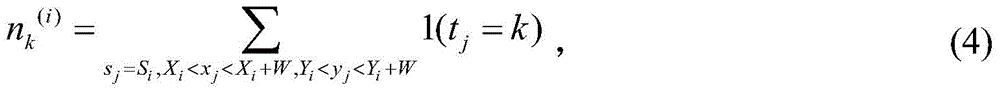Patents
Literature
143 results about "Digital pathology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Digital pathology is an image-based information environment which is enabled by computer technology that allows for the management of information generated from a digital slide. Digital pathology is enabled in part by virtual microscopy, which is the practice of converting glass slides into digital slides that can be viewed, managed, shared and analyzed on a computer monitor. With the advent of Whole-Slide Imaging, the field of digital pathology has exploded and is currently regarded as one of the most promising avenues of diagnostic medicine in order to achieve even better, faster and cheaper diagnosis, prognosis and prediction of cancer and other important diseases.
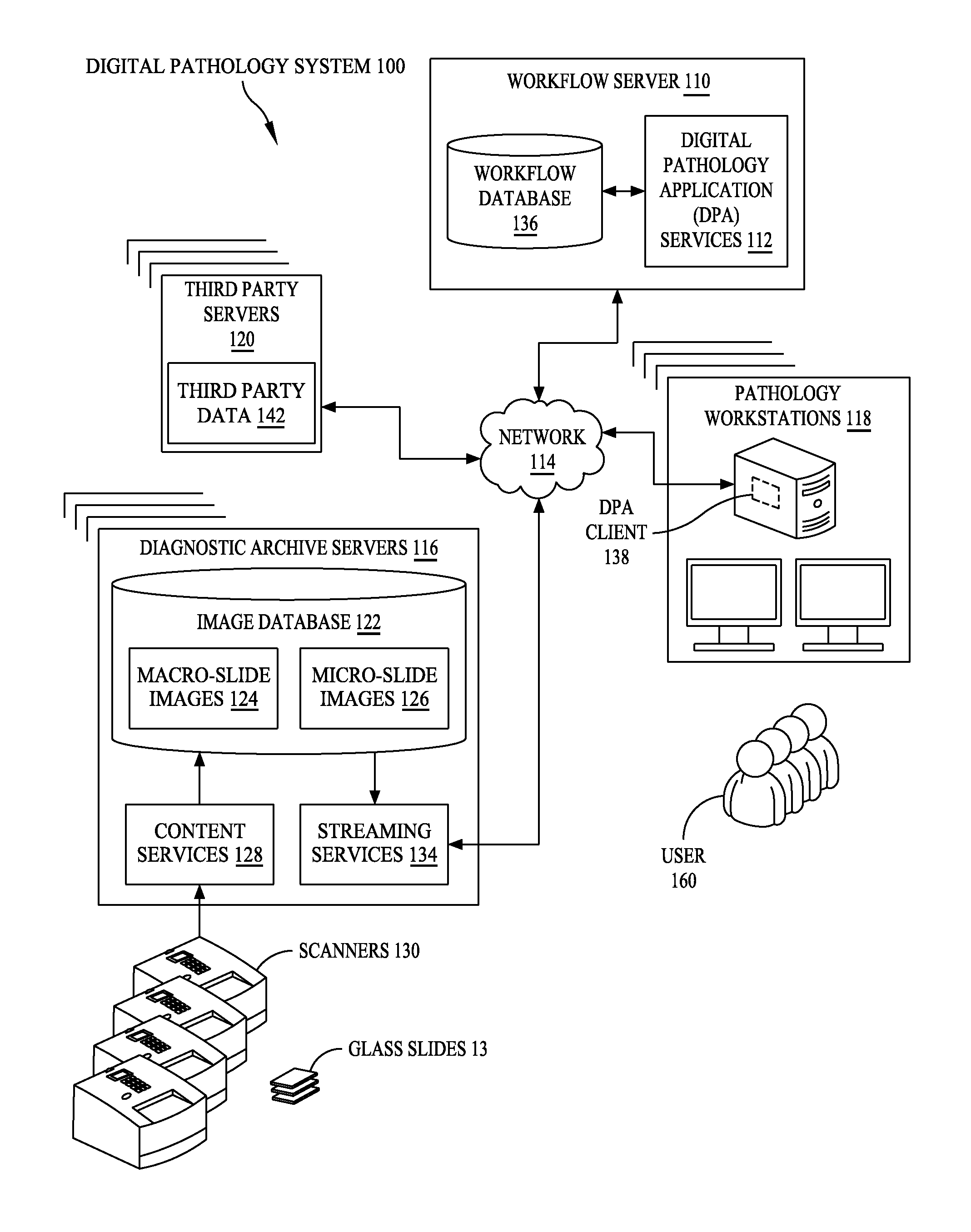
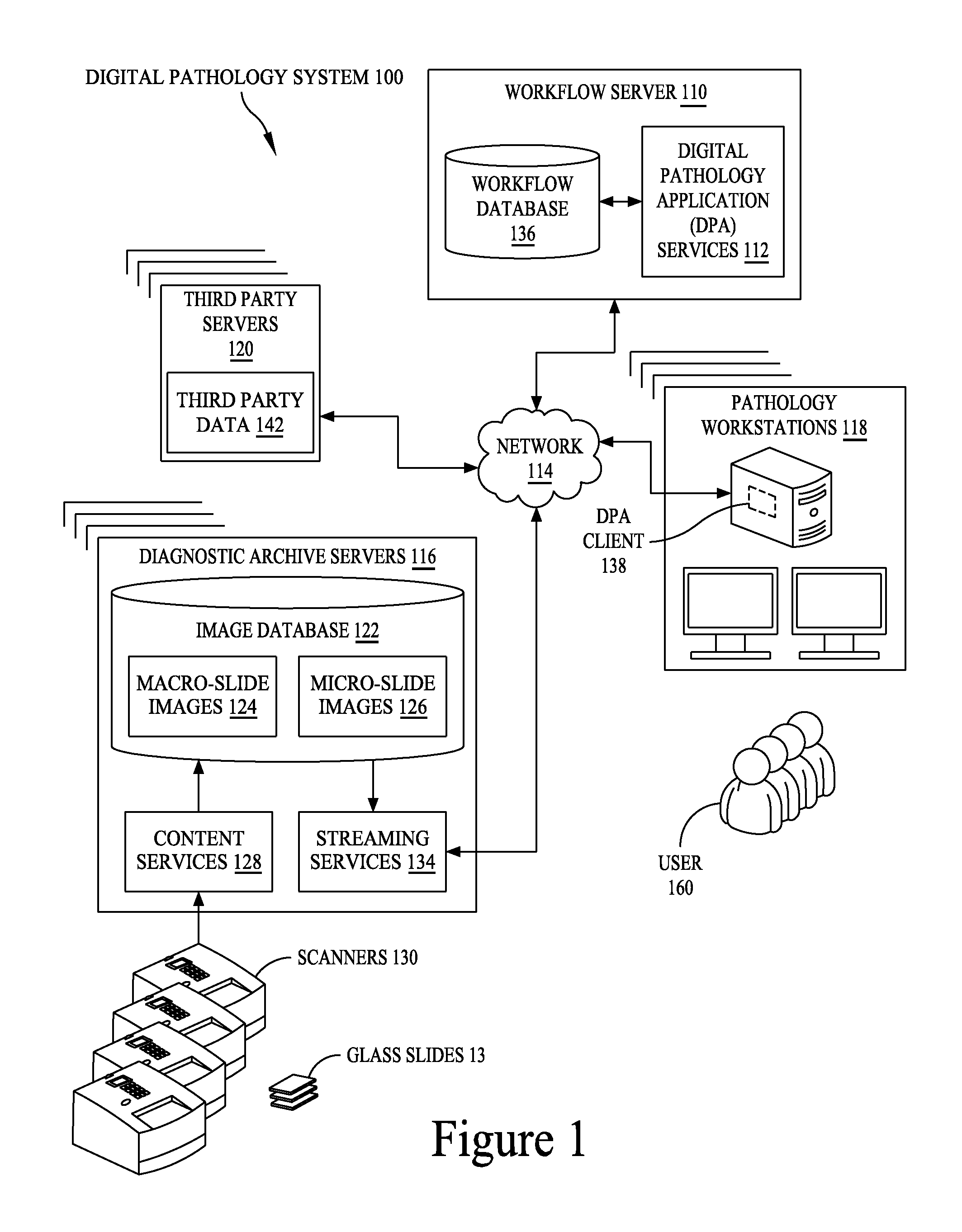
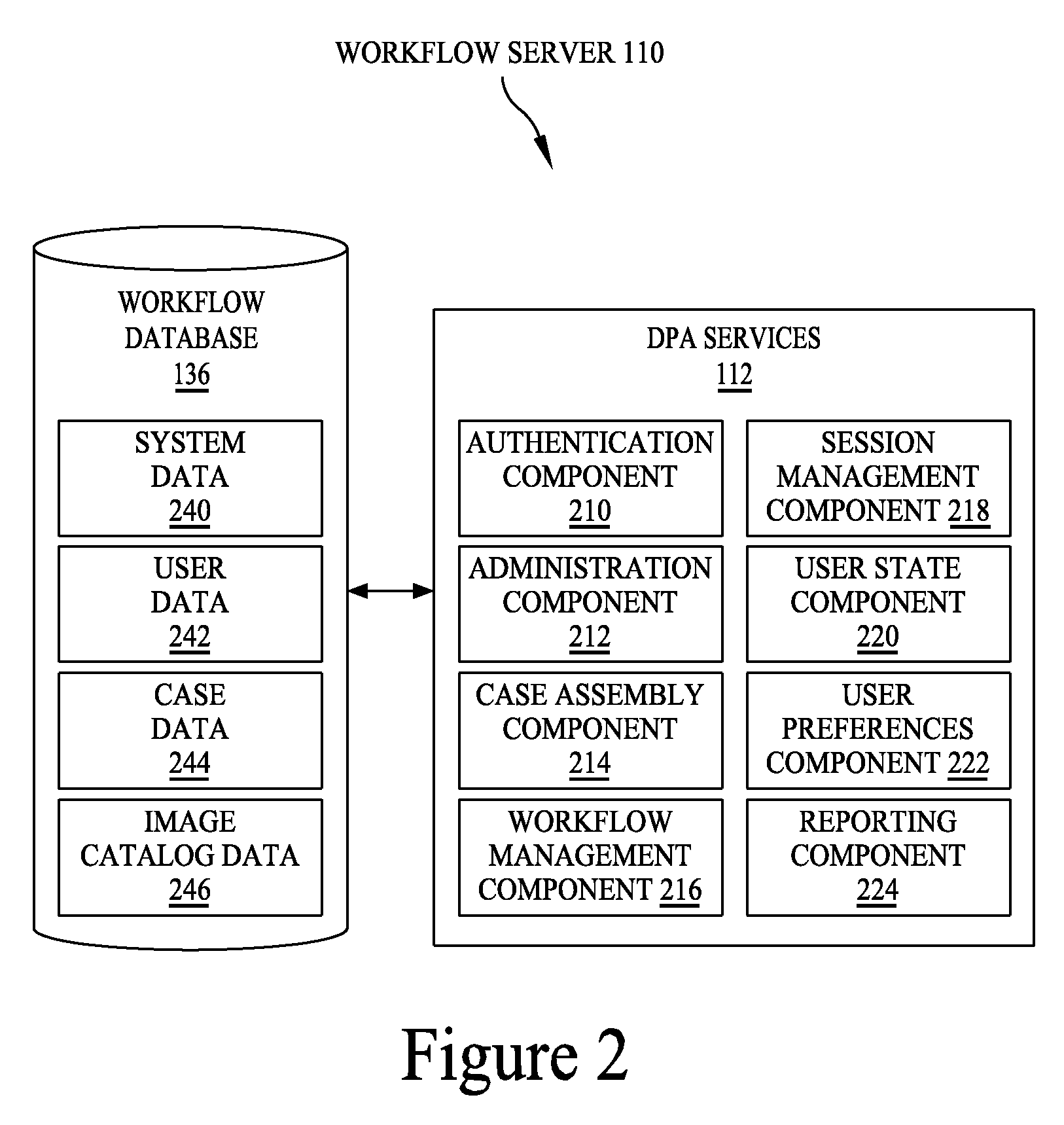
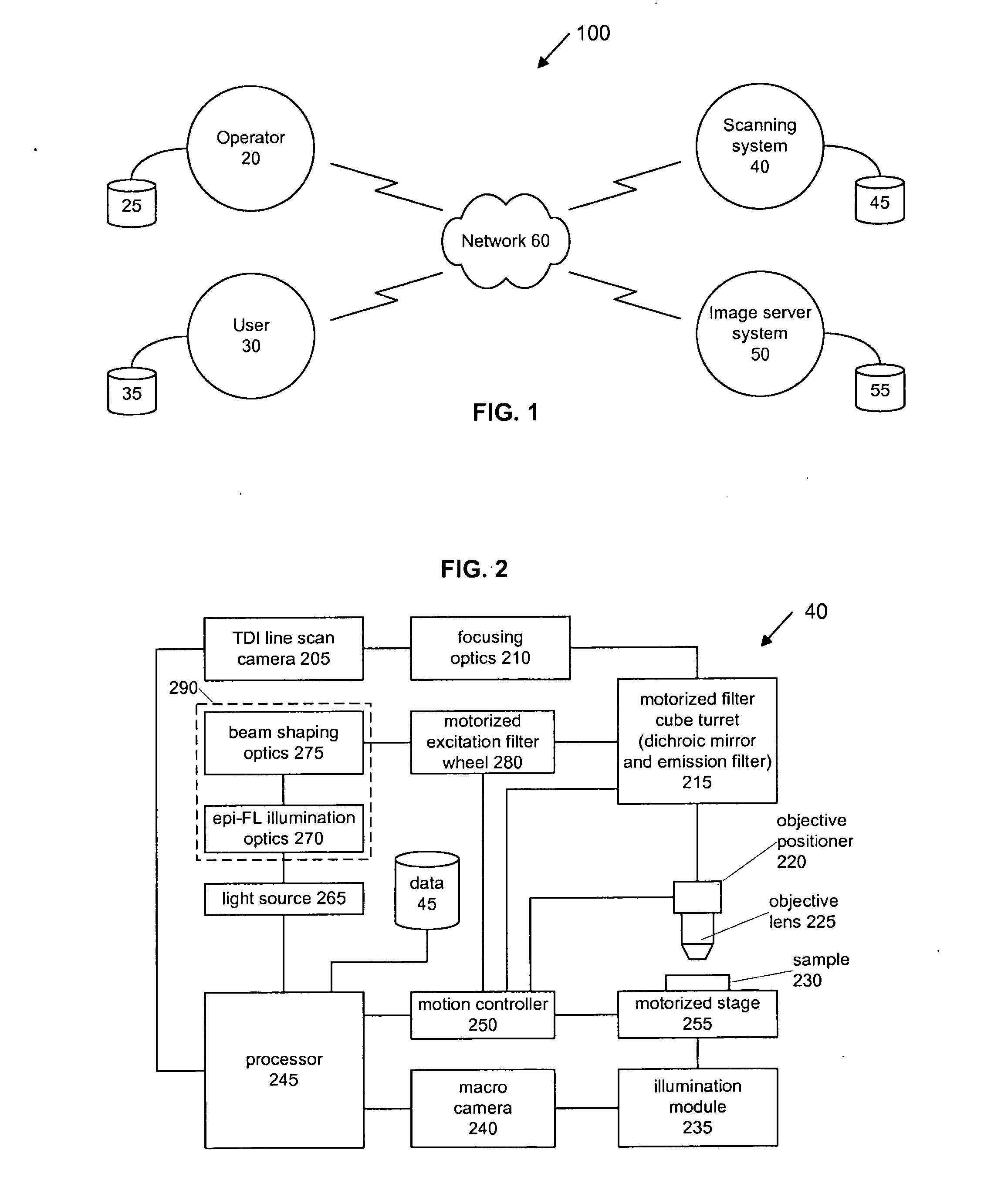
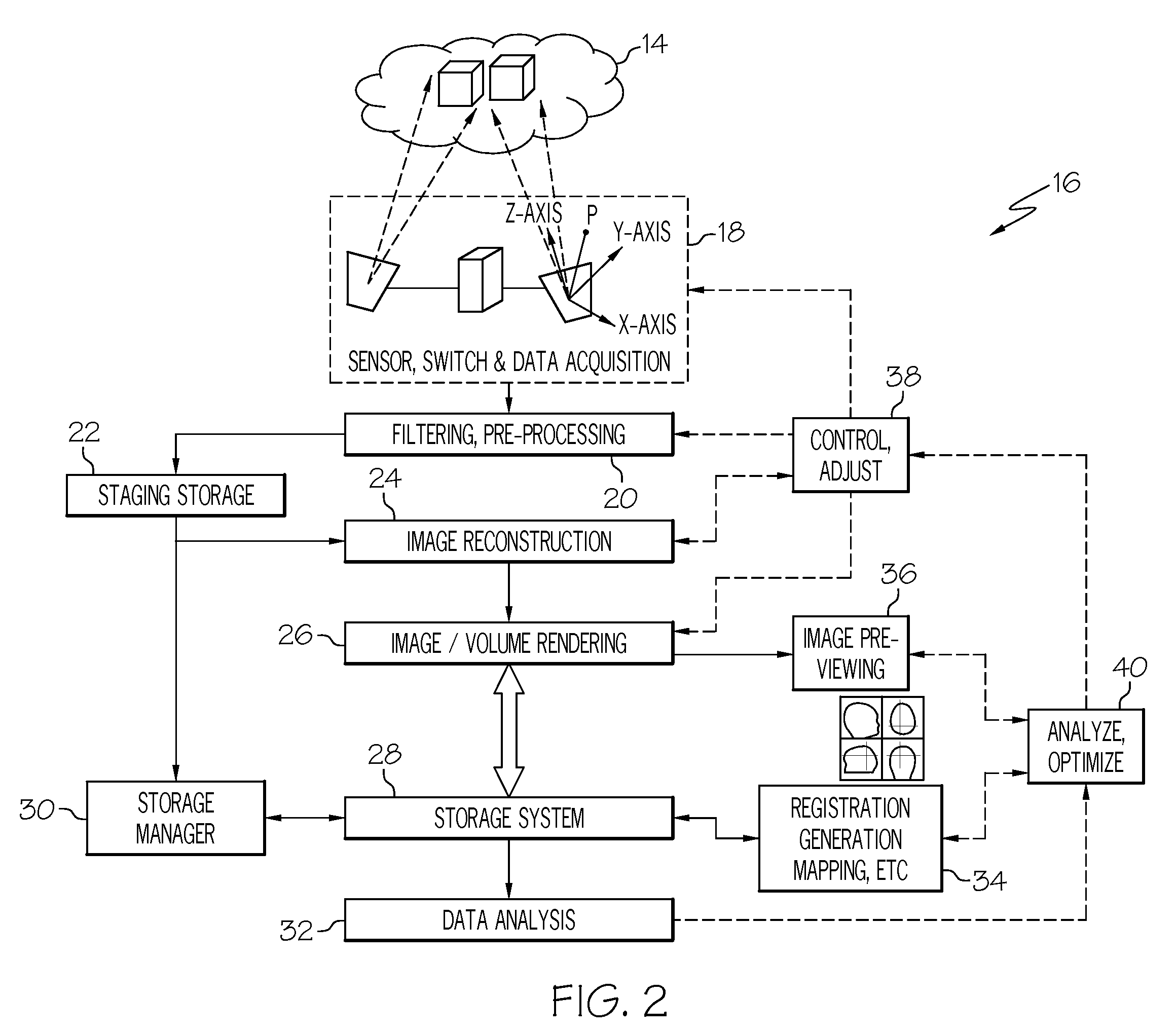
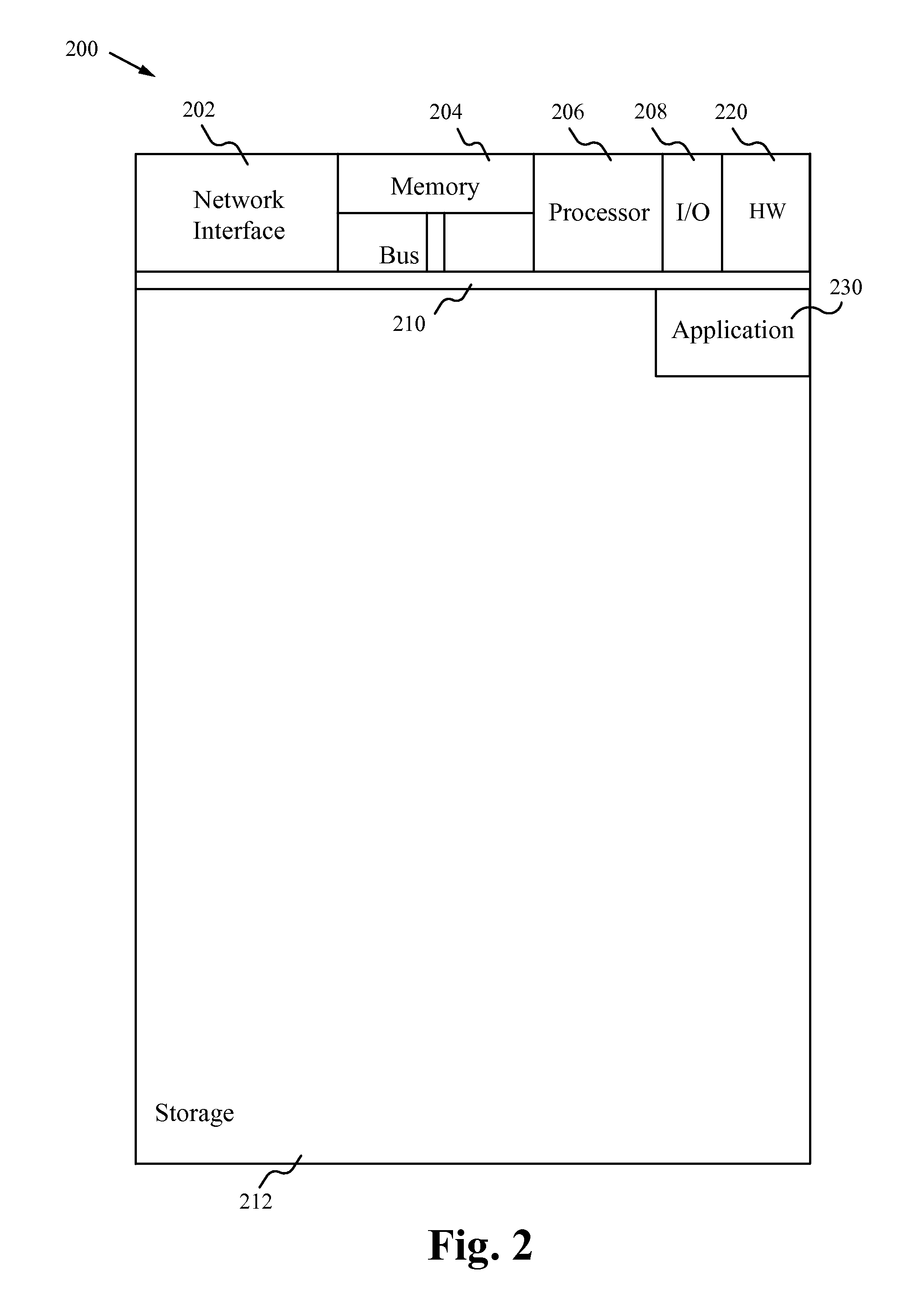
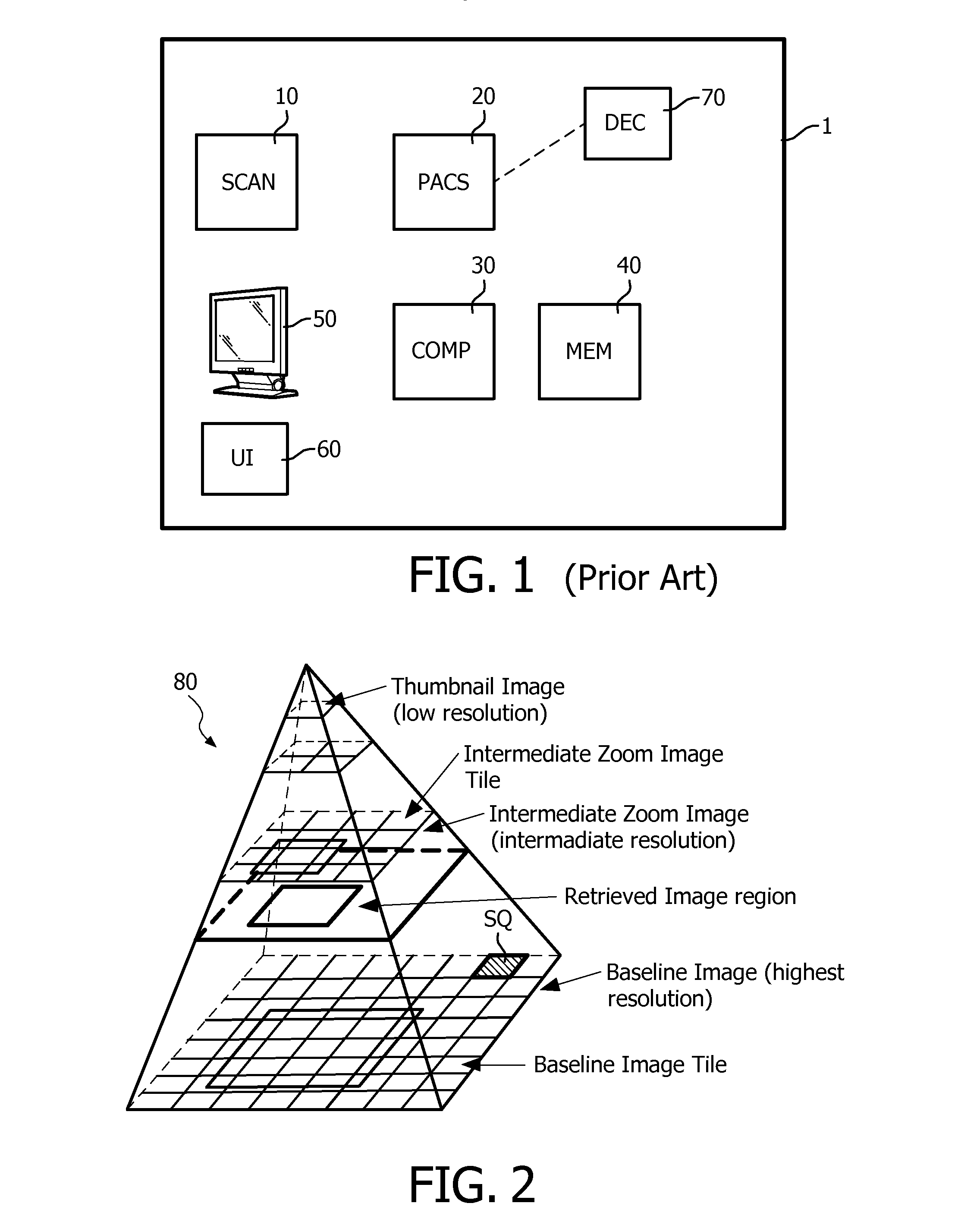
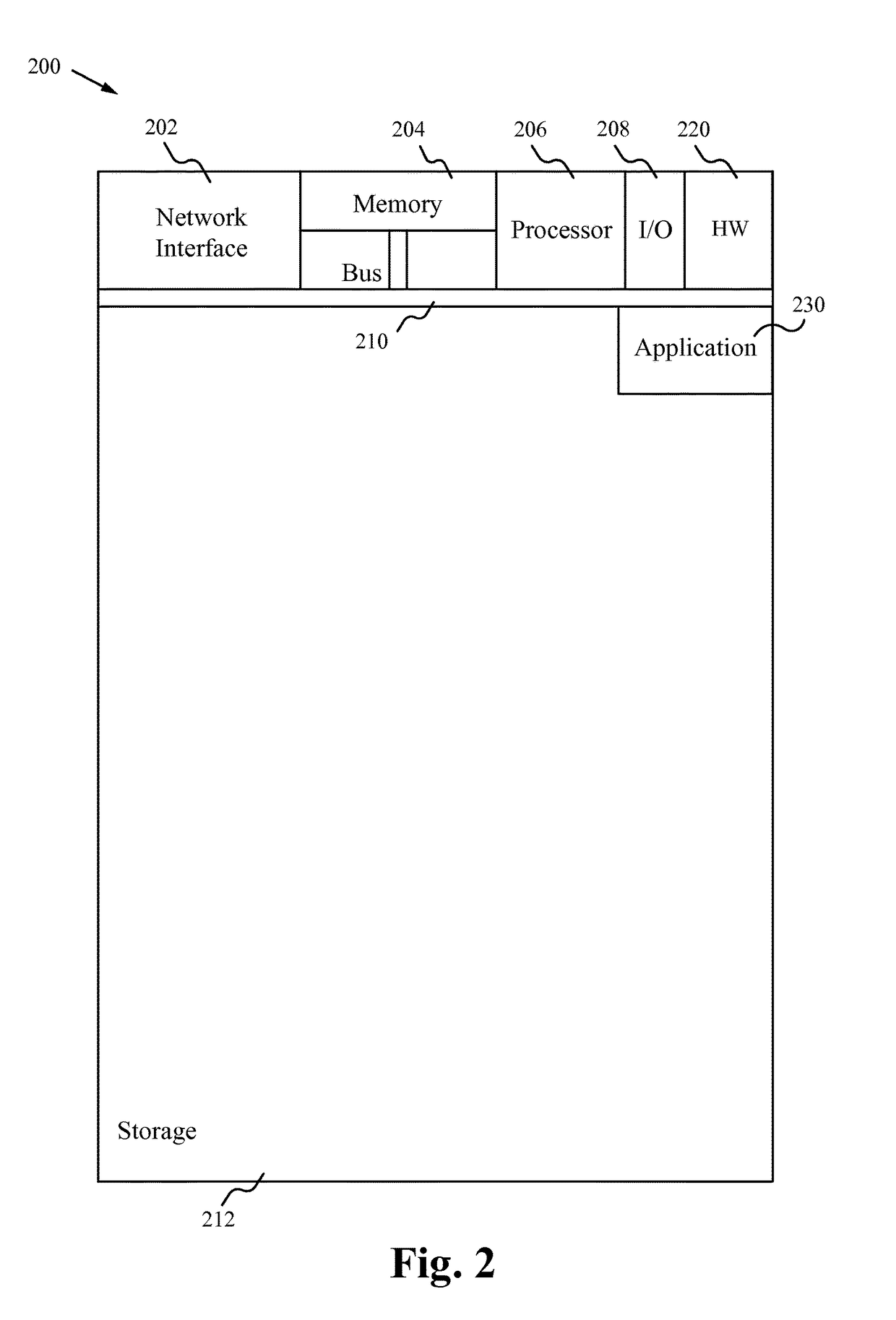
Digital pathology system
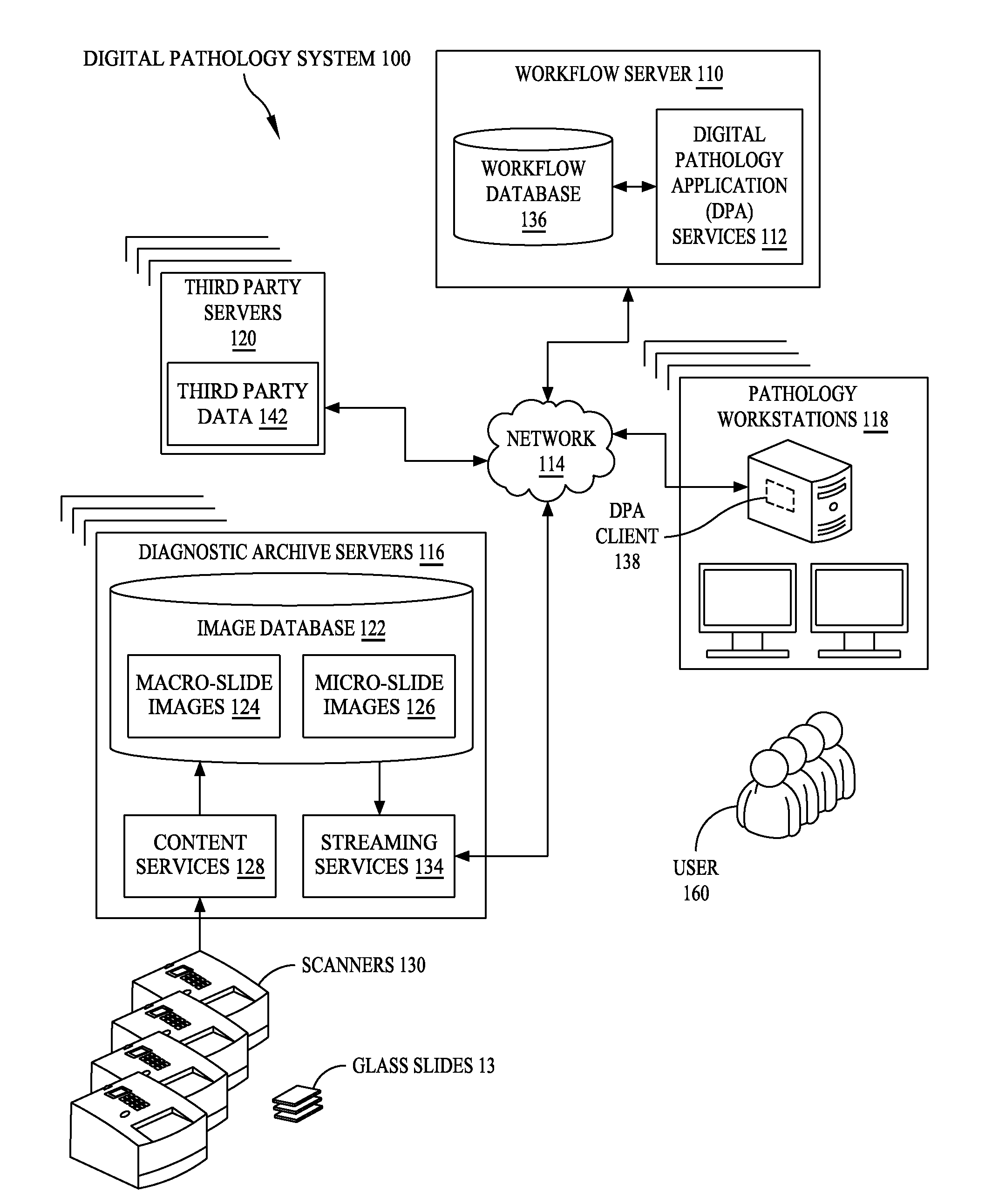
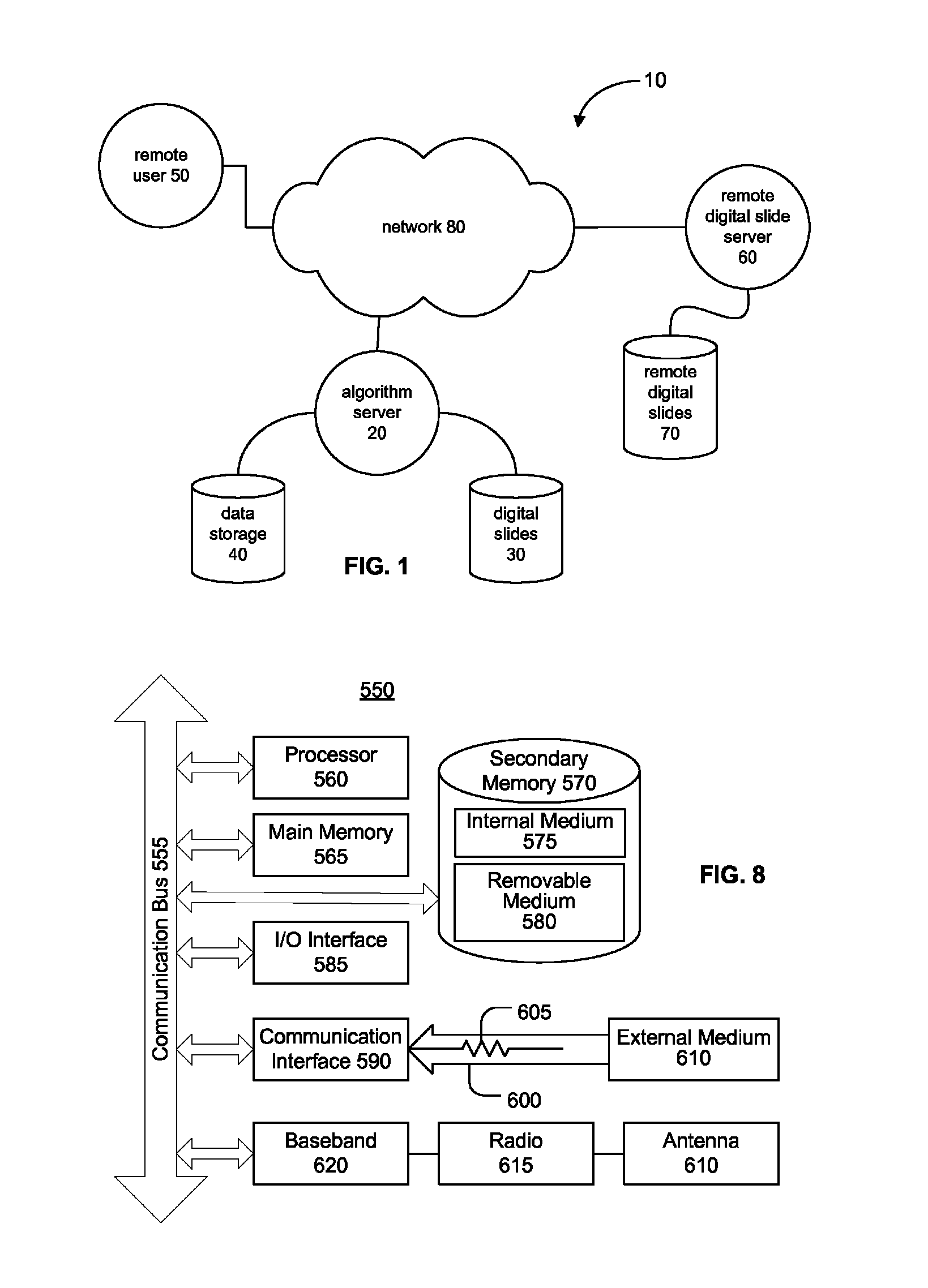
ActiveUS20110060766A1Automated handlingImprove efficiencyDigital data processing detailsMedical report generationImage serverDigital image
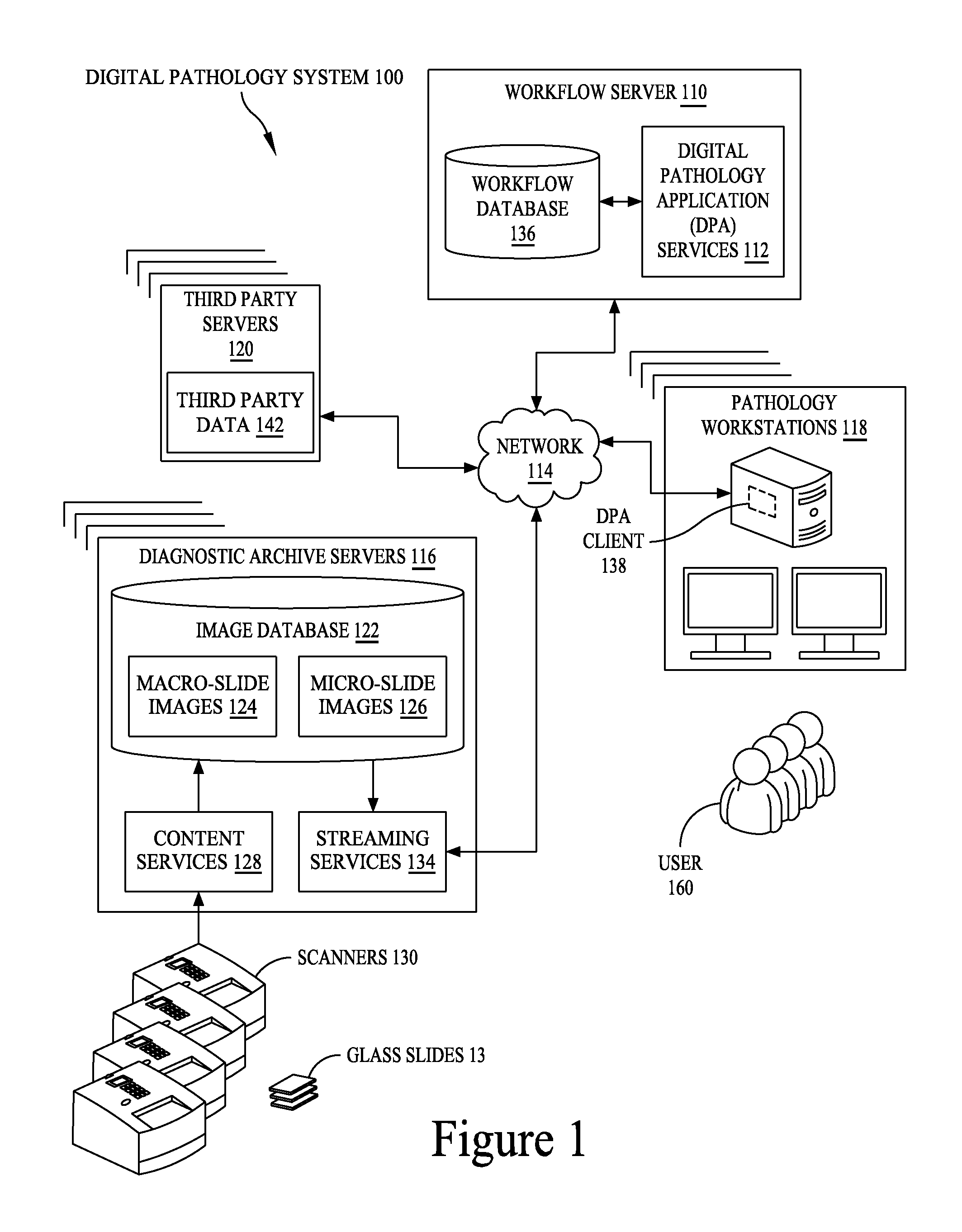
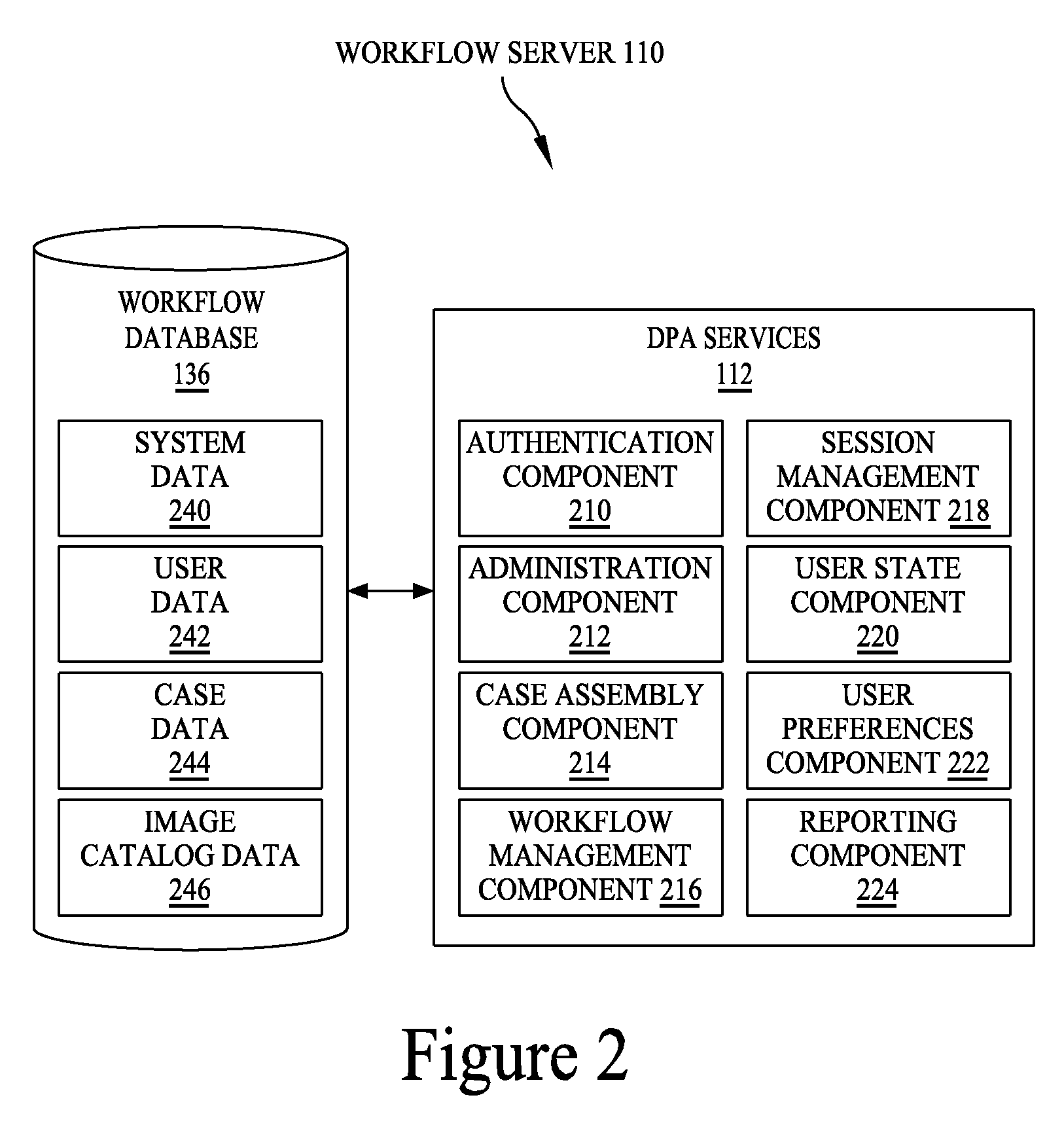
A digital pathology system has a central workflow server hosting digital pathology application services and supporting one or more pathology workstations. The digital pathology system may include one or more image servers, providing digital images of sample specimen slides that are associated with medical cases. Residing at and executing on each pathology workstation is a digital pathology application client, which is the counterpart of digital pathology application services at the central workflow server. The combination of digital pathology application services at the central workflow server and digital pathology application client at each pathology workstation support a pathology workflow software module and a slide viewer software module. The present disclosure also describes a method of operation and / or use of the digital pathology system.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE AMERICAS CORPORATION
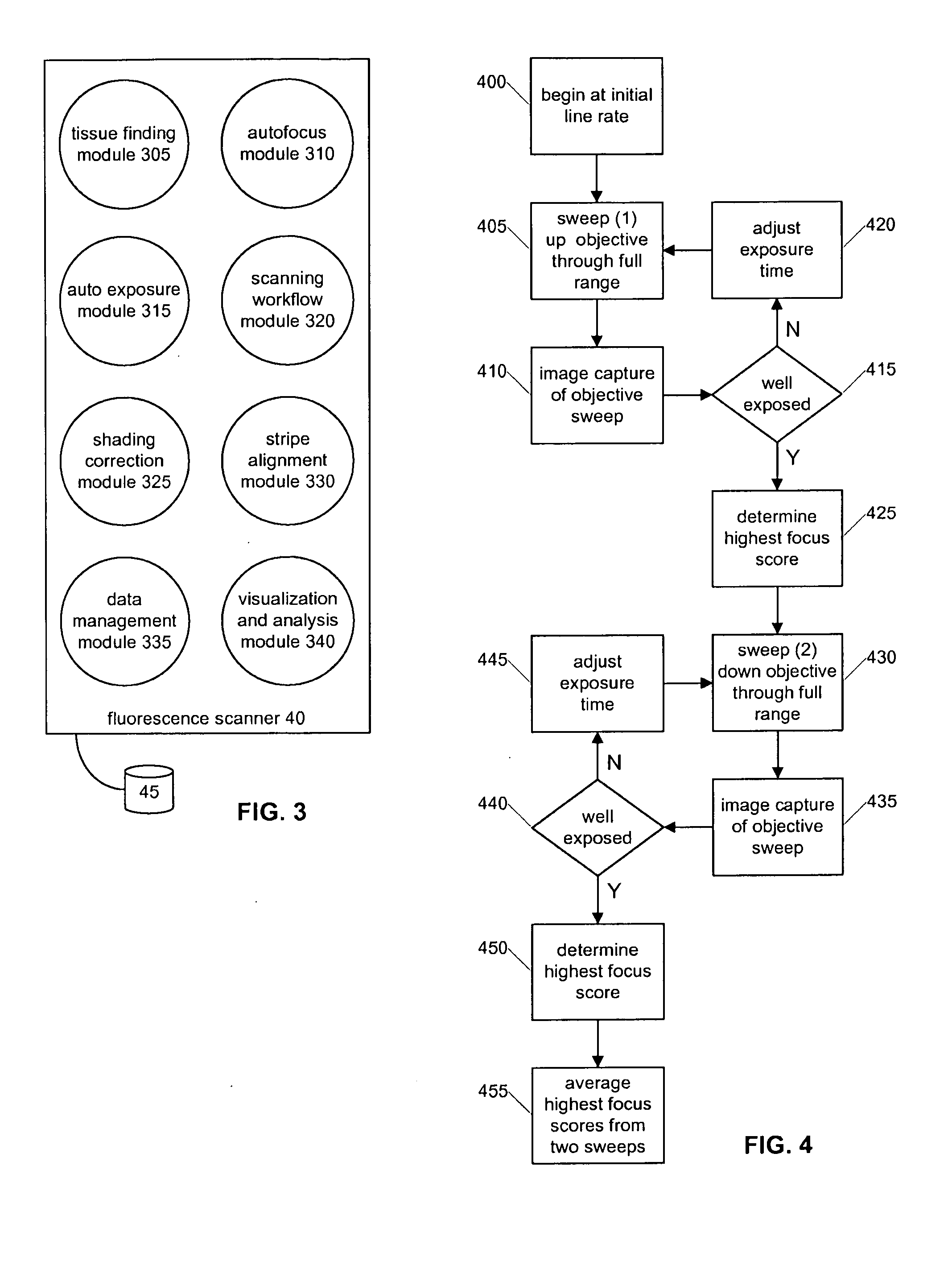
Whole Slide Fluorescence Scanner
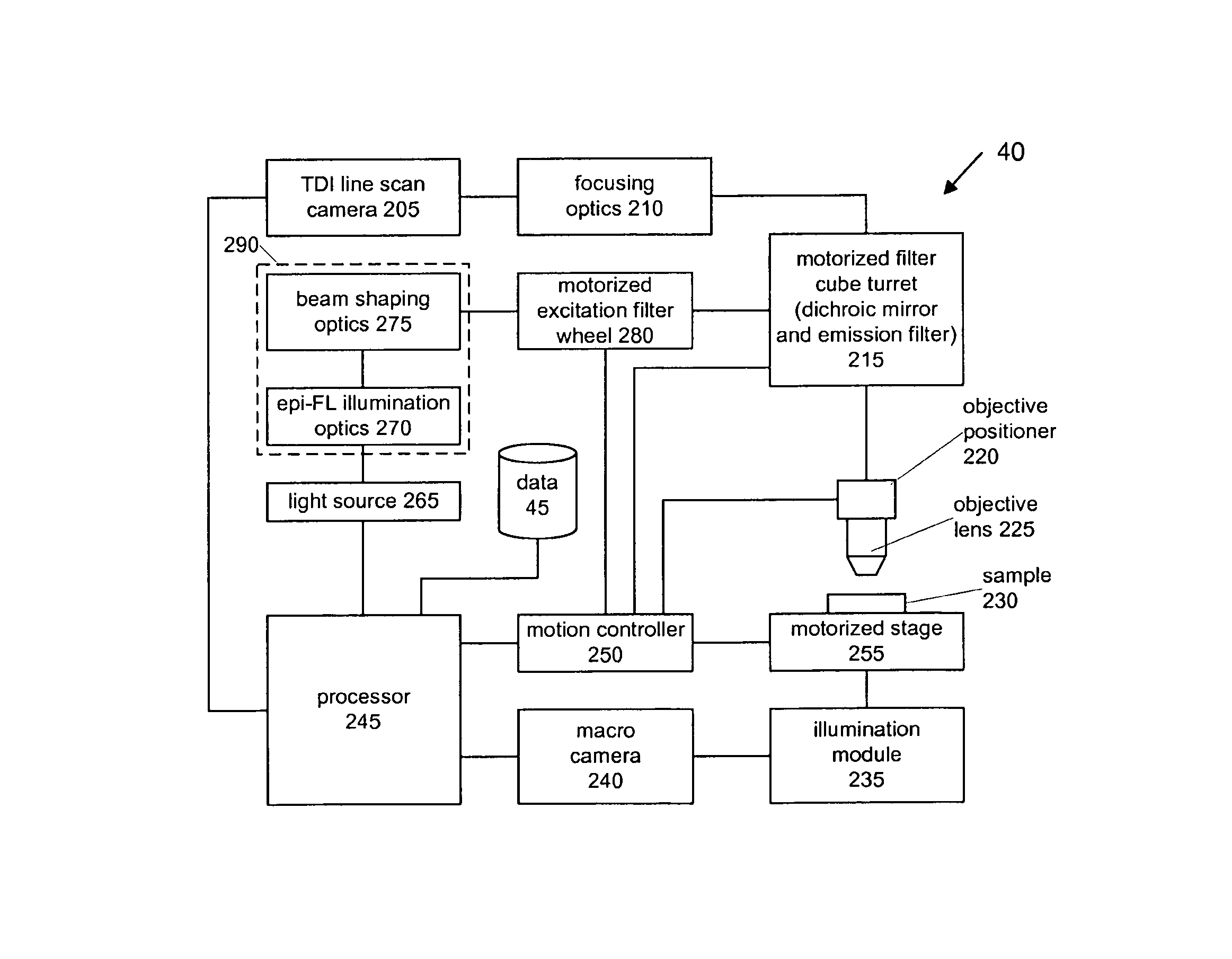
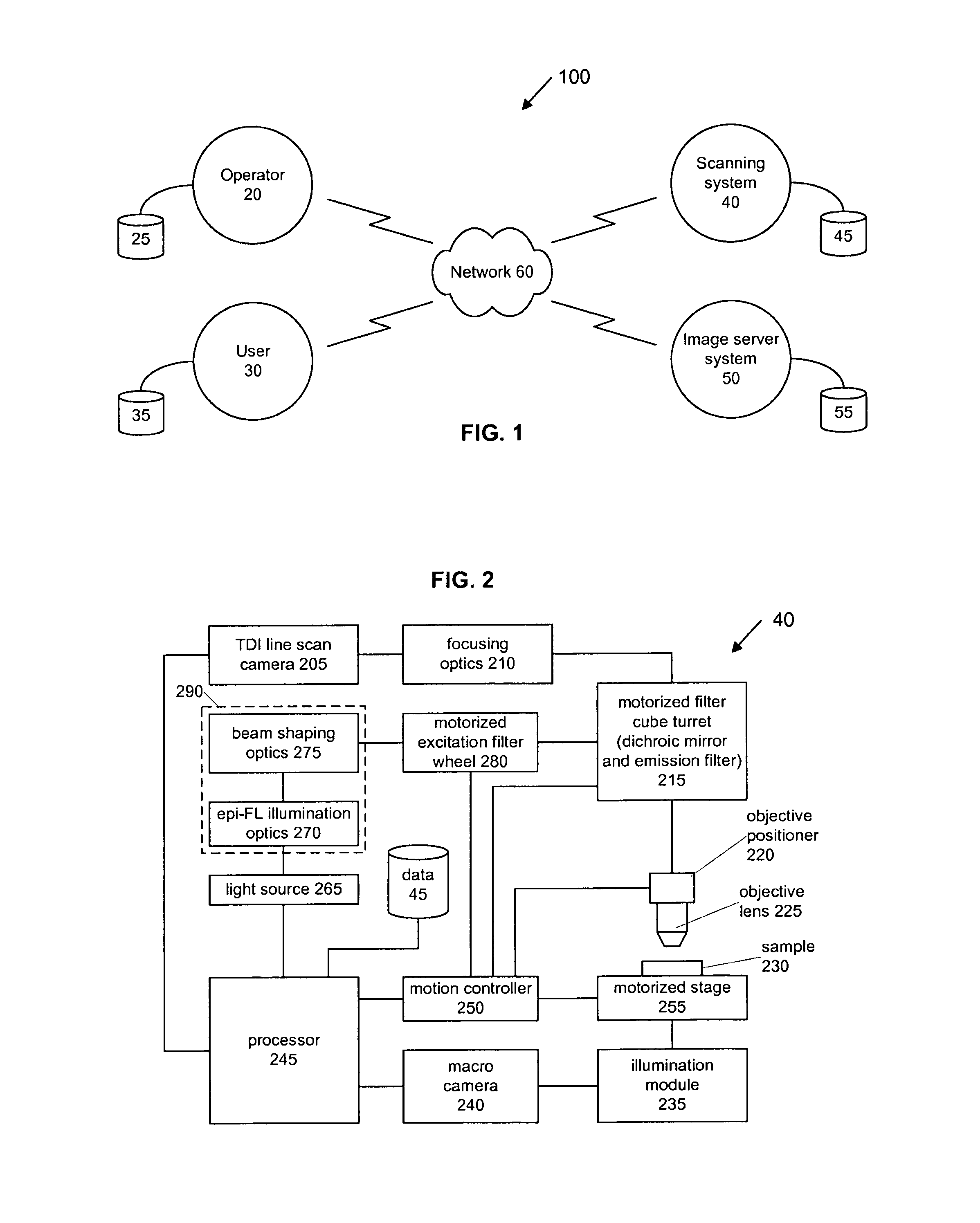
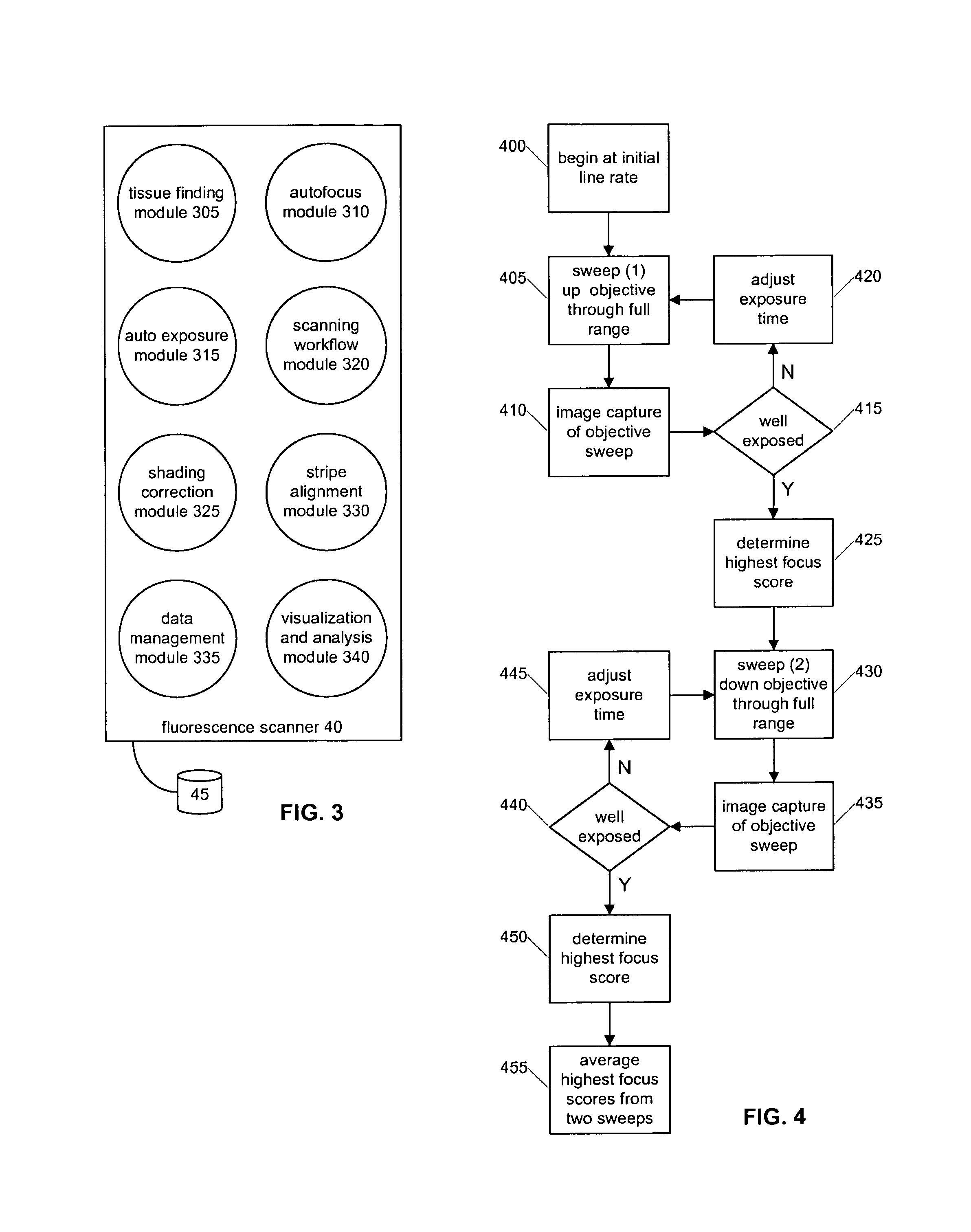
ActiveUS20110115897A1Increase line speedAccuracyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsFluorescenceAutofocus
A whole slide fluorescence digital pathology system is provided that uses a monochrome TDI line scan camera, which is particularly useful in fluorescence scanning where the signal is typically much weaker than in brightfield microscopy. The system uses oblique brightfield illumination for fast and accurate tissue finding and employs a unique double sweep focus scoring and objective lens height averaging technique to identify focus points and create a focus map that can be followed during subsequent scanning to provide autofocusing capability. The system also scans and analyzes image data to determine the optimal line rate for the TDI line scan camera to use during subsequent scanning of the digital slide image and it also creates a light profile to compensate for loss of illumination light due to roll off.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Hybrid medical image processing
The present invention uses a common, hybrid system platform to provide a generalized medical image processing system that can handle the existing medical image application as it is and route the compute intensive medical image processing to a multi-core processor / processing system. The invention allows the processing platform to be shared among healthcare system such as mammography, X-ray, CT Scan MRI, two-photon, laser microscopy, digital pathology, etc. It also allows the processing platform to deliver medical images to a variety of client devices, such as a desktop computer or a handheld device, through the network without high-performance graphical display capabilities because the rendering of the medical images is performed on the Cell BE based platform of the invention.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
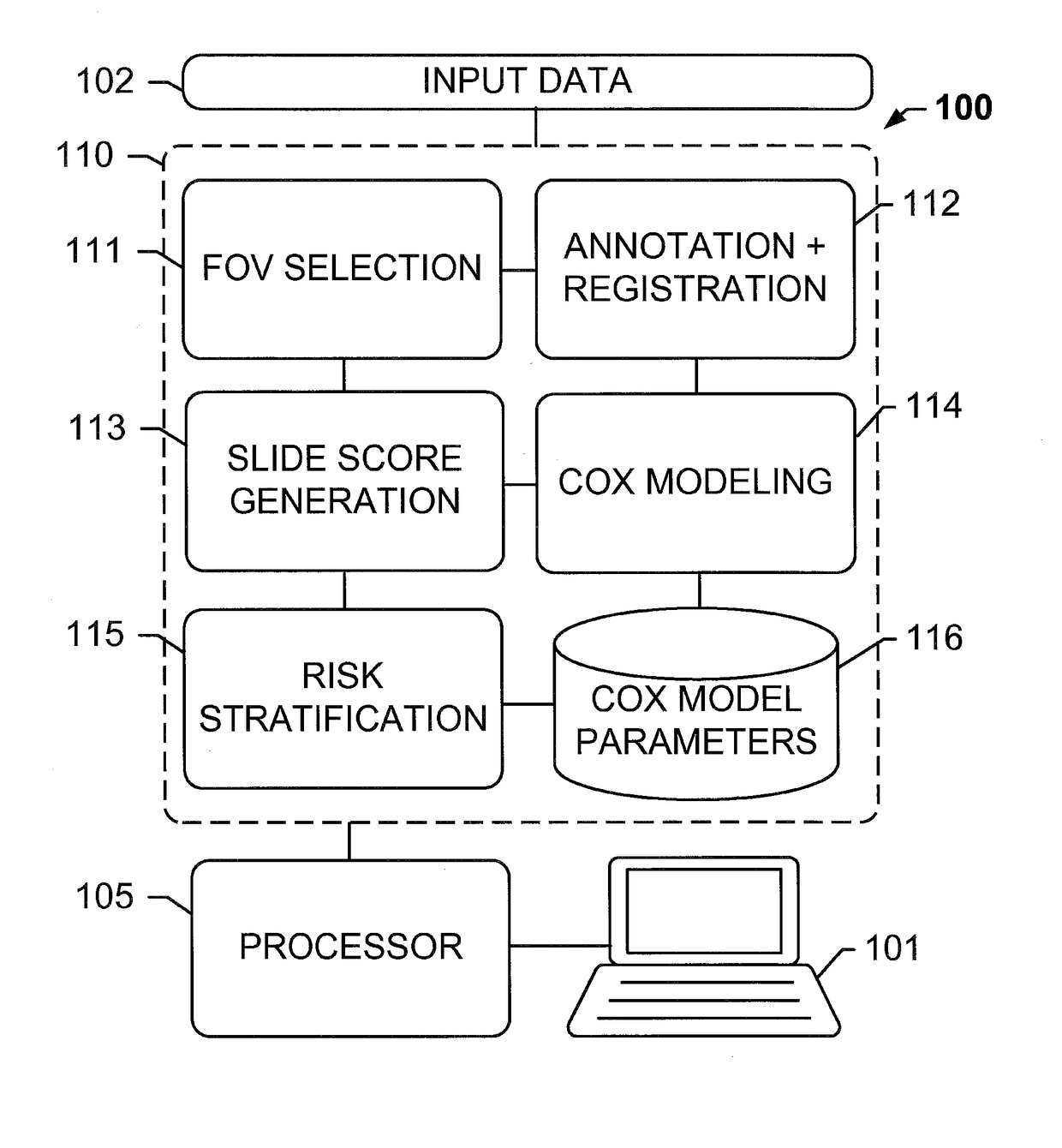
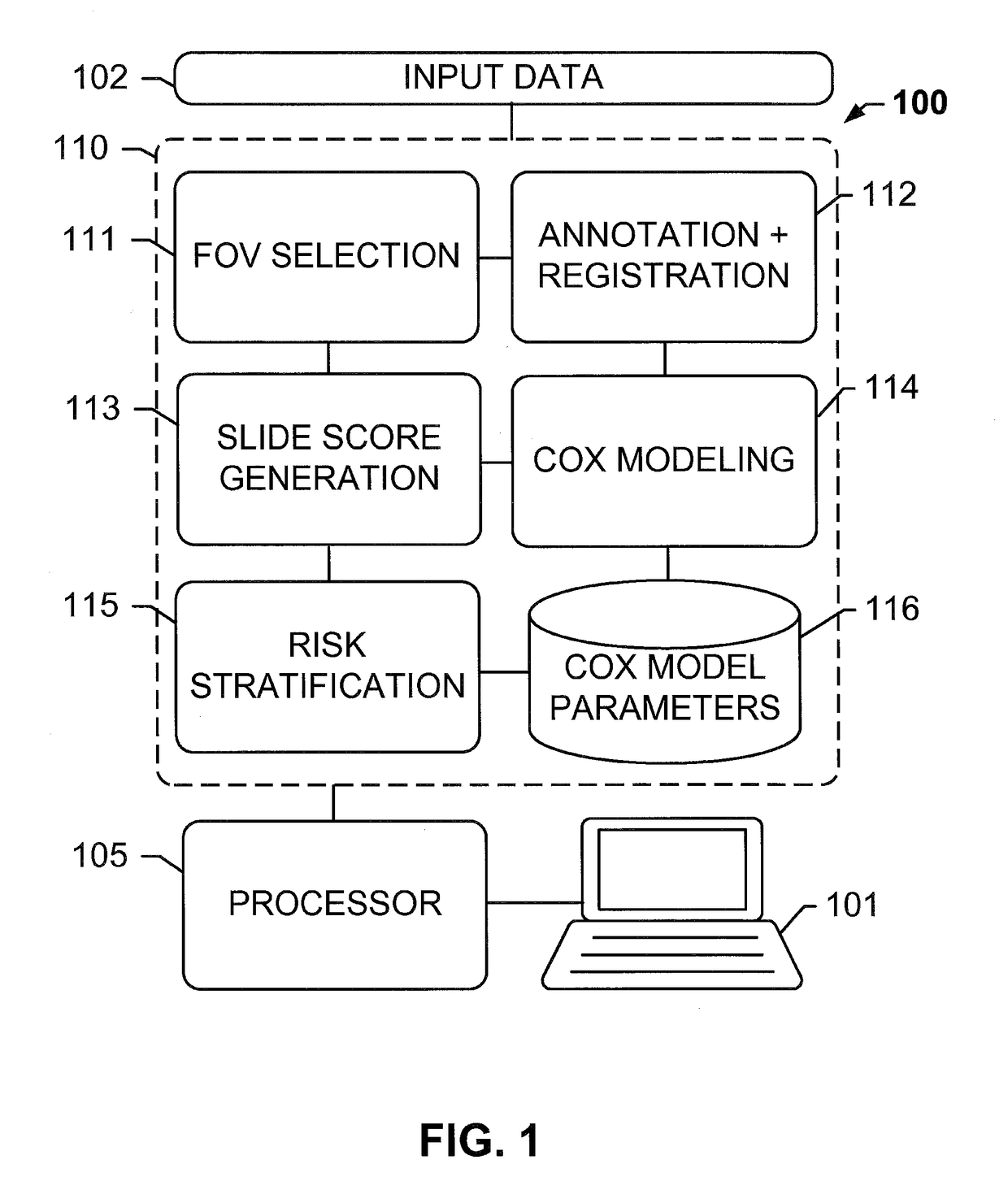
Computational pathology systems and methods for early-stage cancer prognosis
ActiveUS20170270666A1Reduce computing costInformed choiceImage enhancementImage analysisComputational pathologyLow risk group
The subject disclosure presents systems and computer-implemented methods for providing reliable risk stratification for early-stage cancer patients by predicting a recurrence risk of the patient and to categorize the patient into a high or low risk group. A series of slides depicting serial sections of cancerous tissue are automatically analyzed by a digital pathology system, a score for the sections is calculated, and a Cox proportional hazards regression model is used to stratify the patient into a low or high risk group. The Cox proportional hazards regression model may be used to determine a whole-slide scoring algorithm based on training data comprising survival data for a plurality of patients and their respective tissue sections. The coefficients may differ based on different types of image analysis operations applied to either whole-tumor regions or specified regions within a slide.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
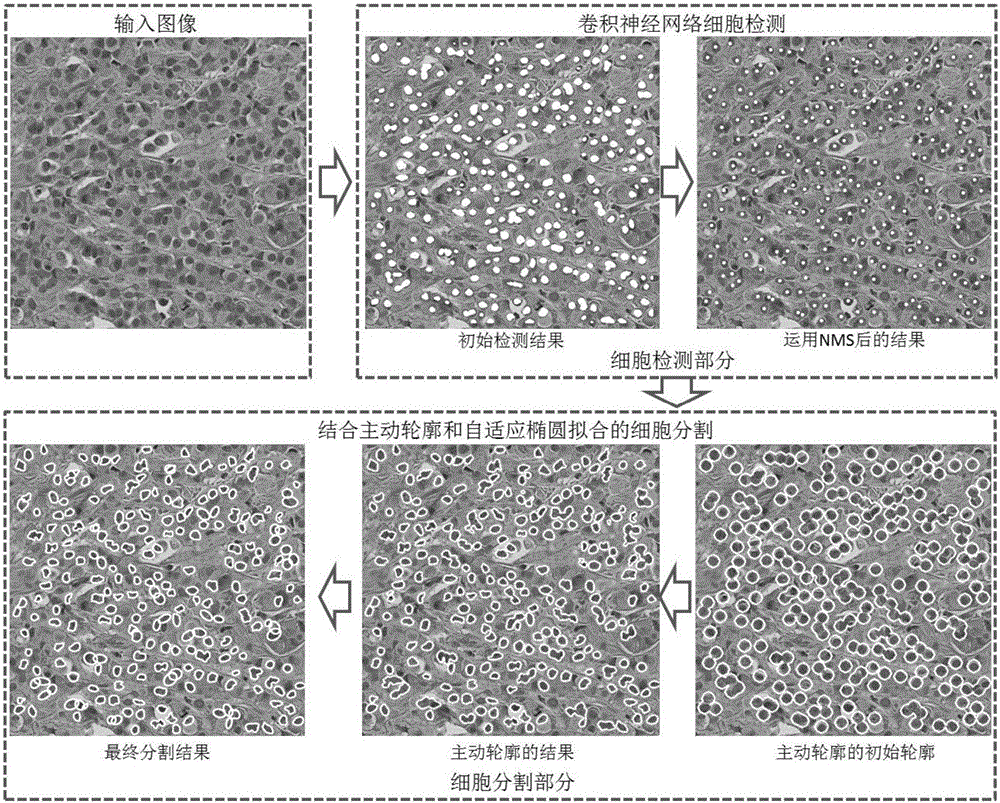
Automatic cell detection and segmentation method based on deep learning and using adaptive ellipse fitting
InactiveCN105931226AImprove detection accuracyImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionResearch Object
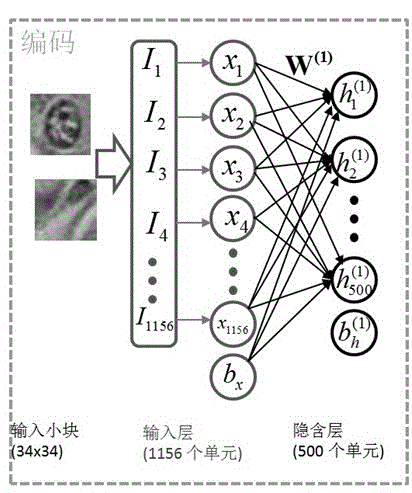
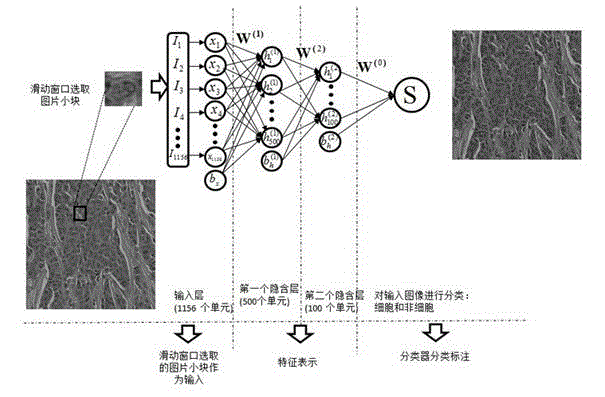
The invention discloses an automatic cell detection and segmentation method based on deep learning and using adaptive ellipse fitting. A deep learning method is used to detect a cell in a pathologic image, an active contour model is used to search an accurate cell contour, and an adaptive ellipse fitting technology is used to segment contours of overlapped cells. According to the method of the invention, large slice images serve as research objects, deep learning is combined with a sliding window, the position of the cell in the image can be found accurately, and the active contour and the adaptive ellipse fitting are combined to effectively segment the overlapped cells. The method can be used to help clinical doctors evaluate cells in the digital pathologic slices in a quantified manner and make clinical diagnosis rapidly and accurately, diagnosis difference between different observers or different time periods of the same observer is reduced, and compared with a present cell detection and segmentation method, the method of the invention is advantageous in the aspects of both accuracy and feasibility.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
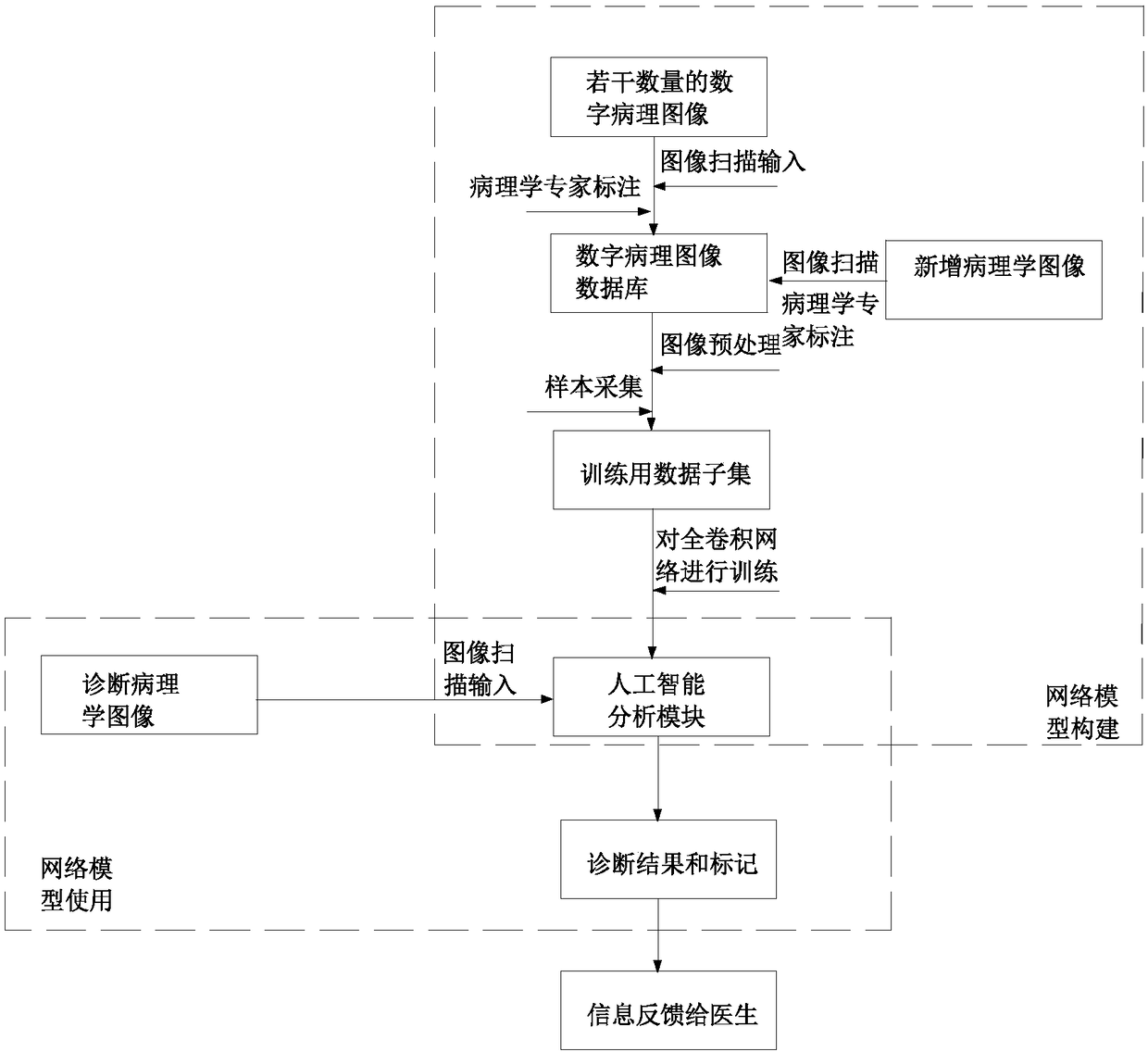
Cancer pathology auxiliary diagnosis method based on artificial intelligence technology
InactiveCN108288506AImprove diagnostic accuracyQuality improvementMedical simulationMedical automated diagnosisDisease areaData set
The present invention discloses a cancer pathology auxiliary diagnosis method based on an artificial intelligence technology. The method comprises the following steps of: canning a plurality of digital pathology images of a system into a computer, performing marking of diseased areas by pathologists to form a digital pathology image database; performing preprocessing of the digital pathology images to form a data set for algorithm training, performing sample collection, and forming a data subset for training; allowing a full convolutional network to use the data subset for training to performiteration training to regulate parameters, and constructing an artificial intelligence analysis module; scanning diagnosis pathology images, and decoding the diagnosis pathology images to access the artificial intelligence analysis module; and performing diagnosis and marking of the diagnosis pathology images by employing the artificial intelligence analysis module, and performing feedback of themarked pathology information to doctors. The cancer pathology auxiliary diagnosis method based on the artificial intelligence technology is high in diagnosis accuracy and can effectively assist doctors in discrimination of cancer pathology information.
Owner:云鲲医疗科技(上海)有限公司
Medical imaging systems
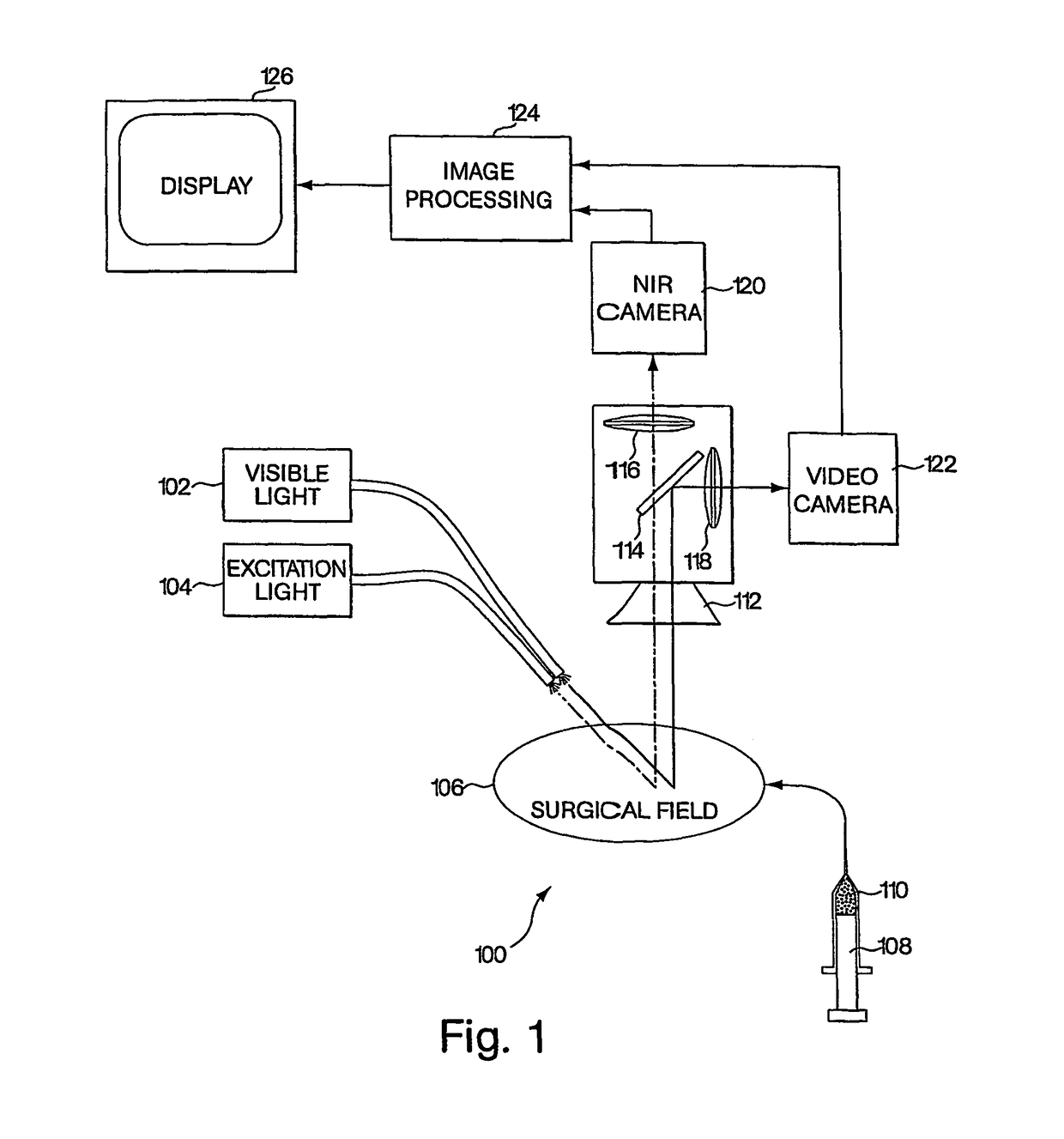
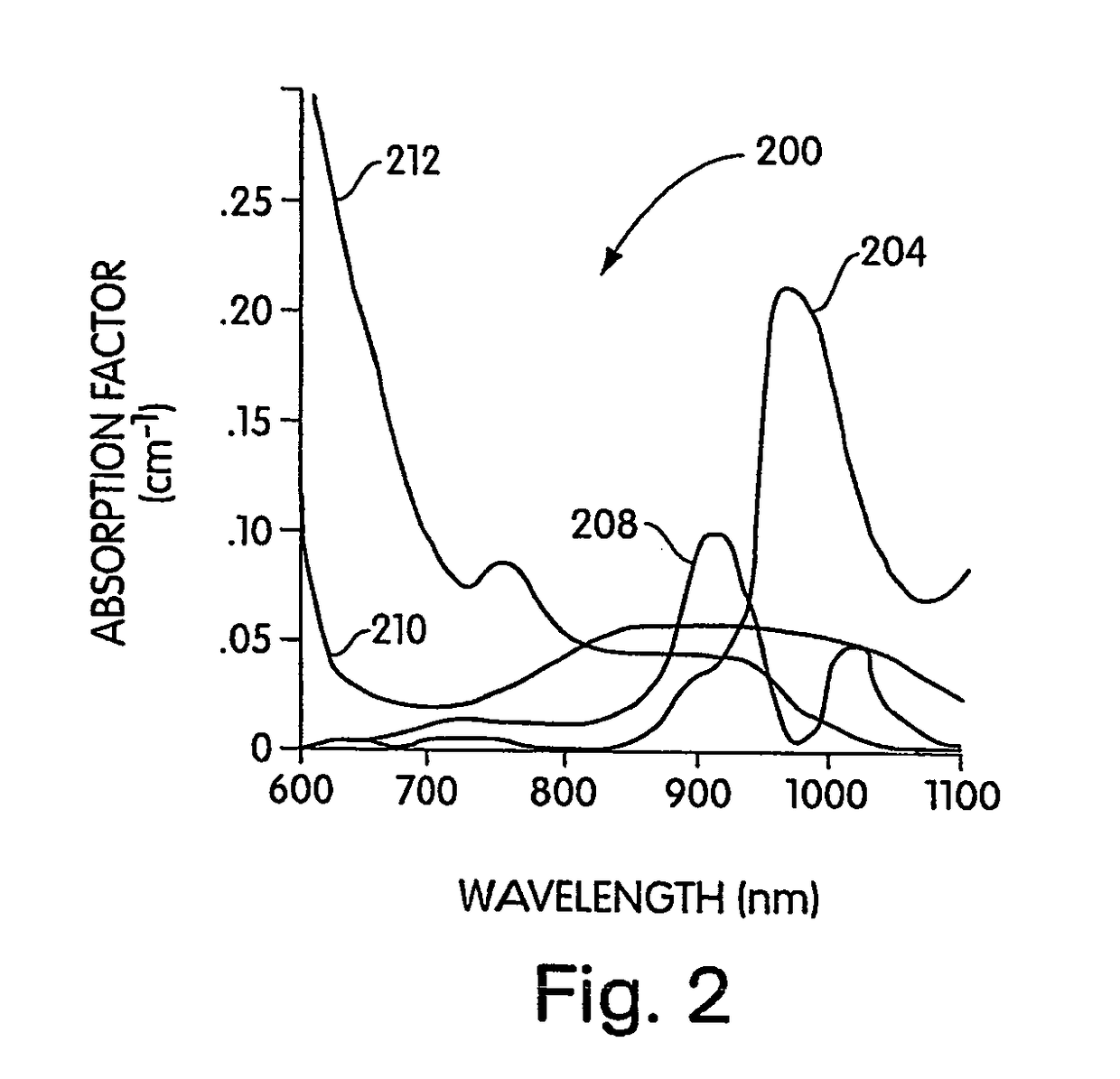
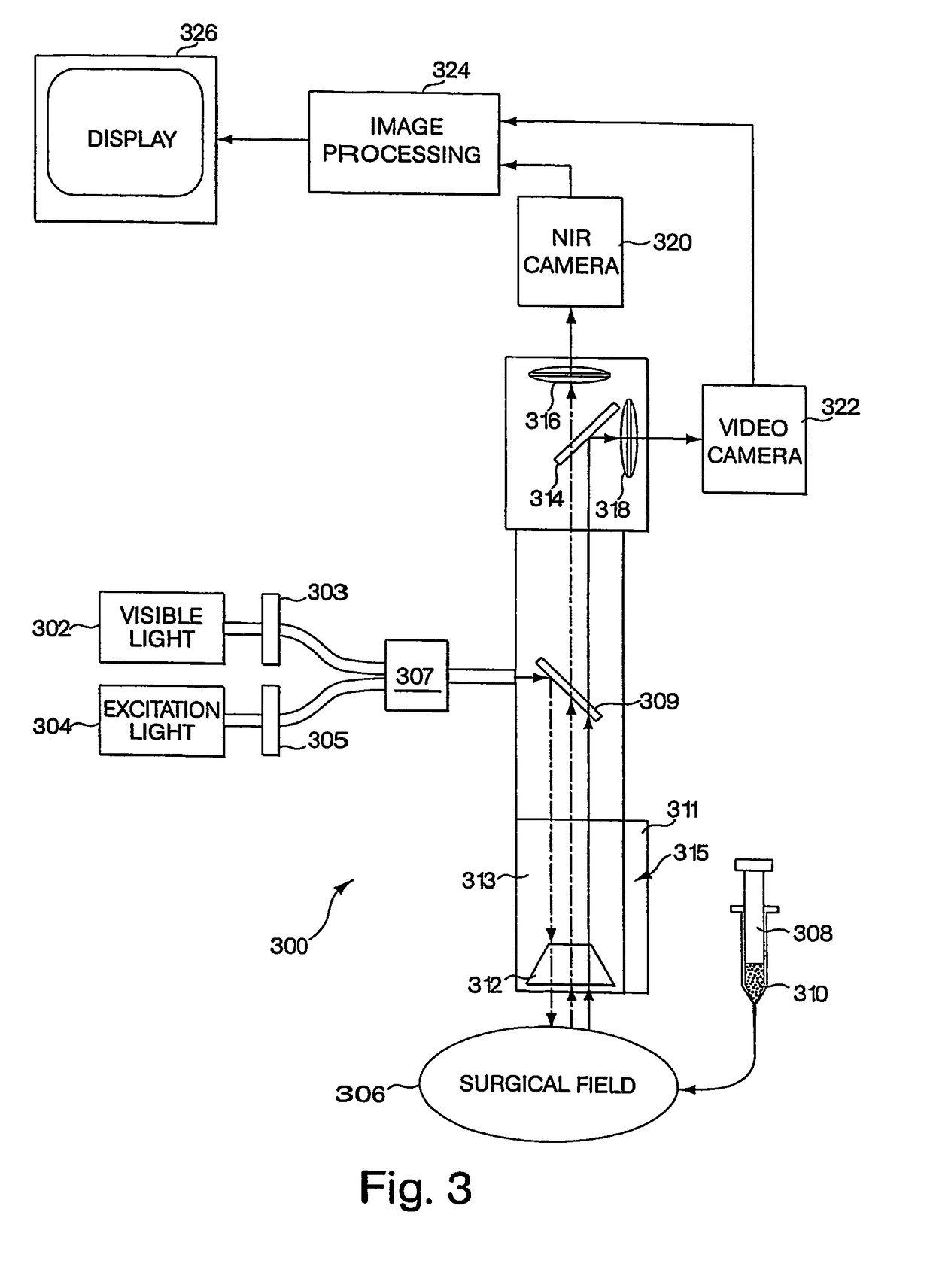
A medical imaging system provides simultaneous rendering of visible light and diagnostic or functional images. The system may be portable, and may include adapters for connecting various light sources and cameras in open surgical environments or laparascopic or endoscopic environments. A user interface provides control over the functionality of the integrated imaging system. In one embodiment, the system provides a tool for surgical pathology.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
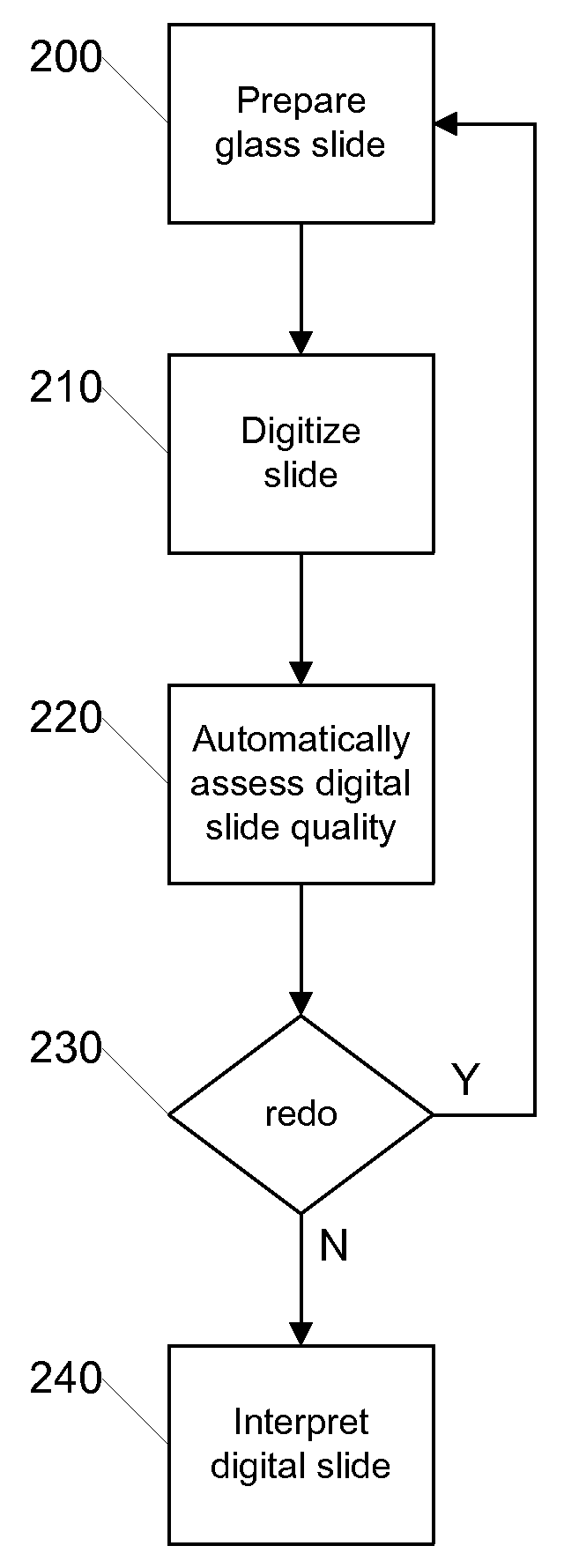
System and Method for Quality Assurance in Pathology
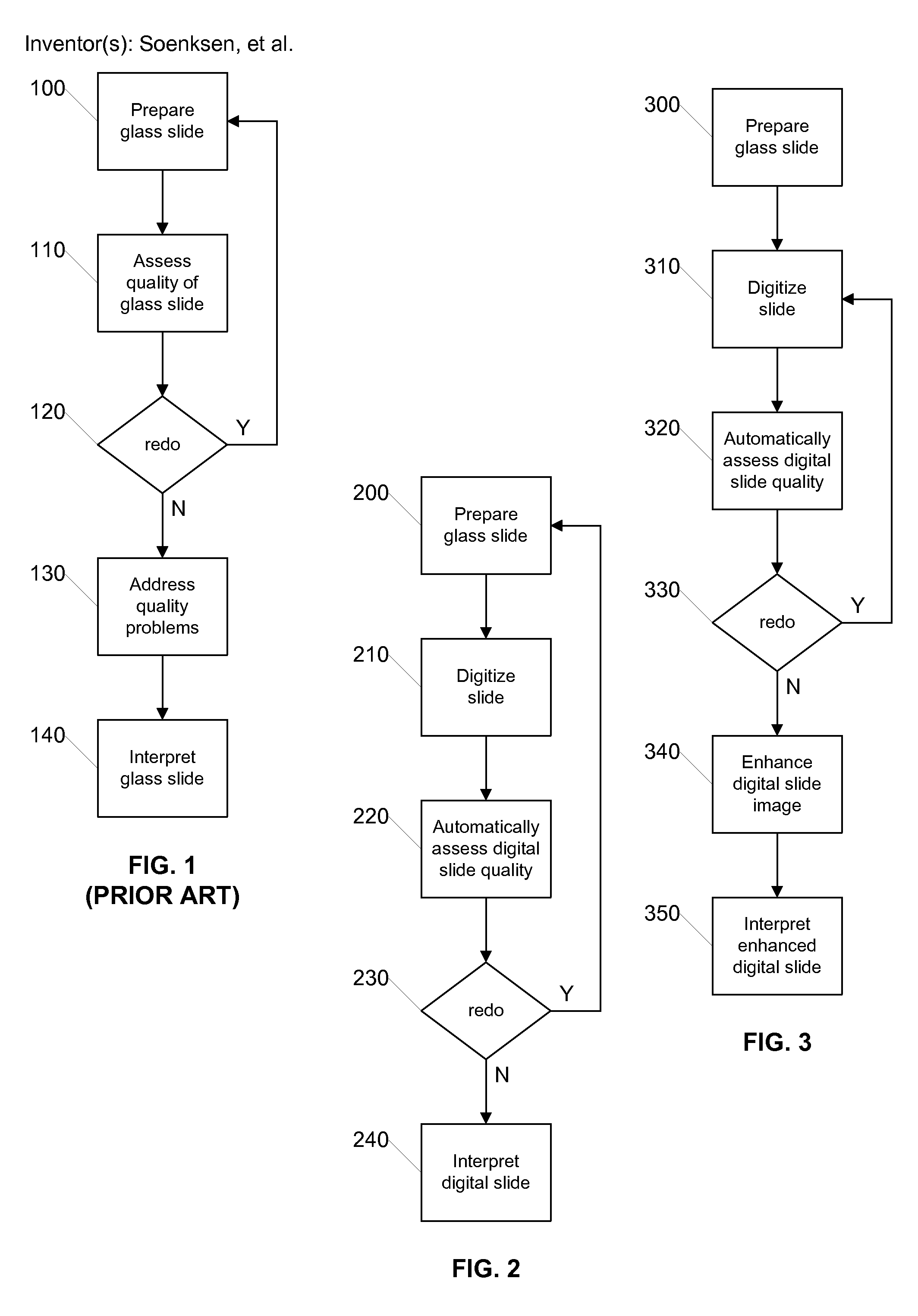
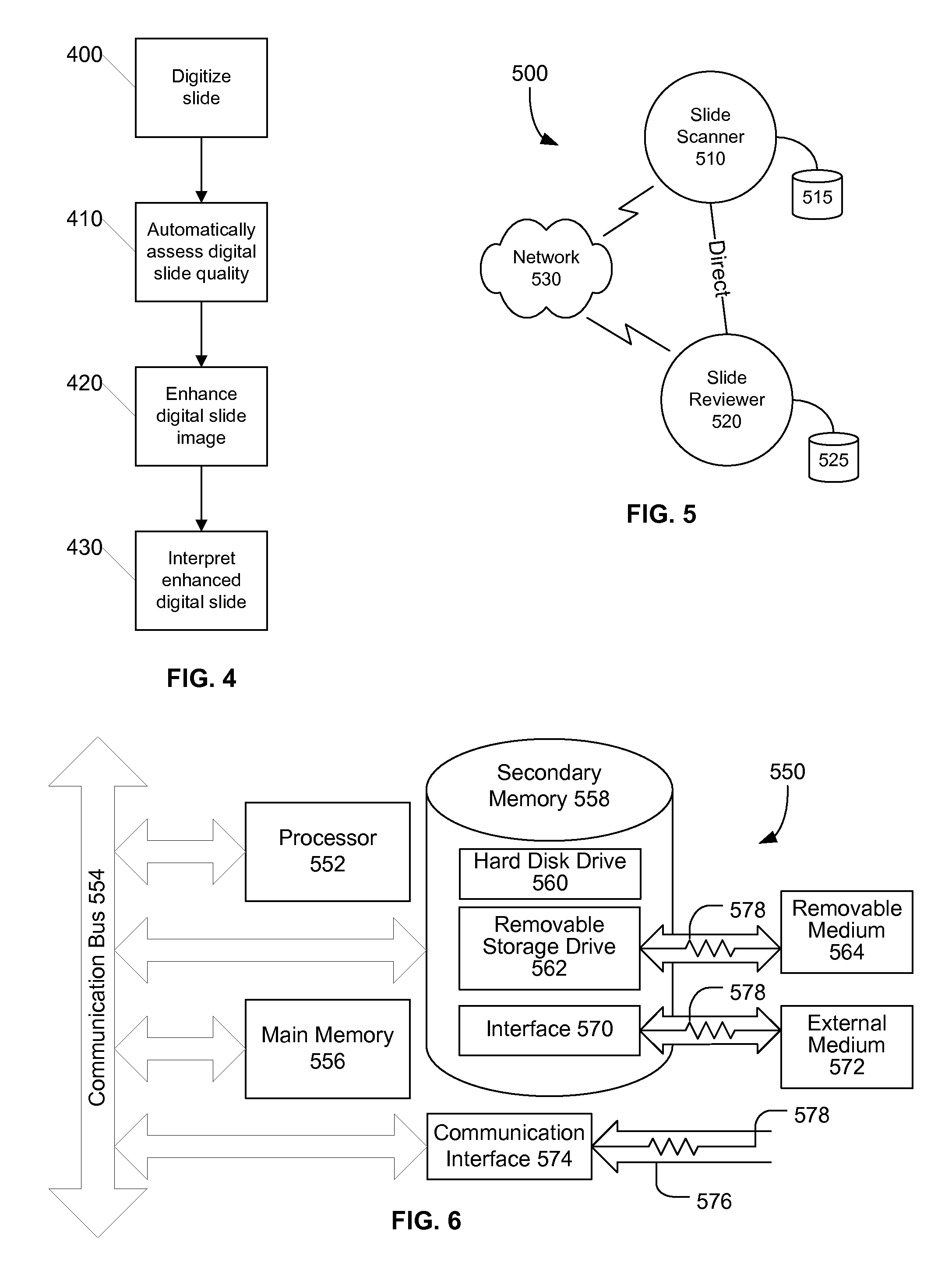
ActiveUS20080273788A1Improve quality assuranceEasy diagnosisImage enhancementData processing applicationsImaging qualityPathology diagnosis
Systems and methods for improving quality assurance in pathology using automated quality assessment and digital image enhancements on digital slides prior to analysis by the pathologist are provided. A digital pathology system (slide scanning instrument and software) creates, assesses and improves the quality of a digital slide. The improved digital slide image has a higher image quality that results in increased efficiency and accuracy in the analysis and diagnosis of such digital slides when they are reviewed on a monitor by a pathologist. These improved digital slides yield a more objective diagnosis than reading the corresponding glass slide under a microscope.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
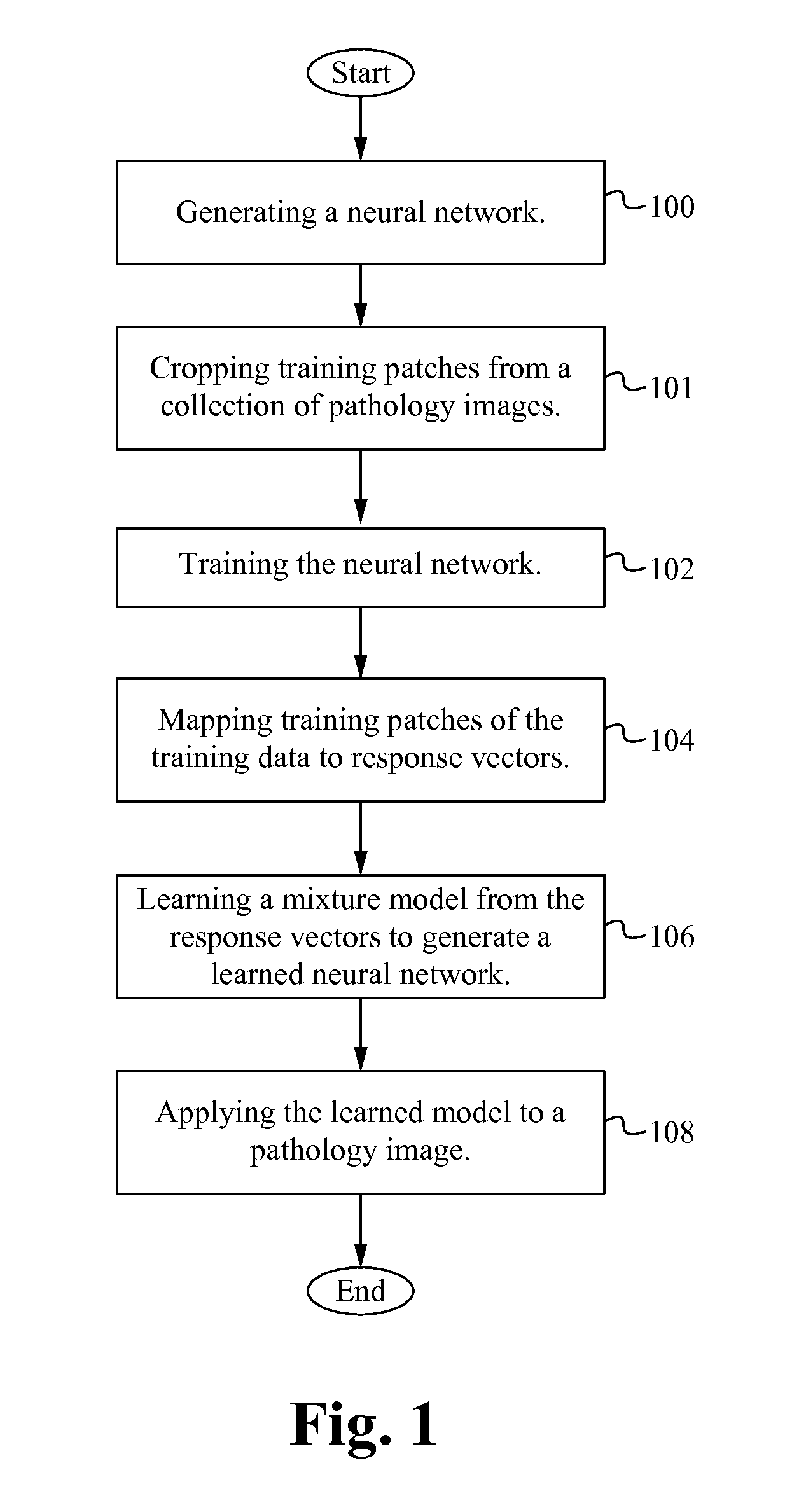
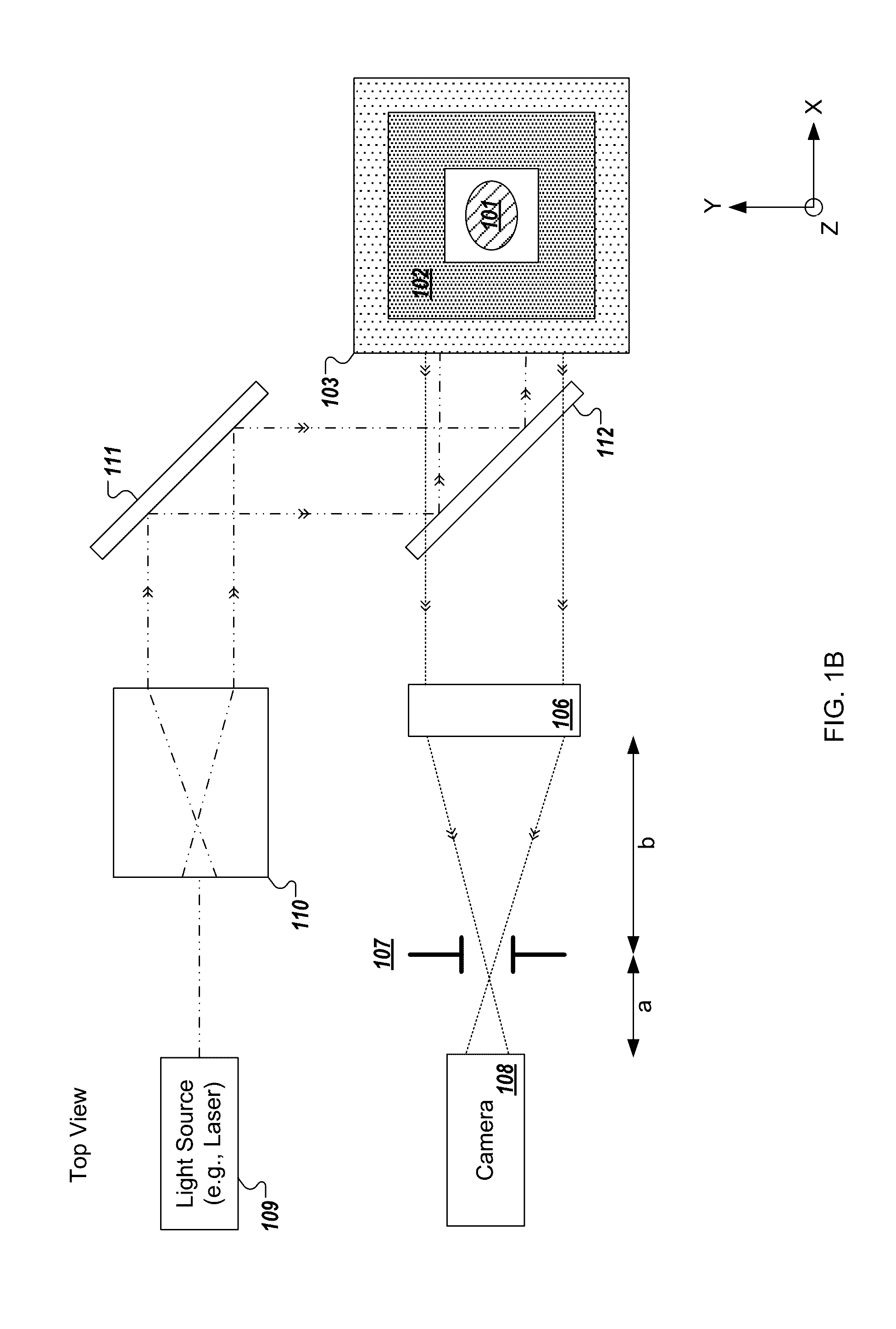
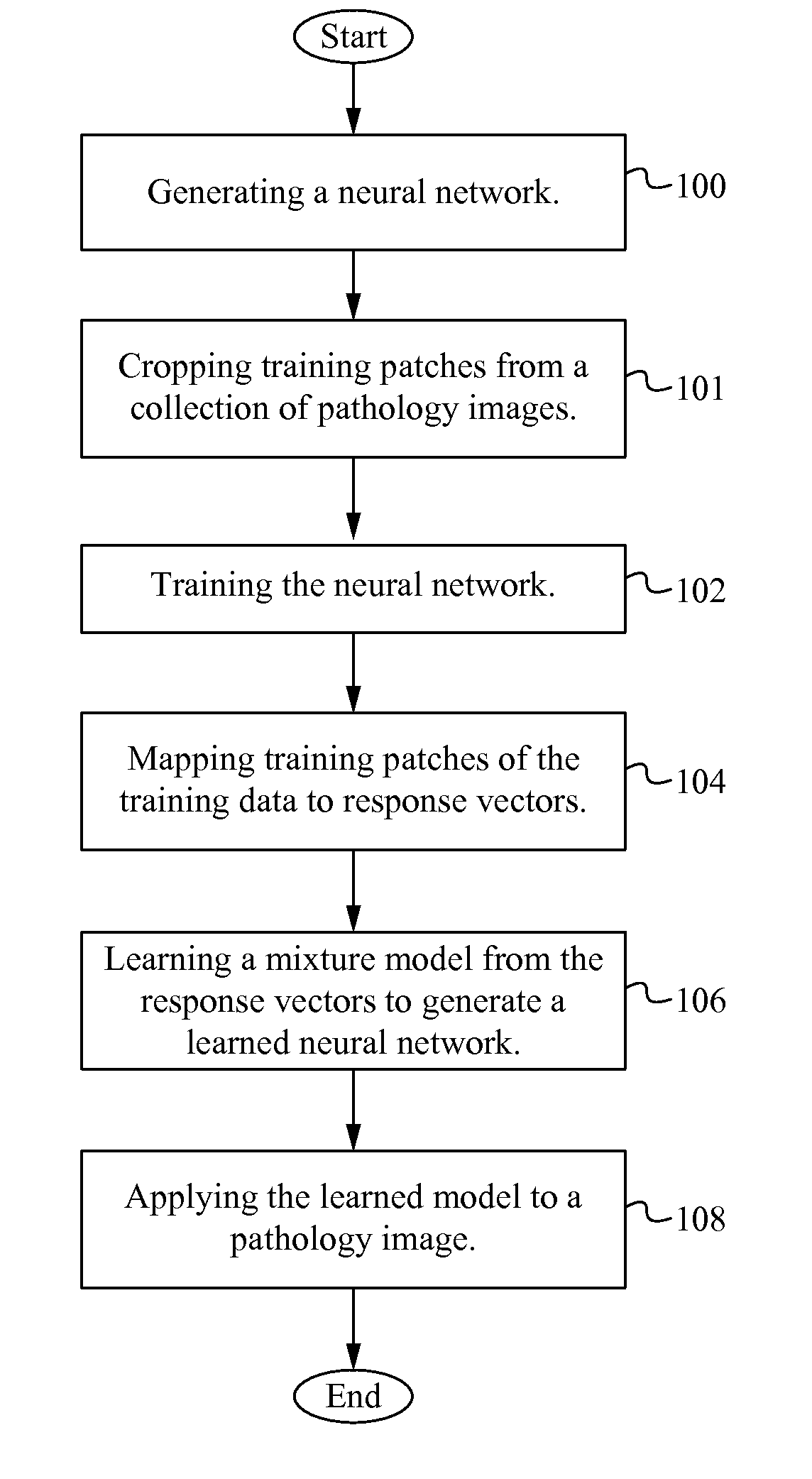
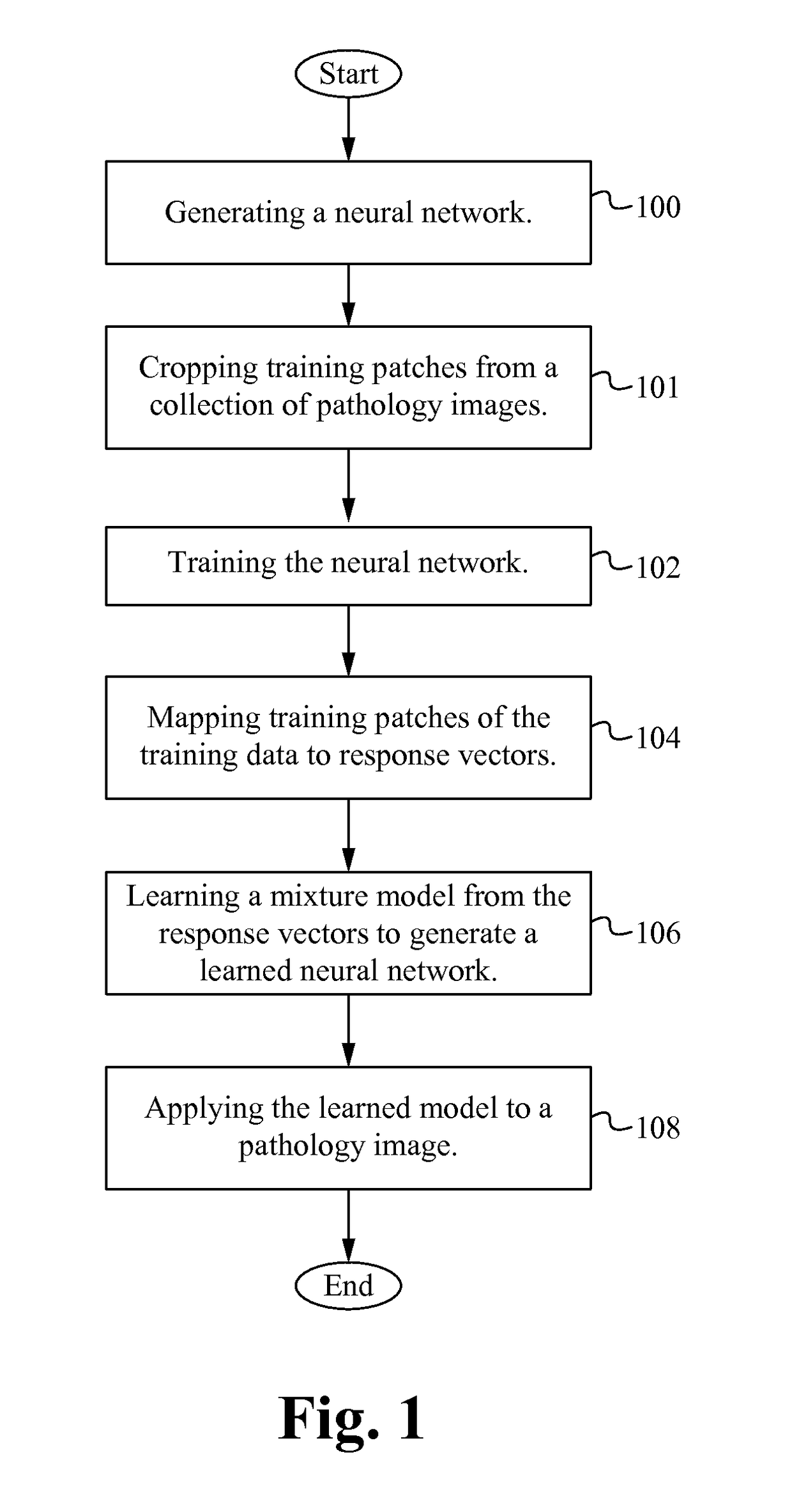
Characterizing pathology images with statistical analysis of local neural network responses
For digital pathology imaging, intelligent processing, such as automatic recognition or content-based retrieval, is one significant benefit that drives the wide application of this technology. Before any intelligent processing on pathology images, every image is converted into a feature vector which quantitatively capture its visual characteristics. An algorithm characterizing pathology images with statistical analysis of local responses of neural networks is described herein. The algorithm framework enables extracting sophisticated textural features that are well adapted to the image data of interest.
Owner:SONY CORP
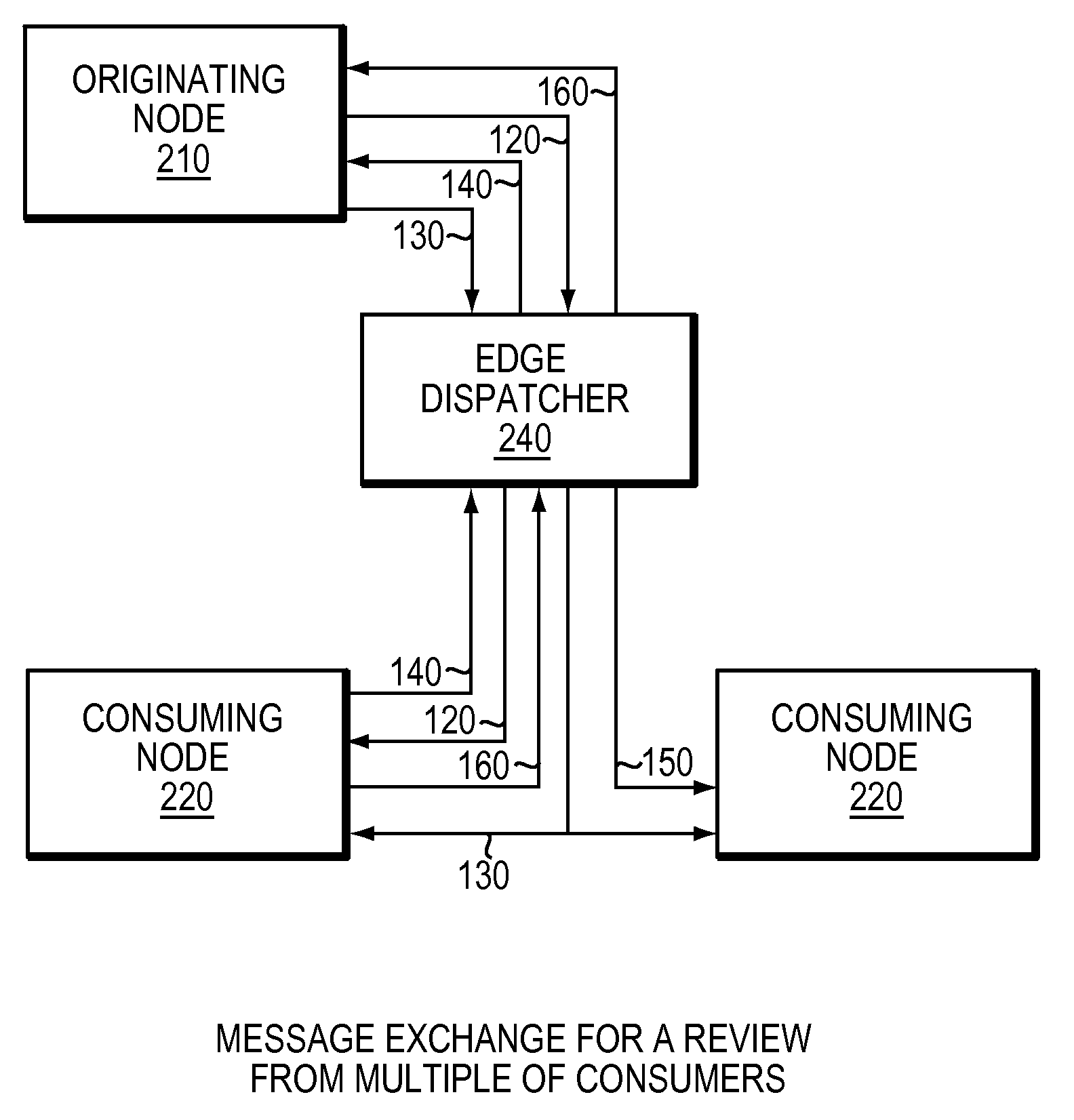
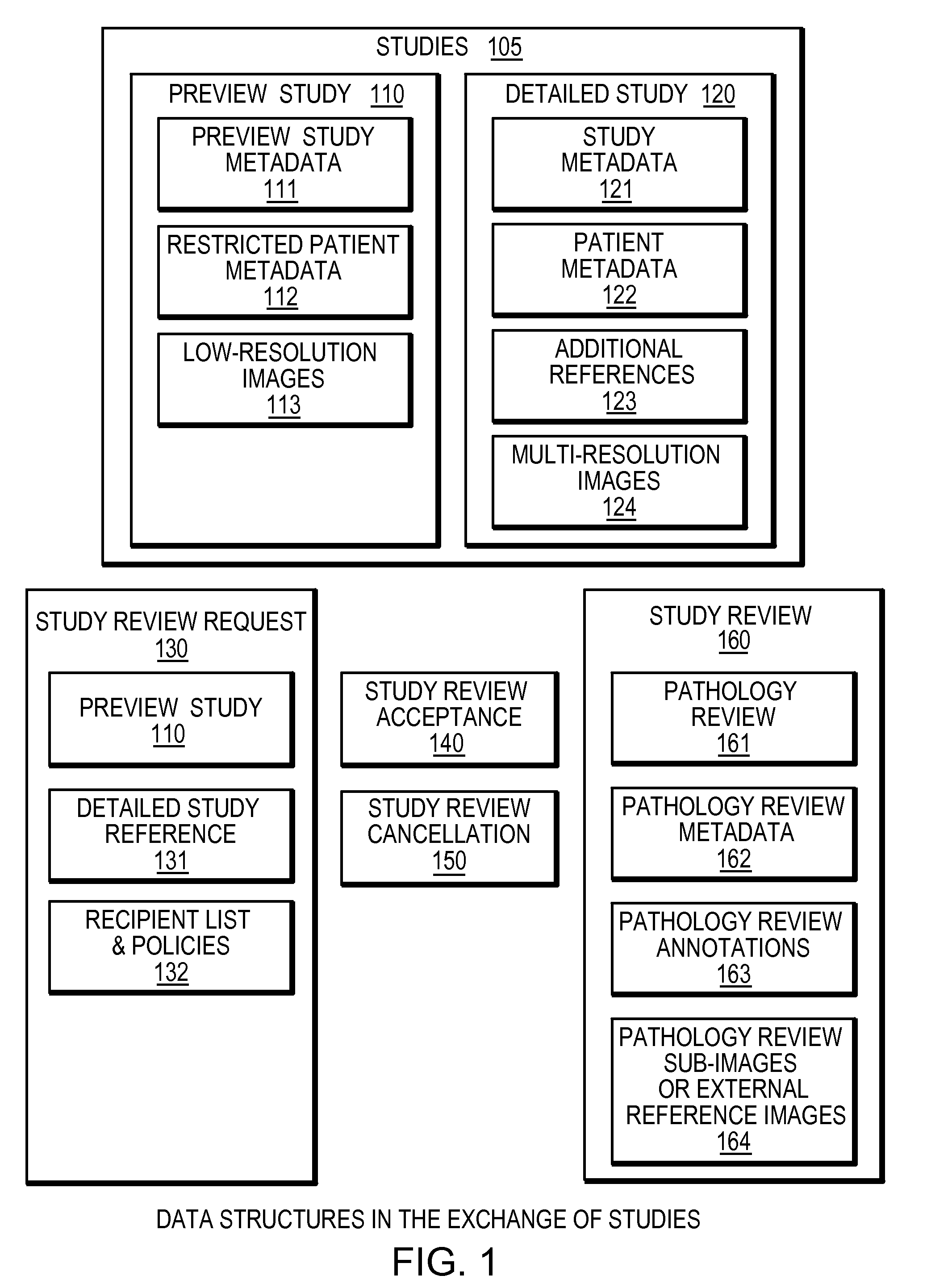
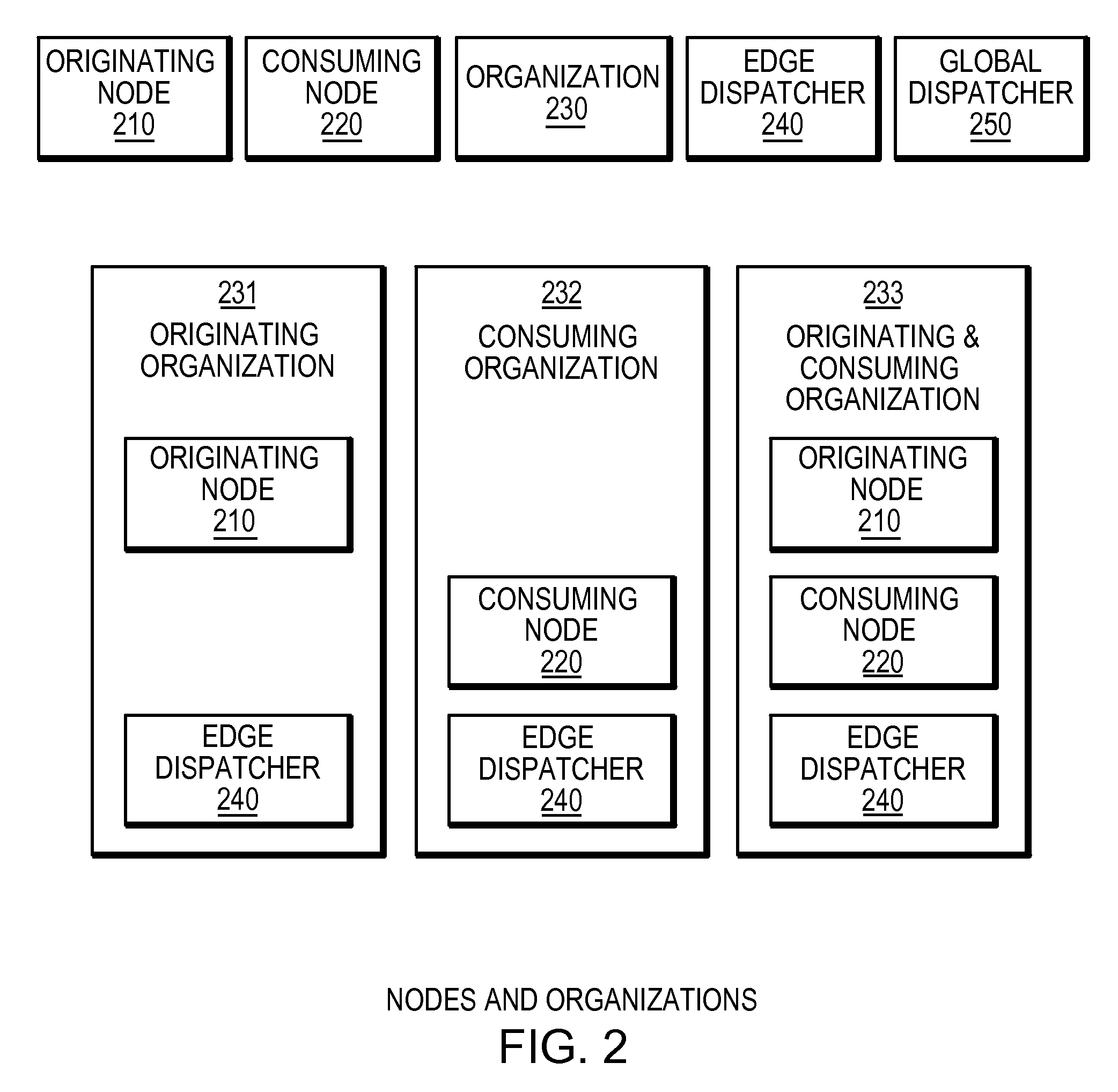
System for networked digital pathology exchange
ActiveUS20110022658A1Facilitate communicationMedical communicationCharacter and pattern recognitionPathology studyHigh resolution image
A computer-based method and apparatus to facilitate the exchange of pathology studies for the purpose of providing a primary or secondary pathological diagnosis. A study consists of one or more lower-resolution images, the references to the corresponding higher-resolution images, associated image metadata, study metadata and patient metadata. The studies are exchanged from one organization (hospital, practice, or individual physician) to another organization through a set of interconnected dispatcher services. In a cloud model, a plurality of dispatchers may be connected through a Global Dispatcher, both facilitating the addition of new organizations to the cloud and allowing for the addressing of studies from any organization in the cloud to any organization, group or individual in the cloud. By this means, the originating organization may obtain the desired level of care through the selection of recipient organizations, groups and individuals according to the organization's existing criteria. Efficiency in diagnosis is improved through the addressing of a study to a plurality of qualified recipients, as the first recipient with an appropriate, available resource may review and provide a diagnosis for the study.
Owner:CORISTA
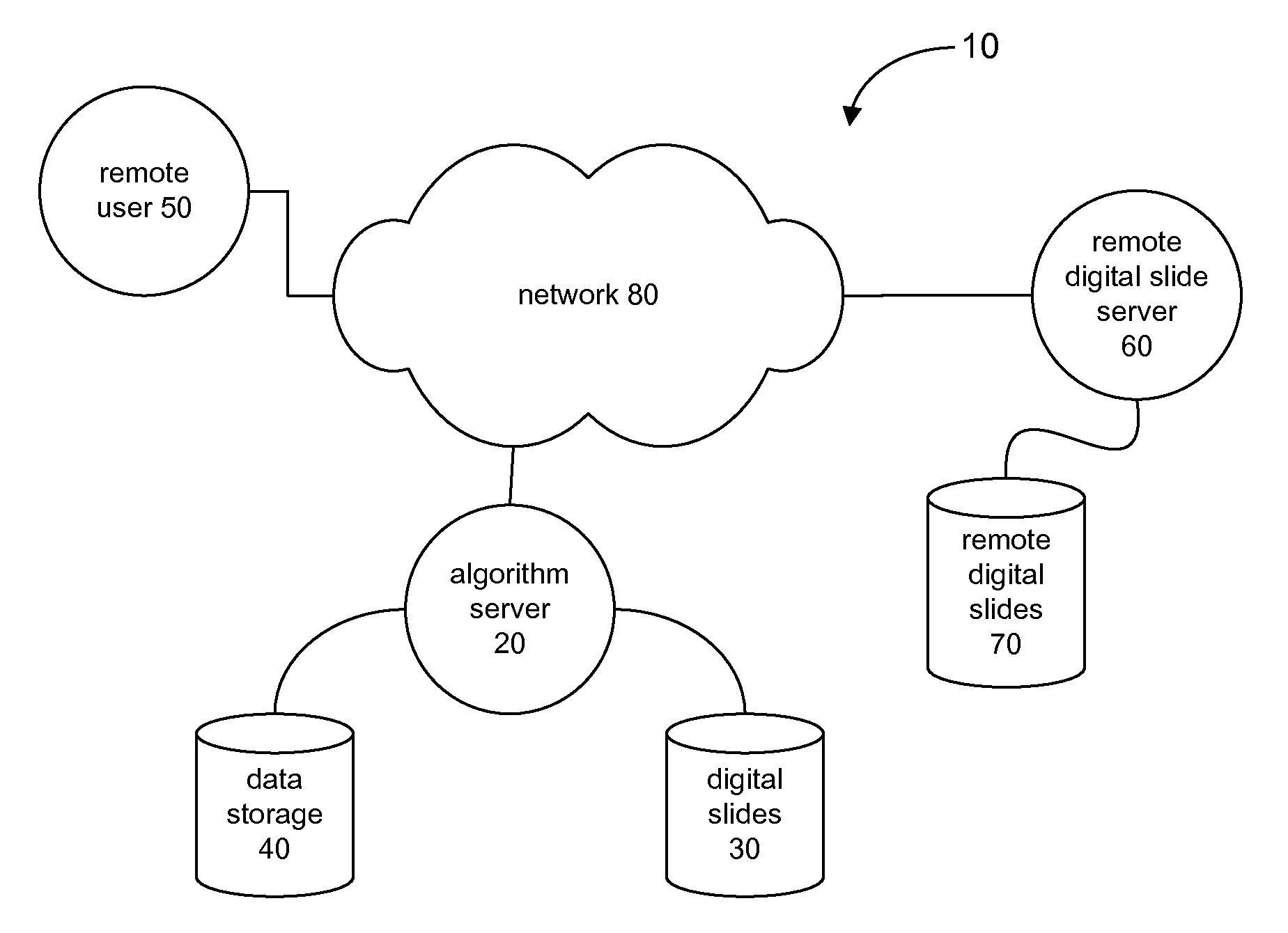
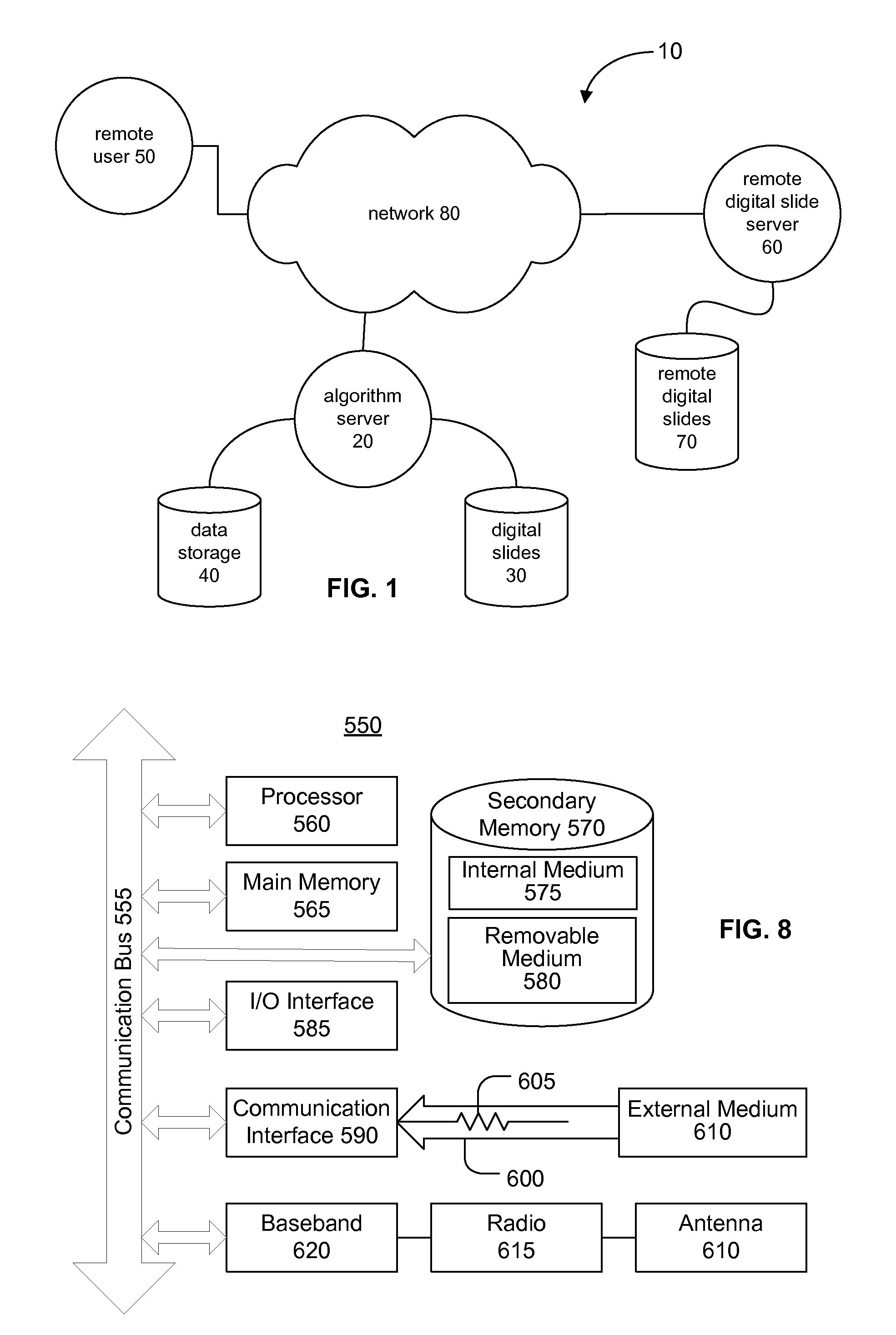
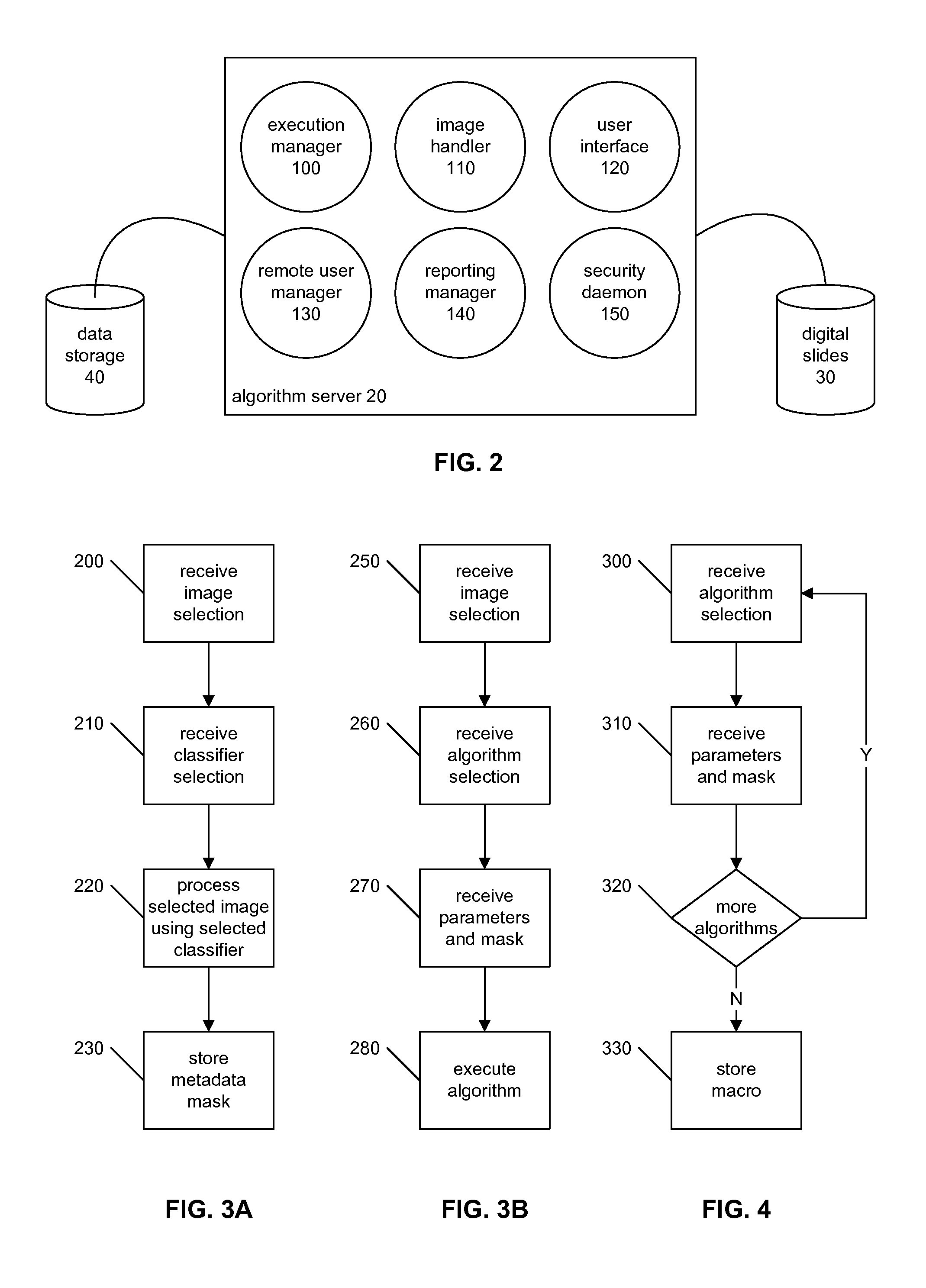
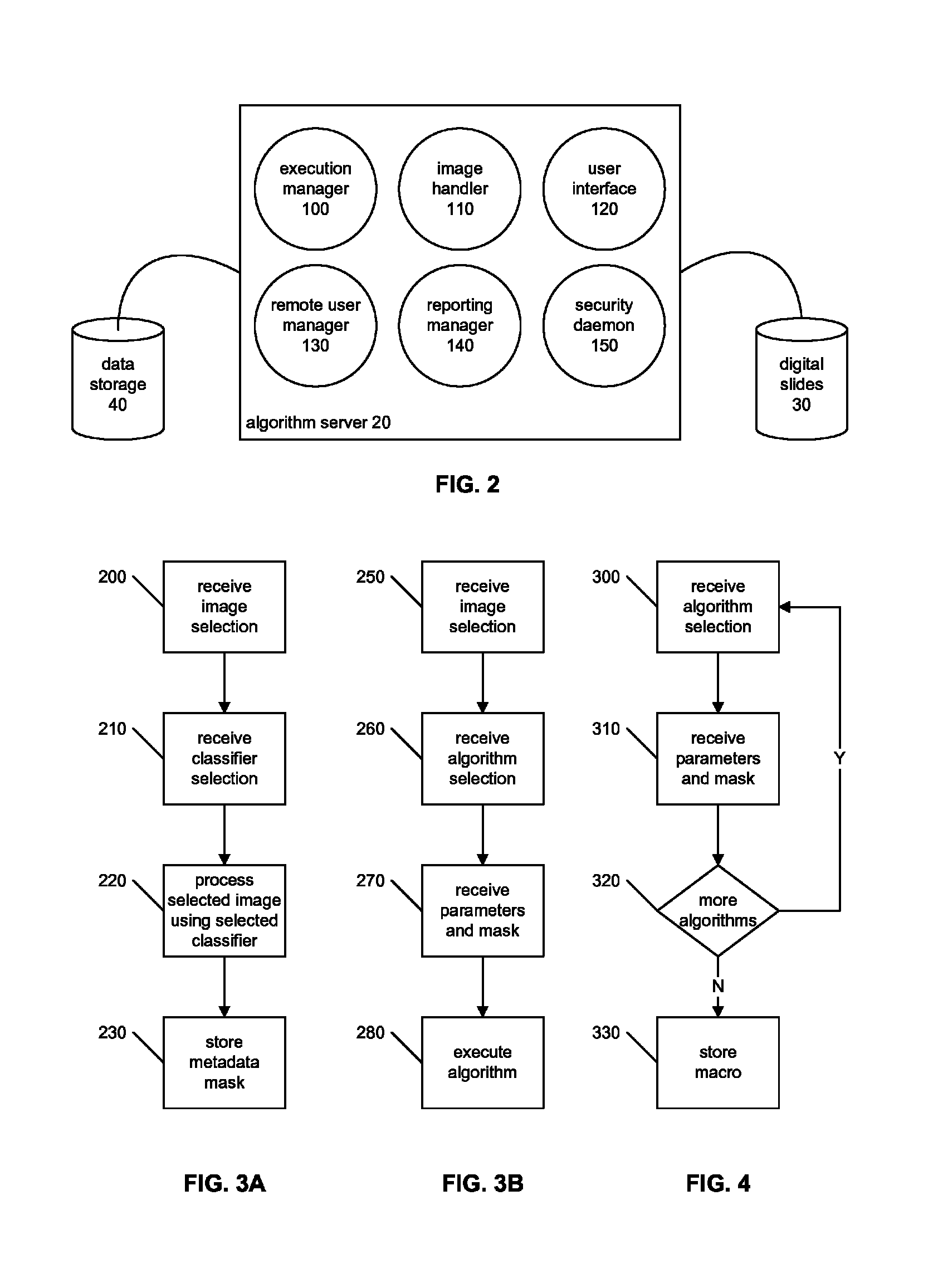
Signal to Noise Ratio in Digital Pathology Image Analysis
ActiveUS20120014576A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReadily apparentImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging data
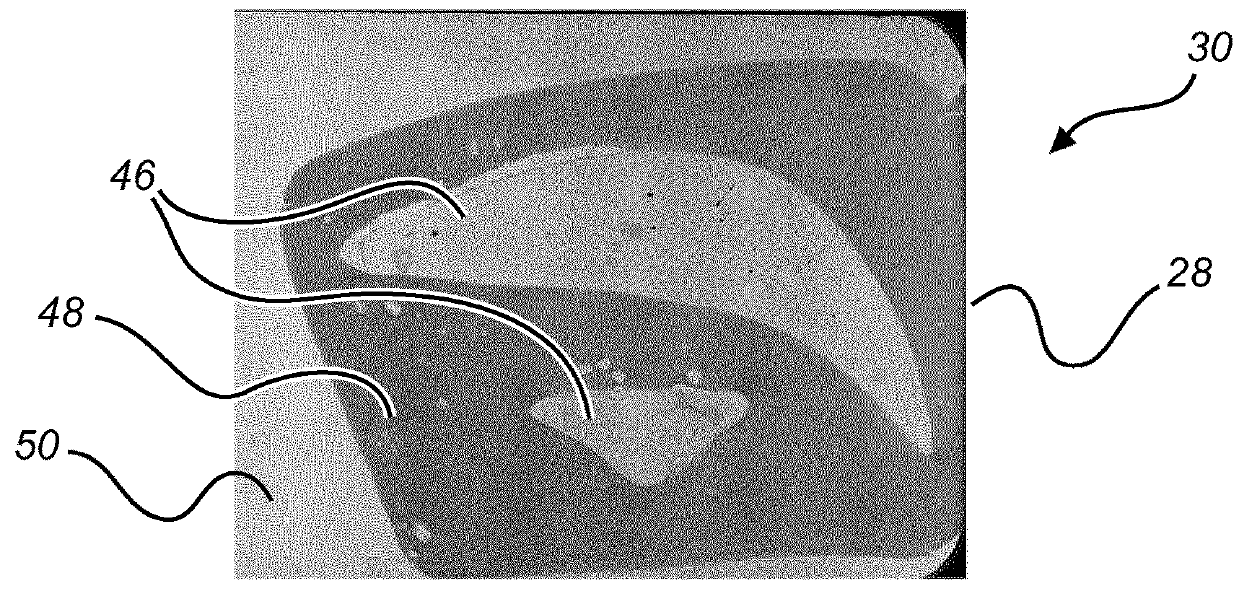
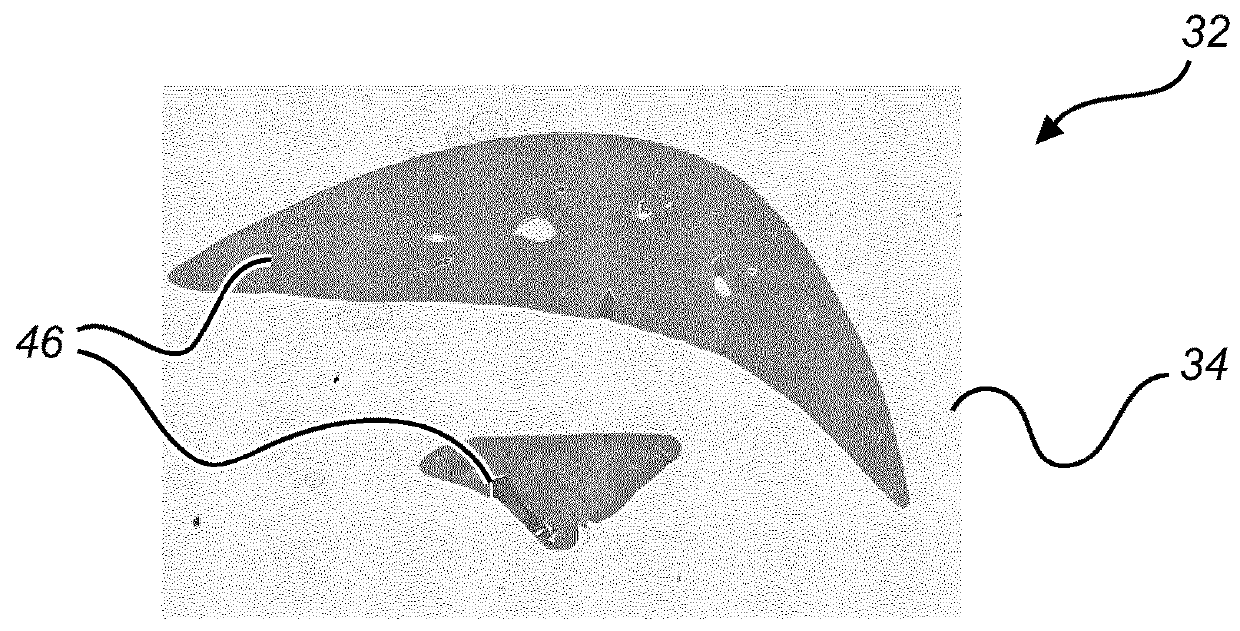
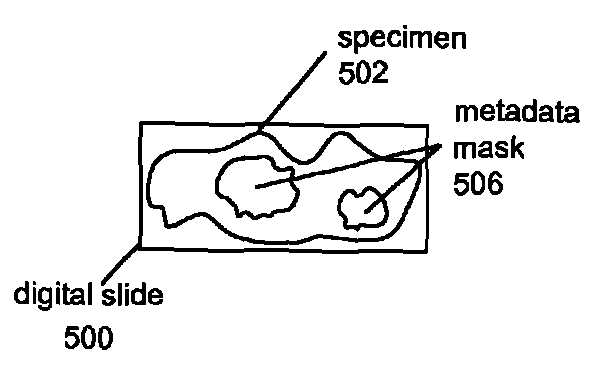
A digital slide analysis system comprises an algorithm server that maintains or has access to a plurality of image processing and analysis routines. The algorithm server additionally has access to a plurality of digital slide images. The algorithm server executes a selected routine on an identified digital slide and provides the resulting data. Prior to the application of selected routine, the system employs a digital pre-processing module to create a metadata mask that reduces undesirable image data such that the image data processed by the selected routine has an improved signal to noise ratio. The pre-processing module uses a classifier that may be implemented as a pattern recognition module, for example. Undesirable image data is therefore excluded from the image data that is processed by the digital pathology image processing and analysis routine, which significantly improves the digital pathology image analysis.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
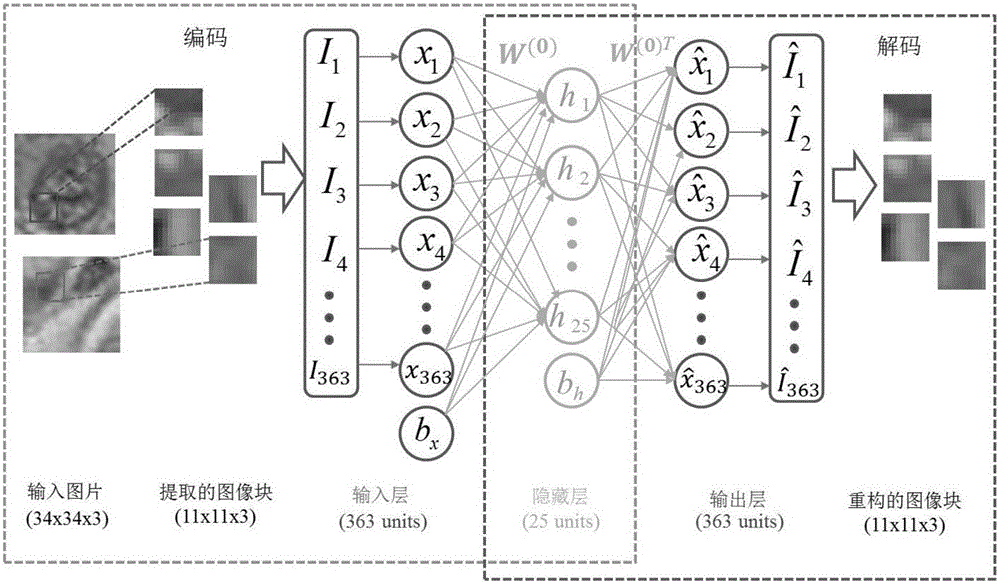
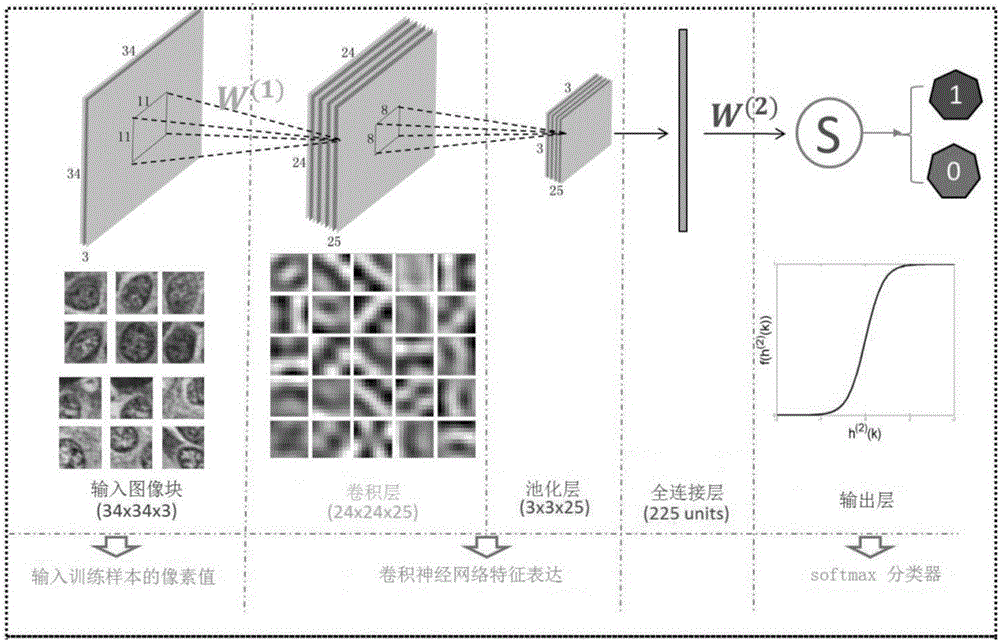
Cell detection method based on sliding window and depth structure extraction features
ActiveCN104346617AImprove detection accuracyImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionModel extractionFeature extraction
The invention discloses a cell detection method based on a sliding window and depth structure extraction features. The cell detection method is used for automatically detecting cells by utilizing depth model extraction features and then applying a sliding window technology to a pathological section image. The cell detection method comprises the following steps: section image blocking, training of stacked and sparse self-coding of a feature extraction model, detector training, scanning of a large image by the sliding window and cell position labeling. According to the cell detection method, the large section image is used as a search object, the positions of cells in the image can be found more accurately, faster and completely by adopting a new method of combining a detector and the sliding window, and a good detection effect can be achieved for some unobvious cells in the image. The automatic cell detection method disclosed by the invention can be used for assisting a clinical doctor in carrying out quantitative evaluation on digital pathological sections and accurately and rapidly carrying out clinical diagnosis, so that the diagnosis difference of different observers or one observer at different time periods is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Display with optical microscope emulation functionality
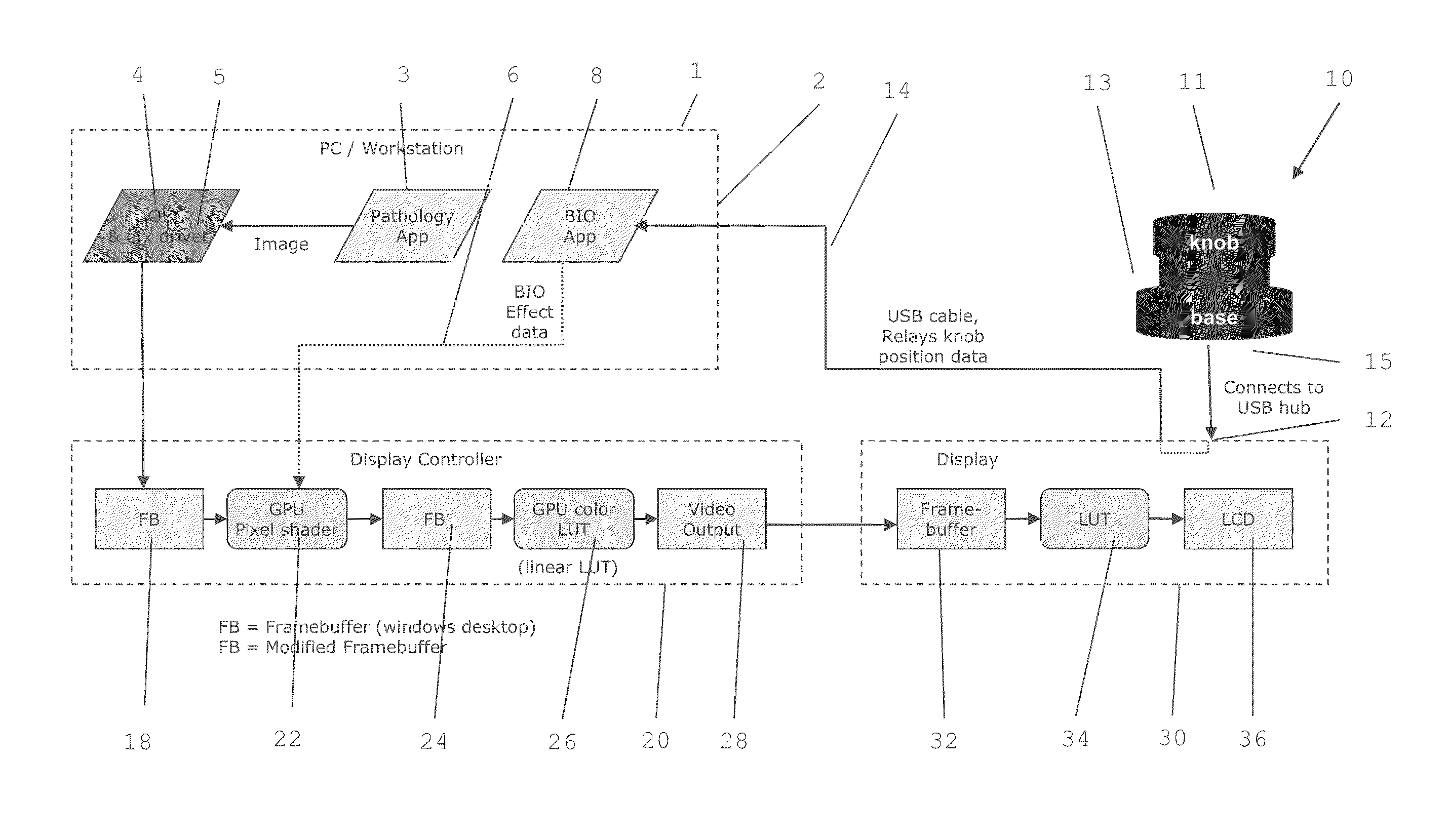
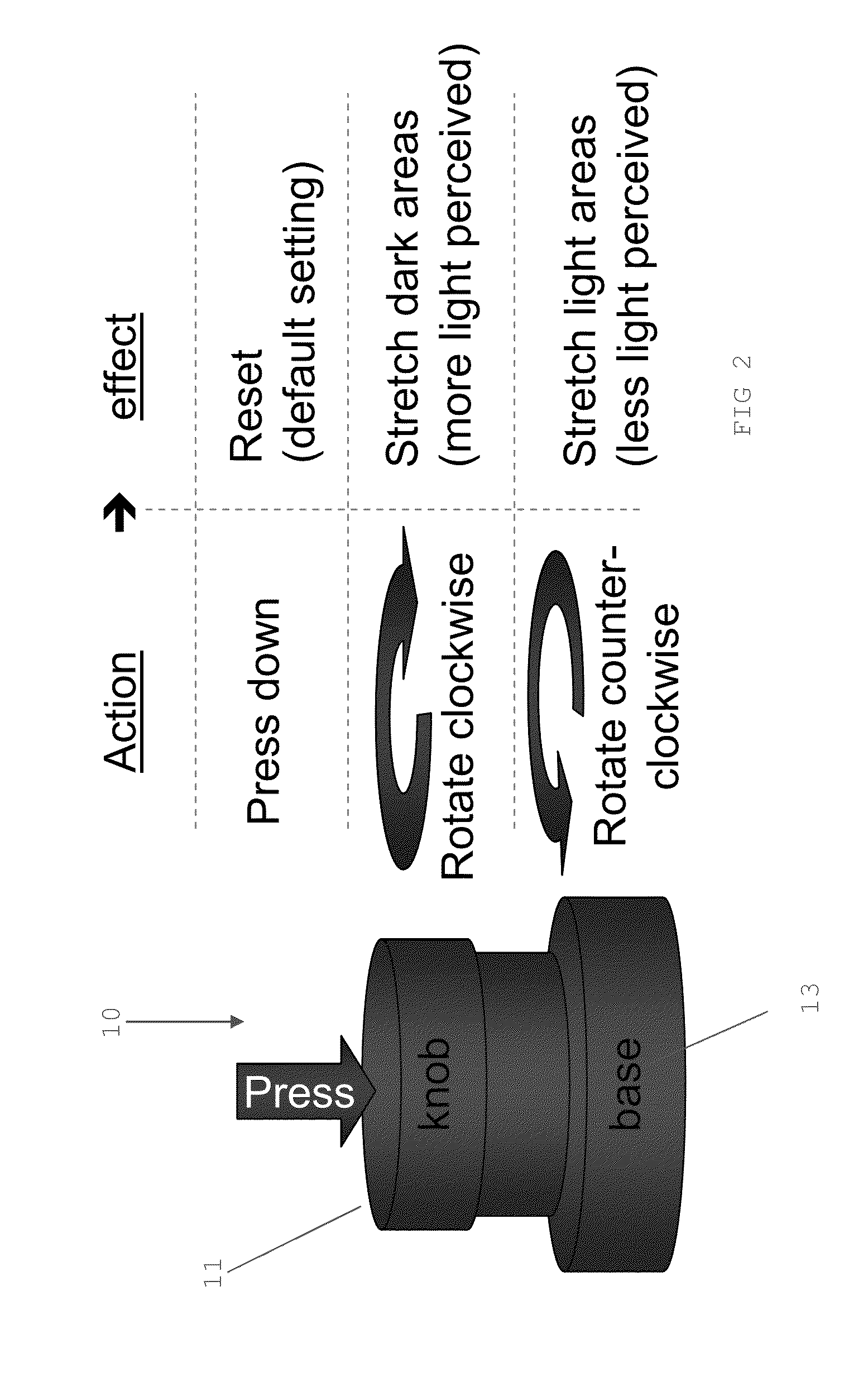
InactiveUS20140139541A1Processing speedGood control over image presentationCathode-ray tube indicatorsMicroscopesDigital signal processingControl signal
An optical microscope digital image processing emulator or emulation is described in which a user input device is used to assist in the emulation of an operation of an optical microscope in a digital image processing system. The emulator or emulation is programmable via a library of processing functions stored in memory. The input device is adapted to generate control signals based on a user input, and to transfer the control signals to a processor, the processor being adapted to alter one or more parameters of the processing functions based on the control signals.Embodiments of the present invention emulate the same control and responsiveness found with an optical microscope on a digital pathology computer system, thereby improving the workflow of pathology specialists by allowing better and faster control over the way images are presented.
Owner:BARCO NV
Image processing method in microscopy
ActiveUS20130089249A1Improvement of image registration efficiencySmall dimensionImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageImaging processing
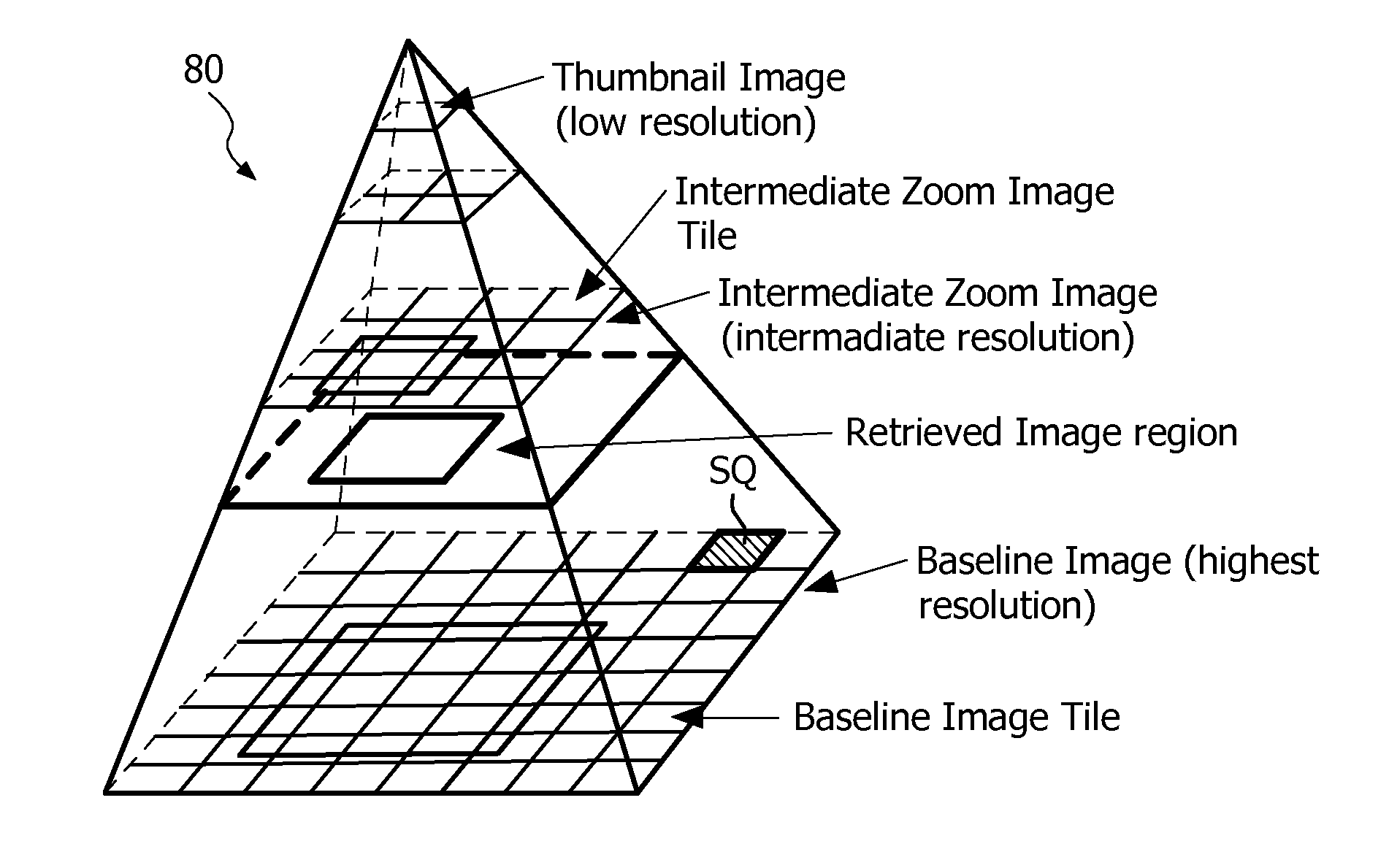
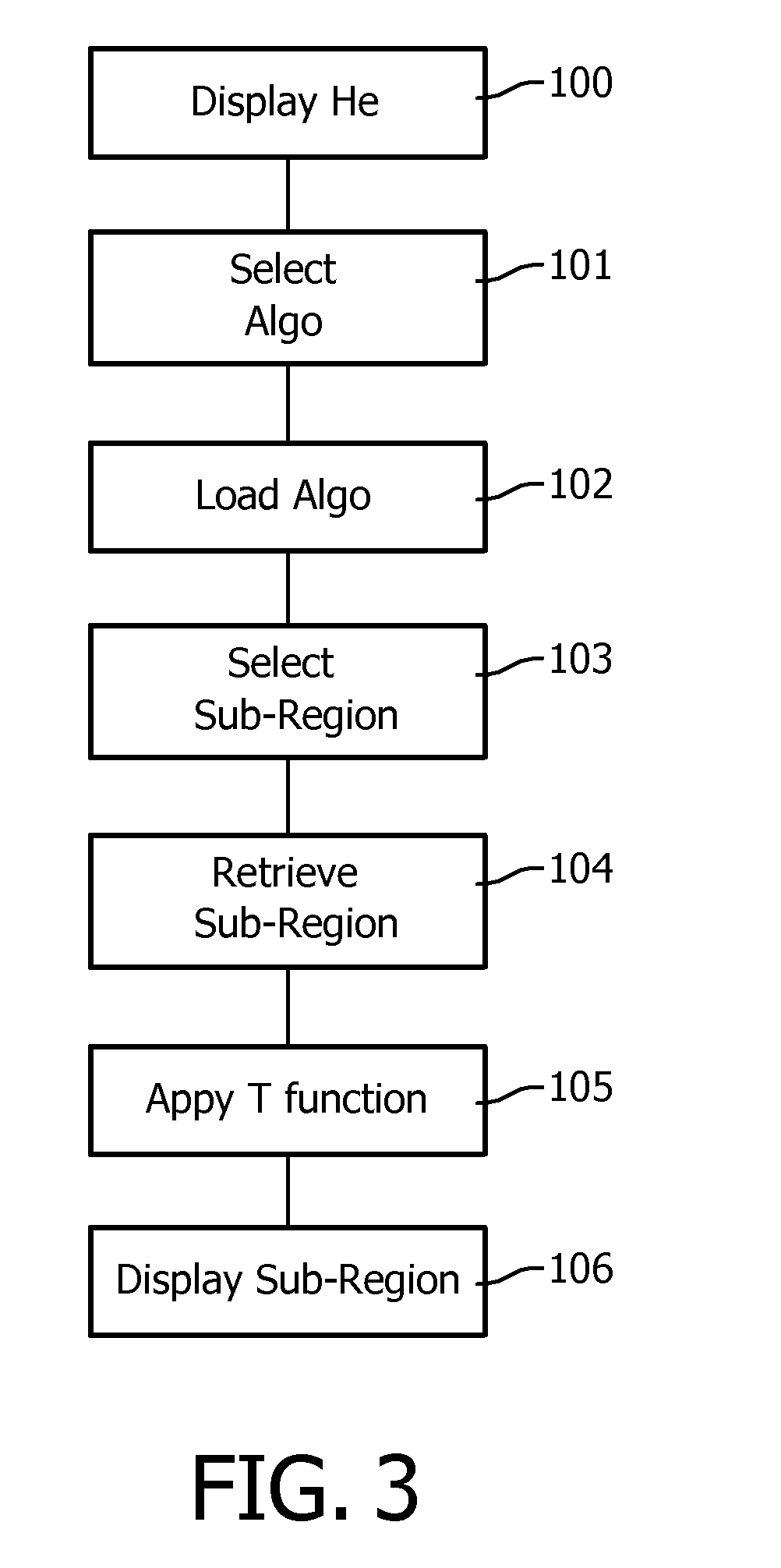
The invention pertains to the field of image processing in digital pathology. It notably proposes a method for processing a first digital image, representing a sample in a region, and which image has been acquired from the sample by means of a microscopic imaging system (1) and is stored in a multi-resolution image data structure (80), comprising the steps of:—retrieving (104) a sub-region of the first digital image at a first resolution, —executing (105) a transform function on the retrieved sub-region, the transform function modifying a content of the sub-region according to at least one metric derived from a second resolution representation of the first digital image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
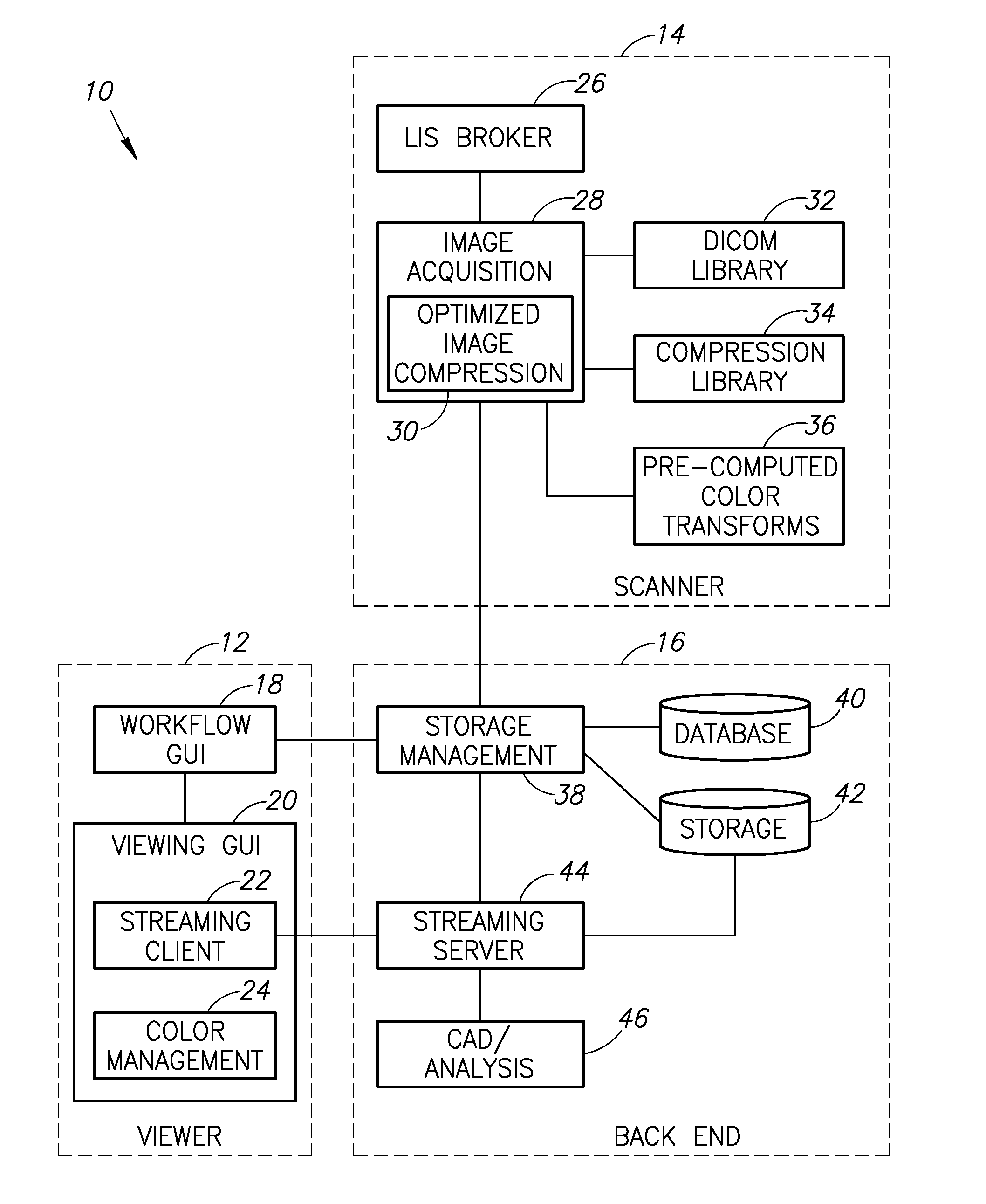
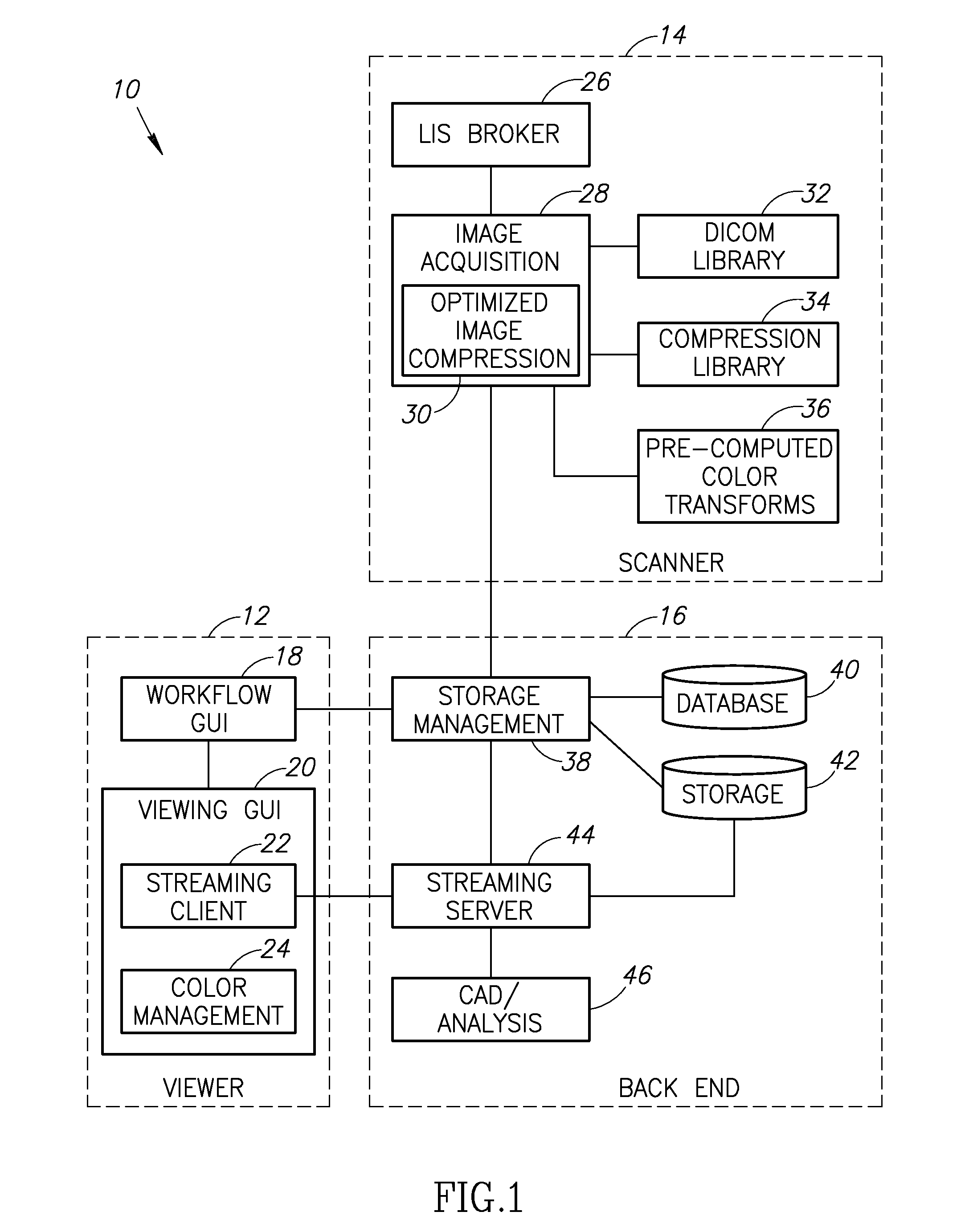
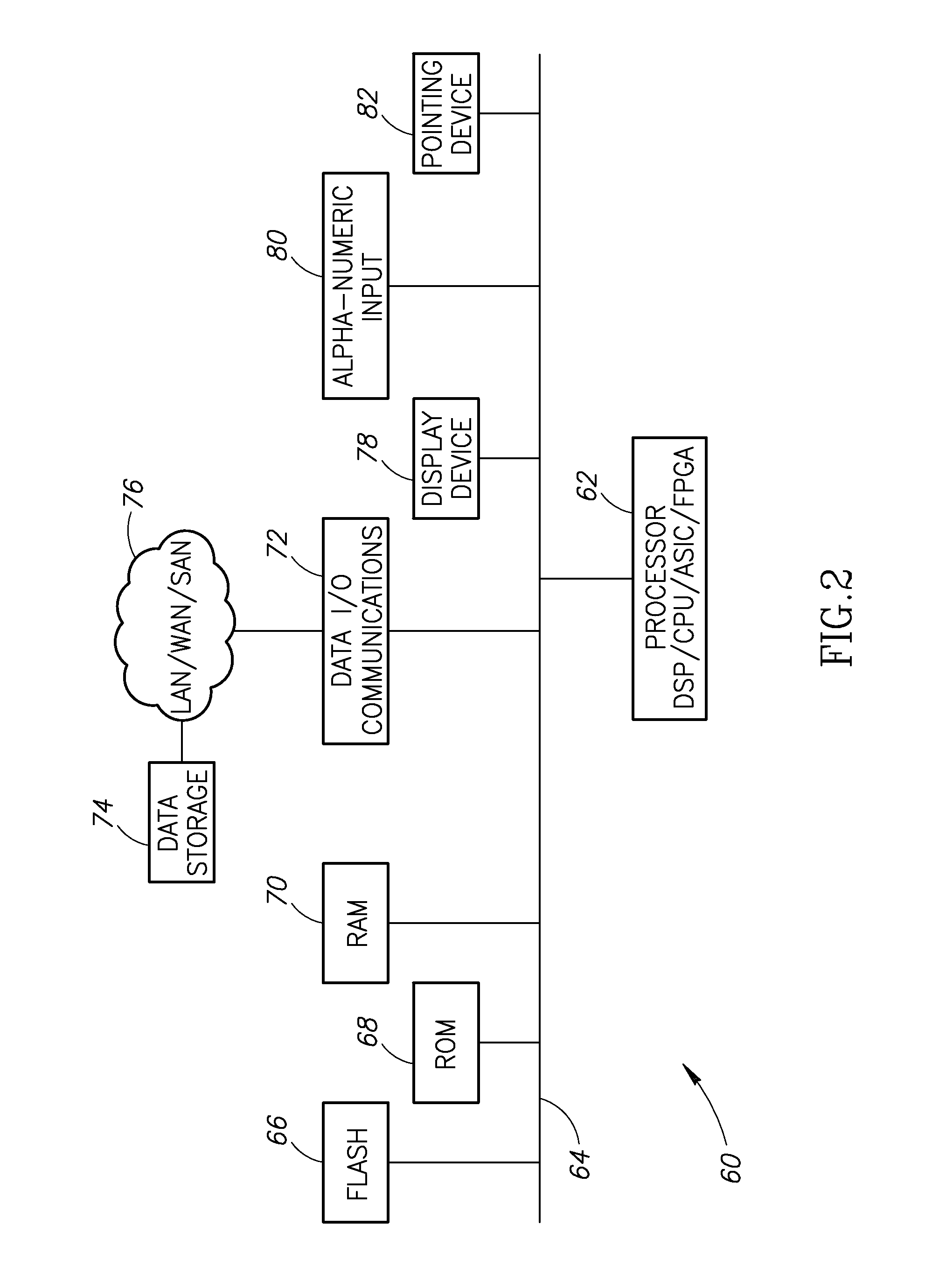
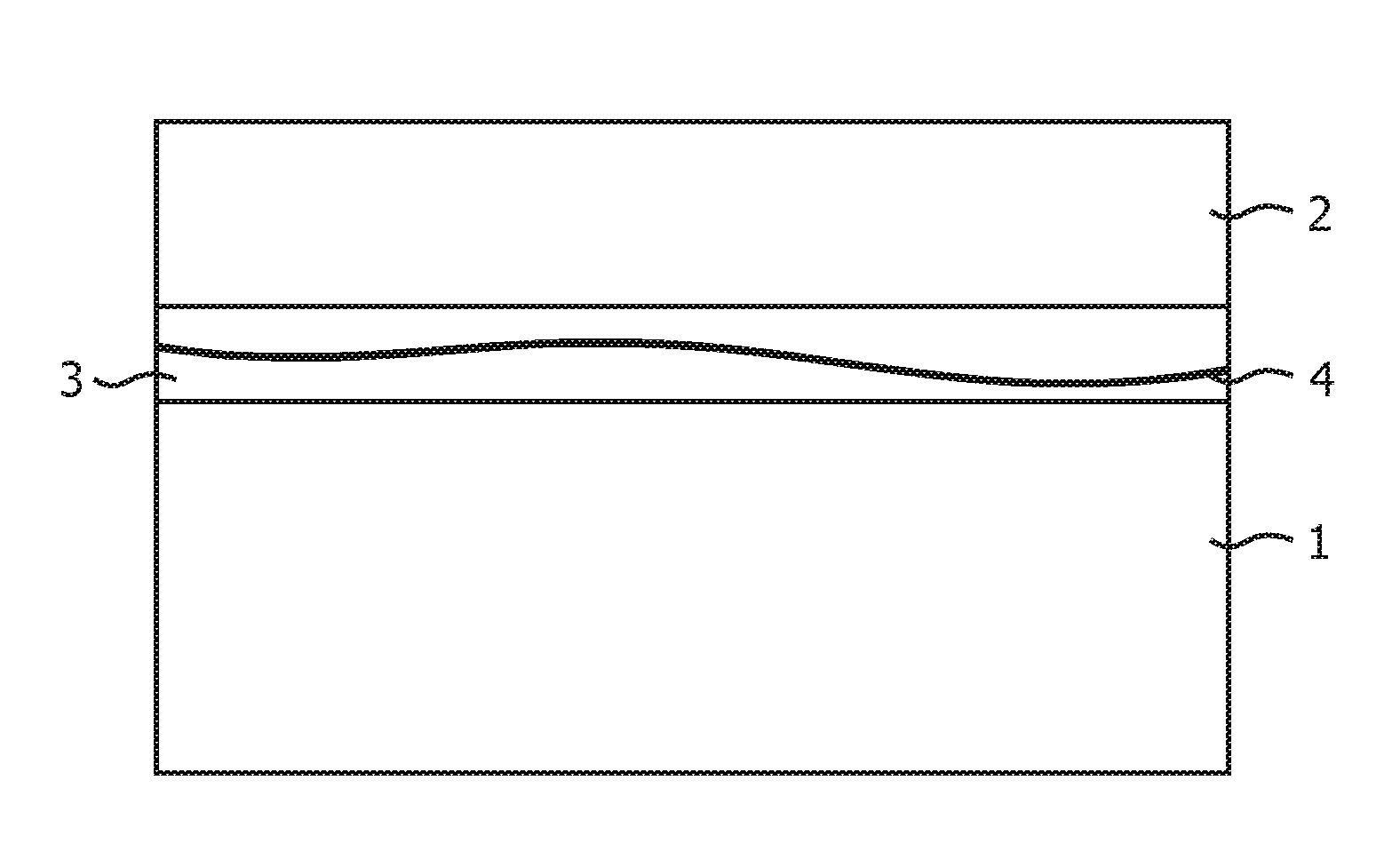
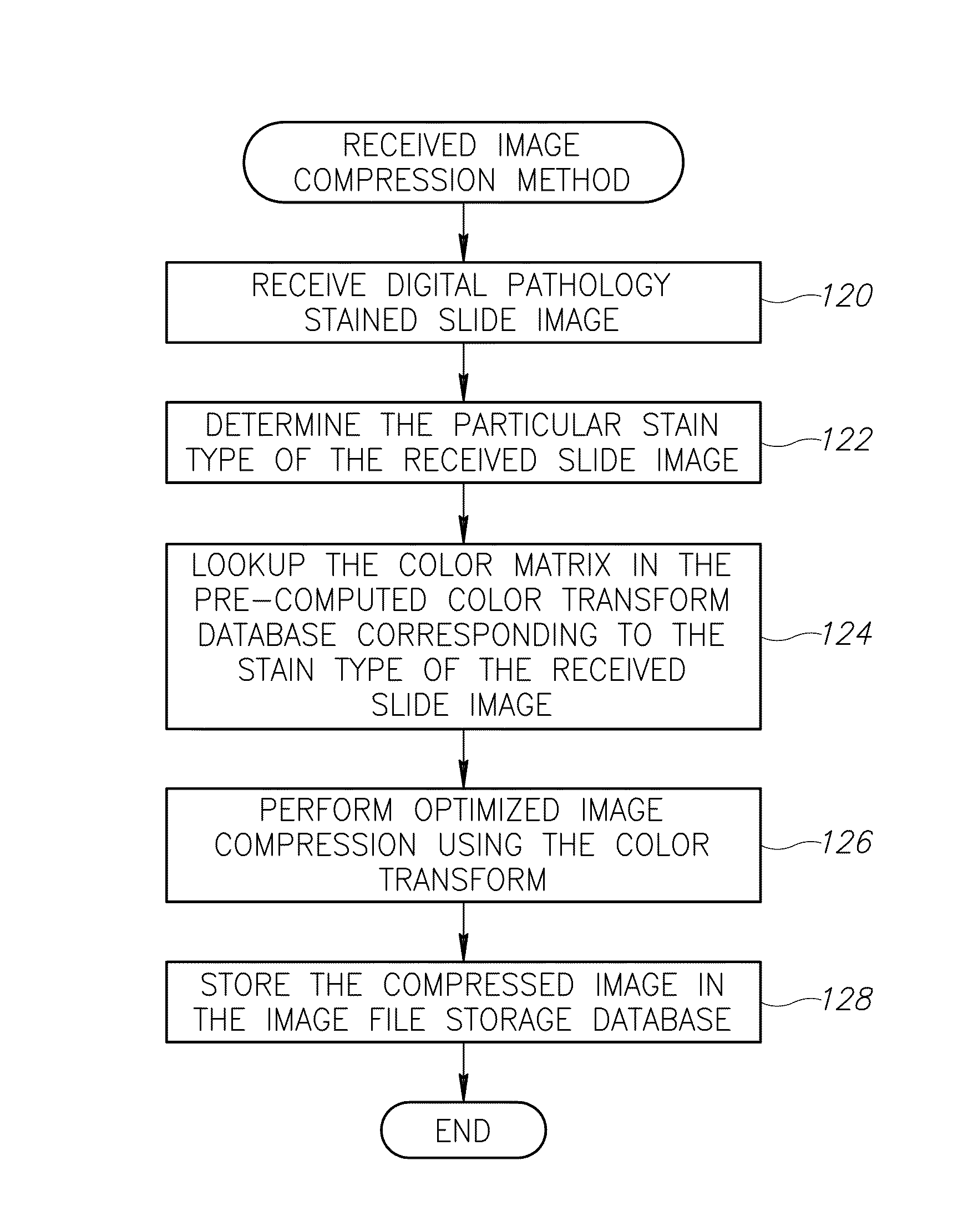
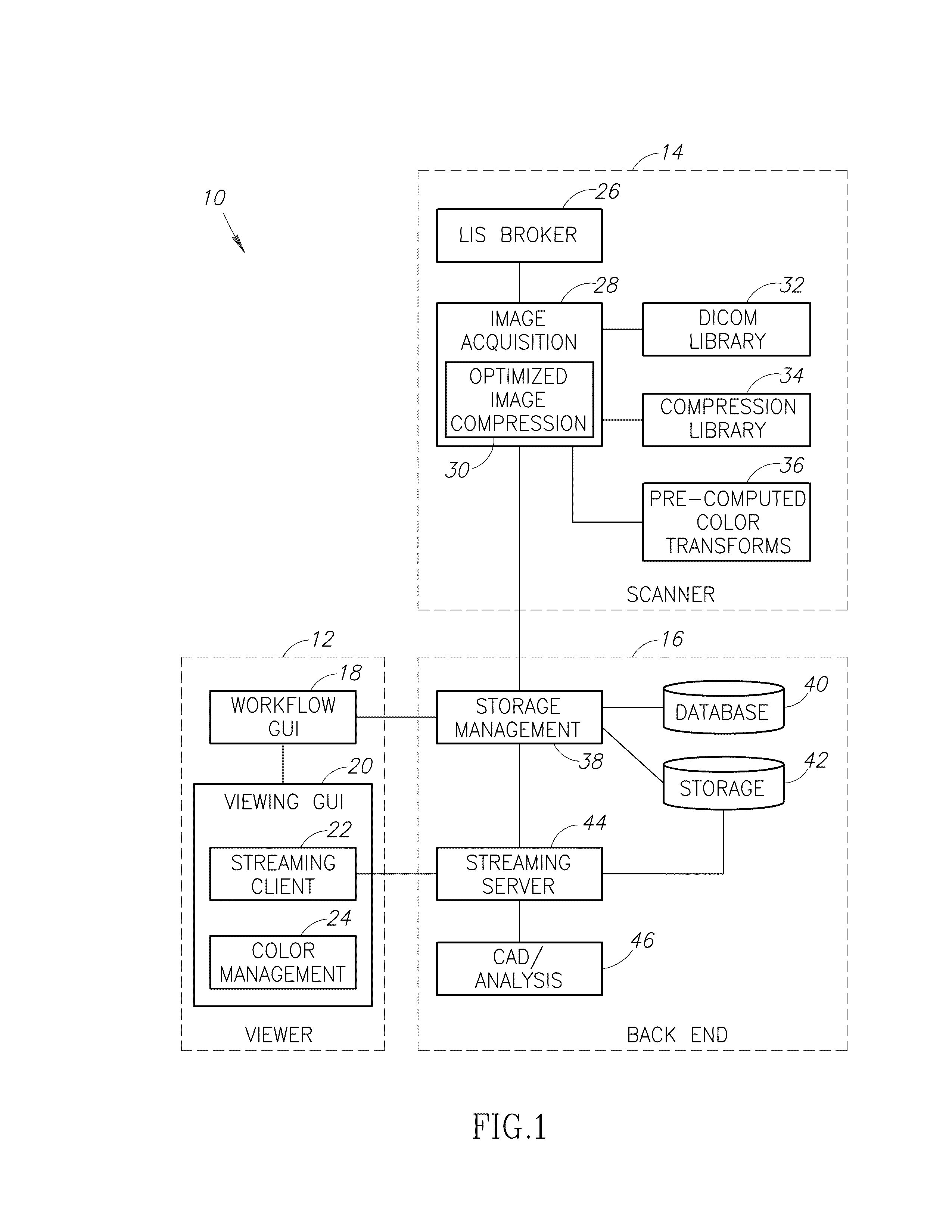
Stain-based optimized compression of digital pathology slides
ActiveUS20110075897A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationColor transformationRate distortion
A novel and useful method and system of optimized image compression of digital pathology slide images. The optimized image compression mechanism exploits the special color properties of the stained tissue represented by the digital pathology slides and provides an image compression algorithm having improved rate-distortion performance. Optimized color transforms are pre-computed using training sets of pathology slide image scan data for each stain type. The optimized color transforms are used to compress input slide image scans resulting in more efficient image streaming enabling users to review extremely large digital slide scans from any connected location, such as in a hospital, satellite center, home or on a mobile telephone.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Digital pathology system
ActiveUS8463741B2Automated handlingImprove efficiencyDigital data processing detailsMedical report generationImage serverDigital image
A digital pathology system has a central workflow server hosting digital pathology application services and supporting one or more pathology workstations. The digital pathology system may include one or more image servers, providing digital images of sample specimen slides that are associated with medical cases. Residing at and executing on each pathology workstation is a digital pathology application client, which is the counterpart of digital pathology application services at the central workflow server. The combination of digital pathology application services at the central workflow server and digital pathology application client at each pathology workstation support a pathology workflow software module and a slide viewer software module. The present disclosure also describes a method of operation and / or use of the digital pathology system.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE AMERICAS CORPORATION
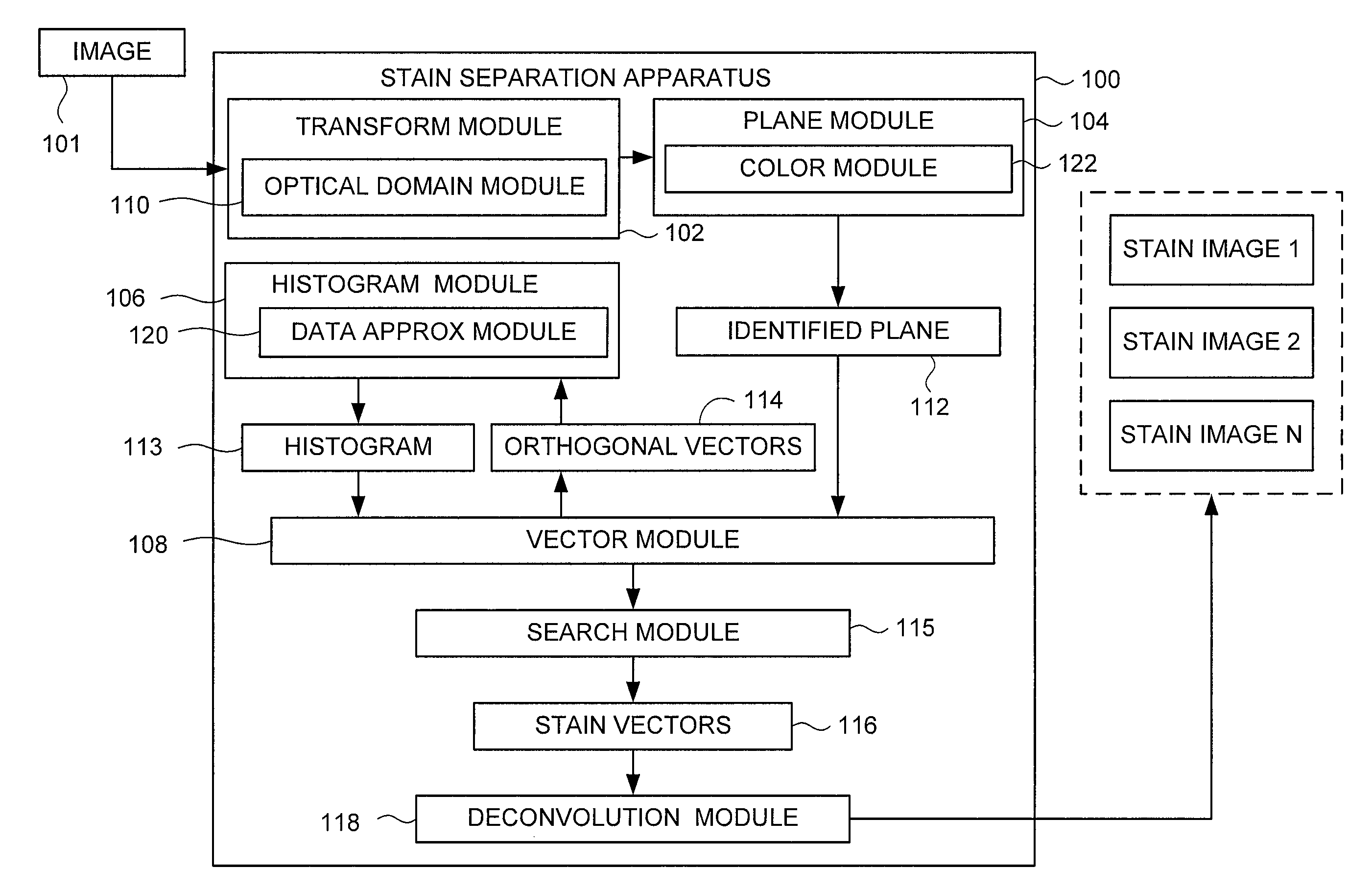
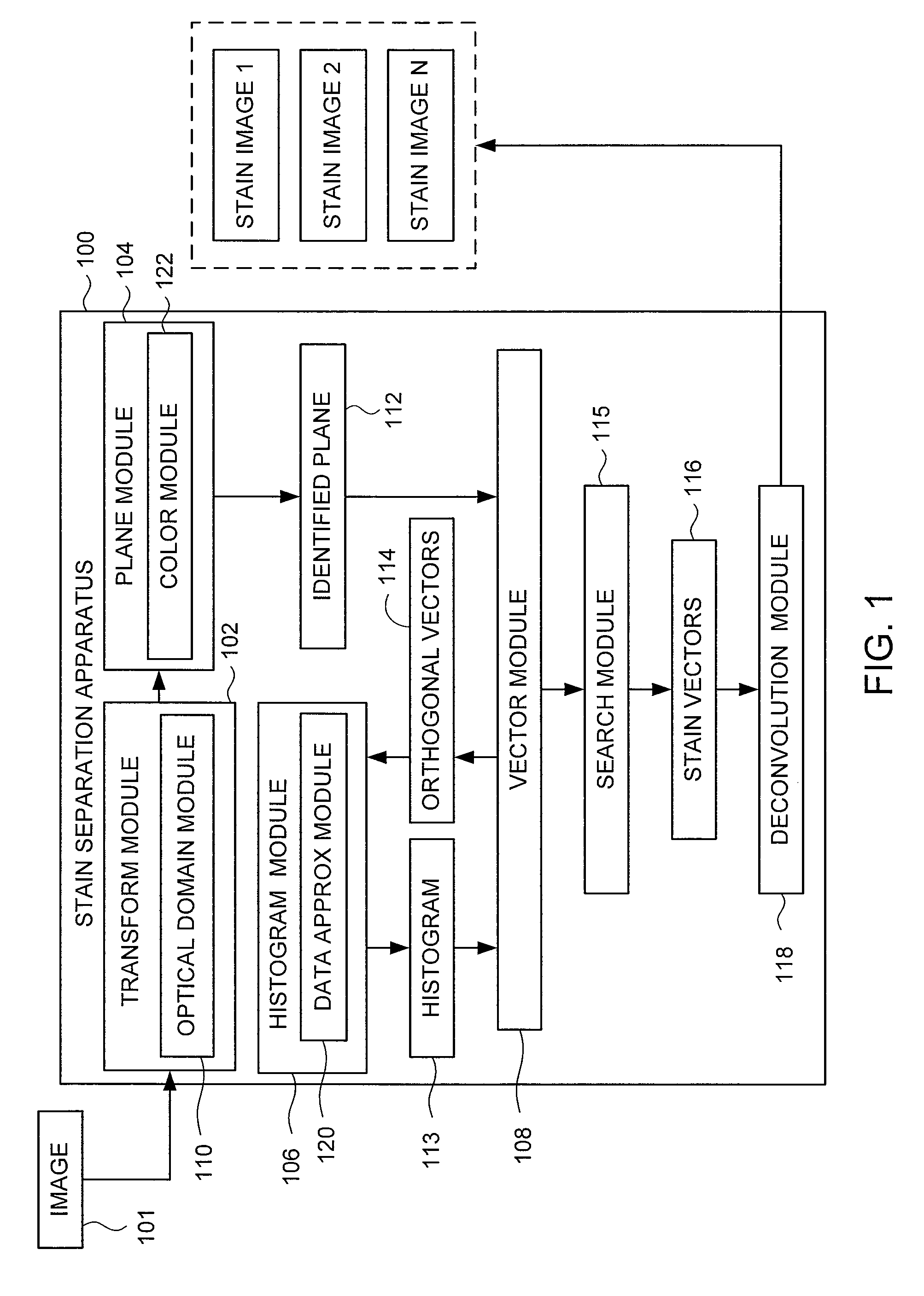
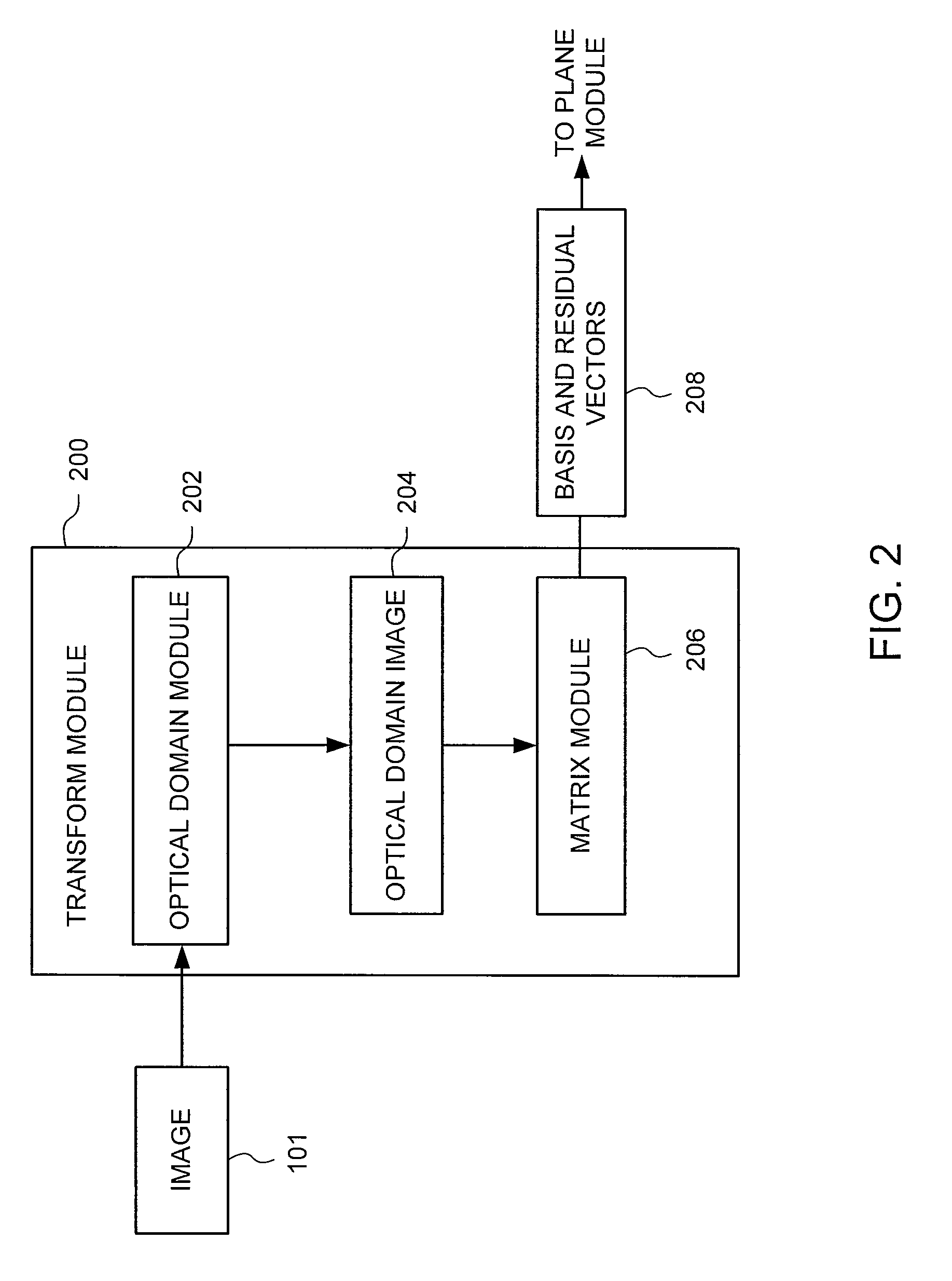
Method and apparatus for stain separation in digital pathology images
A stain separation system of digital pathology images that performs transforming a digital image from a first color domain to an optical domain to form an optical domain image (ODI), identifying a plane containing two or more basis vector which contain the pixels of the ODI, determining a plurality of orthogonal vector within the identified plane, forming a histogram of the digital image represented by the orthogonal vectors and determining one or more final stain vectors by searching for candidate vectors in the plane that minimize a cost function of the histogram.
Owner:SONY CORP
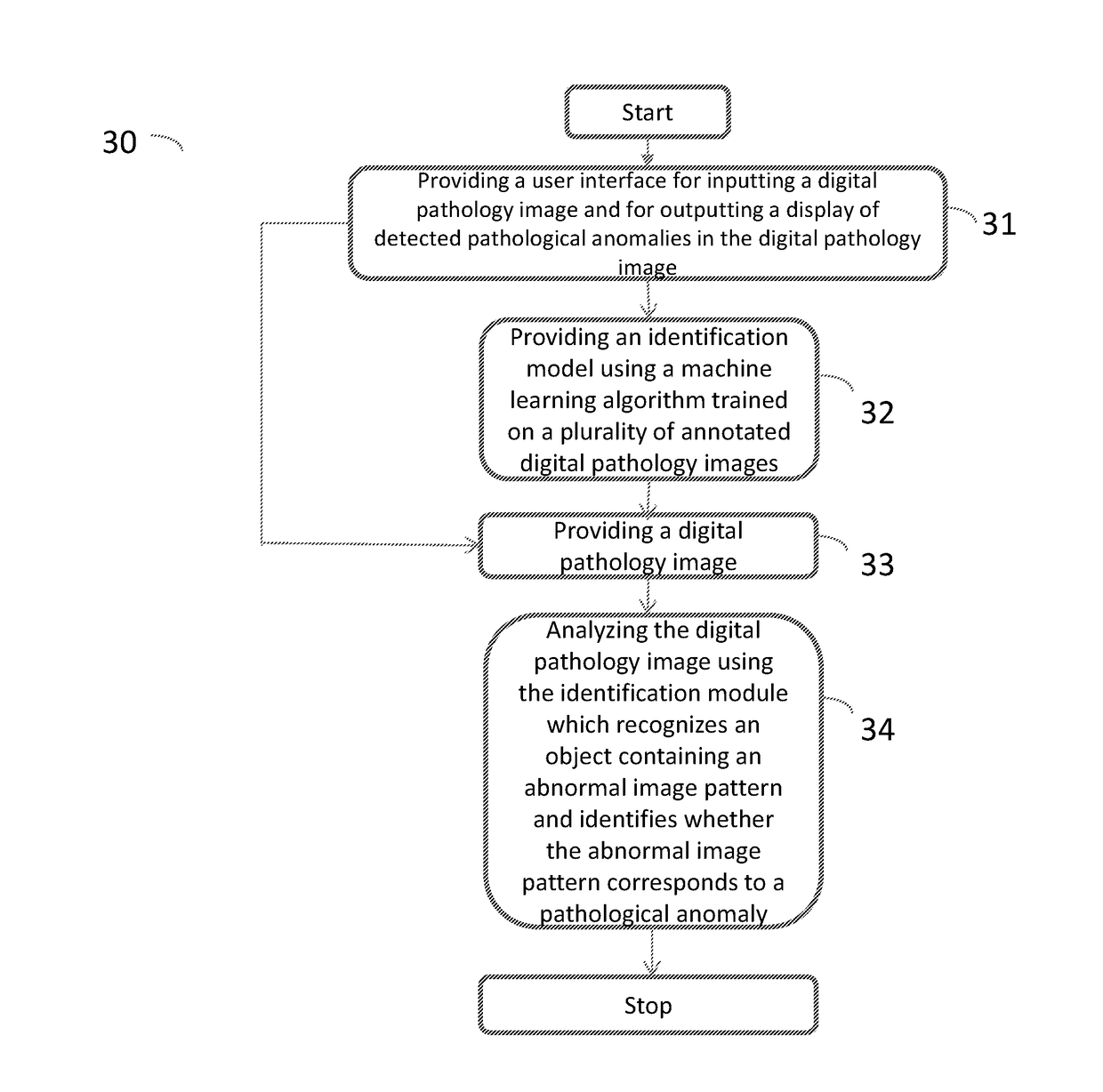
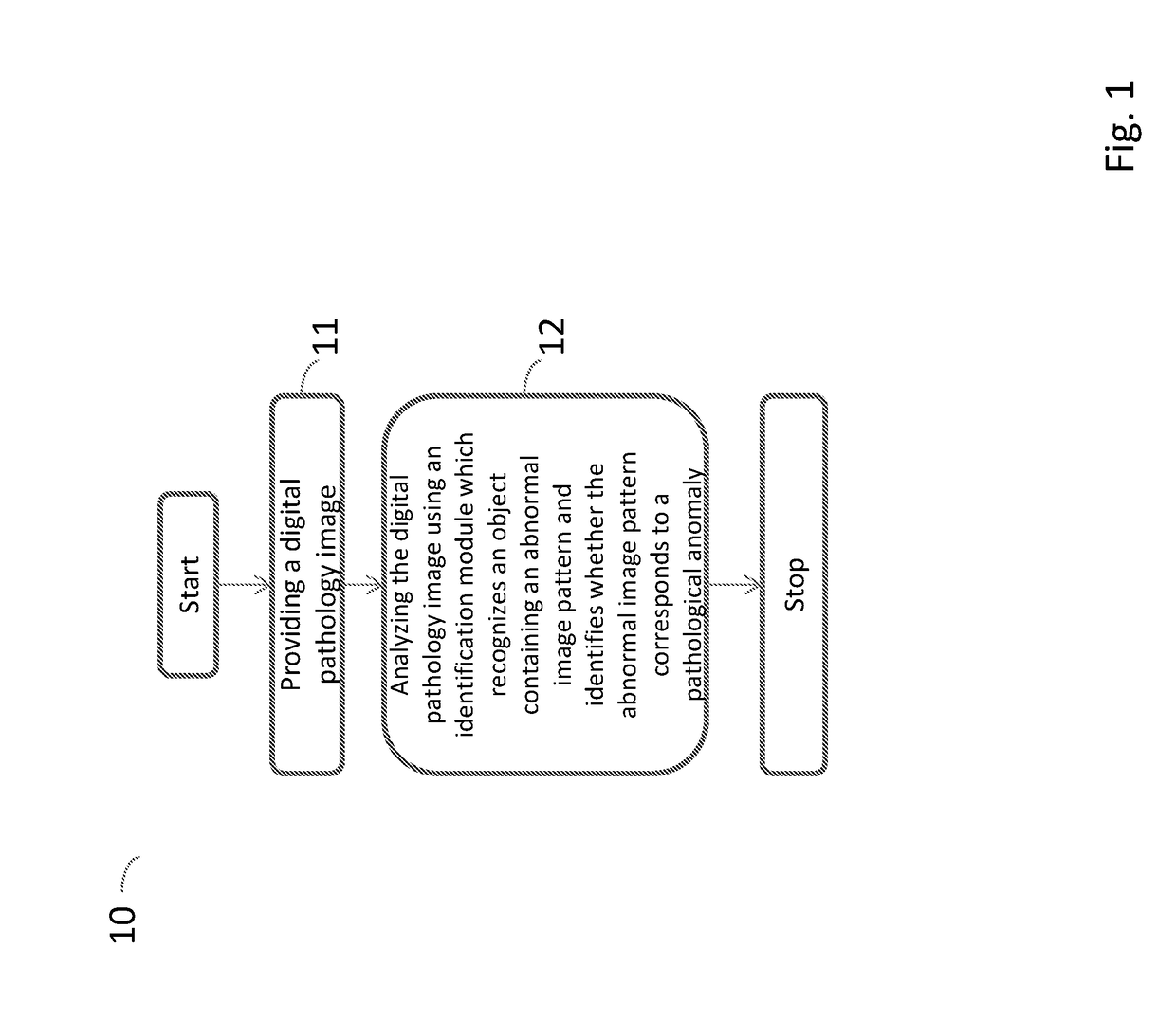
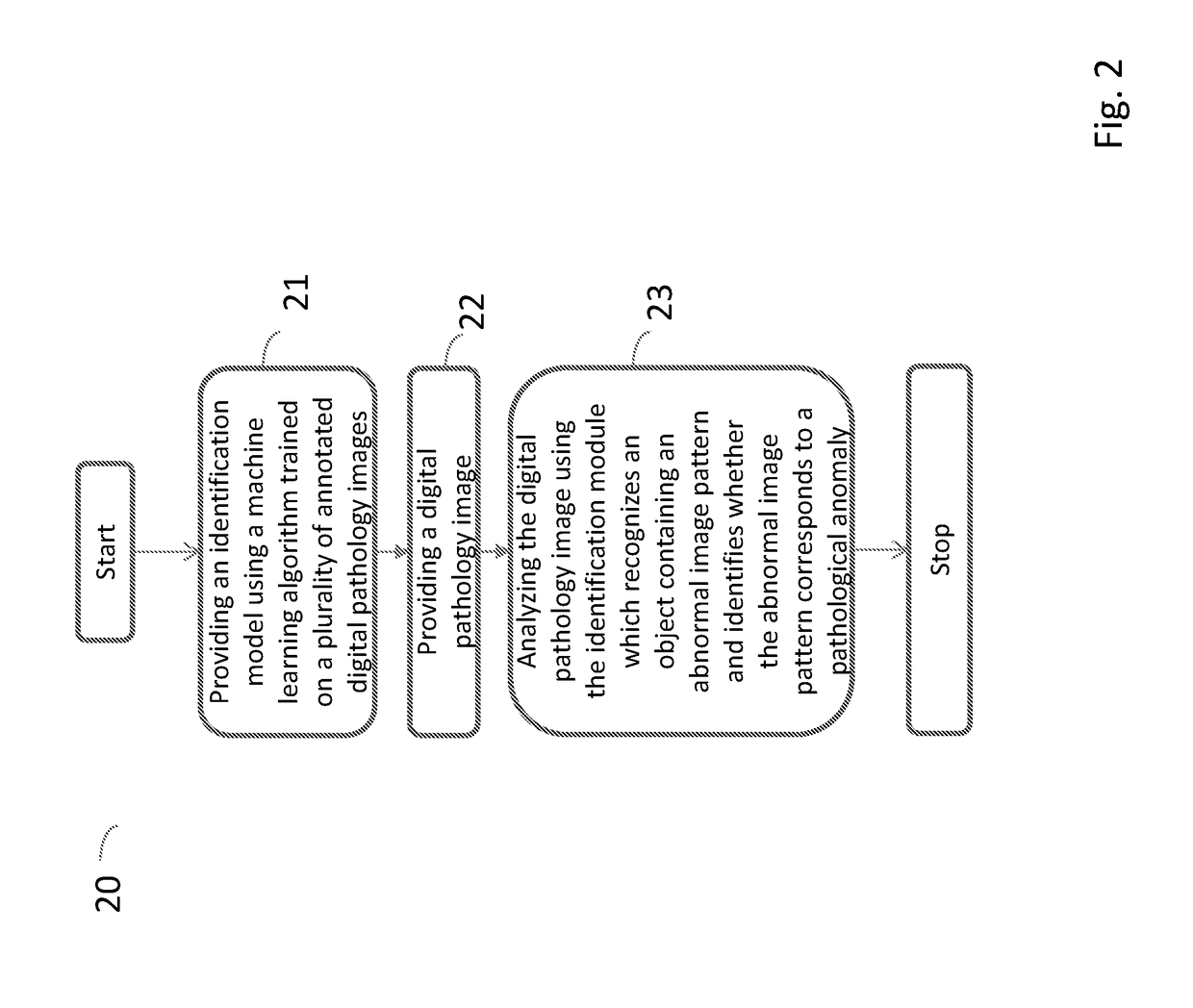
Method and system for detecting pathological anomalies in a digital pathology image and method for annotating a tissue slide
ActiveUS20170372471A1Drawback can be obviatedCorrectly detect pathological anomalyImage enhancementImage analysisComputing systemsComputer science
A method for annotating a tissue slide image, a system and a method performed by a computing system for detecting pathological anomalies in a digital pathology image are disclosed. The method performed by a computing system for detecting pathological anomalies in a digital pathology image includes providing a digital pathology image to the computing system and analyzing the digital pathology image using an identification module arranged on the computing system. The identification module uses a machine learning module to execute recognizing an object containing an abnormal image pattern using an identification model loaded in said identification module and identifying whether the abnormal image pattern corresponds to a pathological anomaly using the identification model.
Owner:INIFY LAB AB
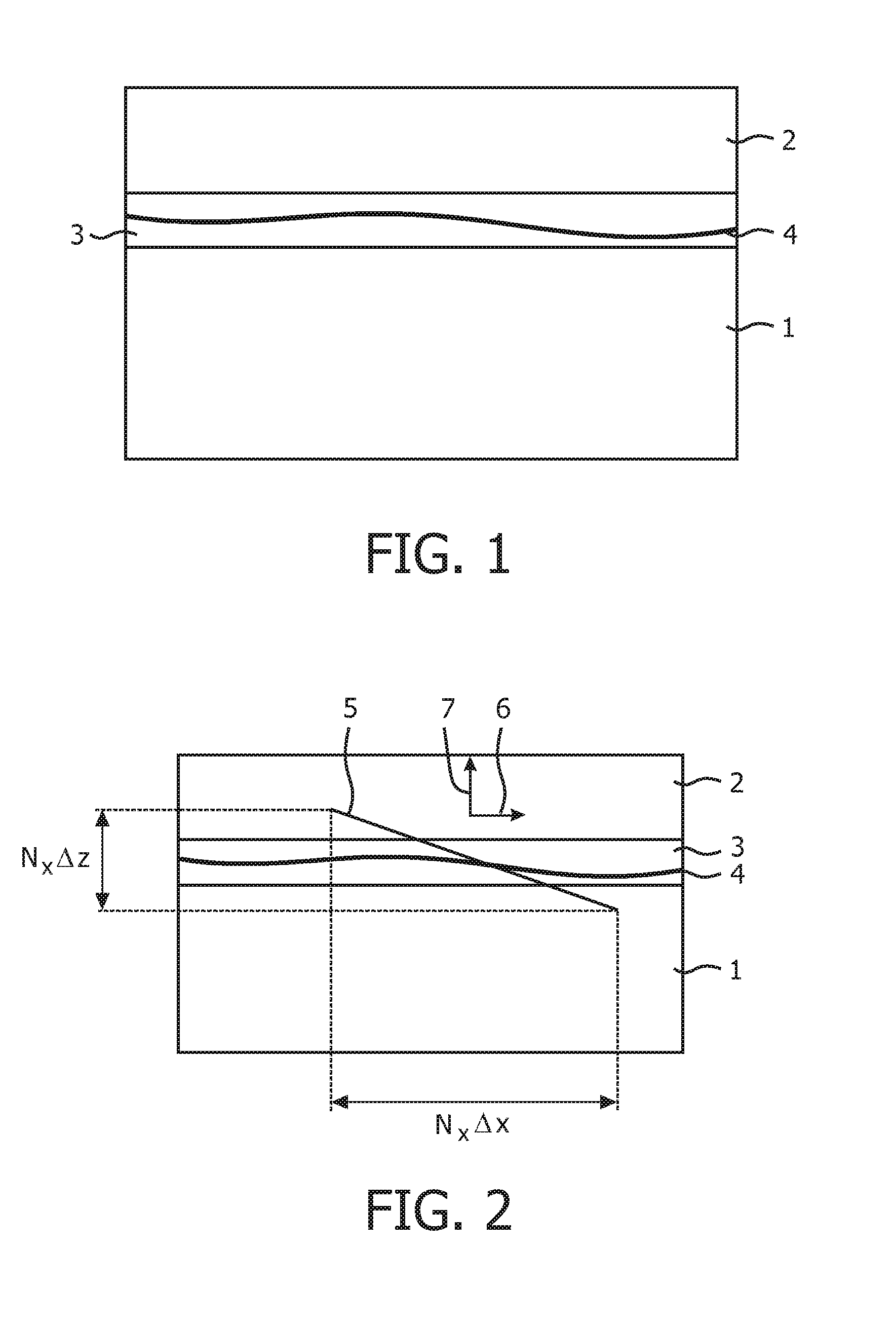
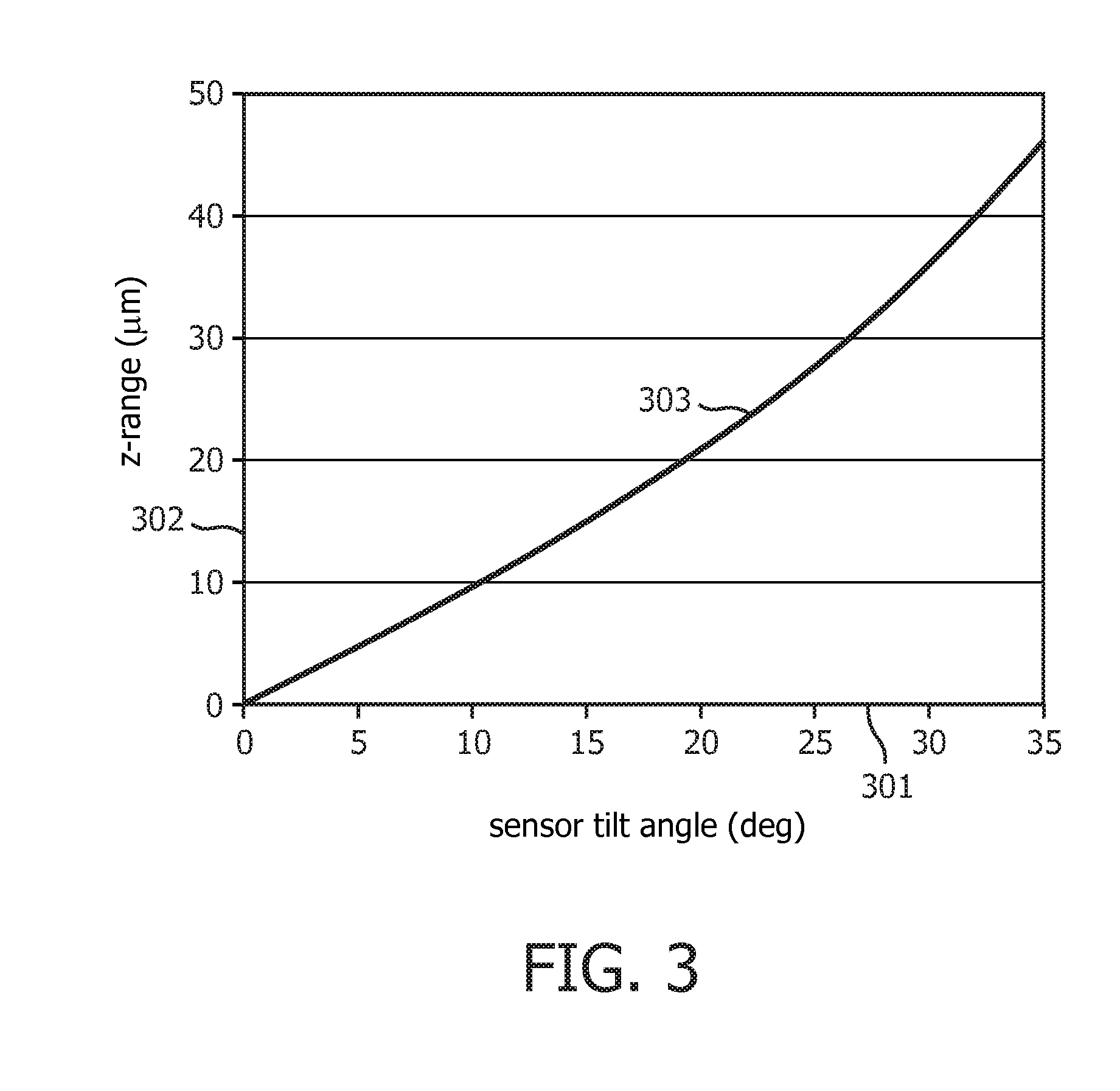
Autofocus based on differential measurements
ActiveUS20130093874A1Less-high-frequency detailImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDifferential measurementAutofocus
The present invention relates to the field of digital pathology and in particular to whole slide scanners. A tilted autofocus image sensor images an oblique cross-section of the slide. For focusing multiple sequential overlapping images, which have been taken by the tilted sensor, are compared. The axial position of the tissue layer can be determined from the polar error signal resulting from this differential measurement.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Stain-based optimized compression of digital pathology slides
ActiveUS8077959B2Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationColor transformationRate distortion
A novel and useful method and system of optimized image compression of digital pathology slide images. The optimized image compression mechanism exploits the special color properties of the stained tissue represented by the digital pathology slides and provides an image compression algorithm having improved rate-distortion performance. Optimized color transforms are pre-computed using training sets of pathology slide image scan data for each stain type. The optimized color transforms are used to compress input slide image scans resulting in more efficient image streaming enabling users to review extremely large digital slide scans from any connected location, such as in a hospital, satellite center, home or on a mobile telephone.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Space orientation computing method for numerical control bracket
InactiveCN102566439AWork quicklyContinuous operationSimulator controlSpatial positioningComputer science
The invention relates to a space orientation computing method for a numerical control bracket, which comprises the following steps of: 1, processing three-dimensional digital analogy of each part; 2, defining a fixed mechanism and a moving mechanism in each digital analogy; 3, setting a drive command for a multiple axis movements of a numerical control bracket; 4, simulating whether each axis movement accords with an actual condition; 5, correcting a movement zero point of the digital analogy of the numerical control bracket; 6, enabling a spindle axes of an automatic drilling and riveting machine to be coincident with a normal line of a riveting point and the riveting point to be coincident with the center of a pressure foot bush; 7, refreshing the digital analogy; 8, figuring out data of five axes of the numerical digital bracket and data of a lifting position and a rotating angle of a lower riveting head under the condition of automatic drilling and riveting on any point on the surface of an airplane; 9, carrying out collision checking and batch output on space orientation data; and 10, carrying out numerical control programming to ensure that the automatic drilling and riveting machine continuously operates. According to the space orientation computing method, the numerical control system can automatically operate according to the space orientation data, and the airplane on the numerical control bracket meets the working requirements of the automatic drilling and riveting machine on the space.
Owner:AVIC SAC COMML AIRCRAFT
Slide Storage, Retrieval, Transfer, and Scanning System for a Slide Scanner
A slide storage, retrieval, transfer and scanning system for a slide scanner presents multiple components which work together in an automated fashion to streamline slide scanning in digital pathology. A slide storage assembly stores several slide baskets and can deliver a particular basket through a rotation mechanism. A slide basket transfer assembly retrieves the basket from the slide storage assembly and transfers the basket to a secondary location, where a slide transfer assembly retrieves a single slide from the basket and delivers the slide to a slide scanning stage for scanning.
Owner:OPTRASCAN INC
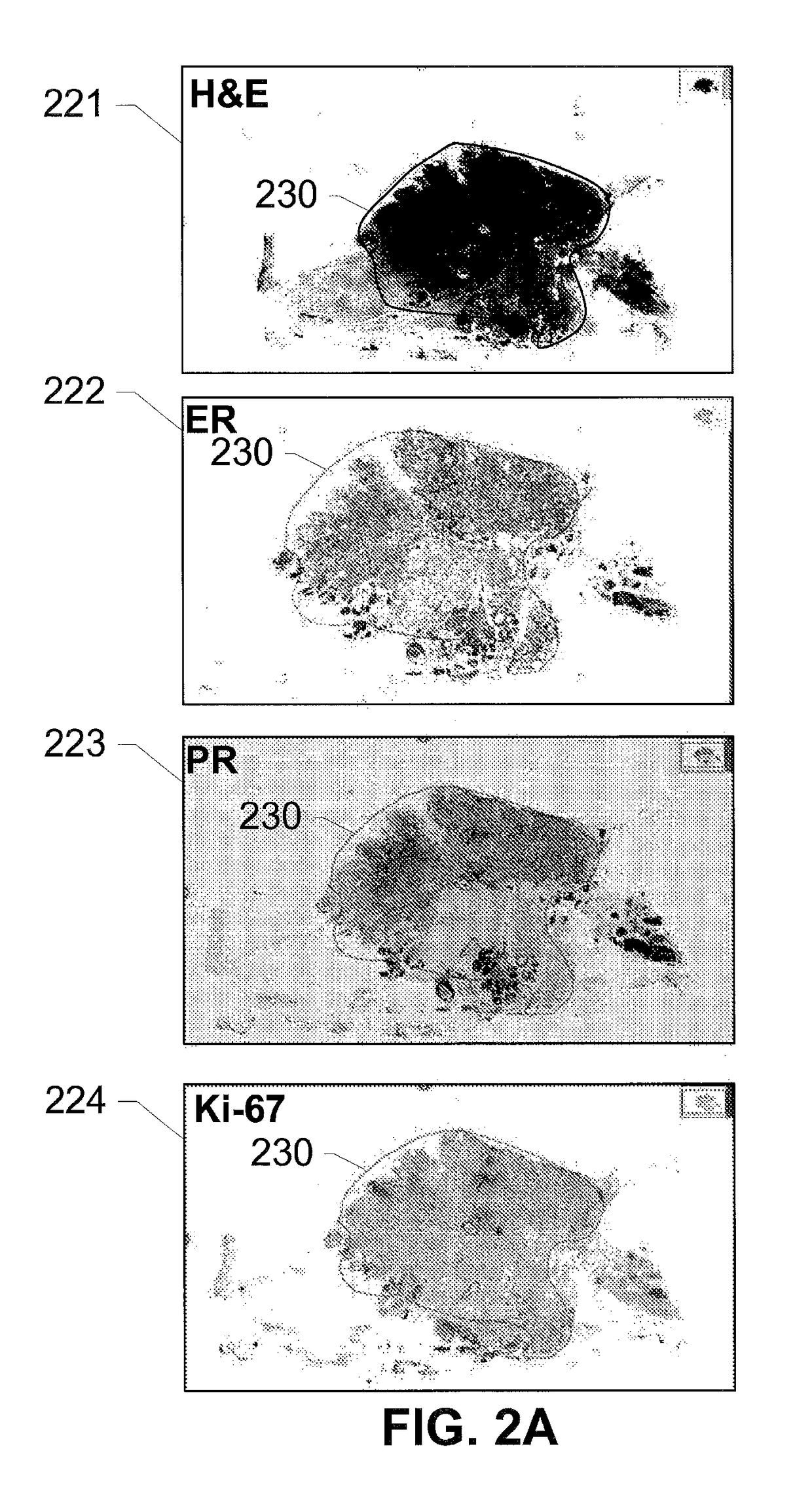
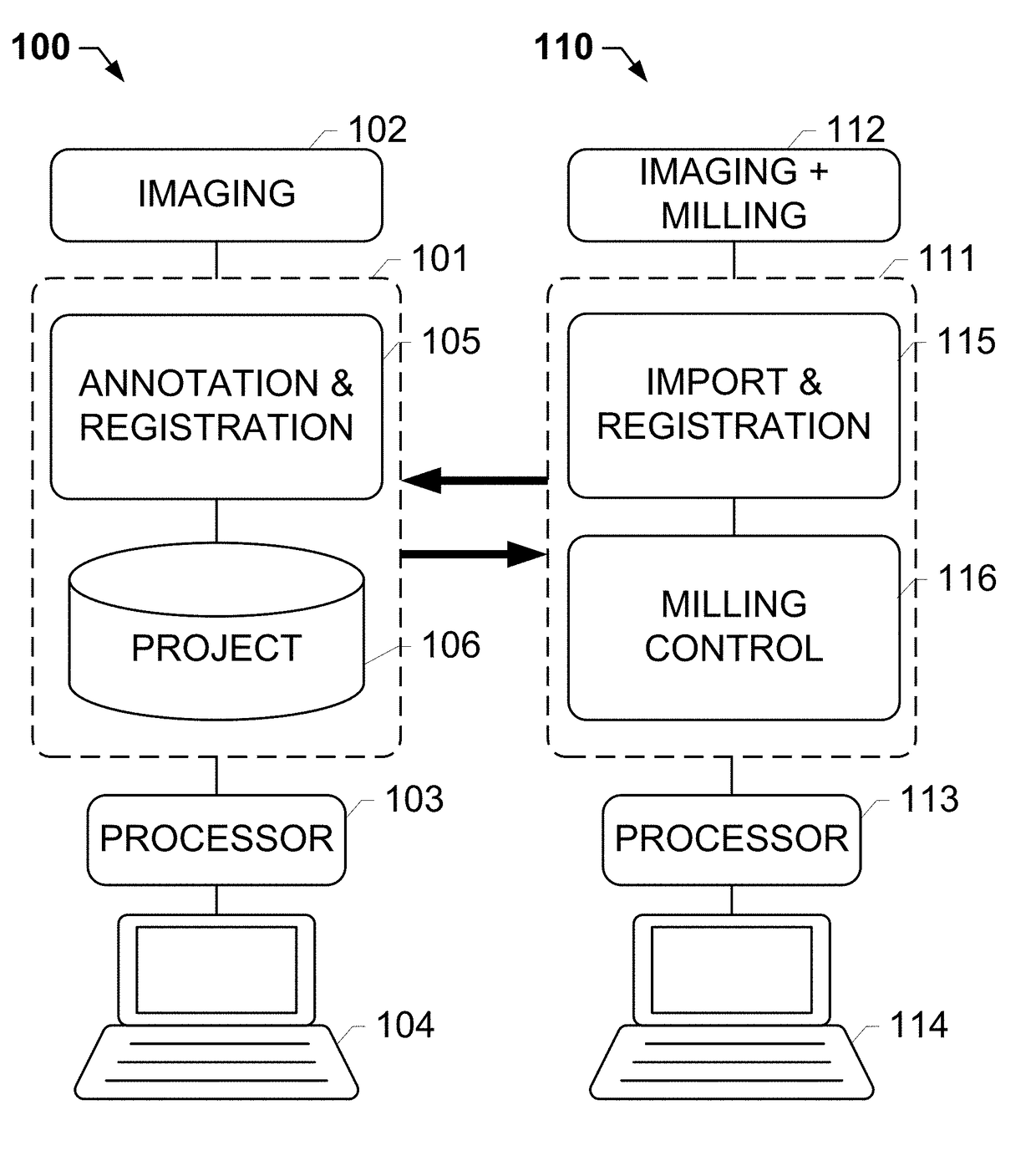
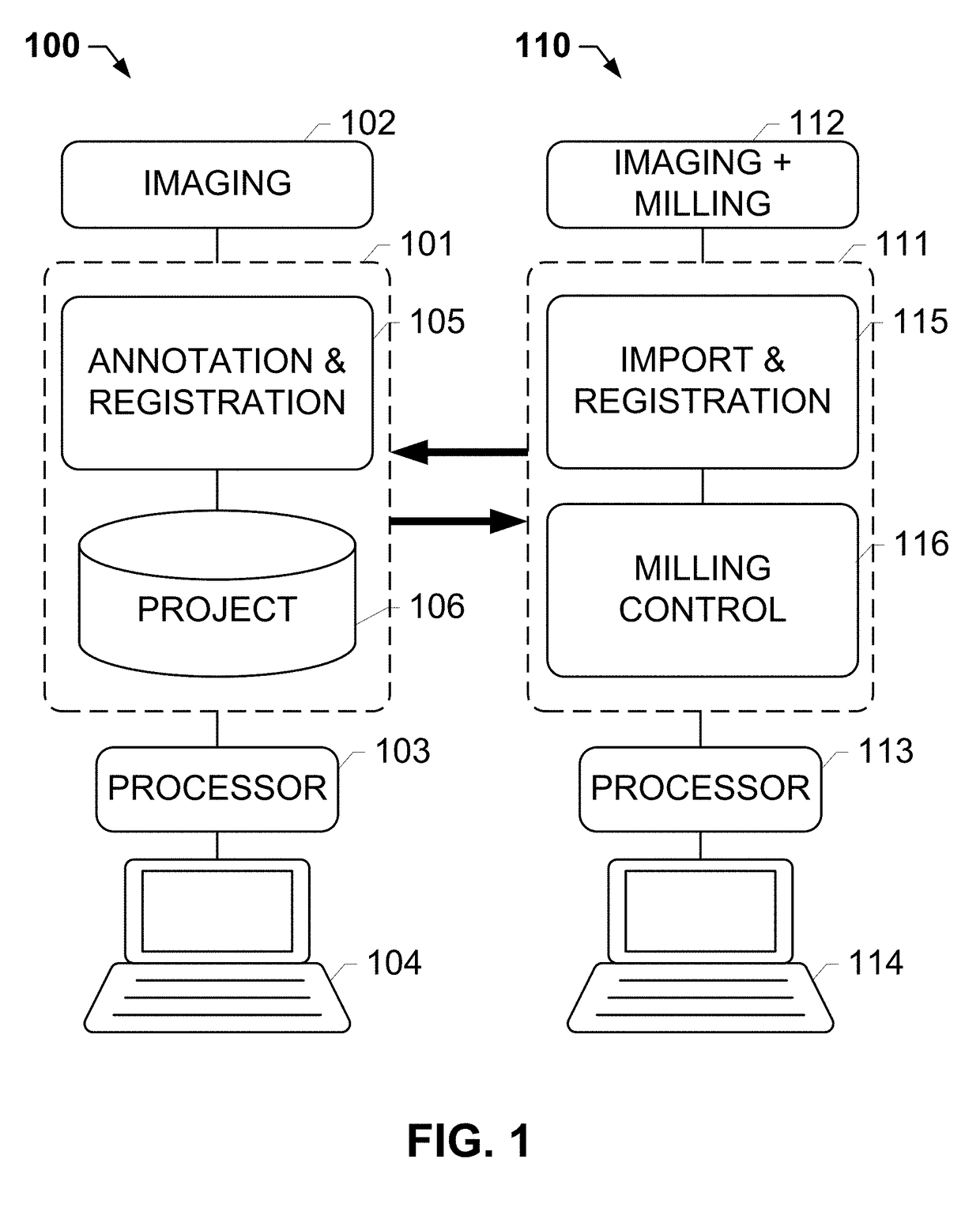
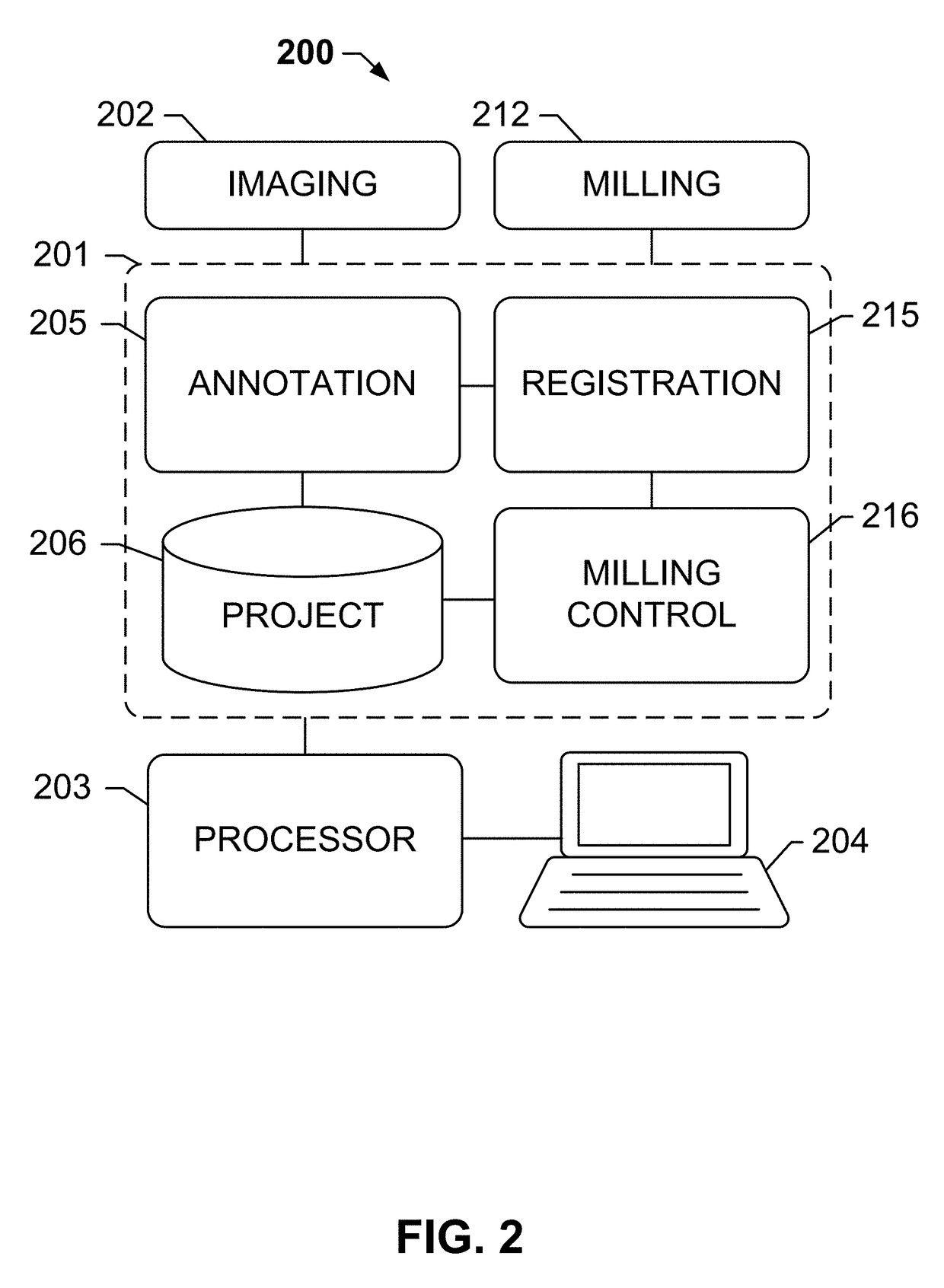
Systems and methods for meso-dissection
The subject disclosure provides systems, computer-implemented methods, and clinical workflows for meso-dissection of biological specimens and tissue slides by incorporating annotation and inter-marker registration modules within digital pathology imaging and meso-dissection (or milling) systems. Images of a reference slide a milling slide may be acquired using the same imaging system, with the annotations on the image associated with the milling slide being based on the inter-marker registration. Each image along with its respective annotations and meta-data may be associated with a project or a case, and stored in an image management system. A same-marker registration may be used to map annotations from the annotated image of the milling slide to a live image of the milling slide. The milling slide may be milled based on the annotations, with milled tissue output into a contained that is labeled in association with the labeled input slides.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Systems and methods for in-operating-theatre imaging of fresh tissue resected during surgery for pathology assessment
ActiveUS20160305926A1Time necessaryFacilitates in-operating-theater analysisMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicroscopesFresh TissueOperating theatres
The disclosed technology brings histopathology into the operating theatre, to enable real-time intra-operative digital pathology. The disclosed technology utilizes confocal imaging devices image, in the operating theatre, “optical slices” of fresh tissue—without the need to physically slice and otherwise process the resected tissue as required by frozen section analysis (FSA). The disclosed technology, in certain embodiments, includes a simple, operating-table-side digital histology scanner, with the capability of rapidly scanning all outer margins of a tissue sample (e.g., resection lump, removed tissue mass). Using point-scanning microscopy technology, the disclosed technology, in certain embodiments, precisely scans a thin “optical section” of the resected tissue, and sends the digital image to a pathologist rather than the real tissue, thereby providing the pathologist with the opportunity to analyze the tissue intra-operatively. Thus, the disclosed technology provides digital images with similar information content as FSA, but faster and without destroying the tissue sample itself.
Owner:SAMANTREE MEDICAL SA
Characterizing pathology images with statistical analysis of local neural network responses
Owner:SONY CORP
Cloud-based digital pathology
Owner:NEC CORP
Digital pathology whole slice image retrieval method
ActiveCN105740378AImprovement can not consider full slice as a wholeIncrease lossCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsImage extractionFeature vector
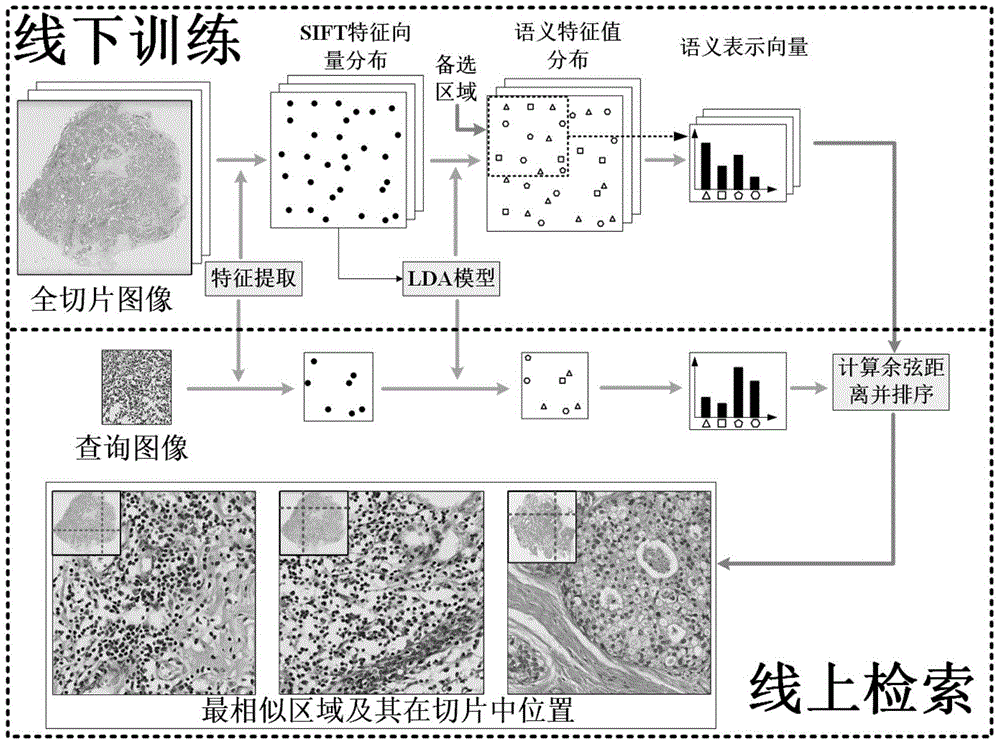
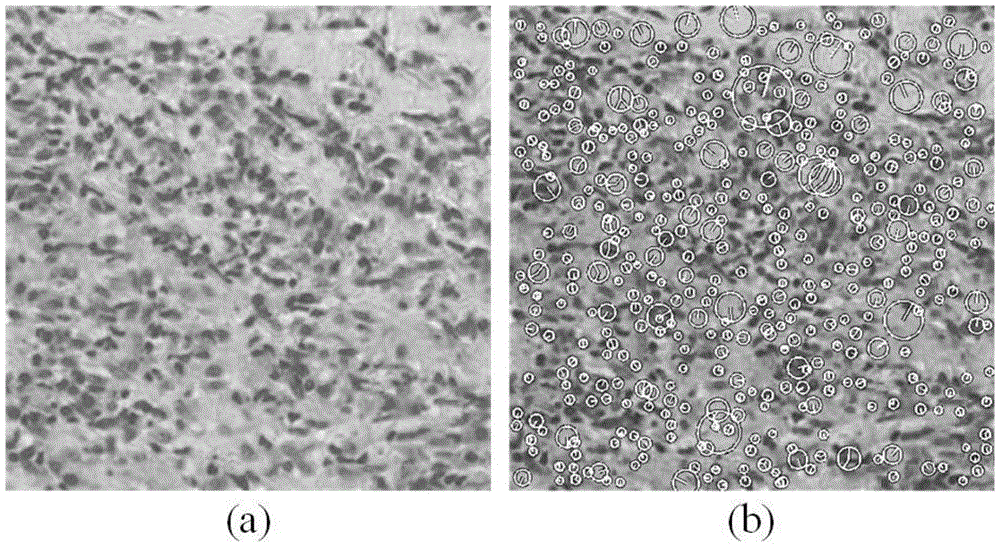
The present invention discloses a digital pathology whole slice image retrieval method, and the method is used in a digital pathology whole slice image database. The method comprises: extracting positions of dispersed SIFT feature points and SIFT feature vectors on a digital pathology whole slice image in the database; using an LDA model to obtain a high-level semantic feature value for each SIFT feature point; using an overlapping sliding window method to select alternative regions, and collecting statistics of semantic feature values of all the SIFT feature points in each alternative region, so as to obtain semantic representation vectors of the alternative region; and taking a query image as a region, using the same method to obtain the semantic representation vector of the query image, calculating cosine distances between the semantic representation vector of the query image and semantic representation vectors of all the alternative regions, sorting the distances, and returning to multiple regions with smallest distance. The method disclosed by the present invention can provide diagnosis reference information for the pathologist, and can be used for a digital pathology whole slice image database management and query system and computer-aided diagnosis.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Digital pathology system
ActiveUS20180267290A1Optimize workflowGeometric image transformationPreparing sample for investigationSample imageWork flow
The present invention relates to digital pathology. In order to improve the workflow in the process of selecting a region of interest of an unstained sample to be removed for molecular diagnostic, a method (100) is provided for selecting a sample removing area of an unstained sample to be removed for molecular diagnostic. The method comprises the following steps: In a first step 102, also referred to as step a), a reference removing area is selected in a reference image of a reference slice of an object, wherein biological material in the reference slice is stained. In a second step 104, also referred to as step b), a digital sample image of a sample slice of the object is obtained under an imaging setting. The biological material in the sample slice is unstained. The sample slice is received on a sample slide and positioned in an optical path between a light source and an image detector. In the optical path between the light source and the image detector, it is further provided a contrast enhancing arrangement for improving contrast between the unstained biological material and background. Light is provided passing through the sample slice to be received by the image detector. In a third step 106, also referred to as step c), the digital sample image is registered with the reference image for translating the reference removing area in the reference image to the digital sample image. In a fourth step 108, also referred to as step d), a sample removing area is identified in the digital sample image based on the translated reference removing area.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Signal to noise ratio in digital pathology image analysis
A digital slide analysis system comprises an algorithm server that maintains or has access to a plurality of image processing and analysis routines. The algorithm server additionally has access to a plurality of digital slide images. The algorithm server executes a selected routine on an identified digital slide and provides the resulting data. Prior to the application of selected routine, the system employs a digital pre-processing module to create a metadata mask that reduces undesirable image data such that the image data processed by the selected routine has an improved signal to noise ratio. The pre-processing module uses a classifier that may be implemented as a pattern recognition module, for example. Undesirable image data is therefore excluded from the image data that is processed by the digital pathology image processing and analysis routine, which significantly improves the digital pathology image analysis.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
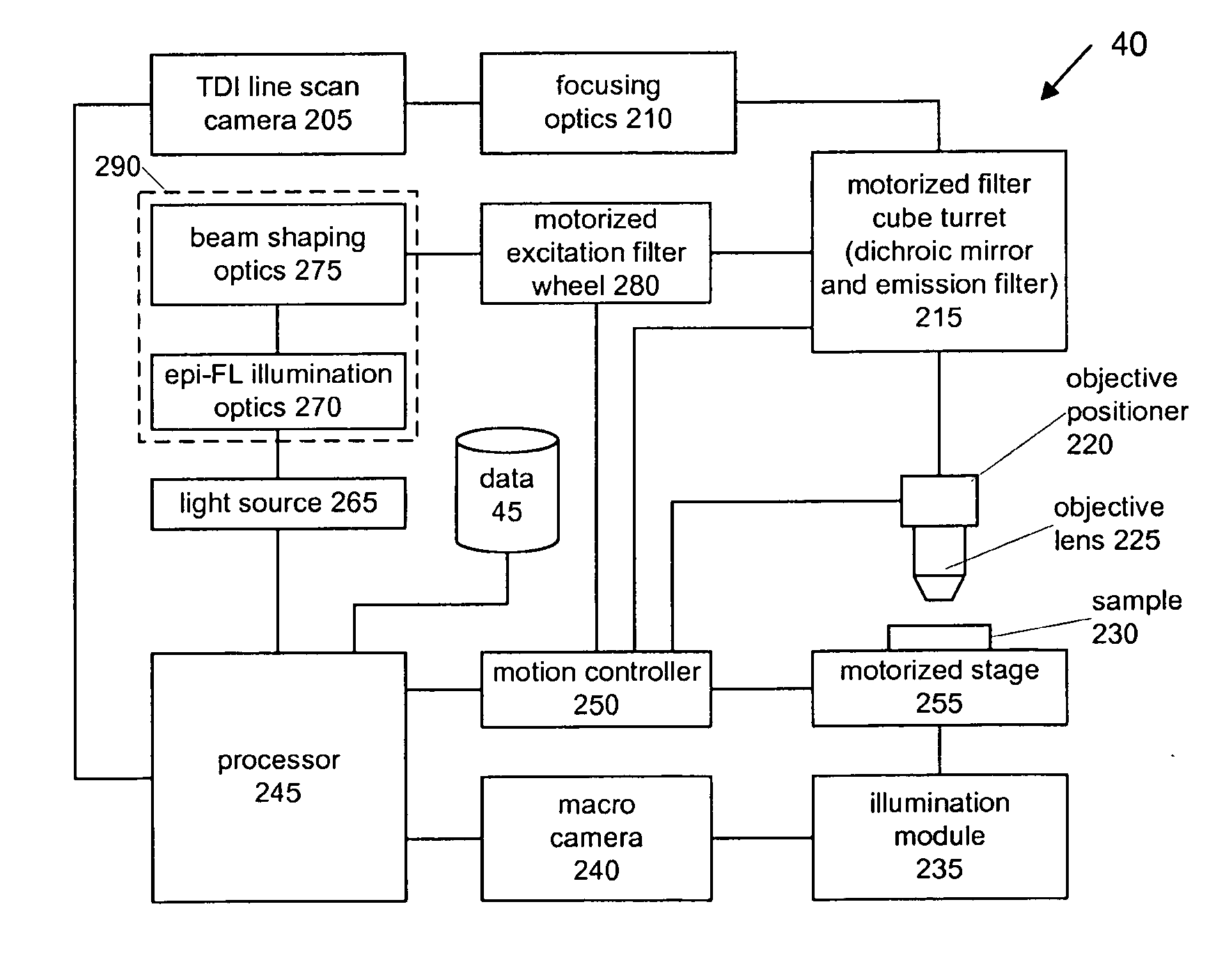
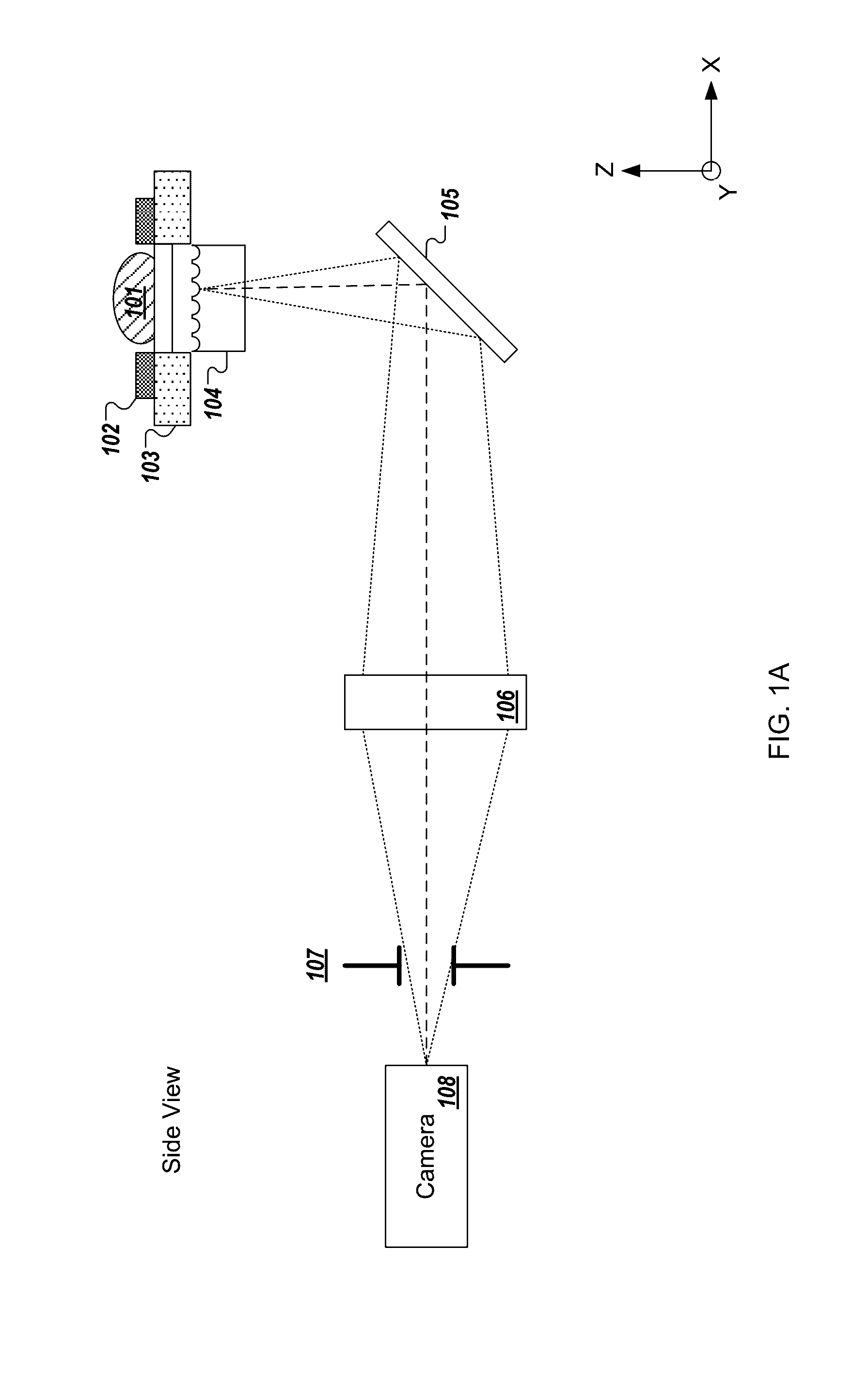
Whole slide fluorescence scanner
ActiveUS8743195B2Increase line speedAccuracyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsFluorescenceAutofocus
A whole slide fluorescence digital pathology system is provided that uses a monochrome TDI line scan camera, which is particularly useful in fluorescence scanning where the signal is typically much weaker than in brightfield microscopy. The system uses oblique brightfield illumination for fast and accurate tissue finding and employs a unique double sweep focus scoring and objective lens height averaging technique to identify focus points and create a focus map that can be followed during subsequent scanning to provide autofocusing capability. The system also scans and analyzes image data to determine the optimal line rate for the TDI line scan camera to use during subsequent scanning of the digital slide image and it also creates a light profile to compensate for loss of illumination light due to roll off.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com