Patents
Literature
66 results about "Spatial response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
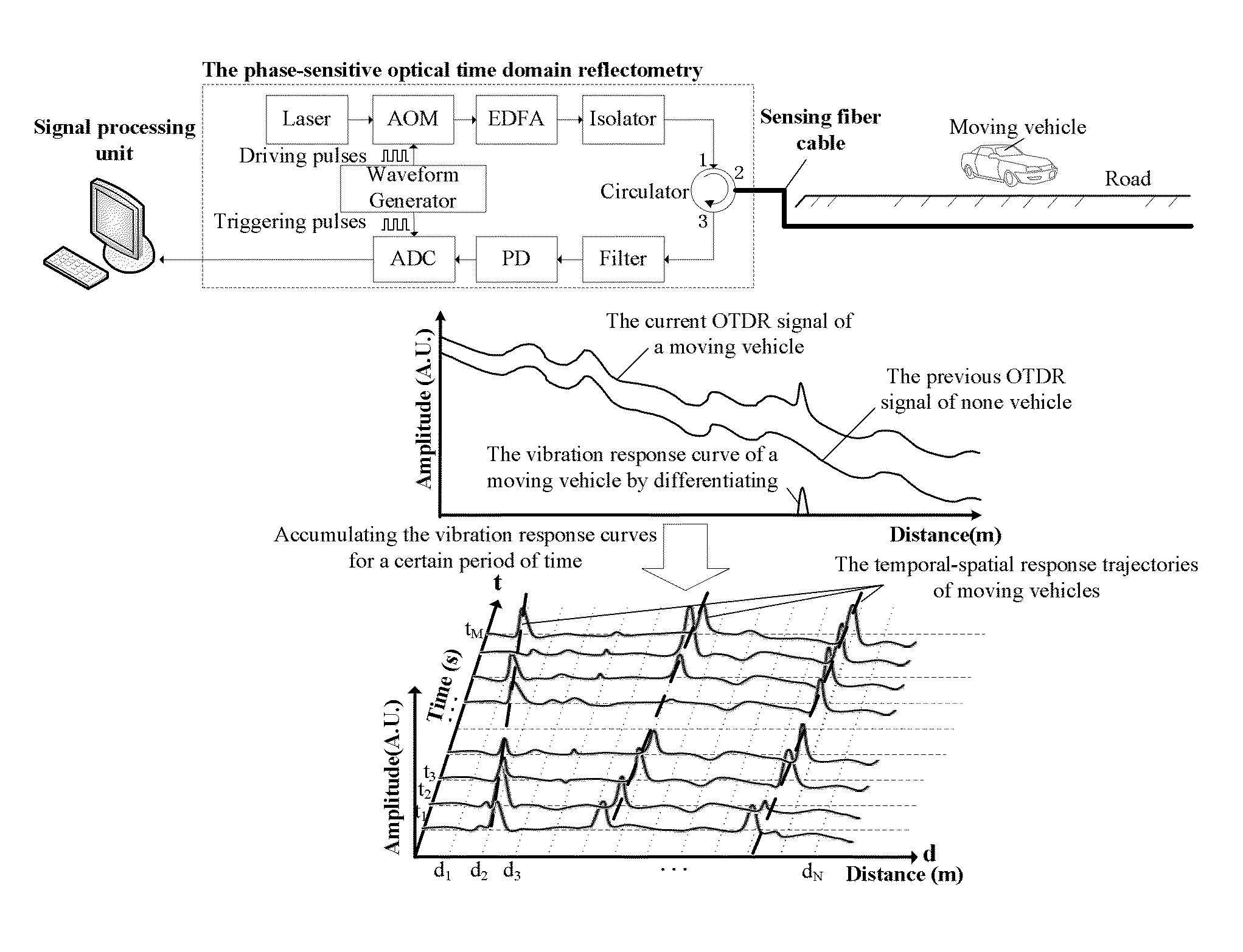
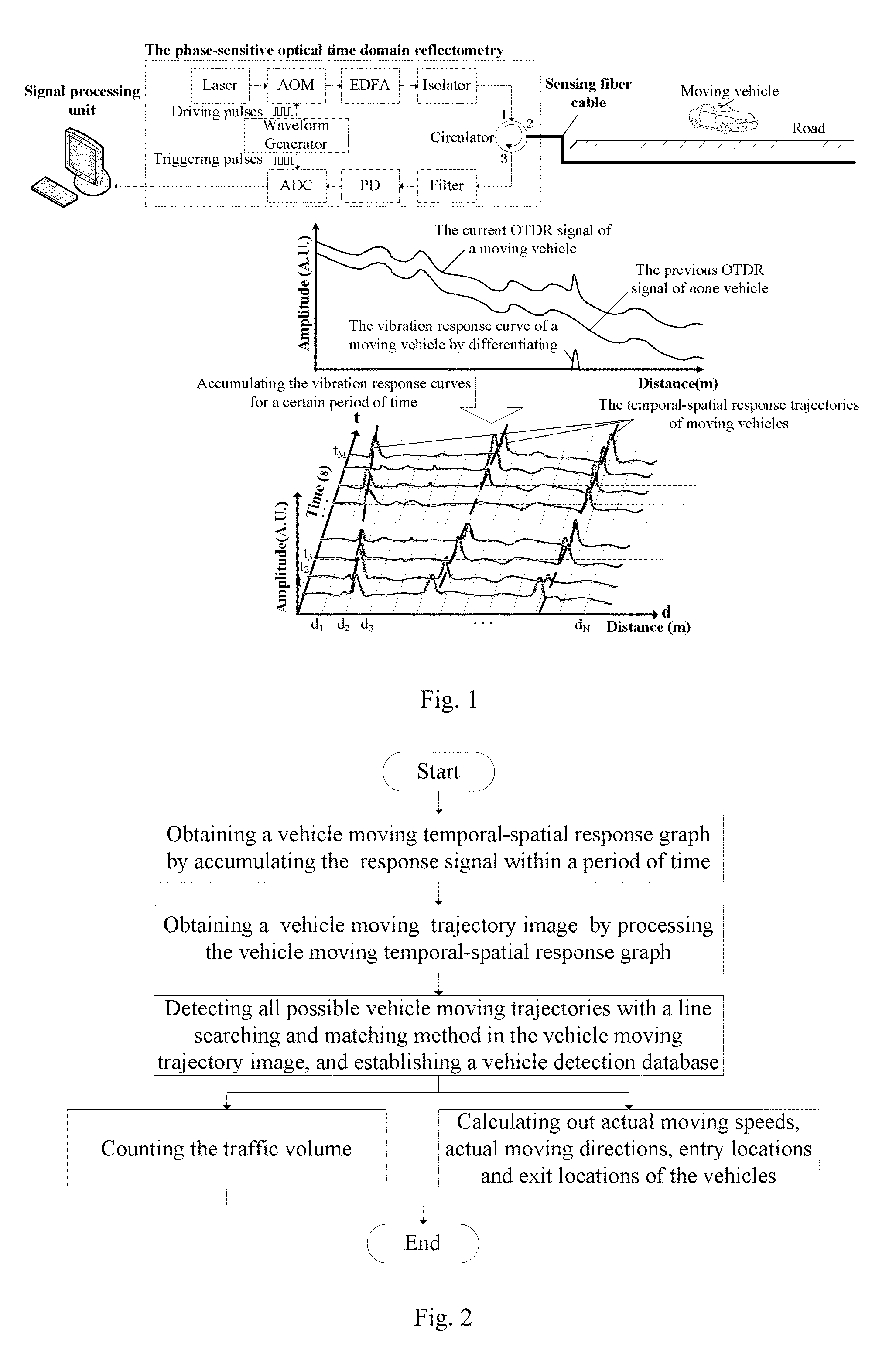
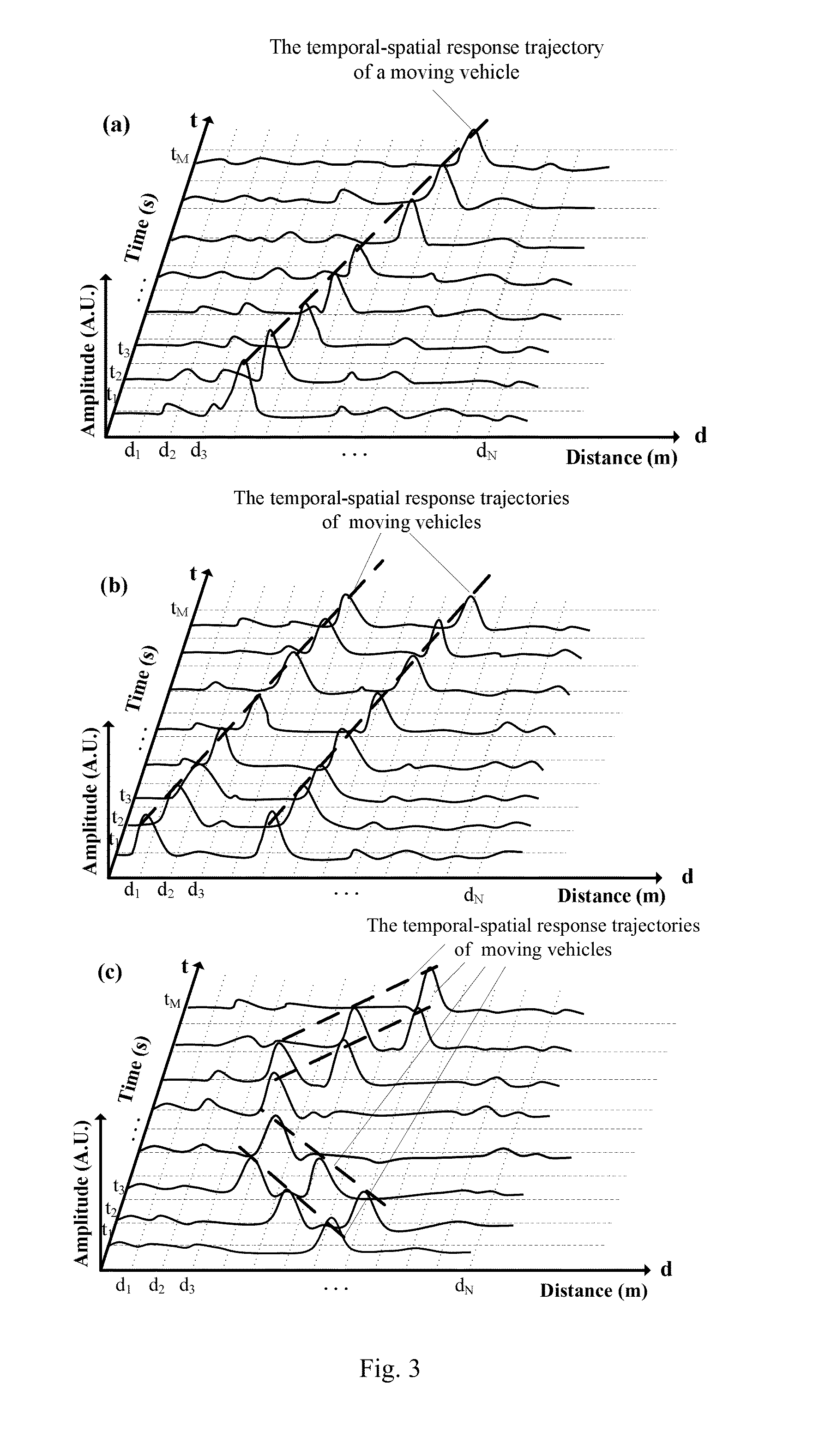
Online traffic volume monitoring system and method based on phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometry
ActiveUS20160275788A1Low costHigh sensitivityDetection of traffic movementCharacter and pattern recognitionFiberPhase sensitive
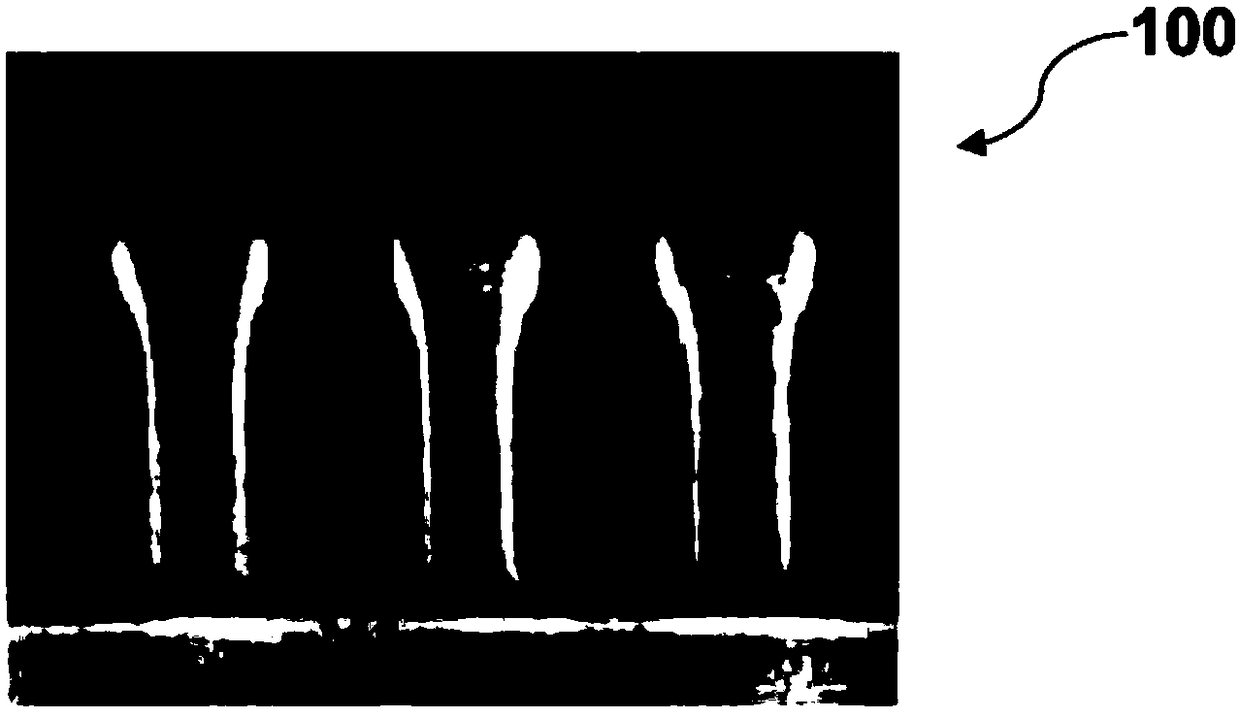
An online traffic volume monitoring system based on a phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometry and its monitoring method are related to a field of intelligent transportation and an application of distributed fiber sensing. A vehicle moving temporal-spatial response graph is generated by accumulating differentiated Optical Time-Domain Reflectometry tracks at different moments in one unit monitoring period for traffic volume statistics, and then converted into a vehicle moving trajectory image through binarization and image pre-processing. Parameters of the moving vehicles are detected by utilizing a search-match method. A traffic volume, moving speeds, moving directions and locations are obtained respectively from detected trajectory number, and a tilt angle and pixel positions. The monitoring method is helpful to solve traffic congestion problem and informing drivers of real-time traffic volume, and contributes to realize an intelligent city traffic regulation.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Short range lidar apparatus having a flat spatial response
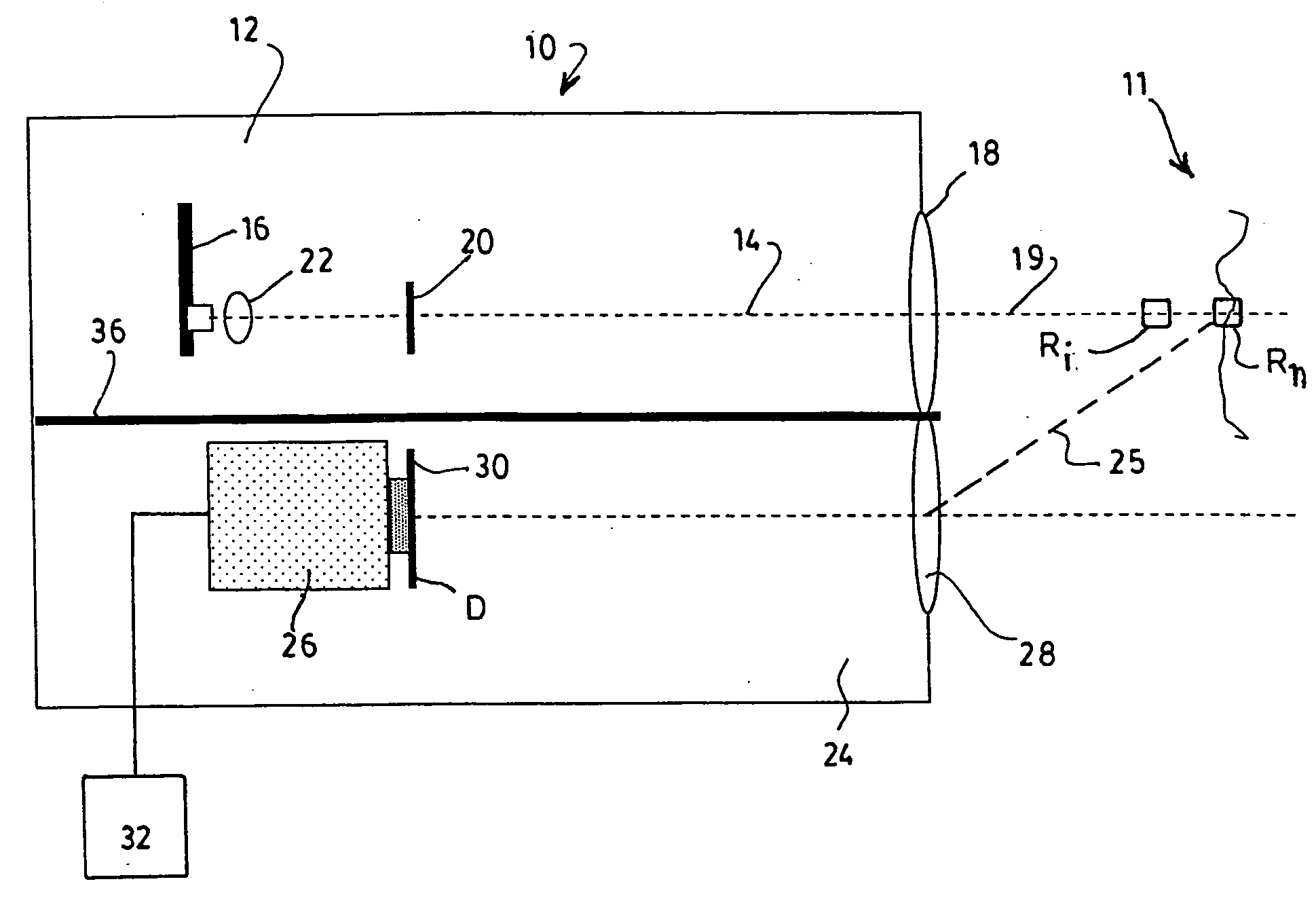
InactiveUS20070076201A1Flatten spatial responseLow costScattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisRadarLight beam
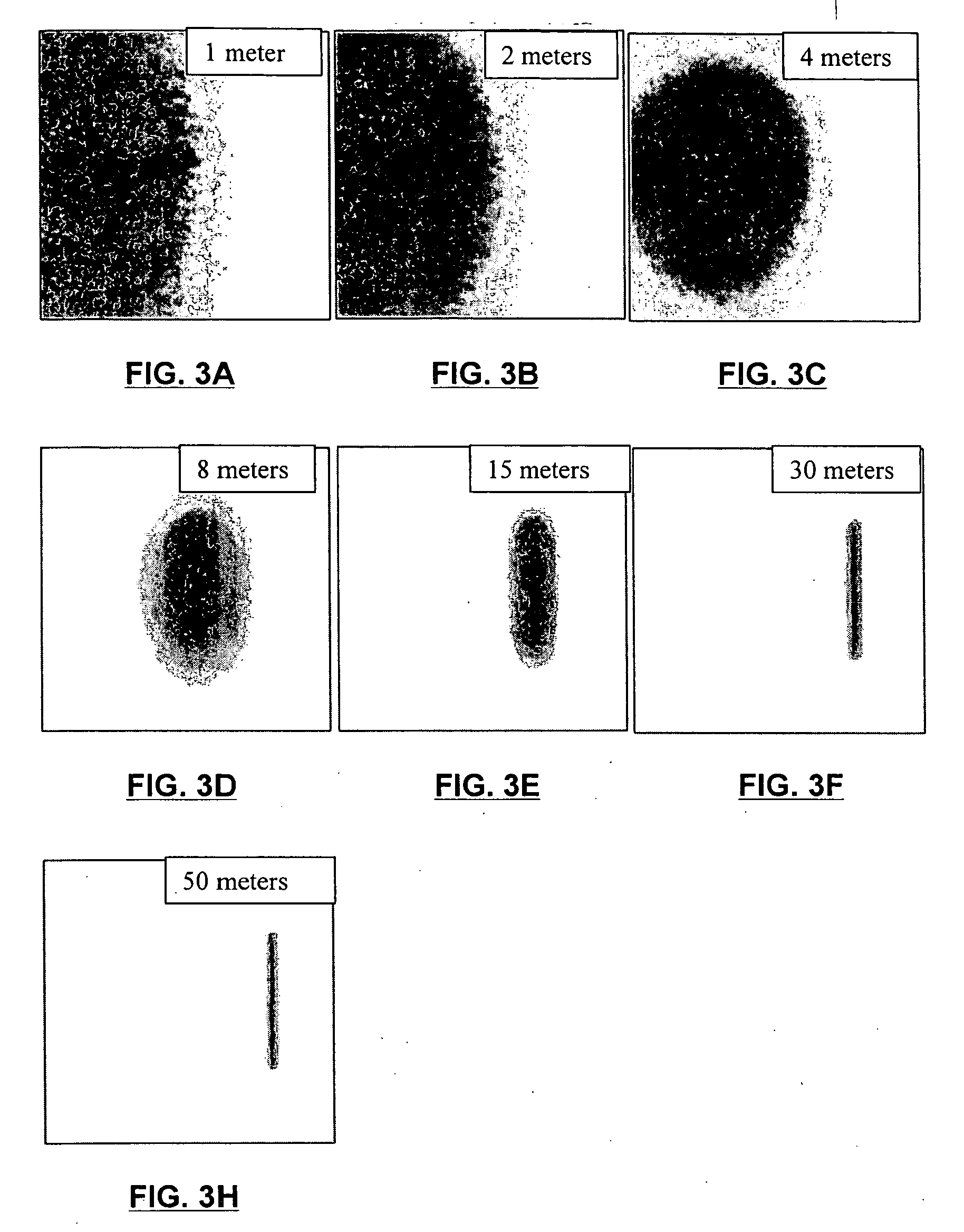
A flat spatial response LIDAR apparatus for detecting particles within a short range is provided. The apparatus includes a light source projecting a light beam which is back-scattered by the particles to be detected. The back-scattered light is received, detected and analyzed. A spatial filter spatially filters the received back-scattered light in order to flatten the spatial response of the apparatus, so that a same concentration of particles at any distance within the short range will generate a signal of substantially the same intensity. This is for example accomplished by a properly profiled mask disposed in front of the detector, or a plurality of spatially distributed waveguides. As a result, the LIDAR apparatus can compensate for the 1 / r2 dependence, or other dependences of the back-scattered light on the distance r.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
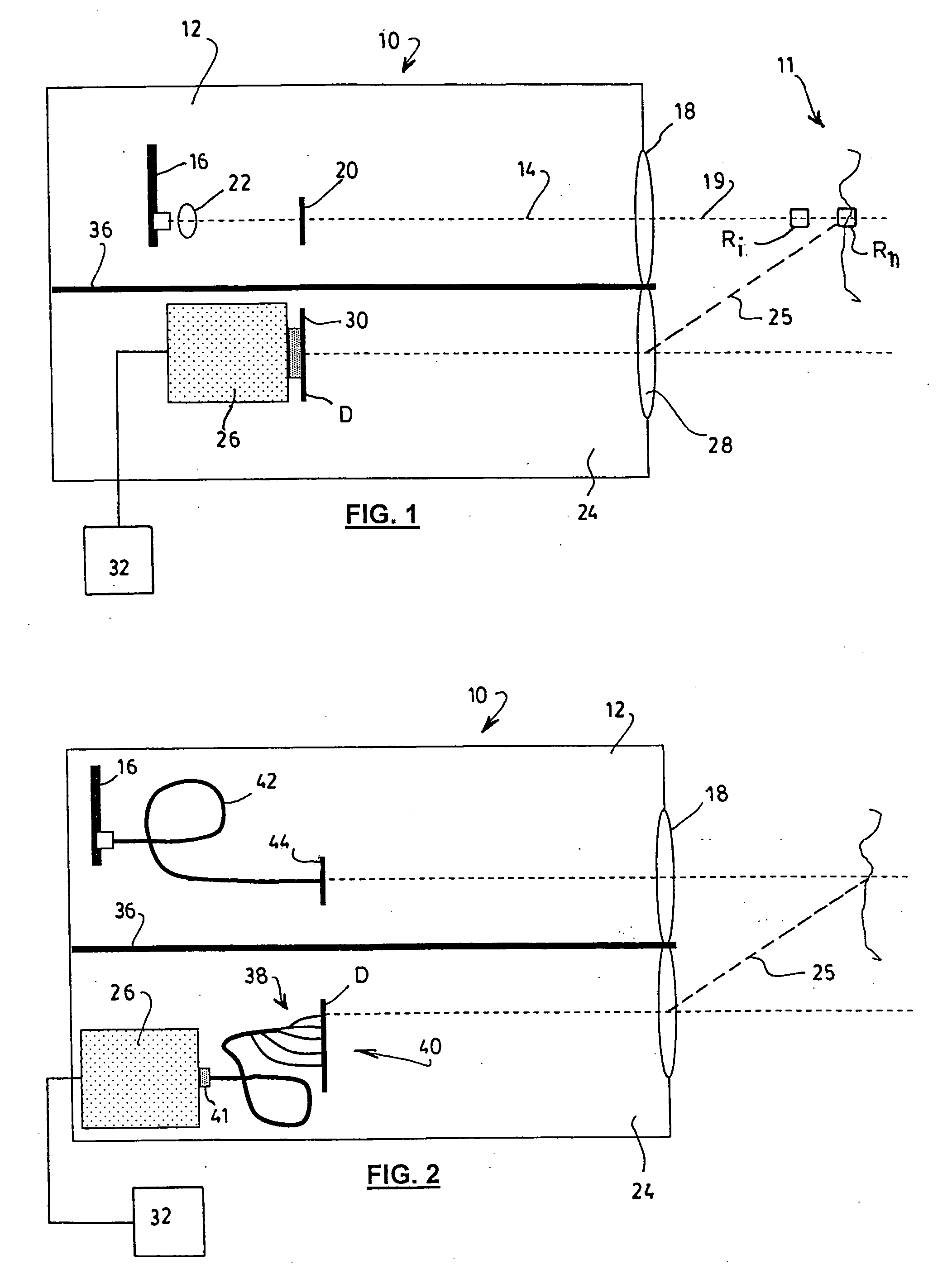
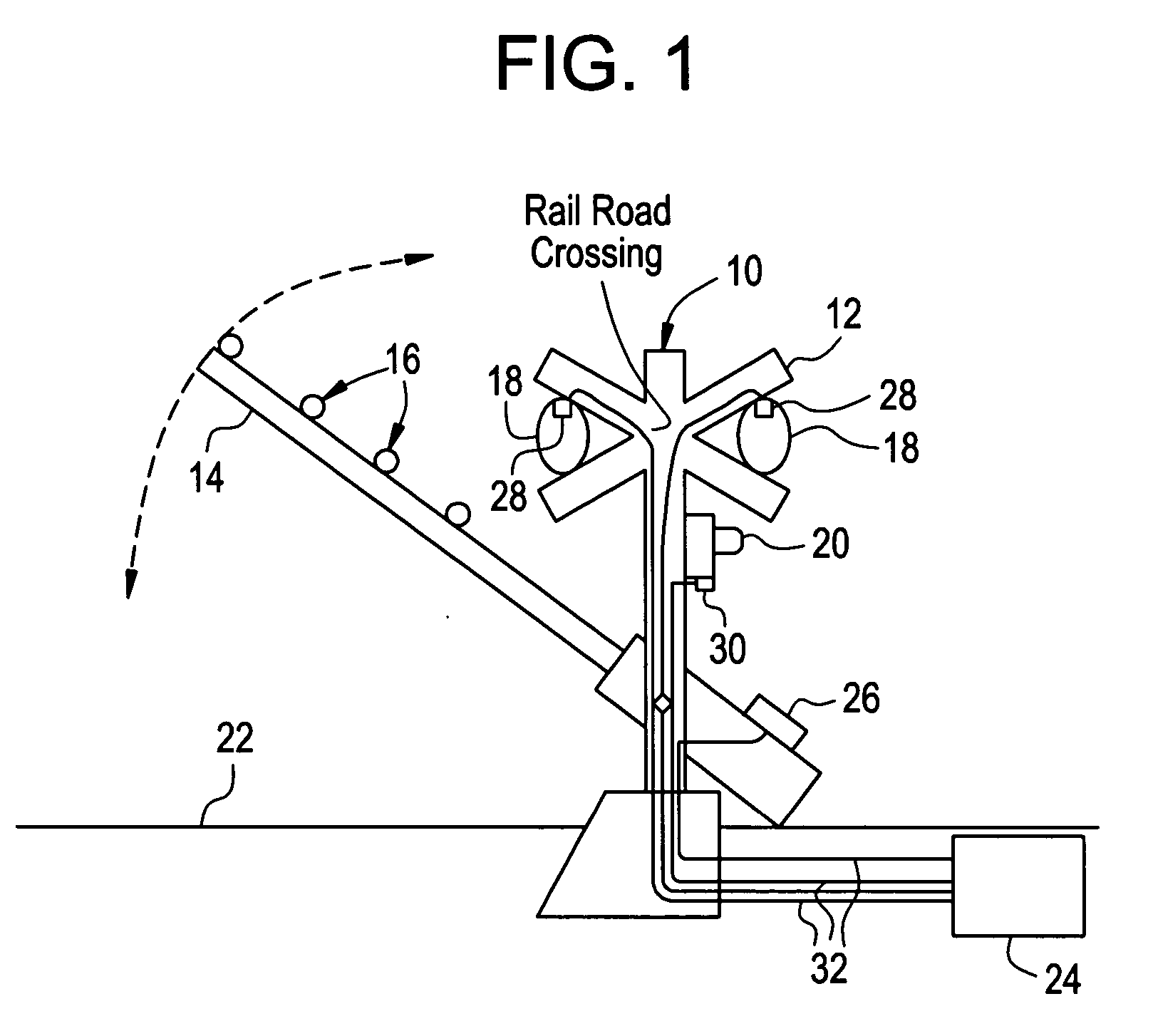
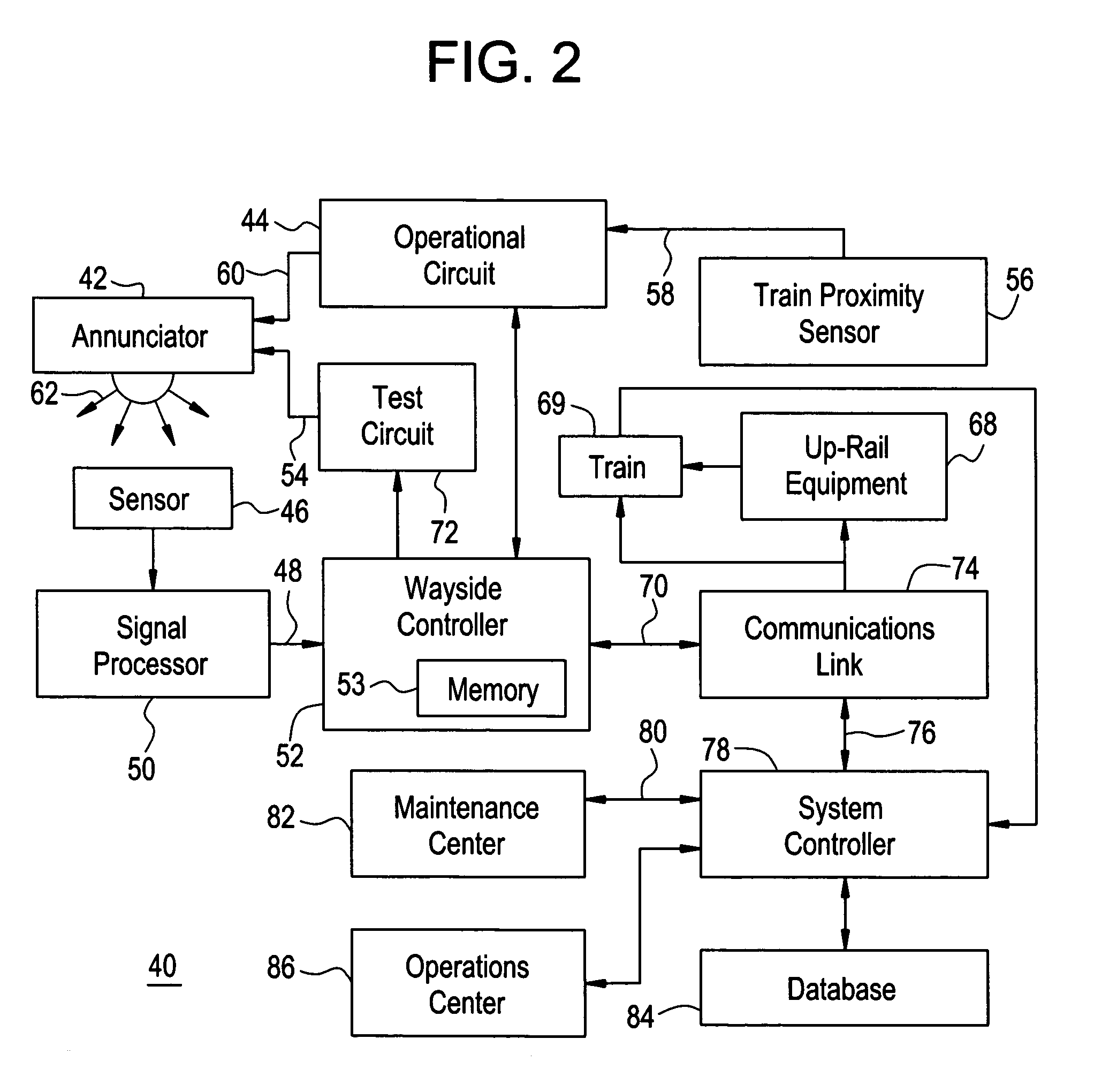
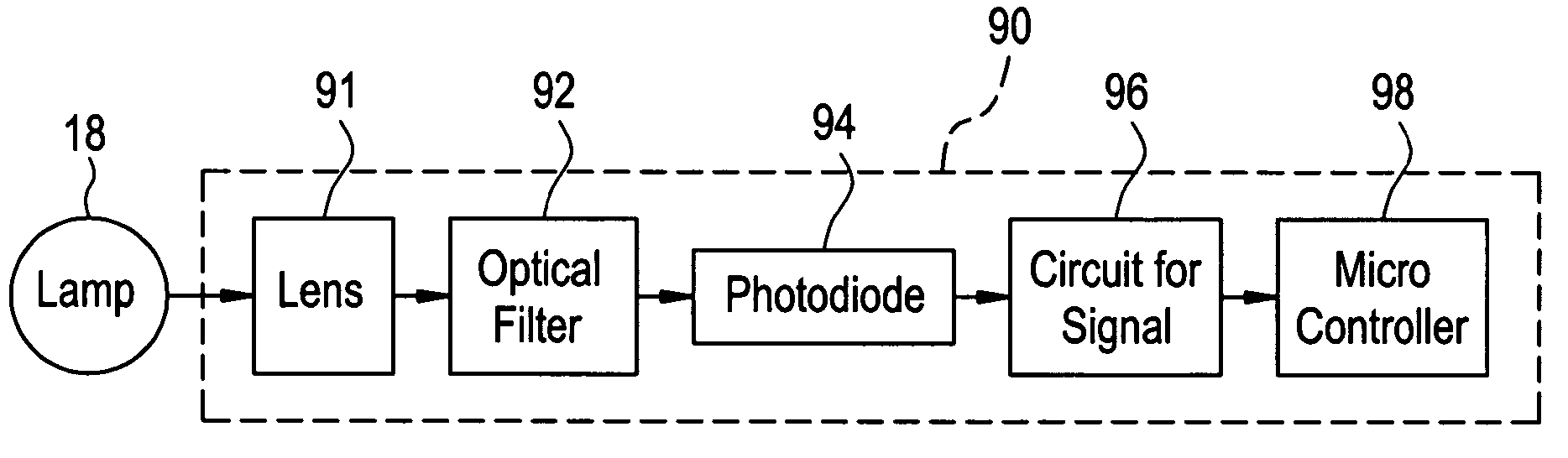
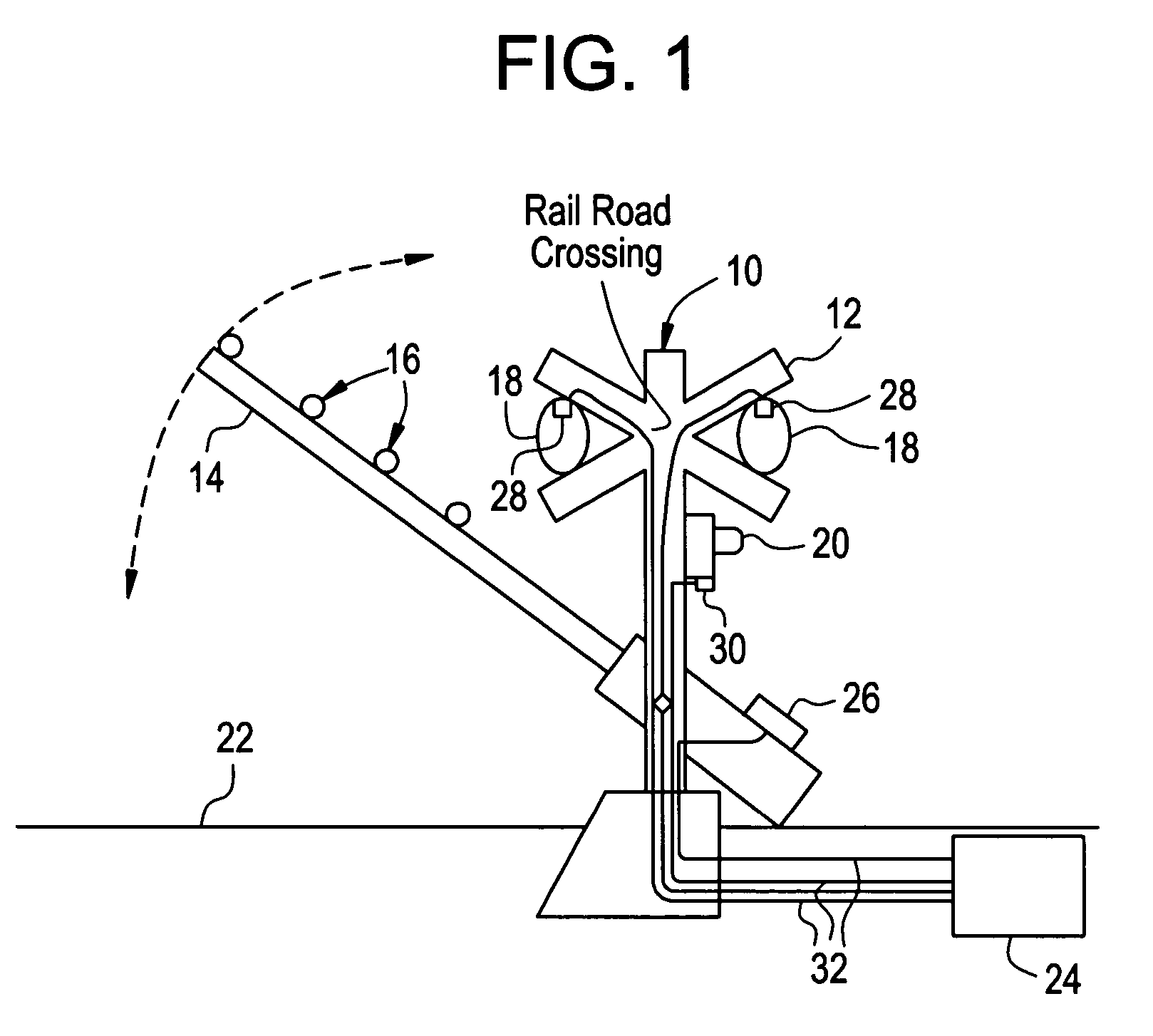
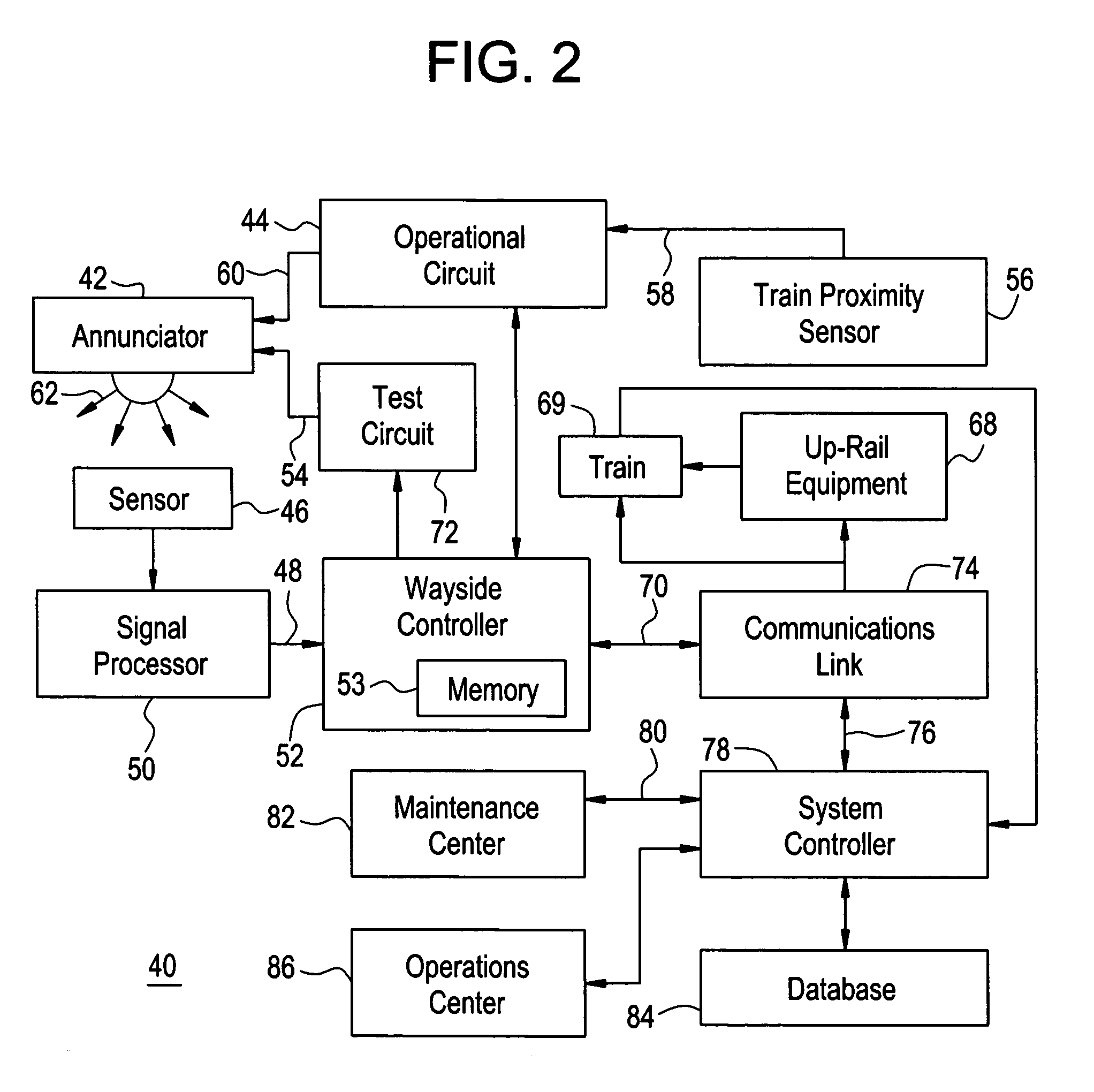
Apparatus and method for monitoring the output of a warning or indicator light
An operational status detection system for a railroad warning device having a warning light, comprising: a photo detector configured to generate a signal corresponding to a light output of the warning light of the railroad warning device, the photo detector comprising a lens, an optical filter and a photodiode, wherein the optical filter is disposed between the photodiode and the lens and the optical filter is configured to provide the light output of the warning light to be presented as a substantially uniform spatial response to the photodiode wherein areas of high intensity of the warning light that are received by the lens are attenuated, the areas of high intensity providing higher light outputs than other areas of the warning light; and a microcontroller for receiving the signal, wherein the microcontroller compares the signal to at least one threshold value, the at least one threshold value corresponding to an acceptable light output of the warning light.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method for monitoring the output of a warning or indicator light
An operational status detection system for a railroad warning device having a warning light, comprising: a photo detector configured to generate a signal corresponding to a light output of the warning light of the railroad warning device, the photo detector comprising a lens, an optical filter and a photodiode, wherein the optical filter is disposed between the photodiode and the lens and the optical filter is configured to provide the light output of the warning light to be presented as a substantially uniform spatial response to the photodiode wherein areas of high intensity of the warning light that are received by the lens are attenuated, the areas of high intensity providing higher light outputs than other areas of the warning light; and a microcontroller for receiving the signal, wherein the microcontroller compares the signal to at least one threshold value, the at least one threshold value corresponding to an acceptable light output of the warning light.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
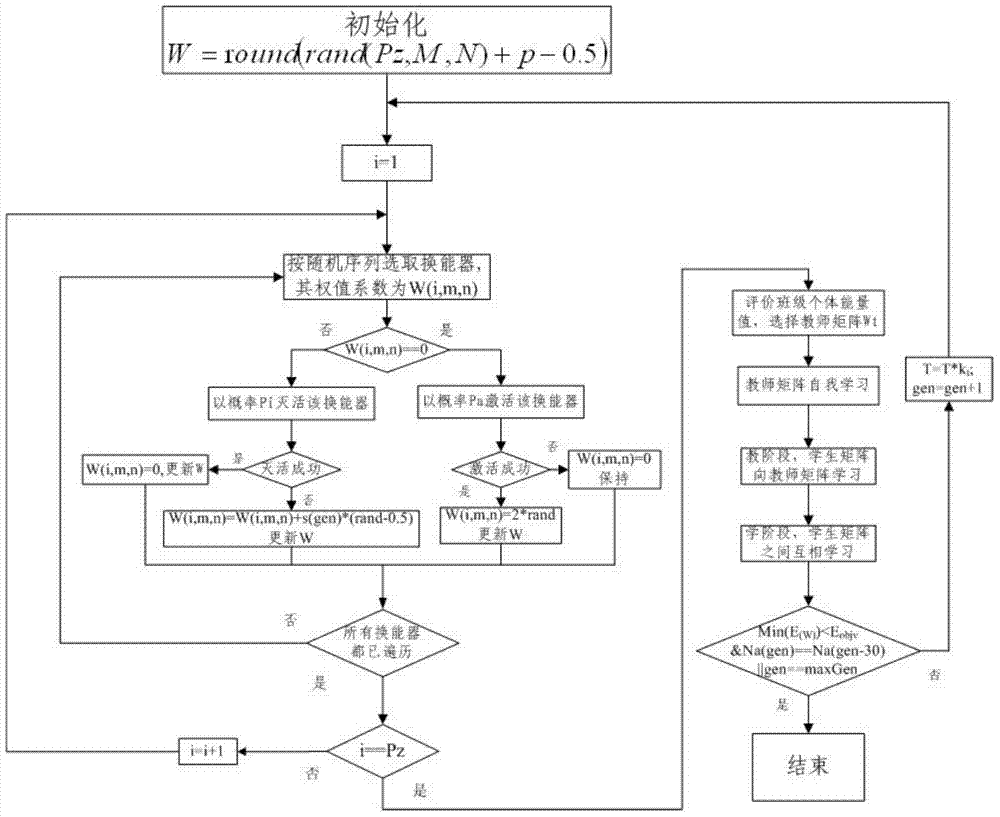
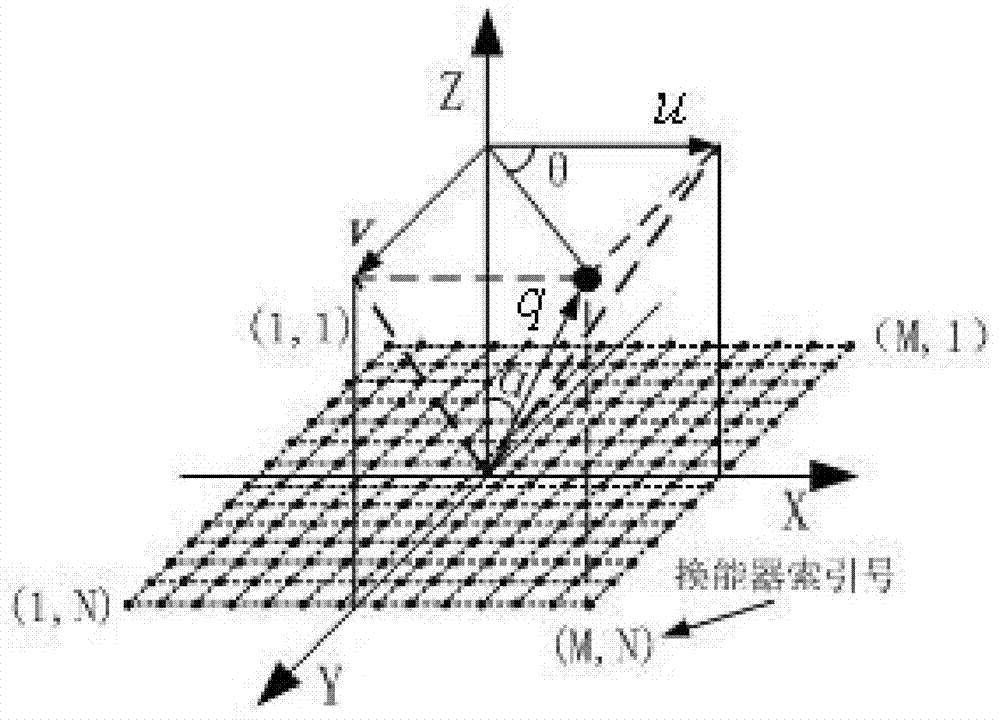
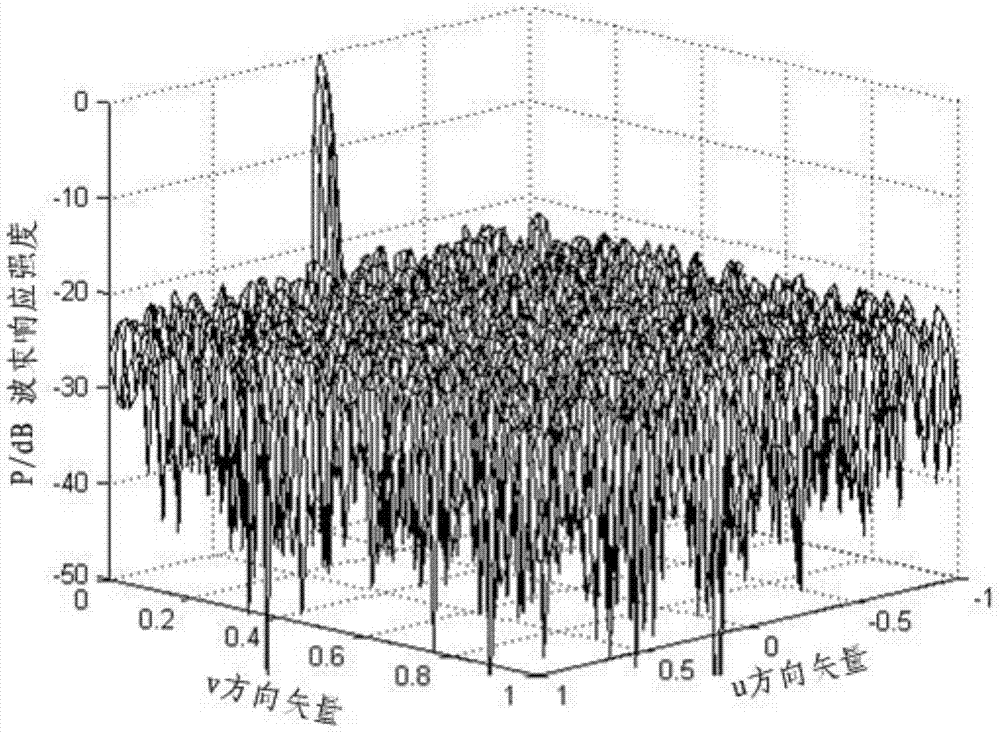
Sparse planar array optimizing method for energy transducers of phased array sonar system
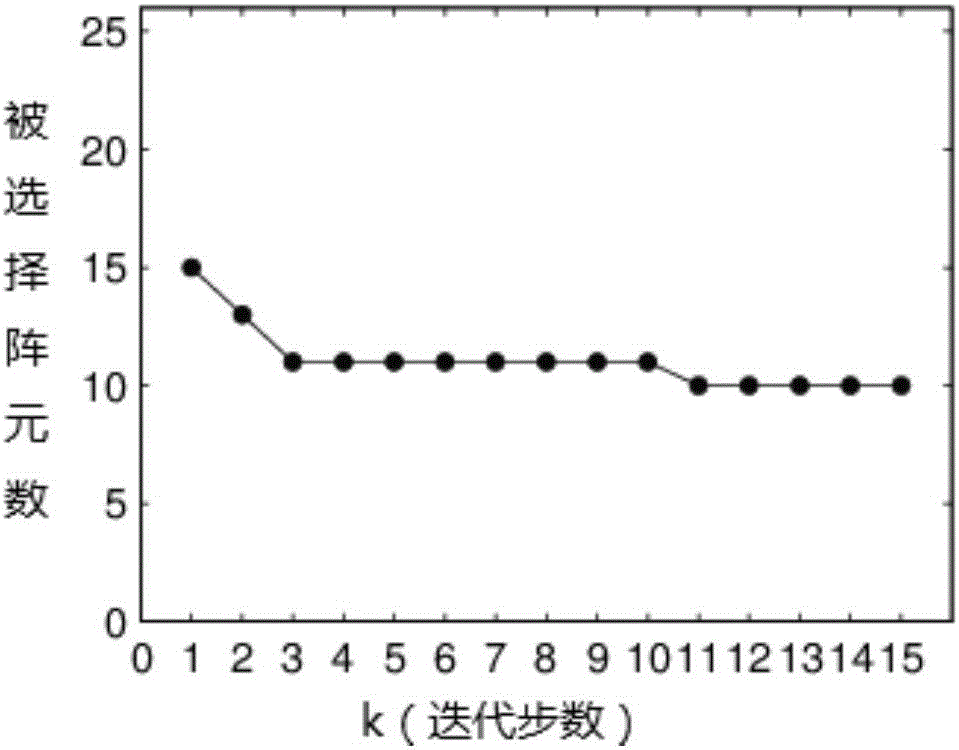
The invention provides a sparse planar array optimizing method for energy transducers of a phased array sonar system. The method comprises the steps of 1) initialization, 2) simulated annealing optimization, 3) teaching and learning optimization and 4) termination. According to the method, the minimal number of energy transducers, which need to be exited to satisfy the spatial response performance, of the sparse planar array is solved by utilizing spatial response performances including the main-lobe width and the side-lobe peak value of the array. The feasible solution obtained by the simulated annealing optimization can be further optimized via teaching and learning optimization, so that higher convergence speed and precision are provided, the optimal solution of the whole situation can be obtained, as few as energy transducers work, the required spatial response performance of the planar array of the energy transducers is obtained, and the required hardware cost of the phased array imaging sonar system can be effectively reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
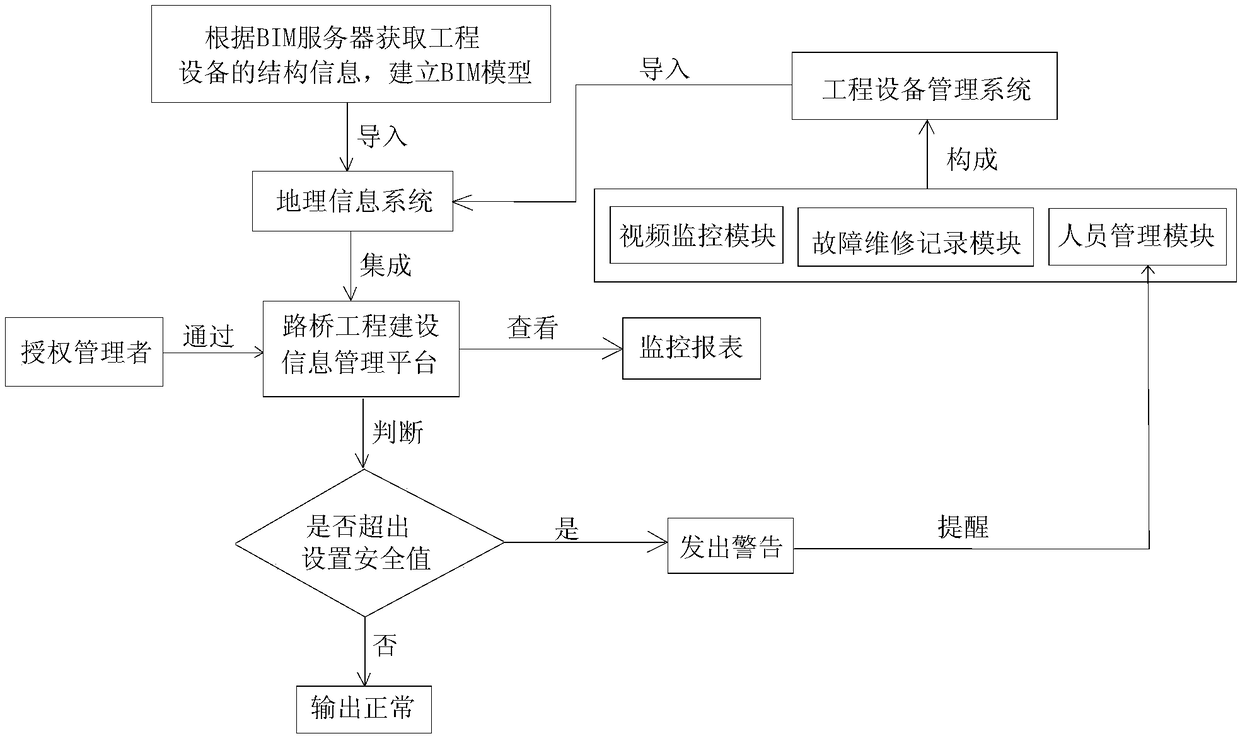
A road and bridge engineering equipment safety monitoring system and method based on BIM + GIS modeling
InactiveCN109447480AQuick ViewFast and seamless browsingOffice automationResourcesBridge engineeringSafety monitoring
The invention belongs to the technical field of digital management, and relates to a road and bridge engineering equipment safety monitoring system and method based on BIM + GIS modeling. The safety monitoring system comprises a BIM server, a geographical information system, an engineering equipment management system and a road and bridge engineering construction information management platform. The BIM server obtains the structure information of the engineering equipment and builds the BIM model. The GIS is connected with the BIM server, and the BIM model data is imported into the GIS by GIStechnology, and is then transmitted to the information management platform of road and bridge engineering construction for display. The engineering equipment management system and the GIS are in remote communication; the information management platform of highway and bridge engineering construction is connected with the equipment management system of the institute. The invention can realize the real-time display of the monitoring state of the engineering equipment, the three-dimensional control of the engineering equipment and the spatial response of the fault maintenance of the engineering equipment, so that the equipment management is ordered and feasible, and the intelligent and efficient safety monitoring management is achieved.
Owner:GUANGXI ROAD & BRIDGE ENG GRP CO LTD
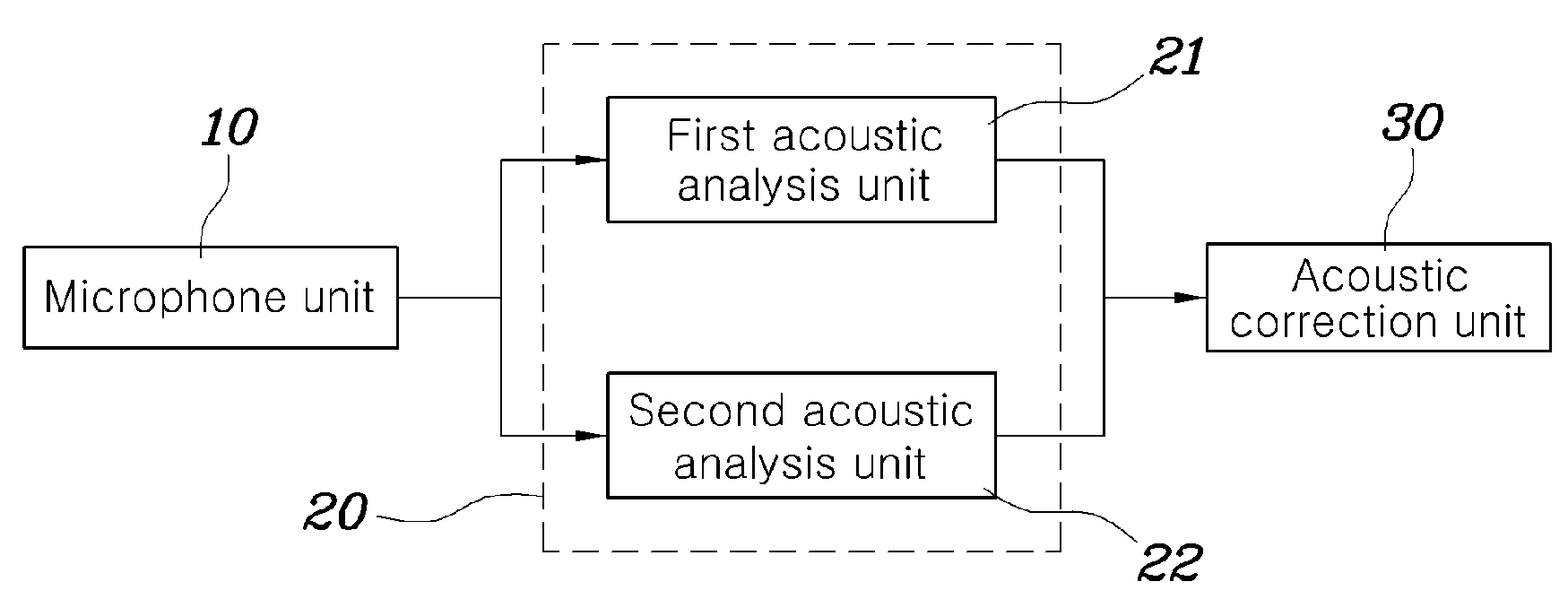
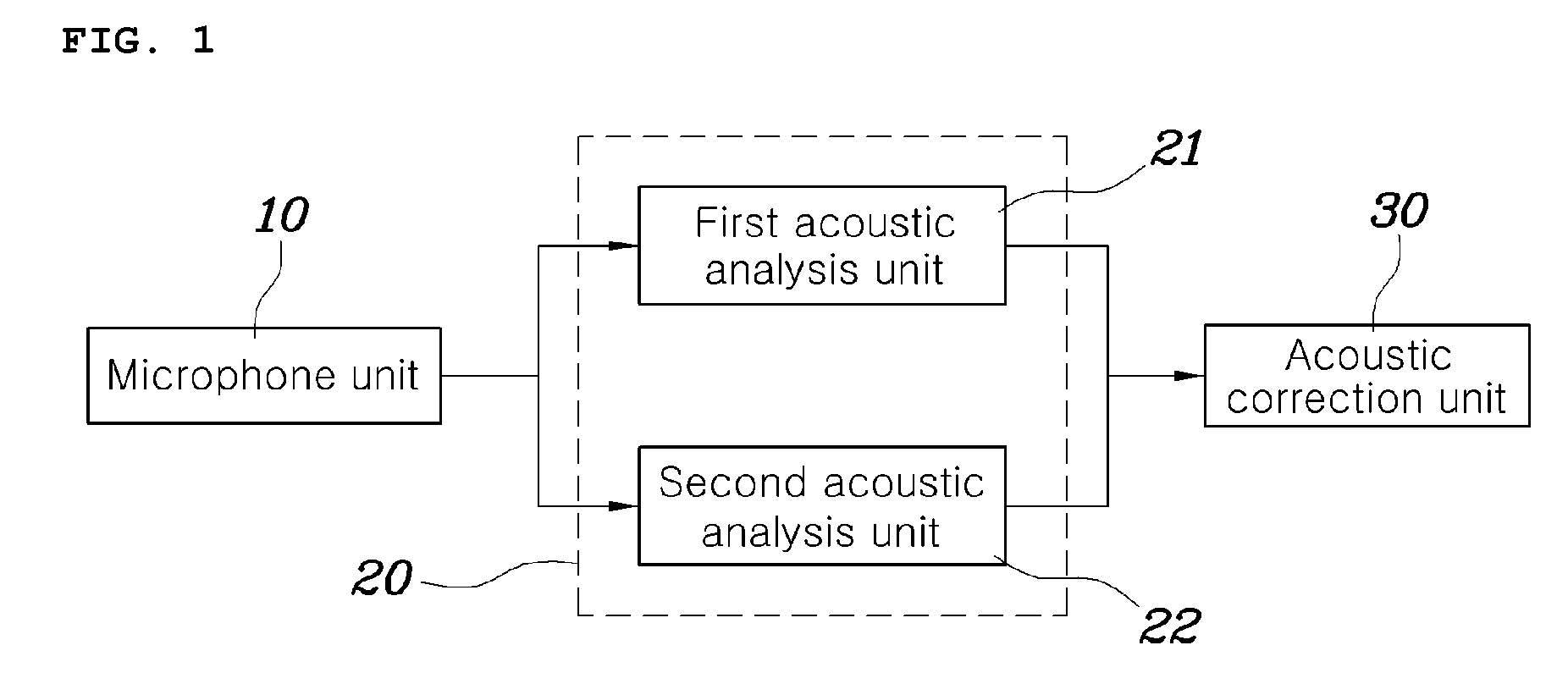
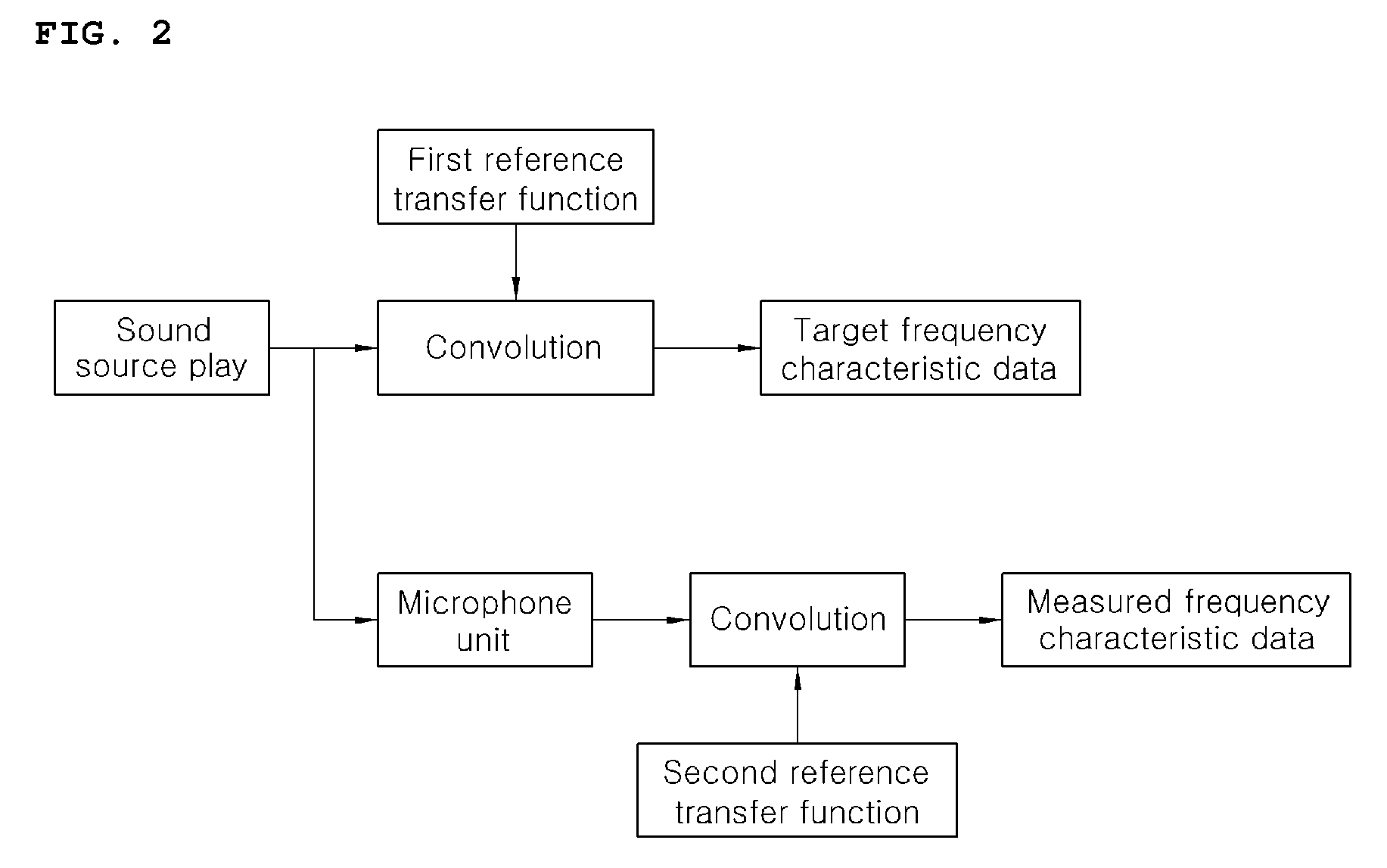
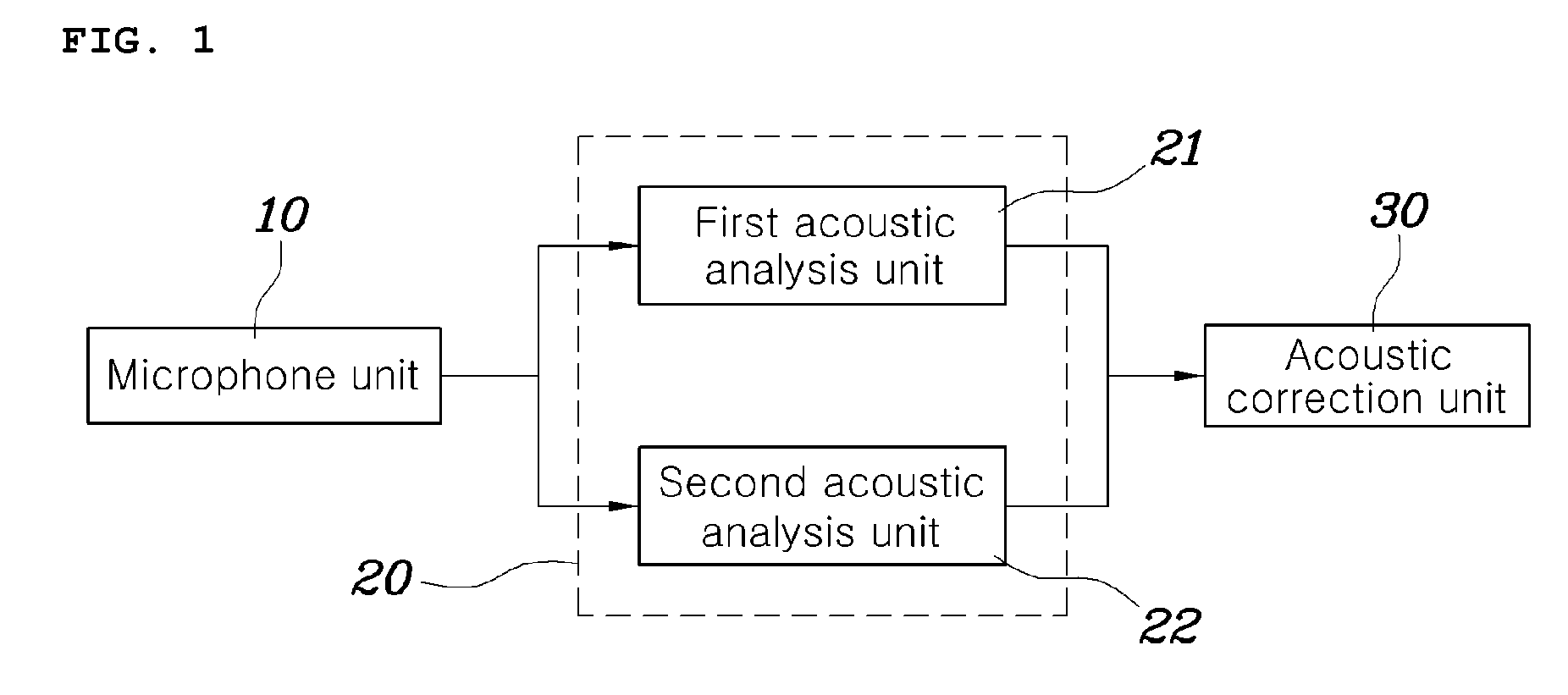
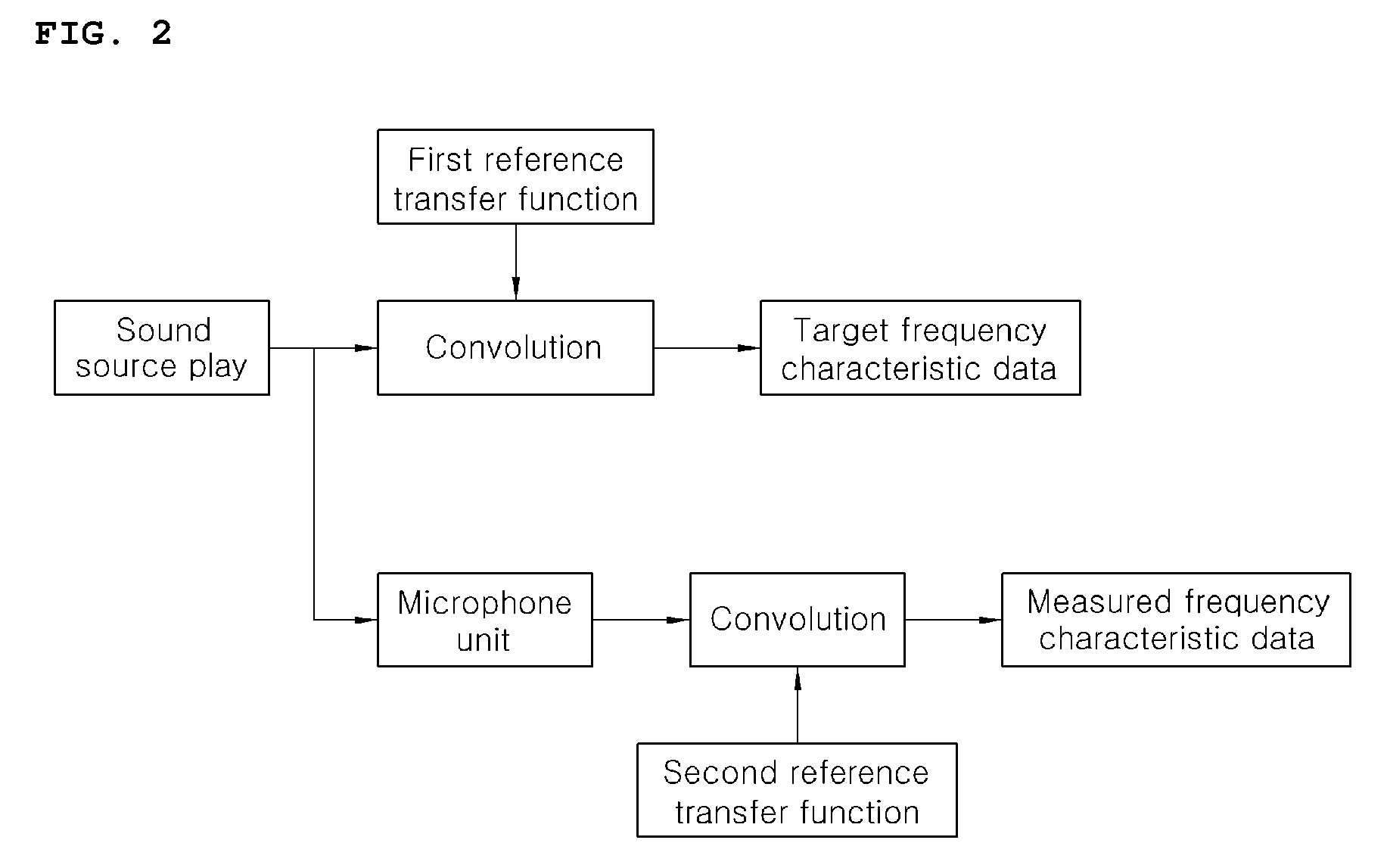
Acoustic correction apparatus and method for vehicle audio system
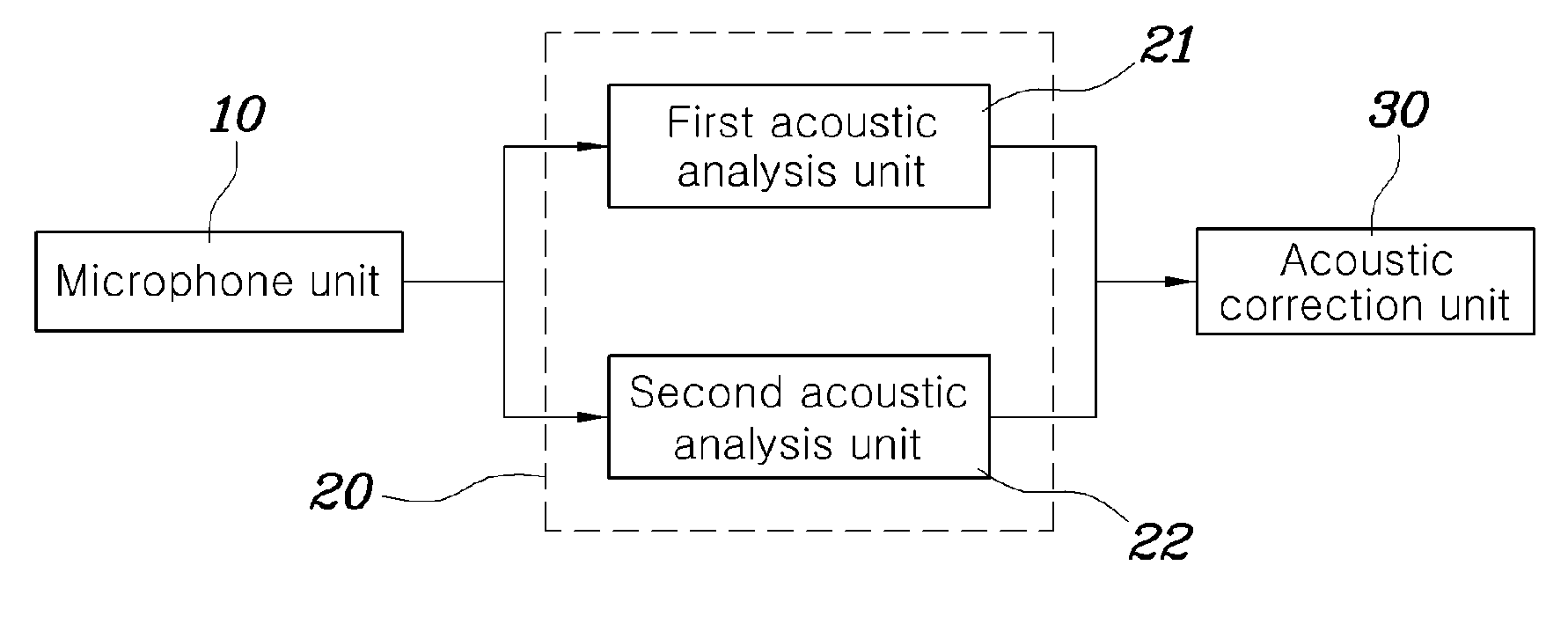
ActiveUS20090154725A1Remove distortionImprove soundFrequency response correctionTransmissionEngineeringFrequency characteristic
Disclosed herein is an acoustic correction apparatus and method for vehicle audio systems which is capable of providing optimal sound at a reference level to a listener even though the acoustic spatial response characteristics in the room of a vehicle vary due to a change in the material of seat covers or the like. A first acoustic analysis unit obtains target frequency characteristic data at a specific listening location based on generated acoustic signals played from an audio system. A second acoustic analysis unit obtains measured frequency characteristic data at the listening location based on measured acoustic signals collected by the microphone unit. An acoustic correction unit adjusts the equalizer of the audio system based on the target and measured frequency data.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
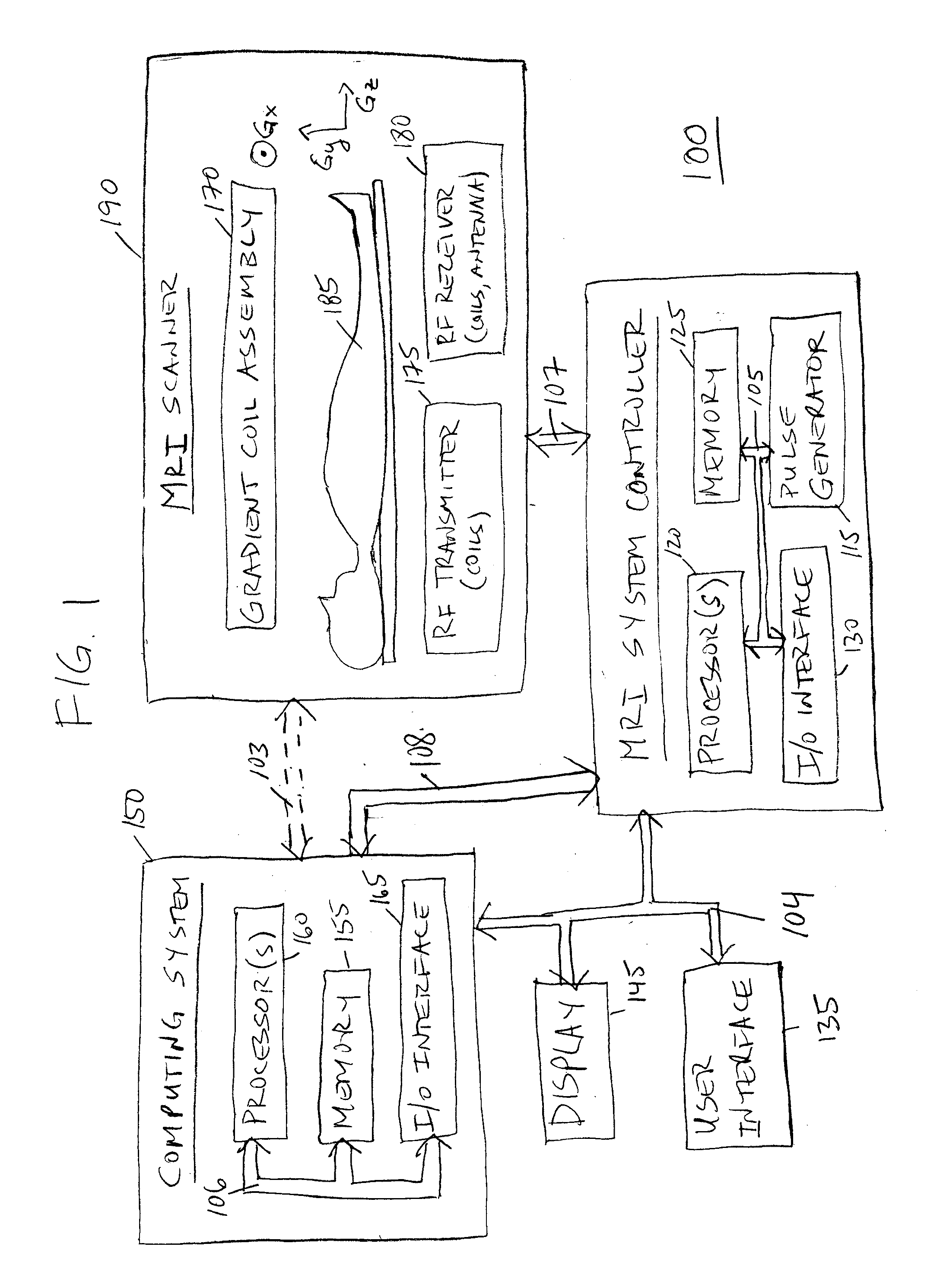
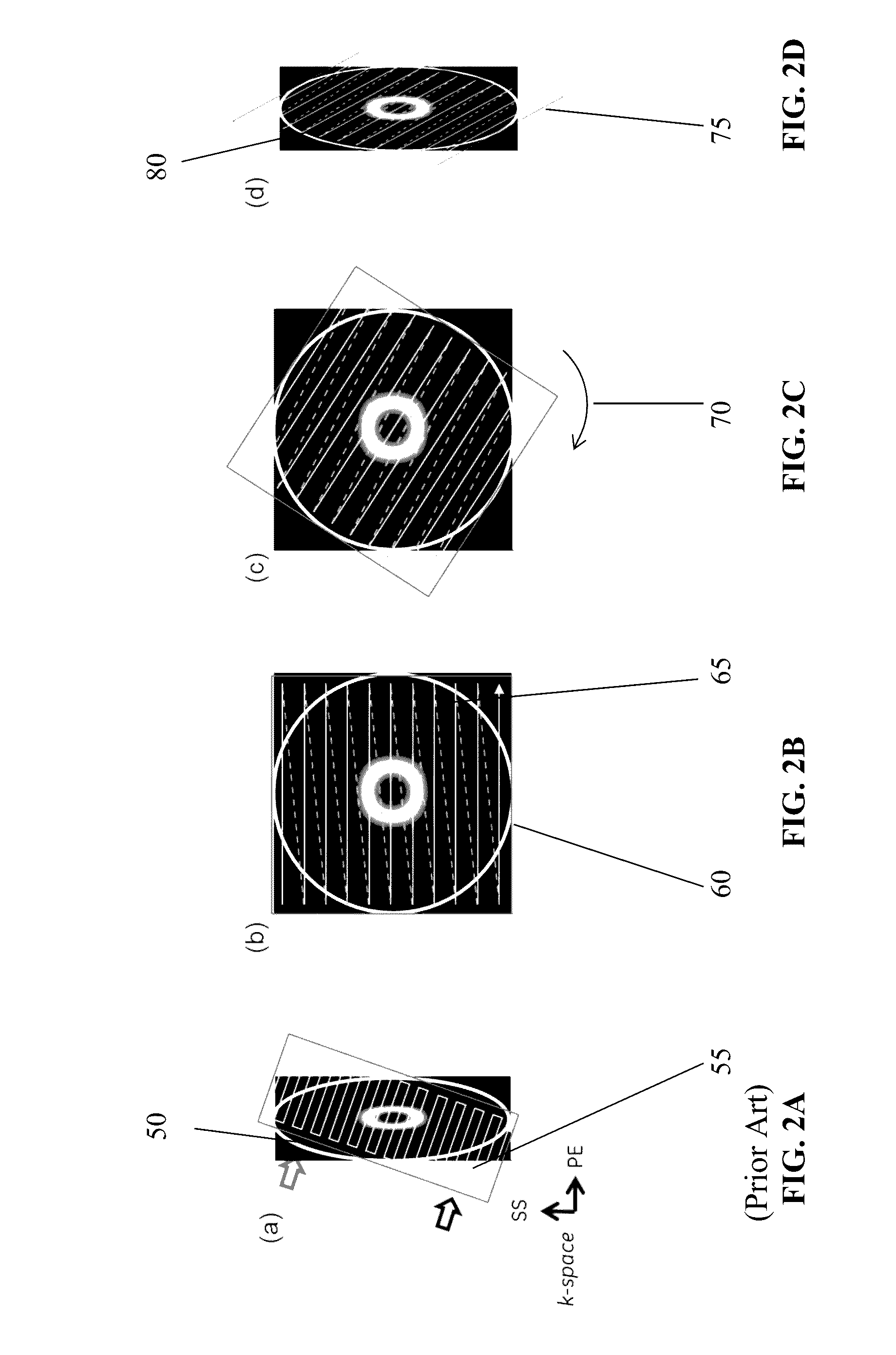
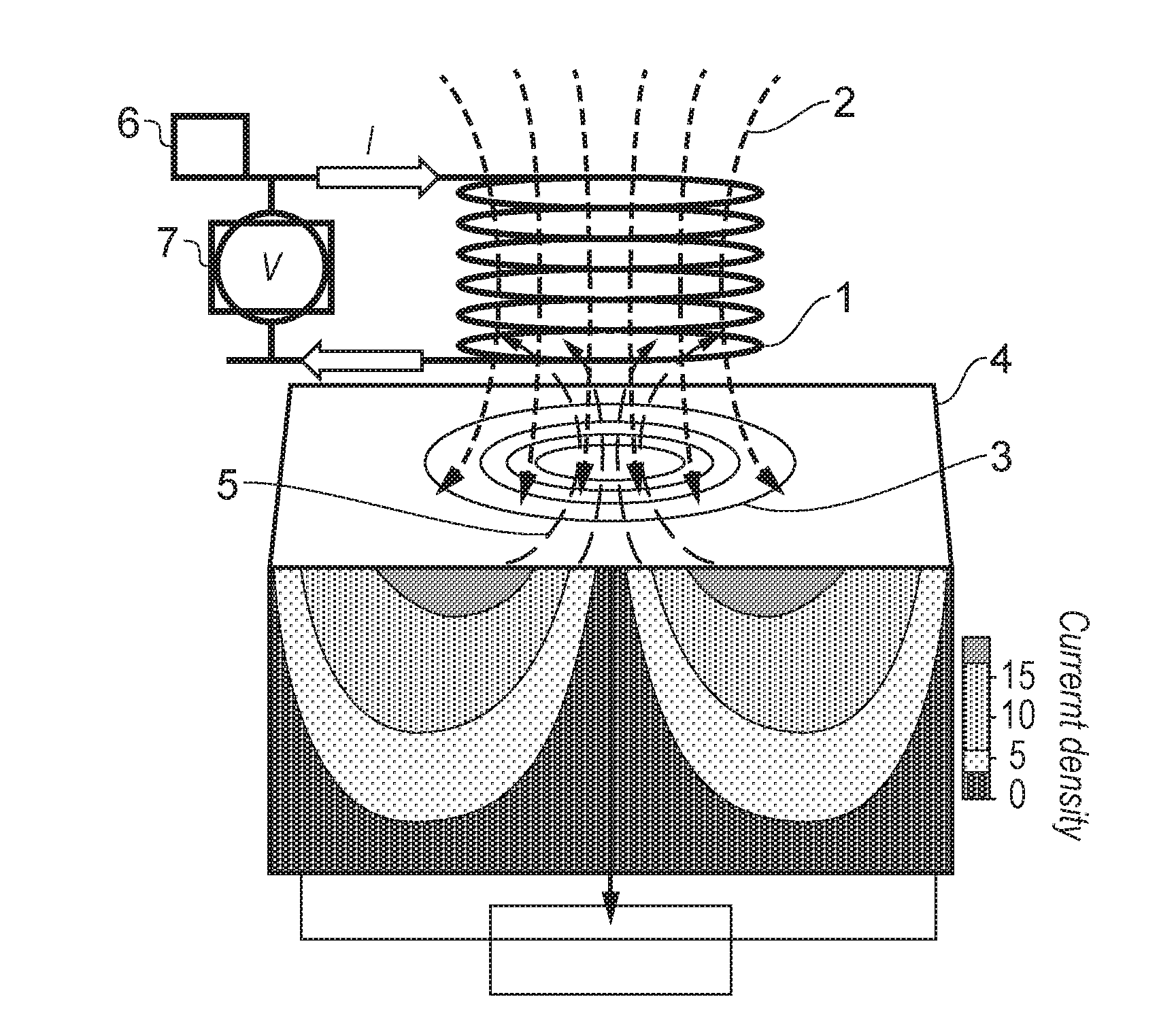
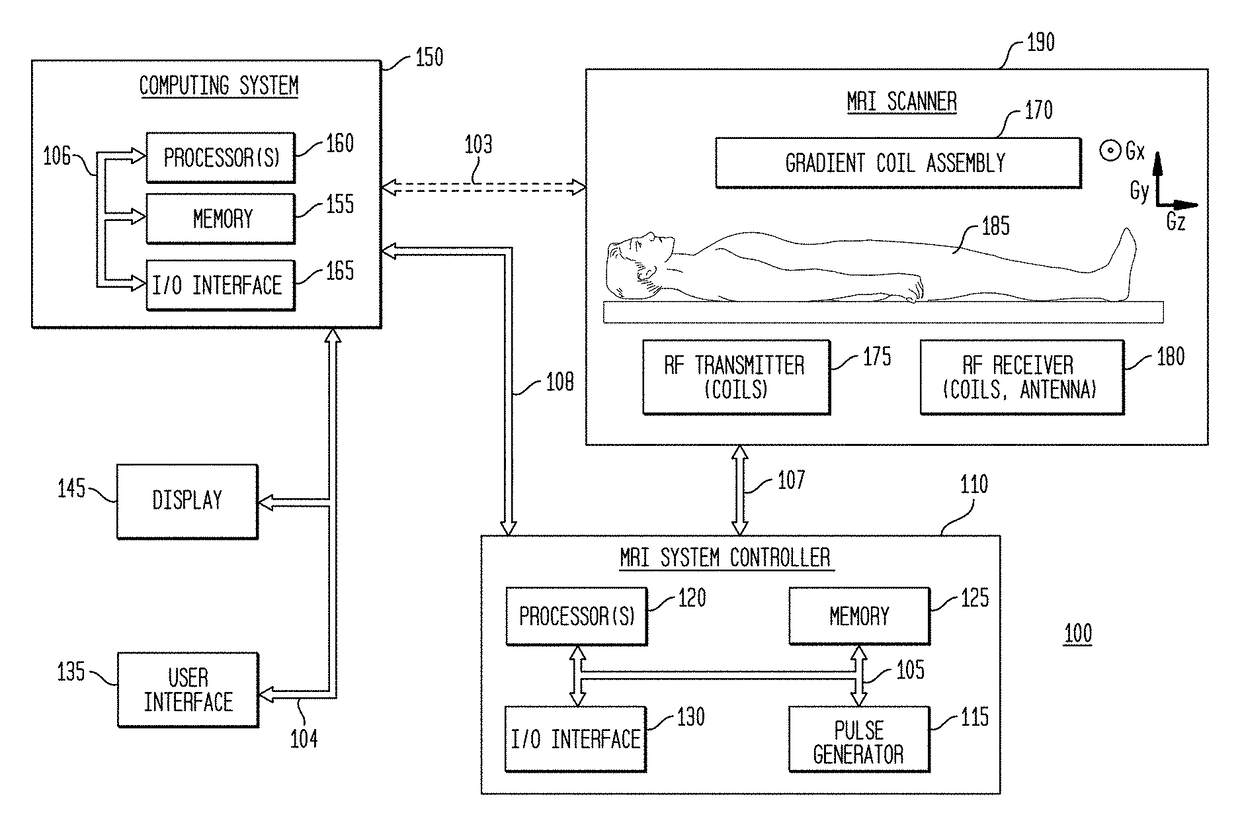
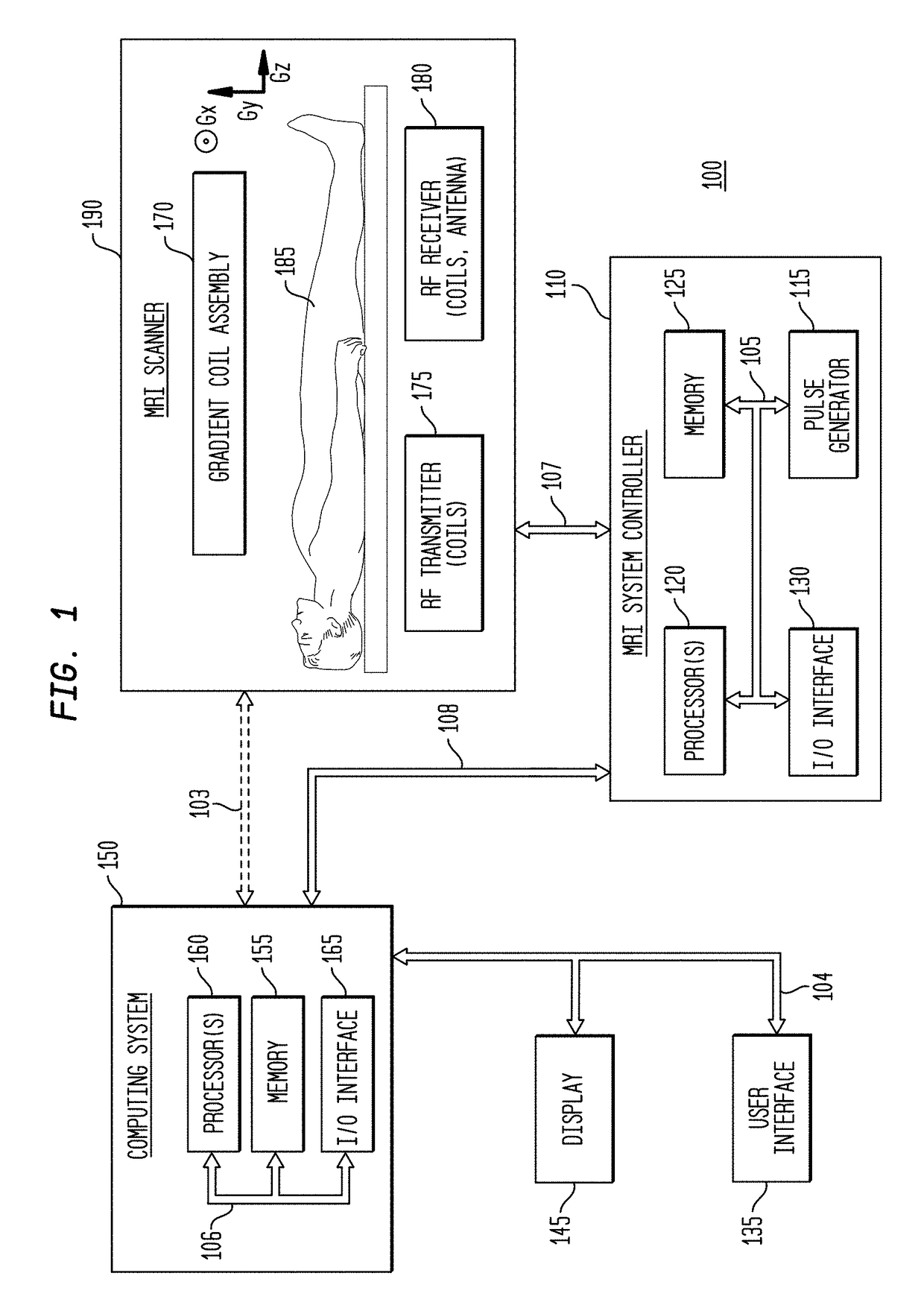
Image Domain Segmented Echo Planar Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using a 2D Excitation Radiofrequency Pulse
ActiveUS20160307301A1Accurate imagingEnhances and enables medical diagnosis and medicalImage enhancementImage analysisMagnetic field gradientImaging data
Representative methods and systems are disclosed for reducing image distortion or increasing spatial resolution in echo planar magnetic resonance imaging. In representative embodiments, a targeted field of view (FOV) image is divided into segments, with each segment having a predetermined overlap region with an adjacent segment, such as in a phase-encoding direction. Image data is acquired for each segment, sequentially or simultaneously, using a reduced phase-encoding FOV with a 2D radiofrequency (RF) excitation pulse, and rotated and scaled magnetic field gradients. The 2D RF excitation pulse may also be modulated, such as onto a plurality of different carrier frequencies, for simultaneous acquisition of multiple segments in the same imaging plane. Using the spatial response of the 2D RF excitation pulse, the acquired image data for each segment of the plurality of segments is combined to generate a combined magnetic resonance image having the targeted field of view.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
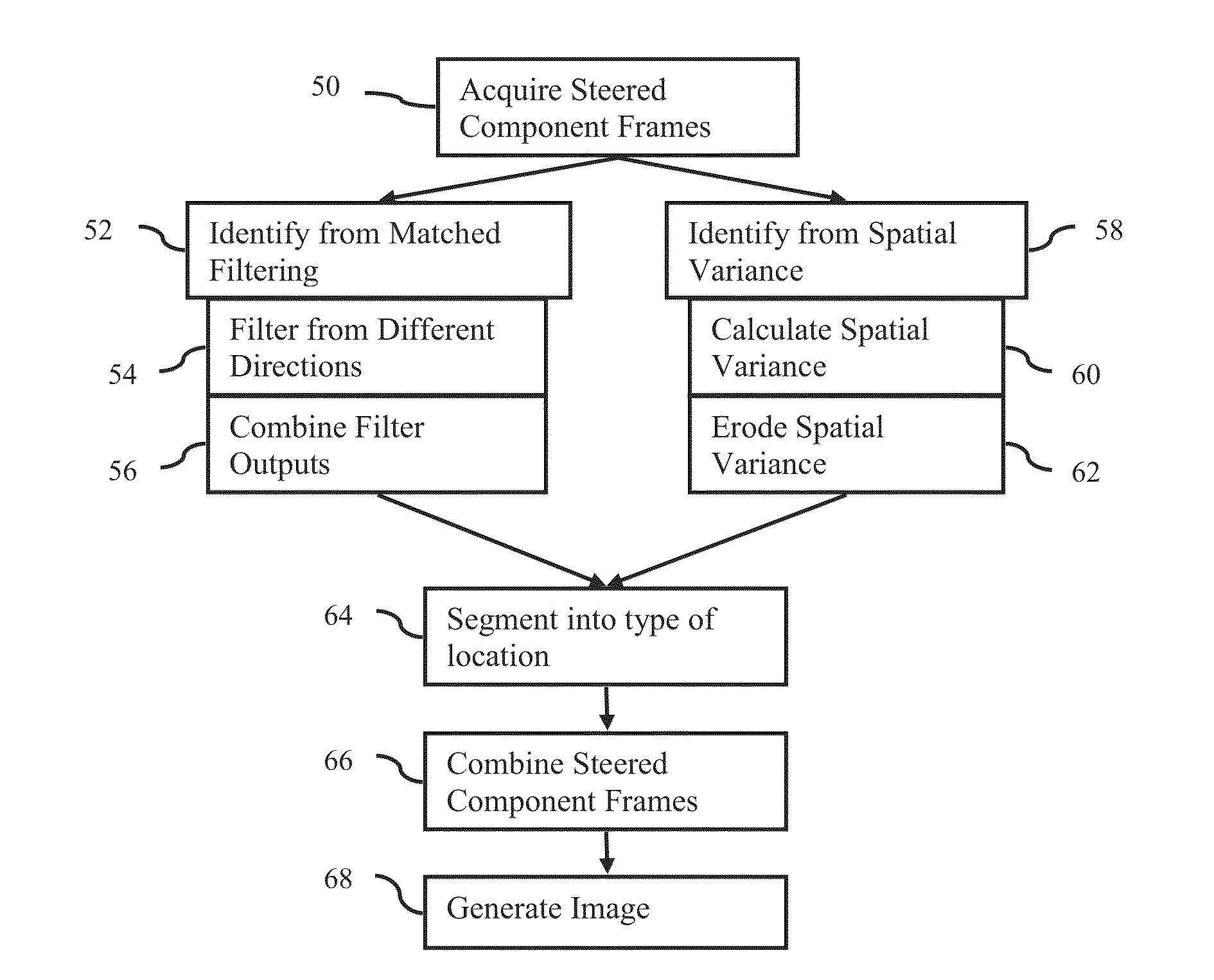
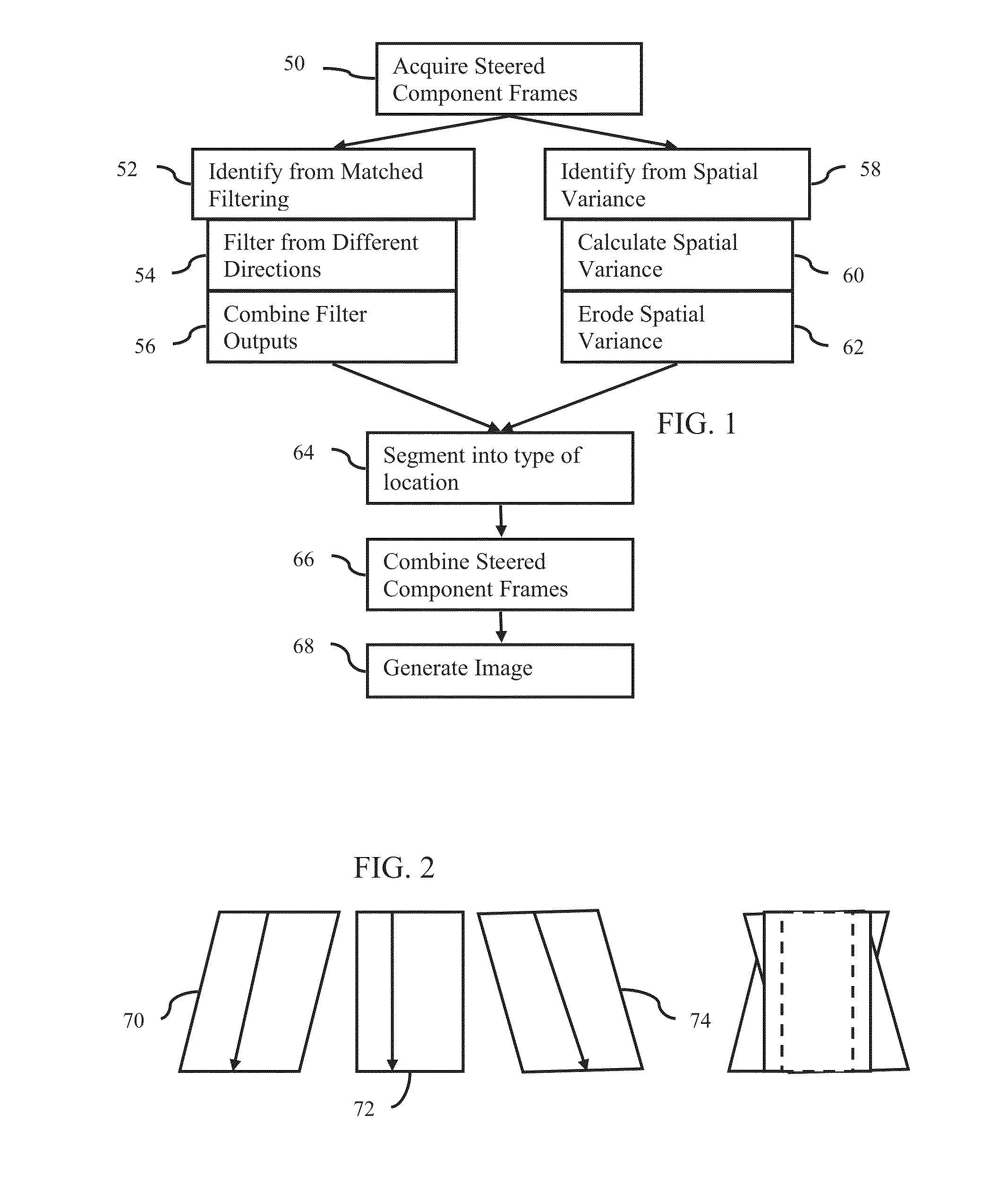
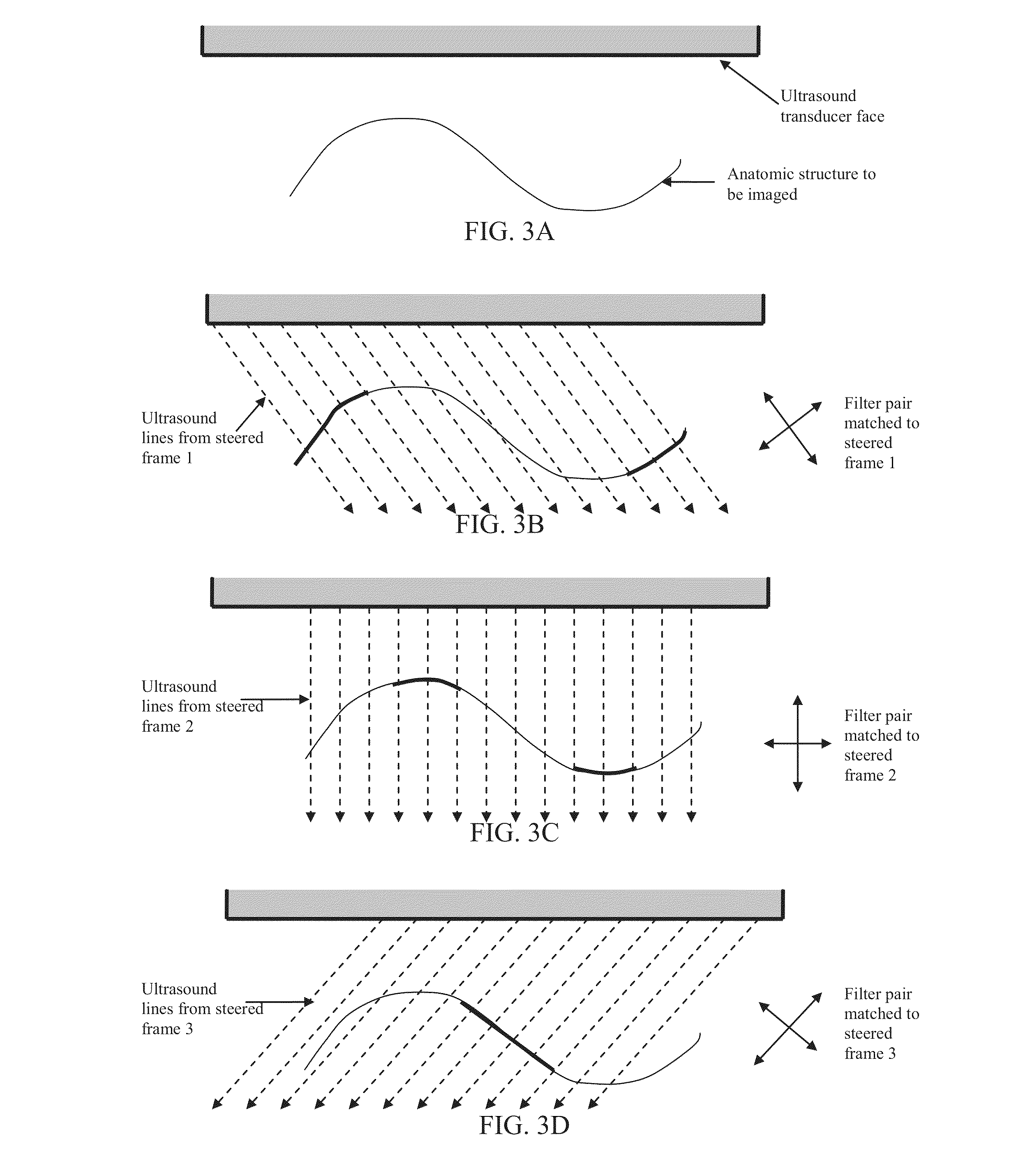
Component Frame Enhancement for Spatial Compounding in Ultrasound Imaging
ActiveUS20130294665A1Character and pattern recognitionAcoustic wave reradiationUltrasound imagingAnatomical structures
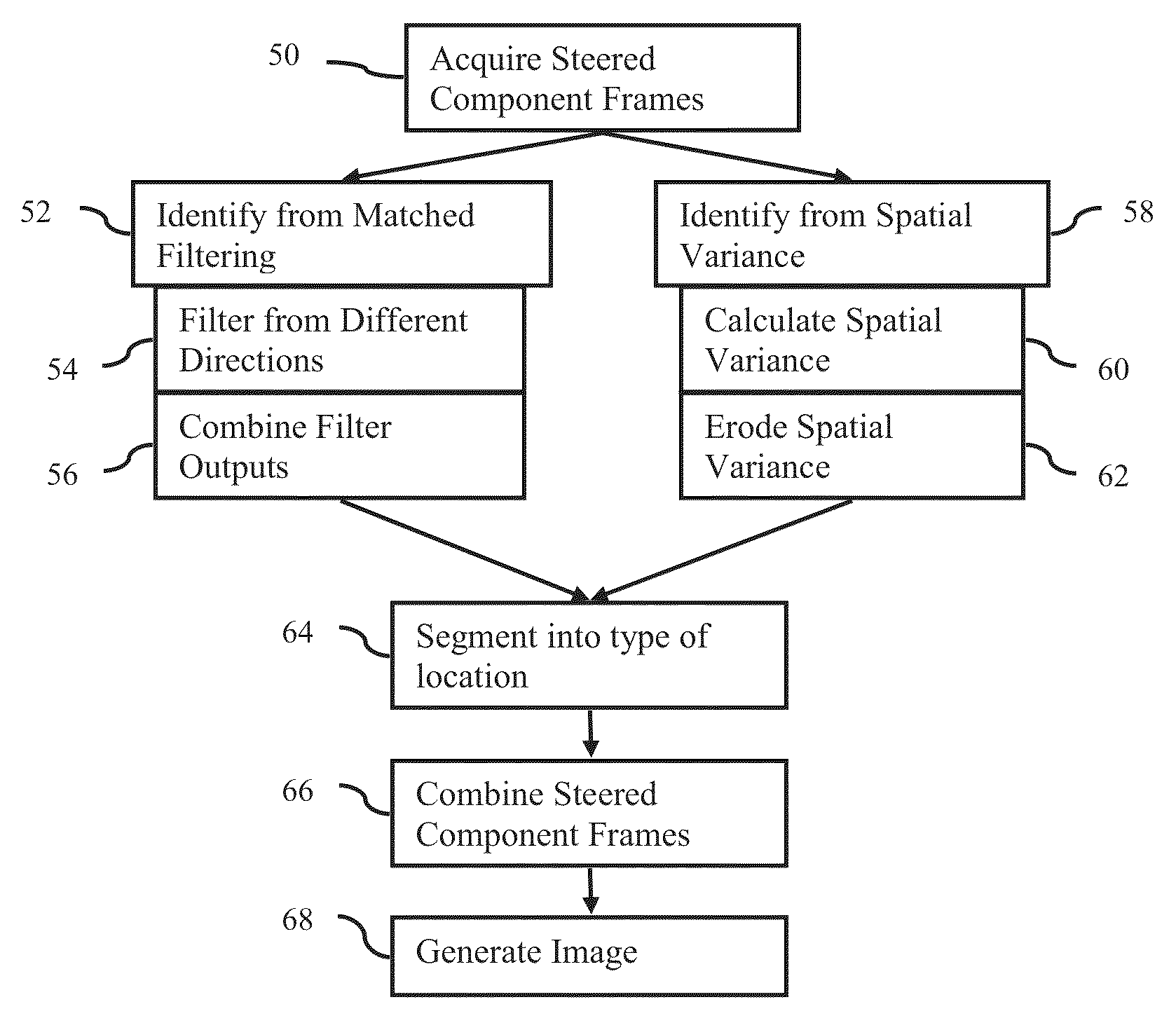
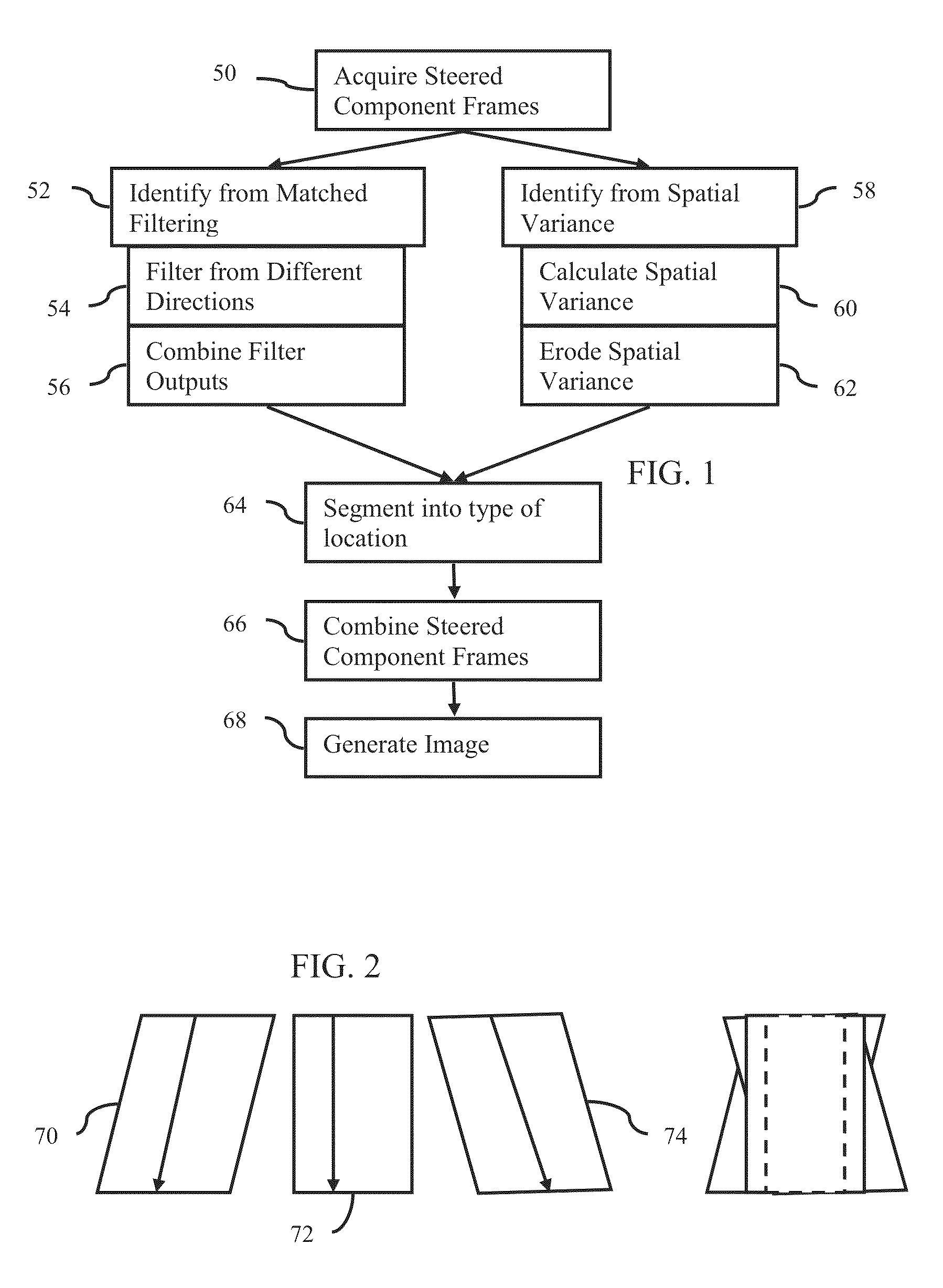
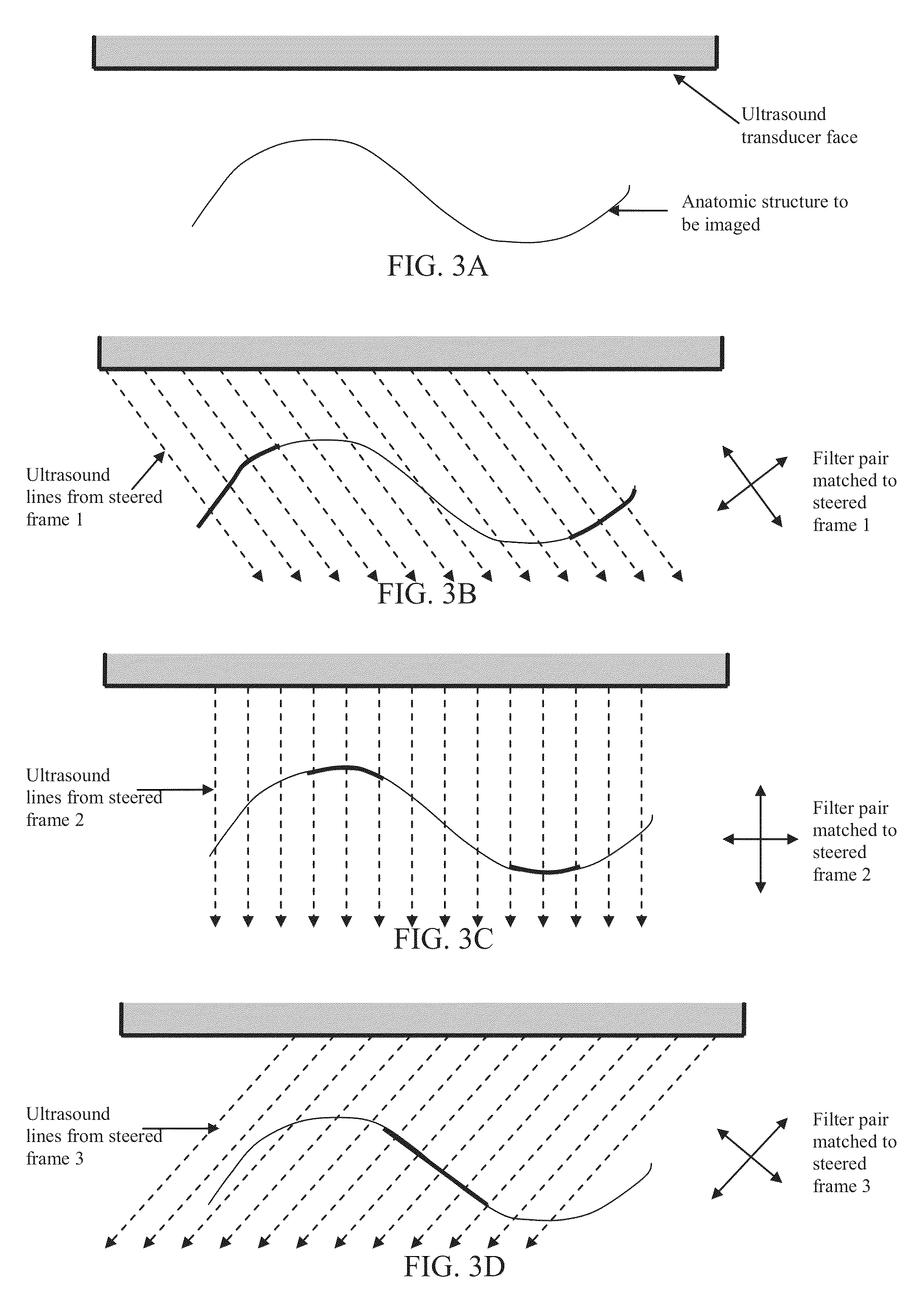
Steered spatial compounding is provided in ultrasound imaging. Component frames of data associated with different spatial response are processed to identify different sources of signals. Matched filtering and / or spatial variance with erosion distinguish between sources of signals, such as distinguishing between (1) anatomical structure and (2) soft tissue and / or noise. The locations in the patient are segmented by the source of signals and different compounding is applied for the different sources.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
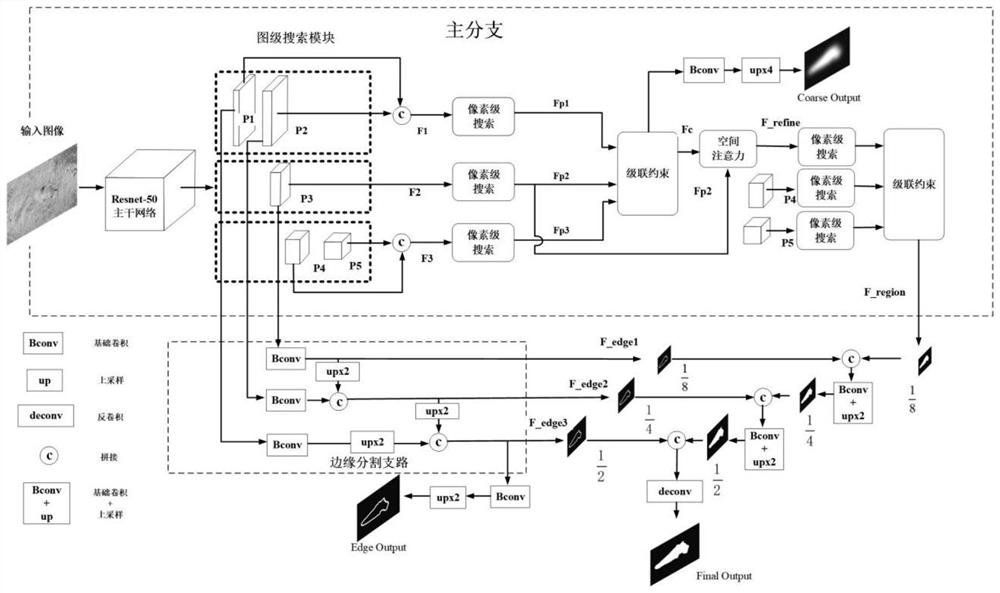
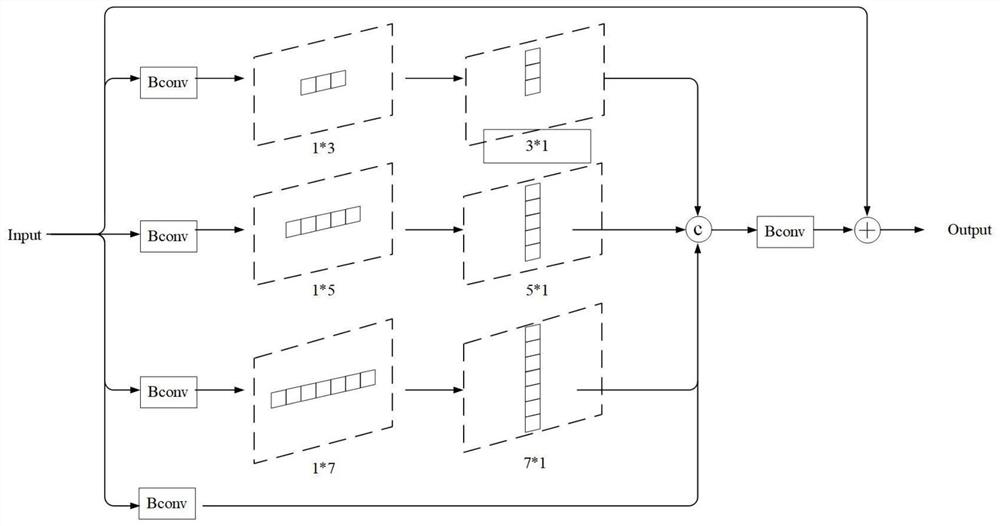
Camouflage object detection model based on edge collaborative supervision and multi-level constraint
ActiveCN112733744AAccurate and effective detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesActivation functionComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a camouflage object detection model based on edge collaborative supervision and multi-level constraint, provides a mature and complete camouflage object detection method based on the model, preliminarily searches a target potential area through graph-level and pixel-level search, and strengthens spatial response through cascade constraint and an attention mechanism. Meanwhile, an edge segmentation branch is established to guide the model to predict a more accurate contour, a Frelu activation function is utilized to extract the spatial activity of an image at a basic convolution part, camouflage object detection can be effectively and accurately carried out through the model, and a gap is filled in the field of camouflage object detection in the prior art.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
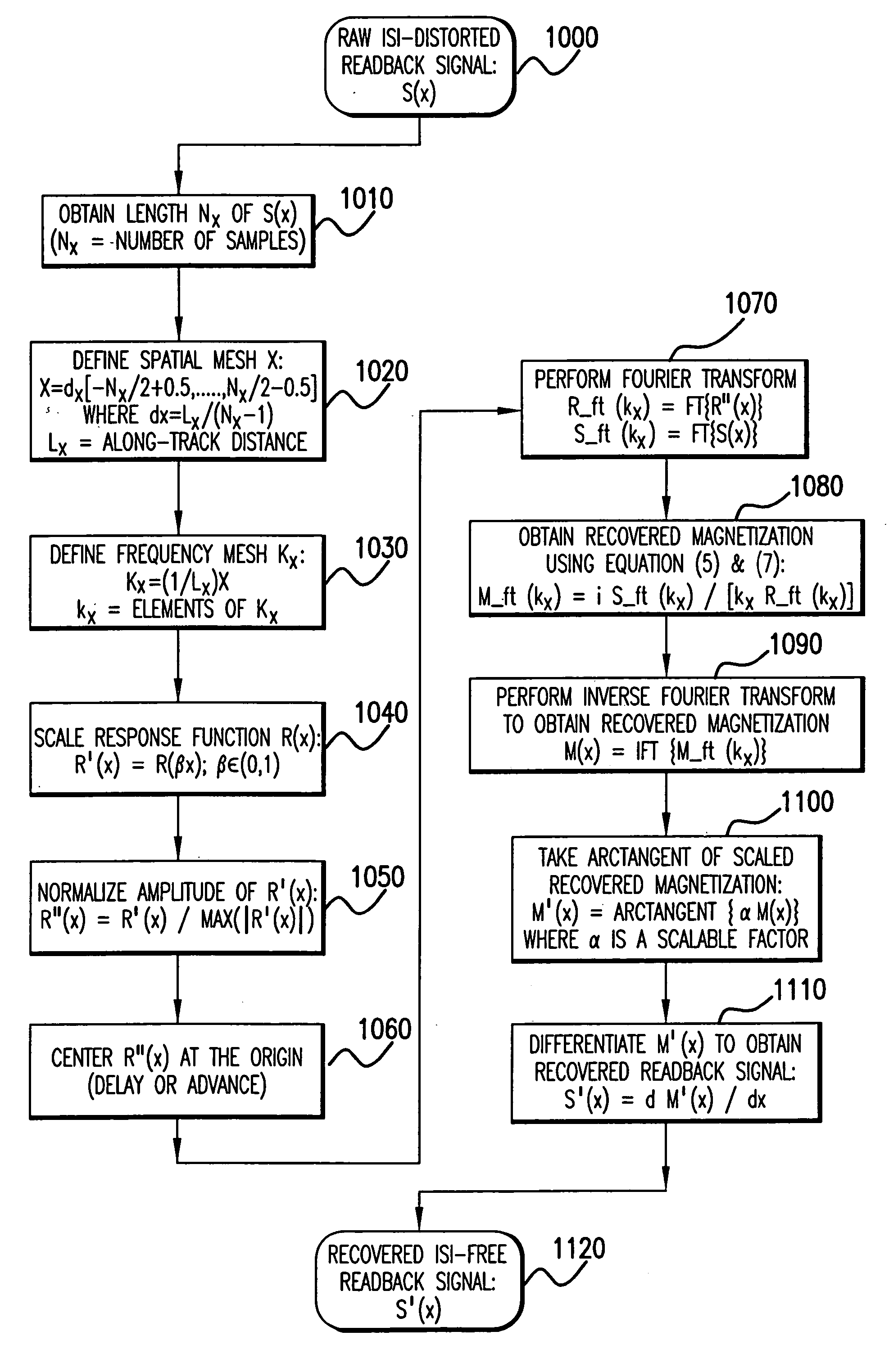
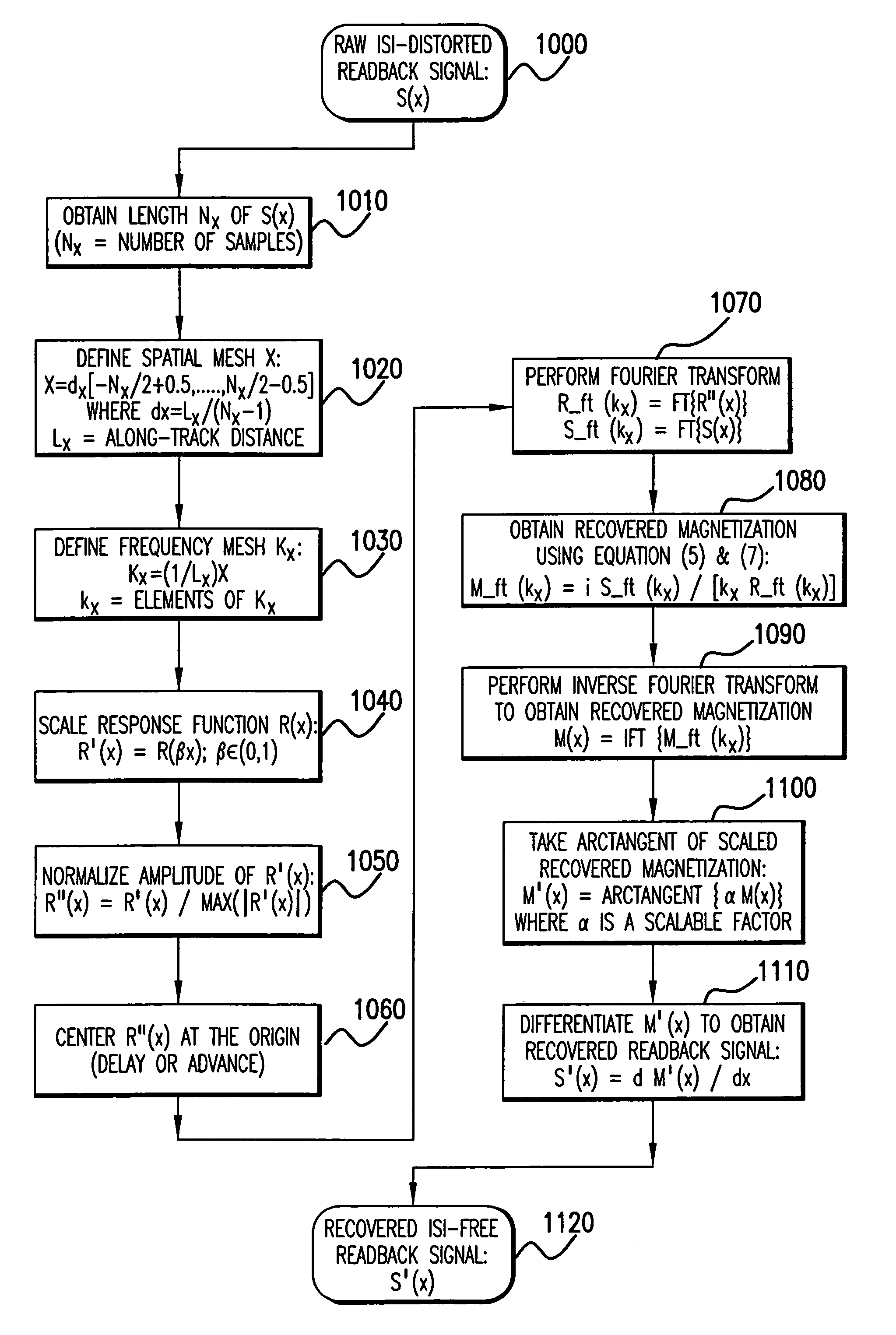
Method for intersymbol interference removal in data recovery
InactiveUS20050180039A1Efficient removalModification of read/write signalsSignal processing for reducing noiseMagnetic mediaImaging quality
In recovering data originally written on a carrier of magnetic media after a catastrophic failure, data may be read without prior knowledge of the write channel by which the data was originally written and in the presence of intersymbol interference of the readback signal. This is accomplished by forming an image of the spatial response function of the magnetoresistive transducer used to recover the data and by forming an image of the raw data read from the carrier of magnetic media by the magnetoresistive transducer for which the response function has been characterized. An image of the distribution of virtual magnetic charge on the carrier of magnetic media is obtained through deconvolution of the image of the response function of the magnetoresistive transducer and the raw readback signal. The readback signal corresponding to the data originally written on the carrier of magnetic media is then recovered by spatial differentiation of the image of virtual magnetic charge. Further improvement in image quality of the resulting image is accomplished through a noise reduction technique such as by the application of an arctangent function to the data prior to differentiation.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Synthesis method of broadband frequency independent thinned array taking mutual coupling effect into account
ActiveCN106650104AReduce the numberReduce complexityAntenna arraysDesign optimisation/simulationThinned arraySynthesis methods
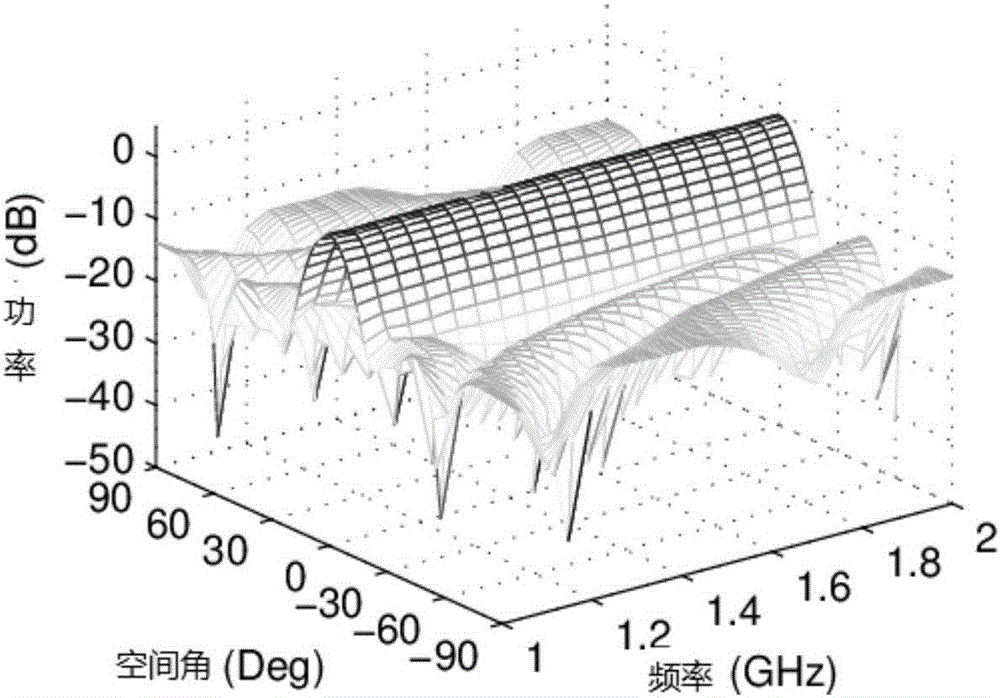
The discloses a synthesis method of a broadband frequency independent thinned array taking mutual coupling effect into account, and relates to array antennae. Iterative weighted first norm is adopted in a plurality of limiting conditions, and the limiting conditions comprise a spatial response change limit, a side lobe level upper boundary limit and an expected direction limit. As the limiting conditions are all convex problems, the problems are optimized through iterative second-order cone programming. In a target working frequency range, low side lobe level can be kept, the quantity of array elements can be effectively reduced under a main lobe frequency independent performance, the hardware complexity and the engineering cost are furthest reduced. In addition, electromagnetic mutual coupling effect met in the practical application is considered, and error, caused by coupling, of an antenna system is effectively avoided.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
System and method to modify the spatial response of a pattern generator
InactiveUS20060019030A1Vacuum evaporation coatingPhotomechanical apparatusGas phasePattern generation
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS7342397B2Low densitySignificant scan-time reductionMagnetic measurementsPulse automatic controlSignal responseSignal statistics
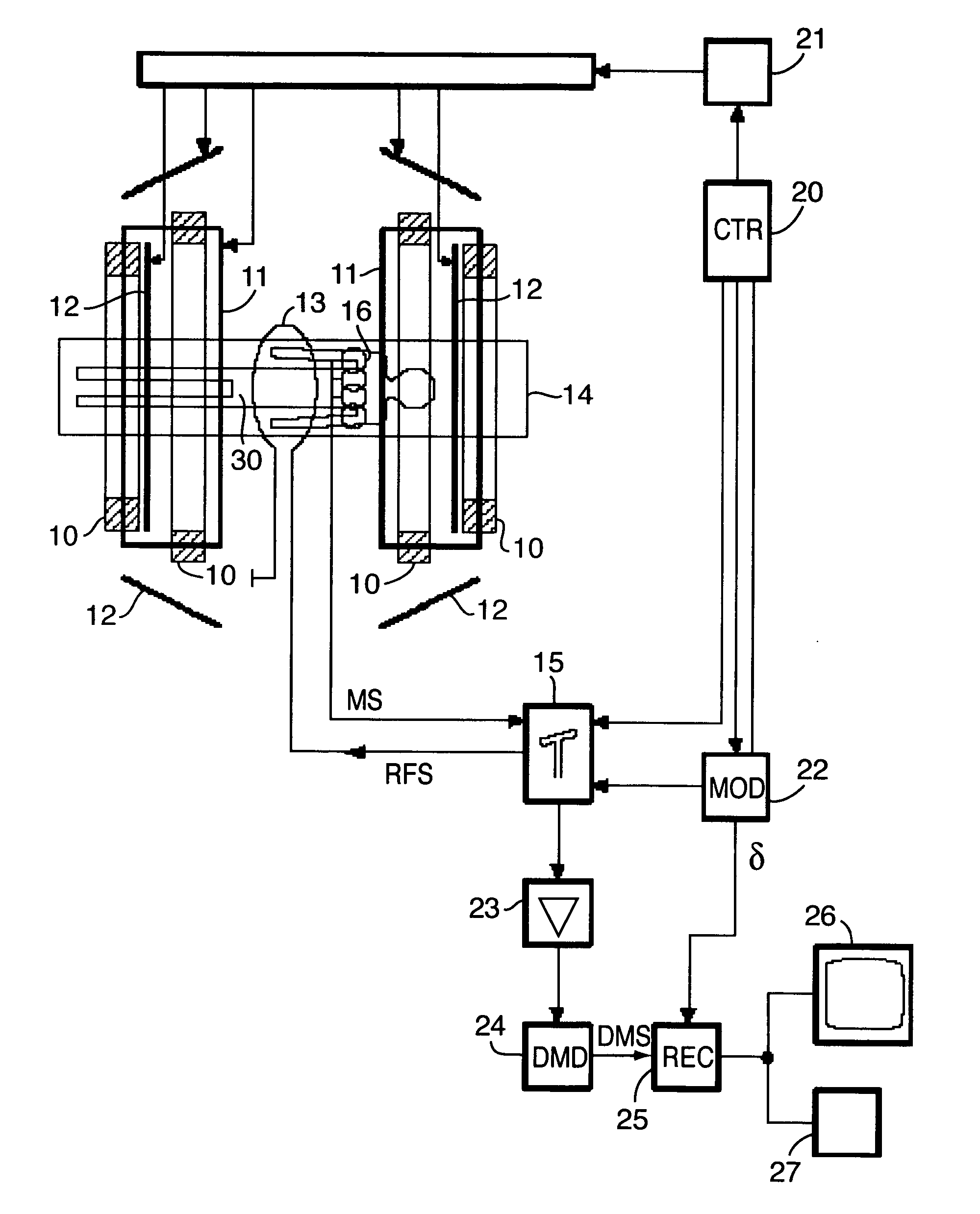
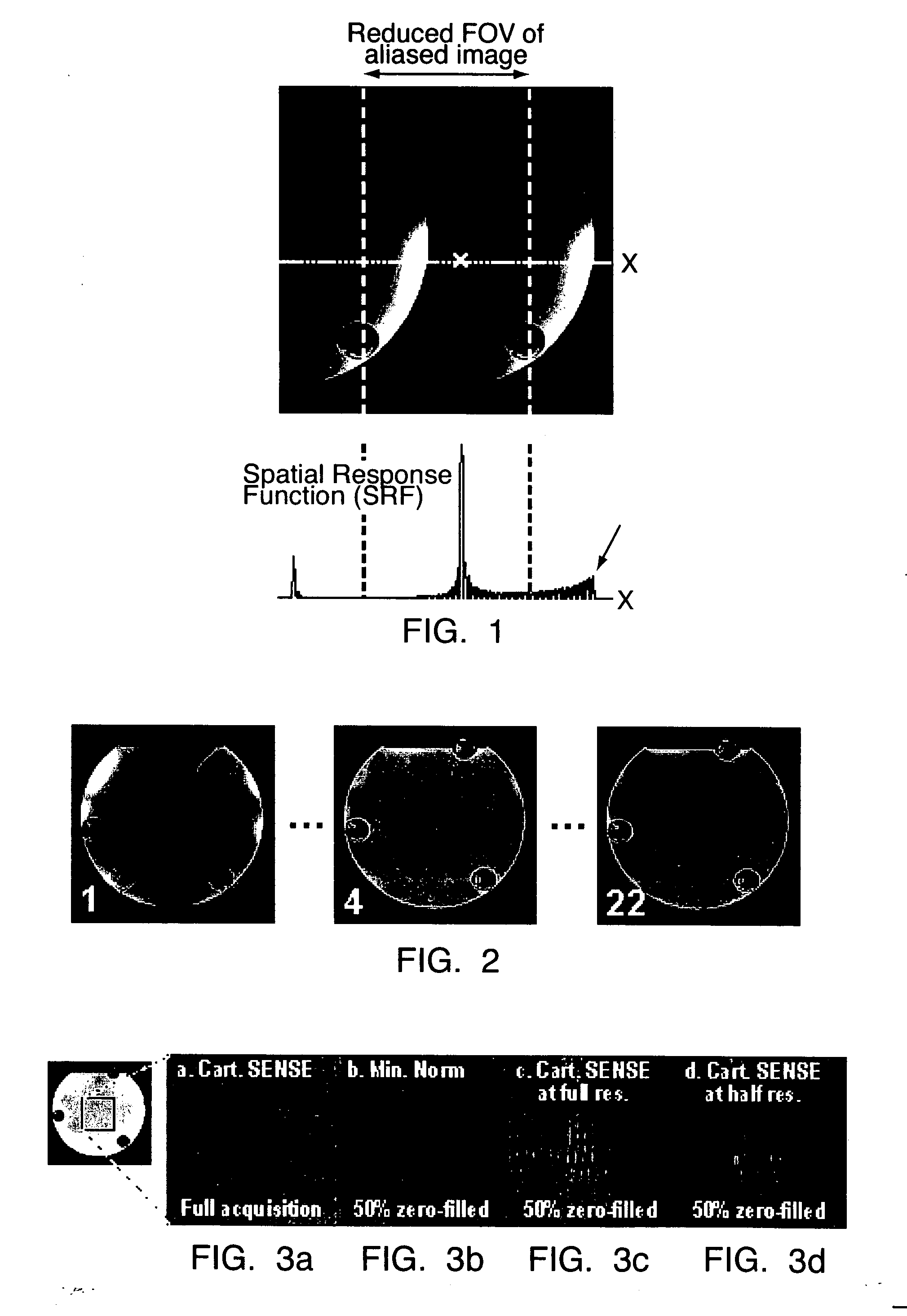
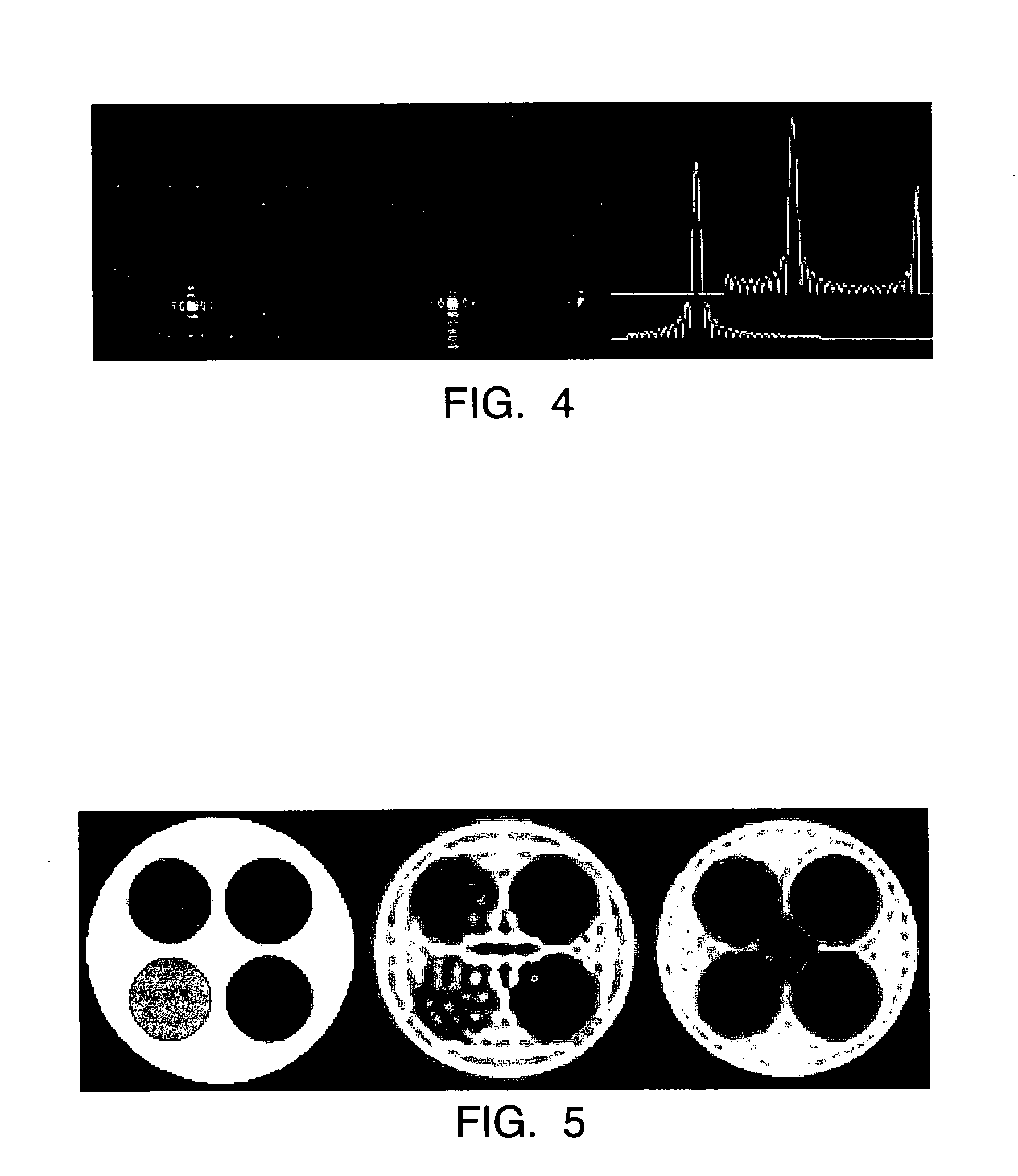
A novel magnetic resonance imaging method is described, wherein undersampled magnetic resonance signals are acquired by a receiver antenna system having spatial sensitivity profiles and the image being reconstructed from the undersampled magnetic resonance signals and the spatial sensitivity profiles. The reconstruction of the image is provided by an optimization of a cost function which accounts for any of noise statistics, signal statistics, and the spatial response function, the latter of which is defined by the spatial signal response from the object to be imaged, separately for each individual pixel.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Near-field linear constrained minimum variance adaptive weighted-frequency-invariant beam forming method
ActiveCN105223544AStructure without limitGood near-field broadband frequency invarianceSystems with undesired wave eliminationInteraction systemsVoice communication
The invention discloses a near-field linear constrained minimum variance adaptive weighted-frequency-invariant beam forming method. The method is based on linear constrained minimum variance. A balance matrix of an array spatial response bias function is defined based on the spatial response bias function, and the matrix is introduced into a near-field linear constrained minimum variance beam forming method to obtain the near-field linear constrained minimum variance weighted-frequency-invariant beam forming method. Then, the weighting coefficient in the near-field linear constrained minimum variance weighted-frequency-invariant beam forming method is defined as a function of the field spot distance and the signal frequency, and the function is dynamic and is updated adaptively. The method of the invention is widely applied to multi-channel speech enhancement, man-machine voice interaction systems, hearing aids, vehicular hands-free voice communication, remote video conferencing systems, robot hearing, and other fields.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Underwater acoustic target radiation noise linear array beam reconstruction method for output signal frequency spectrum
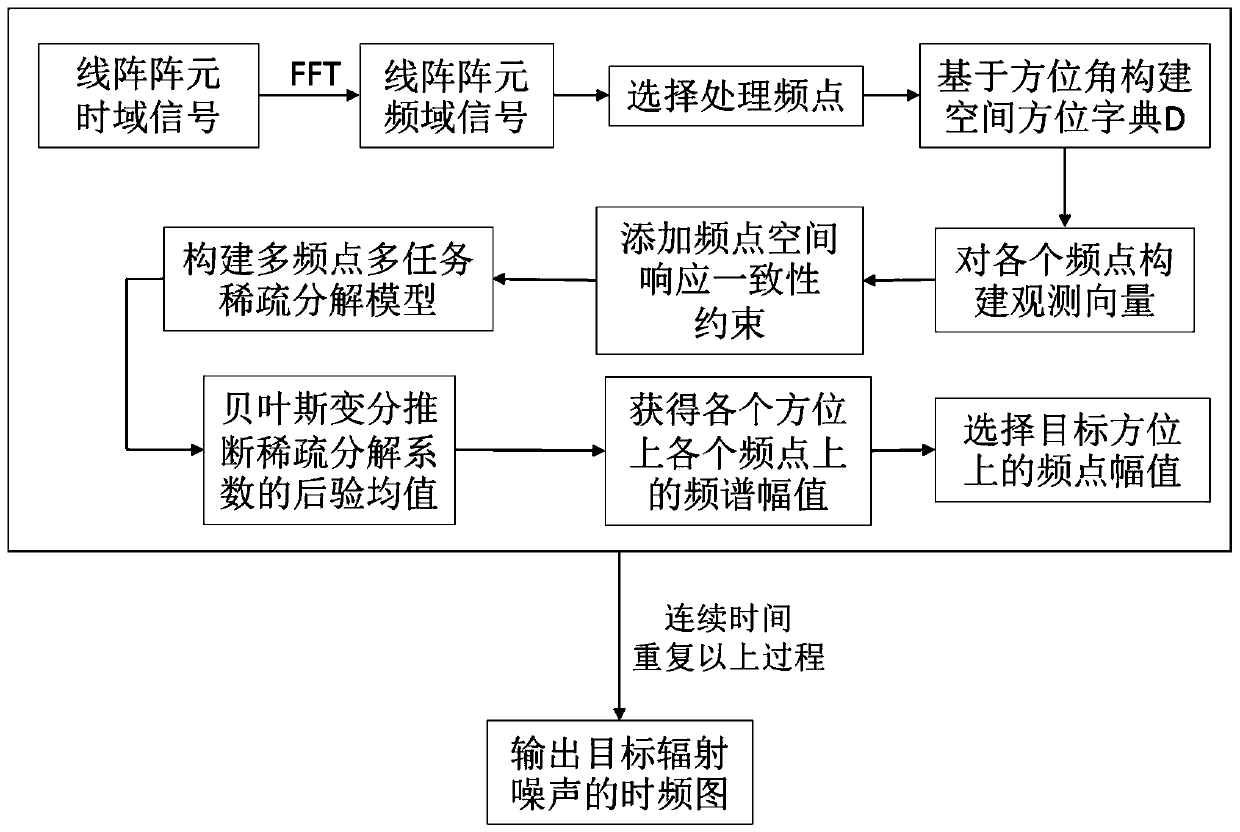
InactiveCN111273301AClear detailsSuppression of interfering signalsAcoustic wave reradiationFrequency spectrumUnderwater acoustics
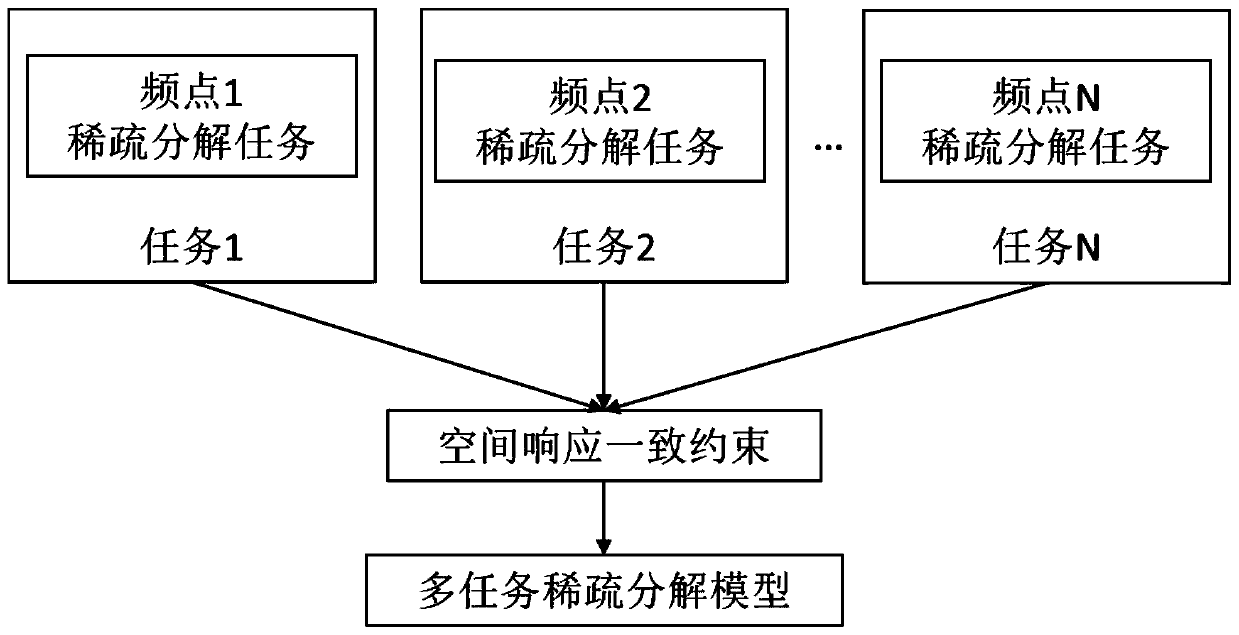
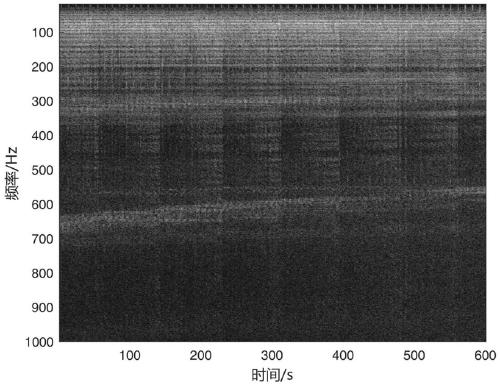
The invention provides an underwater acoustic target radiation noise linear array beam reconstruction method for an output signal frequency spectrum. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, converting a linear array multi-channel signal to a frequency domain through Fourier transform; then, creating a dimensional orientation space, creating observation vectors at all frequency pointswithin the selected frequency spectrum; adding a spatial response consistency constraint for all frequency points to create a a multi-frequency-point multi-task sparse decomposition model; finally, deducing and estimating a posteriori mean value of a sparse decomposition coefficient by using Bayesian variational to obtain frequency spectrum amplitudes on all frequency points in all directionsincluding a target direction. Compared with a traditional conventional beam forming method, the method has the advantage that the target frequency spectrum of the 500-1000Hz medium-high frequency band in the radiation noise signal can be better recovered.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
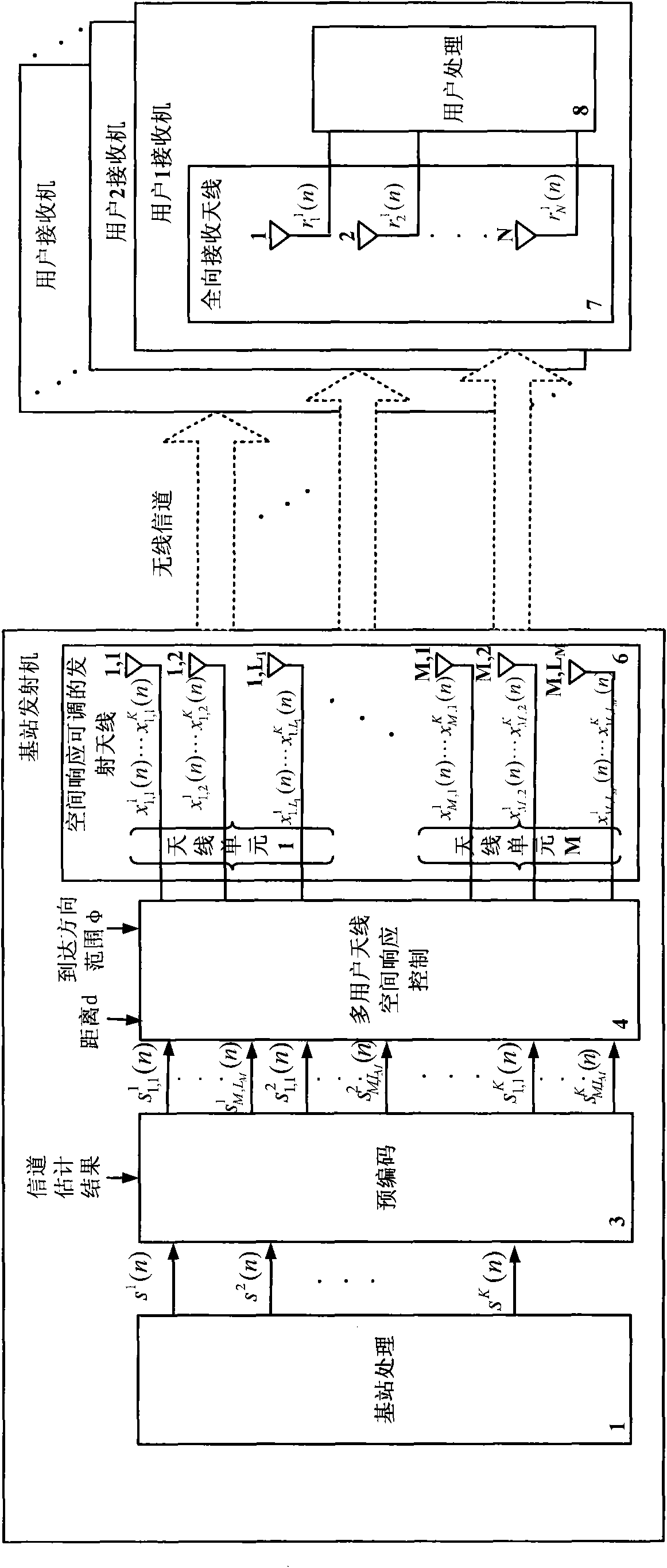
Signal emission method and device of down link in multi-user MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system
InactiveCN101783699AImprove dry ratioThe main lobe energy spectrum is wide and flatSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSignal waveArray element
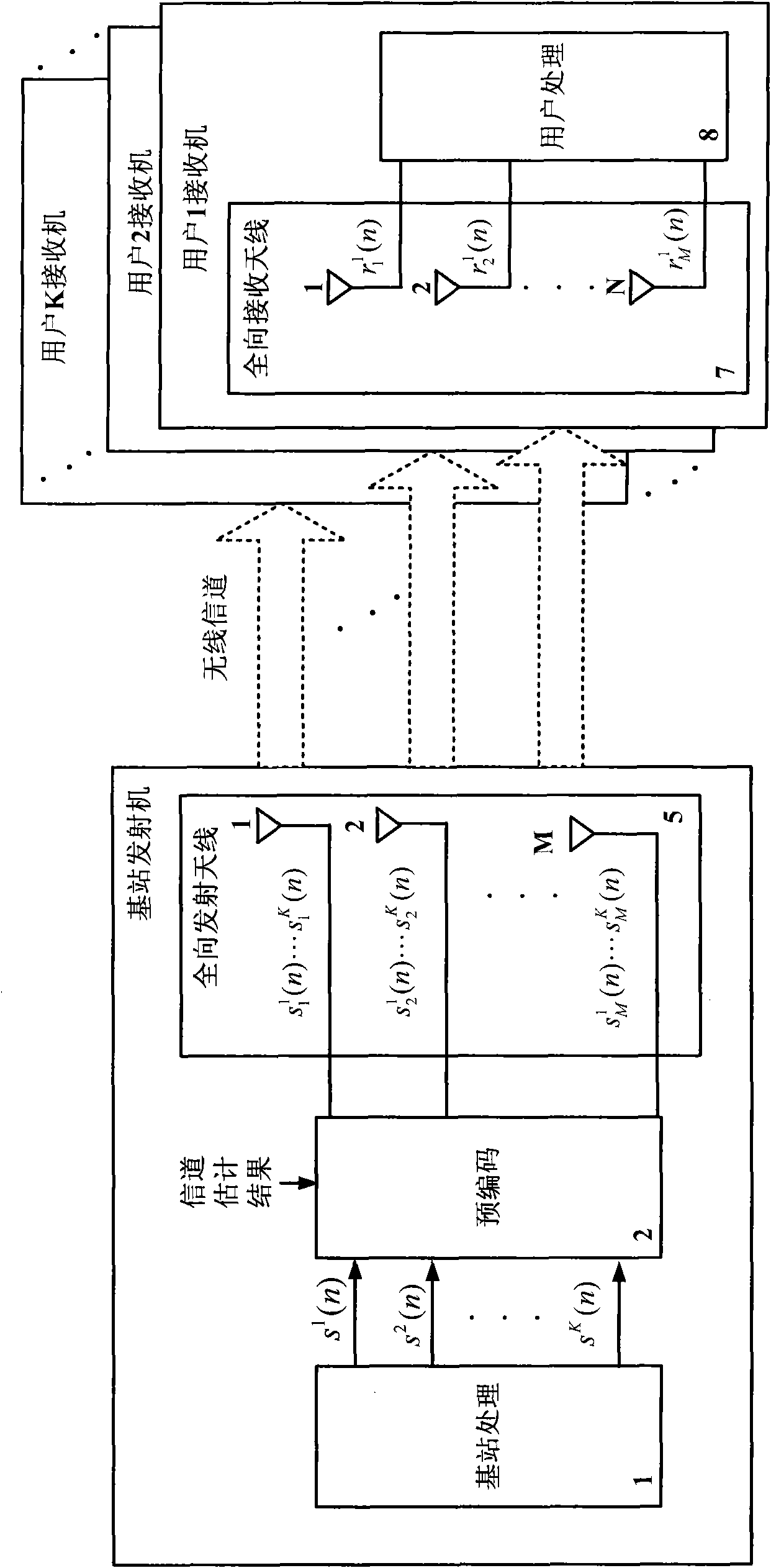
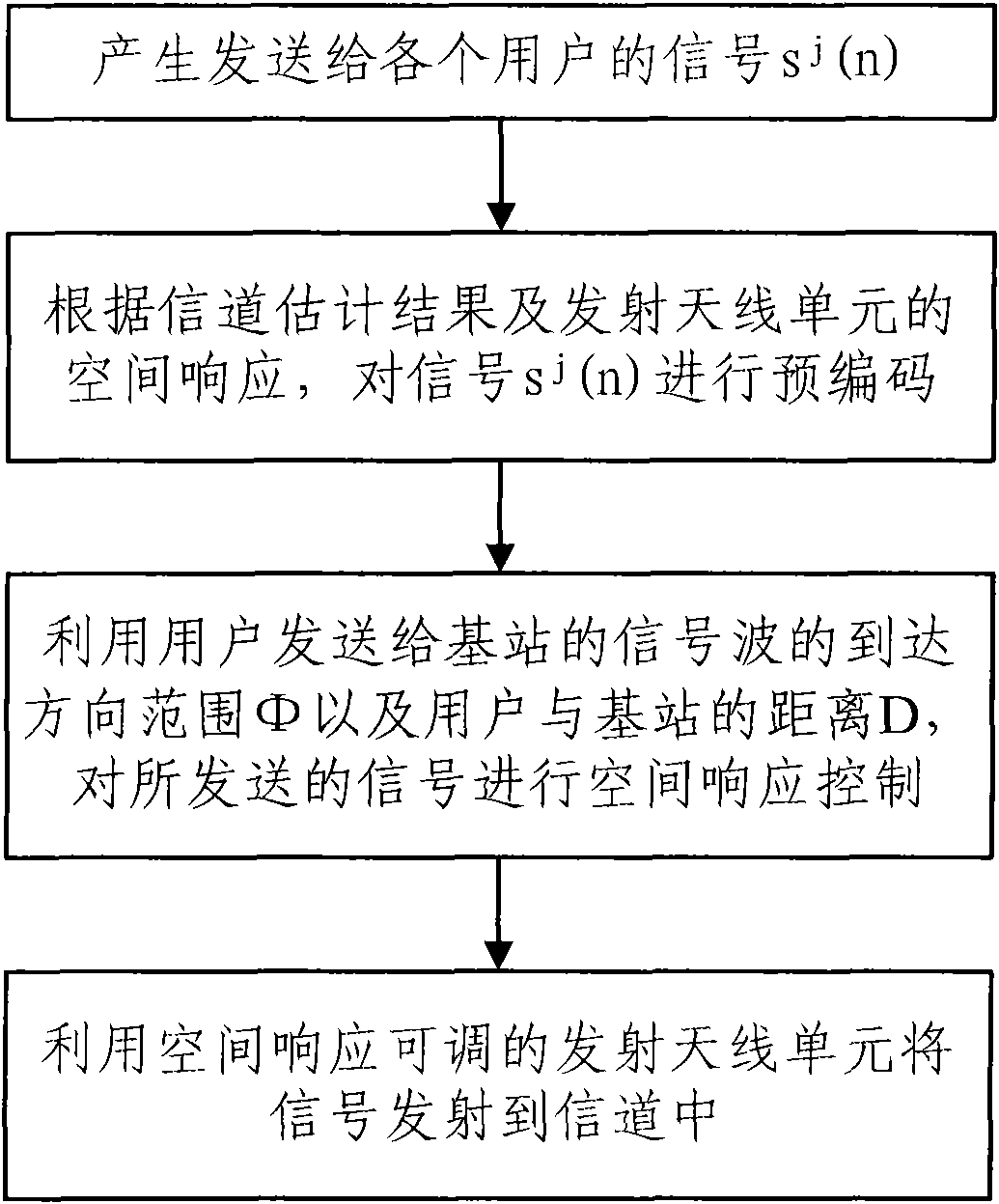
The invention discloses a signal emission method of a down link in a multi-user MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system. The signal emission method comprises the following steps of: generating a signal sj(n) transmitted to each user; pre-coding the signal sj(n) according to a channel estimation result and the spatial response of a transmitting antenna unit; controlling the spatial response of the transmitted signal by utilizing the arrival direction range phi of signal waves transmitted to a base station by the users and a distance D between each user and the base station; and transmitting the signal to a channel by utilizing the transmitting antenna unit with adjustable spatial response. The invention also discloses a signal emission device of the down link in the multi-user MIMO system. The invention adopts the antenna unit with adjustable spatial response to improve the receiving signal to interference ratio and can emit the signal only aiming at the users within a specific direction range through adjusting the weighting amplitudes and the phases of each array element signal in the antenna unit, thereby the emission power and the interferences among multiple users are reduced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for intersymbol interference removal in data recovery
InactiveUS7002762B2Efficient removalModification of read/write signalsSignal processing for reducing noiseImaging qualityOriginal data
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Minimum norm sence reconstruction for optimal spatial response
InactiveUS20060186941A1Low densitySignificant scan-time reductionMagnetic measurementsPulse automatic controlSignal responseMinimum norm
A novel magnetic resonance imaging method is described, wherein undersampled magnetic resonance signals are acquired by a receiver antenna system having spatial sensitivity profiles and the image being reconstructed from the undersampled magnetic resonance signals and the spatial sensitivity profiles. The reconstruction of the image is provided by an optimization of a cost function which accounts for any of noise statistics, signal statistics, and the spatial response function, the latter of which is defined by the spatial signal response from the object to be imaged, separately for each individual pixel.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Acoustic correction apparatus and method for vehicle audio system
ActiveUS8054989B2Improve soundFrequency response correctionTransmissionEngineeringFrequency characteristic
Disclosed herein is an acoustic correction apparatus and method for vehicle audio systems which is capable of providing optimal sound at a reference level to a listener even though the acoustic spatial response characteristics in the room of a vehicle vary due to a change in the material of seat covers or the like. A first acoustic analysis unit obtains target frequency characteristic data at a specific listening location based on generated acoustic signals played from an audio system. A second acoustic analysis unit obtains measured frequency characteristic data at the listening location based on measured acoustic signals collected by the microphone unit. An acoustic correction unit adjusts the equalizer of the audio system based on the target and measured frequency data.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
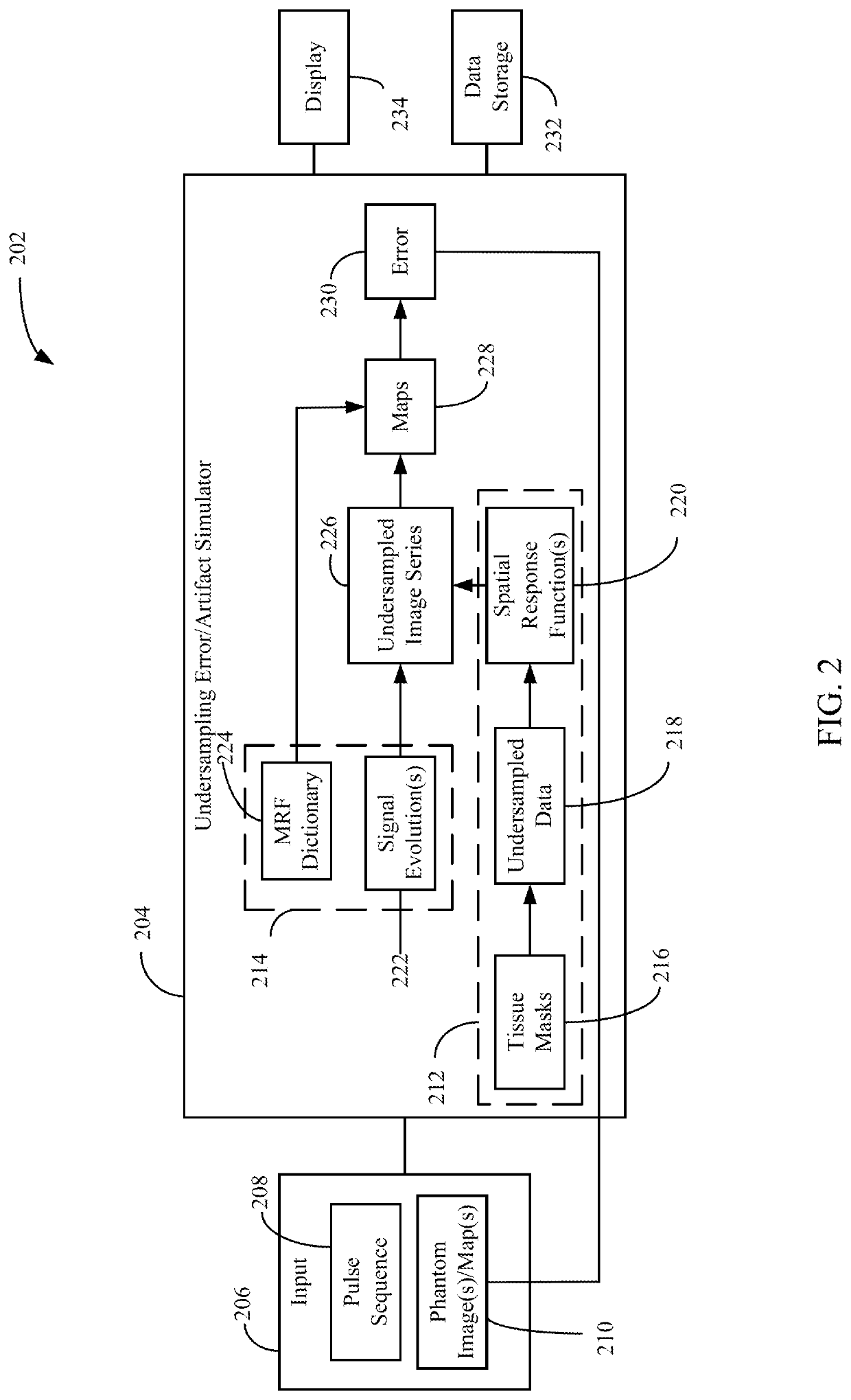
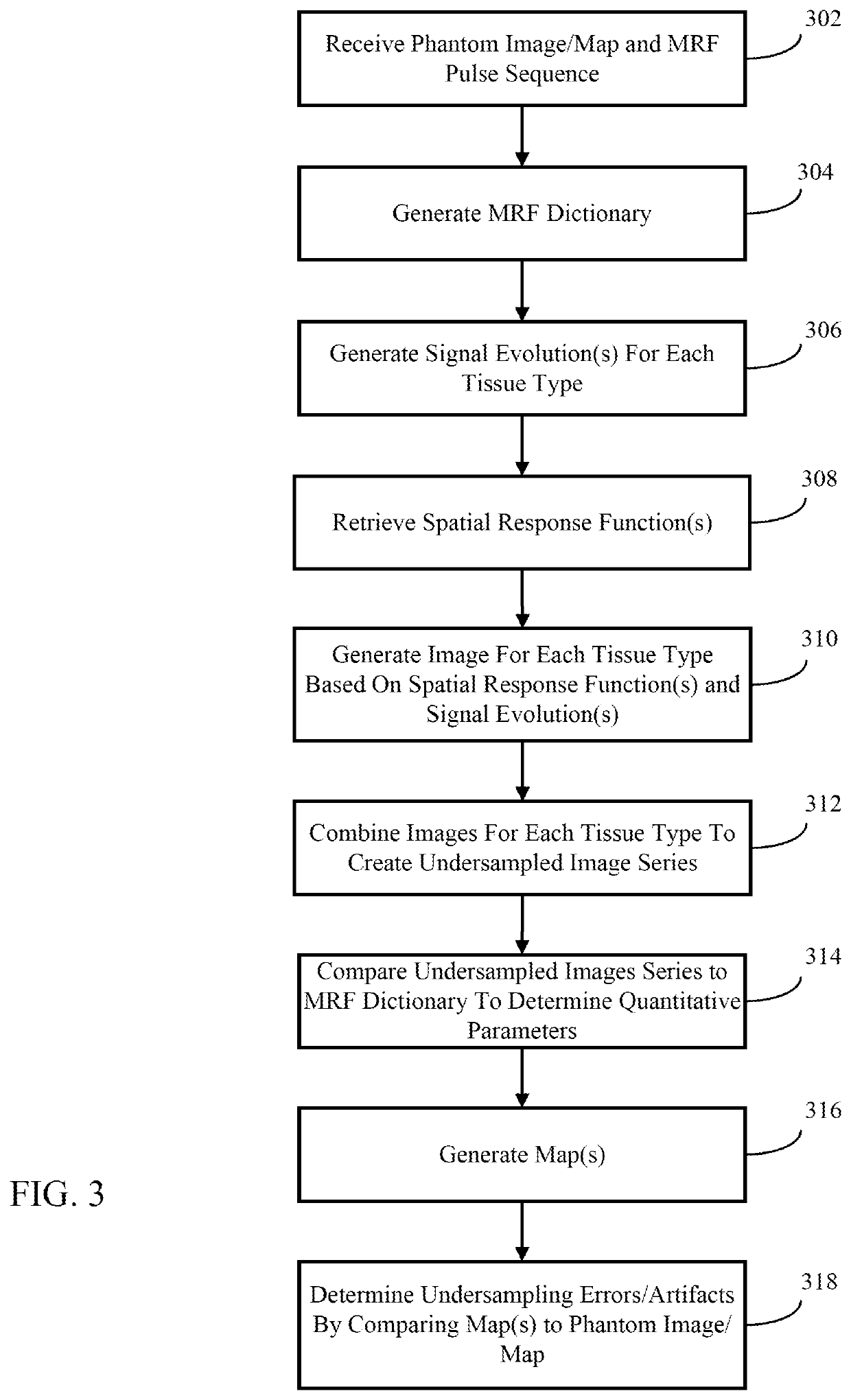
System and method for determining undersampling errors for a magnetic resonance fingerprinting pulse sequence
A method for determining an undersampling error for a magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) pulse sequence includes retrieving a plurality of sets of spatial response functions. Each set of spatial response functions is associated with a tissue type in a reference image and is based on a tissue mask of the reference image for each tissue type. A signal evolution for each tissue type may be generated based on, for example, the MRF pulse sequence, An undersampled image may be generated for each tissue type using the set of spatial response functions and the signal evolutions for the tissue type. At least one quantitative parameter may be determined by comparing an undersampled image series created from the undersampled images to an MRF dictionary. An undersampling error for the MRF pulse sequence may be generated by comparing a quantitative map (or maps) for the quantitative parameter (or parameters) and the reference image.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
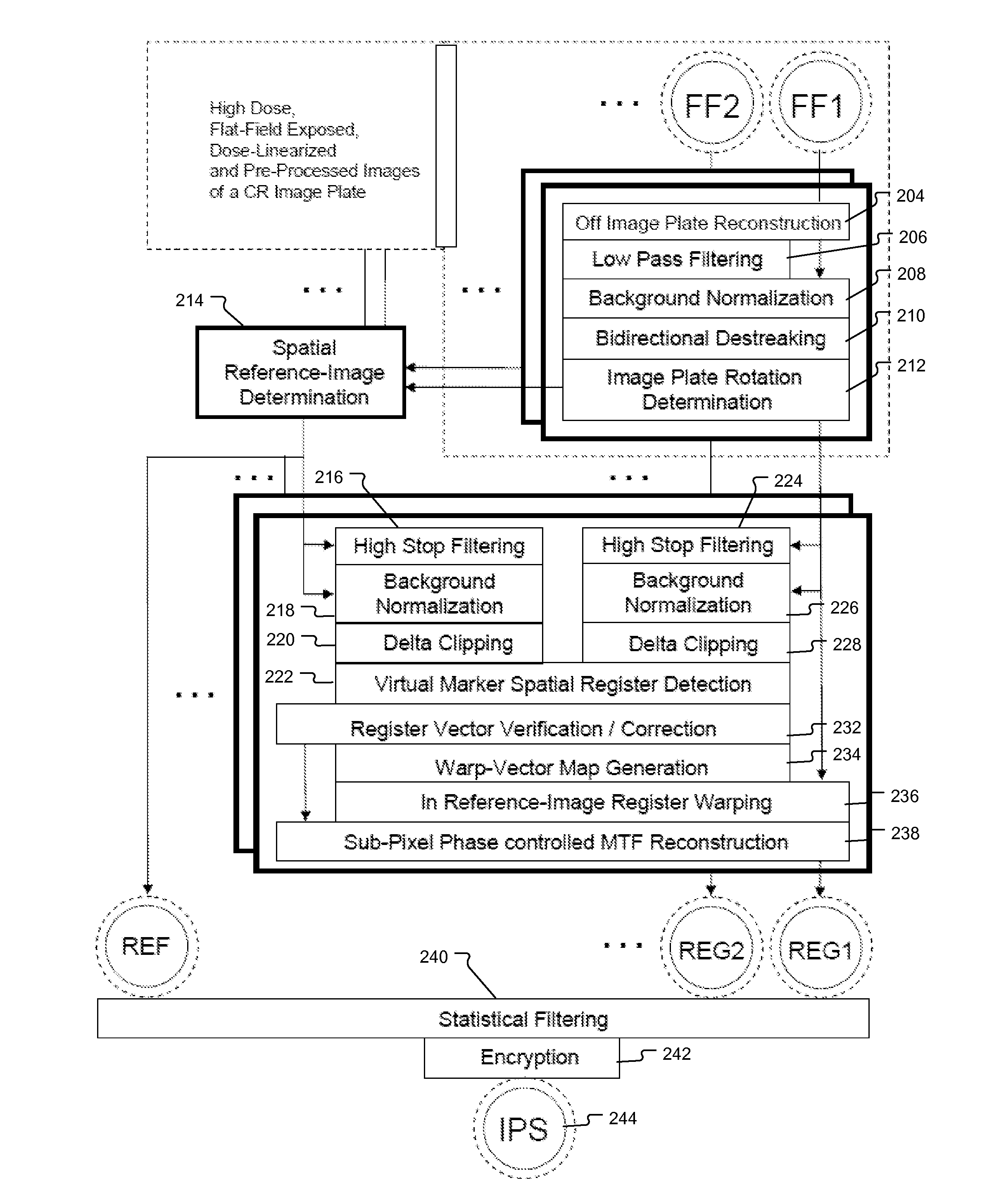
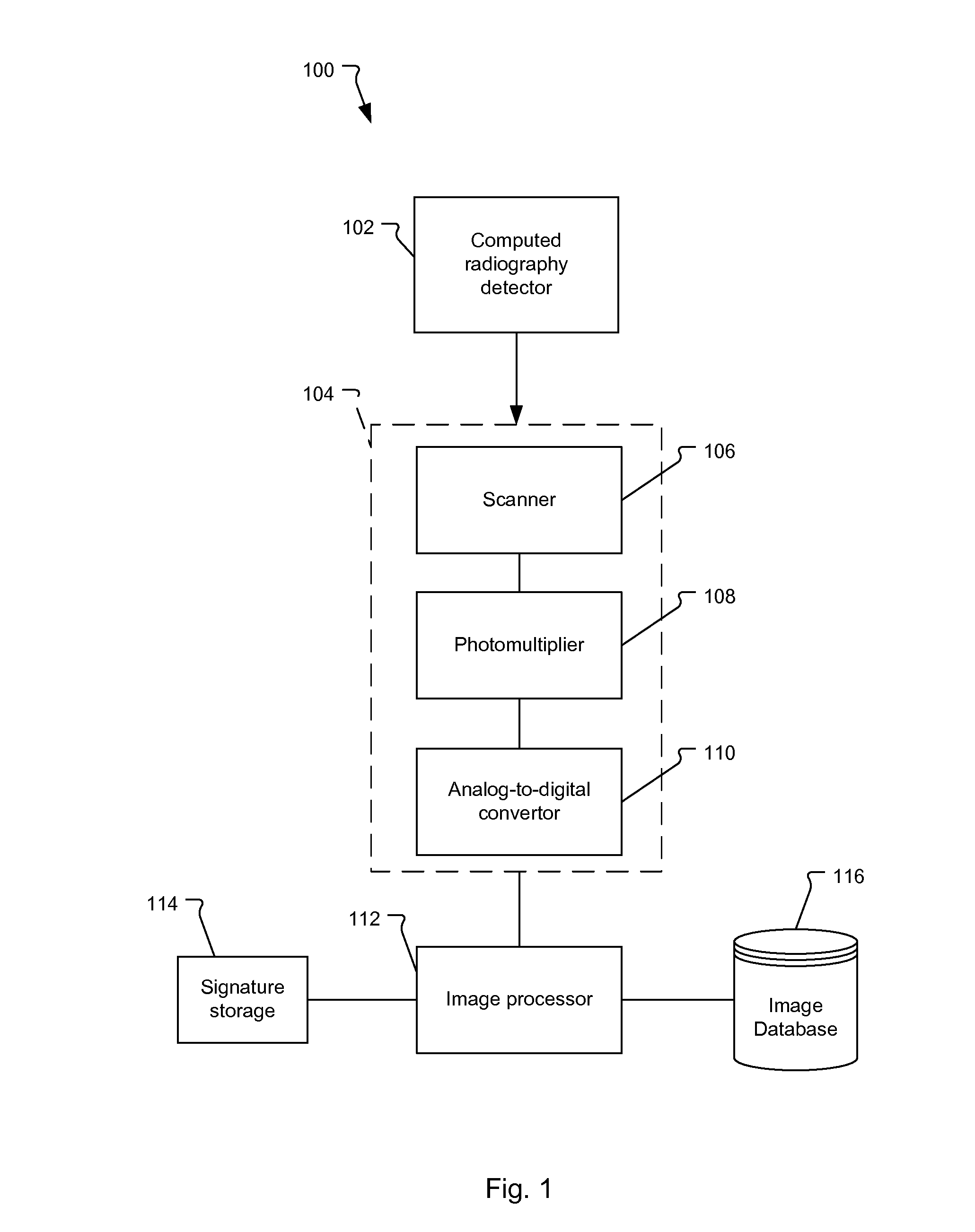
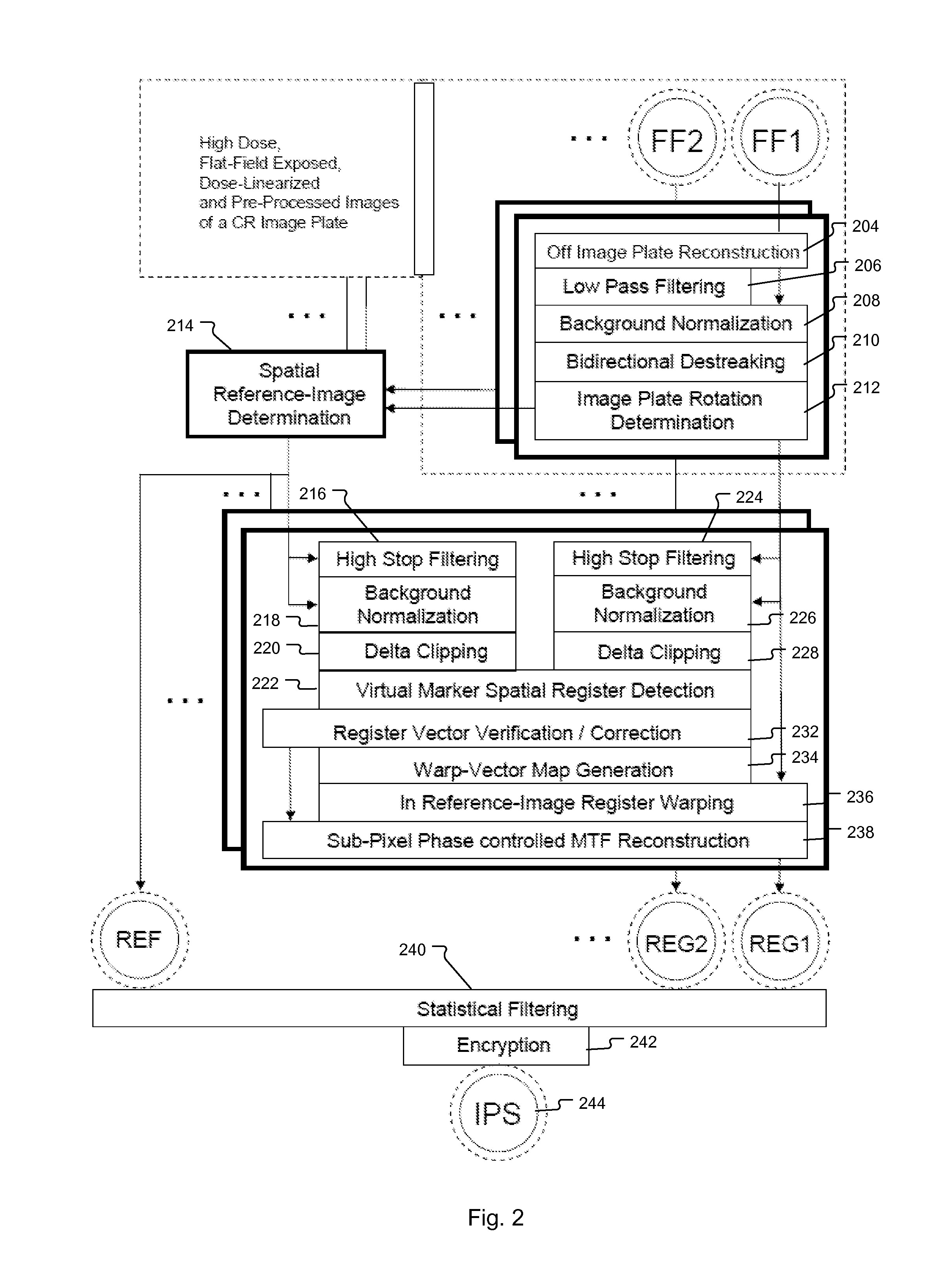
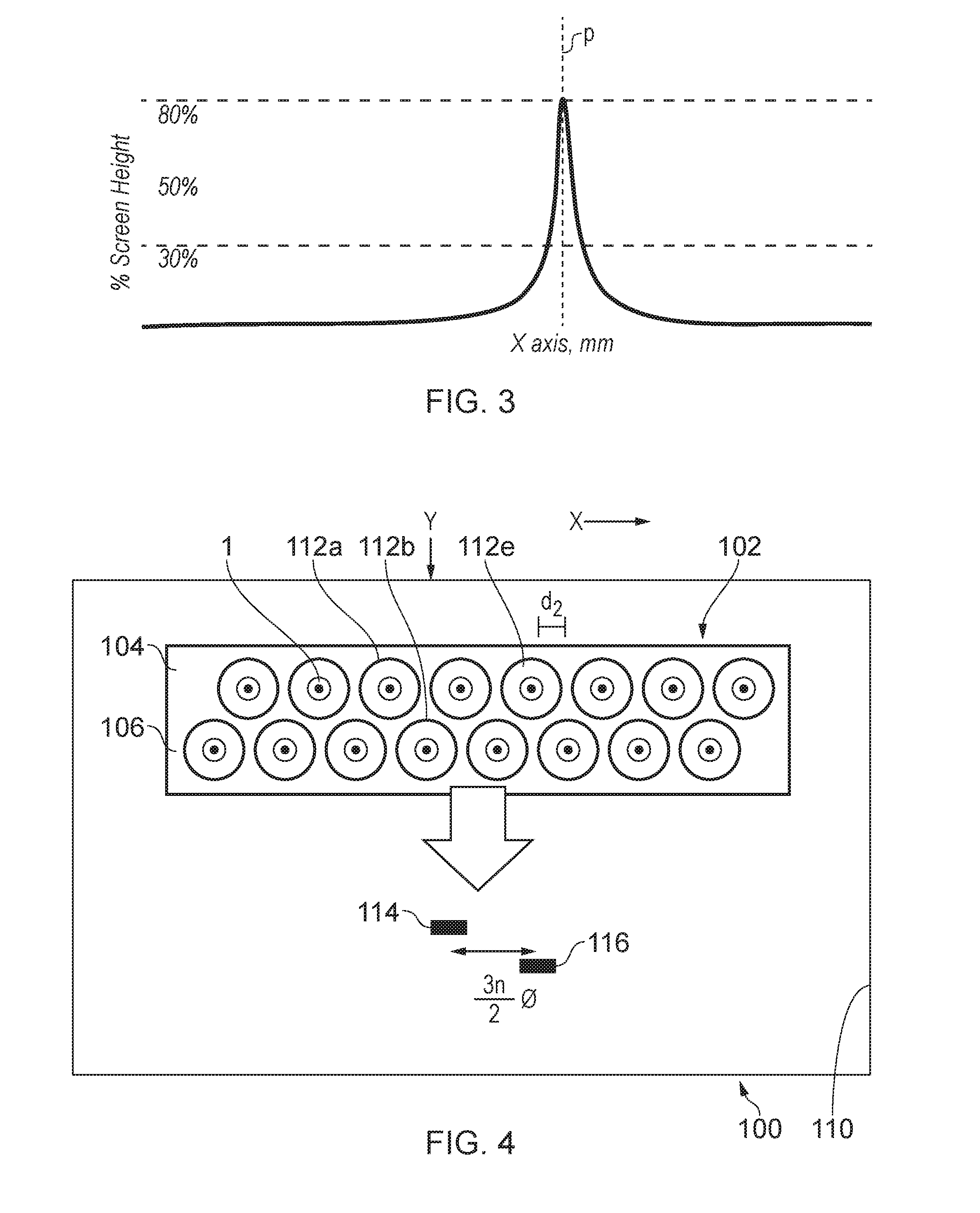
Method of Determining Spatial Response Signature of Detector in Computed Radiography
ActiveUS20130121467A1Sufficient visibilityCostly yield lossMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsPhosphorLow-pass filter
Method and system for determining the spatial response signature of a x-ray detector comprising a photostimulable phosphor by generating a flat field image of the detector, generating a low-pass filtered version of the flat field image and background demodulating the flat field image by pixel-wise dividing it by means of corresponding pixel values in the low-pass filtered version.
Owner:AGFA NV
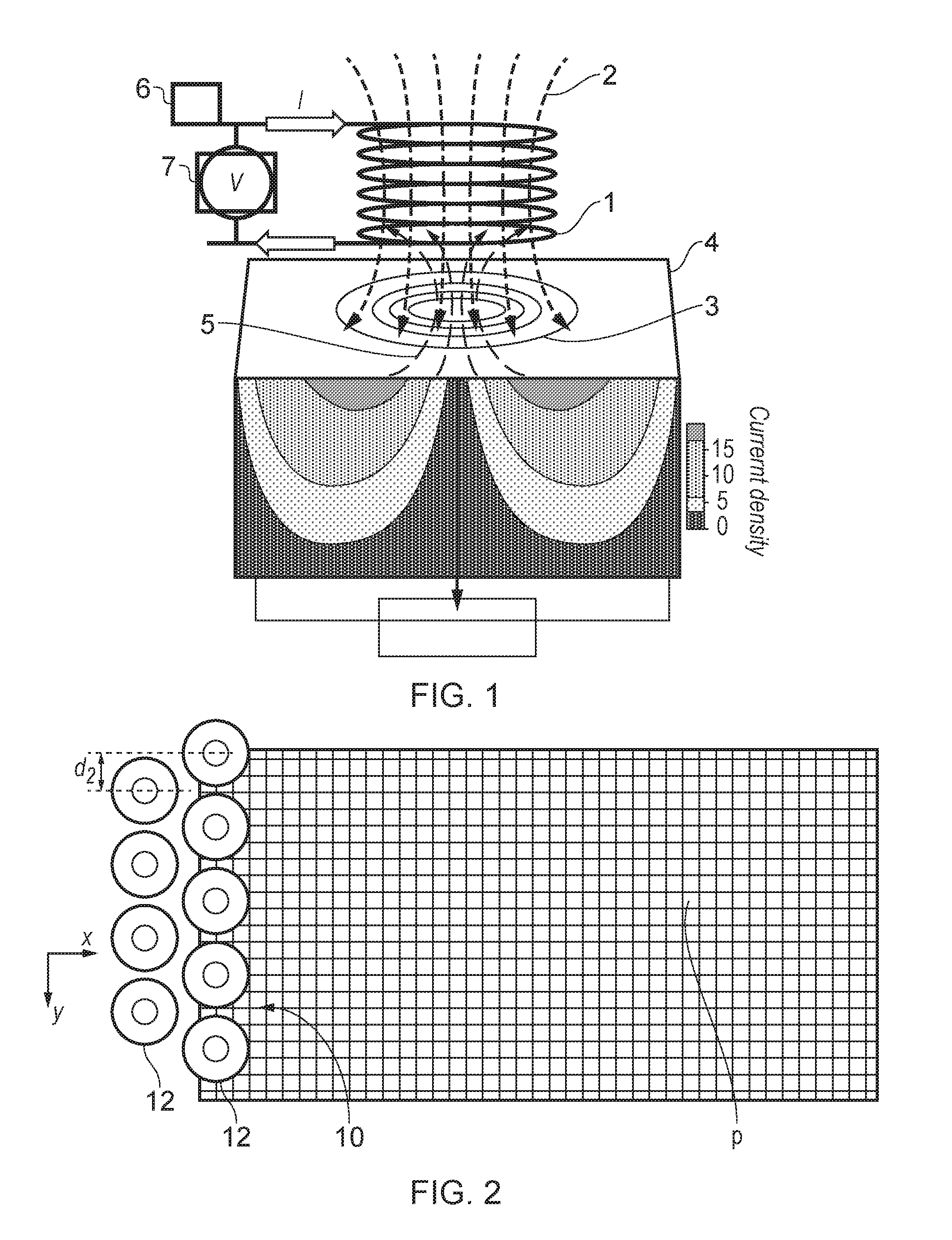
Multi-element sensor array calibration method
ActiveUS20170059683A1Reliable RejectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansApparatus with stored calibration coefficientsElement spaceSensor array
A method of calibrating a sensor array having elements spaced from one another in a first direction, the array defining an array spatial response function, includes: providing a test workpiece having at least first and second calibrated defects spaced apart in the first direction by a characteristic distance such that when the first calibrated surface defect is located at a position corresponding to an array response function maximum, the second calibrated surface defect is located at a position corresponding to an array response function minimum; passing the array across the first and second calibrated surface defects in a direction normal to the first direction and determining a peak sensor signal from at least two of the elements in the array to determine an array spatial response function root mean squared average; and setting a rejection threshold as a predetermined proportion of the array spatial response function root mean squared average.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Image domain segmented echo planar magnetic resonance imaging using a 2D excitation radiofrequency pulse
ActiveUS9797970B2Accurate imagingImprove spatial resolutionCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientRadio frequency
Representative methods and systems are disclosed for reducing image distortion or increasing spatial resolution in echo planar magnetic resonance imaging. In representative embodiments, a targeted field of view (FOV) image is divided into segments, with each segment having a predetermined overlap region with an adjacent segment, such as in a phase-encoding direction. Image data is acquired for each segment, sequentially or simultaneously, using a reduced phase-encoding FOV with a 2D radiofrequency (RF) excitation pulse, and rotated and scaled magnetic field gradients. The 2D RF excitation pulse may also be modulated, such as onto a plurality of different carrier frequencies, for simultaneous acquisition of multiple segments in the same imaging plane. Using the spatial response of the 2D RF excitation pulse, the acquired image data for each segment of the plurality of segments is combined to generate a combined magnetic resonance image having the targeted field of view.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
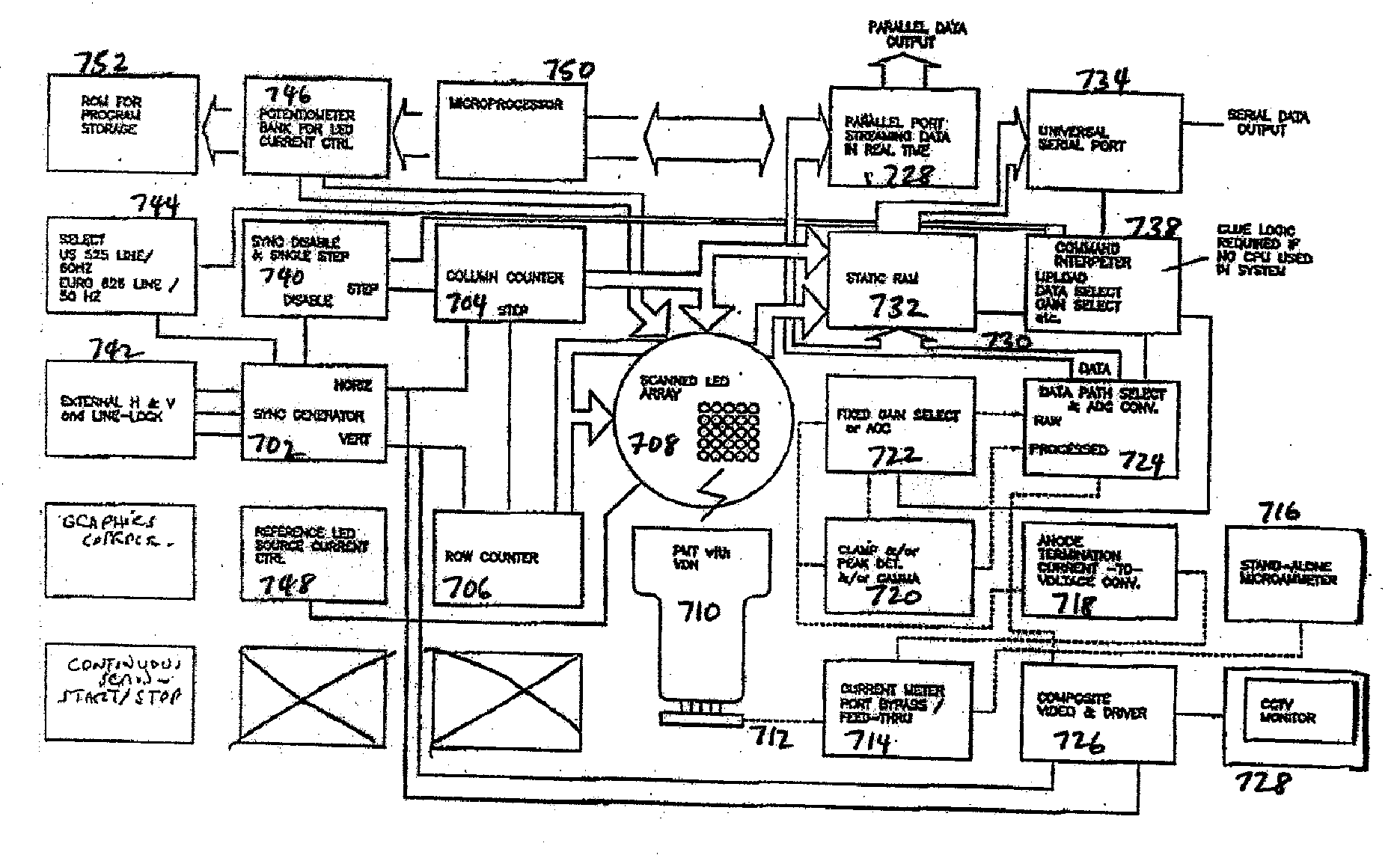
Video Presentation of Photomultiplier Anode Signal
InactiveUS20060273237A1Diminished photoemissionPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansResponsivityDisplay device
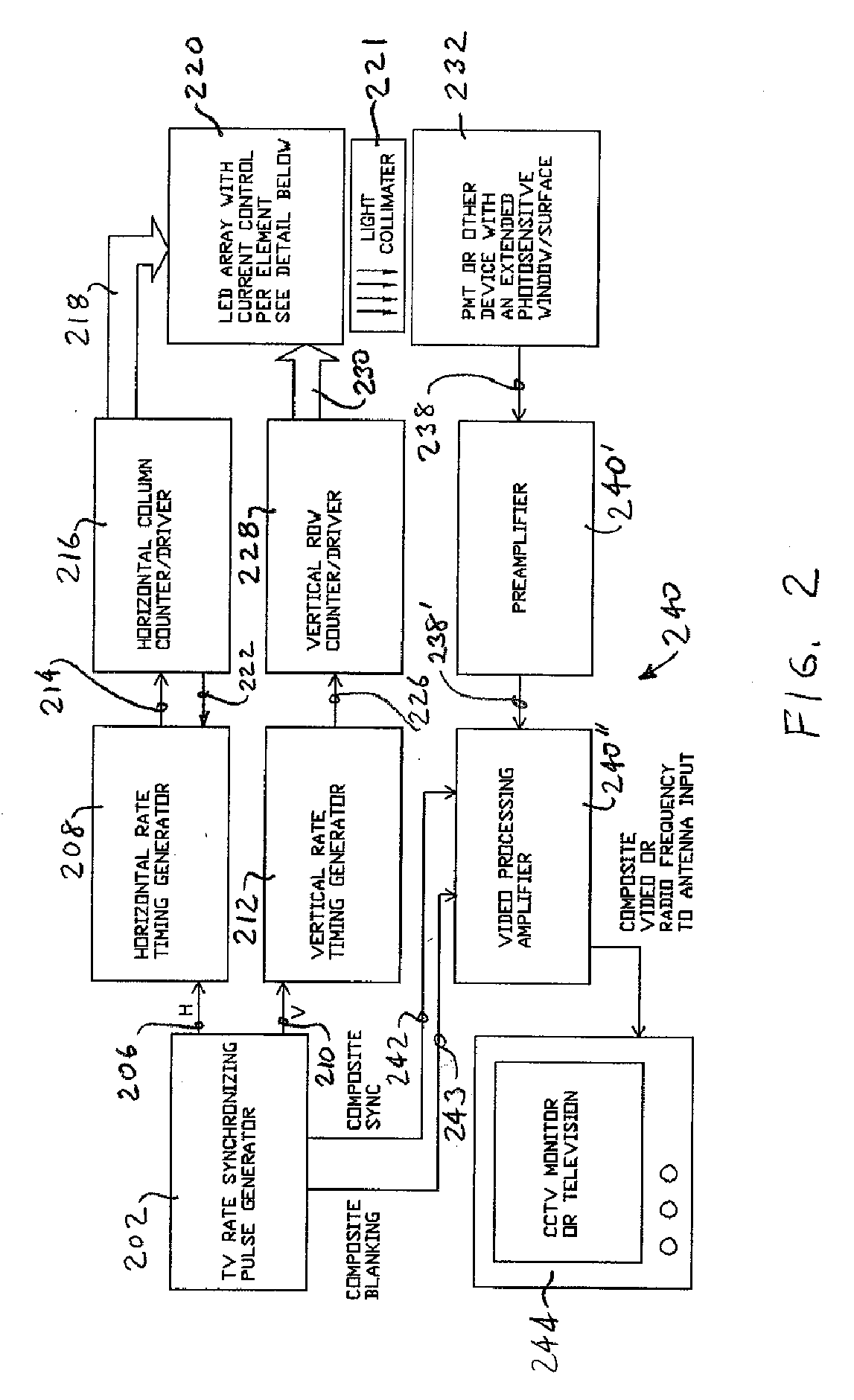
An apparatus and method for video imaging the spatial response of radiation-responsive devices, such as photomultiplier tubes. The apparatus probes the device under-test with an array of radiation emitting elements, such as light-emitting diodes, programmed with a scanning sequence such that the device under-test output response, e.g., the anode current of a photomultiplier tube, may serve as a video signal to a video display device such as a television or monitor. A video image so produced provides a map of the spatial response of the radiation-responsive device which may indicate perturbances, flaws, and inhomogeneities in the spatial responsivity of the device.
Owner:BURLE TECH LLC
Component frame enhancement for spatial compounding in ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS9081097B2Character and pattern recognitionAcoustic wave reradiationAnatomical structuresUltrasound imaging
Steered spatial compounding is provided in ultrasound imaging. Component frames of data associated with different spatial response are processed to identify different sources of signals. Matched filtering and / or spatial variance with erosion distinguish between sources of signals, such as distinguishing between (1) anatomical structure and (2) soft tissue and / or noise. The locations in the patient are segmented by the source of signals and different compounding is applied for the different sources.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method of identifying airborne molecular contamination source
PendingCN108548892ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementAnalysing gaseous mixturesComputer scienceContamination
The present disclosure provides a method of identifying an airborne molecular contamination (AMC) leaking source in a fab. The method includes distributing a sensor in the fab, executing a forward computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation of an air flow in the fab, setting an inversed modeling of the forward CFD simulation of the air flow in the fab, building up a database of a spatial response probability distribution matrix of the sensor using an AMC measurement data in the fab, and identifying the AMC leaking source using the database of the spatial response probability distribution matrix of the sensor.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method of identifying airborne molecular contamination source
InactiveCN103713096ASemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementAnalysing gaseous mixturesComputer scienceContamination
The present disclosure provides a method of identifying an airborne molecular contamination (AMC) leaking source in a fab. The method includes distributing a sensor in the fab, executing a forward computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation of an air flow in the fab, setting an inversed modeling of the forward CFD simulation of the air flow in the fab, building up a database of a spatial response probability distribution matrix of the sensor using an AMC measurement data in the fab, and identifying the AMC leaking source using the database of the spatial response probability distribution matrix of the sensor.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
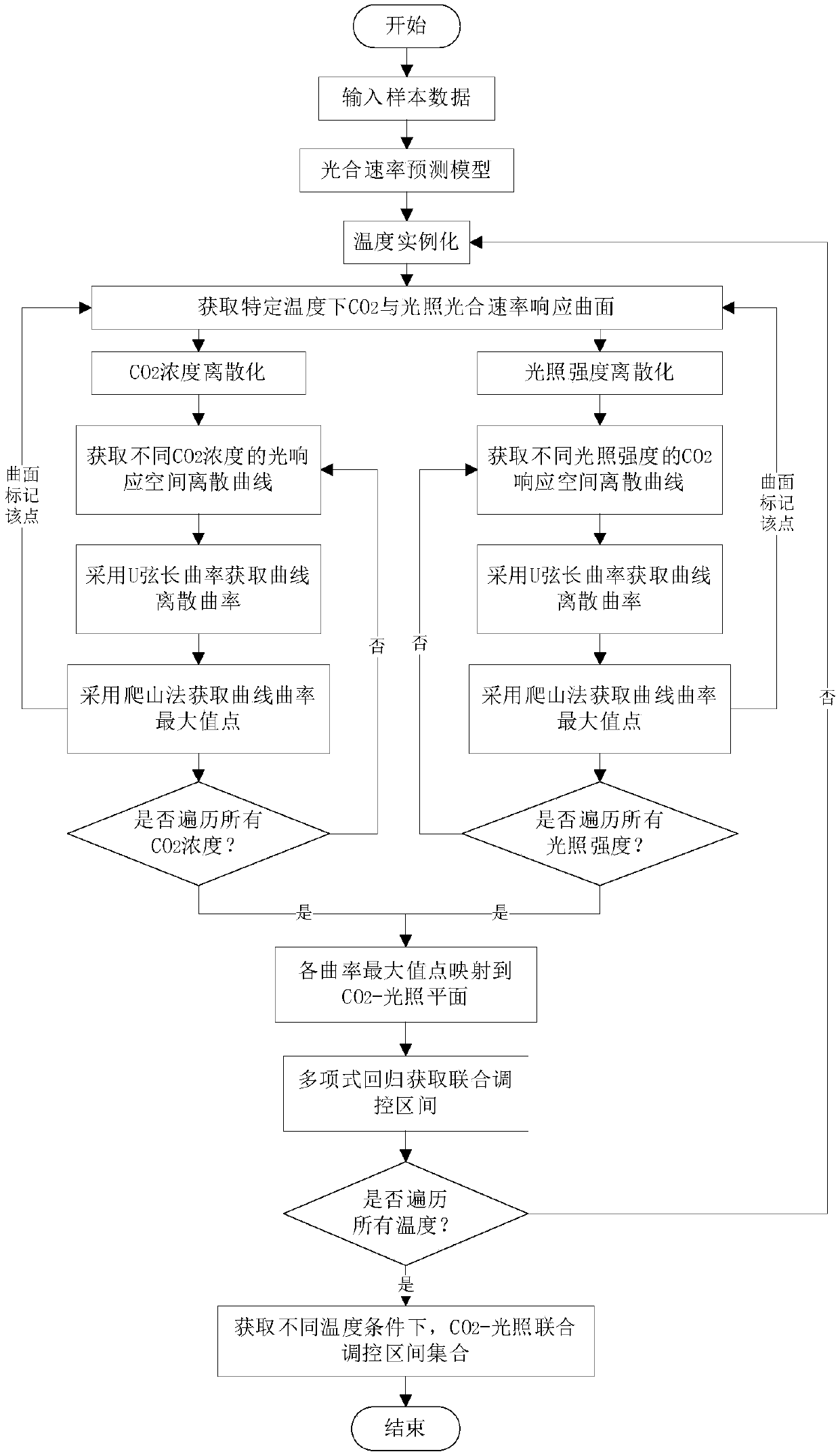
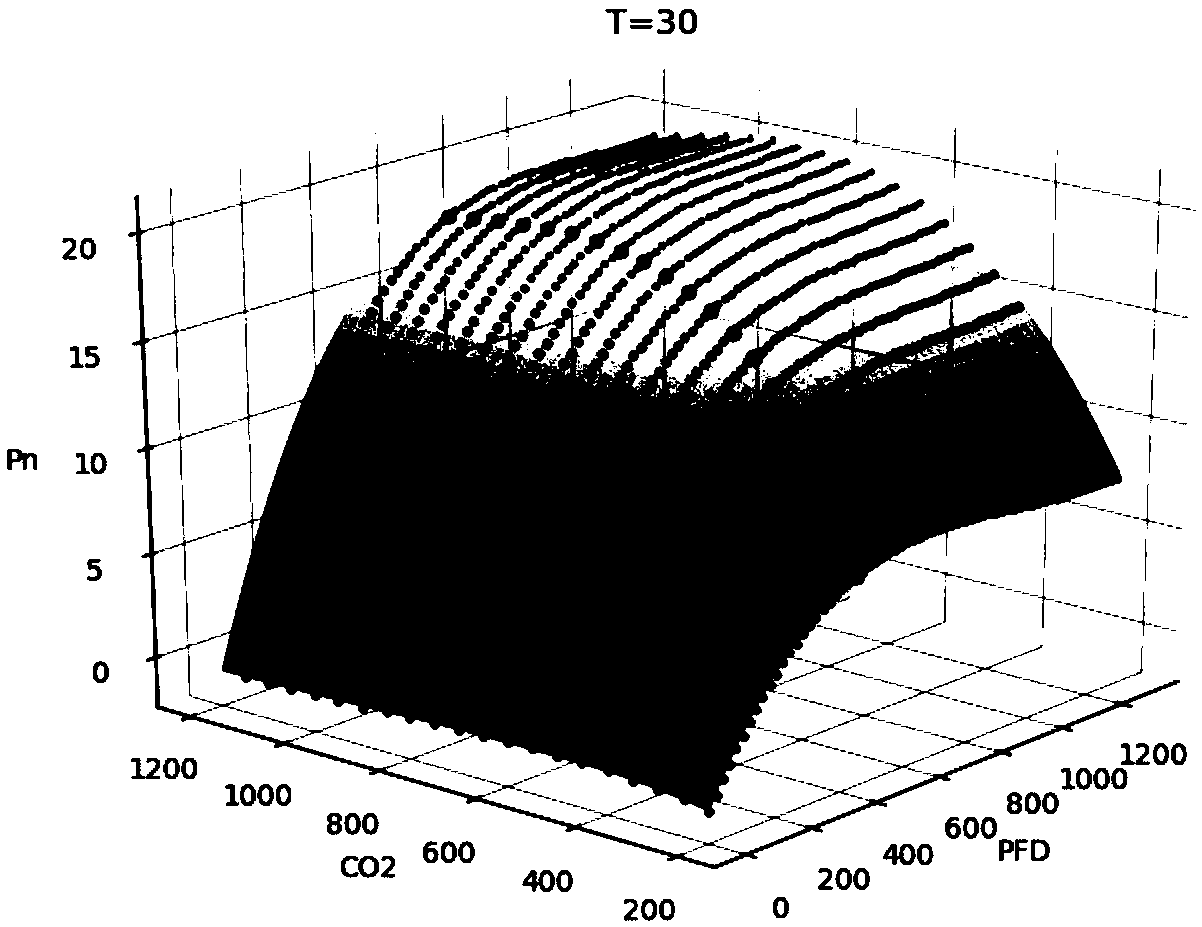
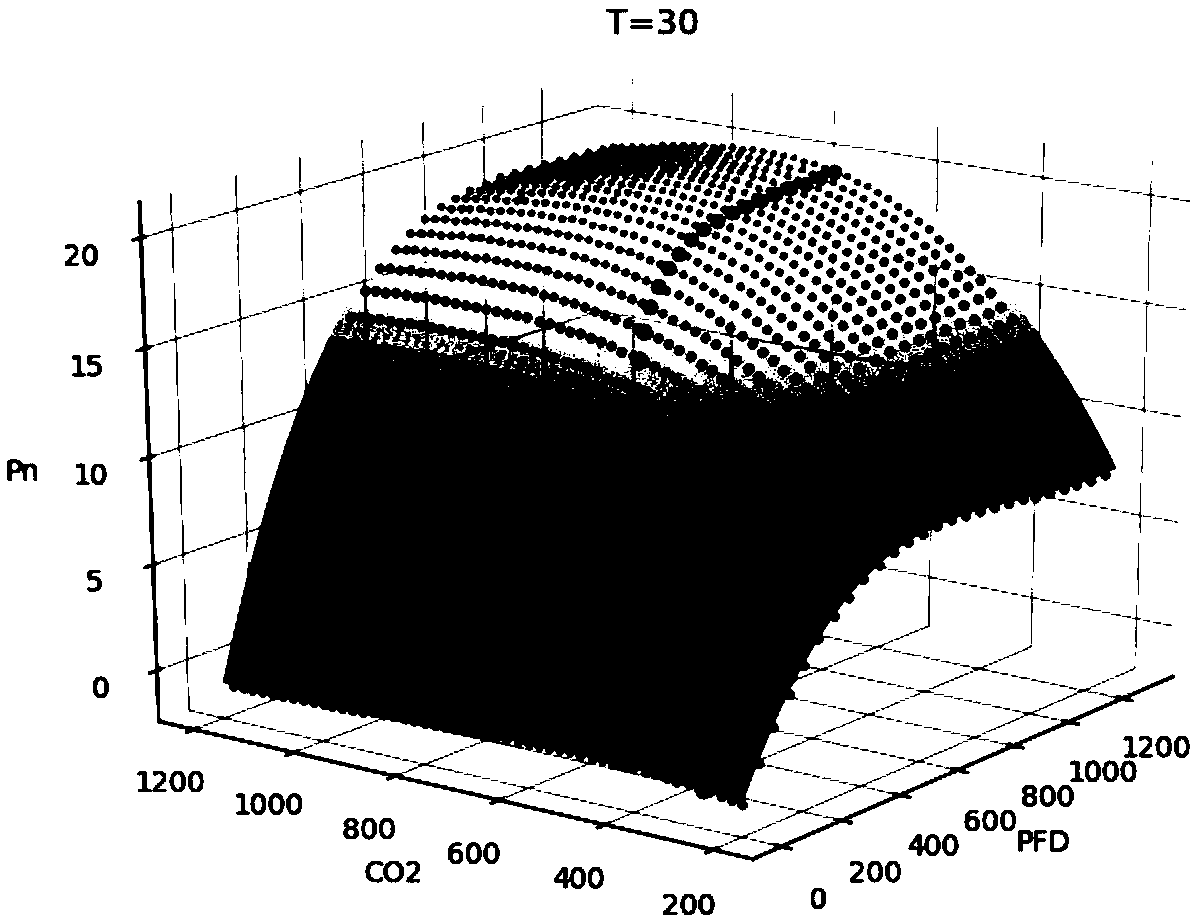
A method for obtaining two-dimensional joint regulation target region based on regulation benefit priority
ActiveCN109102420ASolve the basic theoretical problems of efficient regulationPhotosynthetic rate decreasedForecastingCouplingUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a two-dimensional combined regulation target area acquisition method based on the priority of regulation benefit, which comprises steps: temperature, carbon dioxide concentration and light intensity are taken as inputs and photosynthetic rate is taken as outputs, and SVR is adopted to construct a photosynthetic rate prediction model; using photosynthetic rate at differenttemperatures as objective function, carbon dioxide is extracted at different temperatures; a Photosynthetic Surface of a Light Intensity and Discrete Curve Cluster of Spatial Response with Physiological Significance is obtained; using a U-string length curvature-mountain climbing method, a suboptimal photosynthetic surface of carbon dioxide light intensity is obtained that maps to the part of theconcentration illumination intensity coordinate plane of carbon dioxide, the part of the is the two-dimensional joint control target region, namely the two-dimensional coupling constraint condition; compared with the traditional method which takes the maximum point of photosynthetic rate as the control target, Photosynthetic rate is decreased only by 10.69%, but average light demand is decreased by 38.24%, average carbon dioxide concentration is decreased by 12.10%, which has guiding significance for the actual two-factor regulation of facilities and environment.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Constant width beam forming method based on FIR filter
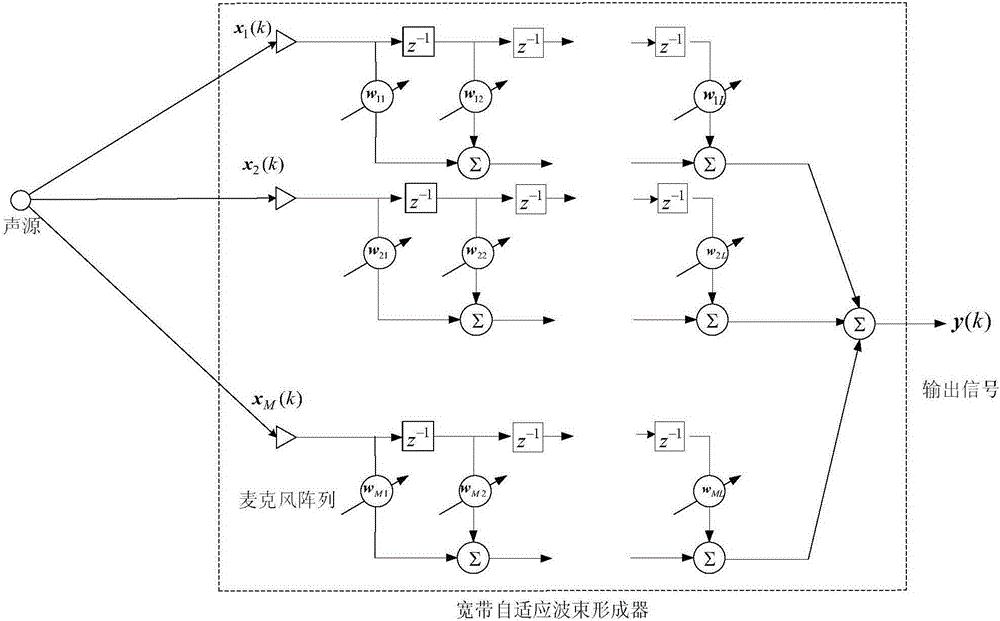
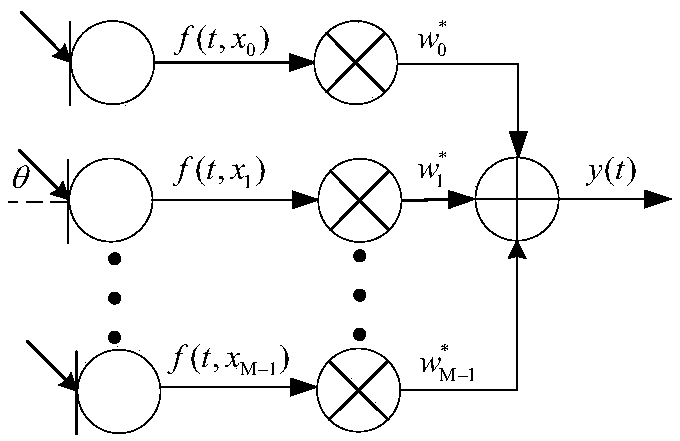
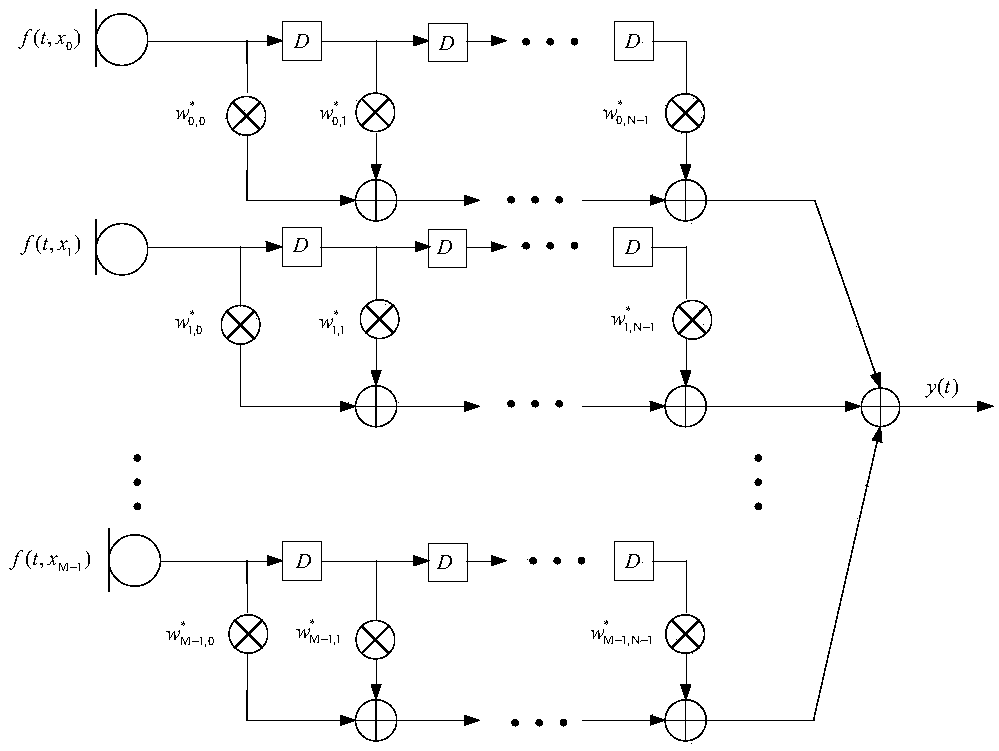
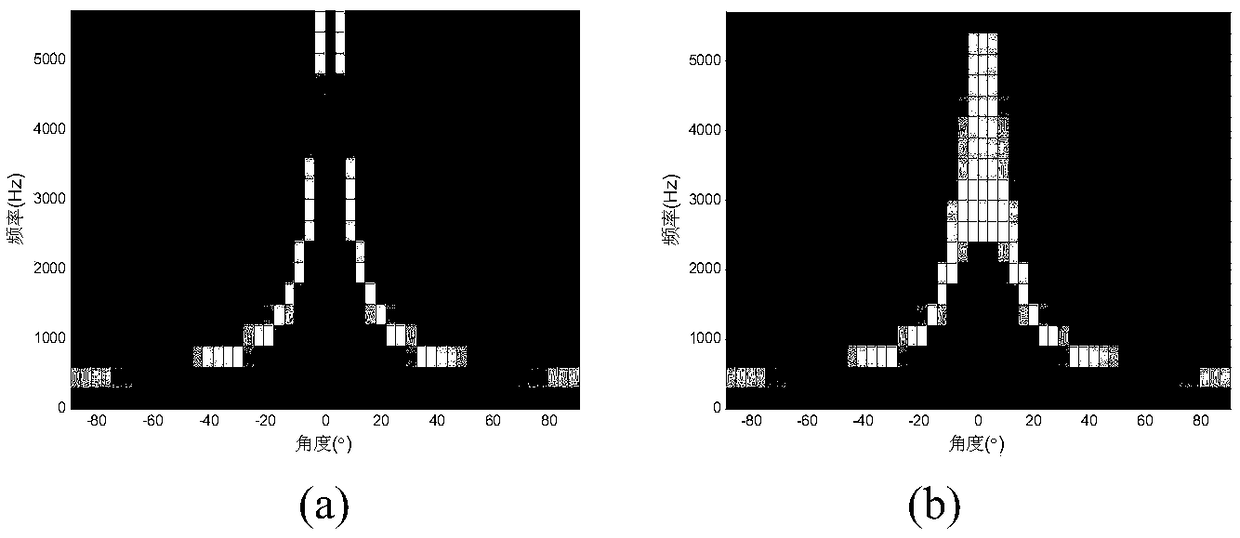
InactiveCN109493844AAchieving frequency invarianceUniform gainSound producing devicesSide lobeArray element
The invention discloses a constant width beam forming method based on an FIR filter, wherein a received signal f (t, x) =[f(t, x0), ..., f(t, xm), ..., f(t, xM-1)] T of a microphone array is processedthrough a beam forming method to obtain an output signal which is shown in the description, wherein f (t, x) represents a sampled signal of the microphone array at a t time position of x, () T represents a matrix transpose, m represents a microphone index, wherein m=0,1,... M-1, M represents the number of microphone array elements, xm represents the array element positions corresponding to the mth microphone, and x=[x0, ... ,xm,... ,xM-1); N represents the order of the FIR filter followed by each microphone, the description represents the coefficient of the n-order FIR filter followed by themth microphone, the superscript * represents the conjugate, and Ts represents the delay between adjacent filters. The method can enable the array to have the same spatial response to input signals with different frequencies within the main lobe width, and the beam forming device with approximately constant beam width and low side lobe array response is designed by utilizing the symmetric properties of the FIR filter array and microphone uniform linear array.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com