Time domain analysis method of thin-layer electromagnetic structure based on surface impedance boundary
A surface impedance, time domain analysis technology, applied in complex mathematical operations, design optimization/simulation, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as no reduction of unknowns, large computer memory and simulation calculation time, and lack of electromagnetic simulation methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
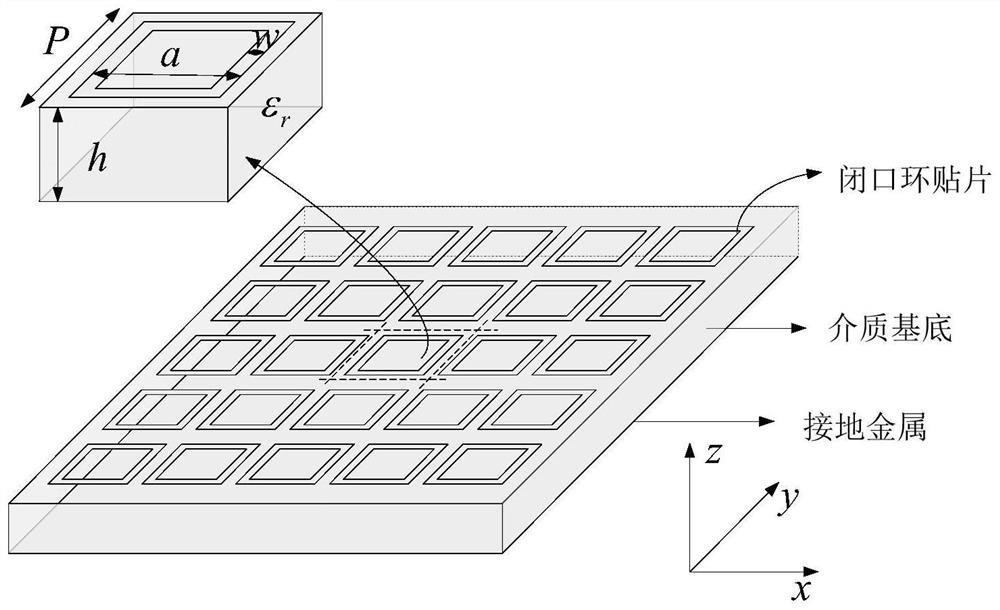
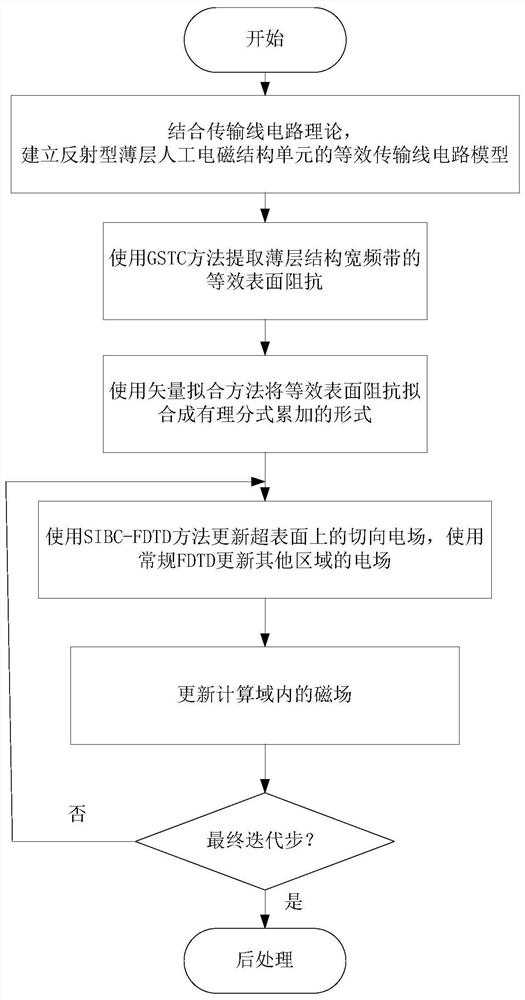
[0109] This embodiment provides a time-domain analysis method for thin-layer electromagnetic structures based on surface impedance boundaries. This method is universal for any thin-layer artificial electromagnetic structure unit. Herein figure 1 Thin-layer artificial electromagnetic structure unit structure as an example. Aiming at the problem of thin-layer artificial electromagnetic structure, the method of the invention greatly saves computer memory, speeds up the calculation time, and has high efficiency and flexibility. The specific process of this method is as follows image 3 As shown, the steps are as follows:
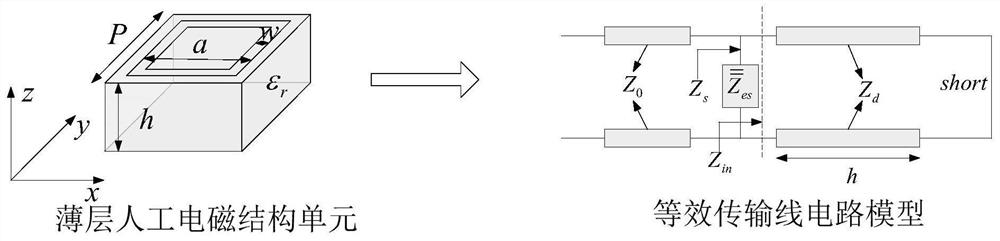
[0110] Step 1: Use the equivalent transmission line circuit theory to establish the equivalent transmission line circuit model of the thin-layer artificial electromagnetic structural unit; combine figure 2 , the thin-layer artificial electromagnetic structural unit can be analyzed by its equivalent circuit model, as follows
[0111] For a thin-layer artifici...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com