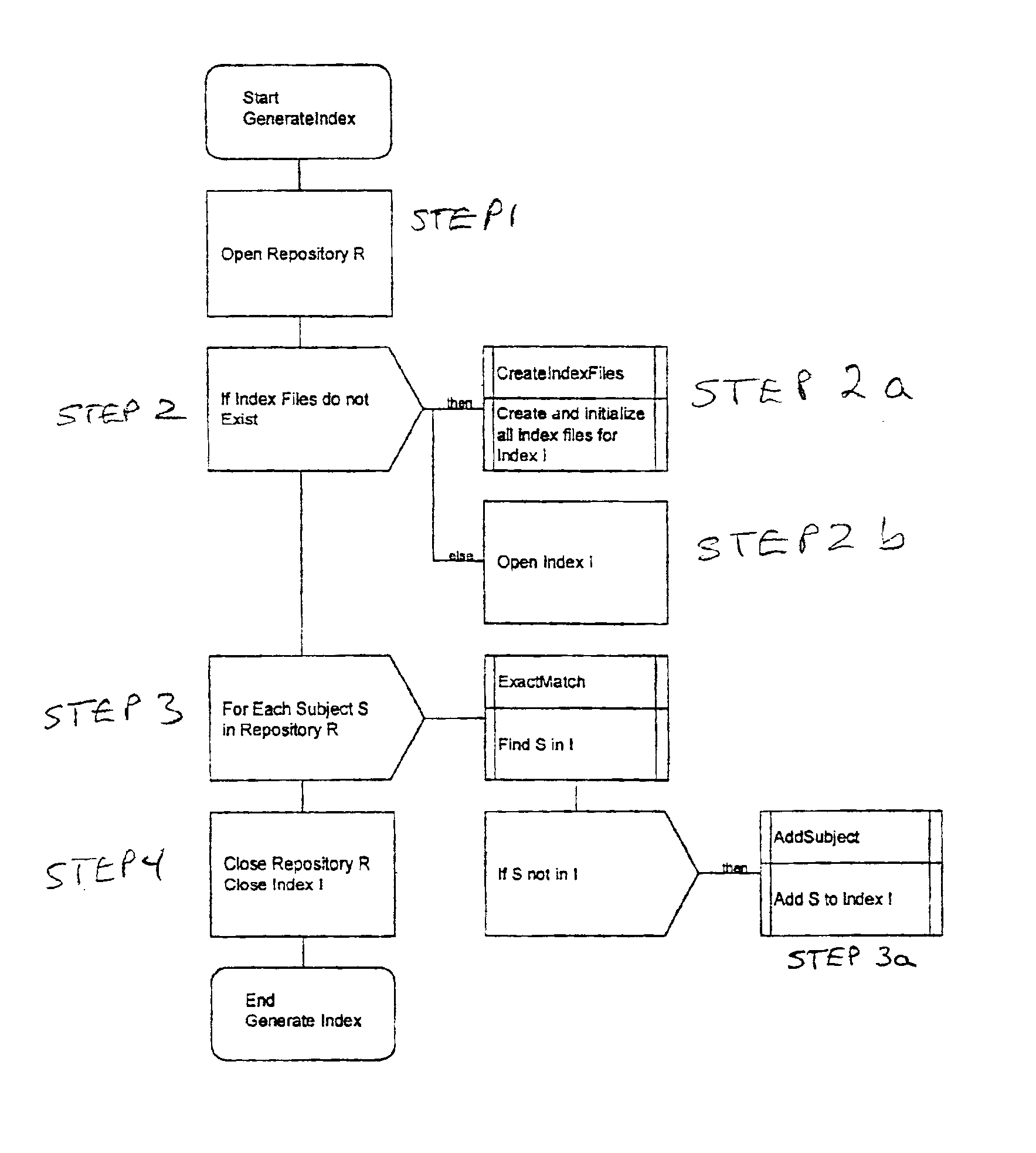
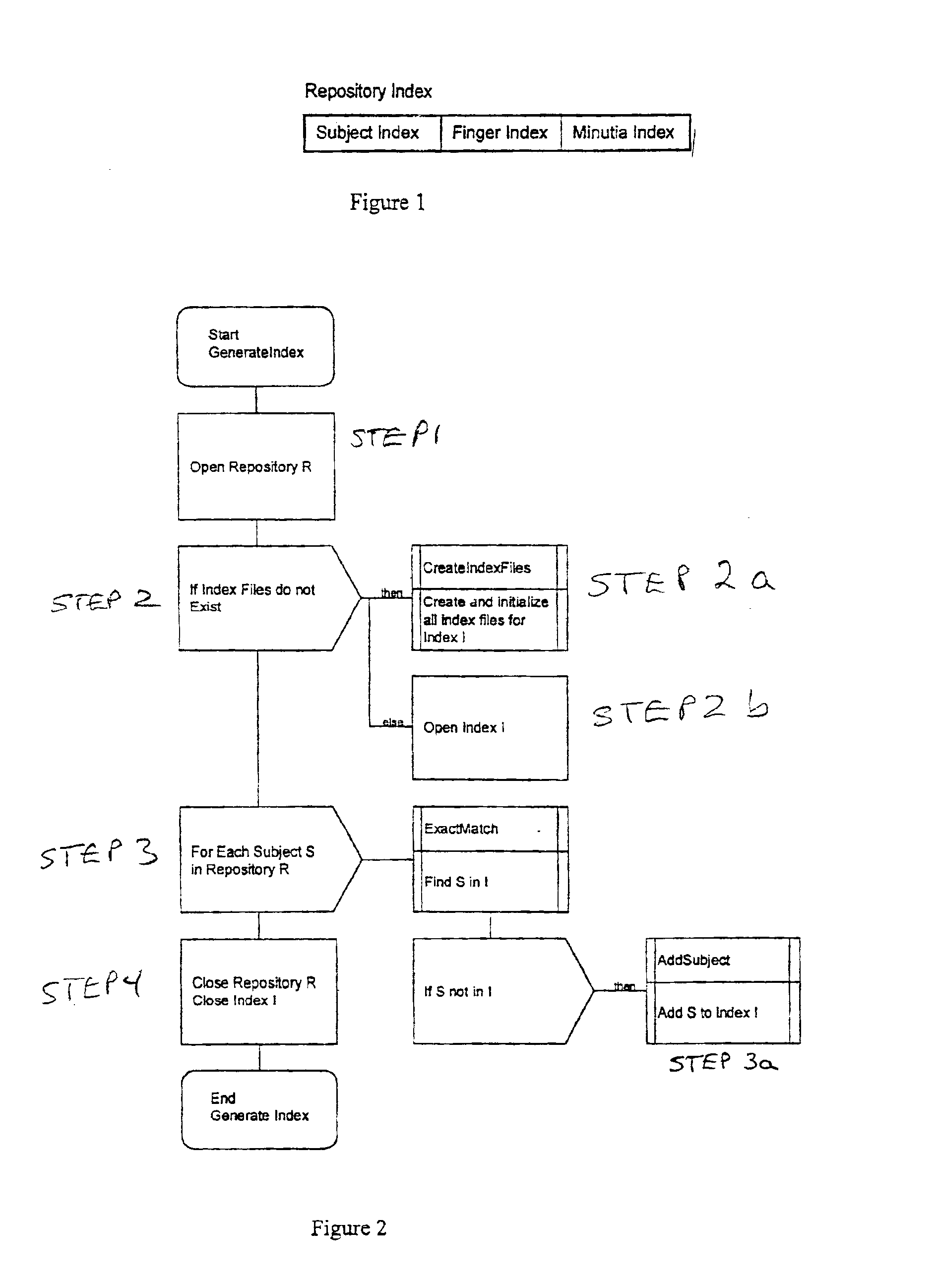
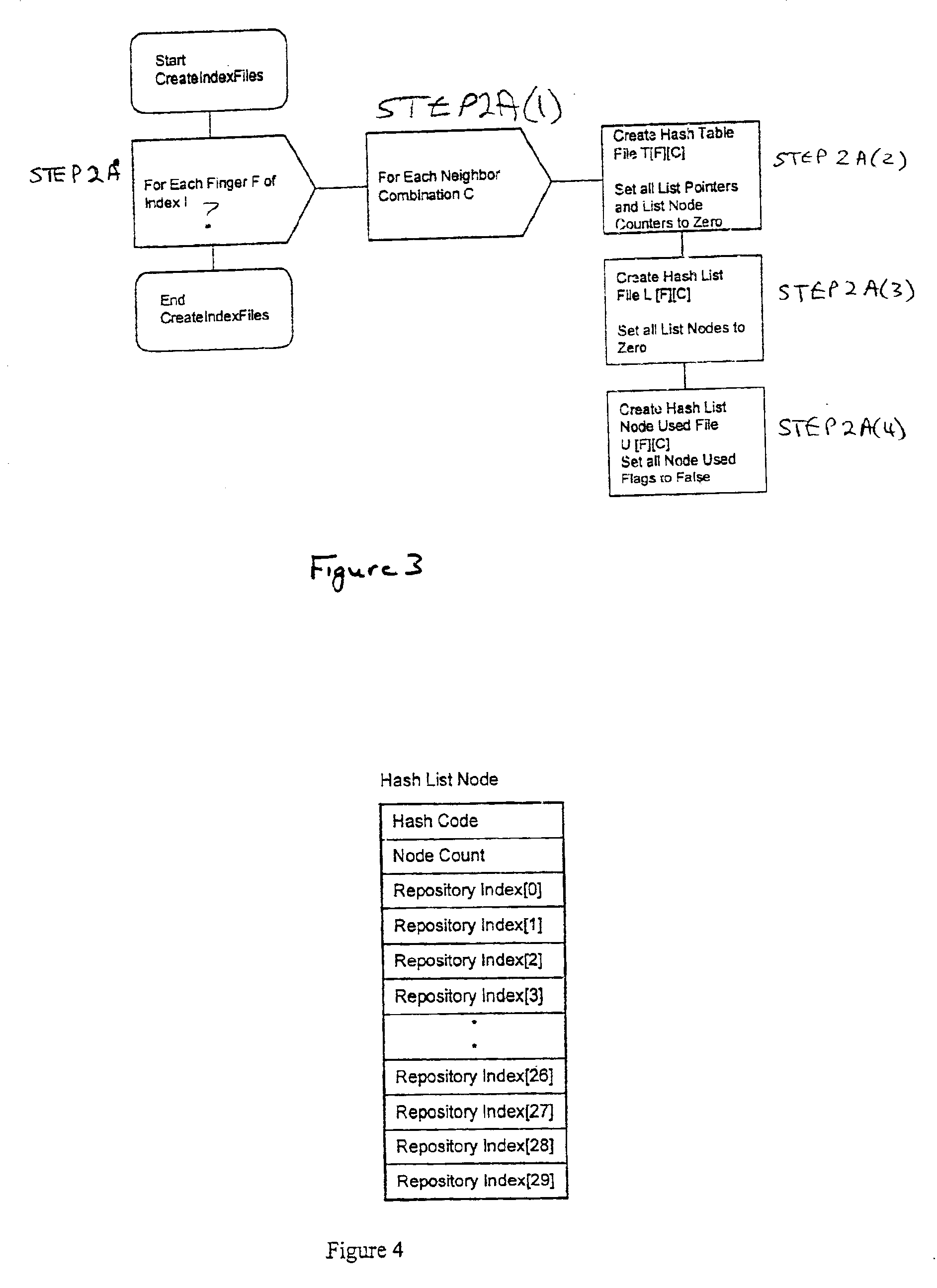
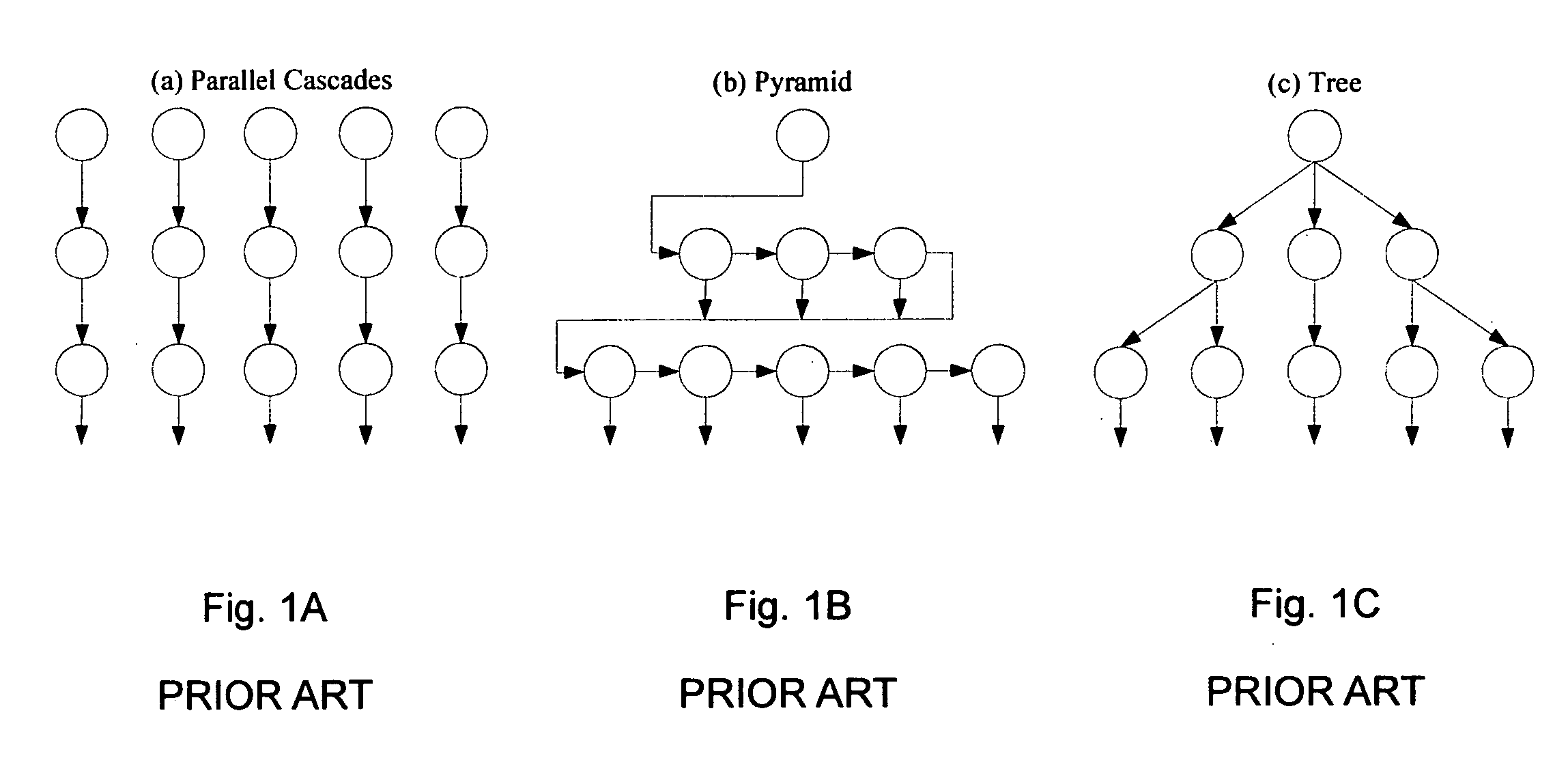
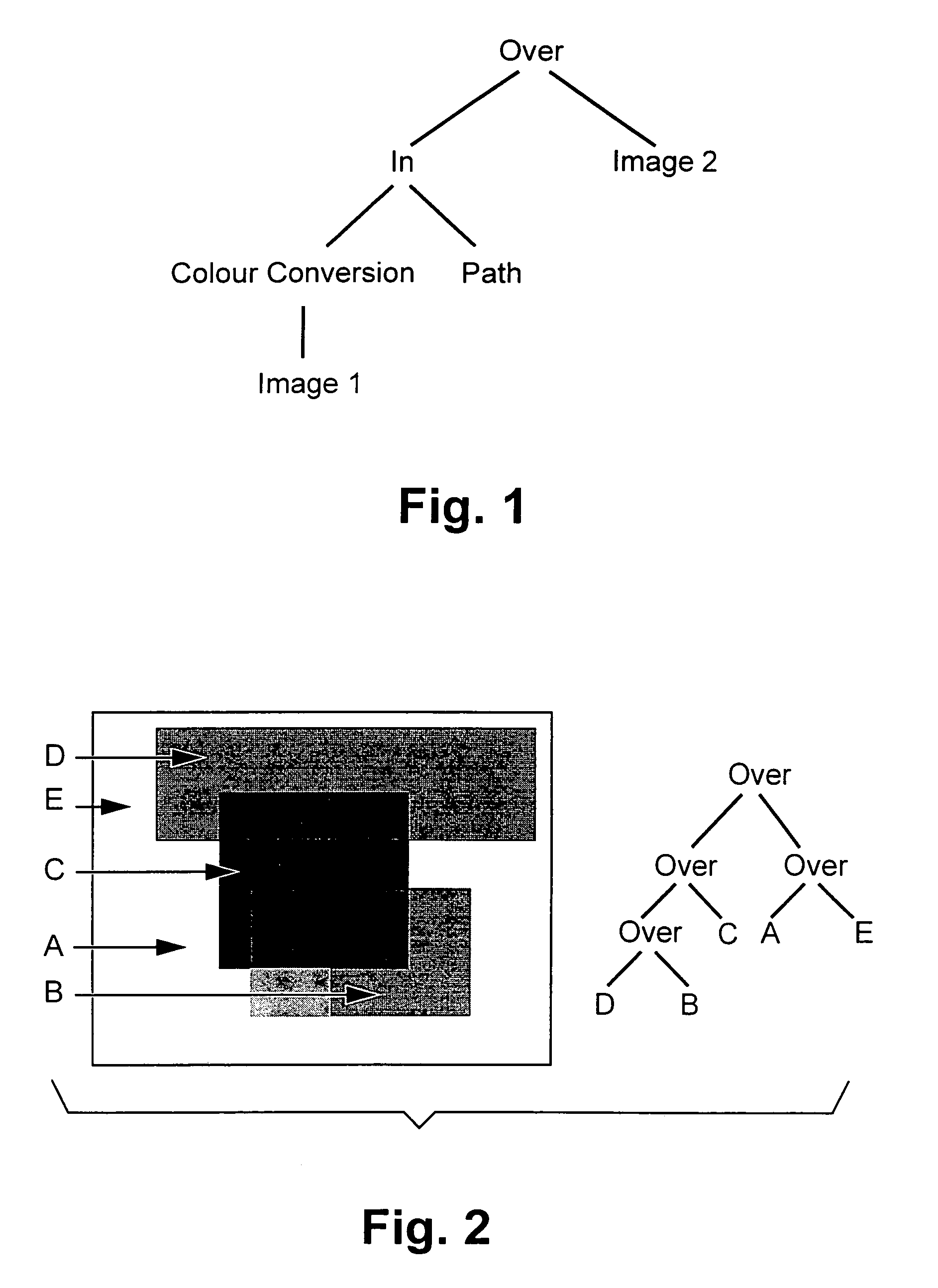
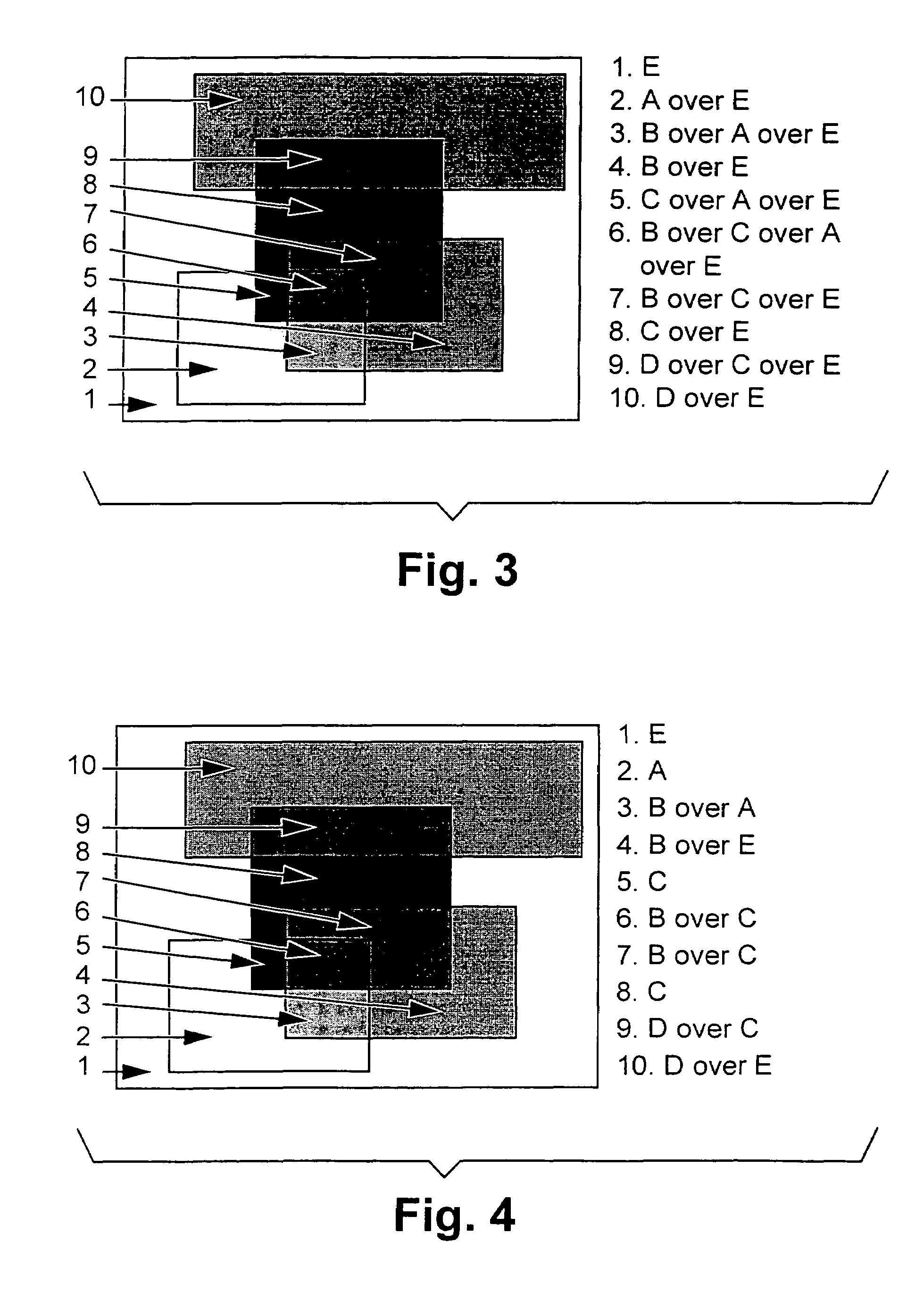
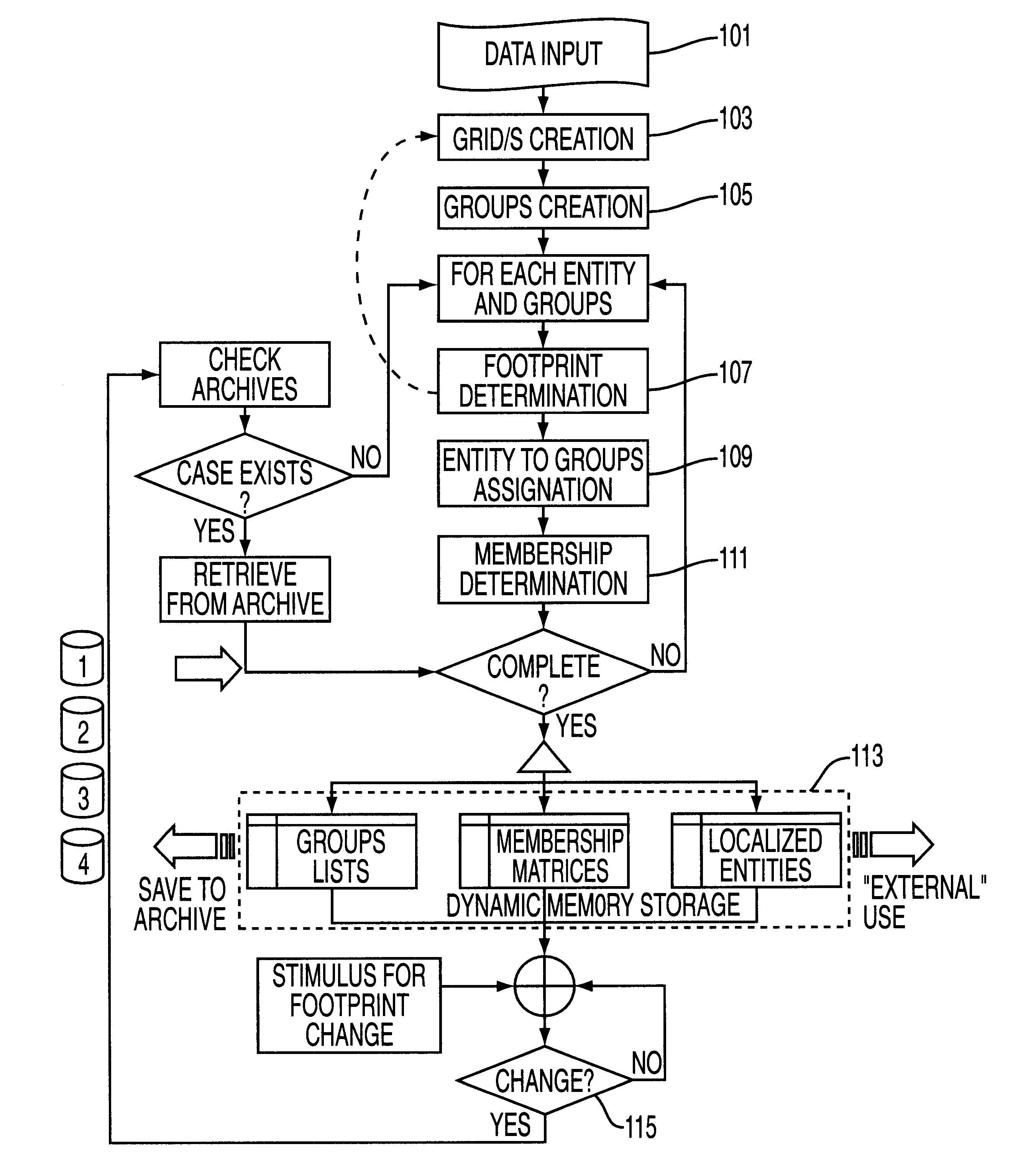
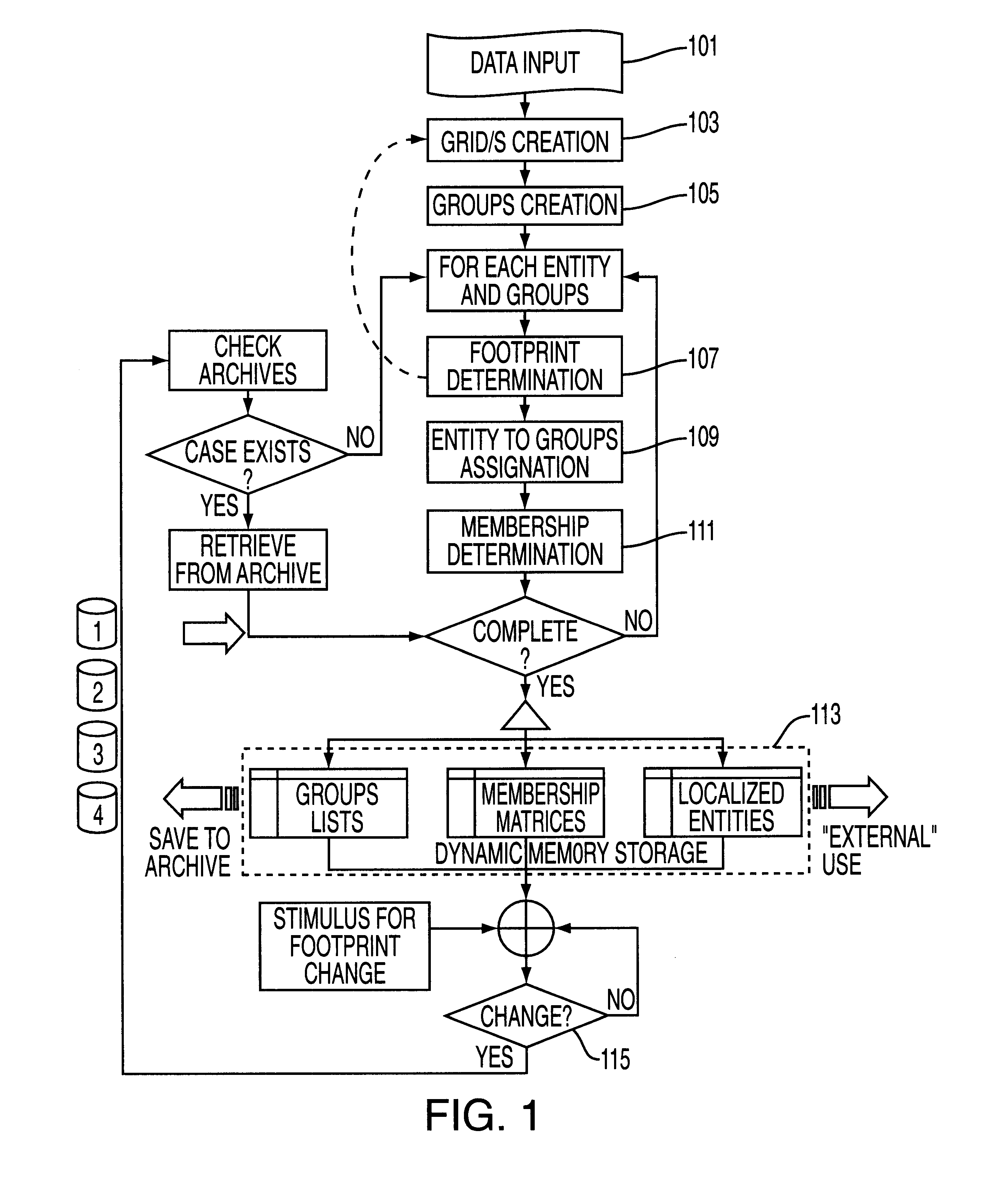
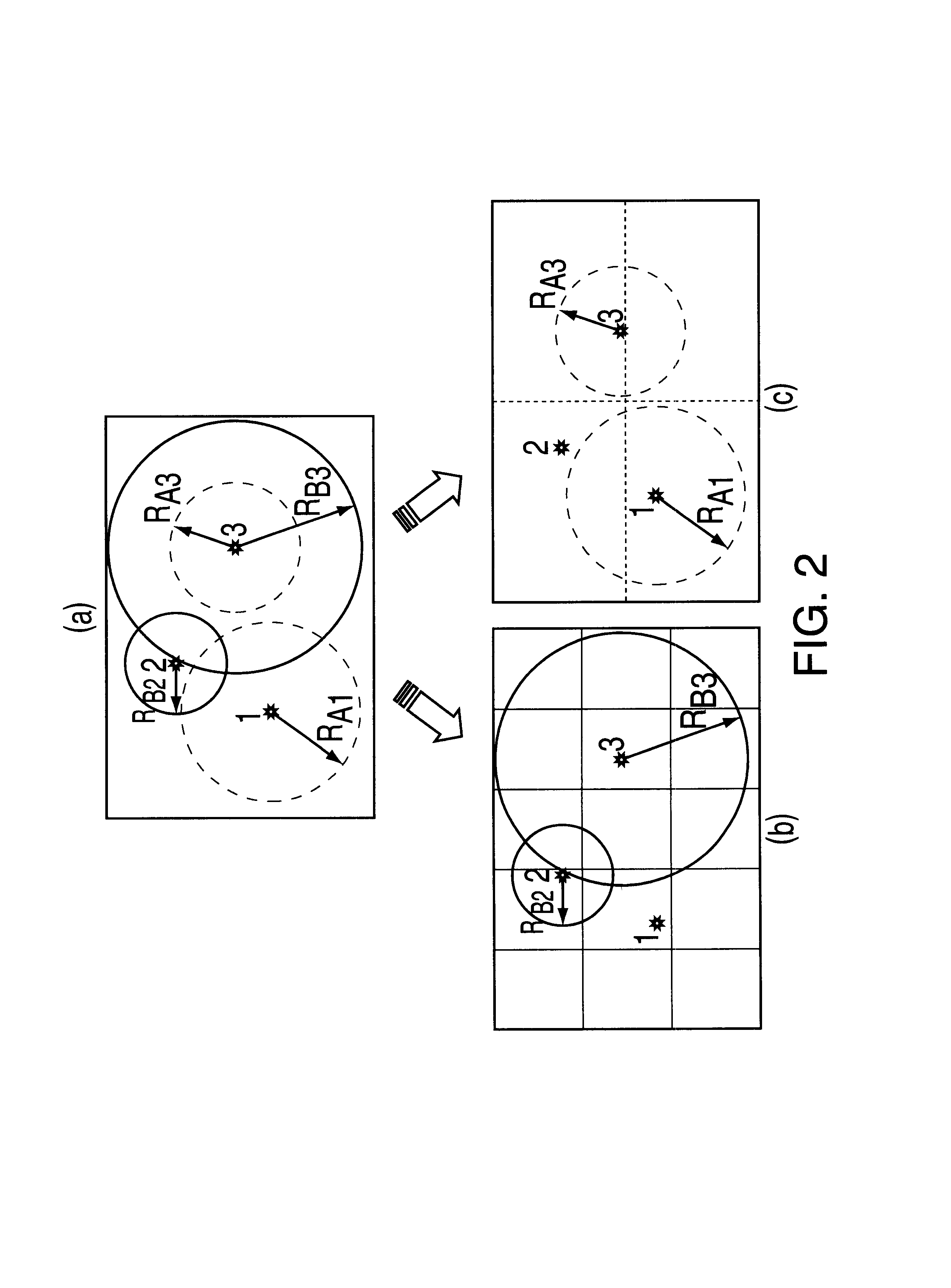
Patents
Literature
251 results about "Space partitioning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In geometry, space partitioning is the process of dividing a space (usually a Euclidean space) into two or more disjoint subsets (see also partition of a set). In other words, space partitioning divides a space into non-overlapping regions. Any point in the space can then be identified to lie in exactly one of the regions.
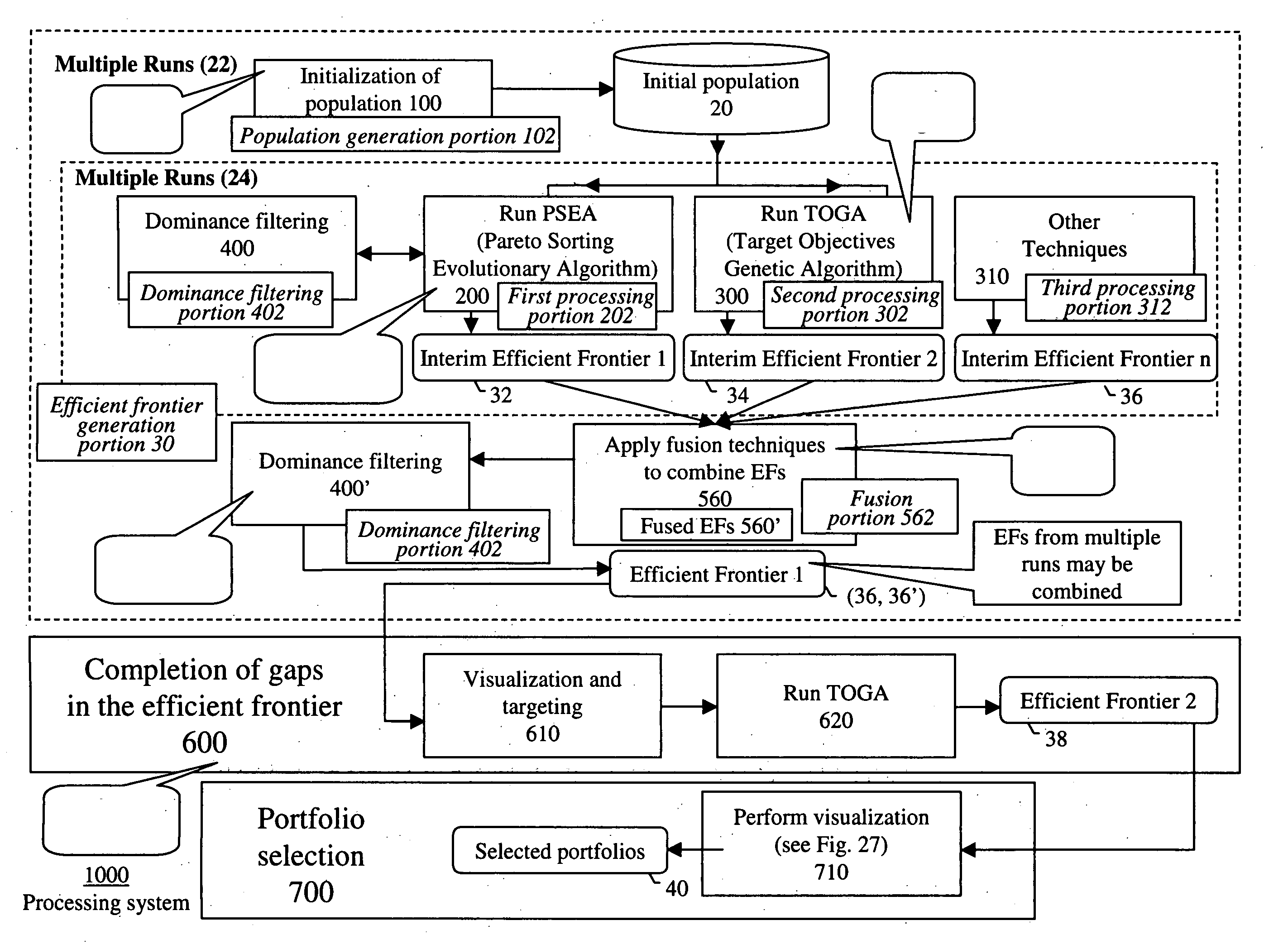
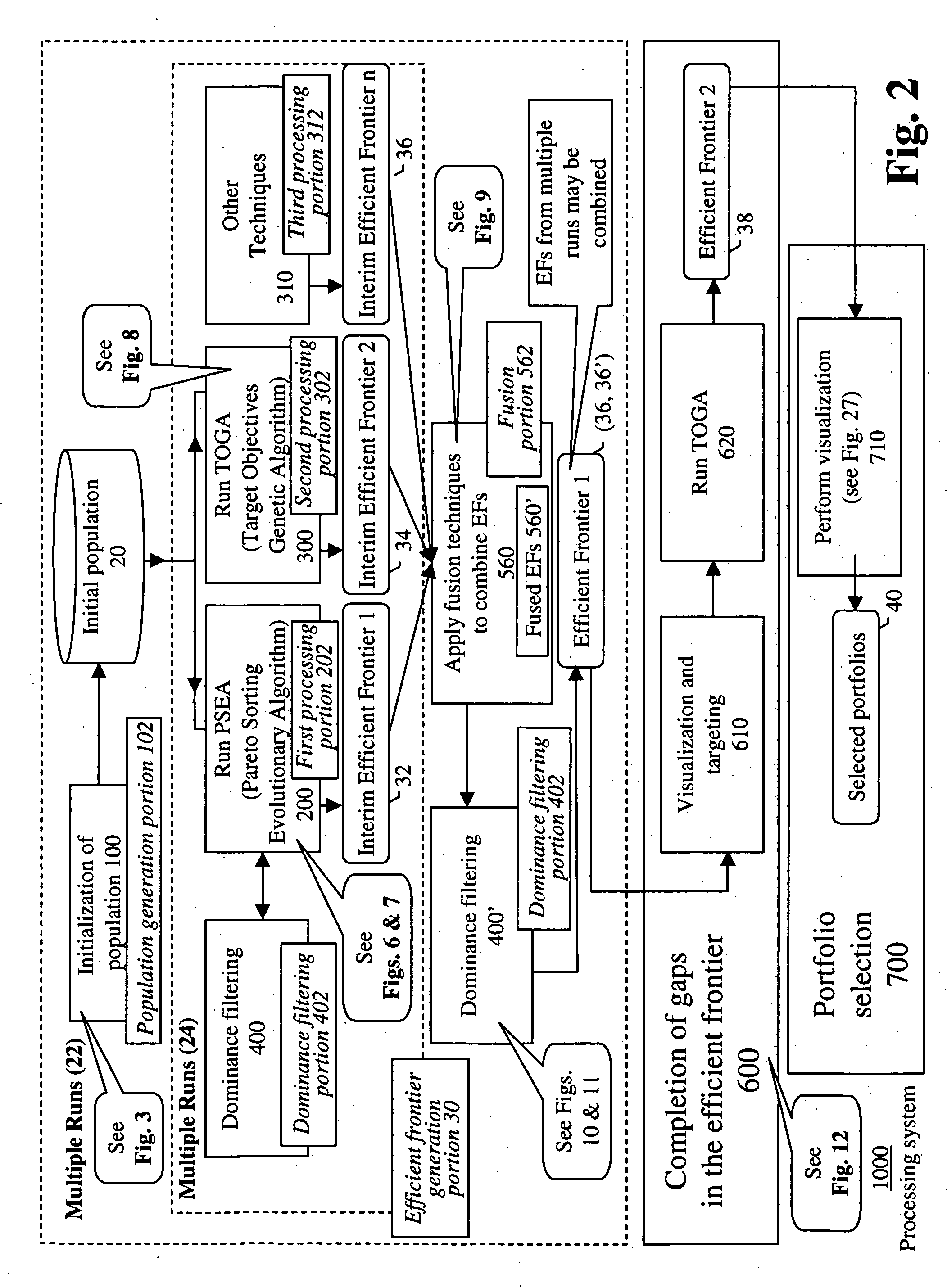
Systems and methods for multi-objective portfolio analysis using dominance filtering
InactiveUS20050187845A1Add settingsReduce settingsFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsCombinatorial optimizationSpace partitioning
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
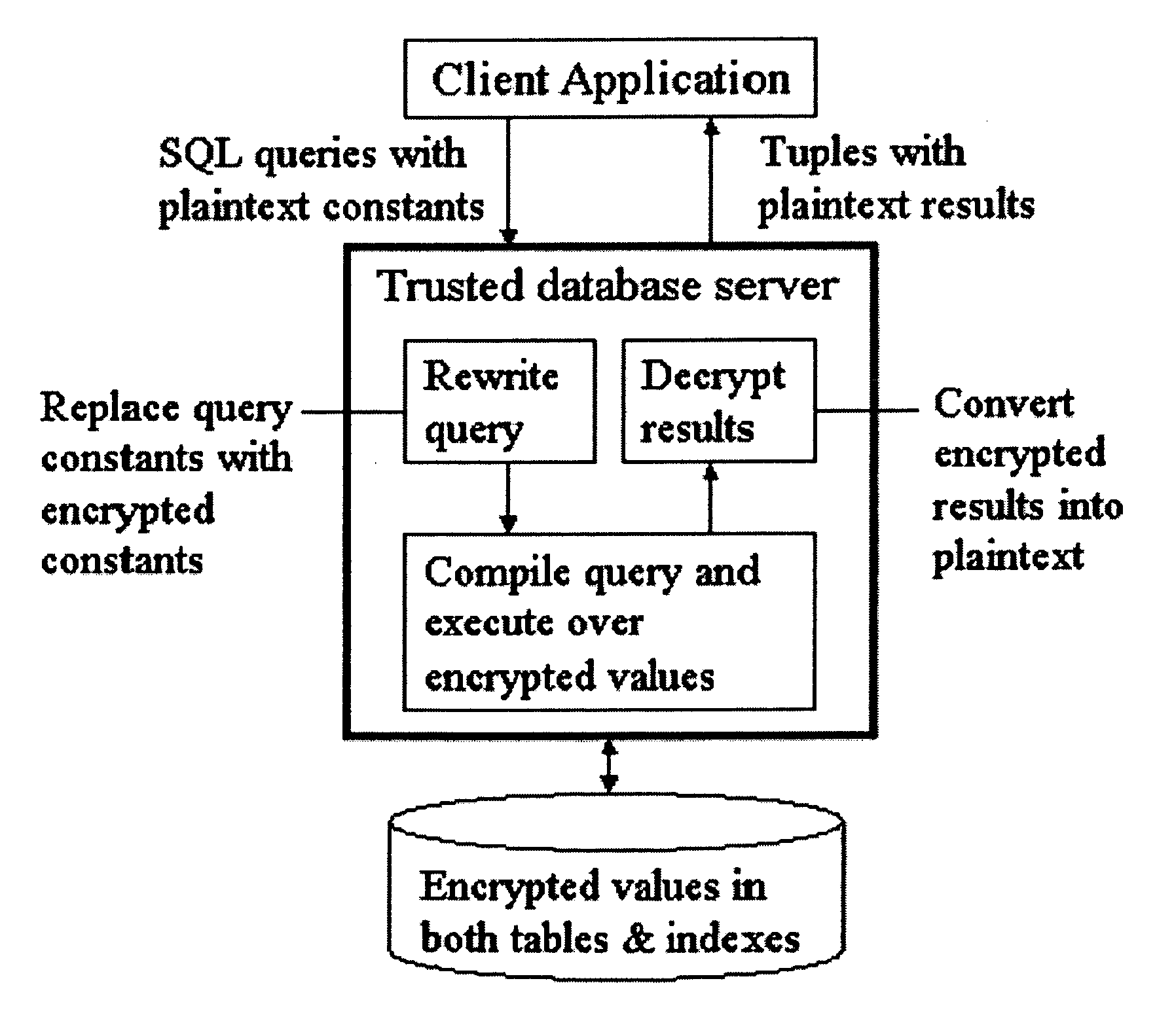
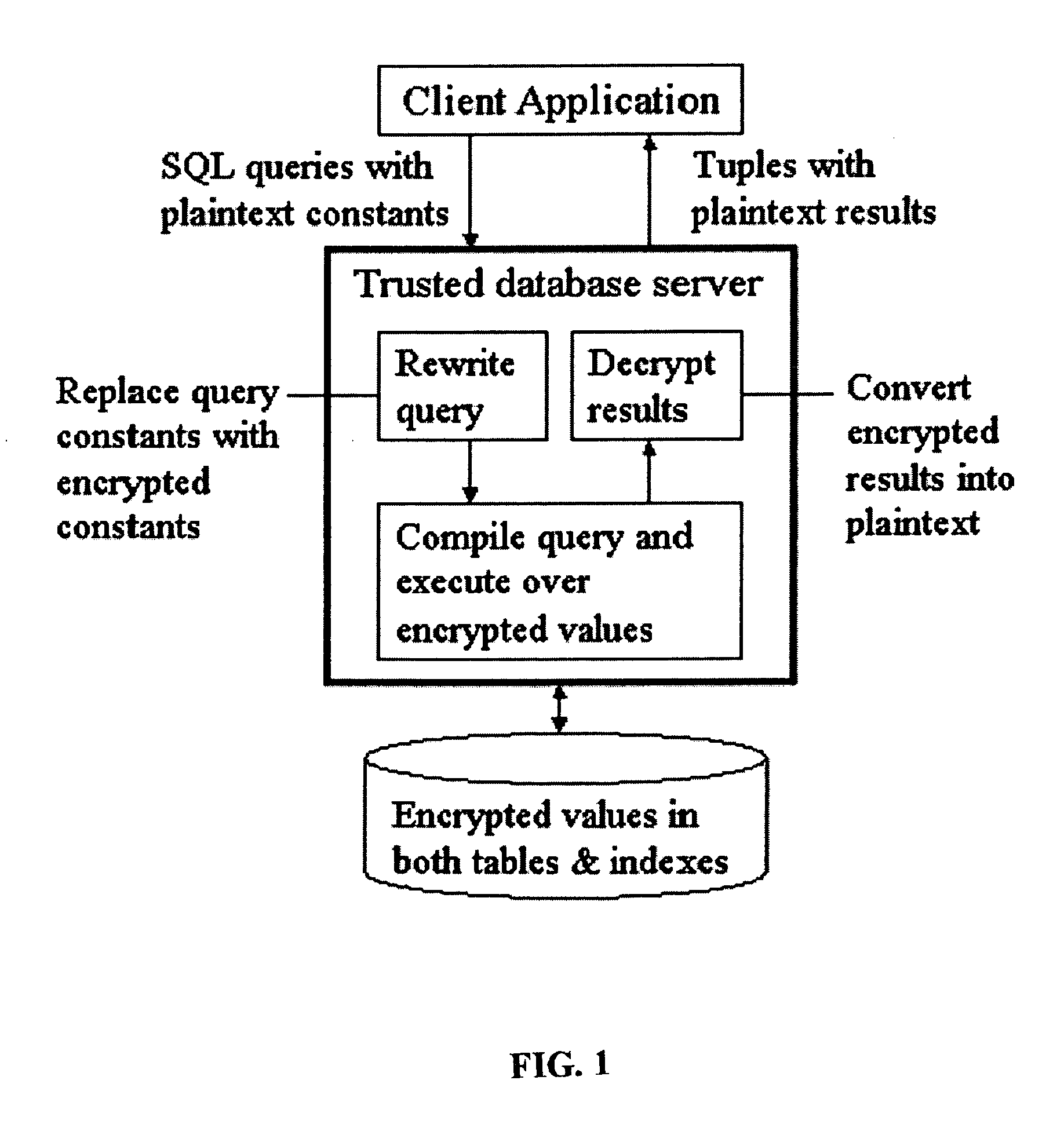
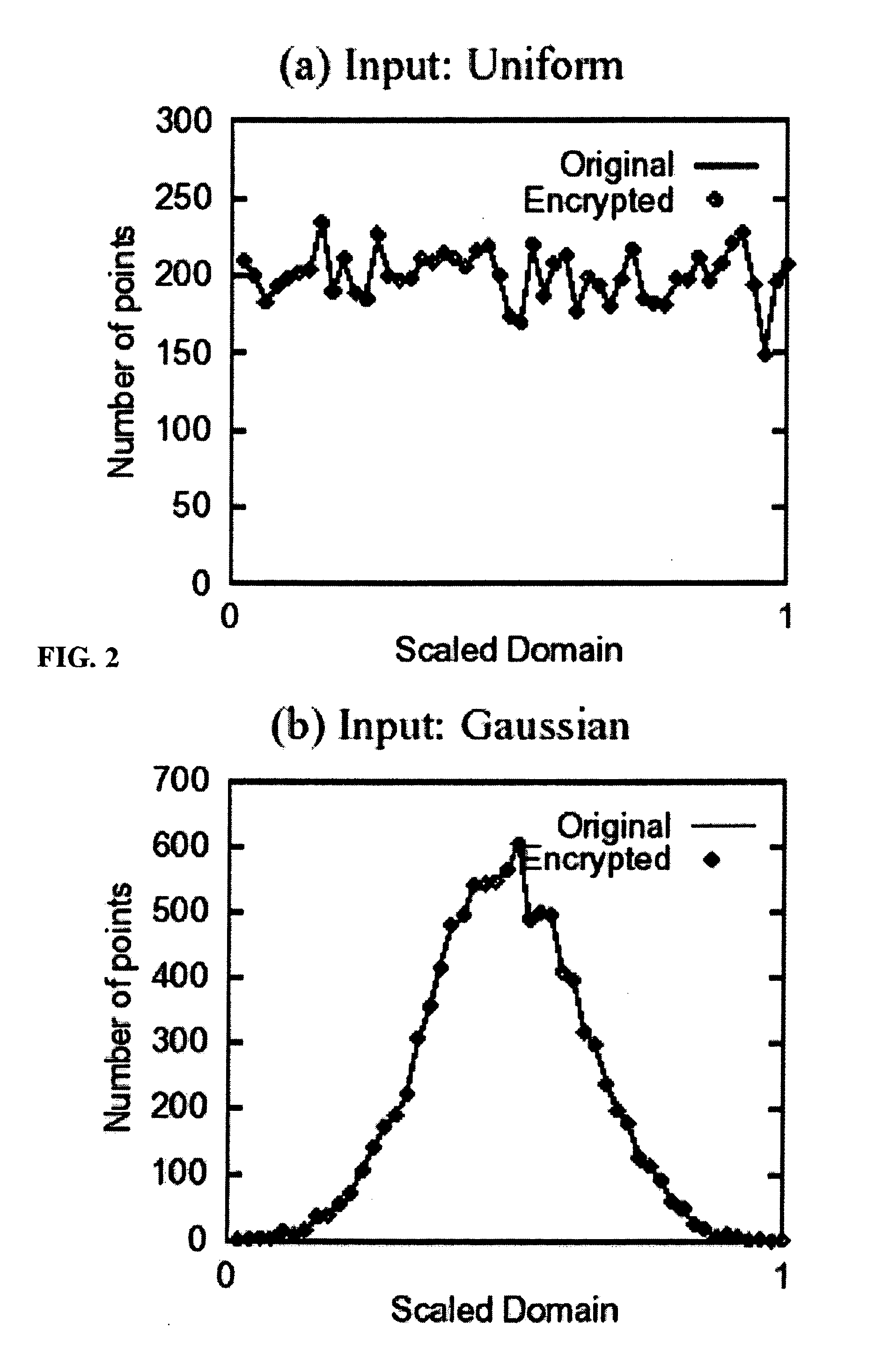
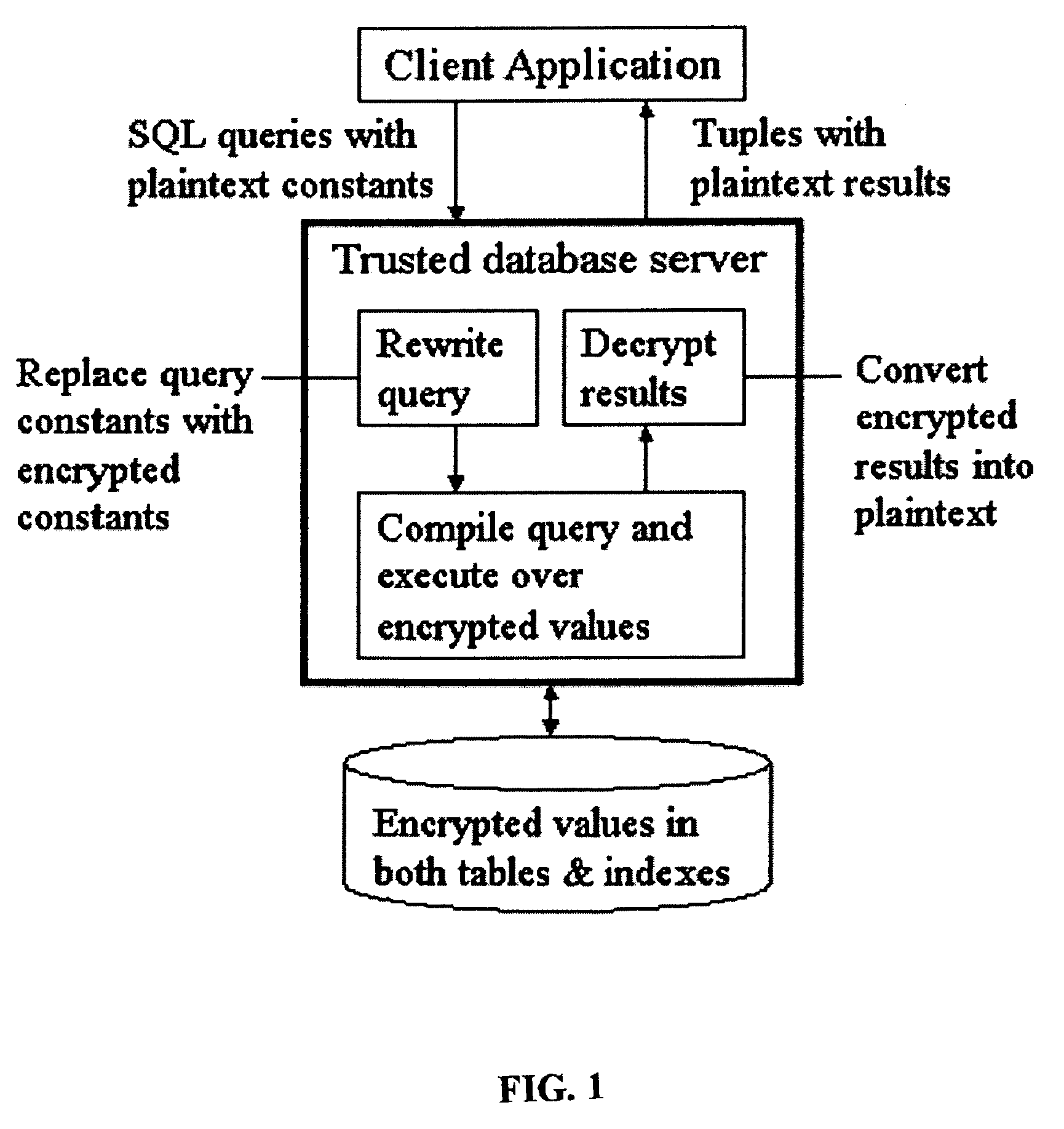
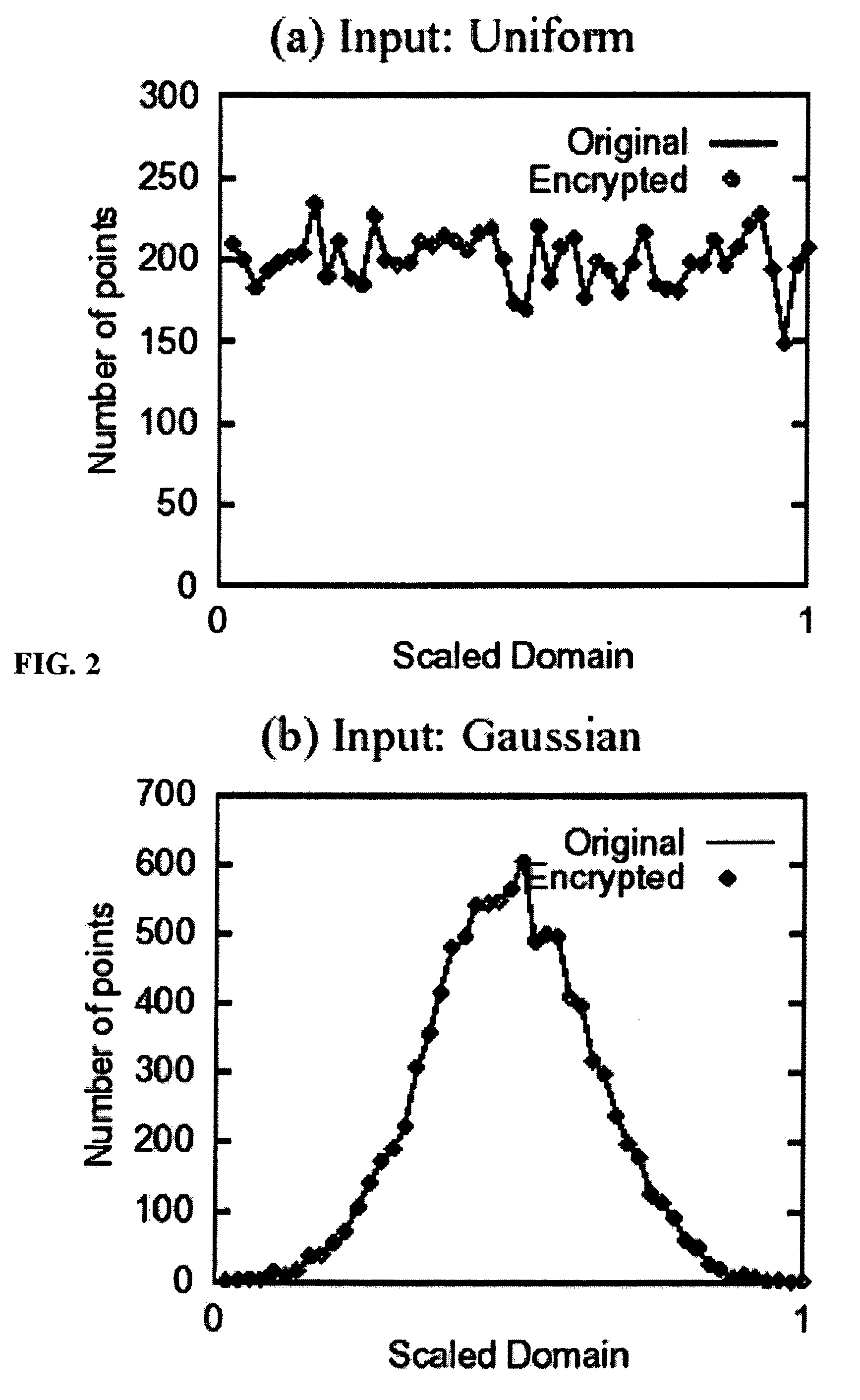
System and method for order-preserving encryption for numeric data
InactiveUS20050147240A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsGrowth phaseData set
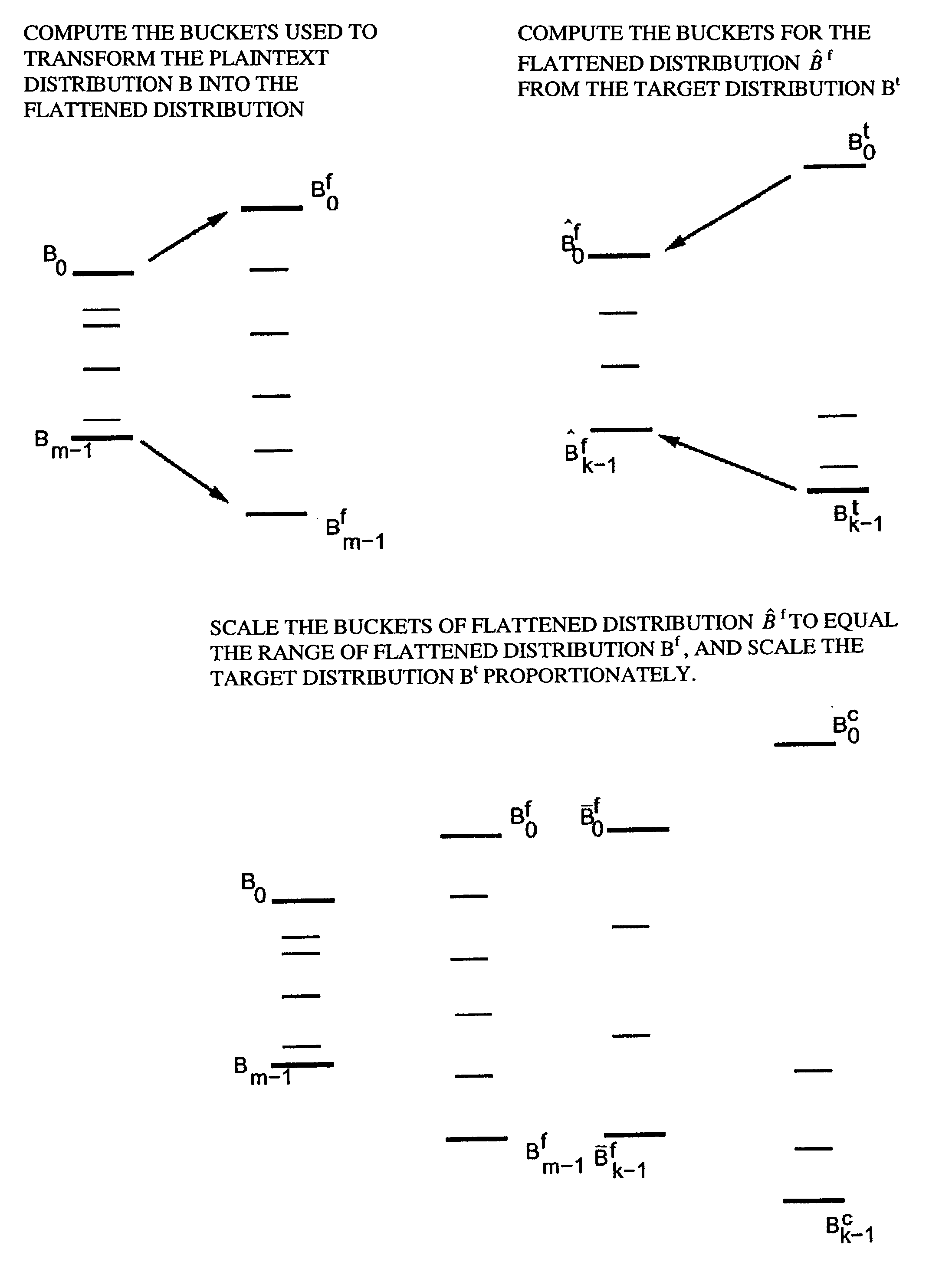
A system, method, and computer program product to automatically eliminate the distribution information available for reconstruction from a disguised dataset. The invention flattens input numerical values into a substantially uniformly distributed dataset, then maps the uniformly distributed dataset into equivalent data in a target distribution. The invention allows the incremental encryption of new values in an encrypted database while leaving existing encrypted values unchanged. The flattening comprises (1) partitioning, (2) mapping, and (3) saving auxiliary information about the data processing, which is encrypted and not updated. The partitioning is MDL based, and includes a growth phase for dividing a space into fine partitions and a prune phase for merging some partitions together.
Owner:IBM CORP
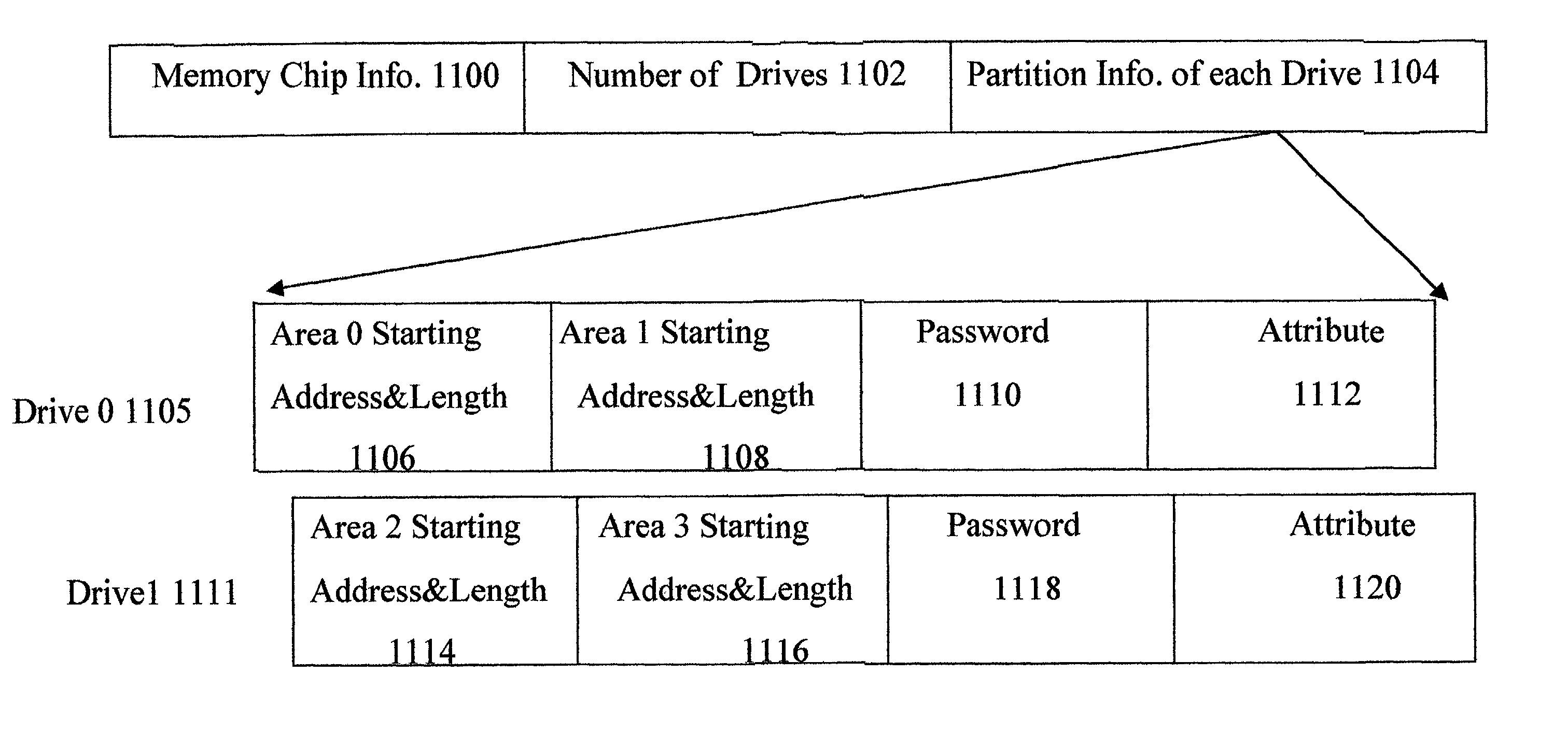
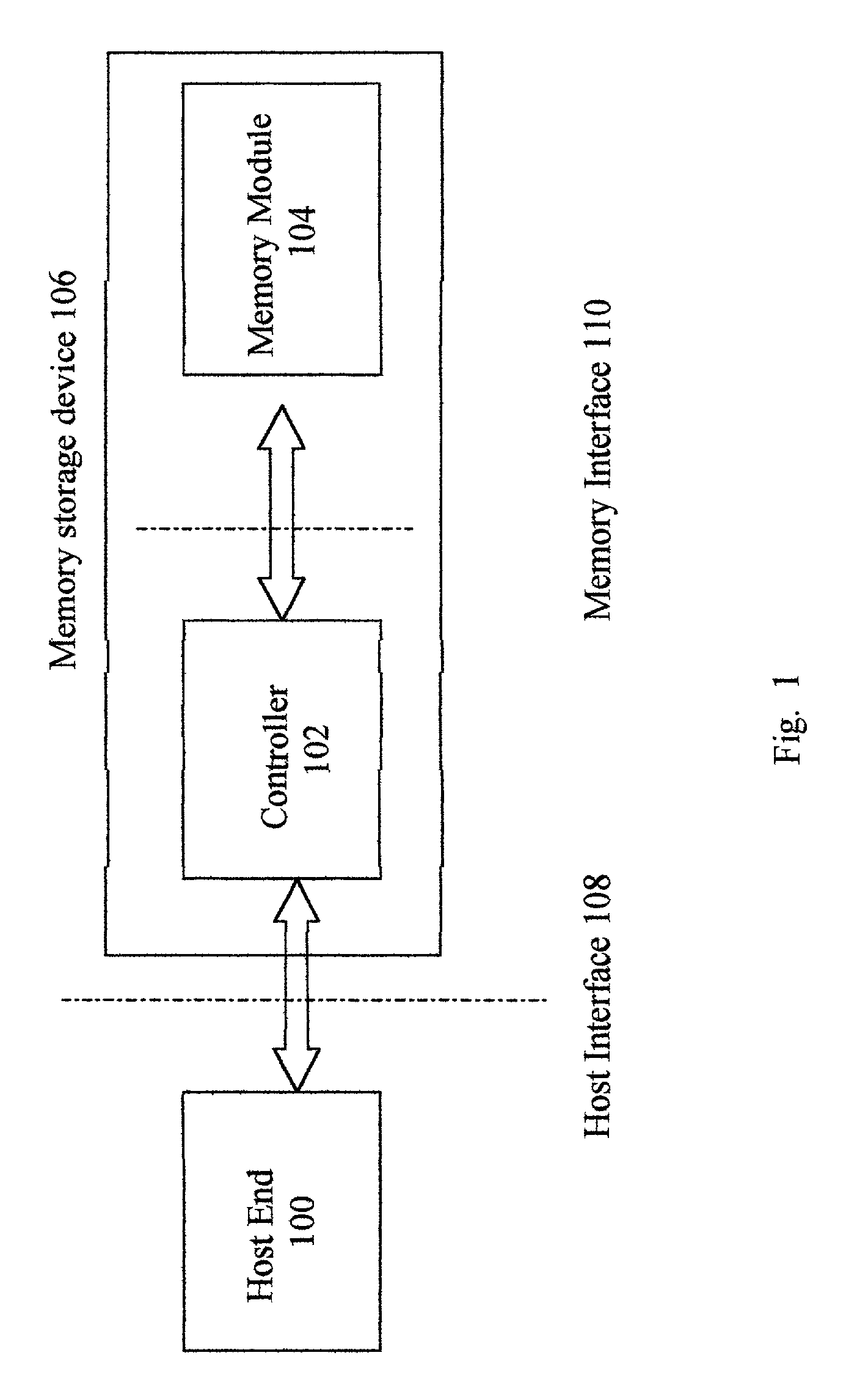
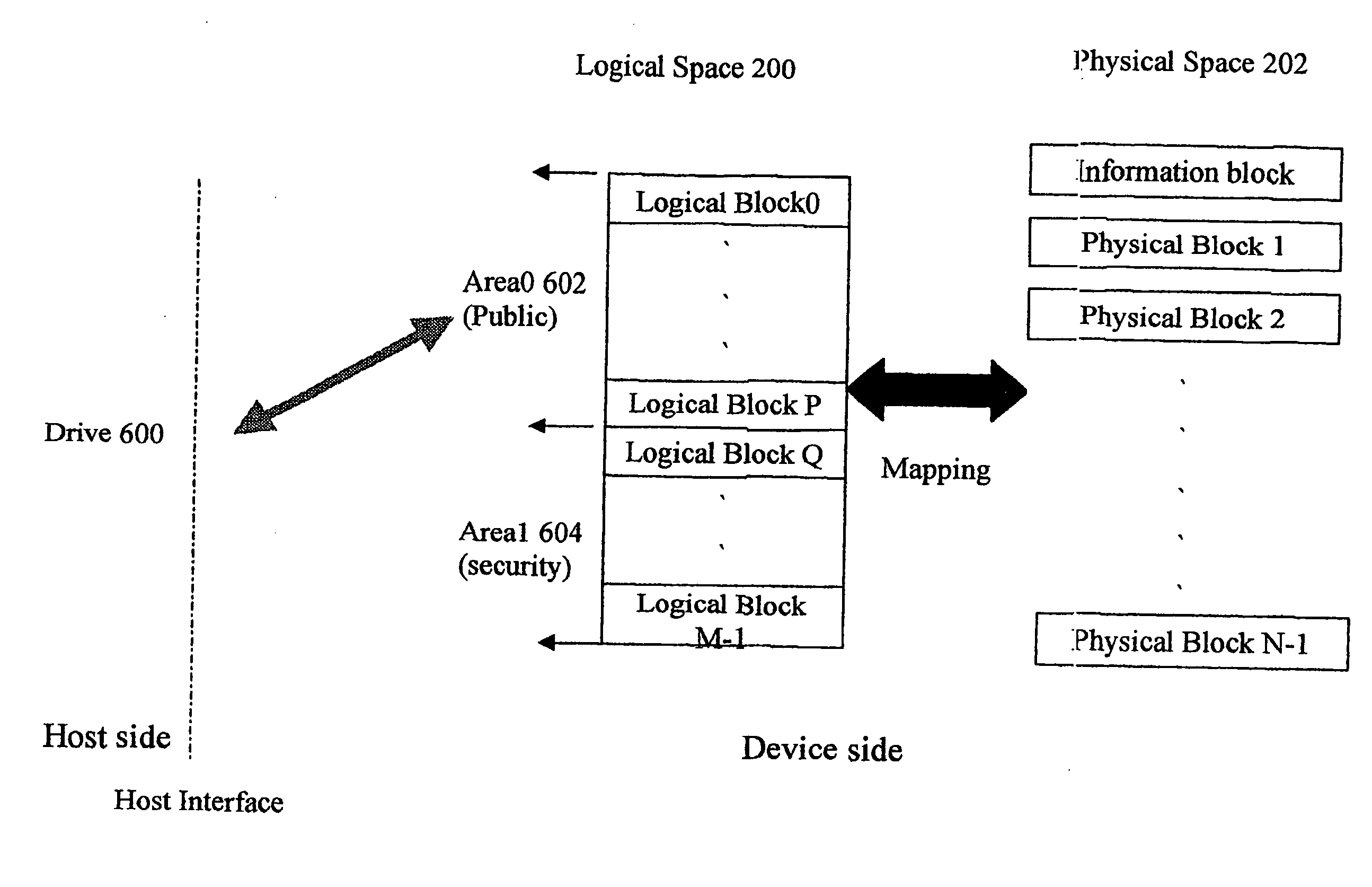
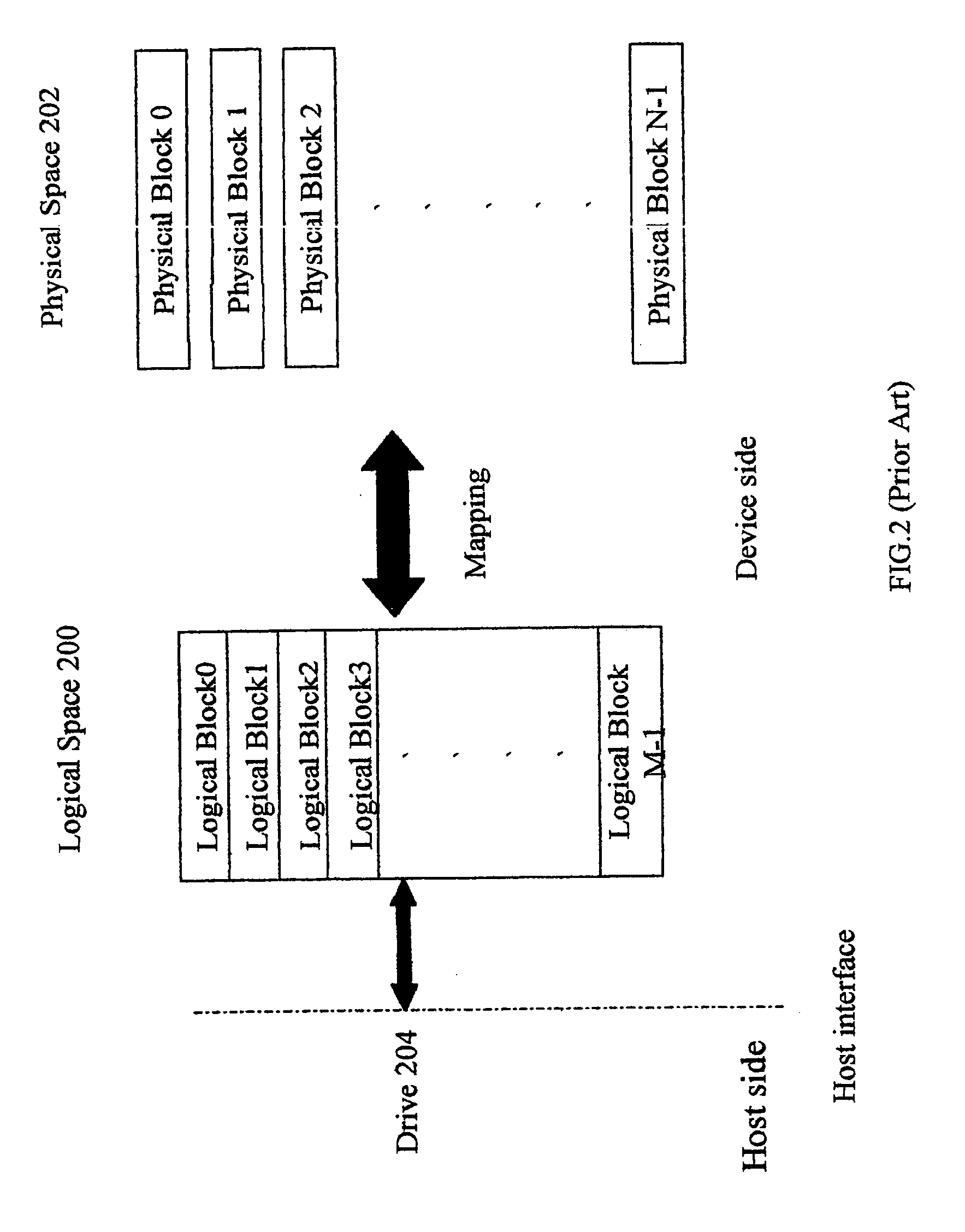
Method for partitioning memory mass storage device
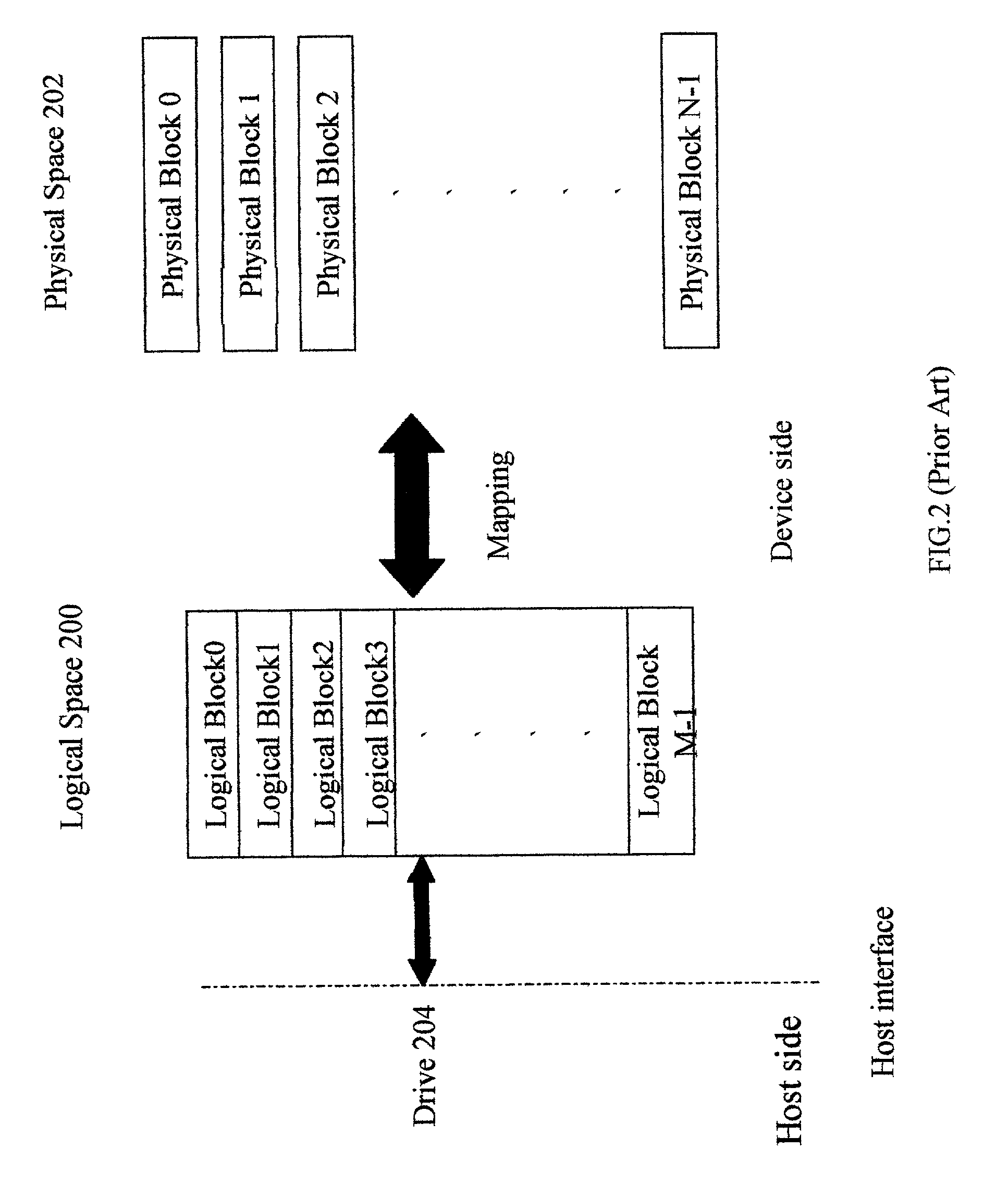
InactiveUS7114051B2Reduce the possibilityInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMass storageSpace partitioning
A method for partitioning a memory mass storage device is disclosed. The partition task is performed by the controller within the memory mass storage device. Firstly, the controller partitions the logical space of the memory storage device into multiple areas, each area belonging to a particular drive. Secondly, the controller partitions the logical space of the memory storage device into a public area and a security area, both areas belonging to the same drive. Finally, the controller partitions the logical space of the memory storage device into multiple areas, which include public areas and security areas and belong to multiple drives.
Owner:SOLID STATE SYST
Compositing images using logically divided object space
InactiveUS20060214949A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsViewpointsSpace partitioning
An apparatus and method of processing object data (e.g., a scene having one or more objects) logically divide the object space into a plurality of contiguous (or noncontiguous) portions. At least two portions each have object data for such object(s). The apparatus and method also determine a positional priority of the at least two portions of the object space for a given viewpoint. Next, the apparatus and method merge rendered object data after at least some of the object data is rendered. This merging is based upon the positional priority of the at least two portions.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Method of fast fingerprint search space partitioning and prescreening
InactiveUS6941003B2Rapid positioningQuick identificationMatching and classificationMinutiaeData mining
Owner:LEIDOS INNOVATIONS TECH INC
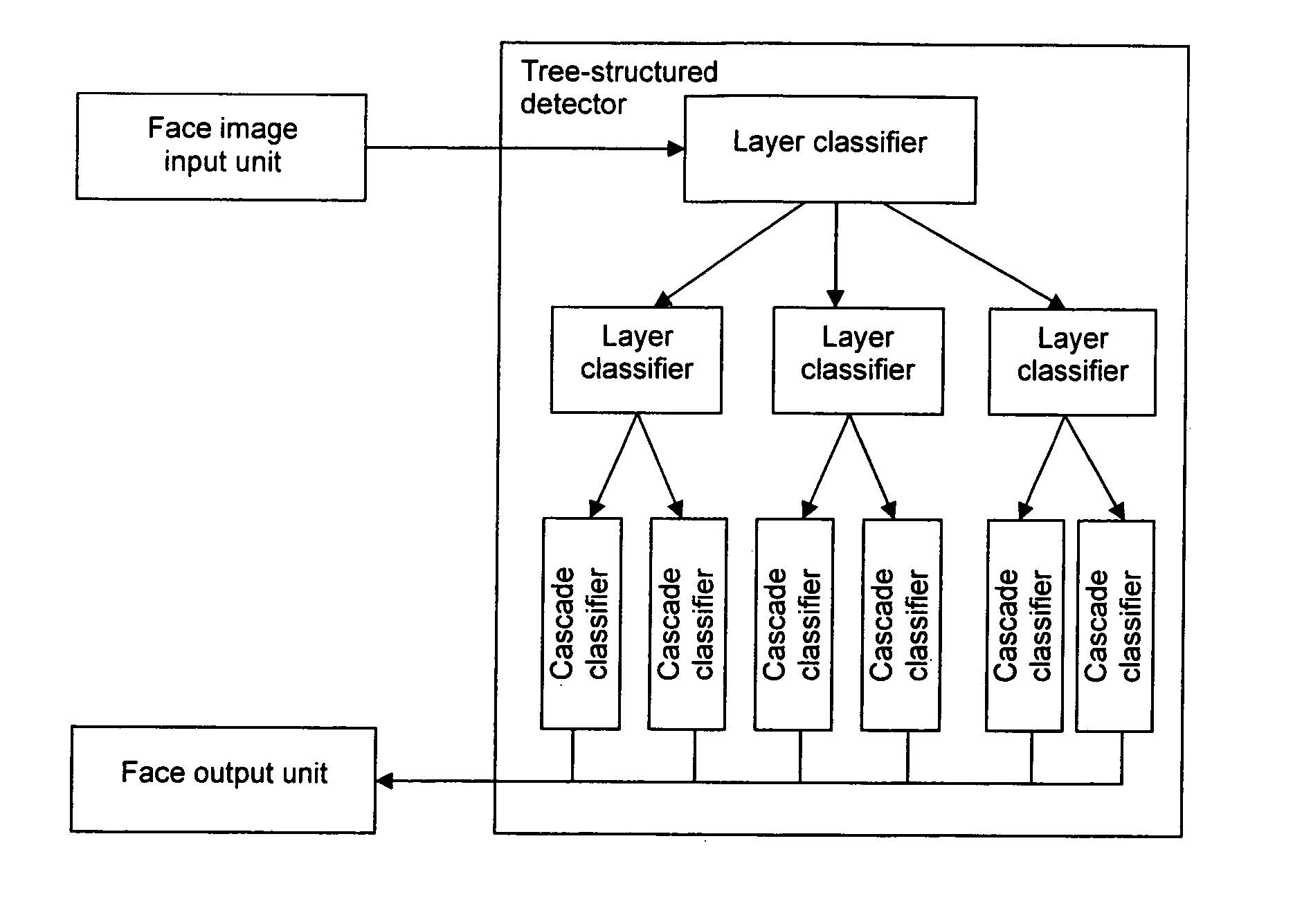
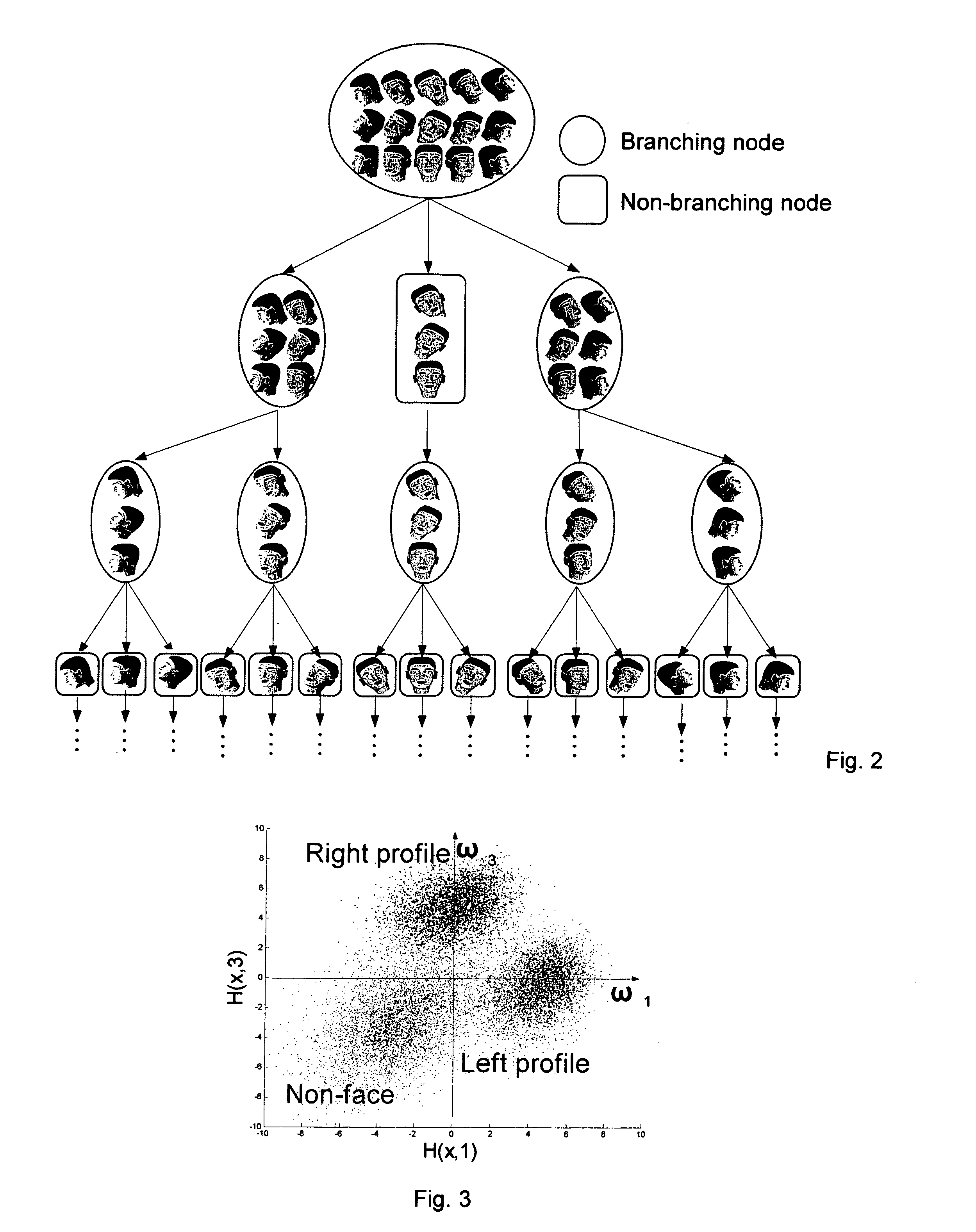
Apparatus and method for detecting a particular subject
ActiveUS20070086660A1Effective calculationImprove accuracyThree-dimensional object recognitionData miningSpace partitioning
An apparatus and a method for detecting from an image a particular subject corresponding to multiple views of the subject by dividing a particular subject space into a plurality of subject subspaces and further dividing a subject subspace into subject subspaces representing multiple views; configuring a tree-structured detector wherein the tree structure has a root node that covers all subject subspaces and has a plurality of branches, each branch corresponding to a child node that covers at least one subject subspace; training each node to determine which nodes in the adjacent lower layer the images of the subject in the corresponding nodes should be sent.
Owner:ORMON CORP +1
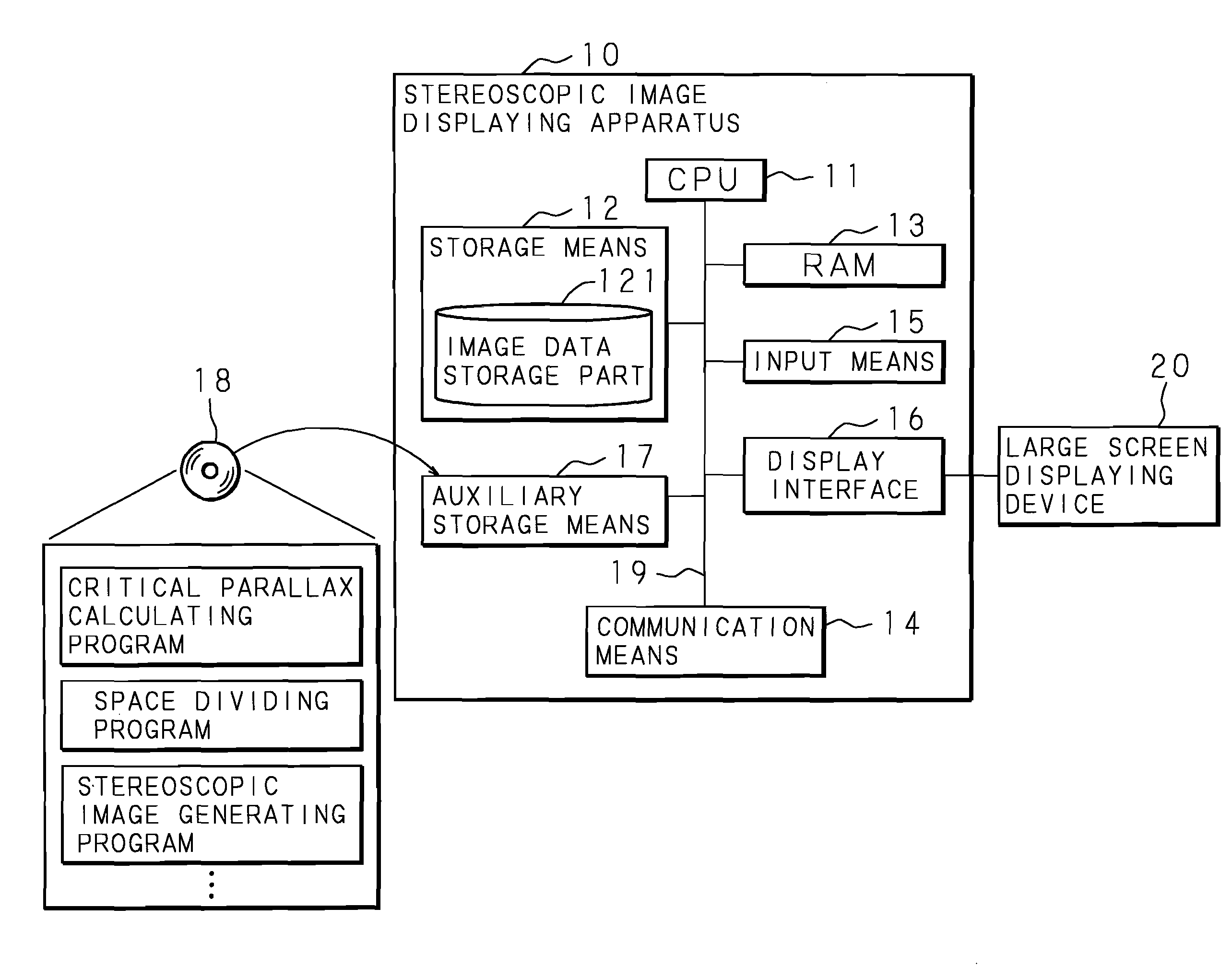
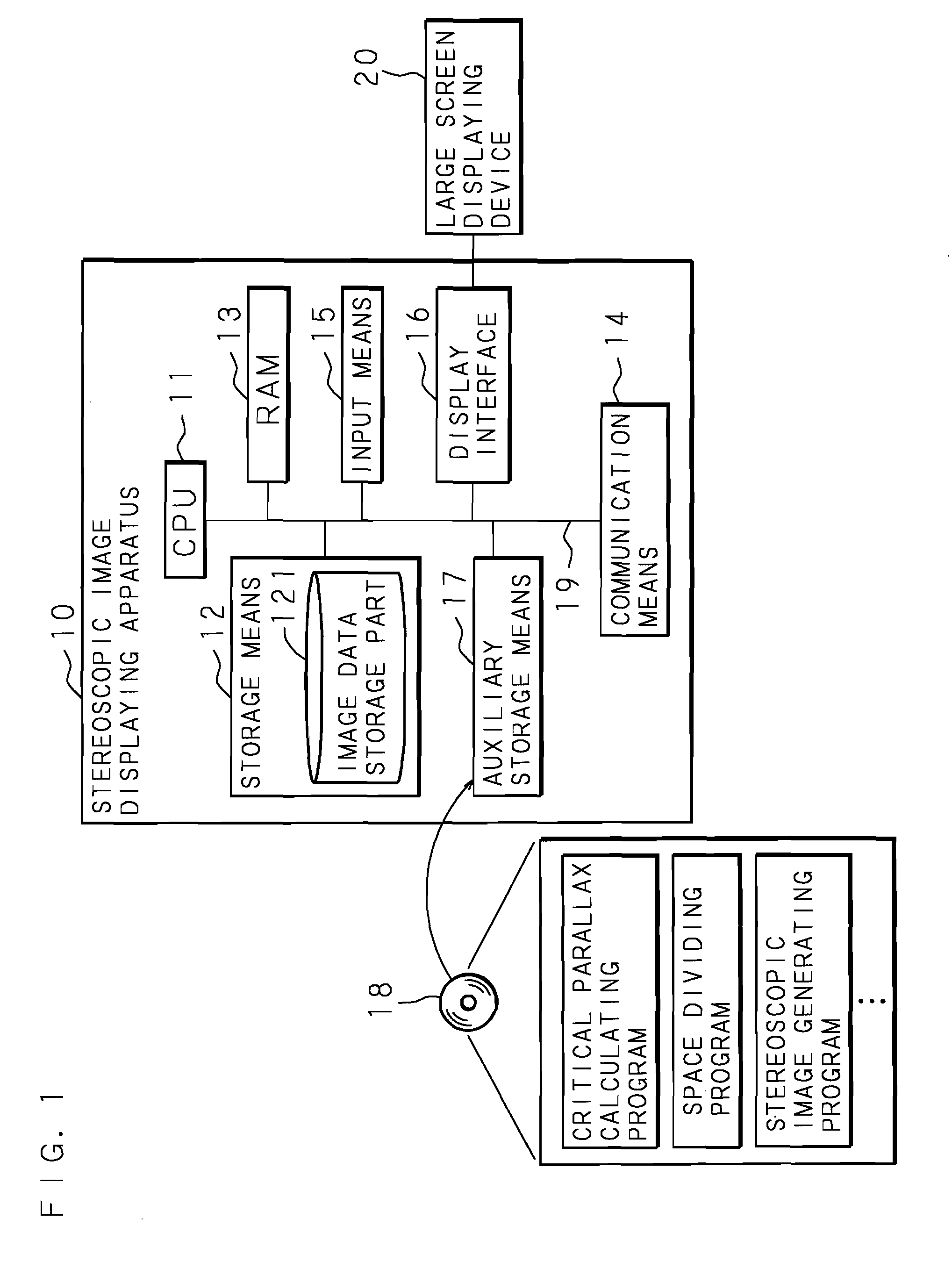
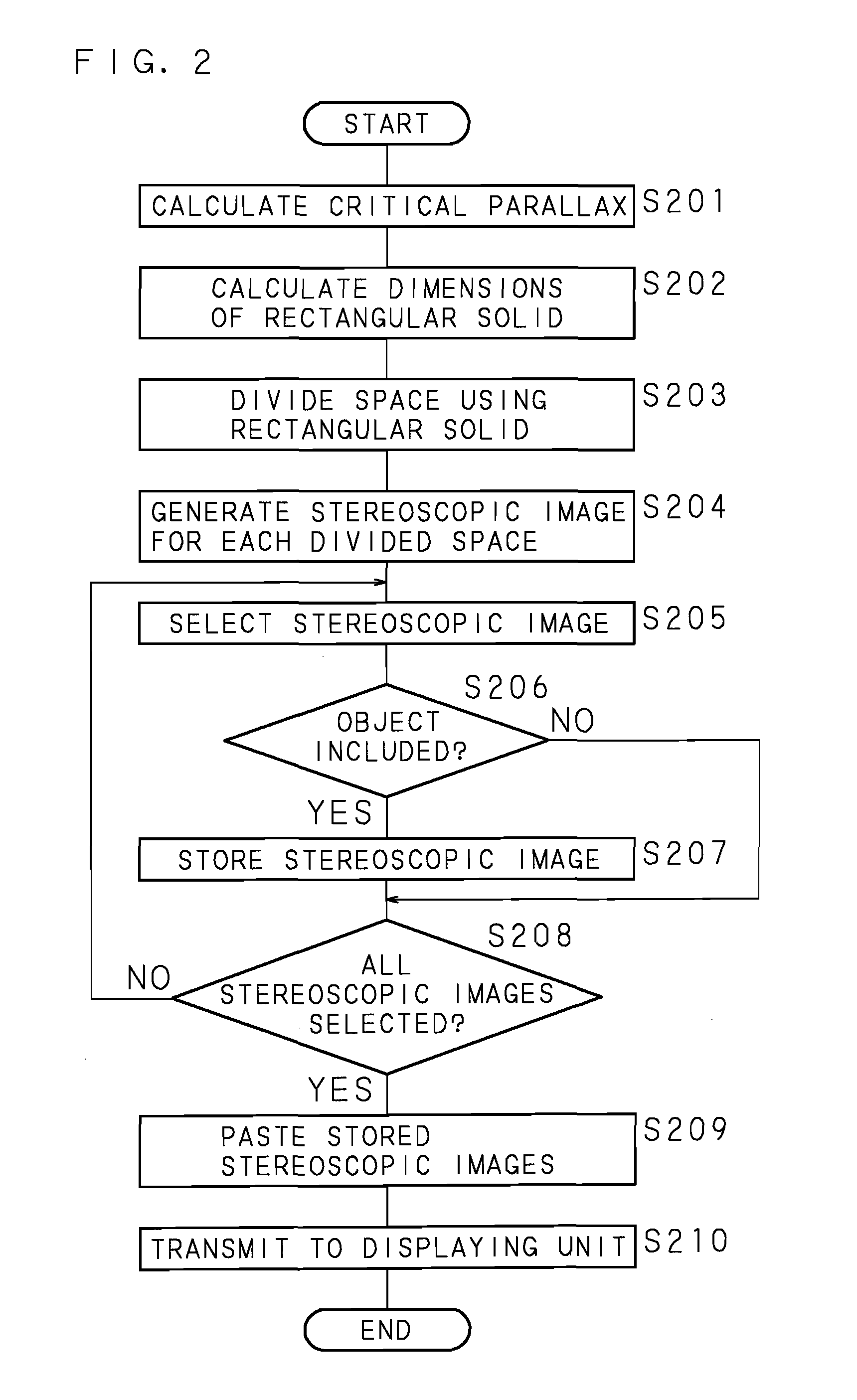
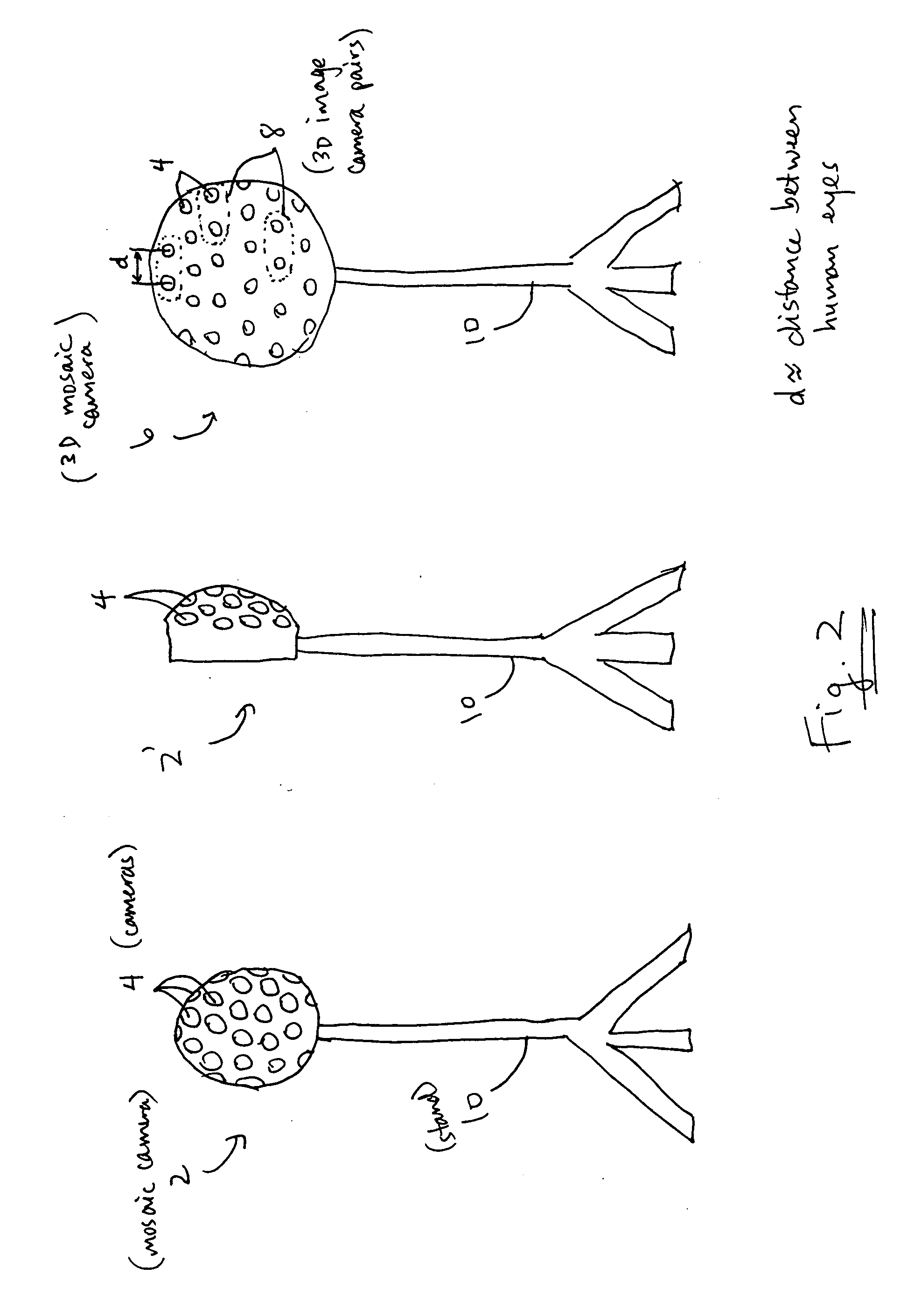
Stereoscopic Image Display Apparatus, Stereoscopic Image Displaying Method And Computer Program Product
A stereoscopic image display apparatus which can accurately visually recognize all the regions of a stereoscopic image without using a varifocal lens, and can form a natural three-dimensional image on a retina with a processing load on a computer eased even if an image is viewed by a plurality of viewers from any positions. A stereoscopic image display apparatus for generating a stereoscopic image that forms three-dimensional image on a retina of a viewer and displaying it, wherein a critical parallax that is the boundary of parallax capable of forming a three-dimensional image on a retina of a viewer is calculated, the dimensions of rectangular parallelepiped inscribing a sphere having a diameter as the calculated critical parallax are calculated, a space including an object is divided into a plurality of spaces using the calculated rectangular parallelepiped, a stereoscopic image of the object with respect to a single gazing point is generated for each divided space, and the plurality of generated stereoscopic images are pasted together to generate a single stereoscopic image and display the generated single stereoscopic image.
Owner:NTT DATA SANYO SYST +1
Method for partitioning memory mass storage device
InactiveUS20050177698A1Reduce the possibilityEasy to understandInput/output to record carriersUnauthorized memory use protectionMass storageSpace partitioning
A method for partitioning a memory mass storage device is disclosed. The partition task is performed by the controller within the memory mass storage device. Firstly, the controller partitions the logical space of the memory storage device into multiple areas, each area belonging to a particular drive. Secondly, the controller partitions the logical space of the memory storage device into a public area and a security area, both areas belonging to the same drive. Finally, the controller partitions the logical space of the memory storage device into multiple areas, which include public areas and security areas and belong to multiple drives.
Owner:KU MAO YUAN +1
Bounding box and space partitioning-based virtual object collision detection method
ActiveCN105469406AImprove accuracyEfficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisSpatial correlationCollision detection
The invention provides a bounding box and space partitioning-based virtual object collision detection method. The method includes the following steps that: virtual object collision pre-detection is performed on two irregular virtual objects; region segmentation is performed on a region to be detected; intersection testing is performed in the sub regions segmented from the region to be detected; virtual object collision detection is performed by using a point vector set representing a moving virtual object and a triangular surface representing a virtual object which does not require assembly at present; and if the virtual objects intersect with each other, the virtual objects collide with each other, otherwise, the virtual objects do not collide with each other. According to the bounding box and space partitioning-based virtual object collision detection method of the invention, a collision detection range of a space is narrowed through using the spatial correlation of the virtual objects, so that time consumption can be reduced, and at the same time, the detection efficiency of the method and the geometric accuracy of collision detection are greatly improved; a bounding box is reduced into the triangular surface and the points, so that the misjudgment of the collision detection can be decreased; and a collision detection process is refined to the interference between the triangular surface and the points, and separate detection is carried out, and therefore, detection efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
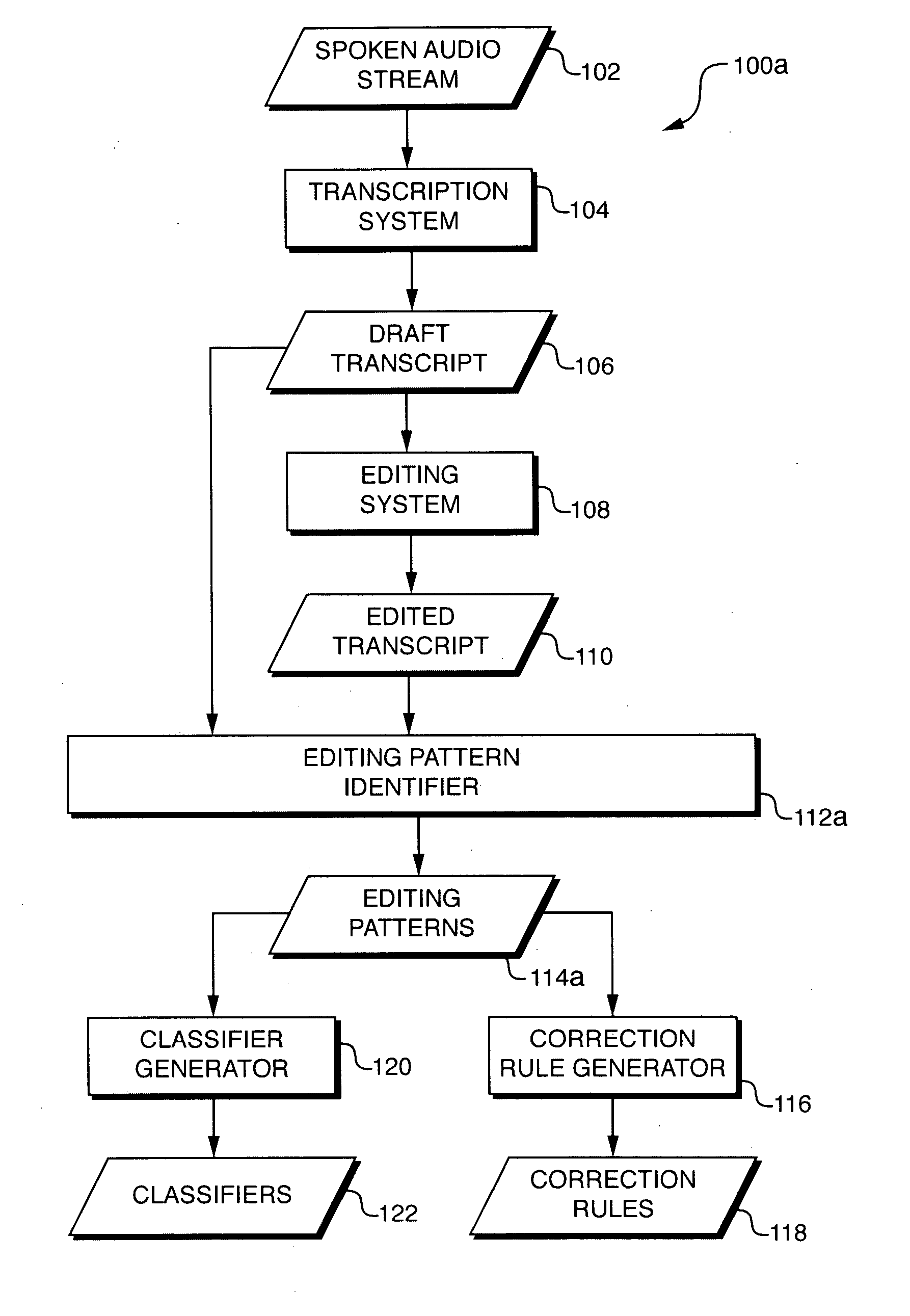
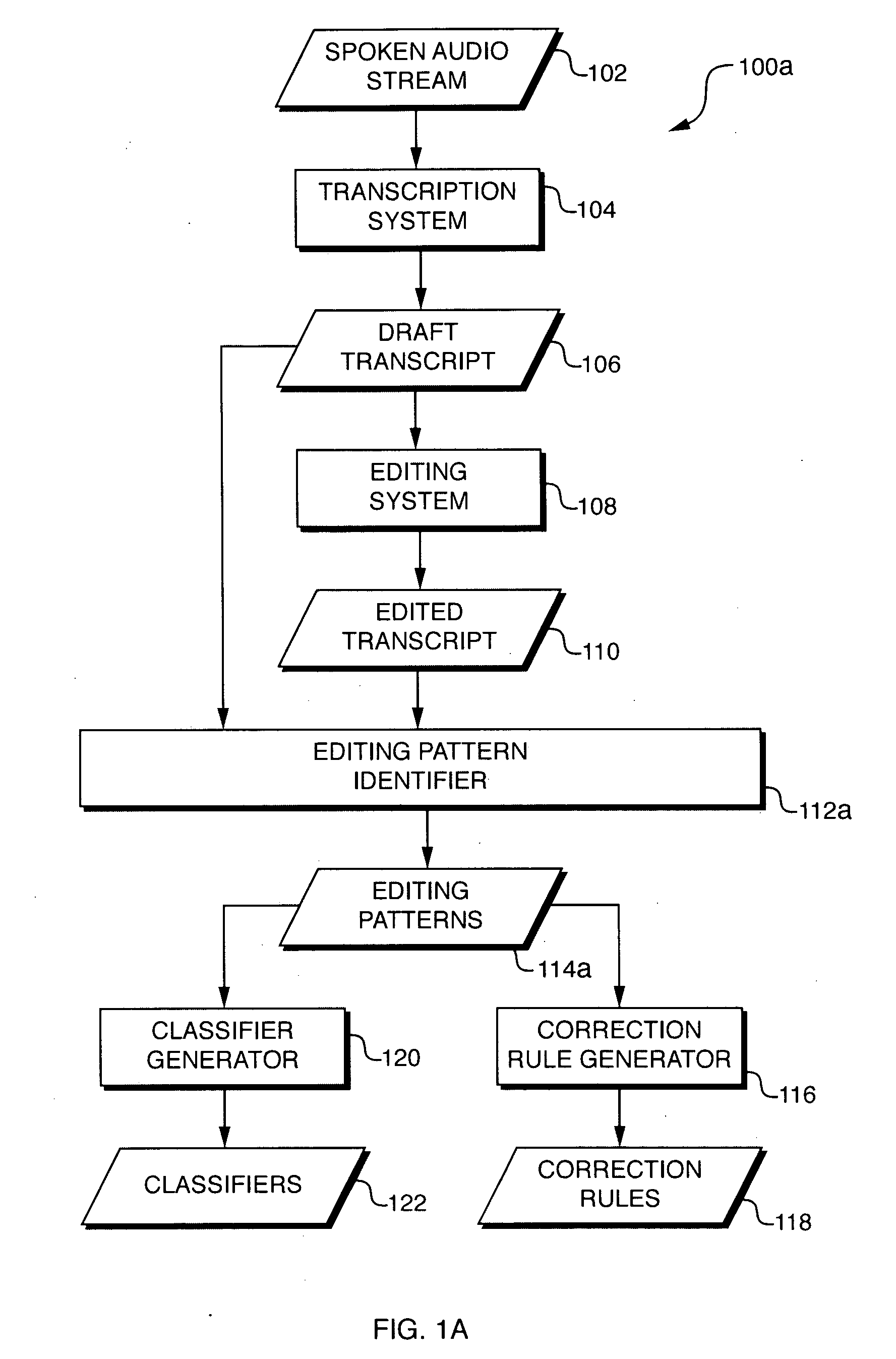
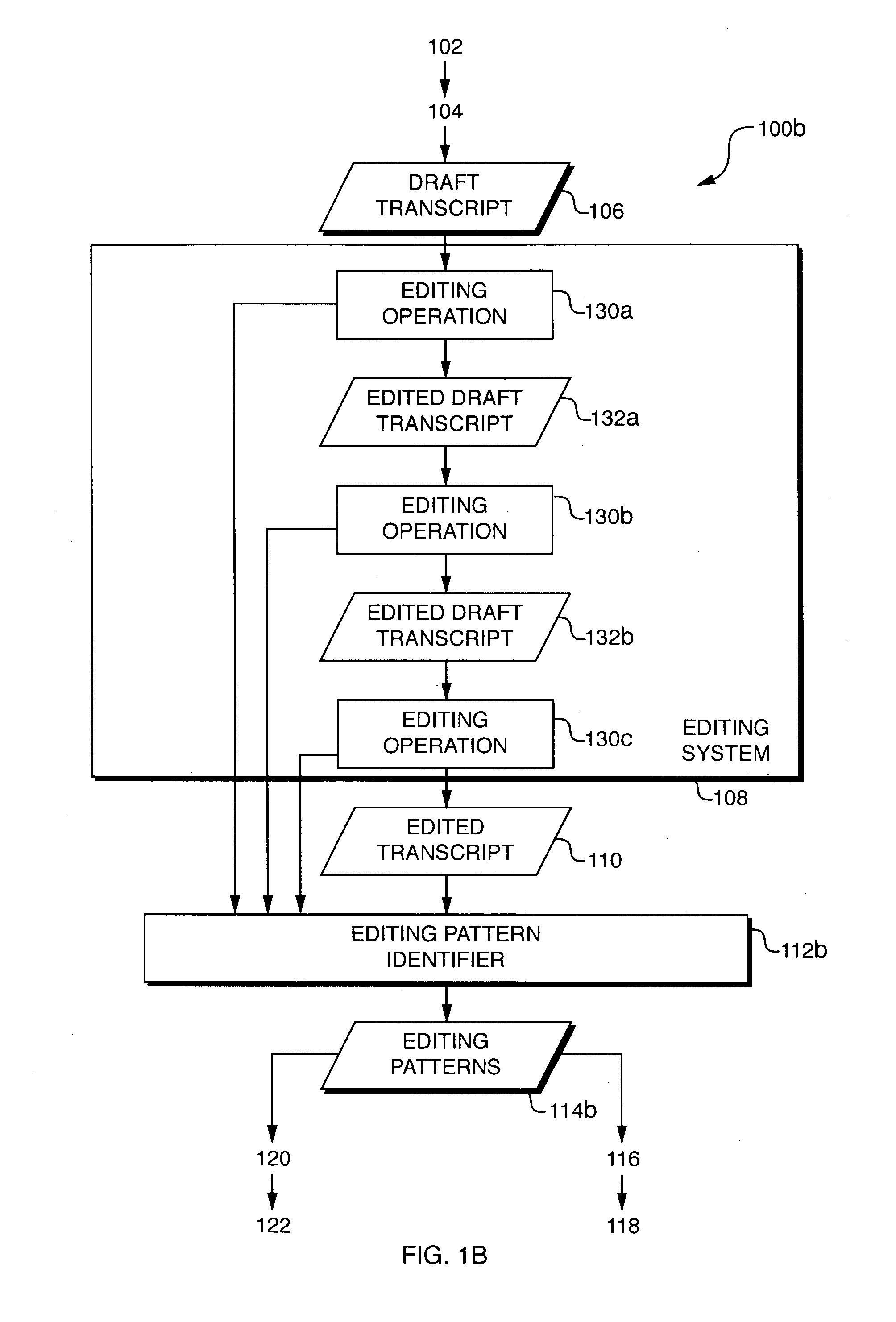
Automatic detection and application of editing patterns in draft documents
ActiveUS20070106494A1Natural language data processingSpeech recognitionContext recognitionPaper document
An error detection and correction system extracts editing patterns and derives correction rules from them by observing differences between draft documents and corresponding edited documents, and / or by observing editing operations performed on the draft documents to produce the edited documents. The system develops classifiers that partition the space of all possible contexts into equivalence classes and assigns one or more correction rules to each such class). Once the system has been trained, it may be used to detect and (optionally) correct errors in new draft documents. When presented with a draft document, the system identifies first content (e.g., text) in the draft document and identifies a context of the first content. The system identifies a correction rule based on the first content and the first context. The system may use a classifier to identify the correction rule. The system applies the correction rule to the first content to produce second content.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
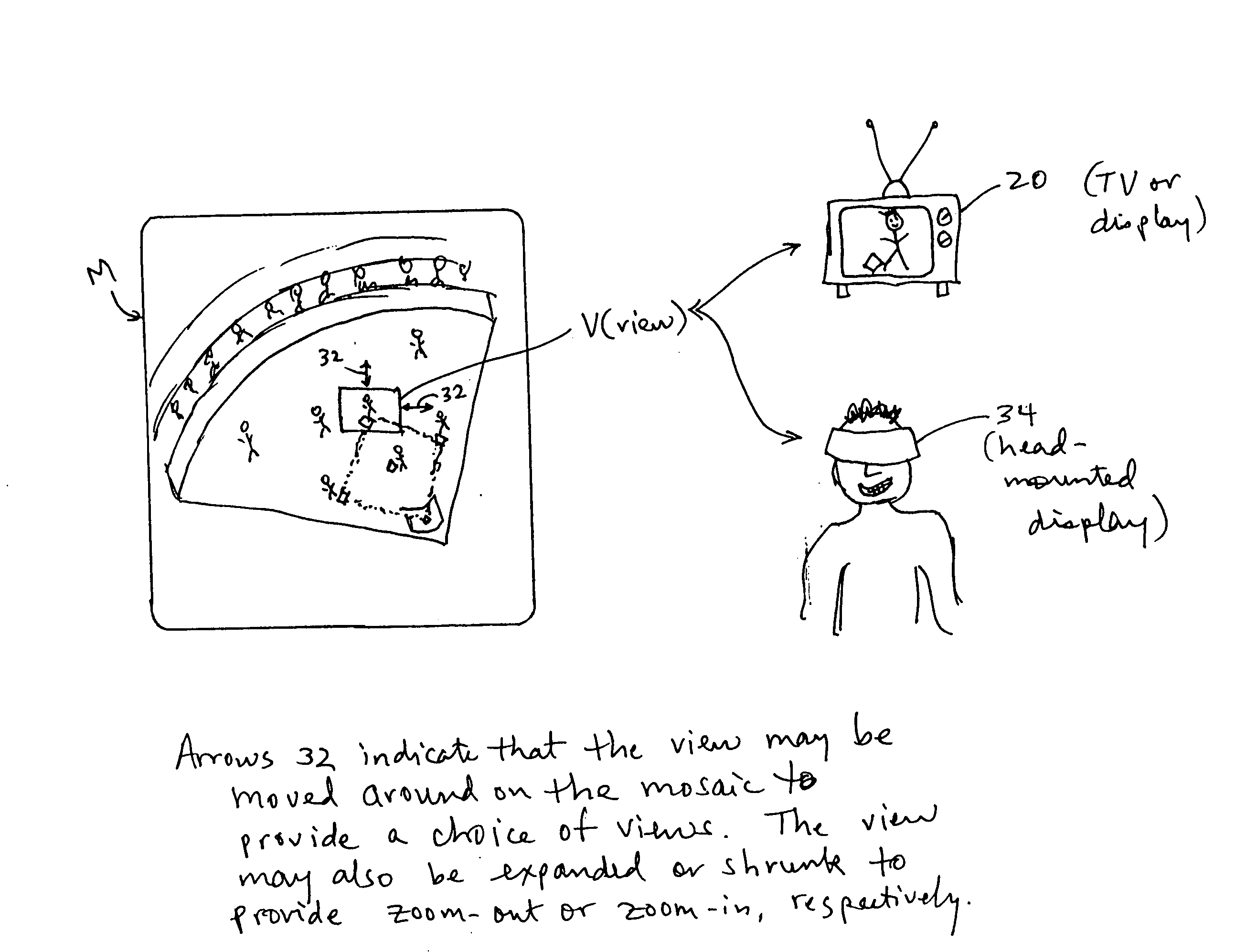
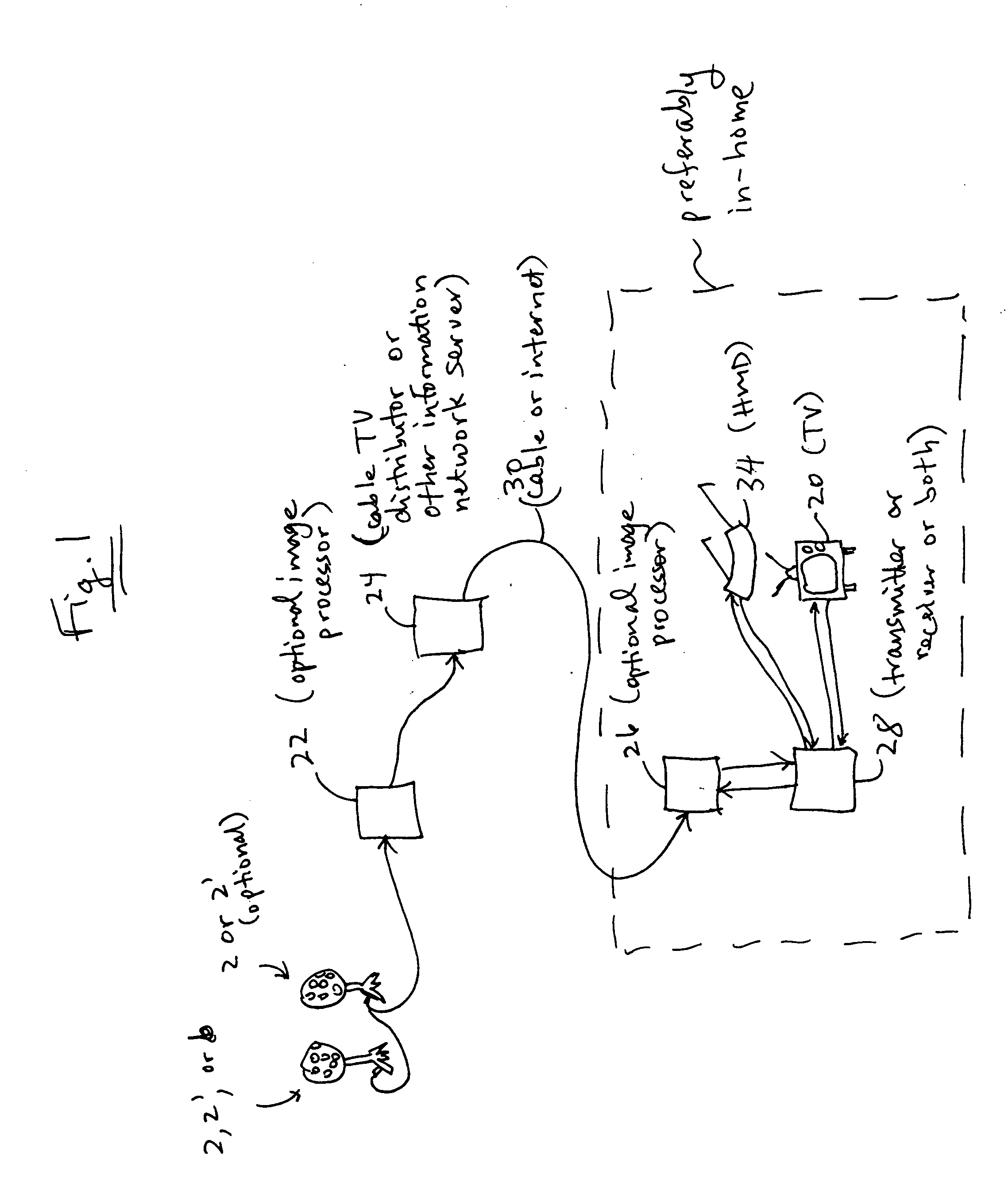
System and method for producing a selectable view of an object space
InactiveUS20050046698A1Increase in sizeSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Display device
A system and method for producing a selectable view of an object space include: a) dividing the object space into n object sections to be imaged; b) providing at least n cameras, where the cameras are configured such that each object section is associated with at least one unique camera configured to image substantially only that object section; and c) imaging each of the object sections with its unique camera, so as to create at least one image of each object section, where the images of the object sections are combined to create a substantially continuous composite mosaic of the object space, where a view of a portion of the mosaic is selectably provided to a user based on selection instructions from the user, and where at least one of the view, the mosaic, and the images of the object sections is sent to the user via an information network, such as a cable network. The view may be provided in 3D to the user via a head-mounted display, and the selection instructions may include a physical orientation of the display.
Owner:KNIGHT ANDREW FREDERICK
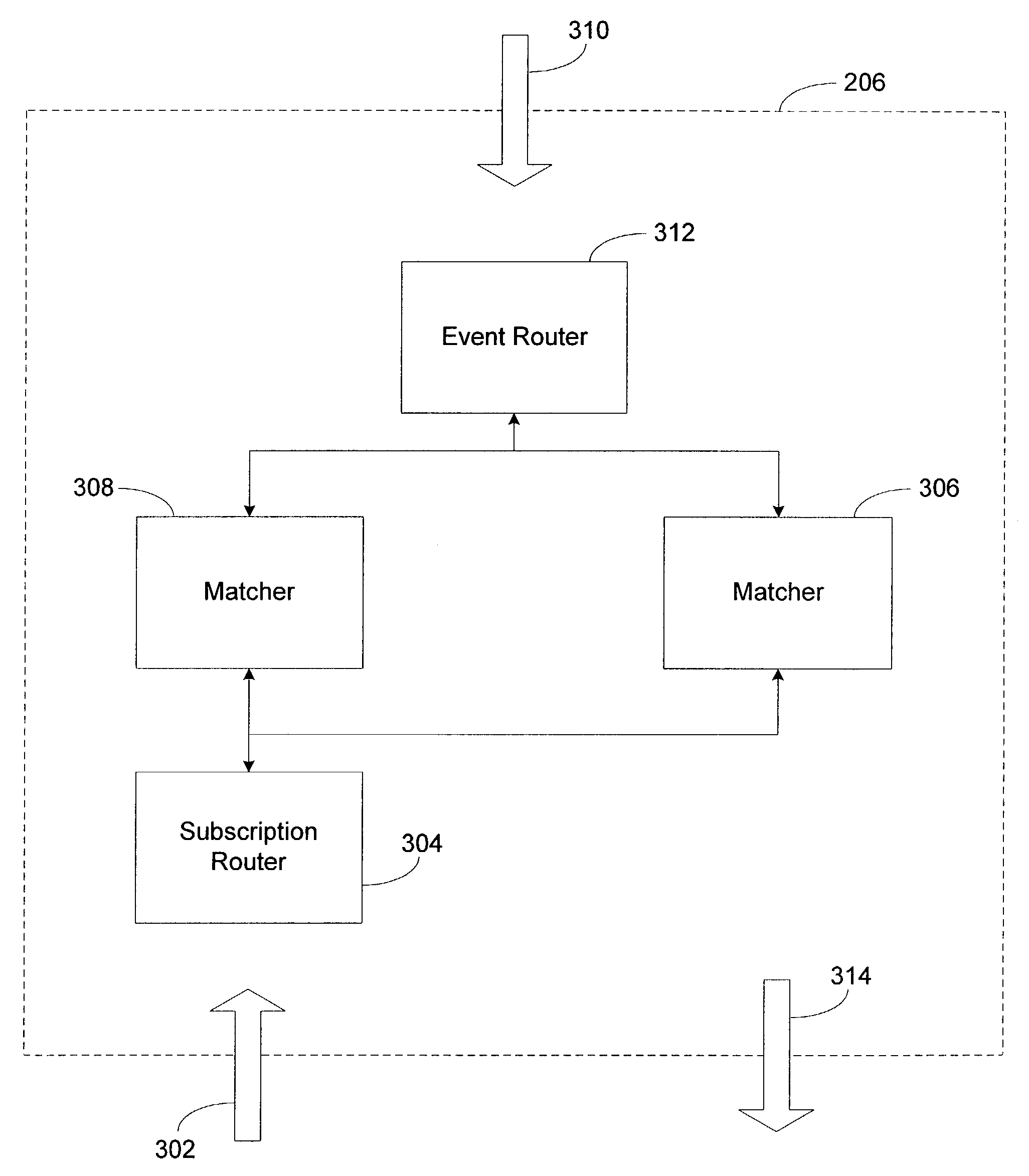
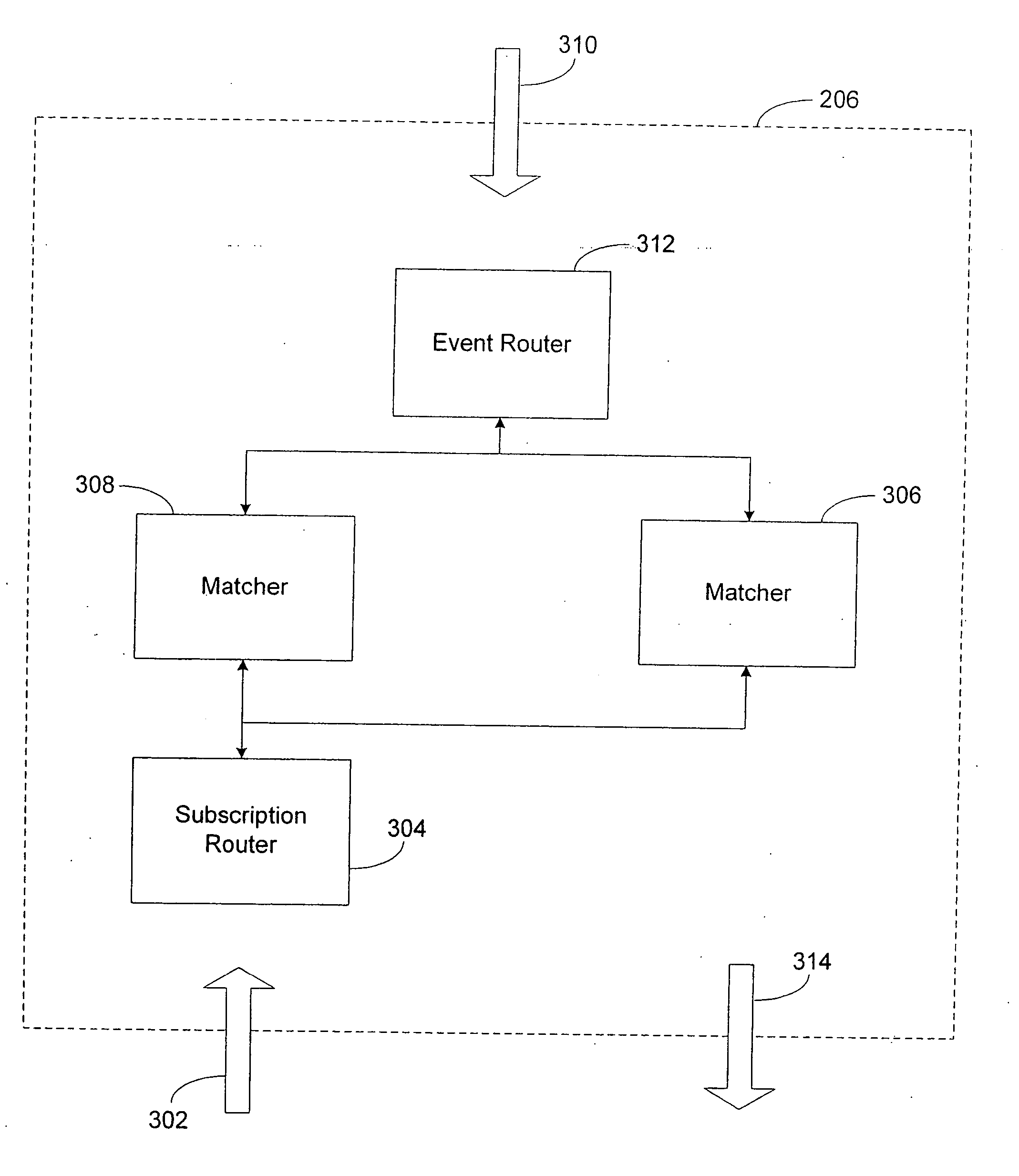
Summary-based routing for content-based event distribution networks
ActiveUS7200675B2Precise cuttingHigh precisionSpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityPublish–subscribe pattern
A system and method for enabling highly scalable multi-node event distribution networks through the use of summary-based routing, particularly event distribution networks using a content-based publish / subscribe model to distribute information. By allowing event routers to use imprecise summaries of the subscriptions hosted by matcher nodes, an event router can eliminate itself as a bottleneck thus improving overall event distribution network throughput even though the use of imprecise summaries results in some false positive event traffic. False positive event traffic is reduced by using a filter set partitioning that provides for good subscription set locality at each matcher node, while at the same time avoiding overloading any one matcher node. Good subscription set locality is maintained by routing new subscriptions to a matcher node with a subscription summary that best covers the new subscription. Where event space partitioning is desirable, an over-partitioning scheme is described that enables load balancing without repartitioning.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
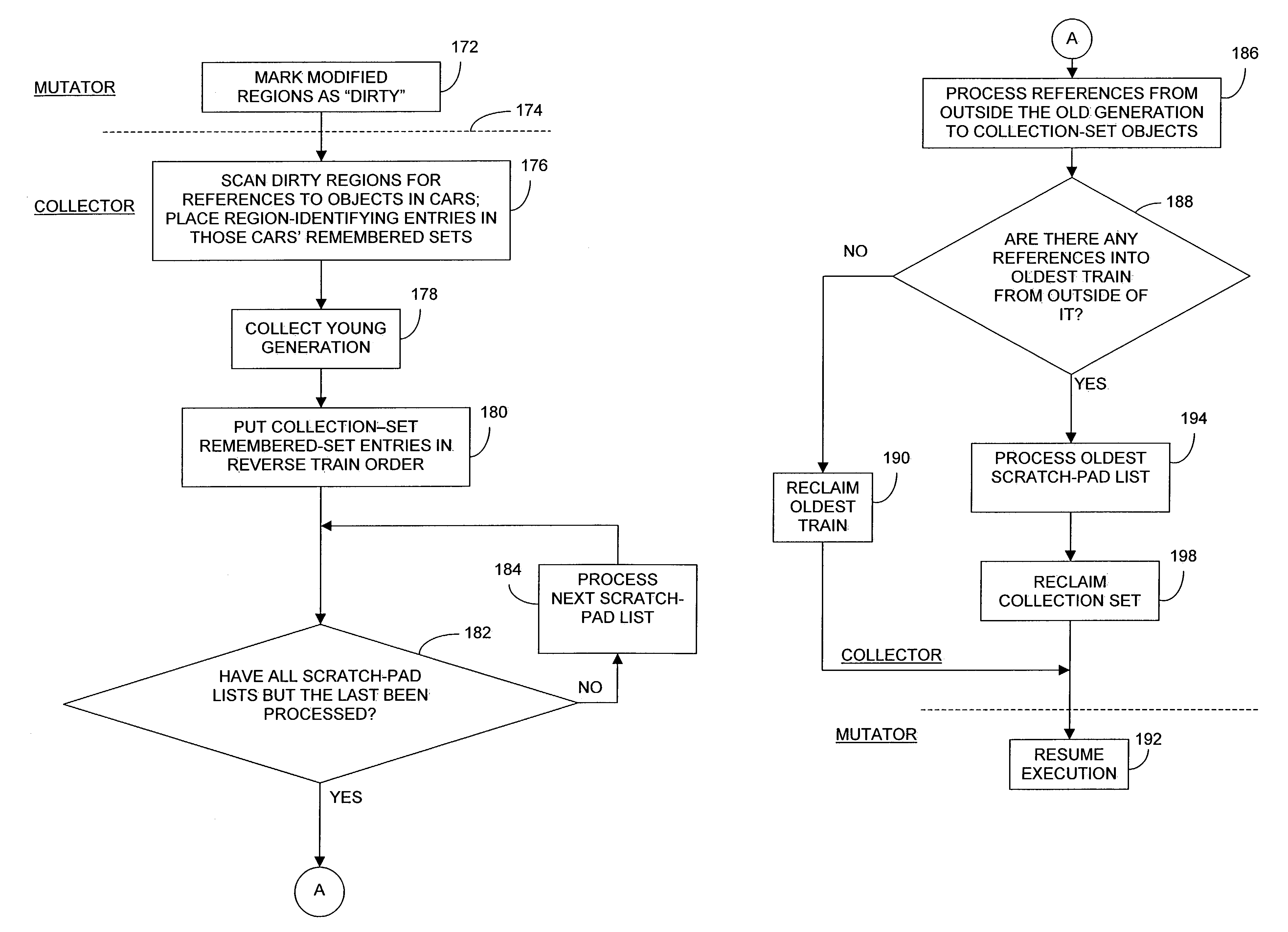
Space-efficient, depth-first parallel copying collection technique making use of work-stealing on the same structures that maintain the stack of items to be scanned
ActiveUS7092978B2Minimize of amountMinimize the numberData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingWaste collection
A copying-type garbage collector operates in multiple concurrent threads. Each thread evacuates potentially reachable objects from the from space to the to space in a depth-first manner: if a thread has evacuated an object containing references to any from-space objects, it evacuates all of that object's descendants before it evacuates any other reachable objects. To keep track of descendants that must be evacuated before non-descendants can be, the thread places objects containing references to non-evacuated objects into a linked list maintained by pointers that it installs in the from-space locations from which the objects on the list were evacuated. Additionally, it divides the to space into local-allocation buffers (“LABs”) to which respective threads exclusively evacuate objects, and each thread maintains a LAB stack representing all the LABs it has filled that still contain references to unevacuated from-space objects. When a thread has completed evacuating the descendants of evacuees in all of its LABs, it “steals” work from other threads. It may do so, for instance, by processing a reference in an object belonging to another thread's list, by transferring to its own list one or more objects from another thread's list, or by transferring to its own LAB stack one or more LABs from another thread's LAB stack.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Summary-based routing for content-based event distribution networks
InactiveUS20070168550A1Precise cuttingHigh precisionSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsAridSpace partitioning
A system arid method for enabling highly scalable multi-node event distribution networks through the use of summary-based routing, particularly event distribution networks using a content-based publish / subscribe model to distribute information. By allowing event routers to use imprecise summaries of the subscriptions hosted by matcher nodes, an event router can eliminate itself as a bottleneck thus improving overall event distribution network throughput even though the use of imprecise summaries results in some false positive event traffic. False positive event traffic is reduced by using a filter set partitioning that provides for good subscription set locality at each matcher node, while at the same time avoiding overloading any one matcher node. Good subscription set locality is maintained by routing new subscriptions to a matcher node with a subscription summary that best covers the new subscription. Where event space partitioning is desirable, an over-partitioning scheme is described that enables load balancing without repartitioning.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for order-preserving encryption for numeric data
InactiveUS7426752B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsGrowth phaseData set
A system, method, and computer program product to automatically eliminate the distribution information available for reconstruction from a disguised dataset. The invention flattens input numerical values into a substantially uniformly distributed dataset, then maps the uniformly distributed dataset into equivalent data in a target distribution. The invention allows the incremental encryption of new values in an encrypted database while leaving existing encrypted values unchanged. The flattening comprises (1) partitioning, (2) mapping, and (3) saving auxiliary information about the data processing, which is encrypted and not updated. The partitioning is MDL based, and includes a growth phase for dividing a space into fine partitions and a prune phase for merging some partitions together.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
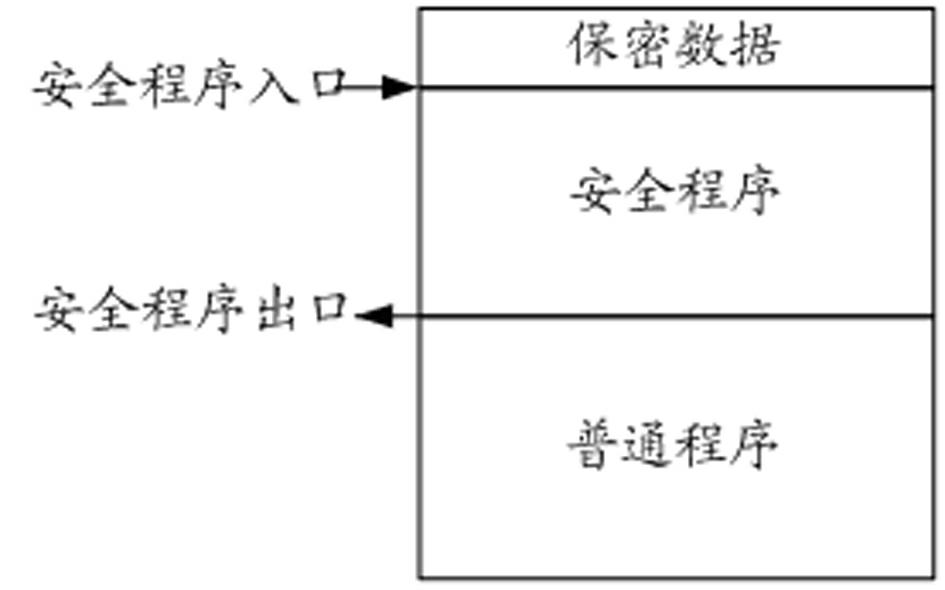
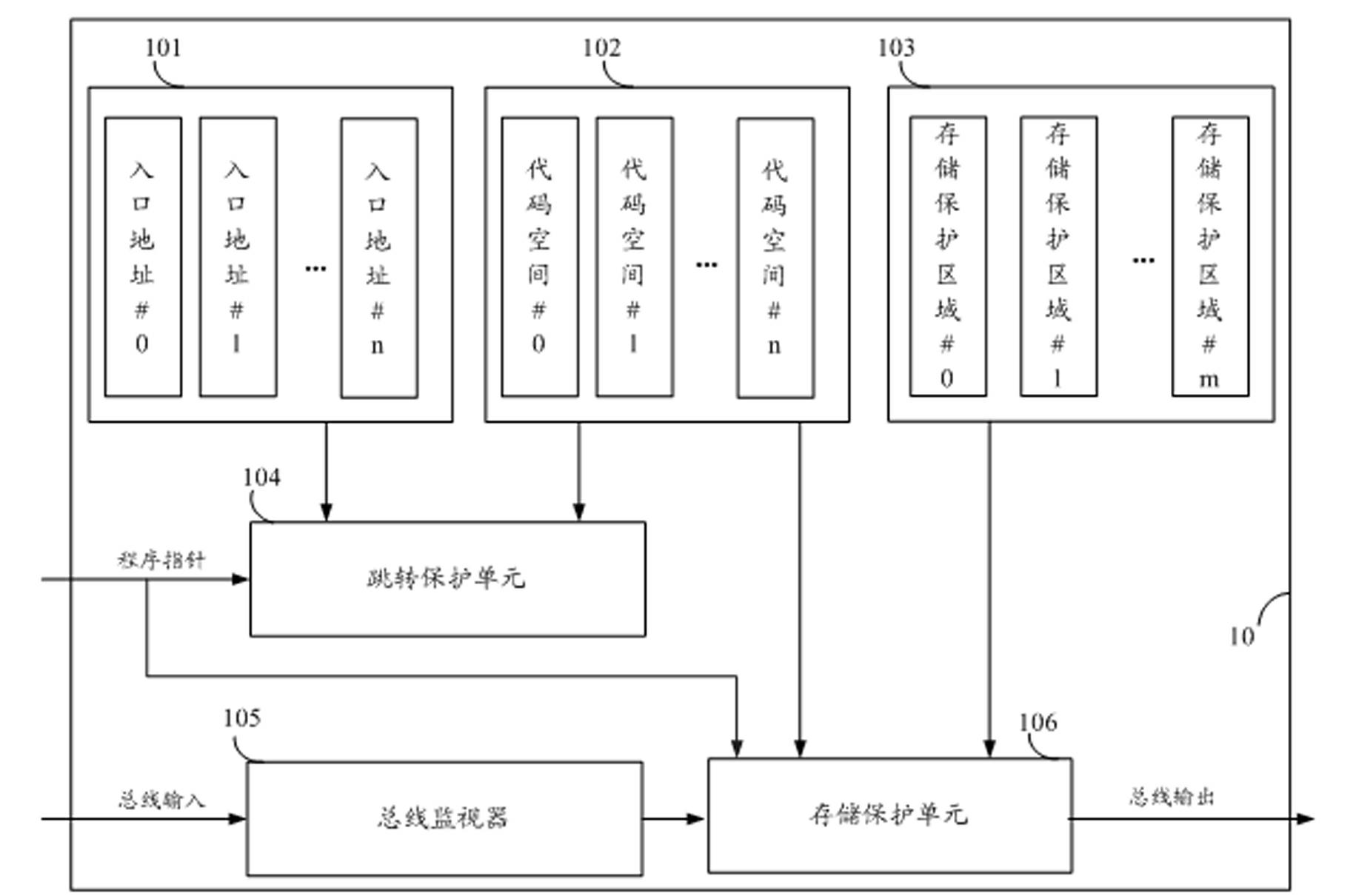
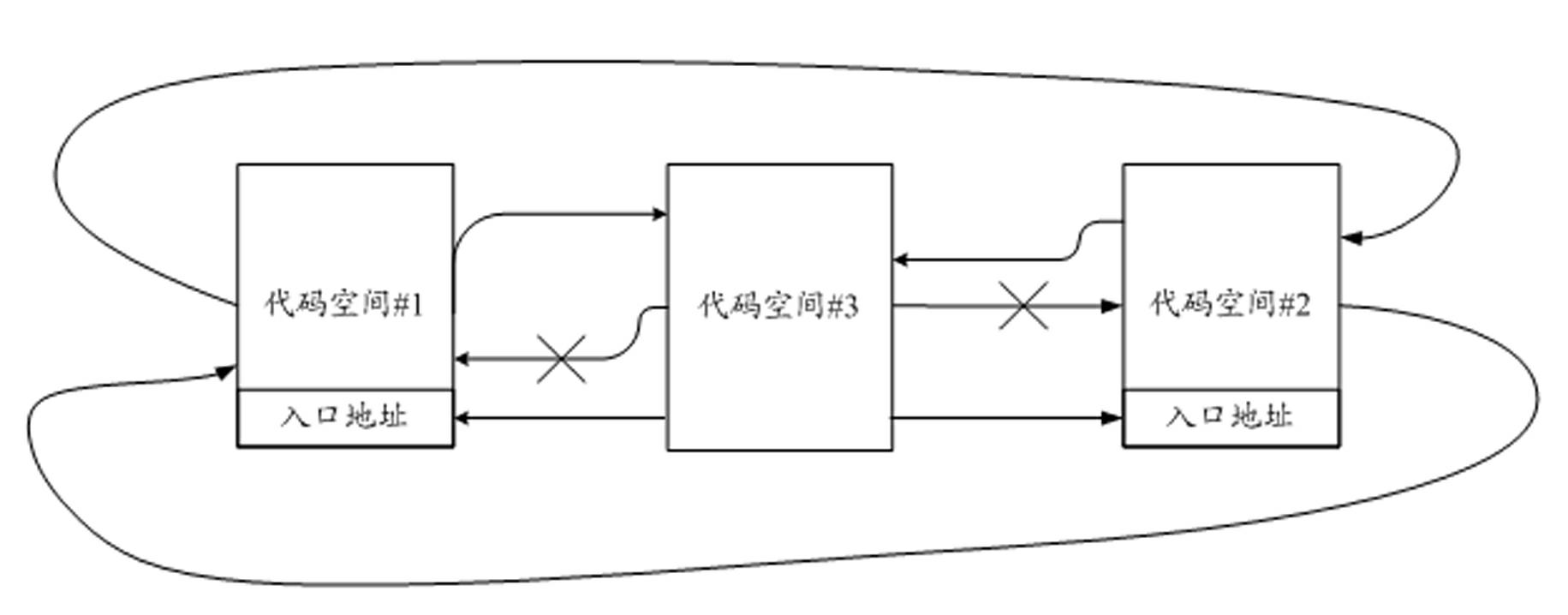
Storage protecting controller and method for improving safety of SOC (system on chip)
ActiveCN102592083AImprove resistance to attackImprove securityUnauthorized memory use protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionCode spaceSpace partitioning
The invention discloses a storage protecting controller and a method for improving safety of an SOC (system on chip). The method includes the steps: dividing a program code space of a processor into a plurality of code spaces, and setting an entry address corresponding to each code space; dividing a storage space into a plurality of storage protecting areas, individually setting access authority attributes of the processor to the storage protecting areas when each code space executes program codes; judging whether a program pointer of the processor skips or not and whether skip is abnormal or not, and generating skip abnormal indication if the skip is abnormal; and monitoring whether access of a current bus to the storage space is abnormal or not, and stopping access of the bus if access of the current bus to the storage space is abnormal, so that the program pointer of the processor is prevented from skipping from one code space to another code space to execute a program, and abnormal access to the storage protecting areas is prevented. The storage protecting controller can effectively improve program code running safety, and can be widely applied to SOC chips of various types.
Owner:SHENZHEN STATE MICRO TECH CO LTD
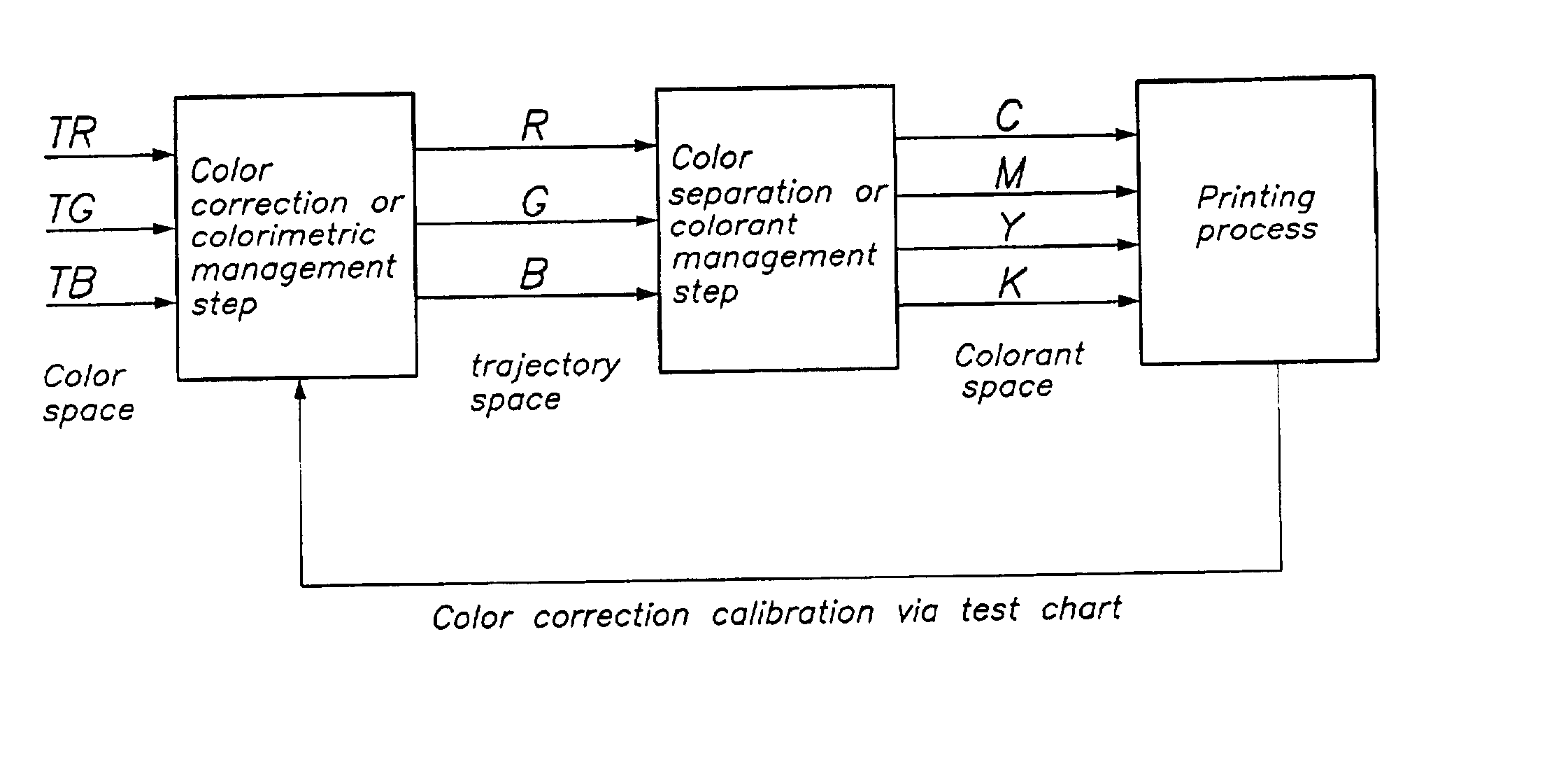
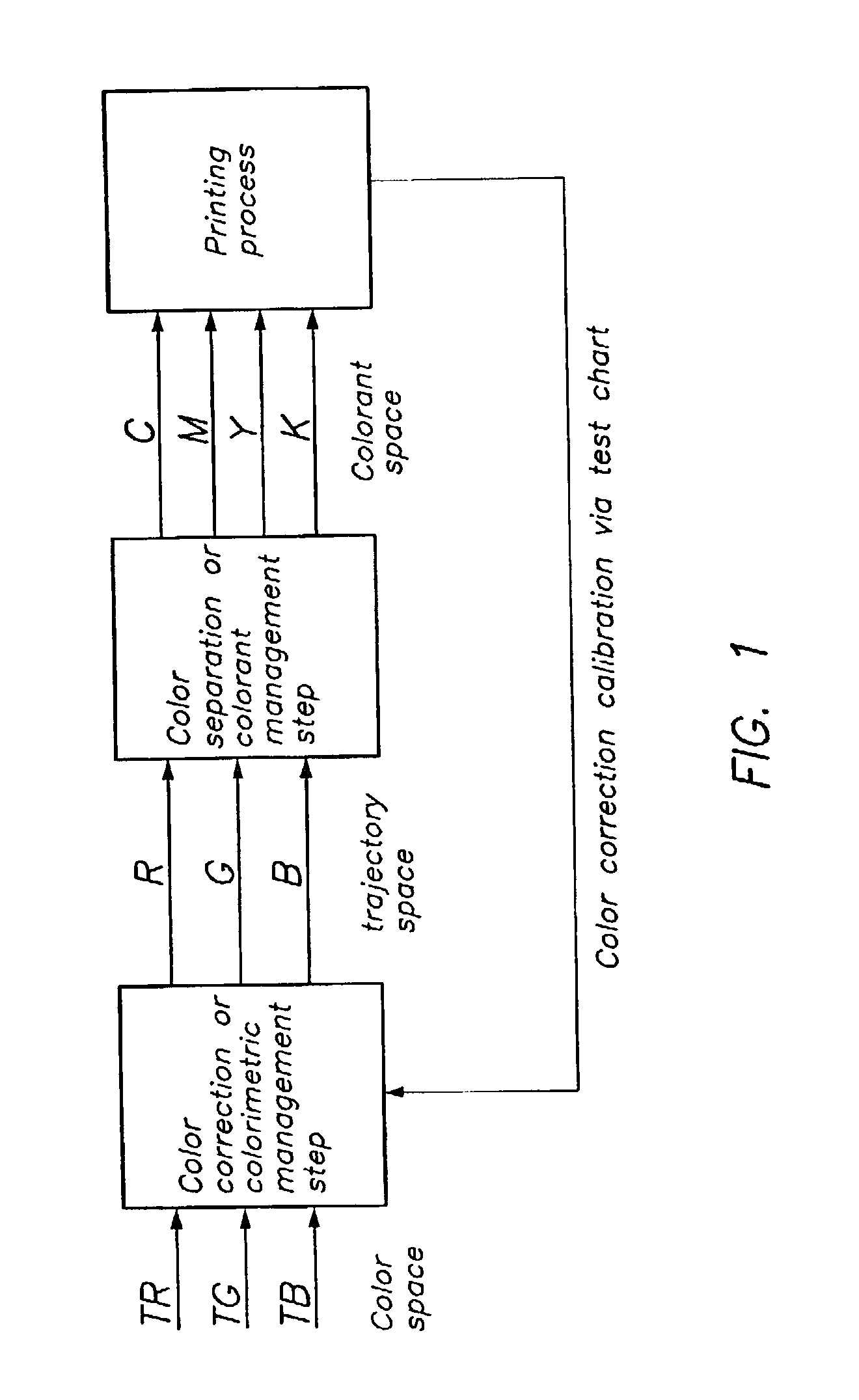
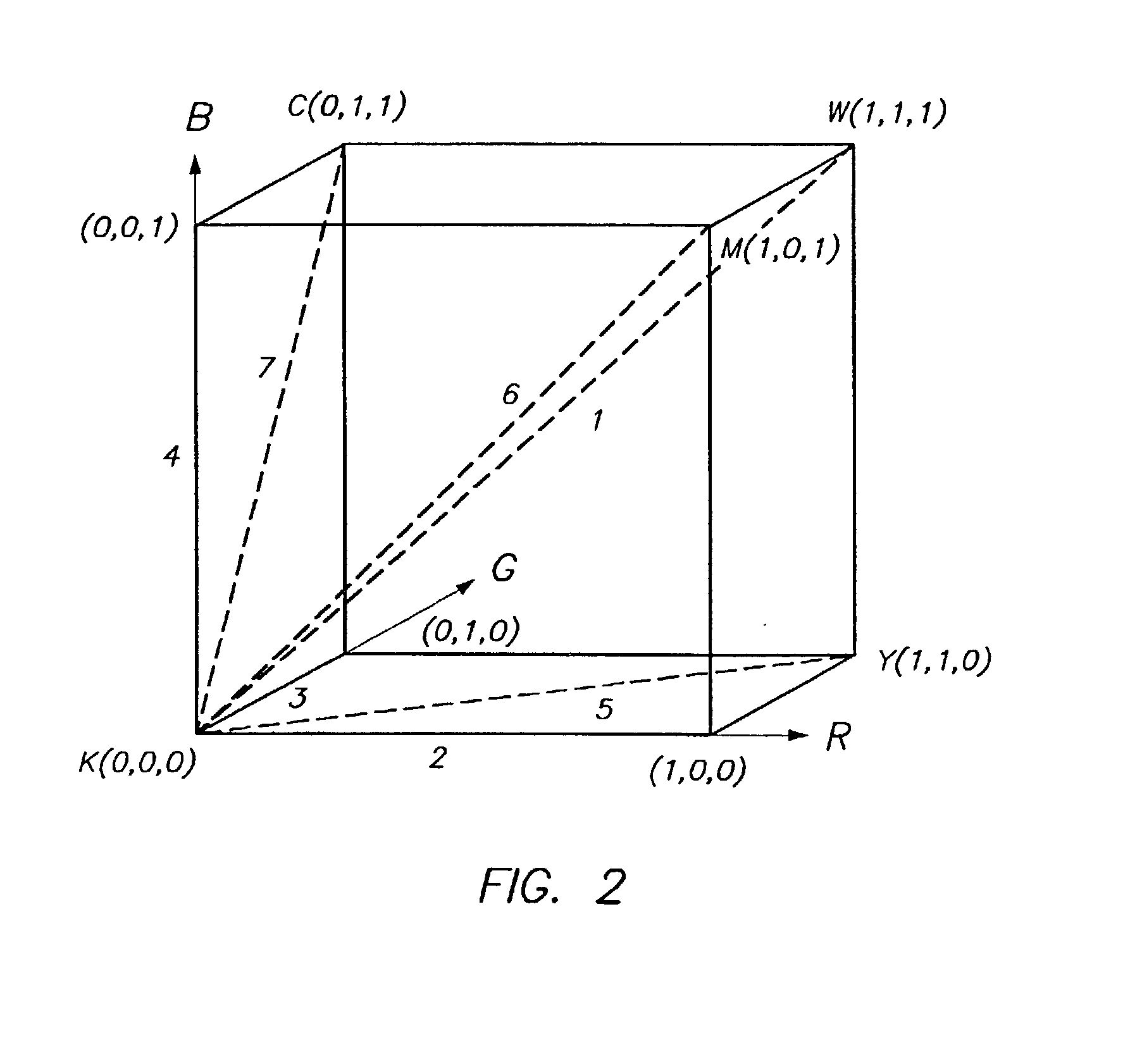
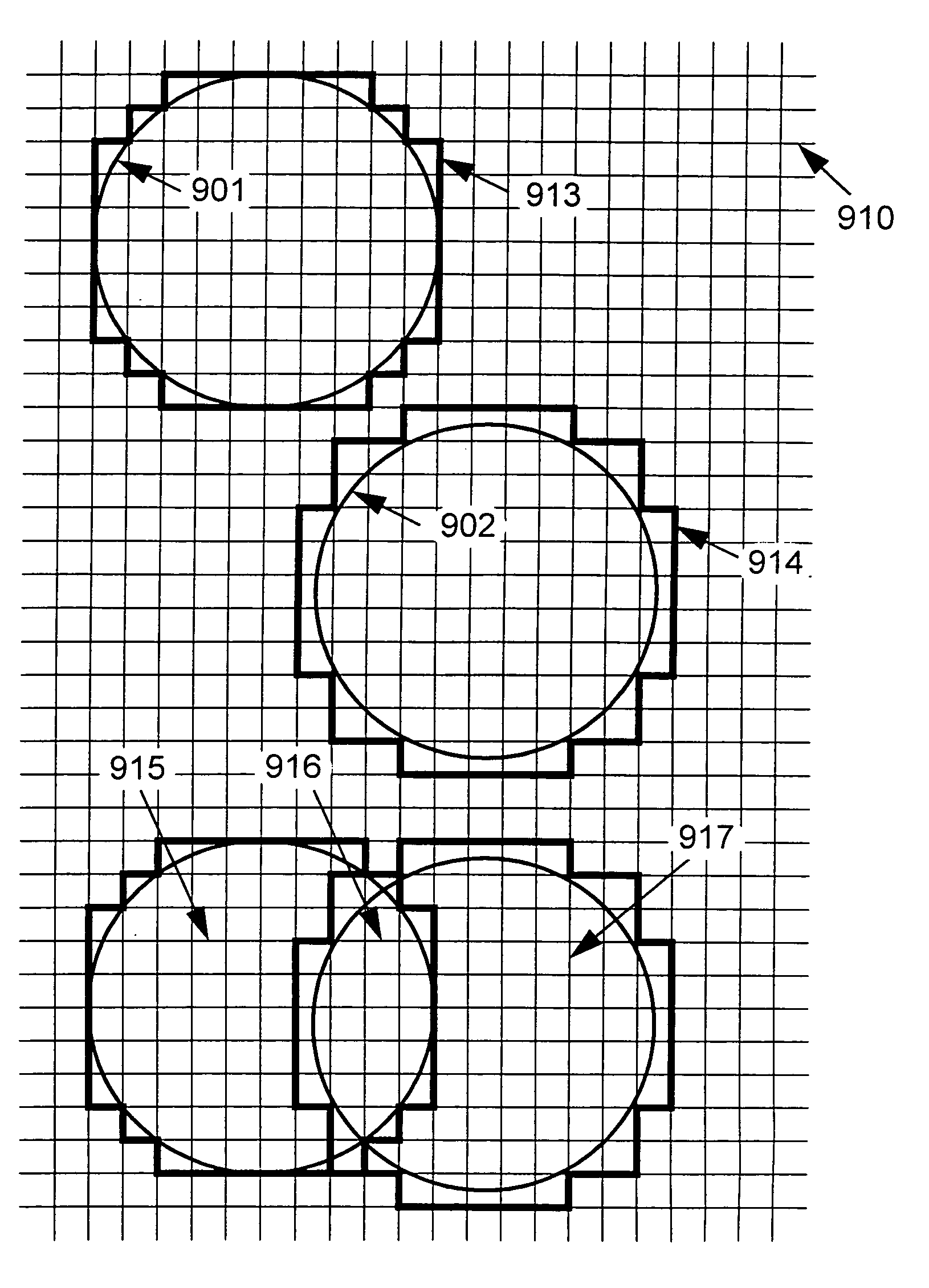
Colour separation method
InactiveUS20030169438A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionColor correction
Owner:AGFA NV
Region based image compositing
InactiveUS6985161B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsEditing/combining figures or textGraphicsSpace partitioning
A method of creating an image is disclosed. The image is formed by rendering and compositing at least a plurality of graphical objects whereby each of the objects has a predetermined outline. The method comprises the following steps. Firstly, dividing a space in which the outlines are defined into a plurality of regions whereby each of the regions is defined by at least one region outline. The region outline substantially follows at least one of the predetermined outlines or parts thereof and is substantially formed by segments of a virtual grid encompassing the space. Secondly, manipulating the regions to determine a plurality of further regions whereby each of the further regions has a corresponding compositing expression. Fourthly, classifying the further regions according to at least one attribute of the graphical objects within the further regions. Fifthly, modifying each of the corresponding compositing expressions according to a classification of each of the further regions to form an augmented compositing expression for each of the further regions. Finally, compositing the image using each of the augmented compositing expression.
Owner:CANON KK
Transformation-based method for indexing high-dimensional data for nearest neighbour queries
InactiveUS6834278B2Easy to deployQuick searchData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData spaceHigh dimensional
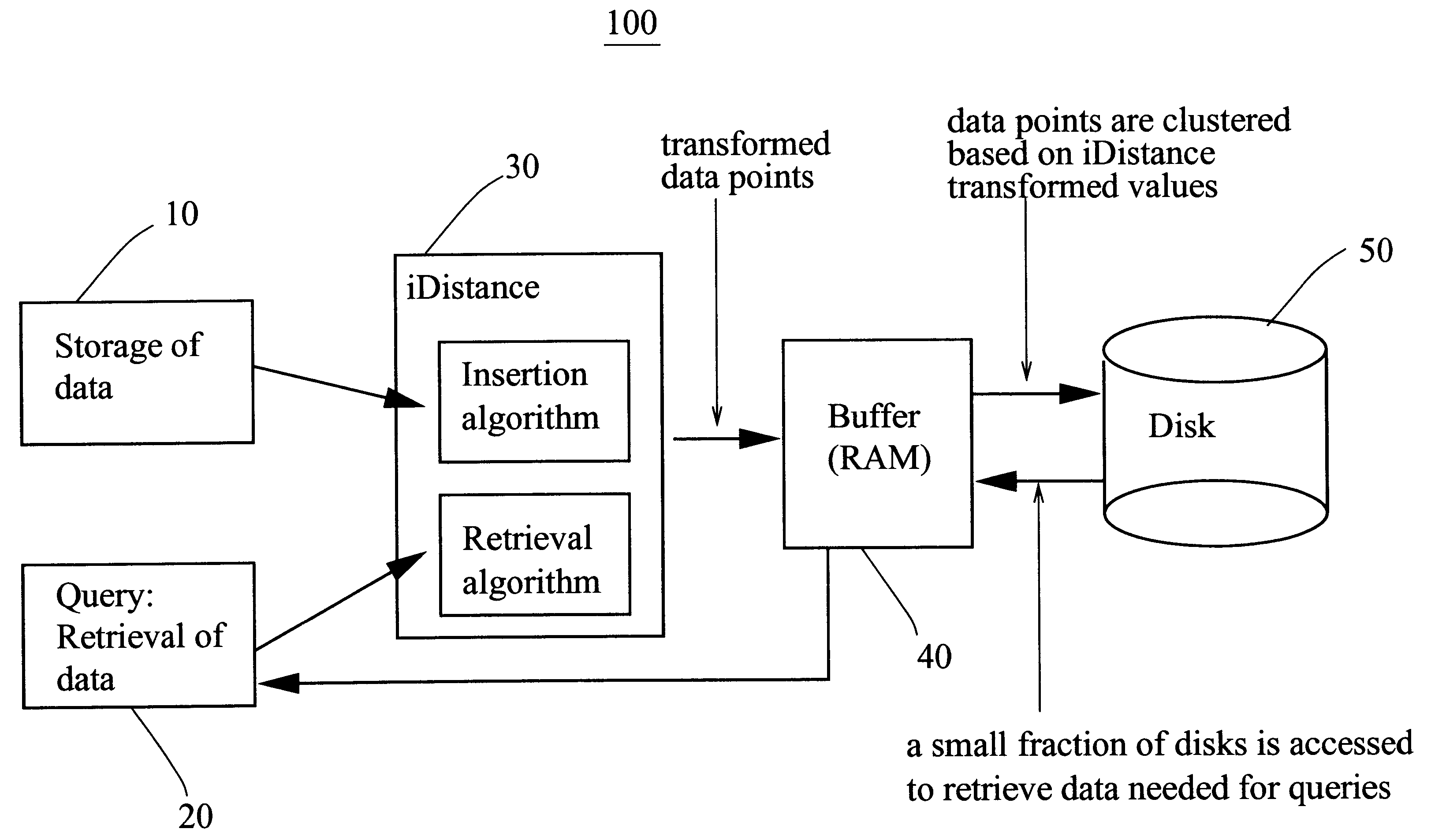
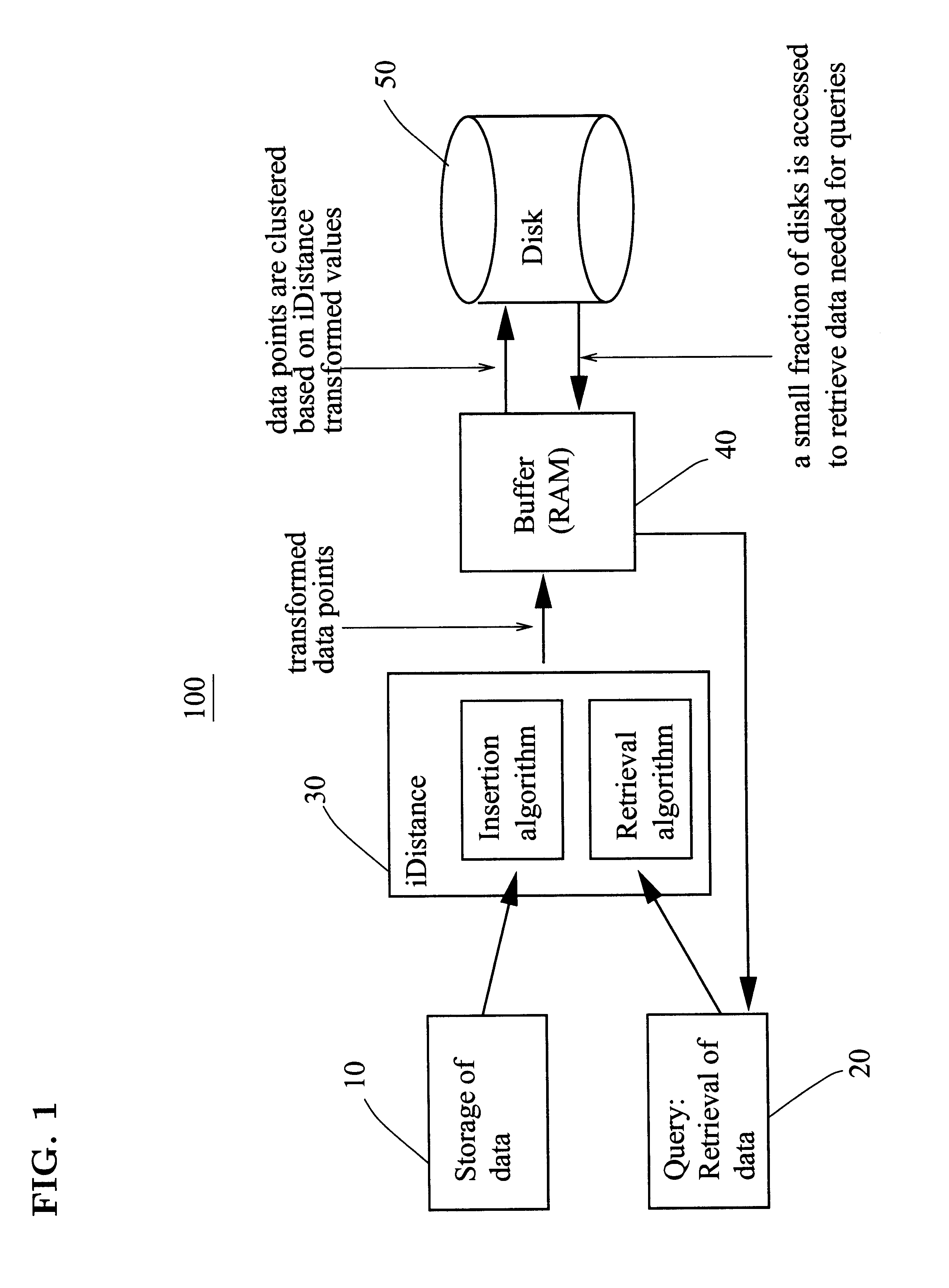
We disclose a transformation-based method for indexing high-dimensional data to support similarity search. The method, iDistance, partitions the data into clusters either based on some clustering strategies or simple data space partitioning strategies. The data in each cluster can be described based on their similarity with respect to a reference point, and hence they can be transformed into a single dimensional space based on such relative similarity. This allows us to index the data points using a B<+>-tree structure and perform similarity search using range search strategy. As such, the method is well suited for integration into existing DBMSs. We also study two data partitioning strategies, and several methods on selection of reference points. We conducted extensive experiments to evaluate iDistance, and our results demonstrate its effectiveness.
Owner:THOTHE TECH PRIVATE
Method for dynamically grouping limited range physical entities in a topological space
InactiveUS6574633B1Geometric CADApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingPhysical entitySpace partitioning
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
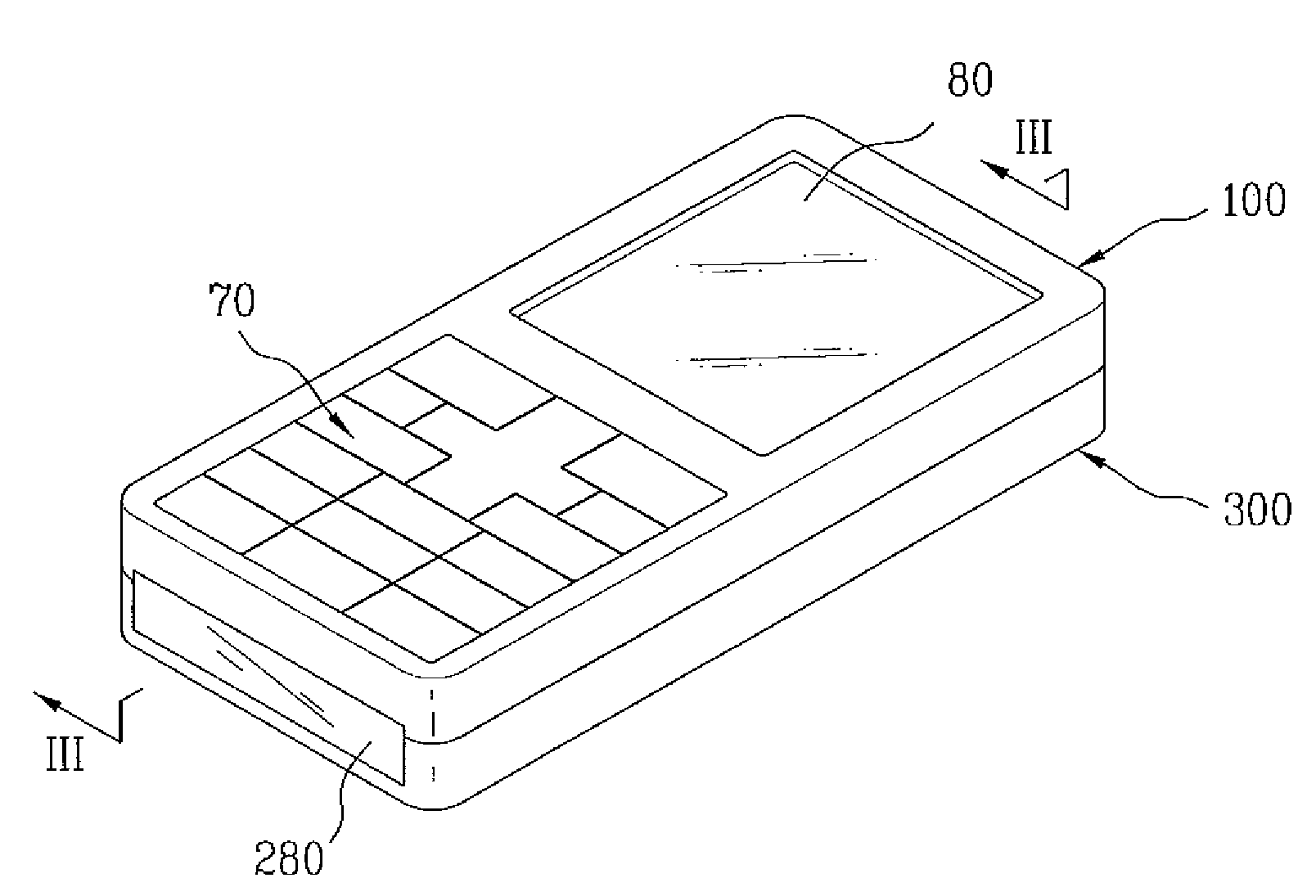
Mobile phone
ActiveUS20080015000A1Avoid enteringSufficient waterproof functionTransmissionTelephone set constructionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A mobile phone is provided. The mobile phone includes a first case, a frame defining a space for elements of the mobile phone, the frame together with the first case dividing the space into a plurality of chambers, and a seal interposed between the frame and the first case for independently sealing more than one of the plurality of chambers.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Three dimension mode compression coding/decoding method based on octree
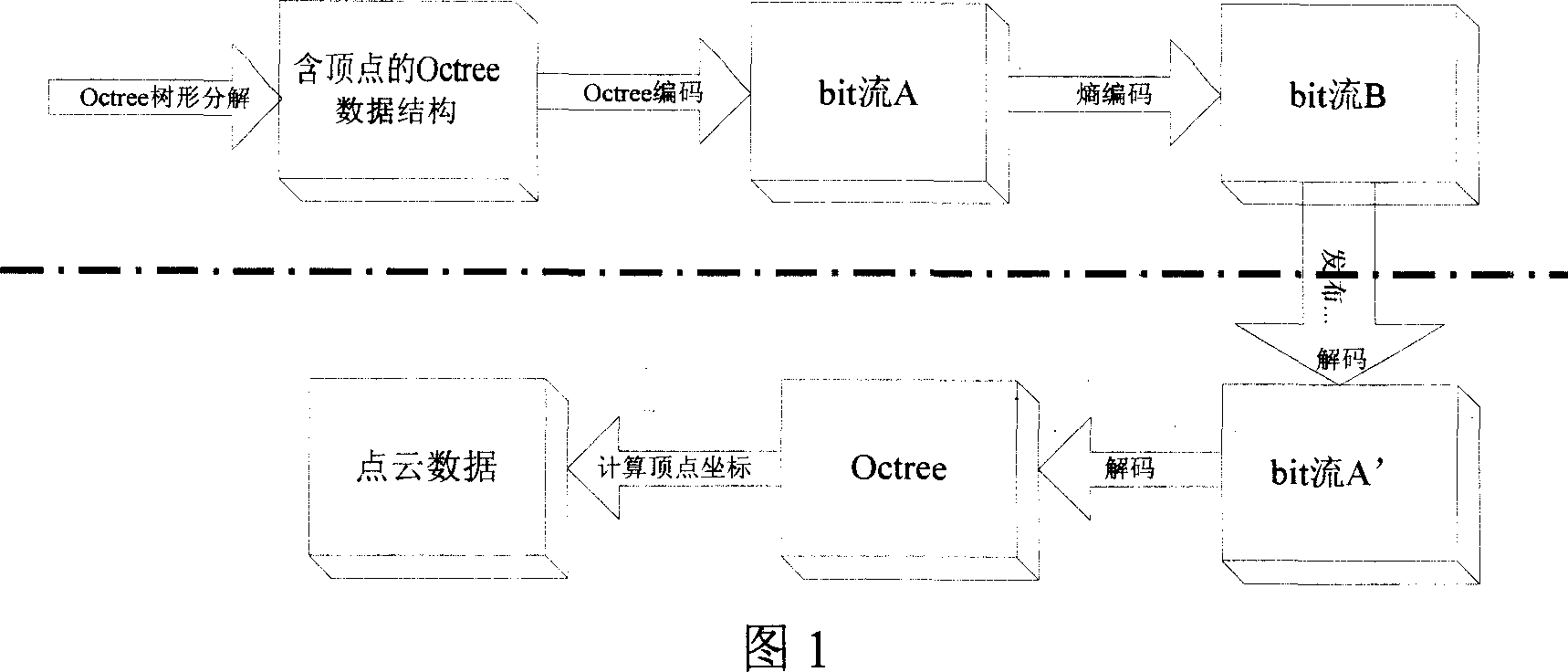
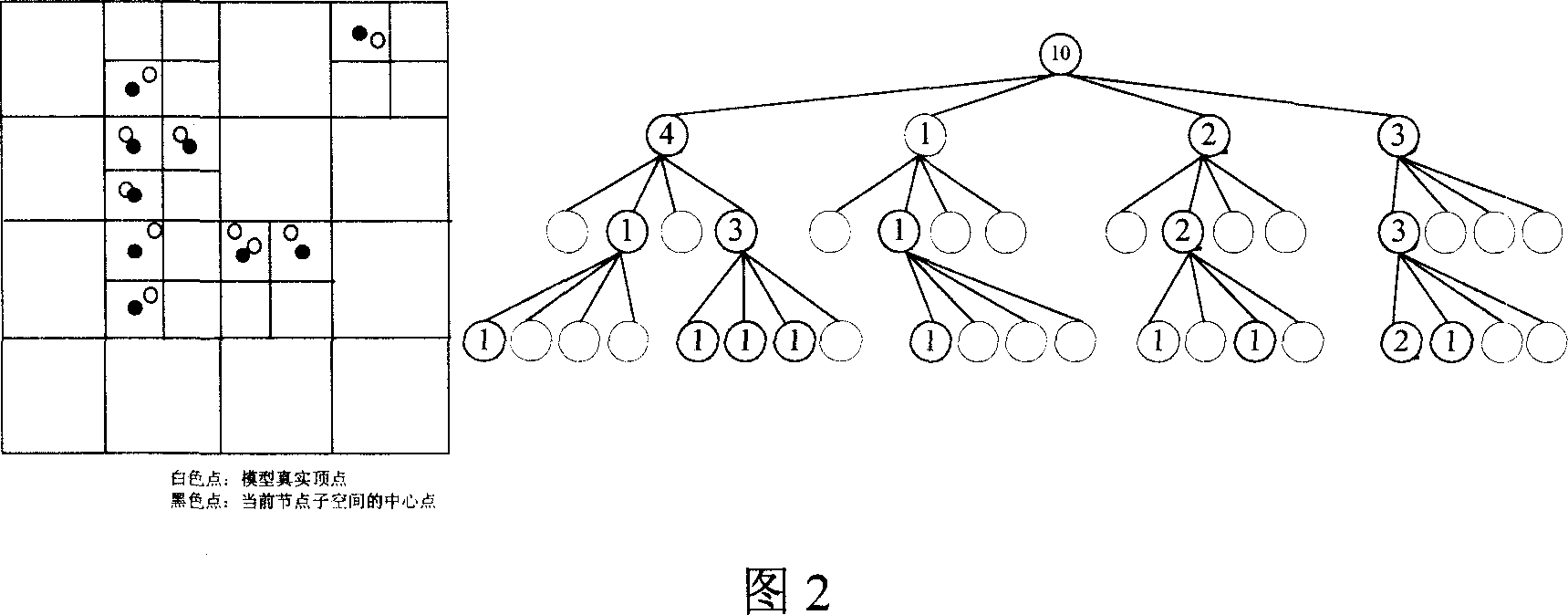
InactiveCN1946180AShort response timeFine-grained controlImage codingTelevision systemsStatistical analysisTheoretical computer science
This invention relates to a compression code / decode method for three-dimension models based on Octree, which redivides the Octree space of the peak information of a three-dimension lattice model to calculate and analyze different kinds of nodes in them to find out one or several with the maximum number of total nodes and carries out less bit coding, re-arranging the topological information and attribute information and code based on the transmission sequence of geometrical information separately and sets separate ascending files to control transmission and display of geometrical information and the synchronous mapping of the topological and attribute information.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Controlling the reactive caching of wildcard rules for packet processing, such as flow processing in software-defined networks
ActiveUS20160050148A1Reduces cache missReduces cache missesError preventionTransmission systemsExact matchTraffic capacity
Software-Defined Networking (“SDN”) enables flexible flow control by caching policy rules at OpenFlow switches. Compared with exact-match rule caching, wildcard rule caching can better preserve the flow table space at switches. However, one of the challenges for wildcard rule caching is the dependency between rules, which is generated by caching wildcard rules overlapped in field space with different priorities. Failure to handle the rule dependency may lead to wrong matching decisions for newly arrived flows, or may introduce high storage overhead in flow table memory. A wildcard rule caching system, which may be used for SDN partitions the field space into logical structures called buckets, and caches buckets along with all the associated wildcard rules. Doing so resolves rule dependency while using control network bandwidth efficiently. Further, controller processing load and flow setup latency are reduced.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Rapid network packet classification method based on network traffic statistic information
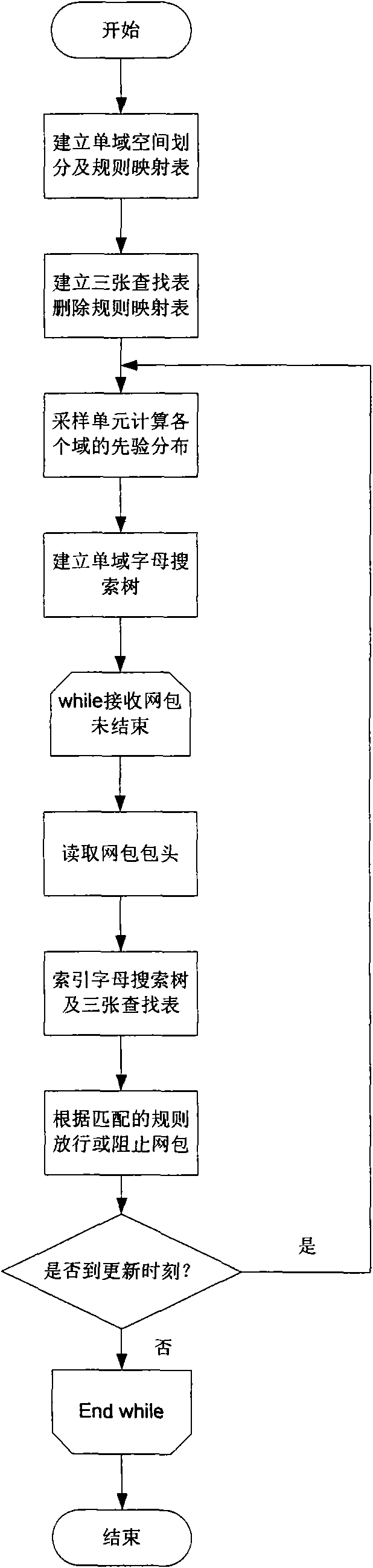
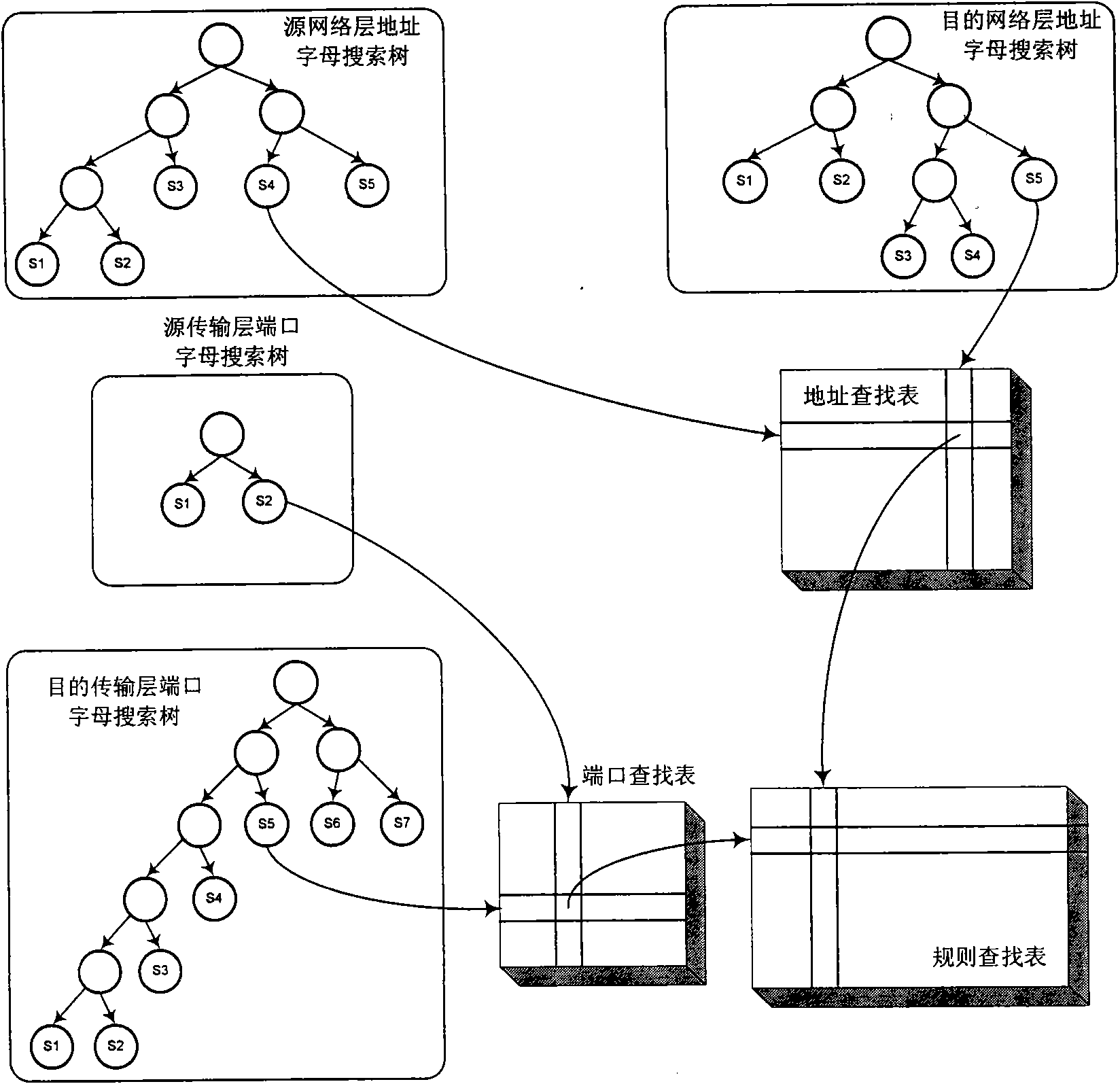
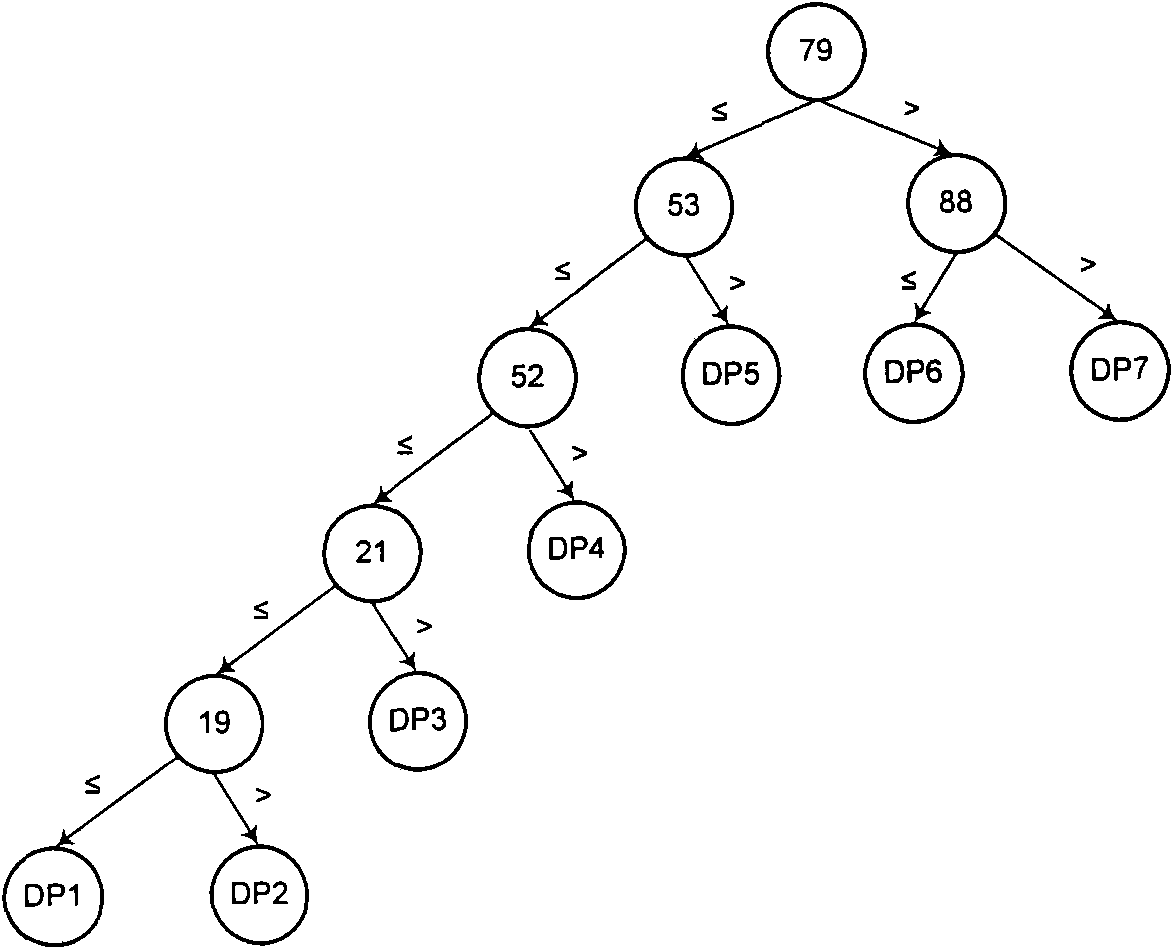
ActiveCN101594303AOptimize data structureAvoid the pitfalls caused by performance dipsData switching networksTraffic capacityFiltration
The invention relates to a rapid network packet classification method based on network traffic statistic information, which belongs to the technical field of filtration and monitoring of network traffic. The method comprises the steps of: determining the space partition of various domains of a header and a rule mapping table thereof according to a classification rule set, and establishing an address lookup table, a port lookup table and a rule lookup table; recording the times that the header of a network packet appears in the space partition of the domains and calculating prior distribution; establishing a letter search tree of the domains according to the prior distribution; performing continuous matching on the received header of the network packet according to the letter search tree and the lookup tables; and re-calculating the prior distribution and updating the letter search tree at update time, and continuing to match the received network traffic. The method uses the classification rule set and heuristic information of the network traffic from two different levels of network packet classification, strengthens the adaptability of the classification method, and improves average classification efficiency. The method has quick lookup speed and strong adaptability, can be realized on a plurality of platforms, and is applicable to the filtration and monitoring of high-performance network traffic.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
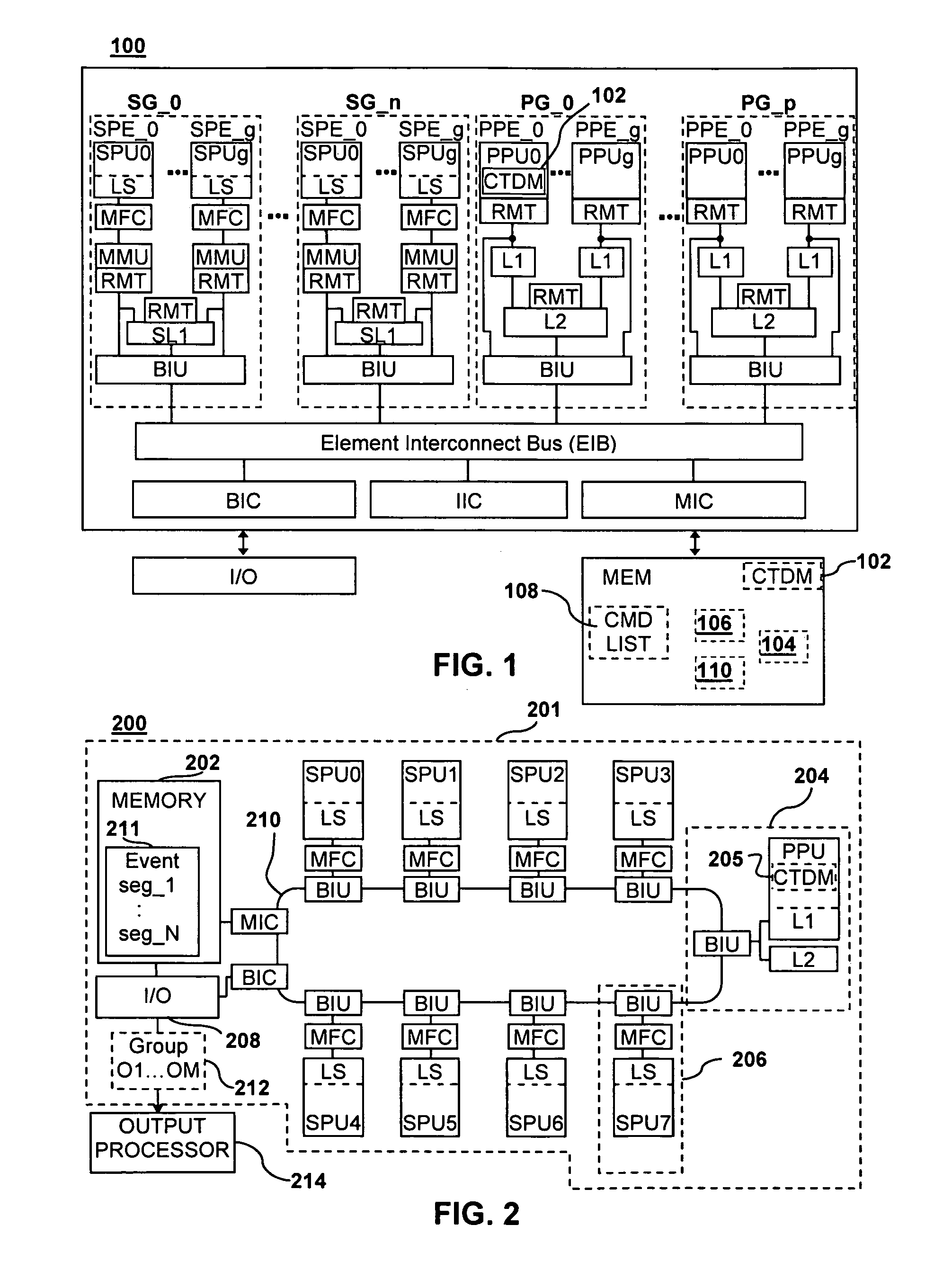
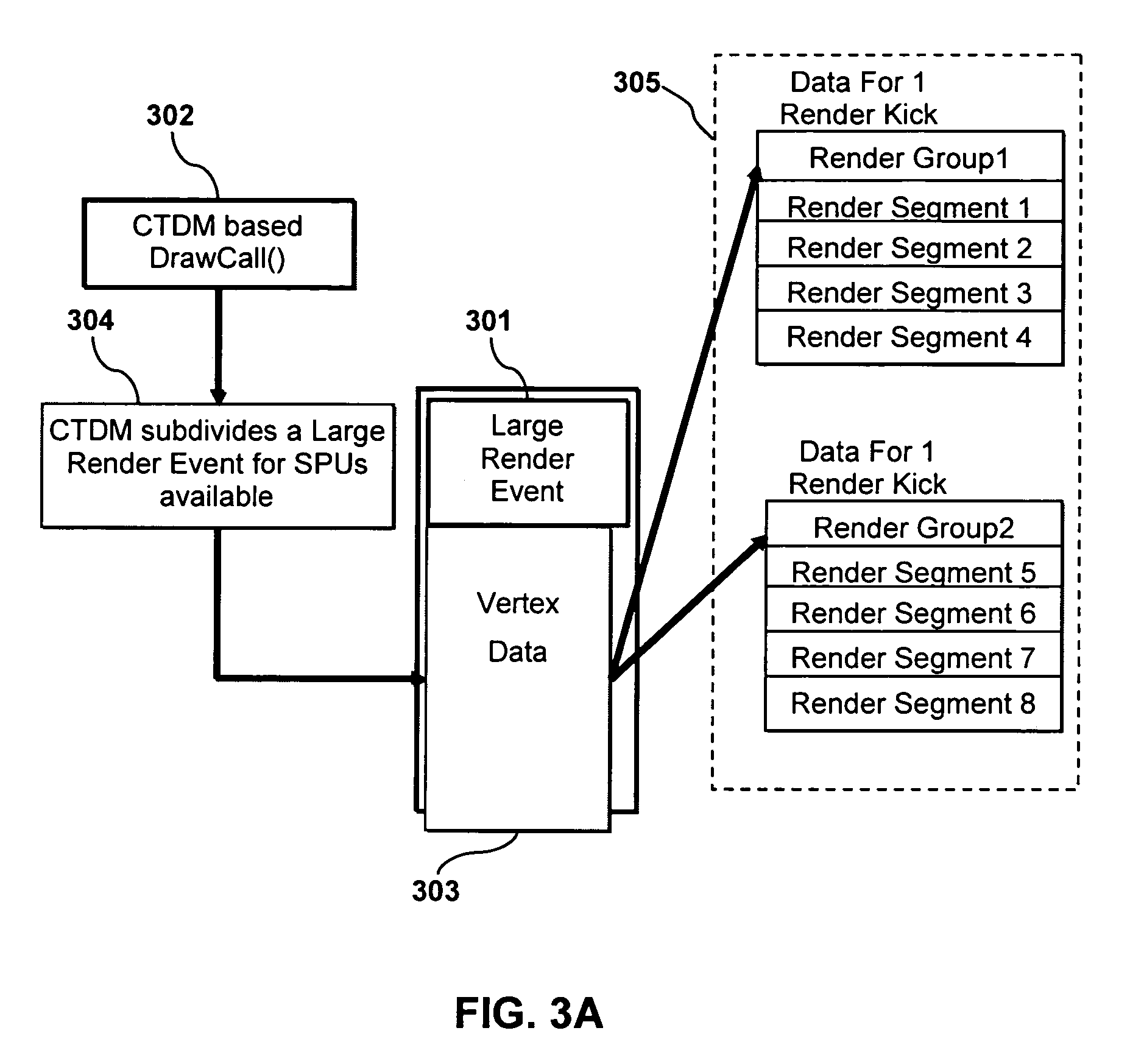
Cell processor task and data management
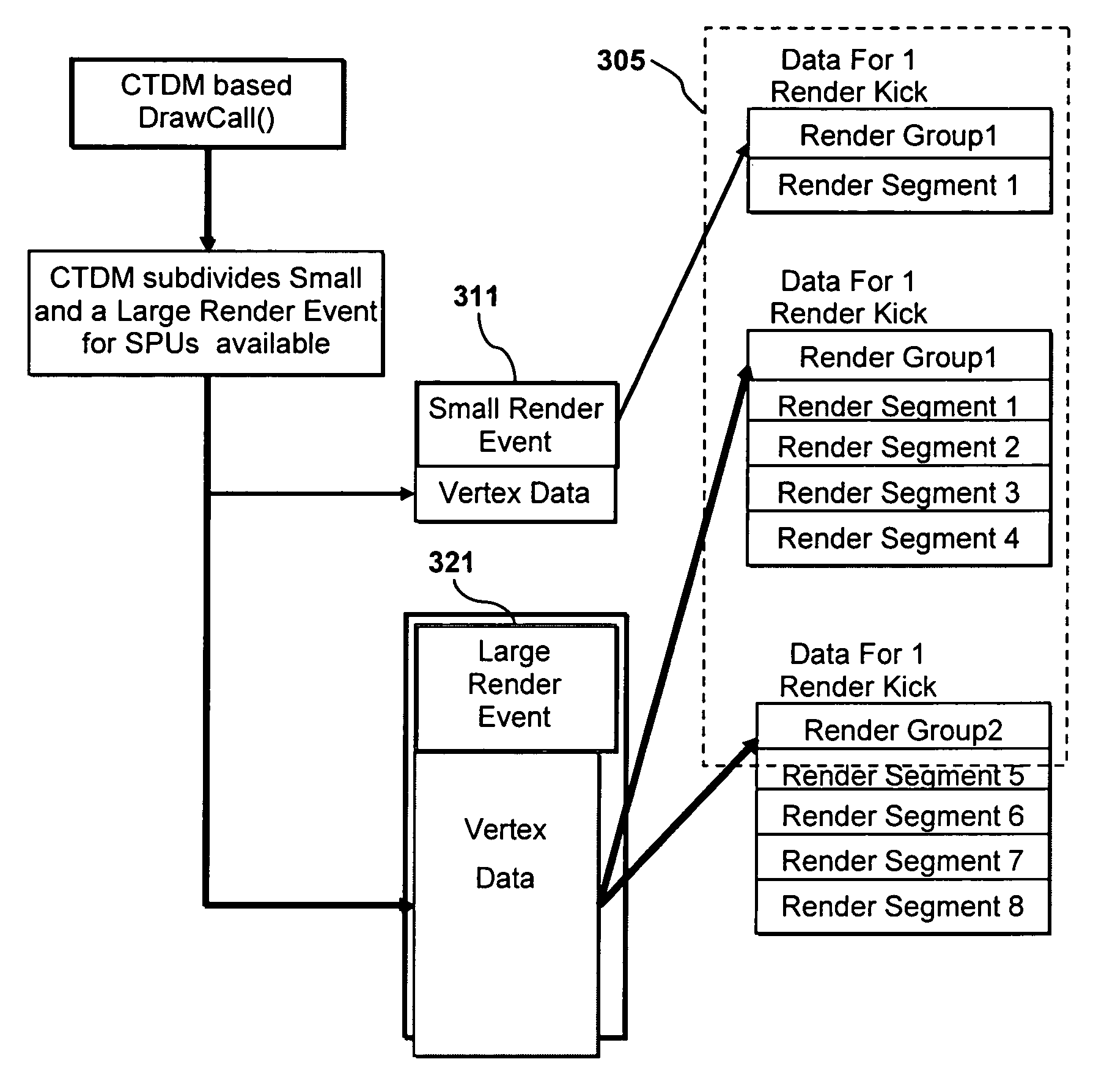
ActiveUS7522168B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationImage memory managementParallel computingData management
Cell processor task and data management systems methods and apparatus are disclosed. A cell processor divides an event that event requires more memory space than is available in a local storage of a synergistic processing element (SPE) into two or more segments. Each segment has a segment size that is less than or the same as an amount of memory space available in the local storage. The segments are processed with one or more SPE of the cell processor to produce two or more corresponding outputs.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
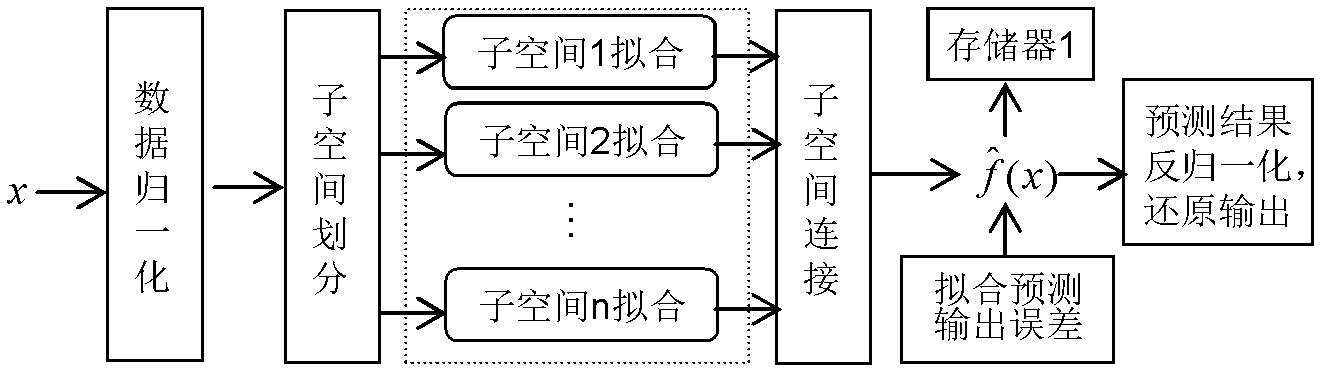
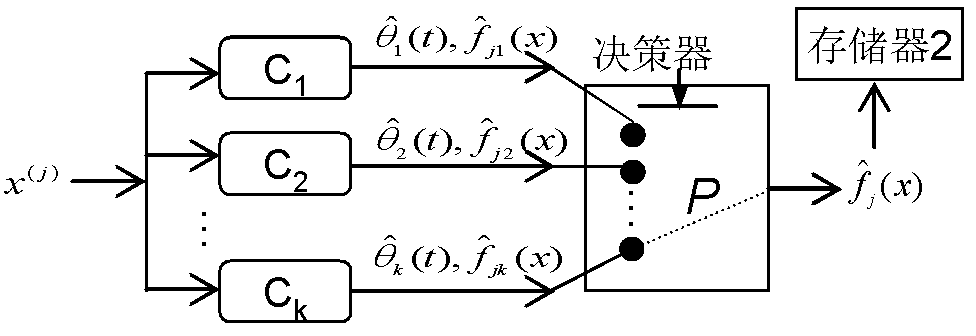
Nonlinear kernelled adaptive prediction method
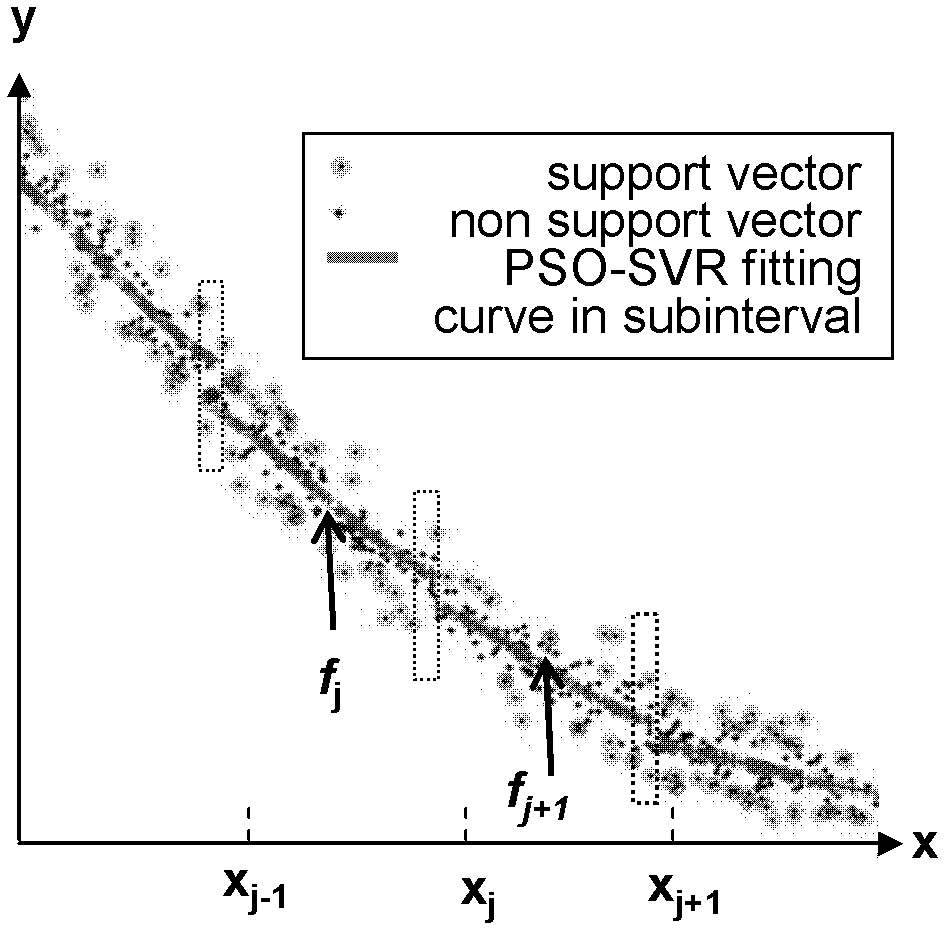
InactiveCN102200759AImprove forecast accuracyGuaranteed to be globally optimalAdaptive controlLocal optimumCharacteristic space
The invention discloses a nonlinear kernelled adaptive prediction method which comprises the following six steps: data preprocessing, subspace subdivision, subspace adaptive fitting control, subspace connection, new sample prediction and prediction output. The method is characterized in that after data is preprocessed, the integral space of the data is subdivided into a plurality of successive subspaces; the optimal kernels and parameters are adaptively selected on each subspace by using an intelligent sliding controller based on particle swarm support vector regression so as to form optimal local fitting hypersurfaces; then the optimal local fitting hypersurfaces are connected by using a three-point Lagrange interpolation method so as to form a final total-space regression prediction function; and finally, new data is predicted and output. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the characteristic space subdivision of data is realized, and the prediction speed for large-scale multi-attribute nonlinear data is improved; and the kernel functions adapting to the data distribution are screened adaptively by using the intelligent sliding controller based on particle swarm support vector regression, thereby optimizing integral parameters, and ensuring the precision and accuracy of fitting prediction.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Dynamic storage method of Flash memory
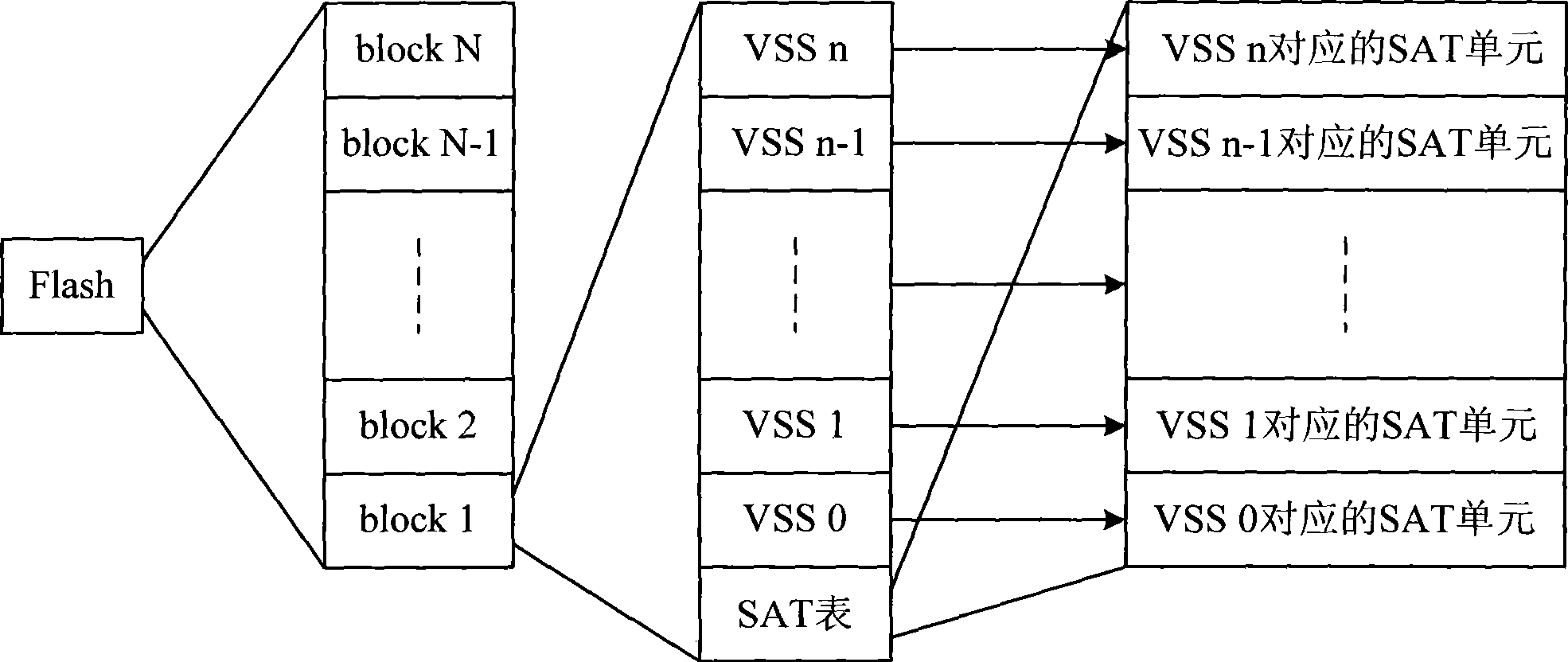
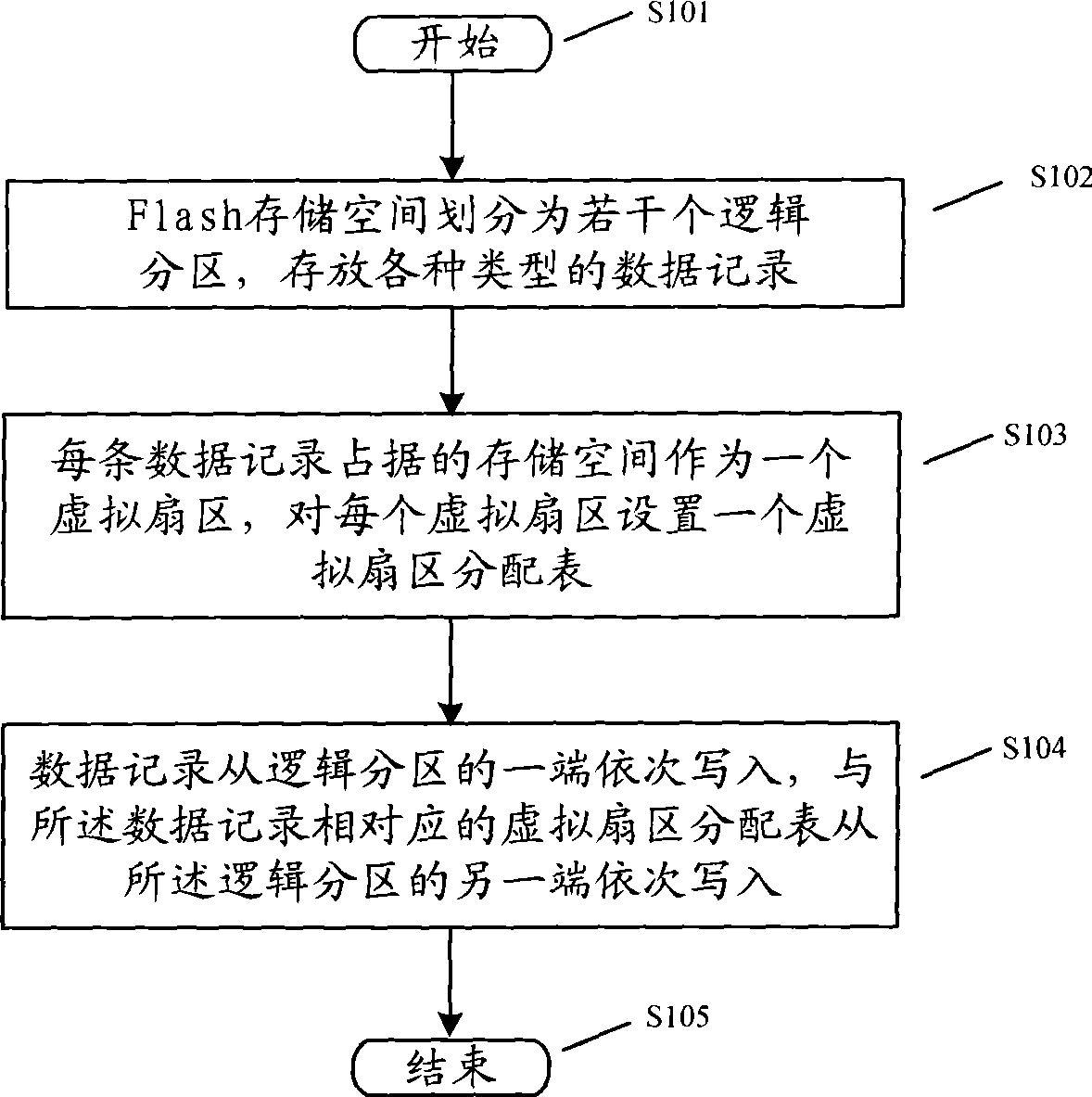
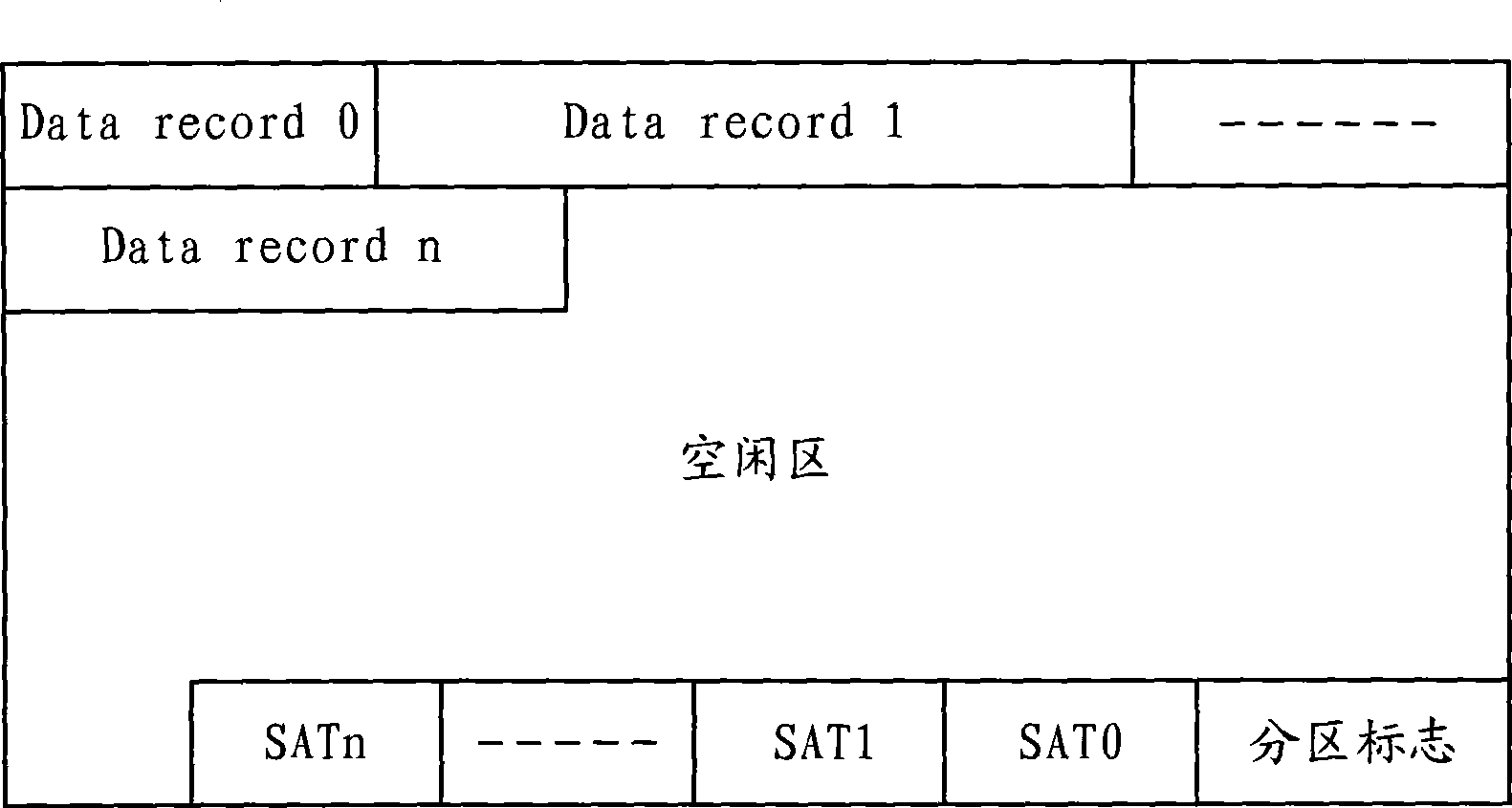
ActiveCN101446921AImprove read and write speedExtend your lifeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRedundant data error correctionDynamic storageData recording
The invention discloses a dynamic storage method of a Flash memory, which comprises the following steps: a. the Flash storage space is divided into a plurality of logical partitions, and the logical partitions can memory at least one type of data record; b. the storage space held by each piece of data record is taken as a virtual sector, and a virtual sector distribution list is arranged for each virtual sector; and c. the data record is read at one terminal of the logical partition in sequence, and the virtual sector distribution list corresponding to the data record is read at the other terminal of the logical partition in sequence; therefore, the dynamic storage method effectively solves the technical problem of low utilization rate of the Flash storage space in the static storage method.
Owner:HISENSE BROADBAND MULTIMEDIA TECH
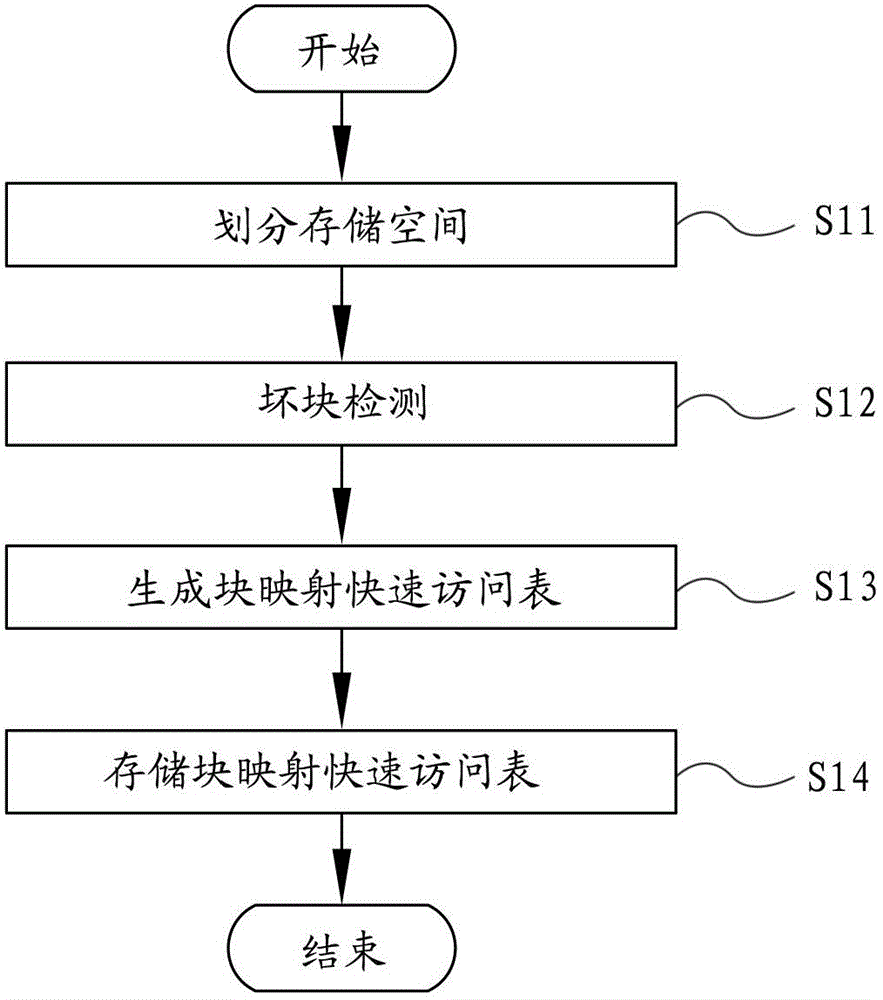
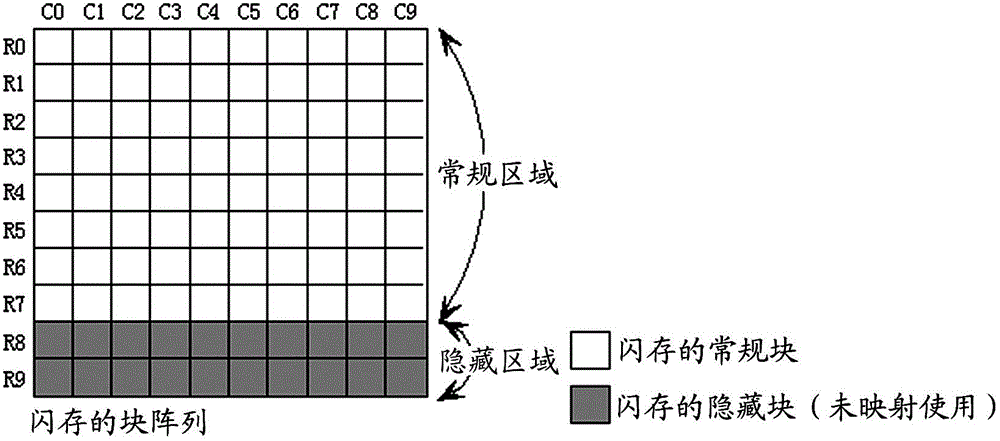
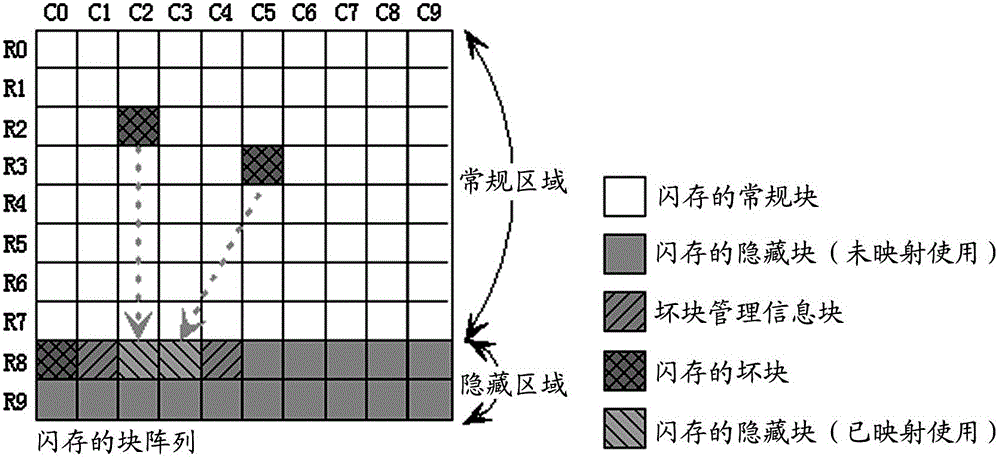
Bad block management method for flash memory
ActiveCN102722443AGuaranteed reliabilityAvoid destructionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationBlock detectionSpace partitioning
The invention provides a bad block management method for a flash memory. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing the storage space of the flash memory into a first area comprising a plurality of blocks and a second area comprising a plurality of blocks; performing bad block detection on the flash memory to acquire information about bad blocks; establishing a mapping relation between the bad blocks in the first area and normal blocks in the second area according to the acquired information about the bad blocks, and generating a block mapping quick access table comprising the information about the established mapping relation; and respectively storing the generated block mapping quick access table into a plurality of bad block management information blocks in the second area, wherein a plurality of bad block management information blocks are any normal blocks which are positioned in the second area and do not have the mapping relation with the bad blocks in the first area.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON CHINA RES & DEV +1
Method and program for generating volume data from boundary representation data
InactiveUS20070057938A1Easy to shapeDesign optimisation/simulationImage data processing detailsComputational scienceBoundary plane
A data input means inputs boundary data of an object to a computer, a data converting means converts the boundary data into a triangle patch having a phase, an associating means divides a space into rectangular parallelepiped cells having boundary planes intersecting perpendicularly and associates the cell with a triangle to be included in the cell, a dividing / arranging means divides a triangle patch having a phase and floating in the space at cell faces and keeps all triangles arranged within and on the boundaries of cells, a ridge line integrating means integrates ridges that do not alter the phase, a cell assigning means assigns each triangle and its vertex to a cell with reference to index data of the vertex, and a labeling means sets an attribute value of each cell.
Owner:RIKEN
Method for simplifying three-dimensional model based on octree space division and culmination deletion
InactiveCN101377857AFor the purpose of simplifyingQuality improvement3D-image rendering3D modellingGraphicsVisualization model
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer graphics processing, and relates to the tridimensional visual model simplification technology. The tridimensional visual model simplification technology uses the method of combining octree and peak abstract of defined new peak weights. Firstly, a model space is divided into a series of leaf node zones through the octree, and all of peaks are dispersed in the zones; subsequently, the peak abstract algorithm with defined new peak weights is adopted for deleting the peaks, thus simplifying a three-dimensional model. By adopting the method of combining the octree and the peak abstract of defined new peak weights provided by the invention, the simplification quality and the simplification speed of the three-dimensional model are effectively improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com