Compensator system and method for compensating angular dispersion
A compensator and angular dispersion technology, applied in the field of compensator systems, can solve the problem that a single prism is not enough to compensate angular dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
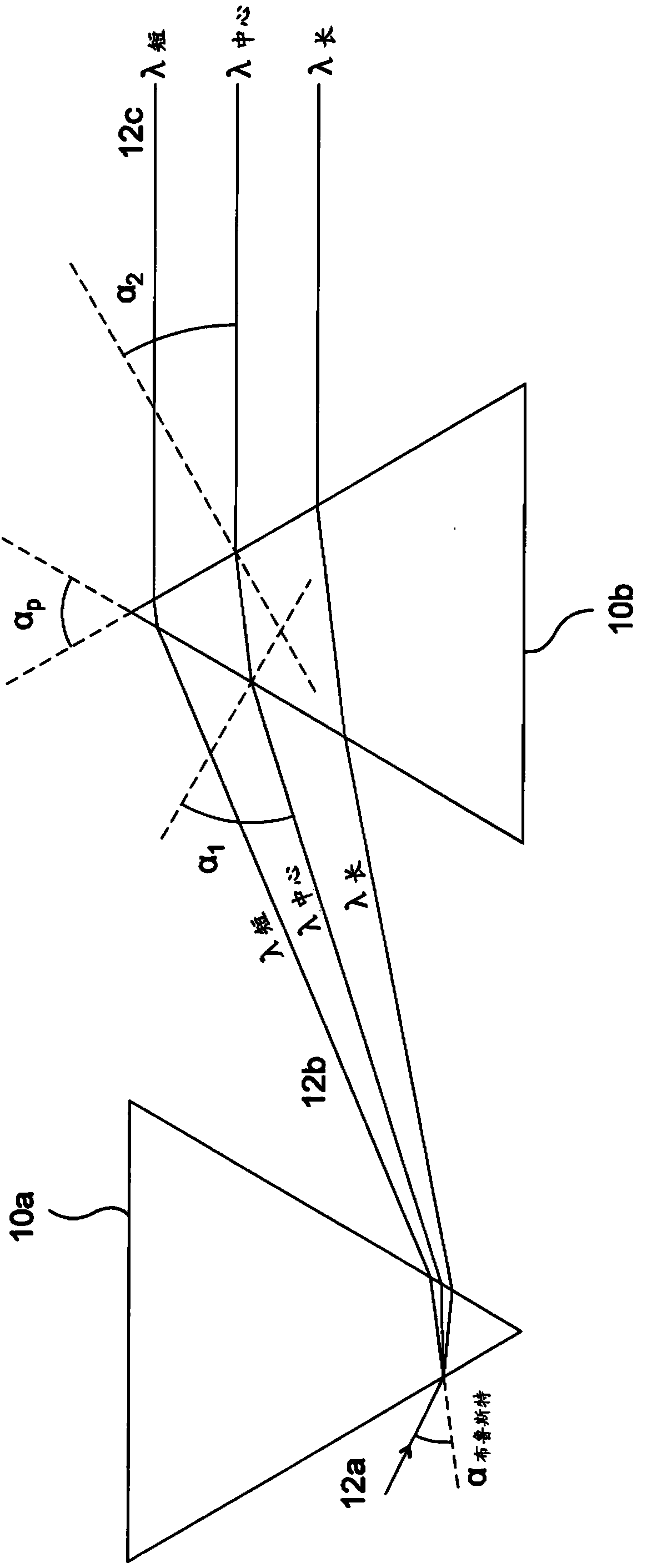
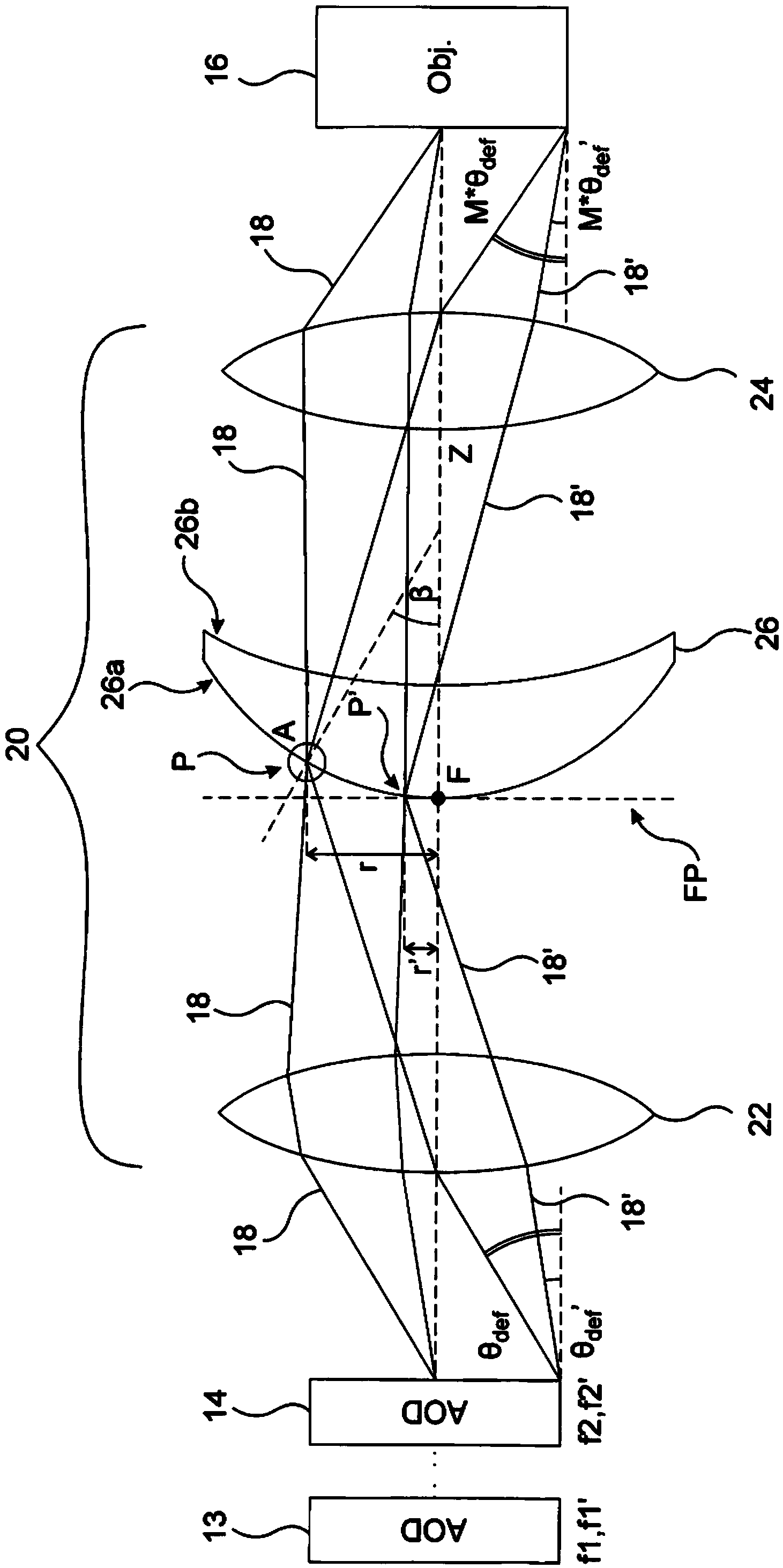
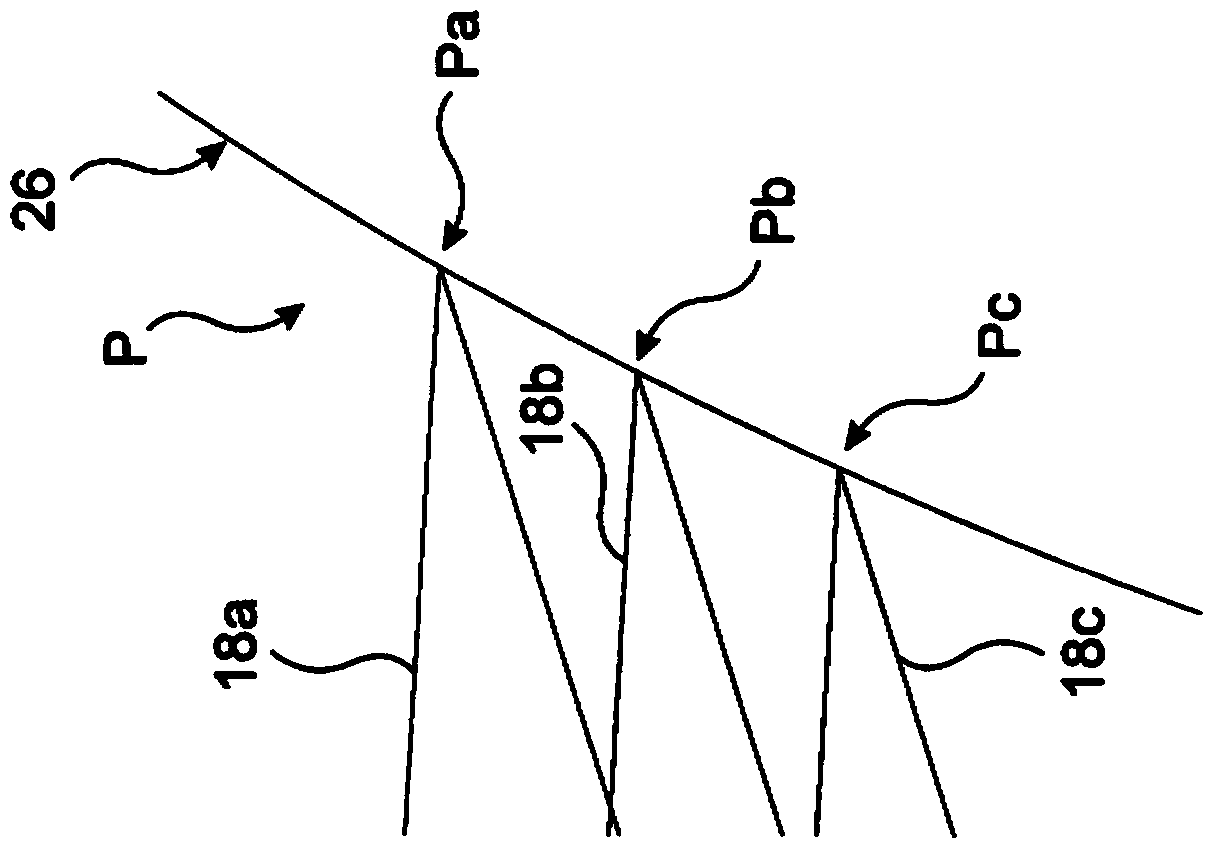
[0026] figure 2 A compensator system 20 according to the invention is shown arranged between a second AOD 14 of a pair of consecutive AODs 13, 14 and an objective lens 16 of an optical system such as a laser scanning microscope (not shown). The optical system may include individual optical elements between two consecutive AODs 13, 14, as discussed in WO2010 / 076579, and additionally, the optical system typically includes a second pair of AODs such that the first pair of AODs is used in the first lateral direction The electromagnetic beam 18 is deflected in x, while the second pair of AODs deflects the beam 18 in a second transverse direction y, perpendicular to the first transverse direction x. For simplicity, only one consecutive pair of AODs 13 and 14 is shown and discussed in the following, however, in the transverse direction corresponding to the second pair of AODs, the beam deflection can be calculated similarly.
[0027] The compensator system 20 includes a first lens ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com