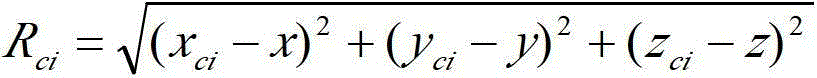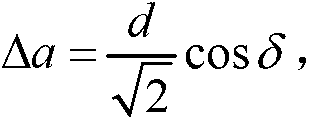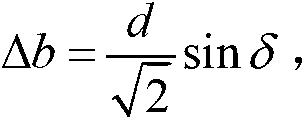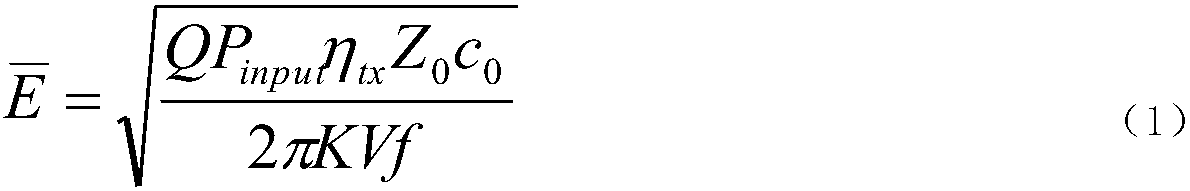Patents
Literature
88 results about "Spatial compounding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
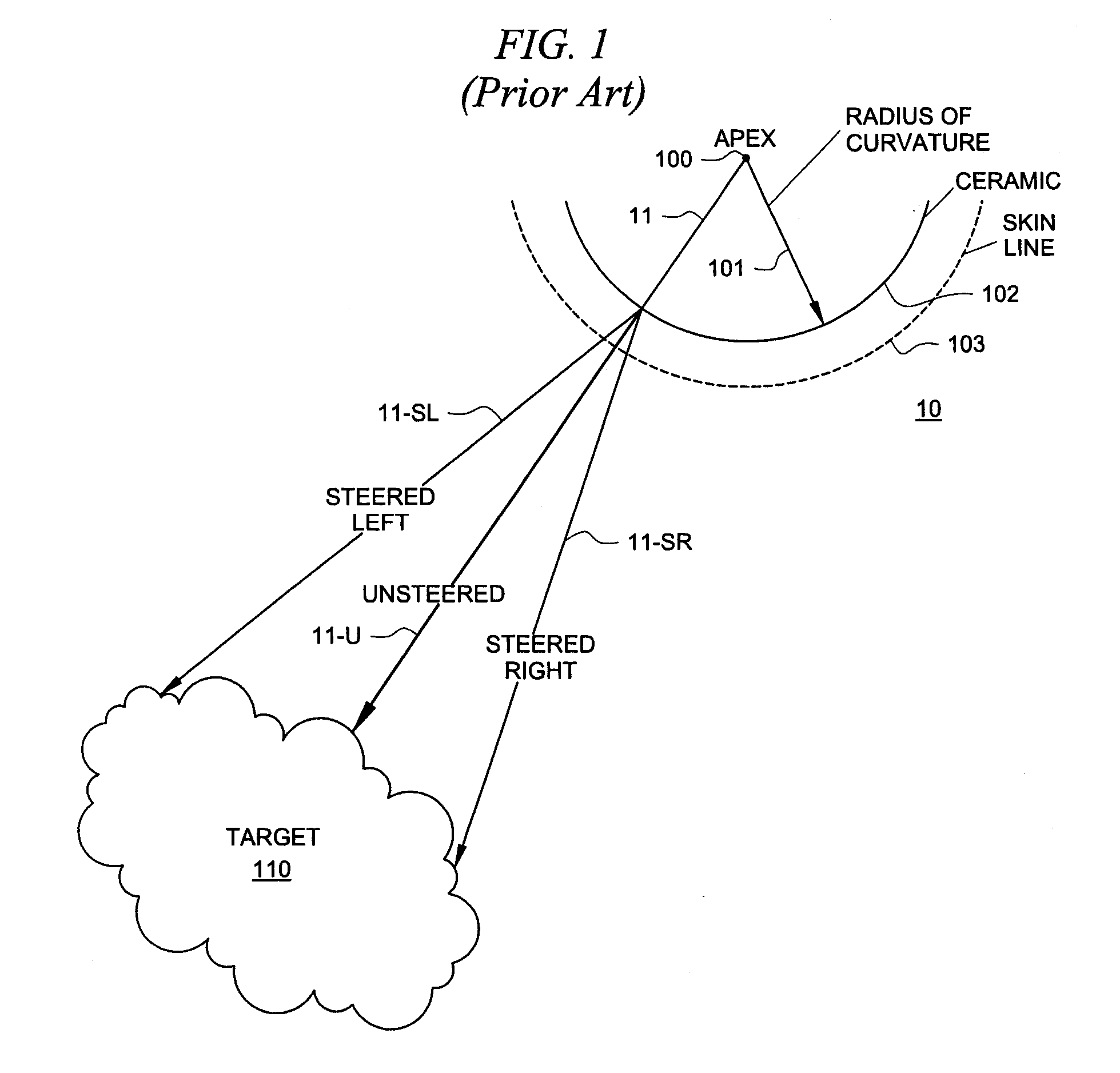
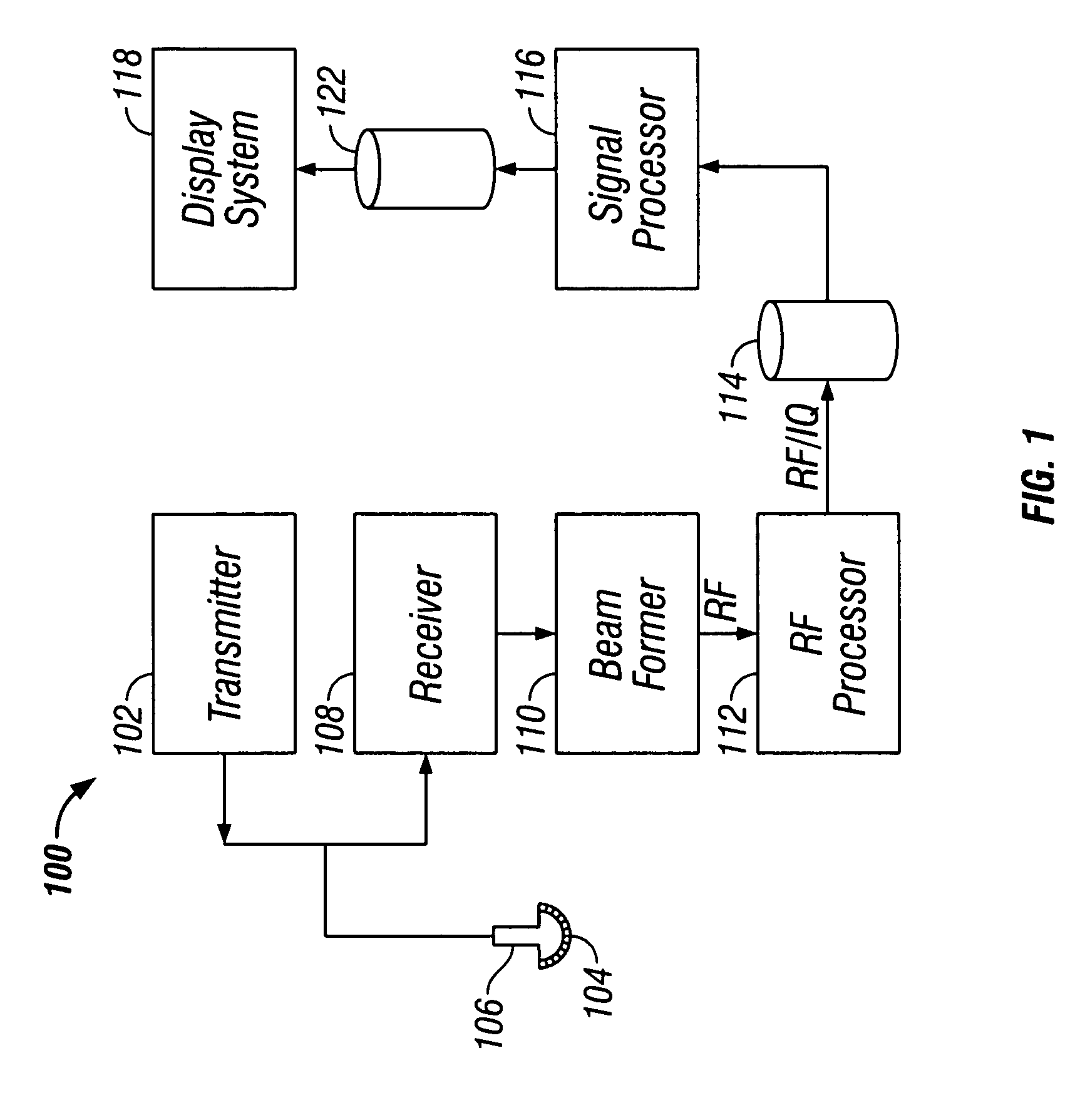
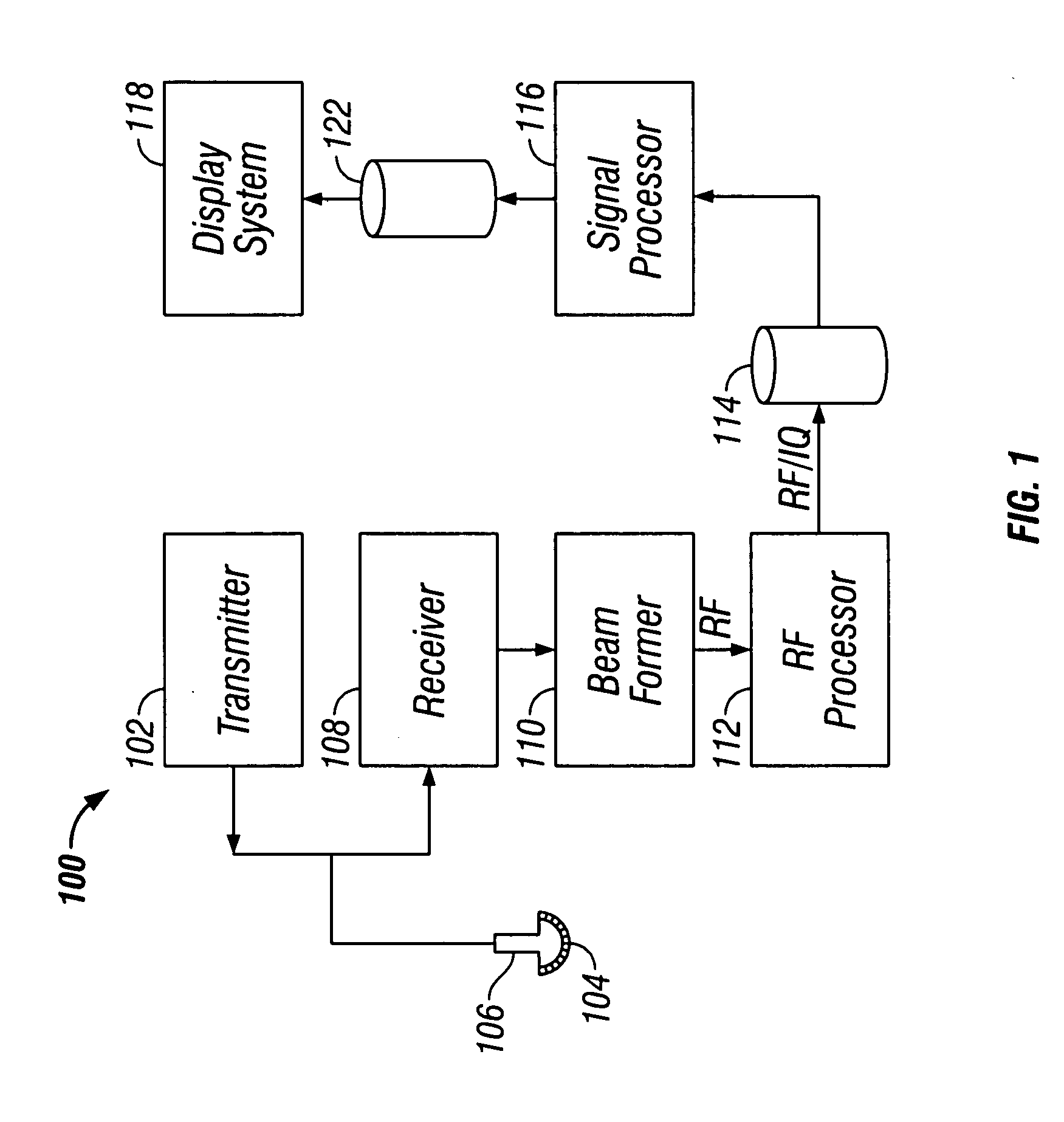
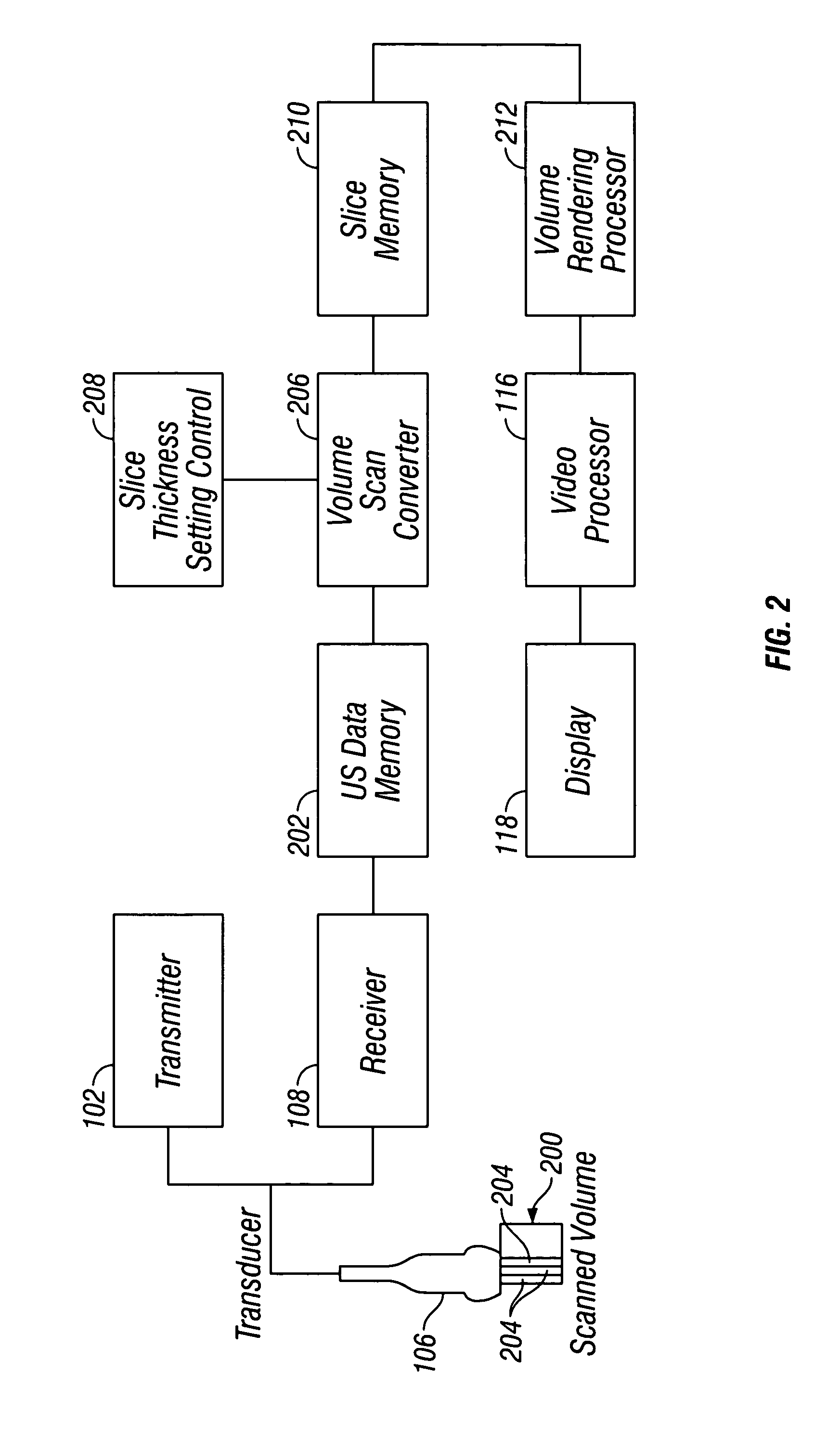
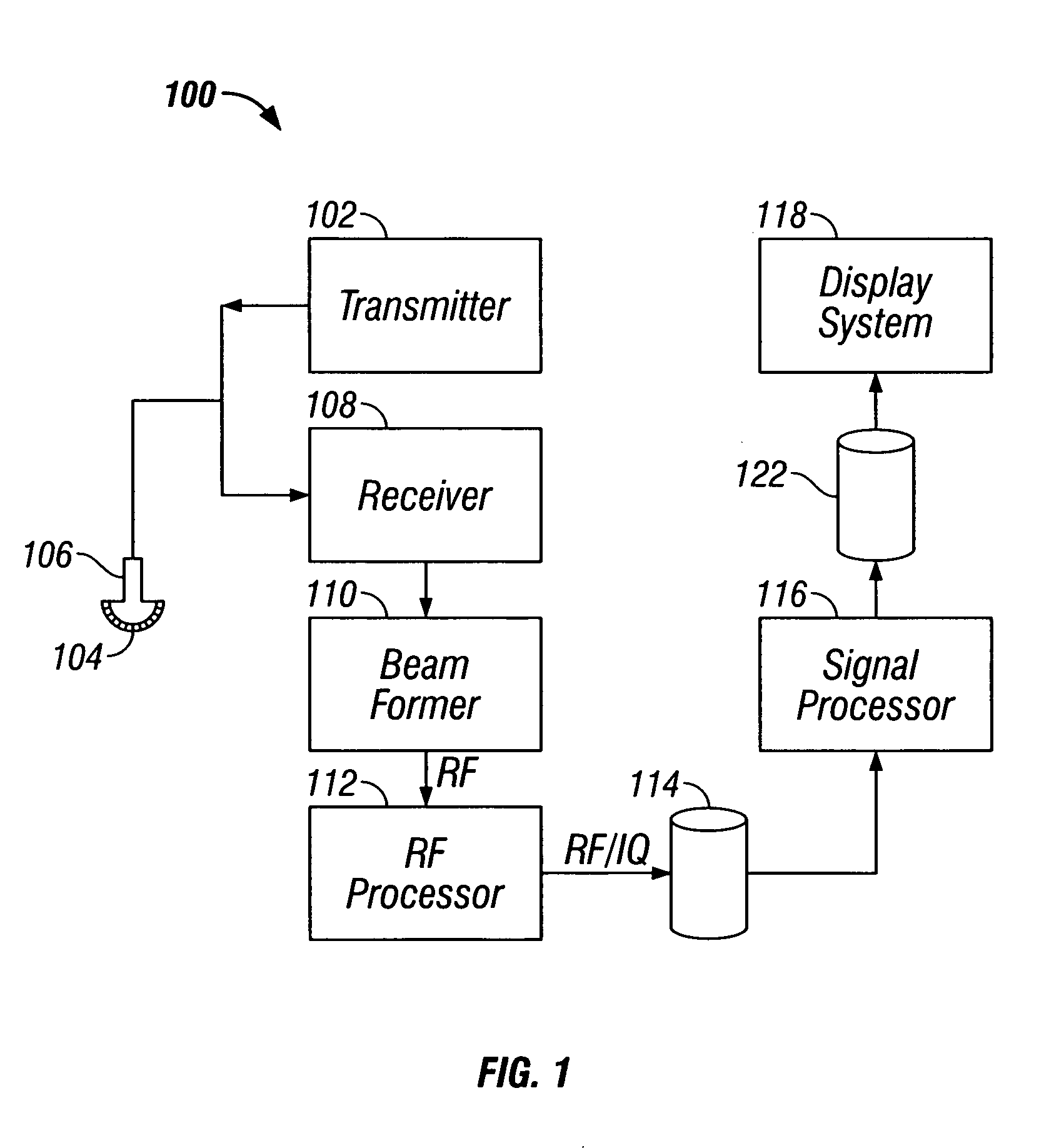
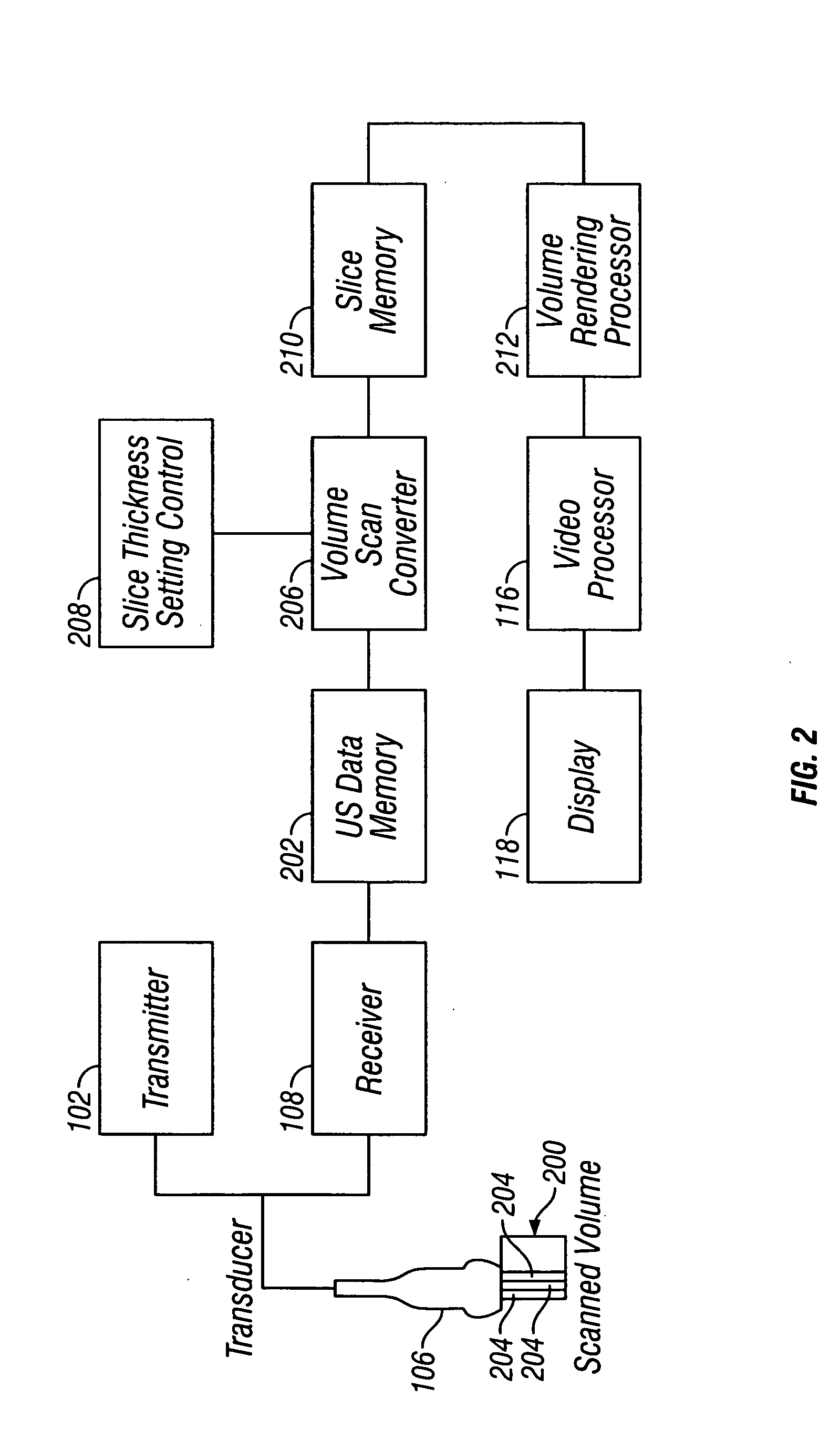
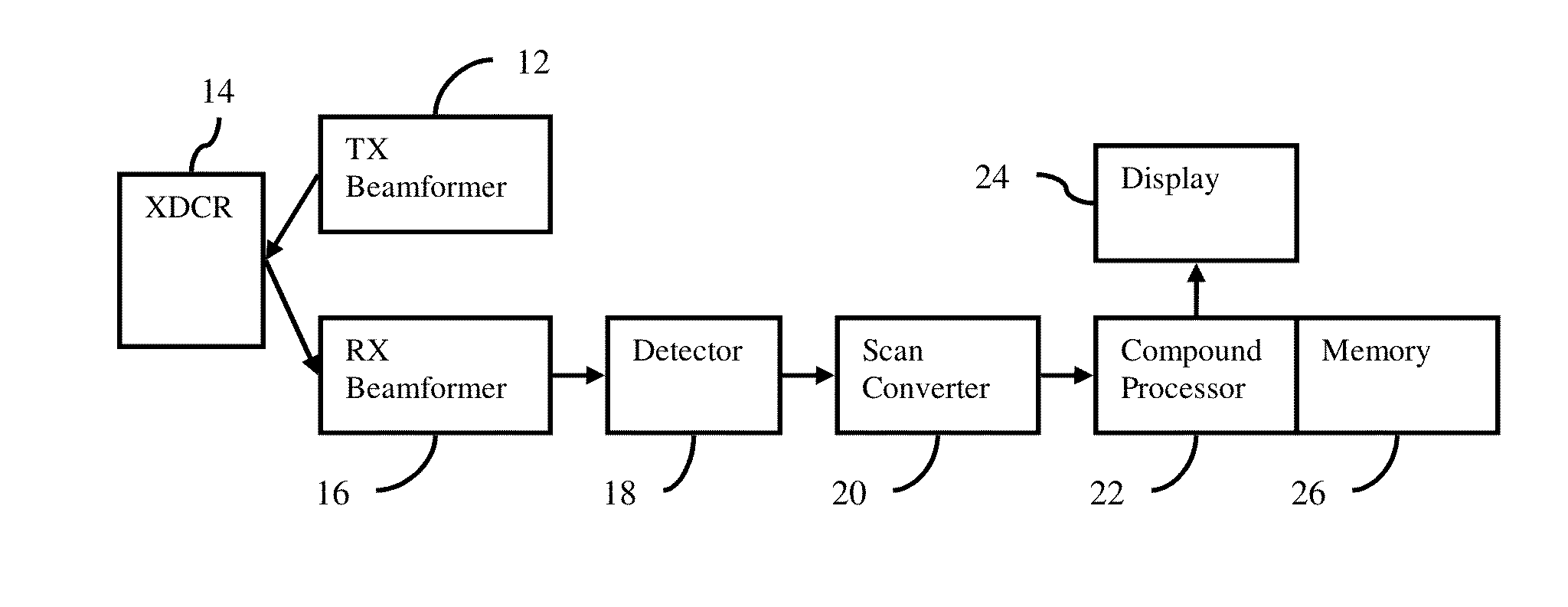
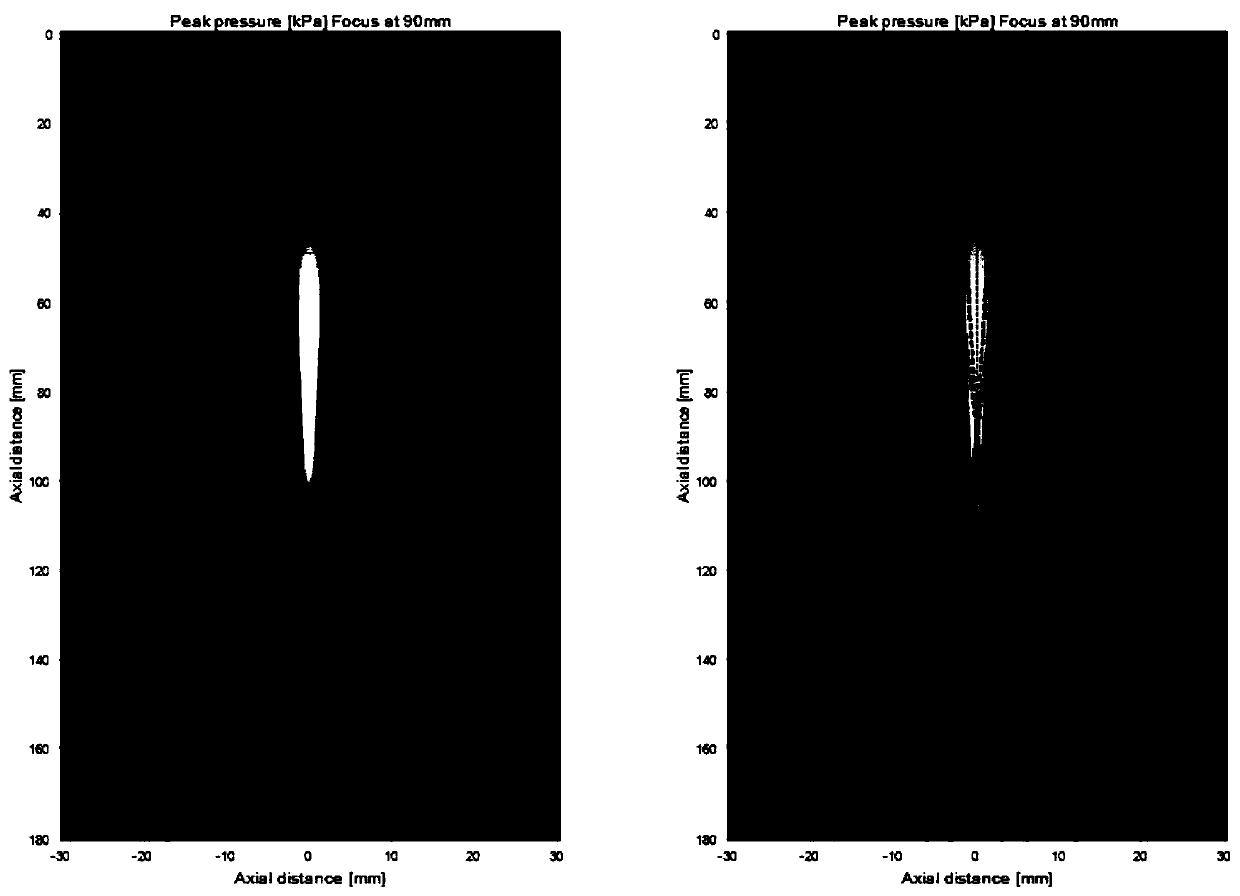
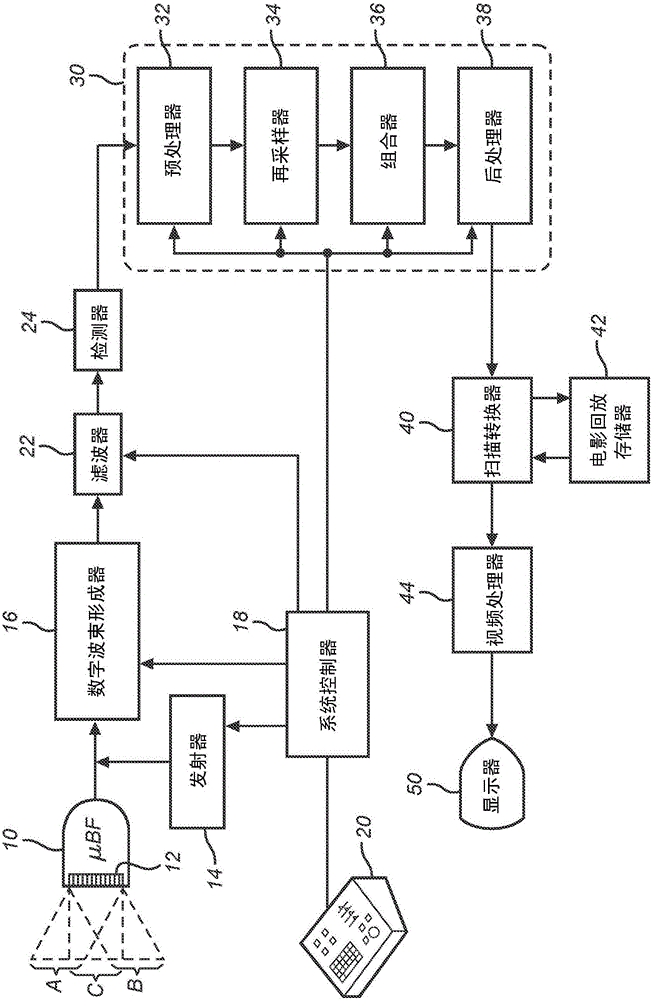
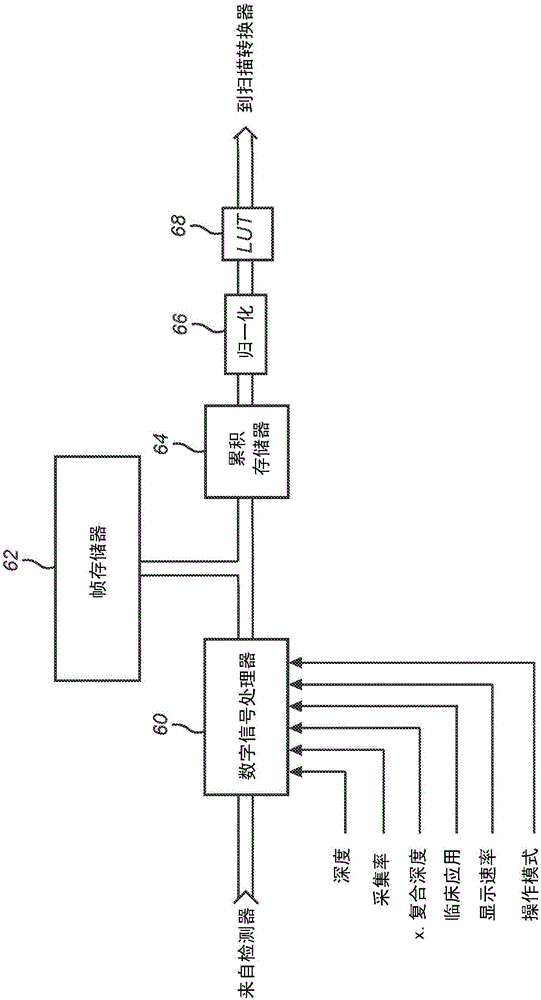
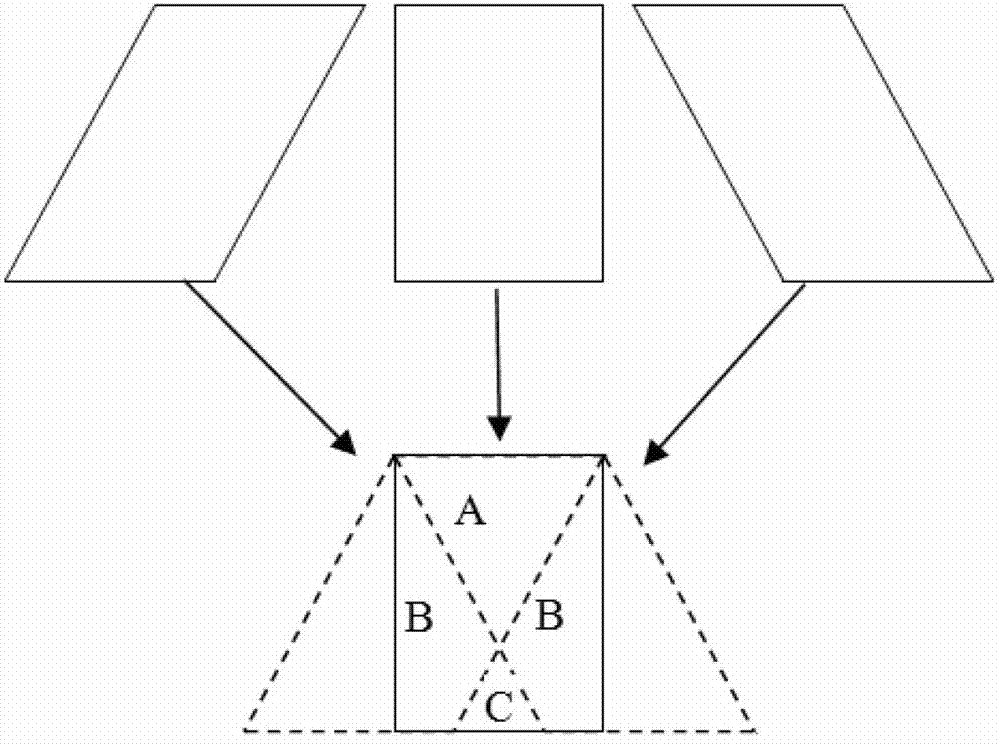
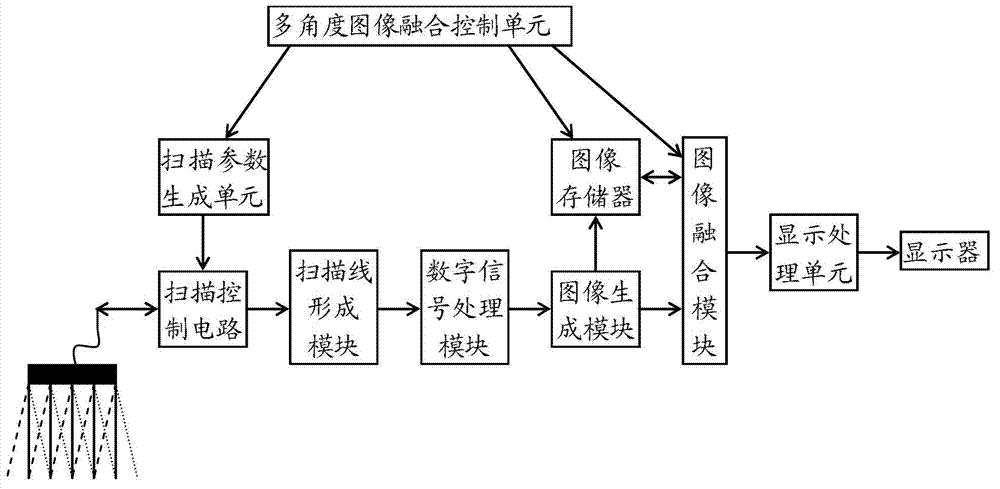
Abstract. Spatial compound imaging is a technique in which a number of co-planar, tomographic ultrasound images of an object are obtained from different directions, then combined into a single compound image. Real-time spatial compounding uses electronic beam steering to rapidly acquire component frames from different view angles.
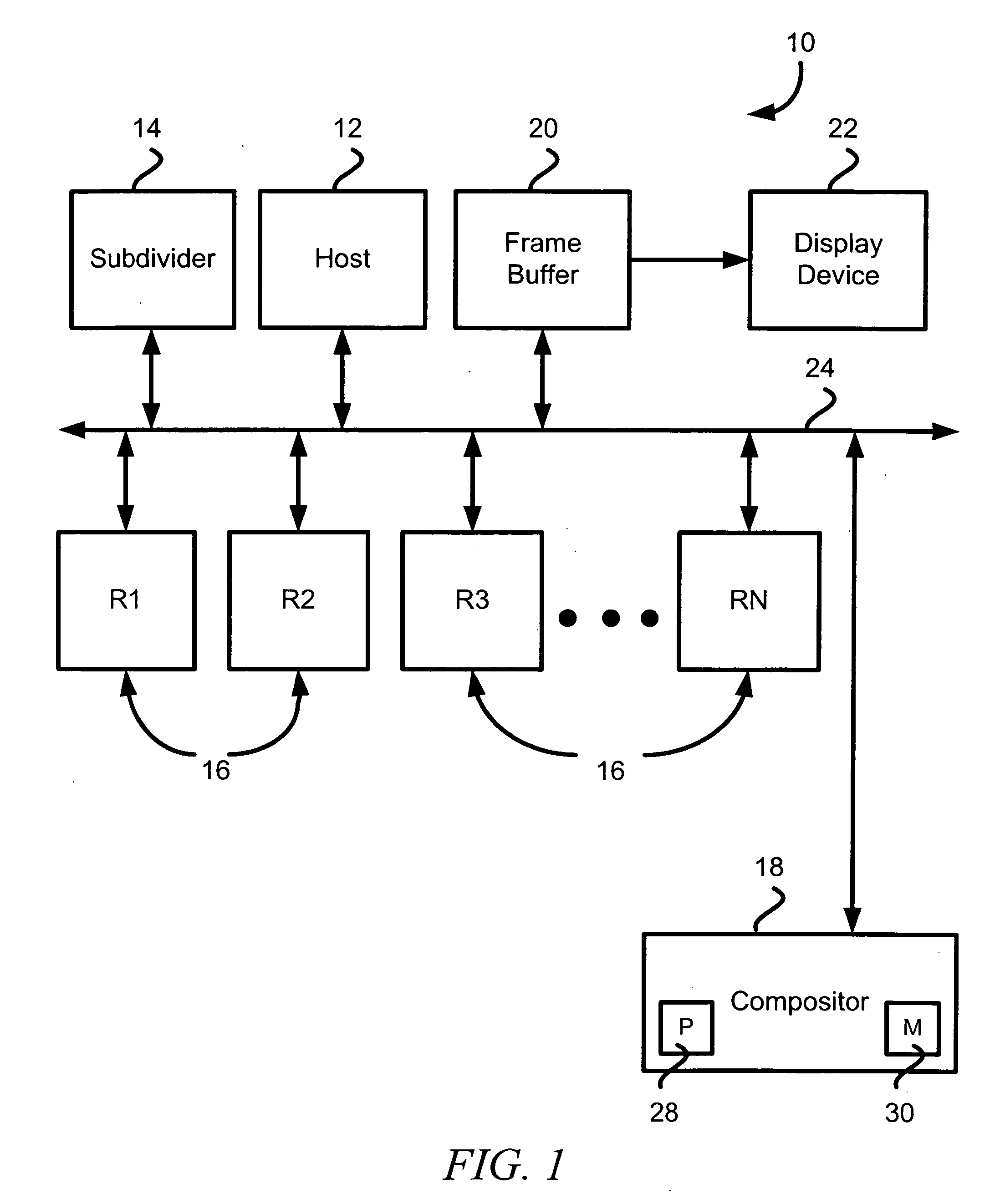
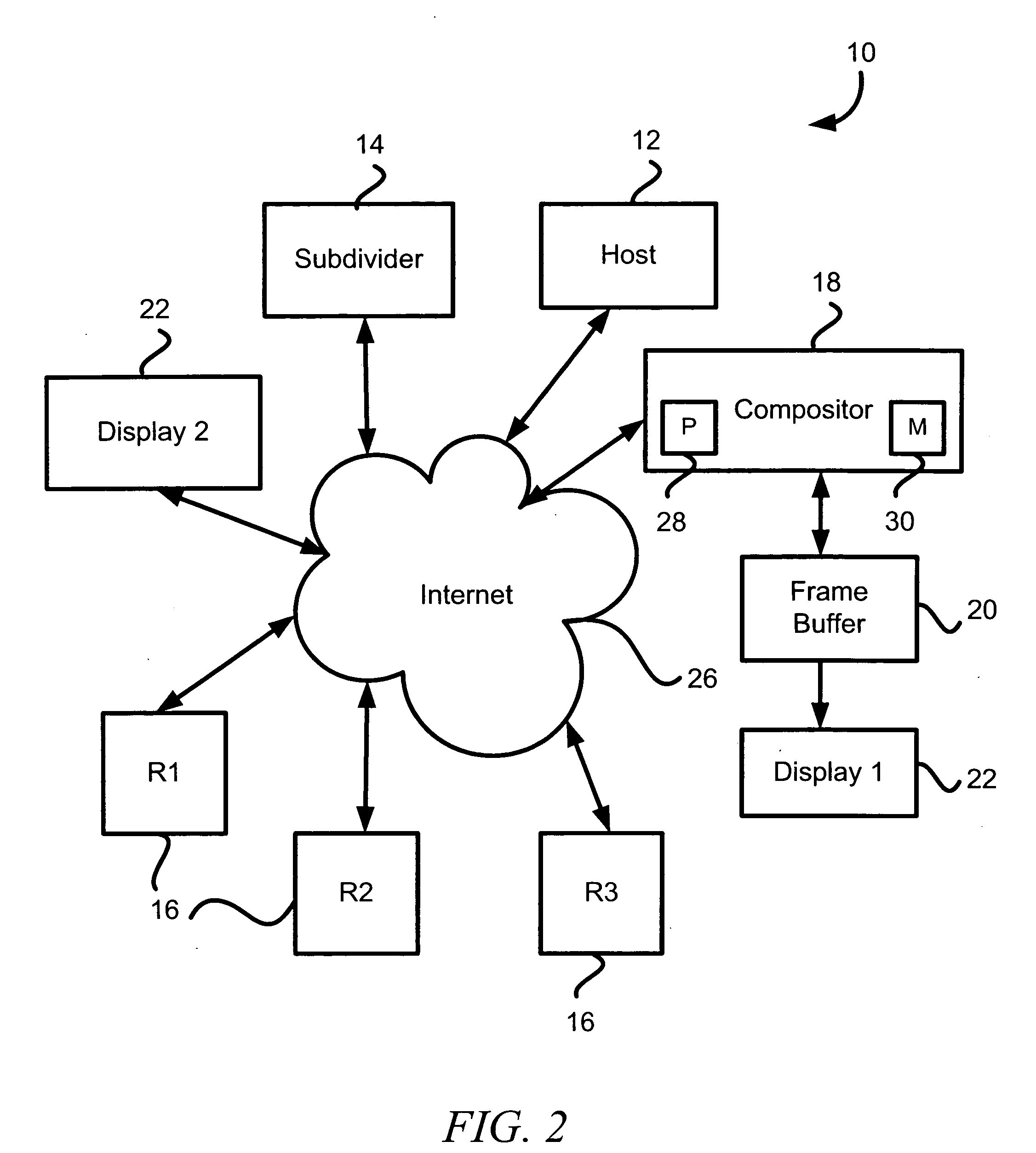
Compositing images using logically divided object space
InactiveUS20060214949A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsViewpointsSpace partitioning
An apparatus and method of processing object data (e.g., a scene having one or more objects) logically divide the object space into a plurality of contiguous (or noncontiguous) portions. At least two portions each have object data for such object(s). The apparatus and method also determine a positional priority of the at least two portions of the object space for a given viewpoint. Next, the apparatus and method merge rendered object data after at least some of the object data is rendered. This merging is based upon the positional priority of the at least two portions.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
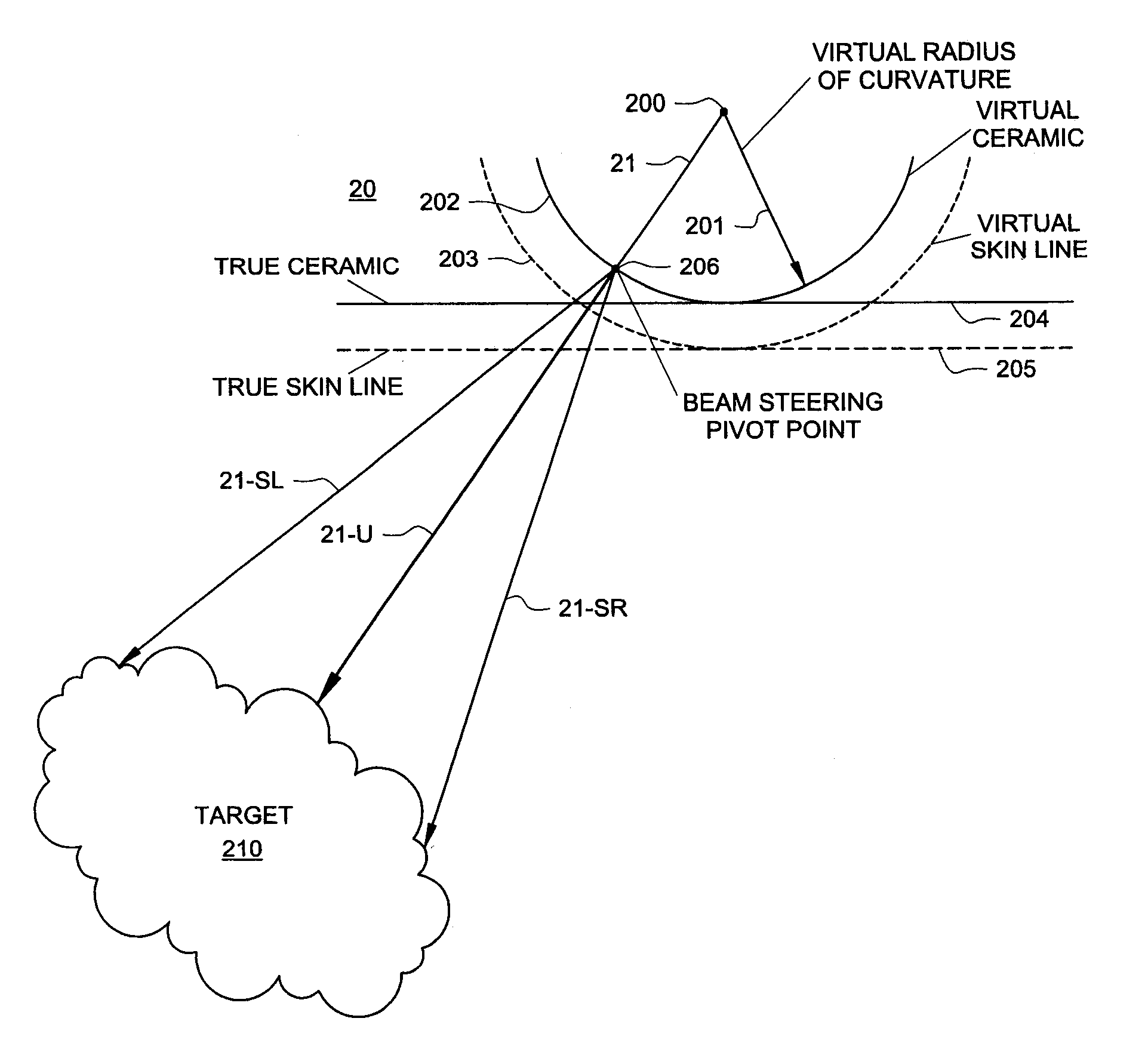
System and method for spatial compounding using phased arrays
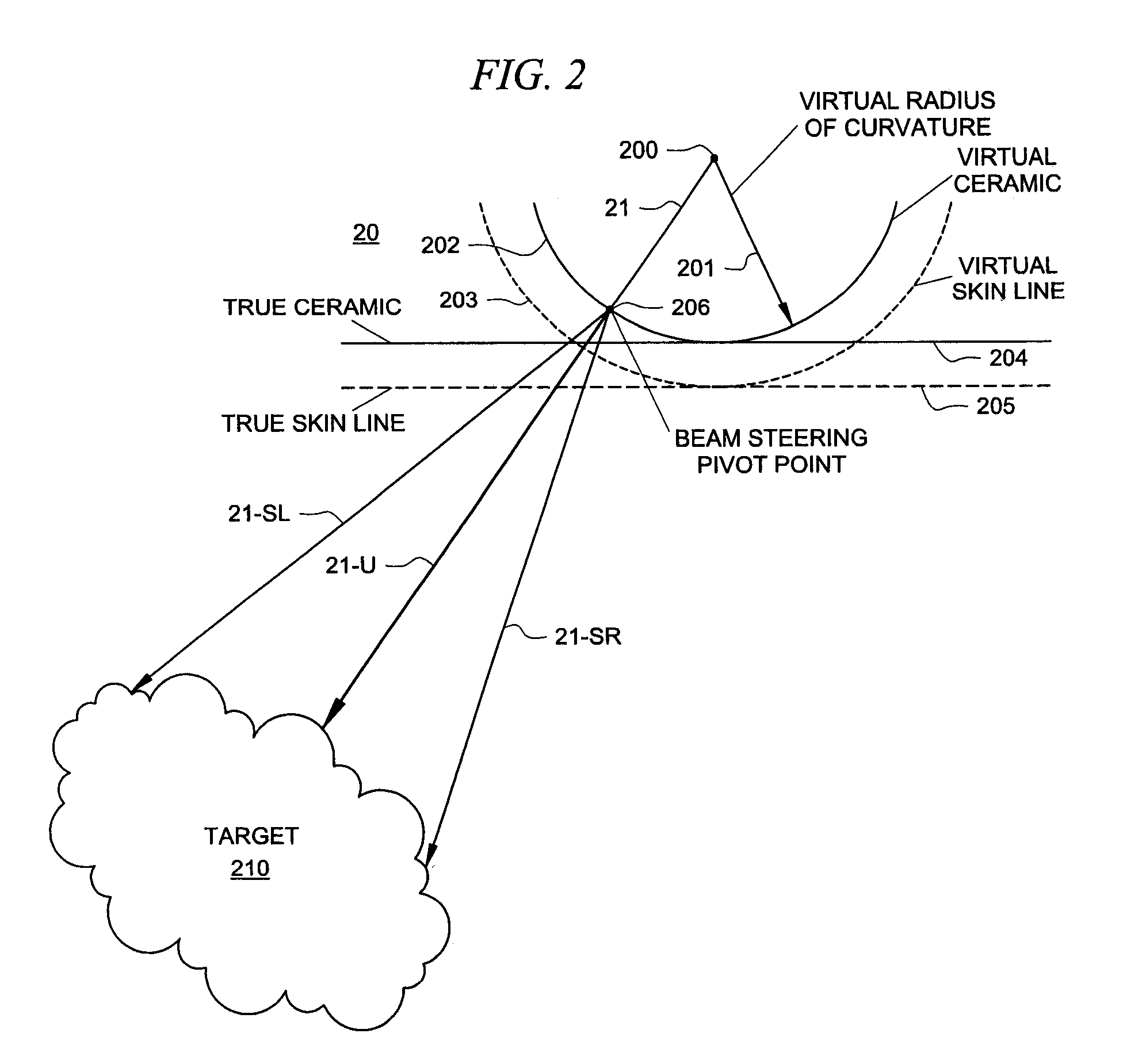
ActiveUS20090069681A1Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsComputer graphics (images)Skin lines
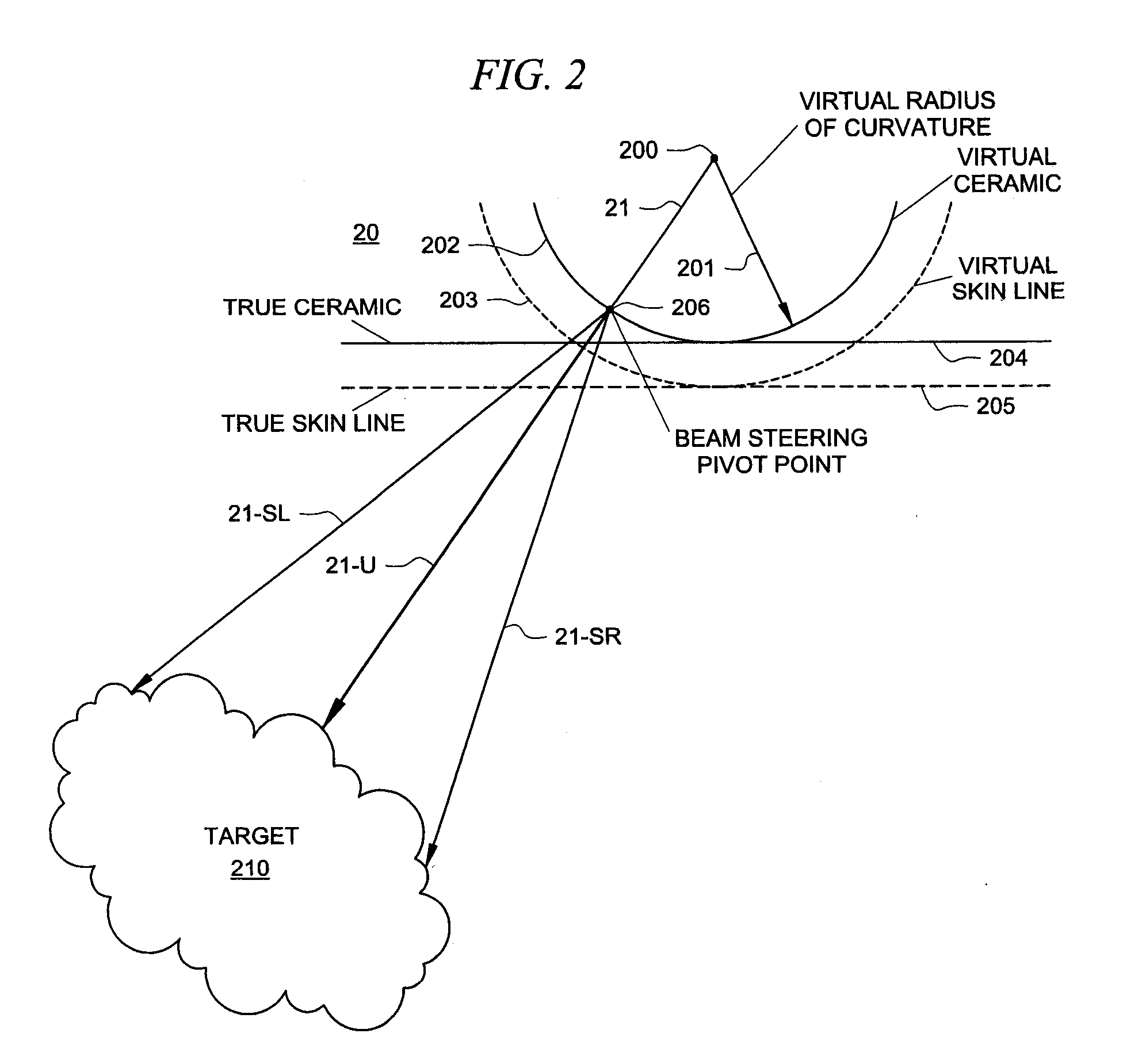
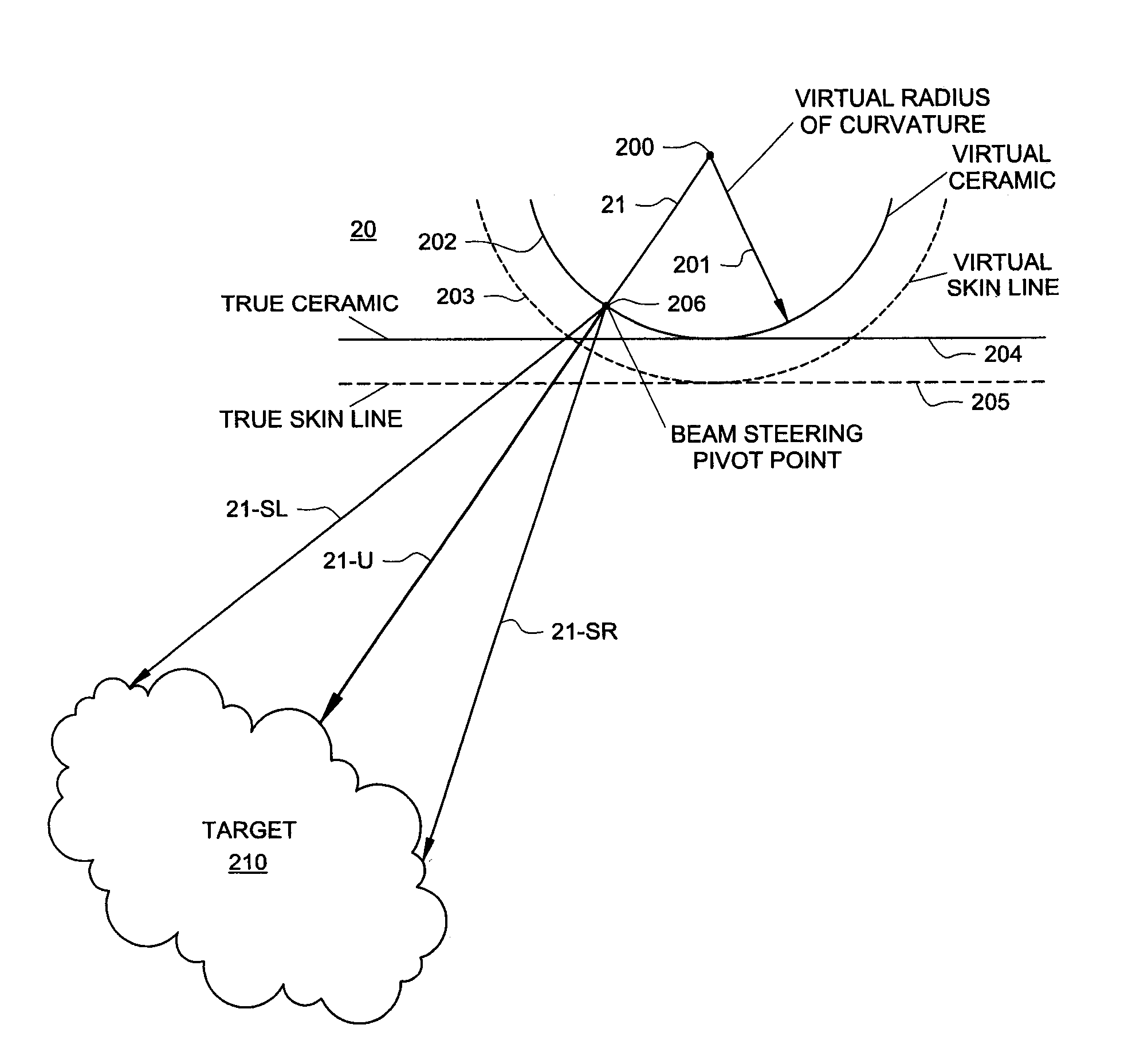
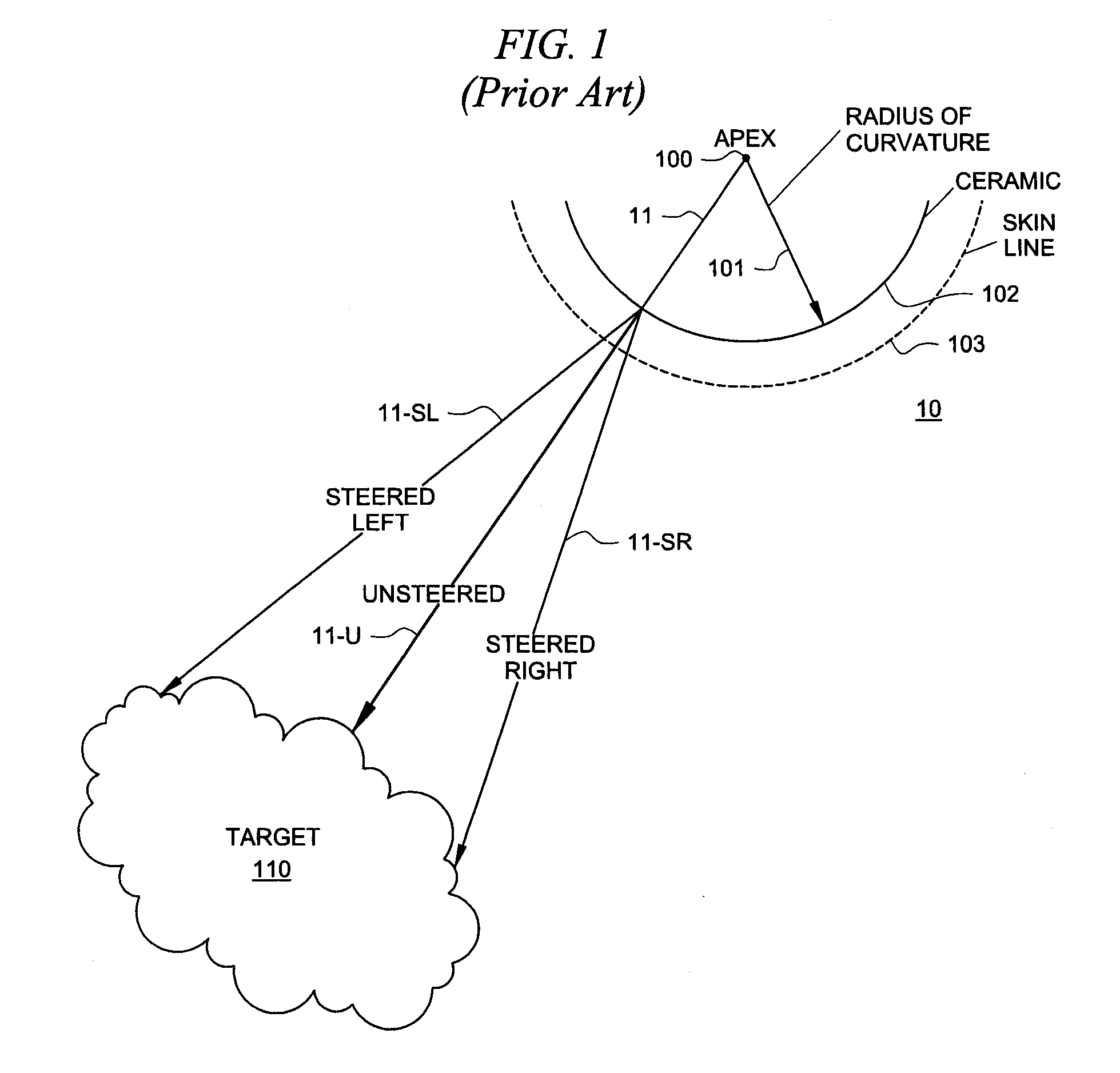
The present invention is directed to a system and method which makes a phased array look like a curved array for purposes of performing spatial compounding calculations. In one embodiment, the phased array is treated as though it were a curved array by creating both a virtual apex and a virtual radius of curvature. Based on this transformation, standard spatial-compounding resampling tables can be used just as they are with curved arrays. In one embodiment, after the data is compounded to form the target image, certain data is removed prior to the actual display. This removed data represents data generated by virtual rays the prior to the physical skin line of the phased array.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
System and Method For Adaptive Spatial Compounding For Ultrasound Imaging
InactiveUS20070232914A1Improve compoundReduce noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionUltrasound imaging
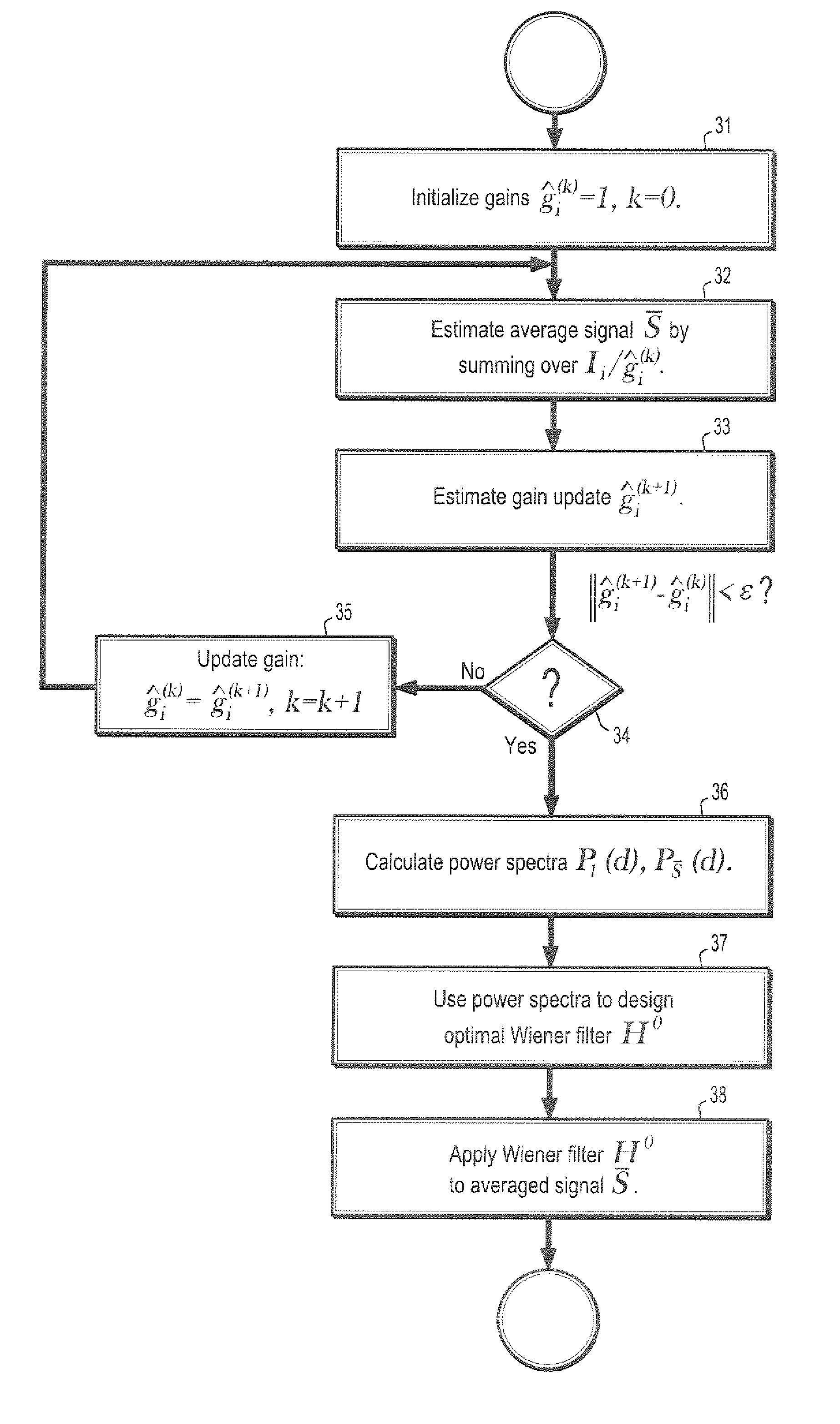
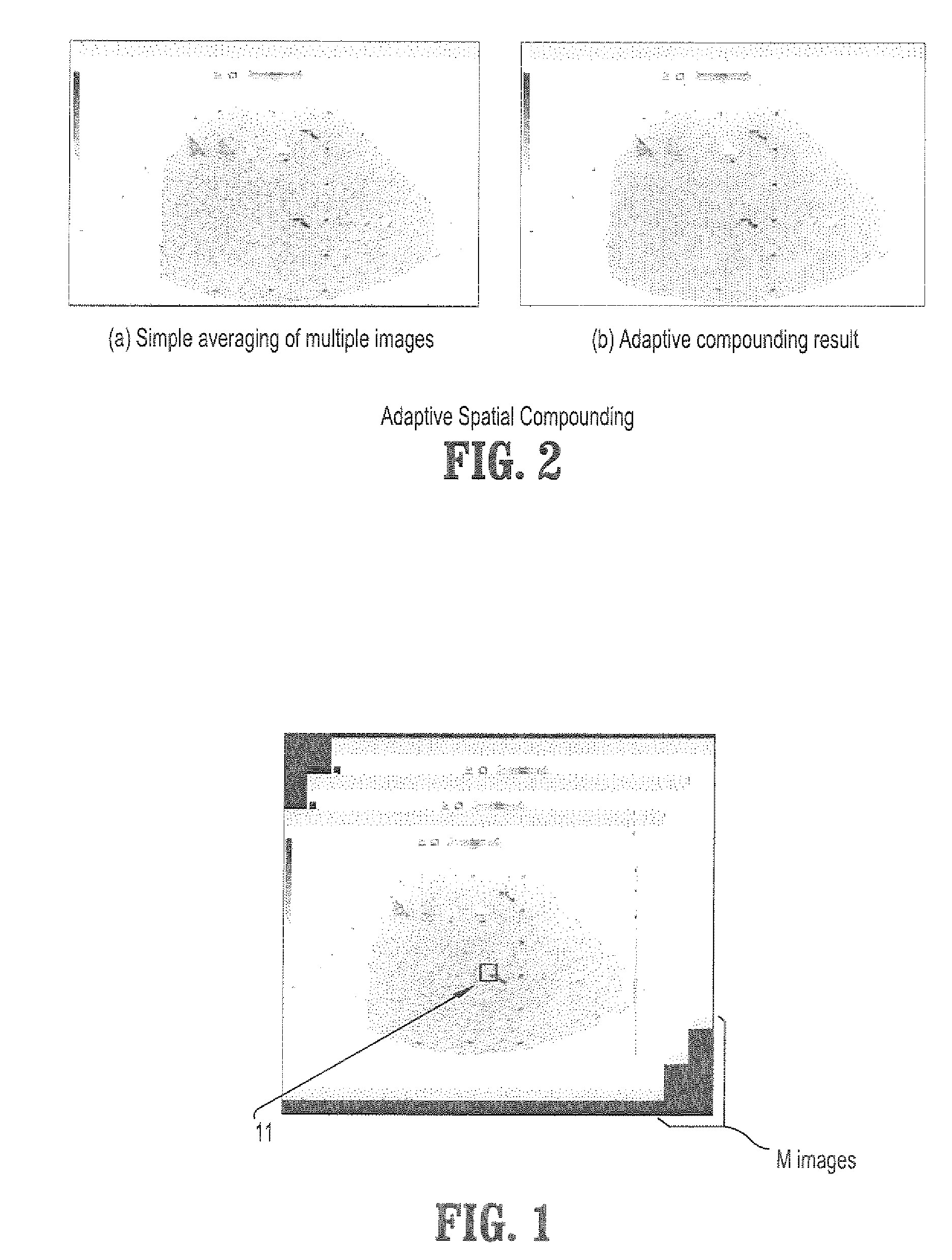
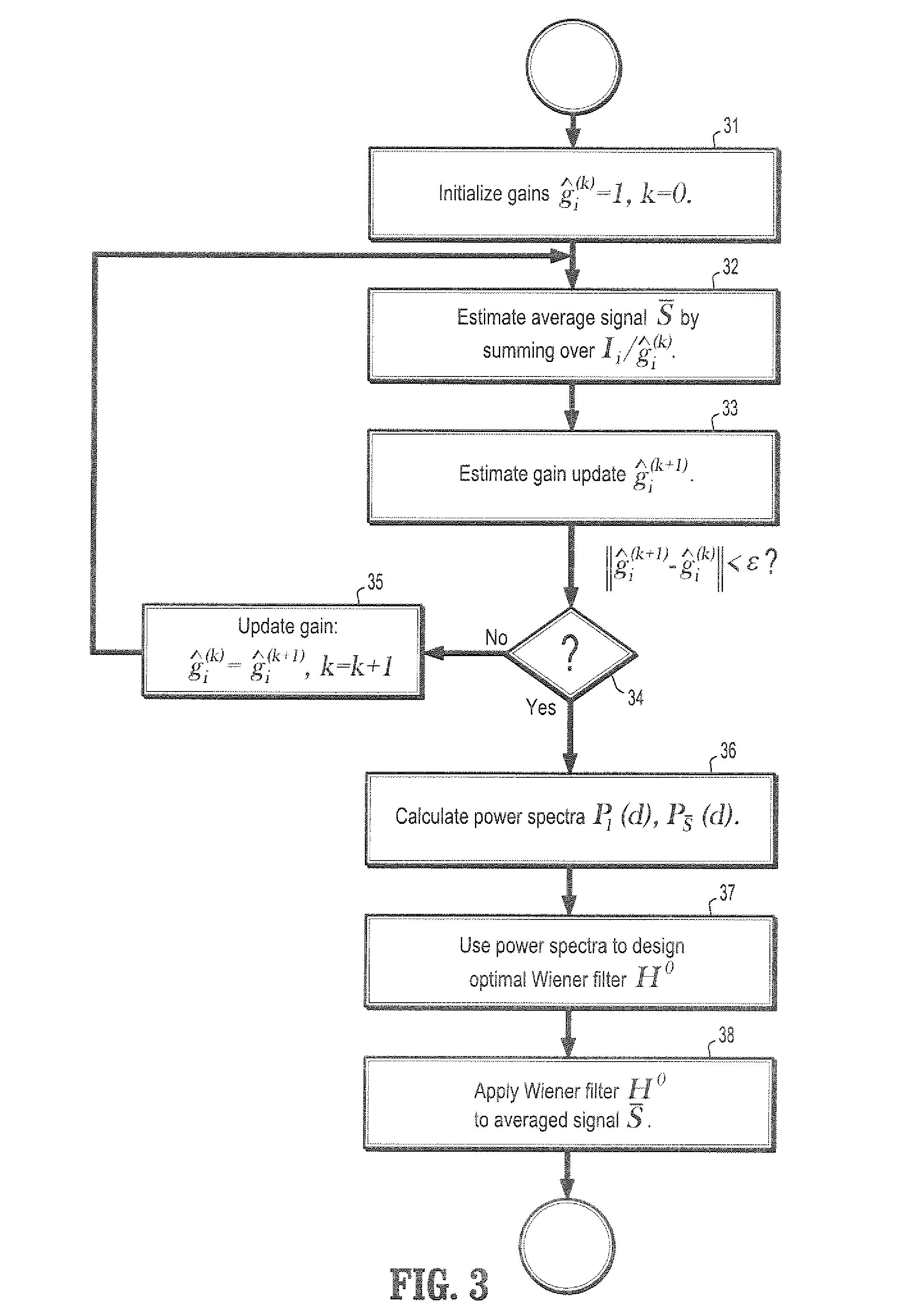
A method for removing speckle noise from ultrasound images includes providing a plurality of digitized ultrasound (US) images, each image comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a domain of points on a 2-dimensional grid, initializing an initial gain associated with each of said plurality of US images, estimating a signal sub-space by averaging over each US image divided by its associated gain, and estimating an updated gain by projecting its associated image into said signal sub-space. If an absolute difference of said updated gain and said initial gain is less than a pre-determined quantity, obtaining an averaged image from said signal sub-space, estimating an optimal Wiener filter from said plurality of US images and said averaged image, and filtering said averaged image with said Wiener filter, wherein said speckle noise is substantially minimized.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Methods and systems for motion adaptive spatial compounding
ActiveUS7101336B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonographySonification
A method of medical ultrasound imaging is provided. The method includes transmitting ultrasound waves into a volume at a first rate, receiving ultrasound echoes for each of the ultrasound waves, each echo is indicative of a density interface within the volume, each set of received echoes that corresponds to a single transmitted wave defines a steering frame, detecting motion of the array transducer, and combining a plurality of steering frames into a compound image based on the detected array transducer motion.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
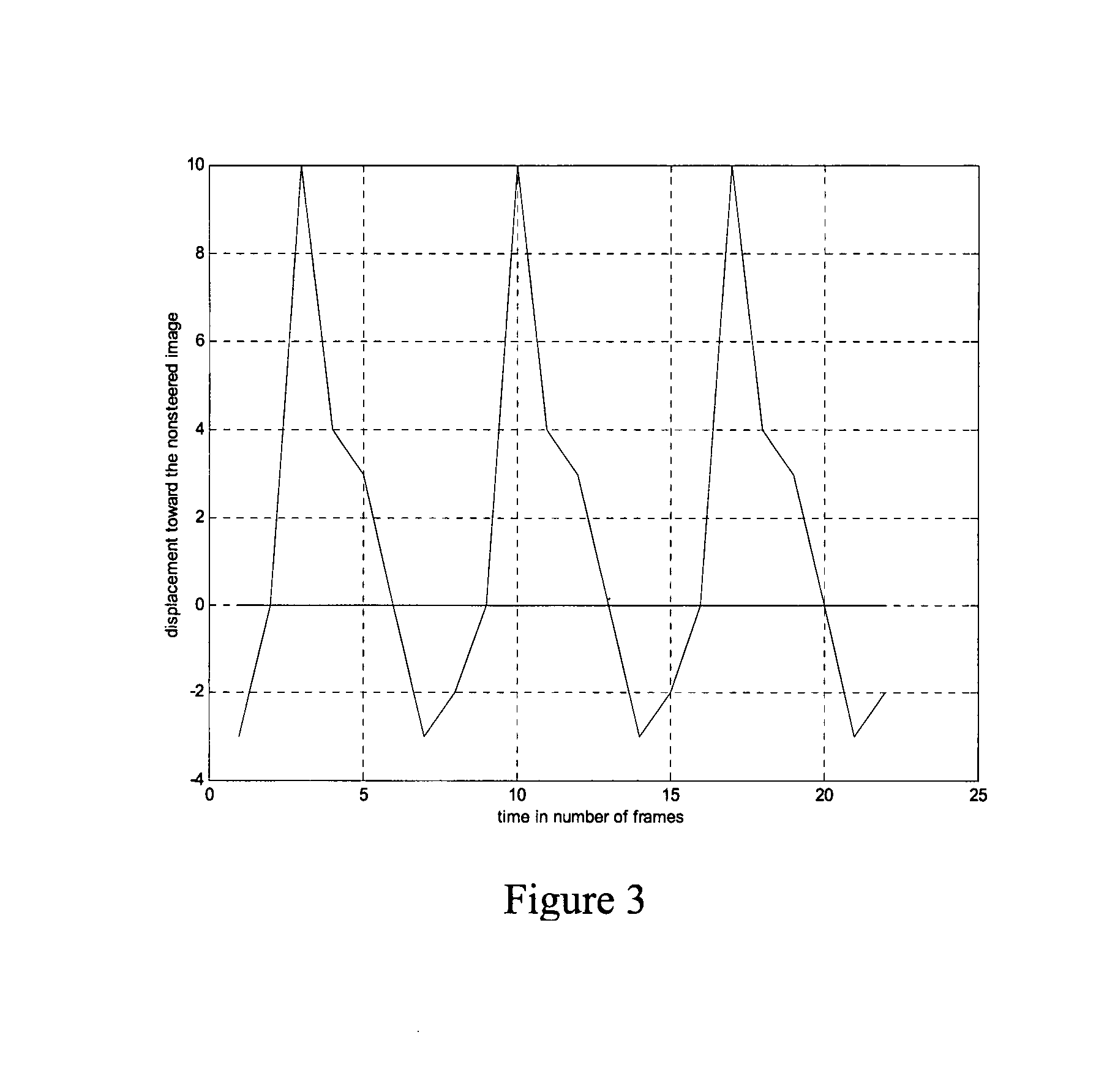
Reducing jittering in medical diagnostic ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS20080175453A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementUltrasound imagingSonification
Jittering in medical diagnostic ultrasound imaging is reduced, such as in steered spatial compounding. A pattern of decorrelation is used to detect motion between component frames, register component frames, and / or reduce jitter in the motion correction. The ultrasound imaging adapts as a function of the pattern.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Methods and systems for motion adaptive spatial compounding
ActiveUS20050113696A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonographyUltrasound imaging
A method of medical ultrasound imaging is provided. The method includes transmitting ultrasound waves into a volume at a first rate, receiving ultrasound echoes for each of the ultrasound waves, each echo is indicative of a density interface within the volume, each set of received echoes that corresponds to a single transmitted wave defines a steering frame, detecting motion of the array transducer, and combining a plurality of steering frames into a compound image based on the detected array transducer motion.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
System and method for spatial compounding using phased arrays
ActiveUS8137278B2Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsComputer graphics (images)Skin lines
The present invention is directed to a system and method which makes a phased array look like a curved array for purposes of performing spatial compounding calculations. In one embodiment, the phased array is treated as though it were a curved array by creating both a virtual apex and a virtual radius of curvature. Based on this transformation, standard spatial-compounding resampling tables can be used just as they are with curved arrays. In one embodiment, after the data is compounded to form the target image, certain data is removed prior to the actual display. This removed data represents data generated by virtual rays the prior to the physical skin line of the phased array.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
Compound image display system and method
InactiveUS6872181B2Reduce noiseIncreasing speckle reductionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCathode-ray tube indicatorsAngle of incidenceExtended field of view
A method and system for displaying an image associated with an extended field of view is provided. One image comprises a compounded sub-set of the extended field of view. Other images may include an extended field of view image or an image absent compounding from the extended field of view image. The compounded sub-set image is associated with reduced noise as compared to the image absent compounding and more closely resembles an area of the extended field of view image. Where plurality of images are associated with a rotated transducer or scan planes or where a sector or Vector® scan pattern is used, the compounded sub-set provides spatial compounding associated with different angles of incidence to the region of interest, increasing speckle reduction.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Digital beam forming method for multi-carrier broadband signal
ActiveCN109116306AEfficiently generate subcarrier signal waveformsAchieve synthesisWave based measurement systemsLocal oscillator signalIntermediate frequency
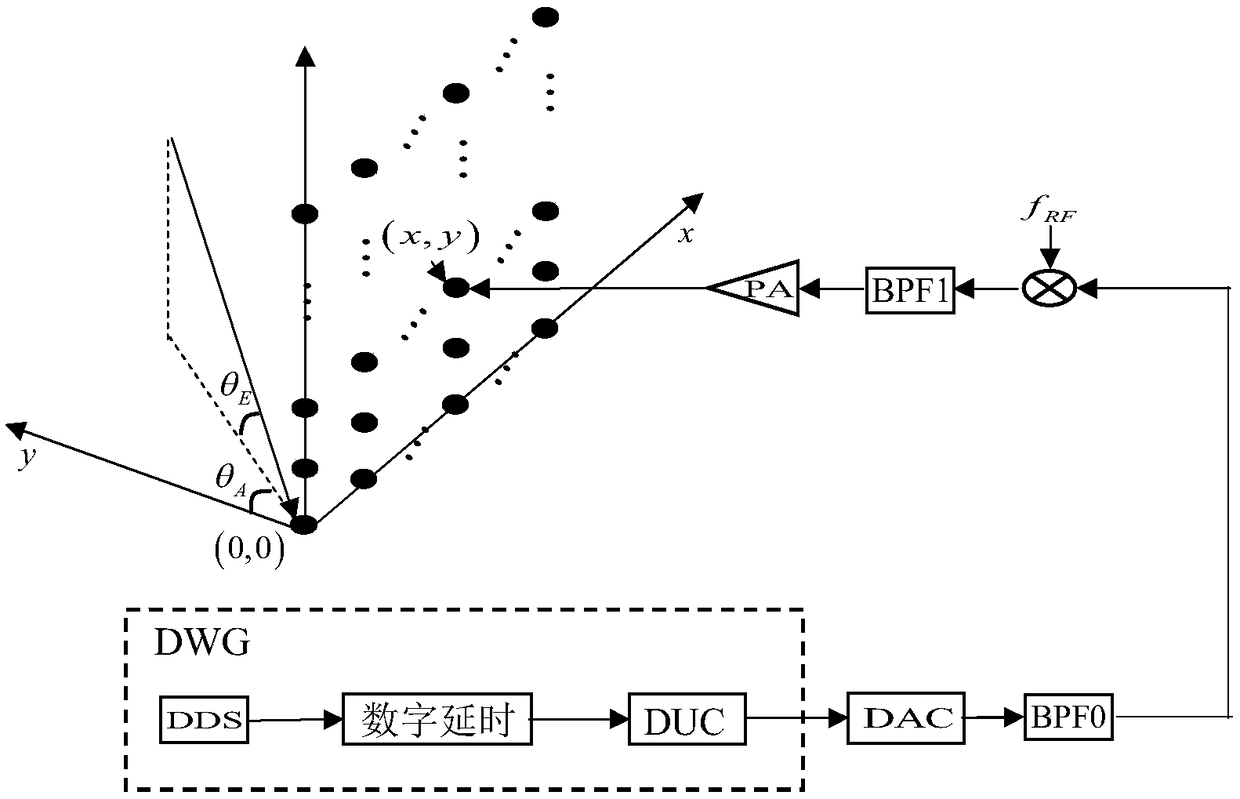
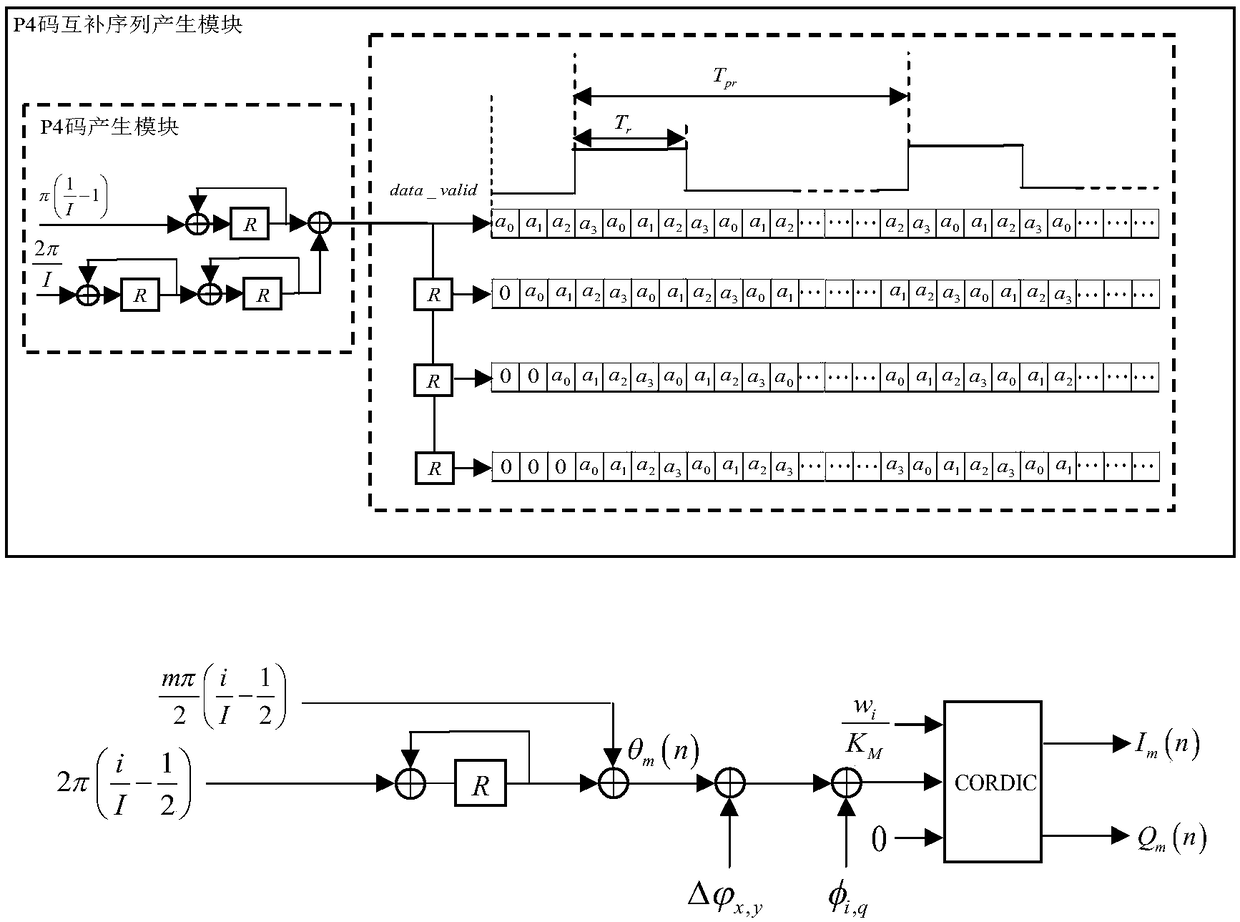
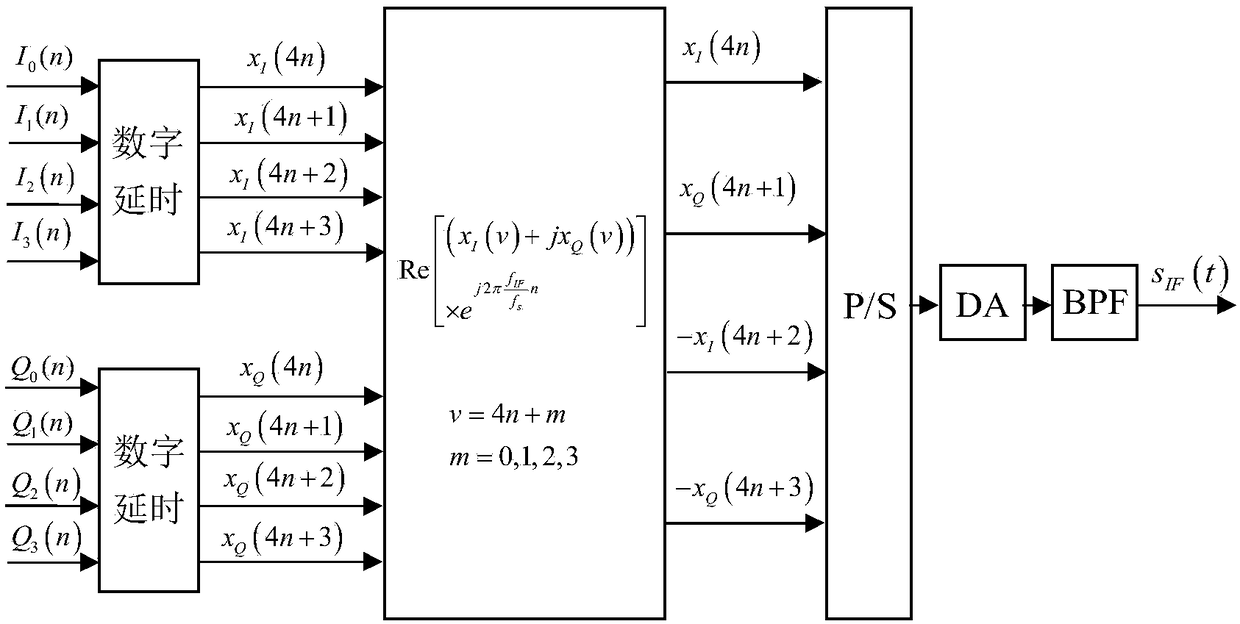
The invention discloses a digital beam forming method for a multi-carrier broadband signal. On the basis of a multi-phase processing technology, a sub-carrier DDS is designed in an FPGA; double accumulators and a register generate a P4 complementary code encoding phase in a delay manner; a compensation phase and a time delay are calculated according to a serial number of a sub carrier radio-frequency signal transmitting antenna unit; a phase code and a sub carrier baseband signal after phase compensation are generated based on a CORDIC algorithm by using the accumulator; digital delay, digitalup-conversion, digital-to-analog conversion, and intermediate-frequency filtering are carried out to output an analog subcarrier intermediate-frequency signal; a frequency-agility local-oscillator signal is generated by using an externally inputted reference clock signal, mixing and filtering are carried out on all sub carrier intermediate-frequency signals and the frequency-agility local-oscillator signal to generate sub carrier radio-frequency signals, power amplification is carried out and the processed signals are transmitted by antenna units; and the sub carrier radio-frequency signals transmitted by all antenna units are synthesized into a multi-carrier broadband signal in space. According to the invention, with phase control and continuously variable digital delay control, digitalbeam forming of the multi-carrier signal is realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
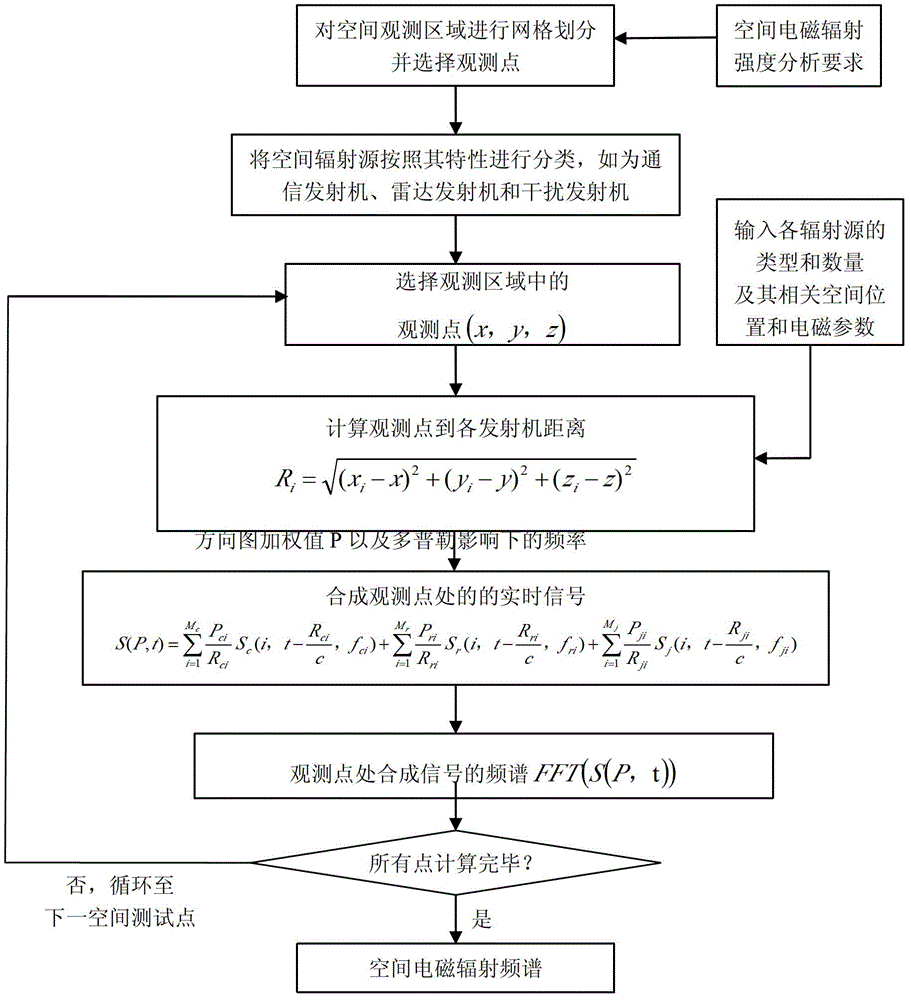
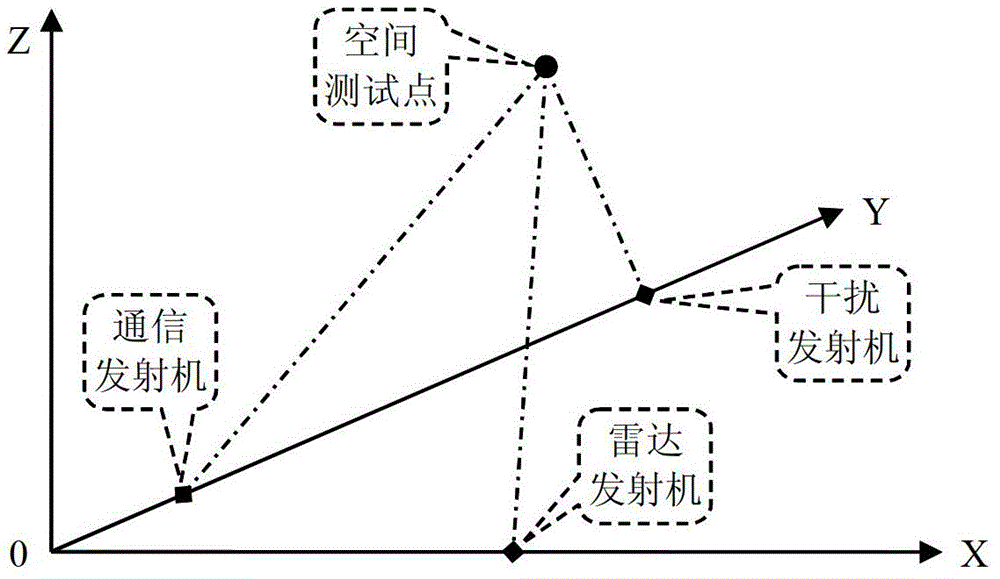
Space electromagnetic intensity distribution analysis method
The invention discloses a space electromagnetic intensity distribution analysis method, which comprises the following steps of: 1, determining an observation and test space region according to space electromagnetic intensity analysis requirements, and meshing the region, wherein a test point in subsequent steps can be selected from mesh regions; 2, calculating a relative distance and a relative direction between the point and each piece of equipment according to the position of the test point; 3, calculating a time-domain signal of the test point according to a formula for a composite signal by utilizing calculation results obtained by the step 2; 4, performing Fourier transform on the time-domain composite signal obtained by the step 3 to obtain the frequency-domain energy distribution of the space composite signal at the test point; and 5, repeating the steps 2 to 4 for the whole observation and test region to obtain the composite electromagnetic radiation intensity data of a space radiation source of the observation and test region. According to the method, the distribution of the space electromagnetic intensity can be analyzed more accurately and efficiently.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Ultrasonic elastography and pressure feedback method based on receive-side spatial-compounding
ActiveCN102626327AEasy to analyzeLow imaging noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Improved algorithm
The invention discloses an ultrasonic elastography andpressure feedback method based on receive-side spatial-compounding, namely, a medical ultrasonic elastography algorithm realized by an improved algorithm based on phase zero. When calculating displacement, the traditional algorithm carries out displacement calculation on a scanning line, which leads to large errors in the case that tissue movement contains a horizontal component; while, the window of noval algorithm covers a plurality of adjacent scanning lines, thereby reducing the errors brought by the horizontal component of tissue movement and improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the ultrasonic elastography. At the same time, the method provided in the invention also employs Receive-Side Spatial-Compounding technology in an elastography system, thereby further reducing the impact of elastography noise and further advancing the signal-to-noise ratio of the system. Finally, an average-strain-based elastography pressure feedback technology is provided to prompt current pressing strength and a normal pressing range for a doctor.
Owner:SASET CHENGDU TECH LTD
Integrated cooling system of high-power amplifier using waveguide space synthesis method
InactiveCN102315506AReduce volumeImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSynthesis methodsEngineering
The invention relates to a novel cooling design for a space synthesis amplifier, which is characterized in that a heat pipe or a high-heat-conducting-factor material is implanted into the card of the amplifier to reduce the thermal impedance of the card; and at the same time, a cooling system for liquid refrigeration is directly implanted into the amplifier to improve the cooling capacity of the system. By using the novel cooling structure in the design of the high-power amplifier, the miniaturization of the system is realized, the internal temperature of the system can be effectively reduced and the service life of the system is improved.
Owner:杨健
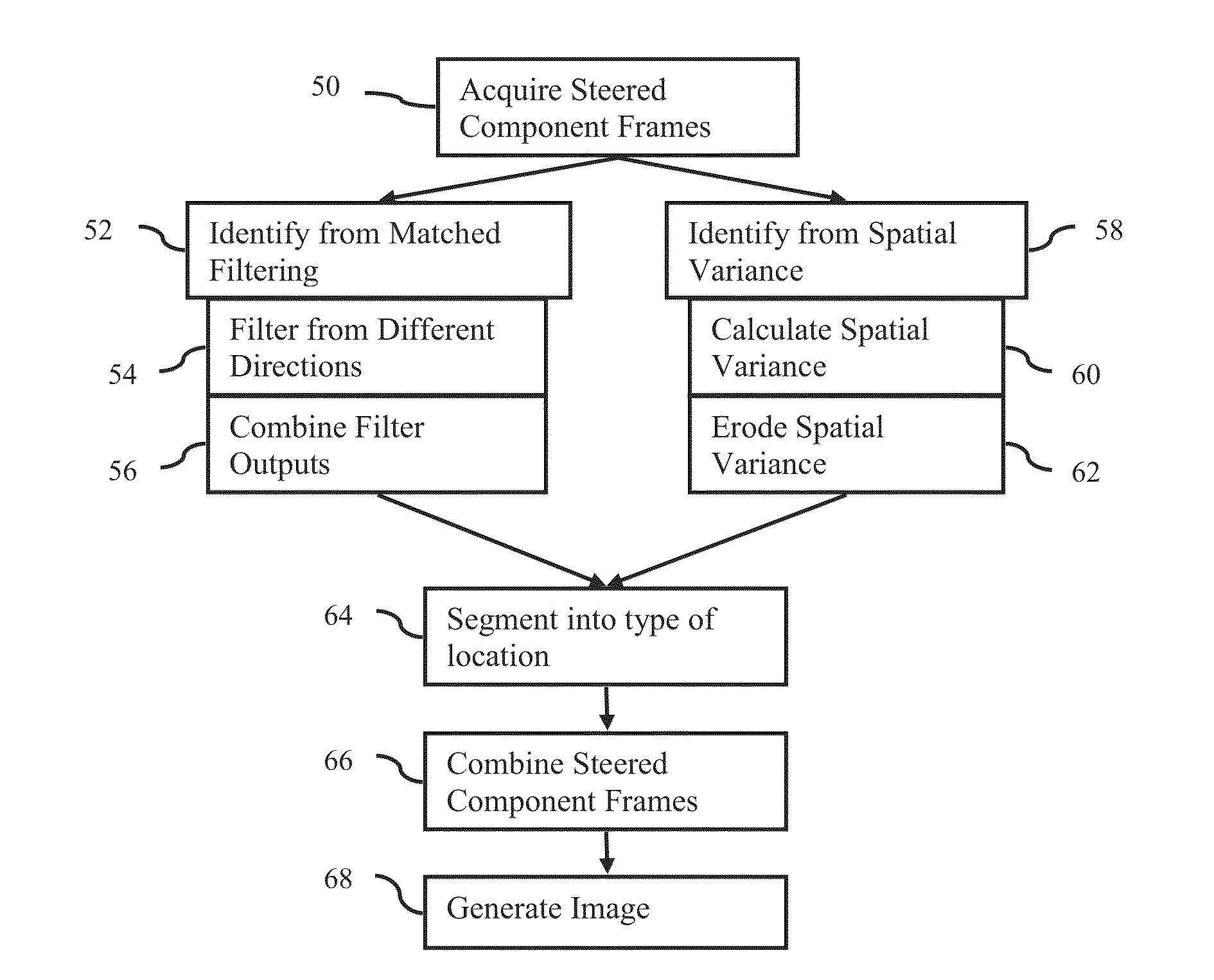
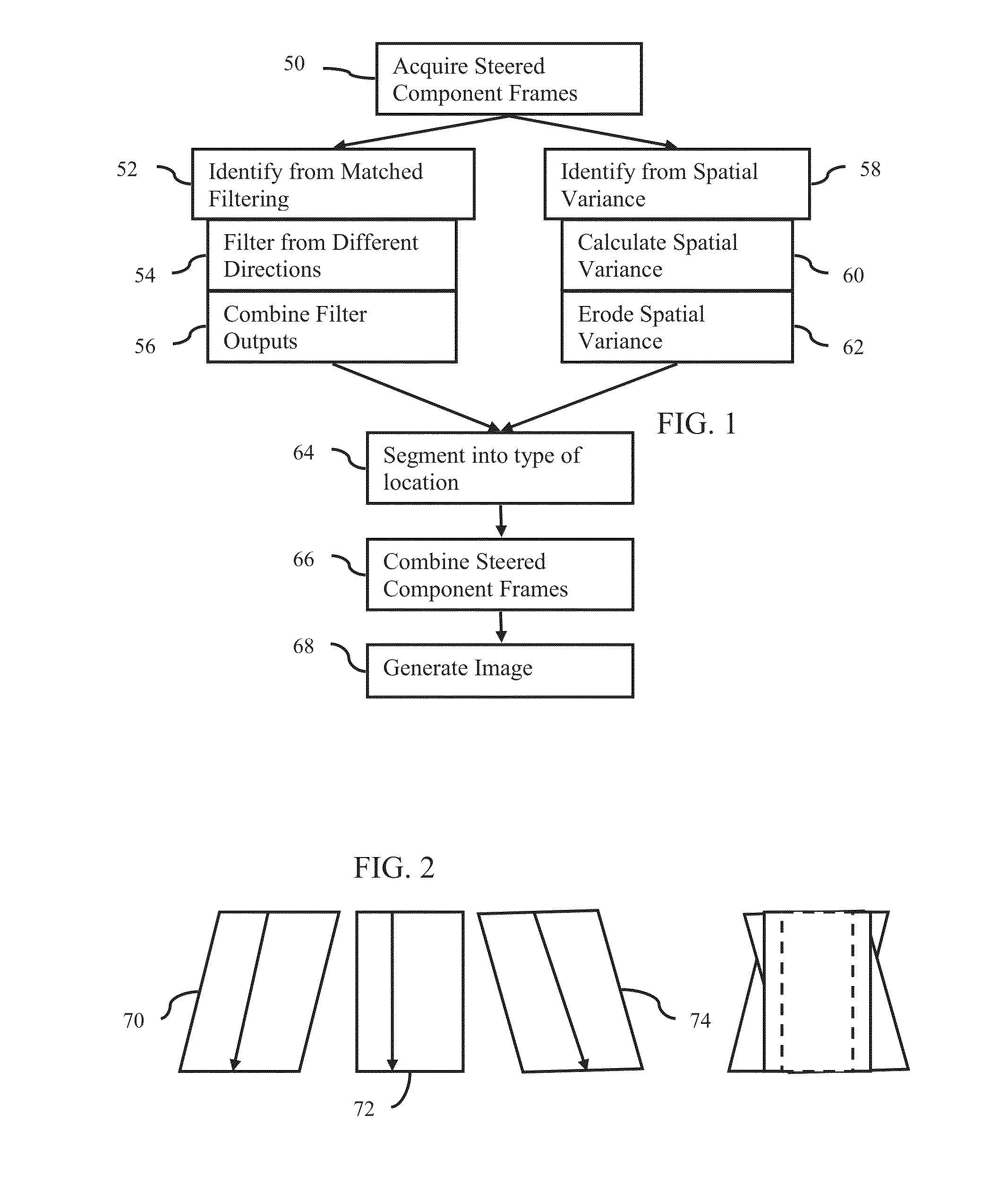
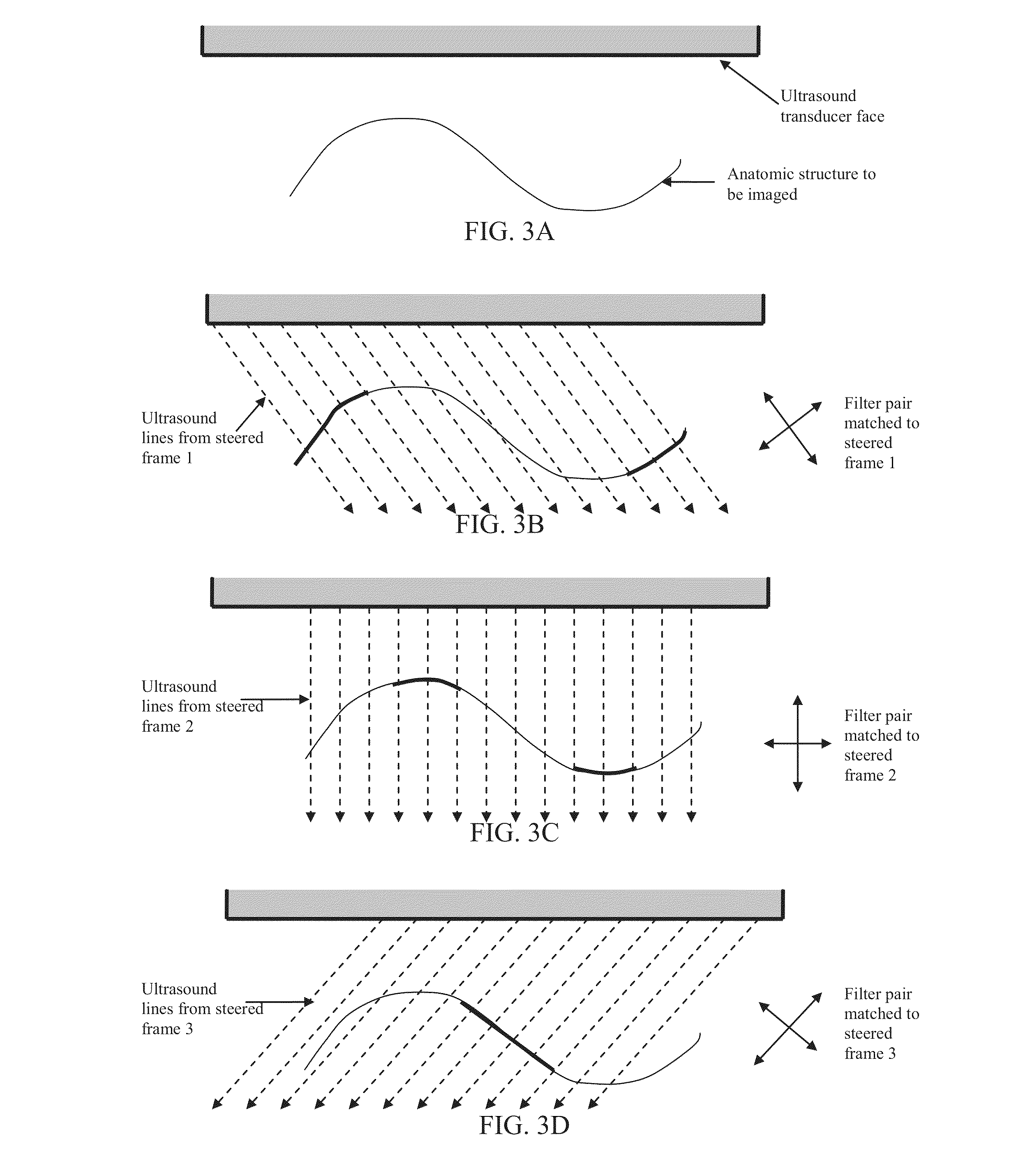
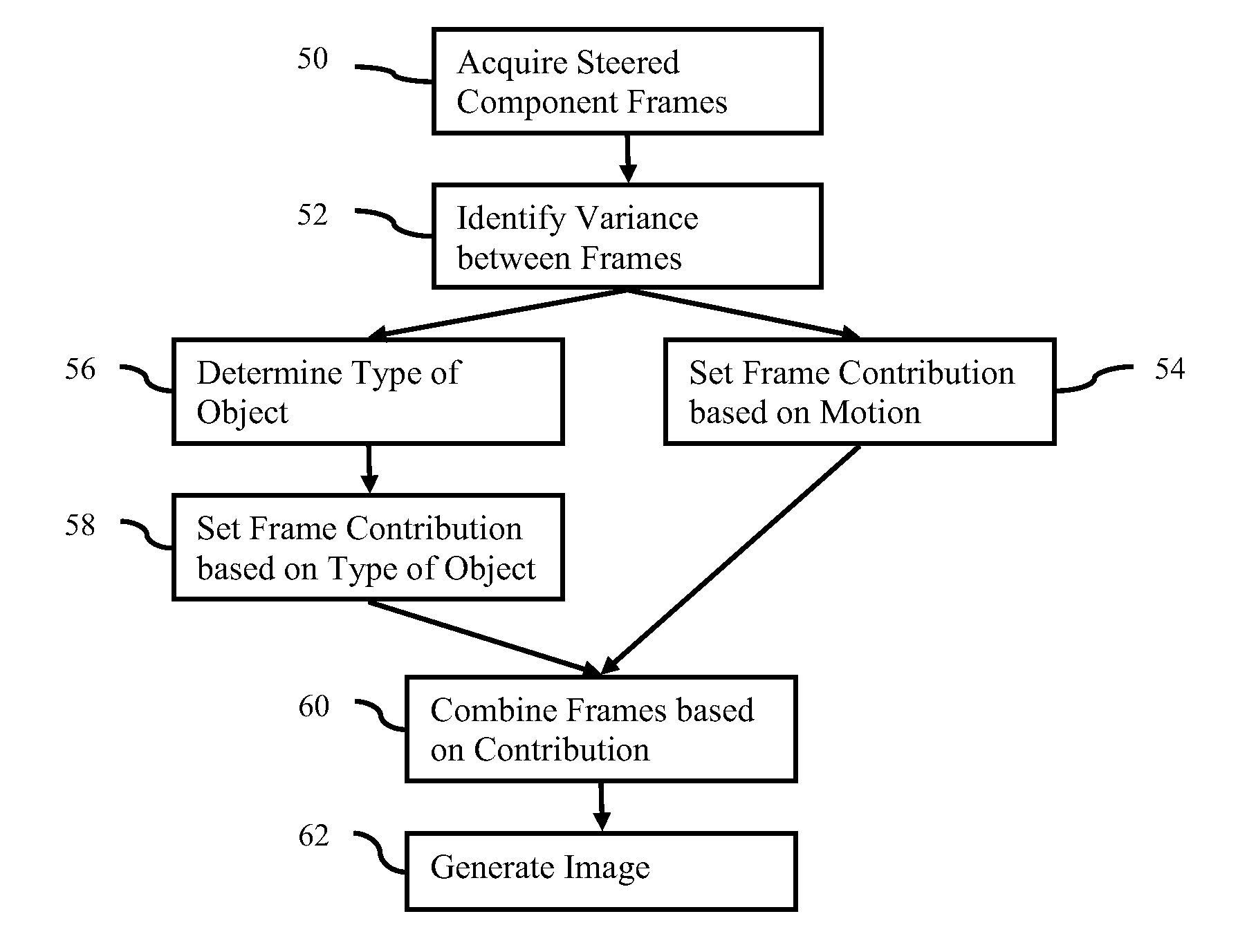
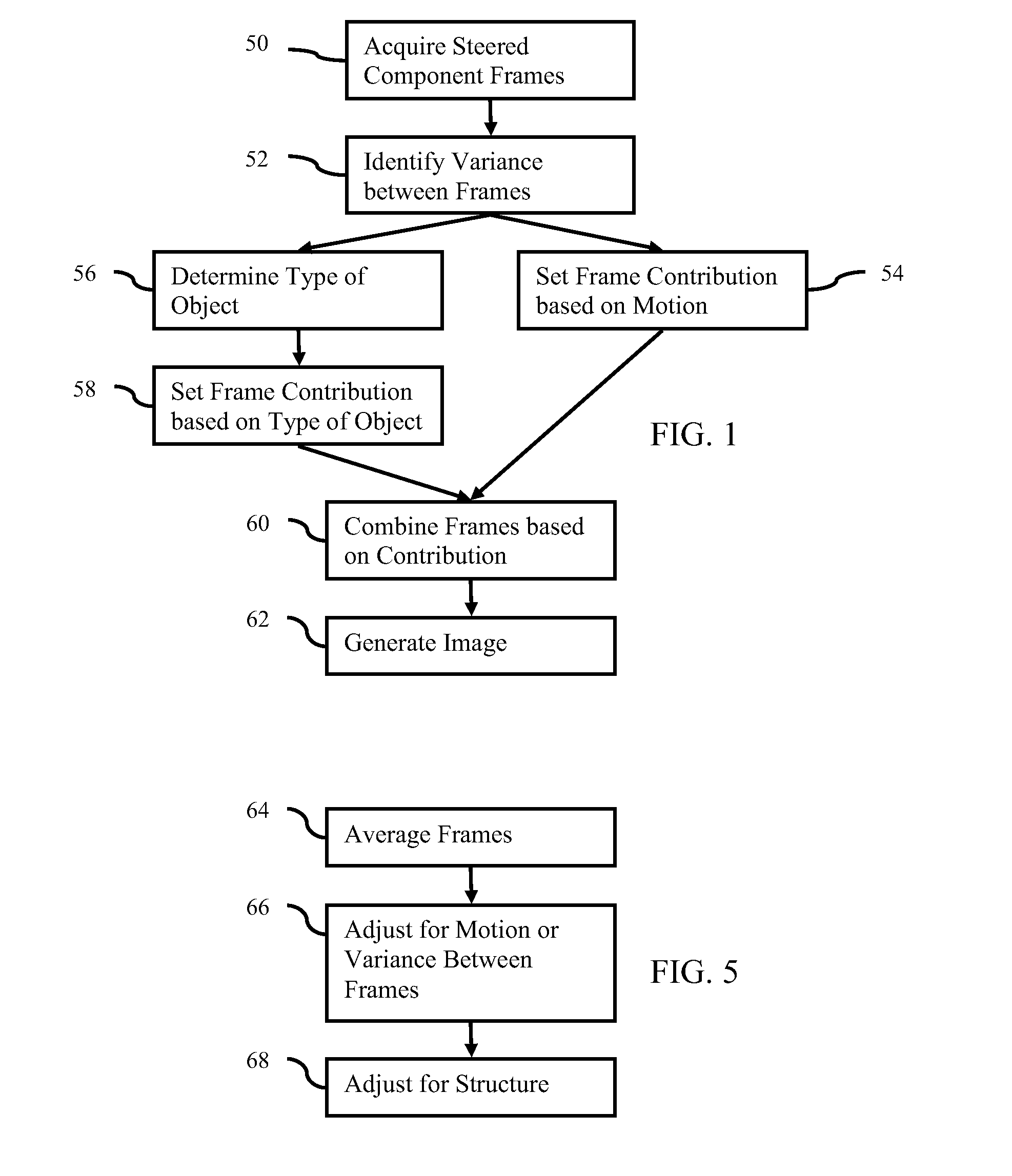
Component Frame Enhancement for Spatial Compounding in Ultrasound Imaging
ActiveUS20130294665A1Character and pattern recognitionAcoustic wave reradiationUltrasound imagingAnatomical structures
Steered spatial compounding is provided in ultrasound imaging. Component frames of data associated with different spatial response are processed to identify different sources of signals. Matched filtering and / or spatial variance with erosion distinguish between sources of signals, such as distinguishing between (1) anatomical structure and (2) soft tissue and / or noise. The locations in the patient are segmented by the source of signals and different compounding is applied for the different sources.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Methods and systems for angular-dependent backscatter spatial compounding
ActiveUS20050113695A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingSteering angle
A method of medical ultrasonic imaging is provided. The method includes transmitting a plurality of ultrasonic waves into a volume such that each successive wave is transmitted into the volume at a steering angle different than each preceding transmitted wave, receiving a plurality of ultrasonic echoes for each of the plurality of transmitted ultrasonic waves, each received echo is indicative of a density interface within the volume, each set of received echoes that corresponds to a single transmitted wave defines a steering frame, combining steering frames into a compound image, and identifying distal shadows in each steering frame.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
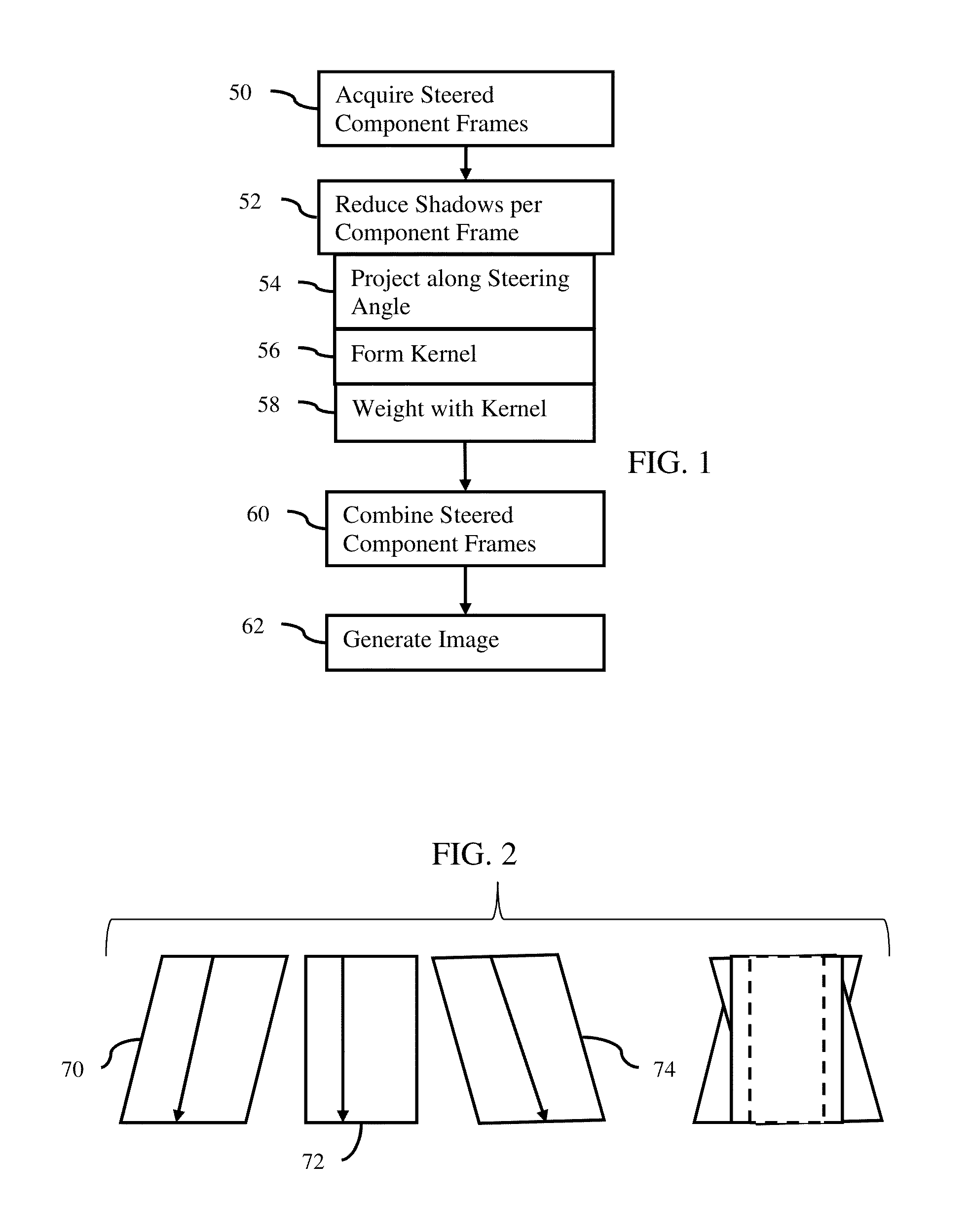
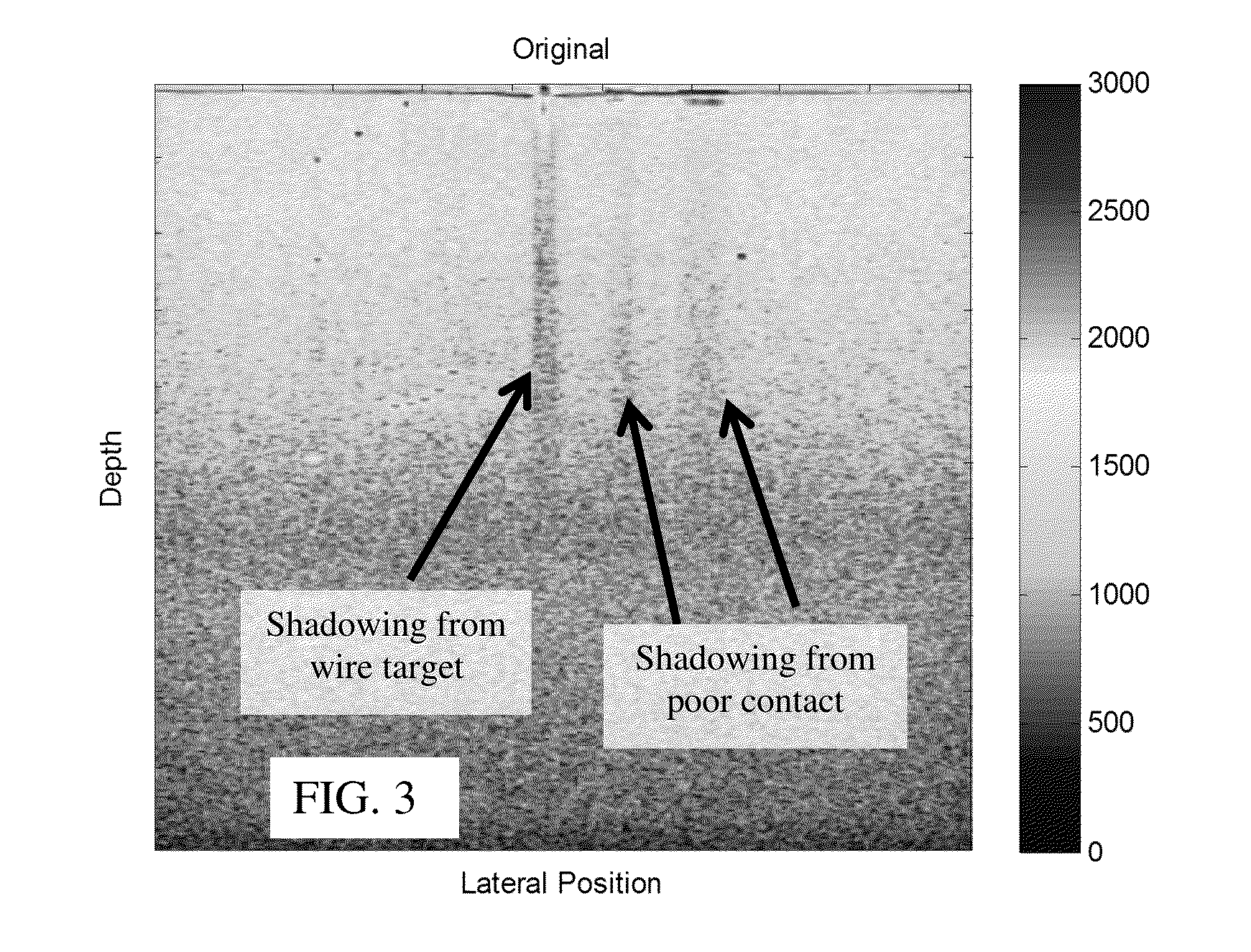
Shadow suppression in ultrasound imaging
ActiveUS20160089116A1Reducing and removing shadowOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound imagingImage Artifact
Shadow suppression is provided in ultrasound imaging, such as in steered spatial compounding. Using a transform or other approach, the data of a frame of data along the steering direction is projected. The projection is used to determine weights. The frame is weighted with the projection-based weights, reducing or removing shadows based on the one frame rather than based on registration with other frames. In the steered spatial compounding example, a compounded frame with independently shadow suppressed component frames may have little or no fork-like image artifacts due to shadowing.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Systems and methods for acquiring images simultaneously
InactiveUS20070073152A1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsComputer visionSpatial compounding
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Calculation method for transmission line clearance spatial synthetic electric field under mountain fire condition
ActiveCN106980712AConvenient researchRealize quantitative analysisDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMulti fieldBody area
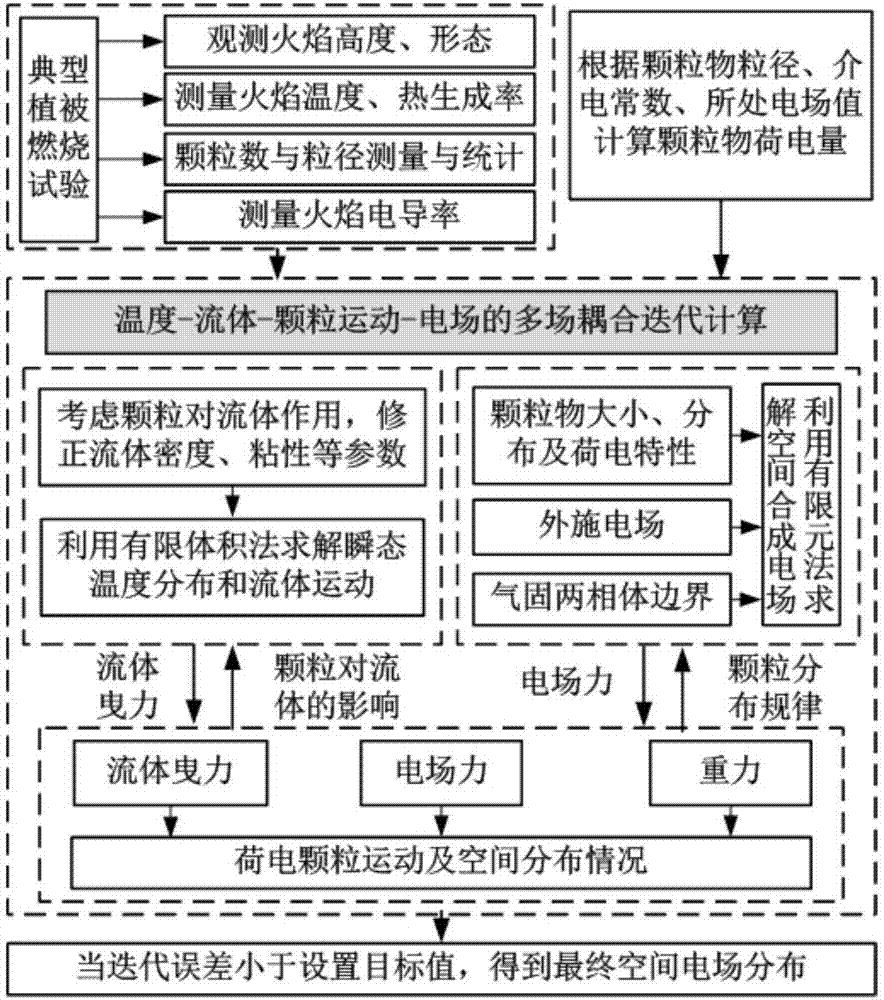
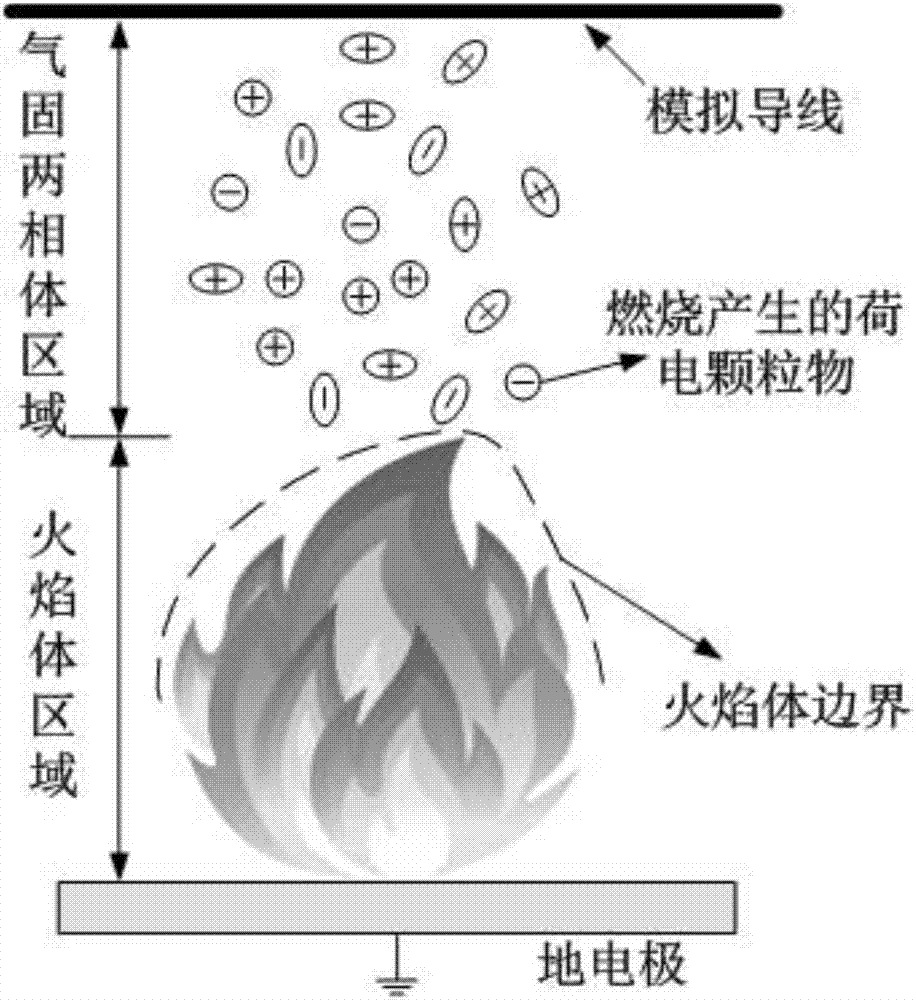
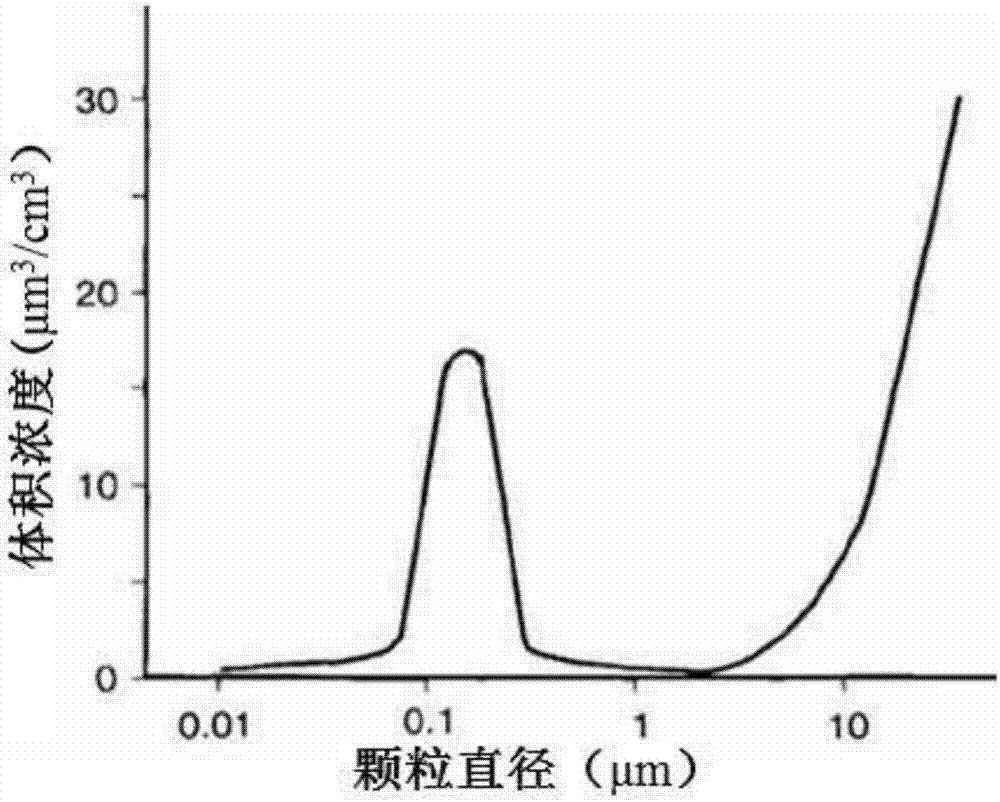
The invention discloses a calculation method for a transmission line clearance spatial synthetic electric field under a mountain fire condition. According to the method, the height, temperature and form of a flame are obtained according to a typical vegetation burning test, a stable burning area is selected, and clearance below a transmission line is divided into a flame body equivalent area and a gas-solid two-phase body area; a difference moving particle sizing instrument is adopted to measure small particles, a vernier caliper is adopted to measure big particles, and the statistical law of particle volume concentration and particle size is obtained; the electric quantity qk of the particles in the flame is calculated; a simulation model is established, and a finite volume method is utilized to solve transient temperature distribution and fluid motion; simulation calculation is performed on particle movement in the flame clearance to obtain particle distribution in the flame clearance; particle positions and carrying capacity are set, and a finite element method is utilized to solve a spatial synthetic electric field to obtain electric fields E at different positions; and initial particle distribution and an initial electric field value are set, temperature-fluid-particle movement-electric field multi-field coupling calculation is performed, and a final spatial synthetic electric field is obtained. The method can provide a basis for research on the discharge mechanism and breakdown characteristics of clearance.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Structural error compensation control method of space phase modulation annular traveling wave ultrasonic motor
InactiveCN103124149AReduce difficultyEffective compensationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesControl signalPhase difference
The invention discloses a structural error compensation control method of a space phase modulation annular traveling wave ultrasonic motor. Piezoelectric ceramics are divided into an A area and a B area, two power supply excitations with same time phase and adjustable amplitude values are exerted on the A area, one power supply excitation or two power supply excitations with the same amplitude value and time phase is / are exerted on the B area, the power supply difference between the A area and the B area is a pi / 2 time phase difference, and space synthesized error standing waves caused by structural errors of the motor are decomposed into two standing wave components with fixed positions for compensation respectively. By means of the structural error compensation control method of the space phase modulation annular traveling wave ultrasonic motor, the defect that traditional schemes for correcting errors through mechanical structures are unrecoverable and not visual is avoided, the error correcting difficulty is reduced, continuous error compensating is achieved, small errors can be effectively compensated, the structural errors are compensated by control signals, and thereby means can be provided for on-line error compensation of the motor.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
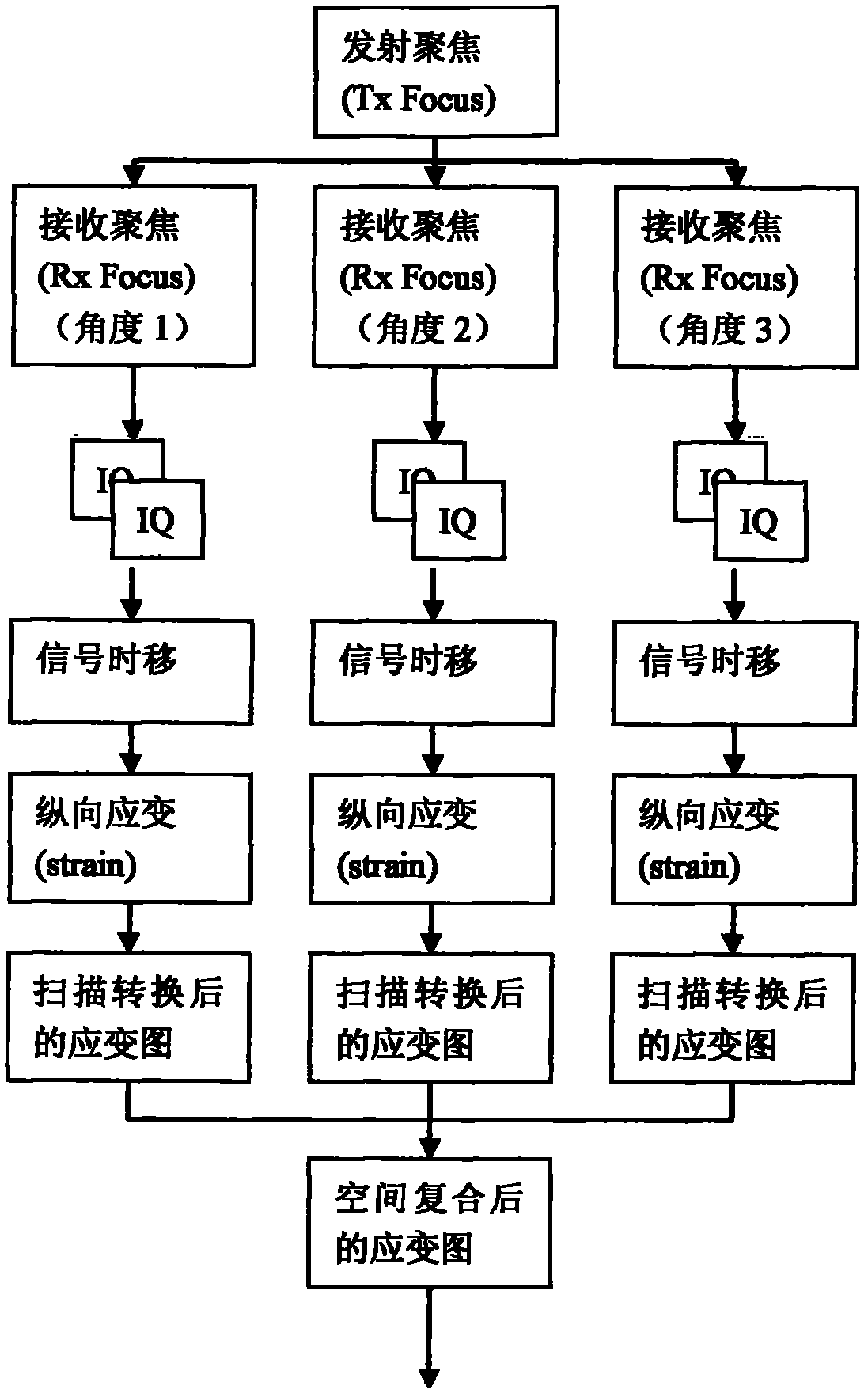
Ultrasonic imaging space compounding method and system
ActiveCN110101411AAvoid dullnessAvoid smearingInfrasonic diagnosticsSonic diagnosticsMultiple frameImage resolution
The invention provides an ultrasonic imaging space compounding method and system. The method comprises the steps that receiving lines with different deflection angles are arranged at a transmitting beam position where each time of scanning is located, wherein the receiving lines are subjected to multi-angle deflection with the normal direction of a probe as the basis and the depth position of a transmitting focal point as a reference point; the receiving lines at different angles are obtained through beam synthesis, and the delay of beam synthesis is compensated according to the wavefront delay of the transmitting beams; after scanning of all positions is completed, the receiving lines at the same deflection angle form a frame of image at the angle, one of multiple frames of images with different deflection angles serves as a basic image, and other frames of images except the basic image are transformed to have a coordinate system same as that of the basic image; spatial compounding iscarried out on the multiple frames of images in the same coordinate system so as to obtain a composite image for outputting. According to the method and system, the time resolution of imaging is notinfluenced, and the phenomena of image dullness and trailing caused by the prior art are avoided.
Owner:VINNO TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Dynamic Steered Spatial Compounding in Ultrasound Imaging
ActiveUS20130208965A1Maintain and increase signal fidelityImage enhancementImage analysisUltrasound imagingSignal variance
Dynamic steered spatial compounding is provided in ultrasound imaging. The compounding adjusts for variance. The compounding dynamically reacts to variance due to motion and / or view direction. For each location, the weights are set based on the motion or signal variance for the respective location. The weighting used for compounding or the results of the compounding adapt to maintain or increase signal fidelity.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
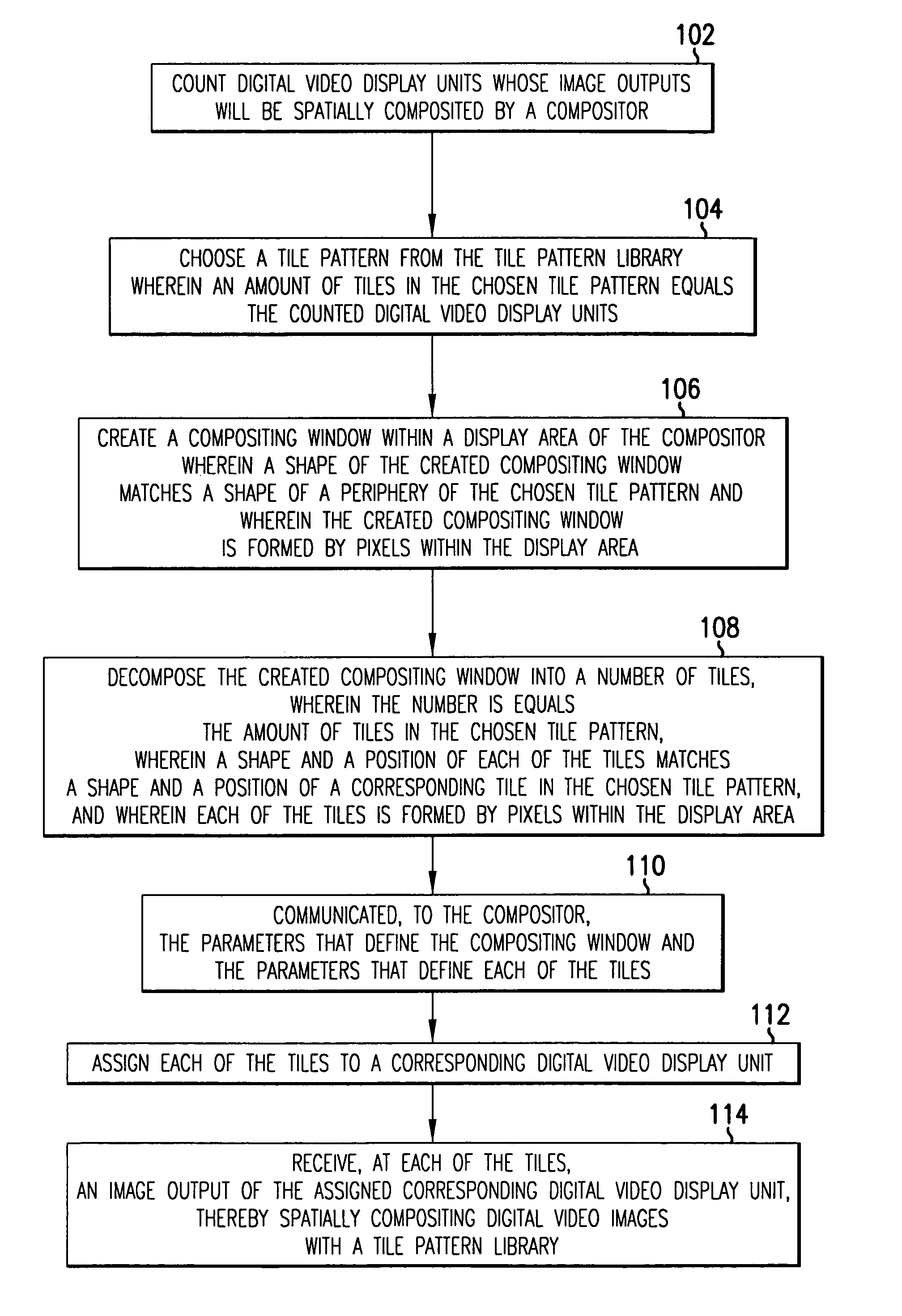
Method and system for spatially compositing digital video images with a tile pattern library
InactiveUS7027072B1Increase probabilityReduce the amount requiredCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage generationDigital videoGraphics
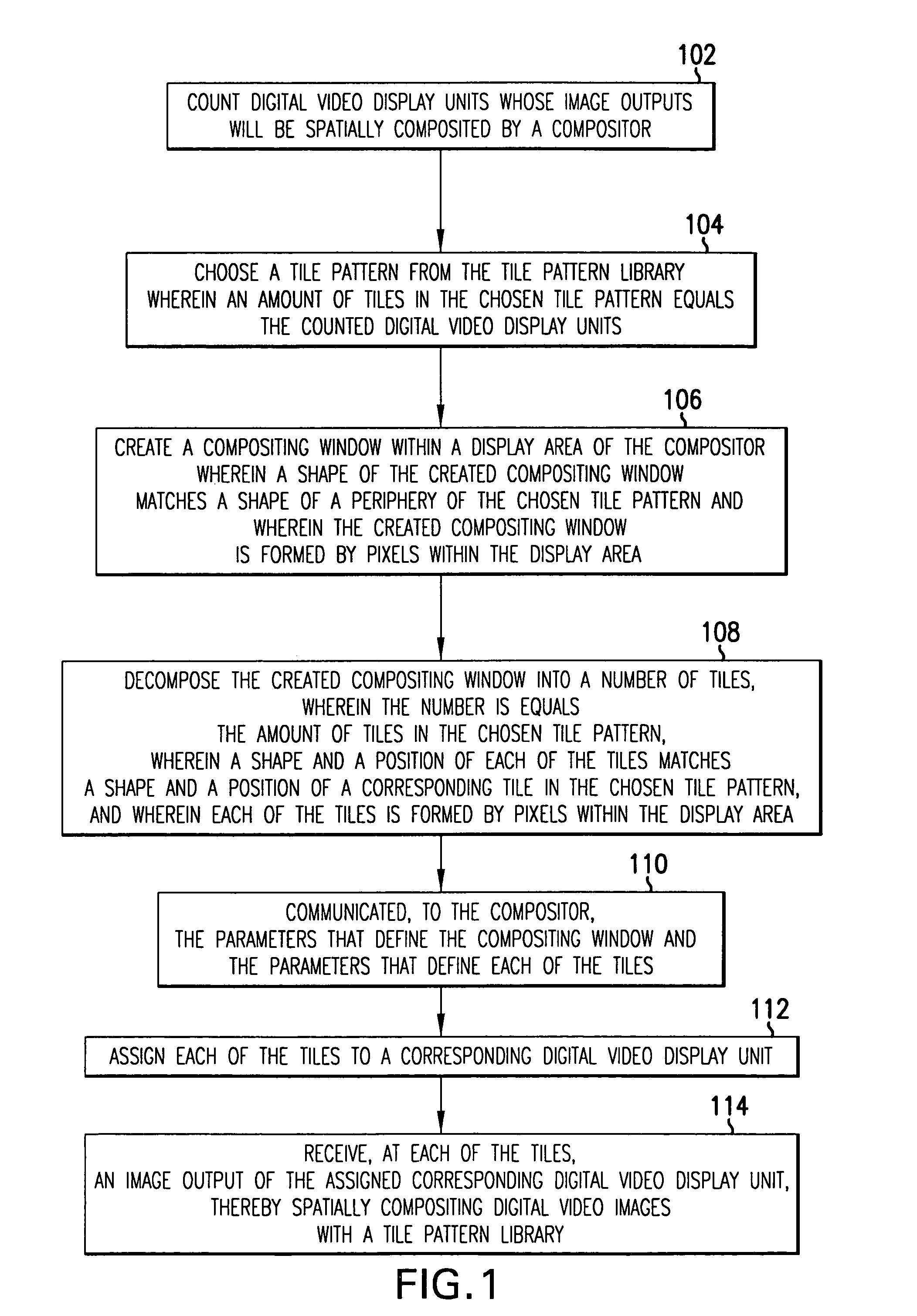
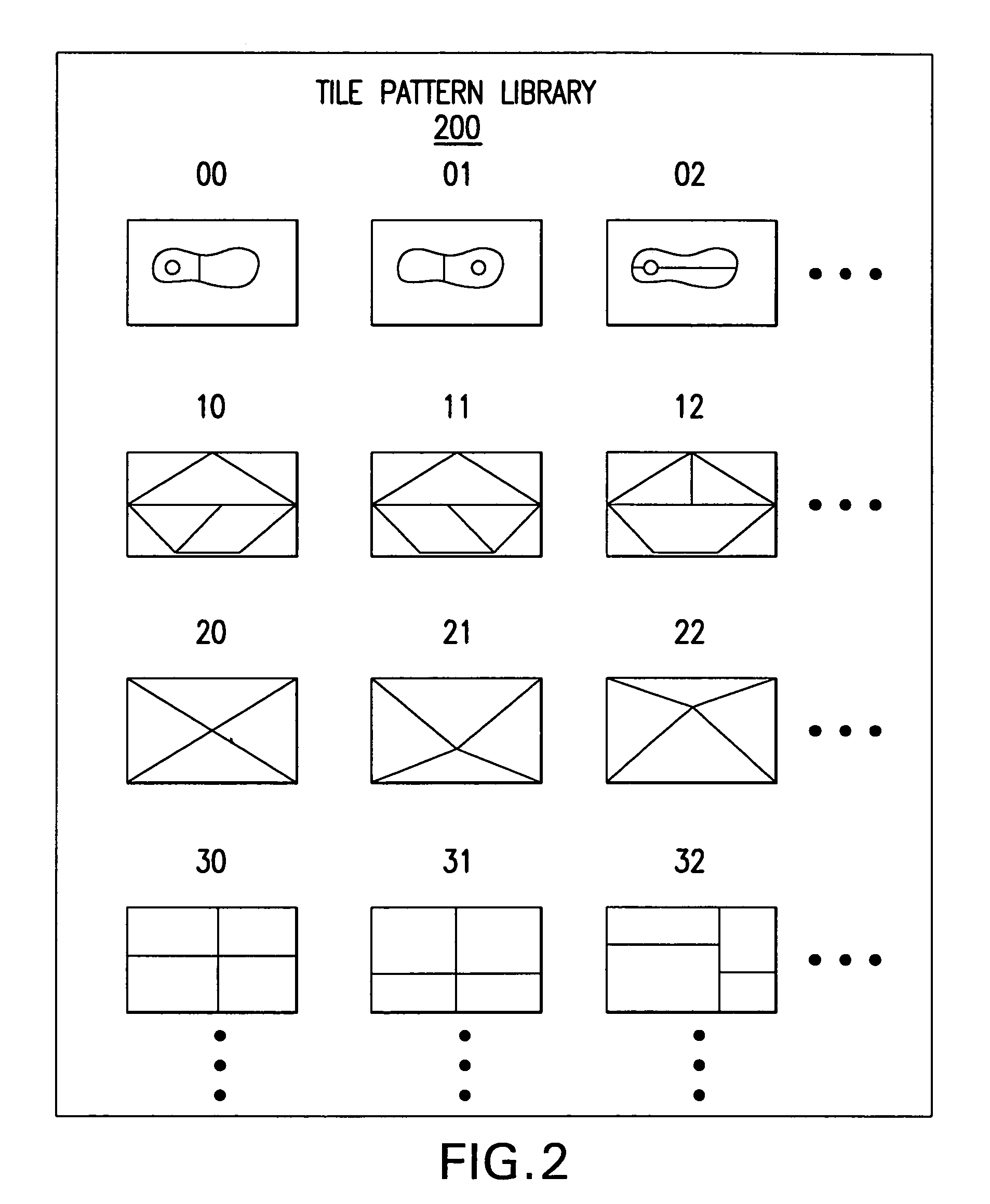
A method and system for spatially compositing digital video images with a tile pattern library. Spatial compositing uses a graphics pipeline to render a portion (tile) of each overall frame of digital video images. This reduces the amount of data that each processor must act on and increases the rate at which an overall frame is rendered. Optimization of spatial compositing depends on balancing the processing load among the different pipelines. The processing load typically is a direct function of the size of a given tile and an inverse function of the rendering complexity for objects within this tile. Load balancing strives to measure these variables and adjust, from frame to frame, the number, sizes, and positions of the tiles. The cost of this approach is the necessity to communicate, in conjunction with each frame, the number, sizes, and positions of the tiles. A tile pattern library is a collection of sample compositing windows of various shapes each of which is decomposed into tiles of various shapes and positions. Associated with each sample in the tile pattern library is an index code that can be used to communicate the overall pattern. This reduces the amount of data needed to convey the parameters that define each tile.
Owner:MORGAN STANLEY +1
Method and system for enhancing reverberation room internal field intensity and simulating compound field electromagnetic environment
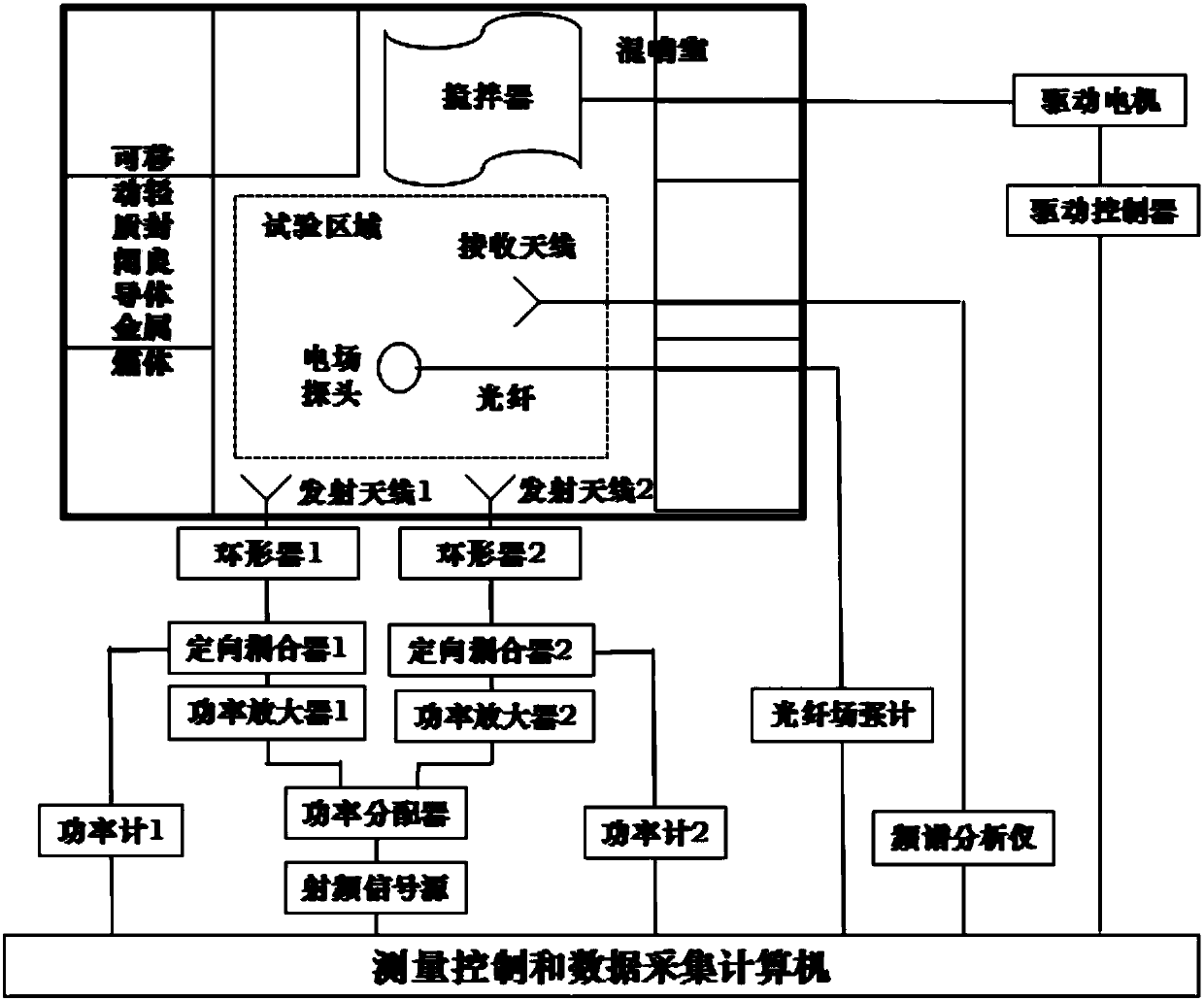
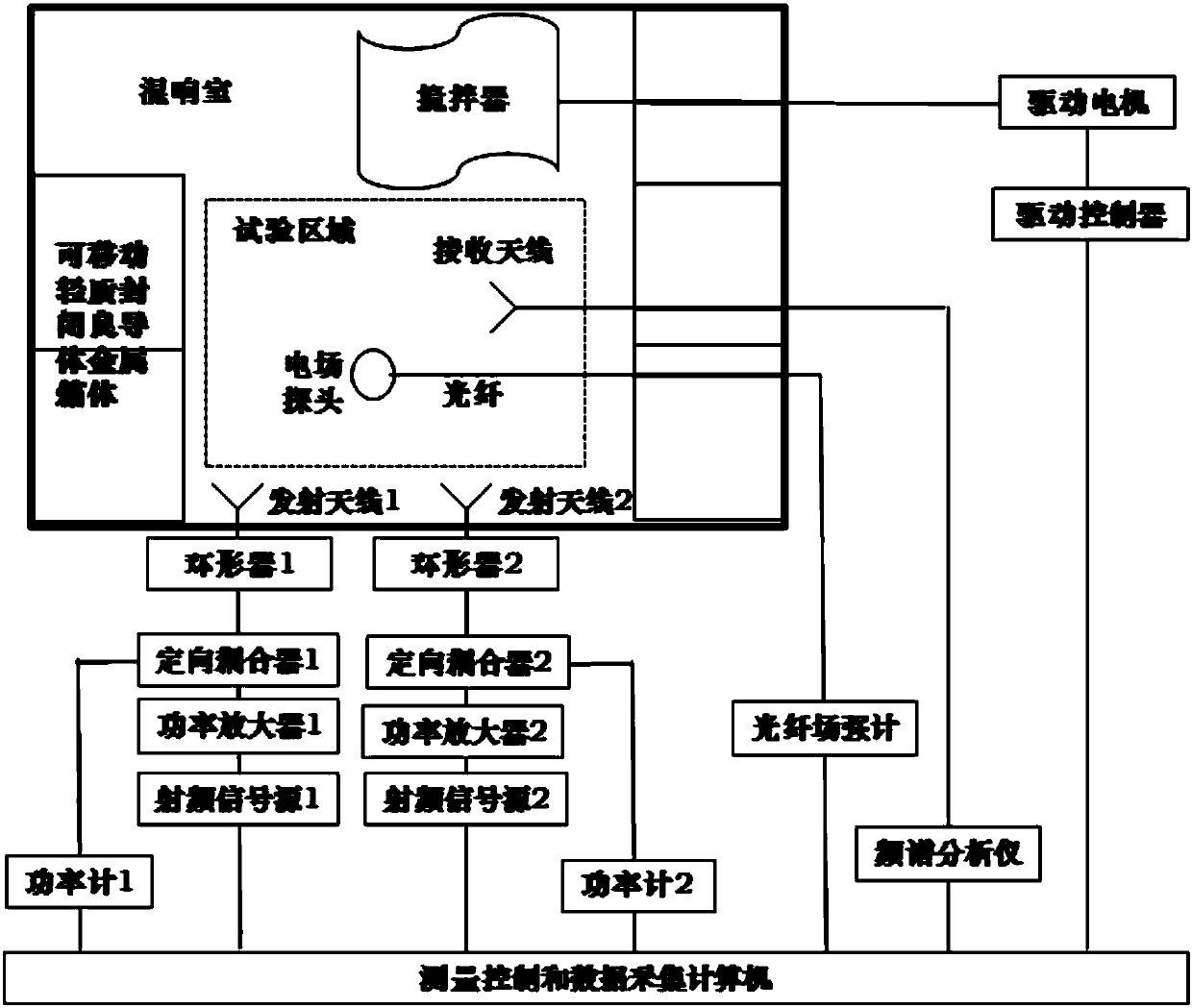
ActiveCN108132390AHigh test spaceHigh field strength test spaceElectromagentic field characteristicsElectrical conductorSynthesis methods
The invention provides a method and a system for enhancing reverberation room internal field intensity and simulating compound field electromagnetic environment. According to the method, the multi-frequency high-field-intensity complex electromagnetic environment is simulated by using a reverberation room, and the high field intensity in the test area is acquired by using the space synthesis method of the same frequency microwave power in the reverberation room; the multi-frequency compound field of the test area is acquired by using a different frequency incoherent resonance method; and multiple movable light closed good conductor metal boxes are arranged in the reverberation room so that the ineffective space of the reverberation room at the high end of frequency can be reduced and the field intensity amplitude of the test area can be enhanced. The system comprises the reverberation room, multiple movable light closed good conductor metal boxes, a radio frequency signal source, a power distributor, power amplifiers, a directional coupler, a circulator, a power meter, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna, an optical fiber field intensity meter, a spectrum analyzer and a measurement and control and data acquisition computer. The internal field intensity amplitude of the reverberation room is enhanced by using multiple power amplifiers and adjusting the internal structureof the reverberation room so as to simulate the multi-frequency complex electromagnetic environment in the reverberation room.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
Method for realizing display of image and character in three-dimensional space by laser scanning
InactiveCN101609210AAchieve normal displayAdvertisingDisplay meansMobile laser scanningThree-dimensional space
The invention relates to a technology for realizing the display of images and characters by laser scanning, in particular to a method for realizing display of image and character in three-dimensional space by laser scanning. The invention is characterized in that the same image or character or the image and the character are synchronously scanned and output at the same time in the same space by the control of a plurality of laser beams emitted by a plurality of lasers. As the laser beams are controlled from different angles, the same image or character or the image and the character are scanned and output in a superposition way simultaneously in the same space, therefore, each beam of laser generates scattered light toward different directions when being converged into a point in the space, and all spectators on the ground can view the image output by scanning at effective distance and effective angle.
Owner:王一诺
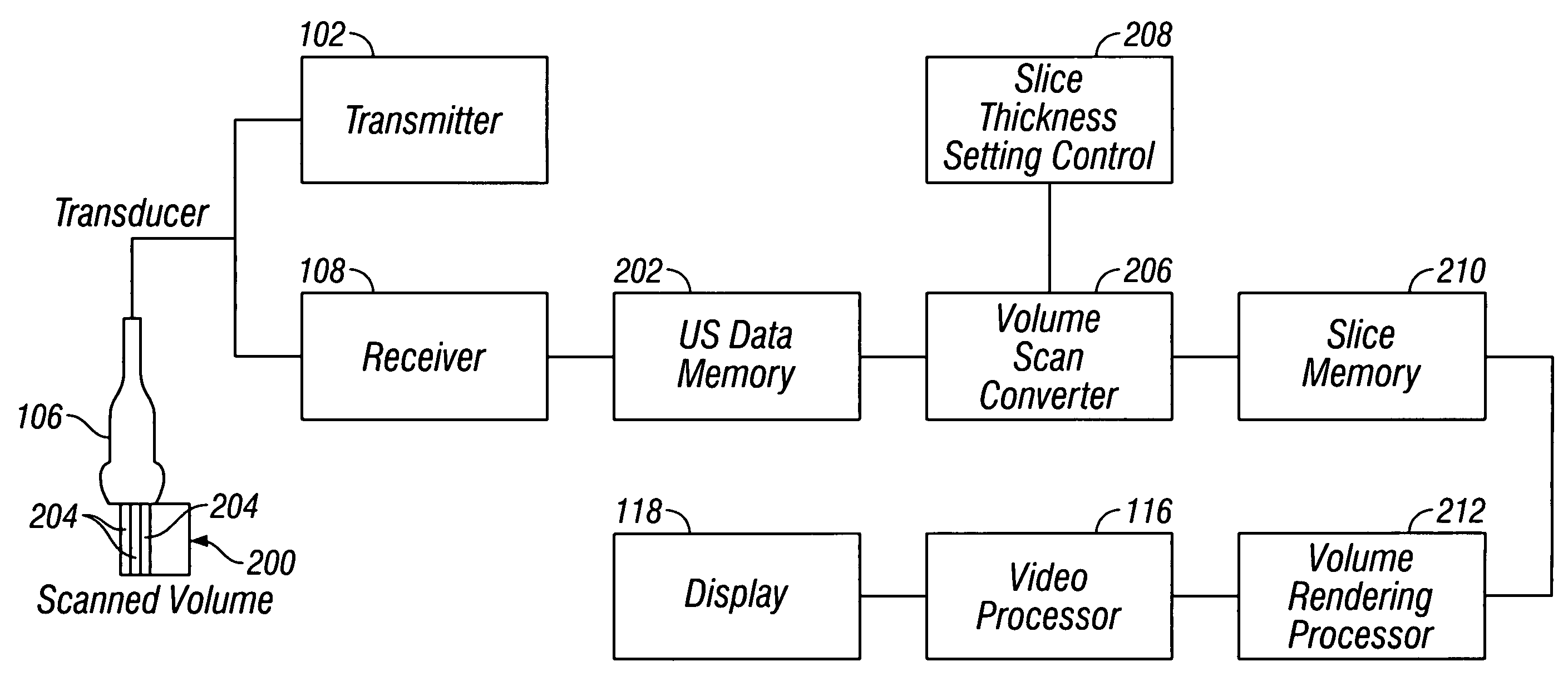
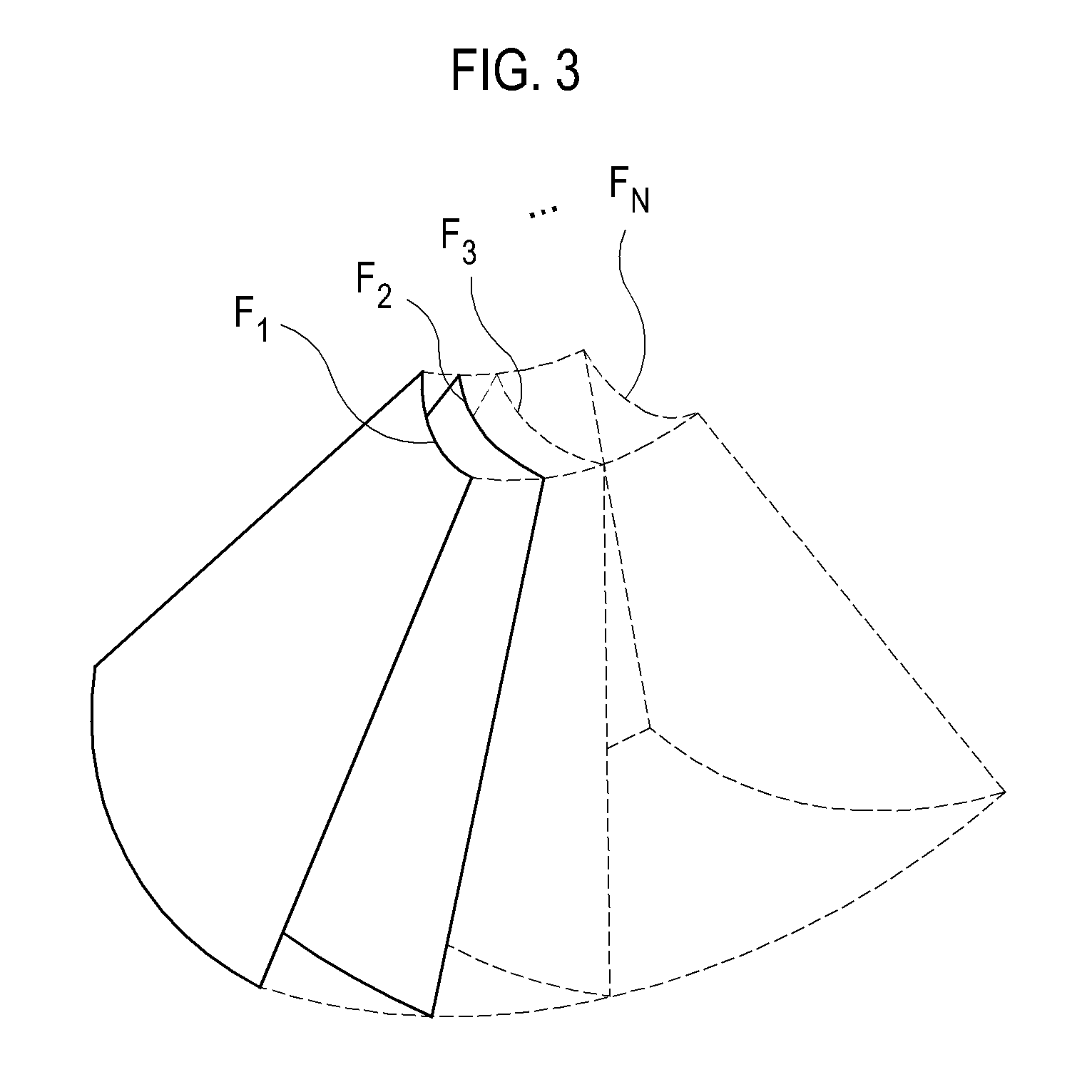
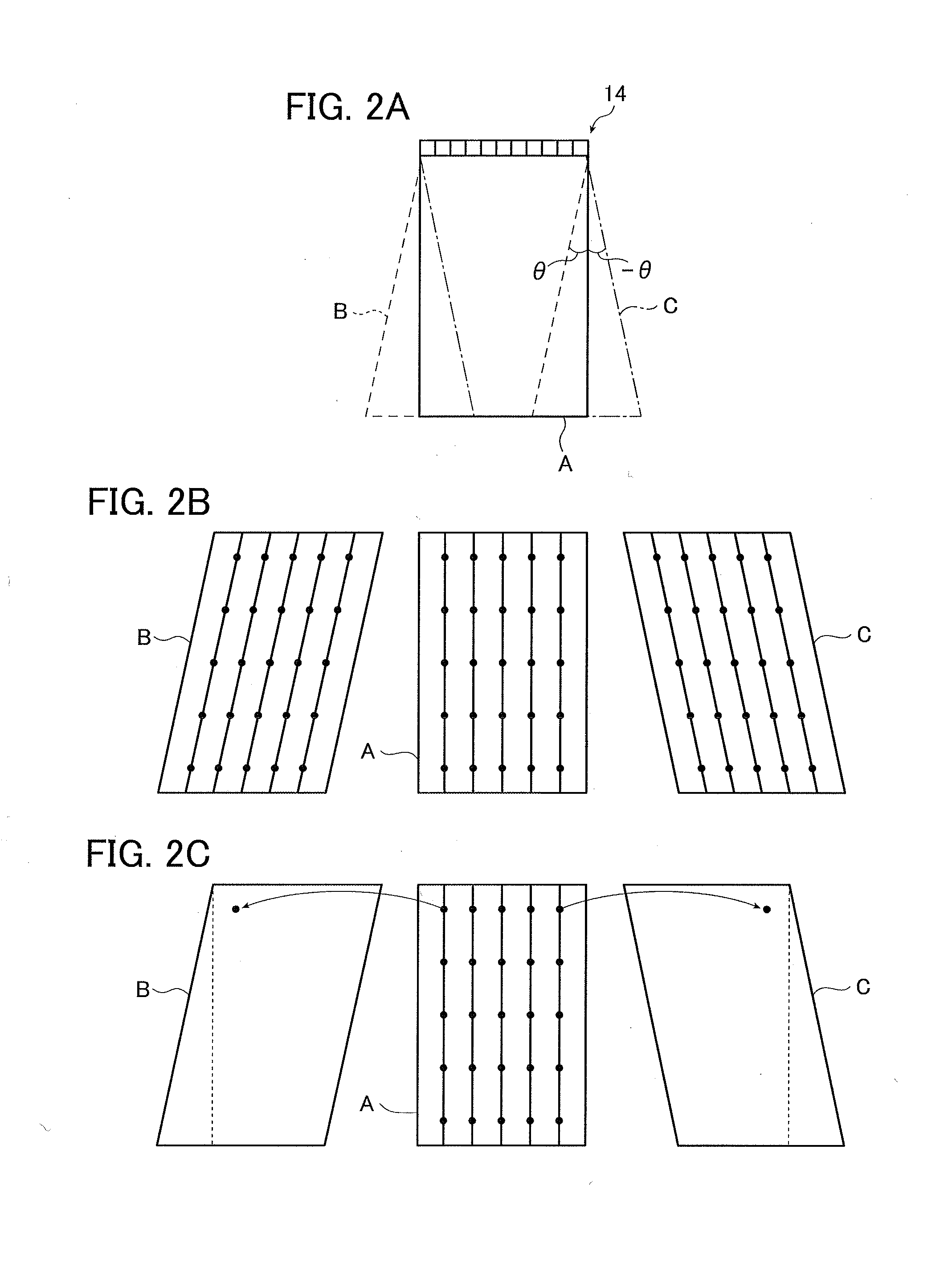
Ultrasonic diagnostic imaging system with spatial compounding of trapezoidal sector
ActiveCN105074498AAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationScan angle
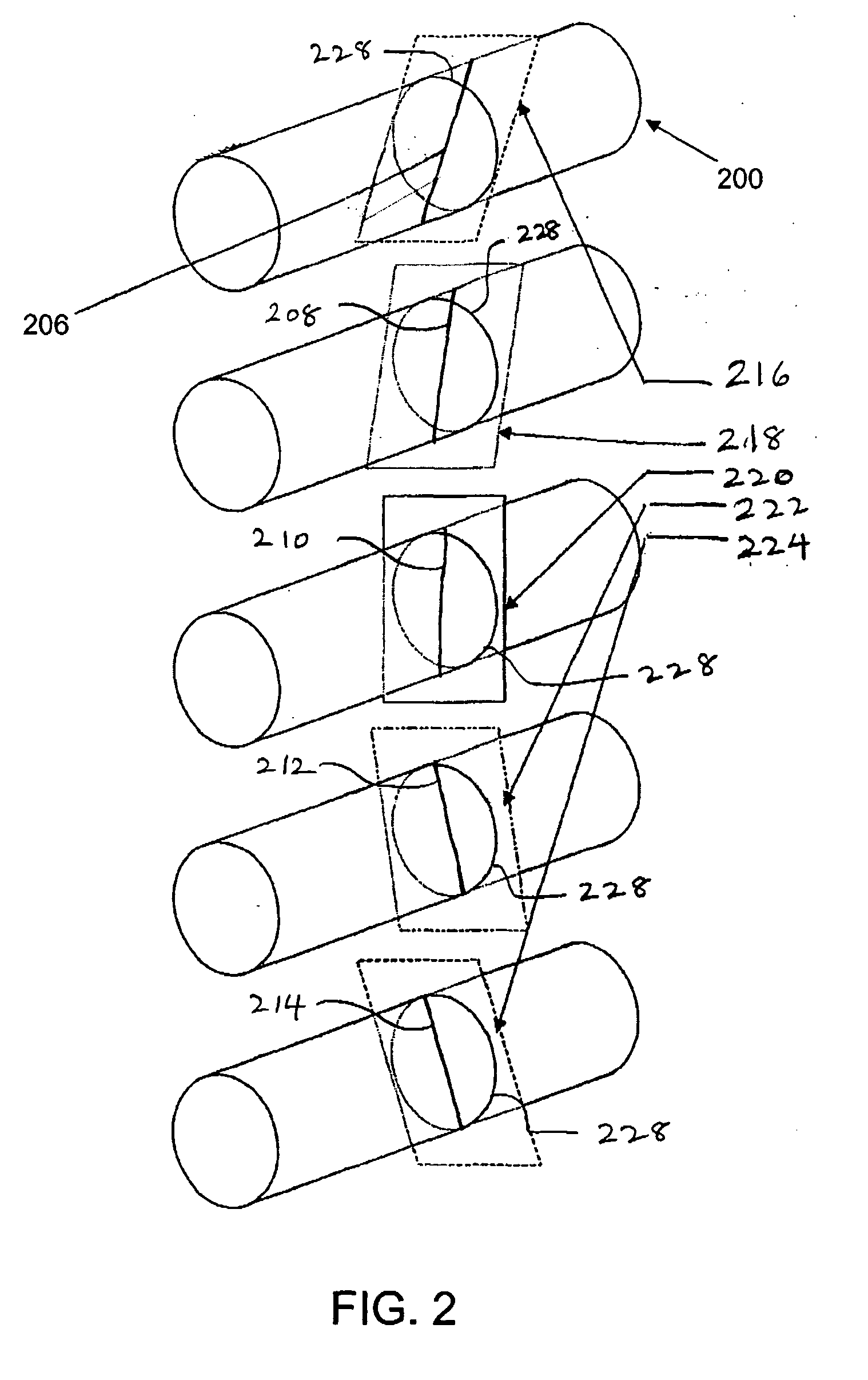
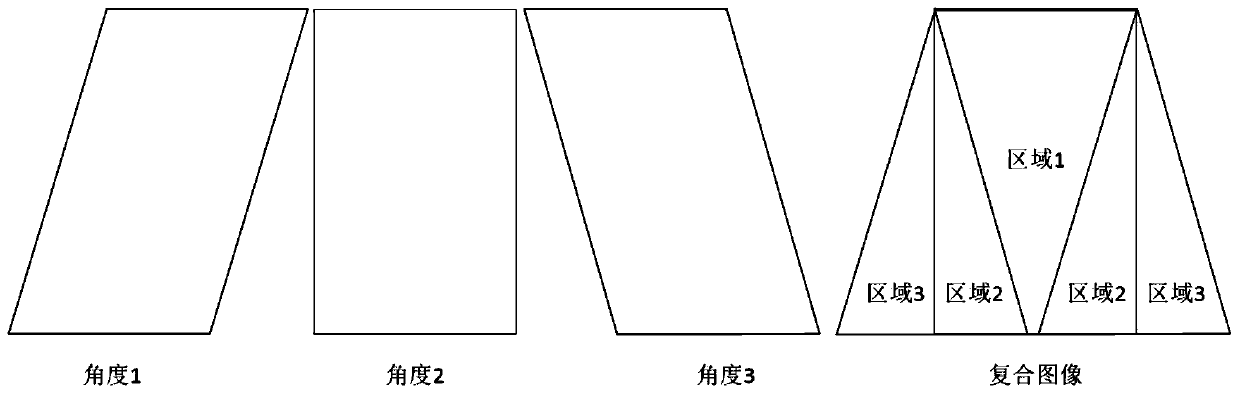
An ultrasonic diagnostic imaging system produces spatially compounded trapezoidal sector images by combining component frames acquired from different look directions. A virtual apex scan format is used such that each scanline of a component frame emanates from a different point (El, En) on the face of an array transducer (12) and is steered at a different scanning angle. For different component frames the scanlines are steered at respectively different angles. In the illustrated example, the scanlines of each component frame are incremented by five degrees relative to the corresponding scanlines in a reference component frame. When the component frames are combined for spatial compounding, the maximum number of component frames are combined over virtually the entire image field.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for measuring noise estimation and data fusion for allowance inertia measuring unit
InactiveCN102679983AAchieve estimatesImprove calculation accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation systemNoise estimation
The invention provides a method for measuring noise estimation and data fusion for an allowance inertia measuring unit, and belongs to the field of inertia navigation. The method specifically comprises steps of obtaining space resultant vector of a carrier shaft; projecting the space resultant vector to different measuring shafts of an allowance sensor to obtain space projection data; obtaining projection residual errors between the space projection data and inertia measured data; weighting the inertia measured data in different axial directions of the allowance sensor; using a weighted least square method to synthesize space resultant vector of a carrier and the like. By means of analyzing an allowance system, measurement errors of the allowance system are estimated, estimation results of measurement noise are utilized sufficiently to reasonably weight the measured data, resultant vector calculating precision is improved effectively, and the precision of an allowance inertia navigation system is improved. Besides, the method is simple in process and easy to operate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
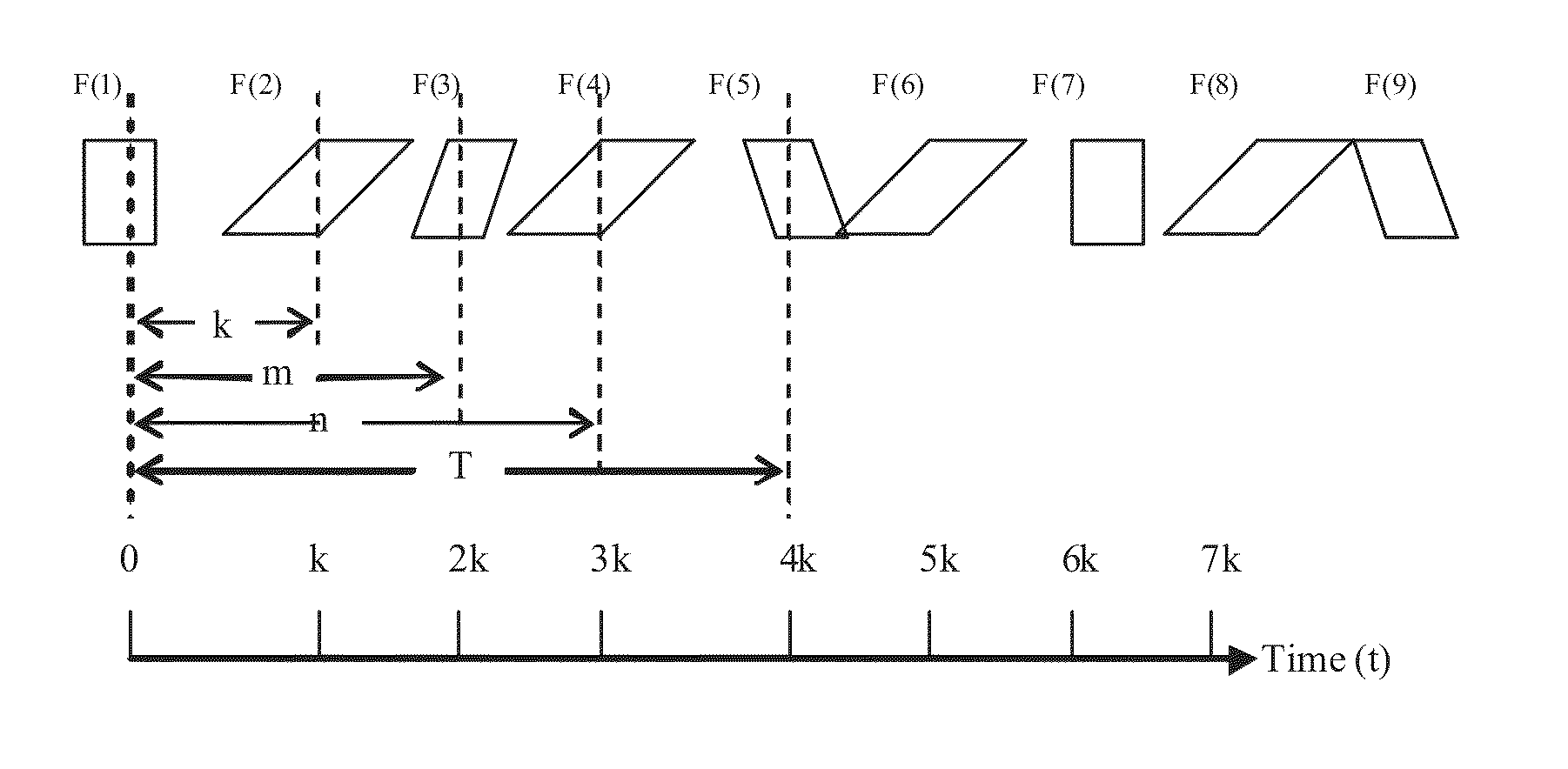
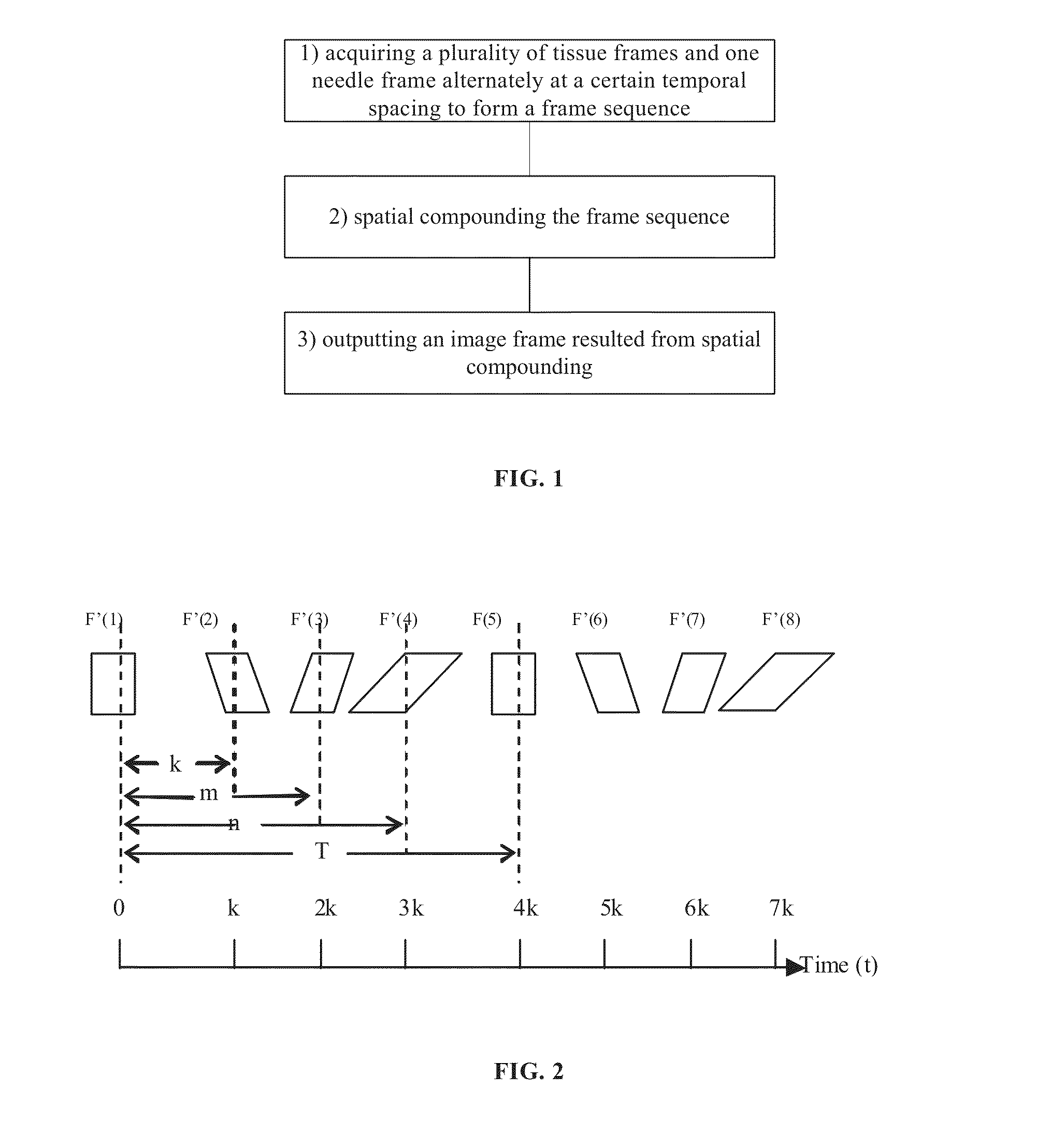
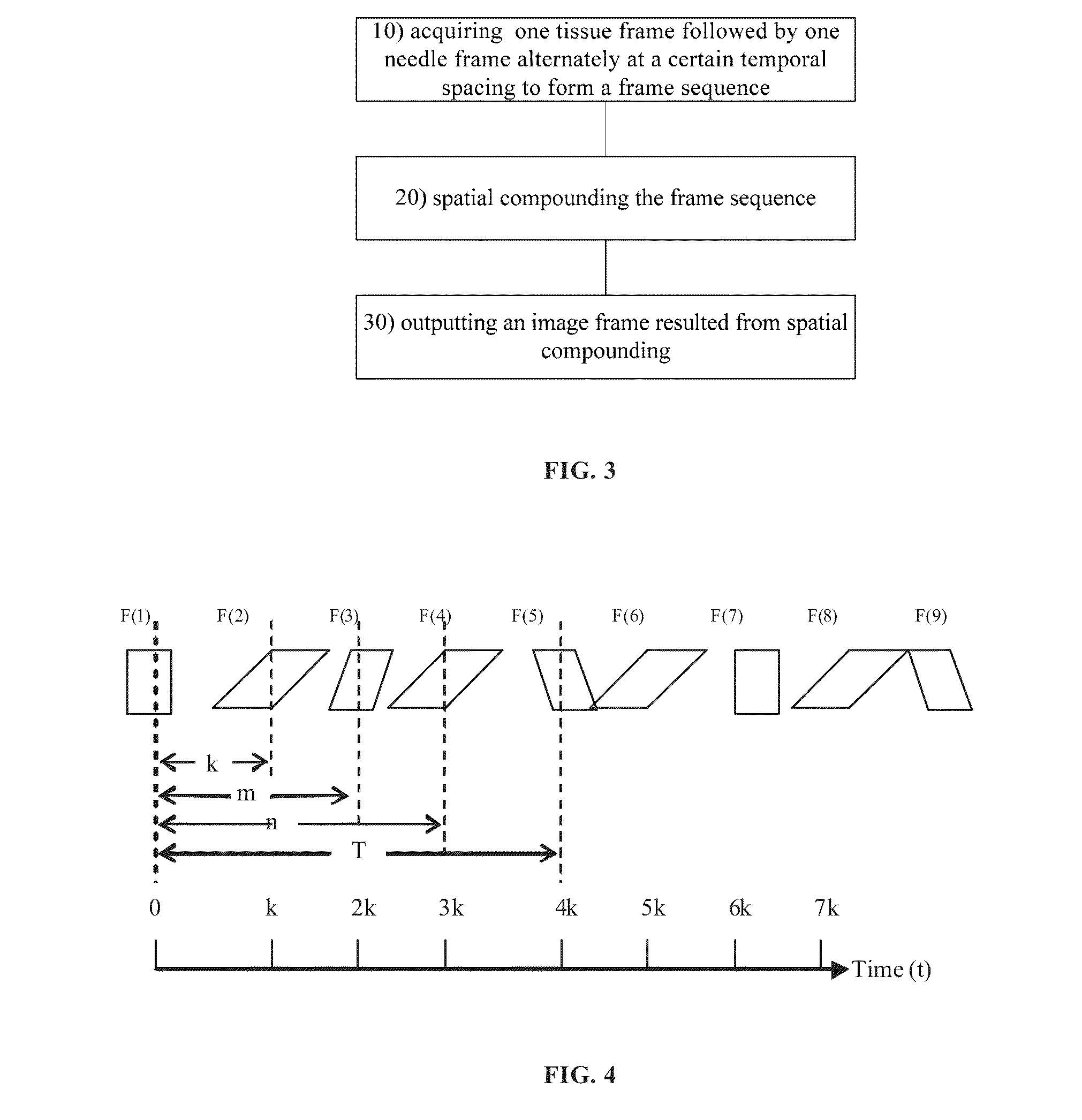
Method and device for needle visualization
ActiveUS20130261432A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingFrame sequence
A method for needle visualization for an ultrasound imaging device, the method comprising alternately acquiring a tissue frame followed by a needle frame at a temporal spacing to form a frame sequence, spatially compounding the frame sequence, and outputting an image frame resulting from spatial compounding.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
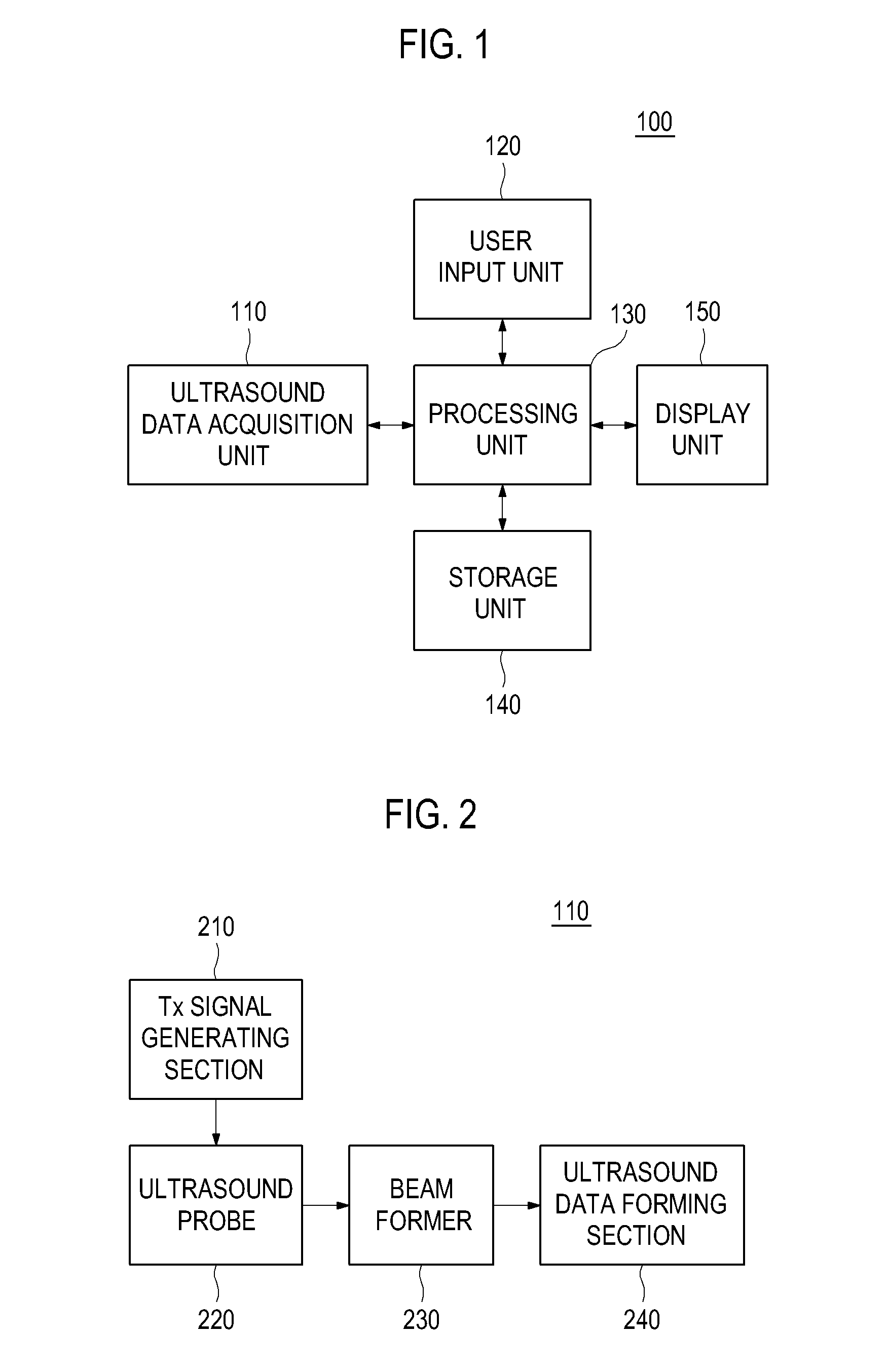
Providing an ultrasound spatial compound image in an ultrasound system
ActiveUS20110137171A1Well formedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage analysisSonificationUser input
Embodiments for providing an ultrasound spatial compound image are disclosed. In one embodiment, by way of non-limiting example, an ultrasound system comprises: an ultrasound data acquisition unit configured to transmit and receive ultrasound signals to and from a target object to output first ultrasound data and a plurality of sets of second ultrasound data corresponding to a region of interest (ROI); a user input unit configured to receive input information for defining the ROI; and a processing unit in communication with the ultrasound data acquisition unit and the user input unit, the processing unit being configured to form volume data based on the plurality of sets of second ultrasound data, compare the first ultrasound data with the volume data to detect geometric information therein, form a two-dimensional (2D) ultrasound image based on the first ultrasound data, and a first three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound image and a second 3D ultrasound data based on the volume data in consideration of the geometric information, and perform a spatial compound upon the 2D ultrasound image, the first 3D ultrasound image and the second 3D ultrasound image based on the geometric information to form an ultrasound spatial compound image.
Owner:SAMSUNG MEDISON
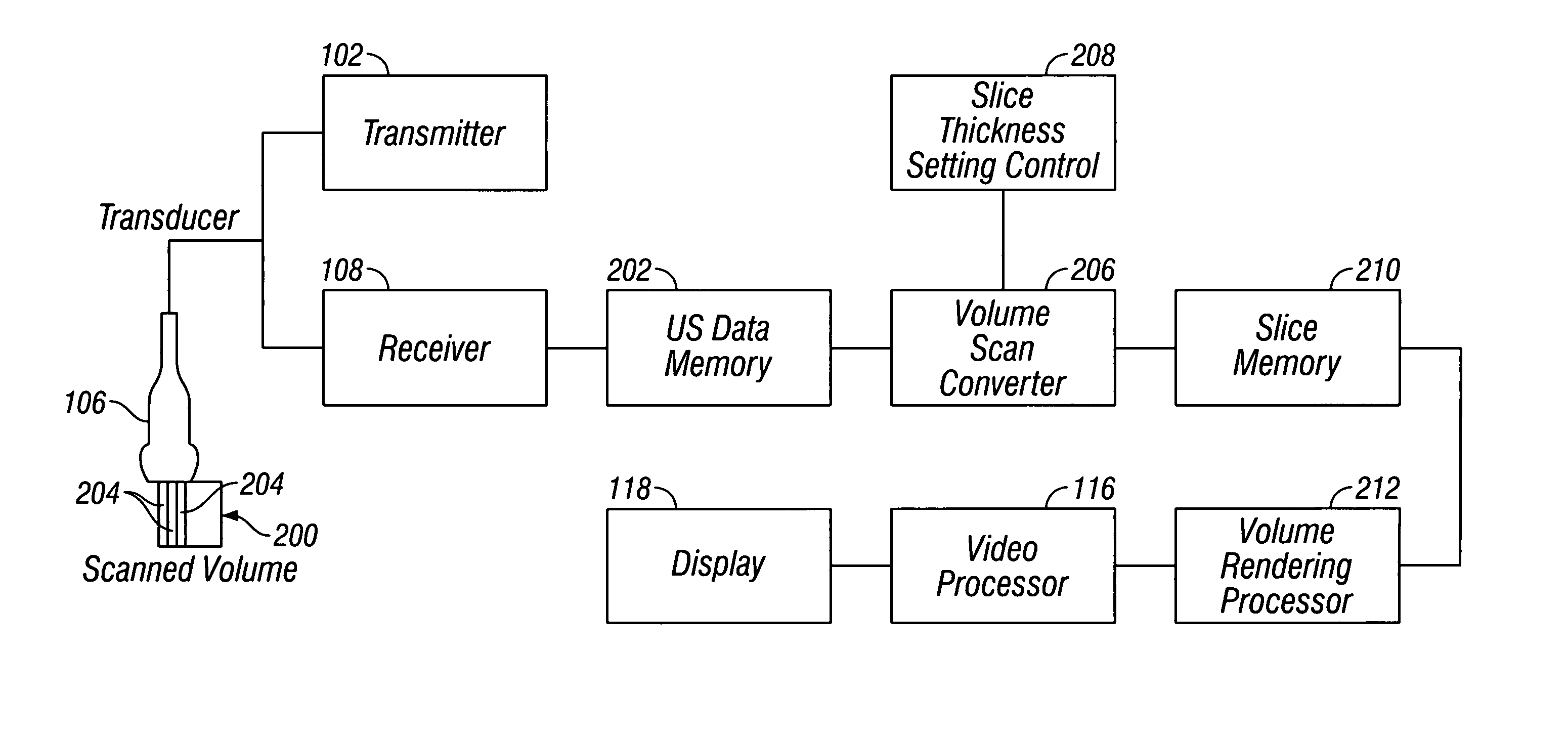
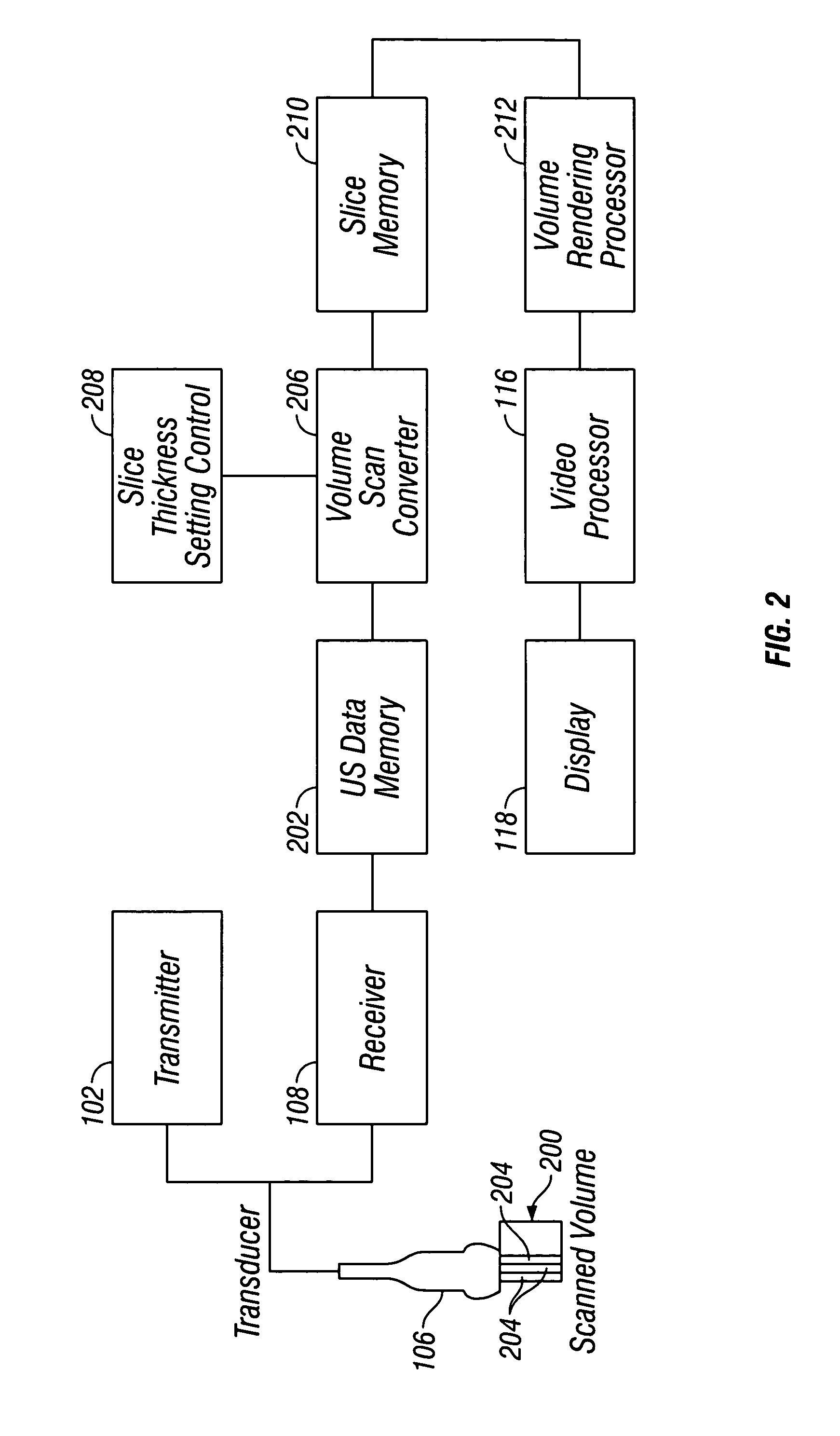
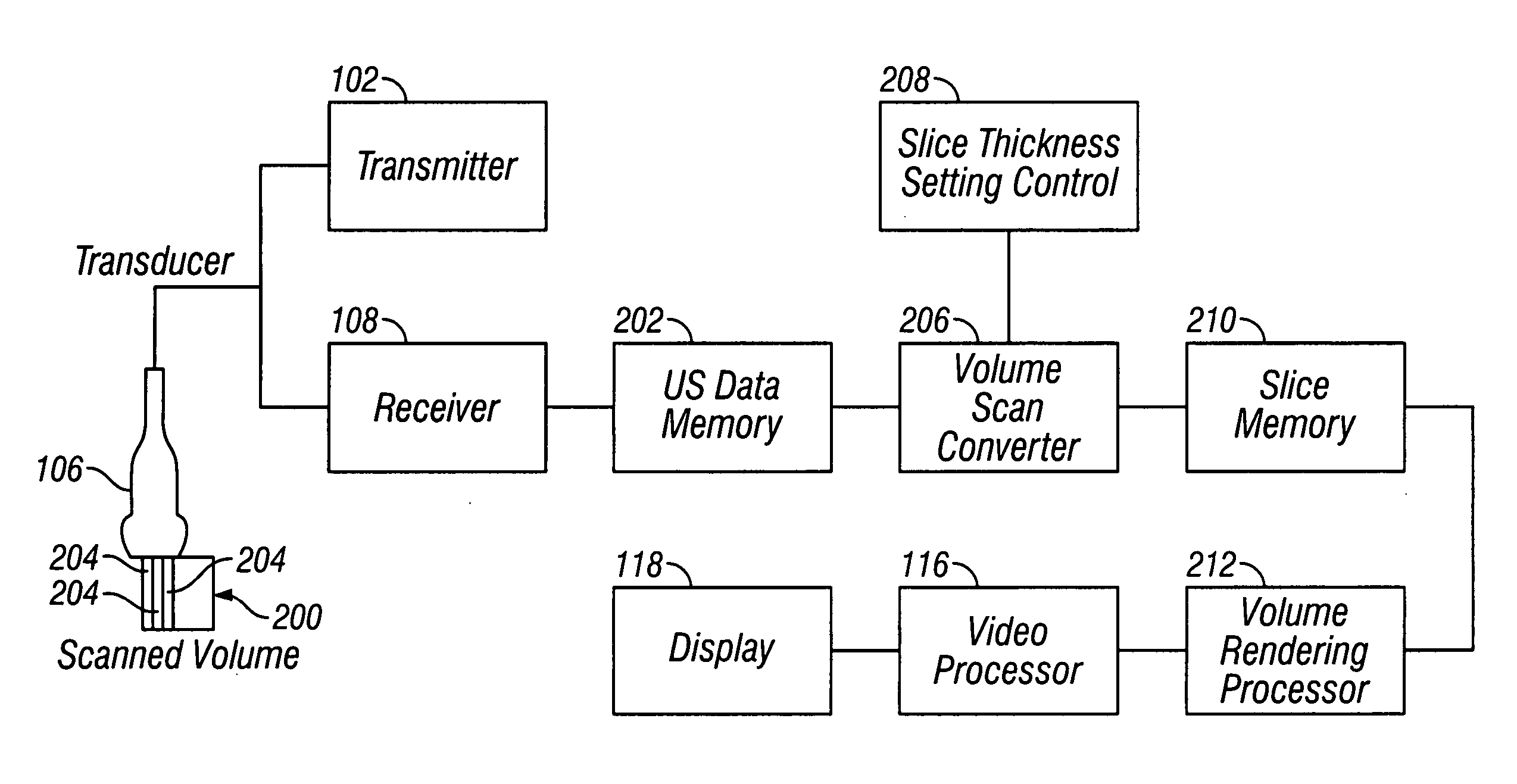
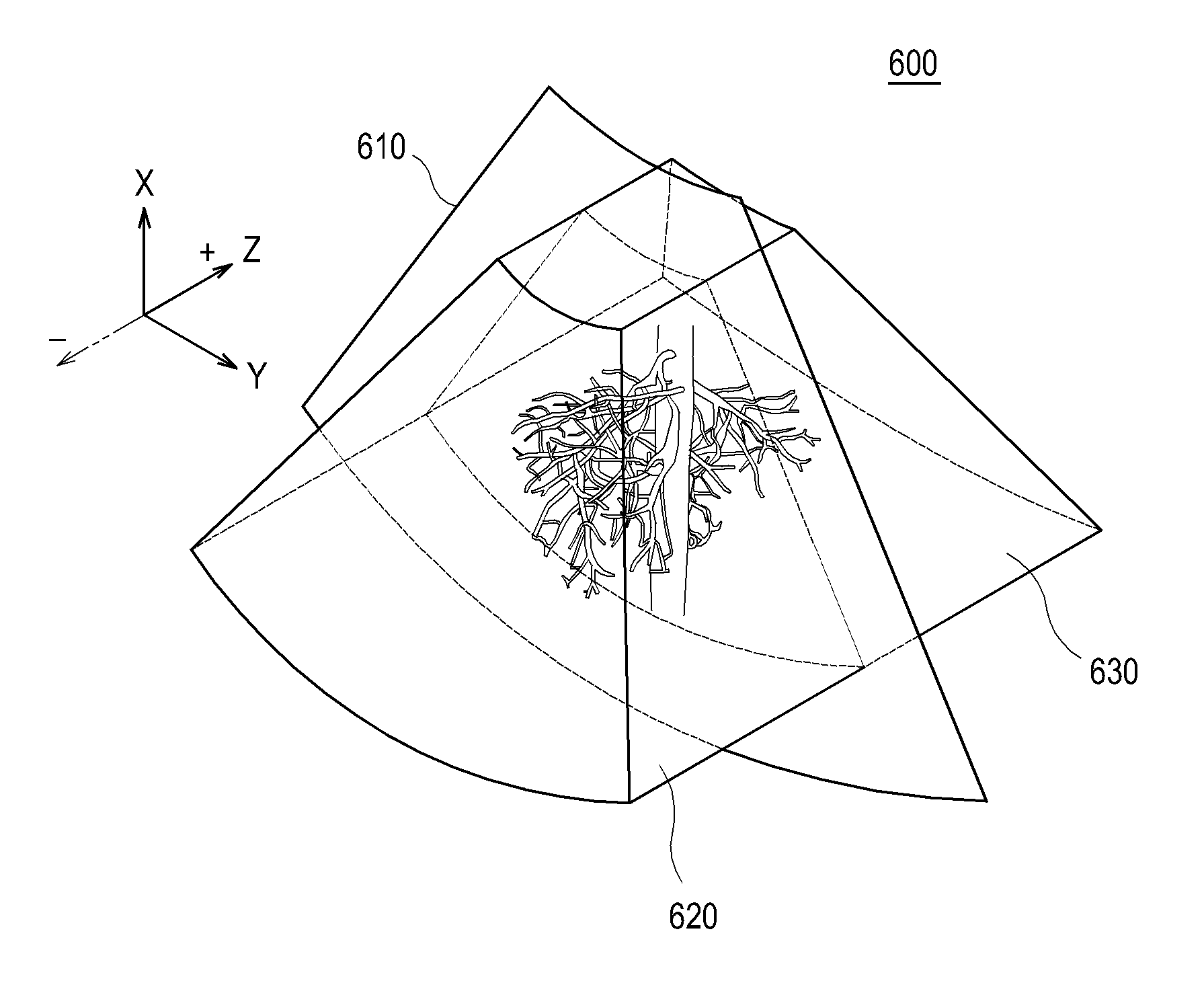
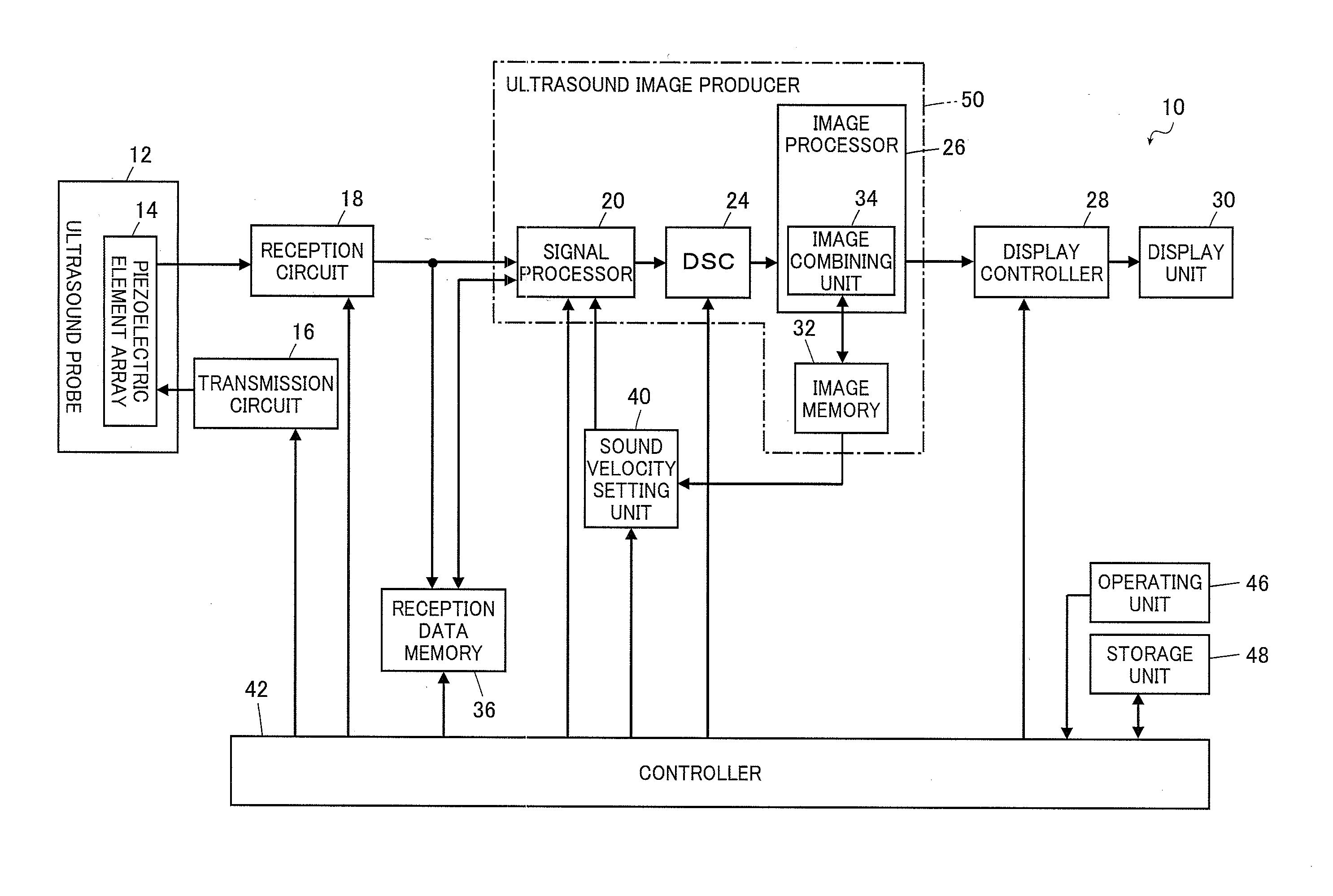
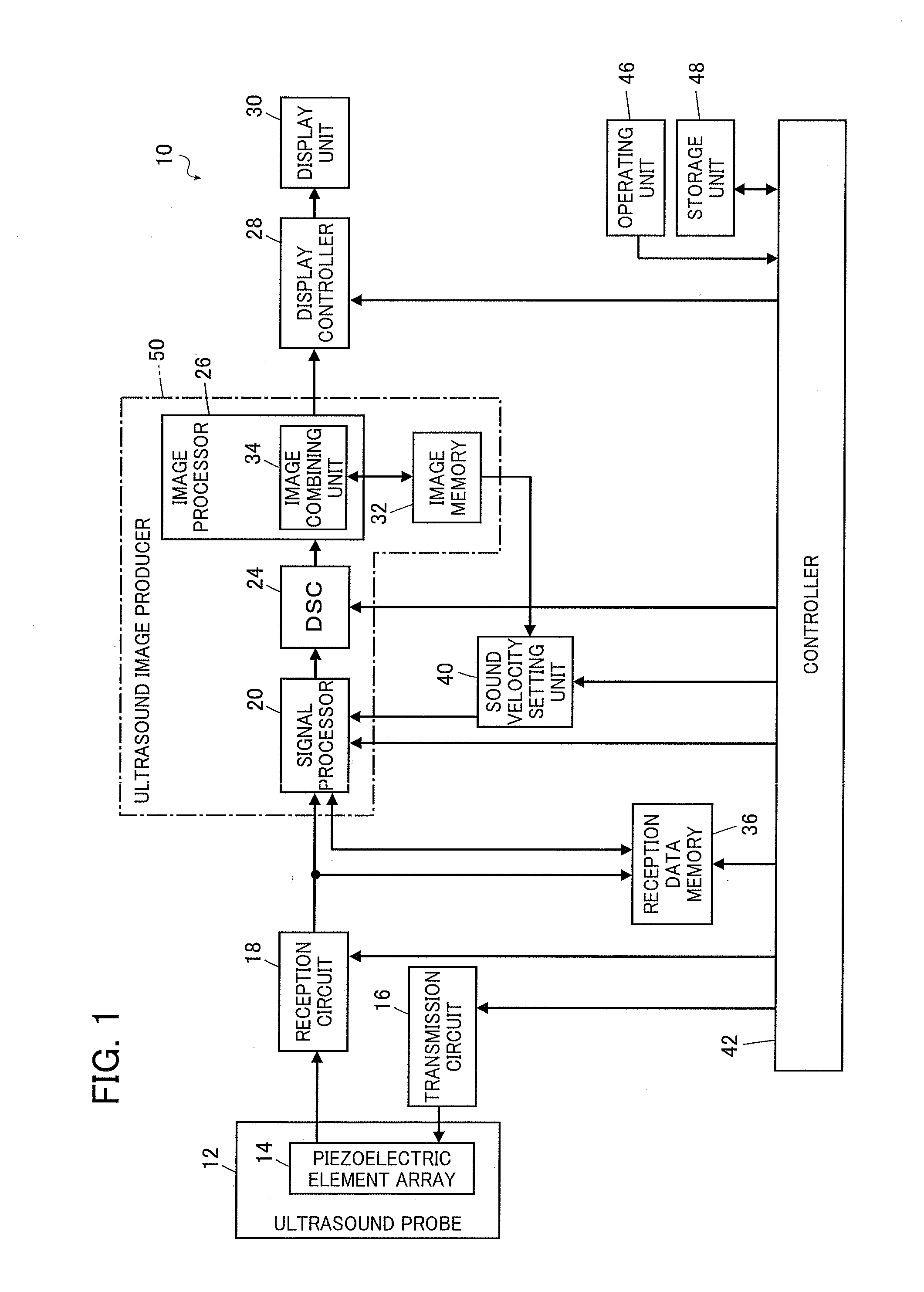
Ultrasound diagnostic apparatus, ultrasound image producing method, and recording medium
InactiveUS20140187953A1Quality improvementDegradation in image qualityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsDistortionSpeed of sound
In an ultrasound diagnostic apparatus, when a compound image is produced, delay correction is performed on all of ultrasound images (sub frames) to be combined based on sound velocities set for respective segment regions obtained by dividing the subject. Owing to this configuration, the ultrasound diagnostic apparatus can produce a high quality compound image by spatial compounding or frequency compounding without being affected by distortion in images.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
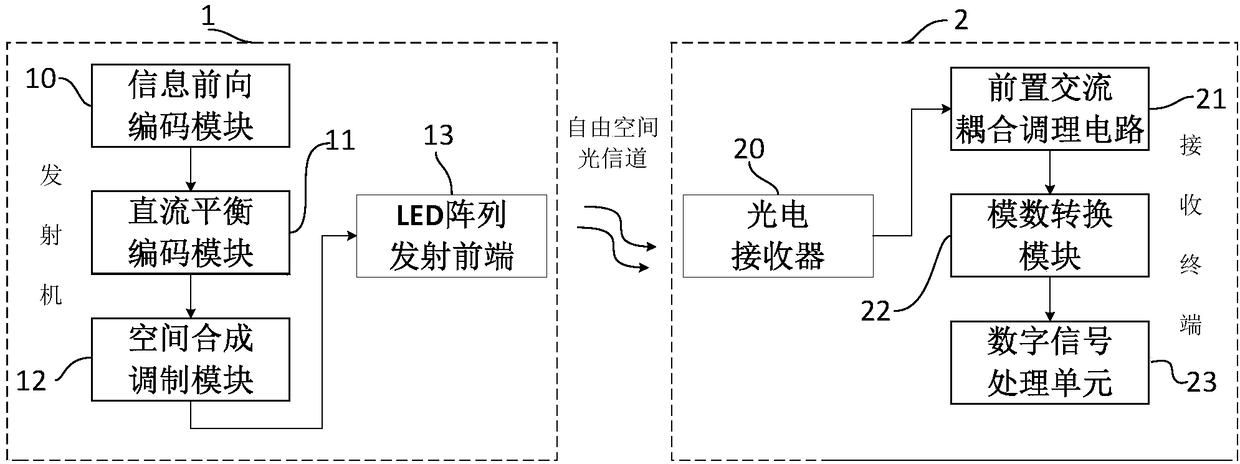
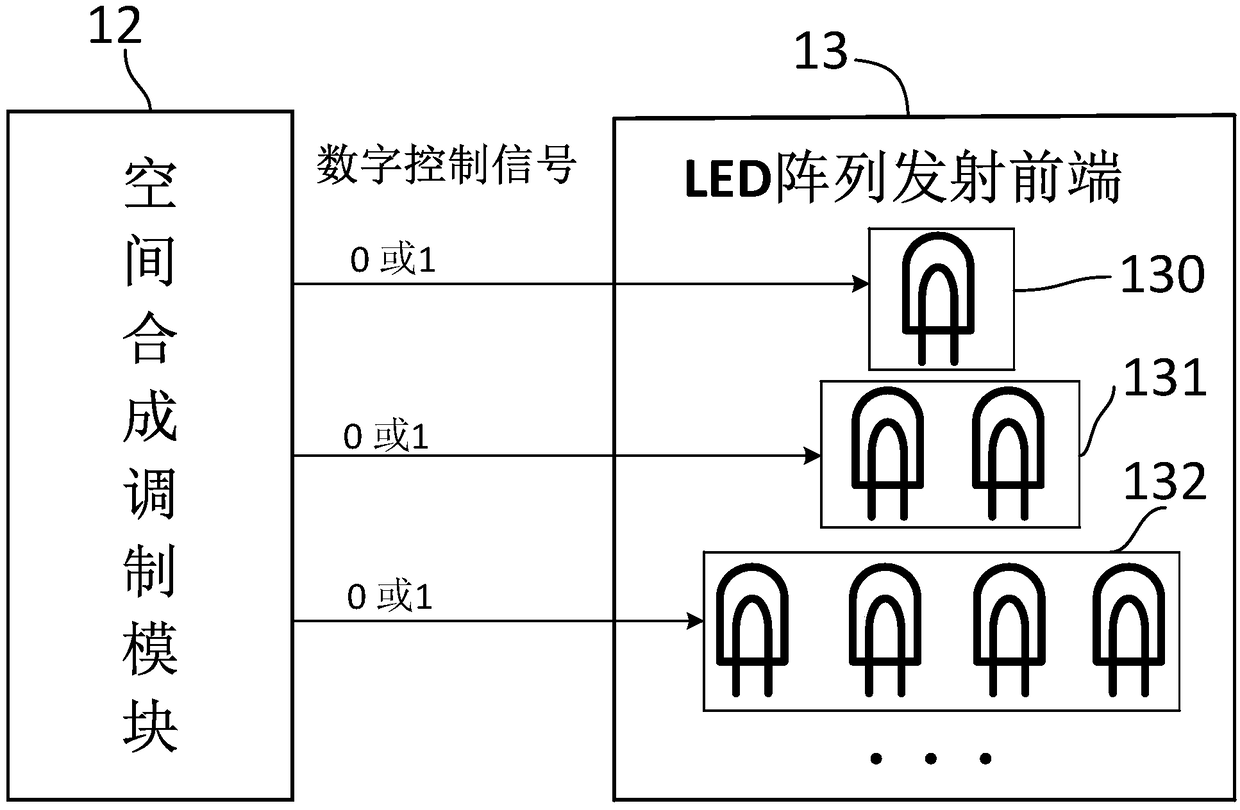
Visible light communication system based on spatial synthesis modulation and implementation method
ActiveCN109462437AAchieve direct controlImprove reliabilityClose-range type systemsDigital signal processingPower Balance
The invention discloses a visible light communication system based on spatial synthesis modulation and an implementation method. The system mainly comprises a transmitter and a receiving terminal, wherein the transmitter part comprises an information forward coding module, a direct current balance coding module, a spatial synthesis modulation module and an LED transmitting front end; the information forward coding module encodes input information by adopting a ratioless coding mode, and divides the information to generate coded data packets; the direct current balance coding module carries outsecondary coding on each data packet, so that the total power balance of each data packet is ensured, and lamplight flickering caused by data communication is avoided; and the spatial synthesis modulation module modulates the data packets to generate corresponding data symbols, and generates a digital control signal to control the LED transmitting module to send the information. The receiving terminal is used for receiving the information sent by a transmitting end and mainly comprises a photoelectric receiver, a front alternating current coupling conditioning circuit, an analog-digital conversion module and a digital signal processing unit.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Spatial compound imaging method and device and ultrasonic imaging system
InactiveCN103584882AInhibition boundarySuppress noiseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingImage conversion
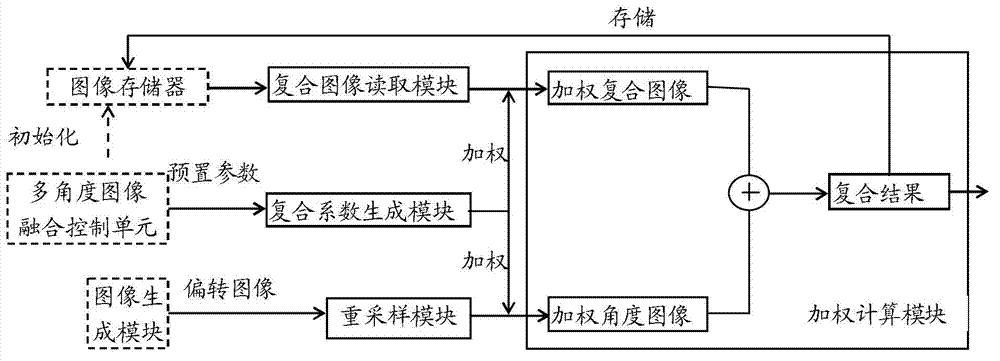
The invention discloses a spatial compound imaging method and device and an ultrasonic imaging system. The spatial compound imaging method comprises the steps of generating a combination coefficient Coefx according to preset parameters; performing resampling on existing deflection image and converting the existing deflection image into a zero-angle image Ax(t) in a coordinate system; reading a result image C(t-1) of the previous spatial compound imaging; utilizing the combination coefficient Coefx to respectively perform multiplied weighting calculation on the result image C(t-1) of the previous spatial compound imaging and the zero-angle coordinate space image Ax(t) obtained through resampling of the existing deflection image to obtain a weighted compound image Coefx*C(t-1) and a weighted angle image (1-Coefx)* Ax(t), performing summation of the weighted compound image and the weighted angle image to obtain a result image C(t) of the existing spatial compound imaging. The multiple-angle spatial compounding is achieved by adopting frame correlation methods, and by combining spatial compounding and time compounding, boundaries caused by different-angle images are effectively inhibited, and image degradation caused by angle deflection is reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDWIND IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com