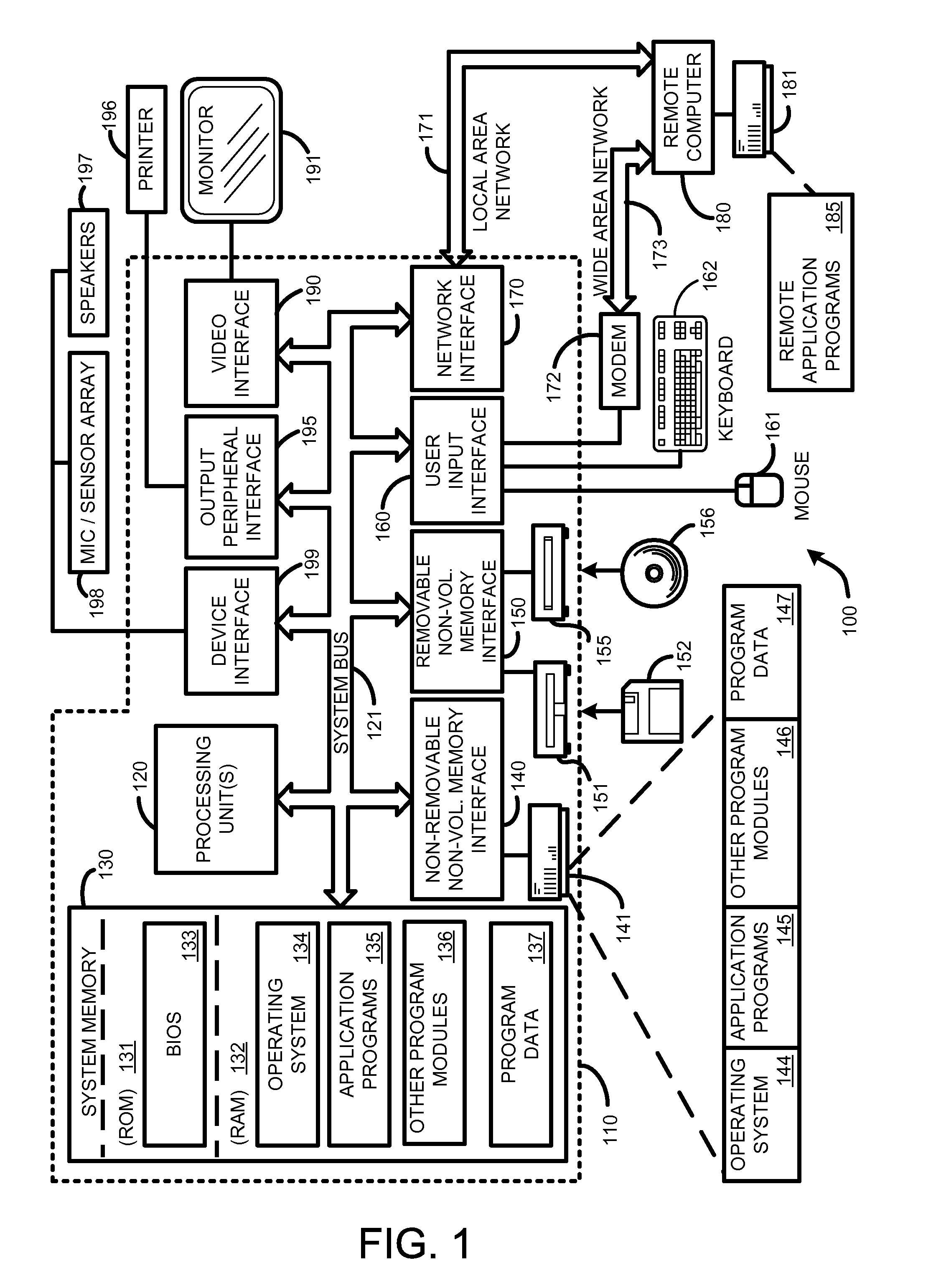
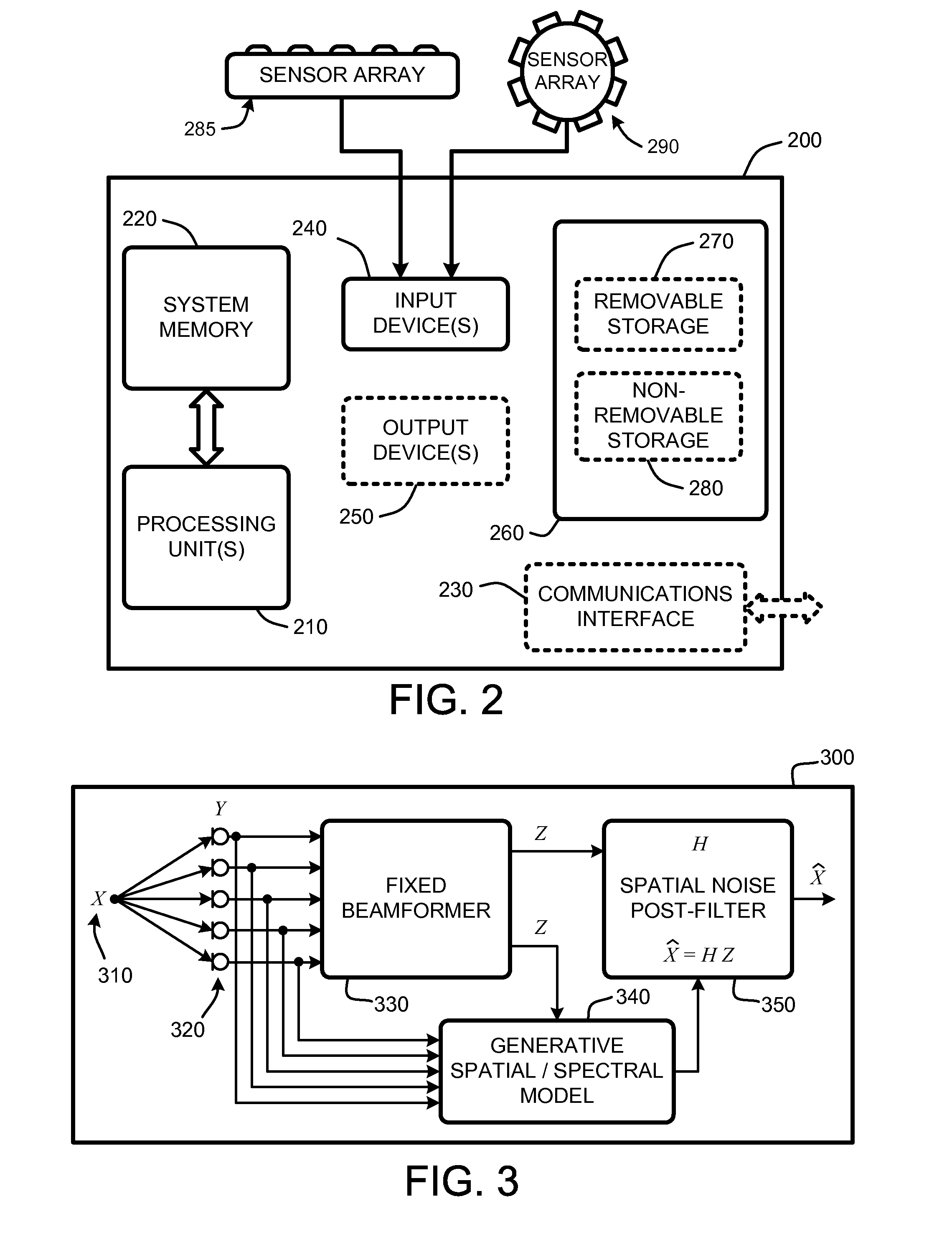
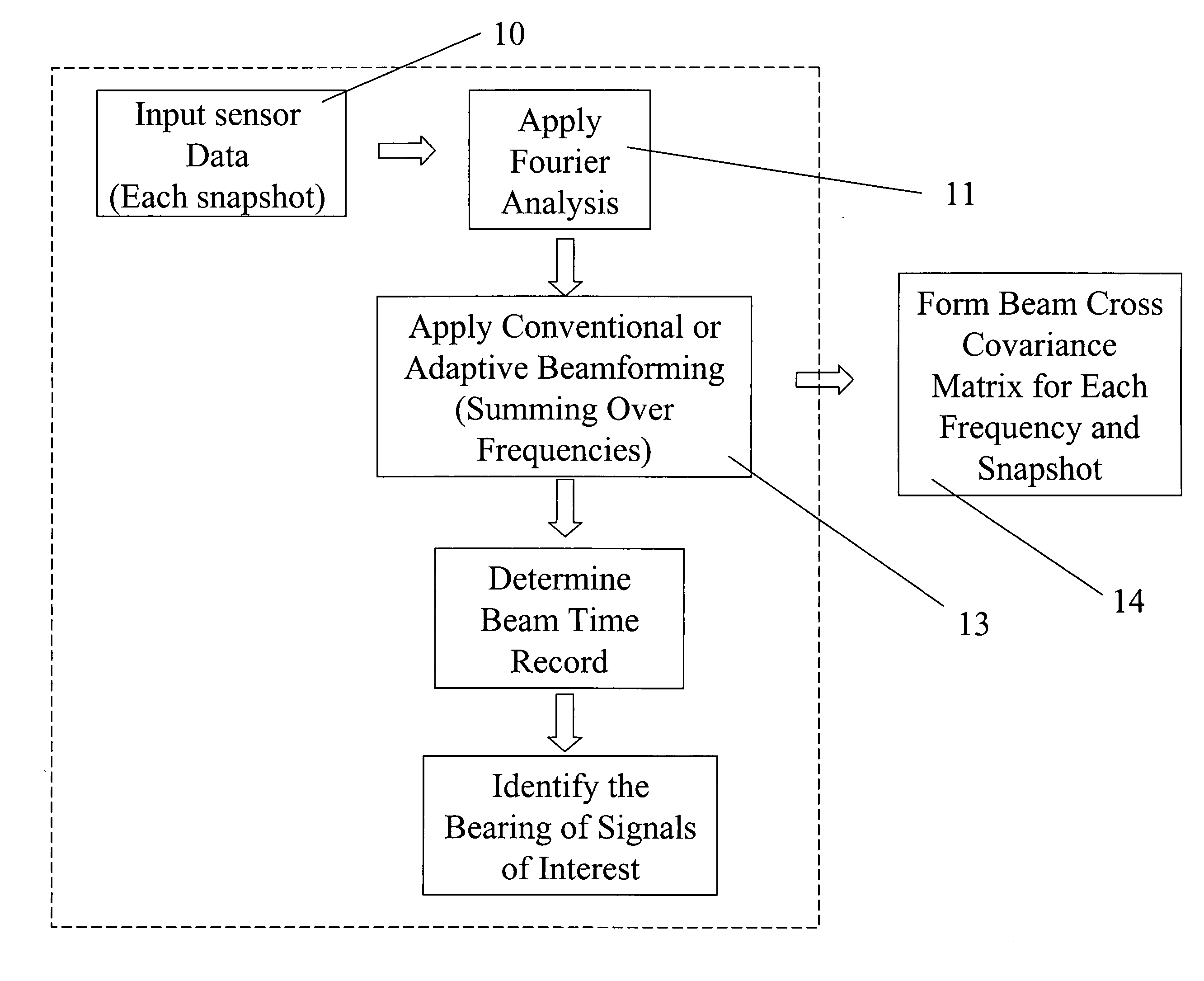
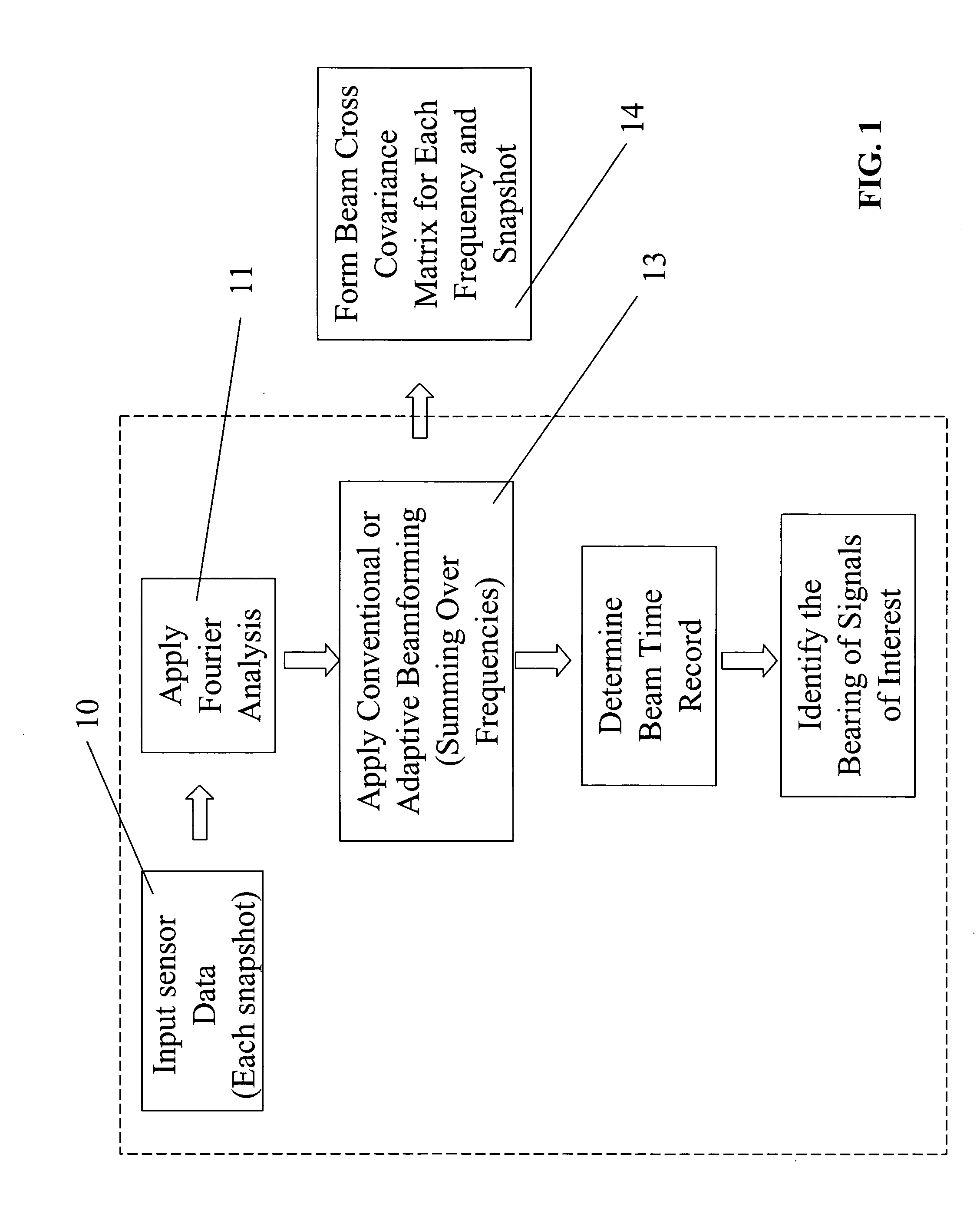
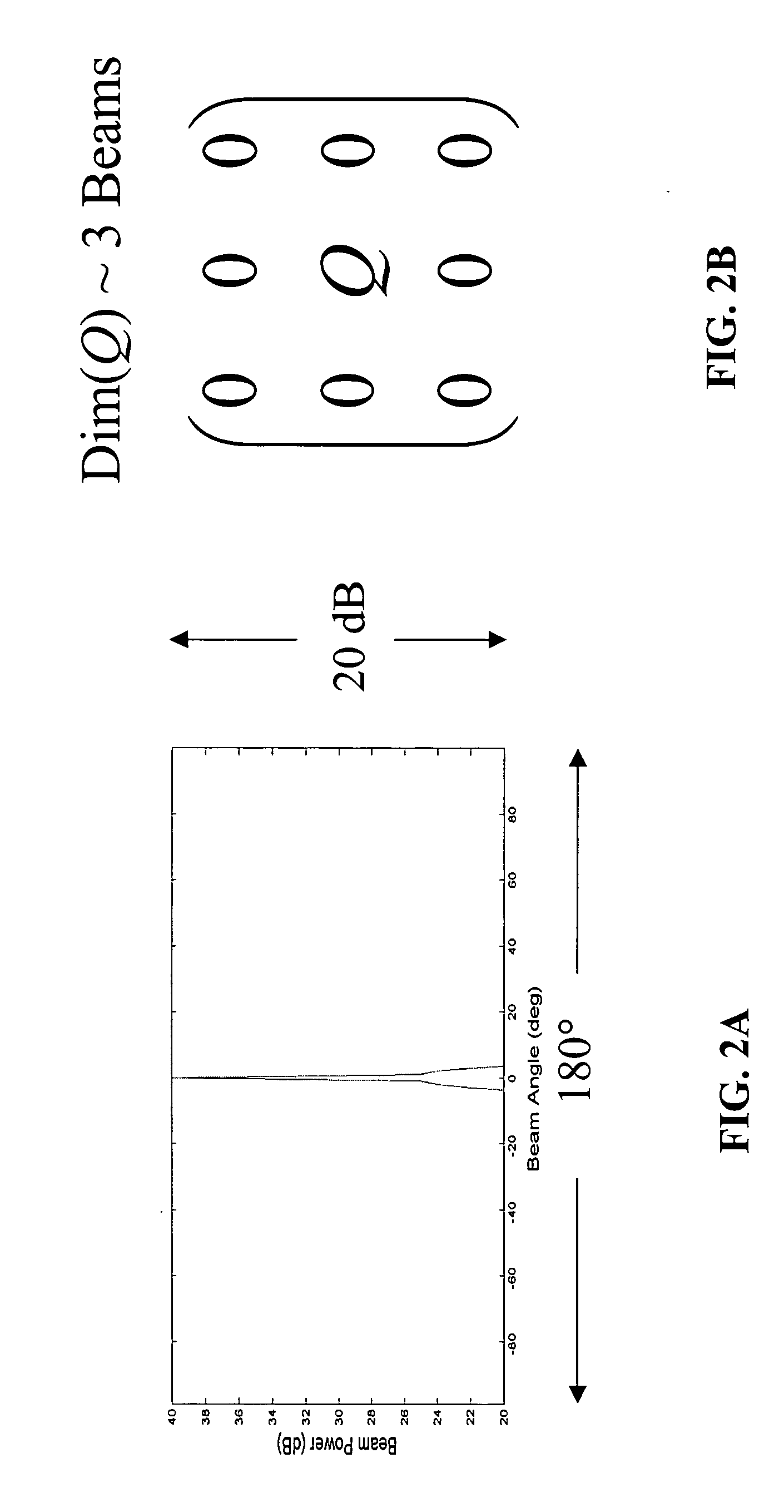
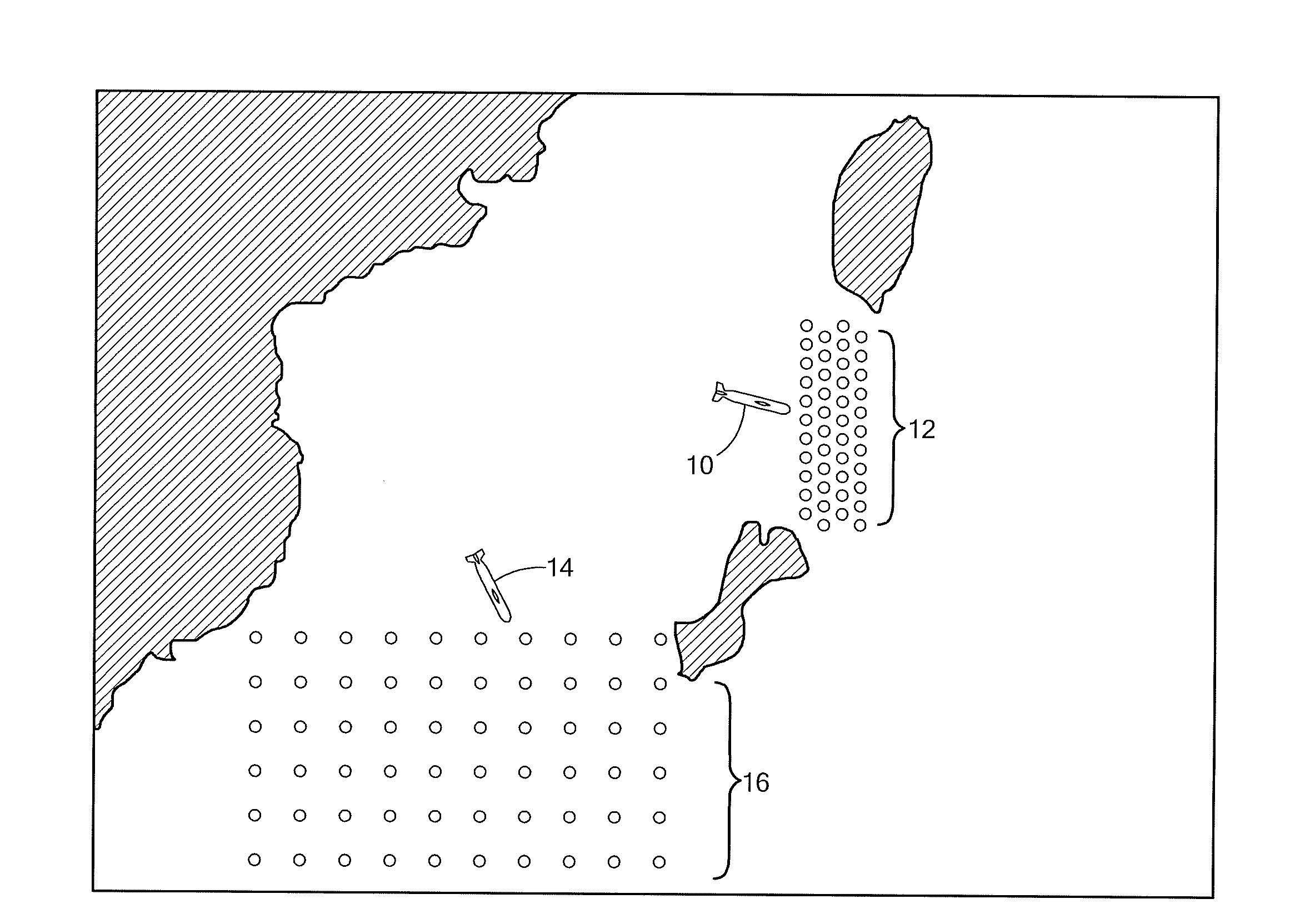
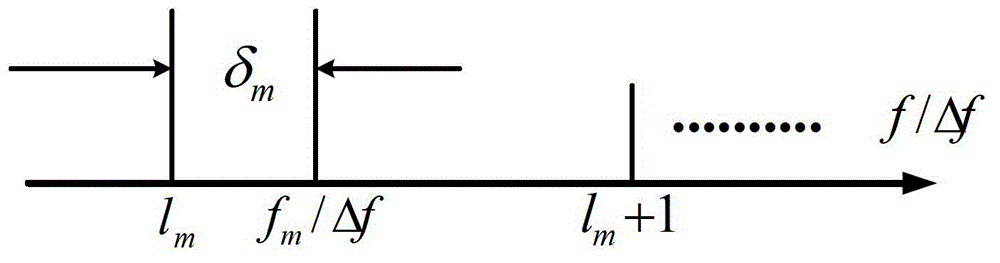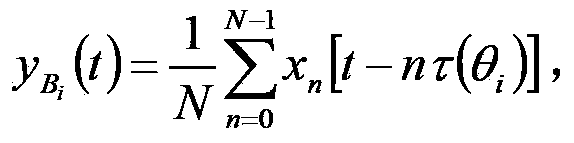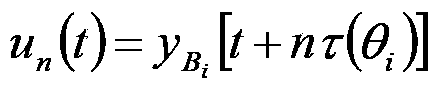Patents
Literature
81results about "Systems with undesired wave elimination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
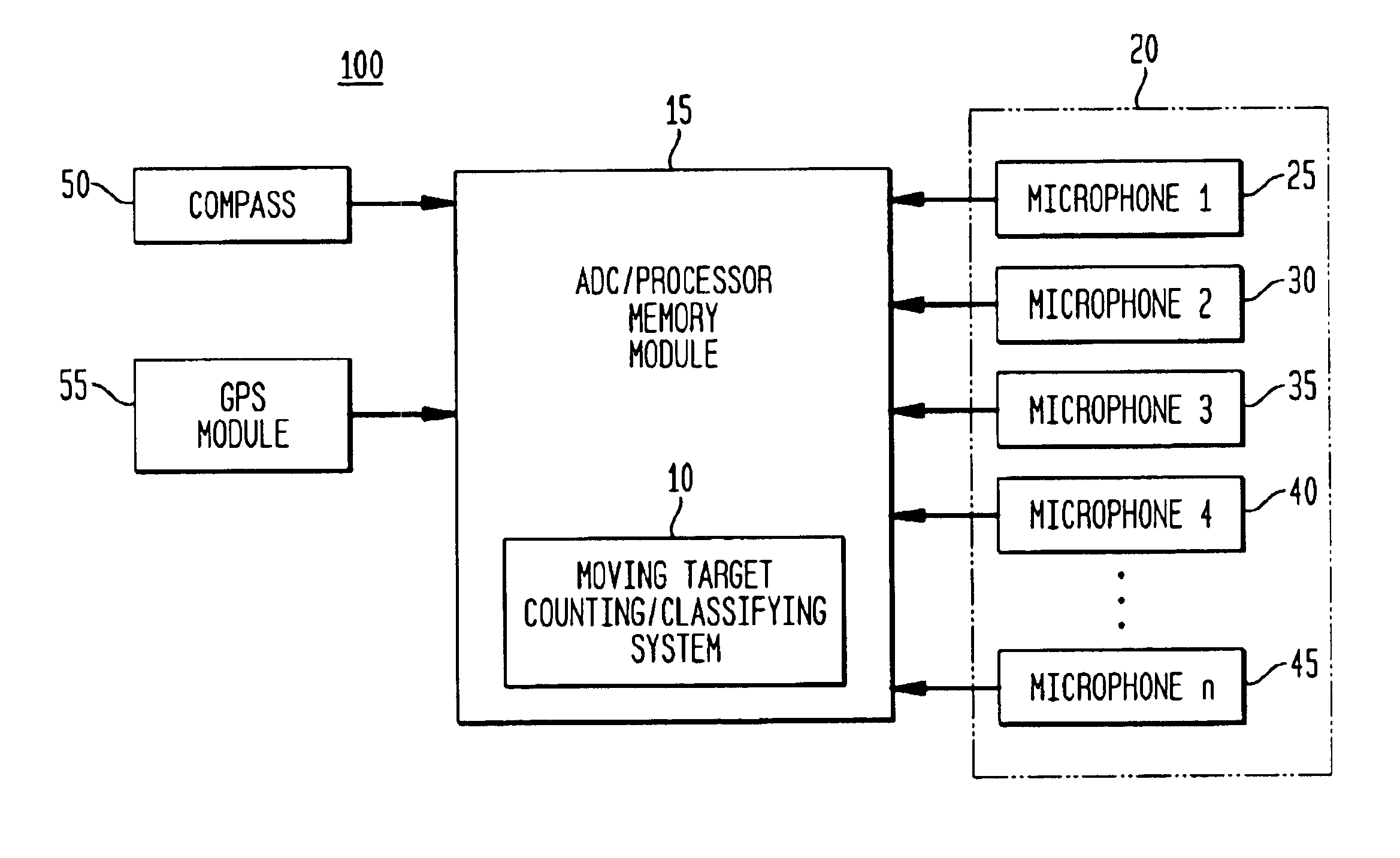
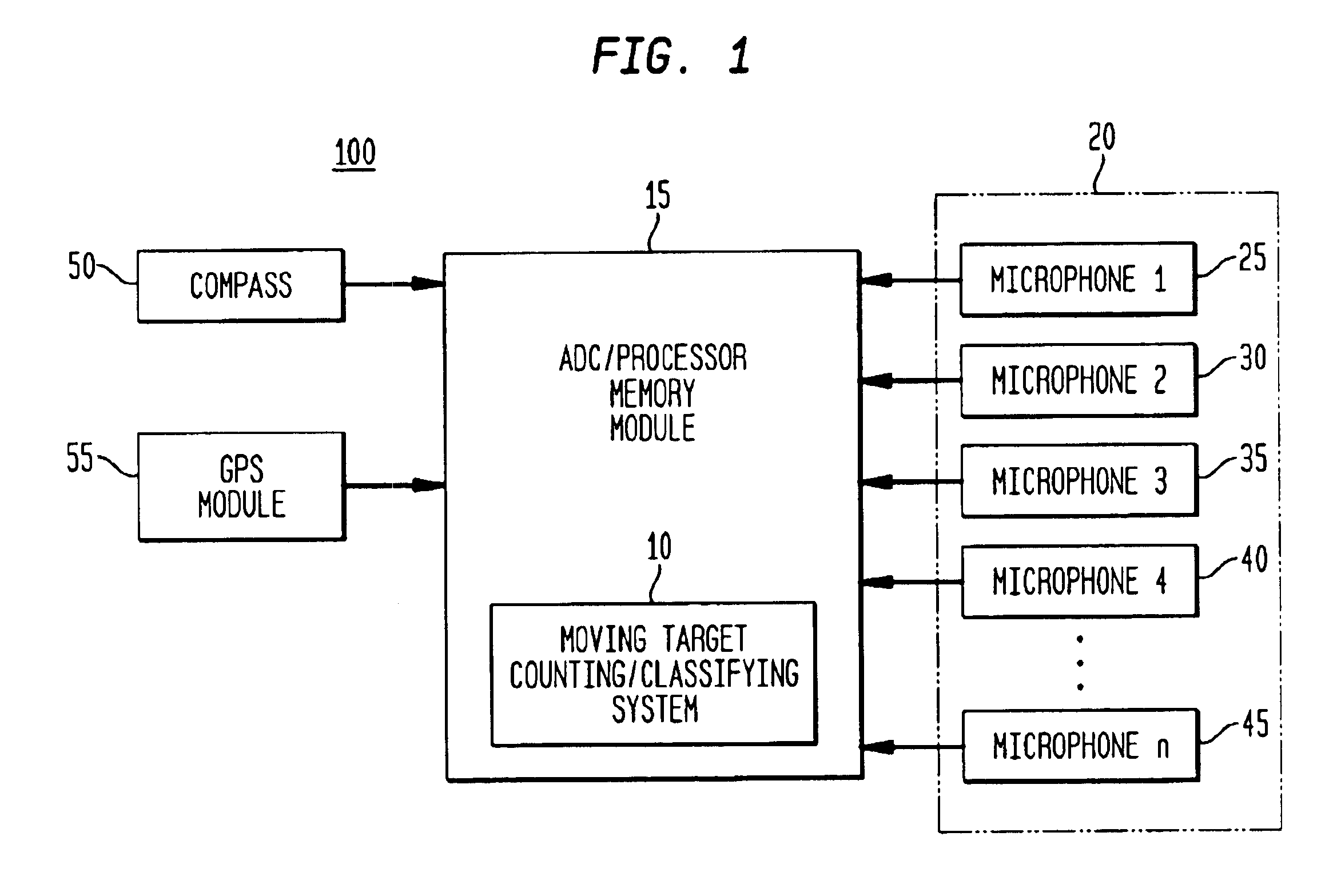
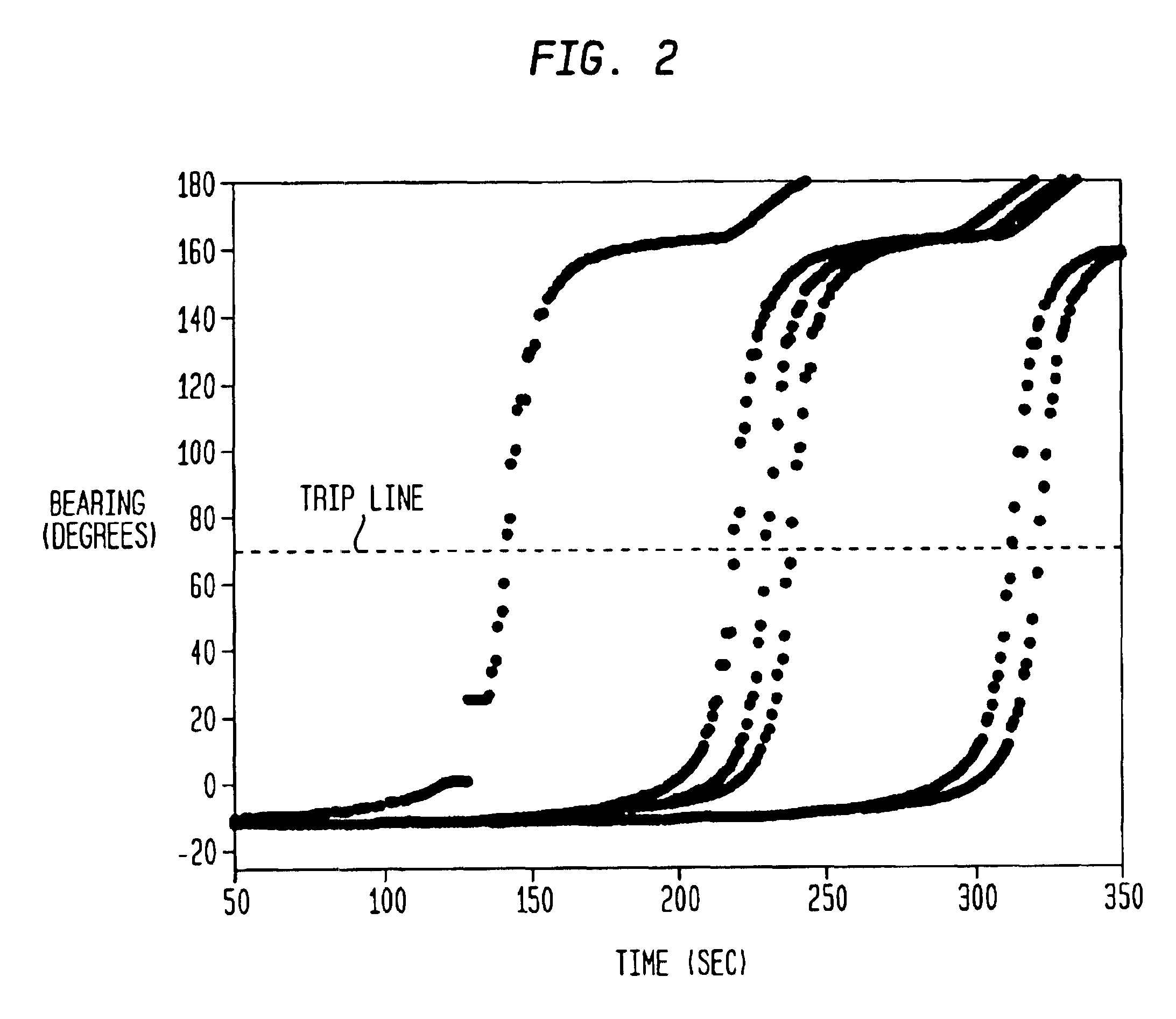
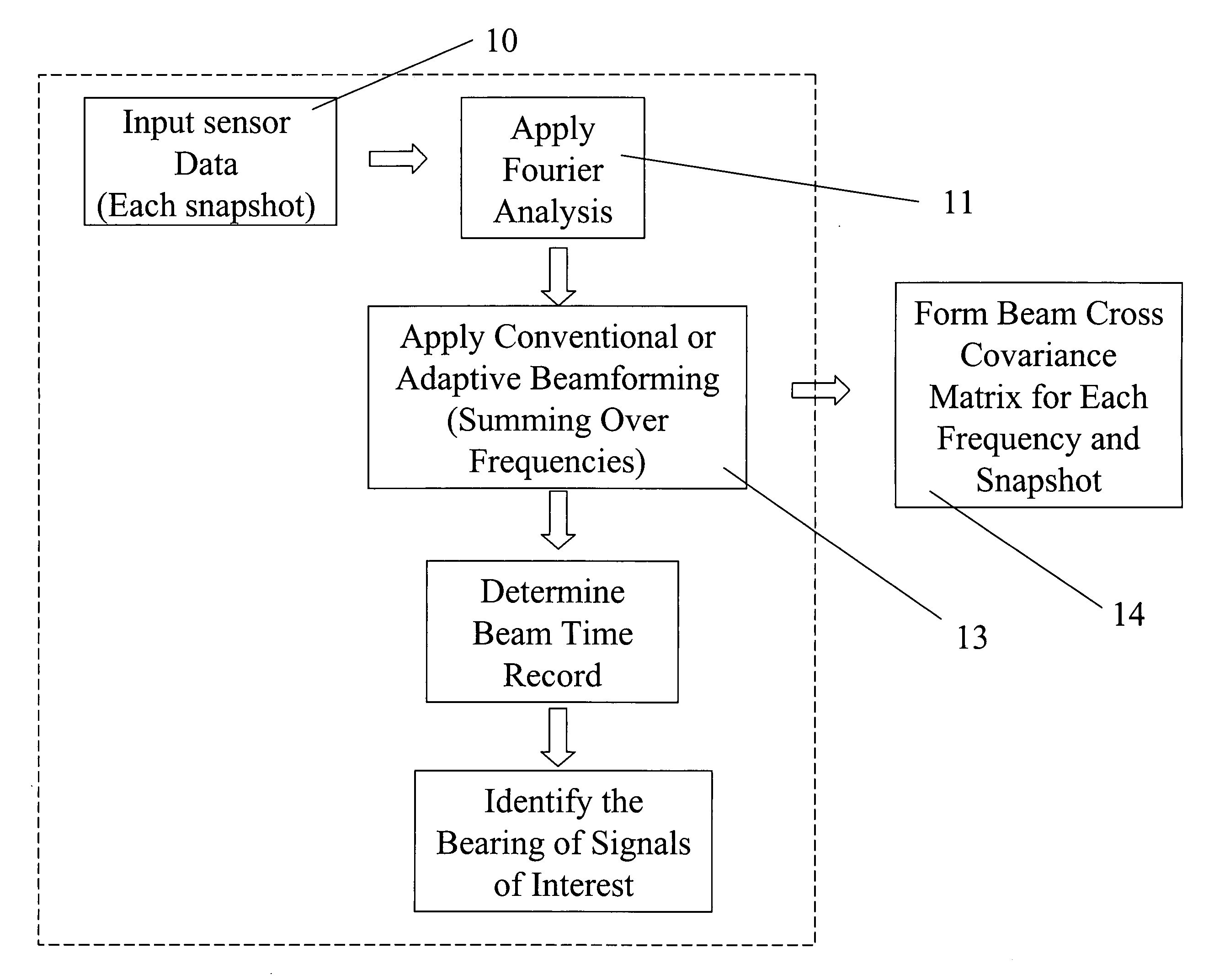
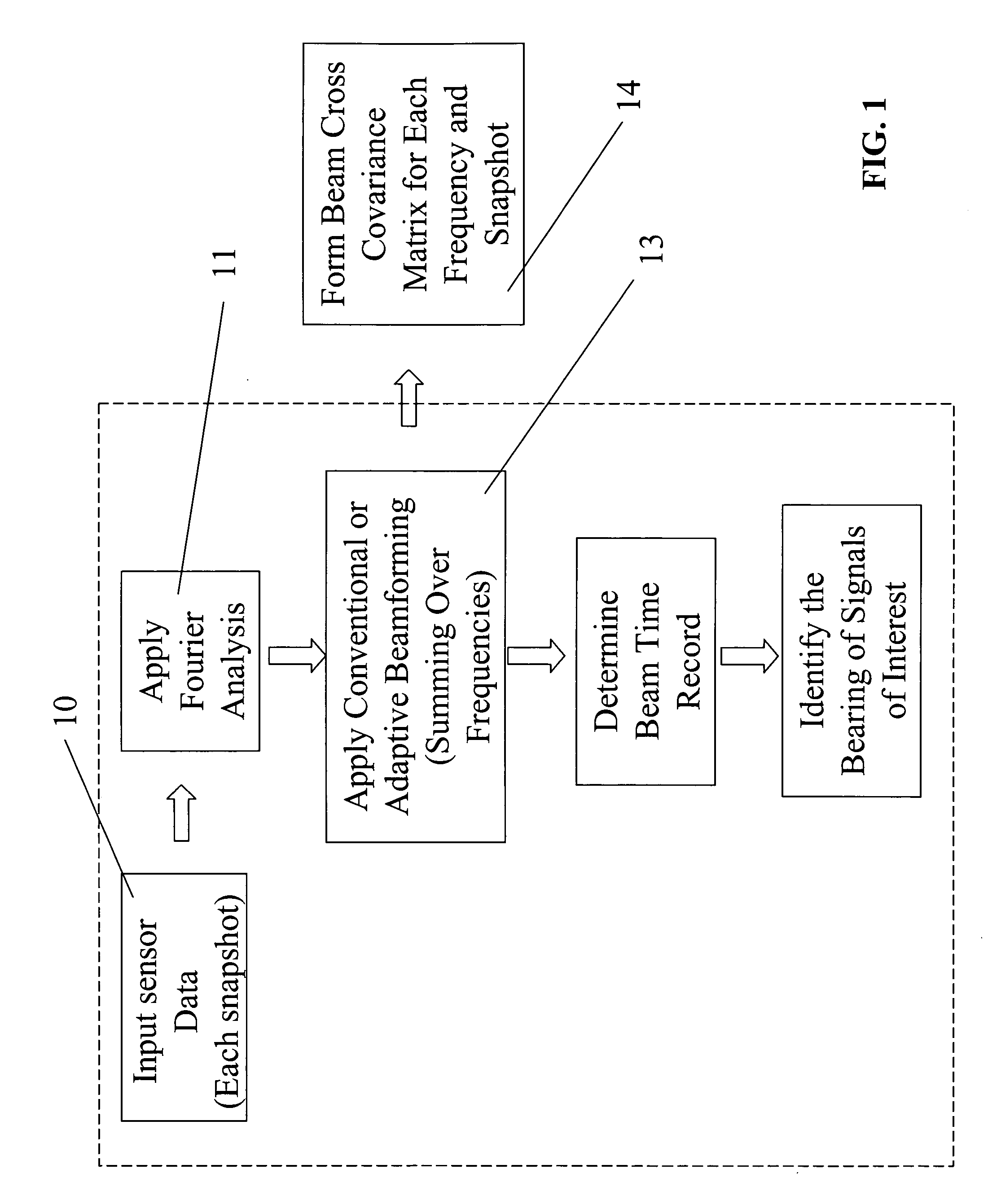
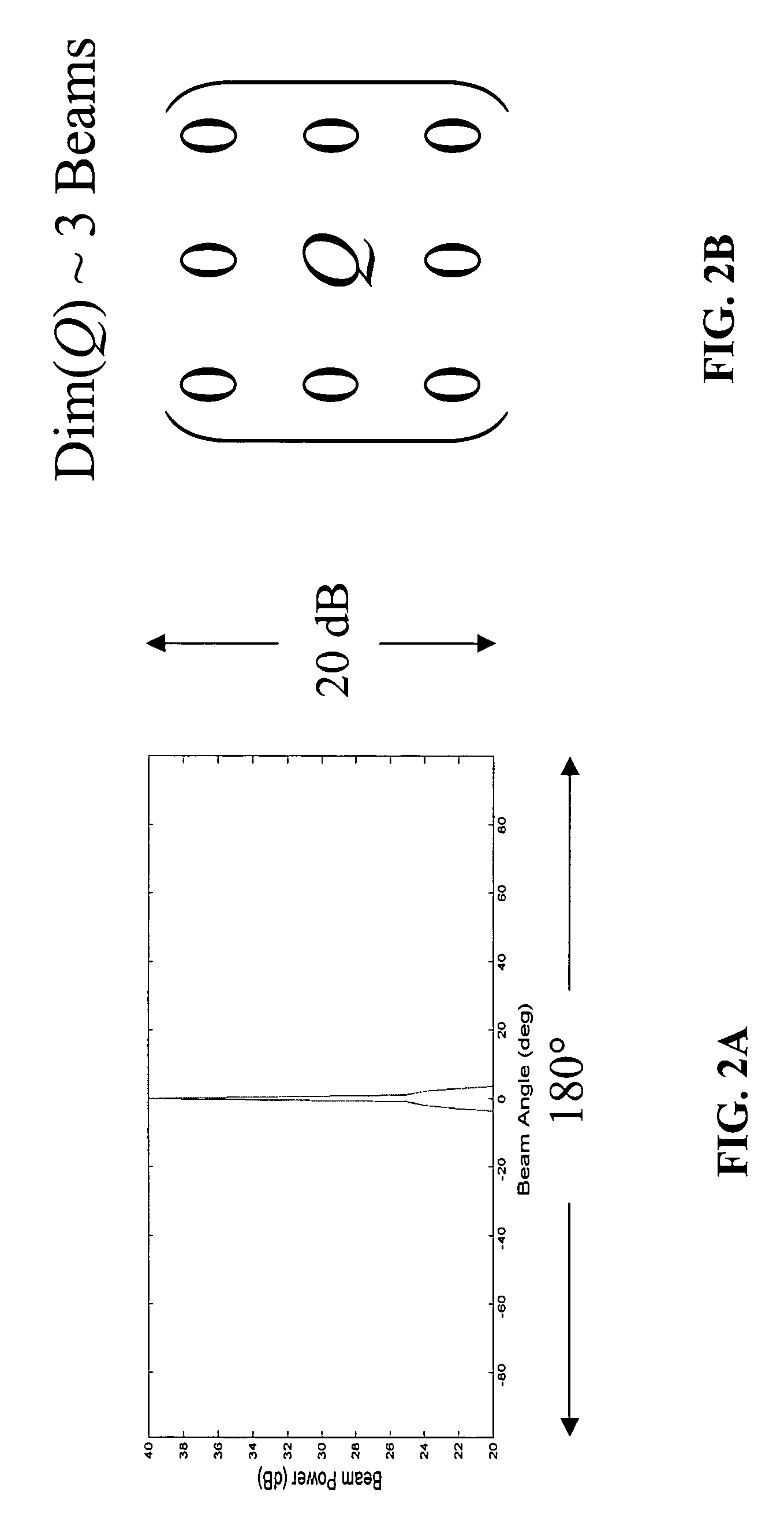
Method for detecting extended range motion and counting moving objects using an acoustics microphone array
InactiveUS6914854B1Reduce uncertaintyHighly accurate vehicle countMulti-channel direction findingUsing reradiationMotion detectorAcoustic array
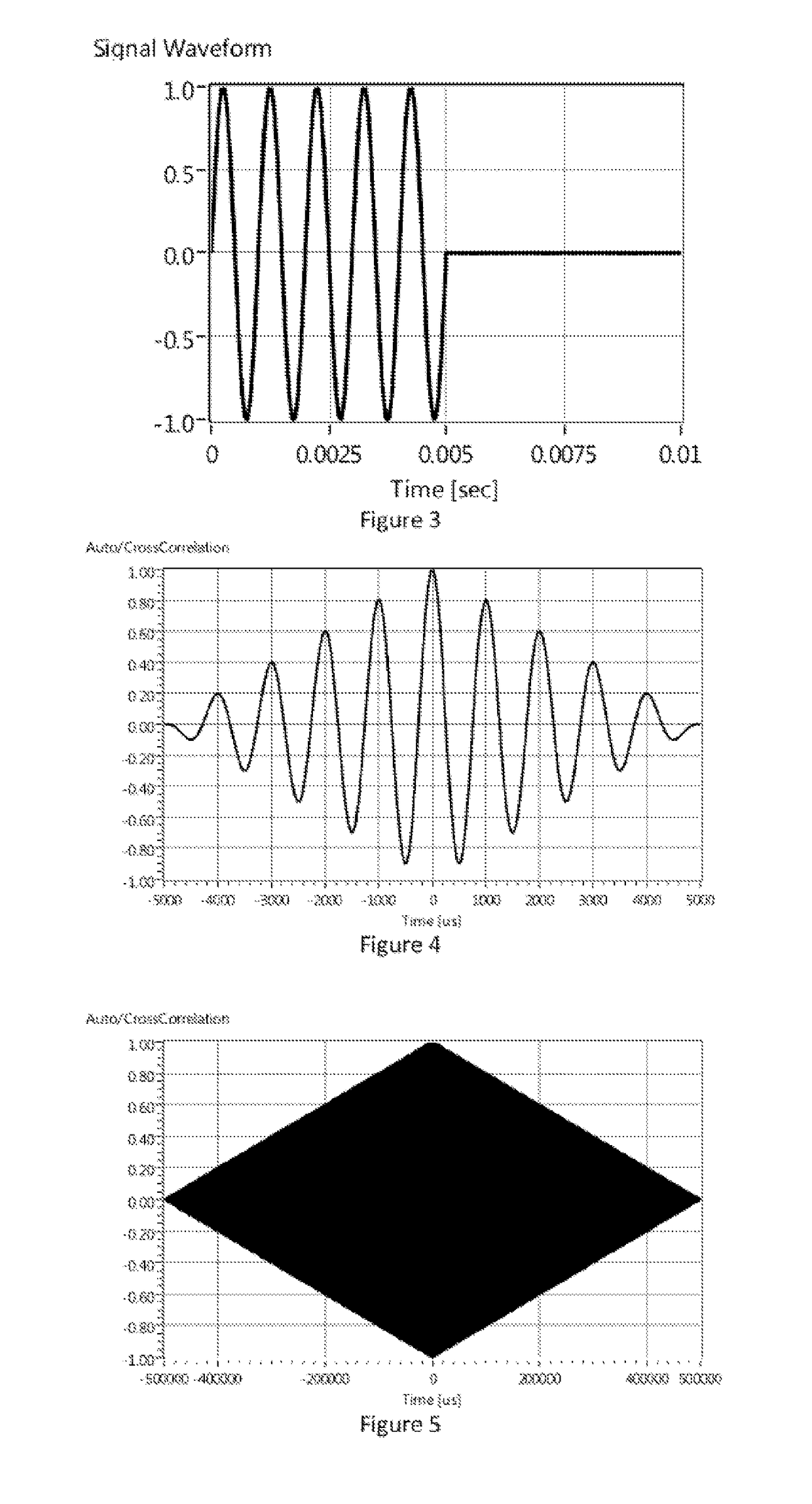
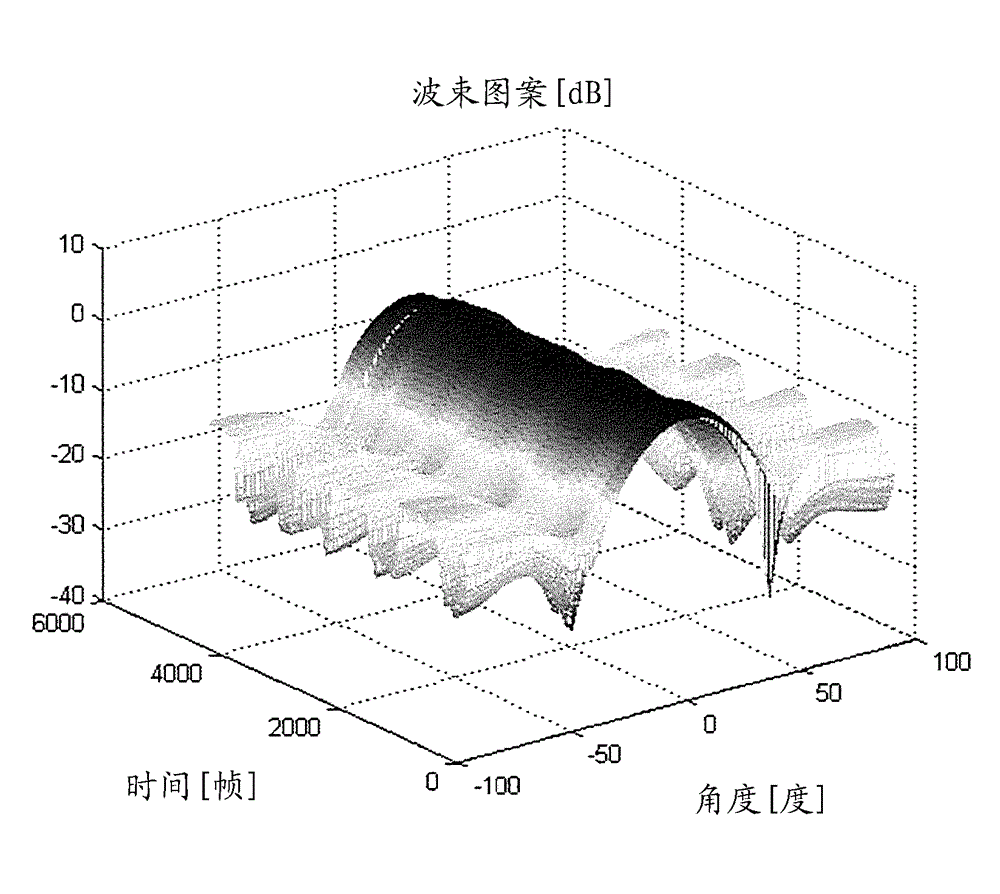
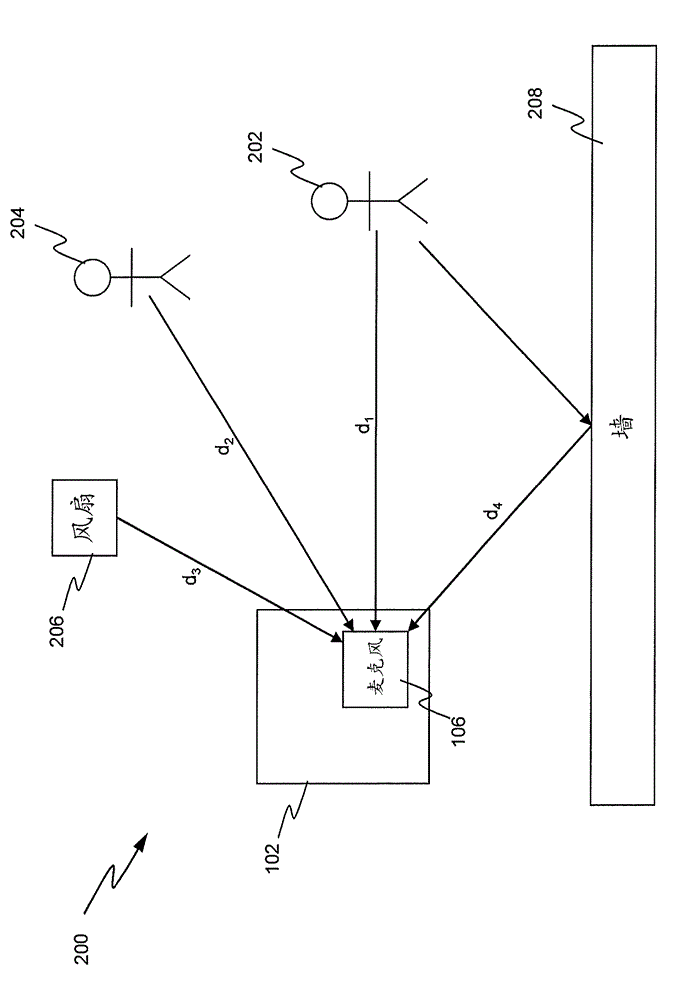
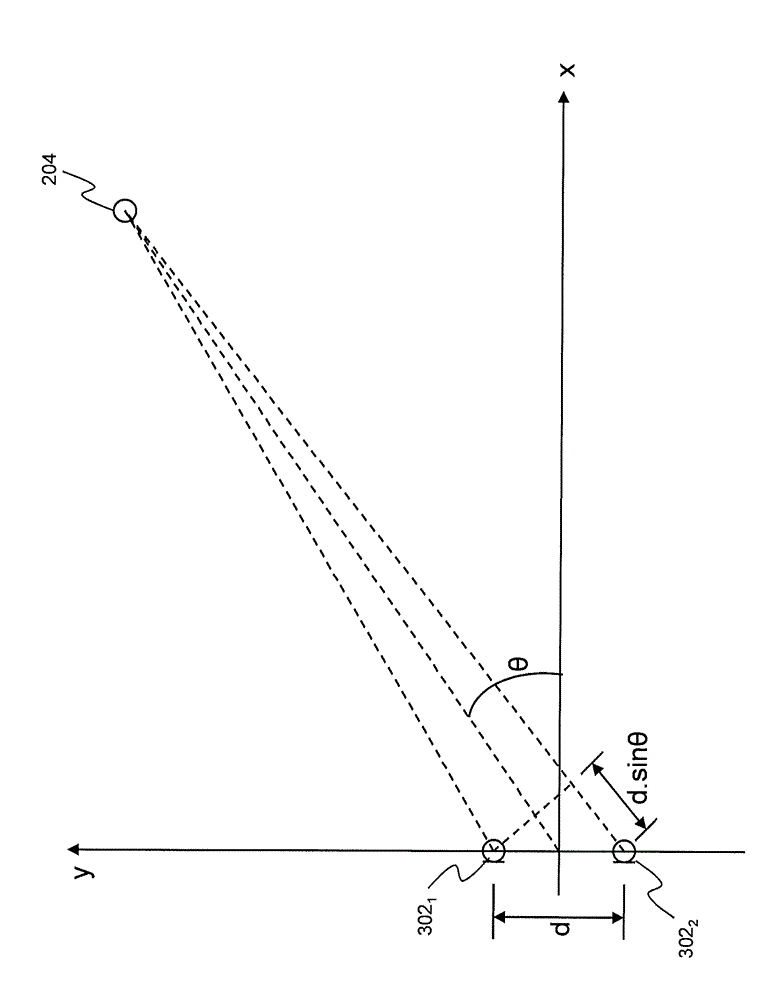
An acoustic array platform comprising multiple spaced microphones and associated processing electronics / algorithms projects distinct beams in a chosen look direction across which moving objects such as vehicles pass. These moving objects are accurately detected, classified and counted at extended ranges. The acoustic microphone array employs optimized beamforming to create specially focused listening directions that function as a “motion detector” and “trip line counter”. Algorithms detect and confirm the appropriate presence of objects moving through the beams and perform other algorithmic tests to verify that the object is a valid object to be counted. The proposed approach is realized with modest sized acoustic arrays and a reasonable number of microphones by employing an adaptive beamforming algorithm that achieves enhanced directivity in a principal look direction and which significantly reduces the effects of interferers outside the precise steering direction of the “trip line”.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
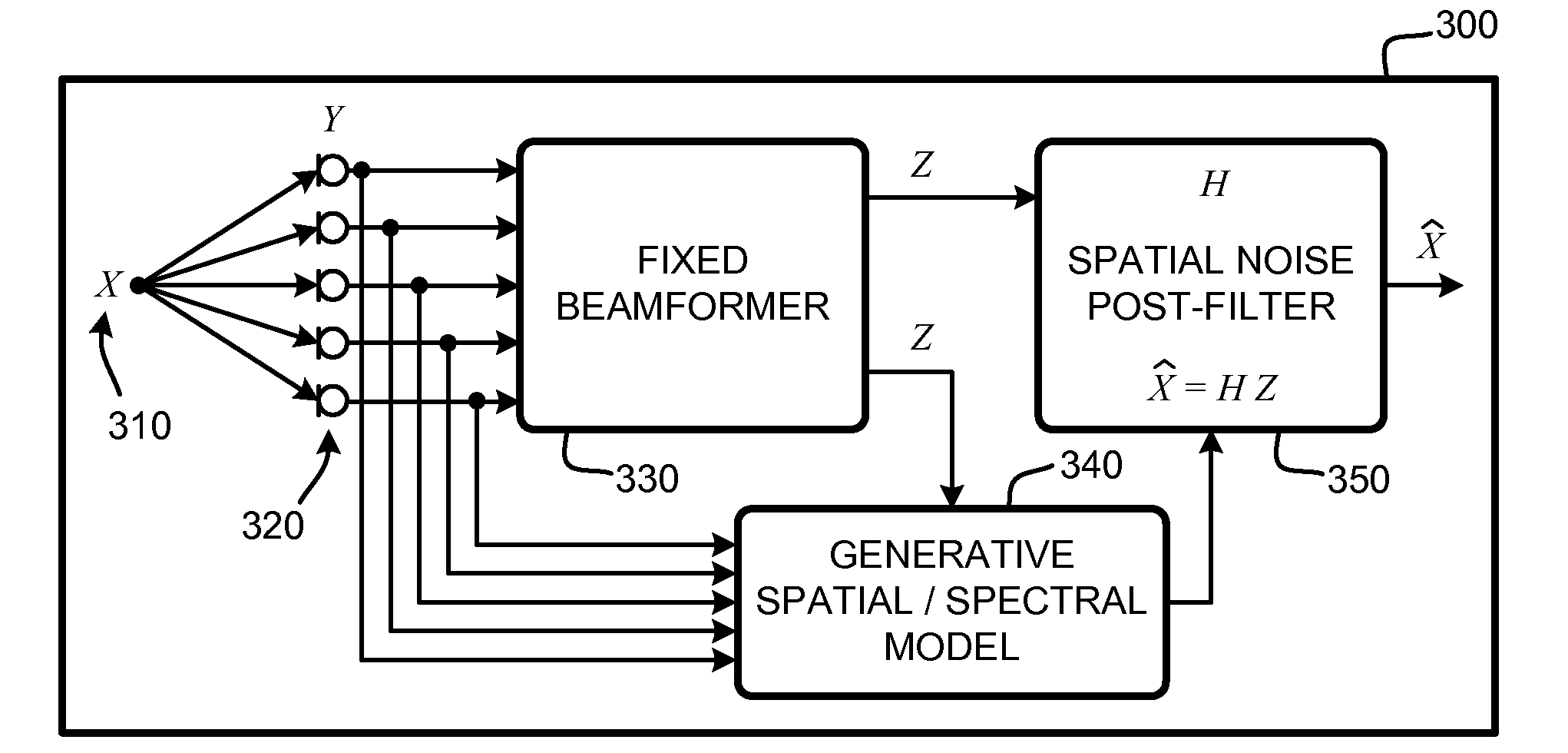
Sensor array post-filter for tracking spatial distributions of signals and noise
ActiveUS20080247274A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioAccurate modelingAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsSensor arraySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A “Sensor Array Post-Filter” provides an adaptive post-filter that accurately models and suppresses both diffuse and directional noise sources as well as interfering speech sources. The post-filter is applied to an output signal produced by a beamformer used to process signals produced by a sensor array. As a result, the Sensor Array Post-Filter operates to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of beamformer output signals by providing adaptive post-filtering of the output signals. The post-filter is generated based on a generative statistical model for modeling signal and noise sources at distinct regions in a signal field that considers prior distributions trained to model an instantaneous direction of arrival for signals captured by sensors in the array.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
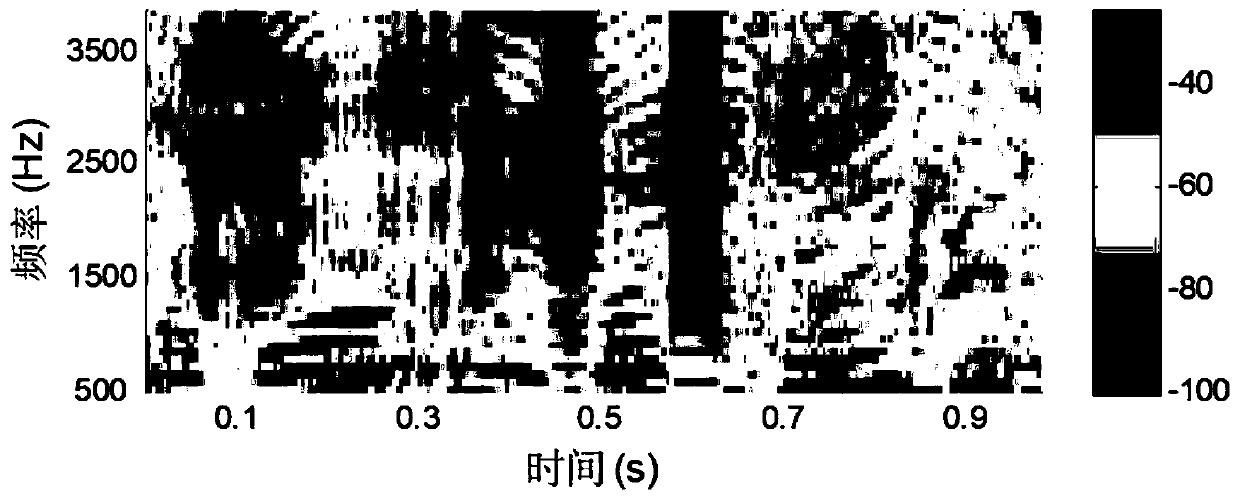
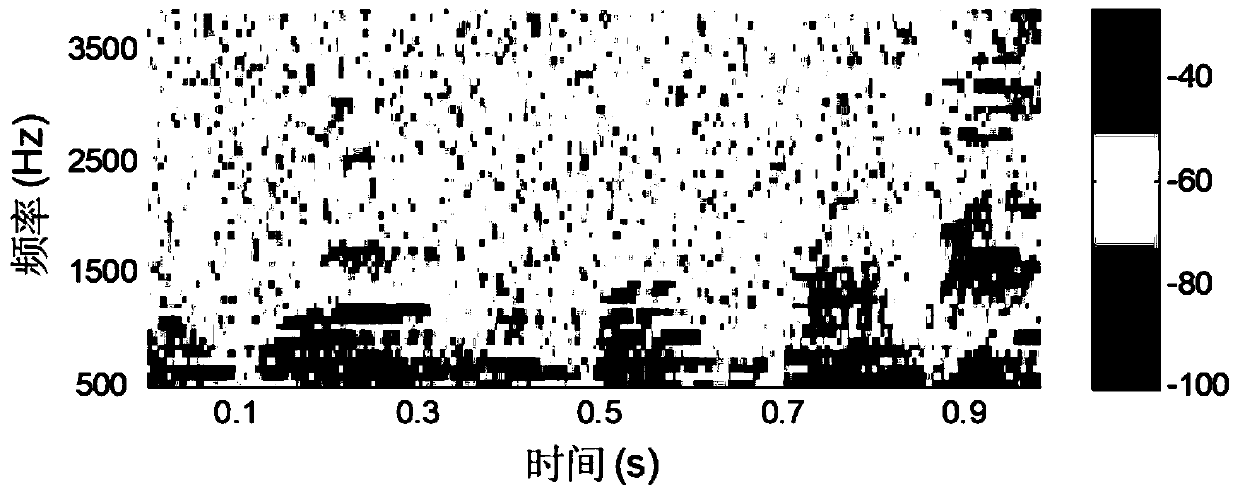
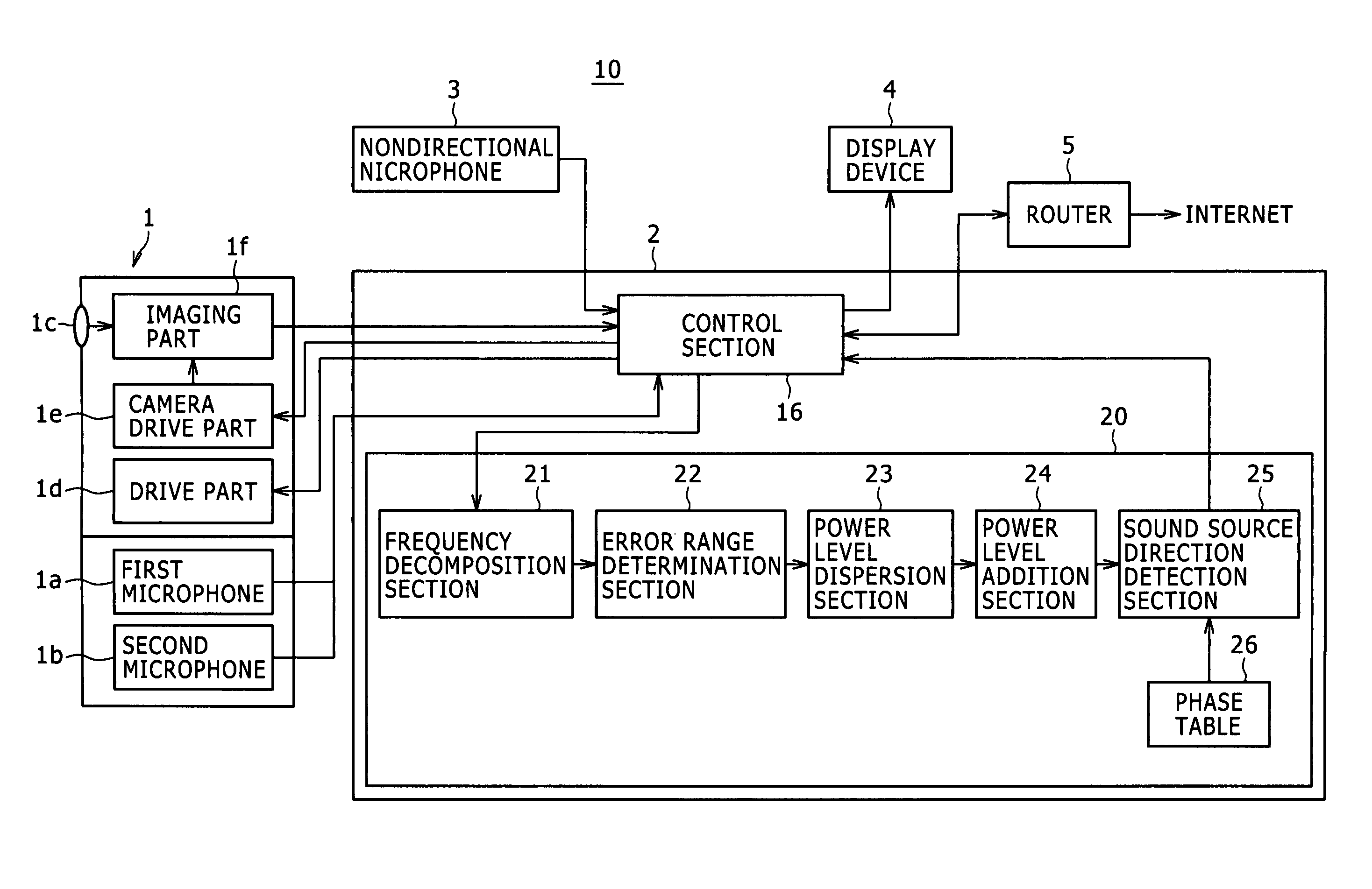
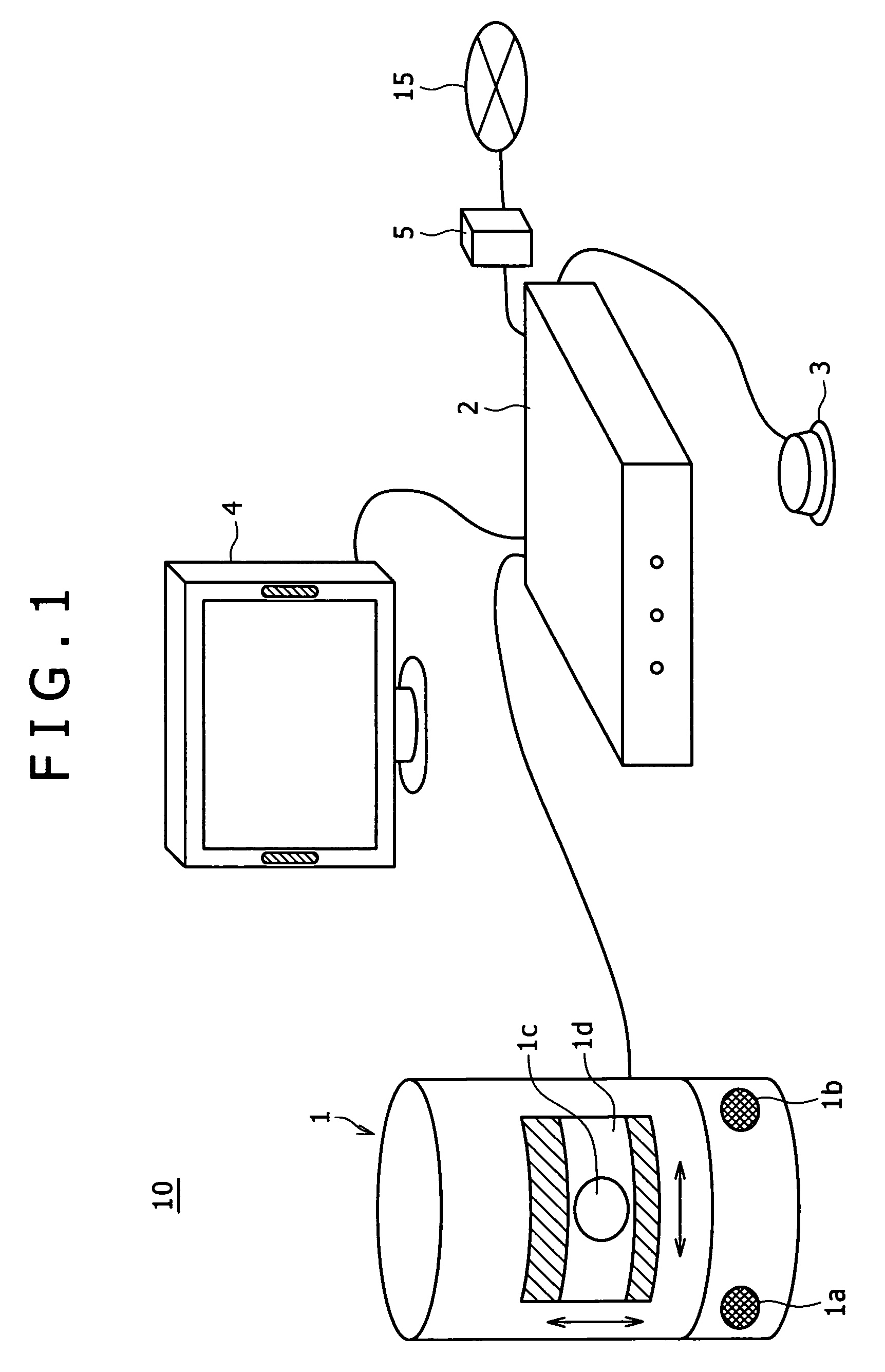
Sound source direction detecting apparatus, sound source direction detecting method, and sound source direction detecting camera
InactiveUS20090086993A1Detect directionReliable detectionTwo-way working systemsSpeech recognitionSound sourcesDecomposition
Disclosed herein is a sound source direction detecting apparatus including: a plurality of microphones configured to collect sounds from a sound source in order to form an audio frame; a frequency decomposition section configured to decompose the audio frame into frequency components; an error range determination section configured to determine the effects of noises collected together with the sounds as an error range relative to phases; a power level dispersion section configured to disperse power levels of the sounds for each of the frequency components decomposed by the frequency decomposition section, on the basis of the error range determined by the error range determination section; a power level addition section configured to add the power levels dispersed by the power level dispersion section; and a sound source direction detection section configured to detect the direction of the sound source based on the phase at which is located the highest of the power levels added by the power level addition section.
Owner:SONY CORP
Underwater detection apparatus
InactiveUS6418080B2Easy to controlEasy to processTransducer circuitsSystems with undesired wave eliminationAudio power amplifierFrequency mixer
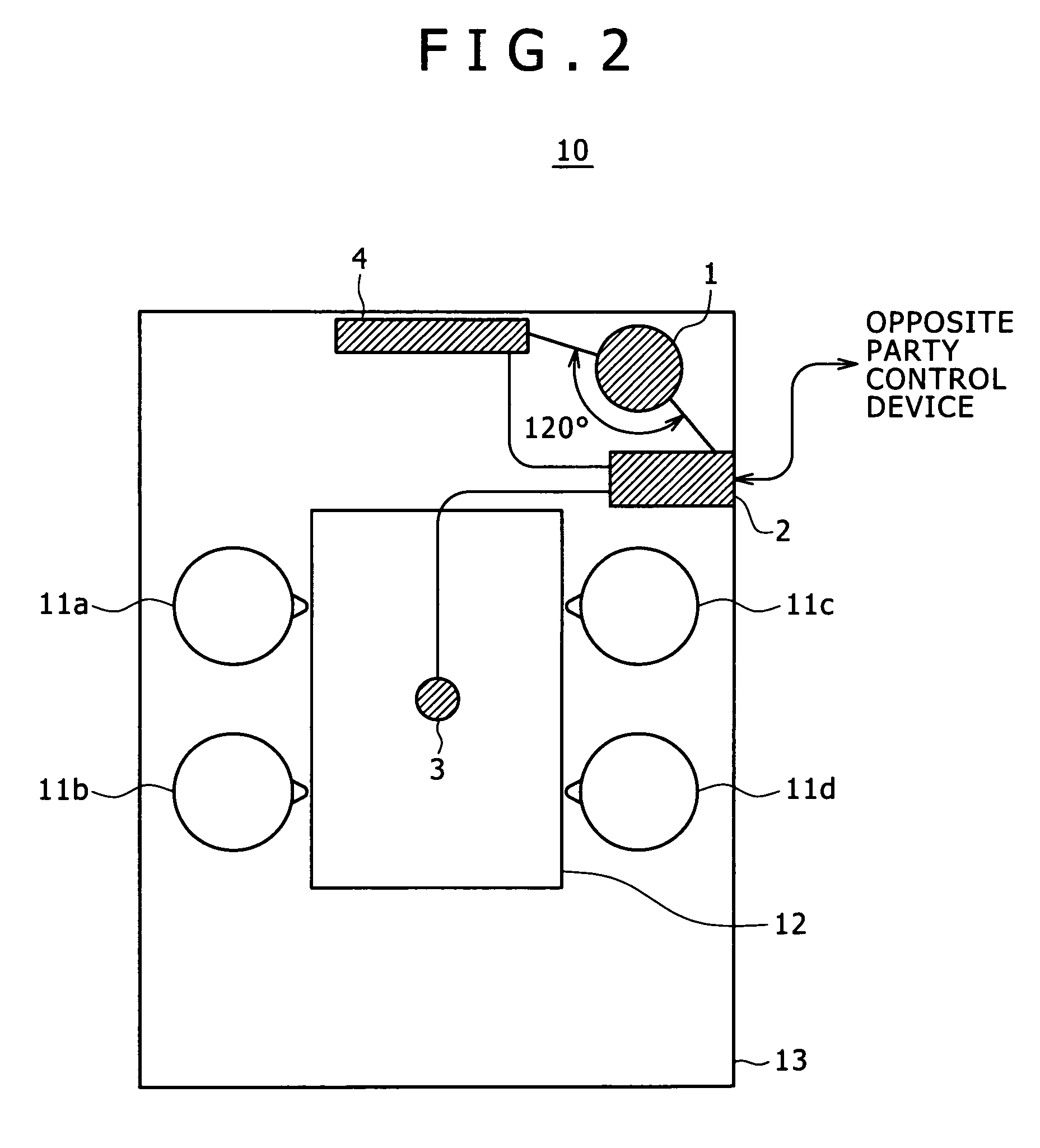
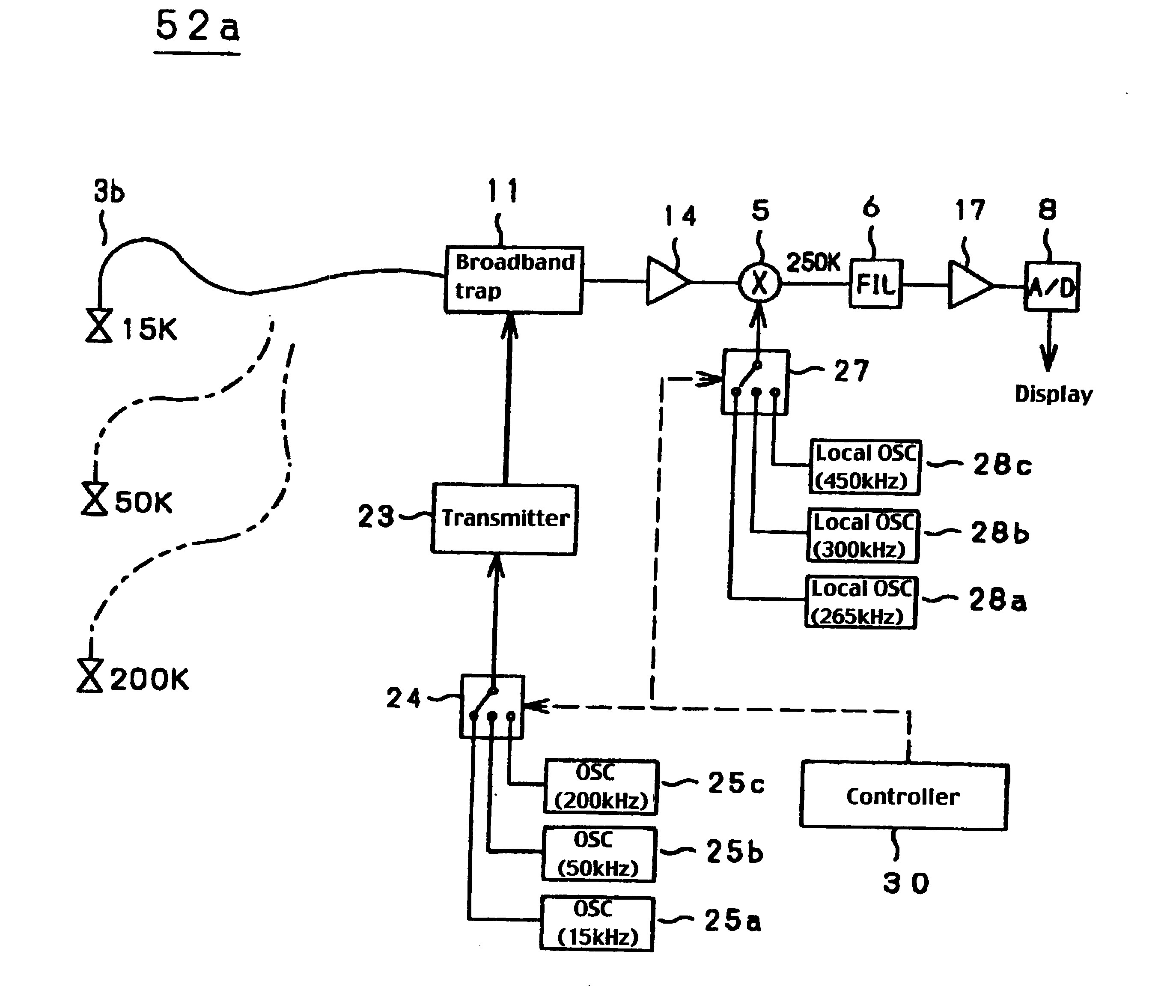
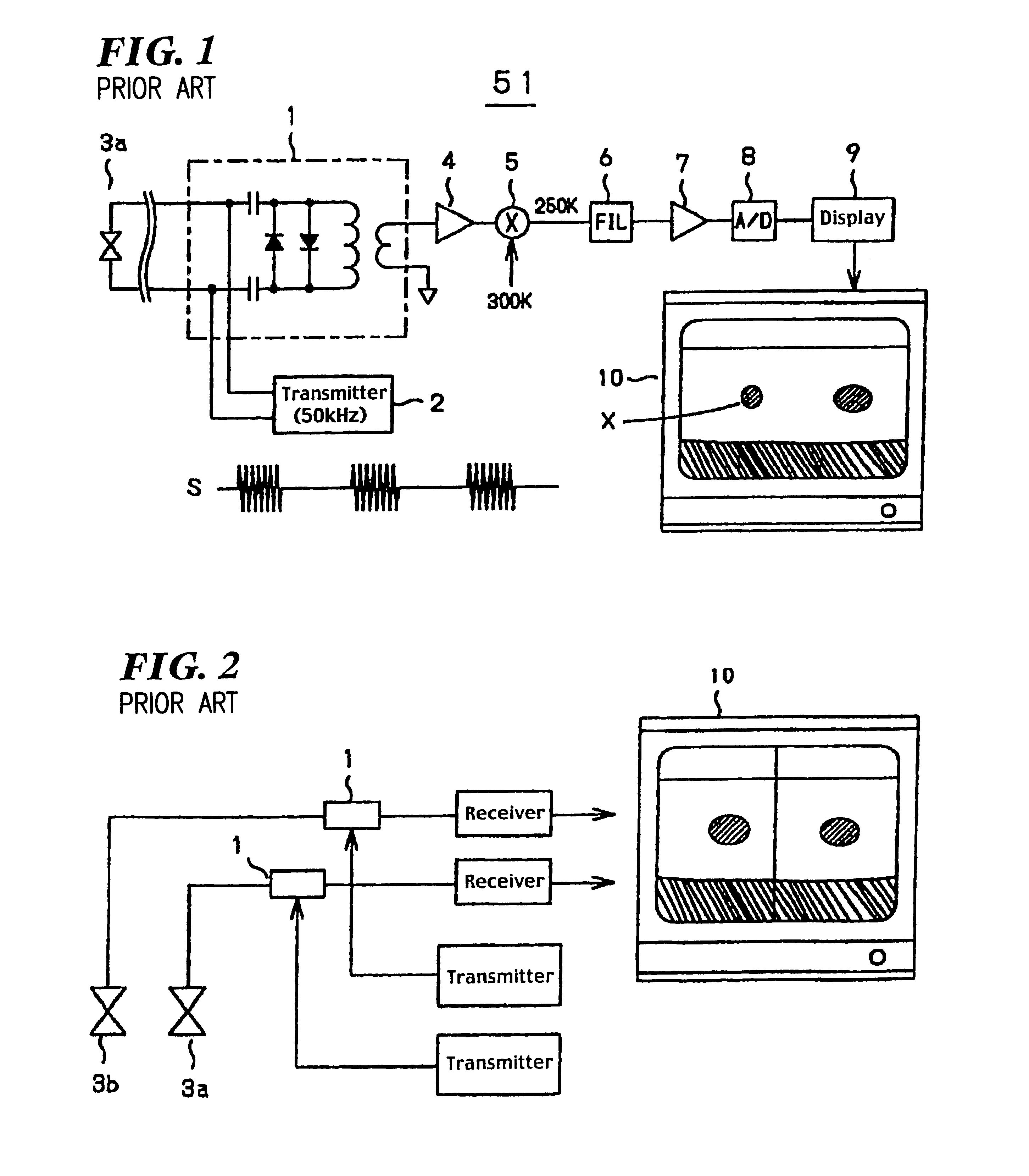
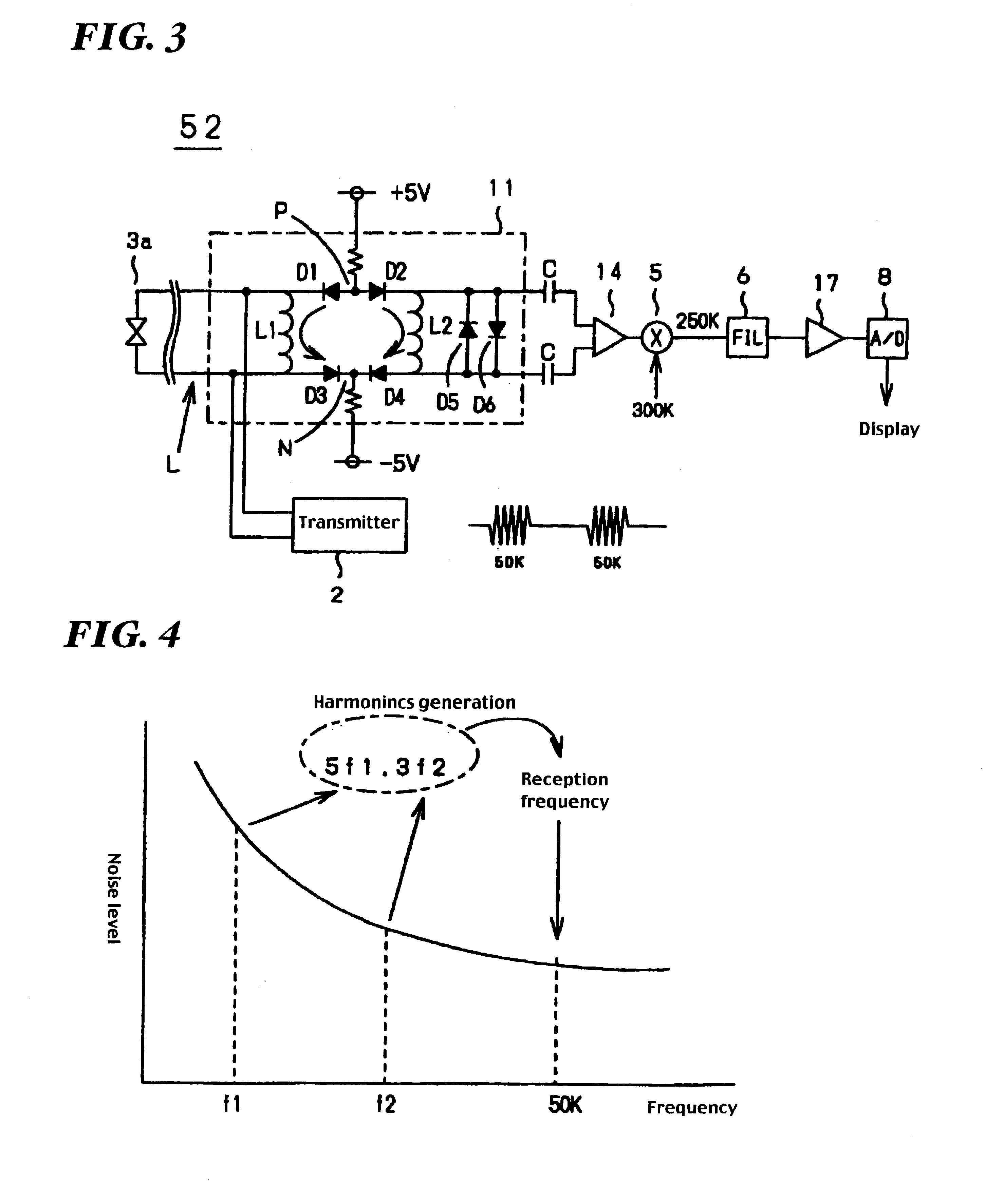
An underwater detection apparatus comprises a transducer, a transmitter capable of generating transmitting signals of a plurality of respective frequencies and for generating a transmitting signal, a broadband trap circuit for transferring the transmitting signal fed from the transmitter to the transducer and for passing an echo signal fed from the transducer, a preamplifier for amplifying the echo signal fed from the broadband trap circuit, a mixer for converting an output of the preamplifier into a signal of a specific frequency, a filter for selectively passing the signal of only the specific frequency-band output from the mixer, a main amplifier for amplifying an output of the filter, an A / D converter for converting an output of the main amplifier into a digital form, and a display circuit for displaying the digitized output of the A / D converter on a monitor, wherein the preamplifier is of a low-gain type.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and apparatus for acoustic source tracking using a horizontal line array
InactiveUS20060133211A1Improve abilitiesEasy to solveSignal processingMicrophones signal combinationSound sourcesEnvironmental acoustics
An apparatus for processing passive acoustic signals received on a horizontal line array that were either emitted from an underwater object or echo returned from an object, is proposed to track the motion (bearing change and range change) of an object (target) relative to the receiver horizontal line array. Adaptive array processing for a moving object is biased for a moving source when the number of data samples is limited by the stationariness condition. Motion compensation can be carried out in the beam domain by beam shifting for a bearing changing object and frequency shifting for a range changing object. The method includes receiving acoustic signals from the target, determining the beam covariance matrices, determining the target bearing rate and range rate, processing the beam covariance matrices by compensating for the target motion, and producing a beam power plot versus time. Interference signal is suppressed when the interference source does not have the same motion (bearing and range rate) as the target. The method does not need detailed environmental acoustic information of the sound channel normally required to model the sound propagation.
Owner:USA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY THE
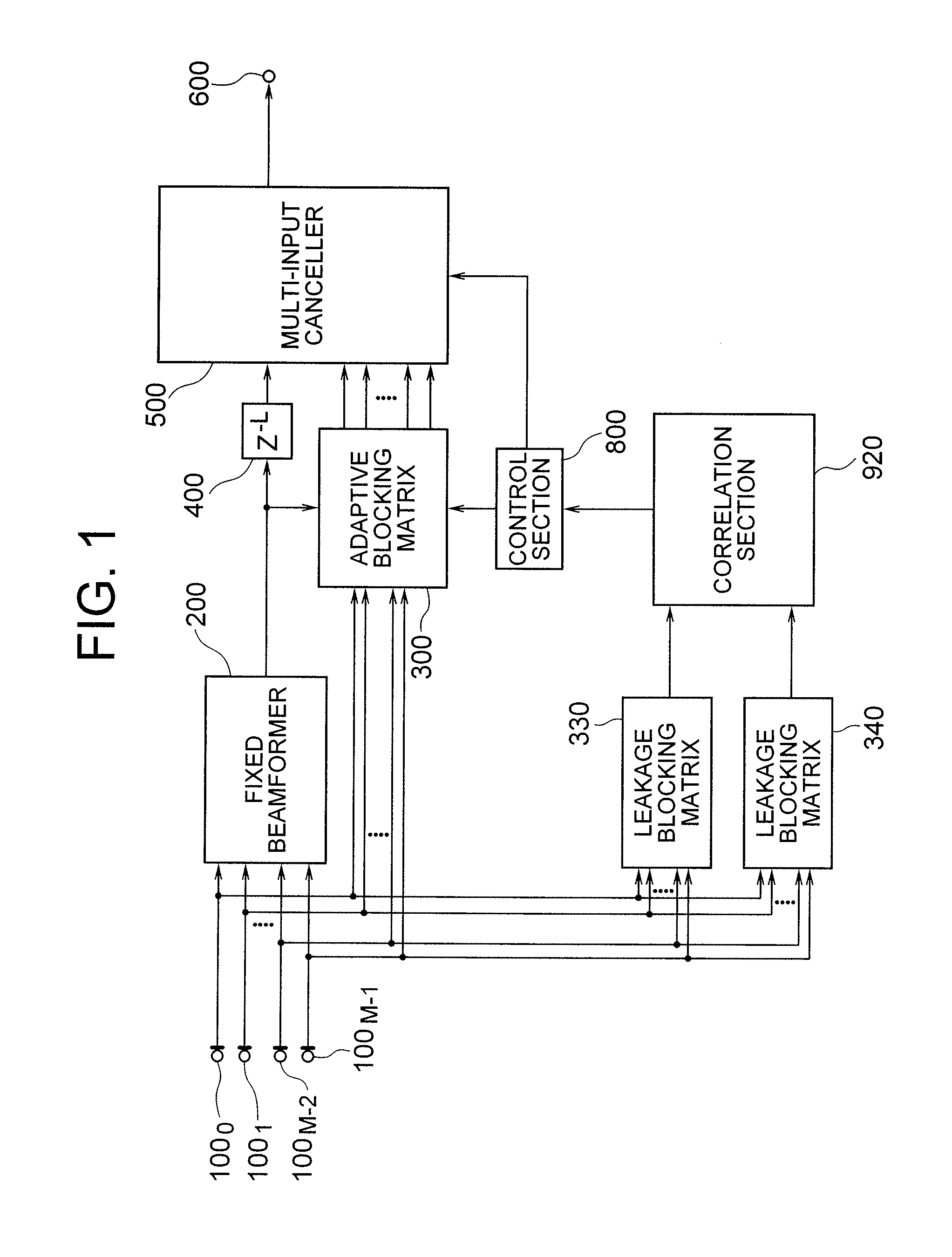
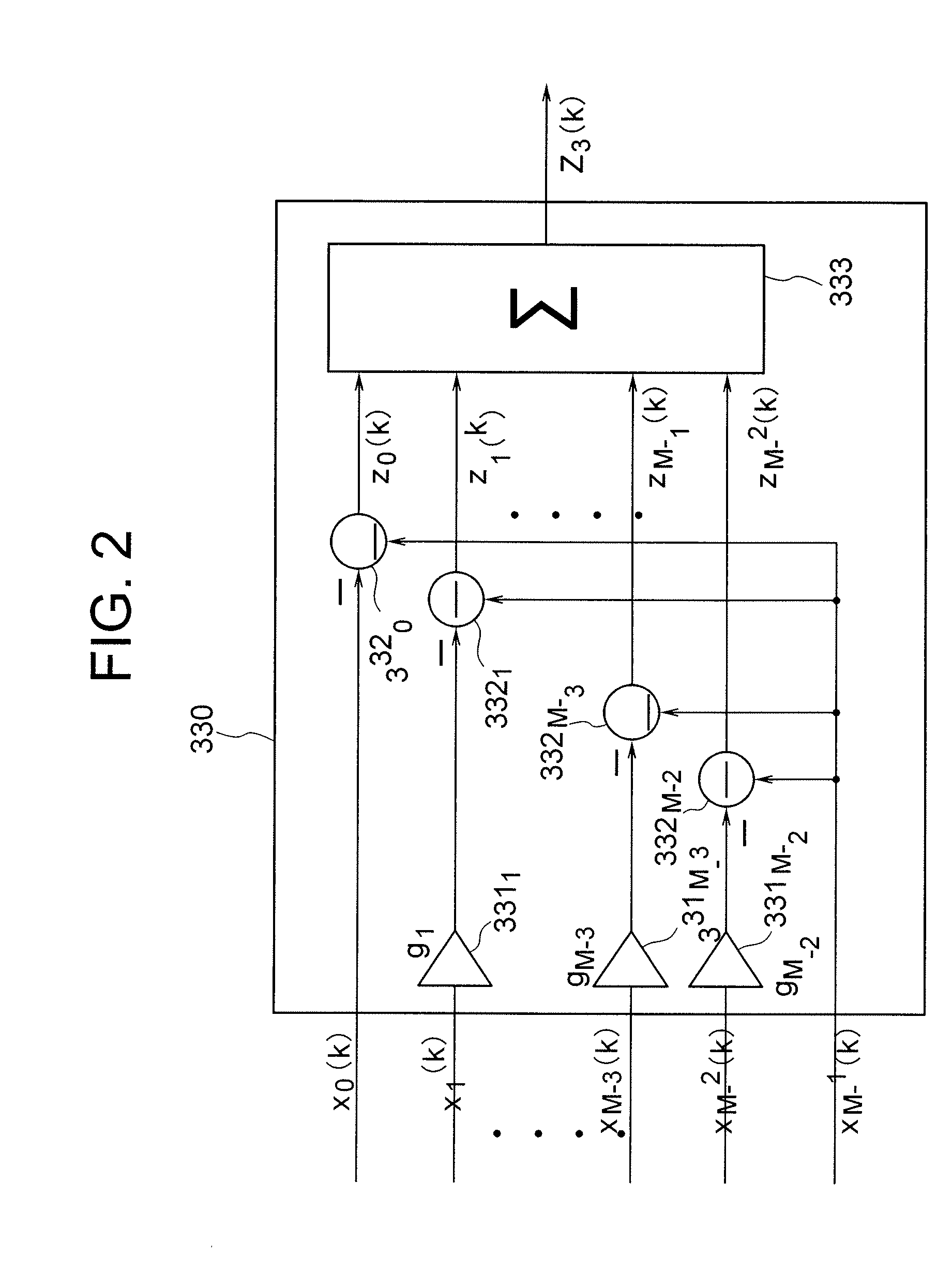
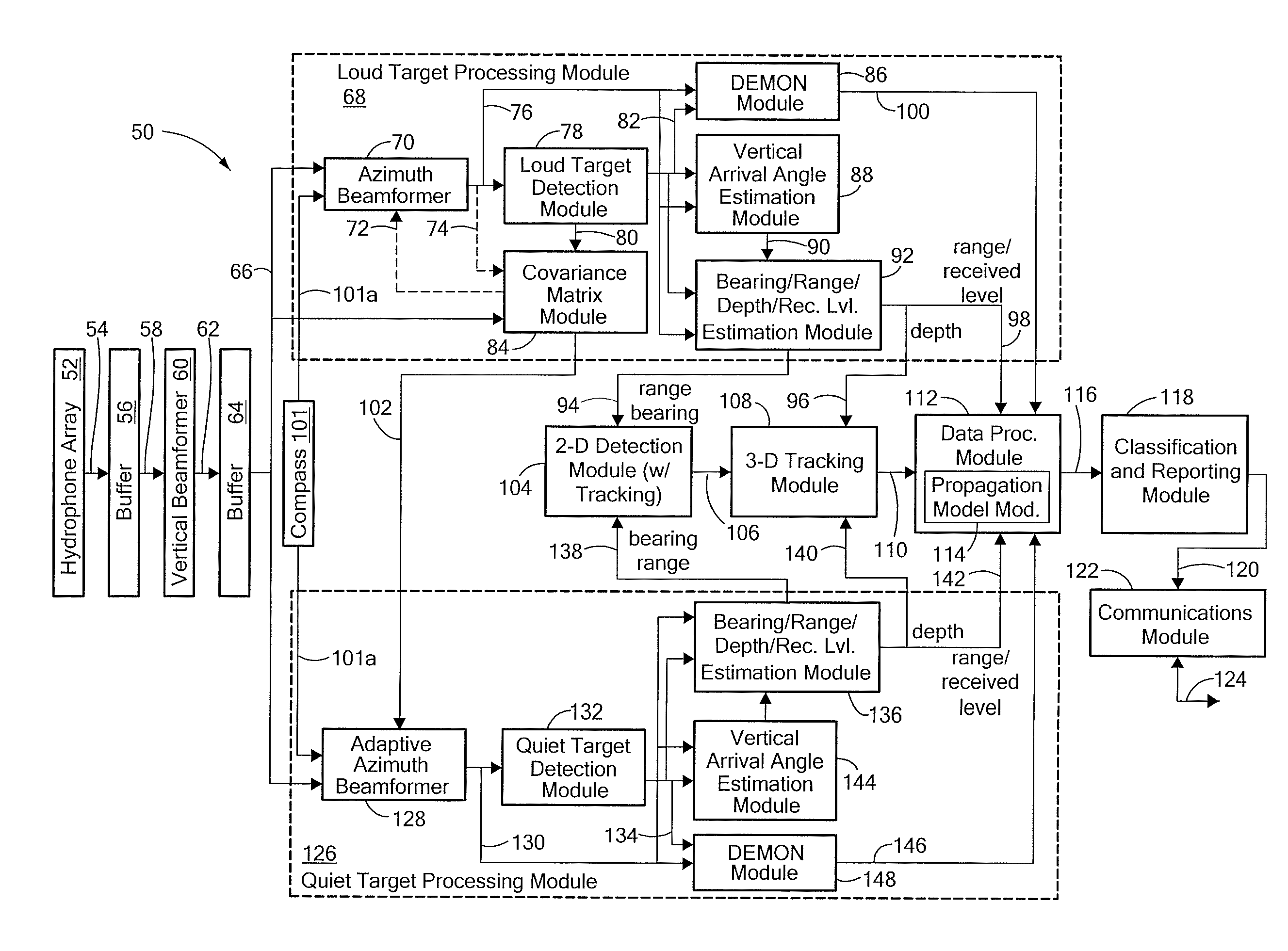
Autonomous Sonar System and Method
ActiveUS20090257312A1Multi-channel direction findingSystems with undesired wave eliminationPropellerSonar system
An autonomous sonar system and method provide an arrangement capable of beamforming in three dimensions, detecting loud targets, adaptively beamforming in three dimensions to avoid the loud targets, detecting quiet targets, localizing the loud or quiet targets in range, bearing, and depth, detecting modulation of noise associated with propellers of the loud or quiet targets, generating three dimensional tracks of the loud or quiet targets in bearing, range and depth, making classification of the loud or quiet targets, assigning probabilities to the classifications, and generating classification reports according to the classifications for communication to a receiving station, all without human assistance.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
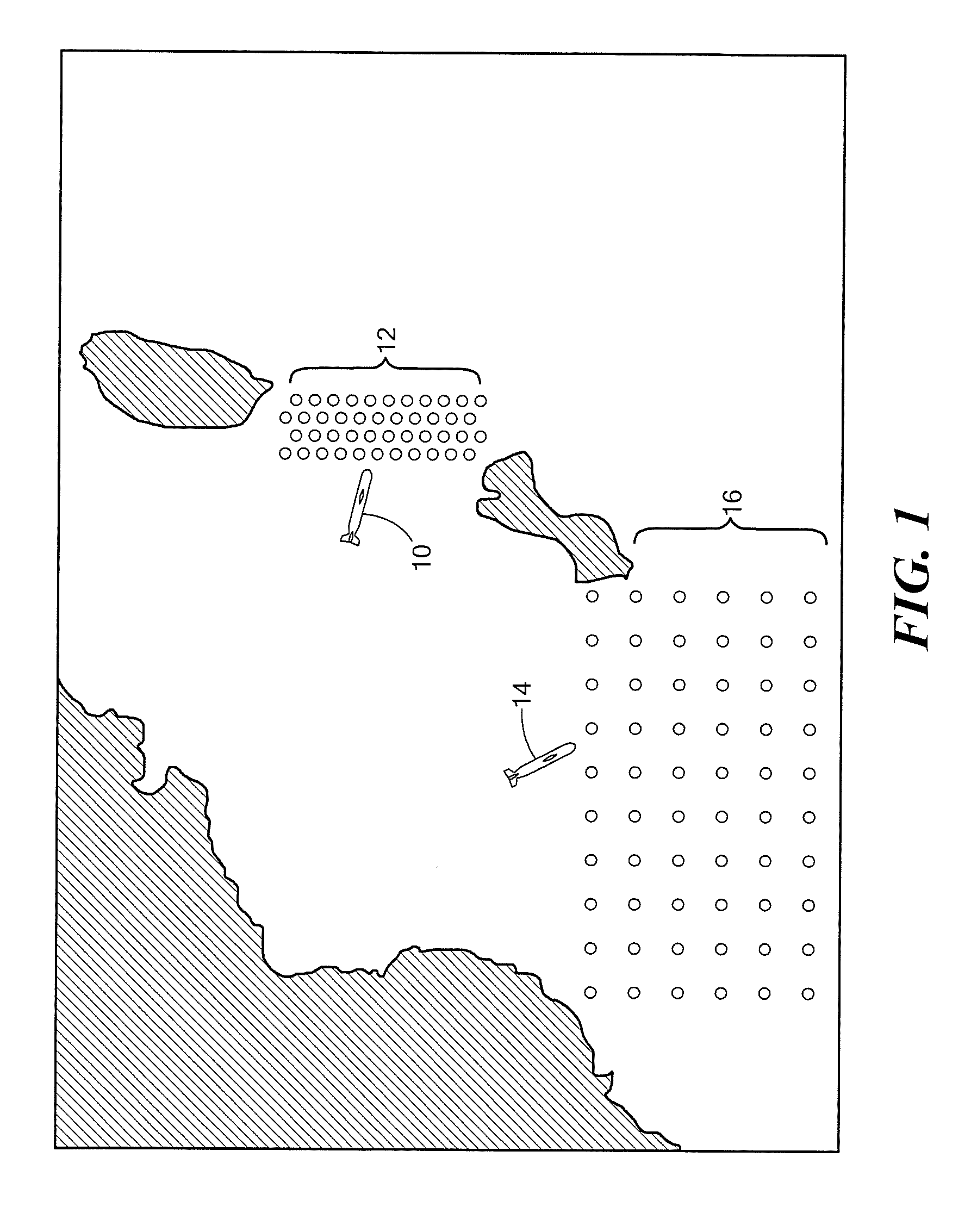
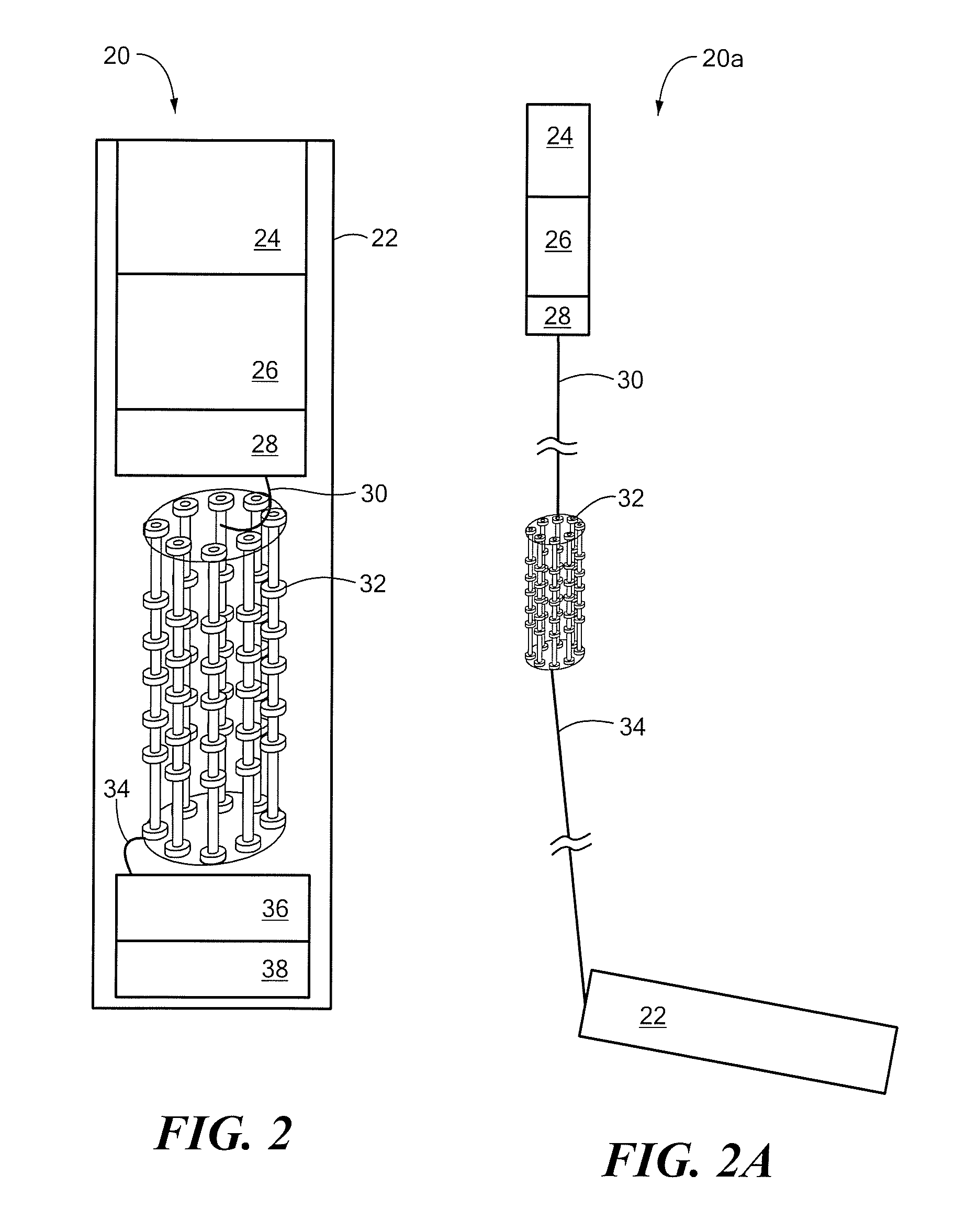
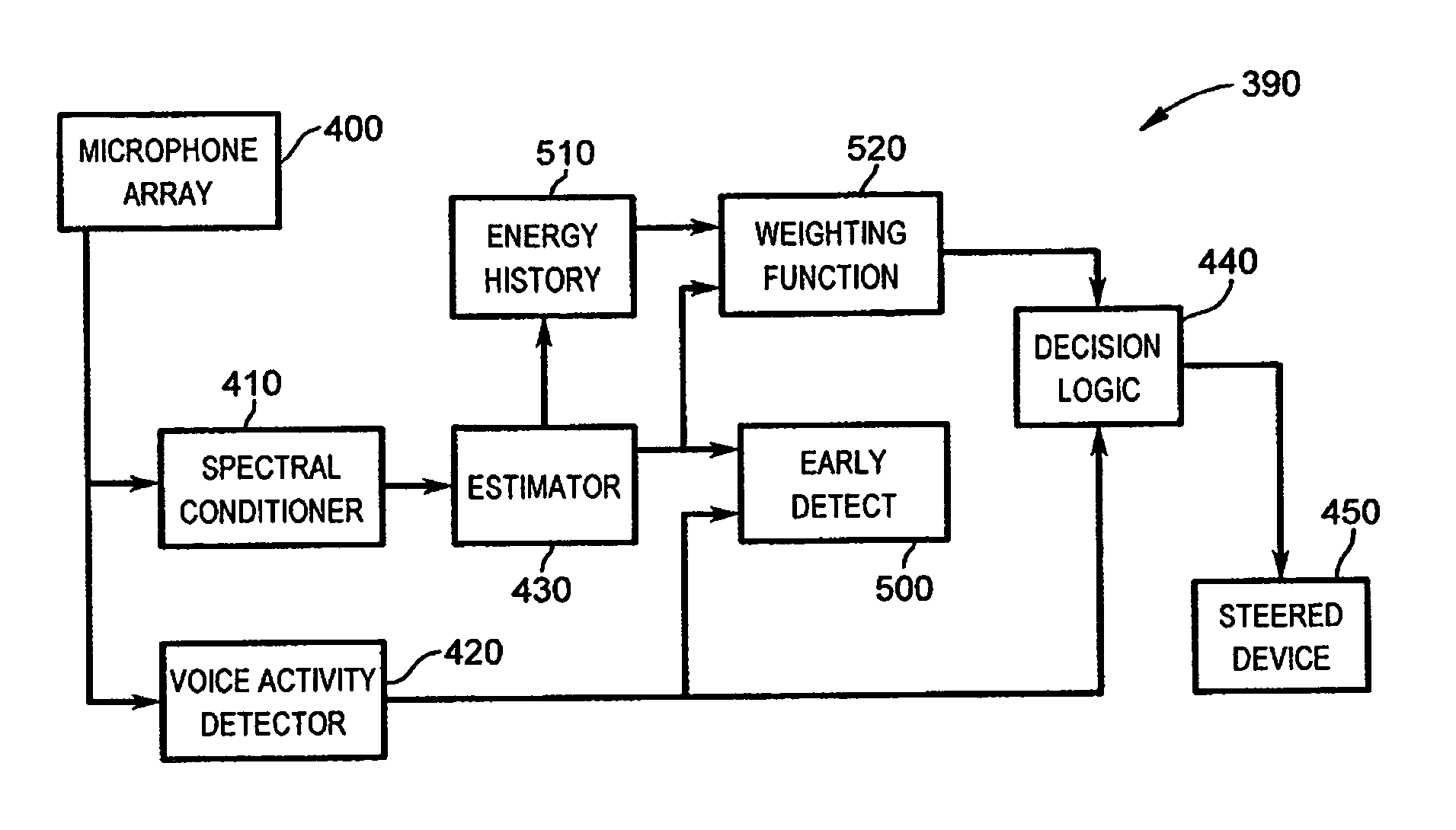
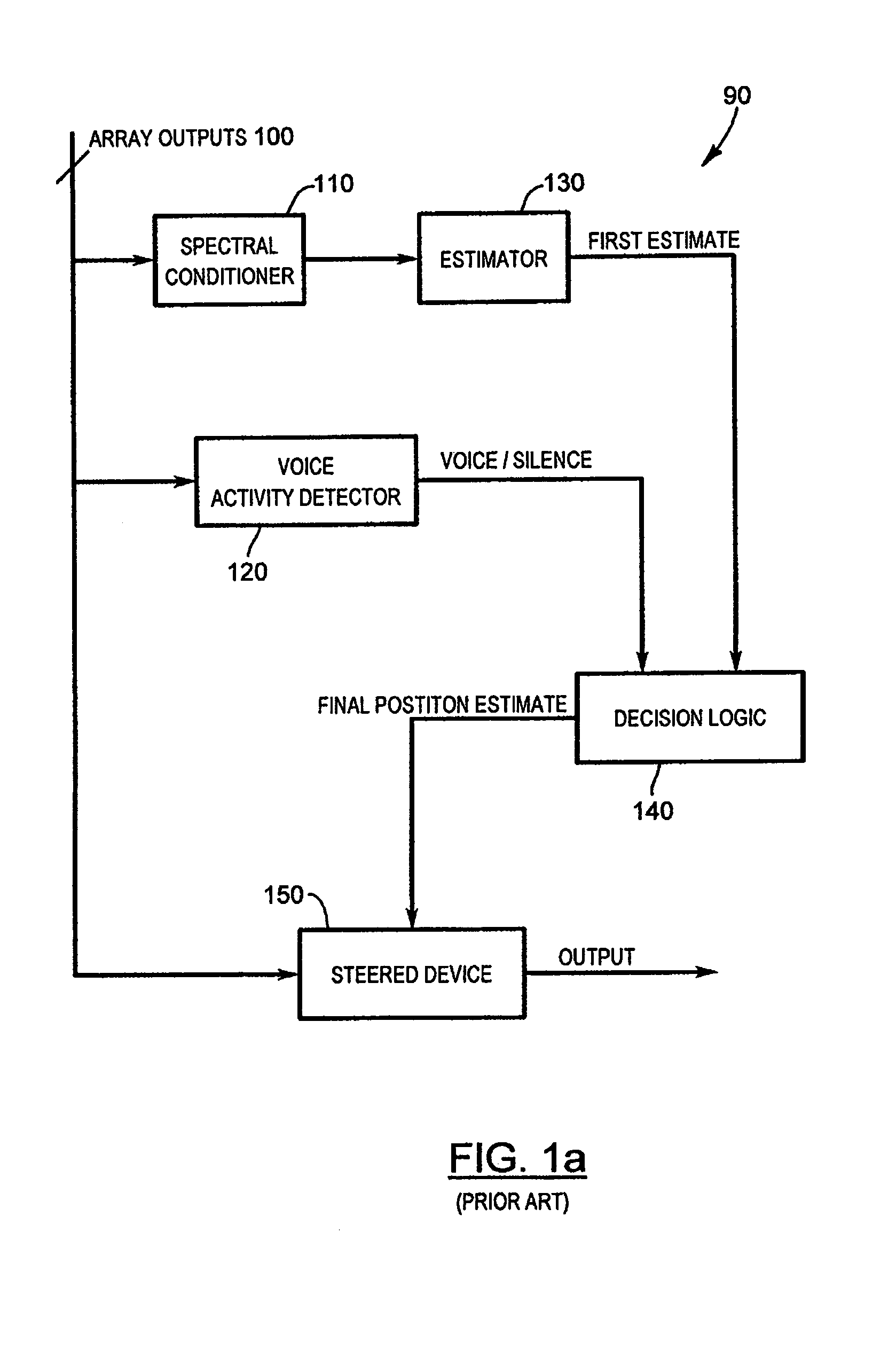
Robust talker localization in reverberant environment
A method of locating a talker in a reverberant environment comprises receiving multiple audio signals from a microphone array that include direct path audio signal and reverberation signal components. The direct path audio signal components of the multiple audio signals are detected and are used to weight the multiple audio signals. A position estimate based on the weighted audio signals is then calculated. Periods of speech activity are detected and a final position estimate is generated during the periods of speech activity.
Owner:MITEL
Adaptive array control device, method and program, and adaptive array processing device, method and program using the same
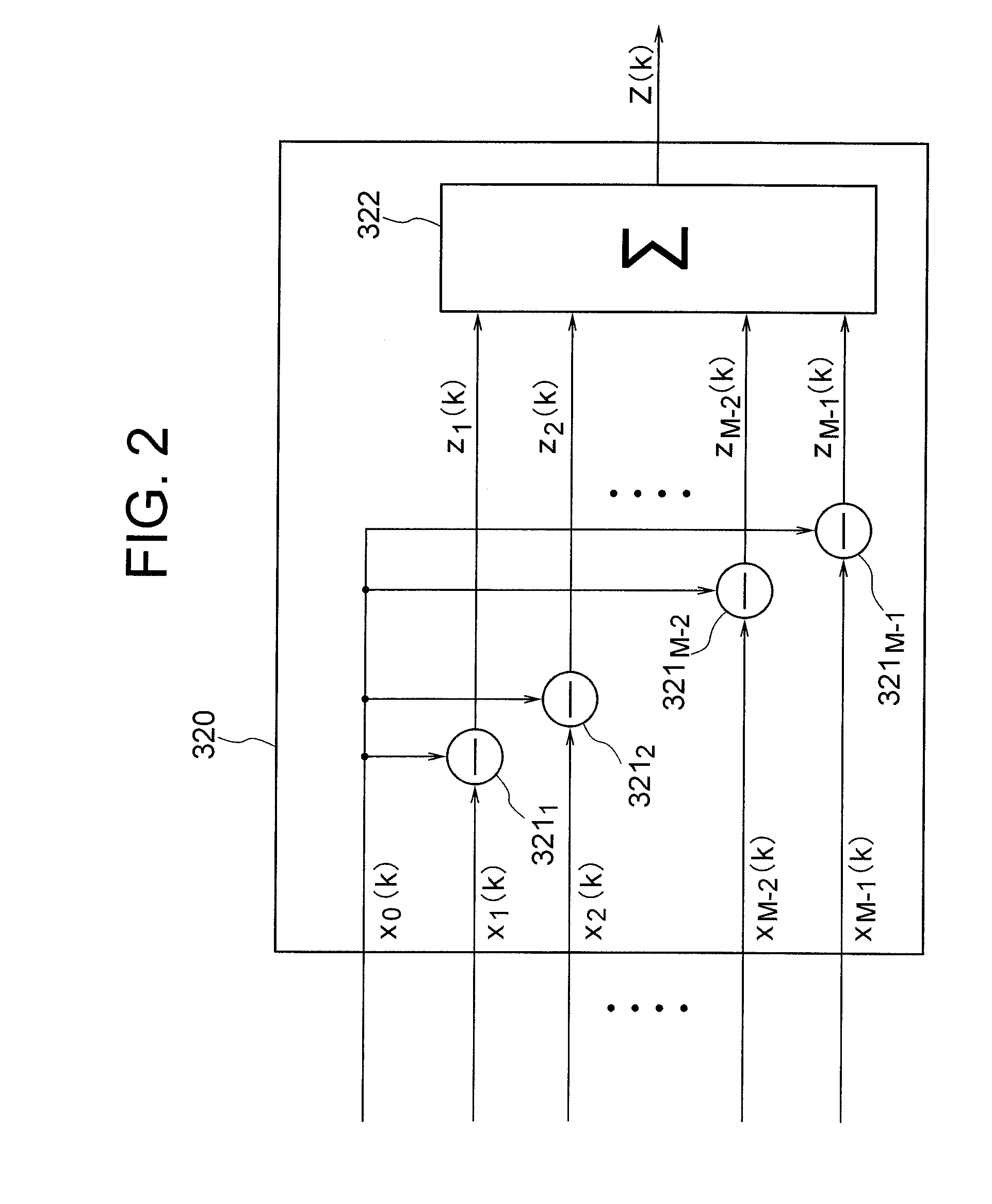
ActiveUS20100171662A1Excellent spatio-frequency selectivityImprove flatnessSignal processingRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsTarget signalFrequency characteristic
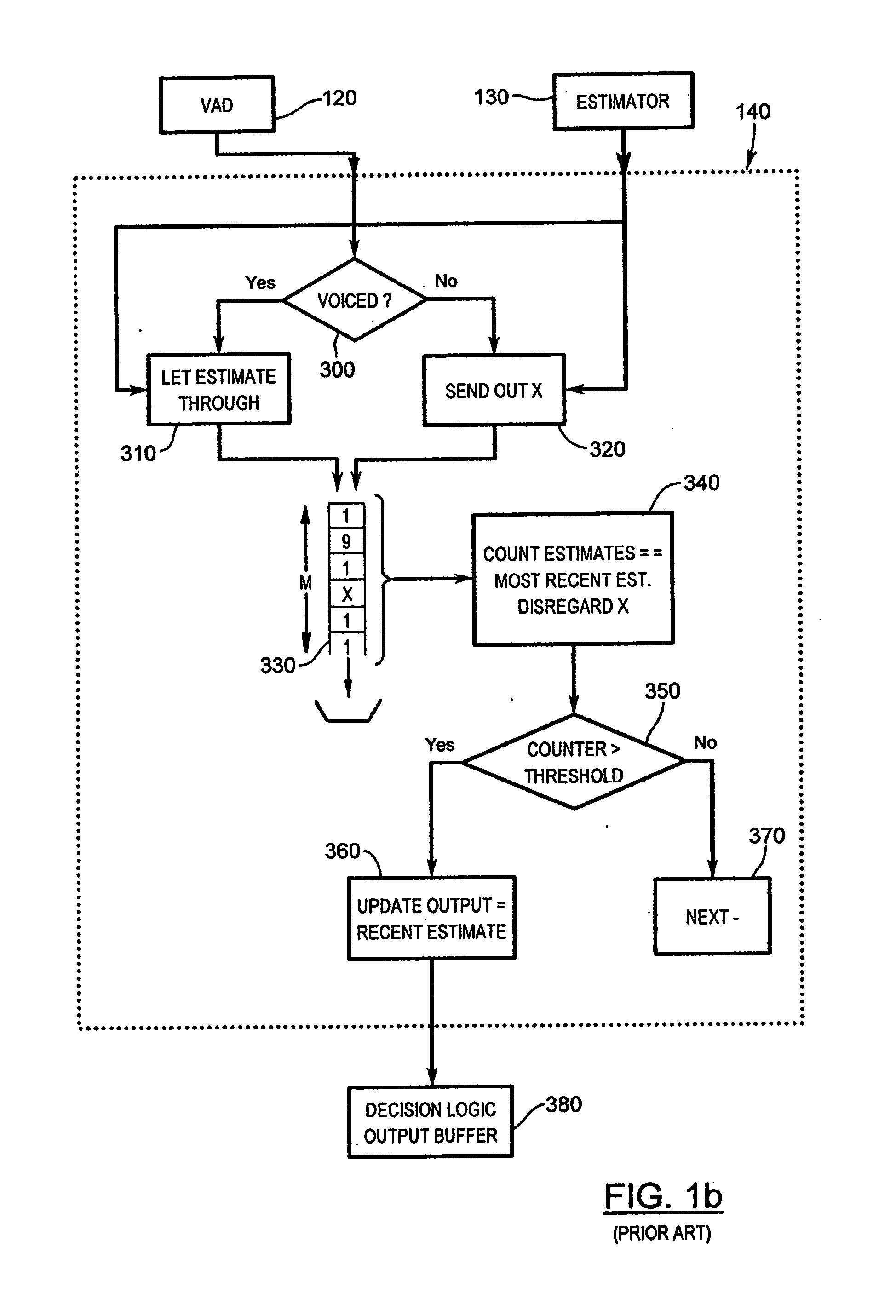
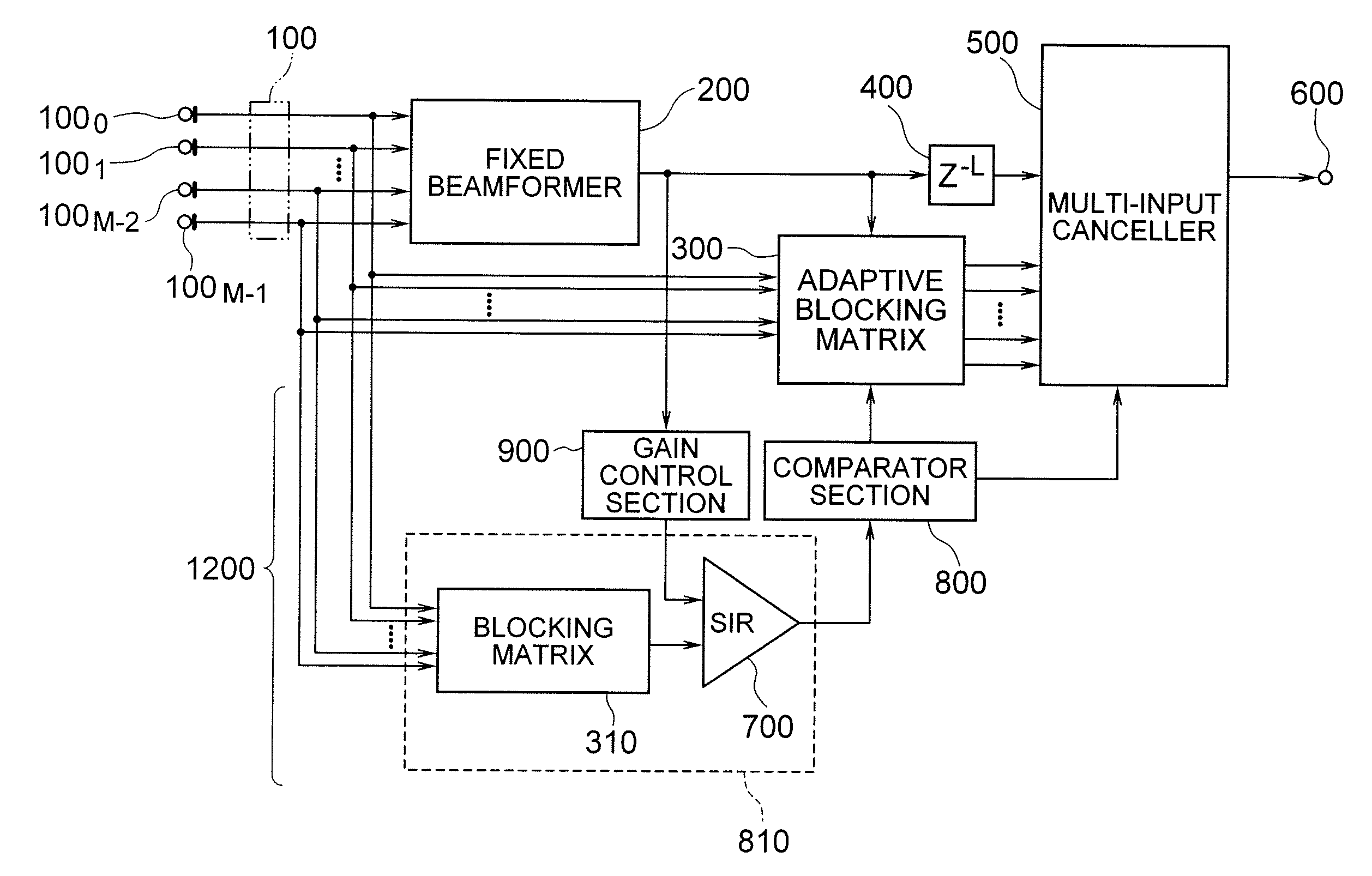
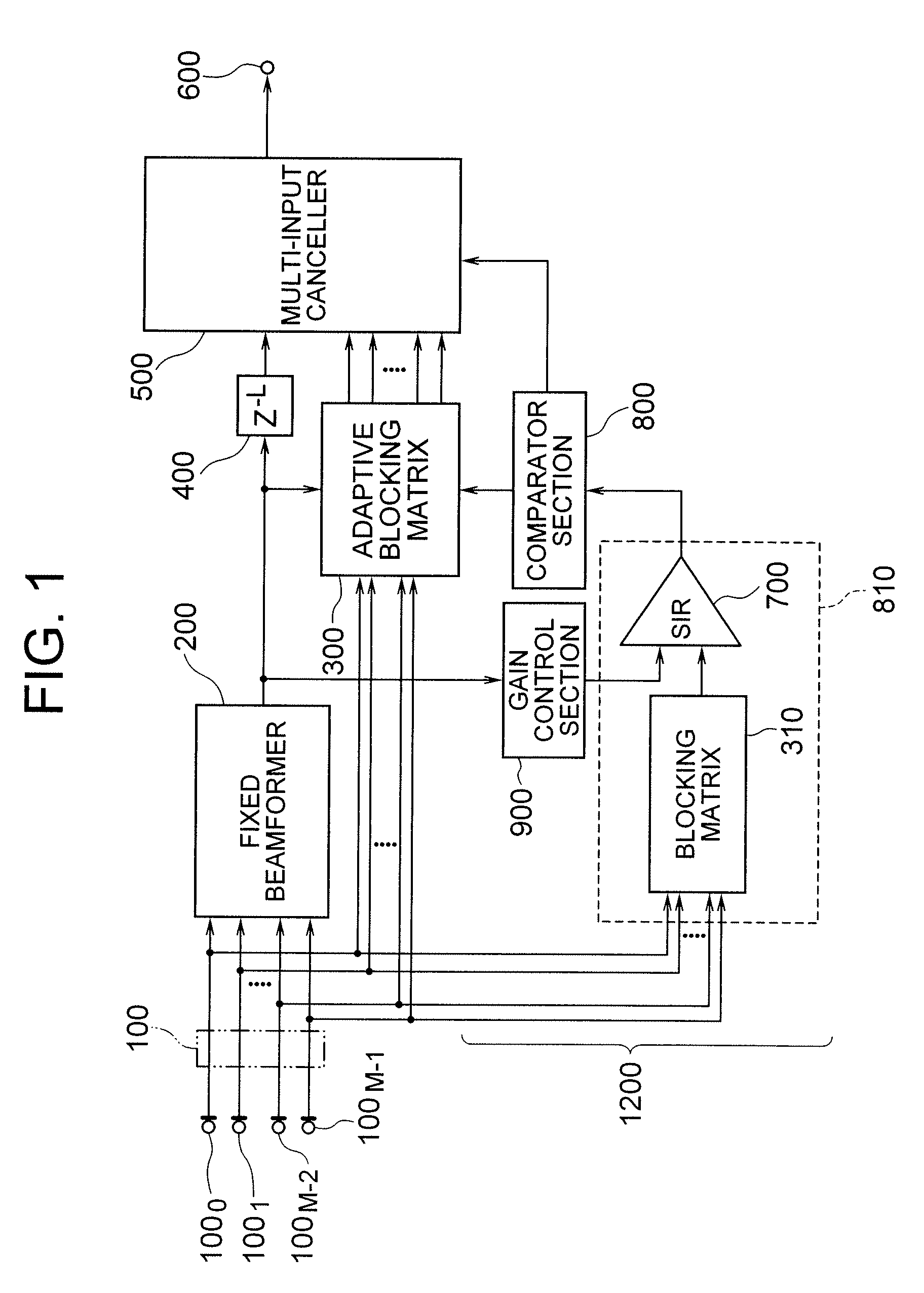
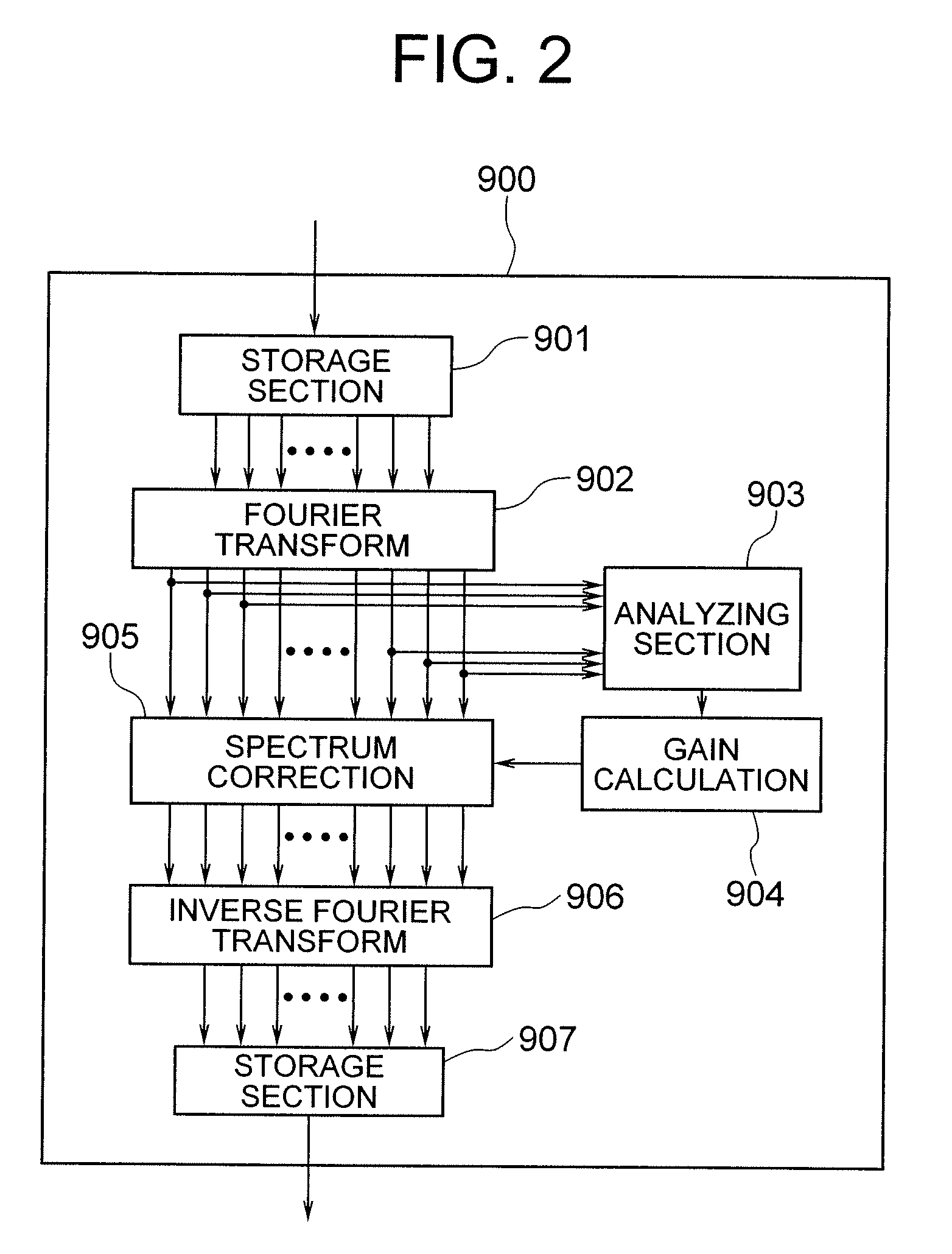
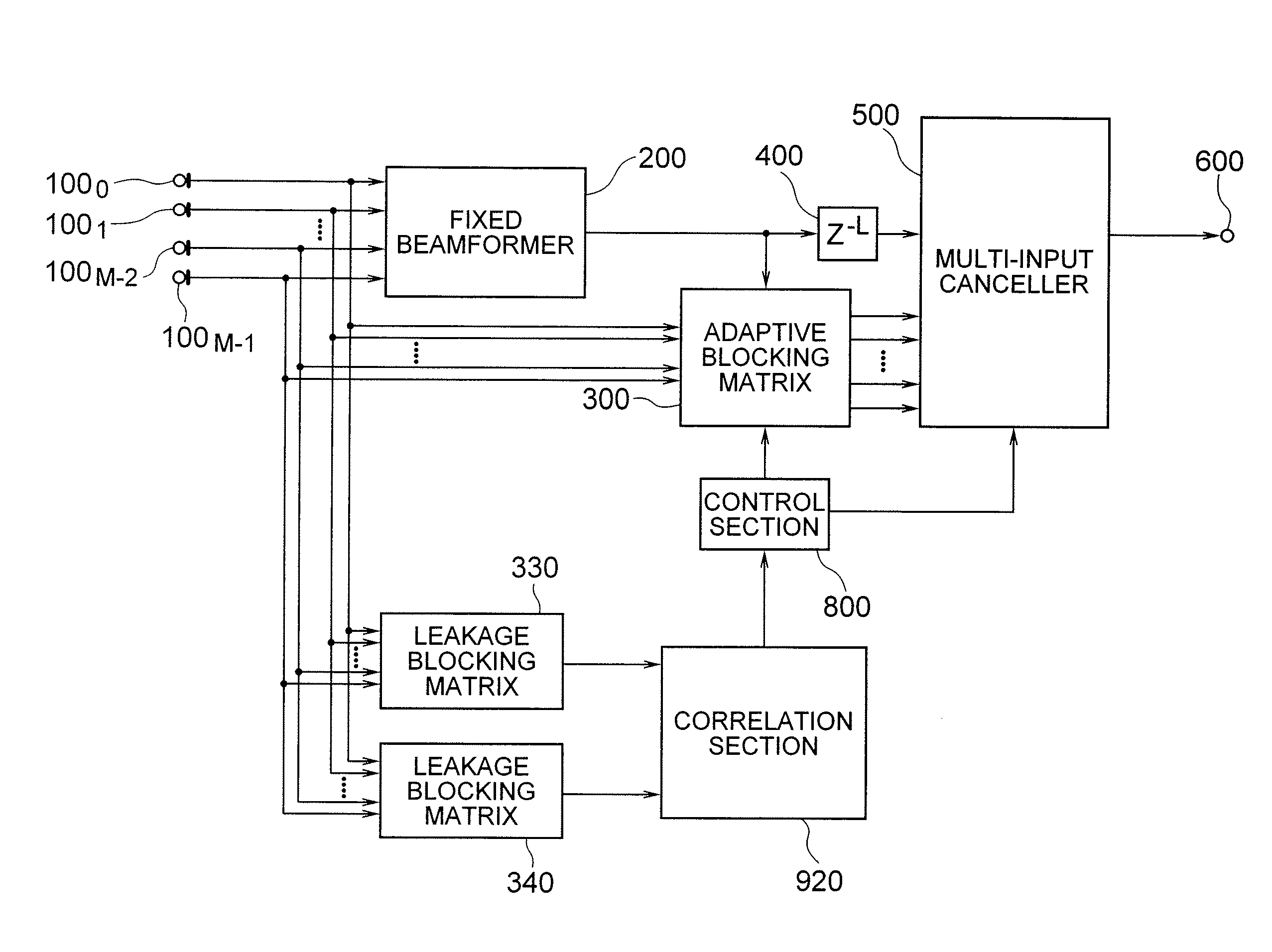
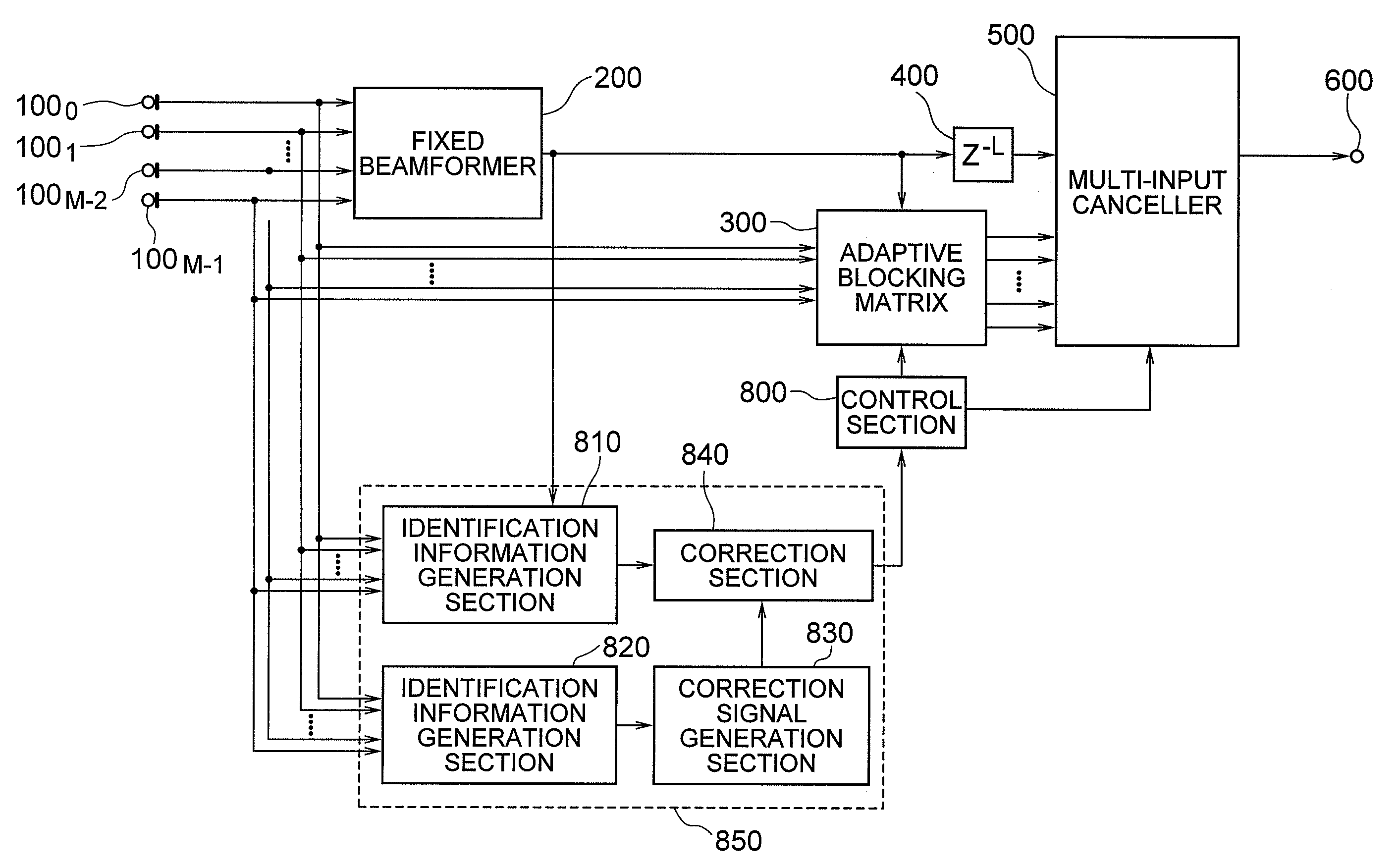
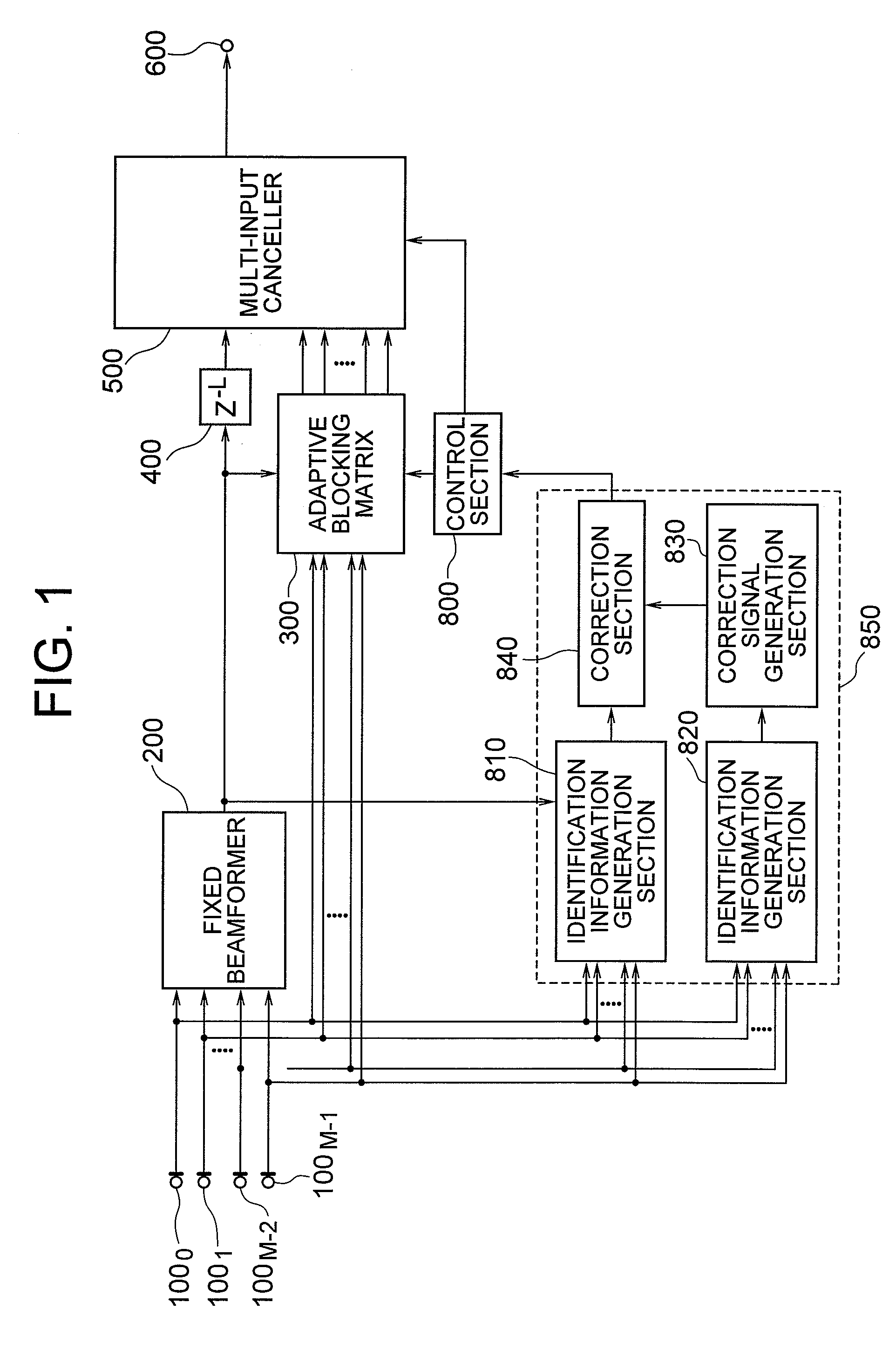
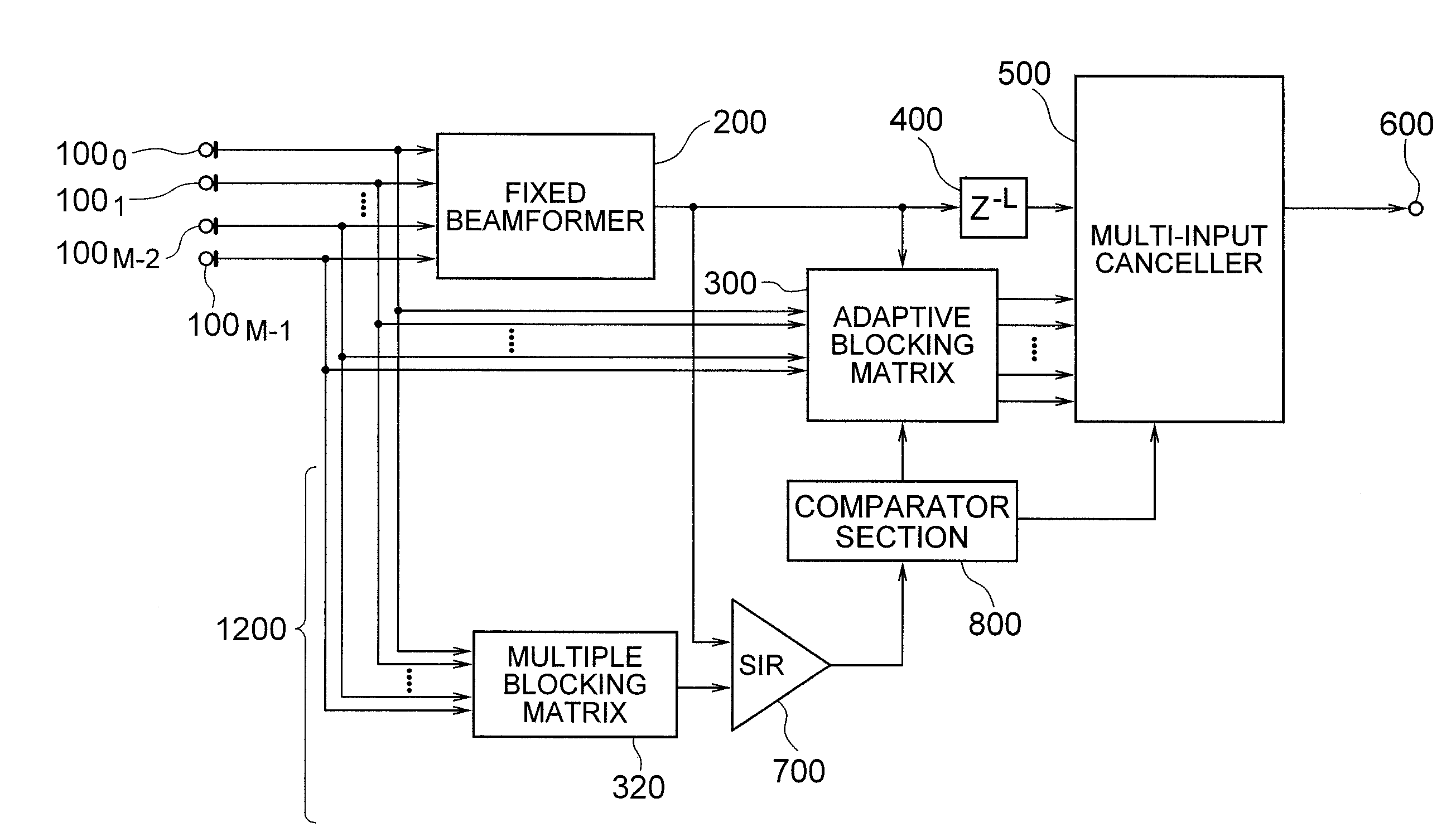
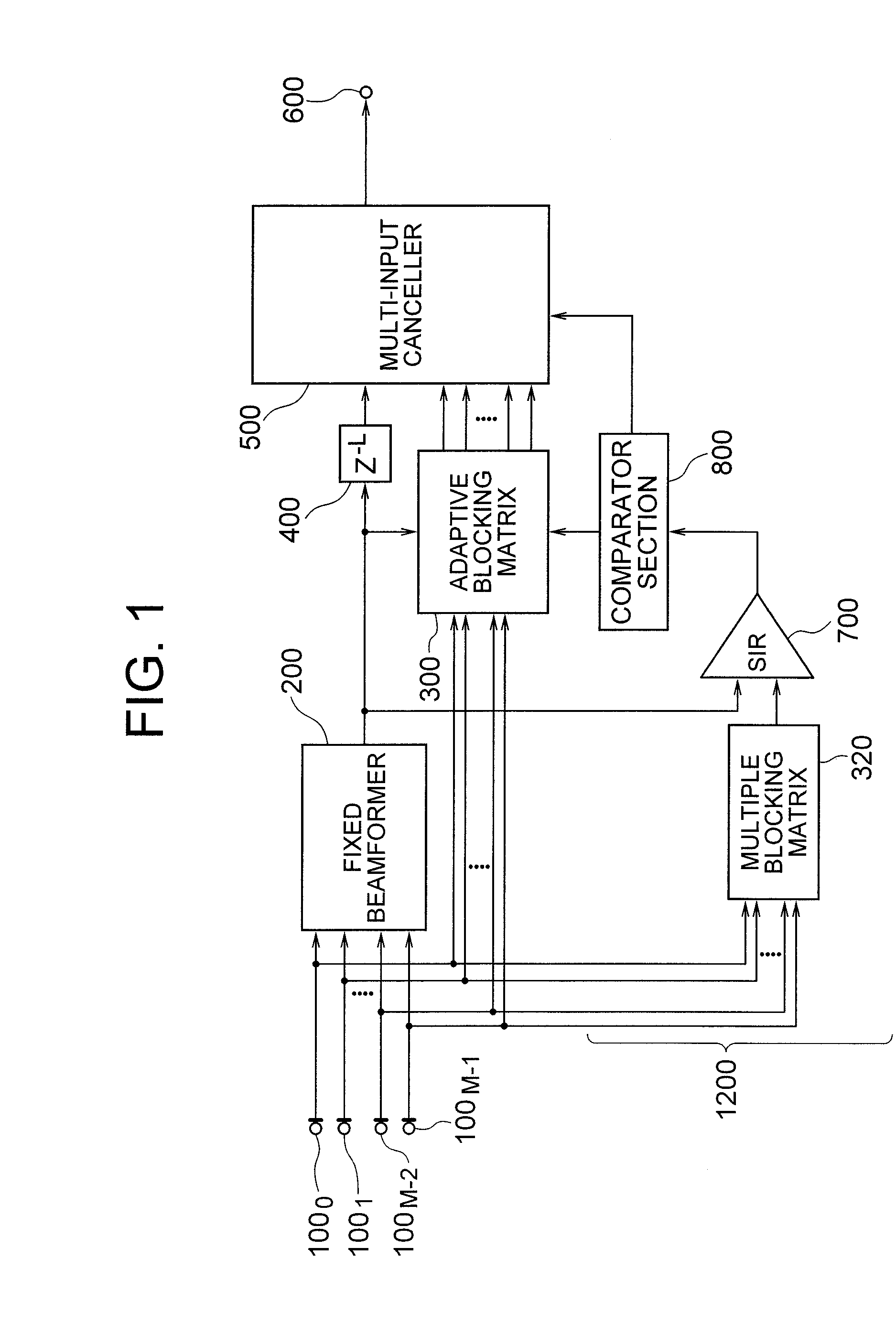
[Object] To provide an adaptive array control device, method, and program adapted to be able to output an enhanced target signal by precisely carrying out a coefficient update control of a plurality of signals input from a group of sensors arranged in an array, the coefficient update control being less influenced by the frequency characteristics of the signals and directions of a target signal and interference.[Achieving Means] The invention includes: a gain control section 900 having an analyzing section 903 which analyzes characteristics of a target signal and a correcting section 905 which corrects a target signal power estimated value in response to the analysis result; and blocking matrix circuits 310 and 320 which receive and process signals from a plurality of sensors having different intervals.
Owner:NEC CORP
Narrowband interference suppression method and narrowband interference suppression system used for passive synthetic aperture
InactiveCN104101871ASuppression of interfering signalsEasy to detectPosition fixationUsing reradiationTarget signalArray element
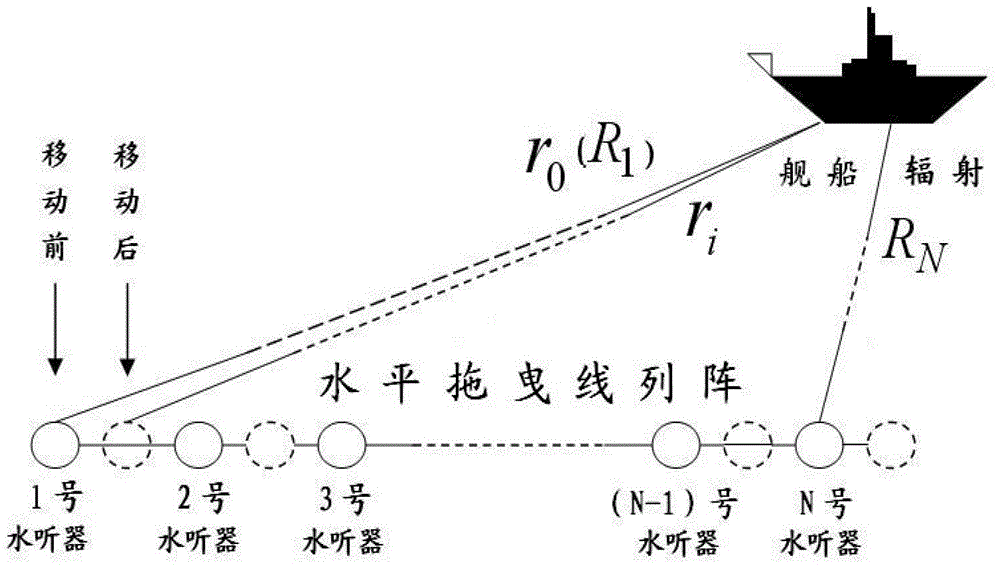
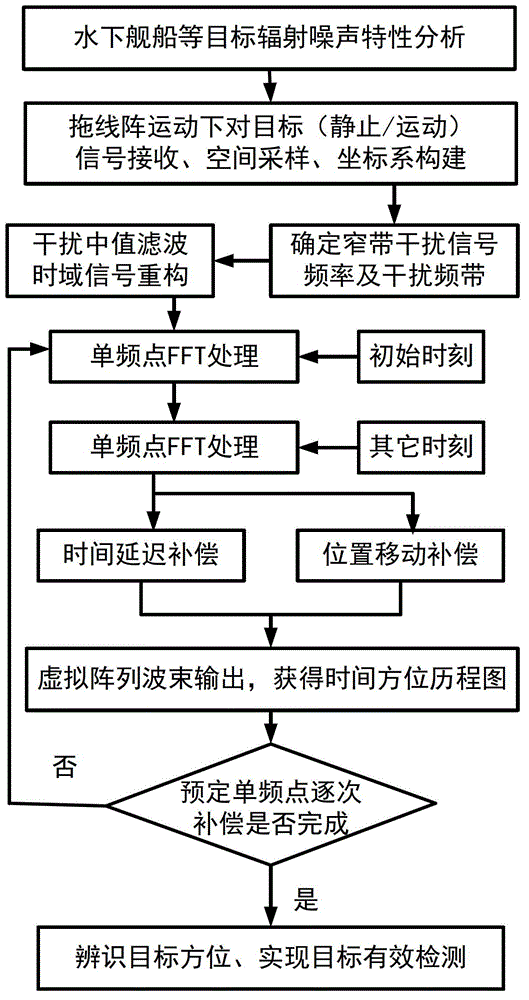
The present invention relates to a narrowband interference suppression method used for a passive synthetic aperture. The method comprises the steps of carrying out fast Fourier transform (FFT) on a signal received by an array element when a towed line array sonar is sampled at one moment, and estimating a center frequency and an interference band of narrowband interference; filtering the signal and reconstructing the filtered signal in a time domain; presetting the total number of frequency compensation; carrying out FFT and frequency-domain beam forming on the signal, and accumulating the frequency-domain beam forming result; after movement for certain time, carrying out FFT and frequency-domain beam forming on a sampling signal, and accumulating the frequency-domain beam forming result; calculating the total phase correction compensation to obtain an output result of an extended virtual array; carrying out coherent accumulation on the output result of the compensated extended virtual array to obtain a time azimuth history plot to detect a detected target signal, determining whether the current number of times of frequency compensation is the preset total number of frequency compensation, if no, changing a current frequency value, and re-executing until the current number of times of frequency compensation is the preset total number of frequency compensation.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adaptive array control device, method and program, and adaptive array processing device, method and program
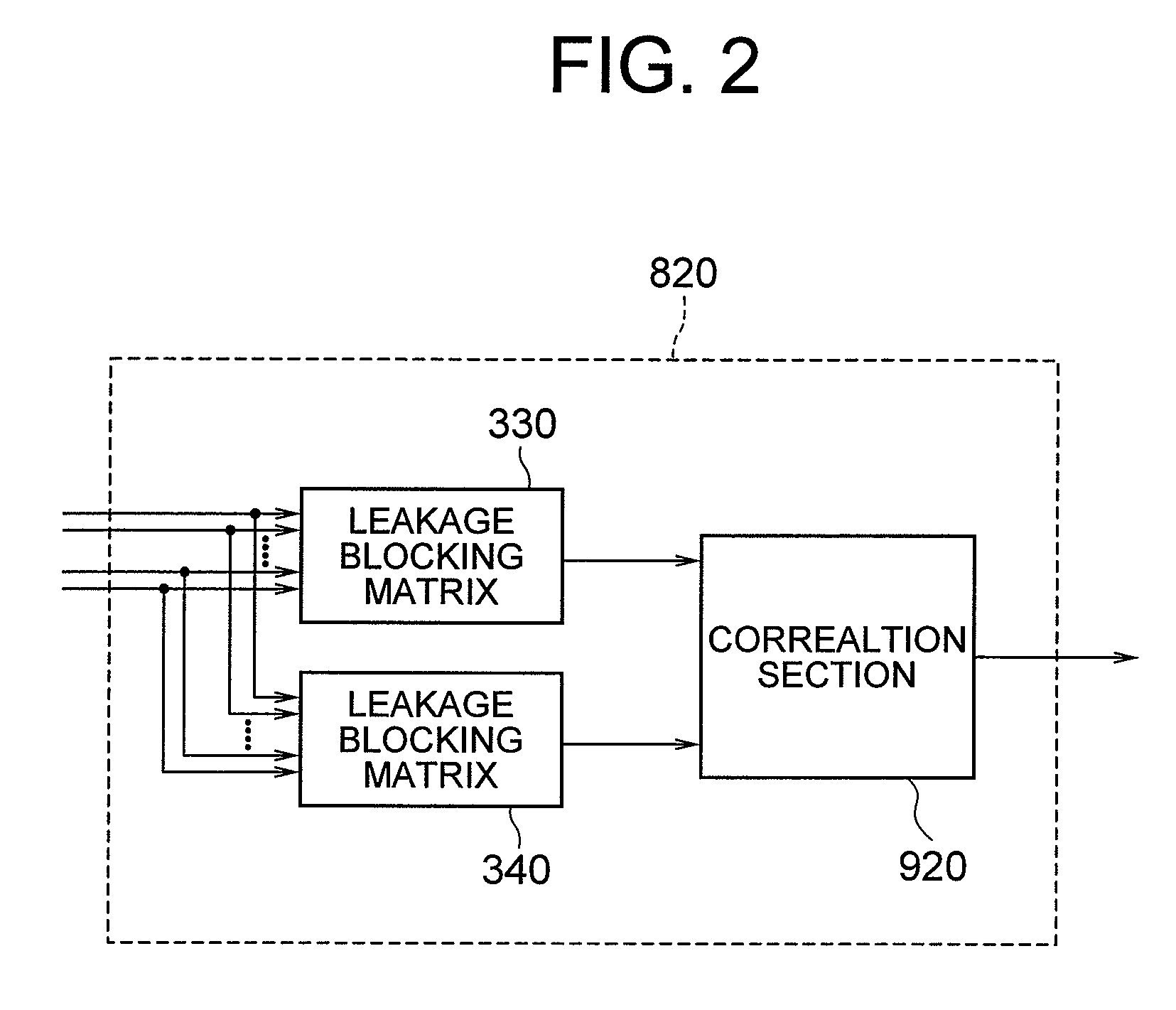
ActiveUS20090121934A1Reducing of breathing noiseMagnitude relationshipRadio wave finder detailsMicrophonesTarget signalPhase difference
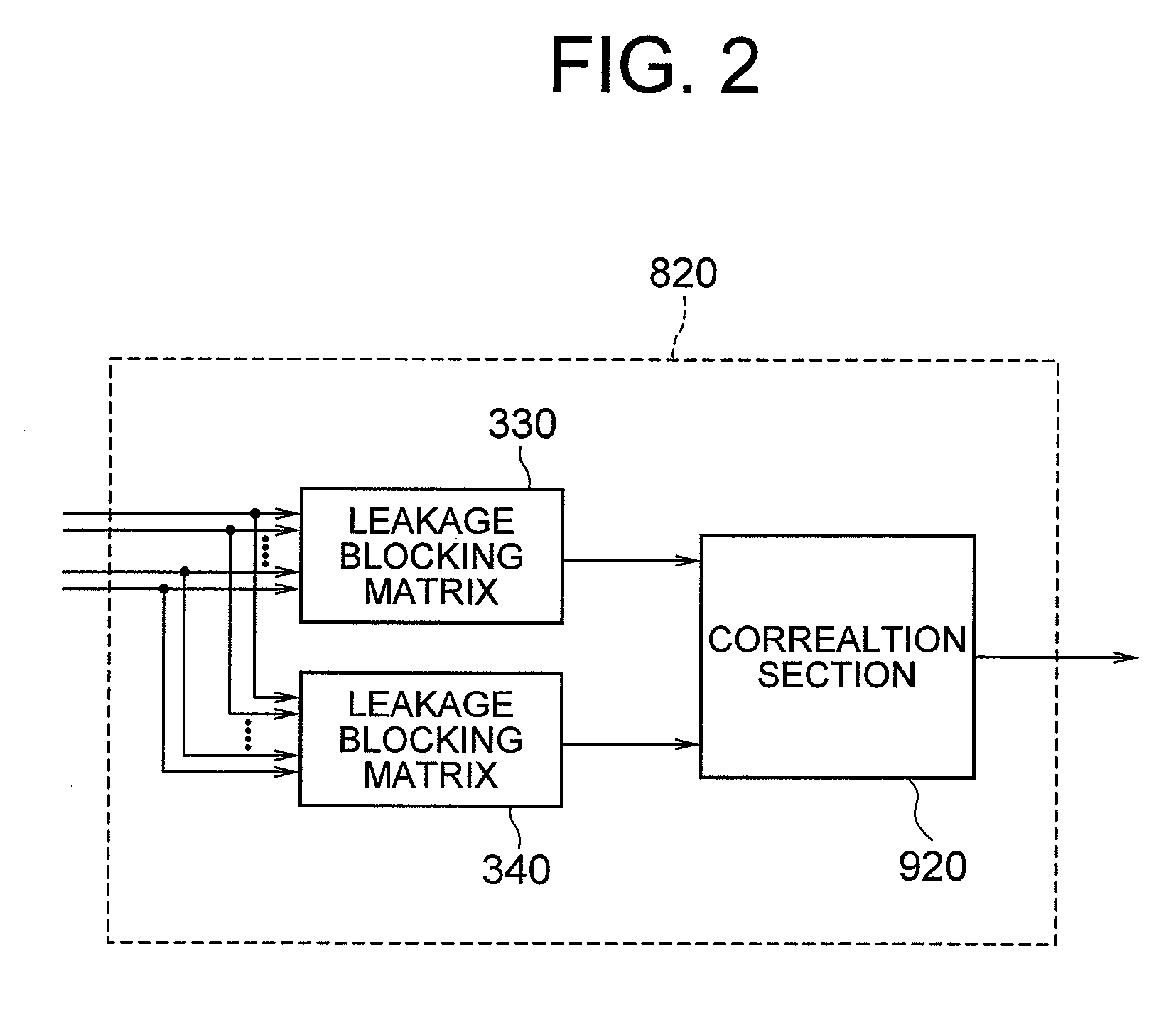
[Object] To provide an adaptive array controlling method, a device, and a program, and an adaptive array processing method, a device, and a program, which are less influenced by frequency characteristics of input signals and directions of a target signal and interference, and capable of performing accurate coefficient update.[Achieving Means] A device includes: a pair of array processing sections 330 and 340 in which a gain is non-zero with respect to a target signal, and a phase difference in processing results with respect to interference becomes close to 180 degrees; and a correlation calculation section 920 which calculates correlation between their outputs.
Owner:NEC CORP
Autonomous sonar system and method
ActiveUS8107320B2Multi-channel direction findingSystems with undesired wave eliminationPropellerSonar system
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Adaptive array control device, method and program, and adaptive array processing device, method and program
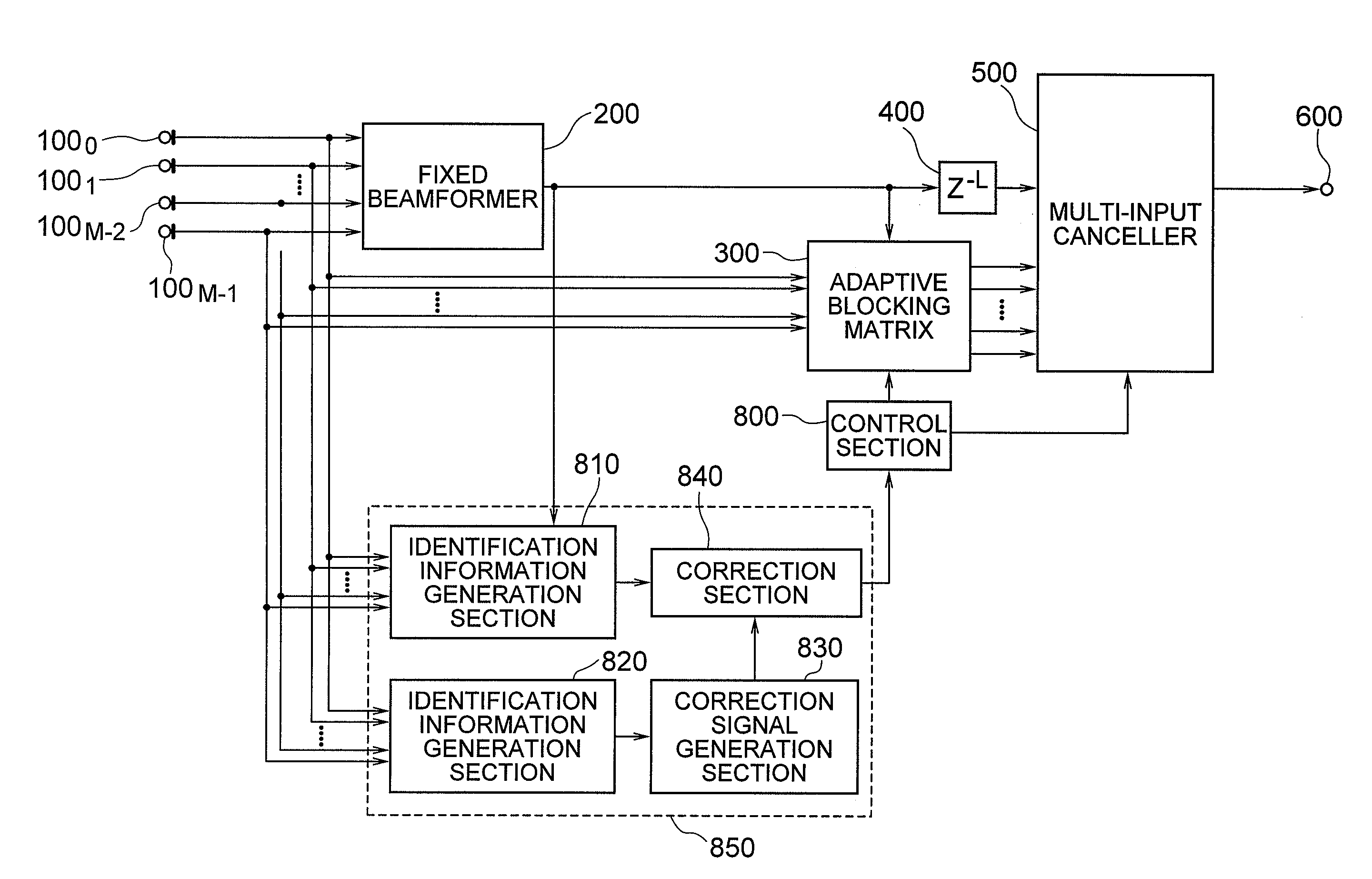
InactiveUS20090073040A1Highly accurate identification informationEasy to controlRadio wave finder detailsMicrophonesTarget signalFrequency characteristic
[Object] By enabling accurate coefficient update, a high-quality array processing output which is less influenced by frequency characteristics and incoming directions of input signals control can be acquired, irrespective of the frequency characteristics and incoming direction of the input signals. [Achieving Means] Identification information of a target signal and interference by amplitude is corrected according to identification information of the target signal and the interference by phase, and with use of the correction result, identification of the target signal and the interference is performed. More specifically, an identification information generation section according to phase, a correction signal generation section, and a correction section are provided.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for acoustic source tracking using a horizontal line array
An apparatus for processing passive acoustic signals received on a horizontal line array that were either emitted from an underwater object or echo returned from an object, is proposed to track the motion (bearing change and range change) of an object (target) relative to the receiver horizontal line array. Adaptive array processing for a moving object is biased for a moving source when the number of data samples is limited by the stationariness condition. Motion compensation can be carried out in the beam domain by beam shifting for a bearing changing object and frequency shifting for a range changing object. The method includes receiving acoustic signals from the target, determining the beam covariance matrices, determining the target bearing rate and range rate, processing the beam covariance matrices by compensating for the target motion, and producing a beam power plot versus time. Interference signal is suppressed when the interference source does not have the same motion (bearing and range rate) as the target. The method does not need detailed environmental acoustic information of the sound channel normally required to model the sound propagation.
Owner:USA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY THE
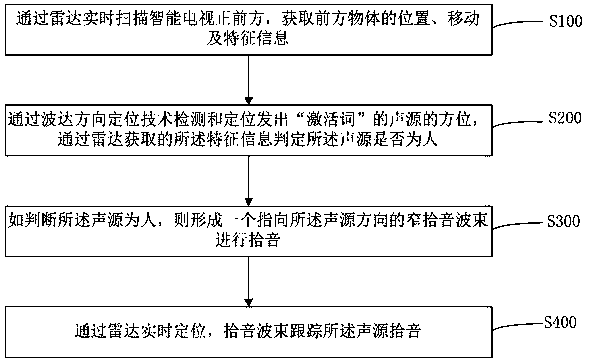
Method and system for improving remote field voice recognition rate, and readable storage medium
ActiveCN110085258APrecise positioningImprove recognition rateSignal processingPosition fixationSound sourcesRadar
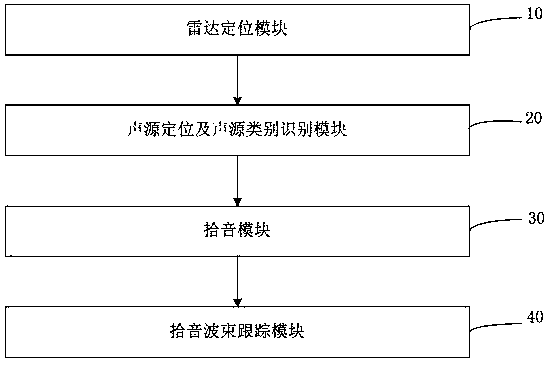
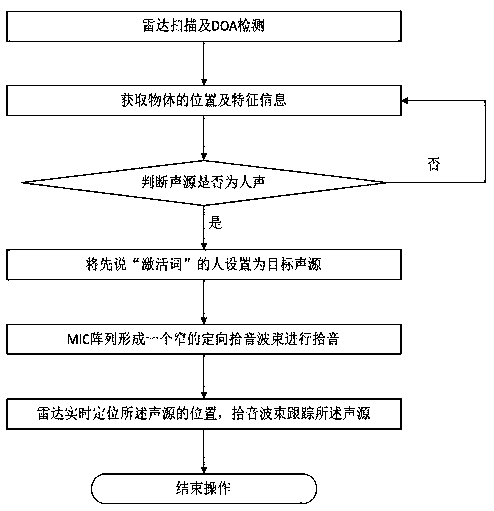
The invention provides a method and system for improving the remote field voice recognition rate, and a storage medium. An intelligent television scans the front side of an intelligent television in real time to obtain the position, the motion and feature information of the front object; the position of a sound source giving out an activation word is detected and positioned through a wave arrivaldirection positioning technology; whether the sound source is people or not is judged through feature information obtained through radar; if the sound source is people, a narrow sound picking wave beam pointing to the sound source direction is formed through an MIC array for sound picking; the sound source is positioned in real time through radar; the sound picking wave bead regulates the angle totrack the sound source in real time according to the position parameter of the sound source provided by the radar; the sound picking stability is improved. Compared with the prior art with the defects of difficult distinguishing between an interference source and a target sound source, unprecise positioning and sound picking incapability during the target sound source movement, the method and thesystem provided by the invention have the advantages that the precise positioning can be realized; the interference source and the target sound source can be distinguished; the target sound source can be tracked; the remote field voice recognition rate is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN TCL NEW-TECH CO LTD
Adaptive array control device, method and program, and adaptive array processing device, method and program using the same
ActiveUS20090086578A1Improve flatnessInterference power can be accuratelyRadio wave finder detailsMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesFrequency characteristicComputer science
[Object] To provide an adaptive array control method, device, and program, and an adaptive array processing method, device, and program, capable of performing accurate coefficient update control independent of frequency characteristics and incoming directions of signals.[Achieving Means] The present invention is characterized as to array-process signals received from a plurality of pairs of sensors having a plurality of different sensor intervals, and using the array processing result, estimate interference power accurately. More specifically, the present invention includes a multiple blocking matrix circuit 320 which processes signals receiving from sensors having a plurality of different intervals, and an accurate coefficient update control is performed based on the output array-processed signal. Thereby, deterioration of output signals and breathing noises are reduced, and high-quality array processing can be performed.
Owner:NEC CORP
Adaptive array control device, method and program, and adaptive array processing device, method and program
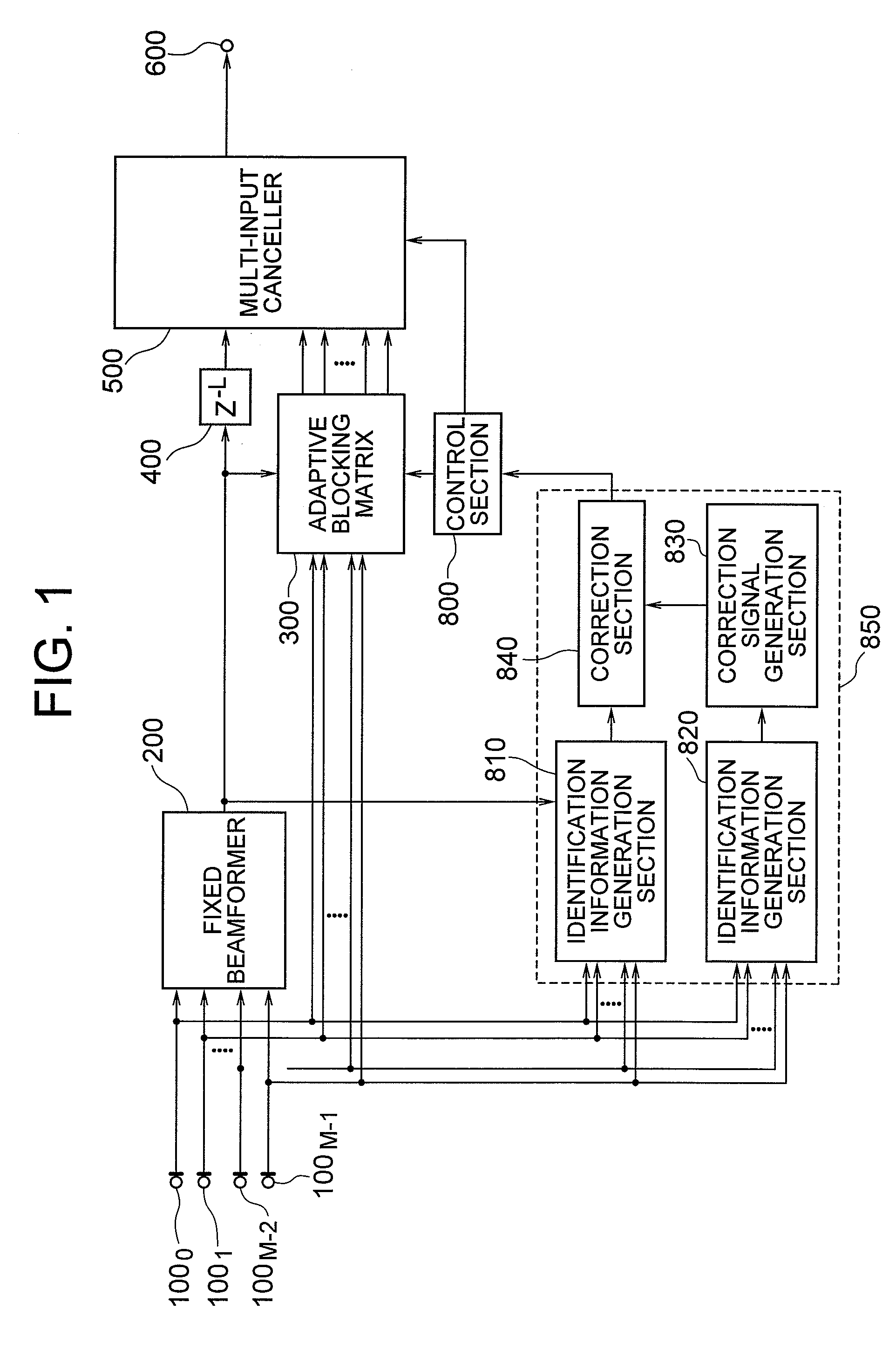
InactiveUS7944775B2Highly accurate identification informationEasy to controlRadio wave finder detailsMicrophonesTarget signalSelf adaptive
[Object] By enabling accurate coefficient update, a high-quality array processing output which is less influenced by frequency characteristics and incoming directions of input signals control can be acquired, irrespective of the frequency characteristics and incoming direction of the input signals. [Achieving Means] Identification information of a target signal and interference by amplitude is corrected according to identification information of the target signal and the interference by phase, and with use of the correction result, identification of the target signal and the interference is performed. More specifically, an identification information generation section according to phase, a correction signal generation section, and a correction section are provided.
Owner:NEC CORP
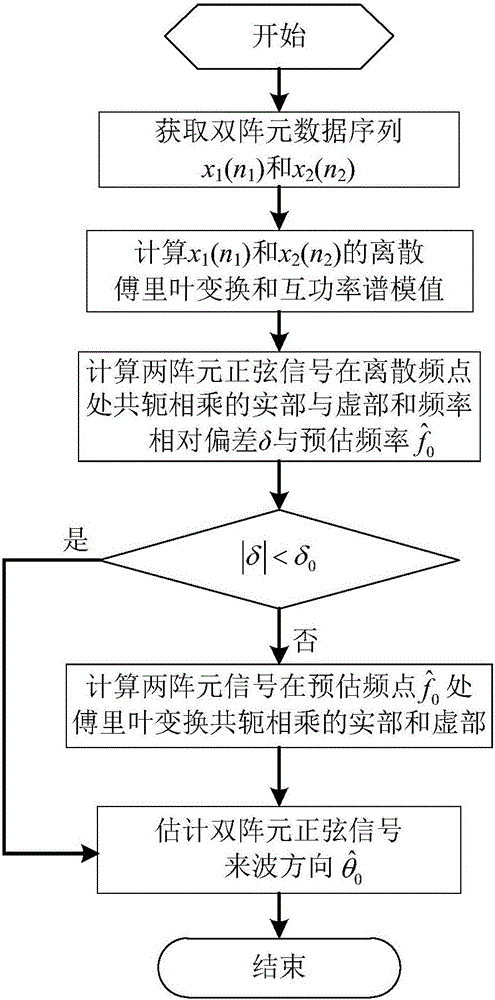
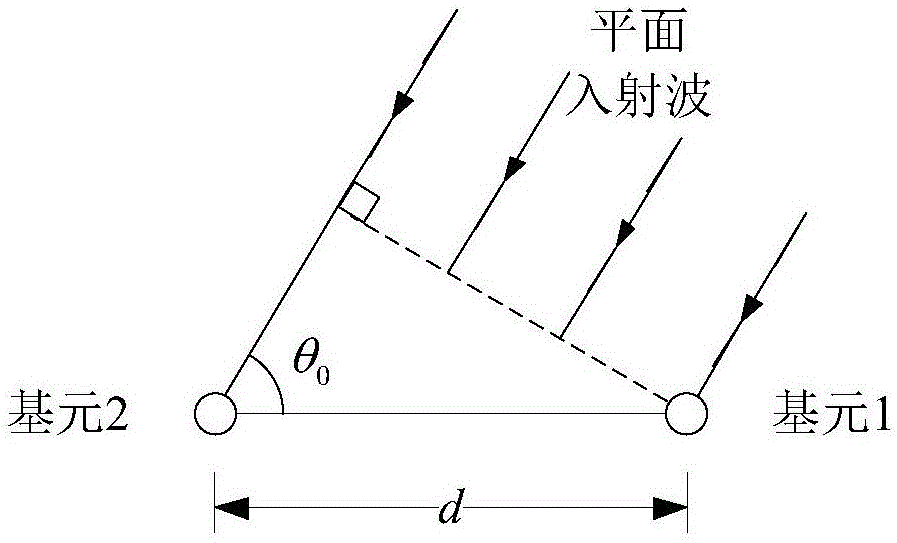
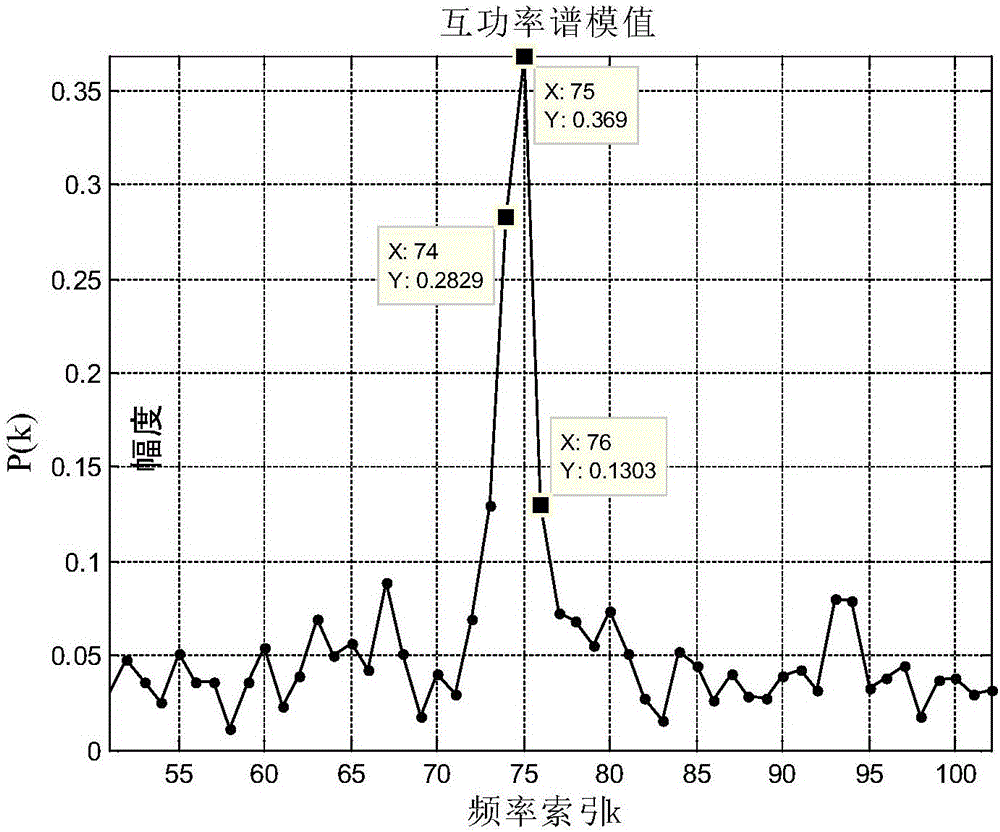
Frequency estimation-based dual-array element sinusoidal signal direction of arrival estimation method
ActiveCN106546949AImprove estimation accuracySNR lower limitRadio wave finder detailsDirection/deviation determination systemsEstimation methodsArray element
The invention relates to a frequency estimation-based dual-array element sinusoidal signal direction of arrival estimation method. The method includes the following steps that: first step, dual-array element sinusoidal signal sampling data sequences x1(n1) and x2(n2) are obtained; second step, the discrete Fourier transformation and cross-power spectral modulus values P(k) of x1(n1) and x2(n2) are calculated; step 3, the real part xid and imaginary part etad of the conjugate multiplication of two array element sinusoidal signals at a discrete frequency point, and the frequency relative deviation delta and estimated frequency f<^>0 of the two array element sinusoidal signals are calculated; fourth step, the absolute value of the frequency relative deviation delta is compared with a relative deviation threshed value delta0, if the absolute value of the frequency relative deviation delta is smaller than the relative deviation threshed value delta0, Fourier transformation is performed on the real part xi which is equal to xid and imaginary part eta which is equal to etad of the conjugate multiplication of the two array element sinusoidal signals at an estimated frequency point, and the method shifts to a sixth step, otherwise, the method shifts to a fifth step; fifth step, the real part xi and imaginary part eta of the conjugate multiplication of the two array element sinusoidal signals at the estimated frequency point, which are subjected to the Fourier transformation, are calculated; and sixth step, the direction of arrival theta of the two array element sinusoidal signals is estimated. With the method adopted, the estimation accuracy of the direction of arrival can be improved. The method has high engineering practicability.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
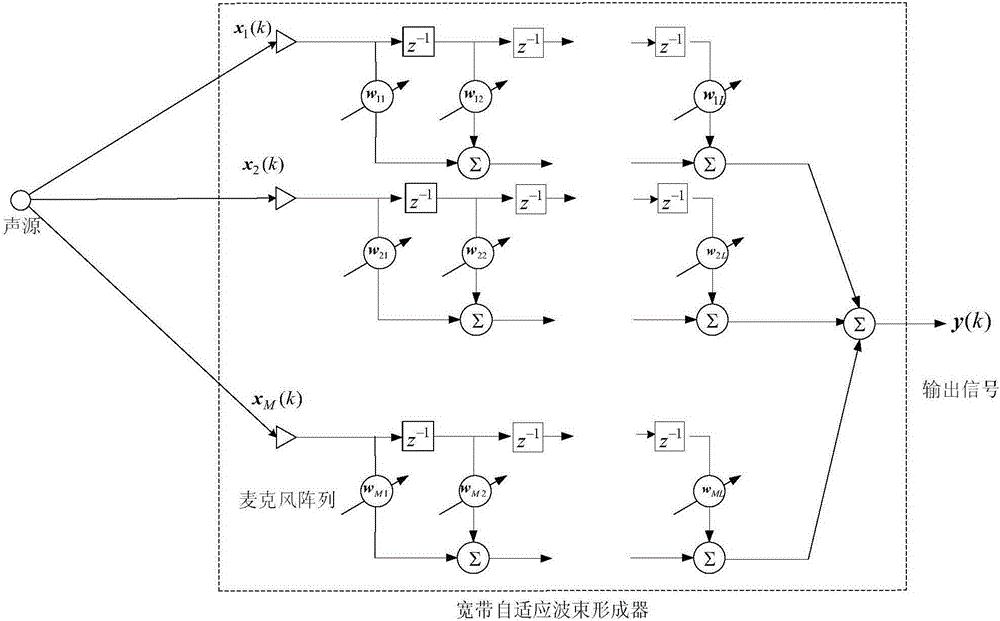
Near-field linear constrained minimum variance adaptive weighted-frequency-invariant beam forming method
ActiveCN105223544AStructure without limitGood near-field broadband frequency invarianceSystems with undesired wave eliminationInteraction systemsVoice communication
The invention discloses a near-field linear constrained minimum variance adaptive weighted-frequency-invariant beam forming method. The method is based on linear constrained minimum variance. A balance matrix of an array spatial response bias function is defined based on the spatial response bias function, and the matrix is introduced into a near-field linear constrained minimum variance beam forming method to obtain the near-field linear constrained minimum variance weighted-frequency-invariant beam forming method. Then, the weighting coefficient in the near-field linear constrained minimum variance weighted-frequency-invariant beam forming method is defined as a function of the field spot distance and the signal frequency, and the function is dynamic and is updated adaptively. The method of the invention is widely applied to multi-channel speech enhancement, man-machine voice interaction systems, hearing aids, vehicular hands-free voice communication, remote video conferencing systems, robot hearing, and other fields.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Systems, methods, apparatus, and computer-readable media for coherence detection
InactiveCN103295579ASpeech analysisMulti-channel direction findingPattern recognitionPhase difference
The invention relates to systems, methods, apparatus, and computer-readable media for coherence detection. Based on phase differences between corresponding frequency components of different channels of a multichannel signal, a measure of directional coherency is calculated. Application of such a measure to voice activity detection and noise reduction are also disclosed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Coprime matrix robust adaptive beamforming algorithm based on matrix filling
ActiveCN110045323AIncrease freedomEfficient use ofRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSystems with adjusting phase/time-lag-errorsCoprime arrayEuclidean vector
The invention provides a coprime matrix robust adaptive beamforming algorithm based on matrix filling. The coprime matrix robust adaptive beamforming algorithm based on matrix filling comprises the following steps that a sample covariance matrix of received data is calculated; the sample covariance matrix is vectorized to obtain vectors, and then elimination of redundancy and vector rearrangementare carried out on the vectors to obtain the received data vectors of a complete coprime matrix differential optimization matrix; zero is arranged between elements with discontinuous wave range difference in the received data vectors in a filling mode to obtain the vectors, and then the vectors are obtained by taking information of the positive half part of the vectors; the vectors are expanded into a Toplitz matrix; the Toplitz matrix is restored to obtain a filled covariance matrix; spectral peak search is carried out in an interference signal angle region to obtain estimation of arrival angles of each interference signal; the estimated arrival angles of interference signals, the physical array information of a coprime array and an interference and noise covariance matrix which reconstructs a coprime array physical array are utilized; weighted vectors of an adaptive beamformer is calculated by using the estimation of the interference and noise covariance matrix and expected signal steering vectors.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Noise suppression system
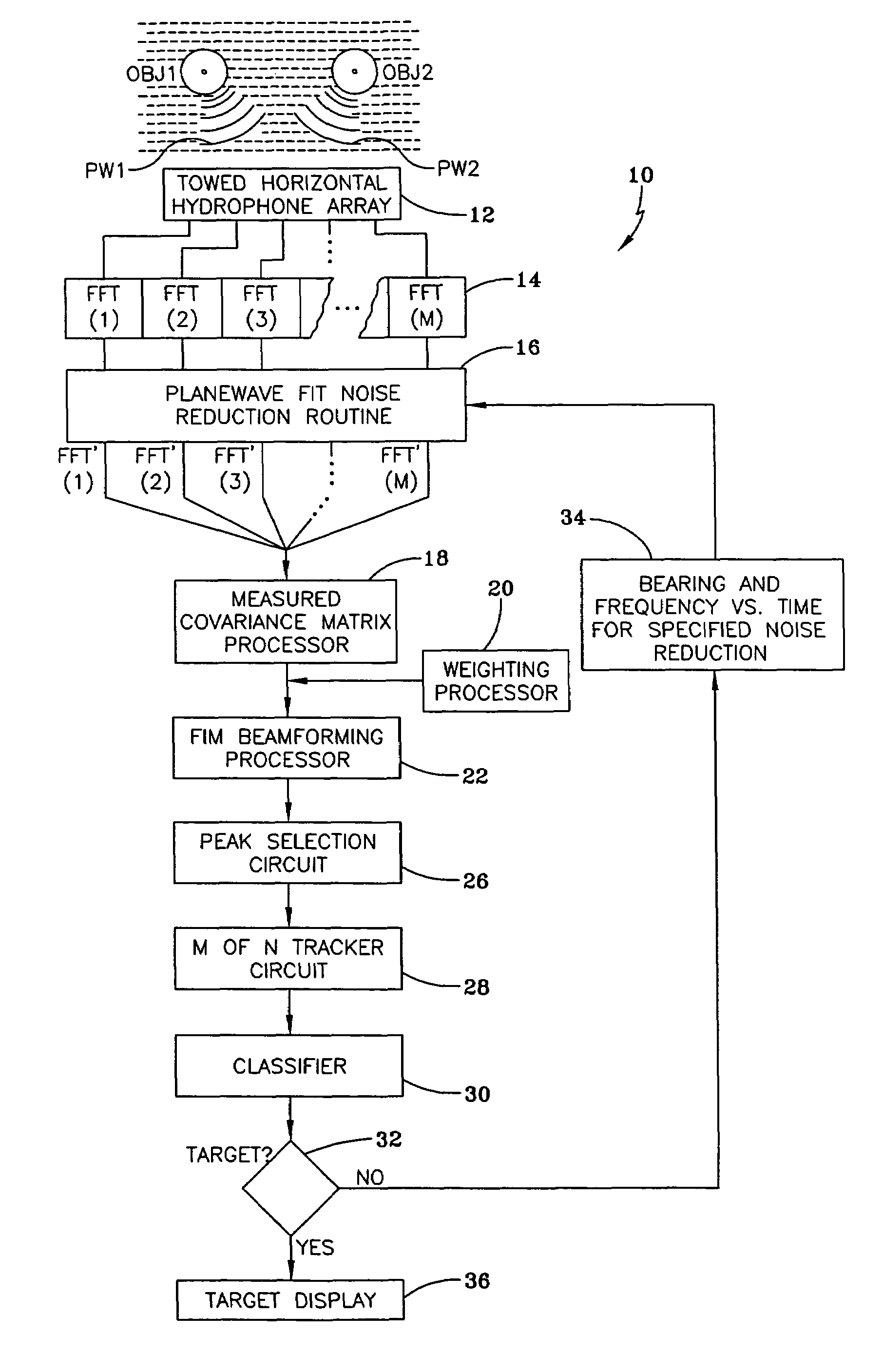
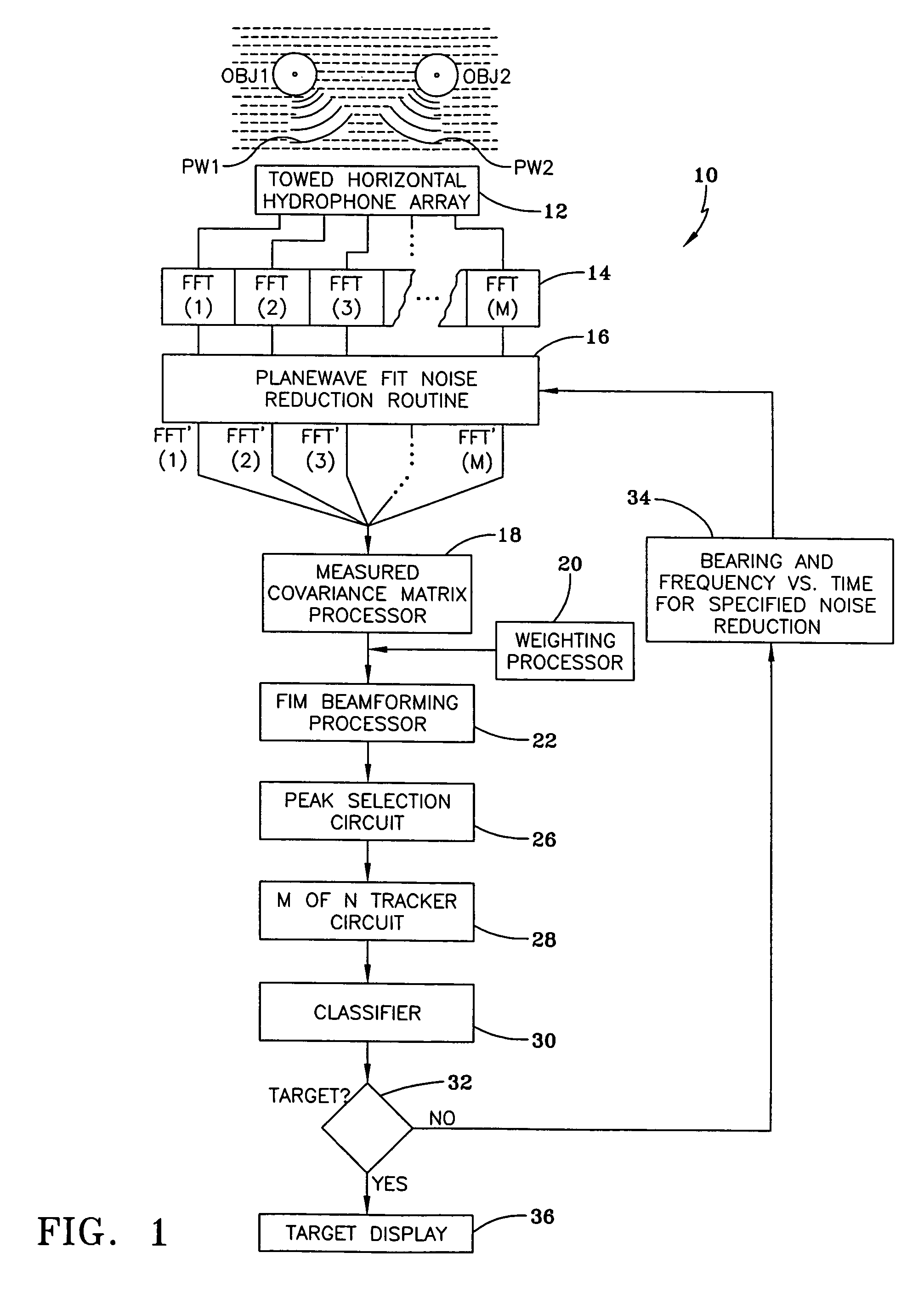
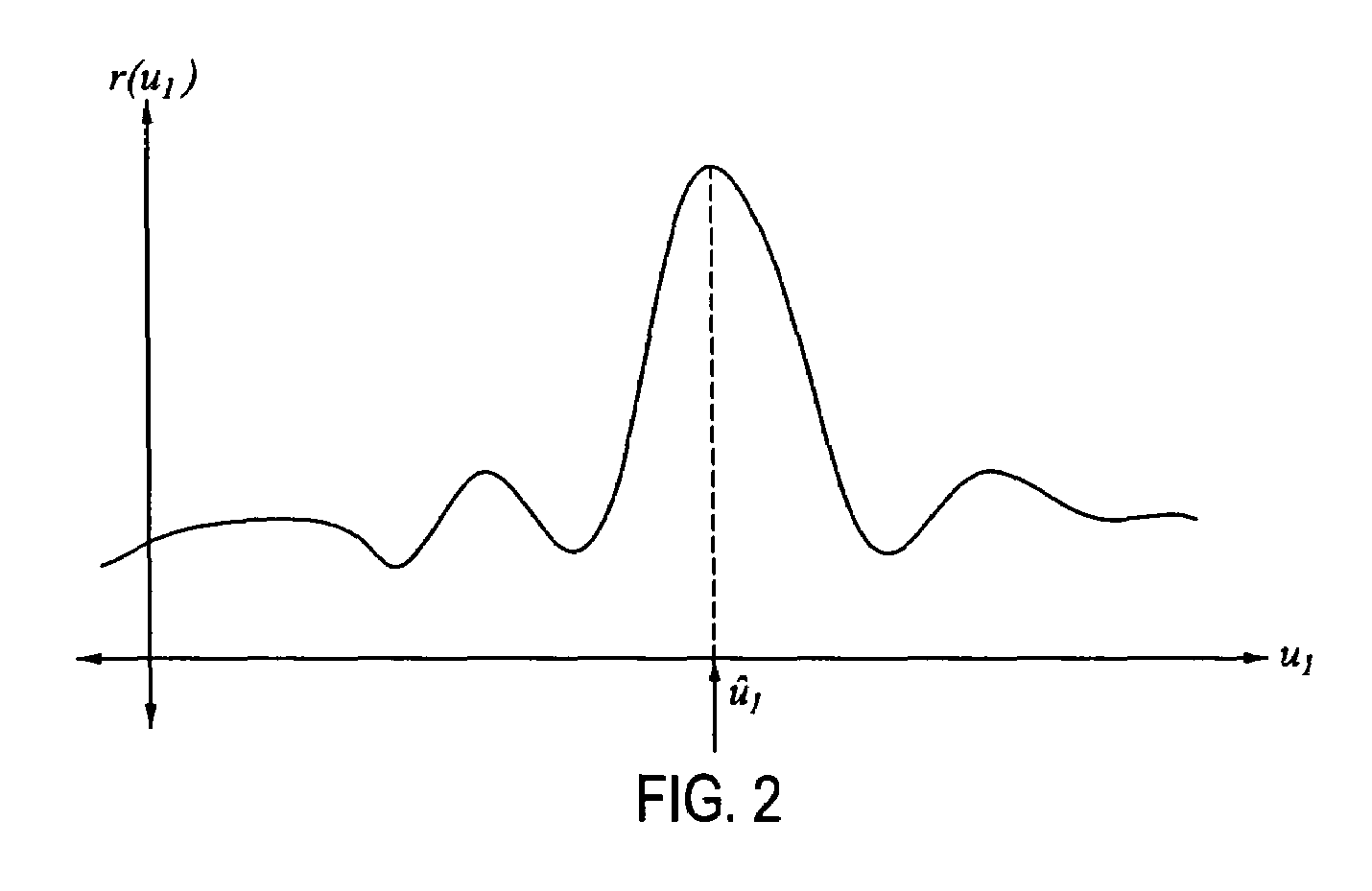
InactiveUS7319640B1Suppress noiseEasy to detectPosition fixationSystems with undesired wave eliminationSensor arrayEngineering
A method and apparatus is provided for suppressing noise which includes receiving a plurality of signals from an array of sensors and transforming each of these signals to the frequency domain. The transformed signals are beamformed so that noise sources can be identified by bearing and frequency range. A planewave-fit noise-suppression routine is then used to remove identified noise sources from the transformed signals and to provide a noise-suppressed transformed signal having signals from said identified noise sources suppressed.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Spherical harmonic order self-adaptive selection method suitable for spherical microphone array sound source orientation
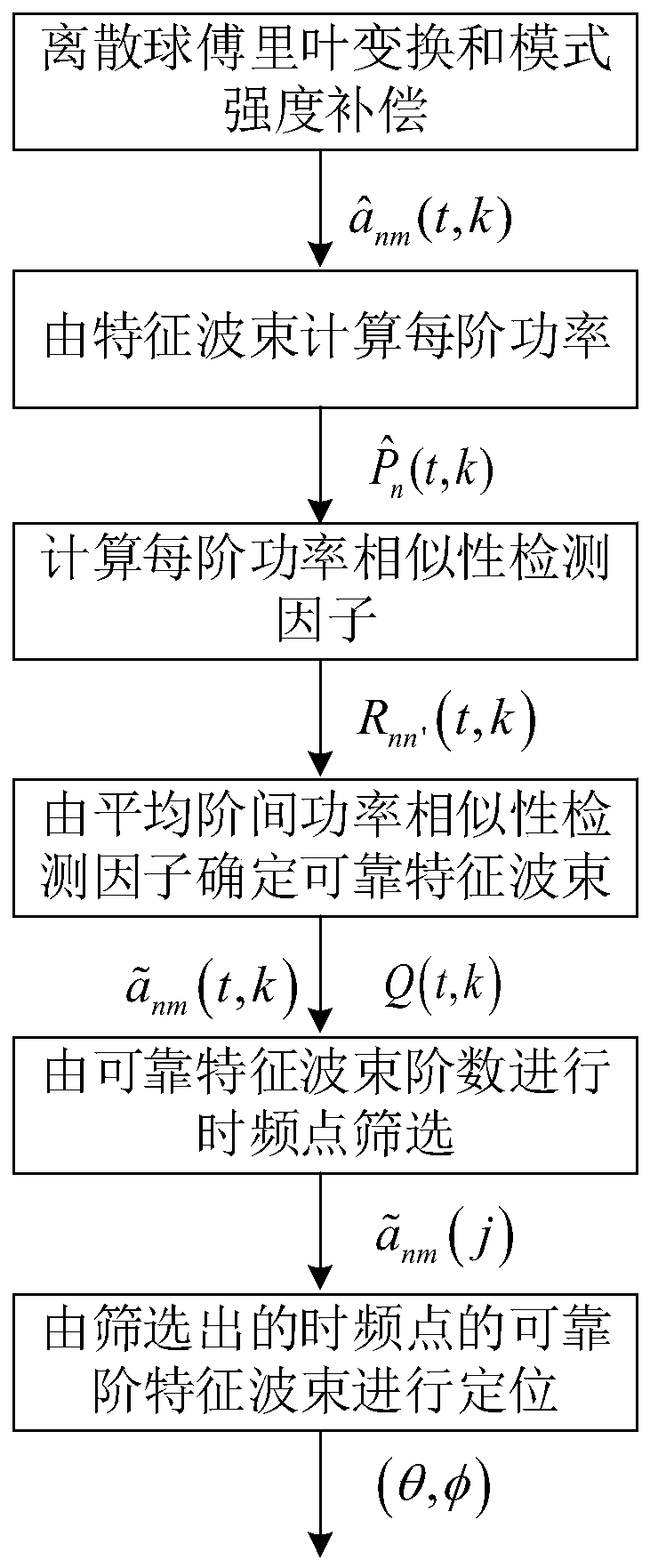
ActiveCN110133579AImprove robustnessHigh precisionDirection/deviation determination systemsSystems with undesired wave eliminationSound sourcesFourier transform
The invention discloses a spherical harmonic order self-adaptive selection method suitable for spherical microphone array sound source orientation, which comprises the following steps of: transformingthe sound field information from a time-frequency domain to a mode intensity compensation characteristic beam form of a spherical harmonic domain by means of discrete sphere Fourier transform and mode intensity compensation, and calculating the power of each order of characteristic beam of the sound field by each order of characteristic beam of the sound field; measuring the power similarity of the characteristic beams of all orders according to the characteristic beam power similarity detection factors among all orders of the sound field; performing reliable order selection processing on theaverage characteristic beam power similarity detection factor according to the set threshold parameter value; and masking the time frequency points according to the reliable order, and positioning the sound field by using reliable-order sound field characteristic beams corresponding to the time frequency points meeting the conditions to obtain an azimuth angle estimation value. The method has higher robustness to reverberation noise and higher sound source azimuth estimation precision.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Sound source direction detecting apparatus, sound source direction detecting method, and sound source direction detecting camera
InactiveUS8098843B2Reliable detectionPointing errorTwo-way working systemsSpeech recognitionSound sourcesDecomposition
Disclosed herein is a sound source direction detecting apparatus including: a plurality of microphones configured to collect sounds from a sound source in order to form an audio frame; a frequency decomposition section configured to decompose the audio frame into frequency components; an error range determination section configured to determine the effects of noises collected together with the sounds as an error range relative to phases; a power level dispersion section configured to disperse power levels of the sounds for each of the frequency components decomposed by the frequency decomposition section, on the basis of the error range determined by the error range determination section; a power level addition section configured to add the power levels dispersed by the power level dispersion section; and a sound source direction detection section configured to detect the direction of the sound source based on the phase at which is located the highest of the power levels added by the power level addition section.
Owner:SONY CORP
Stochastic resonance enhanced acoustic vector signal orientation method
ActiveCN110133580ASolve the problem of large orientation errorsGood orientationDiversity direction findingSystems with undesired wave eliminationHydrophoneSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a stochastic resonance enhanced acoustic vector signal orientation method. The method can realize amplitude linear gain and is suitable for vector acoustic signal noise reduction processing in orientation, can solve the problem of large vector acoustic orientation error under the condition of low signal-to-noise ratio, and has good orientation effect. The stochastic resonance enhanced acoustic vector signal orientation method is mainly applied to the orientation of an underwater weak target in a low signal-to-noise ratio environment, has good resistance to phase inconsistency of actual vector acoustic signals, and is a stable single-vector hydrophone orientation method.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Voice direction searching system and method thereof
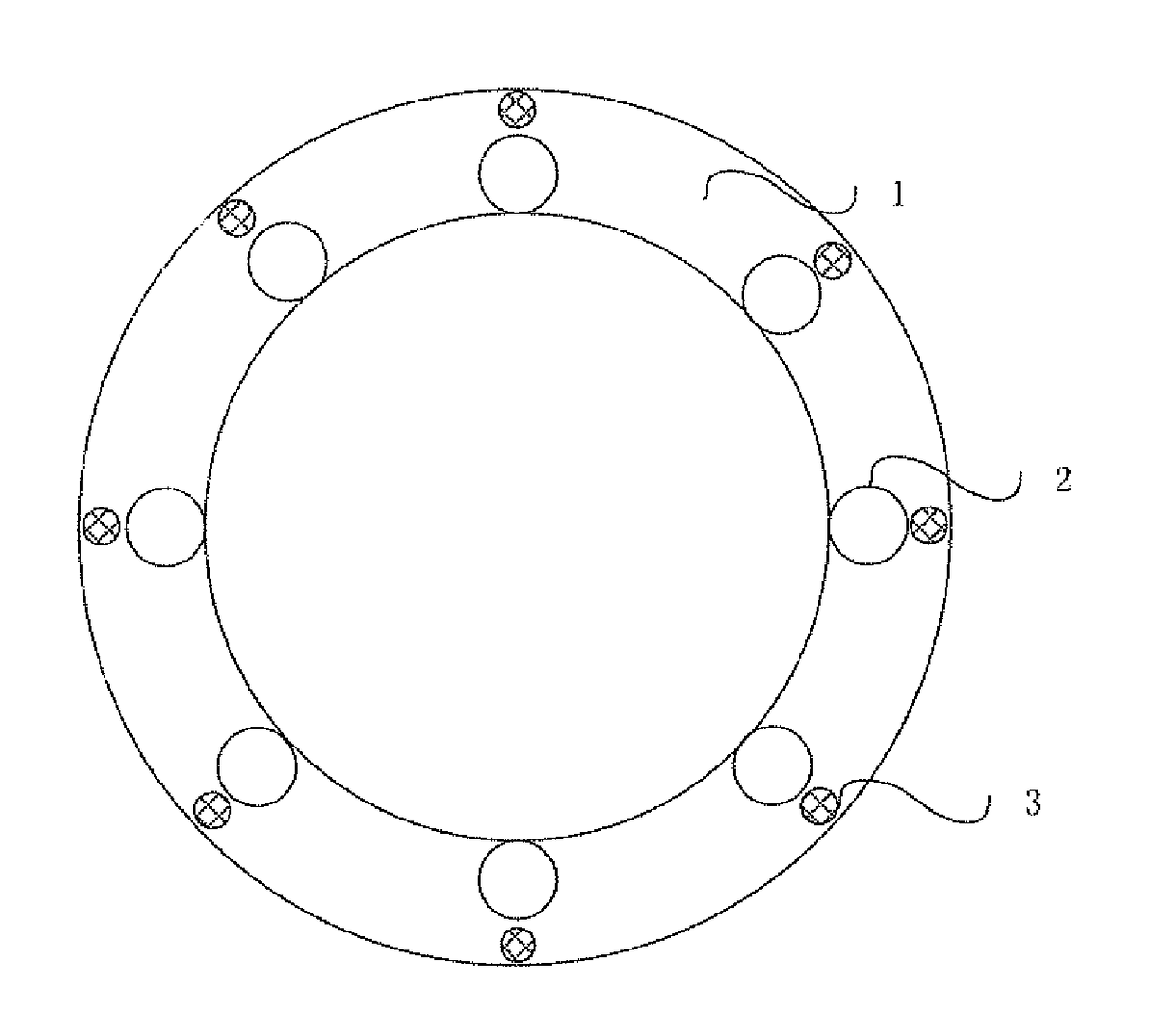
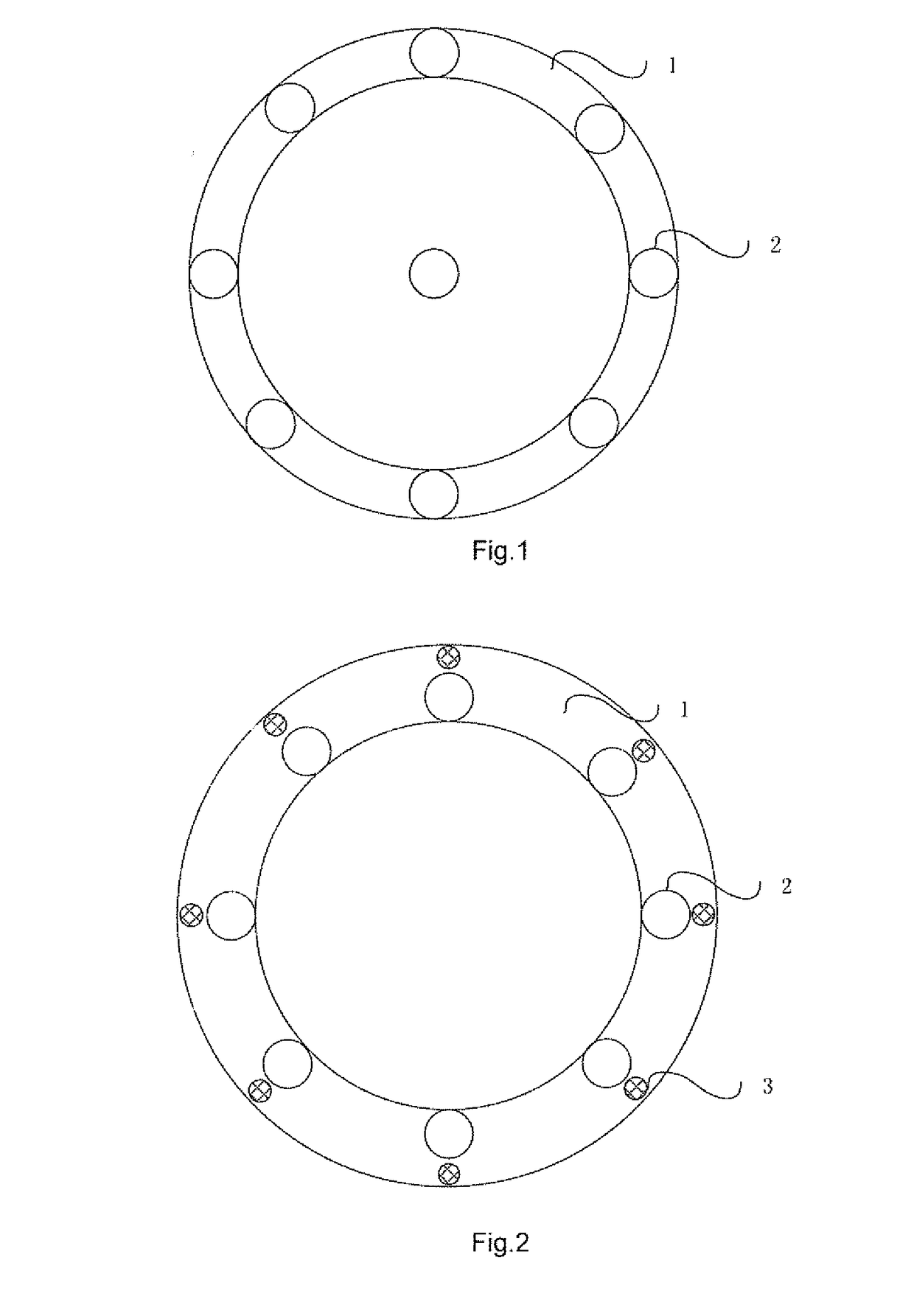
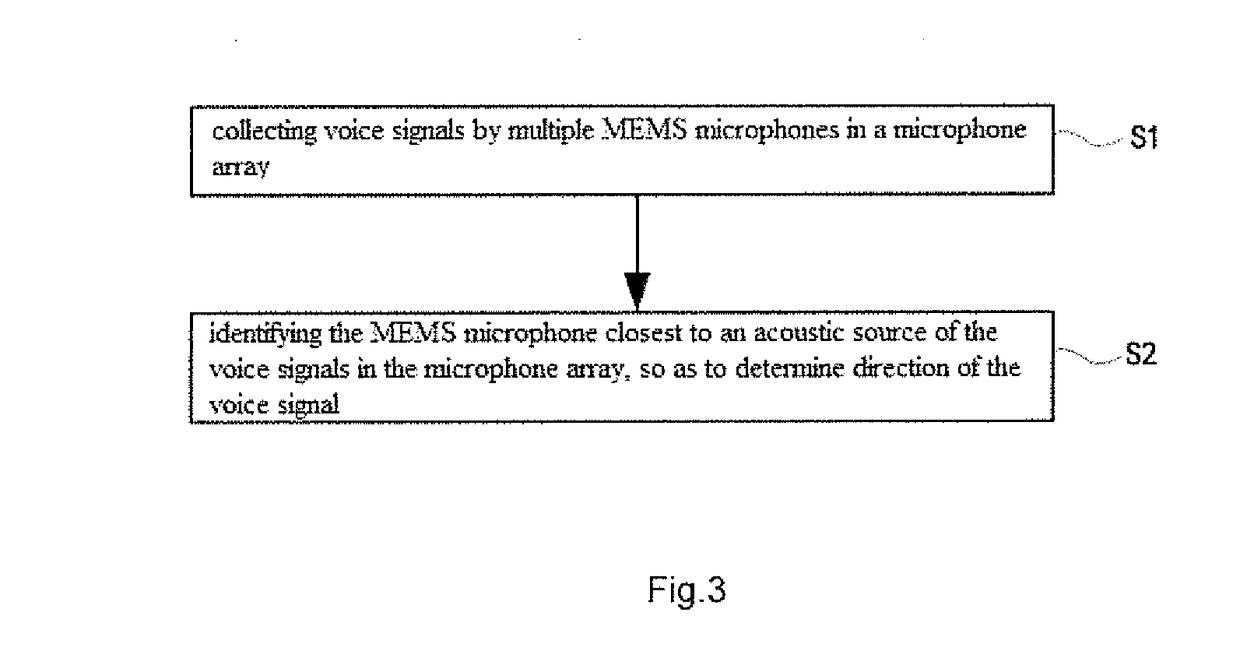
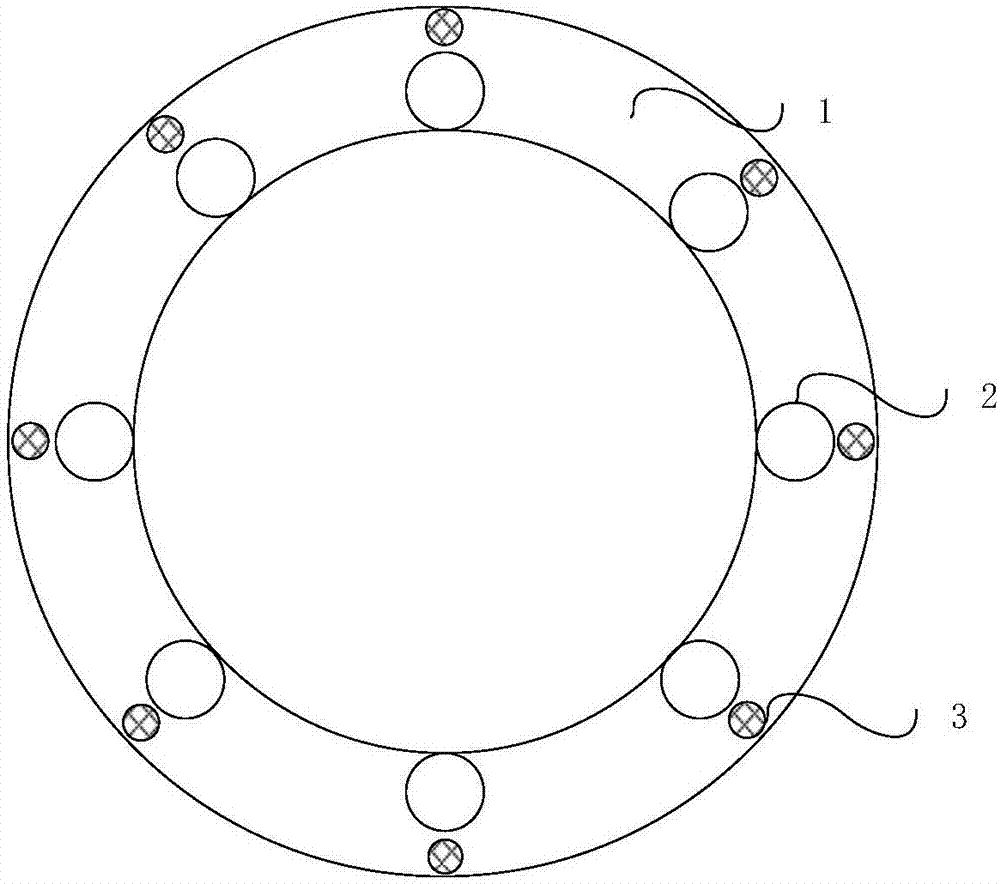
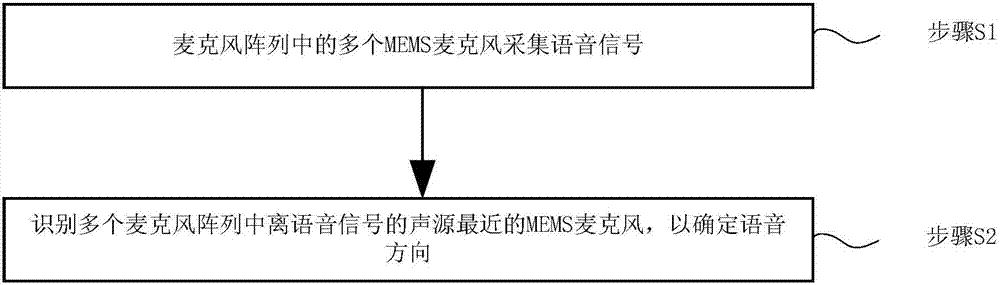
InactiveUS20180188347A1Accurate identificationMicrophones signal combinationDirection/deviation determination systemsMems microphoneSpeech sound
The present invention relates to a technical field of voice interaction, especially to a voice direction searching system and the method thereof. The present invention utilizes a microphone array to collect voice signals made by an acoustic source, and utilizes multiple MEMS microphones to identify an MEMS microphone closest to the acoustic source, so that the voice direction searching system can accurately identify voice direction signals.
Owner:YUTOU TECH HANGZHOU
Sound signal processing device and sound signal processing method
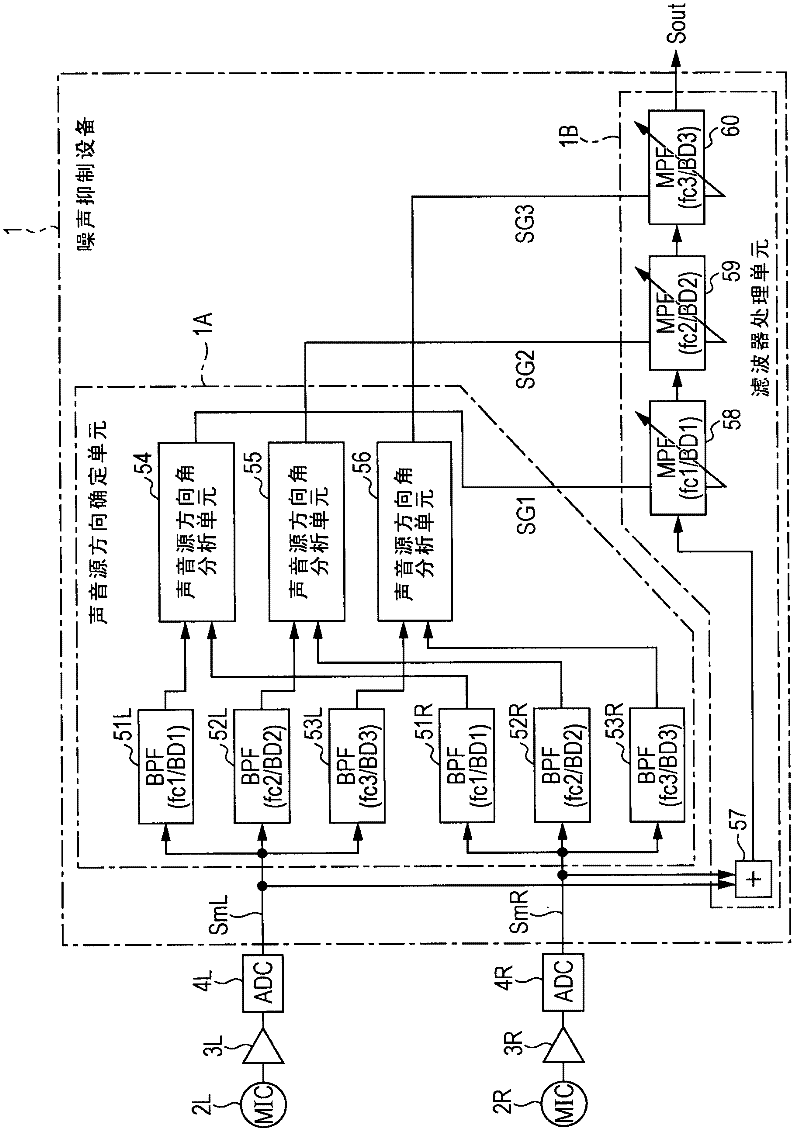
ActiveCN102271299AReduce noiseGuaranteed sound qualitySignal processingHeadphones for stereophonic communicationUltrasound attenuationSound sources
The invention discloses a sound signal processing apparatus and a sound signal processing method. The sound signal processing apparatus includes a sound source direction determination unit and a filter processing unit. The sound source direction determination unit determines sound source directions with respect to sound signals of a plurality of channels for respective first to n-th bands. The filter processing unit includes first to n-th filters which are connected in series and configured to boost or attenuate the sound signals with respect to the first to n-th bands. The respective first to n-th filters perform boosting or attenuation based on the sound source directions of the first to n-th bands which are determined by the sound source direction determination unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
PASS-Tracker: Apparatus and Method for Identifying and Locating Distressed Firefighters
InactiveUS20170270775A1Improve abilitiesRapid positioningPosition fixationAlarmsLeading edgeHand held
According to one aspect of the invention, the PASS-Tracker is a hand-held device that improves the ability of a rescuer to quickly locate a distressed firefighter by two processes: (1) detecting and recognizing the acoustic alarm sound from a PASS device in Alarm Mode, and (2) providing an indication to rescue personnel of the shortest path to the victim. The invention does not require a pre-installed infrastructure in a particular building; rather the device can be used in an ad hoc fashion at any fire scene. The PASS-Tracker utilizes a plurality of small microphones to detect the acoustic signal from the PASS device. Internal electronics in the PASS-Tracker measure the time-of-arrival (TOA) of the leading edge of the acoustic wave at each microphone and calculate and display the angle-of-arrival (AOA) of the wave.
Owner:HAASE WAYNE C +2
Processing signals
ActiveCN103065639ASave energyLittle or no distortionSpeech analysisMicrophones signal combinationPattern matchingVIT signals
A method, a device and a computer program product for processing signals at the device are disclosed. Signals are received, over a range of angles, at a plurality of sensors of the device, the received signals including an interfering signal received from an interfering source location. An interference delay pattern between receipt of signals at the sensors corresponding to receipt of a signal from the interfering source location is determined. A plurality of regularization signals having a delay pattern matching the determined interference delay pattern are generated. The generated regularization signals are used to determine beamformer coefficients to be applied by a beamformer, and the beamformer applies the determined beamformer coefficients to the signals received by the plurality of sensors, thereby generating a beamformer output.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Towed array sonar fixed azimuth large interference source cancellation method and system
InactiveCN104122544AIncrease flexibilitySystems with undesired wave eliminationTime domainArray element
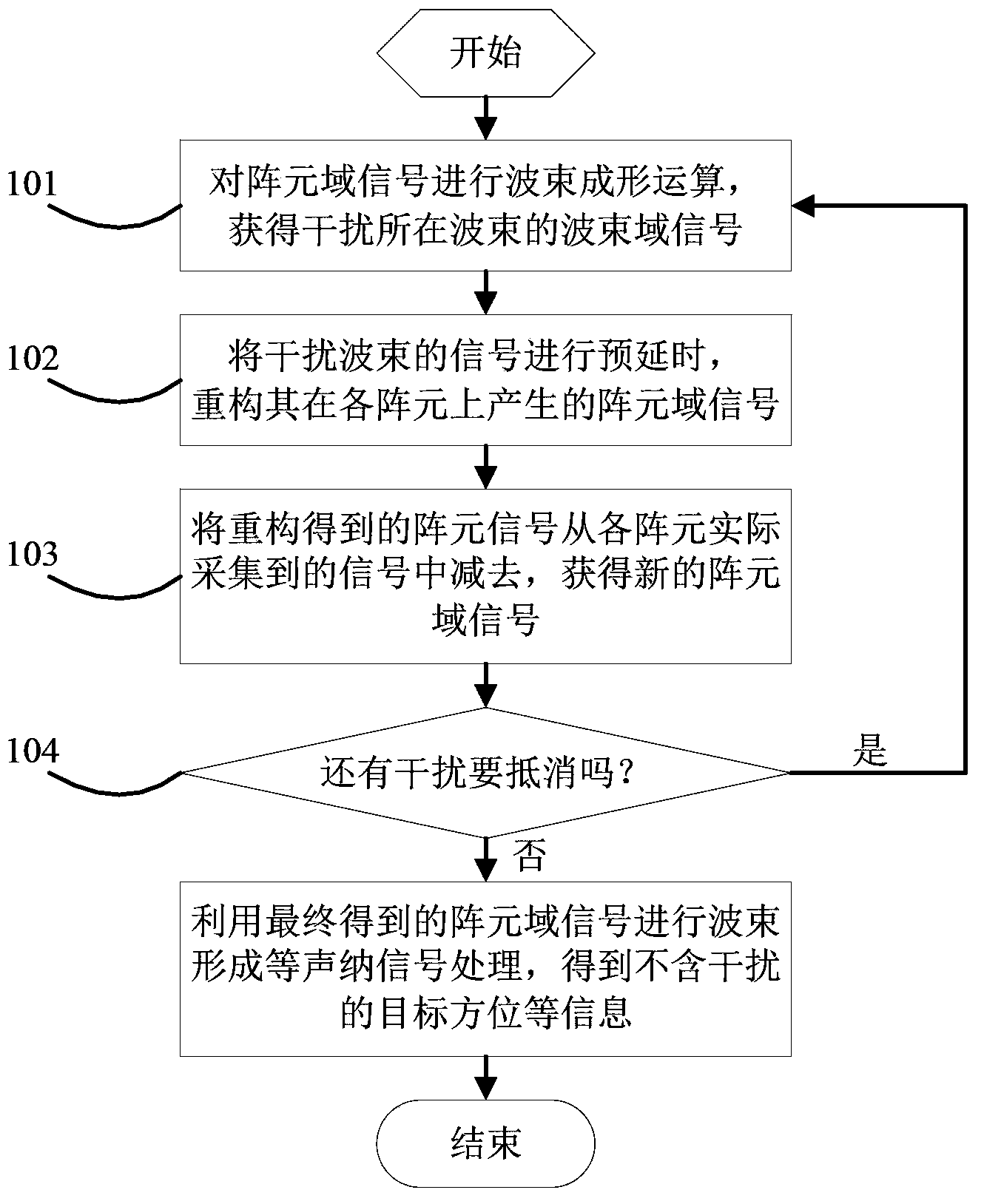
The invention provides a towed array sonar fixed azimuth large interference source cancellation method and a system. The method comprises steps: 101) beam-forming processing is carried out on signals received by towed array elements to obtain corresponding beam space signals of a beam Bi in a theta azimuth; 102) a reconstruction strategy is adopted to obtain interference time domain signals of interference in the theta azimuth in each array element according to the beam space signals; 103) subtraction is carried out between signals actually received by each array element and interference time domain signals of interference in the theta azimuth, and signals of each array element cancelling interference at the theta azimuth is obtained; and 104) the above steps are repeated on interference at another theta<j> azimuth until influences of interference signals from each azimuth on actually-received signals of each array element of the towed array can be cancelled. The reconstruction strategy is that the zeroth array element in the towed array serves as reference and pre delay is carried out on beam space signals of the beam where interference is located according to the delay amount of each array element.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Voice direction finding system and voice direction finding method
InactiveCN107290711AAccurate judgmentMicrophones signal combinationDirection/deviation determination systemsMems microphoneVoice source
Owner:YUTOU TECH HANGZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com