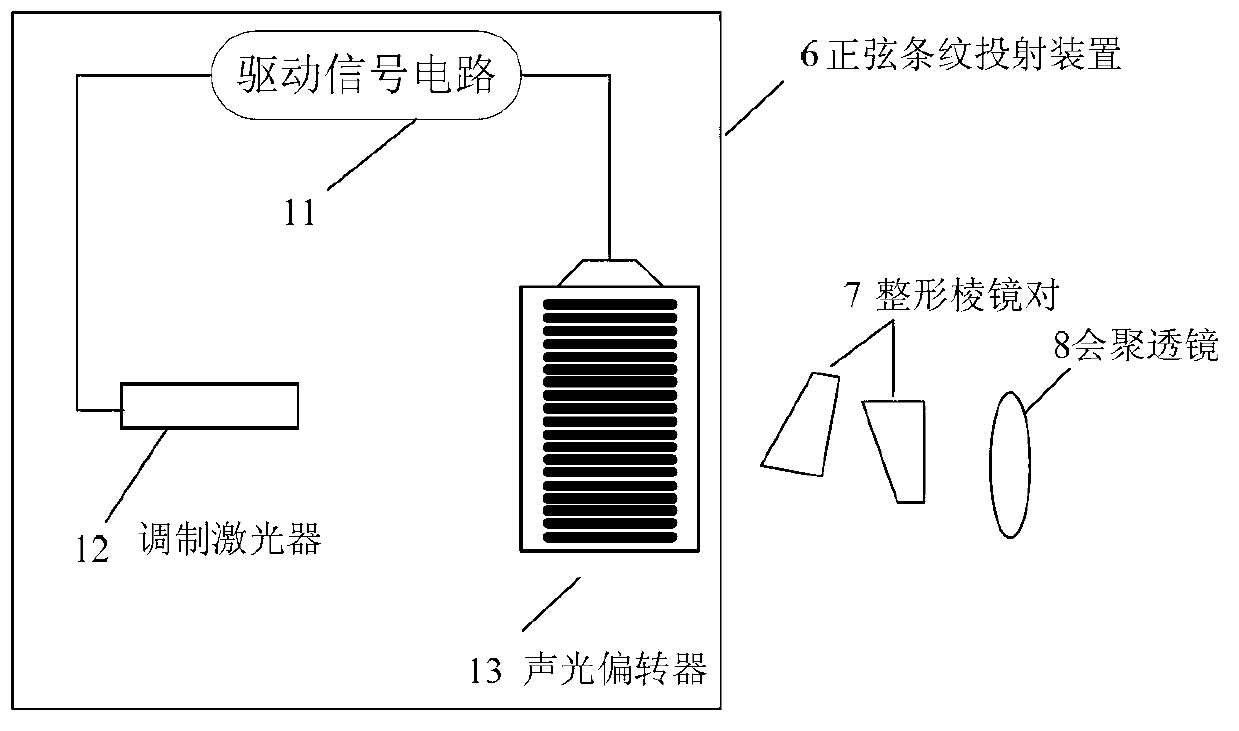
Sinusoidal fringe structural optical projector based on acousto-optic deflection device
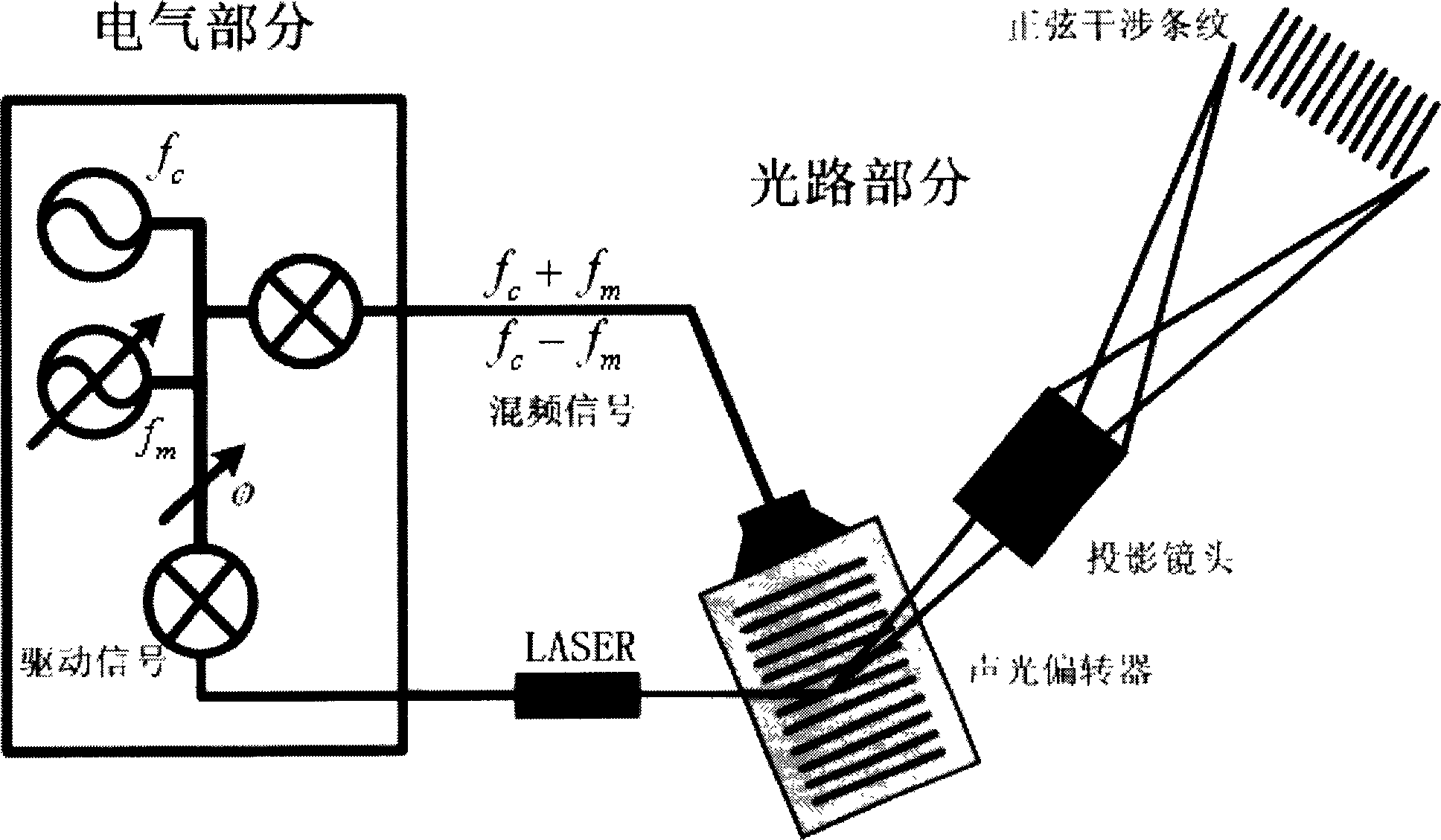
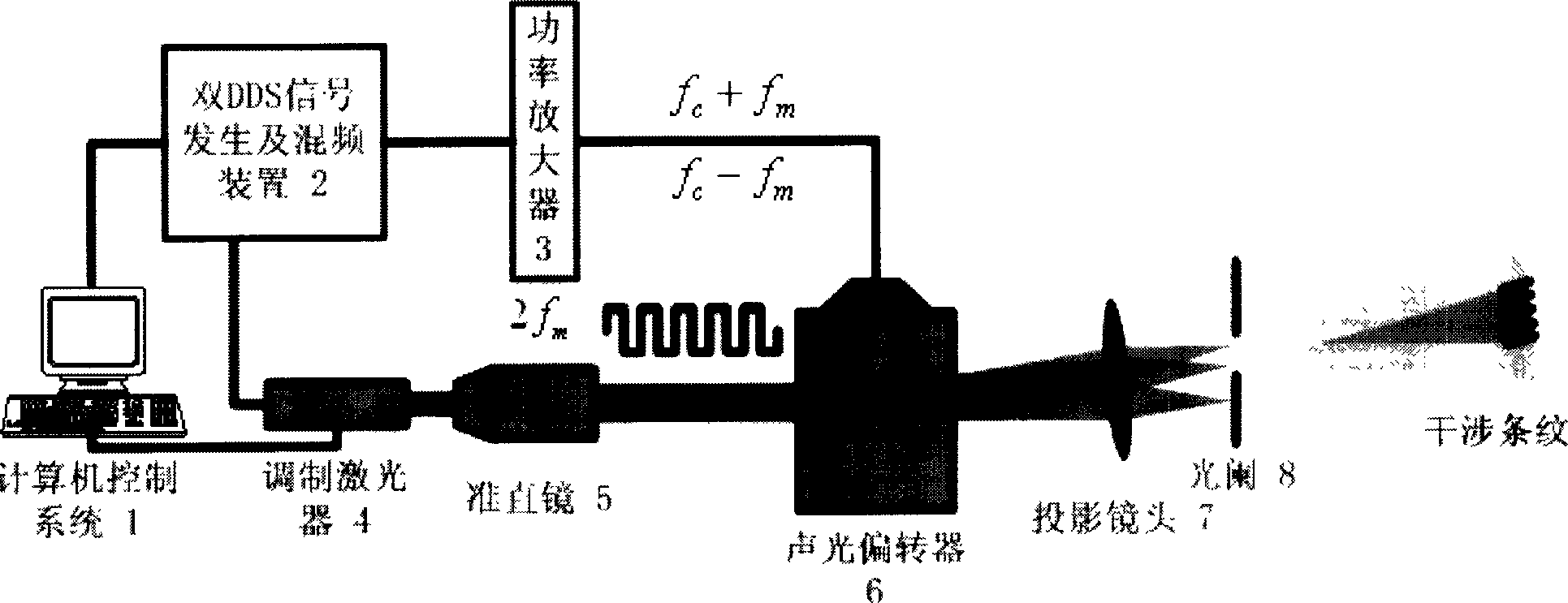
InactiveCN1888818AIncrease flexibilityImprove 3D measurement accuracyUsing optical meansNon-linear opticsCamera lensAcousto-optics
A sine stripe configuration light project equipment based on acousto-optic deflector relates to acousto-optic deflector, double DDS signal generator equipment, mixing multiplier, power amplifier, confection laser, light system and computer controlling system. The acousto-optic deflector produces intervened stripe. Double DDS signal generator equipment produces two-way driving signal. Mixing multiplier mixes the center frequency of the acousto-optic deflector and the confection signal of the DDS. Power amplifier amplifies the power of the mixing signal. Confection laser offers coherent light source and incepts driving signal of laser from DDS. Light system relates to collimating mirror, projection lens and diaphragm which filtrates the 0 level diffraction light from the acousto-optic deflector. Computer control system controls the frequency and phase of the double DDS signal generator equipment to bring the signal, adjusts and controls the brightness and duty ratio of the high frequency confection laser.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Single-optical fiber multiphoton fluorescence scanning endoscope
InactiveCN101485558AEnables early screeningImprove the detection rateEndoscopesDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionCancer cellAcousto-optics
The invention relates to a single-fiber multi-photon fluorescent scanning endoscope, applied in early screening and diagnosis of various mucosa cancers of human body. A single mode fiber is carried inside an endoscope system to enter a human body and guide extracorporeal ultrashort pulse laser into intracorporeal target cell, and an acousto-optic deflector is adopted to carry out laser deflexion in two orthogonal directions; moreover, the endoscope adopts a piezocrystal to perform fine adjustment on the focus of the lens group so as to adjust fluorescence excitation depth, and adopts a multi-photon fluorescent imaging mechanism to eliminate confocal pinholes; therefore, the endoscope reduces the process difficulty of making acousto-optic deflexion scanning front end and also overcomes mechanical inertia of devices adopting micromechanics to realize deflexion scanning so as to ensure convenient integrated molding and miniaturization of an entire scanning imaging tail end. The system provided by the invention can carry out cell morphologic analysis on suspect cancer cells at low cost during routine endoscope examination.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for electronically controlled scanning of micro-area devices
InactiveUS6246046B1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam splitterFluorescence
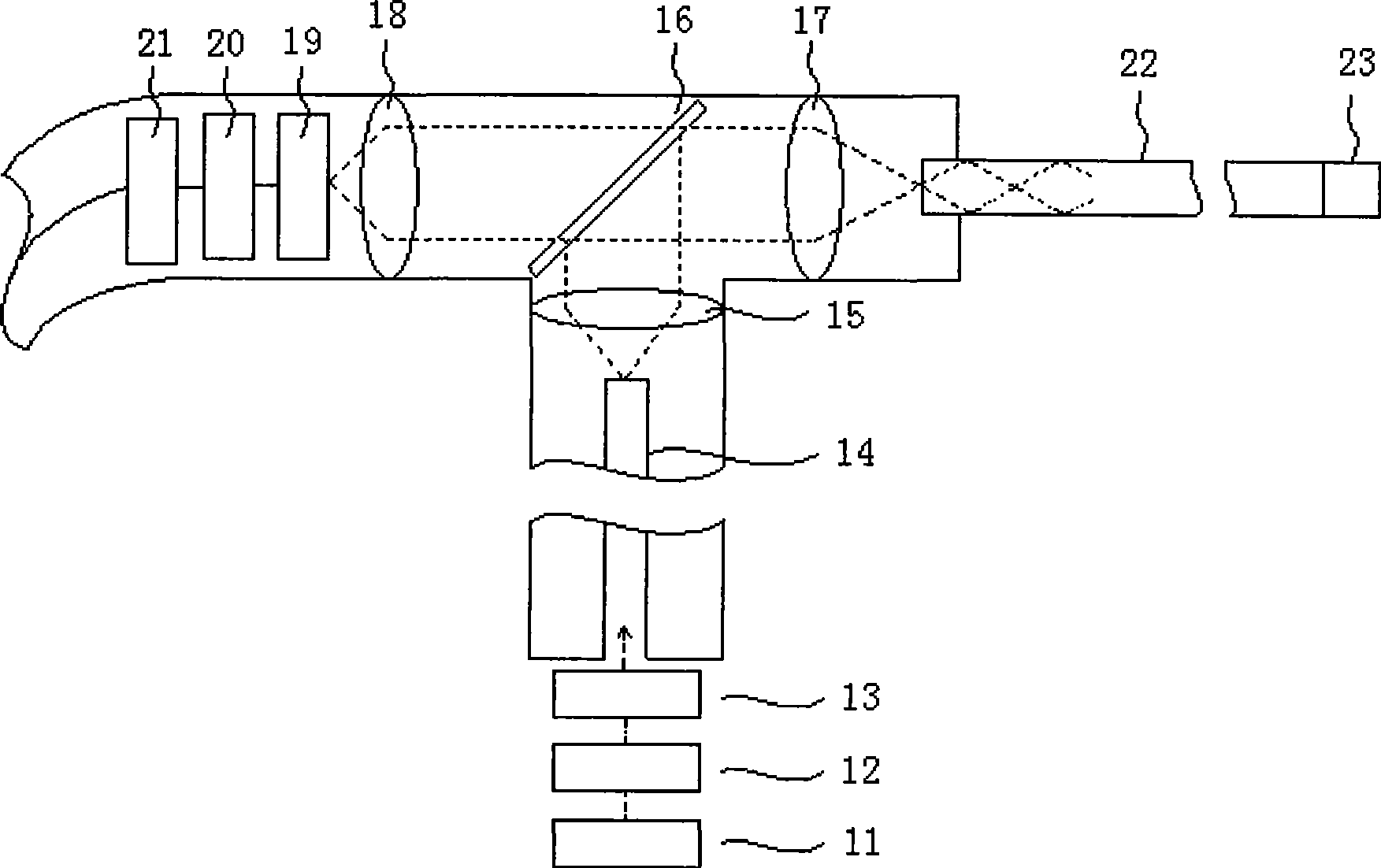
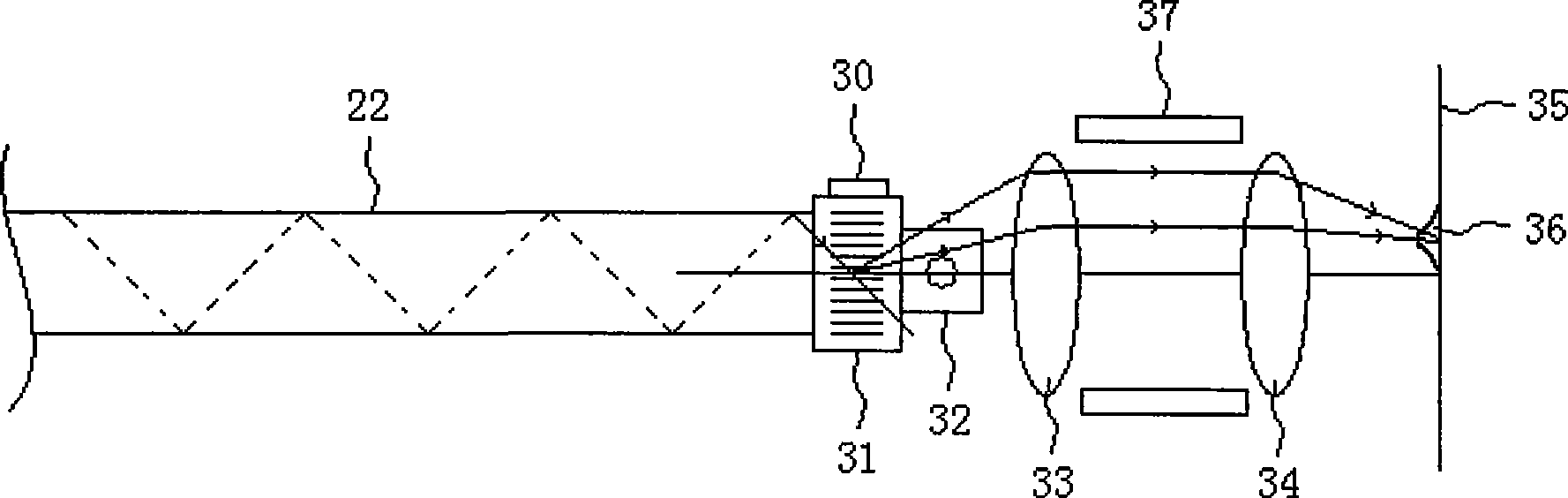
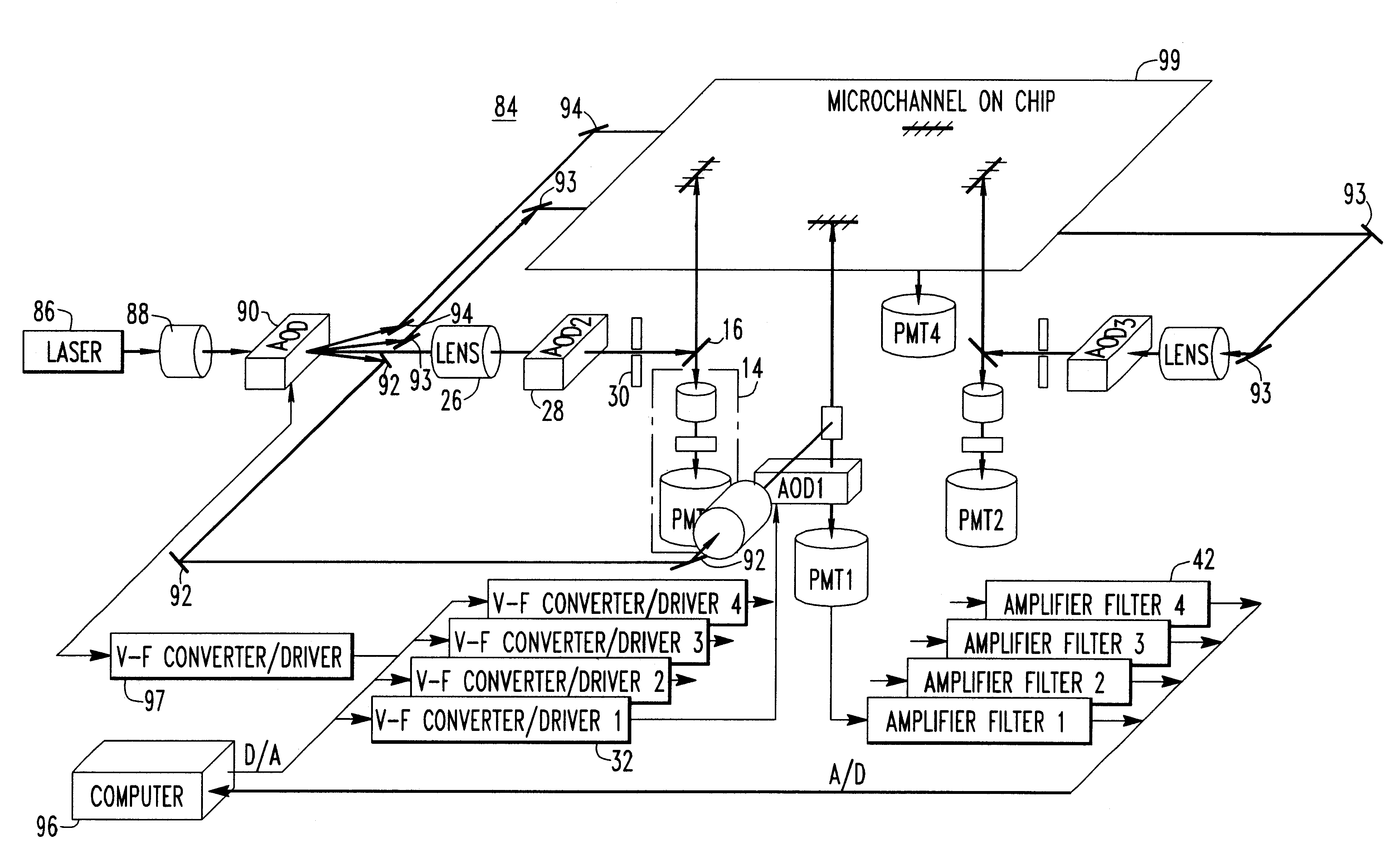
The present invention provides an excitation source which may be used, for example, in conjunction with the scanning of multi-channel electrophoresis chips or capillary arrays. The excitation source is comprised of a source of light, such as a laser beam. A beam expander, an acousto-optic deflector, and a filter are optically aligned with the source of light. A driver is connected to the acousto-optic deflector for controlling the angle of deflection. A system is disclosed which includes the excitation source, a detector for detecting fluorescence from a target chip, and a beam splitter or other device for optically connecting the excitation source to the chip and for optically connecting the chip to the detector. The excitation source may be based on an acousto-optic deflector, an electrooptic deflector, a piezoelectric deflector, or any other electronically controlled device. Methods of focusing a beam of collimated light and electronically exciting a plurality of micro-areas of a target chip, either serially or in parallel, are also disclosed.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
High speed microscope with three-dimensional laser beam scanning including acousto-optic deflector for controlling the lateral position and collimation of the light beam
InactiveUS7227127B2Eliminate dependenceIncrease in sizeBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansAcousto optic deflectorLight beam
A system and method for independently controlling the collimation and lateral positioning of a light beam comprises at least one acousto-optic deflector and a pair of counter propagating acoustic waves with offset frequencies. While the frequency offset controls the lateral positioning of the light beam, a frequency gradient across the acousto-optic deflectors controls the collimation of the light beam.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Device for and method of ray tracing wave front conjugated aberrometry
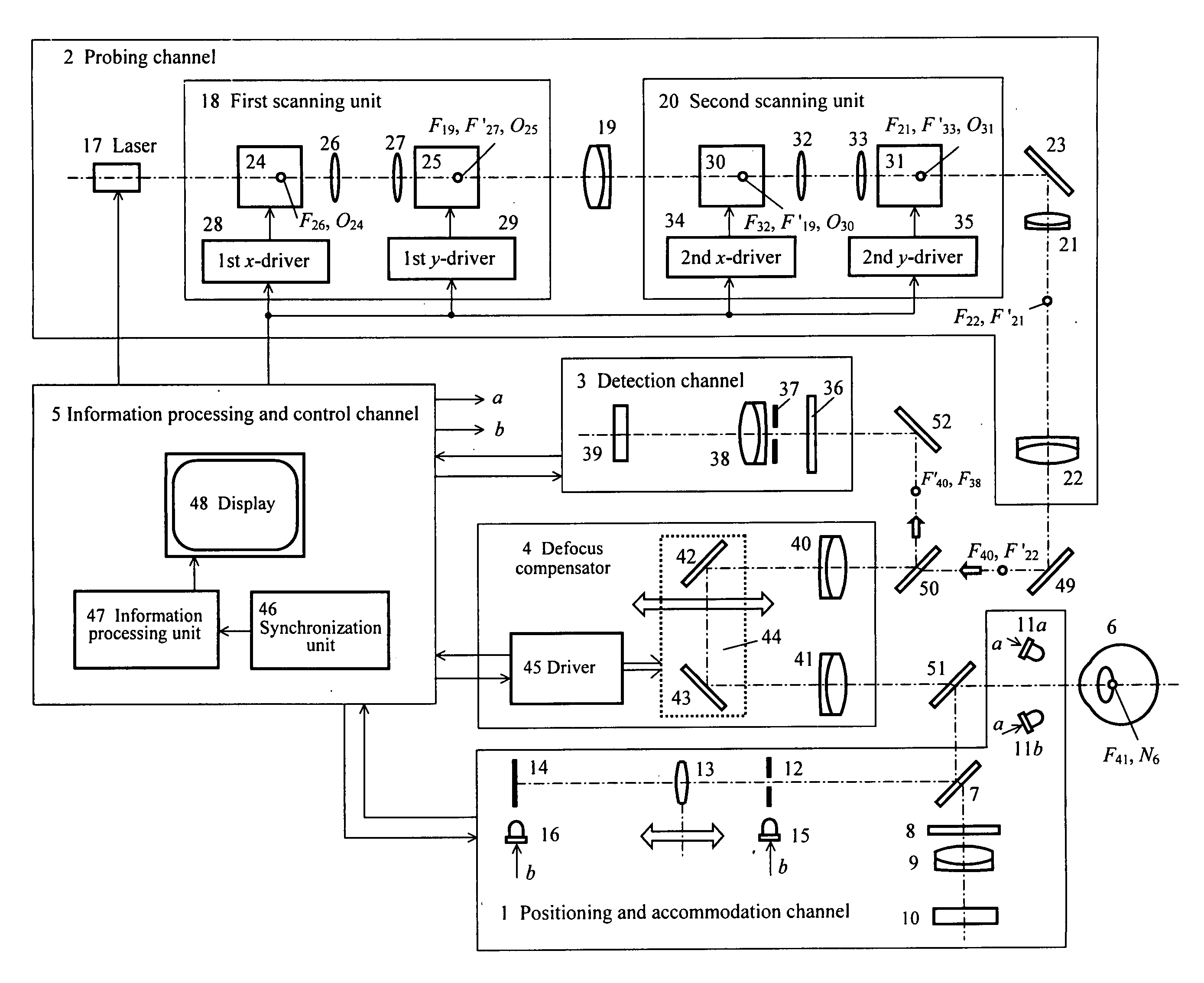
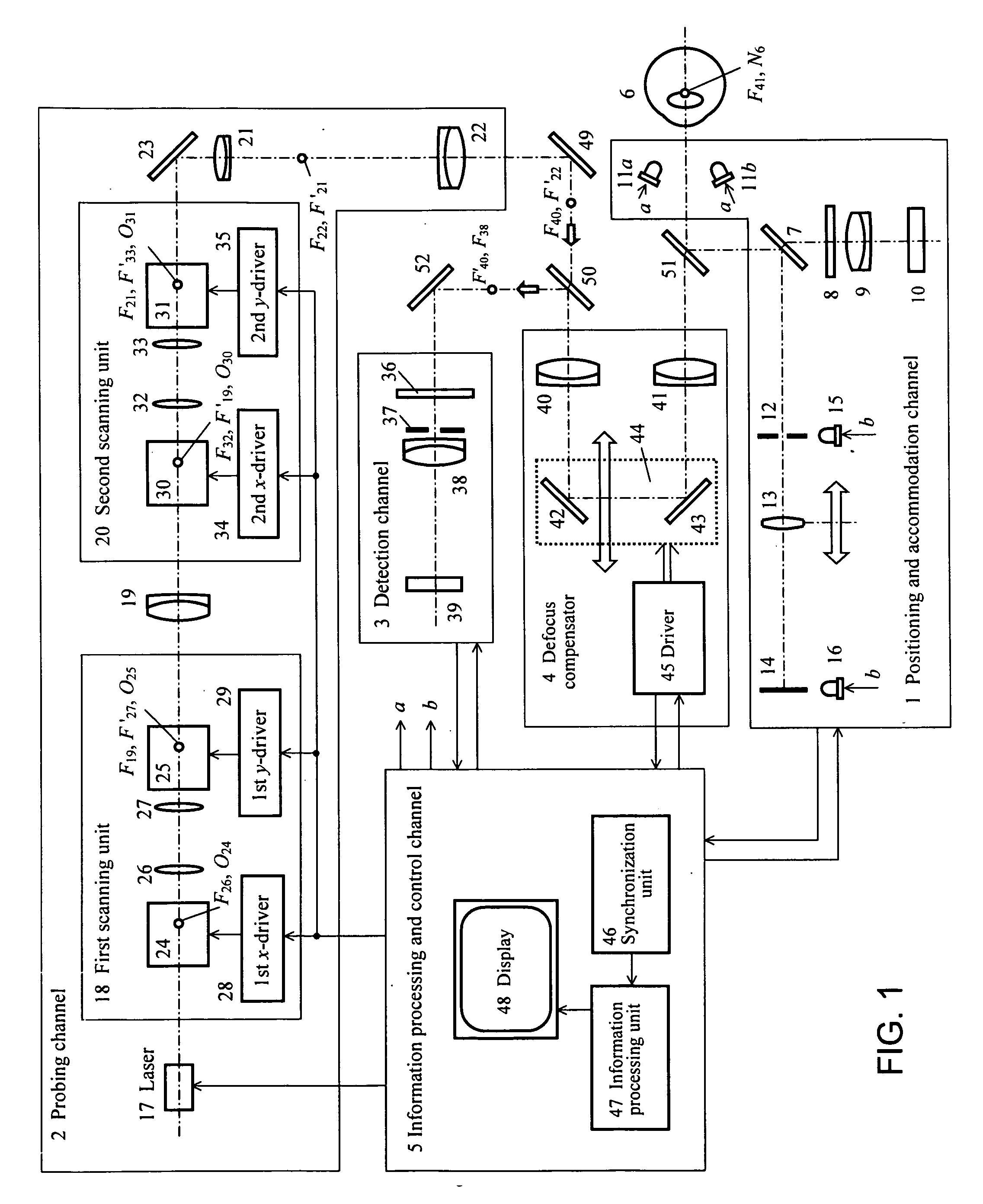
Two stages of ray tracing aberrometry include preliminary stage of measurement with probing beams successively entering the eye in parallel to the optical axis and the main stage of measurement with probing beams successively entering the same points of the eye but tilted in the way to compensate for the refraction variations over the entrance aperture measured in the preliminary stage. The main stage of measurement may be implemented in the combination of units, one compensating for defocus another—compensating for higher order aberrations. In one embodiment, the probing channel contains two two-coordinate acousto-optic deflectors with a collimating lens between them. The procedure of main stage of measurement may be iteratively repeated until the wave front conjugation is achieved with a prescribed accuracy.
Owner:MOLEBNY VASYL
High spectrum full polarization three dimension imaging integrate detecting system
InactiveCN1900741AImprove detection abilityImprove adaptabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationElectronic controllerAcousto-optics
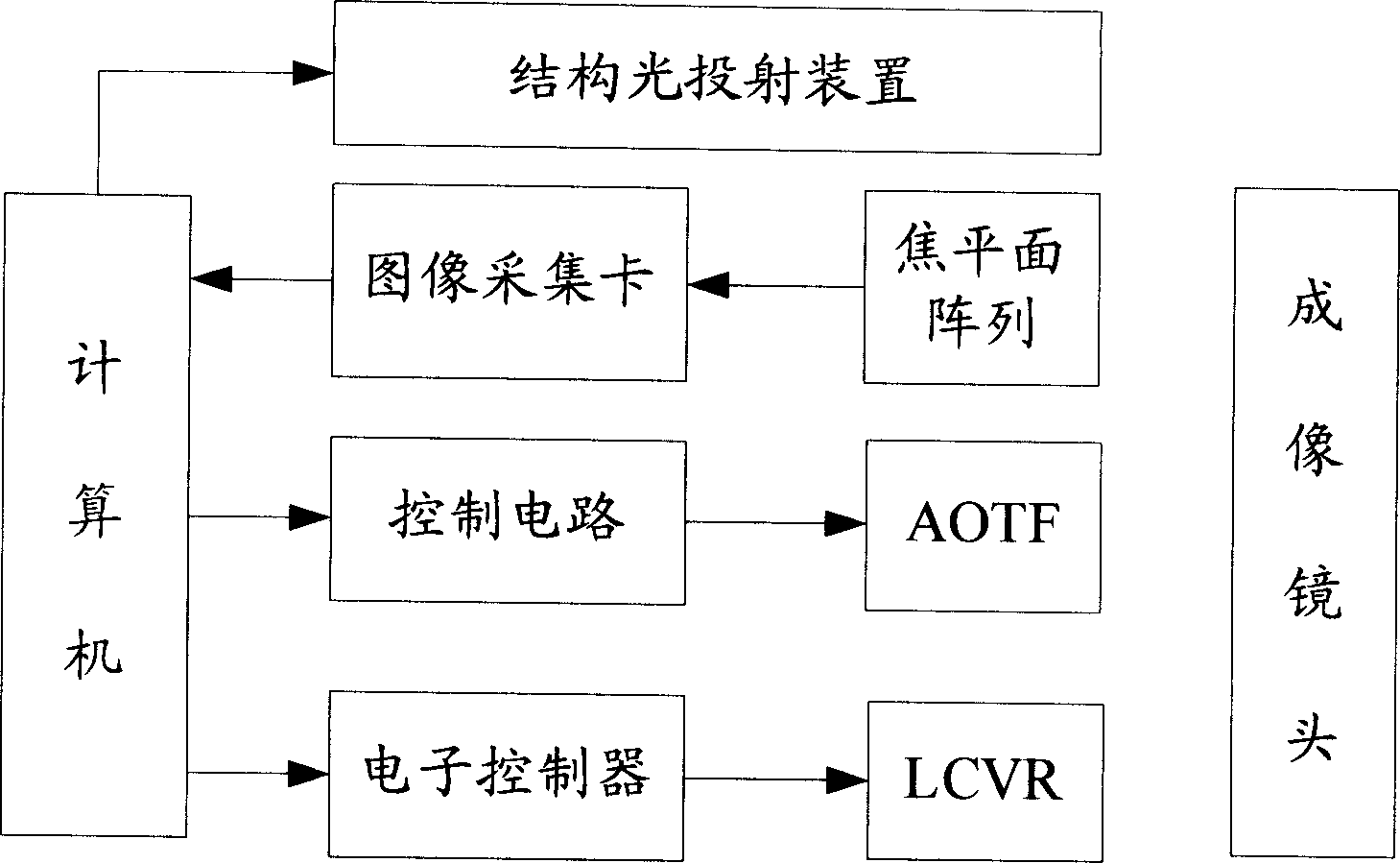
The detection system includes imaging lens, acousto-optic tunable filter plate AOTF, control circuit, linear phase delay LCVR, electronic controller in use for controlling value of voltage applied to LCVR, focal plane array, image collection card, self-adapting structured light projection device, and computer. Being kernel part of whole system, the computer is in use for sending out control commands to control RF drive frequency applied to AOTF so as to change wavelength, and obtain image of object in the wavelength. Also, the computer is in use for controlling value of voltage applied to LCVR so as to change linear phase delay LCVR. Moreover, the computer collects image information of object to be measured, and carries out process for the collected images. The invention possesses integrated capabilities of measuring 3D space, high spectrum and polarization corresponding to scale of object image cell. Features are: good adaptability, and raised detection capability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Acousto-optic deflector with phase-controlled transducer array
InactiveCN102566193AReduce tracking angle rangeHigh bandwidthNon-linear opticsSonificationPhase difference
The invention particularly relates to an acousto-optic deflector with a phase-controlled transducer array. A plurality of transducer electrodes are arranged on a piezoelectric layer on the surface of acousto-optic crystals, and are driven by an independent radio frequency (RF) signal source; the phase difference between RF signals is adjustable; and the acousto-optic deflector works in an abnormal Bragg diffraction mode and can increase the bandwidth by adopting slow-mode incident light and tangent conditions. The range of the tracking angle desired for ultrasonic tracking can be reduced by adopting the tangent conditions of abnormal Bragg diffraction, thereby further increasing length of a single transducer electrode, improving acousto-optic interaction length, or reducing the number of desired transducer electrodes, and reducing system complexity. The acousto-optic deflector can be widely used in the application fields of microscopic imaging, laser display and record system, laser processing, laser measurement and control, and so on.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Light stimulation device
InactiveCN101776791AGuaranteed beam scanning qualityReduce volumeMicroscopesNon-linear opticsAcousto-opticsNerve cells
The invention discloses a light stimulation device, which can be applied to the fields of biology, chemistry, life sciences and the like. The structure of the device is that a laser, a scanning unit and a lens are arranged sequentially and are coincident with the center of an optical axis; the center of the scanning unit is positioned on an object focal plane of the lens; and the scanning unit comprises two acousto-optic deflection devices arranged orthogonally. The device adopts the acousto-optic deflection devices as the scanning elements and can carry out high-speed random light stimulation on cell biological samples comprising nerve cells, tissues and the like so as to carry out various psychological research. The device adopts the optical fiber and the optical fiber bundle to guide light to make the system miniaturized and convenient for integration, and is very convenient to carry out cooperative work with other systems such as the microscope and the patch clamp.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
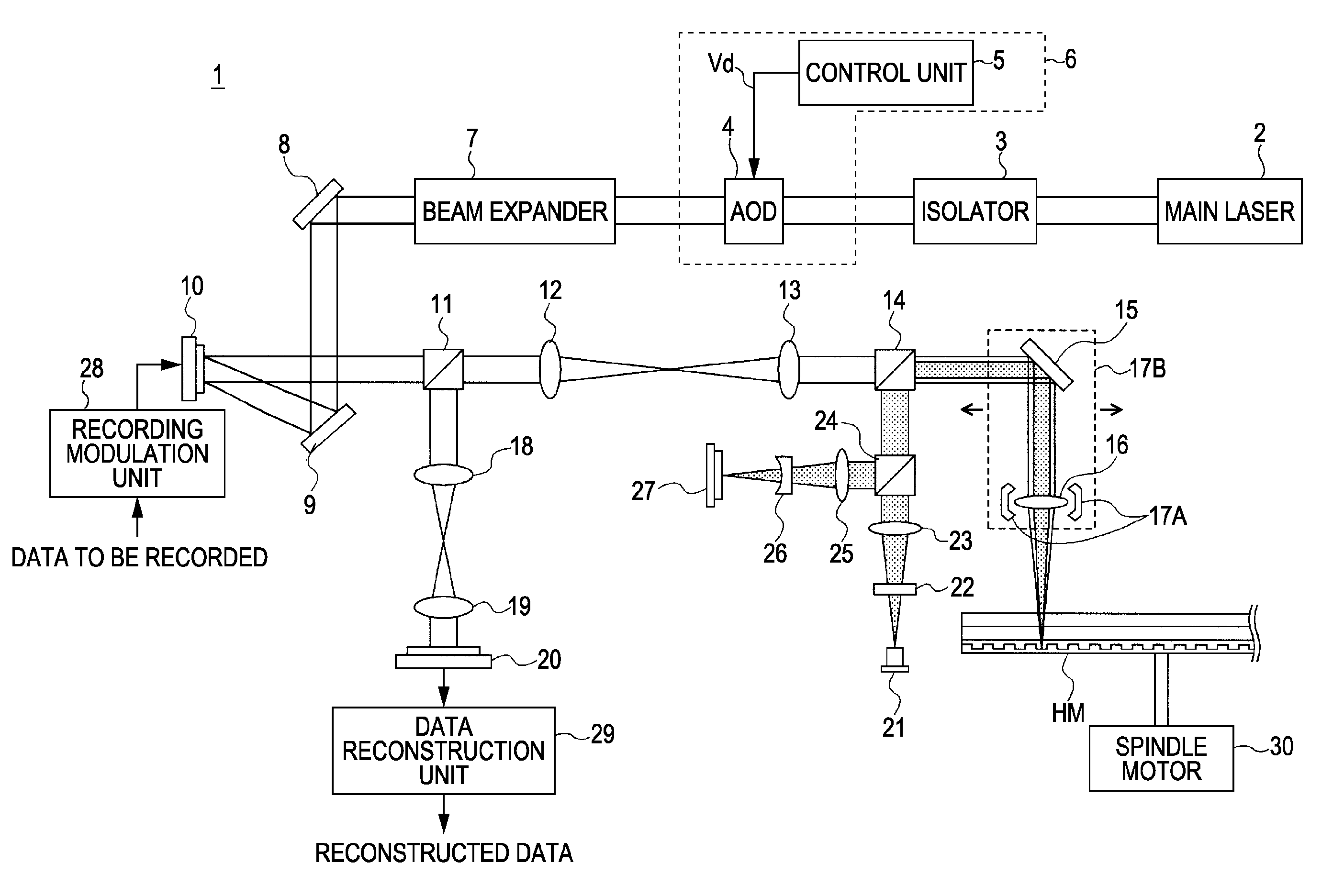
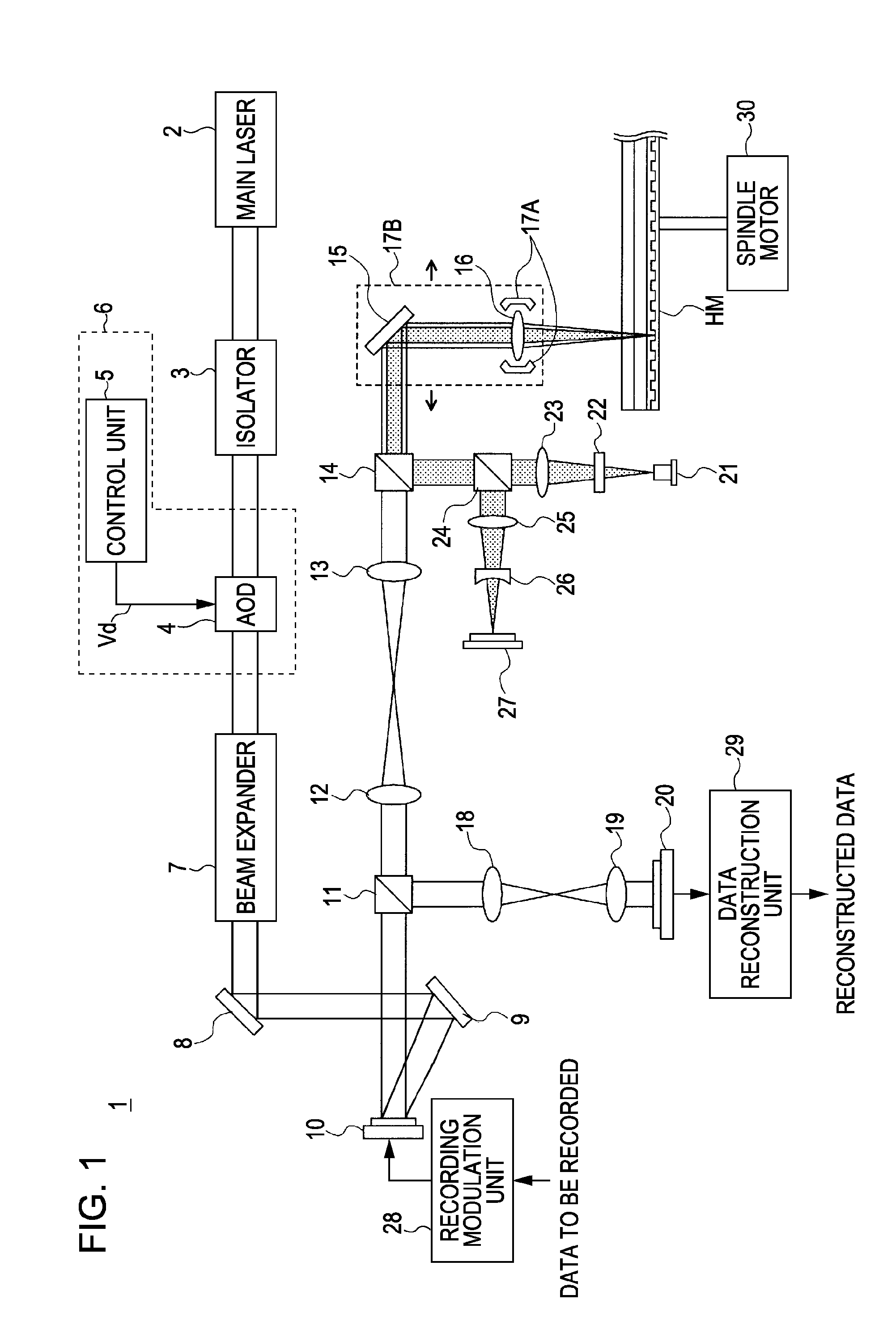
Optical unit, method for controlling drive, and holographic apparatus
InactiveUS20090116088A1Reduce necessityConstant levelOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageAcousto optic deflectorTransmittance
An optical unit includes an acousto-optic deflector and a drive control unit. The drive control unit controls the acousto-optic deflector by changing a frequency of a voltage applied to an acousto-optic medium of the acousto-optic deflector to a frequency in a first frequency range during a first period representing a deflection control period and changing the frequency of the voltage to a frequency in a second frequency range different from the first frequency range during a second period representing a transmittance control period.
Owner:SONY CORP
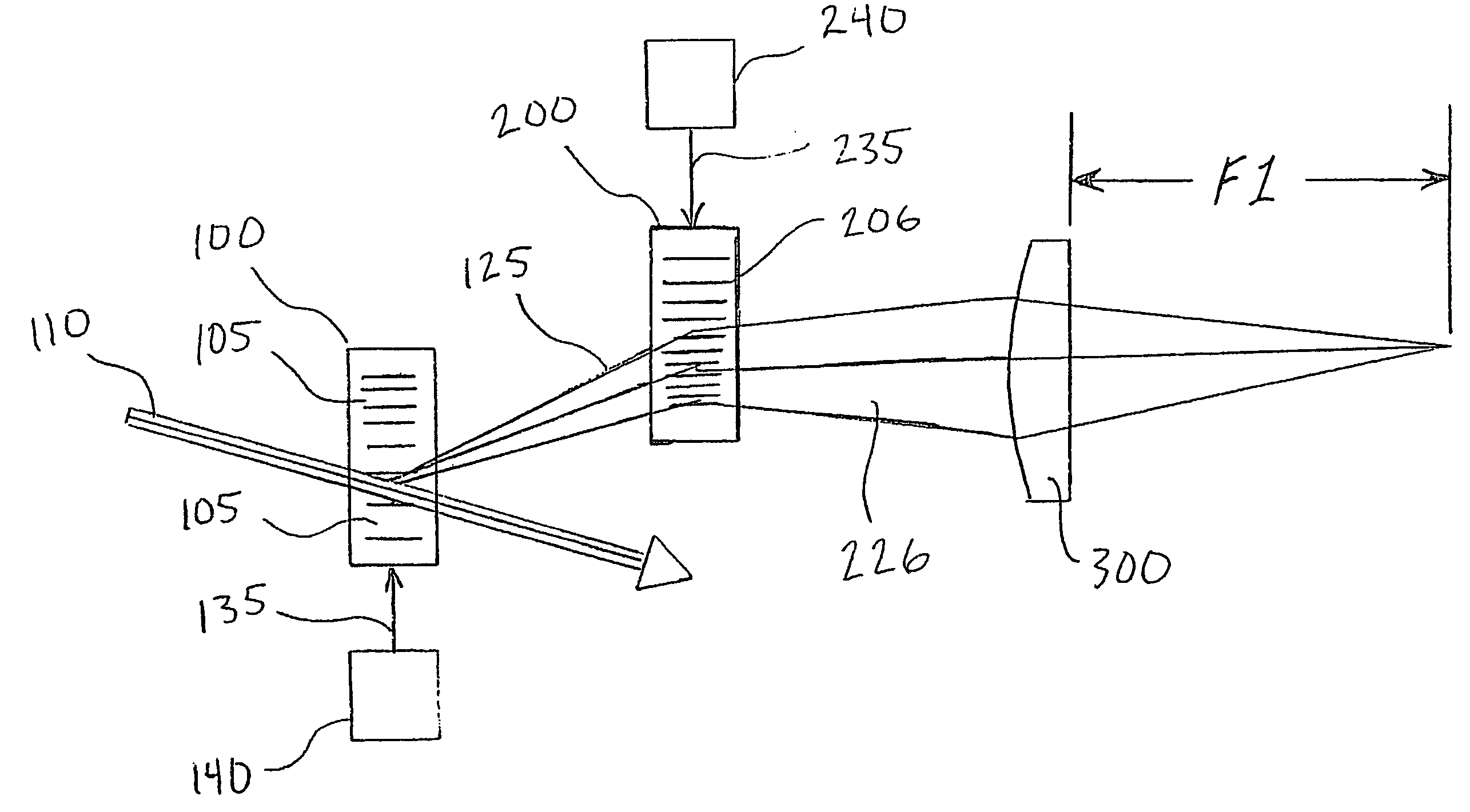
Focusing system comprising acousto-optic deflectors for focusing an electromagnetic beam
The present invention relates to a focusing system (100) for focusing an electromagnetic beam for three-dimensional random access applications, the system comprising a first pair of acousto-optic deflectors (10) for focusing an electromagnetic beam in an X-Z plane, and a second pair of acousto-optic deflectors (20) for focusing an electromagnetic beam in a Y-Z plane being substantially perpendicular to the X-Z plane, characterised in that the second pair of acousto-optic deflectors (20) are arranged between the acousto-optic deflectors (12, 12') of the first pair of acousto-optic deflectors (10), such that the first and fourth acousto-optic deflectors (12, 12") of the system belong to the first pair of acousto-optic deflectors (10) and the second and third acousto-optic deflectors (22, 22") of the system belong to the second pair of acousto-optic deflectors (20).
Owner:FEMTONICS
Solid state microoptoelectromechanical system (moens) for reading photonics diffractive memory
InactiveUS20060018182A1Increase speedSmall sizeRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansAcousto optic deflectorPhotonics
The present invention comprises a solid-state system for reading information from a photonics diffractive memory. An acousto-optic deflector directs a convergent light beam onto a micr-mirror array which then reflects the light beam onto the photonics diffractive memory at a predetermined point and angle so as to access a packet of information. The compact architecture for this diffractive optics systems in accordance with the present invention integrates a number of components into a compact package, including an acousto-optic deflector and a microoptoelectromechanical system (MOEMS) mirror array whose elements oscillate with a sznchronized frequency adapted to that of the acousto-optic deflector. This architecture reduces the addressing component of a reading system for a photonics diffractive memory to a matchbox size.
Owner:RES INVESTMENT NETWORK
Compensator system and method for compensating angular dispersion
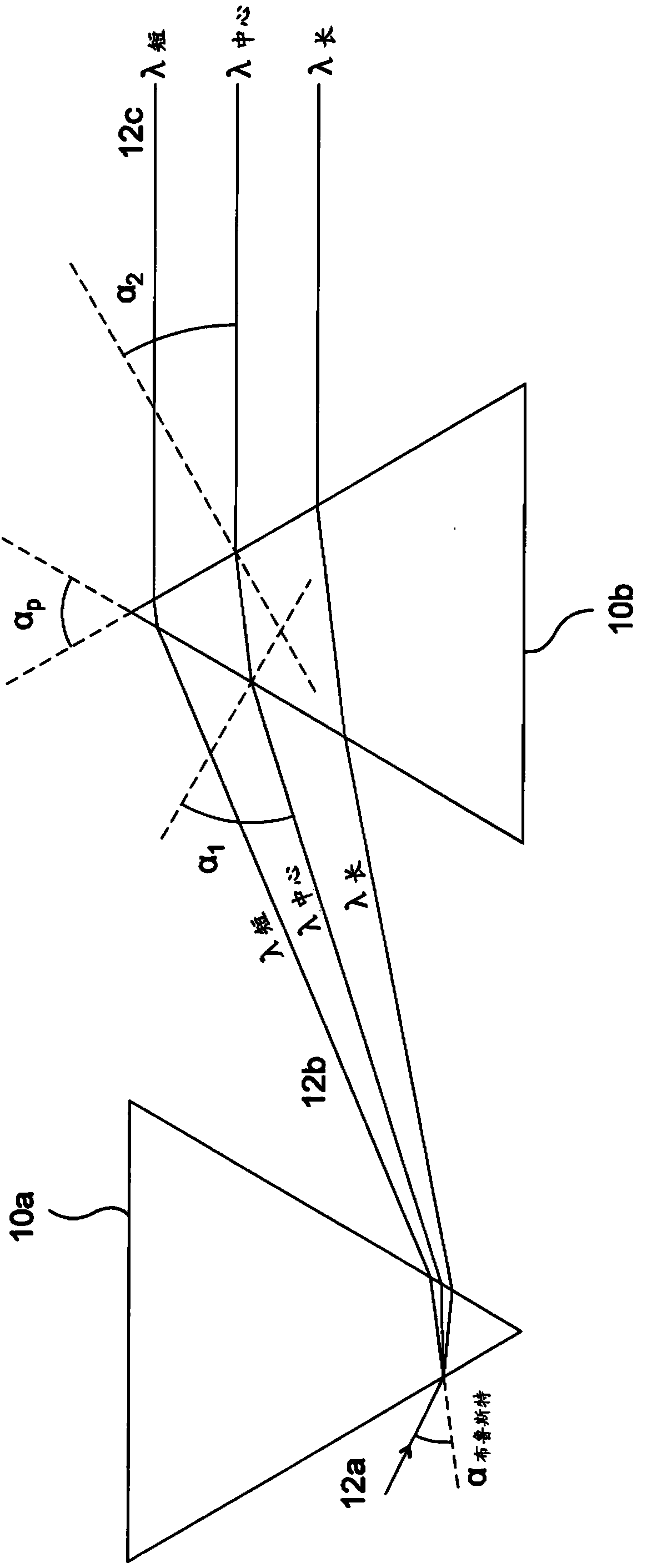
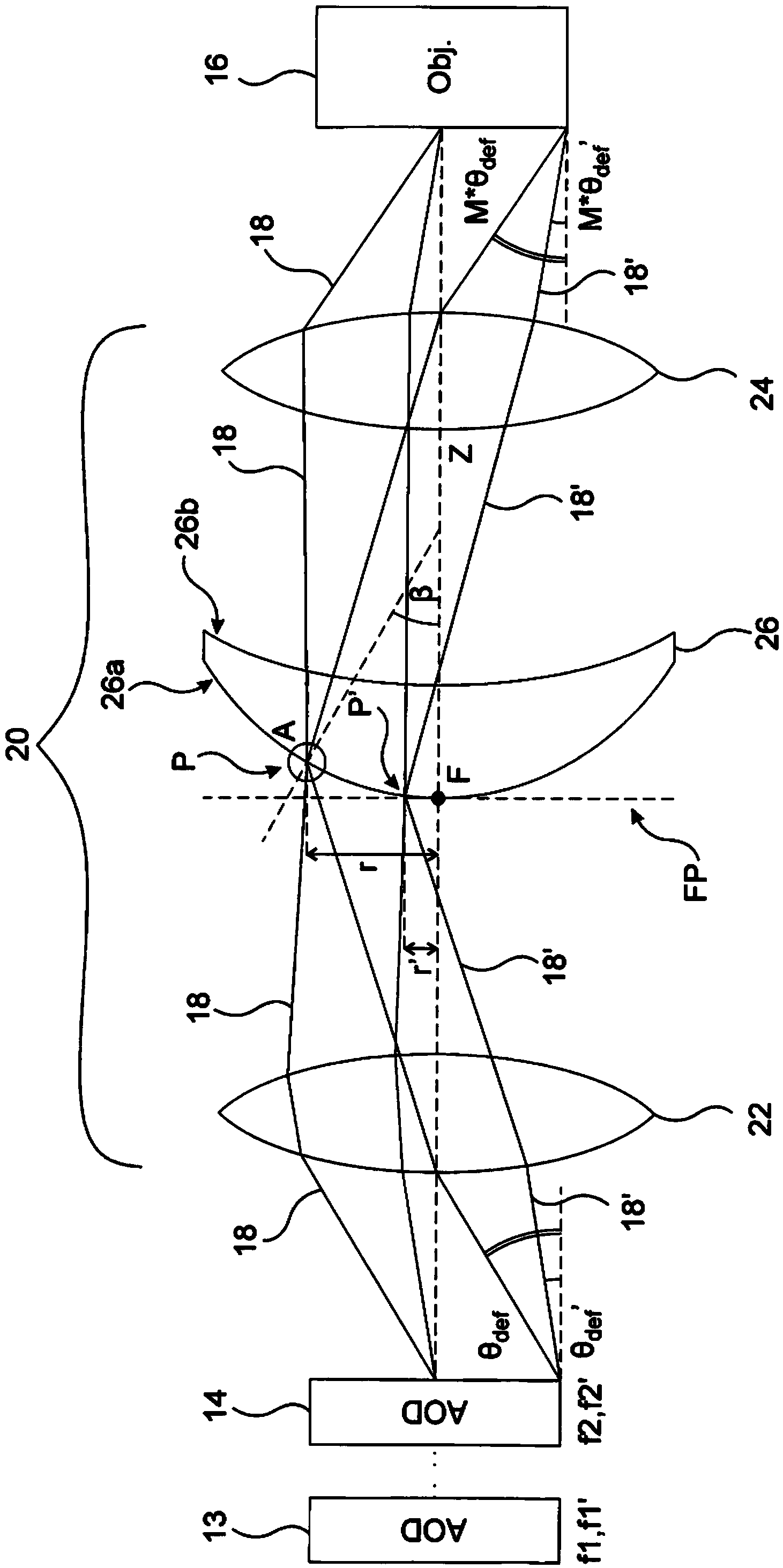
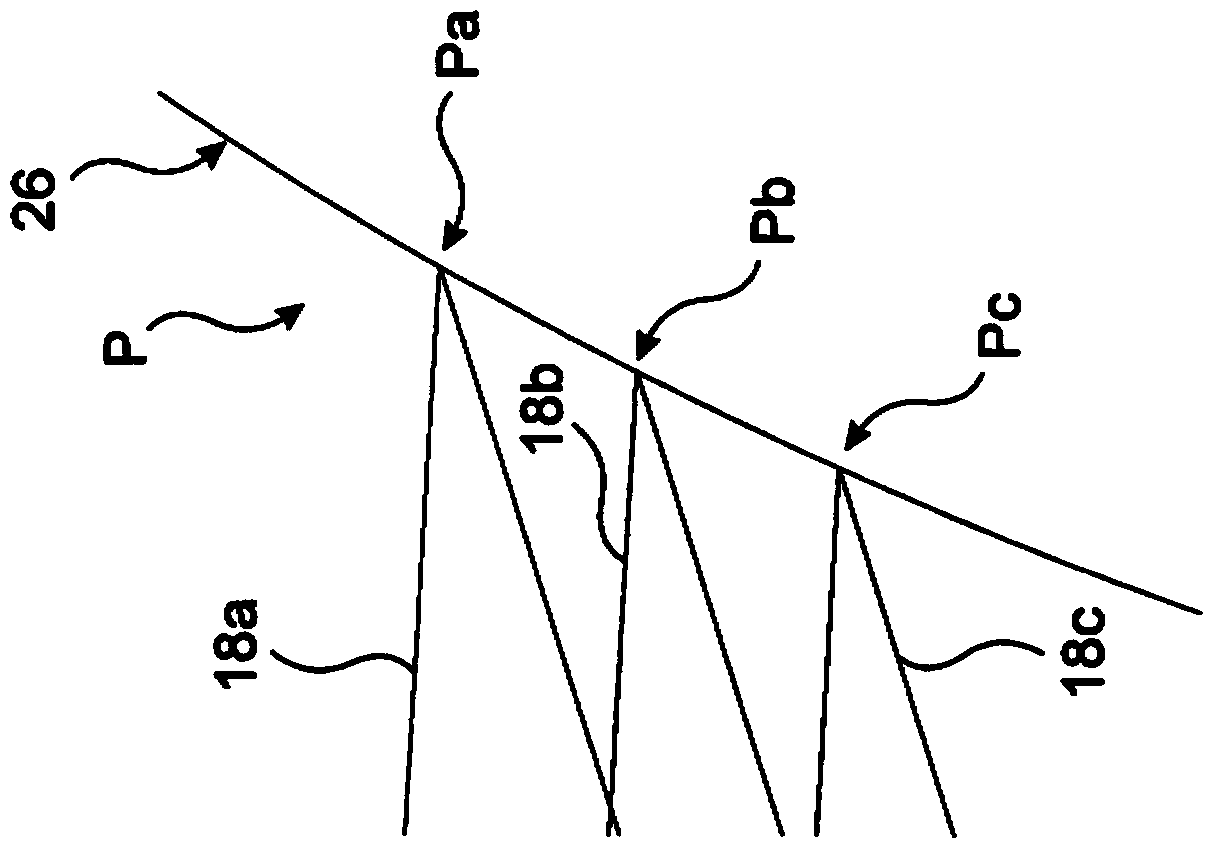
The invention relates to a compensator system adapted to compensate for the angular dispersion of electromagnetic beams deflected by at least one acousto-optic deflector of an optical system, wherein the angular dispersion of each deflected beam is dependent on the deflection angle obtained by the deflecting acoustic frequency of the acousto-optic deflector, characterised in that the compensator system comprises: - a first lens group for spatially separating the deflected beams of different deflection angle and angular dispersion by focusing the beams substantially into the focal plane, - a compensator element having a first surface and a second surface, and being arranged such that the first surface of the compensator element lies substantially in the focal plane of the first lens group, and the first and second surfaces of the compensator element have nominal radiuses R1 and R2 that together work as prisms with tilt angles beta and prism opening angles alphap that vary with the distance from the optical axis so as to compensate for the angular dispersion of the spatially separated deflected beams, - a second lens group arranged so as to substantially parallelise the different wavelength components of each deflected beam exiting the compensator element while maintaining the angular variation of the beams deflected at different acoustic frequencies. The invention further relates to method for compensating for the angular dispersion of electromagnetic beams deflected by at least one acousto-optic deflector of an optical system, wherein the angular dispersion of each deflected beam is dependent on the deflection angle obtained by the deflecting acoustic frequency, characterised by - spatially separating the deflected beams of different deflection angle and angular dispersion by focusing the beams via a first lens group substantially into the focal plane of the first lens group, - compensating for the angular dispersion of the spatially separated deflected beams in accordance with the angular dispersion of the given beam, - substantially parallelising the spectral components of each deflected beam while maintaining the angular variation of the beams deflected at different acoustic frequencies.
Owner:FEMTONICS
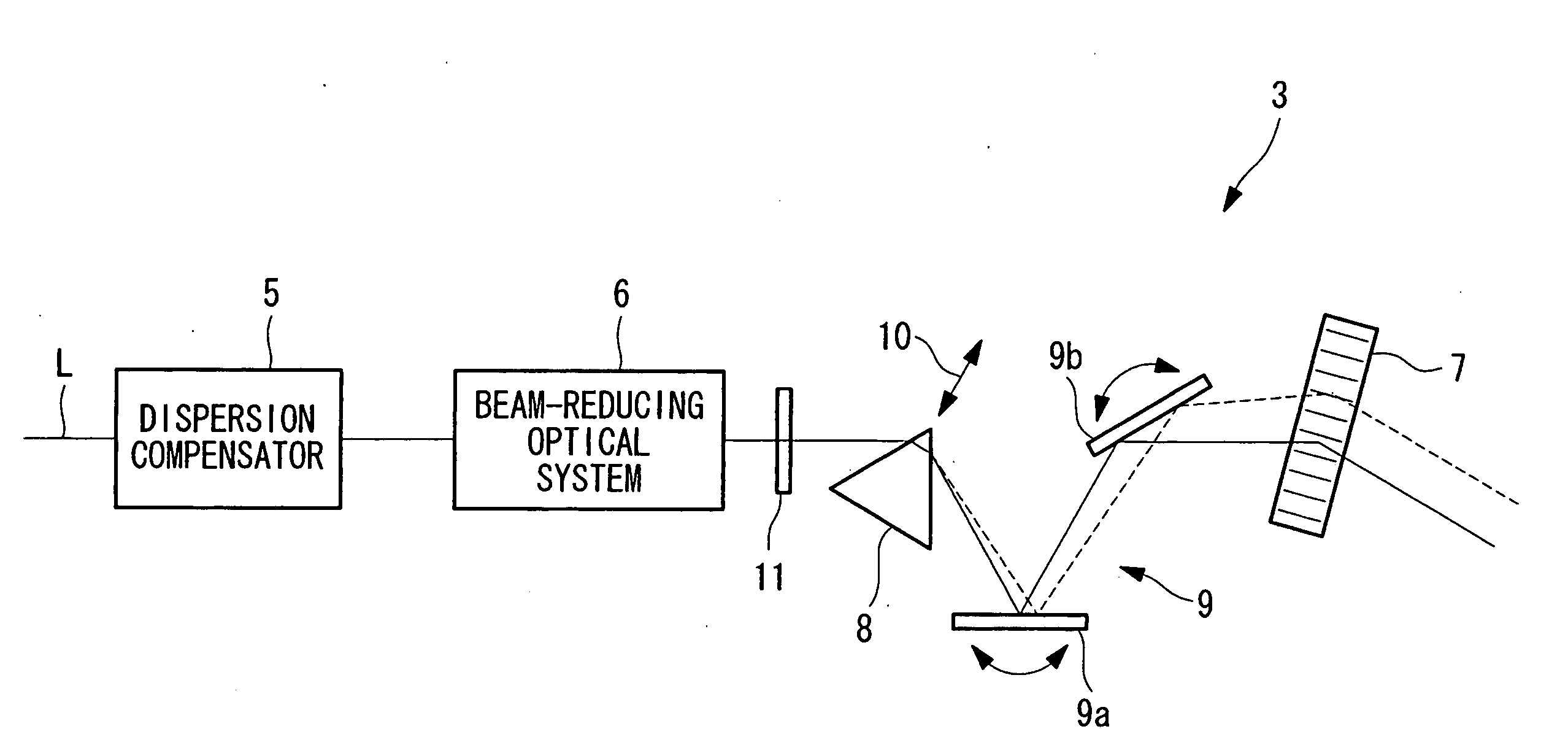
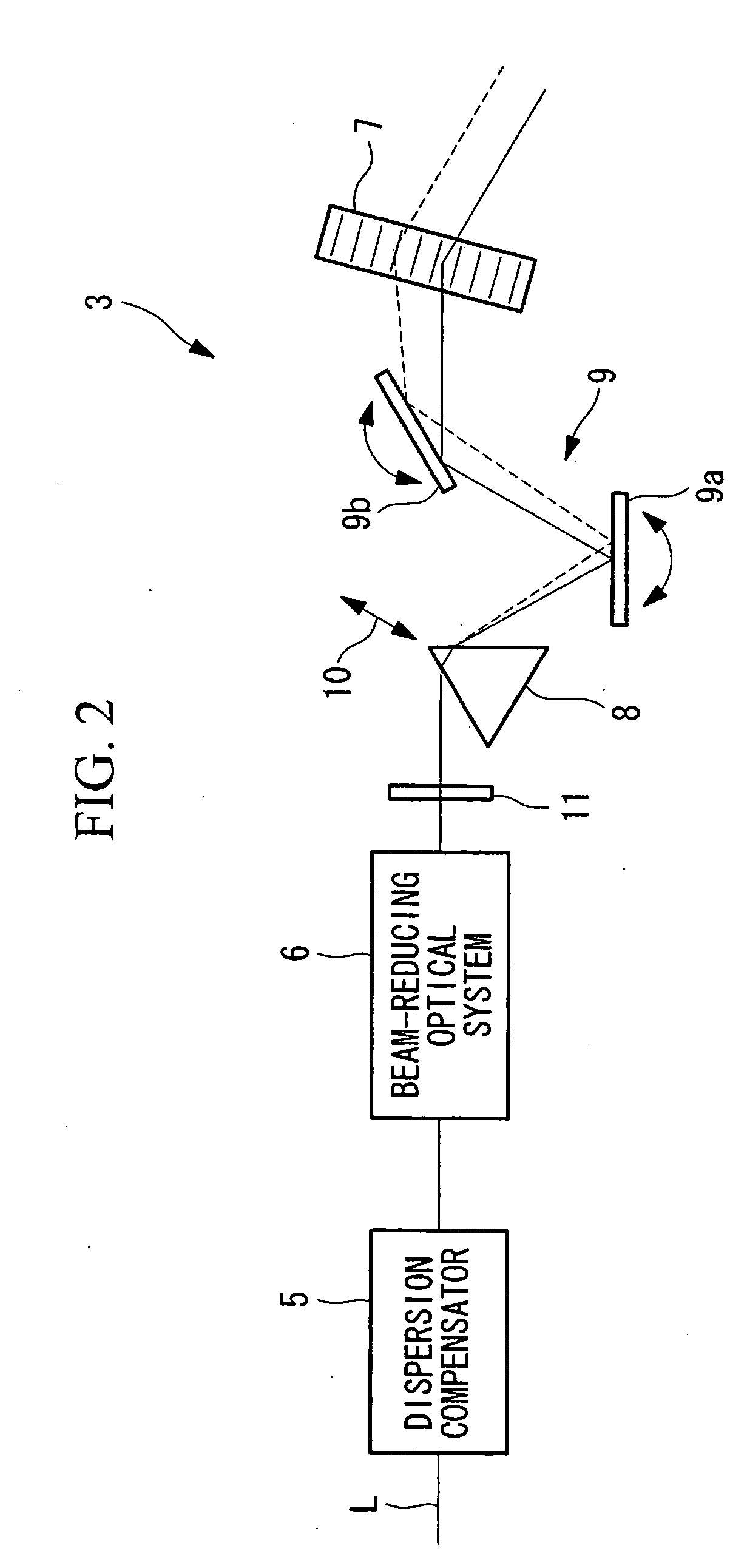
Laser microscope
InactiveUS20090290209A1Reduce variationSimple configurationMicroscopesNon-linear opticsAcousto optic deflectorLaser Microscopy
It is an object to perform high-precision observation by compensating group-velocity-delay dispersion and angular dispersion with a simple structure. The invention provides a laser microscope 1 including a light source; an acousto-optic deflector 7 that deflects ultrashort-pulse laser light L emitted from the light source; an angular-dispersion element 8, disposed in front of or after the acousto-optic deflector 7, that applies angular dispersion in a direction opposite to the acousto-optic deflector 7; and a group-velocity-delay dispersion-amount adjusting unit 10 that adjusts the amount of dispersion compensation by moving the angular-dispersion element 8 so as to vary the optical path length at each wavelength between the angular-dispersion element 7 and the acousto-optic deflector 8.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Acousto-optic filter
ActiveCN101706617AEliminate Dispersion ProblemsCompact structureNon-linear opticsAcousto-opticsMicrosecond
The invention discloses an acousto-optic filter. The acousto-optic filter comprises two lenses, two acousto-optic deflectors and a liquid crystal spatial light modulator. The focal distances of the two lenses are equal, and the two lenses are arranged in a confocal way; the two acousto-optic deflectors are completely the same and are respectively arranged at the front focal points and the back focal points of the two lenses; and the liquid crystal spatial light modulator is arranged at the common focal point of the lenses and provides an adjustable phase for carrying out color dispersion effect. The invention can realize microsecond stage quick switching between a plurality of wavelength lasers. Furthermore, the collinearity of emergent light beams and incident light beams can be kept, the adjustment of a light path is convenient, and the color dispersion effect of femtosecond lasers is completely eliminated. The invention has compact structure and easy adjustment and can be widely applied to a plurality of research fields of femtosecond laser biologic imaging, optical storage, micro-machining and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Image interference photoetching method using end acousto-optical deflector and its system
InactiveCN1752847AAchieving Exposure Dose RatioEasy to optimizePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusResistAcousto optic deflector
The present invention relates to an imaging interference photoetching method by adopting one acousto-optic deflector and its system. It is characterized by that said invention only uses one acousto-optic deflector to make laser beam sent out by laser produce deflection, and utilizes the control of exposure intensity and exposure dose and utilizes the change of ultrasonic frequency to real-time control deflection angle size so as to implement triple exposure required for imaging interference photoetching process and raise exposure efficiency and resist pattern quality.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-channel dual phase lock-in optical spectrometer
InactiveUS20070252988A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationHigh resolution imagingPhase sensitive
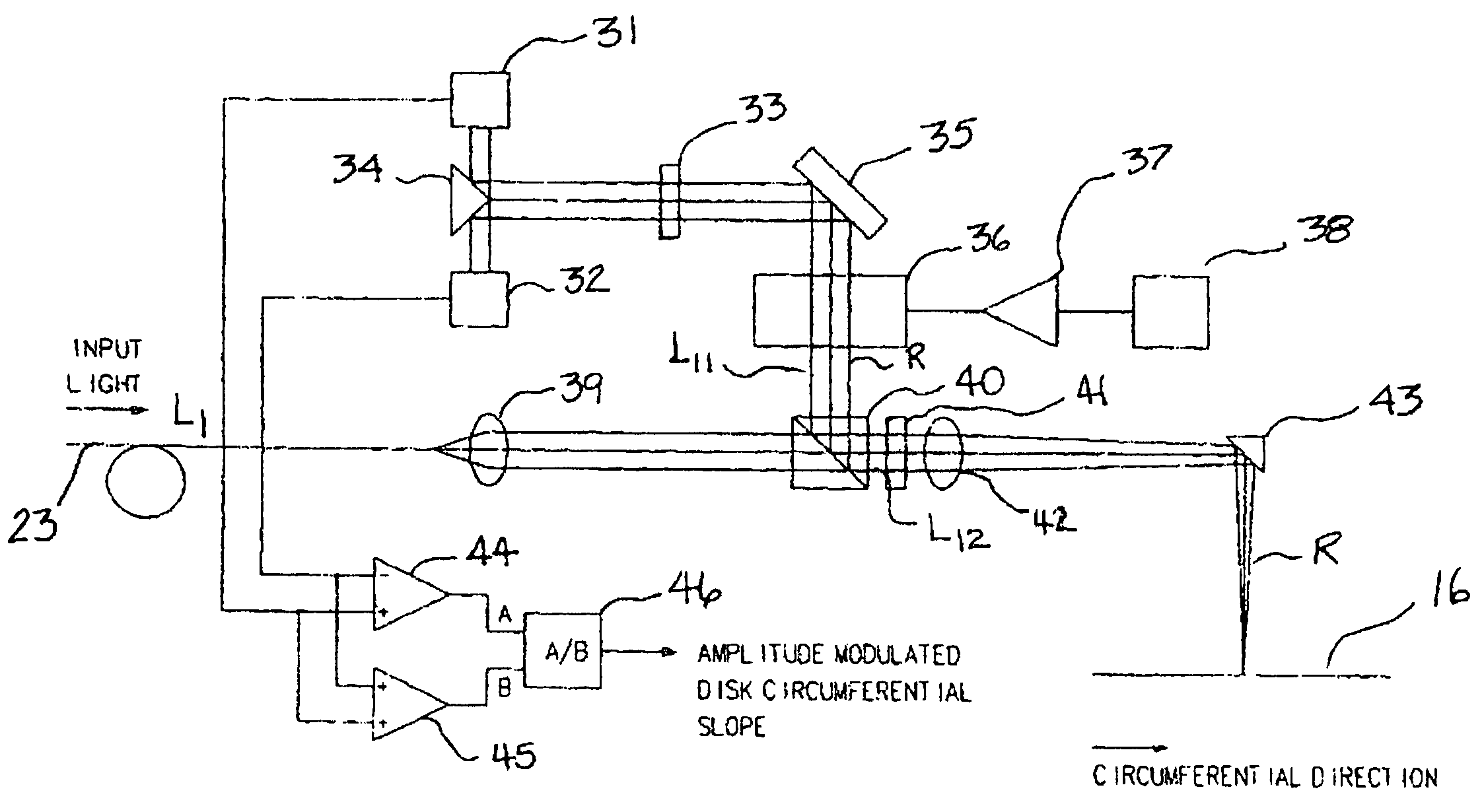
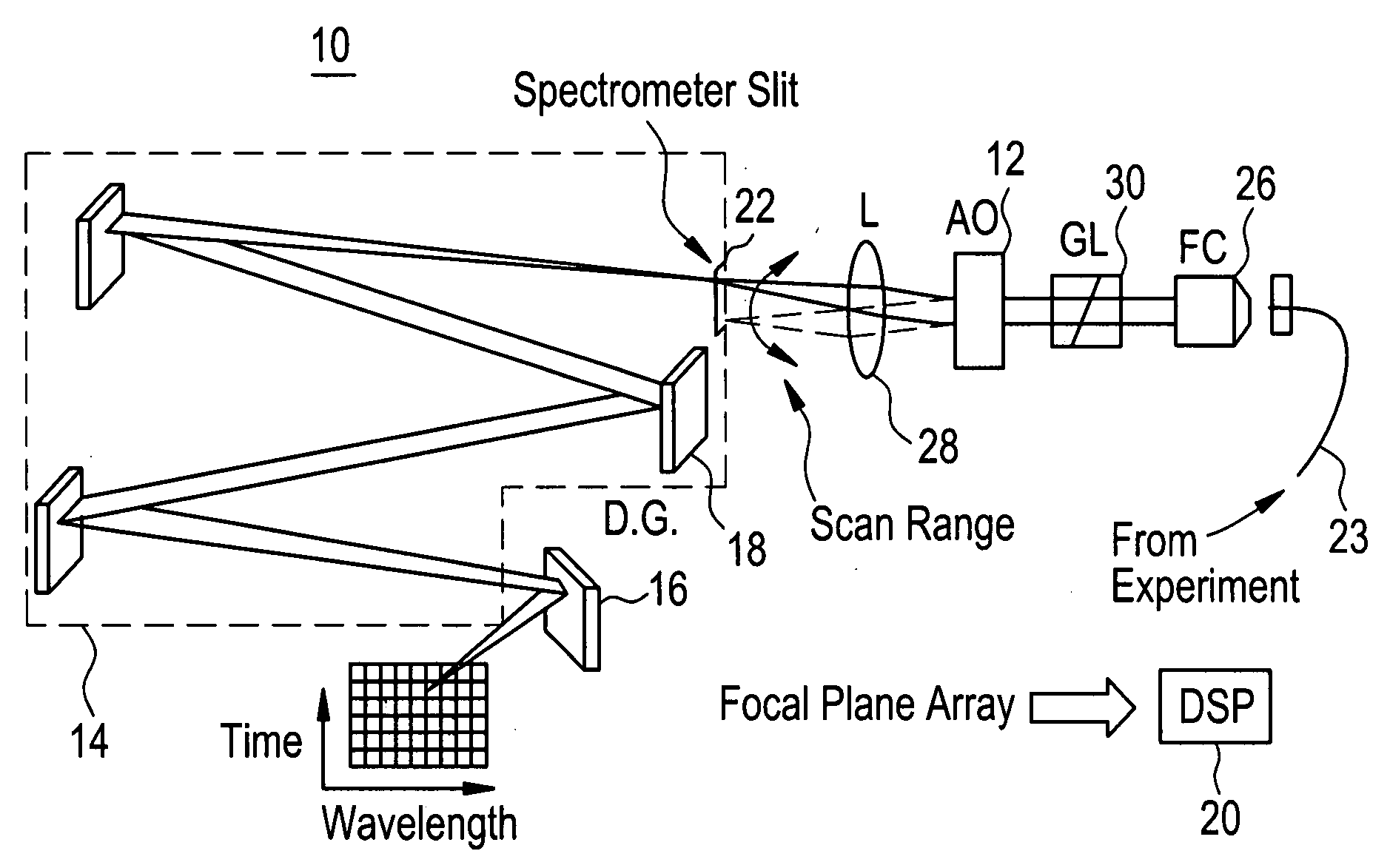
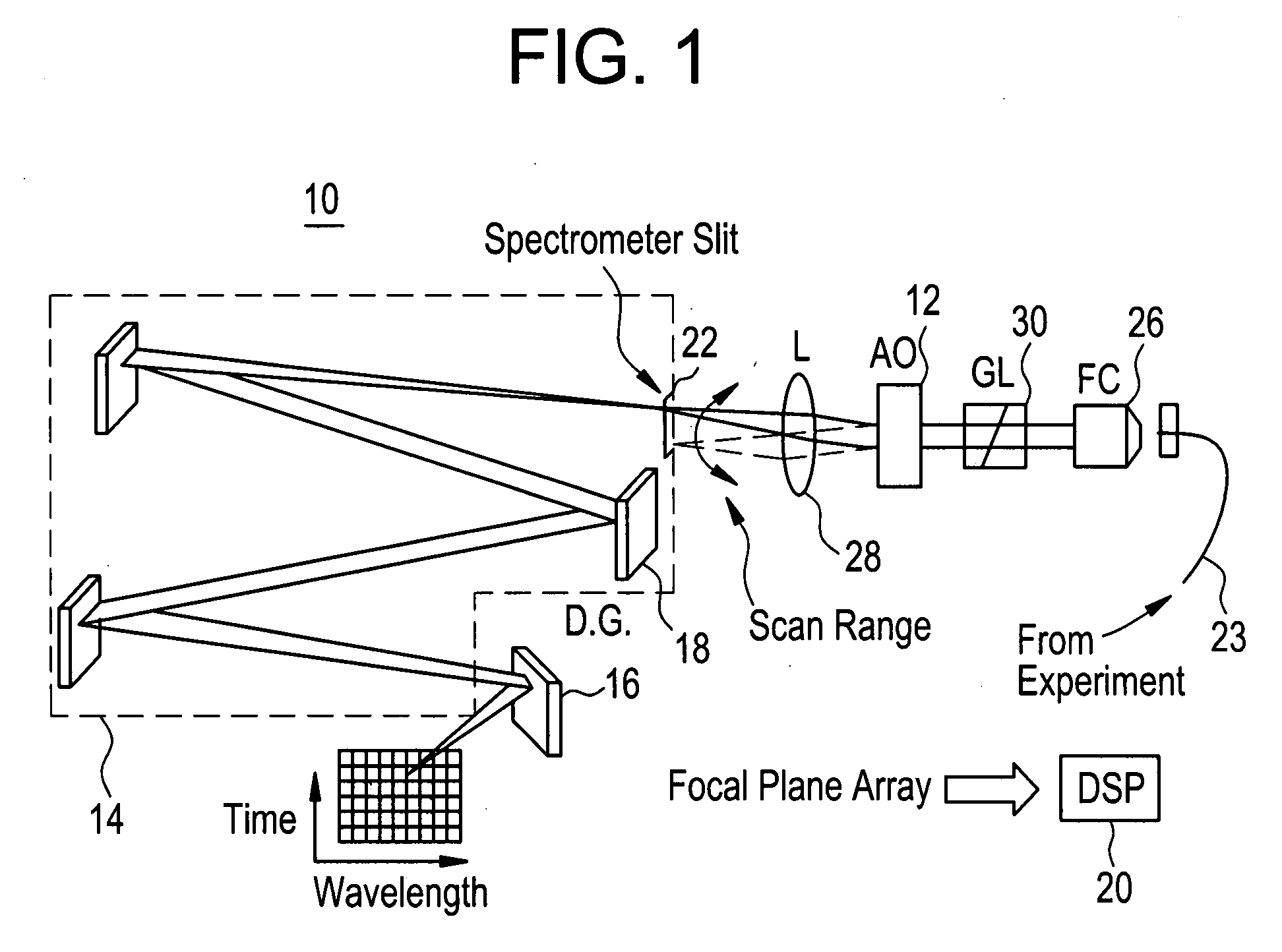
The development of a multiple-channel dual phase lock-in optical spectrometer (LIOS) is presented, which enables parallel phase-sensitive detection at the output of an optical spectrometer. The light intensity from a spectrally broad source is modulated at the reference frequency, and focused into a high-resolution imaging spectrometer. The height at which the light enters the spectrometer is controlled by an acousto-optic deflector, and the height information is preserved at the output focal plane. A two-dimensional InGaAs focal plane array collects light that has been dispersed in wavelength along the horizontal direction, and in time along the vertical direction. The data is demodulated using a high performance computer-based digital signal processor. This parallel approach greatly enhances (by more than 100×) the speed at which spectrally resolved lock-in data can be acquired.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
Laser scanner
InactiveCN103048811AFast scanningHigh precisionNon-linear opticsOptical elementsAcousto optic deflectorRadar
The invention discloses a laser scanner which comprises an acousto-optic deflection device and a mechanical galvanometer system. Light beams sent out by the laser diffract through the acousto-optic deflection device, and diffraction light beams can achieve rapid and accurate regulation by controlling input electrical signals; and then the diffraction light beams are reflected through the galvanometer system, and large-breadth scanning is achieved through wide-angle twisting of the galvanometer system. Therefore, the laser scanner can achieve high-speed high-precision and large-breadth optical scanning, and can be widely applied to aspects such as laser precision marking, laser rapid molding and laser radars.
Owner:LAIZE PHOTONICS CO LTD
Micro-imaging system with combined optical tweezers function and expanded focal depth
The invention discloses a micro-imaging system with a combined optical tweezers function and expanded focal depth. The micro-imaging system comprises a first laser, a first reflector, a first spectroscope, a first lens, a second lens, a first acousto-optic deflector, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens, a second acousto-optic deflector, a sixth lens, a second spectroscope, a first dichroic mirror, a second dichroic mirror, a first object lens, a sample table, a second object lens, a third dichroic mirror, a third spectroscope, a fourth spectroscope, a fifth spectroscope, a first four-quadrant position detector, a second four-quadrant position detector, a position detector, an LED light source, a first detector, a second laser, a first cylindrical lens, a cylindrical lens group, a fourth dichroic mirror, a scanning galvanometer, a first telescope system, an electric control lens, a second telescope system, a second reflector, a third telescope system, a slit, a third reflector, asecond cylindrical lens, and a second detector. The system utilizes an electric control lens to scan planes with different focal depths and has the advantages of no mechanical vibration and high imaging quality.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Anti-counterfeiting laser boring method and device of cigarette tipping paper
InactiveCN101870038AAesthetically pleasingAnti-counterfeitingLaser beam welding apparatusAcousto optic deflectorControl signal
The invention discloses an anti-counterfeiting laser boring method of cigarette tipping paper, which comprises the following steps: leading a pulse laser beam outputted by a pulse laser to sequentially pass through a two-dimensional acousto-optic deflection system and an F-theta lens for transmission and focusing, and forming a pulsed focal spot on the surface of the tipping paper in continuous motion; and simultaneously leading a control system to emit a control signal for respectively carrying out centralized control on light-emitting time sequence and pulse interval time of the pulse laser and light beam deflection angles of an X-axis acousto-optic deflector and a Y-axis acousto-optic deflector in the acousto-optic deflection system at different time according to the motion velocity of the tipping paper and information of a pattern, characters or a curve which is inputted into a boring pattern and character data storage module in advance, and boring small holes which are arranged and distributed like the required pattern, the characters or the curve on the surface of the tipping paper by being matched with the continuous motion of the tipping paper. The invention simultaneously provides a device capable of realizing the method, and the device has simple structure, stable working and high processing efficiency.
Owner:苏州市博海激光科技有限公司
Laser roller film engraving machine
InactiveCN101746152AIncrease the diameterIncrease the light receiving anglePrintingNon-linear opticsAcousto optic deflectorLaser processing
The invention relates to the field of roller laser processing system, more particularly to a laser roller film engraving machine. Being a relatively advanced plate making way at present, roller film engraving technology is mainly characterized in processing in that: according to the trace of plate pattern, laser is applied to a protective layer which is pre-coated over the surface of a roller, the part of the surface of the roller, which is exposed due to the falloff of the protective layer, is the plate pattern to be processed, and the roller is then subject to corrosion treatment to finally form the plate pattern. As a special machine aiming at the above processing way, the laser roller film engraving machine comprises: a graphic and image processing system, a control system, a mechanical system, a laser and an optical system, wherein the optical system comprises an acoustic optic deflector to achieve the light-splitting and time-sharing control for laser, so that the processed plate pattern is more exquisite, and a double-layer optical fiber laser generator is adopted to realize high stability of laser power and excellent quality of light beam.
Owner:东莞东运机械制造有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com