Damage Identification Method for Stochastic Structures Based on Genetic Algorithm and Static Measurement Data
A technology of structural damage and genetic algorithm, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, calculations, etc., can solve problems such as non-optimal results and misjudgment, so as to reduce misjudgment, increase stability and reliability , the effect of fast convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
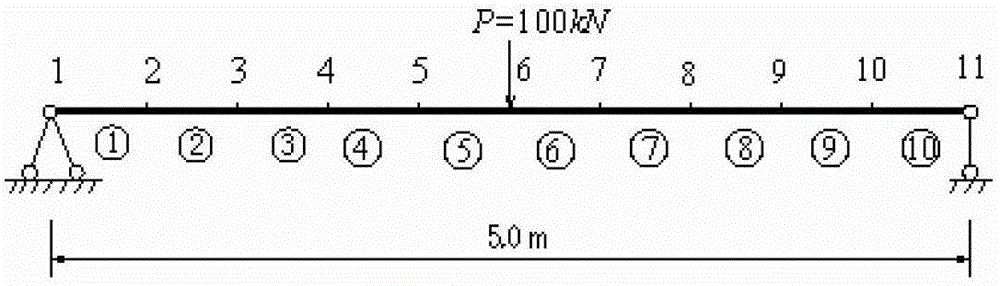
[0071] Example 1: Damage identification for a simply supported beam structure
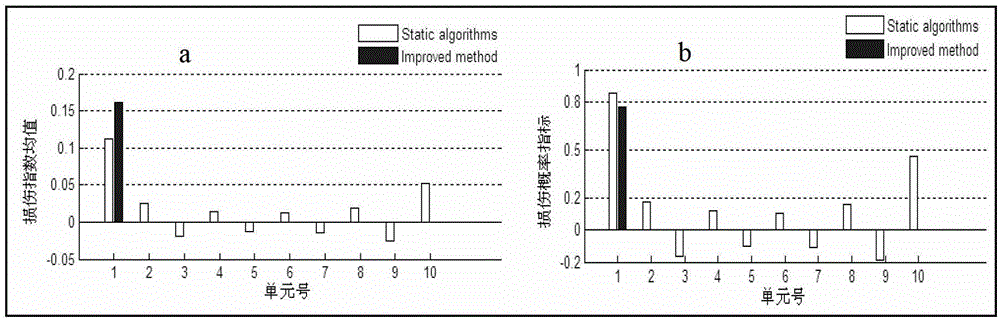
[0072] a. The first step: through the random structure damage identification method based on static measurement data, the statistical characteristics of the random structure damage index are initially obtained α 0 , α 1 , α 2
[0073] Such as figure 1 For the simply supported beam with rectangular cross-section shown, the parameters of the given material are: beam length l=5.0m, cross-sectional area A=0.3m×0.8m, moment of inertia I=0.0128m 4 , density ρ=2.5×10 3 Kg / m 3. The simply supported beam is discretized into 10 equally spaced planar beam units, each unit node has two degrees of freedom of vertical deflection and rotation angle, and there are 20 degrees of freedom in total. Assume that the randomness of the stiffness in the initial model of simply supported beams is caused by the uncertainty of the elastic modulus, and the mean value of the elastic modulus is E=2.8×10 10 Pa, and assum...
Embodiment 2
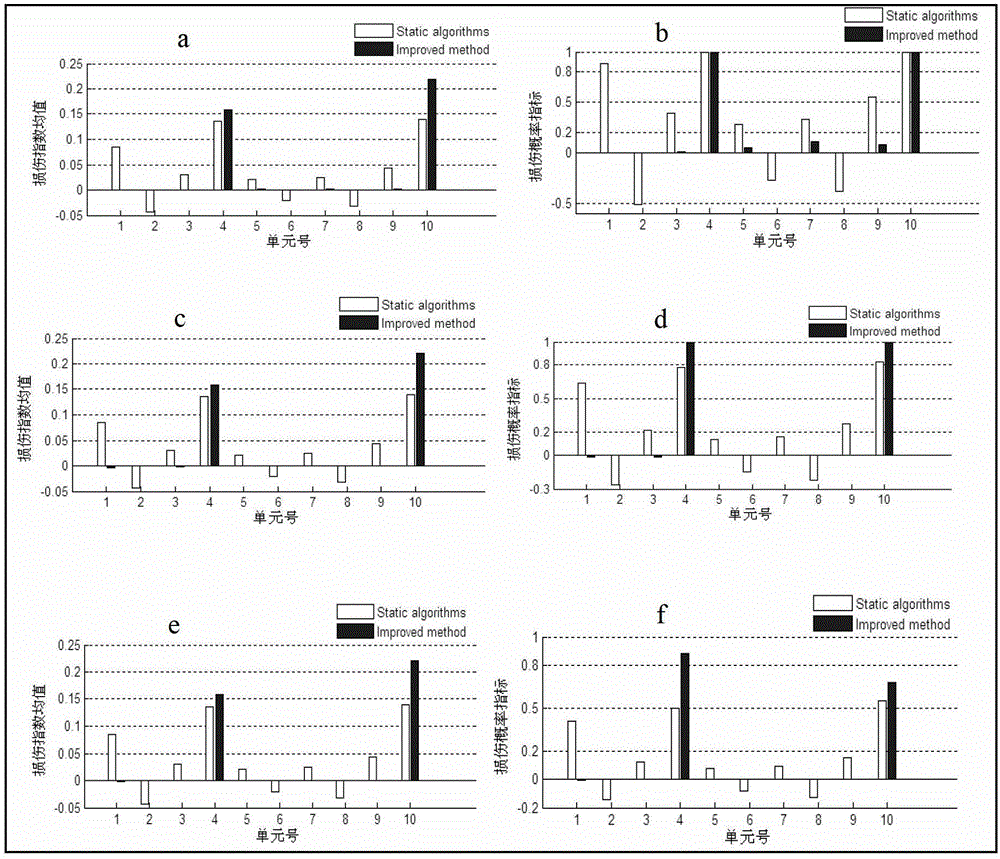
[0090] Example 2: Damage identification for a continuous beam structure
[0091] Such as Figure 5 For the three-span continuous beam with rectangular section shown, the parameters of the given material are: beam length l=15.0m, cross-sectional area A=0.3m×0.8m, moment of inertia I=0.0128m 4 , density ρ=2.5×10 3 Kg / m 3 . The beam is discretized into 30 equally spaced planar beam units, each unit node has two degrees of freedom of vertical displacement and rotation angle, a total of 62 degrees of freedom, and then the influence of the degree of freedom of rotation angle can be removed by the agglomeration method. Assume that the elastic modulus of the initial stiffness of the continuous beam is random, and assume that the elastic modulus of each span unit of the continuous beam is a random variable, a total of three independent random variables.
[0092] Working condition one: the modulus of elasticity of the beam unit 16 is reduced by 20%; only considering the initial mode...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com