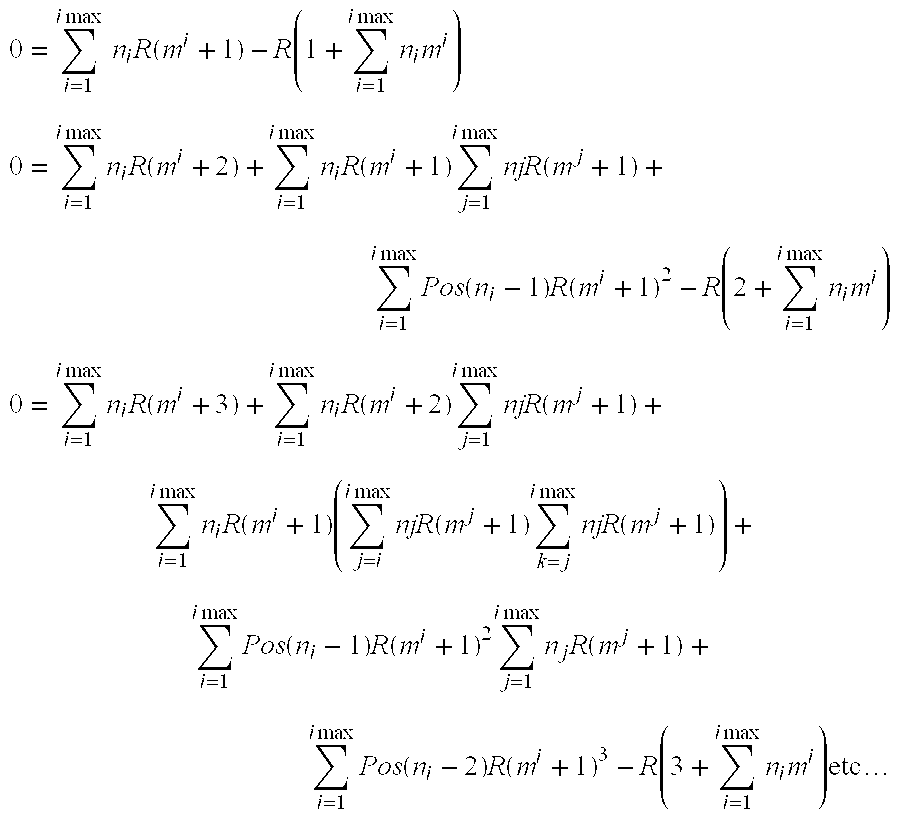
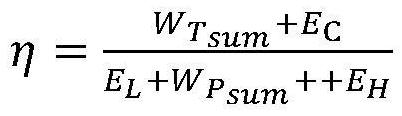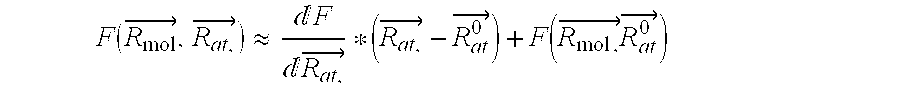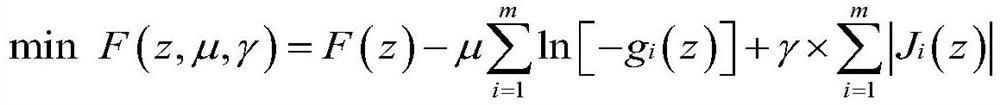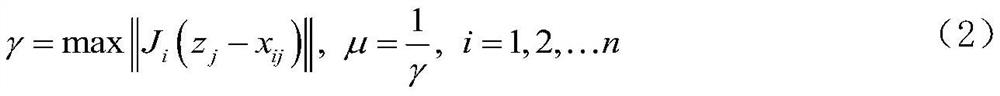Patents
Literature
57 results about "Numerical methodology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
CD metrology analysis using a finite difference method
ActiveUS6919964B2Directly computeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyDirect evaluation
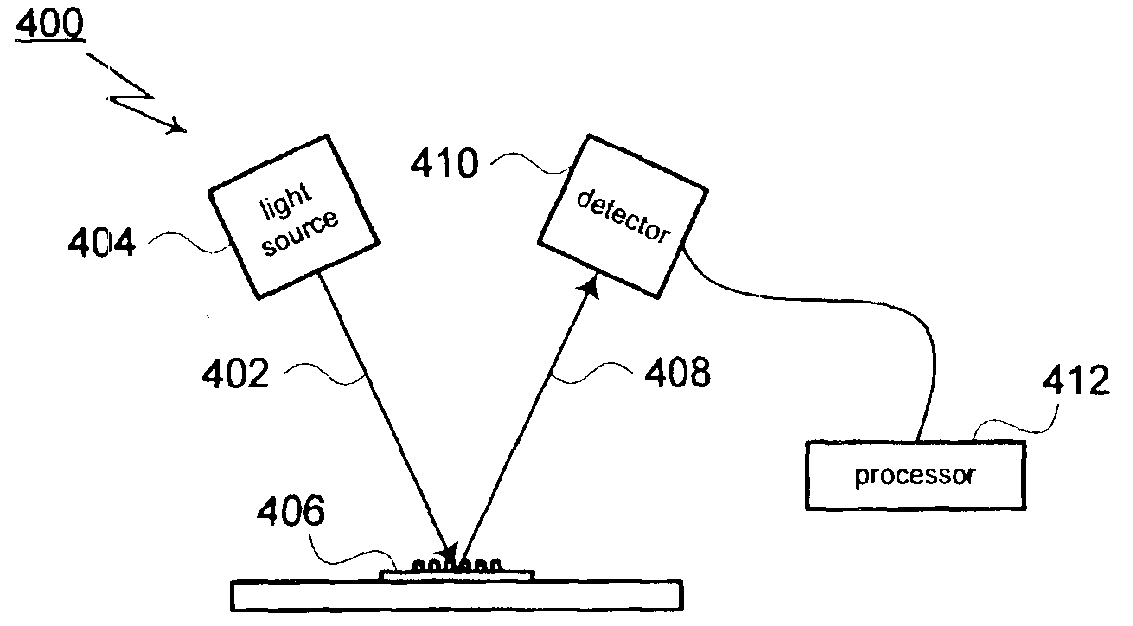
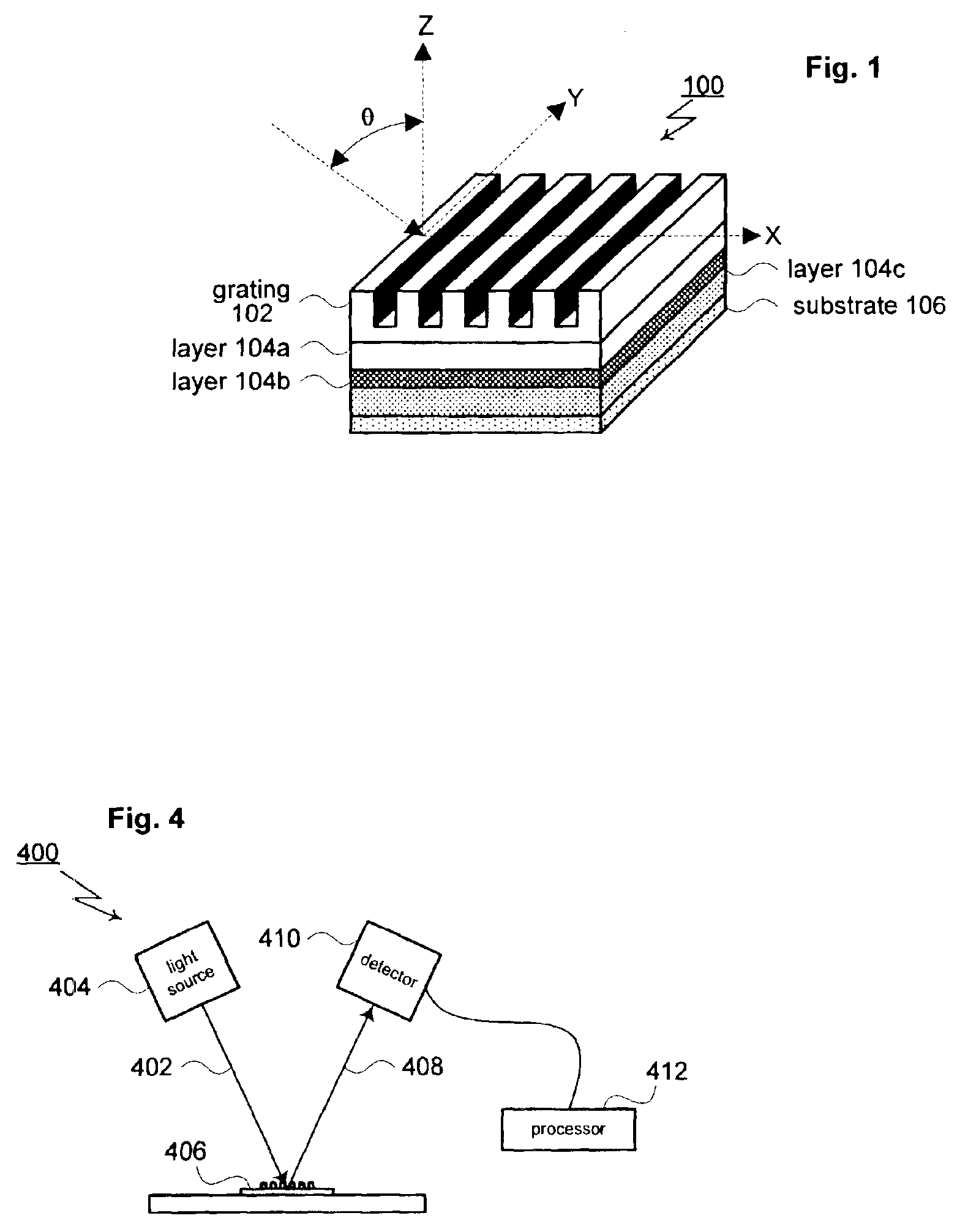
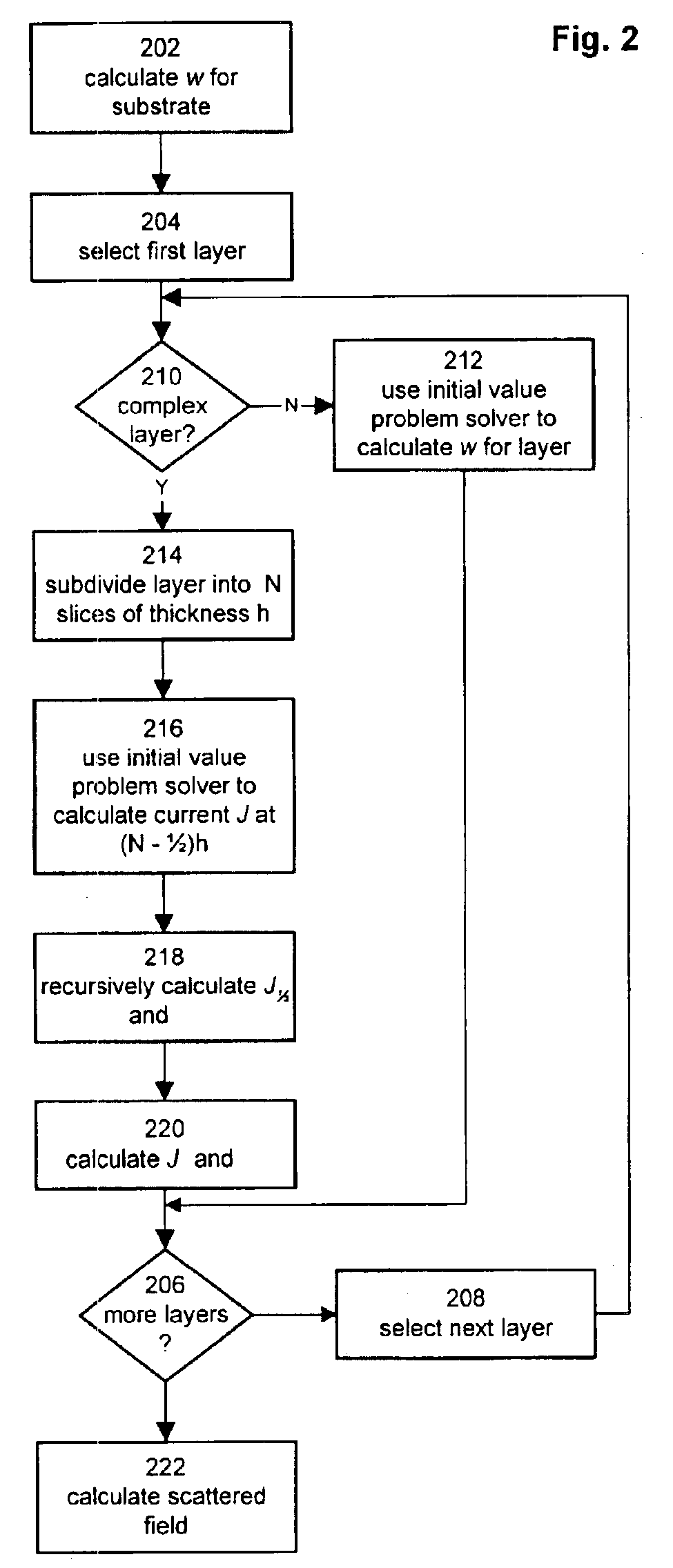
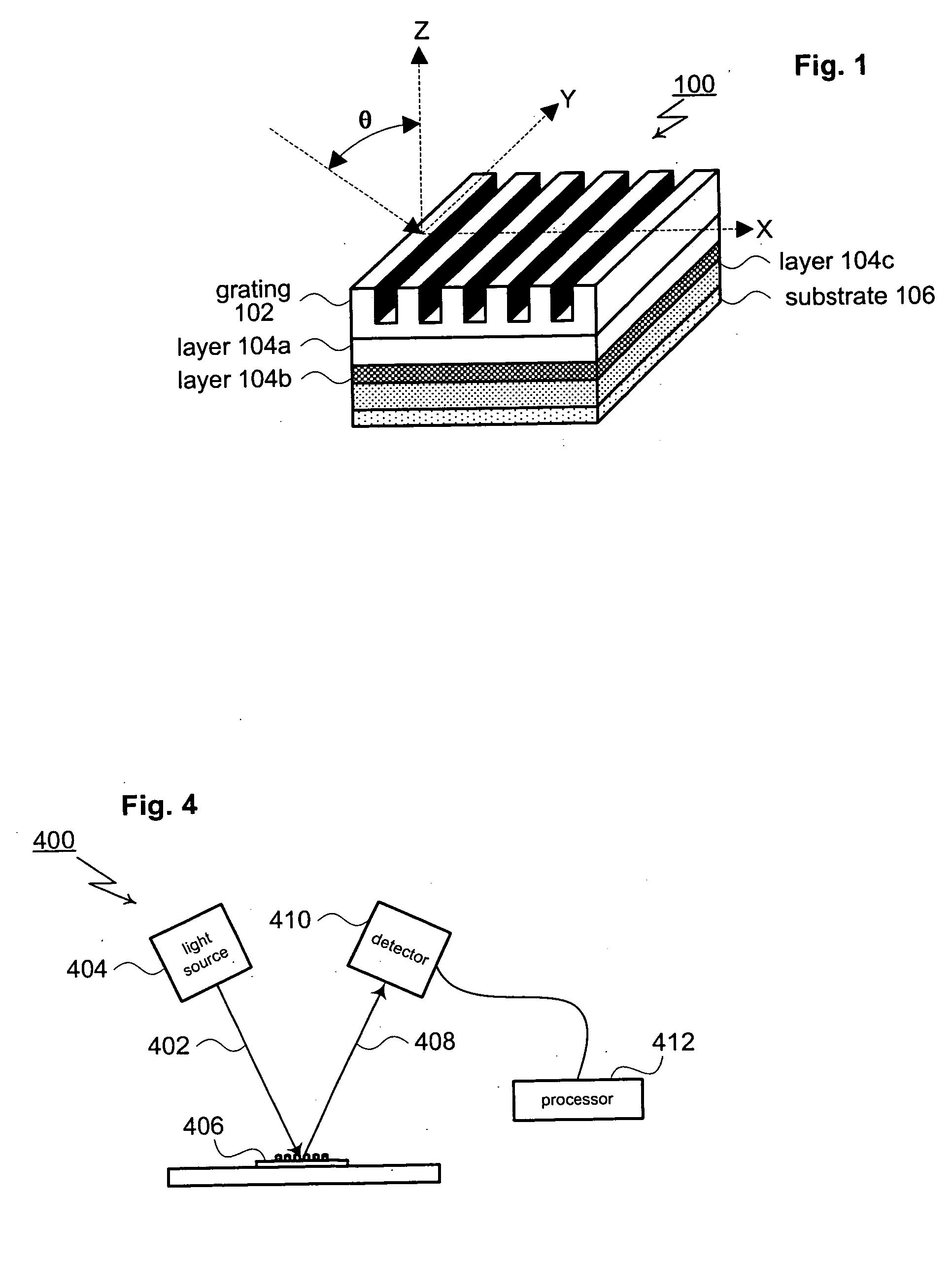
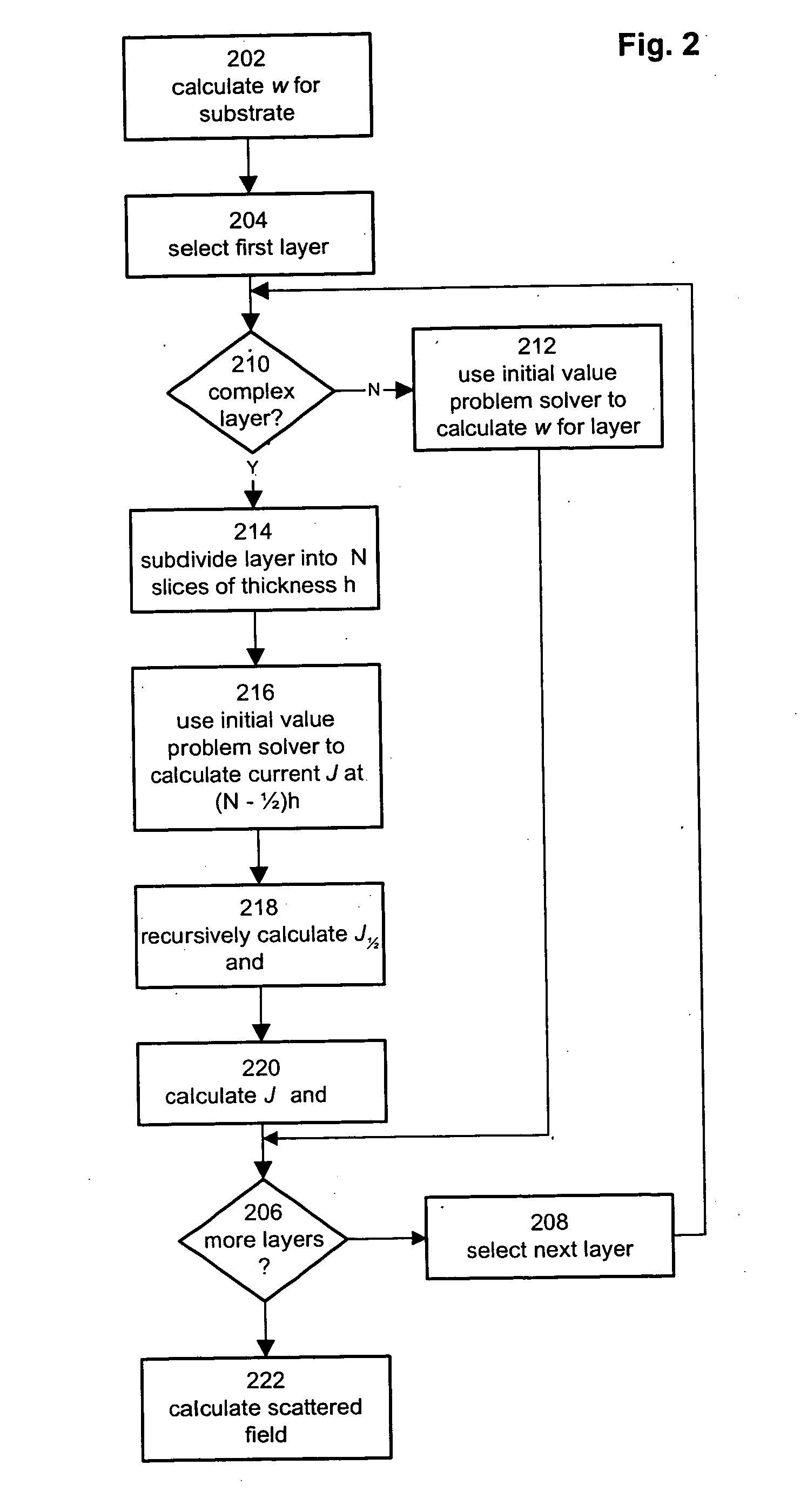
A method for modeling diffraction includes constructing a theoretical model of the subject. A numerical method is then used to predict the output field that is created when an incident field is diffracted by the subject. The numerical method begins by computing the output field at the upper boundary of the substrate and then iterates upward through each of the subject's layers. Structurally simple layers are evaluated directly. More complex layers are discretized into slices. A finite difference scheme is performed for these layers using a recursive expansion of the field-current ratio that starts (or has a base case) at the lowermost slice. The combined evaluation, through all layers, creates a scattering matrix that is evaluated to determine the output field for the subject.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
Financial methodology to valuate and predict the news impact of major events on financial instruments
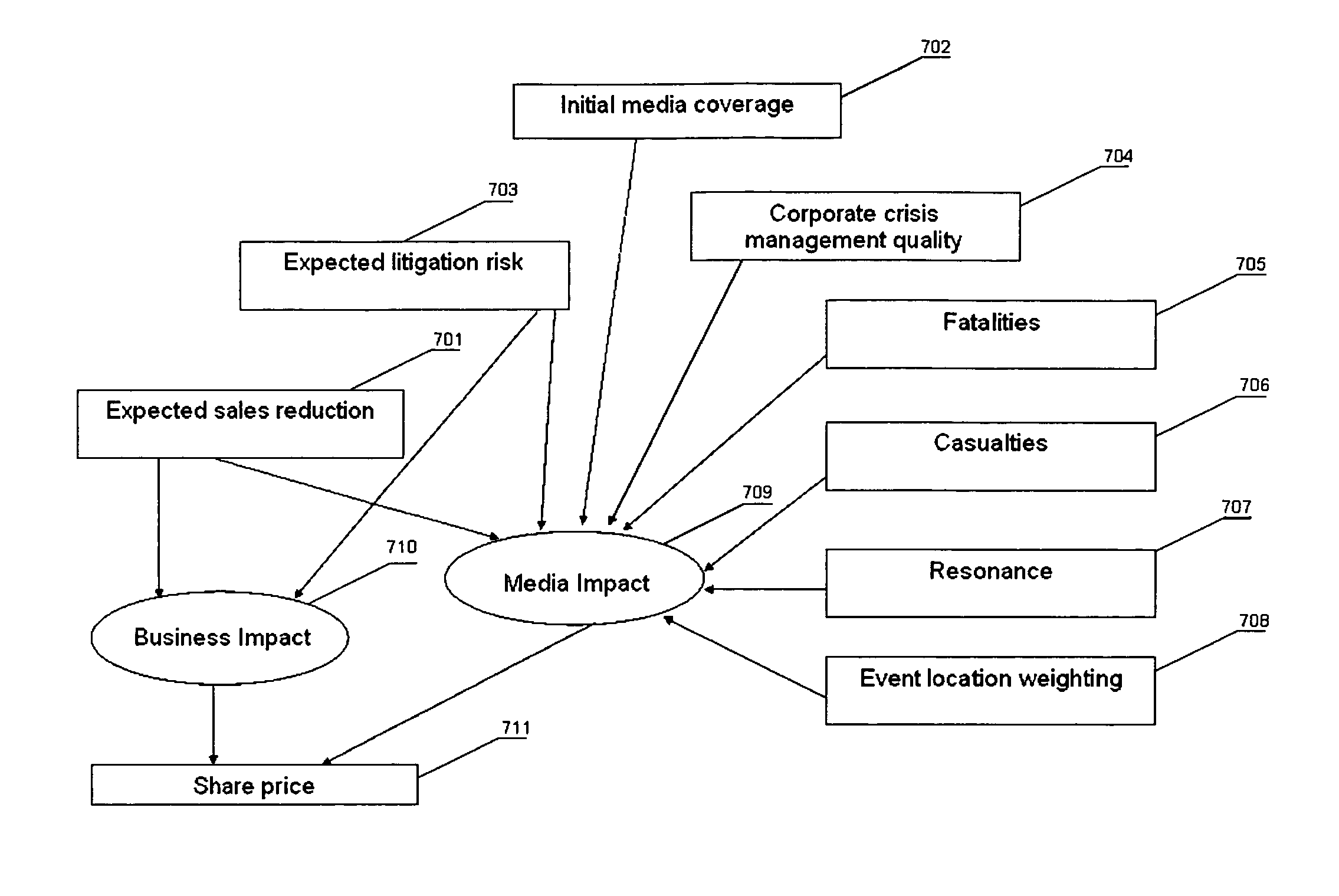
A financial methodology for the analysis of events' impact on media coverage and business, and predictive indications of movements of stock prices (or other financial instruments) triggered by media and business impact is described. The methodology is based on a numerical approach suitable for processing by a computer. It takes into account data outside the traditional realm of finance, such as public sensitivity to certain classes of events, and the correlation between media coverage and stock price performance during the course of an event.
Owner:SIGMAI LTD
Dynamical method for obtaining global optimal solution of general nonlinear programming problems
InactiveUS7277832B2Reliability of computationDigital computer detailsComputation using non-denominational number representationNumerical methodologyDynamic method
A method for obtaining a global optimal solution of general nonlinear programming problems includes the steps of first finding, in a deterministic manner, all stable equilibrium points of a nonlinear dynamical system that satisfies conditions (C1) and (C2), and then finding from said points a global optimal solution. A practical numerical method for reliably computing a dynamical decomposition point for large-scale systems comprises the steps of moving along a search path φt(xs)≡{xs+ t×ŝ, tε+} starting from xs and detecting an exit point, xex, at which the search path φt(xs) exits a stability boundary of a stable equilibrium point xs using the exit point xex as an initial condition and integrating a nonlinear system to an equilibrium point xd, and computing said dynamical decomposition point with respect to a local optimal solution xs wherein the search path is xd.
Owner:BIGWOOD SYST
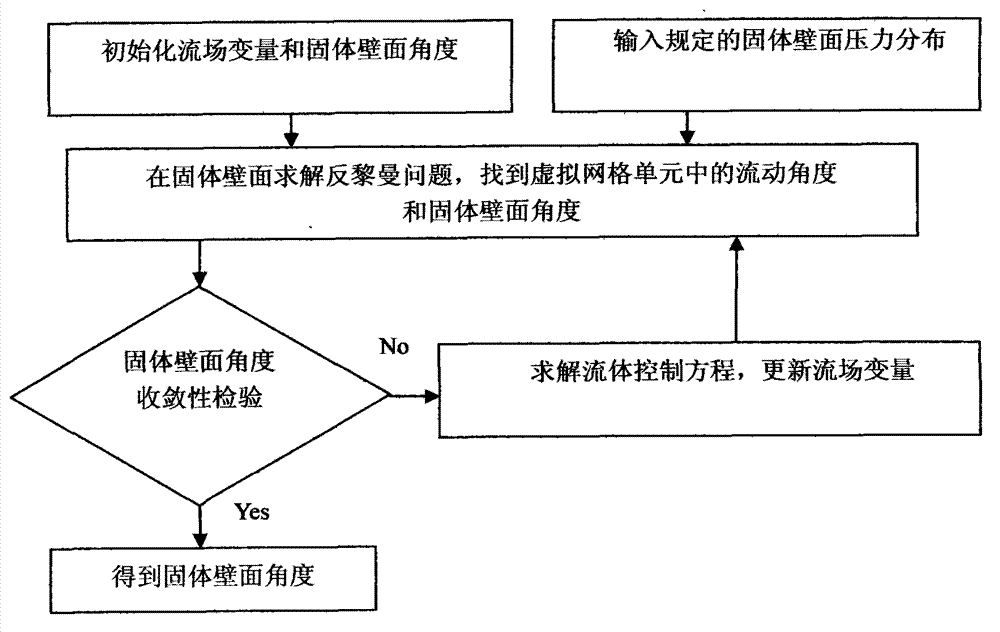
Numerical method for solving two-dimensional Riemannian problem and simulating subsonic non-viscous stream
The invention belongs to the field of computational fluid mechanics, in particular to a numerical method for solving a two-dimensional Riemannian problem, and is applied to solve an Euler equation and perform the numerical simulation of subsonic non-viscous stream. By the numerical method, the Euler equation on an Euler plane is transformed to a stream function plane; in a two-dimensional Cartesian grid, the Riemannian problem of a translational stream line and the Riemannian problem along the stream line are solved, so that the error of a numerical solution is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
Scalable finite element simulation of additive manufacturing
ActiveUS20170337307A1Additive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyComputer moduleDevice simulation
Methods and systems for providing accurate, scalable, and predictive 3D printing simulations using numerical methods for part-level simulations. Complex parts can be discretized into finite elements using independent and arbitrary meshing. The real additive manufacturing tooling path and printing time of a printing machine are simulated and applied to the mesh of finite elements using an intersection module that combines the finite element mesh with the tool path information of the printing machine in a geometric sense. This allows for localized heating effects to be simulated very accurately, and for cooling assessments to be precisely computed given the intersection module's computation of partial facets and volumes of the finite elements at any given time in the printing simulation.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES SIMULIA CORP
Solid-liquid multiphase dynamic numerical simulation method suitable for debris flow
ActiveCN109657322AGood serviceSatisfy H<<L dynamic characteristicsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDependabilityLandform
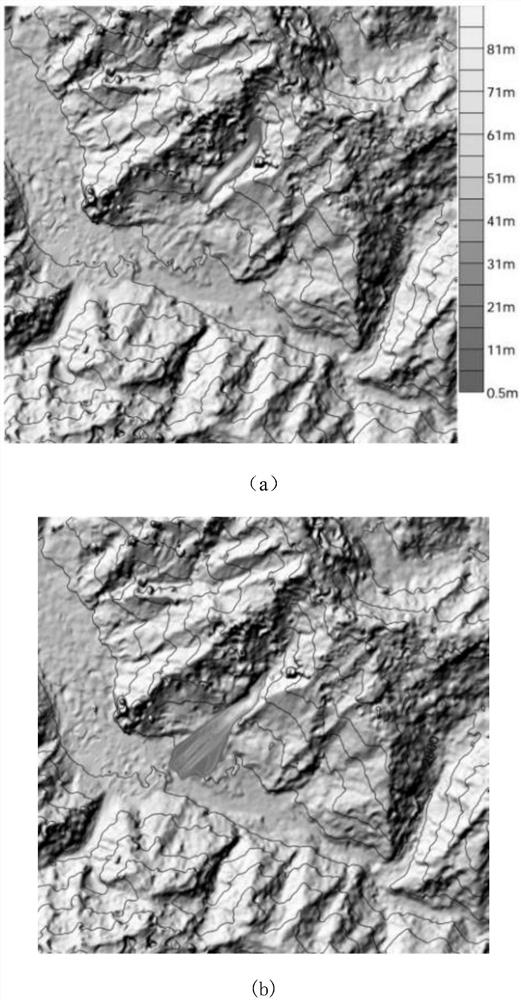
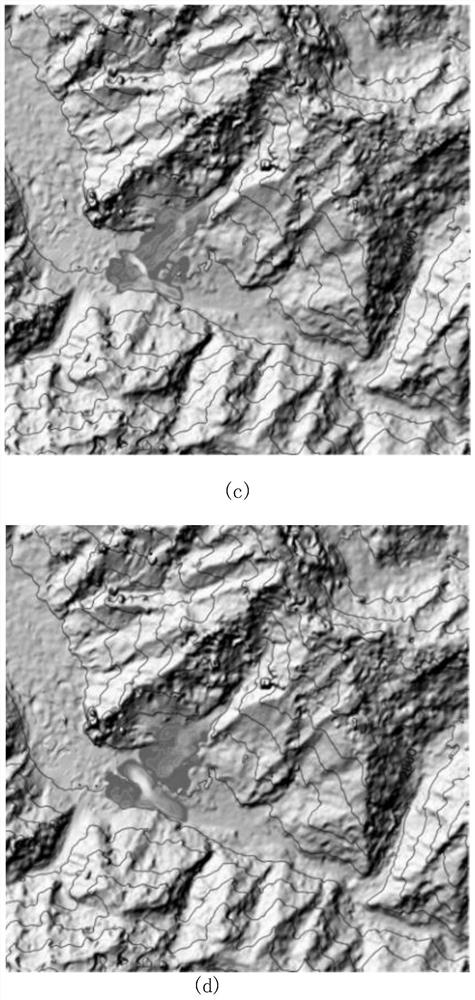
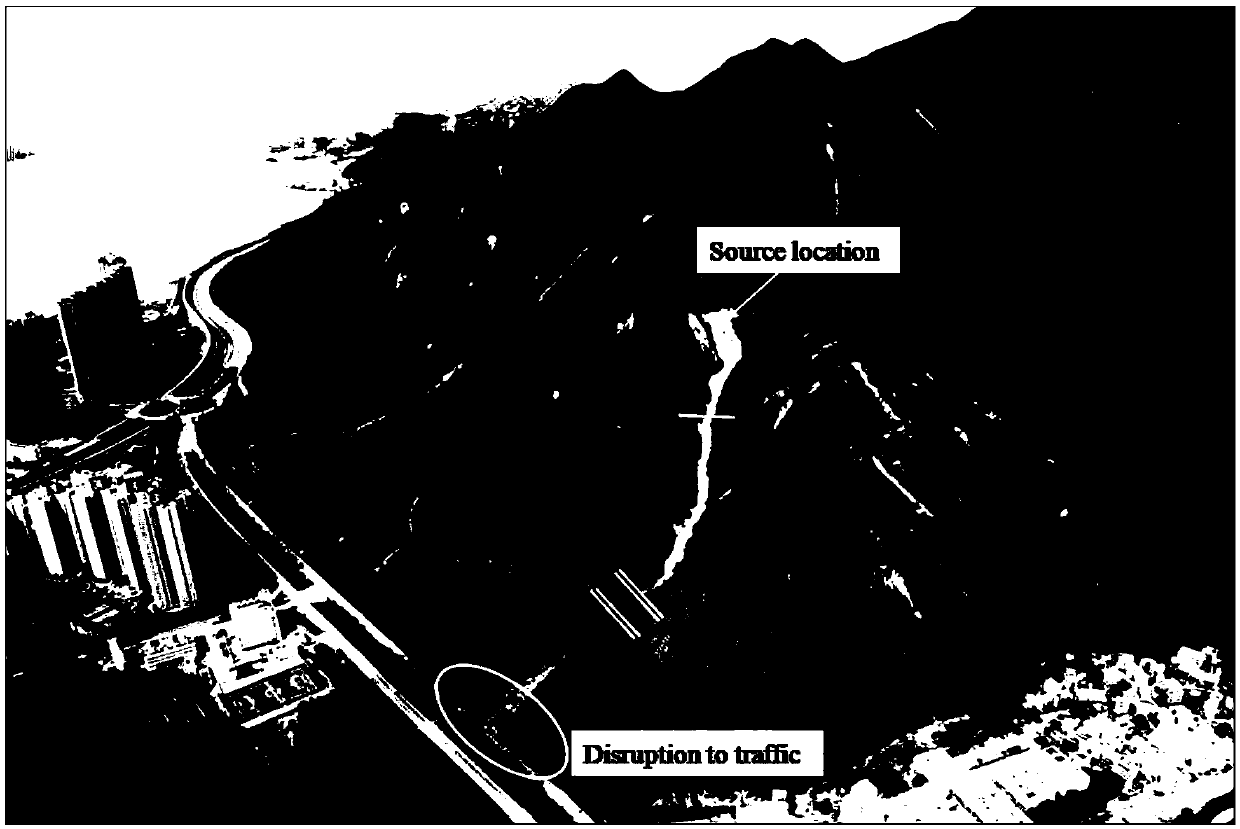
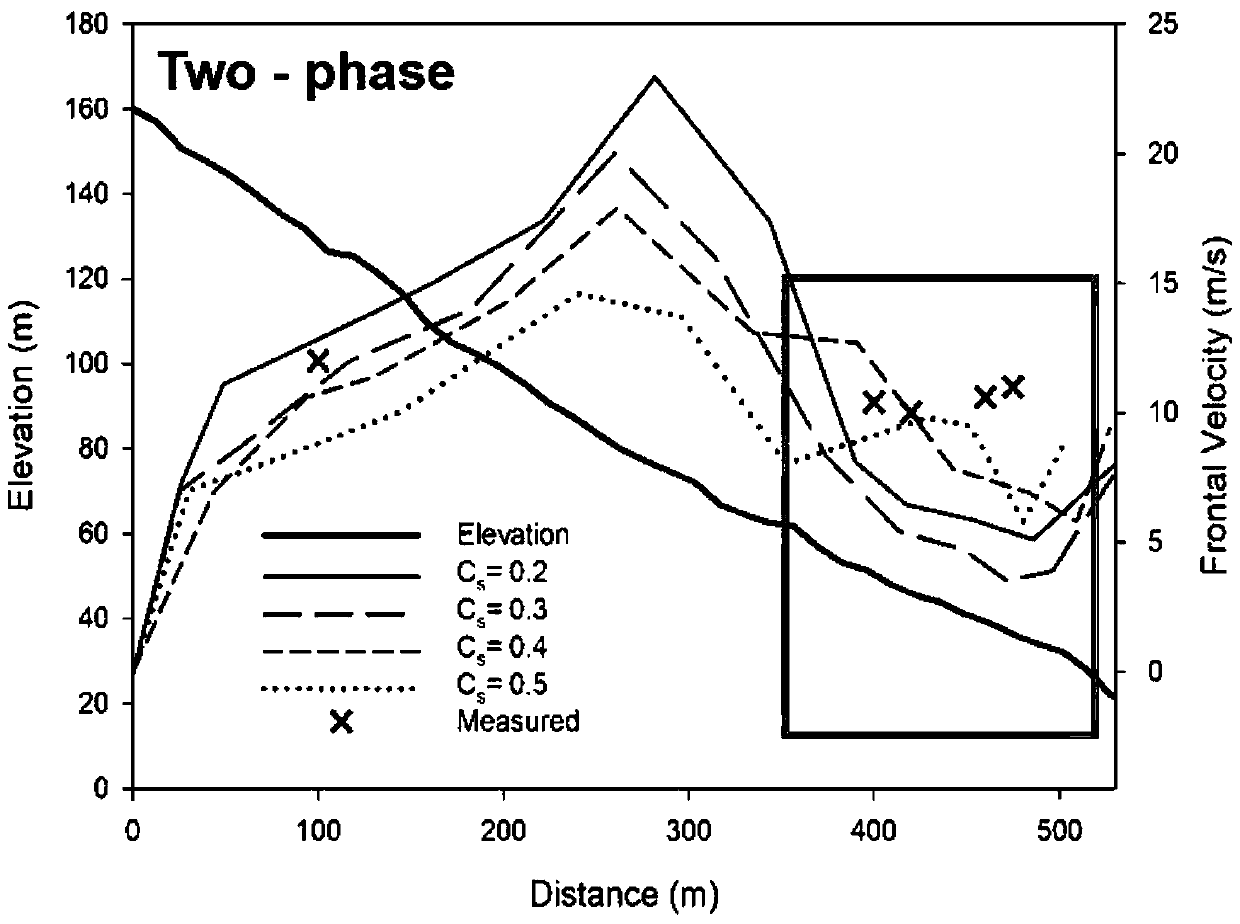
The invention relates to a solid-liquid multiphase dynamic numerical simulation method suitable for debris flow, which adopts a numerical simulation model of a solid-liquid multiphase debris flow power process, and comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring debris flow channel starting, movement and accumulation dynamic information through field scientific investigation and physical and mechanical experiments; Determining high-precision topographic data and object source data in the calculation area through a geographic information system or a high-precision 3D topographic scanner, expressing the high-precision topographic data and the object source data as (x, y, h) grid data through grid coordinate conversion, and respectively representing x, y and h as x, y coordinates and elevation values h of topographic points; Soil and fluid parameters are determined and estimated from a proper amount of soil samples in the channels in the calculation area through indoor physical and mechanical experiments, so that all parameters needing to be prepared in the pretreatment stage of the numerical method are obtained; According to the method, the scientificity and reliability of numerical simulation research in the debris flow dynamic process are improved, the pertinence of disaster prevention and control is improved, the prevention effect is enhanced, and technical support is provided for debris flow disaster reduction.
Owner:INST OF MOUNTAIN HAZARDS & ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
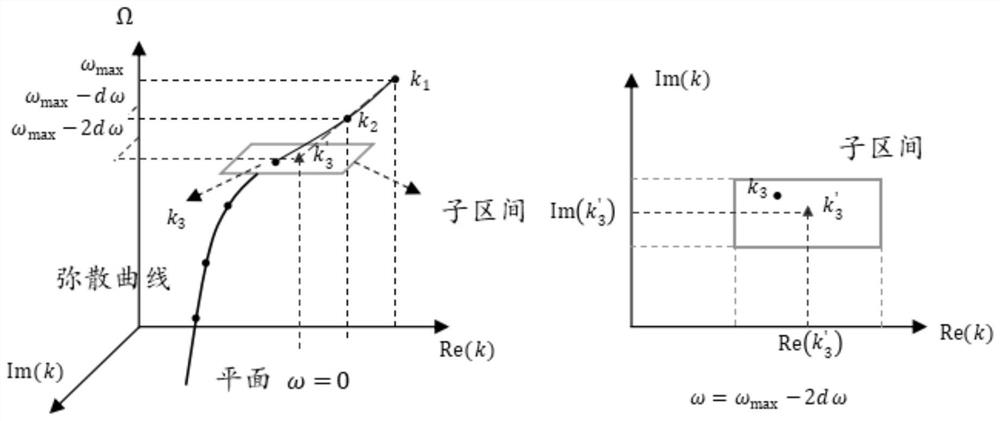
Method for solving numerical value of dispersion curve in sonic sensor
ActiveCN105590025AInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical methodologyDispersion curve
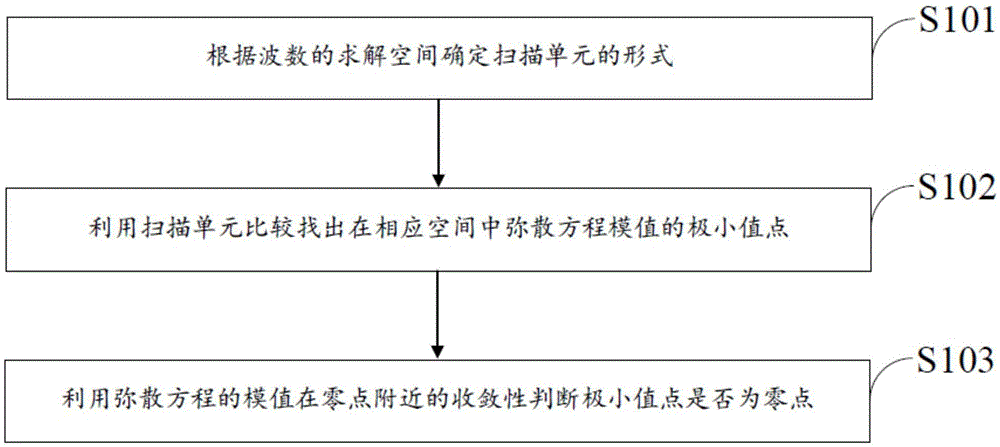
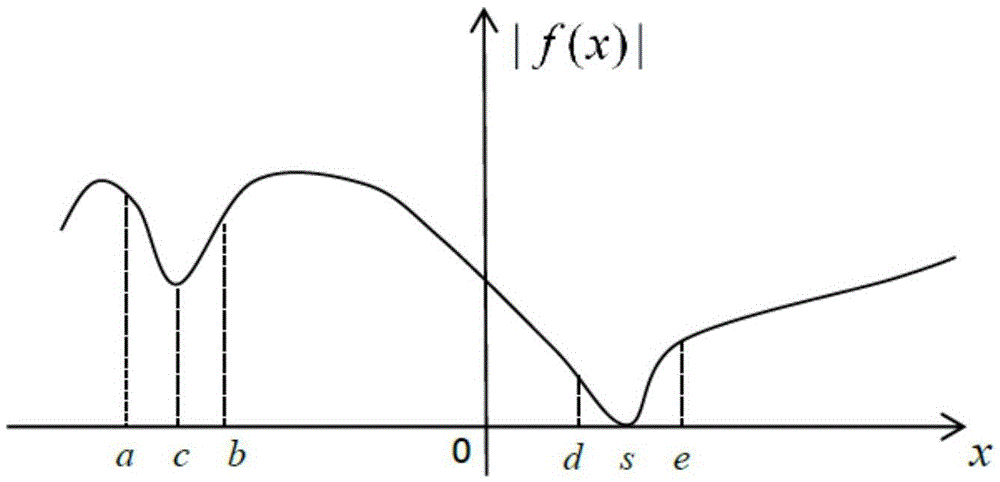
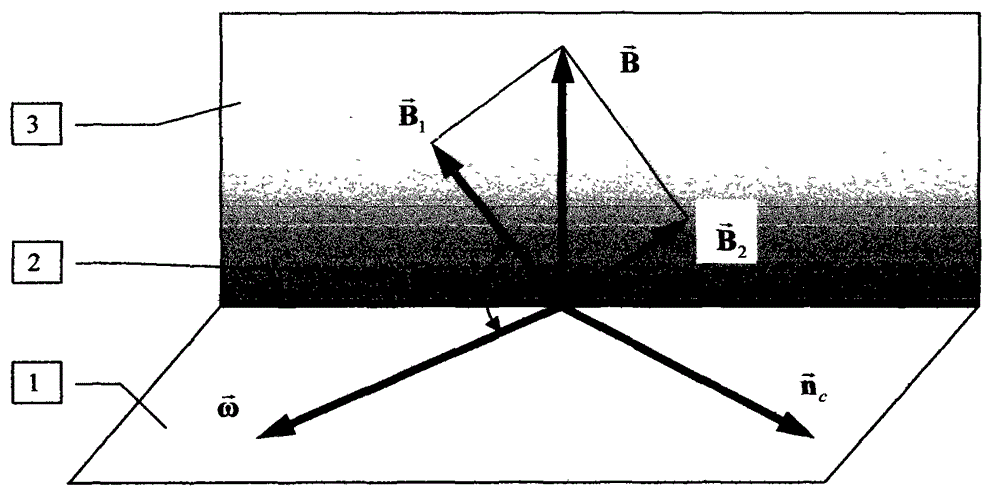
The invention discloses a method for solving a numerical value of a dispersion curve in a sonic sensor. A method for solving a numerical value of a dispersion curve in a real-wave number field and a complex-wave number field is used for solving the frequency of a dispersion equation in the real-wave number field and the complex-wave number field and the solution of a wave number by utilizing the convergence of the module value of the dispersion equation near a zero point. The method comprises the following steps: determining the form of a scanning unit according to a wave number solving space; comparing and finding out the minimal value point of the module value of the dispersion equation in a corresponding space by utilizing the scanning unit; and judging whether the minimal value point is the zero point or not by utilizing the convergence of the module value of the dispersion equation near the zero point. According to the invention, the problem of being difficult to solve the numerical value of the dispersion equation in the real-wave number field and the complex-wave number field can be effectively solved; the method can be used for solving dispersion equations in all kinds of wave propagation problems; and the method is applied to wave propagation and analysis in multiple sensor models.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Numerical method simulating ultrasonic cavity dynamics behavior
ActiveCN105975700AReduce mistakesIncreased Ultrasound Radiation PowerDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical methodologySonification
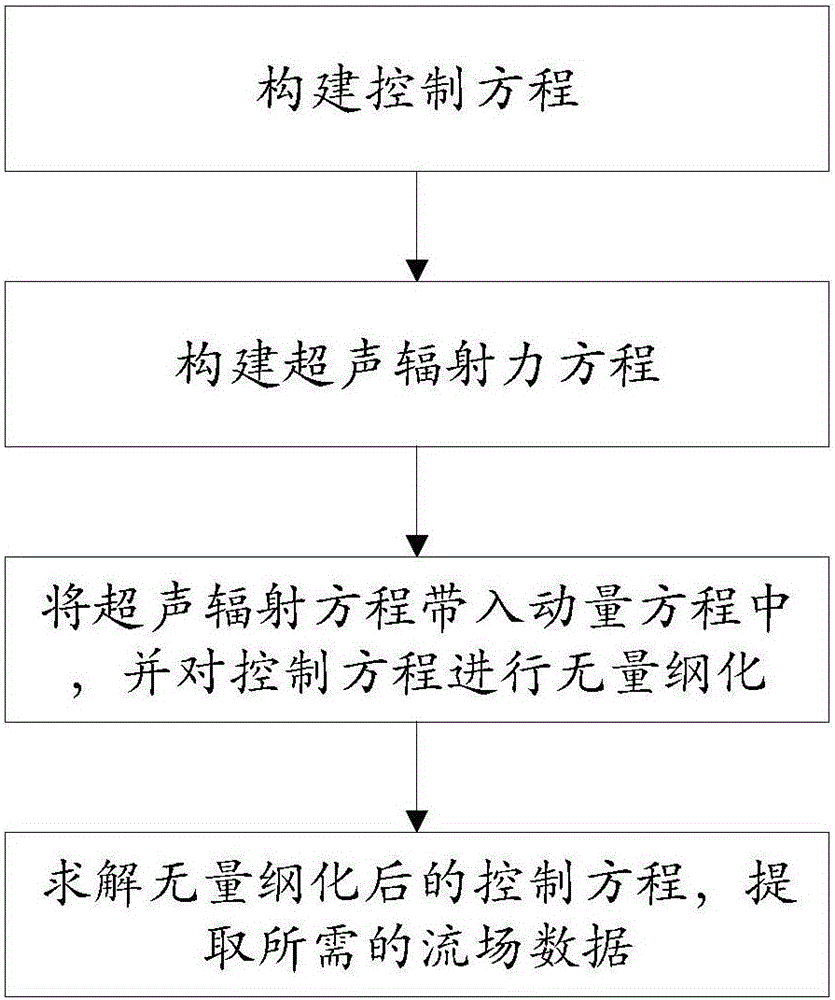
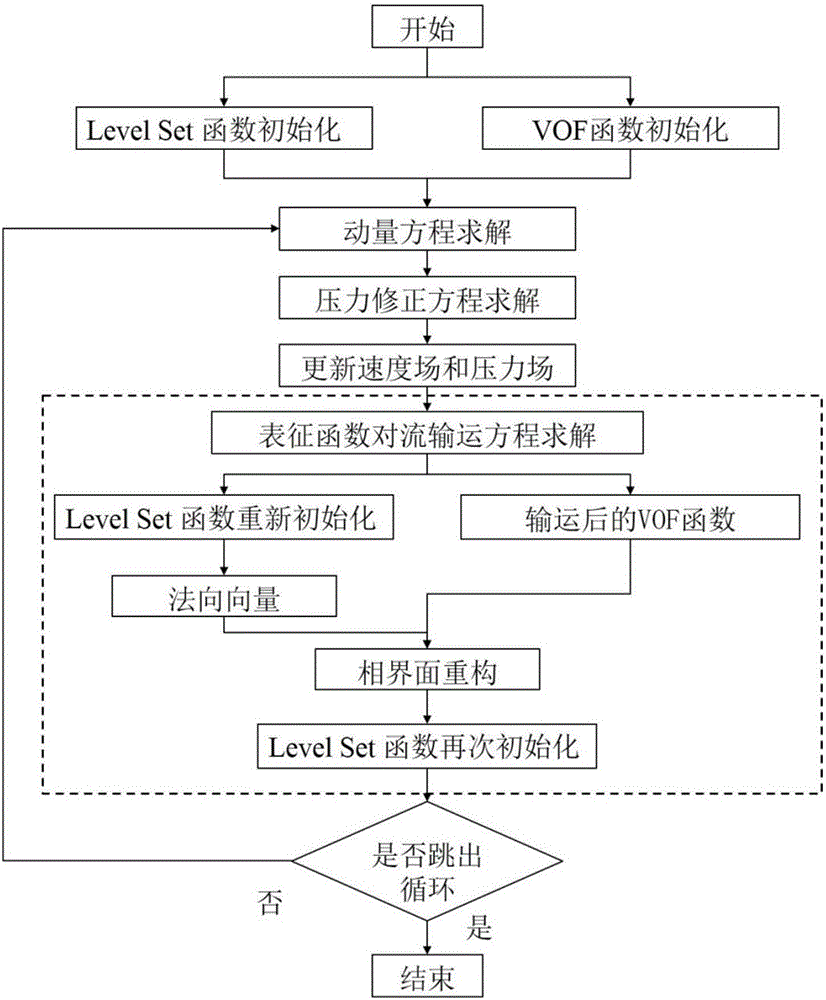
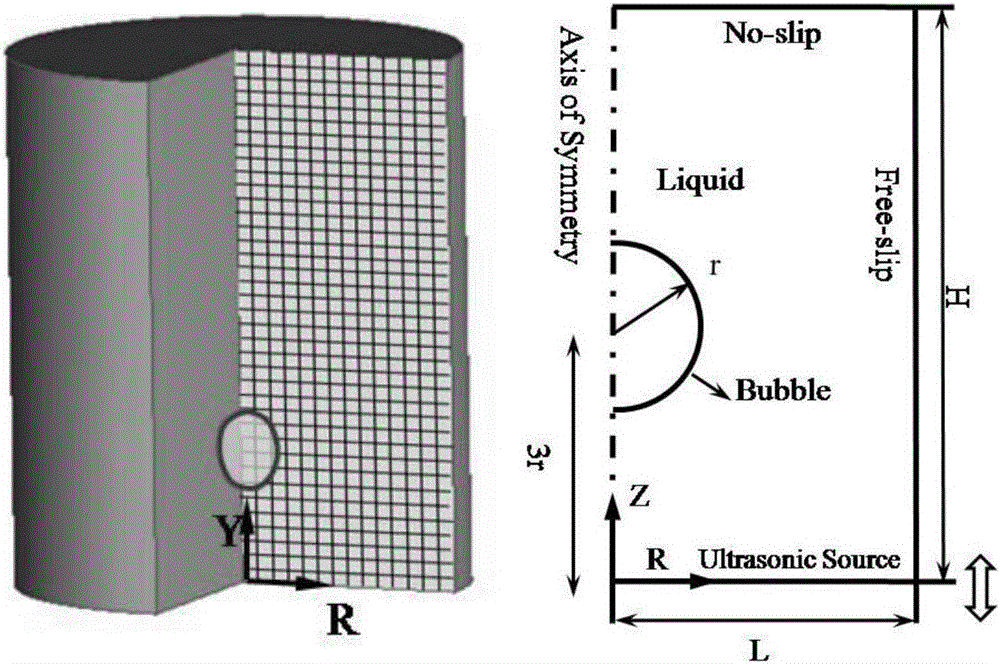
The invention provides a numerical method simulating ultrasonic cavity dynamics behaviors; the method comprises the following steps: 1, building control equations including an ultrasonic field conservation of mass equation and a momentum equation; 2, building an ultrasonic radiation force equation; 3, substituting the ultrasonic radiation force equation into the momentum equation, and nondimensionalizing the control equation; 4, resolving the nondimensionalized control equation, extracting needed flow field data, and thus simulating the ultrasonic cavity dynamics behavior. The numerical method can simulate ultrasonic cavity form changes, wherein the simulated ultrasonic cavity form change has small error with the real ultrasonic cavity form change, thus capturing ultrasonic cavity transient evolution rules and cavity collapse characteristics.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
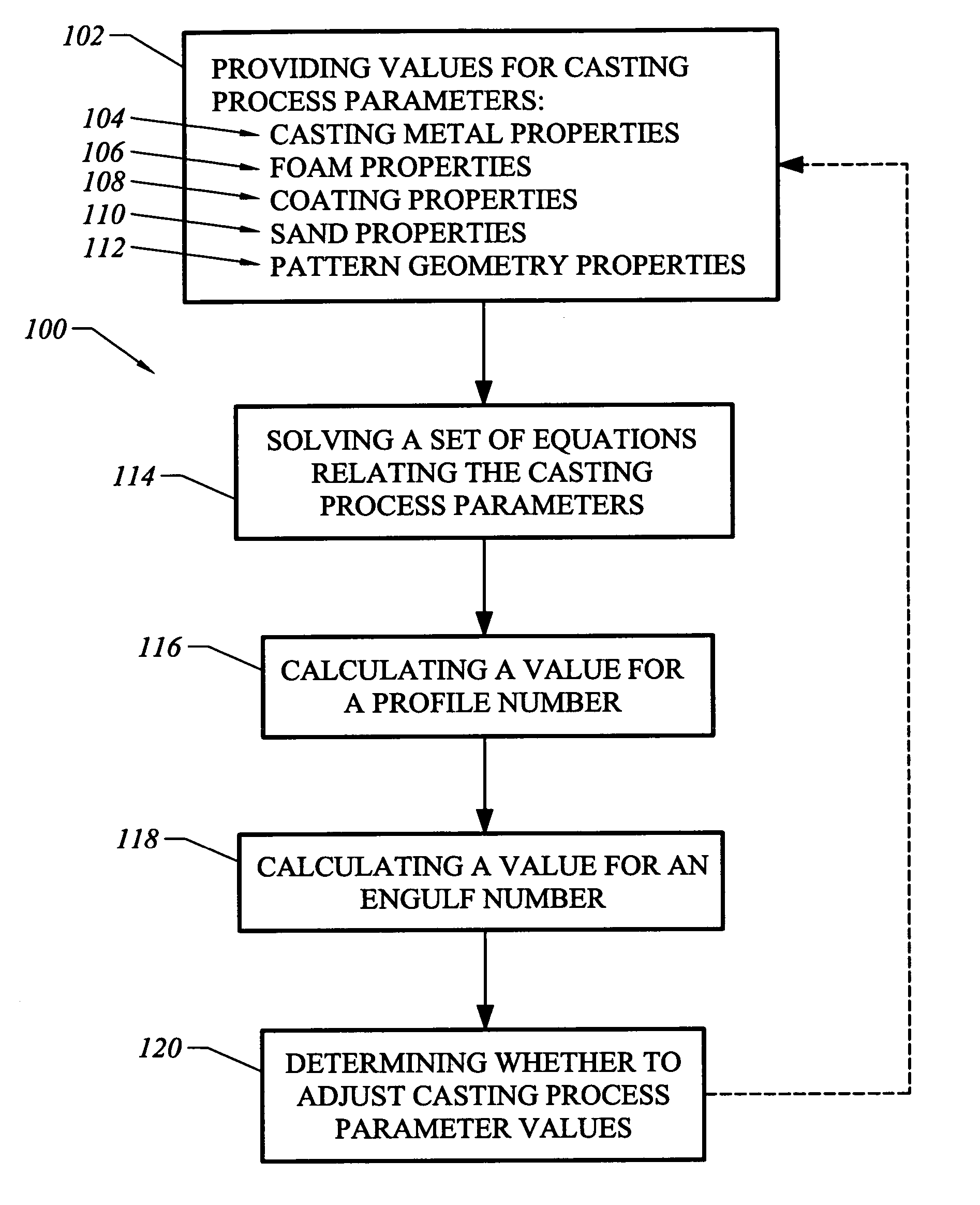
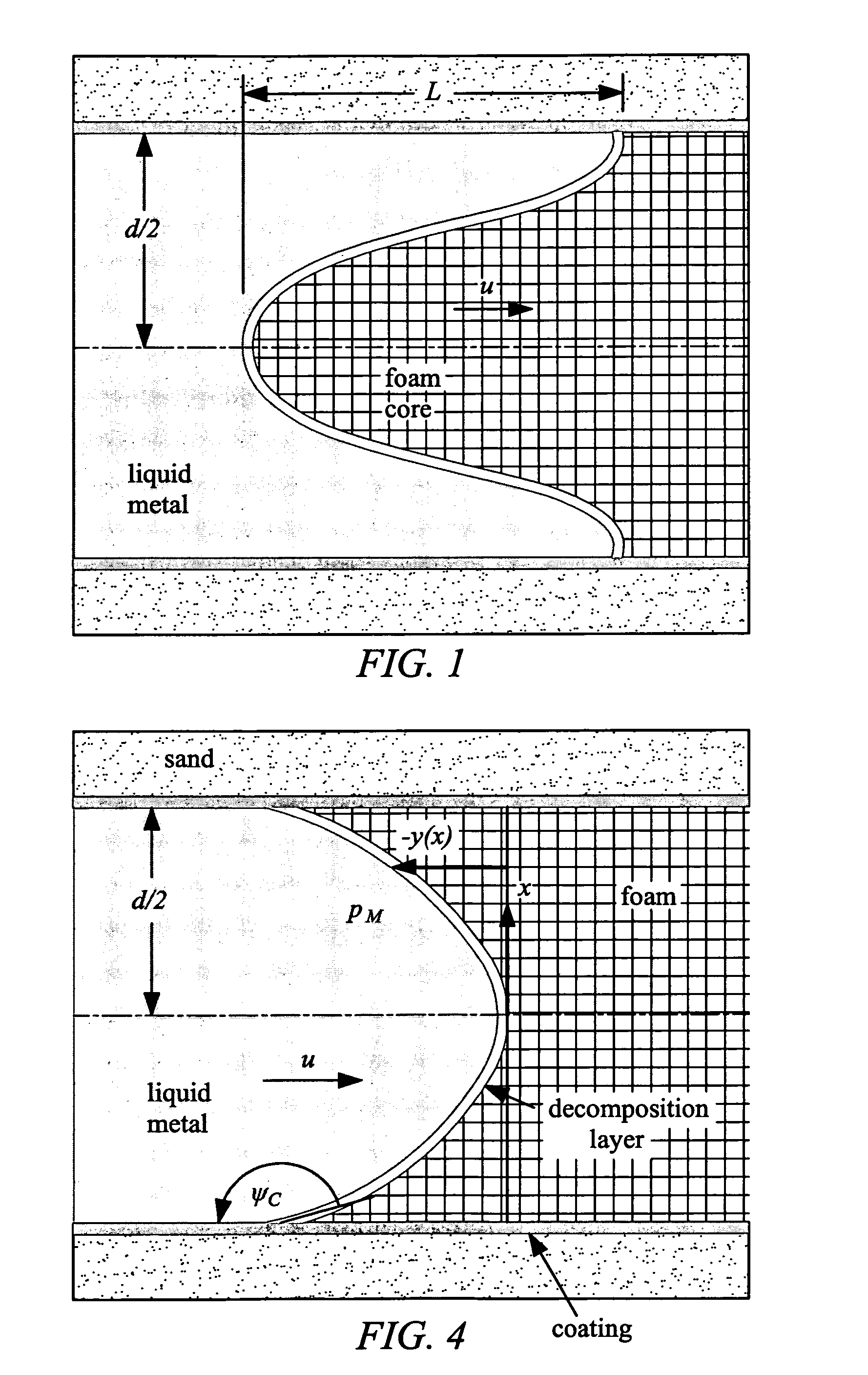
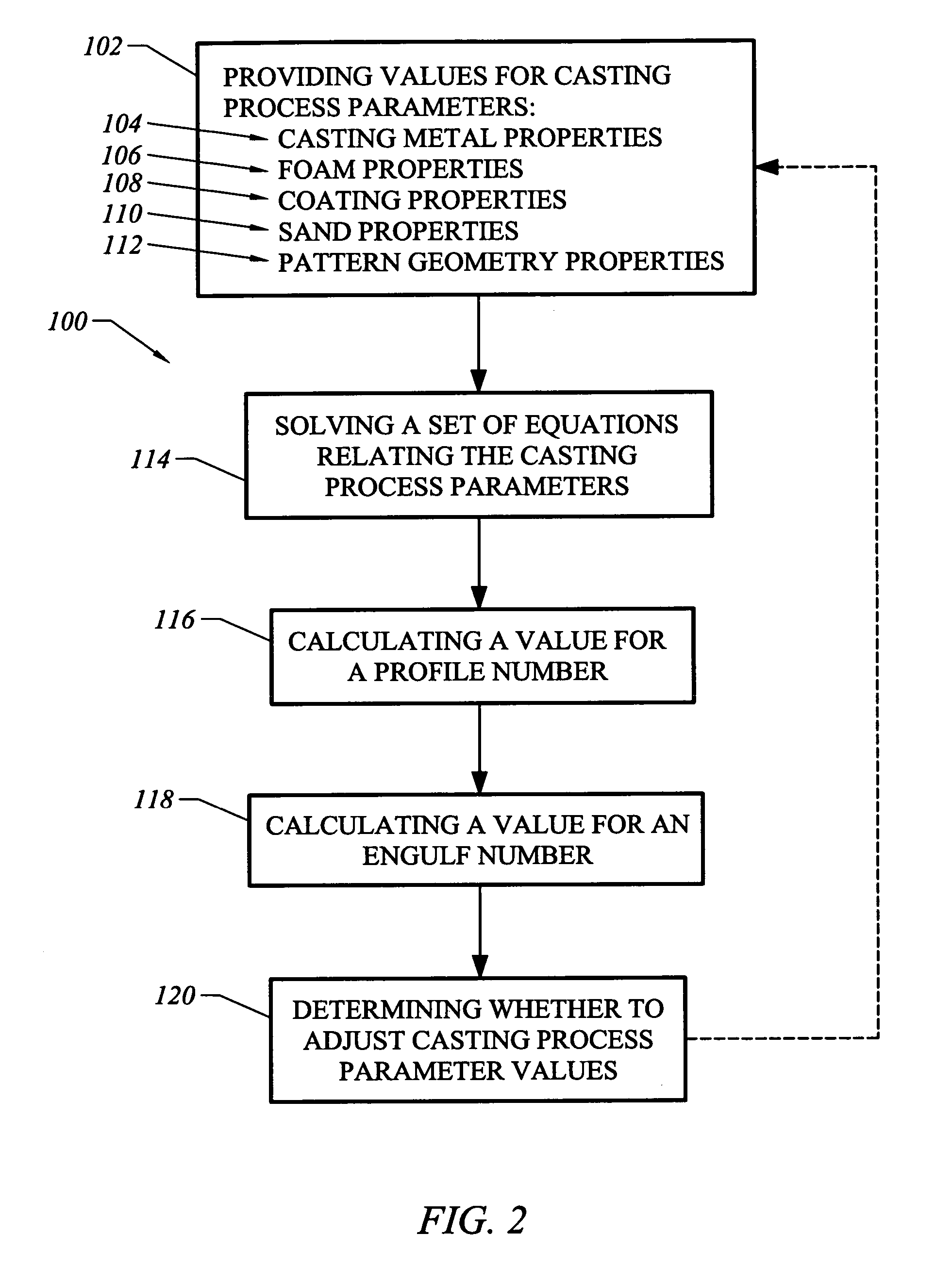
Lost foam casting analysis method
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
CD metrology analysis using a finite difference method
A method for modeling diffraction includes constructing a theoretical model of the subject. A numerical method is then used to predict the output field that is created when an incident field is diffracted by the subject. The numerical method begins by computing the output field at the upper boundary of the substrate and then iterates upward through each of the subject's layers. Structurally simple layers are evaluated directly. More complex layers are discretized into slices. A finite difference scheme is performed for these layers using a recursive expansion of the field-current ratio that starts (or has a base case) at the lowermost slice. The combined evaluation, through all layers, creates a scattering matrix that is evaluated to determine the output field for the subject.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
Numerical method of using Euler equation in Lagrange form to solve inverse problems of one kind
InactiveCN102880588ASave CPU timeComplex mathematical operationsNumerical methodologyEuler equations
The invention relates to a numerical method, and provides and solves a novel two-dimensional Euler equation in Lagrange form to solve inverse problems of solid wall face geometric shape design. The invention provides a mapping mode for deducing the Euler equation on a Lagrange plane, computational grid is simplified, and numerical dissipation of convective terms is lowered furthest. Using the numerical method of using the Euler equation in Lagrange form to solve the inverse problems of one kind can simultaneously obtain solution of flow field physical quantity and solution of the solid wall face geometric shape design.
Owner:西安远景动力模拟技术有限公司
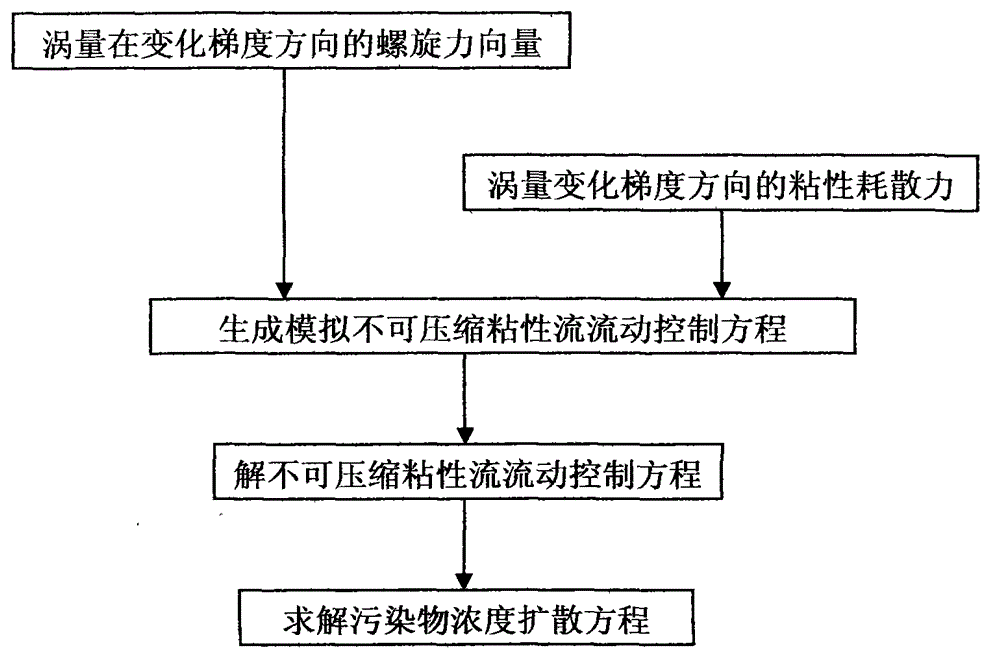
Numerical method for simulating pollutant dispersion in swirling flow field
InactiveCN103064996AHigh precisionFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumViscous dissipation
The invention provides a numerical method for simulating pollutant dispersion in a swirling flow field. According to characteristics of incompressible flows, two forms of force are added in a momentum equation to improve numerical simulation accuracy of the vortical-motion-oriented flow field. The two forms of force are respectively vortical force and viscous dissipation force of a vorticity in the changing gradient direction. The numerical method enables integral calculation of the vortical force of the vorticity in a computational grid in the changing gradient direction to be converted into flux calculation of force on a boundary of the computational grid and can enable spatial dispersion to have a high-order accuracy form. In addition, the viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the changing gradient direction is retained by a source item of the momentum equation so as to improve convergence and stability of a numerical solution. The two forms of force adopt different amplification coefficients, the accuracy of the vorticity can be further kept, and pollutant dispersion movement in the swirling flow field can be accurately simulated.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
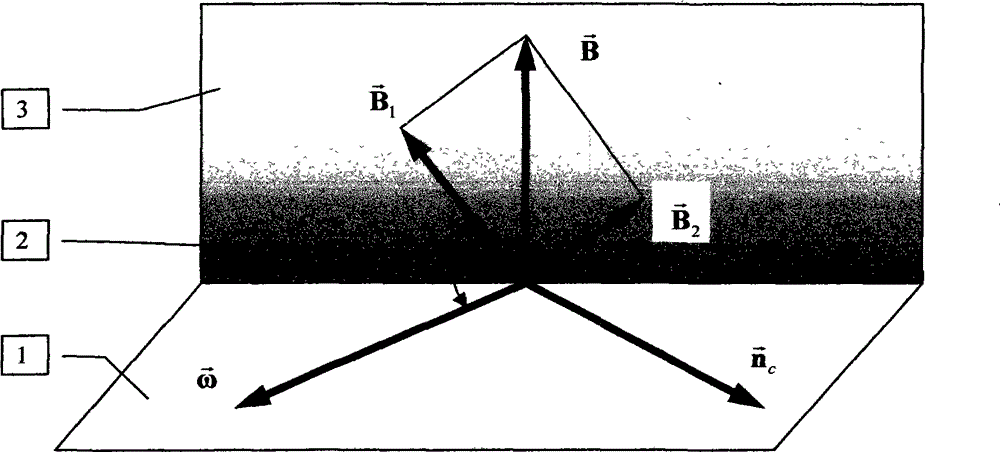
Numerical method for simulating wingtip vortex flow of aircraft
InactiveCN102930134AHigh precisionFast convergenceAerodynamics improvementSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumEngineering
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
Nonlinear constitutive relation analysis method, system and device for negative poisson ratio structure
PendingCN111191378AImprove calculation accuracyIncrease the scope of applicationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical methodologyEngineering
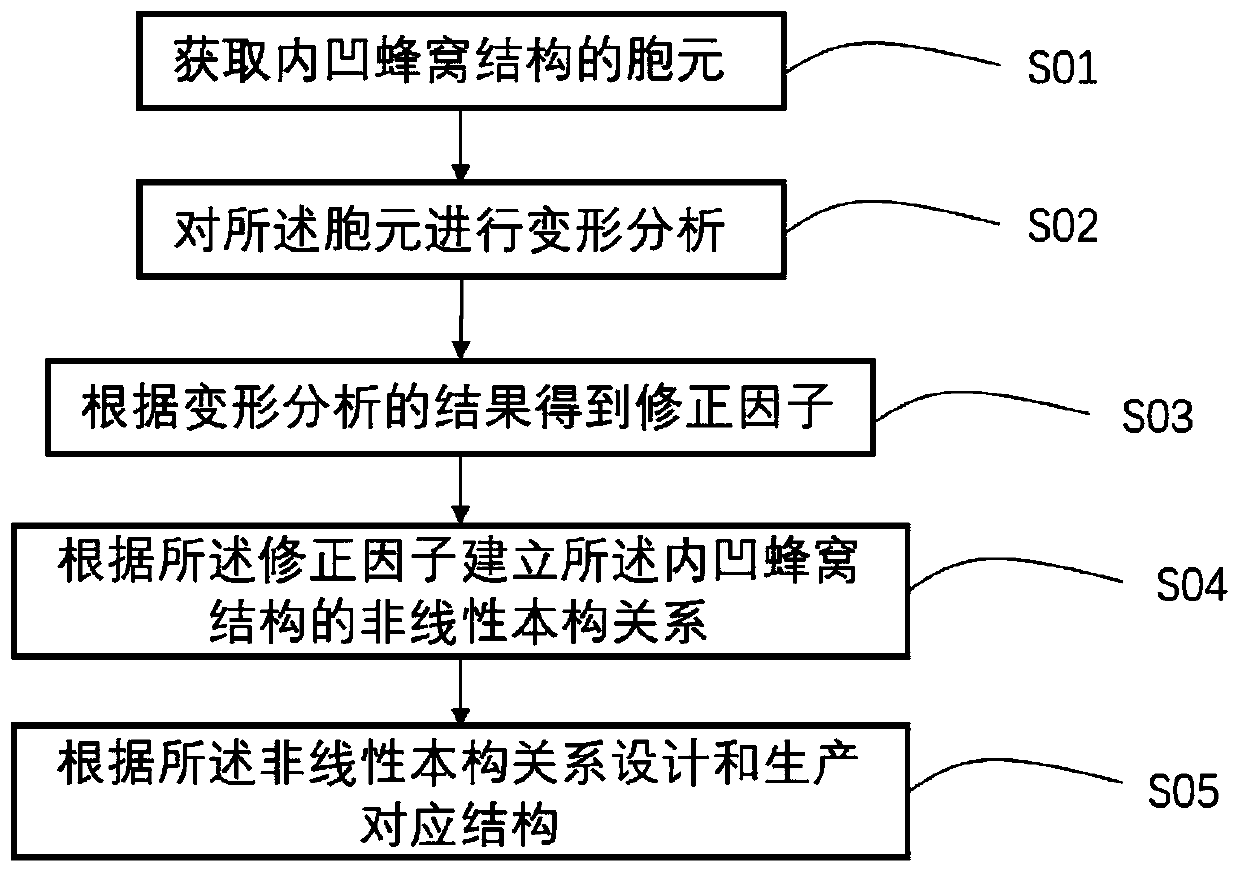
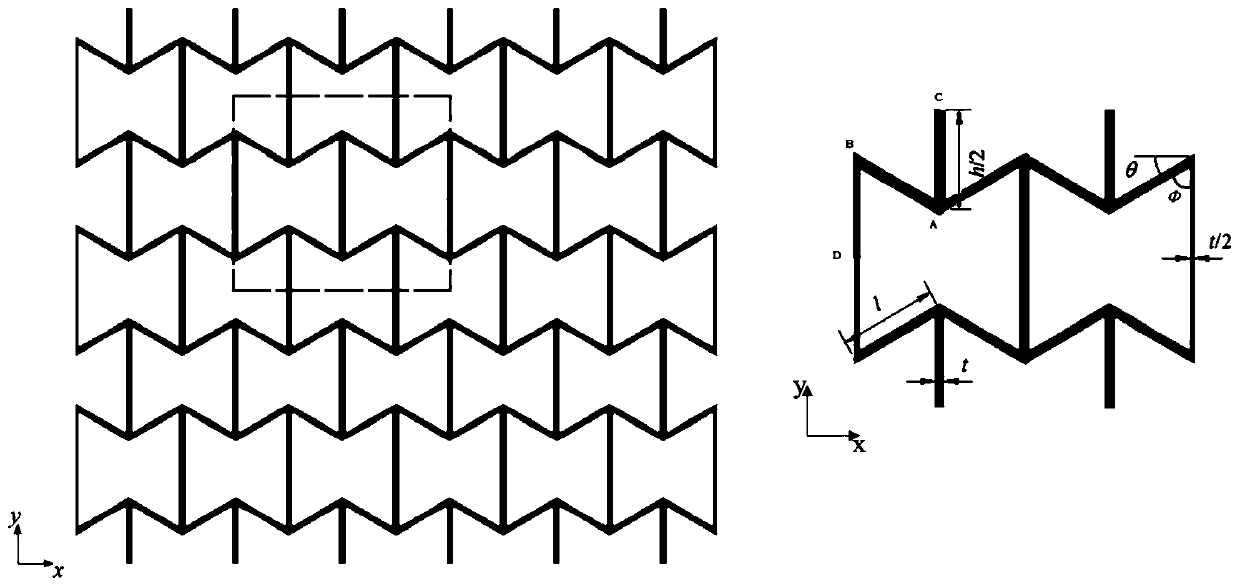
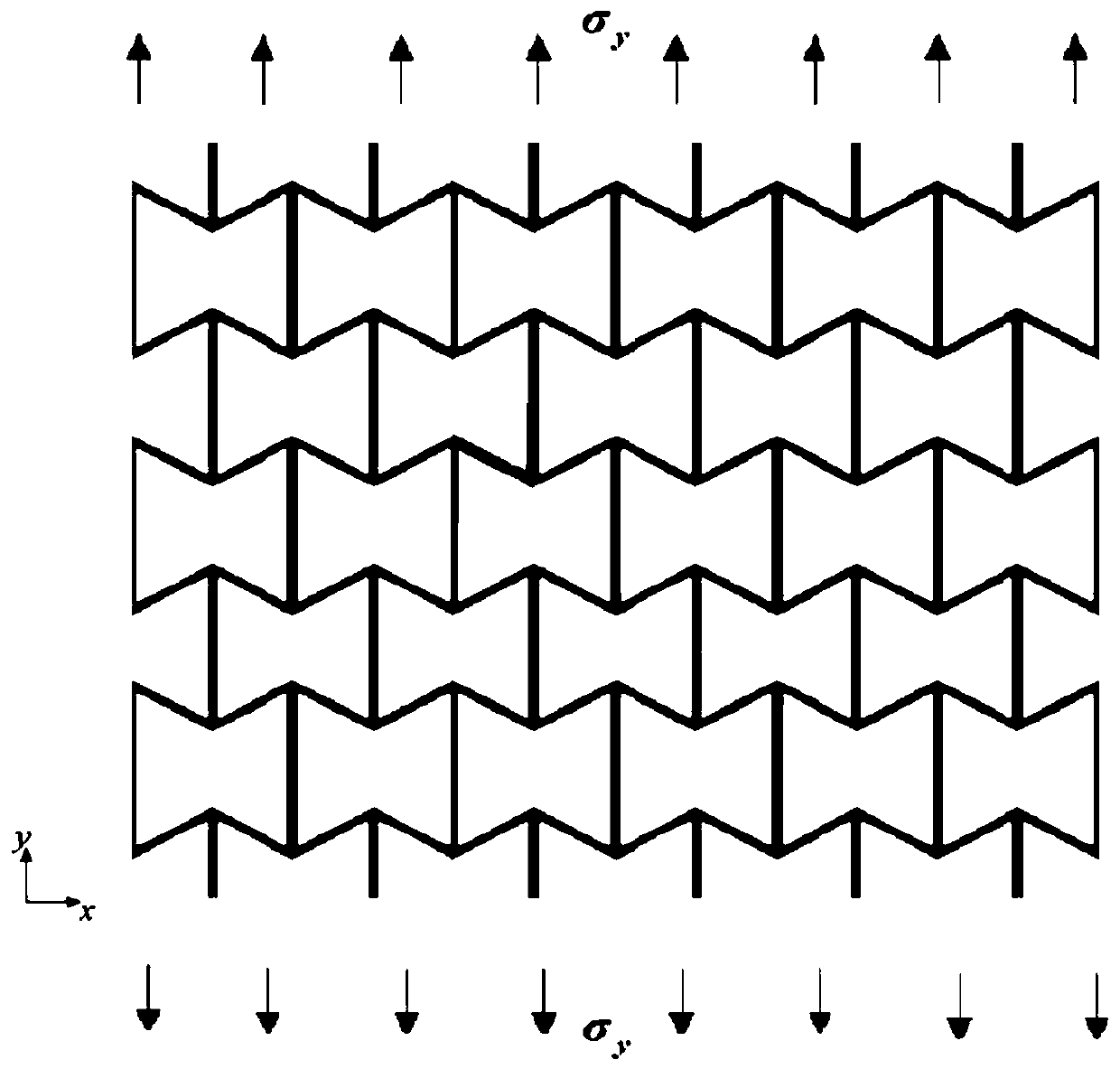
The invention discloses a nonlinear constitutive relation analysis method, a system and a device for a negative poisson ratio structure. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a unit cellwith a concave honeycomb structure; carrying out deformation analysis on the unit cell; obtaining a correction factor according to a deformation analysis result; establishing a nonlinear constitutiverelation of the concave honeycomb structure according to the correction factor; and designing and producing a corresponding structure according to the nonlinear constitutive relation. By using the method provided by the invention, the design, production and manufacturing processes are more convenient in a scene with special requirements on materials or structures, the design period of the productis further shortened, and the method provided by the invention has better calculation precision and application range compared with a numerical method and a test method in the prior art. The method can be widely applied to the technical field of material science.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Vorticity-refinement based numerical method for simulating aircraft wing-tip vortex flows
InactiveUS20140343905A1Fast convergenceImprove simulation accuracyGeometric CADSustainable transportationNumerical methodologyEngineering
The present invention relates a numerical method to simulate the incompressible wing-tip vortex flows. This method is called Vorticity-Refinement, which refines the added vorticity as two different forms of force multiplied by two different factors to counteract the numerical diffusions in the numerical solutions by utilizing the high-order spatial discretization and improving the stability and convergence of the governing equations for incompressible flows.
Owner:XIAN VIRTUAL DYNAMICS SIMULATION TECH
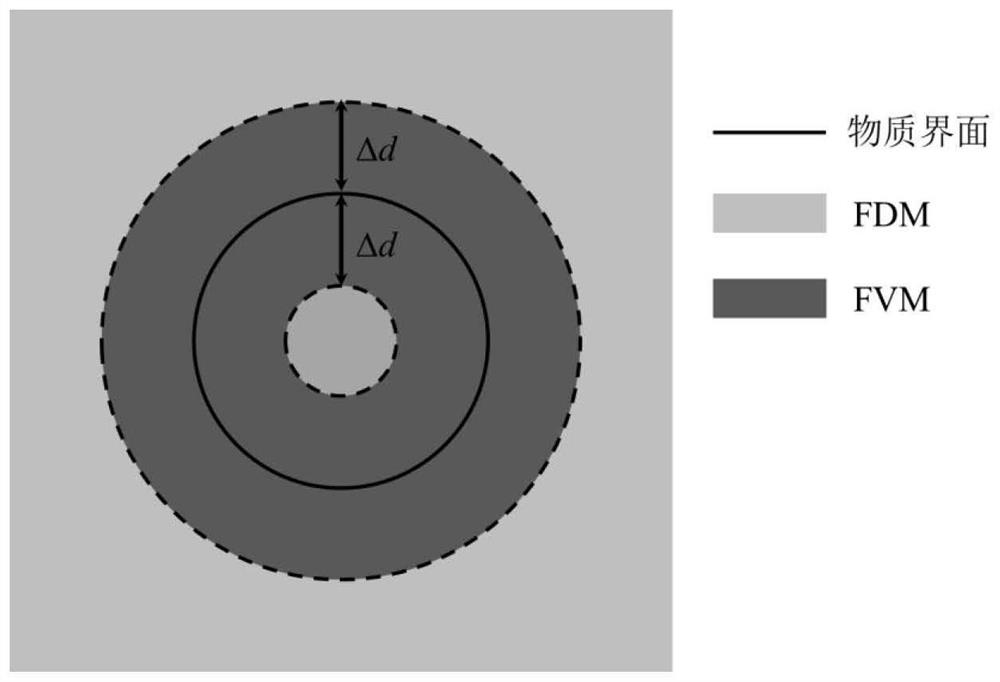
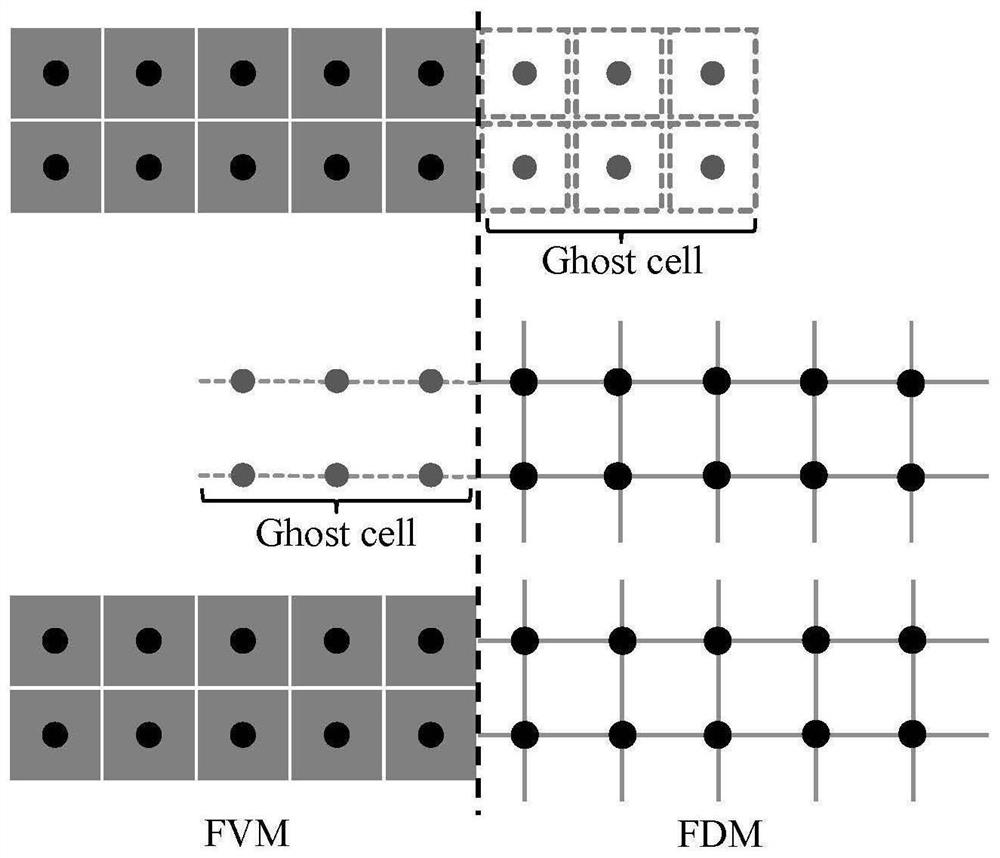
High-precision adaptive finite volume-finite difference coupling numerical simulation method
PendingCN114169184AHigh resolutionMaintain conservationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsUltra high speedNumerical methodology
The invention discloses a high-precision self-adaptive finite volume-finite difference coupling numerical simulation method, and belongs to the field of multi-substance coupling effect high-precision numerical simulation. According to the method, adaptive coupling of two numerical methods of finite volume and finite difference can be realized, different numerical formats are selected for calculation at different positions of a calculation domain according to an adaptive algorithm judgment rule, and different high-precision algorithm calculation areas are coupled by adopting an adaptive algorithm coupling method, so that the calculation accuracy is improved. According to the method, the high-resolution shock wave discontinuous capture effect of the high-order finite difference method can be obtained, the inherent good conservation characteristic of the finite volume method can be considered, the accuracy of a numerical simulation prediction result can be remarkably improved, and then the engineering technical problem related to the high-precision numerical simulation field can be effectively predicted. The high-precision numerical simulation field comprises the fields of high-speed / ultrahigh-speed warhead penetration and protection, underwater explosion, bubble dynamics, aerospace and mechanical engineering.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
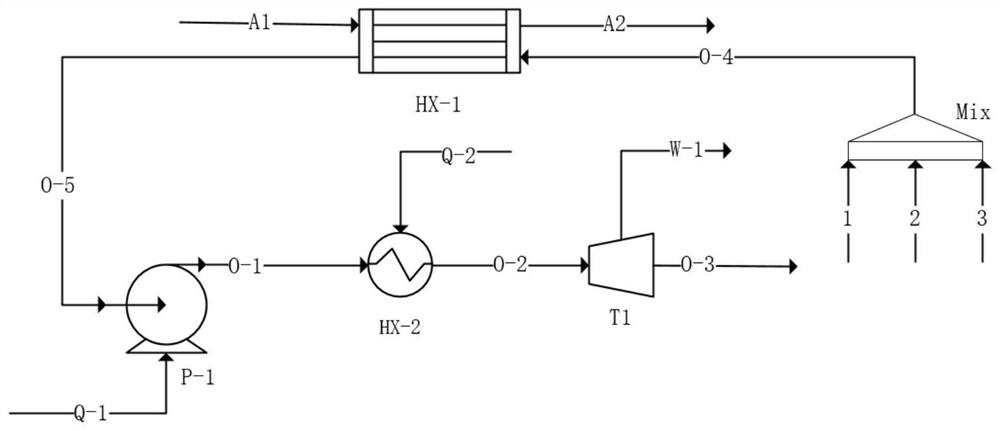
Numerical method for optimizing performance of organic Rankine cycle system
ActiveCN113027556AReduce engagementReduce adverse effectsSteam engine plantsBoiler controlNumerical methodologySystems design
The invention discloses a numerical method for optimizing the performance of an organic Rankine cycle system. The numerical method comprises the steps of optimizing cycle parameters to improve the system performance, and optimizing cycle working medium components to improve the system performance. According to the step for optimizing the cycle parameters to improve the system performance, parameters which have great influence on the system performance are selected, sensitivity analysis is conducted on the parameters, a sensitivity change interval serves as an independent variable change interval, and the system performance is optimized through an optimization algorithm; and according to the step for optimizing the cycle working medium components to improve the system performance, control over the working medium components is achieved by optimizing the mass flow / molar flow of all the components in a working medium, the mass flow / molar flow of all the components of the working medium serves as an independent variable, a system performance evaluation index serves as a dependent variable, and the system performance is optimized through an optimization algorithm. According to the numerical method for optimizing the performance of the organic Rankine cycle system provided by the invention, optimization work of system node parameters and working medium components can be rapidly completed, the system design optimization process is simplified, and the participation degree of technicians in the optimization process is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for determining atomic isotope masses
ActiveUS7193705B2Not easy to make mistakesEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryNumerical methodologyMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A method for determining atomic isotope masses in mass spectrometry, atomic isotope ratios being determined from molecular isotope ratios measured by means of an isotope mass spectrometer—ion correction, the determination of the atomic ratios being carried out by setting up and solving a system of equations which describes relationships between the atomic and the molecular ratios, and the system of equations having to have at least as many independent equations as there are atomic ratios. The entire system of equations is linearized by means of suitable numerical methods in a first step, in particular by means of a Taylor expansion or similar method, and in which the linearized system of equations is subsequently solved as a whole without transforming the individual equations.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
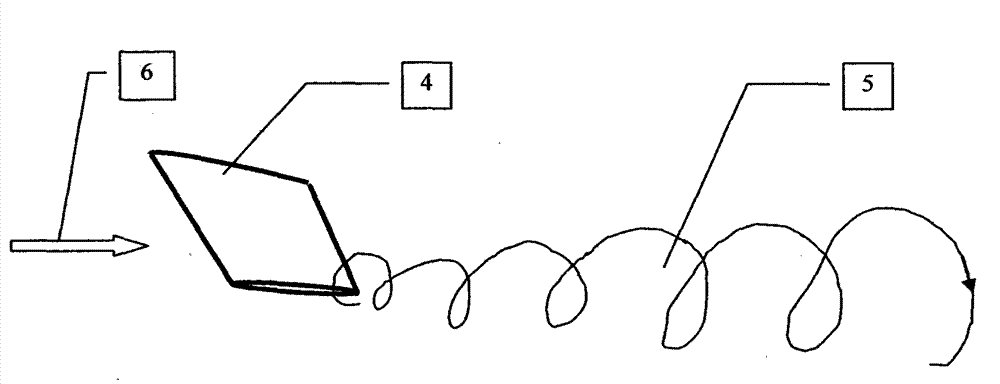
Numerical method for simulating ship propeller wake field
InactiveCN102945293AHigh precisionFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumPropeller
The invention relates to a numerical method for simulating a ship propeller wake field. The numerical simulation accuracy of a type of flow fields predominant in vortex motion is improved by forces of two different forms in a momentum equation according to the feature of incompressible flows. The forces of two different forms include a spiral force whose vorticity is in a variable gradient direction and a viscous dissipation force whose vorticity is in the variable gradient direction. The method converts an integral calculation of the spiral force in the calculation grid, of which the vorticity is in the variable gradient direction, into a flux calculation of a force on the boundary of the calculation grid, so that the spatial discretization of the force has a format of higher order accuracy. Meanwhile, the source item of the momentum equation maintains the viscous dissipation force whose vorticity is in the variable gradient direction, so as to improve the convergence and stability of numerical solution. The two forces have different amplification coefficients, so that the accuracy of vorticity can be further maintained, and as a result, the vortex motion of the ship propeller wake field is simulated more accurately.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
Numerical method for quickly drawing dispersion curve in complex wave number domain in waveguide structure
PendingCN112069447AImprove solution efficiencyImprove completenessComplex mathematical operationsNumerical methodologyScreening method
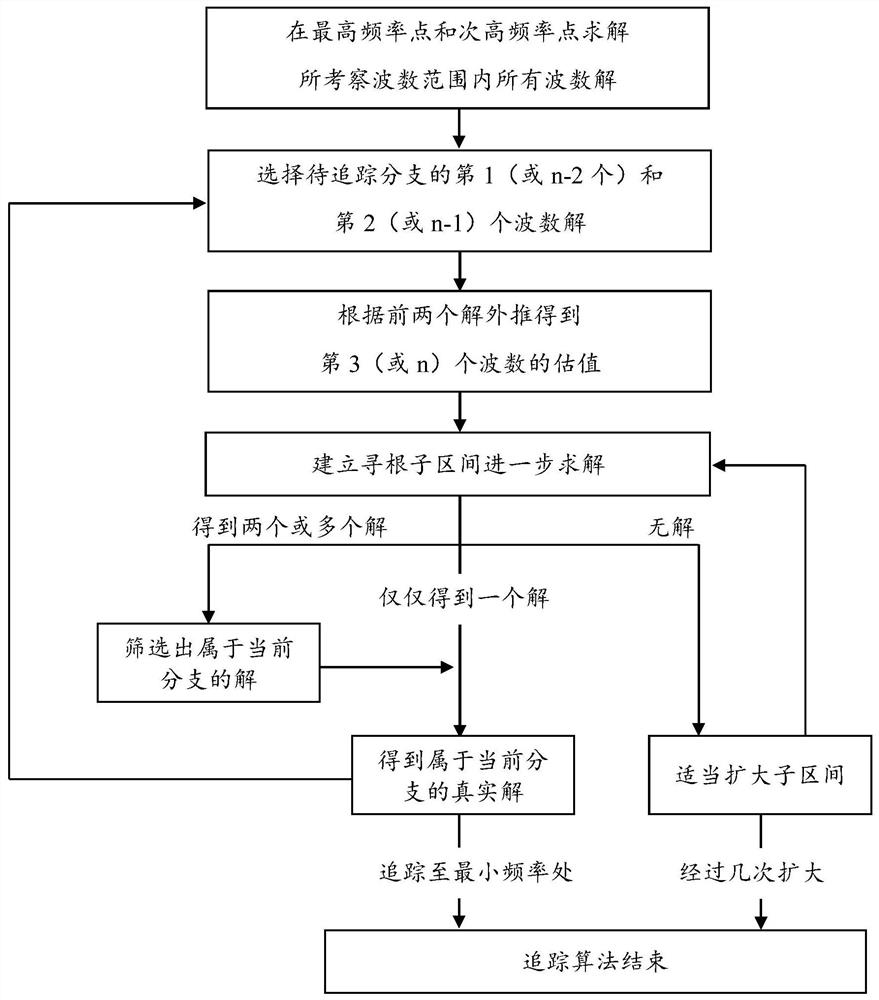
The invention discloses a numerical method for quickly solving a dispersion curve in an acoustic wave sensor. The numerical method utilizes a method of sequentially tracking and drawing single dispersion curve branches to form a complete space dispersion curve. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a subinterval for solving the next wave number by utilizing the first two wave numbers of a current tracking branch; and employing a screening method when multiple solutions appear in a sub-interval in the tracking process. According to the method, the problem that a large amount ofoperation time is consumed due to the fact that the solving accuracy and completeness are improved when a space dispersion curve is solved through a conventional method is effectively solved, separated storage of each piece of modal data can be achieved to a certain extent, and a data storage structure is optimized. The method can be suitable for drawing and solving spatial dispersion curves in various types of waveguide structures, and brings great convenience to propagation analysis and subsequent application of waves in various sensor models.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
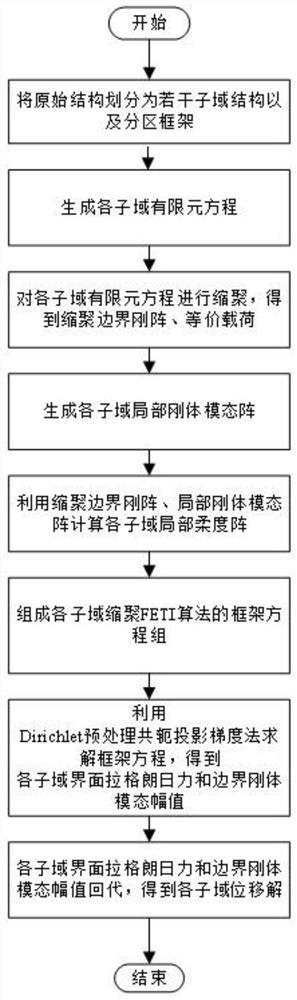
Method for condensing FETI engineering numerical values based on regional decomposition
ActiveCN113779831AEconomically feasibleImprove efficiency of triangular decomposition solutionSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationHat matrixNumerical methodology
The invention discloses a method for condensing FETI engineering numerical values based on regional decomposition. The method comprises the steps of solving a generalized flexibility matrix and a boundary flexibility matrix through constructing a rigid matrix only related to the boundary freedom degree of a floating sub-domain and a rigid body modal matrix of the rigid matrix. The formed new 'hat' matrix can fully utilize and maintain the sparsity of the floating sub-domain rigid matrix, and the order of the new 'hat' matrix is equal to the number of floating sub-domain boundary degrees of freedom and is far smaller than the scale of the original 'hat' matrix, so that the storage space is greatly reduced, and the triangular decomposition solving efficiency of the generalized stiffness matrix is improved; and the calculation of the local flexibility matrix becomes economical and feasible. Meanwhile, an intermediate result of the new 'hat' matrix calculation just provides a Dirichlet preprocessor with a better convergence characteristic for PCPG iterative solution of a frame equation set.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
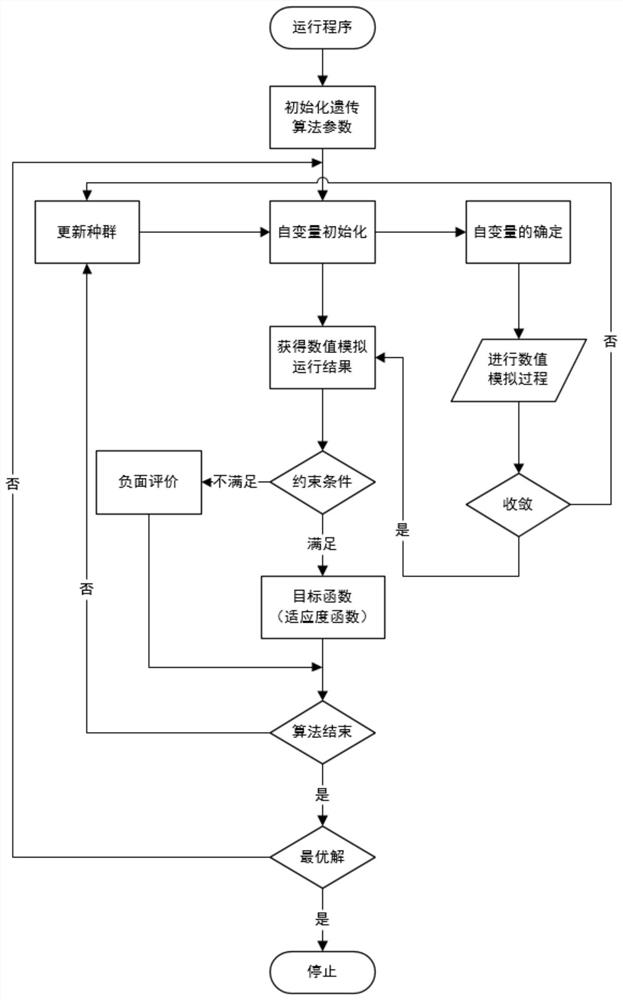
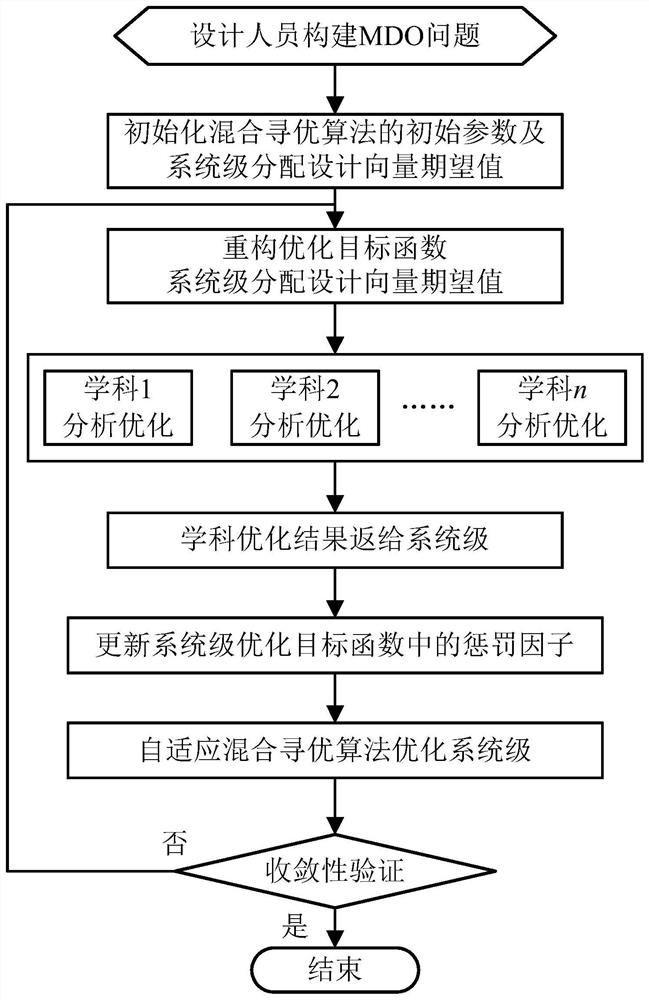
Parallel configurable intelligent optimization method based on collaborative optimization strategy
PendingCN112100909AExpand application spaceImprove quality and efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationMulti-objective optimisationNumerical methodologySelf adaptive
The invention provides a parallel configurable intelligent optimization method based on a collaborative optimization strategy, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, building an MDO optimization problem according to requirements, and determining an optimization model and a system-level optimization model; 2, determining parameters of an adaptive hybrid optimization method according to aspecific optimization problem; 3, converting and optimizing an objective function based on a penalty function method; 4, distributing an initial value to the subsystem level by the system level, carrying out subsystem level optimization by the subsystem by adopting a conventional numerical method, and returning an optimization result of the subsystem level to the system level; 5, comparing to obtain the difference between the subject optimization solution and the system-level optimization solution, calculating a penalty factor, and reconstructing a system-level optimization model; 6, performing system-level optimization coordination and solution by adopting a hybrid intelligent method; 7, judging convergence. According to the invention, a complex product engineering digitization and networking design optimization system is perfected, the application space of collaborative optimization and intelligent optimization methods in the field of design optimization is expanded, and the design quality and design efficiency of products are effectively improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
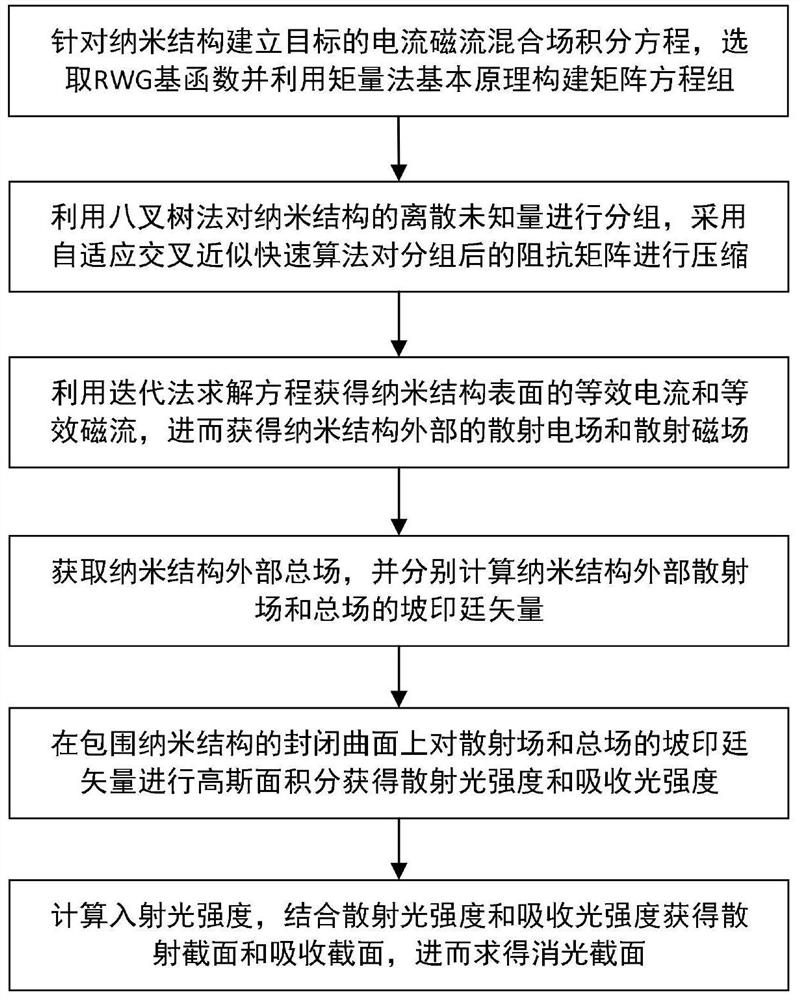
Nanostructure extinction characteristic simulation method based on moment method in combination with adaptive cross approximation fast algorithm
InactiveCN112711856AHigh precisionLittle unknownDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingNumerical methodologyFast algorithm
The invention discloses a nanostructure extinction characteristic simulation method based on a moment method in combination with an adaptive cross approximation fast algorithm. According to the method, a moment method in an integral equation method is adopted for solving, and compared with a traditional numerical method such as a finite element method based on a differential equation method, dispersion errors do not exist, and the accuracy is high. According to the method, the extinction characteristic of the large-scale nanostructure can be solved by combining the adaptive cross approximation fast algorithm on the basis of the moment method, transplantation can be conveniently carried out under different background media, and the application range is wide.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Numerical method for simulating serious bias large deformation of tunnel
ActiveCN112648017AAccurately reflectReal interactionMining devicesDesign optimisation/simulationNumerical methodologyClassical mechanics
The invention provides a numerical method for simulating serious bias large deformation of a tunnel, and relates to the field of tunnel construction simulation. The numerical method comprises the steps that a load structure plane calculation model and a concrete layer plastic damage constitutive model are established; different tension and compression stress deformation characteristics and nonlinear contact attributes of different contact areas are defined through nonlinear spring simulation; and interaction between a supporting structure and surrounding rock can be truly reflected, deformation and stress response of the tunnel load structure after the surrounding rock is subjected to bias stress are analyzed, and an analysis means is provided for revealing the bias deformation damage mechanism of the supporting structure after tunnel construction.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nonlinear energy trap optimal rigidity solving method based on platform phenomenon
PendingCN112182881AWeaken energyMeet the robustnessDesign optimisation/simulationProtective buildings/sheltersNumerical methodologyLower limit
The invention discloses a nonlinear energy trap optimal rigidity solving method based on a platform phenomenon, belongs to the technical field of structure control. According to the method, with combination of the actual situation of civil engineering, on the premise of small initial conditions, multi-scale analysis is carried out on a two-degree-of-freedom system composed of a linear main structure and a cubic rigidity nonlinear energy trap, a "platform" phenomenon in a slow-varying equation is observed, so that an excitation amplitude interval in which the damper can generate effective target energy transfer under the condition that system parameters are fixed is obtained; an analytical solution of the optimal design rigidity of the nonlinear damper is derived through formulas of the upper limit and the lower limit of the interval, and through inspection of a numerical method, the design value has outstanding advantages in the aspects of the vibration reduction effect and robustness.The obtained optimized stiffness analytical solution gets rid of constraints on initial conditions, is applied to the design of nonlinear dampers, is simple in actual operation and good in optimization effect, and has great application value and development prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
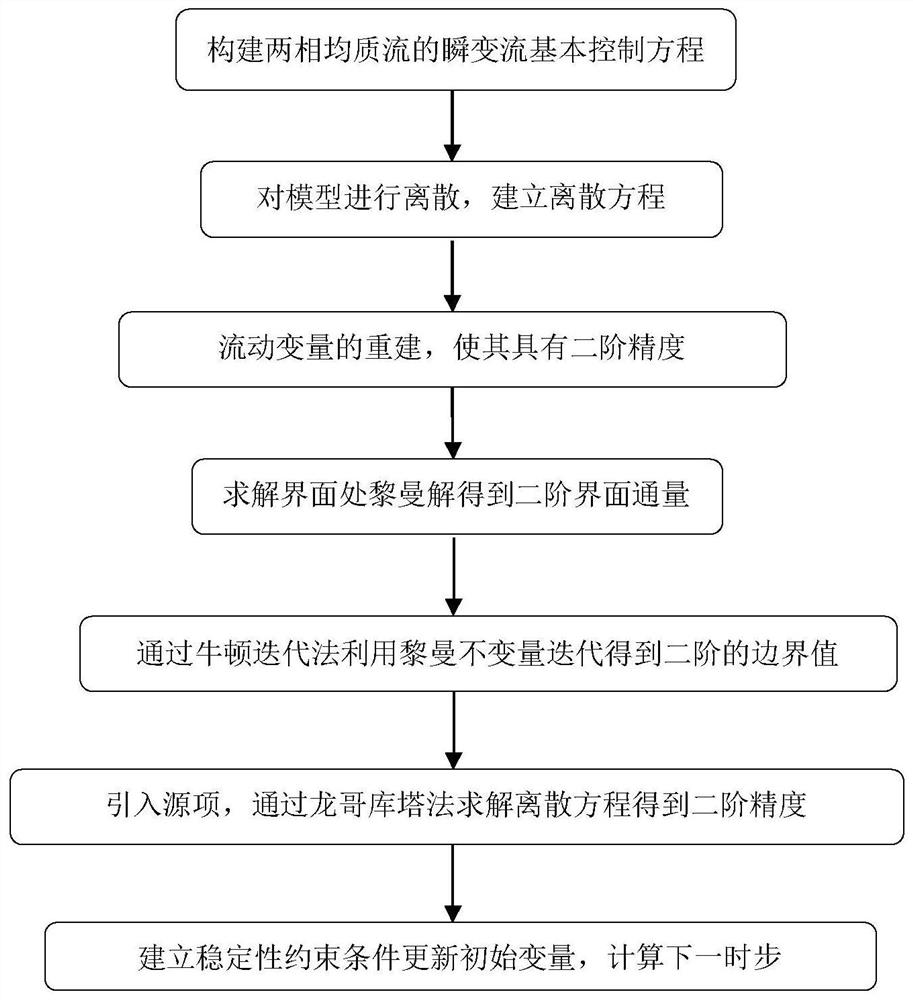
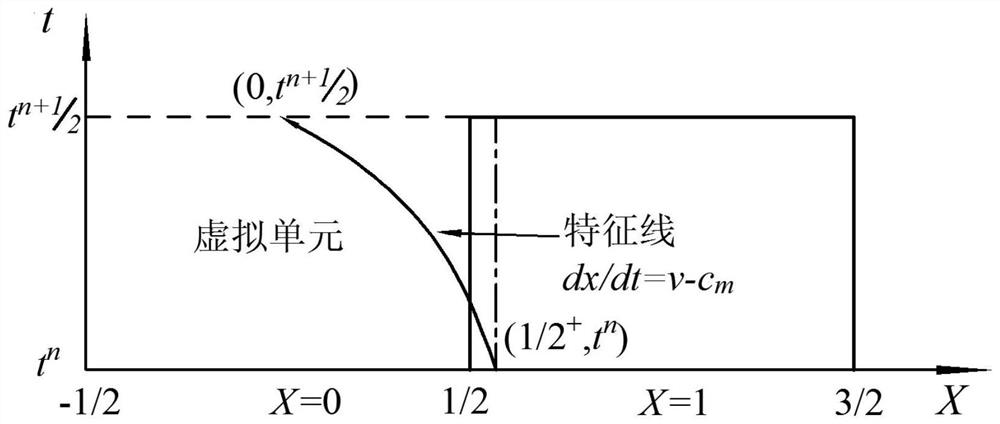
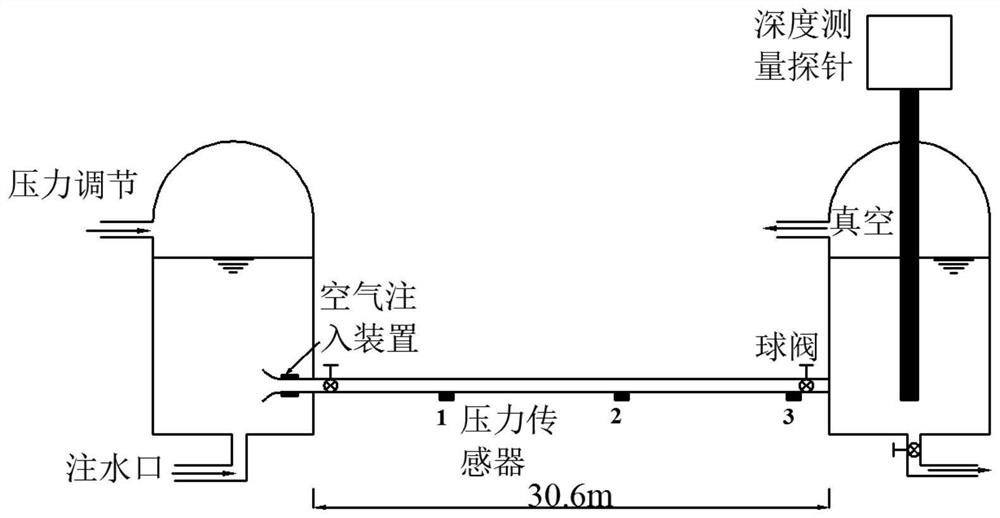
Simulation method of gas-liquid two-phase homogeneous flow in water pipeline based on finite volume method
ActiveCN109918787BThe MOC class method is simpleEasy to implementDesign optimisation/simulationNumerical methodologyRiemann invariant
The invention discloses a method for simulating water-air two-phase homogeneous flow in a water pipeline based on a finite volume method. The method is based on a non-conservative form; the model pipeline is discretized in time and space by the finite volume method; Then, through the MUSCL-Hancoke format containing TVD, the reconstructed flow variables are obtained to have second-order precision; then, the Riemann solution at the internal interface of the model is solved to obtain the calculated interface flux value; then, for the boundary conditions of the model, Use the Newton iteration method to use the Riemann invariant to wait until the second-order boundary value; then, enter the source item in the model, and use the numerical method to discretize it to make it have second-order accuracy; finally, based on the initially given parameters (free Gas content, pure water water hammer wave velocity under normal pressure, etc.), to simulate the pressure fluctuation in the pipeline at any time. The results show that the calculation accuracy and efficiency of the model are higher than those of the traditional conservative homogeneous flow model.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Smooth particle dynamics modeling method for solid structure
ActiveCN111353229AGuaranteed first-order completenessHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationNumerical methodologyParticle dynamics
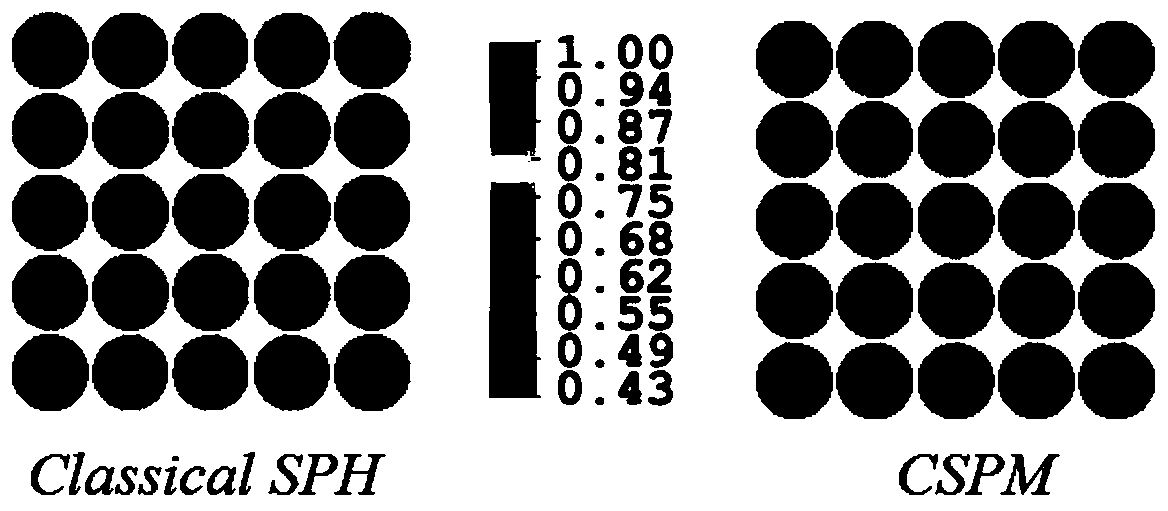
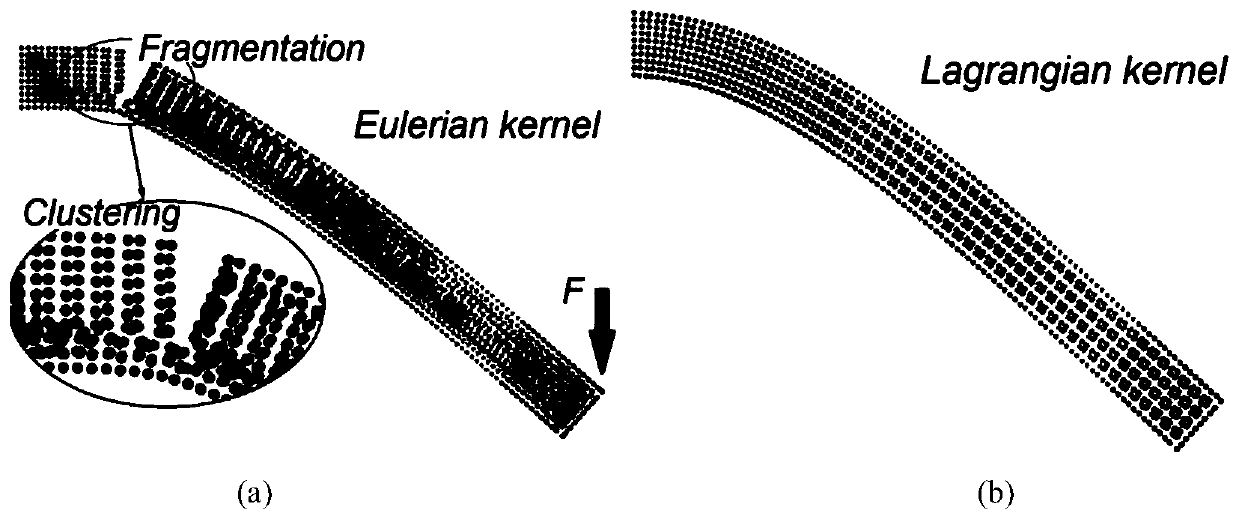
The invention relates to the field of materials, and provides a solid structure smooth particle dynamics modeling method. The method comprises the steps: discretizing a planar solid structure into SPHparticles, wherein each particle carries at least one kind of same physical information; deformation occurs at a spatial point xi, and calculating a correction mode of a smooth function derivative atthe spatial point xi; then calculating the deformation of the spatial point xi; and finally, in a deformation state, calculating the deformation gradient at the spatial point xi. According to the invention, a smooth function correction method and a complete Lagrange SPH method are combined to obtain the correction mode of the smooth function derivative as an integral kernel, so the first-order completeness of the numerical method is ensured, the boundary calculation accuracy is improved, the stretching instability phenomenon is eliminated, the calculation time is greatly saved, and the boundary defects and instability of the traditional SPH are overcome.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A CFD-Based Analysis Method for Free Motion in Low-Speed Inclined Entry into Water
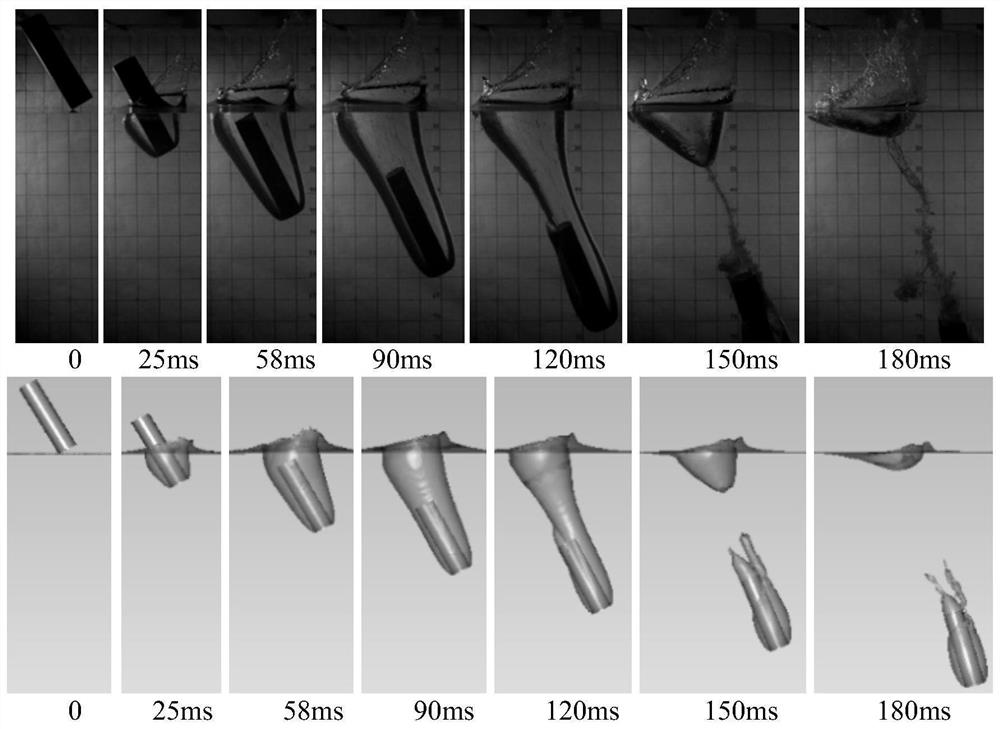
ActiveCN108319793BHigh precisionImprove consistencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical methodologyLow speed
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
A Reentry Prediction Method for Small Ellipse Targets in Sparse Data
ActiveCN109992927BDesign optimisation/simulationSelf-propelled projectilesNumerical methodologyKepler
The invention discloses a re-entry prediction method for a small elliptical target under the condition of sparse data, which processes N-circle data collected in the past 5 days, uses a numerical method to determine the orbit of the single-circle data respectively, and uses the Kepler square root as the root. Compared with the prior art, the present invention proposes a numerical system based on the characteristics of sparse data and small elliptical orbits, and uses the semi-numerical method for orbit integration, and uses the least squares method to fit the ballistic coefficient of the re-entry target. A reentry forecasting method combining the method with the semi-numerical method. It effectively solves the problems that the residual error of joint orbit determination of multi-turn data is too large or does not converge in the case of sparse data, and it is difficult to determine the ballistic coefficient of orbit determination of single-turn data.
Owner:中国人民解放军32035部队
A numerical simulation analysis method and system for debris flow dynamics
ActiveCN107506566BImprove targetingImprove the level of scienceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical methodologyClassical mechanics
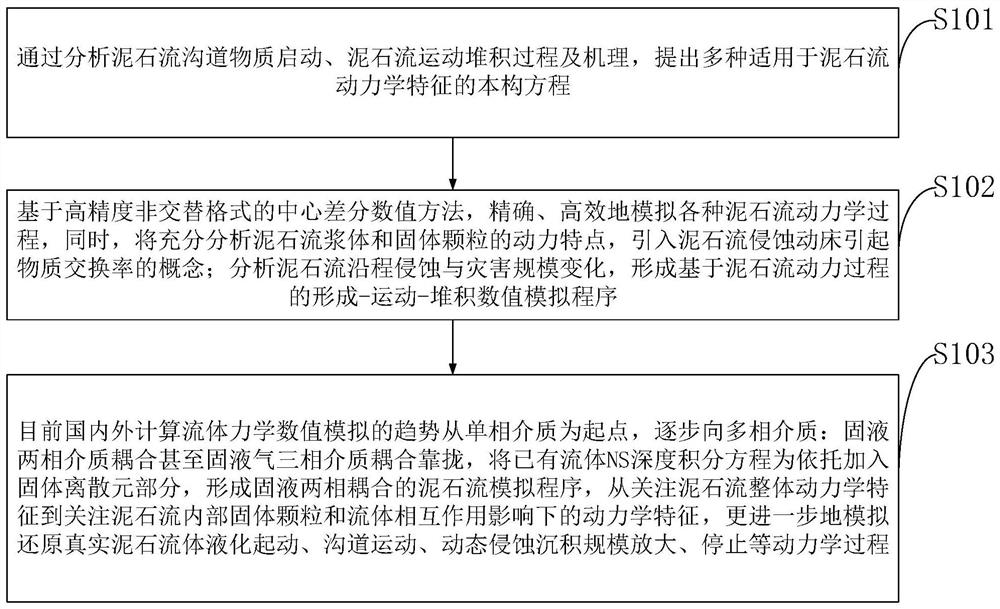
The invention belongs to the technical field of debris flow disaster prevention and environmental management, and discloses a new type of debris flow dynamics numerical simulation analysis method and system. By analyzing the debris flow channel material start, debris flow movement and accumulation process and mechanism, a variety of debris flow dynamics are obtained. The characteristic constitutive equation; at the same time, based on the non-alternating format central difference numerical method, simulate various debris flow dynamic processes; and analyze the dynamic characteristics of debris flow slurry and solid particles, introduce the concept of material exchange rate caused by debris flow erosion dynamic bed, analyze The erosion and scale changes along the debris flow form a numerical simulation program of formation-movement-accumulation based on the dynamic process of debris flow. The numerical simulation program and numerical calculation method of the present invention have the characteristics of simplicity and high efficiency, and are suitable for use by workers in related disaster fields to improve the scientific level of debris flow prevention and environmental protection.
Owner:INST OF MOUNTAIN HAZARDS & ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com