Patents
Literature
152 results about "Laser Microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM or LSCM) is a valuable tool for obtaining high resolution images and 3-D reconstructions. The key feature of confocal microscopy is its ability to produce blur-free images of thick specimens at various depths.
Multi-photon laser microscopy
InactiveUS6344653B1Less photodamageExpand the scope of useLaser detailsPhotometryConfocal laser scanning microscopeLaser scanning microscope
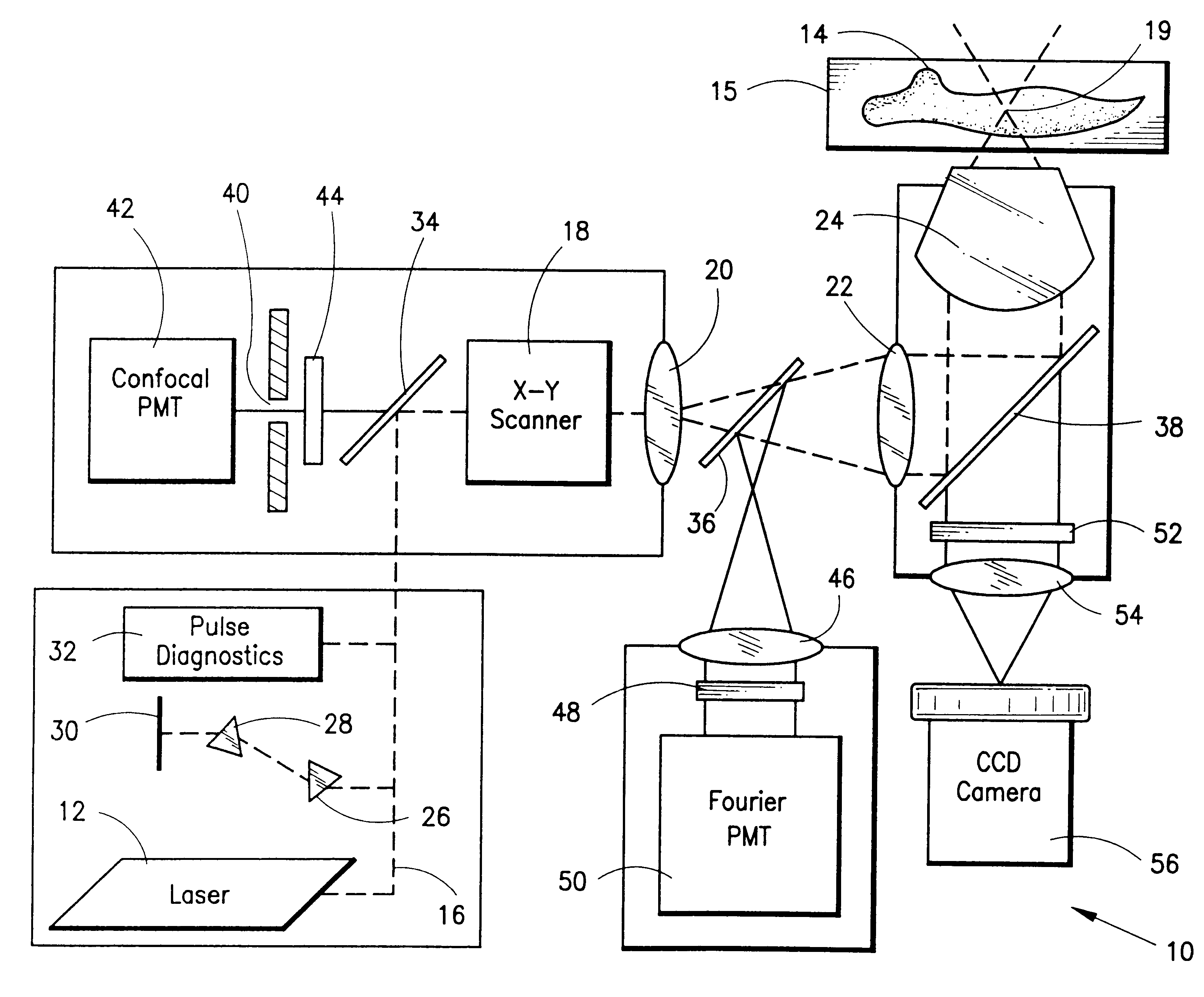
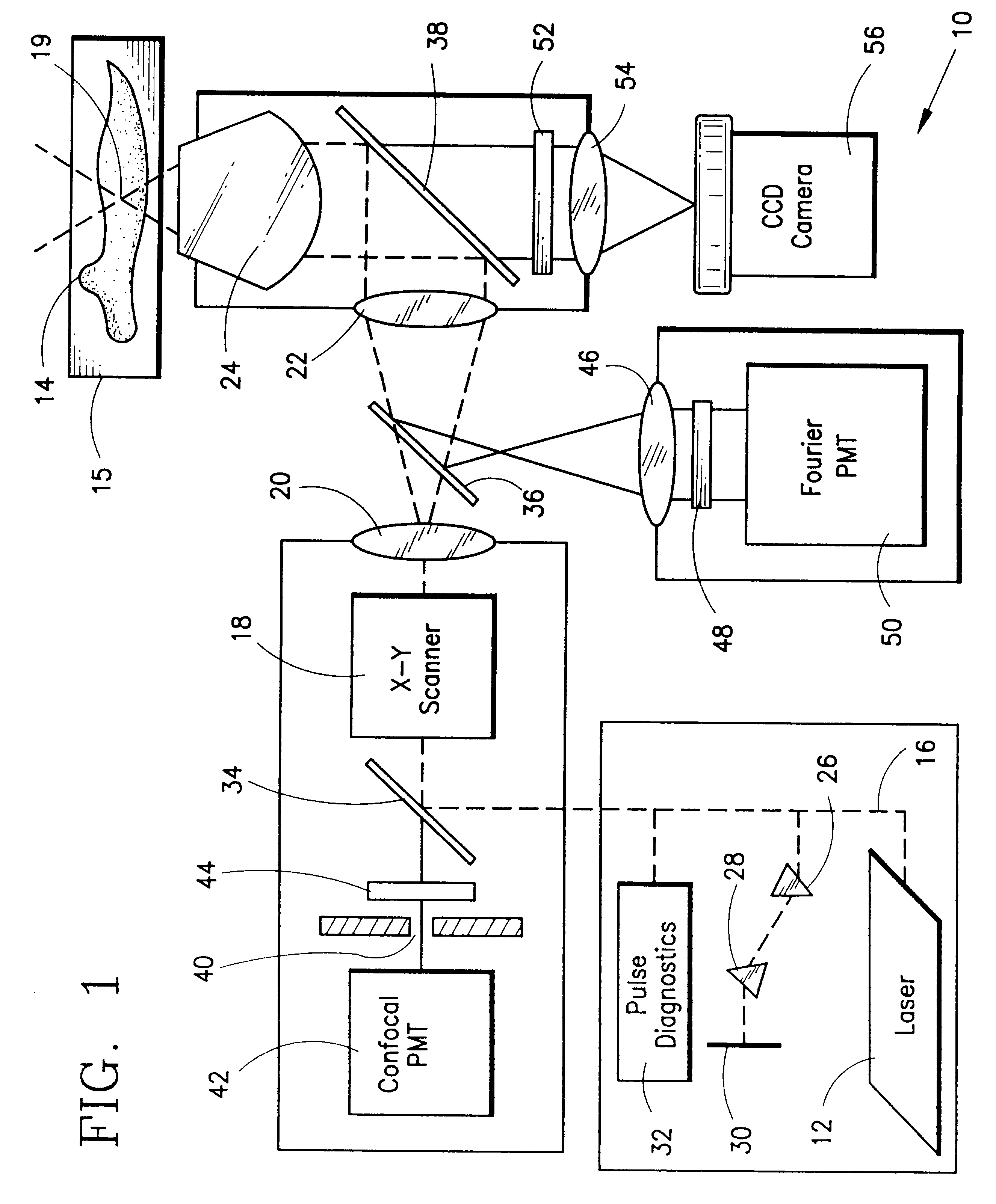
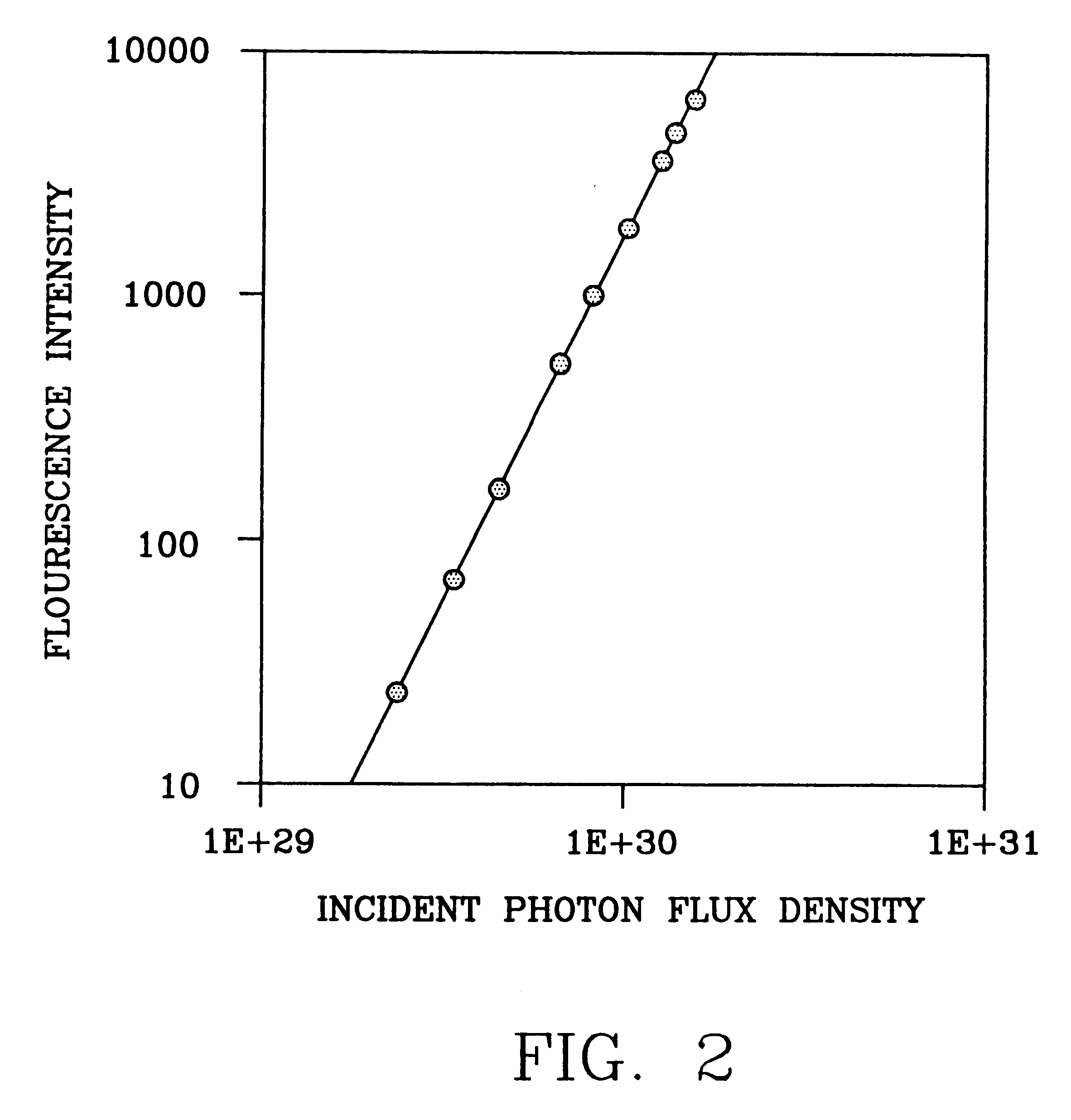
A laser scanning microscope produces molecular excitation in a target material by simultaneous absorption of three or more photons to thereby provide intrinsic three-dimensional resolution. Fluorophores having single photon absorption in the short (ultraviolet or visible) wavelength range are excited by a beam of strongly focused subpicosecond pulses of laser light of relatively long (red or infrared) wavelength range. The fluorophores absorb at about one third, one fourth or even smaller fraction of the laser wavelength to produce fluorescent images of living cells and other microscopic objects. The fluorescent emission from the fluorophores increases cubicly, quarticly or even higher power law with the excitation intensity so that by focusing the laser light, fluorescence as well as photobleaching are confined to the vicinity of the focal plane. This feature provides depth of field resolution comparable to that produced by confocal laser scanning microscopes, and in addition reduces photobleaching and phototoxicity. Scanning of the laser beam by a laser scanning microscope, allows construction of images by collecting multi-photon excited fluorescence from each point in the scanned object while still satisfying the requirement for very high excitation intensity obtained by focusing the laser beam and by pulse time compressing the beam. The focused pulses also provide three-dimensional spatially resolved photochemistry which is particularly useful in photolytic release of caged effector molecules, marking a recording medium or in laser ablation or microsurgery. This invention refers explicitly to extensions of two-photon excitation where more than two photons are absorbed per excitation in this nonlinear microscopy.
Owner:WEBB WATT W +1
Agile-beam laser array transmitter
ActiveUS8301027B2Turn fasterWave based measurement systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLaser arrayBeam steering
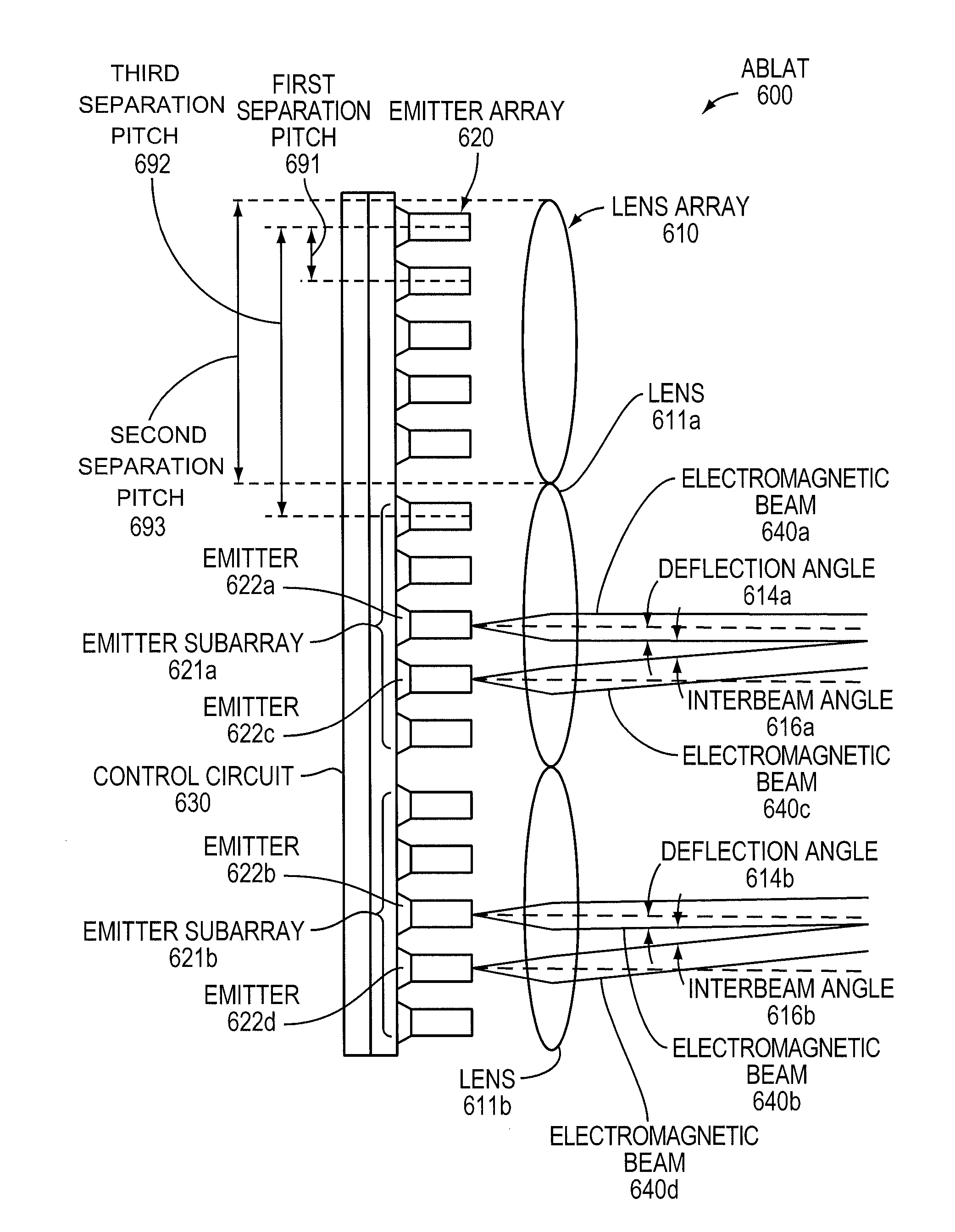
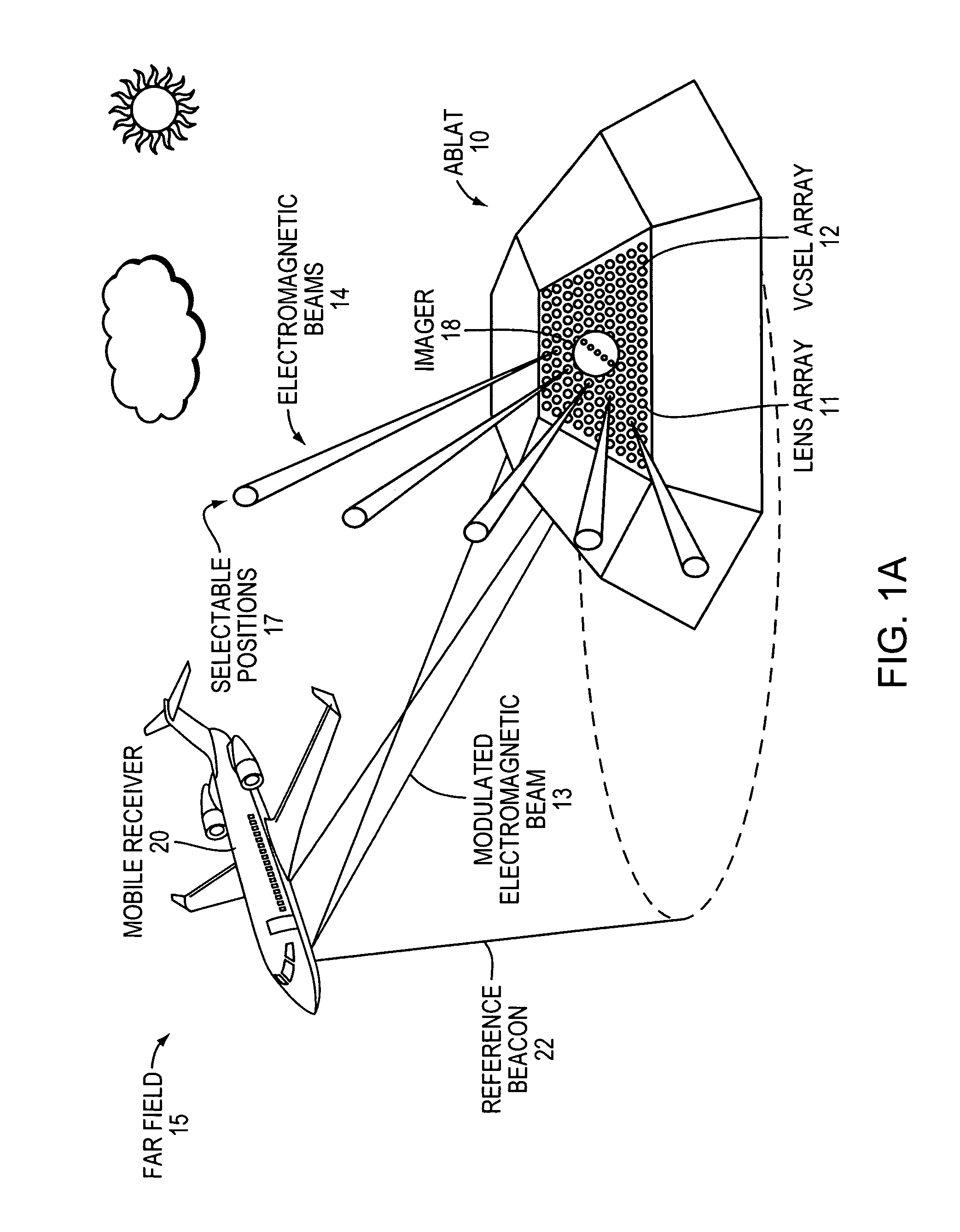
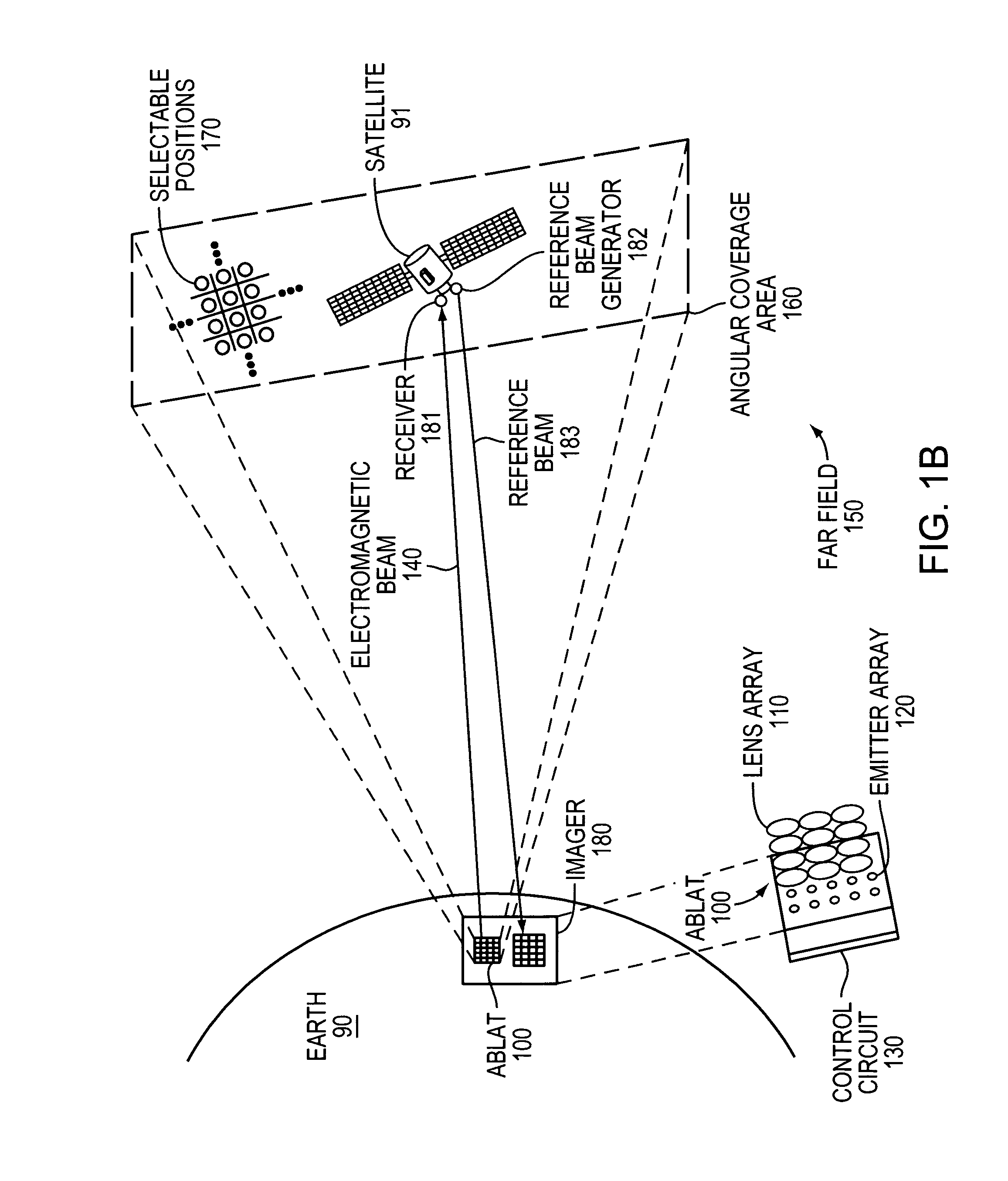
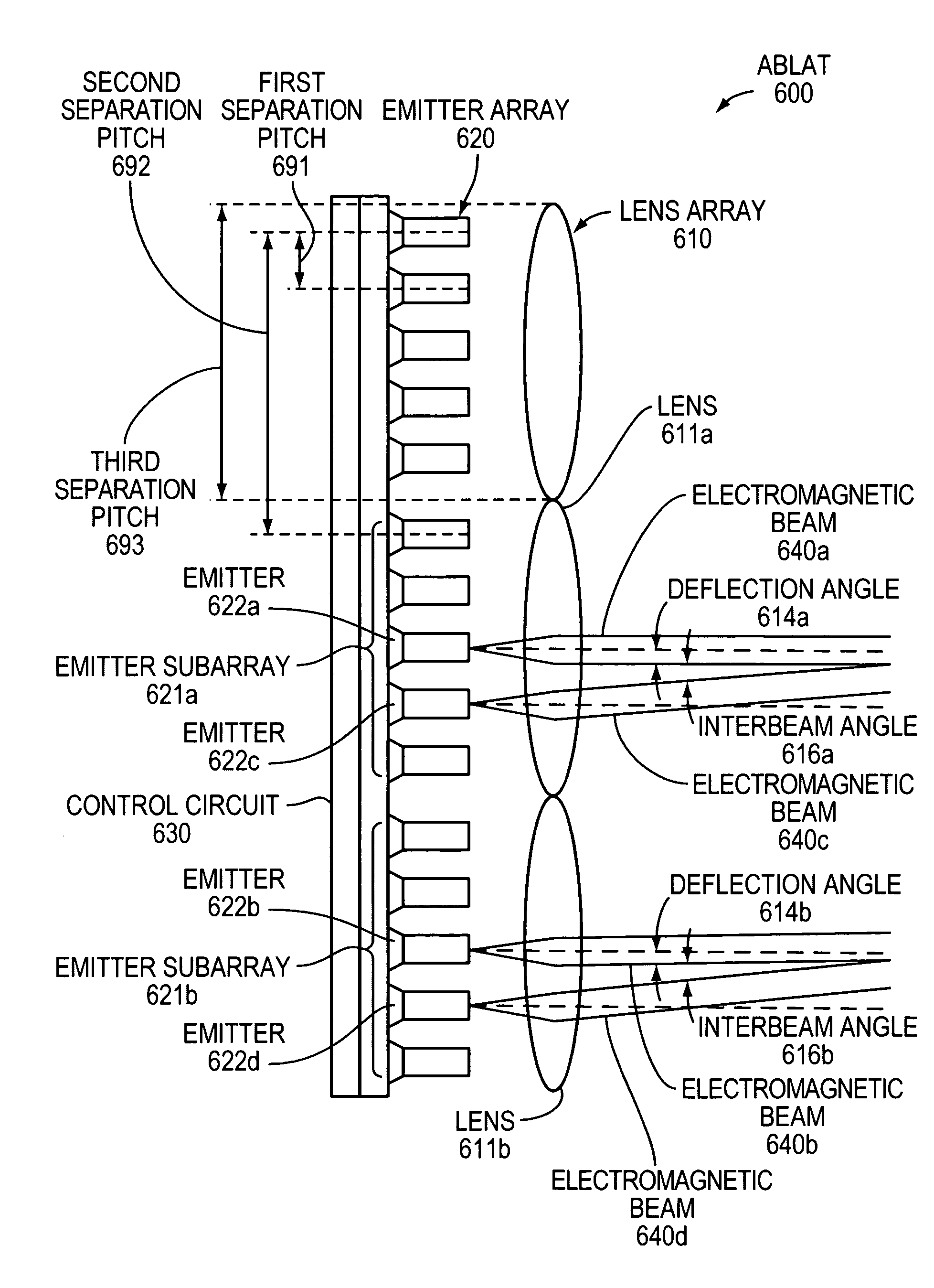
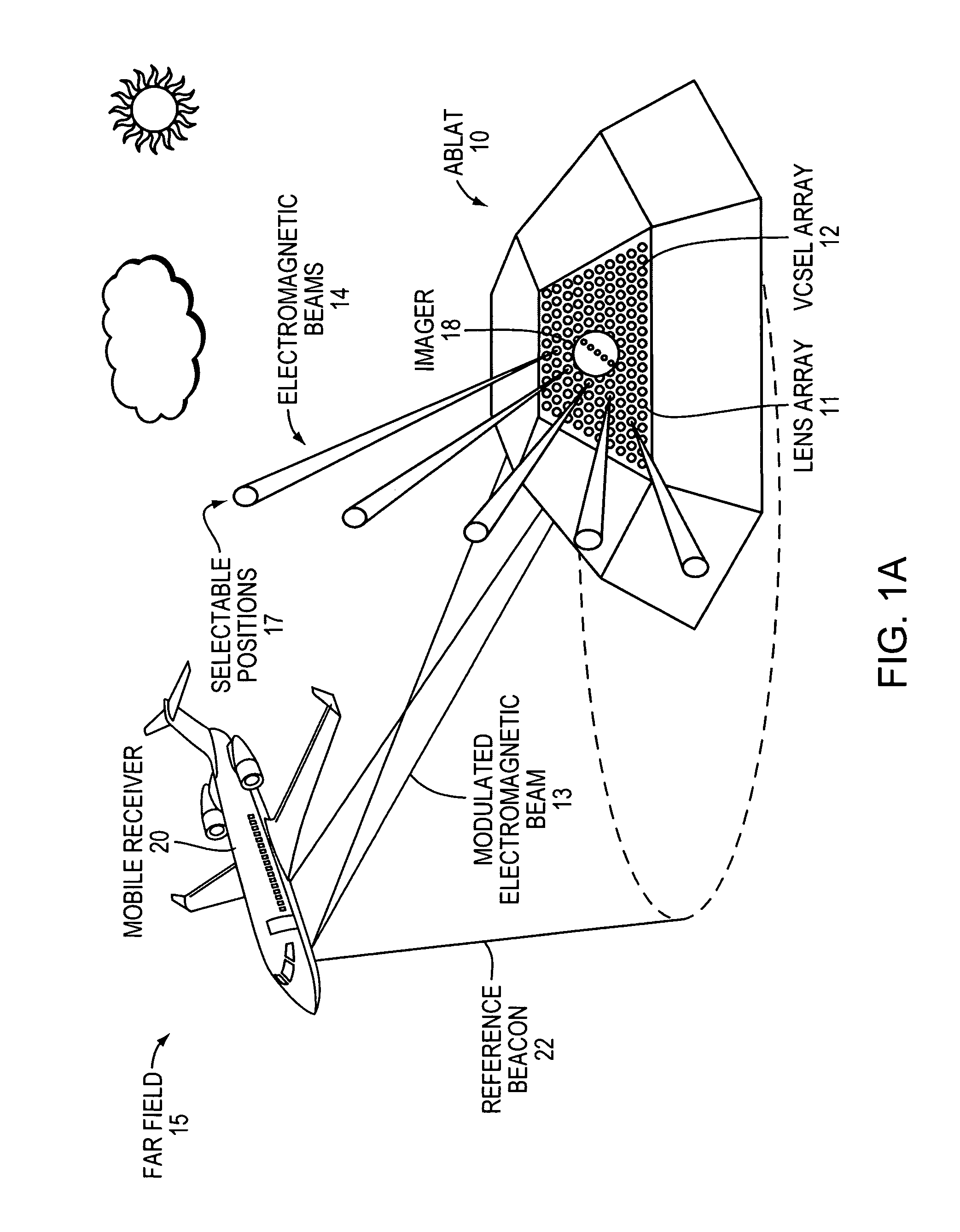
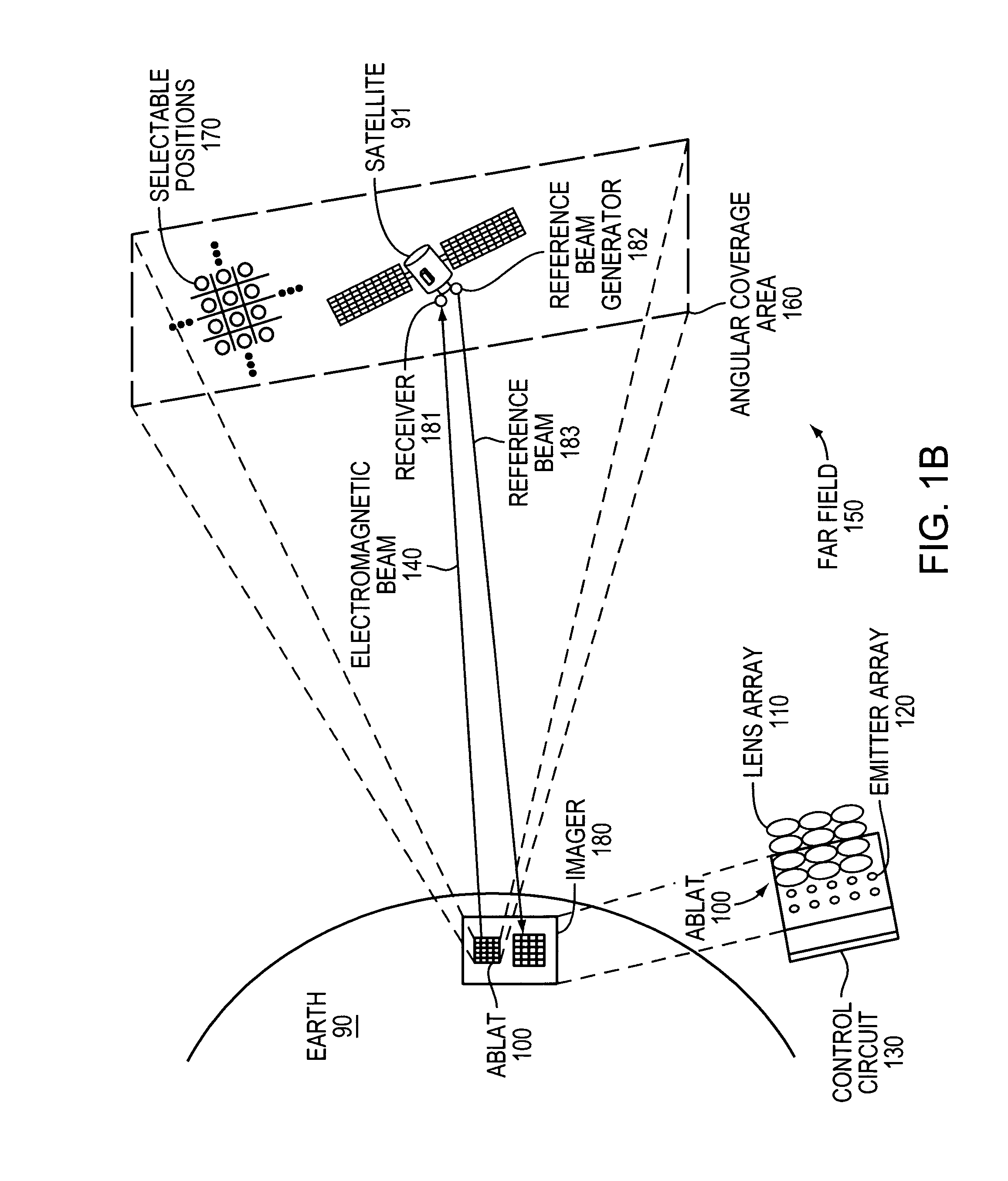
An Agile-Beam Laser Array Transmitter (ABLAT) uses an array of emitters and an array of lenses to project electromagnetic beams over a wide angular coverage area in the far field. Differences in the separation pitches of the two arrays allows the ABLAT to project beams to contiguous and / or overlapping positions, depending on the ratio of the separation pitches and the lens focal length. Compared to other beam steering technology, the ABLAT is a smaller, lighter, and more efficient means of projecting beams over wider angular coverage areas. Various embodiments can be used in any beam steering application, including, but not limited to: free-space optical communications; light detection and ranging (lidar); optical scanning (e.g., retinal or bar-code scanning); display projection; image capture; optical character recognition; scanning laser microscopy; non-destructive testing; printing; facsimiles; map making; web inspection; color print processing; phototypesetting and platemaking; laser marking; material processing; DNA analysis; and drug discovery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Agile-beam laser array transmitter
ActiveUS20100046953A1Turn fasterWide field of viewWave based measurement systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLaser arrayColor printing
An Agile-Beam Laser Array Transmitter (ABLAT) uses an array of emitters and an array of lenses to project electromagnetic beams over a wide angular coverage area in the far field. Differences in the separation pitches of the two arrays allows the ABLAT to project beams to contiguous and / or overlapping positions, depending on the ratio of the separation pitches and the lens focal length. Compared to other beam steering technology, the ABLAT is a smaller, lighter, and more efficient means of projecting beams over wider angular coverage areas. Various embodiments can be used in any beam steering application, including, but not limited to: free-space optical communications; light detection and ranging (lidar); optical scanning (e.g., retinal or bar-code scanning); display projection; image capture; optical character recognition; scanning laser microscopy; non-destructive testing; printing; facsimiles; map making; web inspection; color print processing; phototypesetting and platemaking; laser marking; material processing; DNA analysis; and drug discovery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
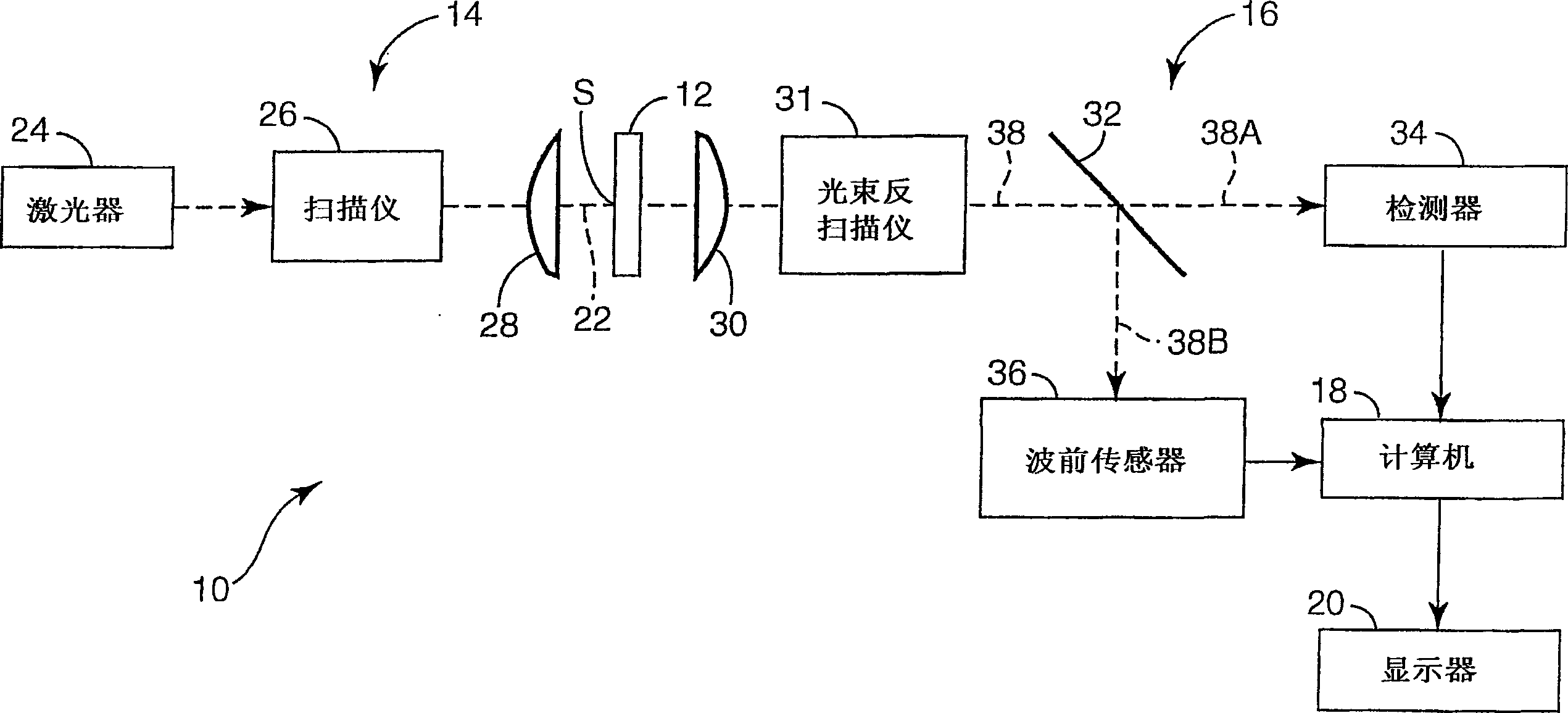
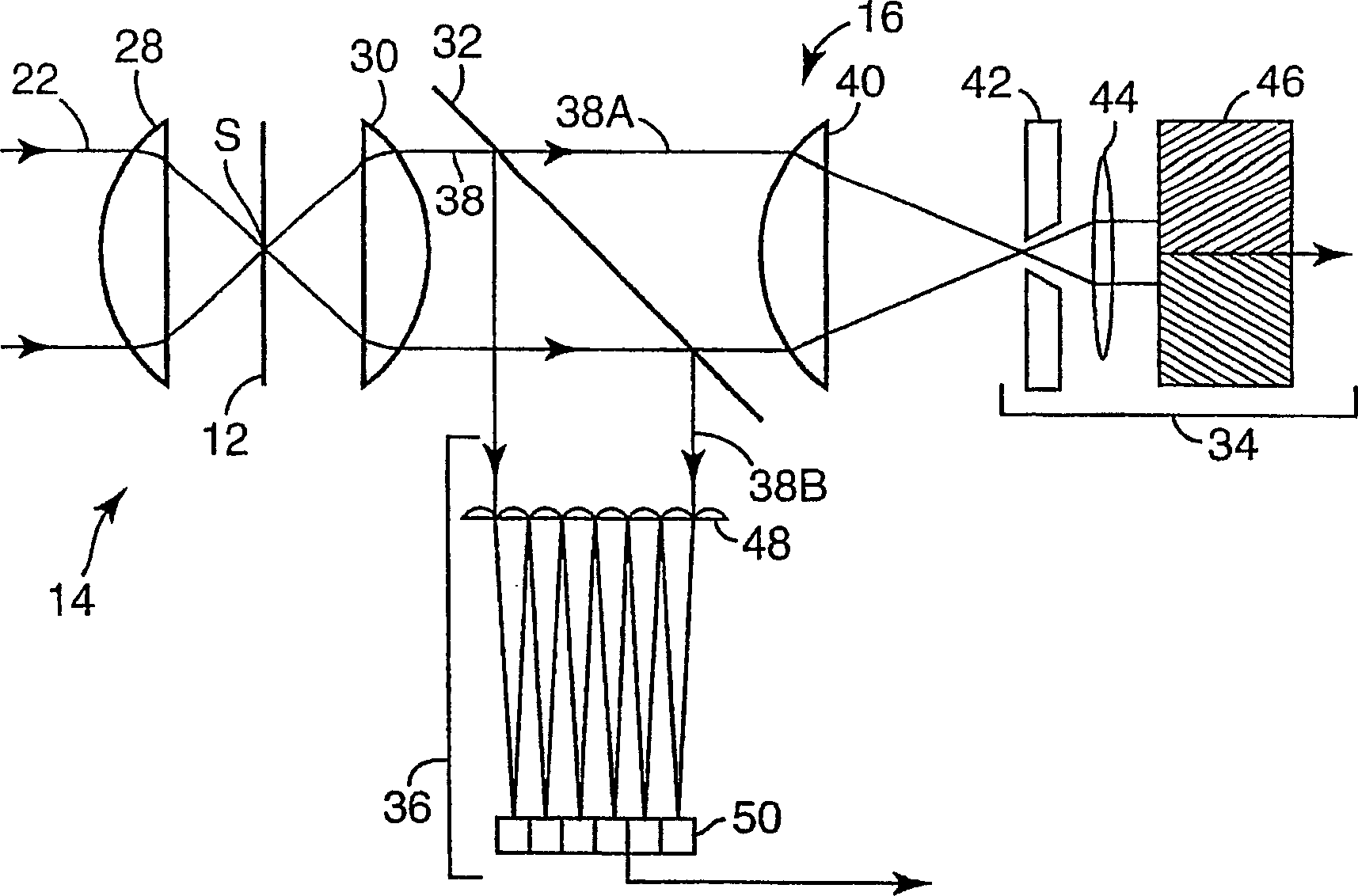
Scanning laser microscope with wavefront sensor
InactiveUS7057806B2High resolutionEnhanced resolution imagePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansFrequency spectrumWavefront sensor
An enhanced resolution scanned image of an object is produced by a scanning laser microscope which includes an illumination arm for scanning an object with a focused probe beam and a detection arm for receiving light from the object. The detection arm includes a detector which collects and detects light from the object to produce pixel data for a plurality of pixels. In addition, the detection arm includes a wavefront sensor for sensing phase variations of the light from the object to produce wavefront data for scanned pixel locations. From the wavefront shape of the collected light at each pixel location, a high frequency spectrum is determined which corresponds to uncollected scattered light from small scale features of that pixel location. An enhanced resolution image of a region of interest is produced based on the high frequency spectra of the scanned pixel locations.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Hybrid medical image processing
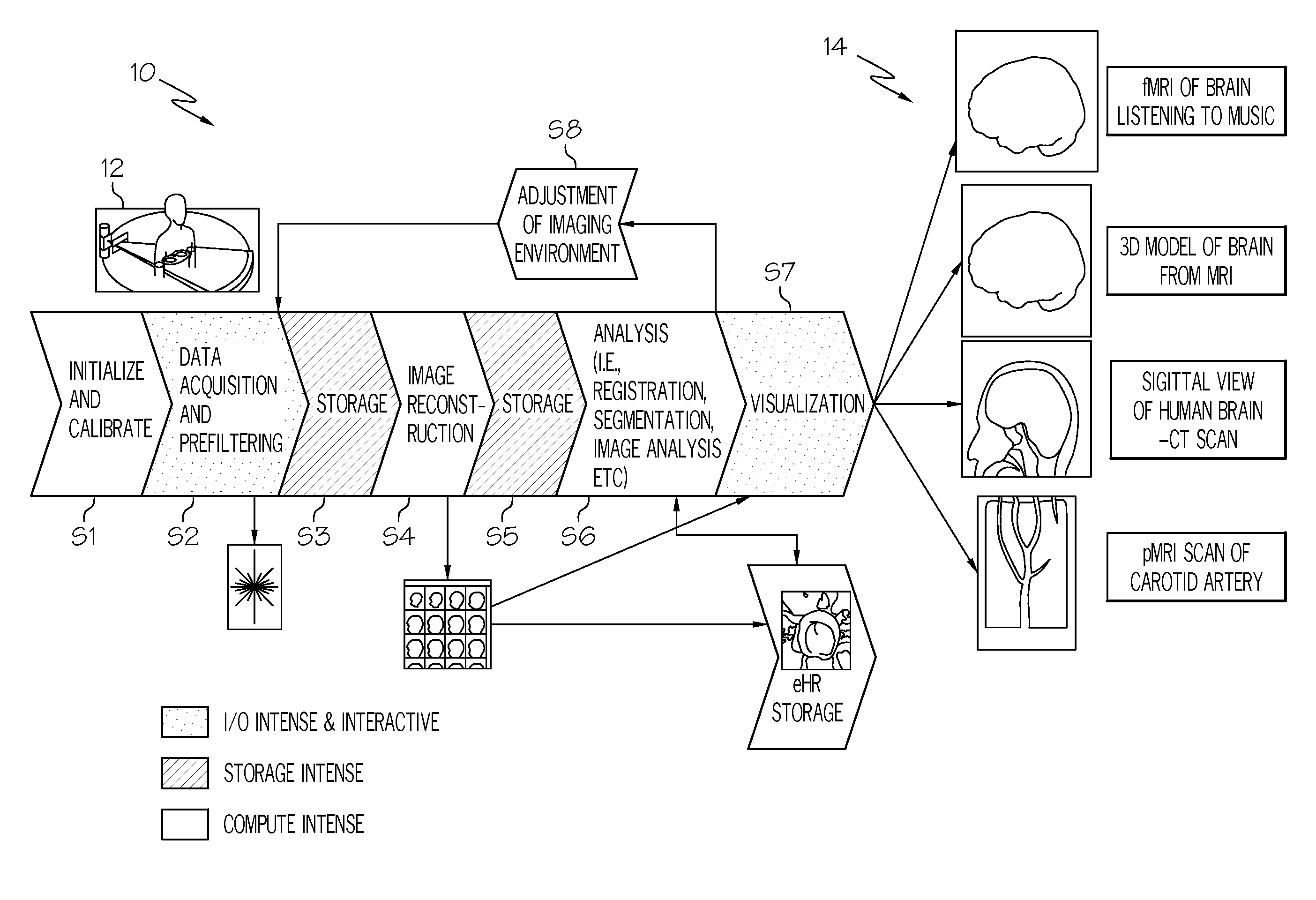
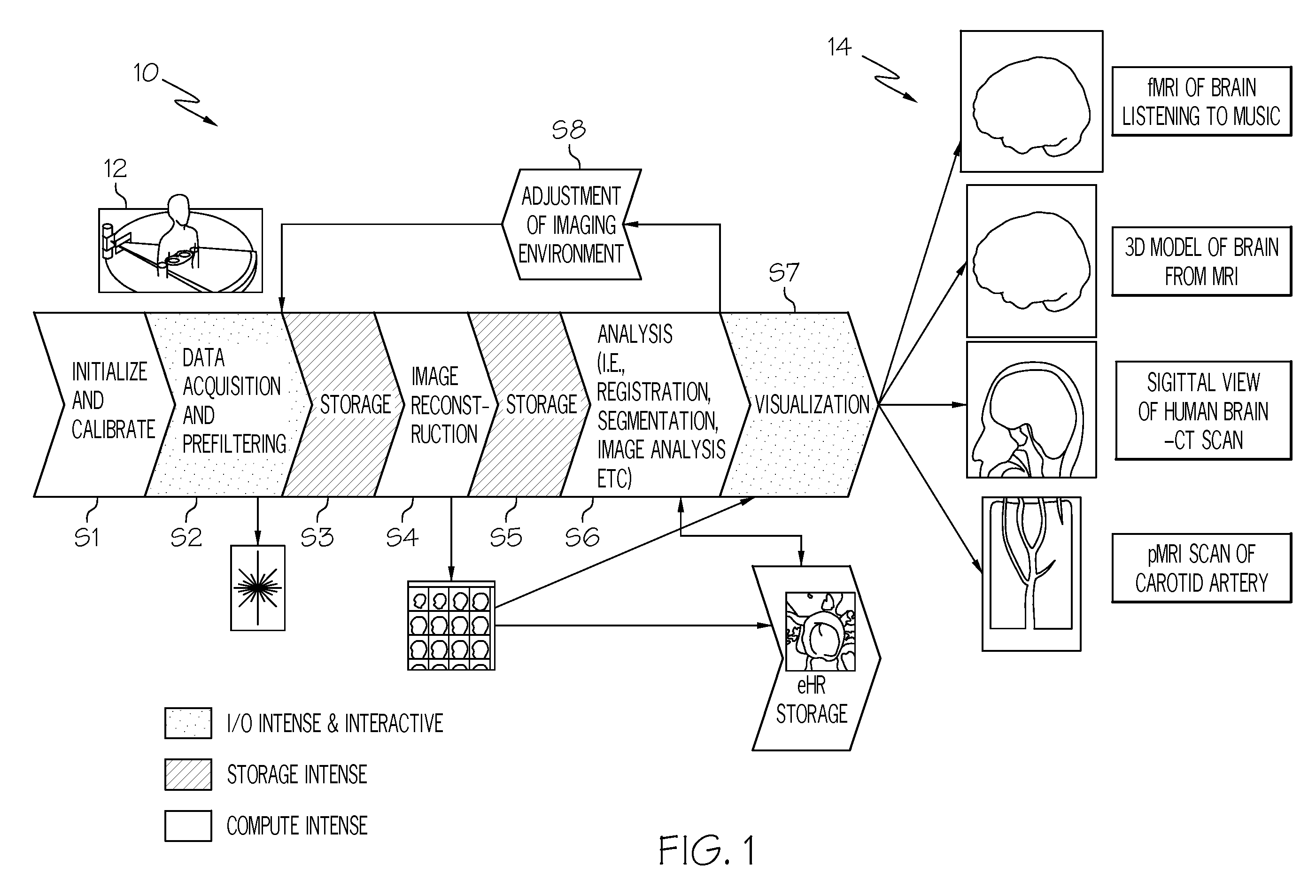
The present invention uses a common, hybrid system platform to provide a generalized medical image processing system that can handle the existing medical image application as it is and route the compute intensive medical image processing to a multi-core processor / processing system. The invention allows the processing platform to be shared among healthcare system such as mammography, X-ray, CT Scan MRI, two-photon, laser microscopy, digital pathology, etc. It also allows the processing platform to deliver medical images to a variety of client devices, such as a desktop computer or a handheld device, through the network without high-performance graphical display capabilities because the rendering of the medical images is performed on the Cell BE based platform of the invention.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
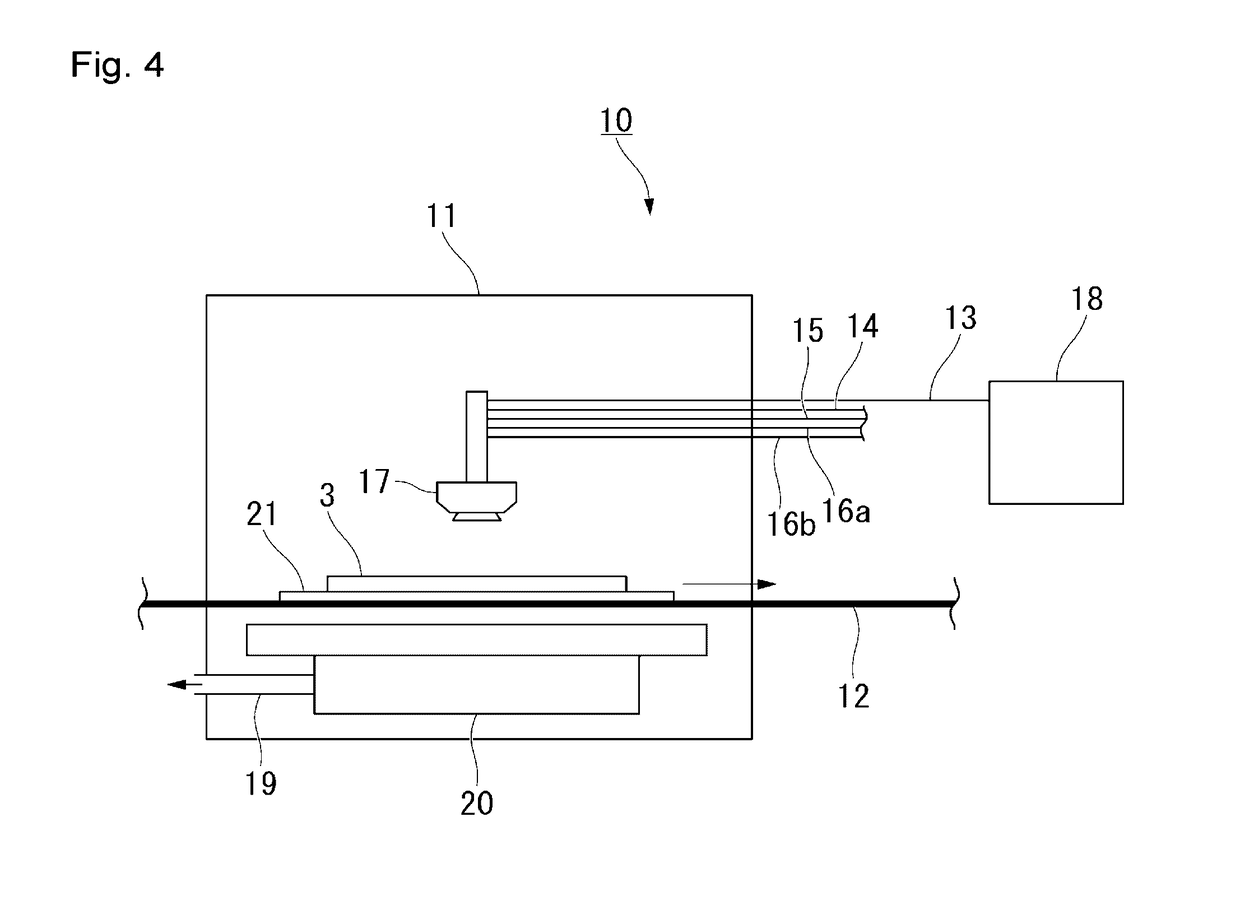
Laser microscope
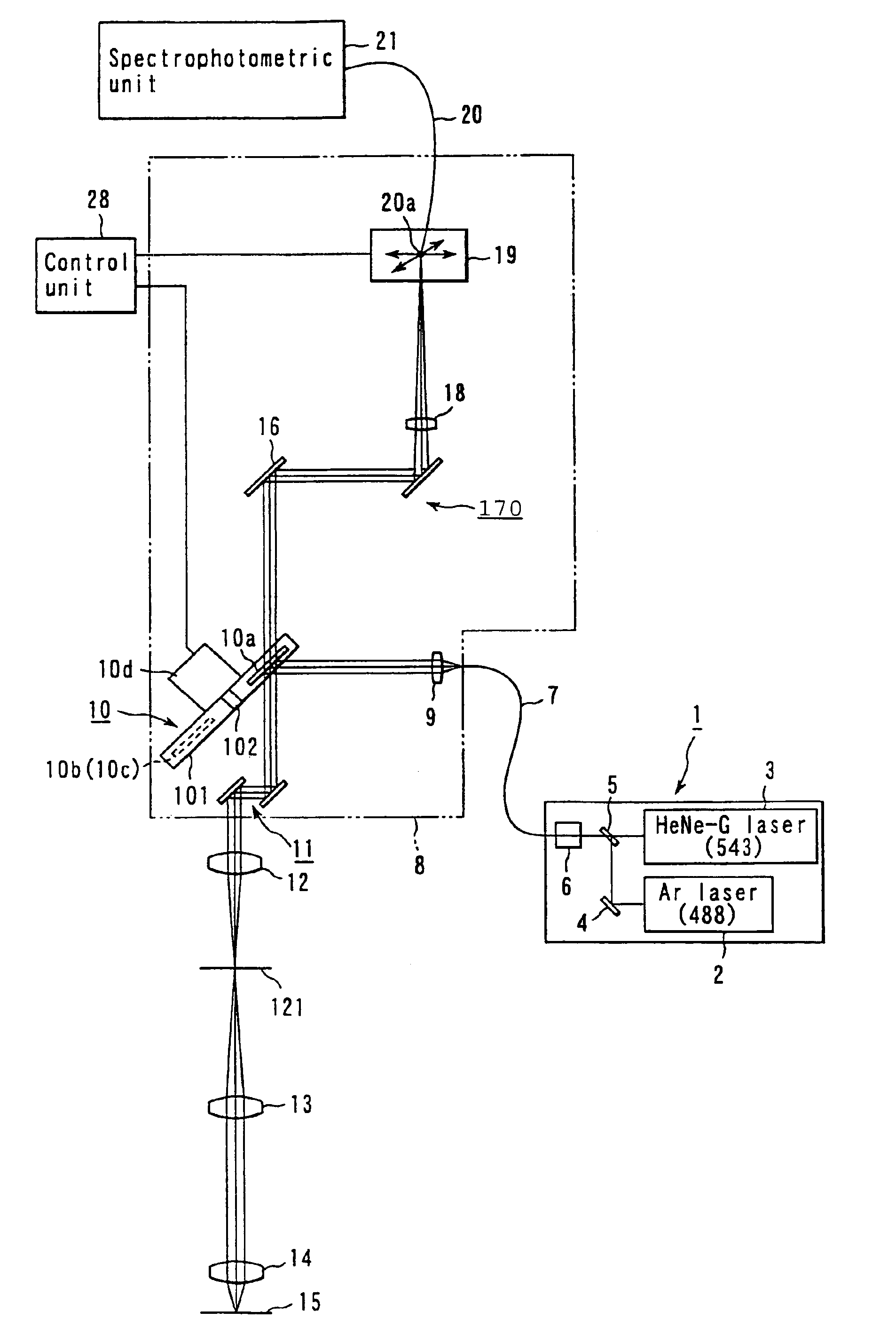
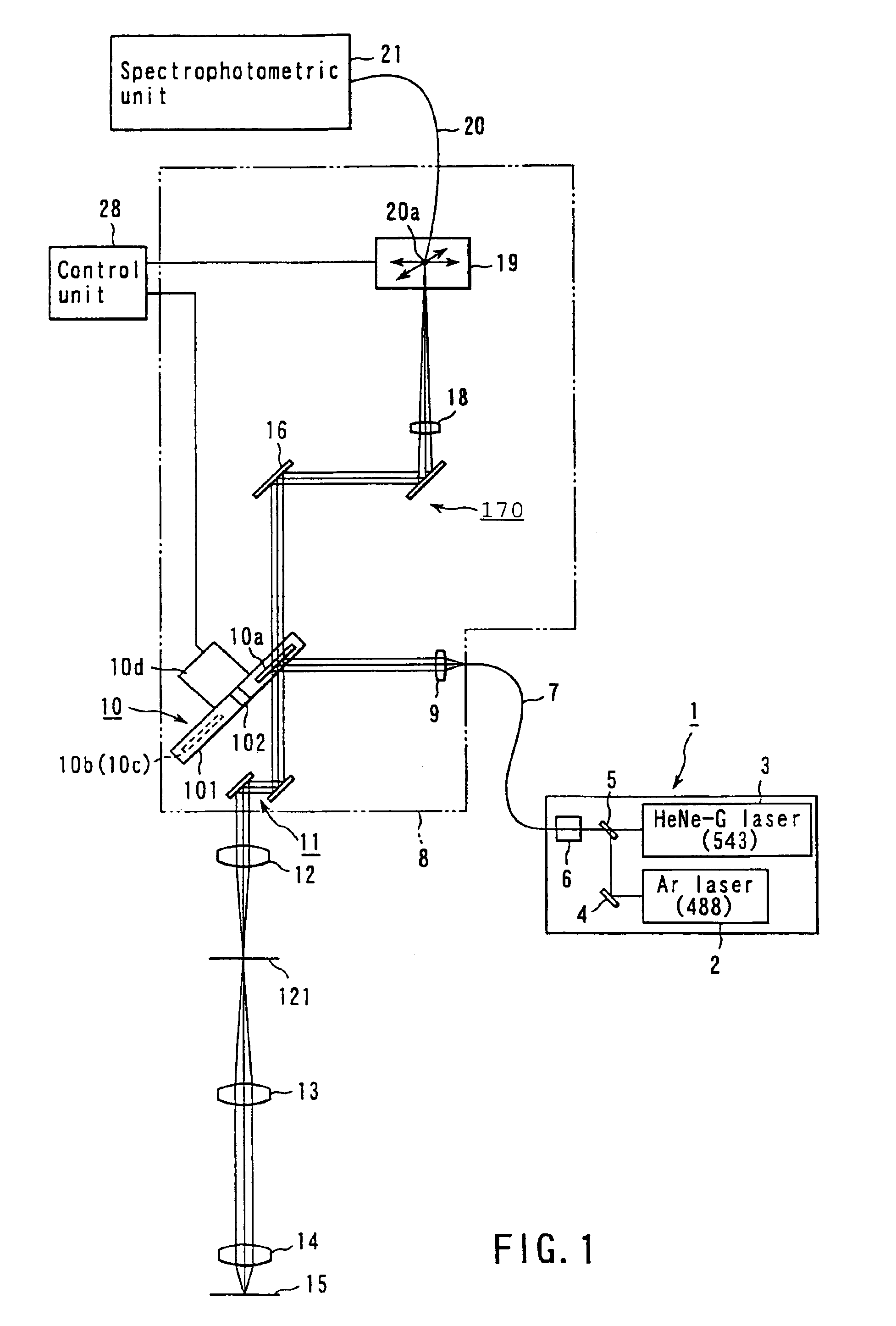
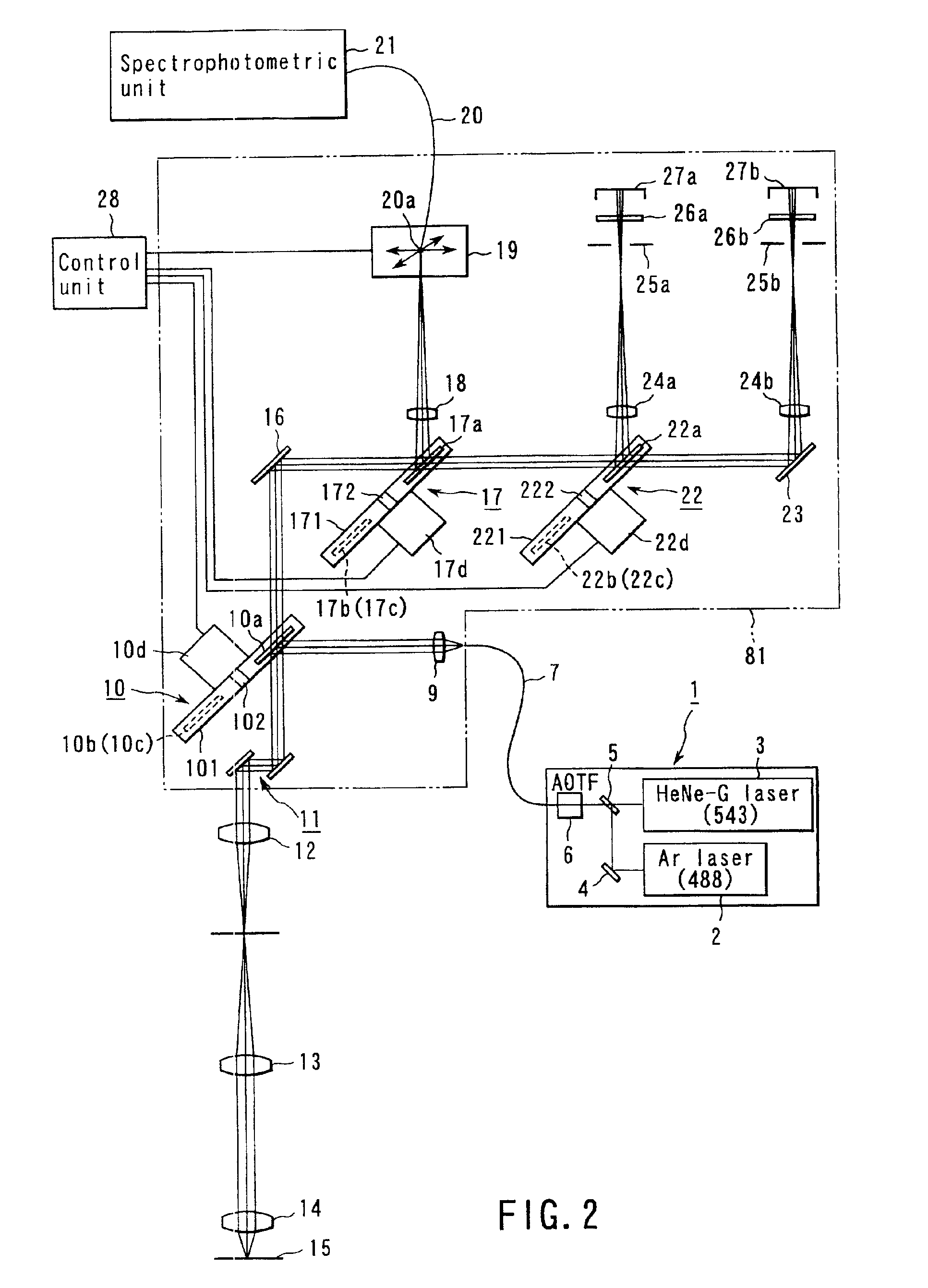
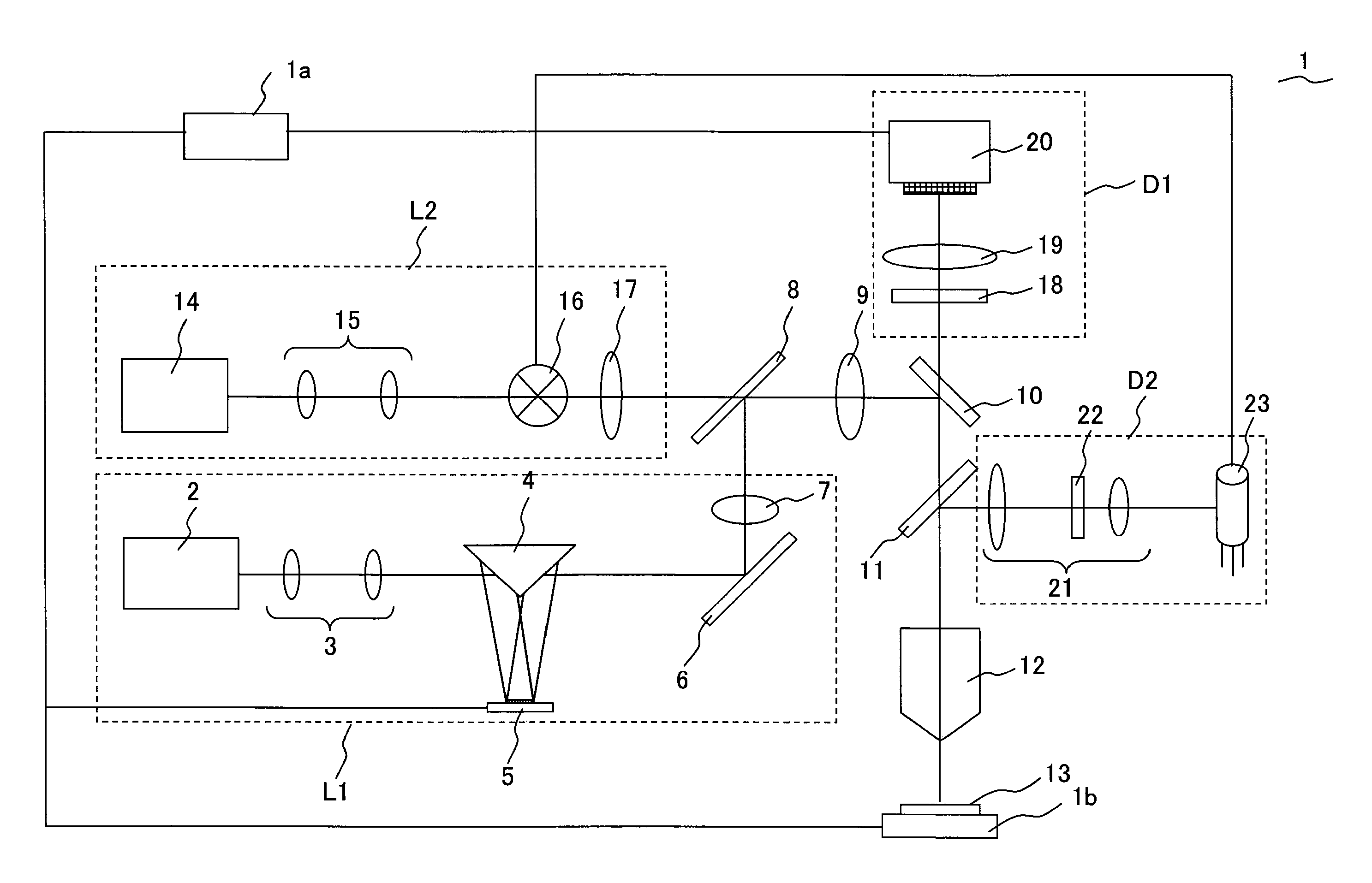
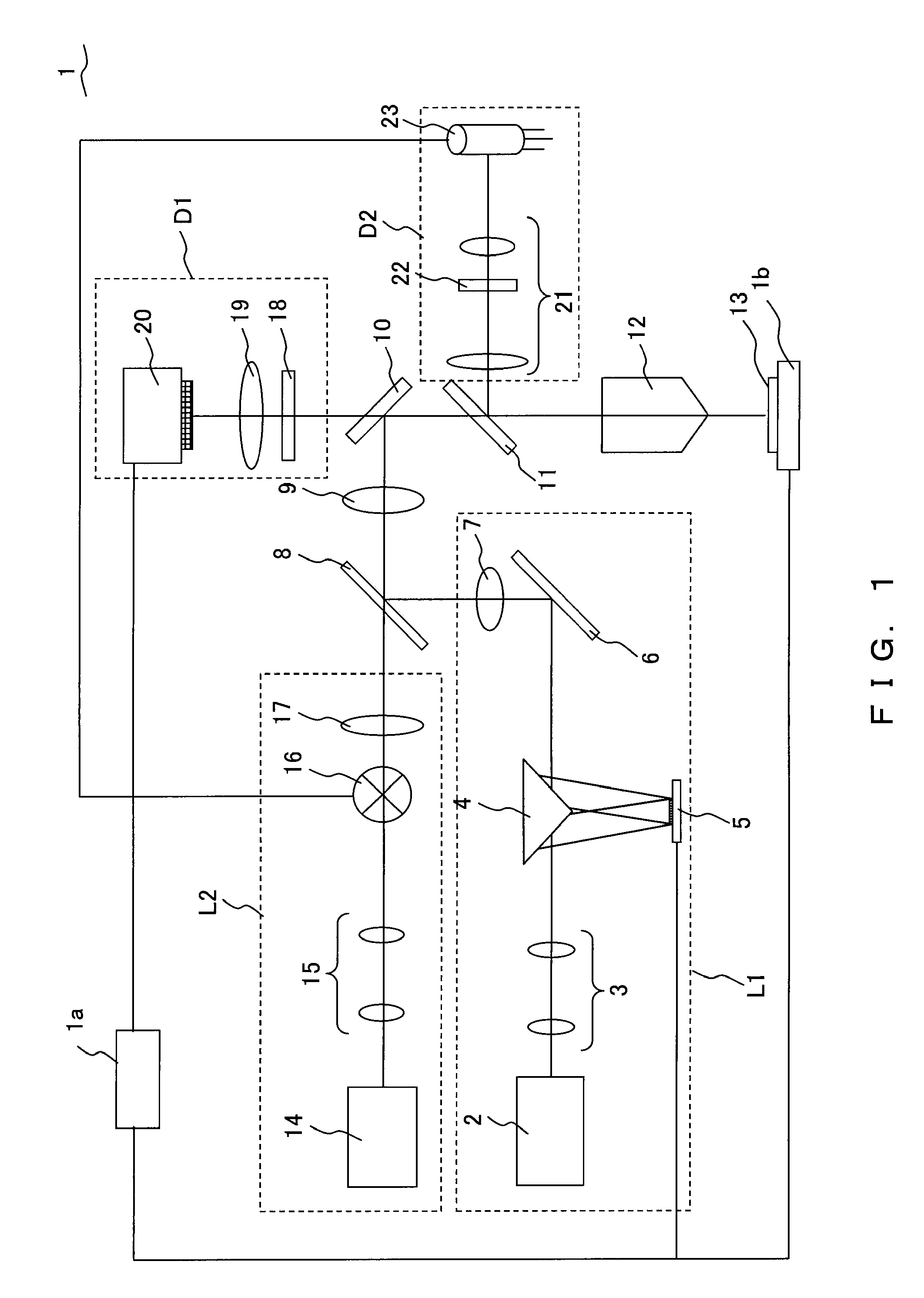
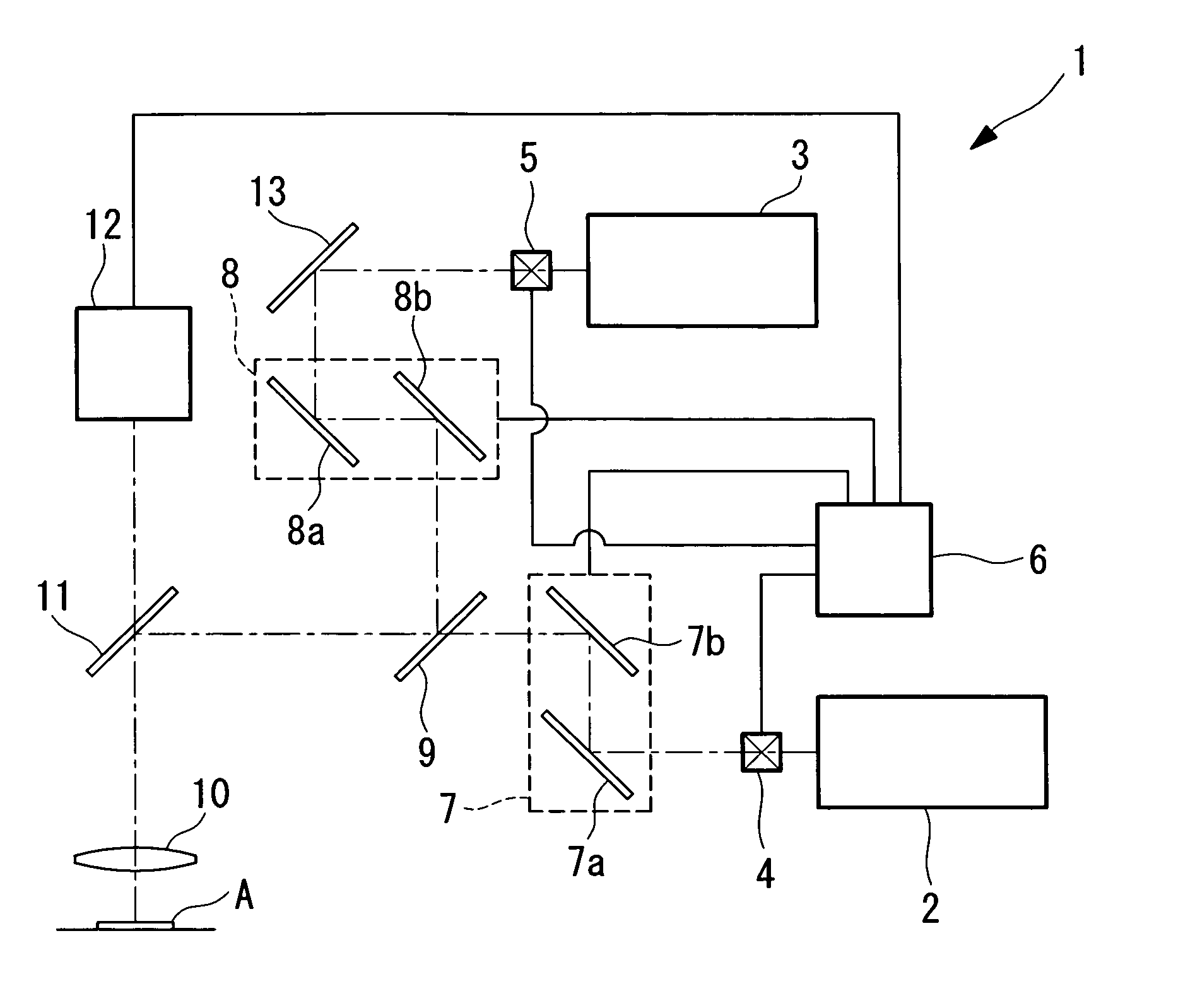
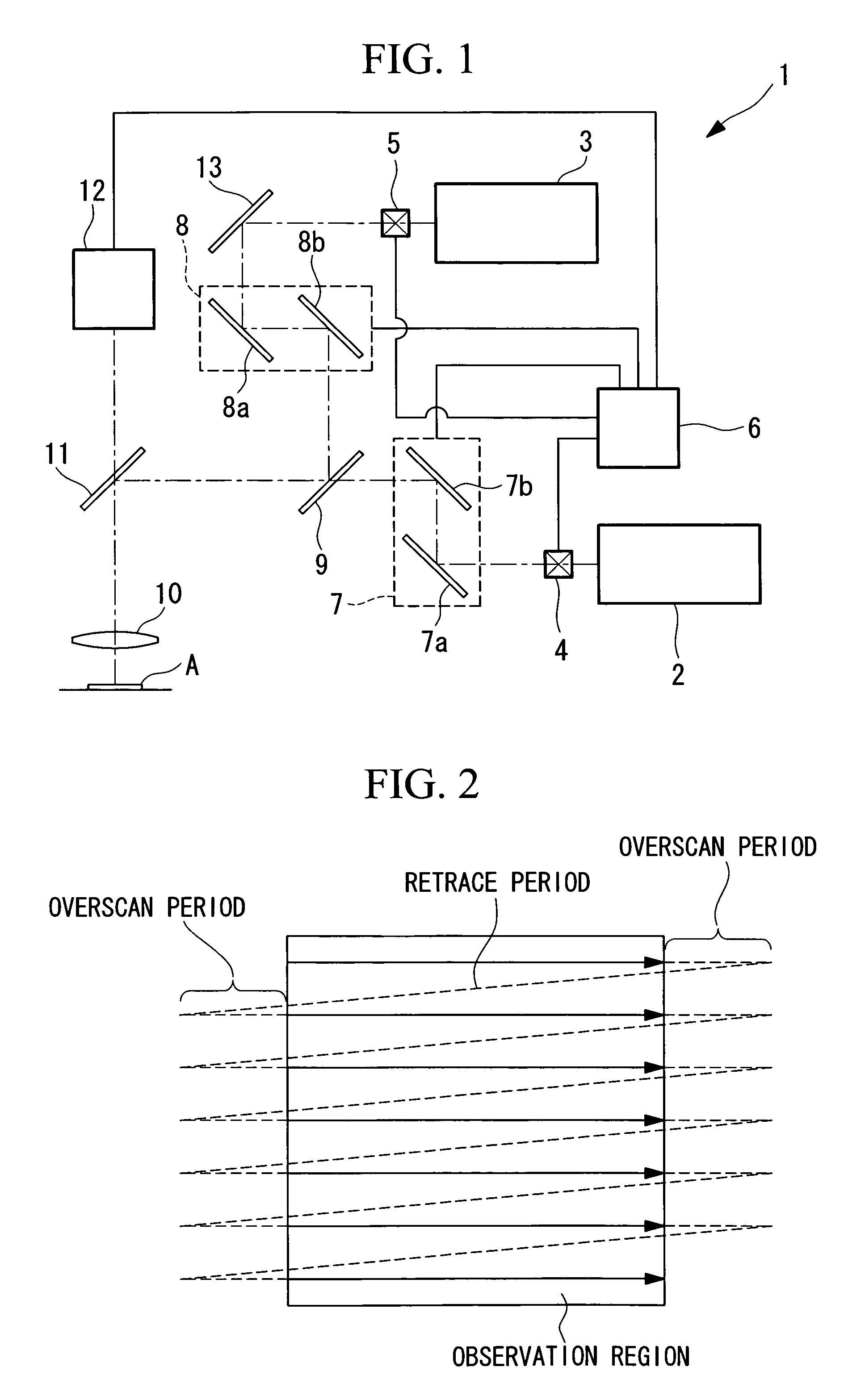
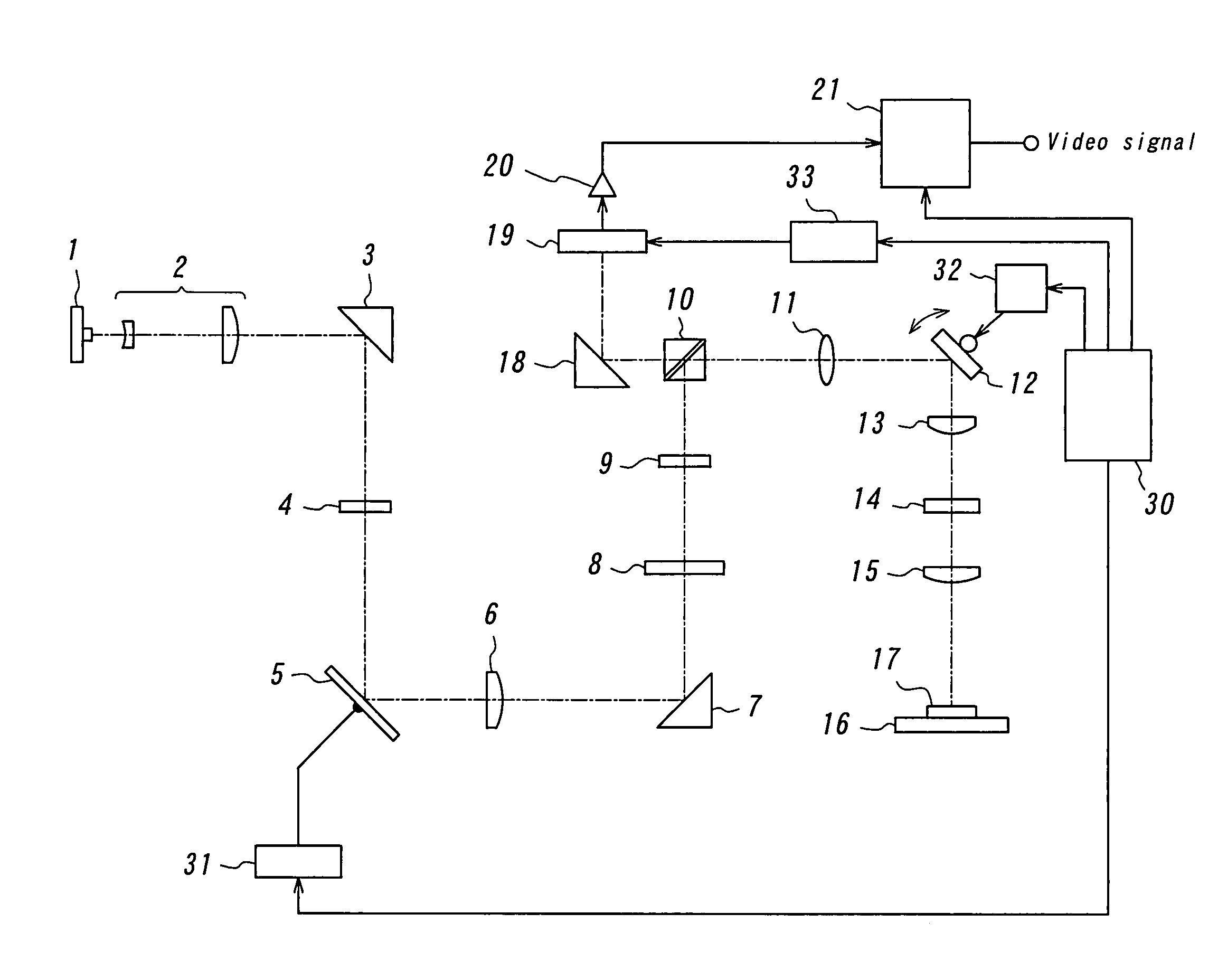
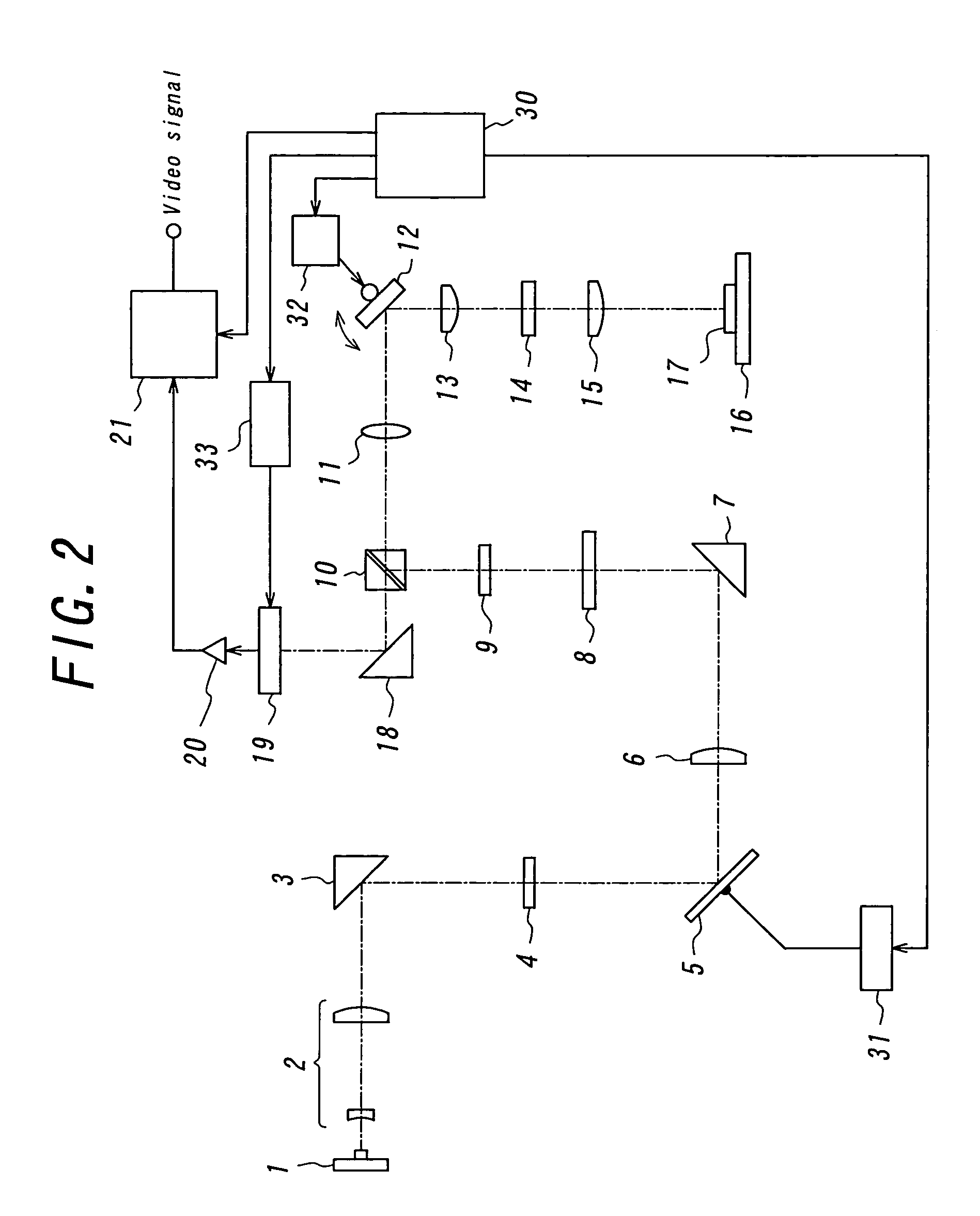
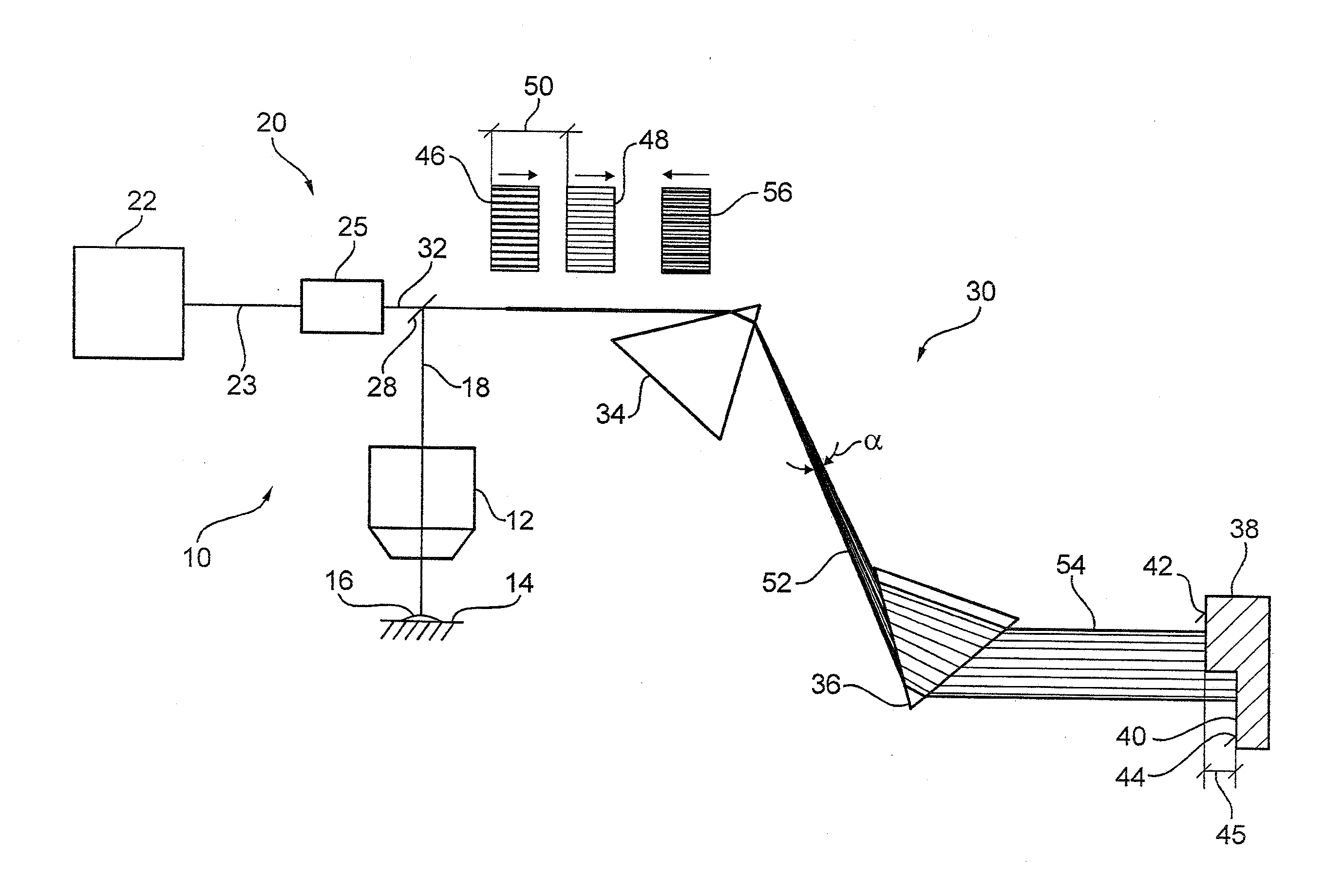
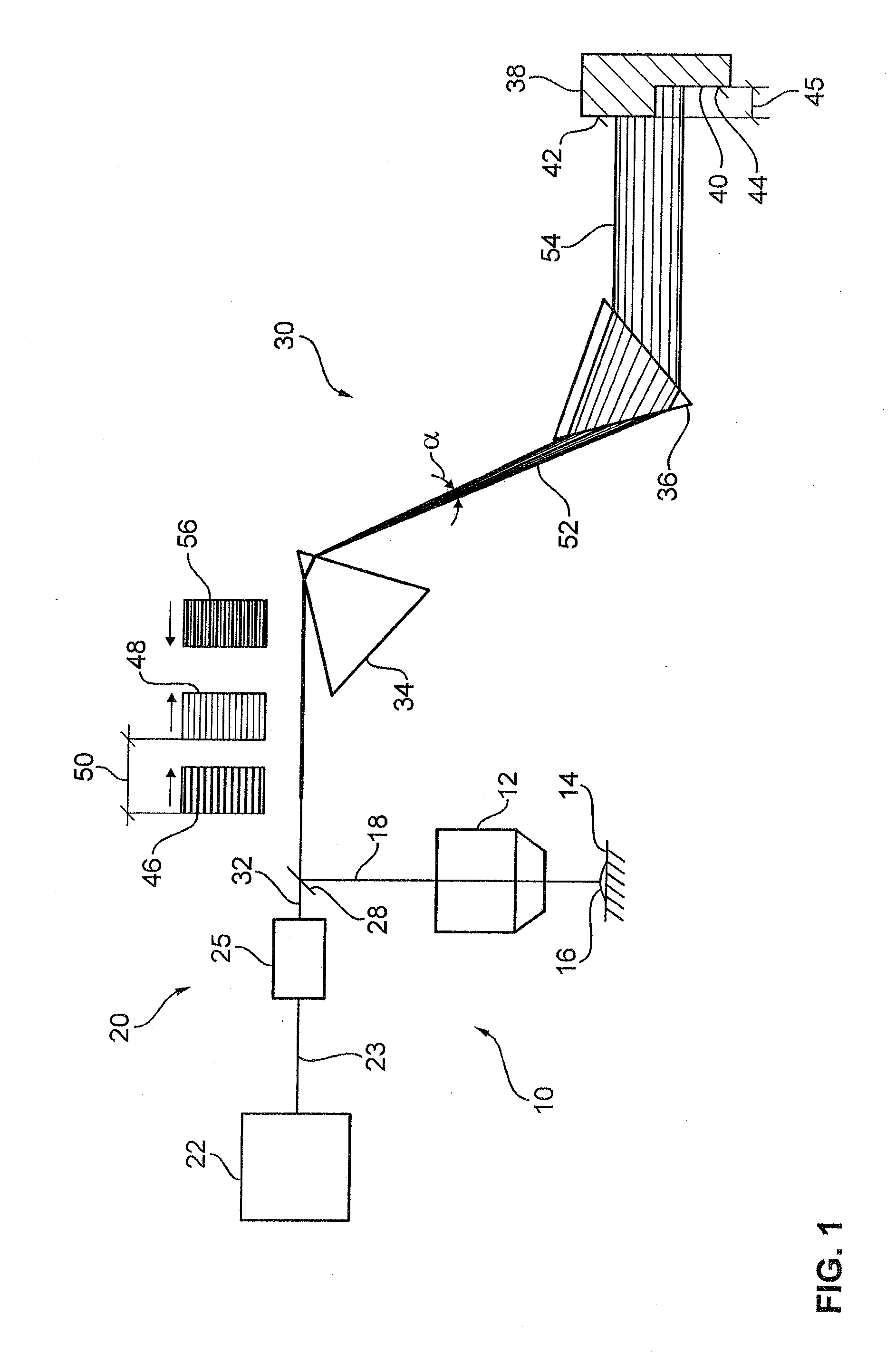
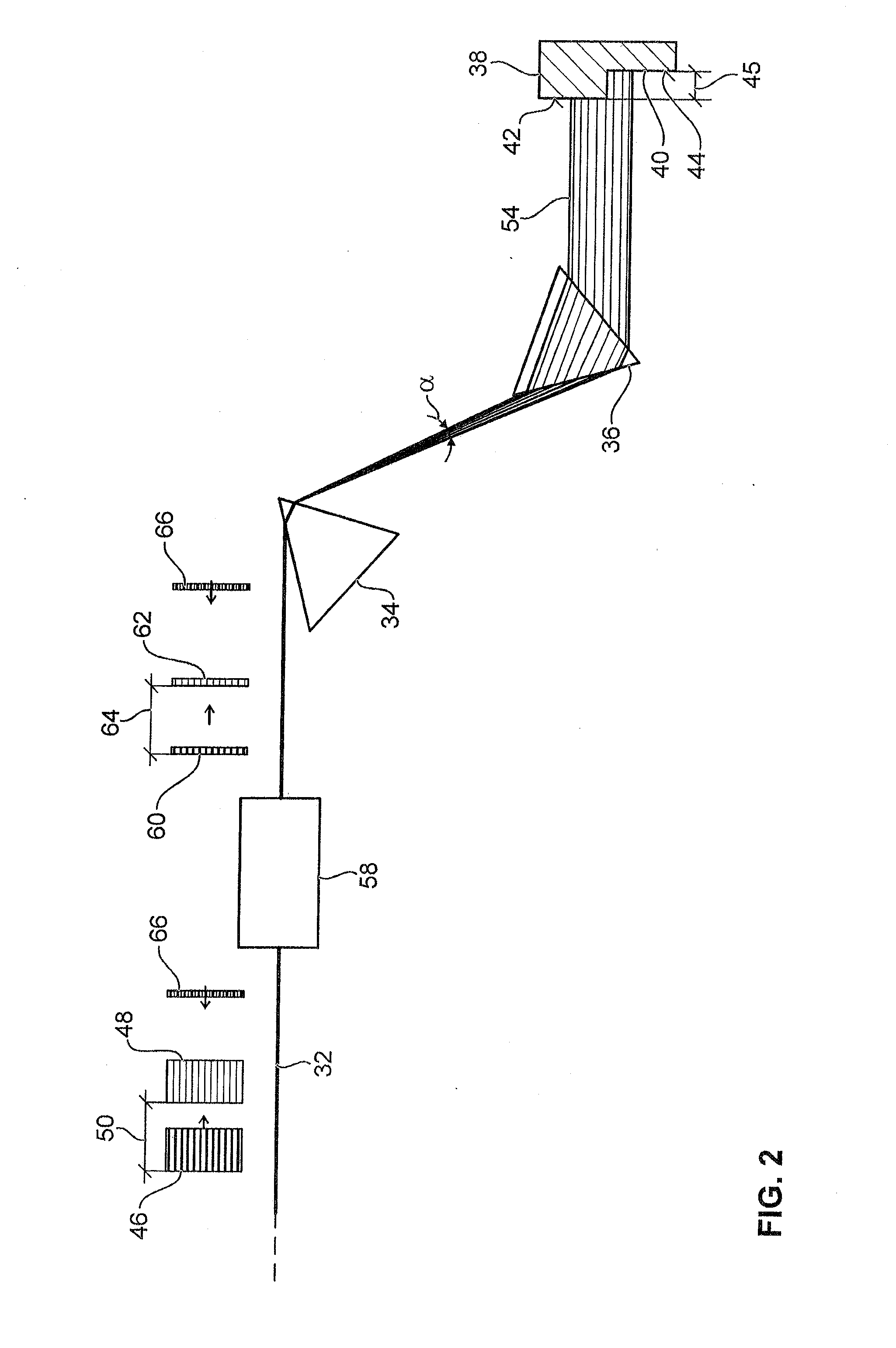
A laser microscope according to the present invention comprises a laser light source which generates a laser beam, an optical path split portion which has a plurality of optical path split elements with different characteristics for separating the laser beam irradiated to a sample from the laser light source and light returned from the sample and includes a selection mechanism to switch these optical path split elements on an optical path, an imaging lens to converge light which is returned from the sample and is separated in the optical path split portion, a spectrophotometric detection unit which obtains spectral data of light from the sample, an optical fiber which guides light from the sample imaged by the imaging lens to the spectrophotometric detection unit, wherein an incident end face of the fiber is arranged to a position substantially conjugate to the sample, and a transfer mechanism which moves an incident end face of the optical fiber in a plane orthogonal to an optical axis of light incident on the optical fiber.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Laser microscope using phase-modulation type spatial light modulator
A laser microscope comprises a laser light source emitting illumination light; an objective applying the illumination light on a sample; a light path compounding unit compounding a first illumination light path and a second illumination path between the laser light source and the objective; a phase-modulation type spatial light modulator placed on a position on the first illumination path, the position also being optically conjugate with a pupil position of the objective, modulating a phase of the illumination light; and a two-dimensional scanning unit placed on the second illumination light path, scanning the sample in a plane orthogonal to an optical axis of the objective.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Laser microscope
InactiveUS20070076199A1Amount of second harmonic light emitted backward can be increasedIncrease volumeRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotovoltaic detectorsPhase difference
A laser microscope according to an embodiment of the invention includes: a laser beam source; a phase plate providing a phase difference for laser beam from the laser beam source in accordance with an incident position; an objective lens focusing light transmitted through the phase plate onto a sample; a first separating unit separating second harmonic light emitted from the sample in a direction opposite to a traveling direction of the laser beams from a fundamental light reflected by the sample; and a photodetector detecting the second harmonic light separated from the fundamental light by the first separating unit.
Owner:NANOPHOTON
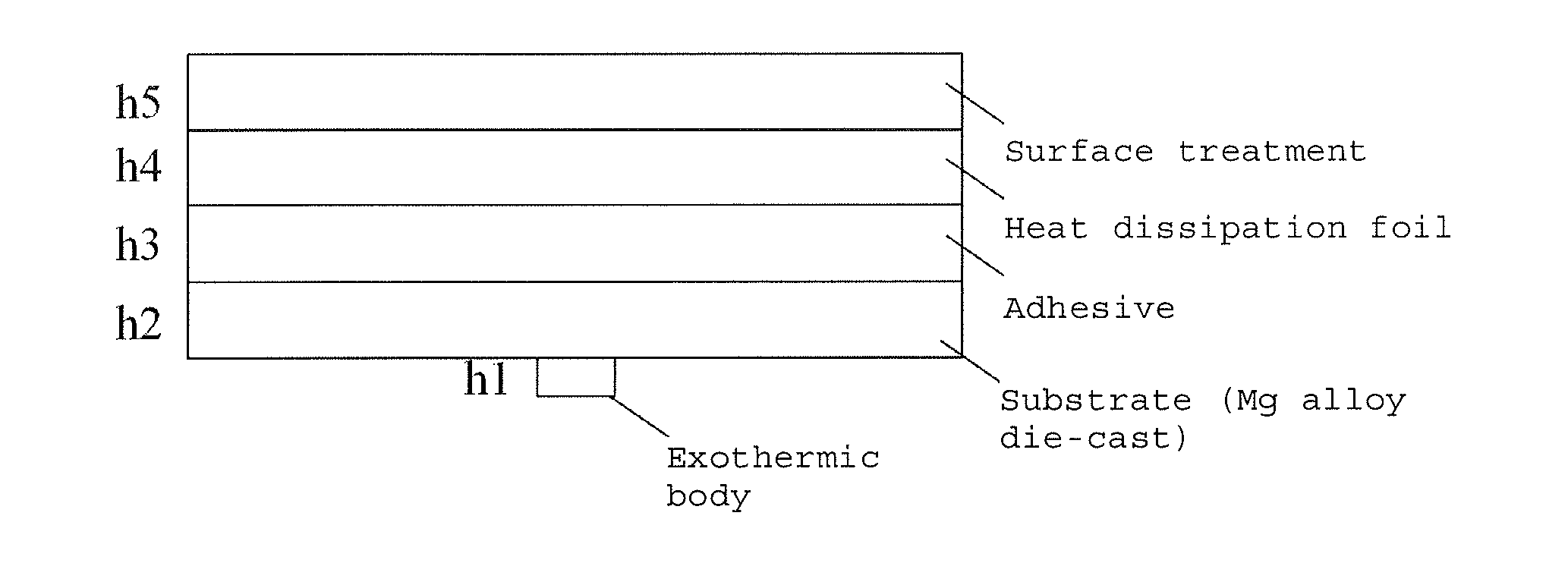
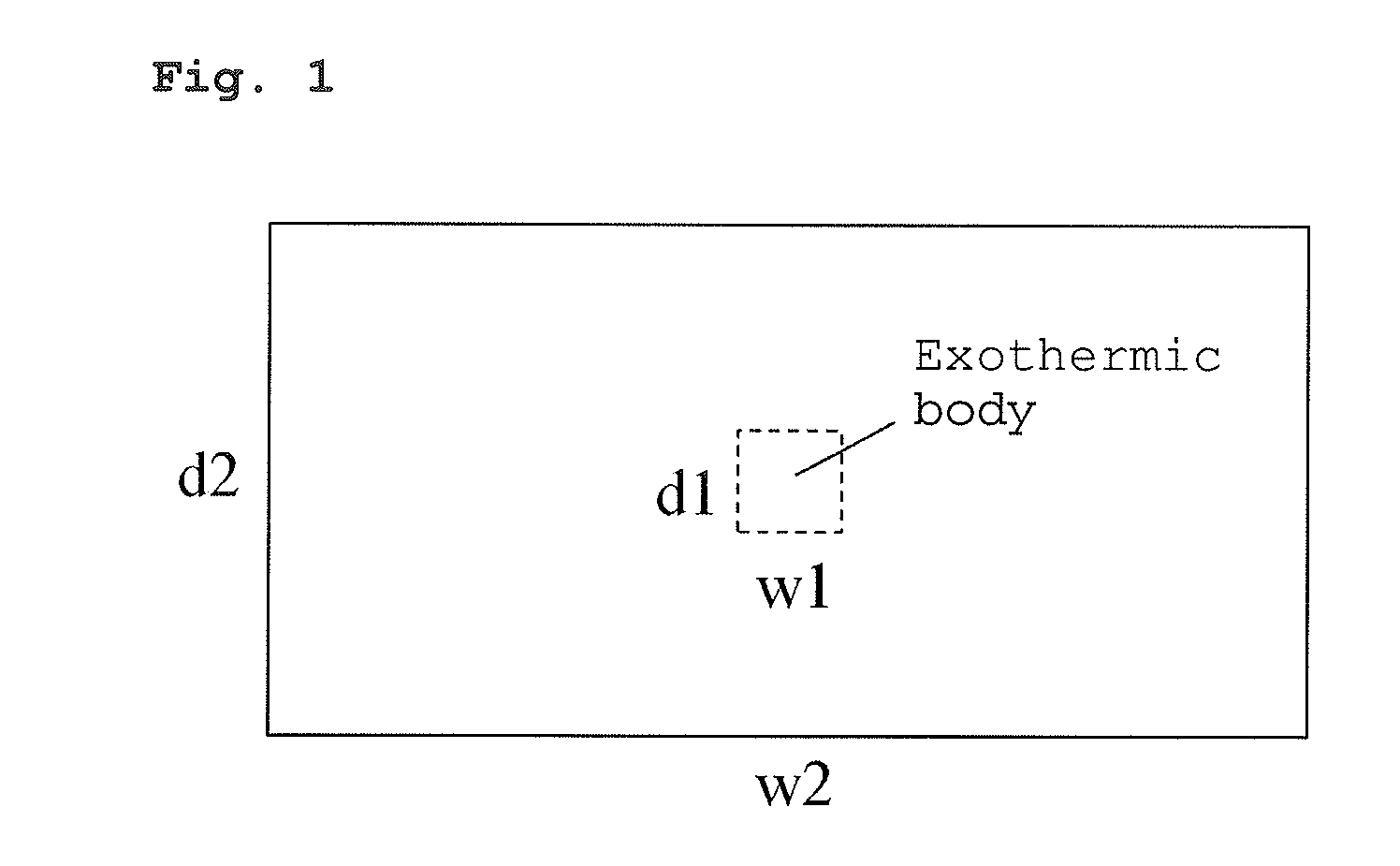
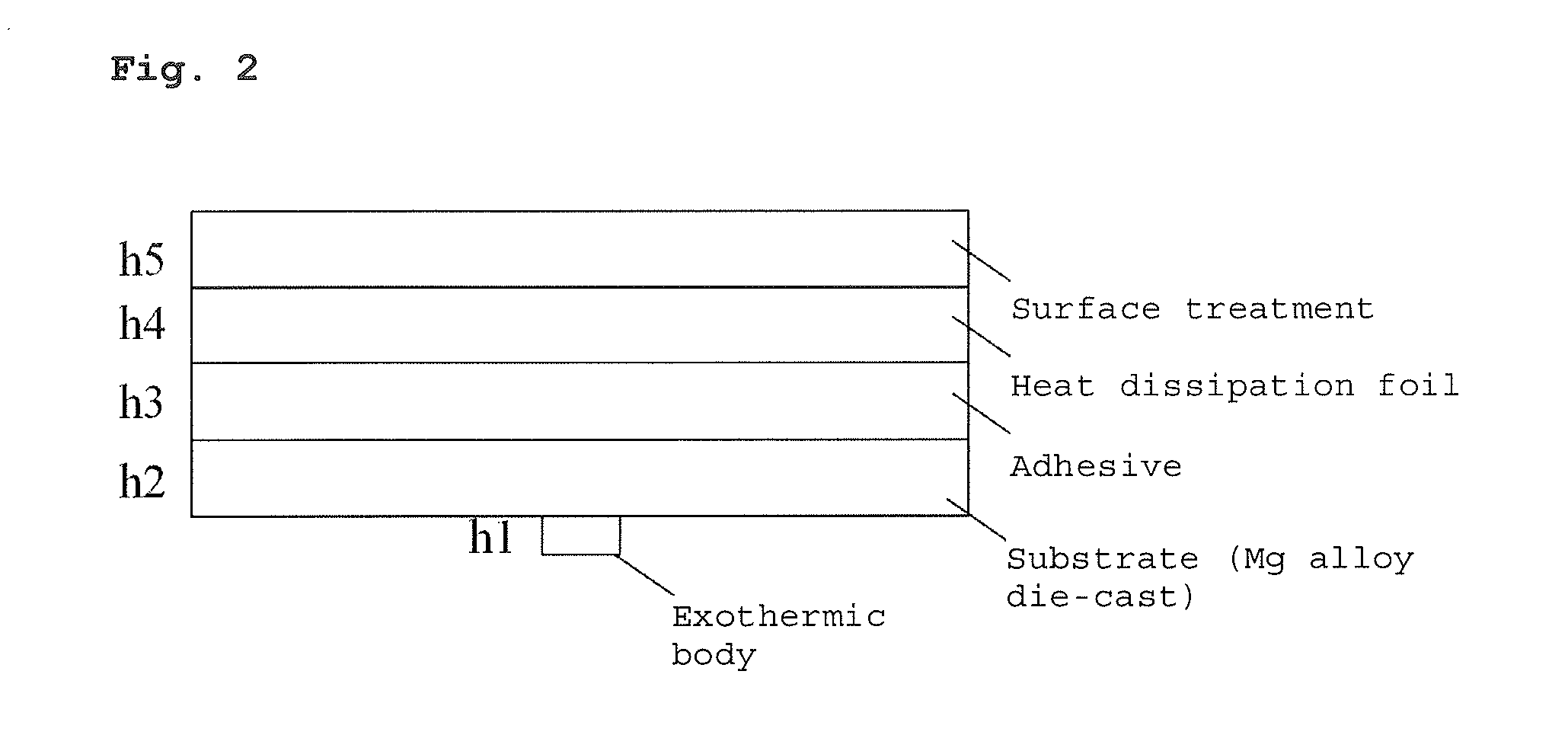
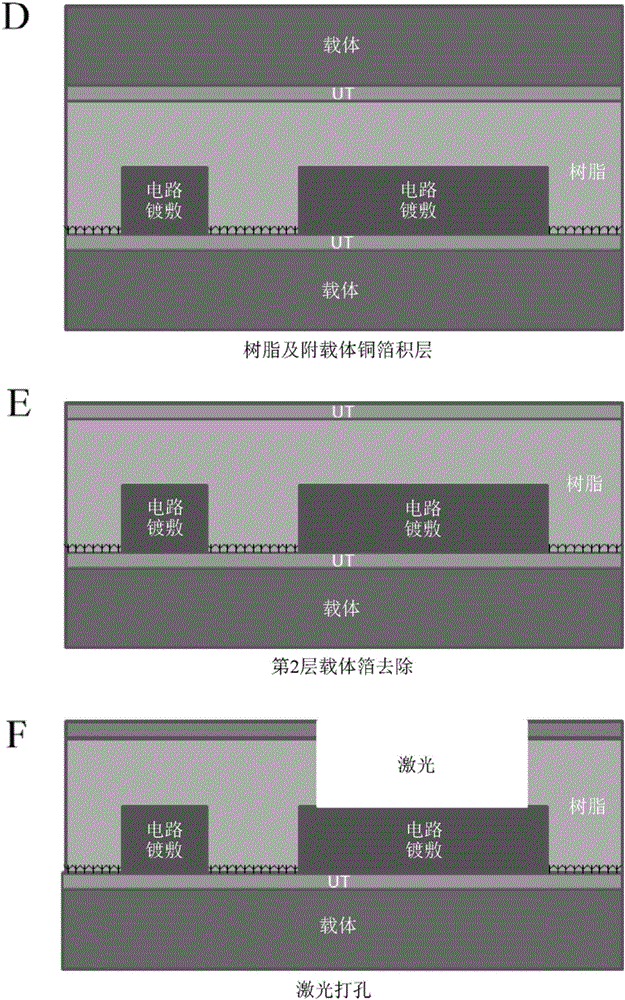
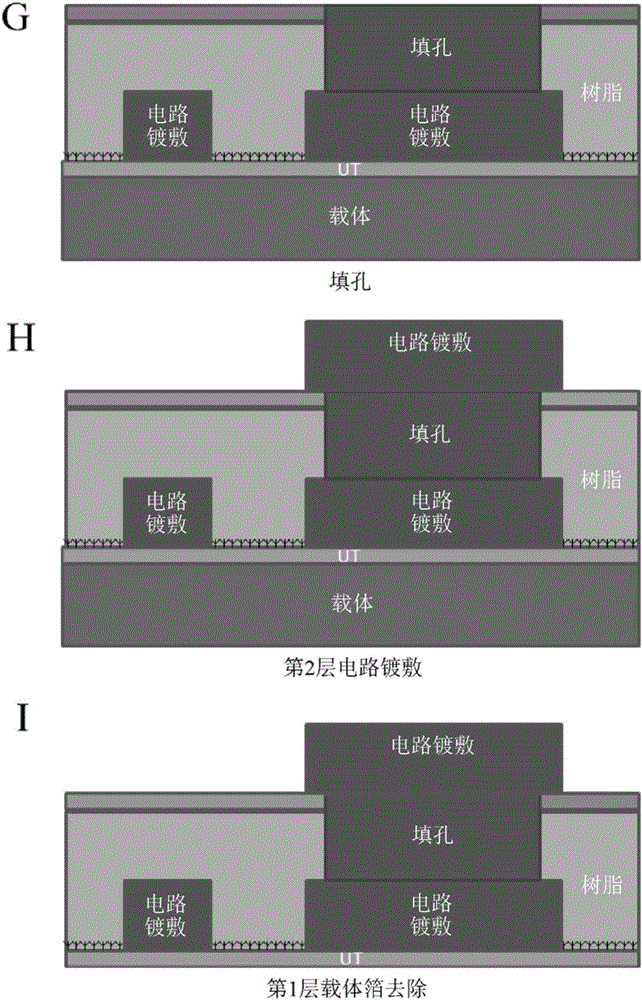
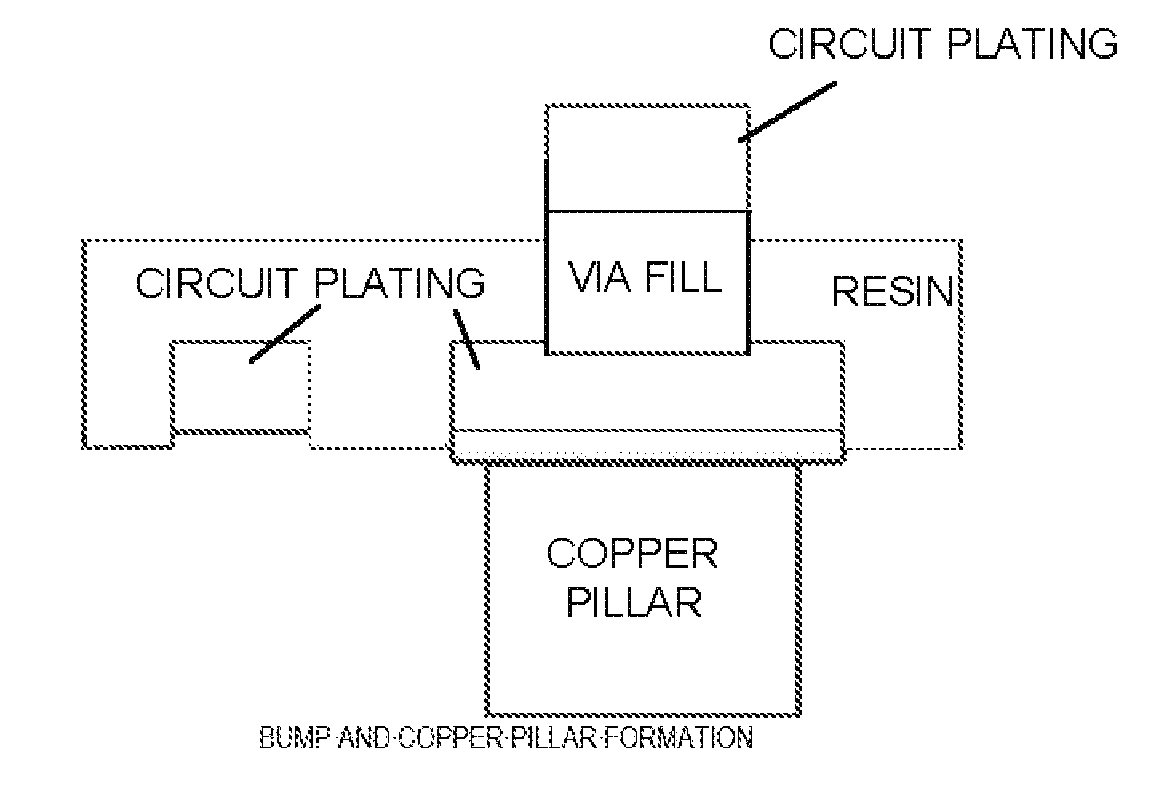
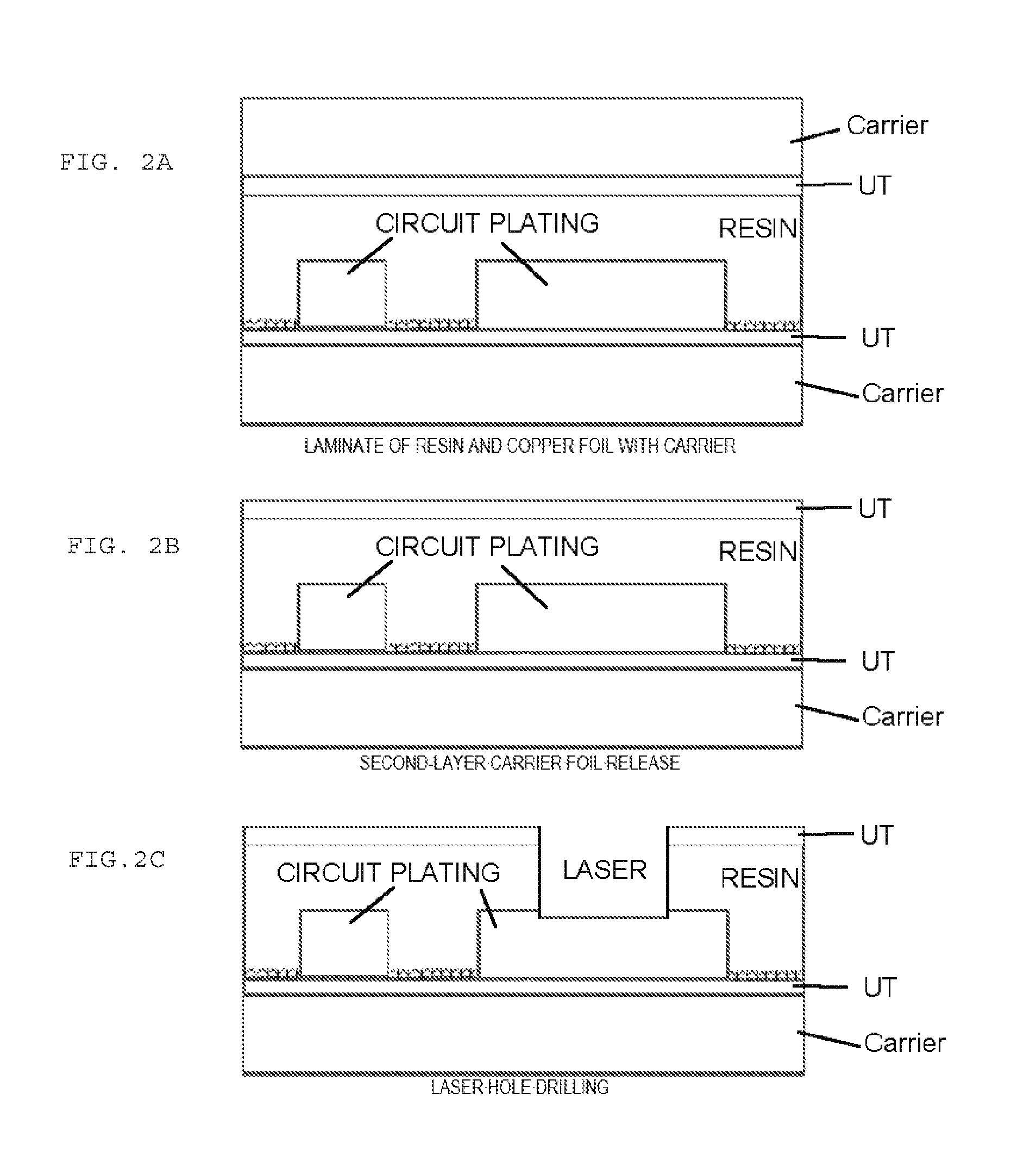
Copper Heat Dissipation Material, Carrier-Attached Copper Foil, Connector, Terminal, Laminate, Shield Material, Printed-Wiring Board, Metal Processed Member, Electronic Device and Method for Manufacturing the Printed Wiring Board
ActiveUS20160120017A1Satisfy heat dissipationSatisfactory performanceCoupling device connectionsCell electrodesSurface roughnessAlloy
A copper heat dissipation material having a satisfactory heat dissipation performance is provided. The copper heat dissipation material has an alloy layer containing at least one metal selected from Cu, Co, Ni, W, P, Zn, Cr, Fe, Sn and Mo on one or both surfaces, in which surface roughness Sz of the one or both surfaces, measured by a laser microscope using laser light of 405 nm in wavelength, is 5 μm or more.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
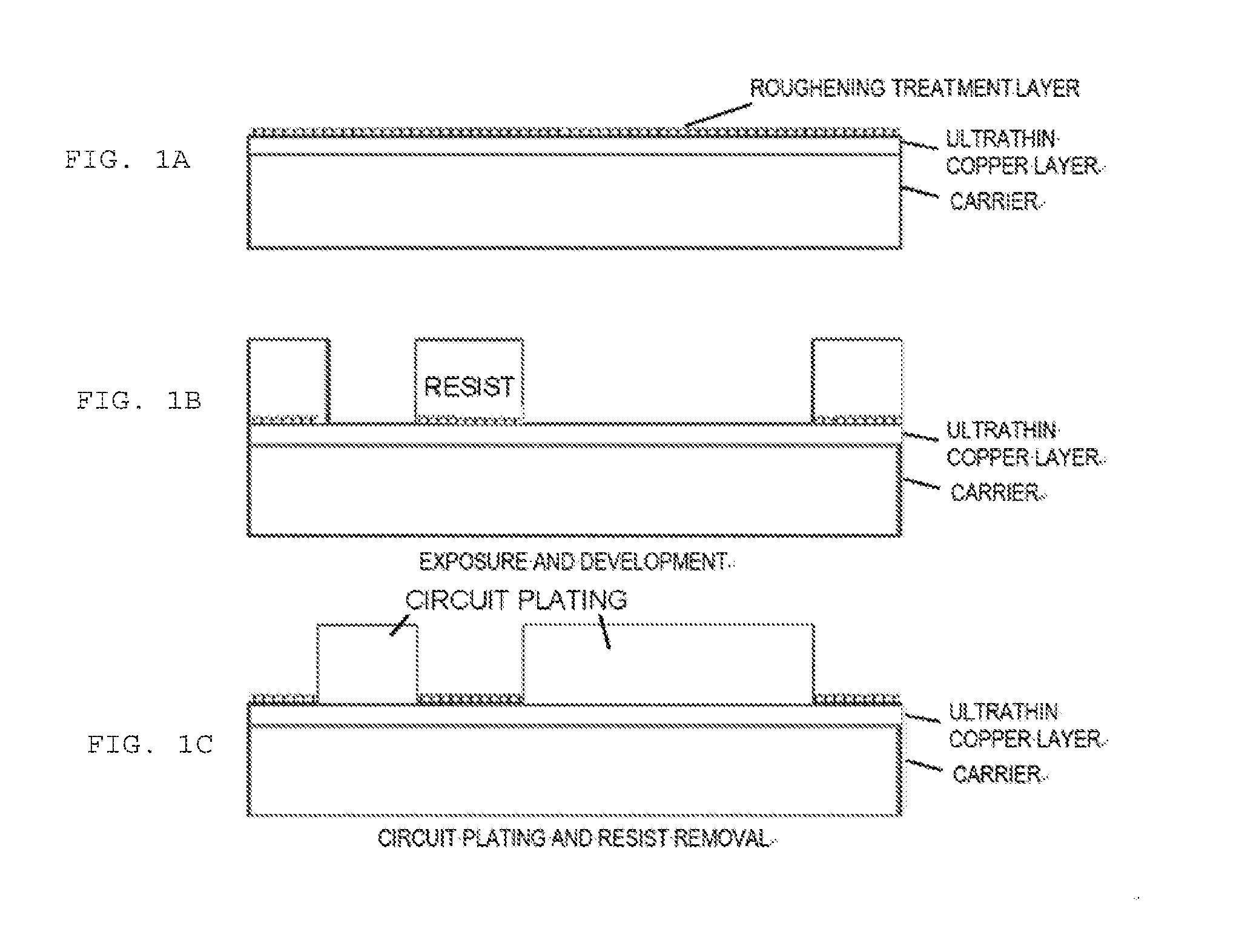
Carrier-Attached Copper Foil, Laminate, Method For Producing Printed Wiring Board, And Method For Producing Electronic Device
ActiveCN106455341AFormation effect is goodInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementPrinted circuit aspectsISO 25178Copper foil
Provided herein is a carrier-attached copper foil having desirable fine circuit formability. The carrier-attached copper foil includes a carrier, an interlayer, and an ultrathin copper layer in this order. The maximum ridge height Sp as measured with a laser microscope according to ISO 25178 on the surface of the carrier-attached copper foil on the side of the ultrathin copper layer is 0.193 to 3.082 [mu]m.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CO LTD
Scanning laser microscope
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Laser microscope apparatus
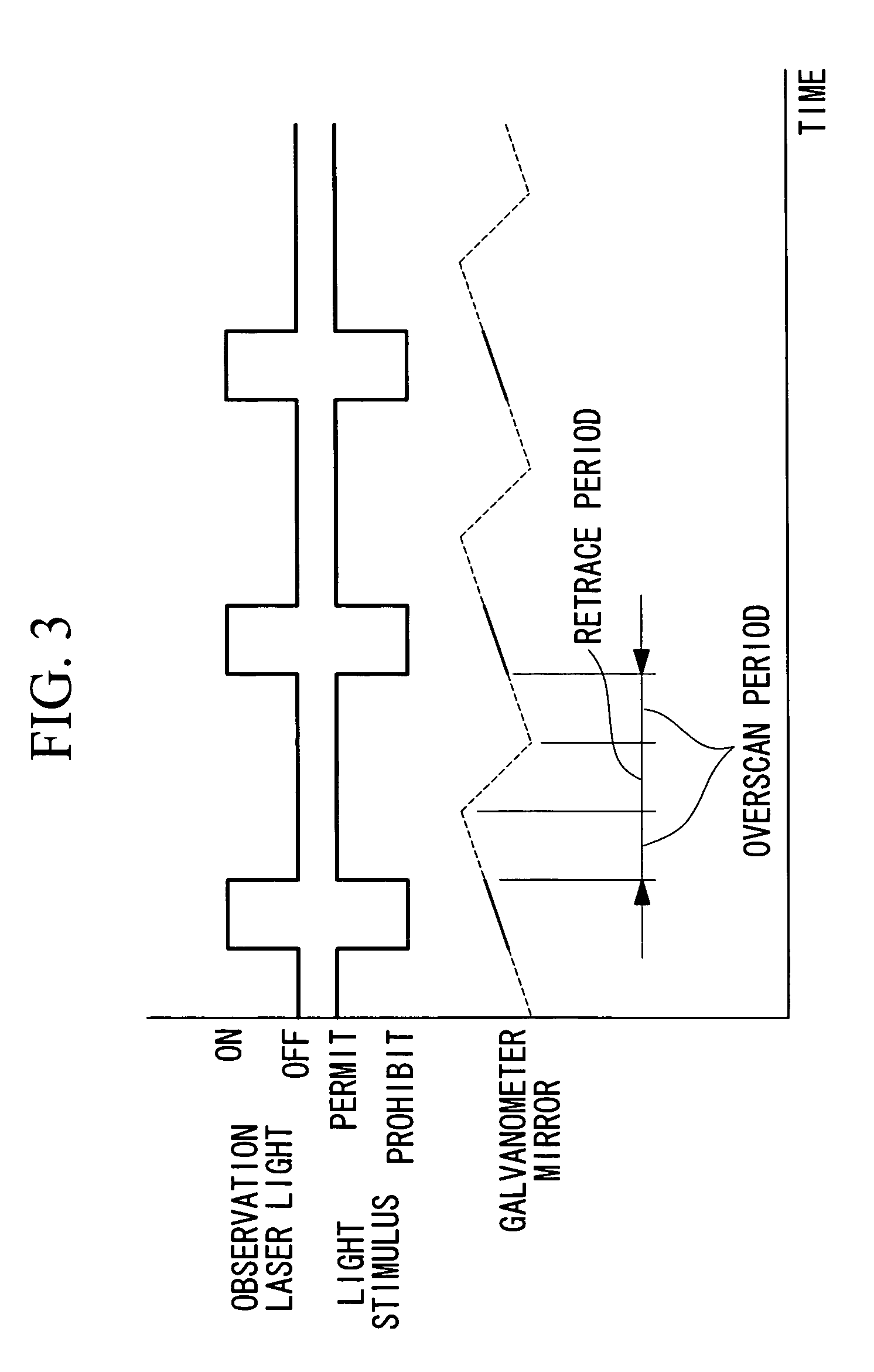
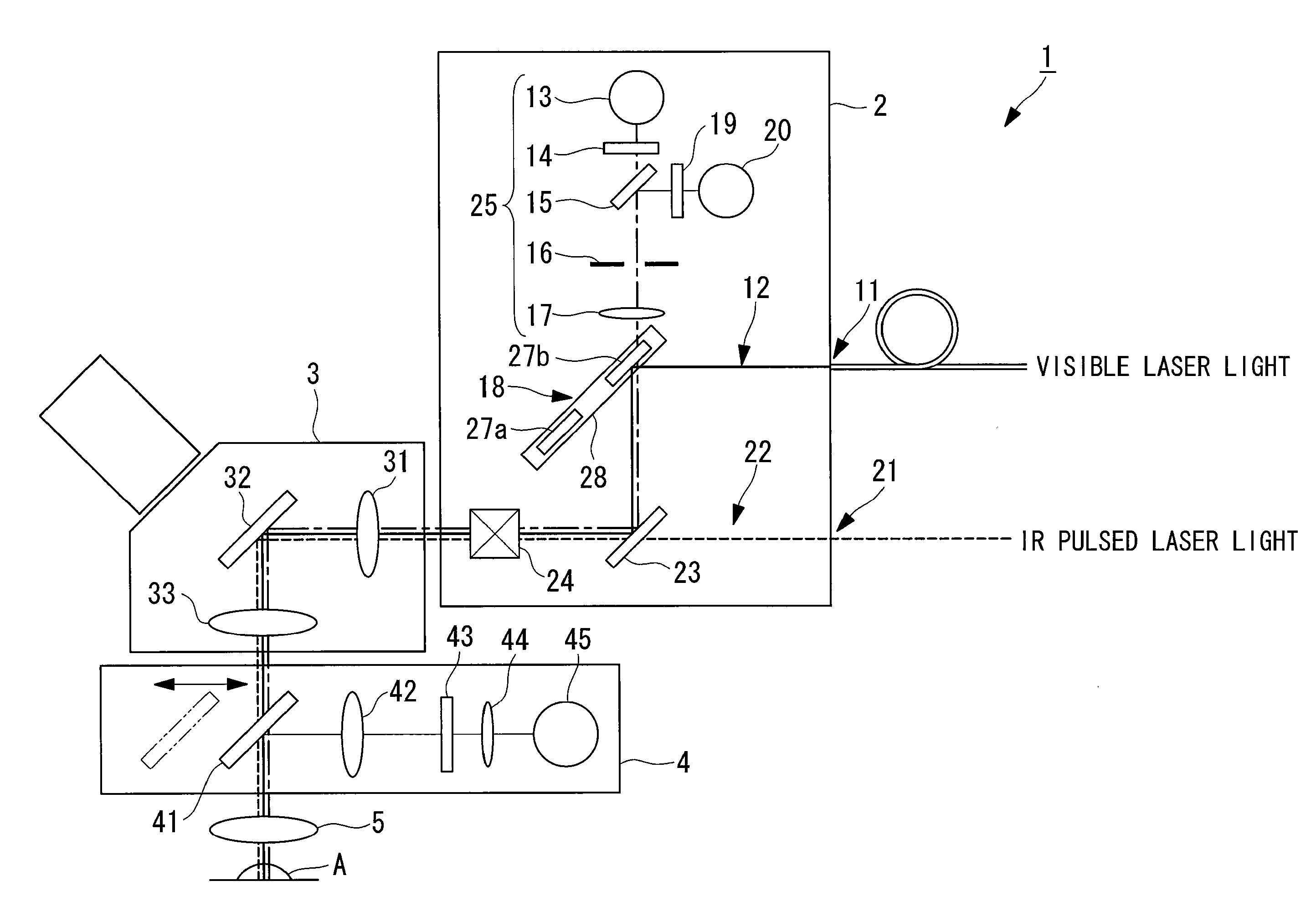
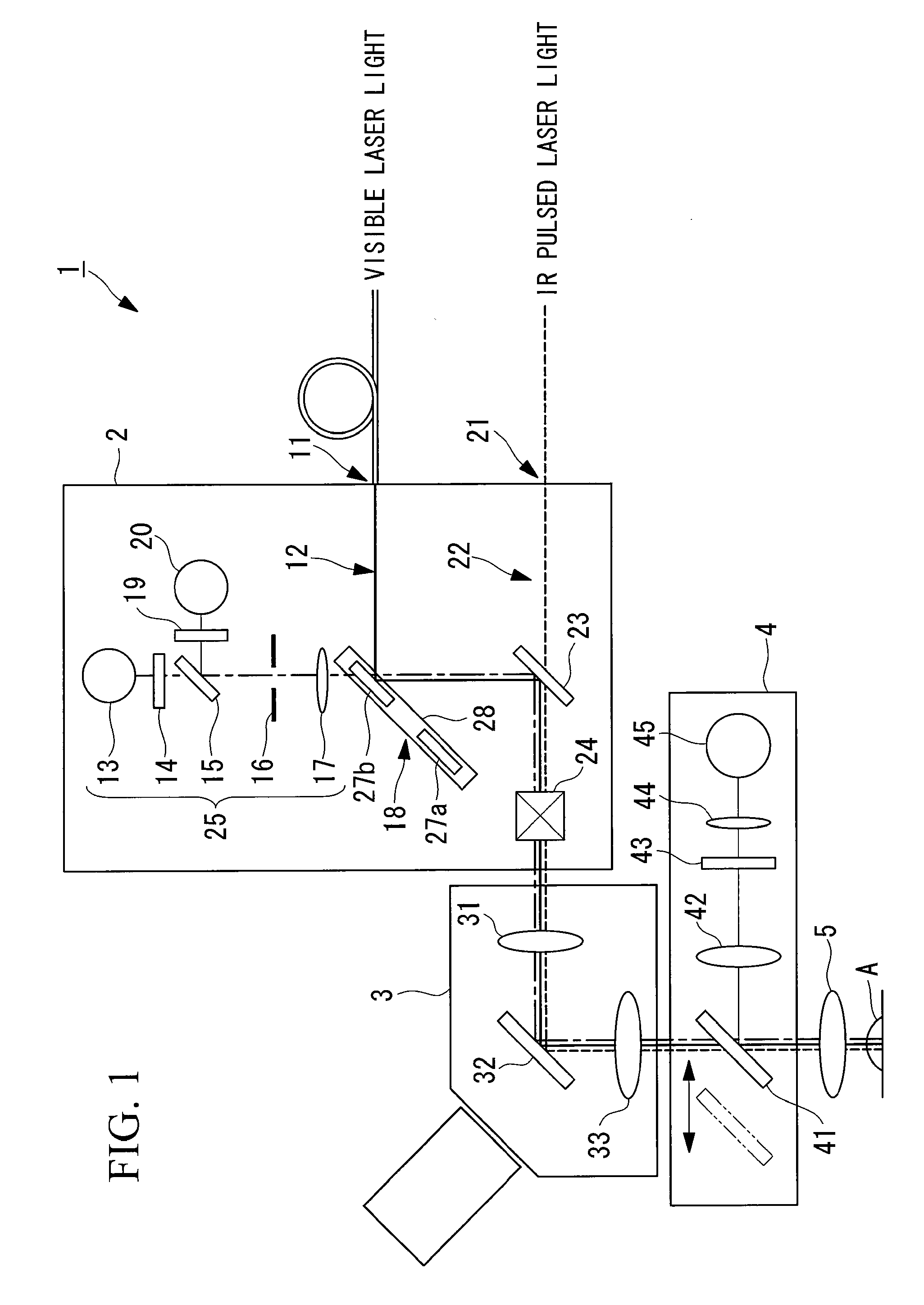
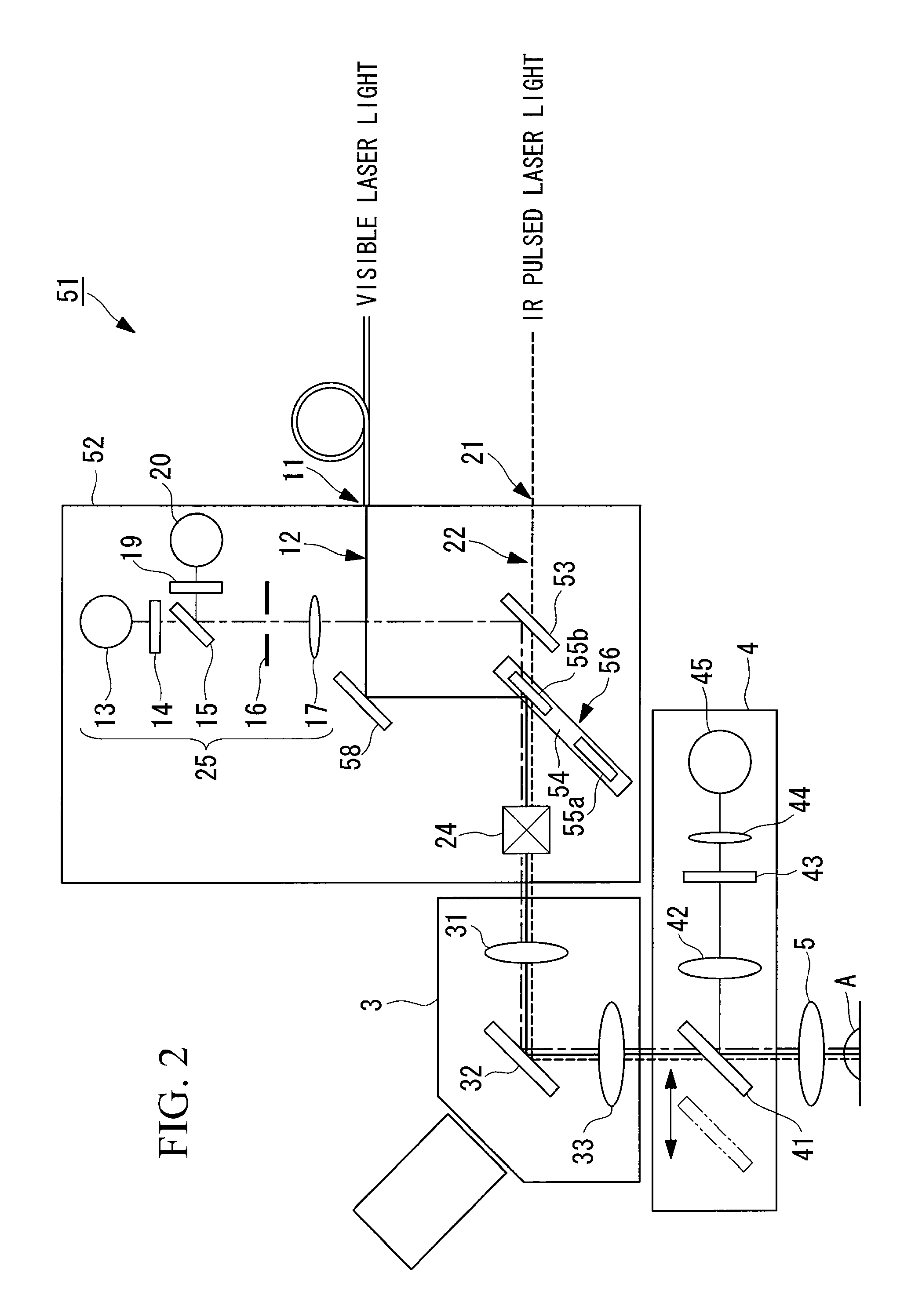
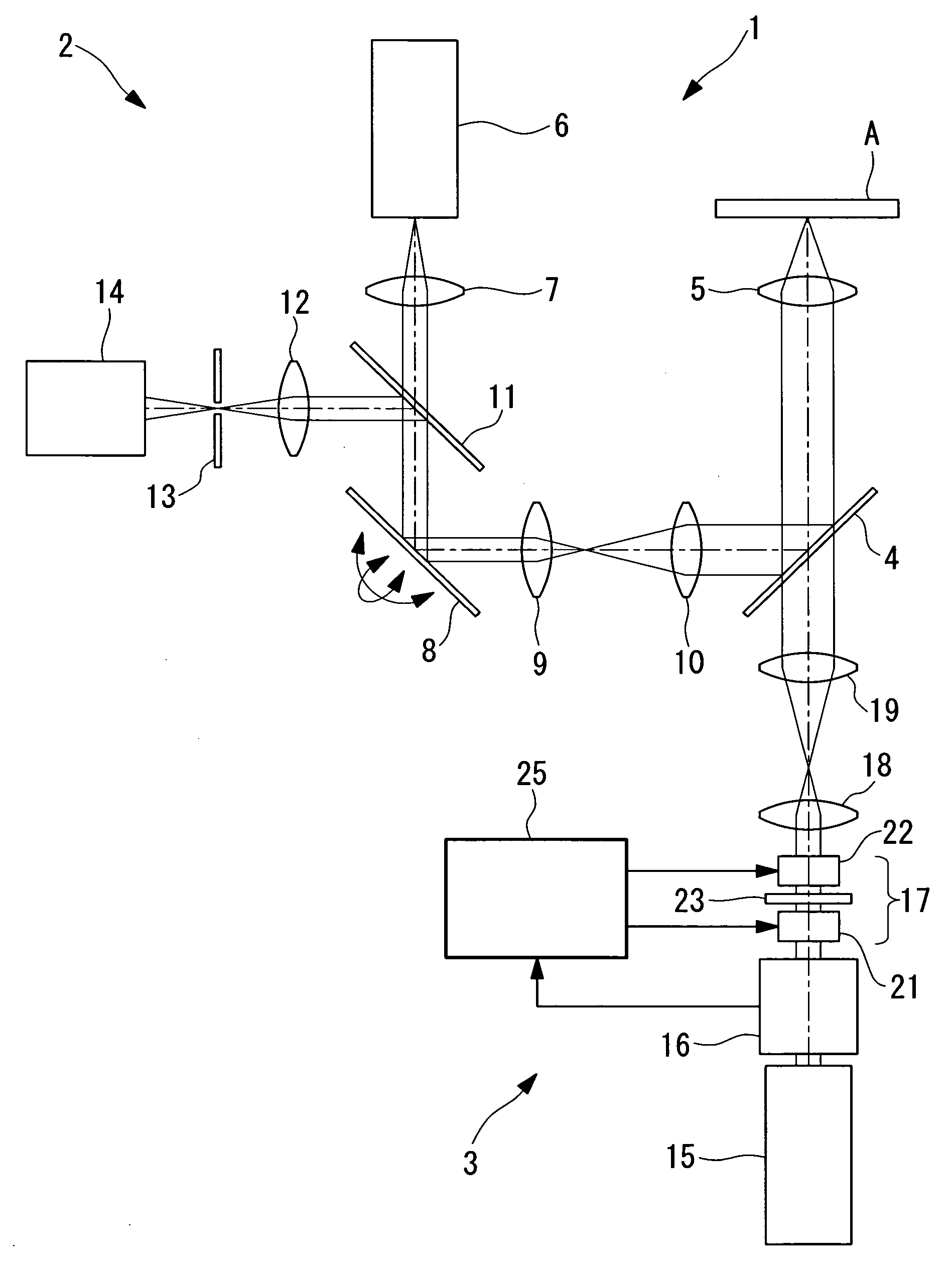
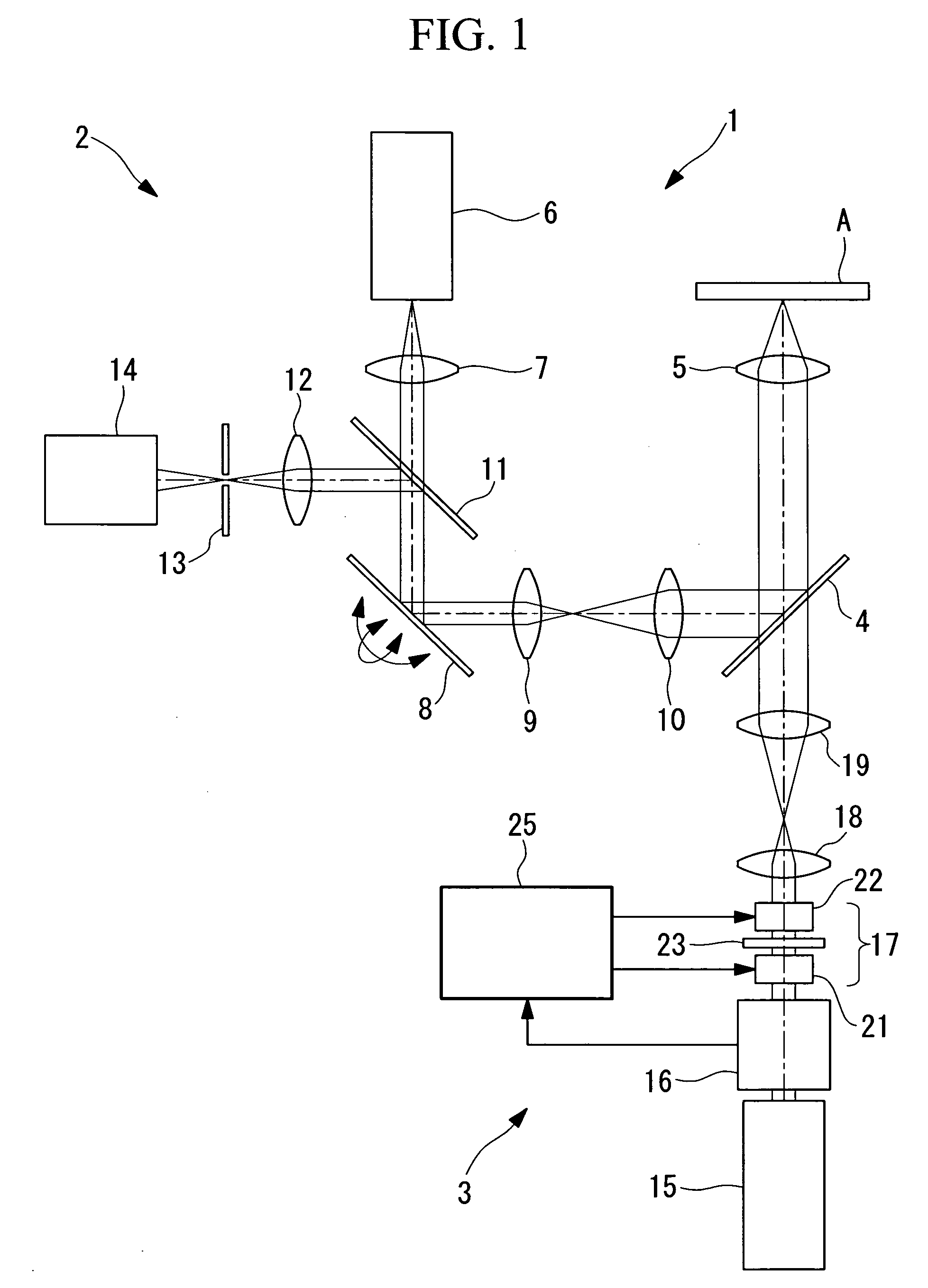
Observation is performed using bright, clear multiphoton fluorescence images produced by efficiently generating a multiphoton excitation effect, without the need for a complex interference film structure. The invention employs a laser microscope apparatus including a first dichroic mirror that reflects visible laser light guided via a first light path and that transmits IR pulsed laser light guided via a second light path to combine the first light path and the second light path; an XY galvanometer mirror that scans the laser light from the first dichroic mirror on a specimen; an objective lens that irradiates the specimen with the scanned laser light and that collects fluorescence produced in the specimen; a second dichroic mirror that reflects the visible laser light and transmits the fluorescence from the specimen; and a detection unit that detects the fluorescence transmitted through the second dichroic mirror.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Method for quantitatively analyzing inclusions in steel under laser microscope
InactiveCN103063576AQuick scanQuick distinctionMaterial analysis by optical meansSingle sampleMicroscopic observation
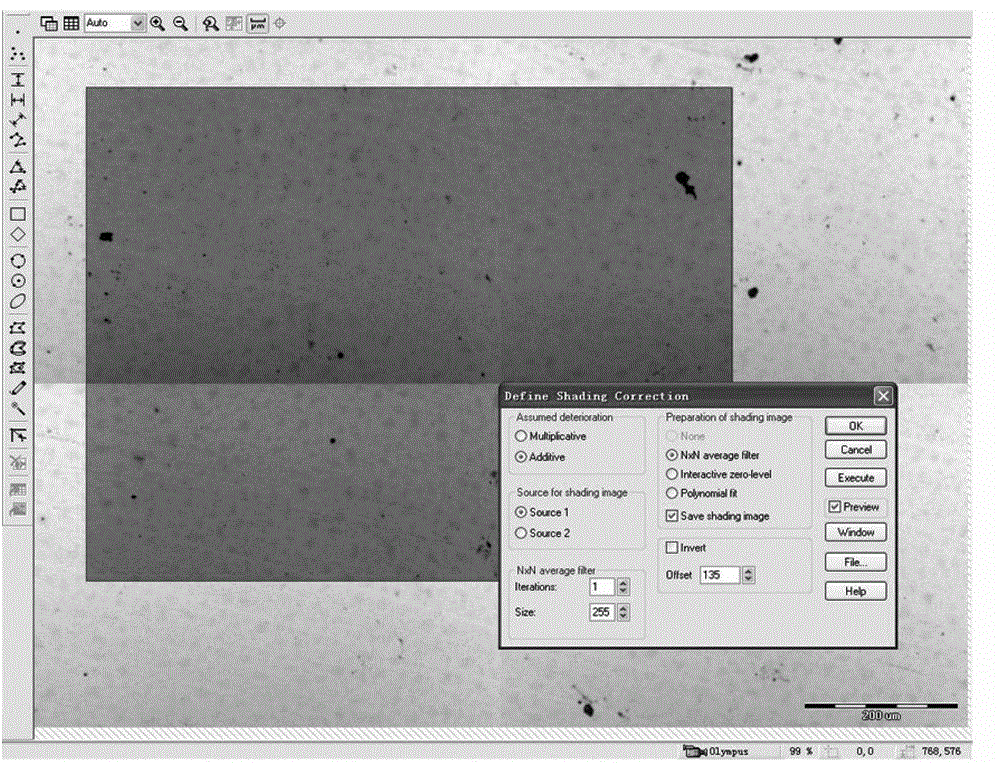
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively analyzing inclusions in steel under laser microscope, comprising the following steps: 1) sampling; 2) polishing; 3) observing and imaging under a microscope; 4) analyzing data, wherein the data of inclusions in each digitalized photo is directly obtained after analysis, and the inclusion A method grading of single sample is obtained; and 5) splicing and analyzing the photo, wherein the inclusion B method grading of single sample is calculated through measurement. Through the application of the laser microscope and accessories, the surface of the whole metallic phase sample can be quickly scanned, the light microscope photos with different areas on a detection surface are obtained respectively by scanning one or more photos continuously, micro deviation of light on the surface of the sample is eliminated through software shadow rectification processing, the inclusions on the surface of the steel sample are sieved by utilizing the gray difference in the photo, the information of different types of inclusions in the whole surface to be detected such as size, length-diameter ratio, shape and the like are automatically calculated and counted through software after laser imaging, and the inclusions are graded with reference to national standard.
Owner:TIANJIN IRON & STEEL GRP
Scanning laser microscope
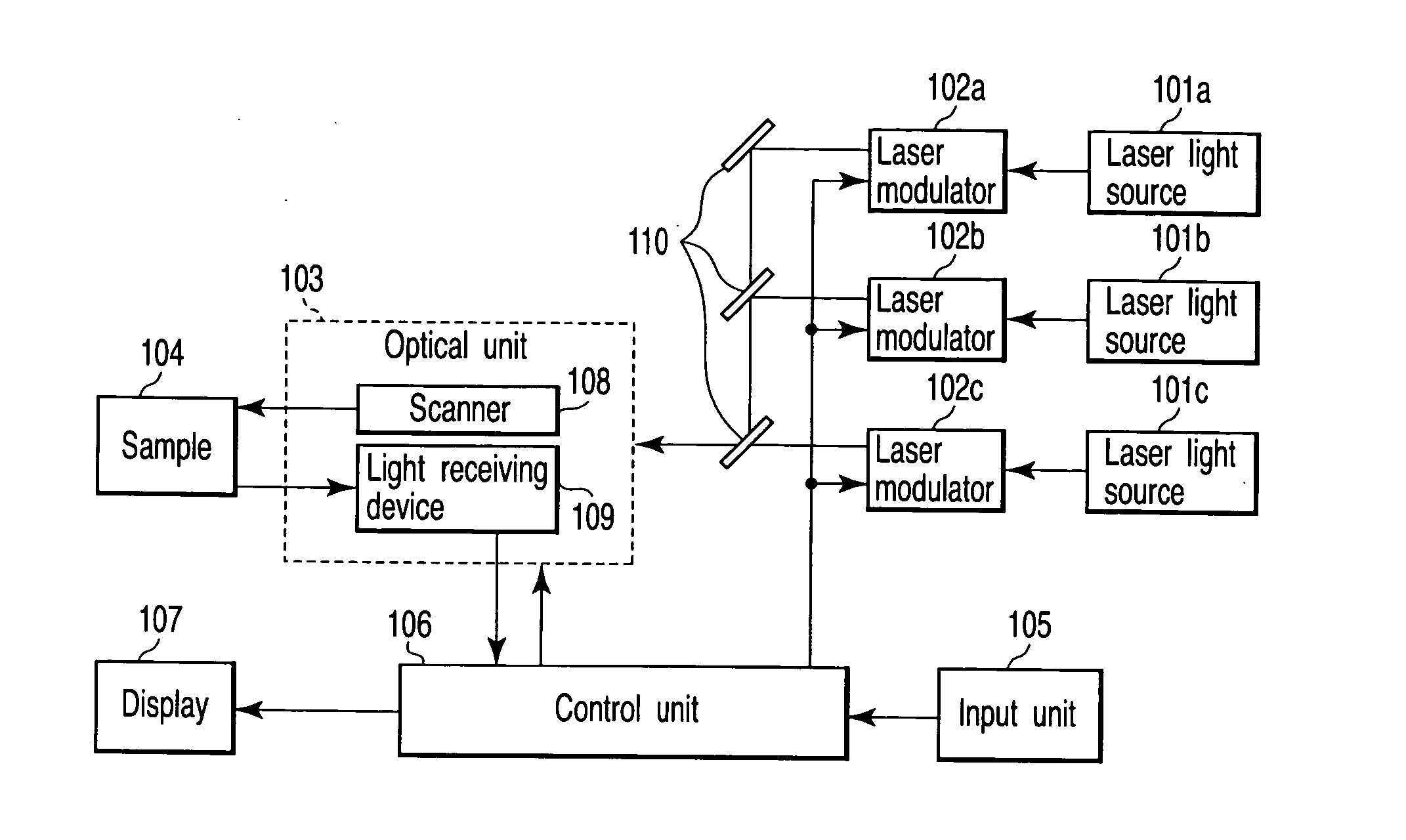
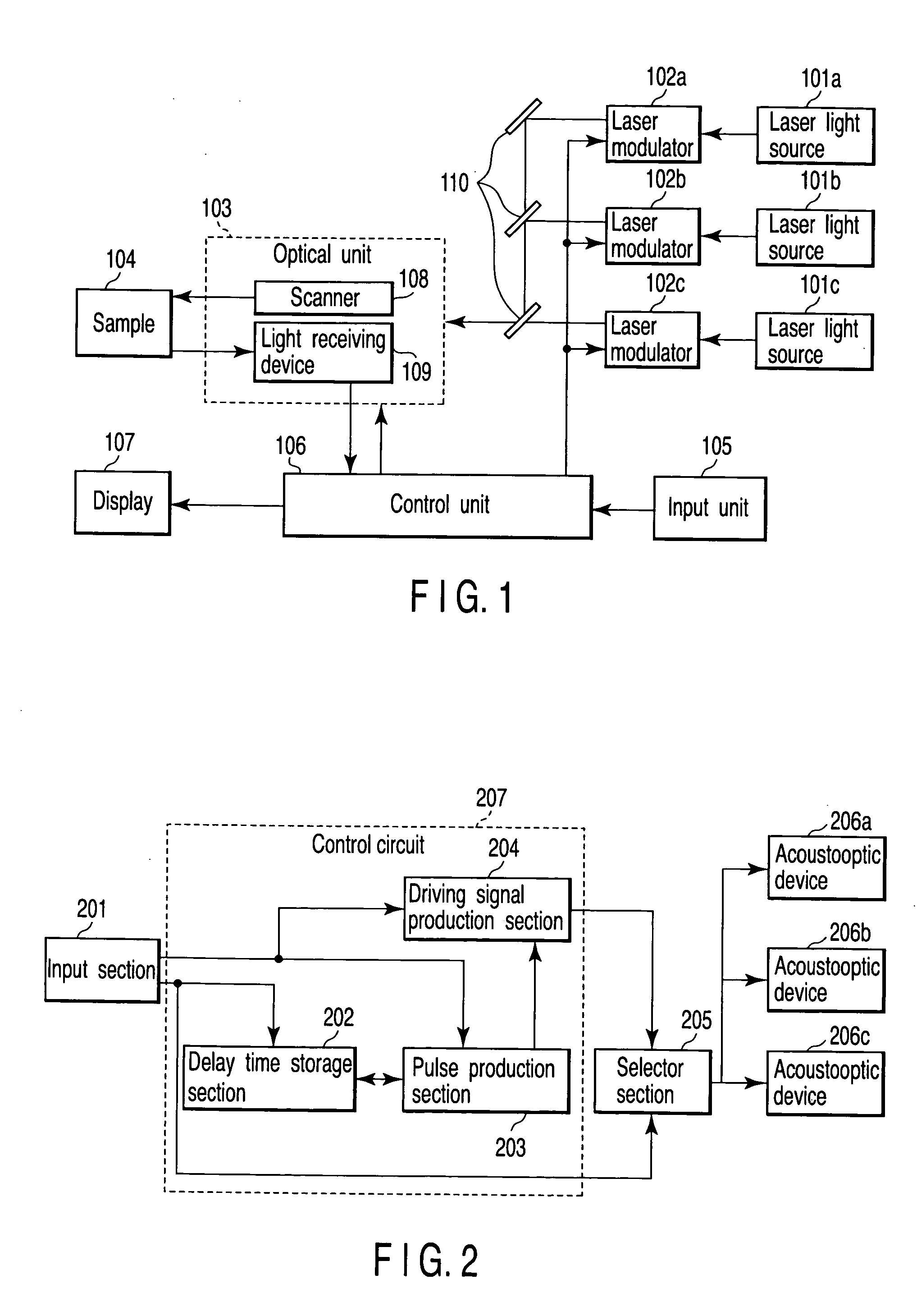
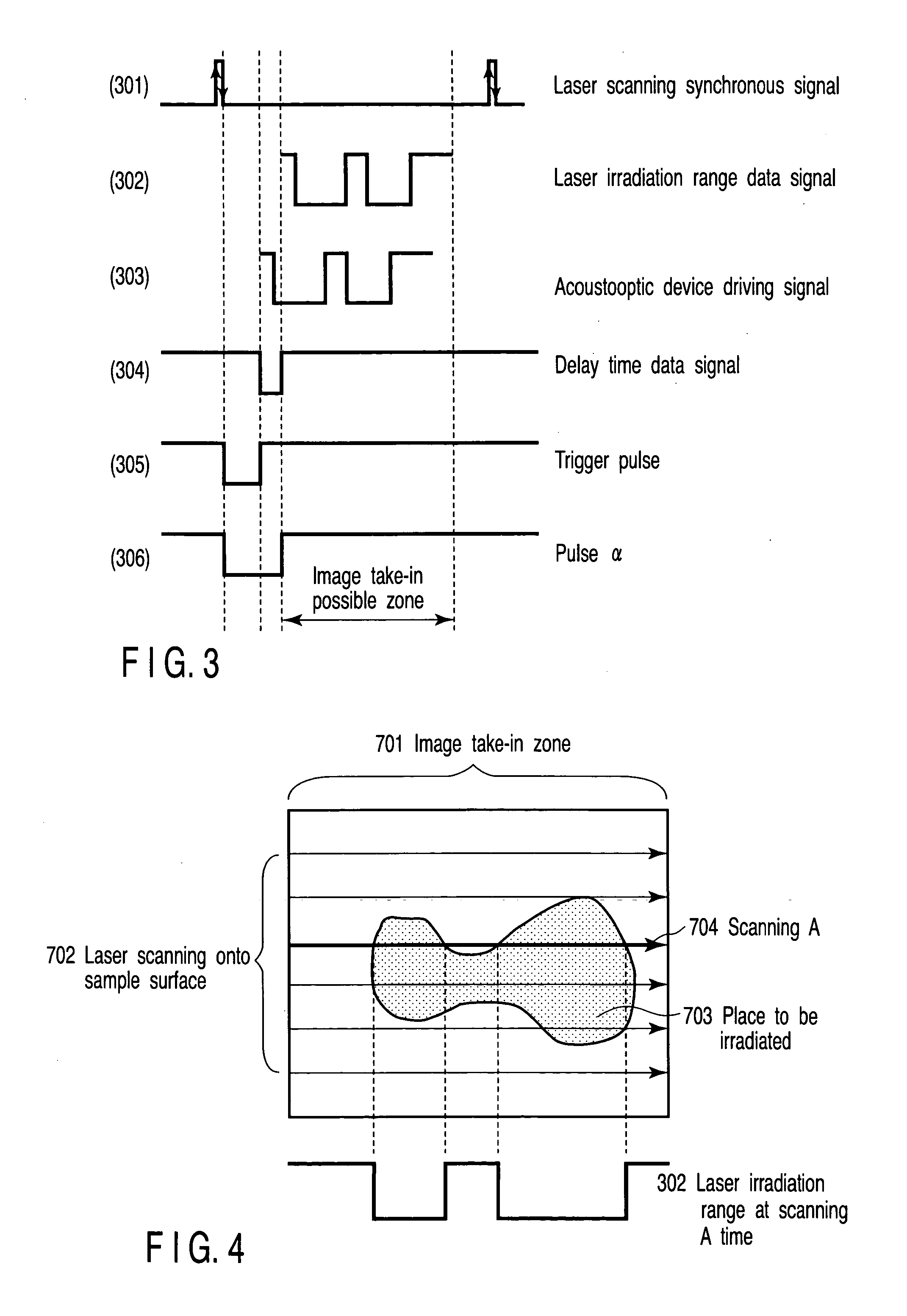
A scanning laser microscope of the present invention comprises at least one laser light source, a plurality of modulating sections for adjusting each laser light emitted from each laser light source, storage section for storing delay time information on an input / output of each modulating section, and signal production section for producing a driving signal to drive the modulating section selected from the plurality of modulating section based on the delay time information of the selected modulating section.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
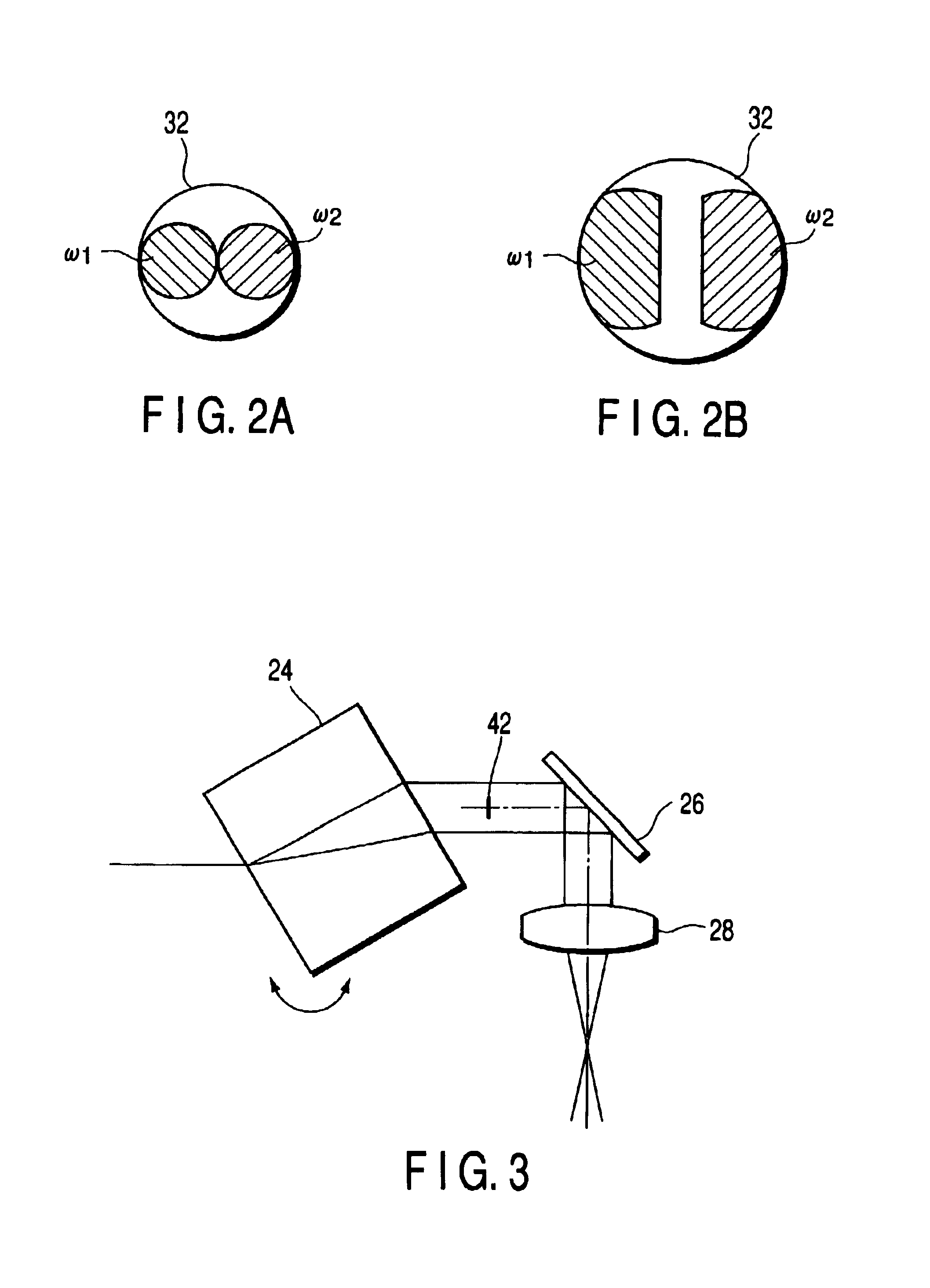
Device for generating line-shaped light beam and laser microscope
A laser microscope is provided, which is low in manufacturing costs and compact in structure. A laser beam emitted from a semiconductor laser is converted into a rectilinear light beam which has divergence in one direction by use of a micromirror device. The micromirror device comprises a plurality of micromirrors arranged in a two-dimensional array, and each micromirror is vibrated at a high speed by a driving pulse. Since each micromirror is movably supported by a hinge, a mirror layer of the micromirror is displaced in a curved manner by the electrostatic attractive force caused by the driving pulse. By this curved displacement of the mirror layer, each micromirror operates as a cylindrical mirror to convert an incident laser beam into an incoherent light beam which diverges in one direction. The rectilinear beam is projected to a sample through a beam deflection device and an objective lens, and a reflected light from the sample is made incident on a linear image sensor. Since the micromirror device is relatively low in costs and a relatively large diverging angle is obtained, the laser microscope low in manufacturing costs and compact in structure can be achieved.
Owner:OHKURA IND
Method and device for optical detection of the eye
InactiveUS20090304591A1High transparencyHigh optical contrastSenses disorderDiagnostics using lightDiseaseLaser Microscopy
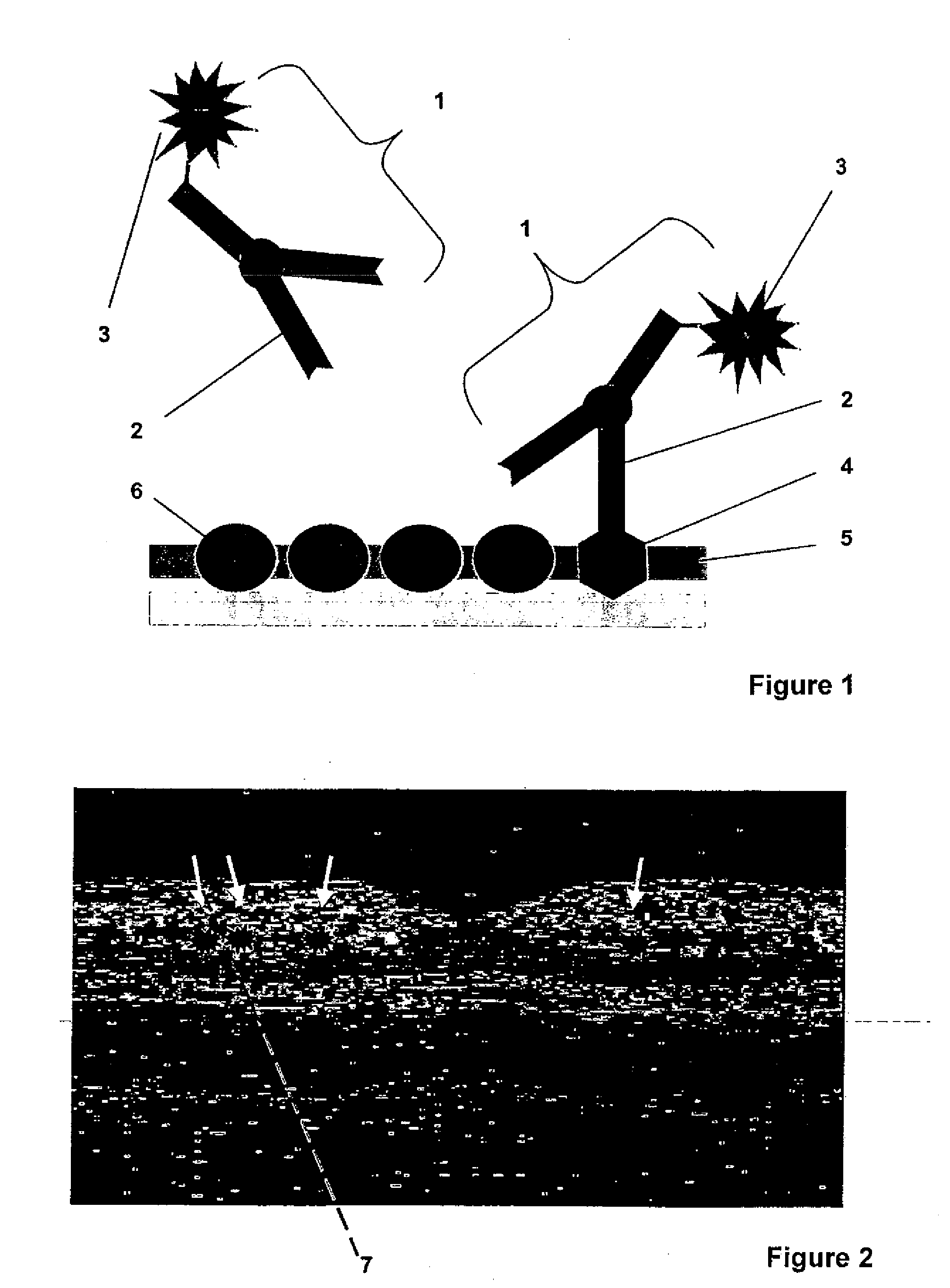
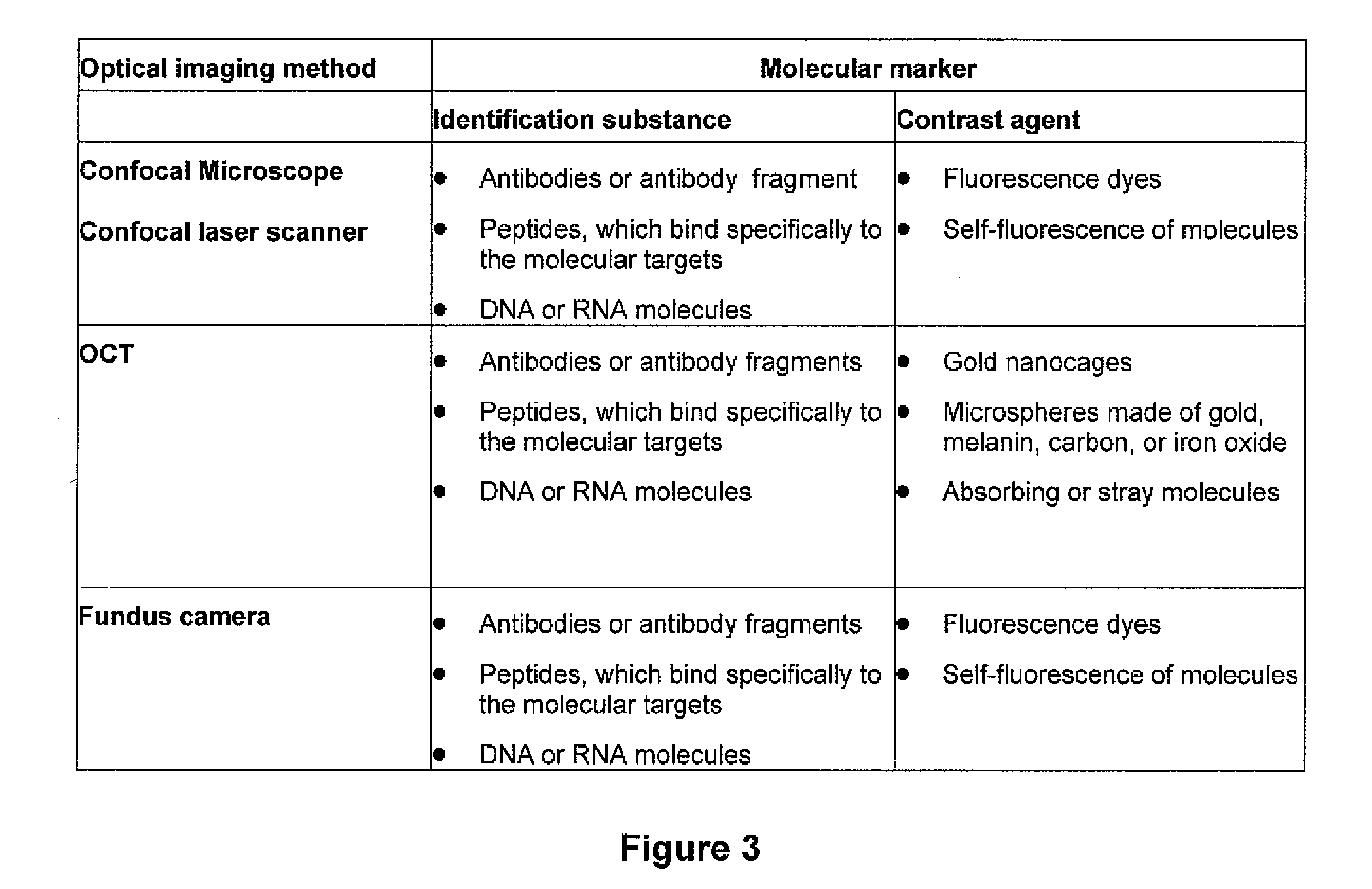
A solution for optical detection of the eye. Molecular markers are used for high-contrast diagnosis of eye diseases, other diseases, and other vital parameters which can be diagnosed in the eye. For optical detection of the eye, a molecular marker with spectral characteristics of absorption and / or scattering in the visual and infrared spectral region is introduced into the eye and bound to a specific target. The interaction of the molecular marker with the target is detected by means of optical imaging methods, such as fundus photography, confocal laser microscopy, polarisation-optical imaging methods, holographic methods or especially OCT methods. The use of optical methods is strongly preferred for the diagnosis of the eye as a result of the high transparency of the optical system of the eye compared to other body parts.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Translucent structure
ActiveUS20170139082A1Good anti-glare effectSparkle of it is sufficiently suppressedOptical elementsConvex structureEngineering
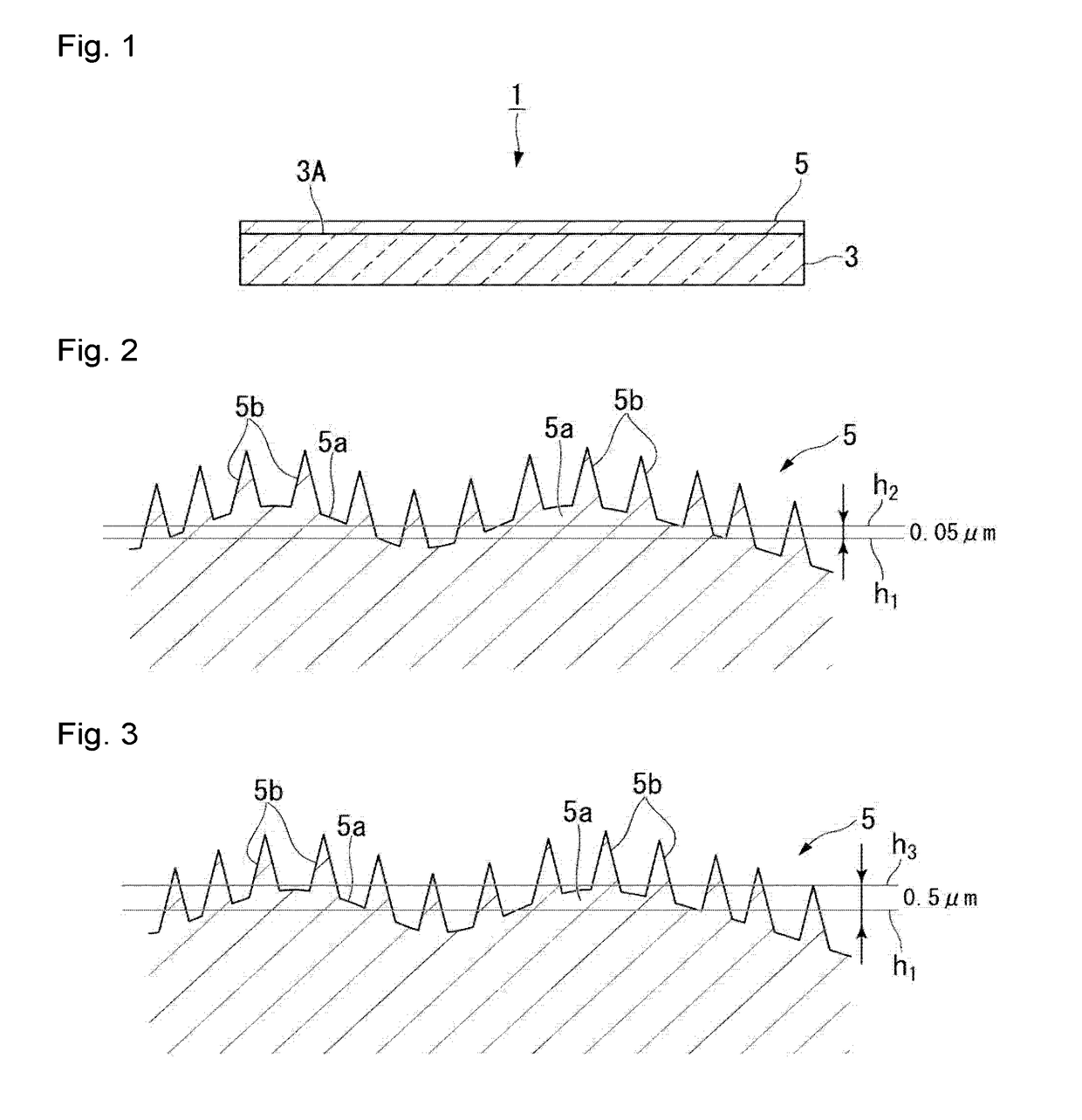
To provide a translucent structure, which is excellent in the antiglare property, and which has its sparkle sufficiently suppressed.The translucent structure of the present invention has the following concavo-convex structure on its surface. The concavo-convex structure: having first convex portions having a diameter of larger than 10 μm in a cross section at a height of 0.05 μm+the bearing height of a surface shape obtained by measuring a region of 101×135 μm to 111×148 μm by a laser microscope, and second convex portions having a diameter of larger than 1 μm in a cross section at a height of 0.5 μm+the above bearing height of the surface shape; the average diameter of the first convex portions being larger than 10 μm and at most 185 μm in a cross section at a height of 0.05 μm+the above bearing height of the surface shape; the maximum height of the first convex portions being from 0.2 to 8 μm based on a height at the lowest portion in the above region; and the number of the second convex portions being from 0.0004 to 1.2 per 1 um2, and the average height of the second convex portions being from 0.1 to 8 μm based on the above bearing height.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
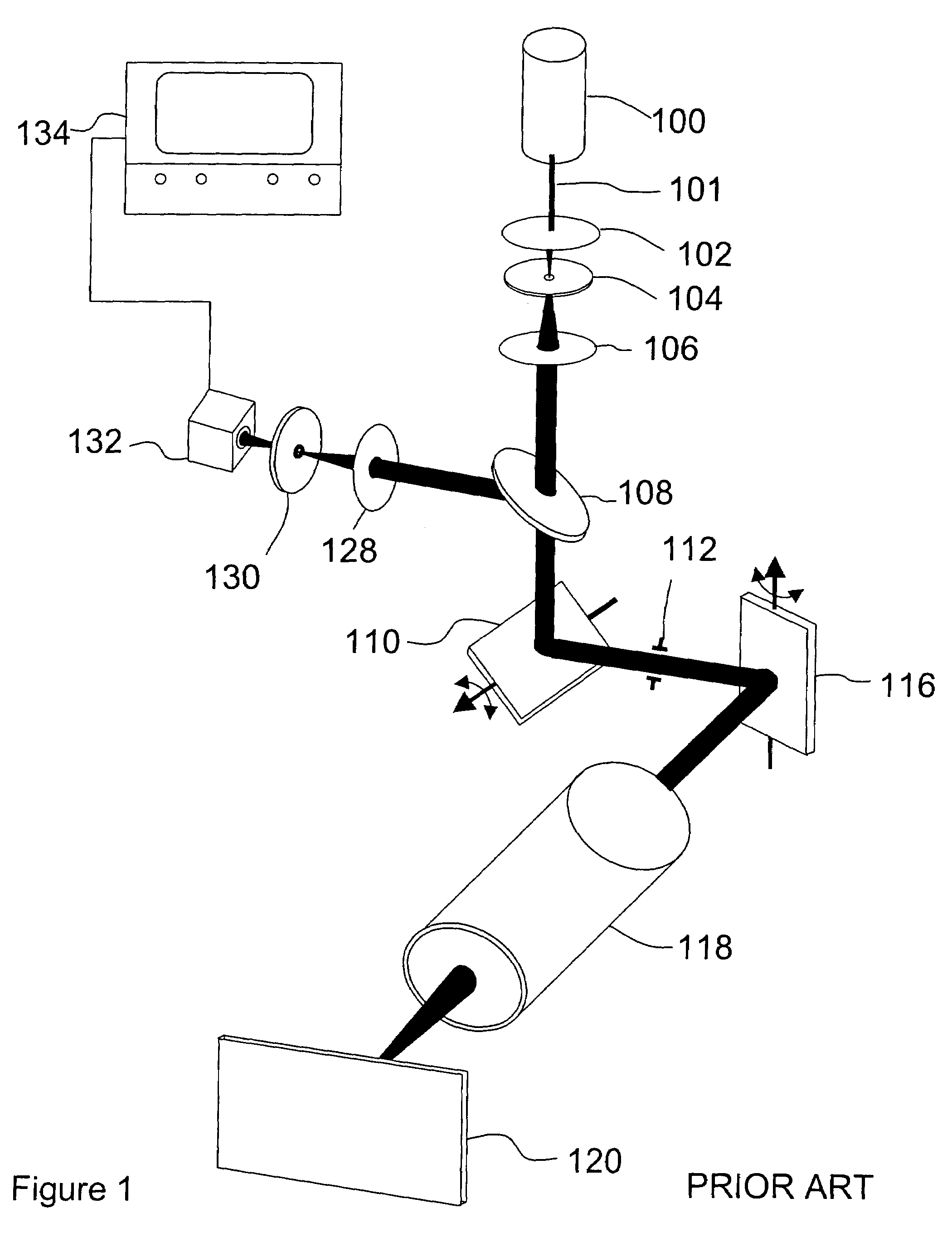
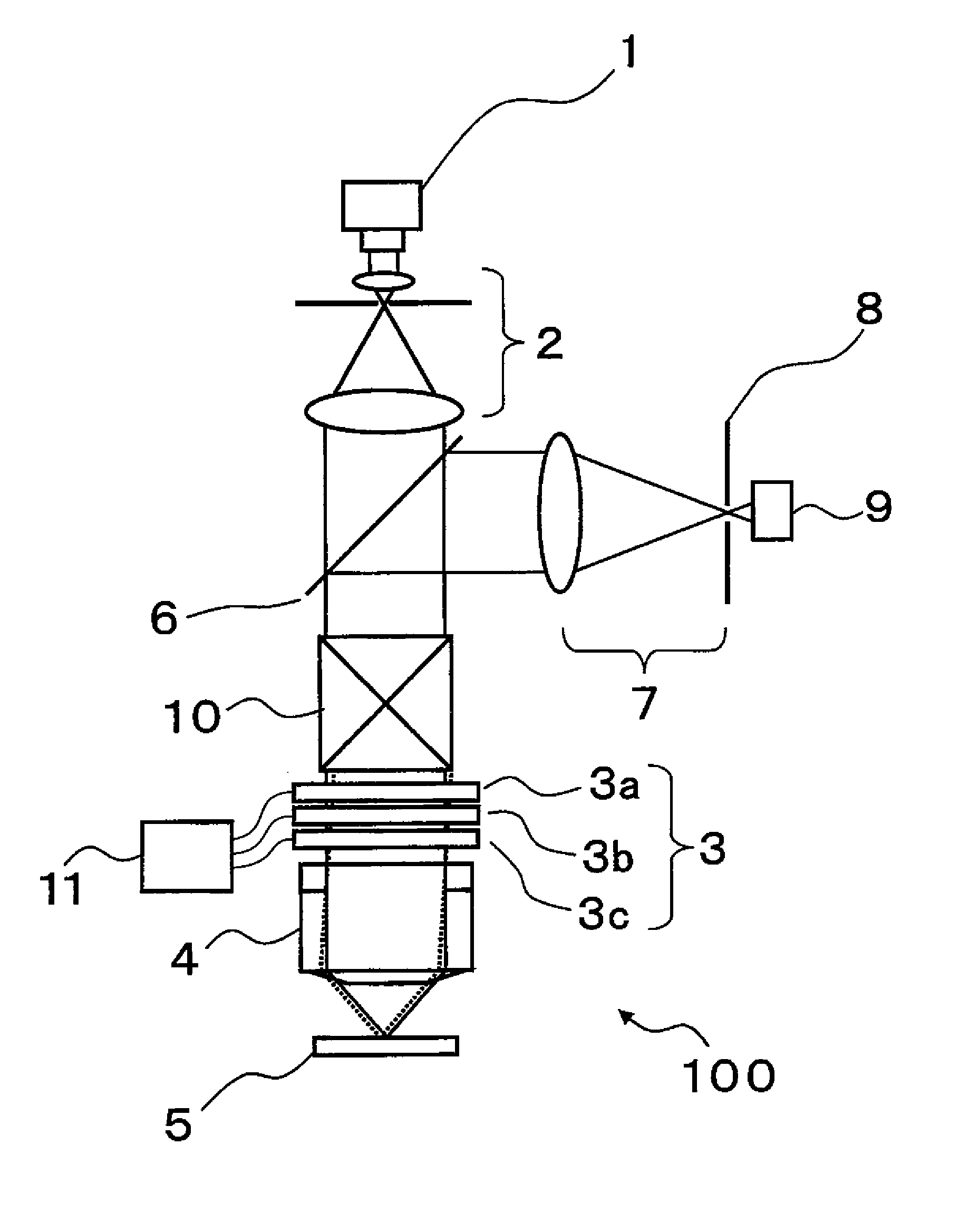
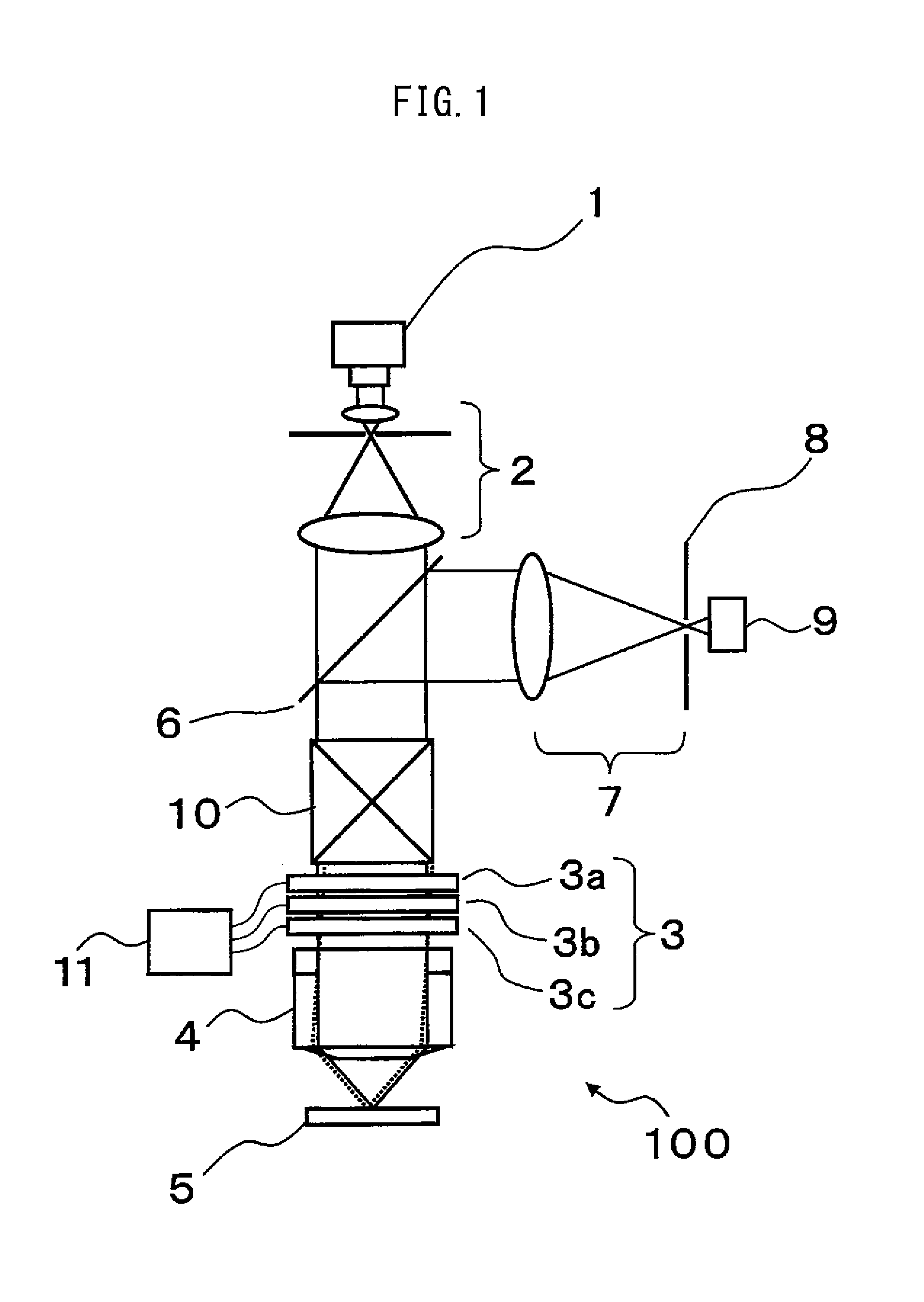
Imaging system having a fine focus
A new high resolution confocal and non-confocal scanning laser macroscope is disclosed which achieves fine focus and control of focus position by moving a lens in the intermediate optics. This arrangement is particularly useful for imaging specimens where it is difficult to focus by changing the distance between the scan lens and the specimen, for example for in-vivo imaging, photodynamic therapy, and image-guided surgery. It is also important to keep the lens-to-specimen distance constant when a liquid-immersion scan lens is used, in order to maintain a constant thickness of liquid between the lens and the specimen. In addition to being useful for confocal slicing, motion of the intermediate lens under computer control also enables dynamic focus and the ability to move the focal spot along a general path inside the specimen. Several applications of the imaging system are described. The macroscope images macroscopic specimens in reflected light, transmitted light, fluorescence, photoluminescence and multi-photon fluorescence.
Owner:HURON TECH INT
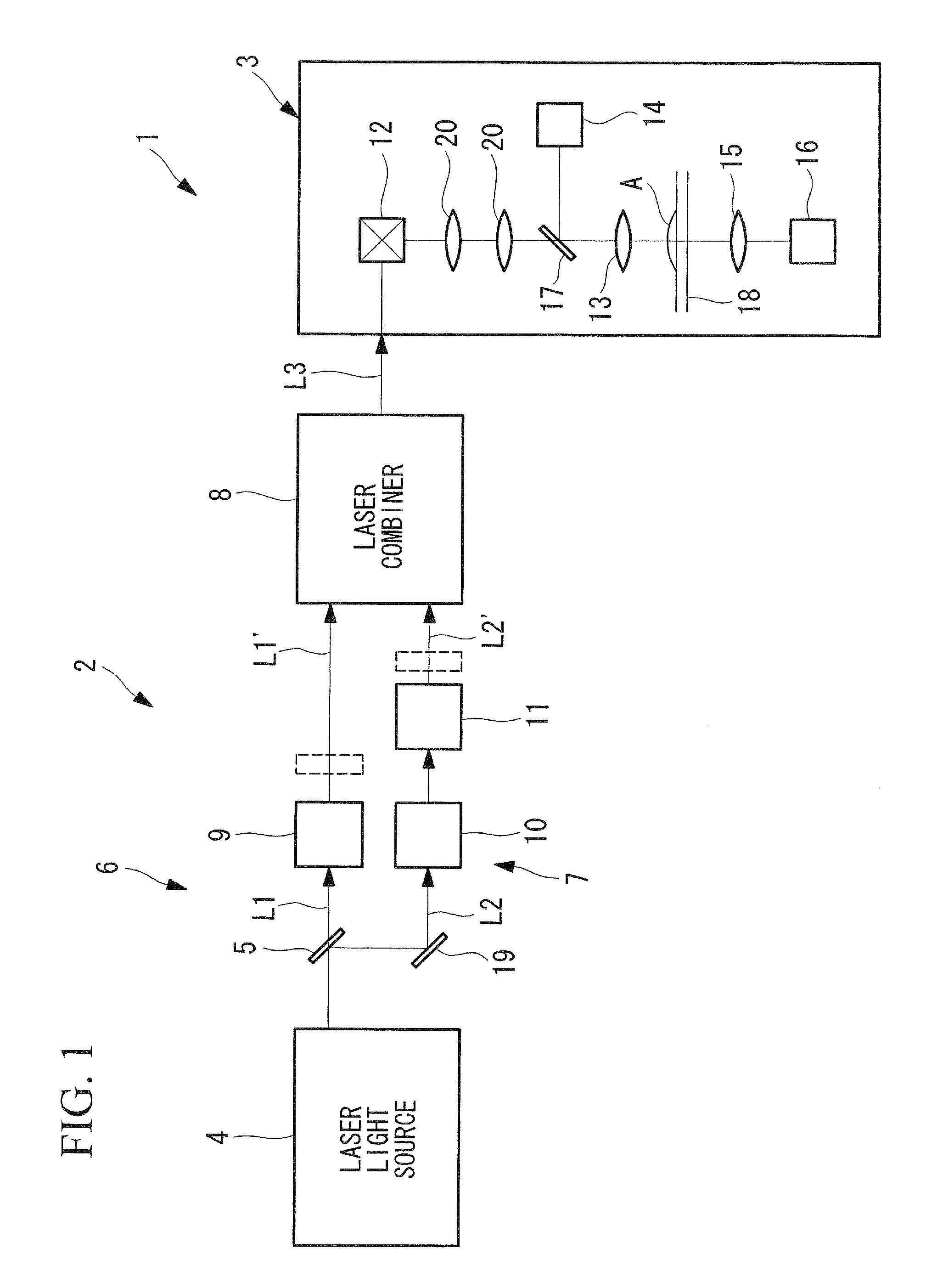
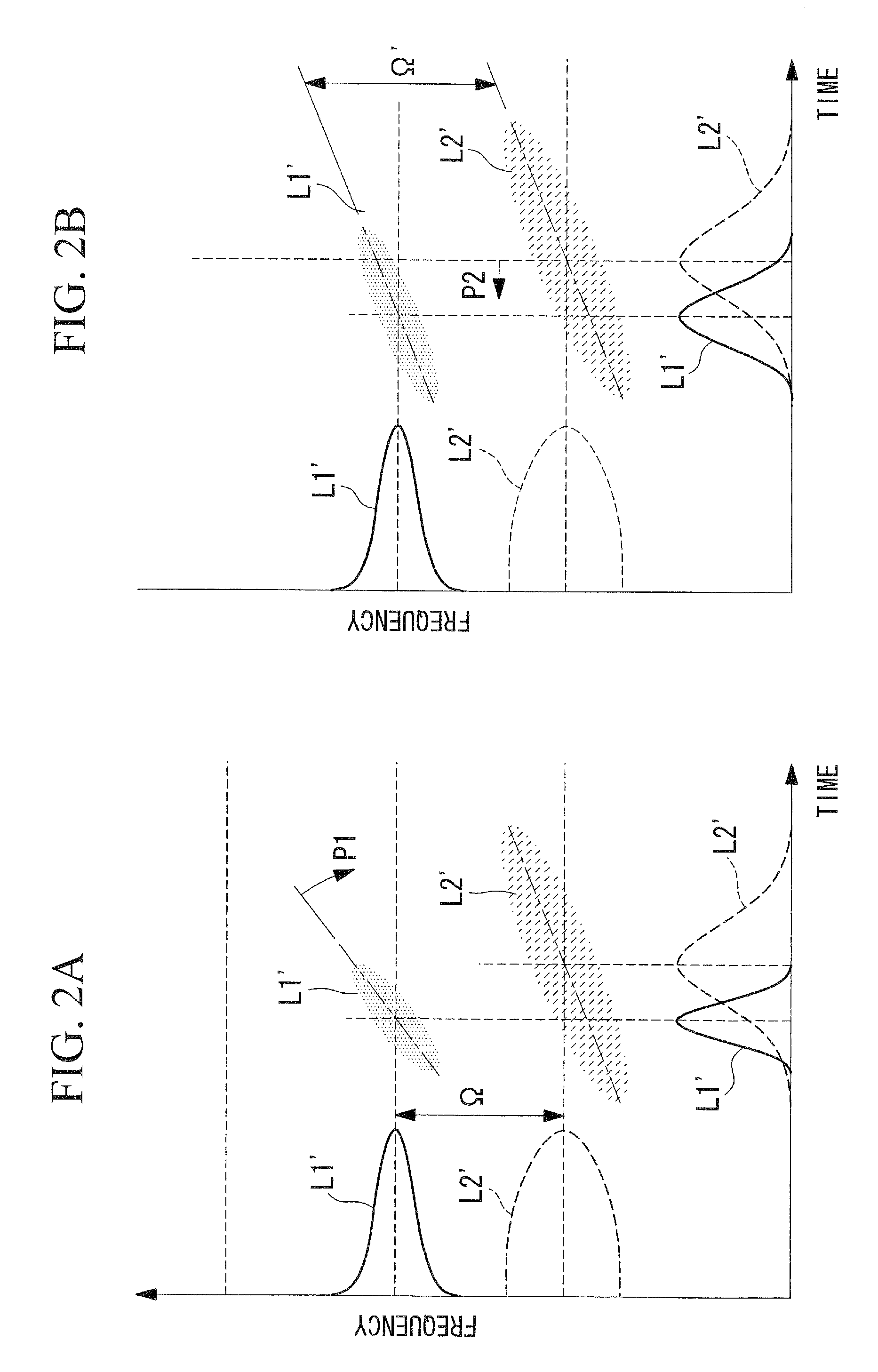
Apparatus for Temporal Displacement of White Light Laser Pulses
ActiveUS20120050849A1Accurate measurementEasy to measureLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPath lengthLaser light
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
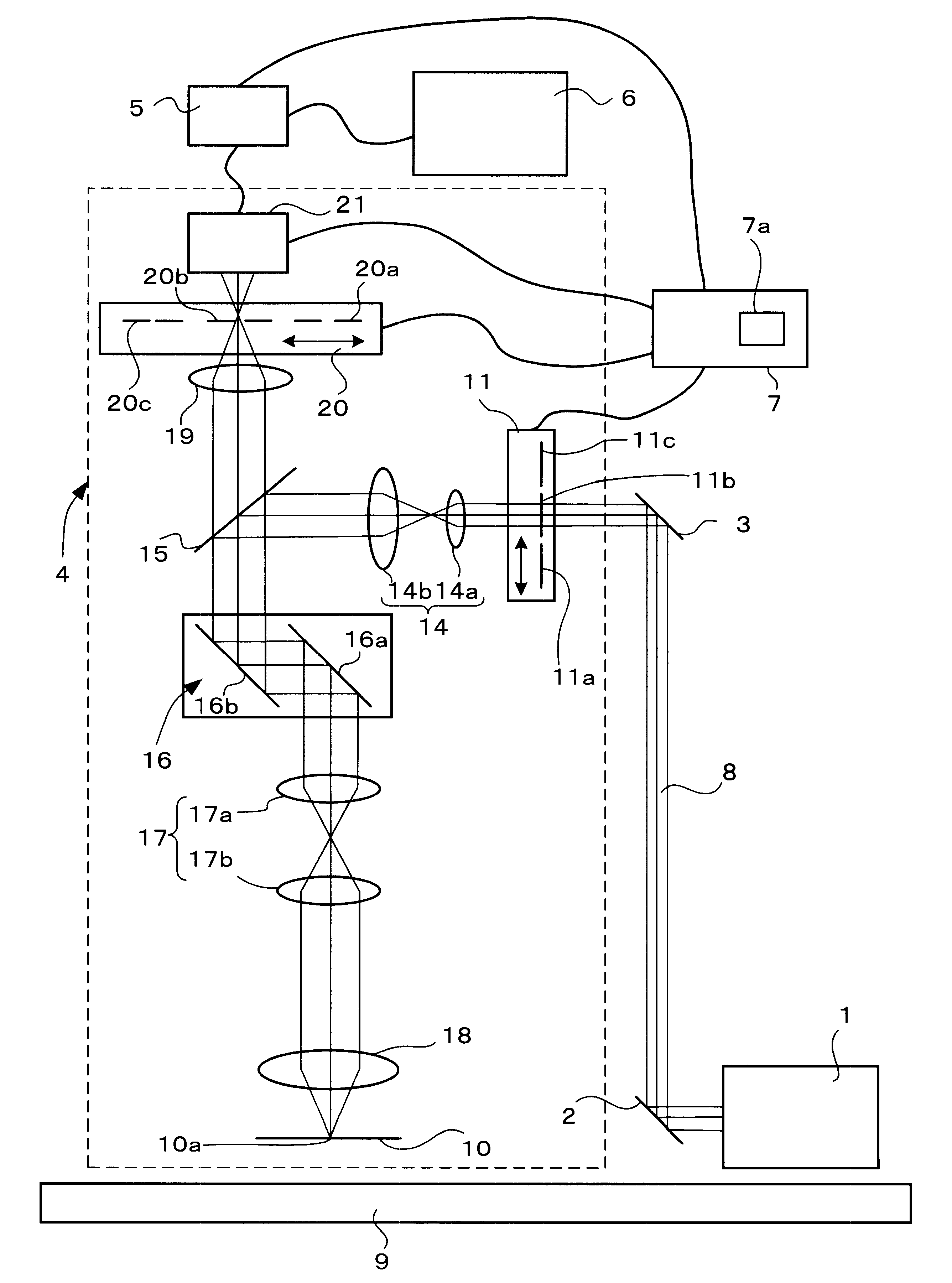
Laser microscope and confocal laser scanning microscope
InactiveUS6621628B1Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansConfocal laser scanning microscopeConfocal scanning microscopy
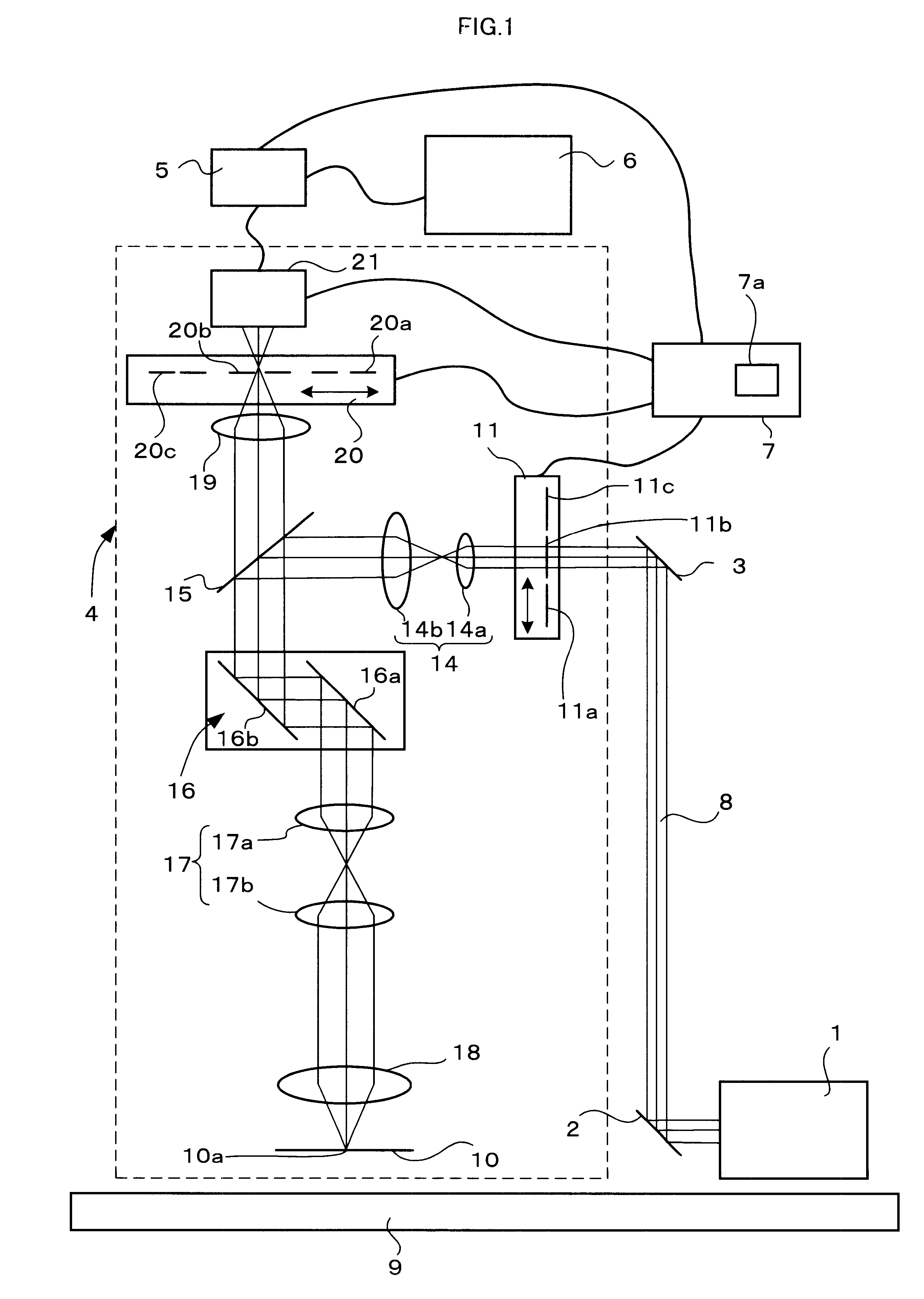
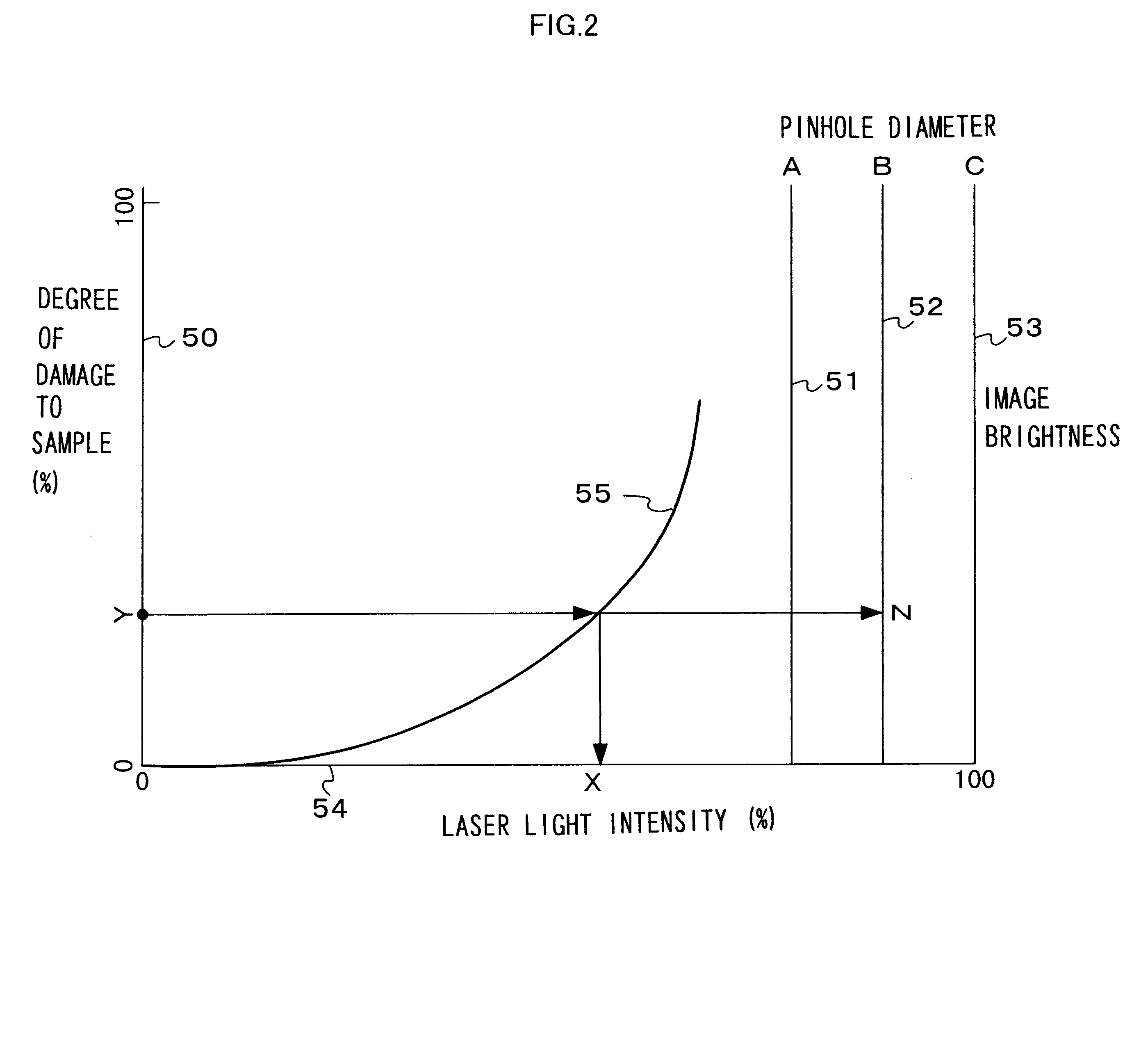
A laser microscope includes: a light source that emits deep ultraviolet laser light to be irradiated on a sample; a limiting device that sets a limit to an intensity of the deep ultraviolet laser light irradiated on the sample; a detection device that detects the deep ultraviolet laser light having been reflected from the sample; a storage device that stores first information related to damage to the sample corresponding to the intensity of the deep ultraviolet laser light; and a control device that controls the limiting device based upon the first information when a sample damage limit is input from outside.
Owner:NIKON CORP
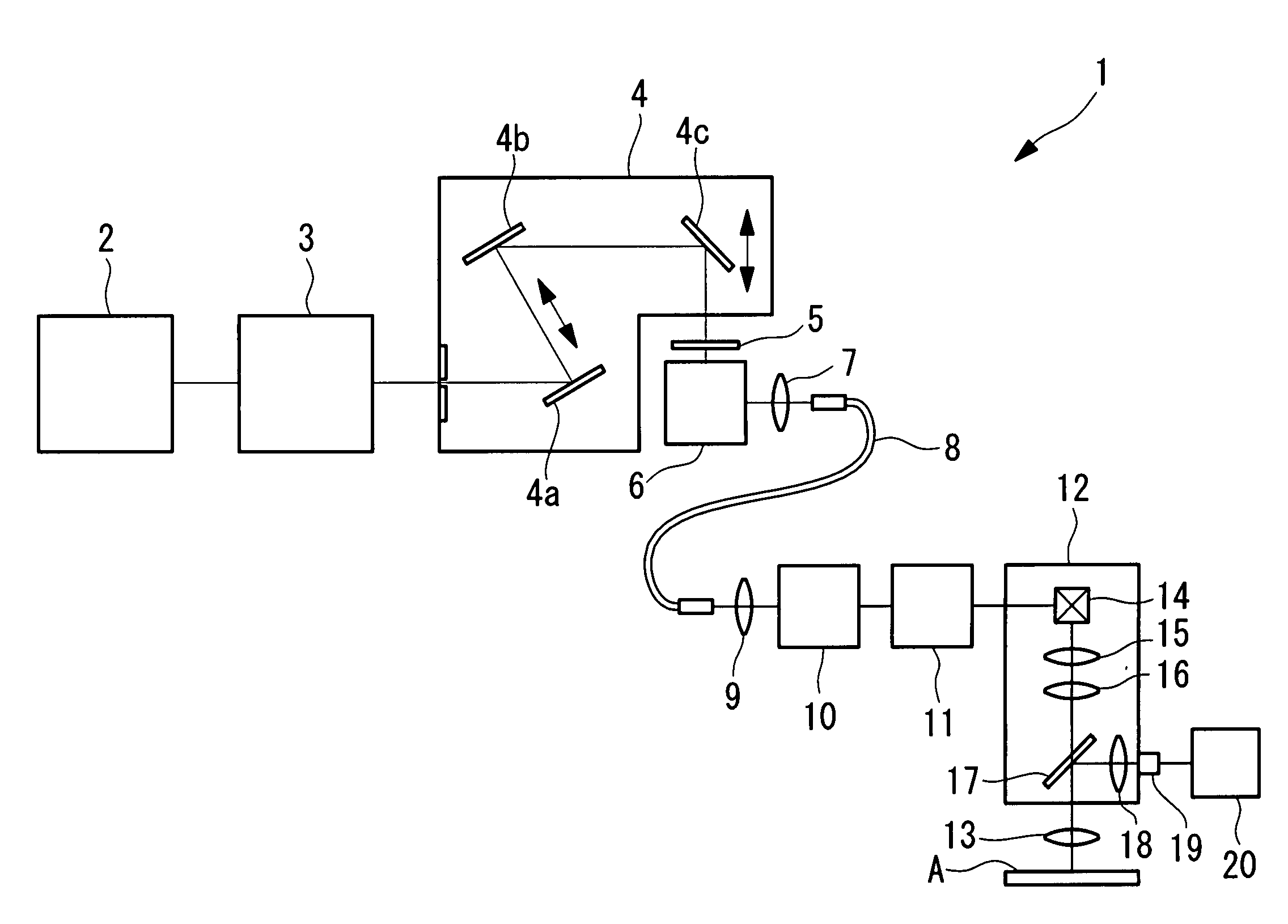
Laser microscope and control method for the same
It is possible to achieve a required field number and numerical aperture for microscope observation at a scanning speed equal to video-rate or higher and also to change the scanning speed with a simple configuration. The invention provides a laser microscope including a laser light source; a scanning unit configured to scan a specimen with laser light emitted from the laser light source; and an objective lens configured to focus the laser light scanned by the scanning unit on the specimen. The scanning unit is provided with an electro-optical deflecting element including an electro-optical crystal in which a refractive index gradient is induced by injecting electric current.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Method of manufacturing electrode laminate and method of manufacturing all-solid-state battery
ActiveUS20170092987A1Reduce thicknessShort-circuiting can be preventedElectrode rolling/calenderingFinal product manufactureAll solid stateSurface roughness
A method of manufacturing an electrode laminate, which includes an active material layer and a solid electrolyte layer formed on the active material layer, includes: an active material layer forming step of forming an active material layer; and a solid electrolyte layer forming step of forming a solid electrolyte layer on the active material layer by applying a solid electrolyte layer-forming slurry to the active material layer and drying the solid electrolyte layer-forming slurry. In this method, a surface roughness Ra value of the active material layer is 0.29 μm to 0.98 μm when calculated using a laser microscope.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Laser microscope apparatus
ActiveUS20090290150A1Generate efficientlyLow priceRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFluorescenceMolecular vibration
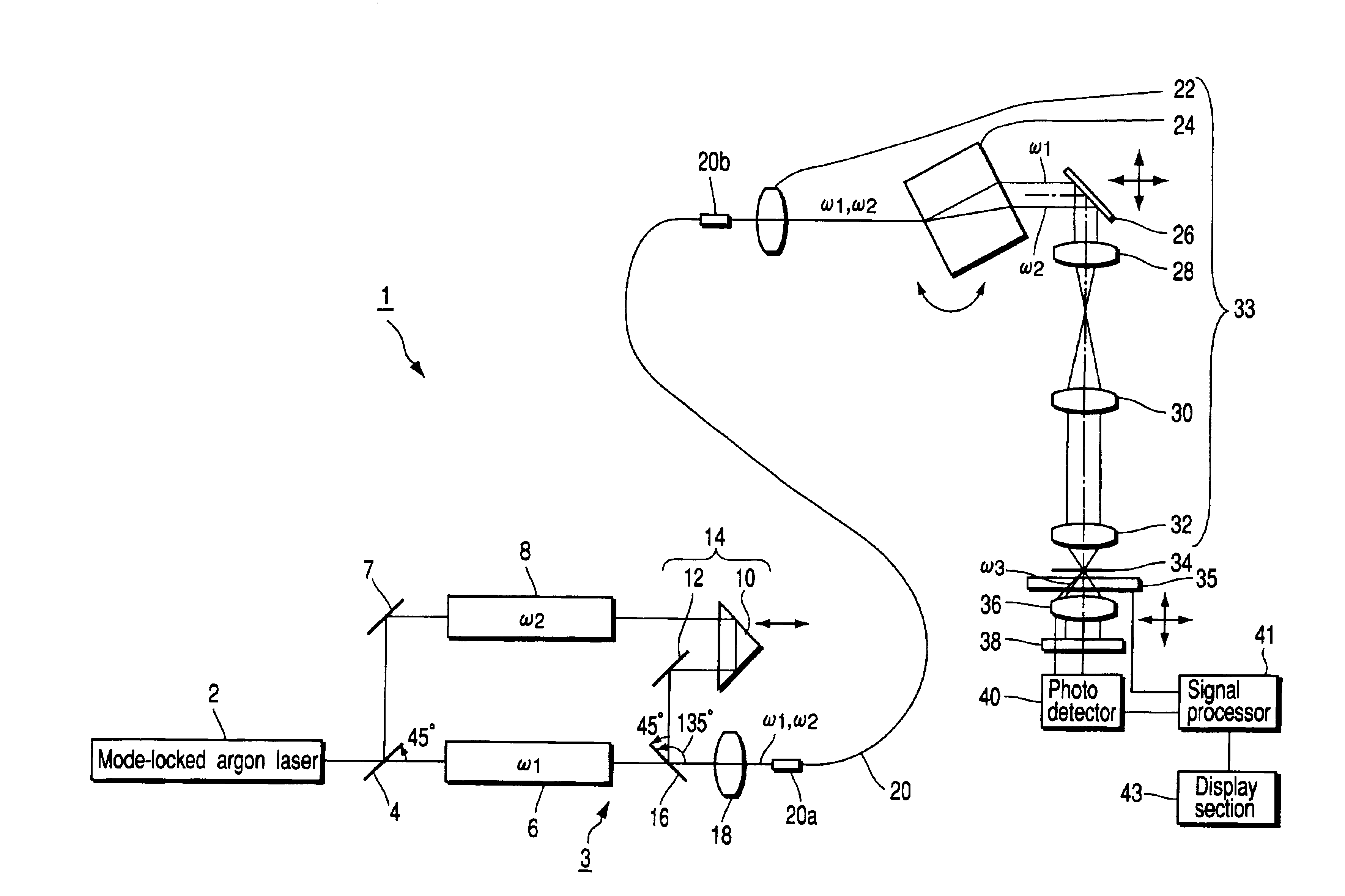
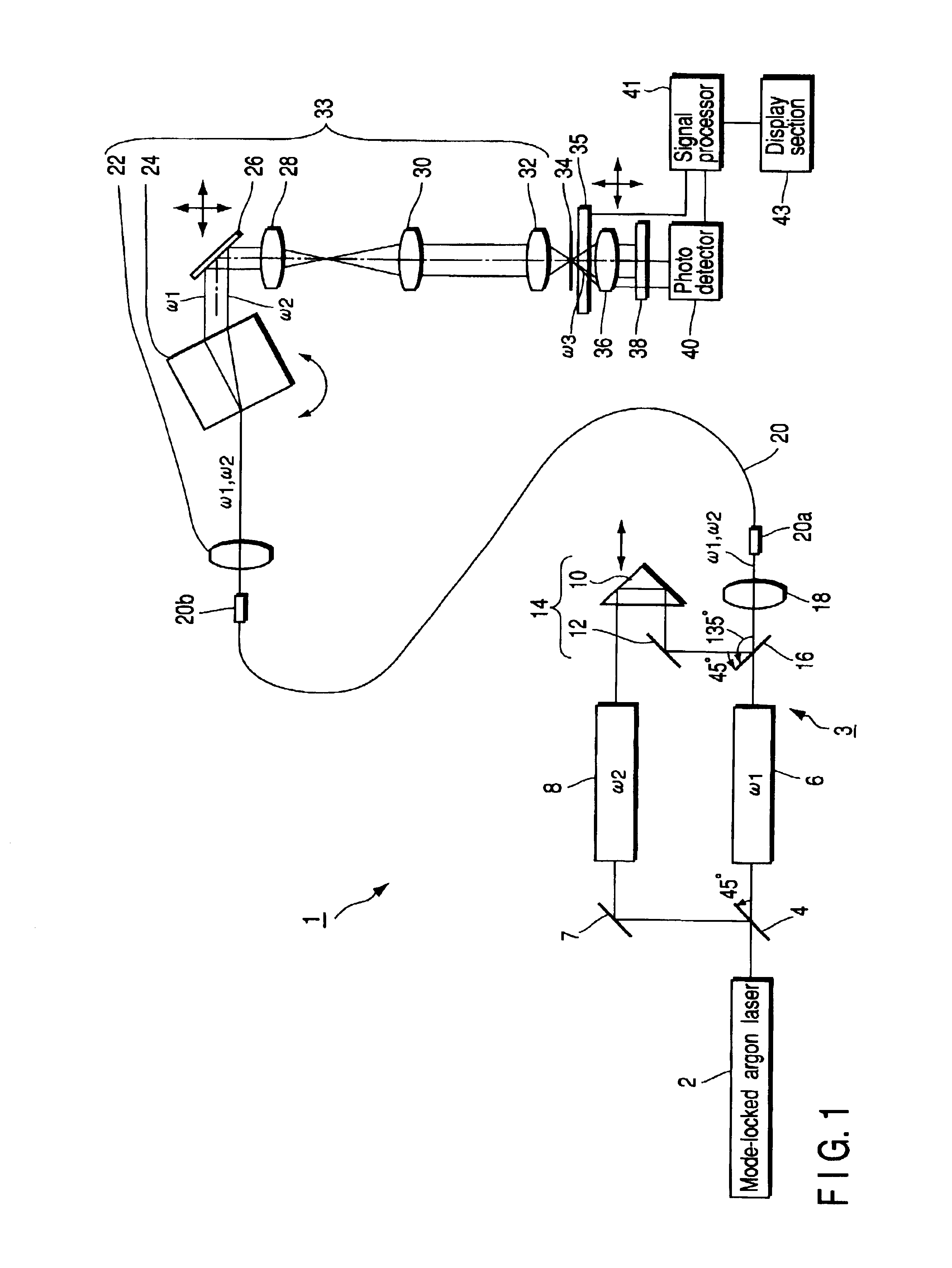
To enable both observations of coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering light and multiphoton fluorescence in a same apparatus so as to observe a specimen by various observation methods. There is provided a laser microscope apparatus comprising: two optical paths for guiding pulsed laser beams having two different frequencies whose frequency difference is approximately equal to a specific molecular vibration frequency in a specimen; a multiplexer for combining the pulsed laser beams guided through these two optical paths; and a frequency dispersion adjuster which is provided on at least one of these two optical paths, and is capable of adjustment to approximately equalize frequency dispersion quantities of the pulsed laser beams guided through the two optical paths.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Laser microscope
InactiveUS6934020B2Suppress generationEasy to detectRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringLight beamLaser light
A laser microscope includes a laser light emitting system which emits a pump beam and a Stokes beam having different frequencies, and a common optical fiber having one end and the other end. The pump beam and the Stokes beam emitted from the laser light emitting system are incident on the one end thereof and emitted from the other end thereof. A beam irradiating mechanism condenses and irradiates the pump beam and the Stokes beam emitted from the other end of the optical fiber, onto a sample via the objective lens, thereby making an anti-Stokes beam be emitted from the sample. A photo detector detects the anti-Stokes beam emitted from the sample. A beam selecting mechanism allows only the anti-Stokes beam of the pump beam, the Stokes beam and the anti-Stokes beam to be received on the photo detector.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD +1
Device for generating line-shaped light beam and laser microscope
ActiveUS20050036197A1Reduce manufacturing costCompact structureMicroscopesLight beamLaser Microscopy
A laser microscope is provided, which is low in manufacturing costs and compact in structure. A laser beam emitted from a semiconductor laser is converted into a rectilinear light beam which has divergence in one direction by use of a micromirror device. The micromirror device comprises a plurality of micromirrors arranged in a two-dimensional array, and each micromirror is vibrated at a high speed by a driving pulse. Since each micromirror is movably supported by a hinge, a mirror layer of the micromirror is displaced in a curved manner by the electrostatic attractive force caused by the driving pulse. By this curved displacement of the mirror layer, each micromirror operates as a cylindrical mirror to convert an incident laser beam into an incoherent light beam which diverges in one direction. The rectilinear beam is projected to a sample through a beam deflection device and an objective lens, and a reflected light from the sample is made incident on a linear image sensor. Since the micromirror device is relatively low in costs and a relatively large diverging angle is obtained, the laser microscope low in manufacturing costs and compact in structure can be achieved.
Owner:OHKURA IND
Carrier-Attached Copper Foil, Laminate, Method For Producing Printed Wiring Board, And Method For Producing Electronic Device
ActiveUS20170042036A1Improve surface smoothnessReduce etch timeElectrical connection printed elementsCircuit susbtrate materialsISO 25178Inter layer
Provided herein is a carrier-attached copper foil having desirable fine circuit formability. The carrier-attached copper foil includes a carrier, an interlayer, and an ultrathin copper layer in this order. The maximum trough depth Sv as measured with a laser microscope according to ISO 25178 on a surface of a bismaleimide-triazine resin substrate exposed by detaching the carrier and etching and removing the ultrathin copper layer after the carrier-attached copper foil is heat pressed against the resin substrate from the ultrathin copper layer side under the pressure of 20 kgf / cm2 at 220° C. for 2 hours is 0.181 to 2.922 μm.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Copper foil for secondary battery negative electrode power collector
InactiveCN102725892AImprove adhesionReduce weight thickness deviationElectrolytic inorganic material coatingElectrode carriers/collectorsWeather resistanceElectrical battery
Provided is a copper foil for a secondary battery negative electrode power collector, which is obtained by performing a roughing process on both of the front and back surfaces of a rolled copper alloy foil. The copper foil is characterized in that, in the case where an average surface roughness Ra of the front and back surfaces which is measured by a laser microscope is 0.04 to 0.20 [mu]m, and a calculation value (C) is obtained from (A) / (B) = (C) in which (A) represents a three-dimensional surface area that is obtained by measuring the surface of the roughed surface by the laser microscope, and (B) represents a two-dimensional area, which is a projection area at the time of the measurement of the three-dimensional surface area, and in the case where a calculation value (C') is obtained from (A') / (B') = (C') in which (A'); represents a three-dimensional surface area that is obtained by measuring the surface of a rolled copper foil and a copper alloy foil which are not subjected to the roughing process by the laser microscope, and (B') represents a two-dimensional area, which is a projection area at the time of the measurement of the three-dimensional surface area, 1.0 < (C) / (C') < 1.1 is satisfied. The copper foil for a secondary battery negative electrode power collector is excellent in adhesion of secondary battery active materials, is capable of reducing the variation of weight thicknesses of the secondary battery active materials, and is also excellent in weather resistance and heat resistance.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
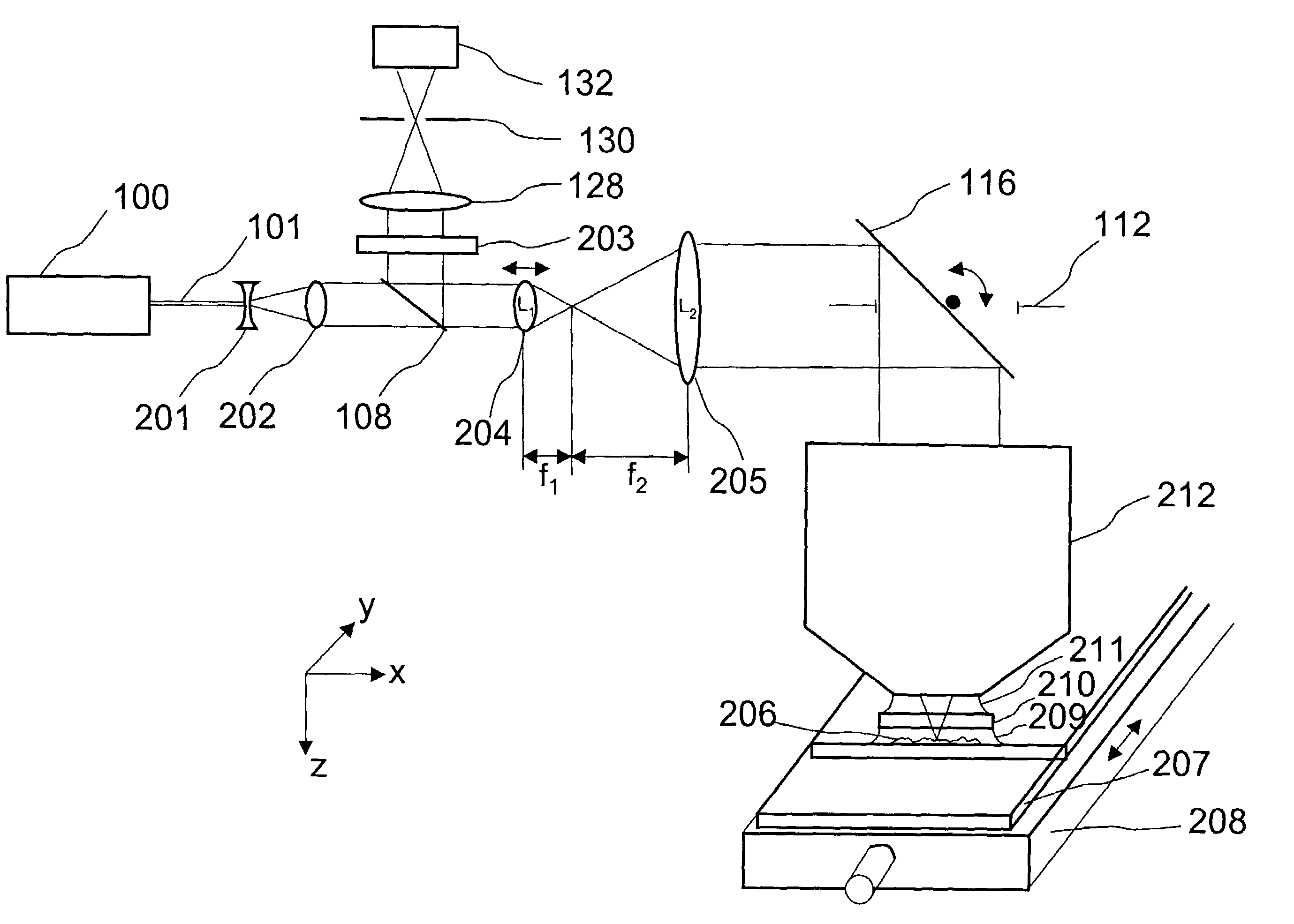
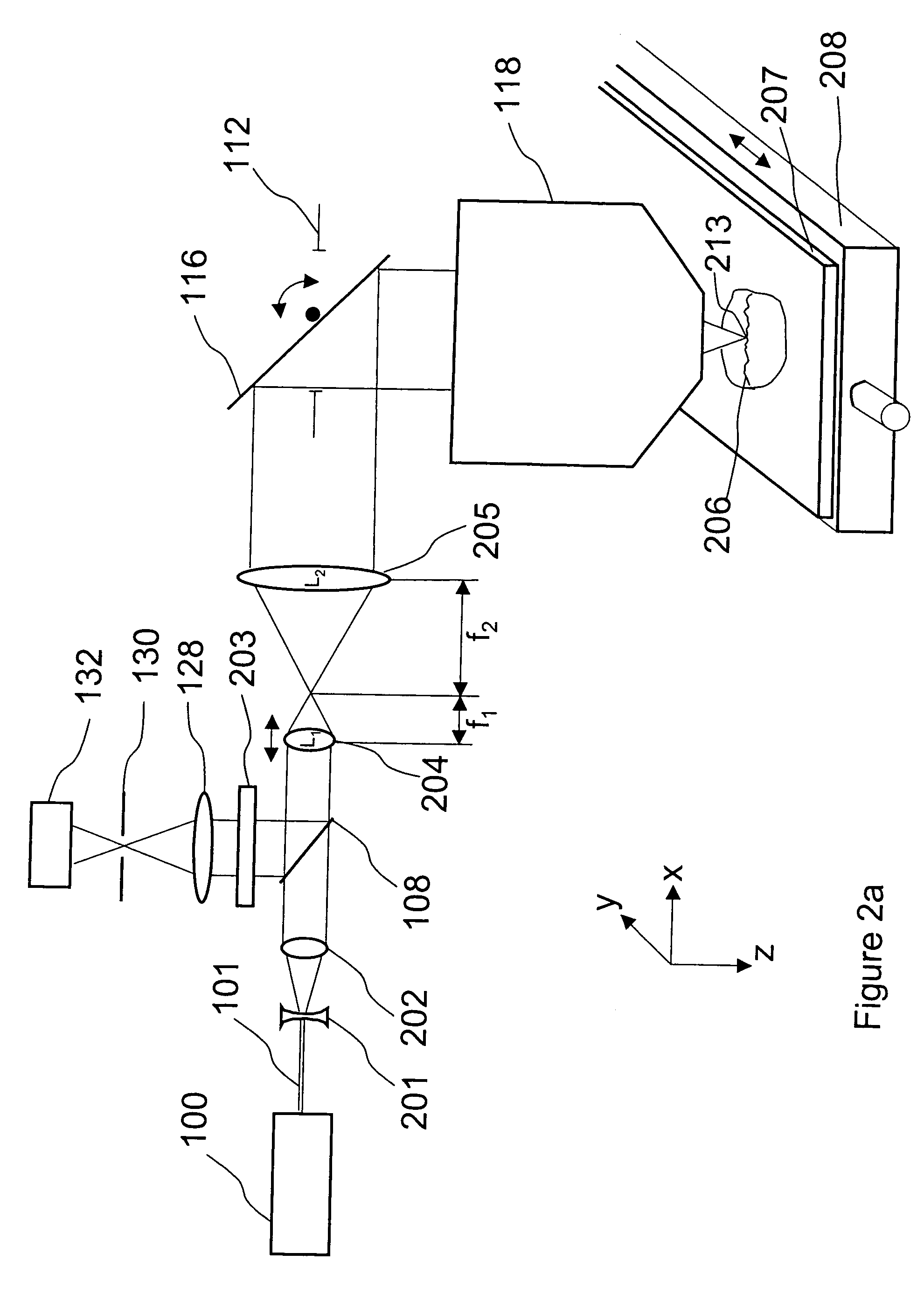
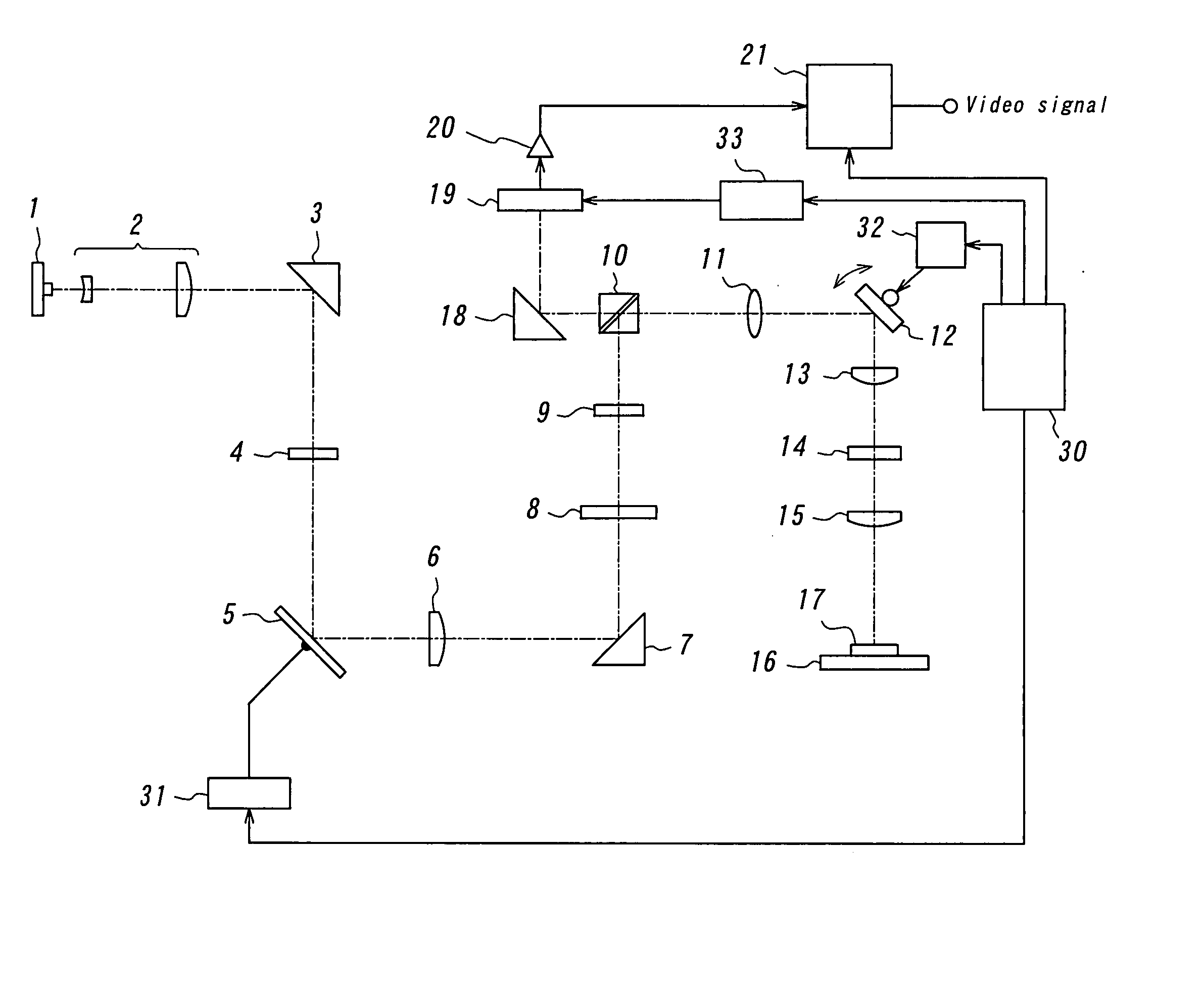
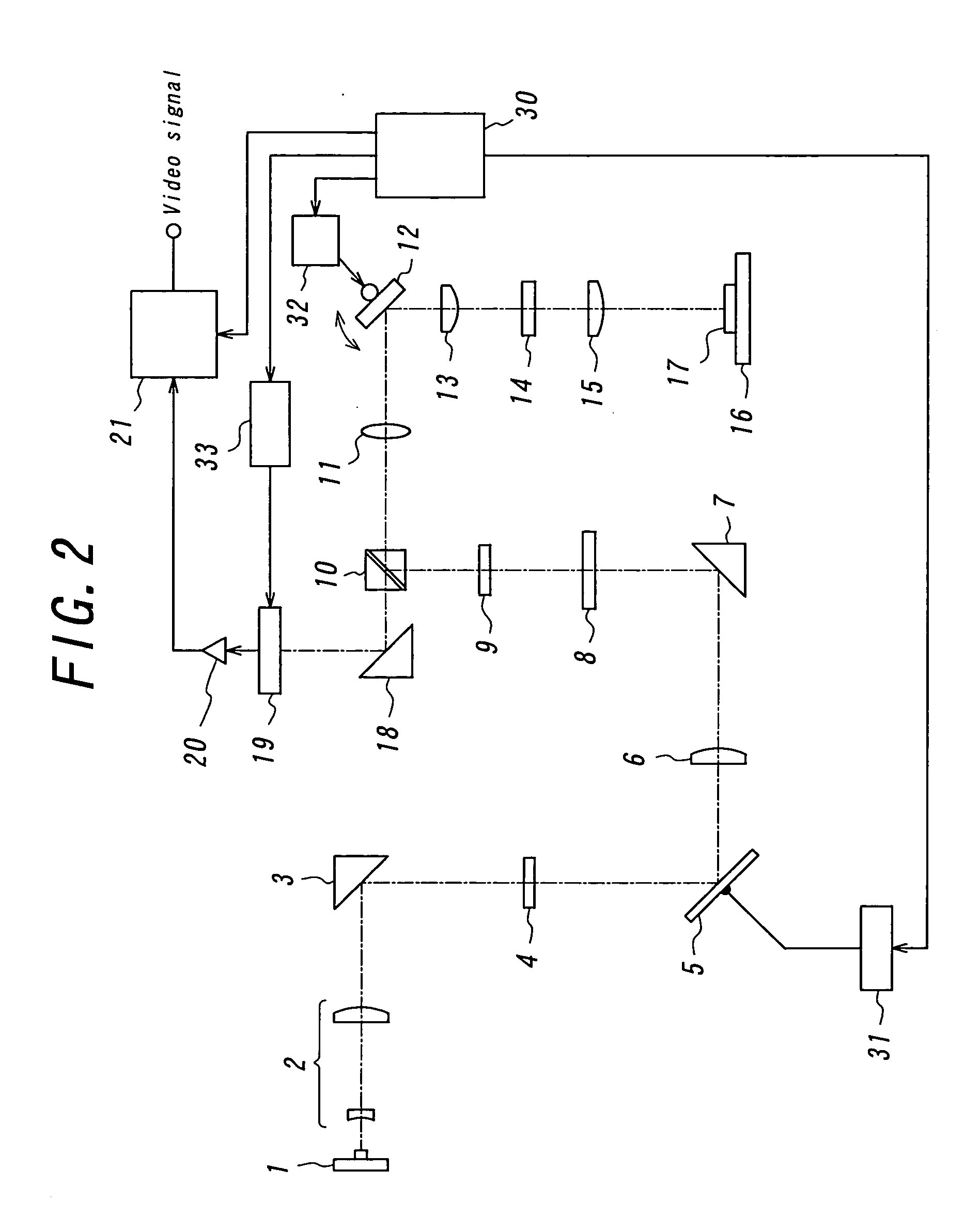
Scanning laser microscope with wave-front sensor
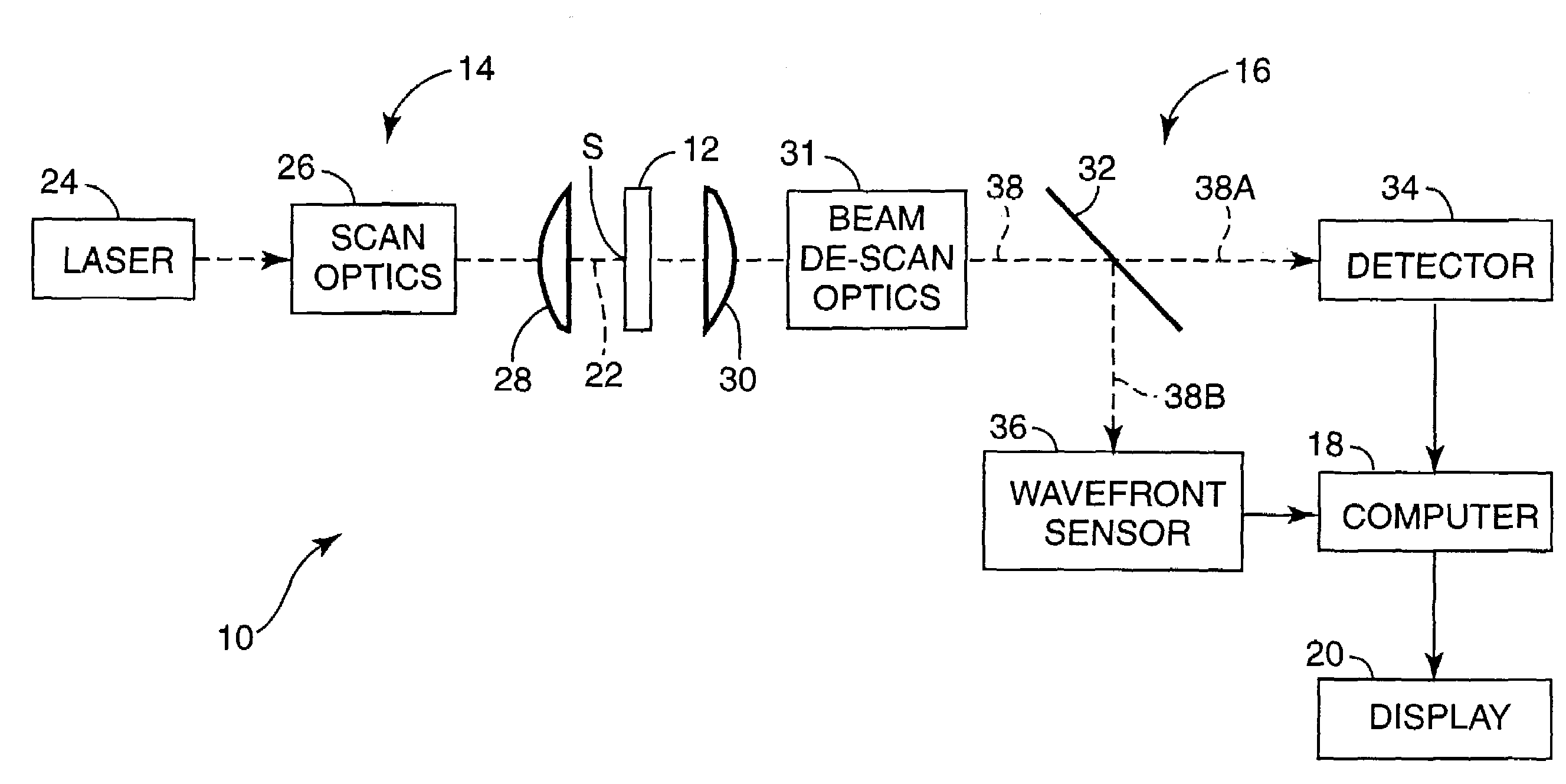
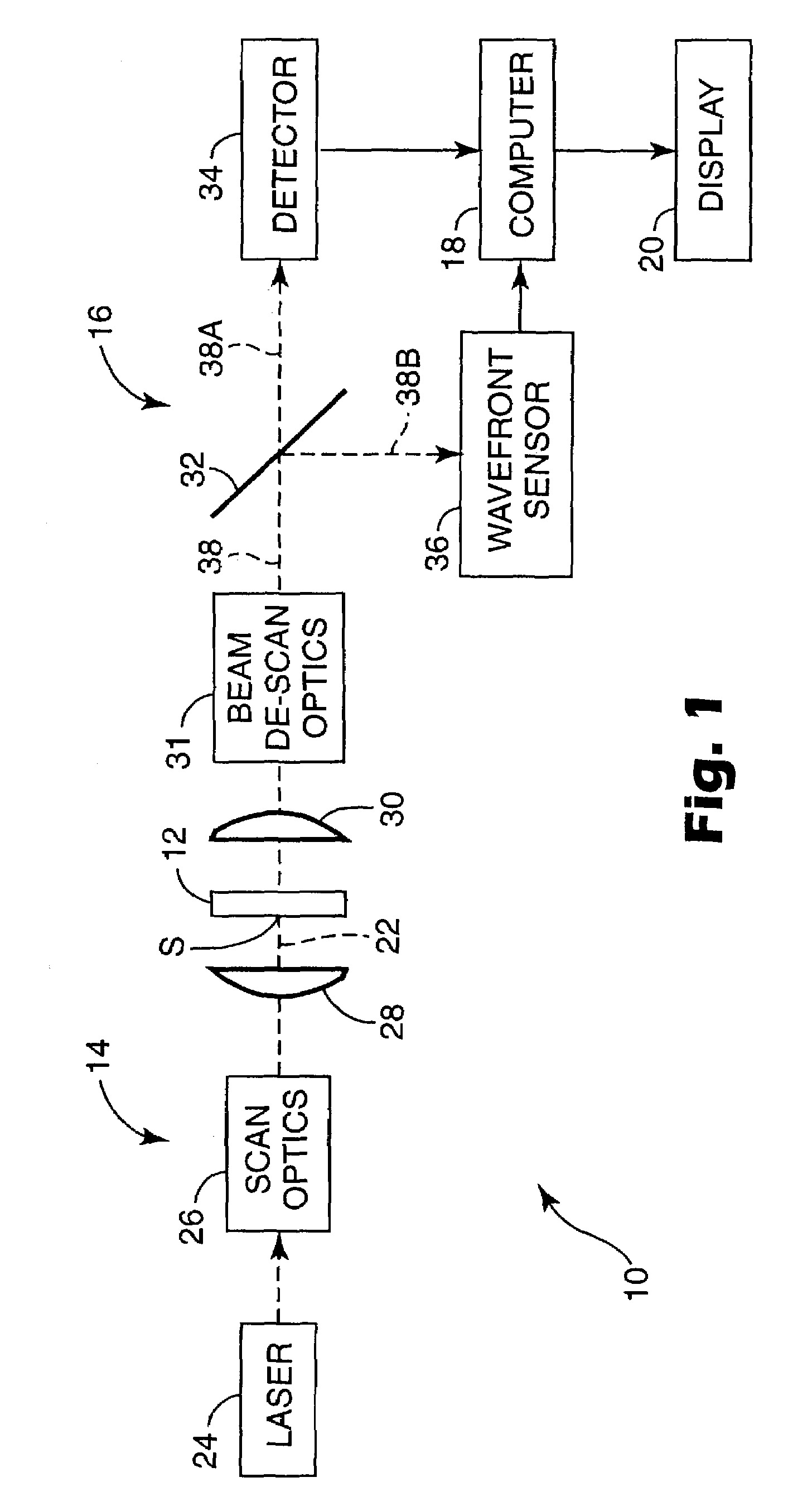
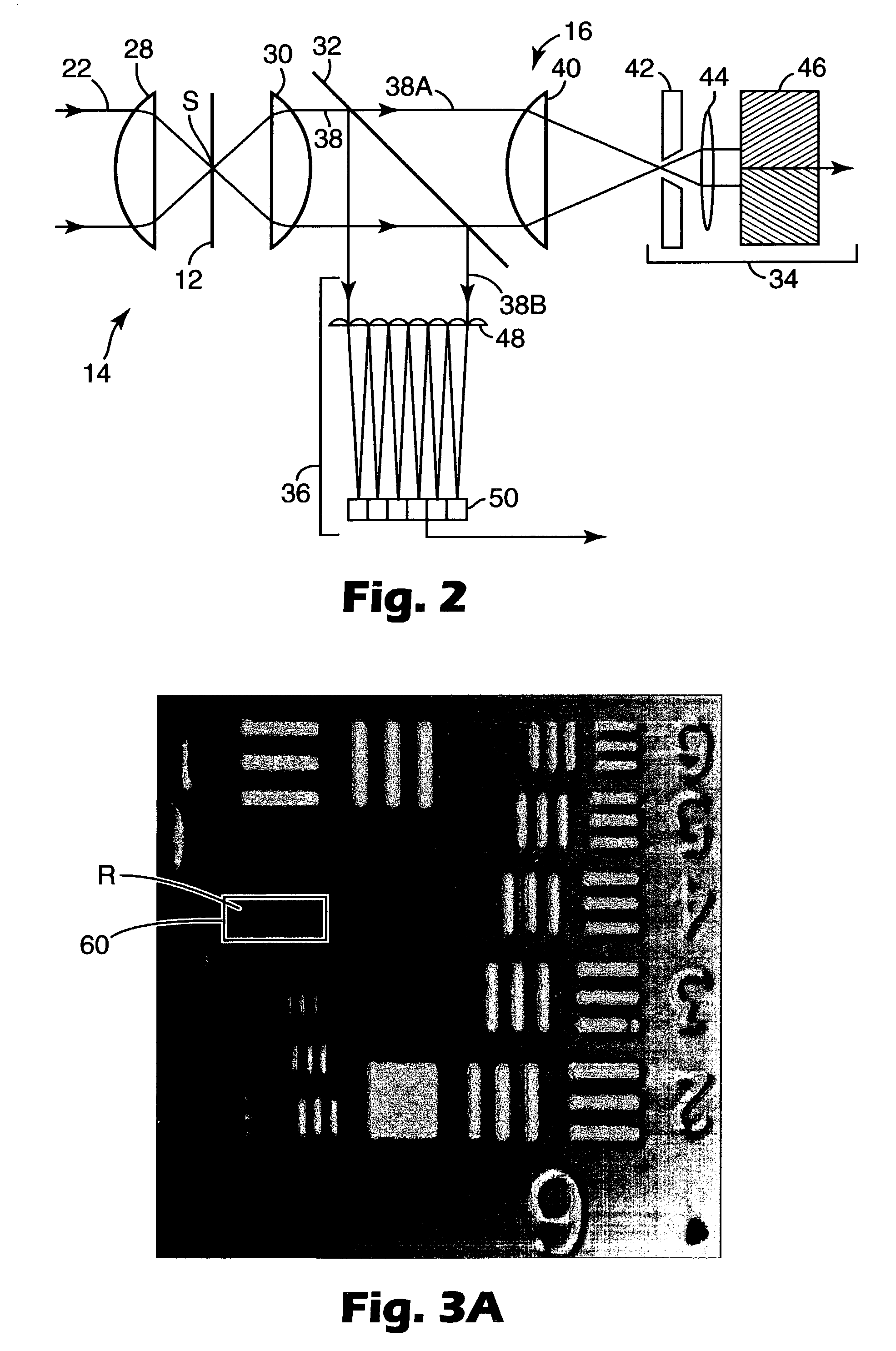
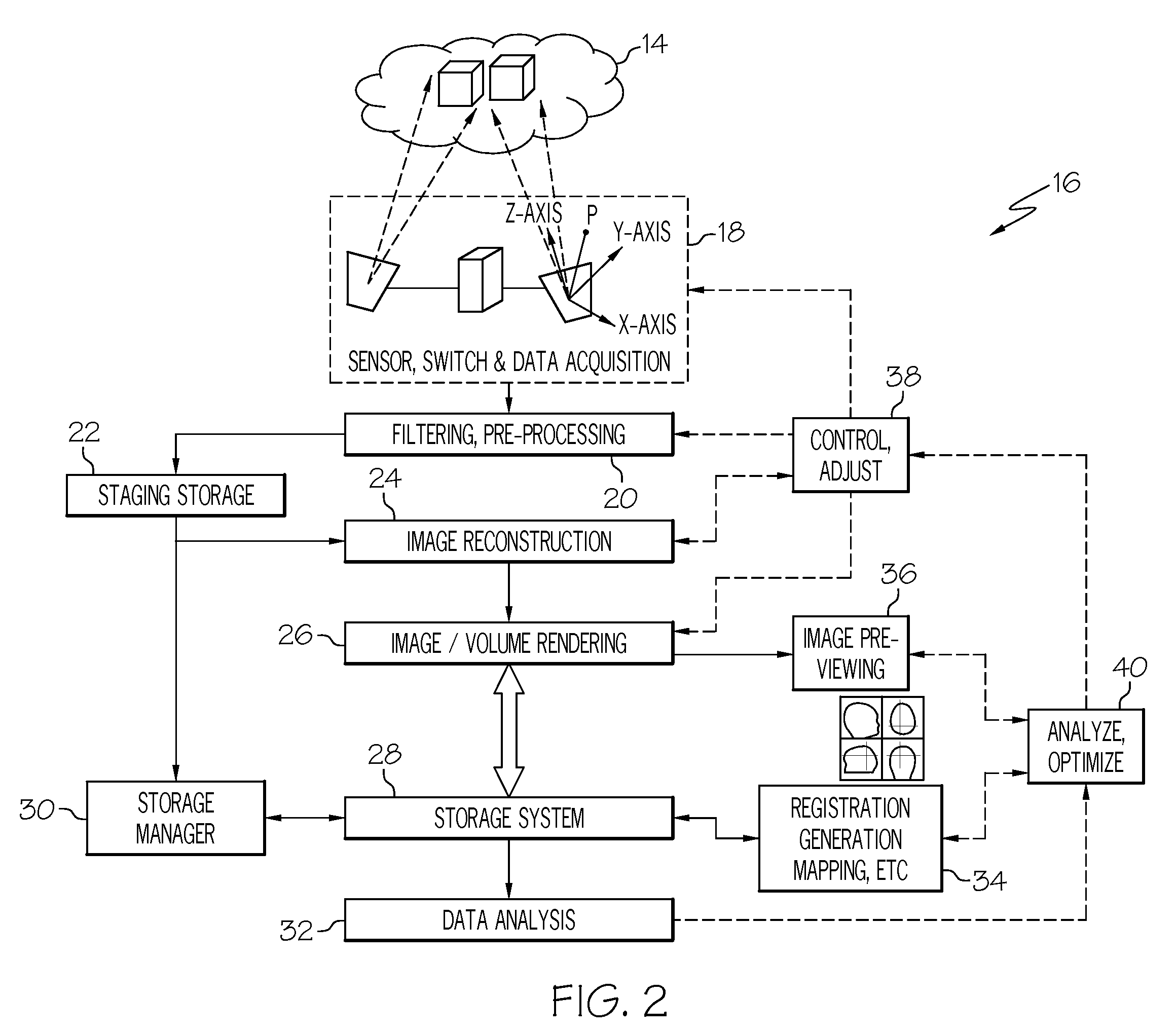
An enhanced resolution image of the object is produced by a scanning laser microscope (10) that includes an illumination arm (14) for scanning the object (12) by a focused probe beam (22) and a detection arm for receiving light from the object (16). The detection arm includes a detector (34) that collects and detects light from the object (12) to generate pixel data for a plurality of pixels. Additionally, the detection arm includes a wavefront sensor (36) for detecting phase changes of light from the object to generate wavefront data for the scanned pixel locations. From the wavefront shape of the light collected at each pixel location, a high frequency spectrum can be determined, which corresponds to the uncollected light diffracted from small scale features at that pixel location. Based on the high frequency spectrum of these scanned pixel locations, an enhanced resolution image of the target area is produced.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Laser Microscope
It is possible to reduce a drop in output power in a positive-dispersion element used as a pulse compressor, thus improving multiphoton-excitation efficiency. Also, reducing the size of the positive-dispersion element makes it easier to attach it to a microscope main body and to accommodate it therein, thus improving maneuverability. The invention provides a laser microscope including a laser light source for emitting ultrashort-pulsed laser light; a pulse expander for expanding the ultrashort-pulsed laser light emitted from the laser light source; a large-diameter single-mode fiber for transmitting the ultrashort-pulsed laser light expanded by the pulse expander; a pulse compressor for compressing the ultrashort-pulsed laser light transmitted by the single-mode fiber; and a microscope main body for irradiating a specimen with the ultrashort-pulsed laser light compressed by the pulse compressor.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
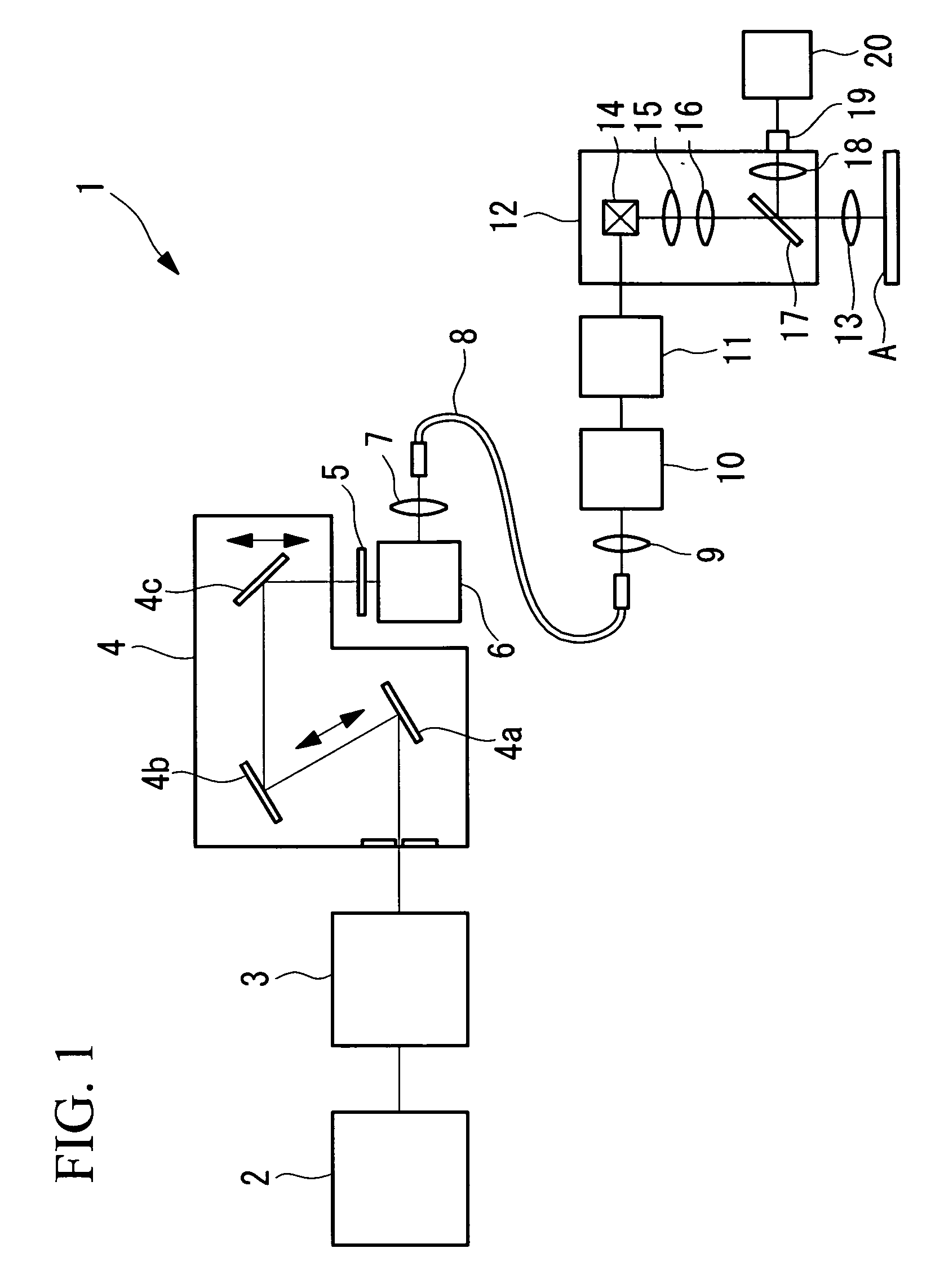
Aberration correction optical unit and laser microscope
ActiveUS20150293337A1High resolutionFor automatic positioningMicroscopesNon-linear opticsOptical axisOptoelectronics
An aberration correction optical unit (3) disposed in an optical system includes: a first phase modulation element (3a) and a second phase modulation element (3c) each having a polarization characteristic; and a variable waveplate (3b) disposed between the first and second phase modulation elements so that an optical axis of the variable waveplate has a predetermined angle with respect to optical axes of the two phase modulation elements, in order to correct an aberration generated by the optical system.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com