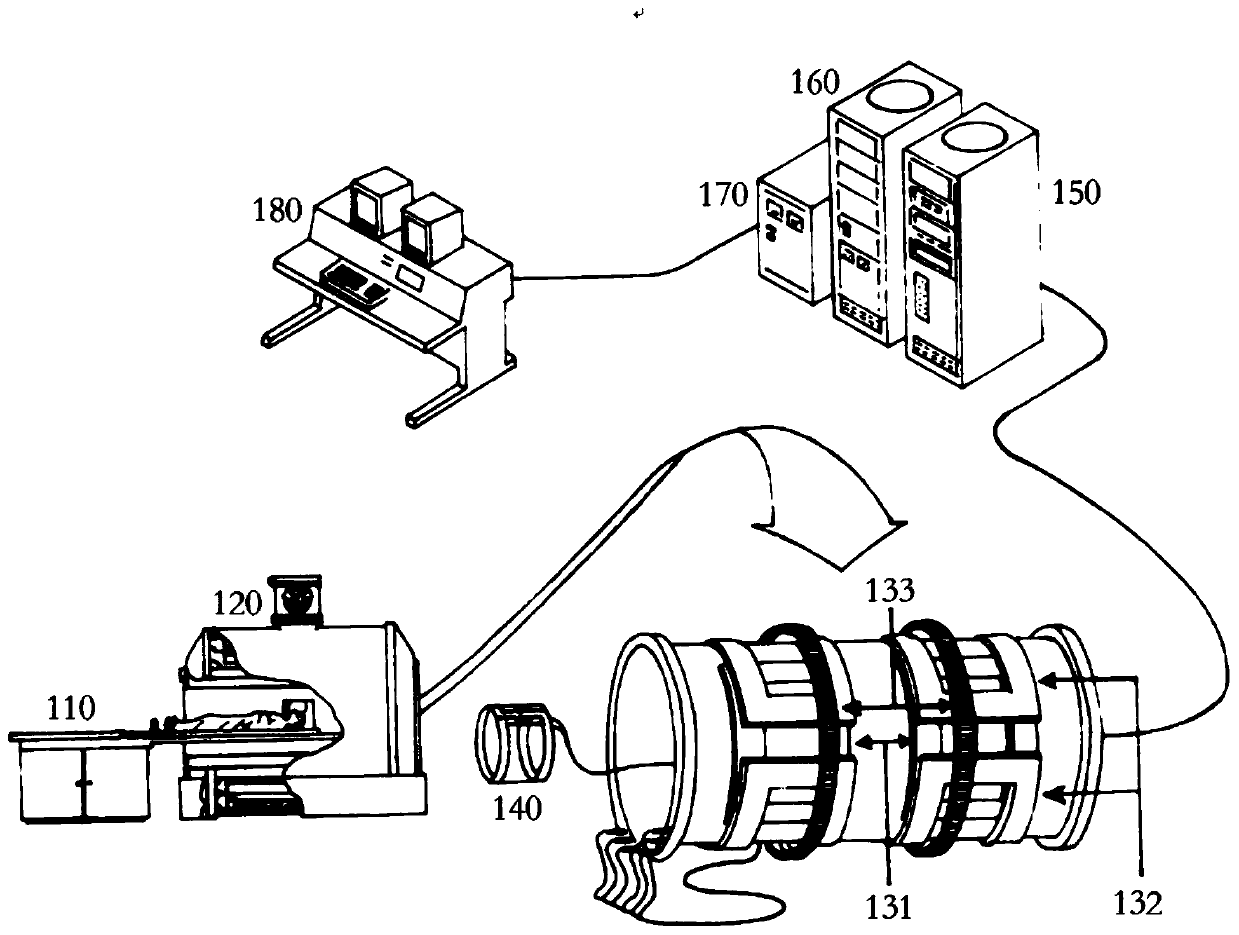
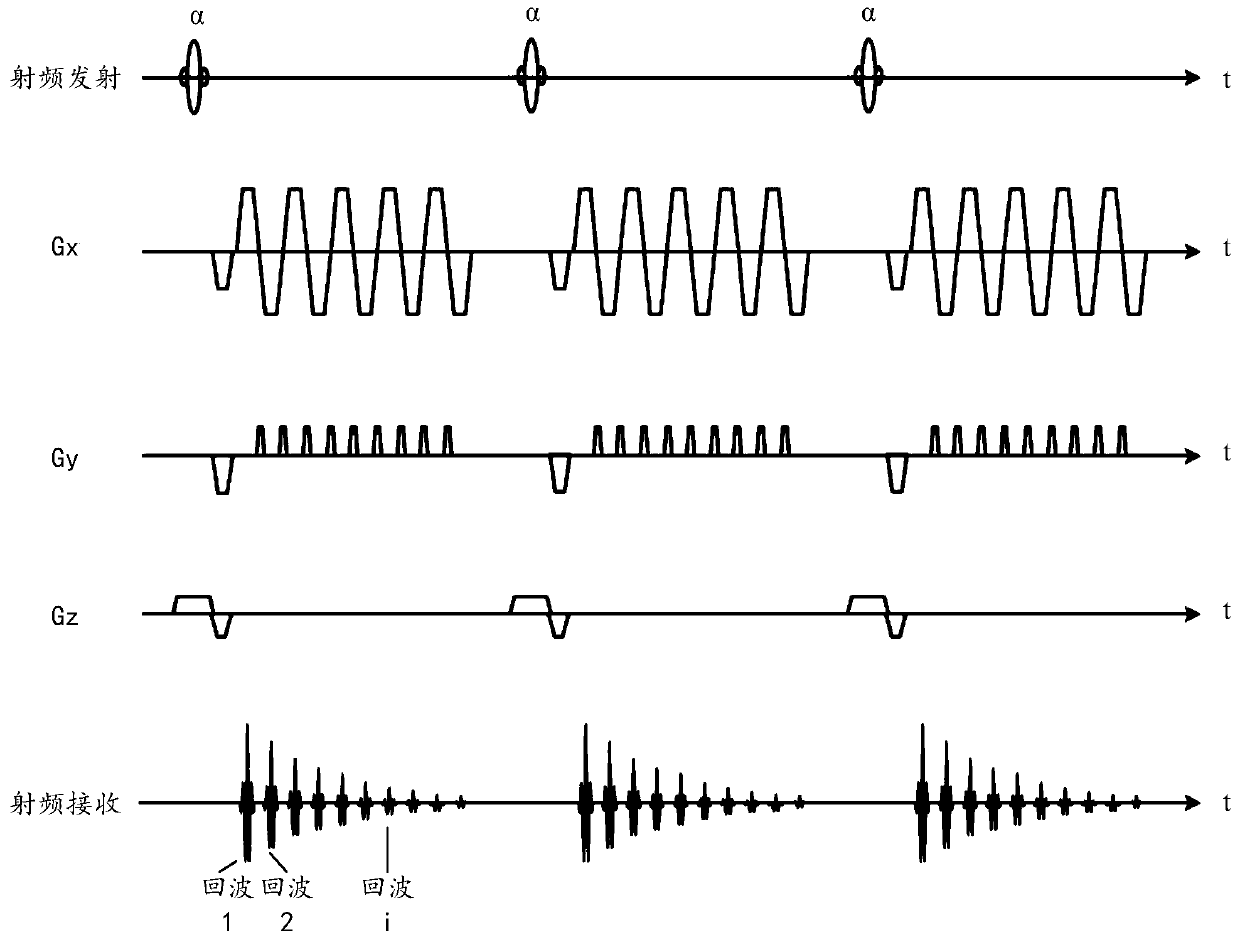
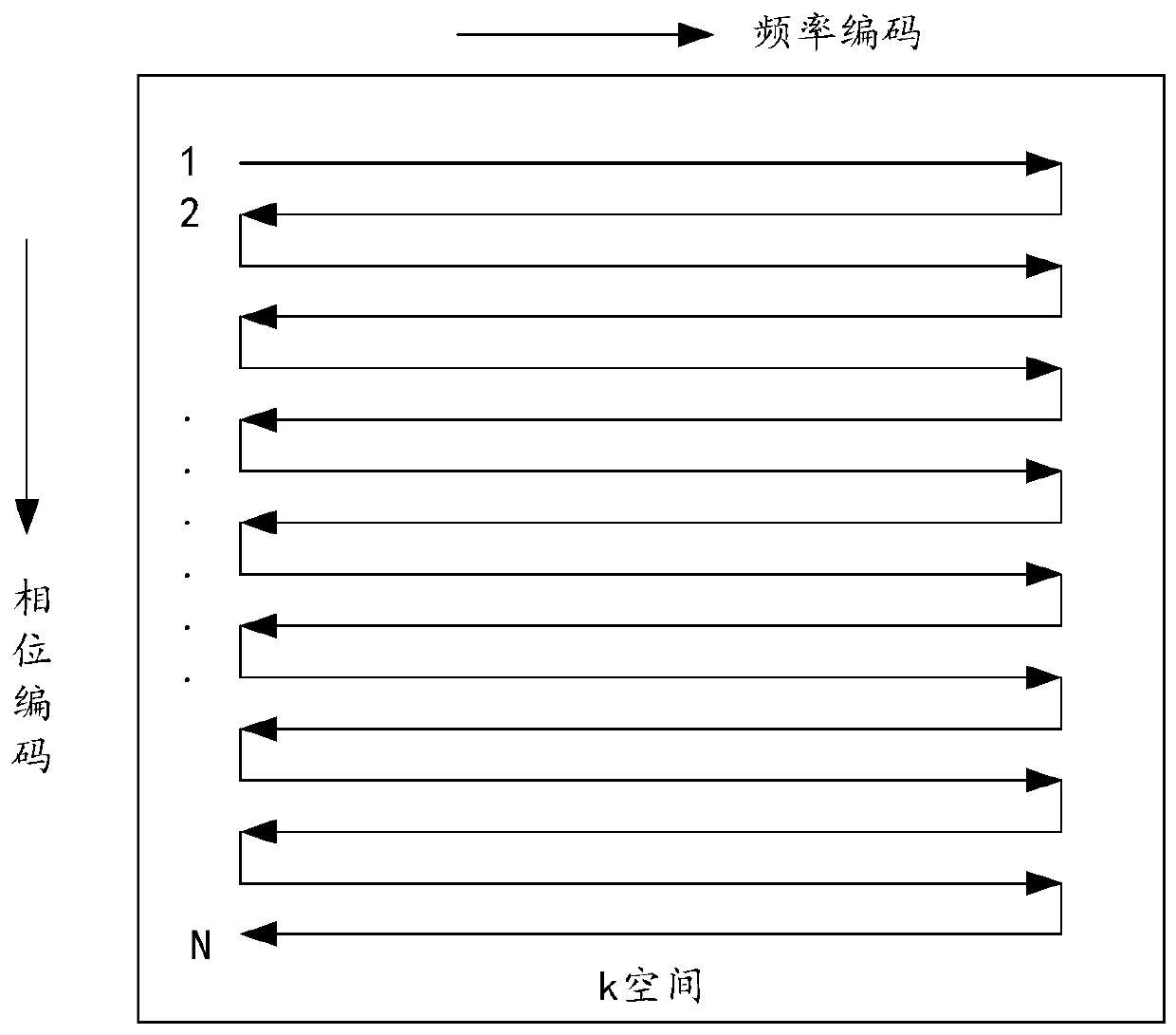
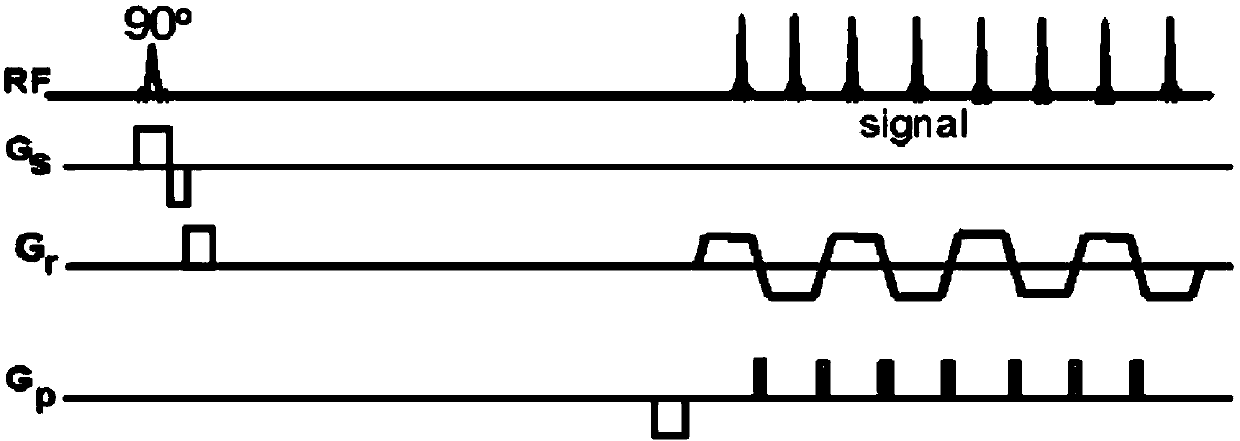
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Echo planar" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
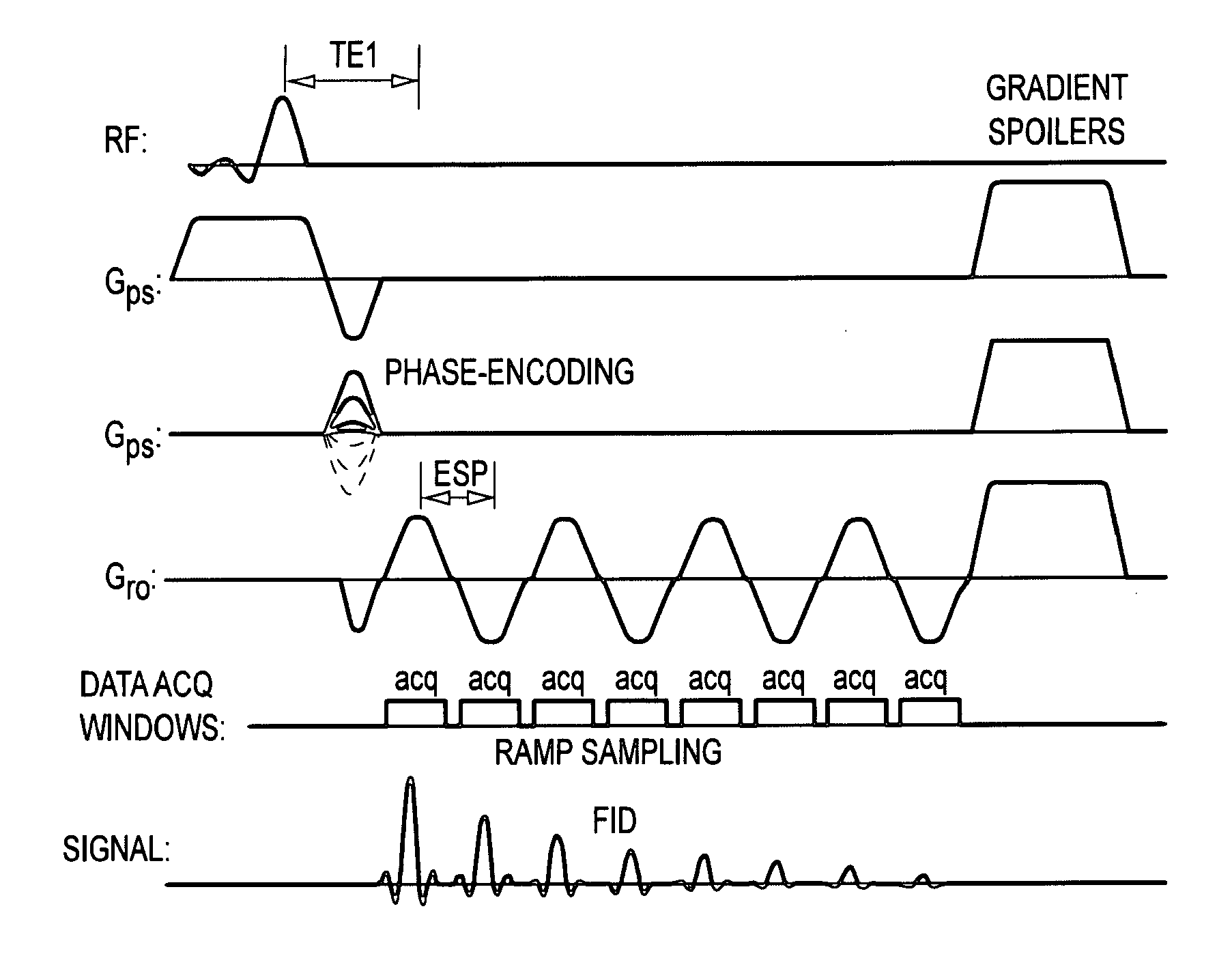
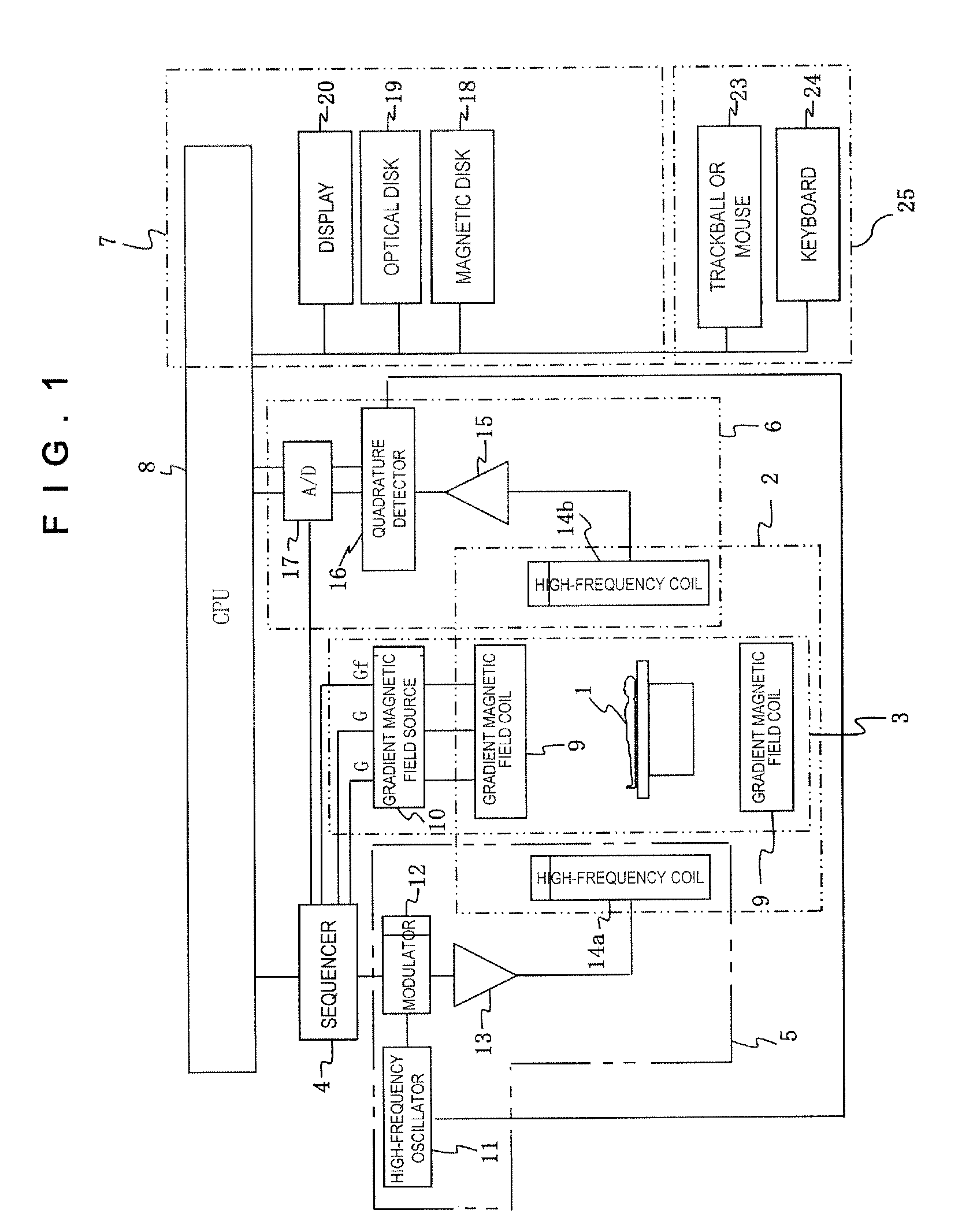
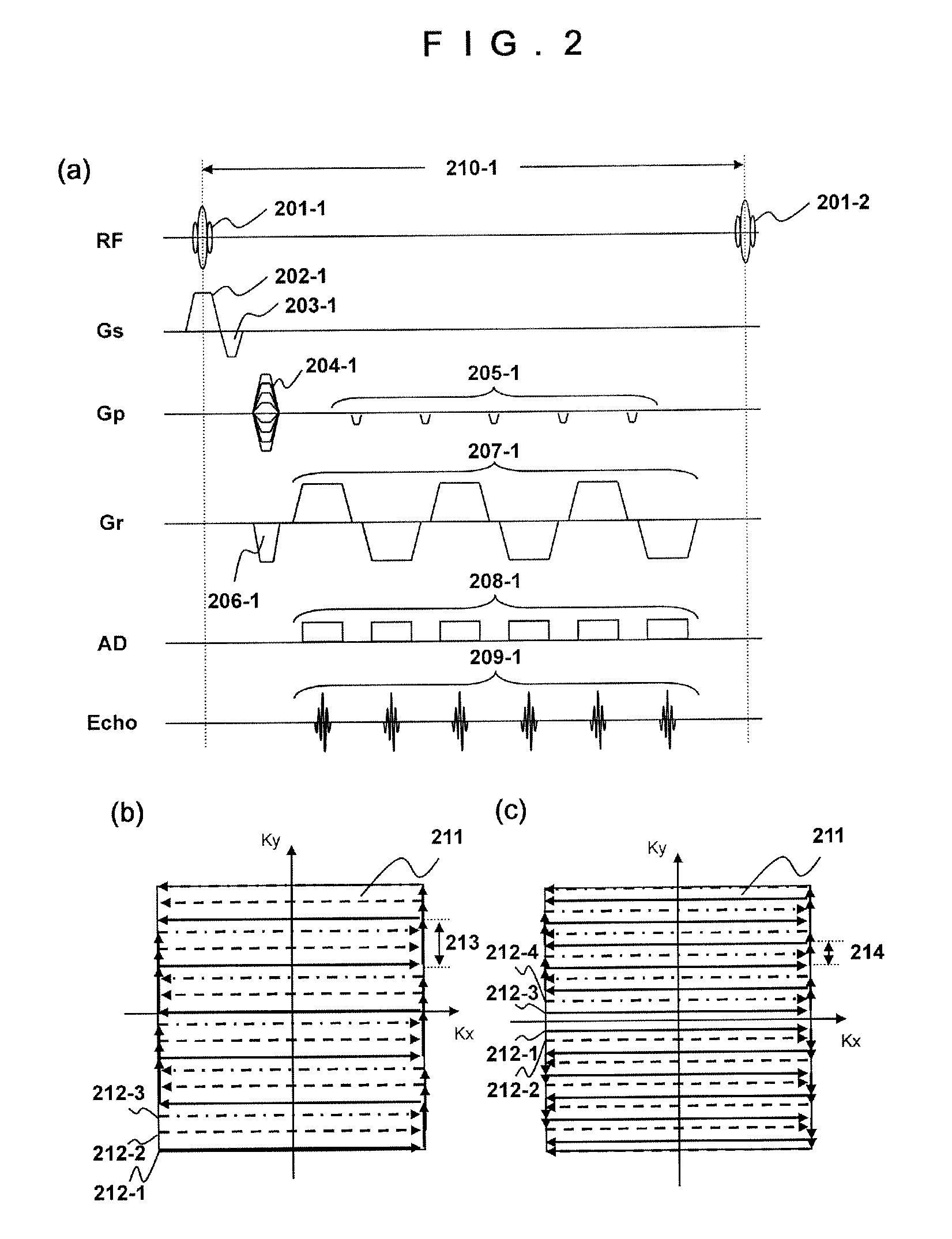
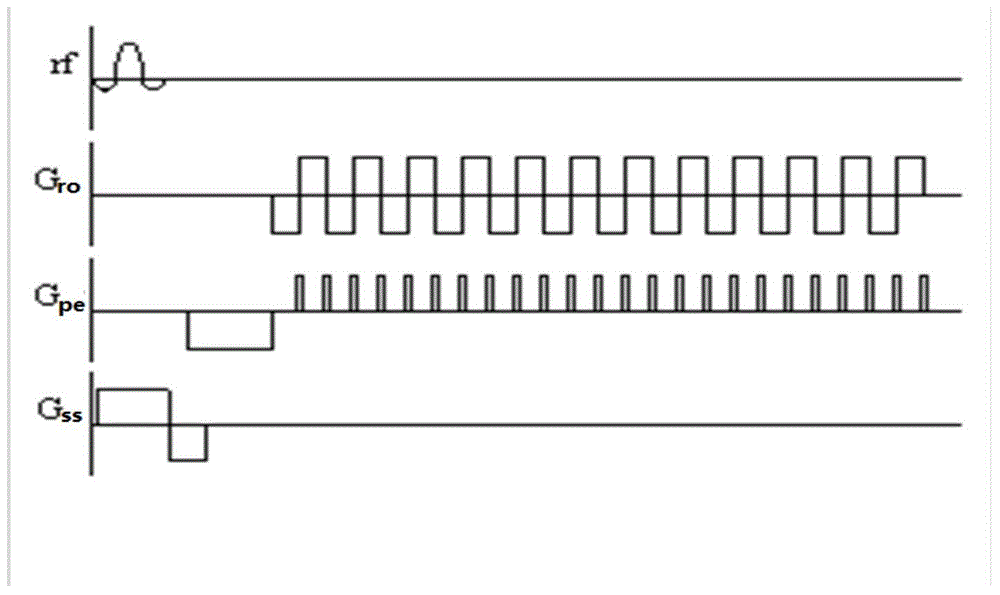
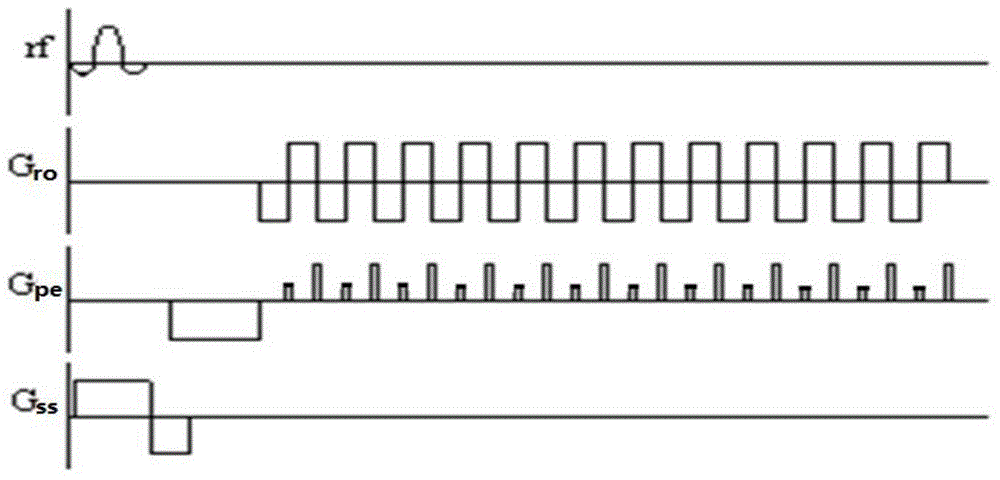
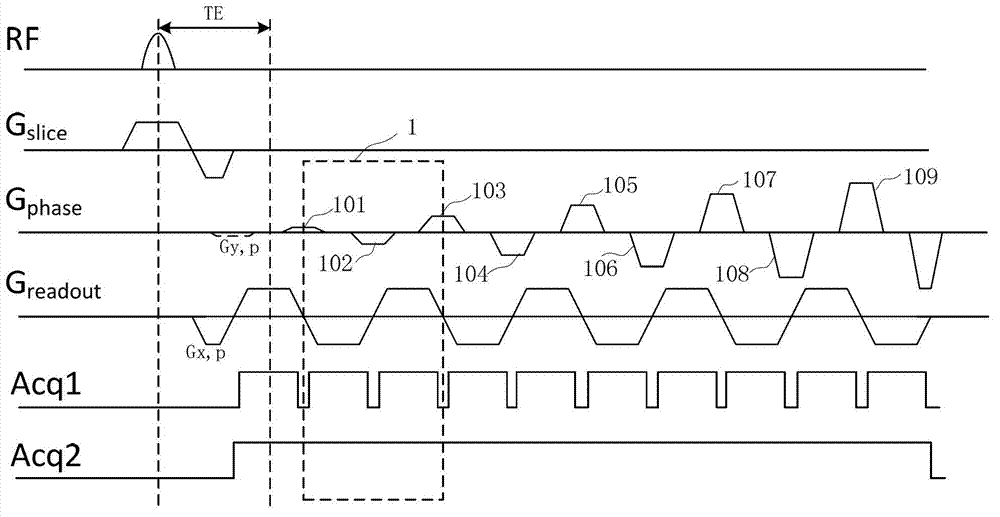
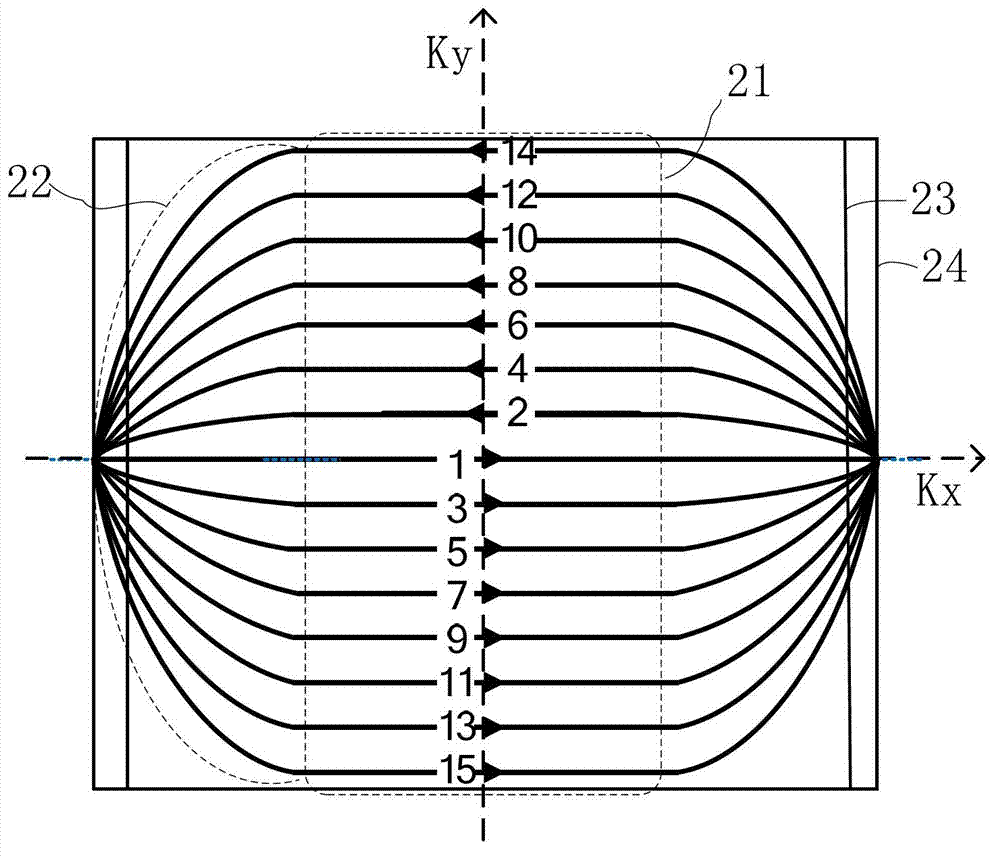
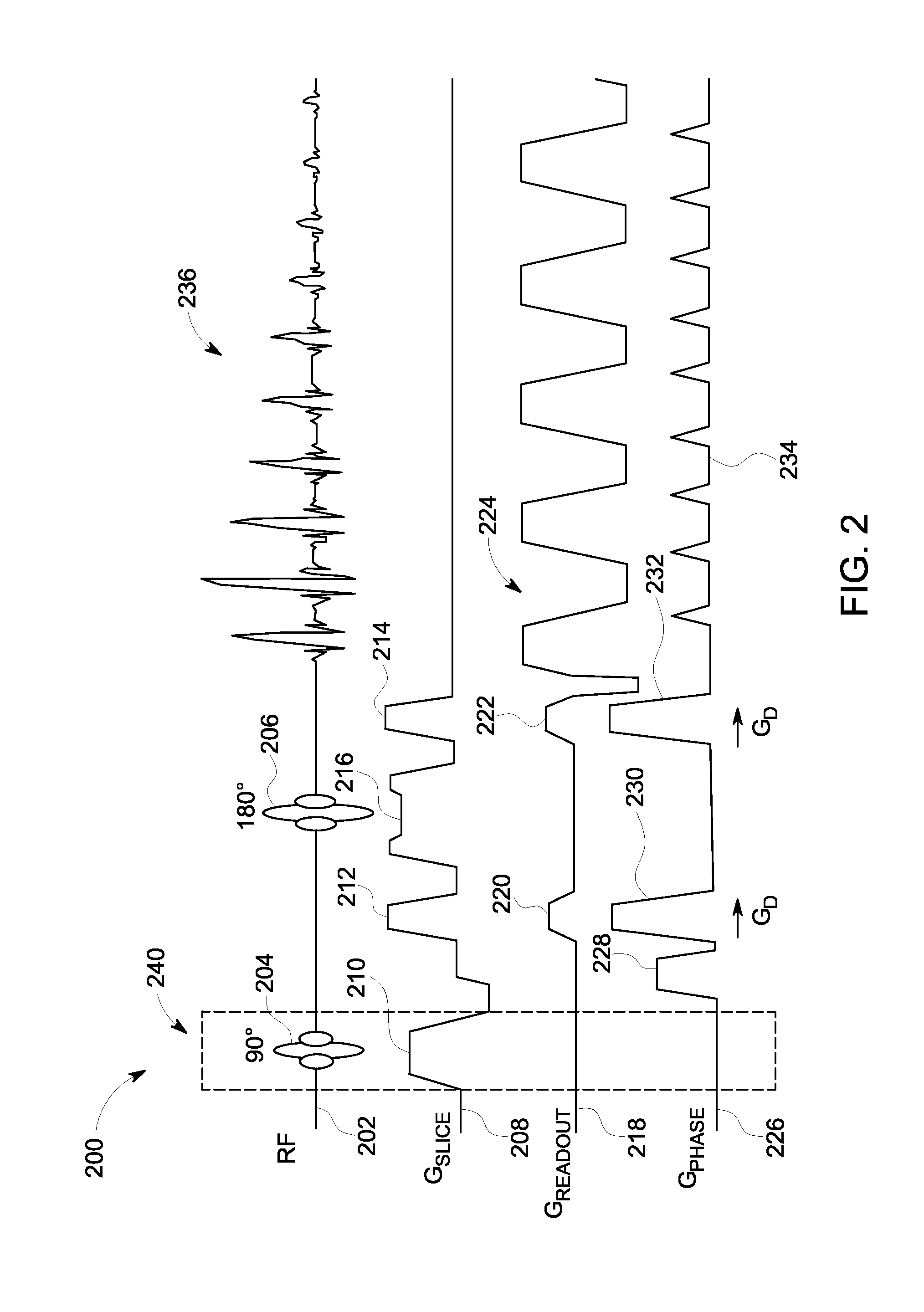
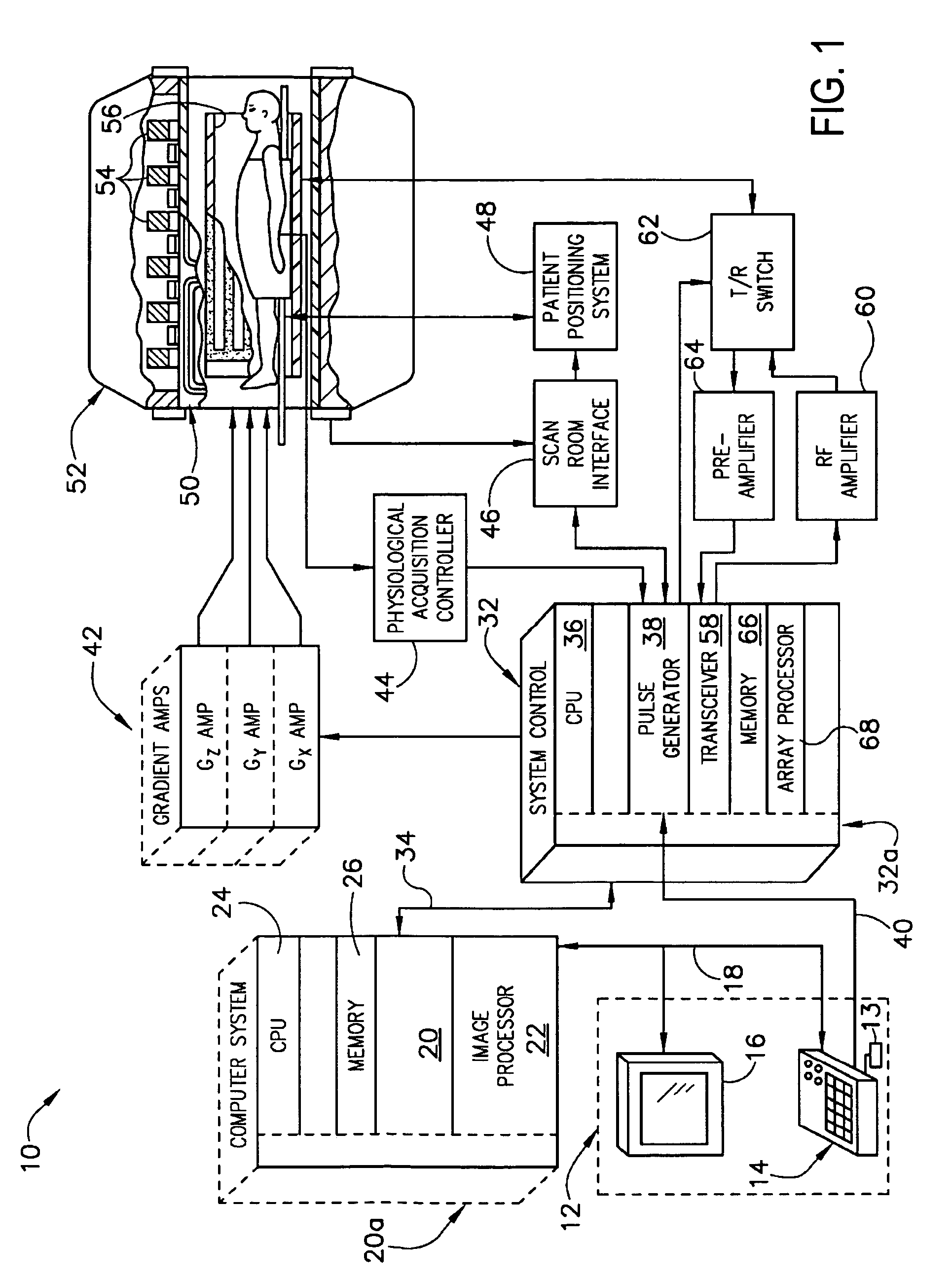
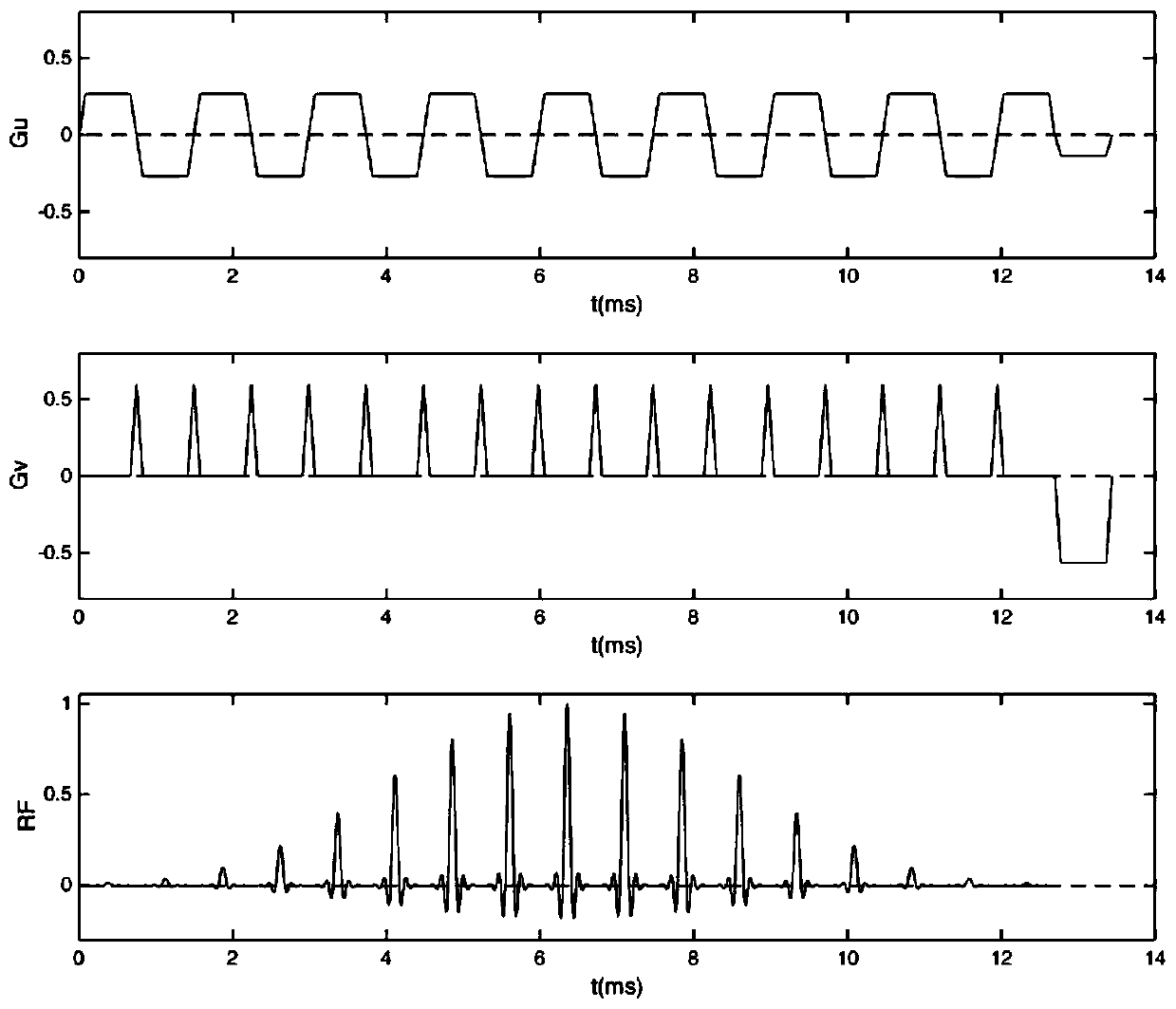
Echo planar imaging. An MRI term for the utilisation of rapid gradient reversal pulses of the readout gradient, resulting in a series of gradient echo signals to reduce fast dephasing or signal loss. Abbreviation: EPI. A fast magnetic resonance imaging technique in which an image is acquired after a single radiofrequency excitation.
Method for fast multi-slice mapping of myelin water fraction
InactiveUS20090312625A1Increasing volume coverageShorten the construction periodMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionDiseaseMulti slice
Mapping of myelin water content in white matter may provide important information for early diagnosis of multiple sclerosis and the detection of white matter abnormality in other diseases. It is disclosed here that free induction decay (FID) of each voxel at multiple slice locations is acquired in the brain using an echo-planar spectroscopic imaging (EPSI) pulse sequence. The multi-slice EPSI acquisition is designed to have a short first echo time (˜2 ms) and echo-spacing (˜1 ms) in order to acquire multiple sampling points during the fast decay of the myelin water signal. Multi-compartment analysis is then applied to the FID in each pixel using a 3-pool model of white matter to obtain quantitative maps of the myelin water fraction. Using this technique, the MR data for whole brain mapping of the myelin water can be acquired in less than 10 minutes, making this technique feasible for routine clinical applications.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
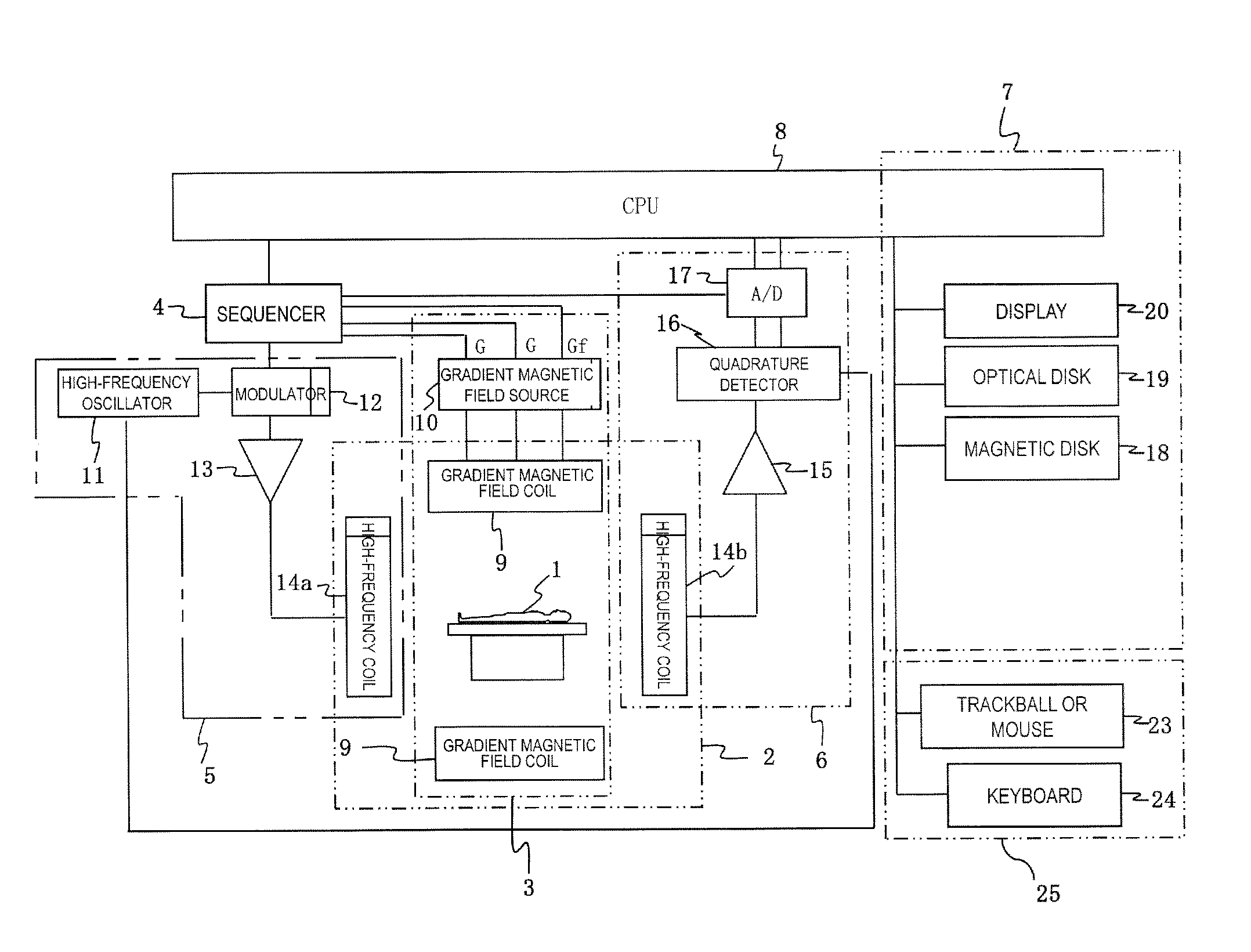
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and susceptibility-emphasized imaging method
ActiveUS20100277172A1Preferable signal-to-noise ratioSusceptibility-emphasizedMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic susceptibilitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
When performing susceptibility-emphasized imaging using the echo planar method in an MRI apparatus, it is possible to obtain a susceptibility-emphasized image having a preferable signal-to-noise ratio.When measuring a plurality of echo signals by applying a phase blip gradient magnetic field to inverse the polar characteristic of the frequency encode gradient magnetic field, the echo signals are divided into a first echo signal group and a second echo signal group.Image data is acquired from the first echo signal group while mask data is acquired from the second echo signal group.A susceptibility-emphasized image is obtained from the image data and the mask data.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
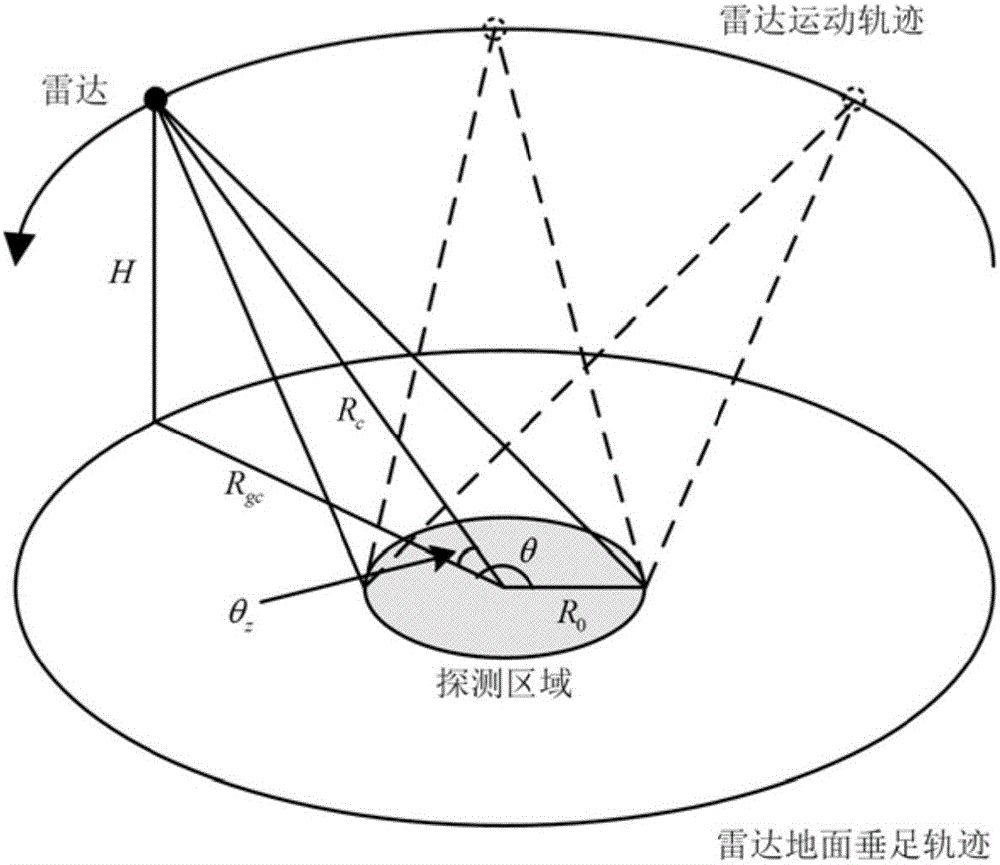
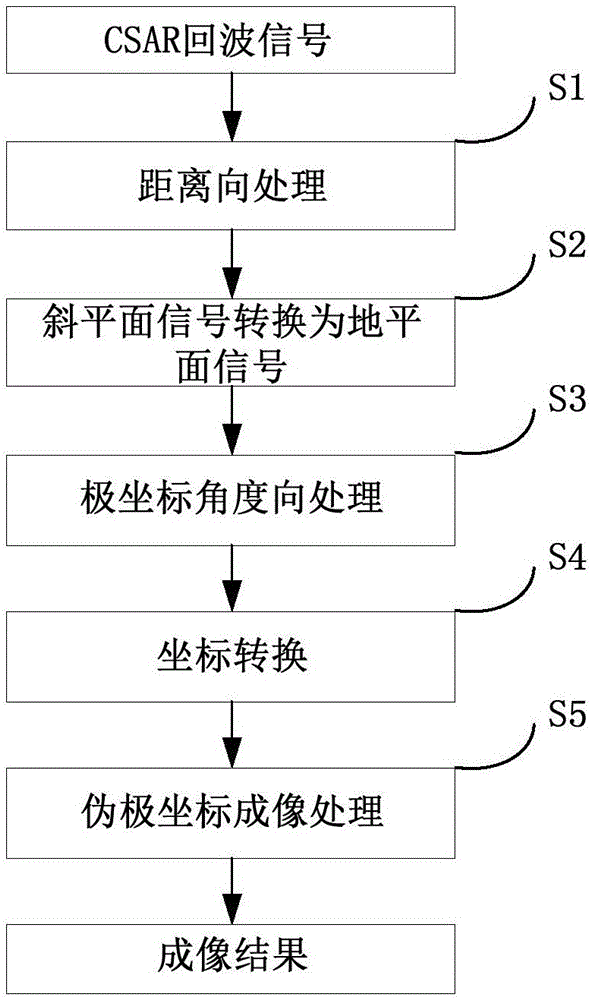
Circular synthetic aperture radar imaging method
InactiveCN106772380AHigh resolutionHigh resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInformation processingRapid imaging
The invention discloses a circular synthetic aperture radar imaging method, belonging to the technical field of electronic signal processing. The invention relates to a spatial remote sensing and air-to-ground observation information processing technology, in particular to an onboard circular synthetic aperture radar imaging technology. According to the imaging method, an original oblique plane echo is mapped to the ground plane by solving the inverse of a system kernel function, and the distribution of signals in a wave number domain is obtained by multiplying an azimuth frequency domain with a reference function, so that plane wave approximation is avoided, the problem that the size of an imaging area of the traditional polar format algorithm is limited can be solved, and the imaging of a large imaging scene can be realized; pseudo-polar coordinates are used for replacing rectangular coordinates as an intermediate interpolation transition matrix, and the distribution density characteristic of the signals in the wave number domain is considered, so that the interpolation precision is higher, the obtained image resolution is higher, and the high resolution imaging can be realized; the imaging process only involves one-dimensional interpolation, and fast algorithms such as chirp z transform (CZT) and inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) are adopted, so that the method has very high computational efficiency and can realize rapid imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Sequence preconditioning for ultra-fast magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6933720B2Improve image qualityQuality improvementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVolumetric imagingUltra fast
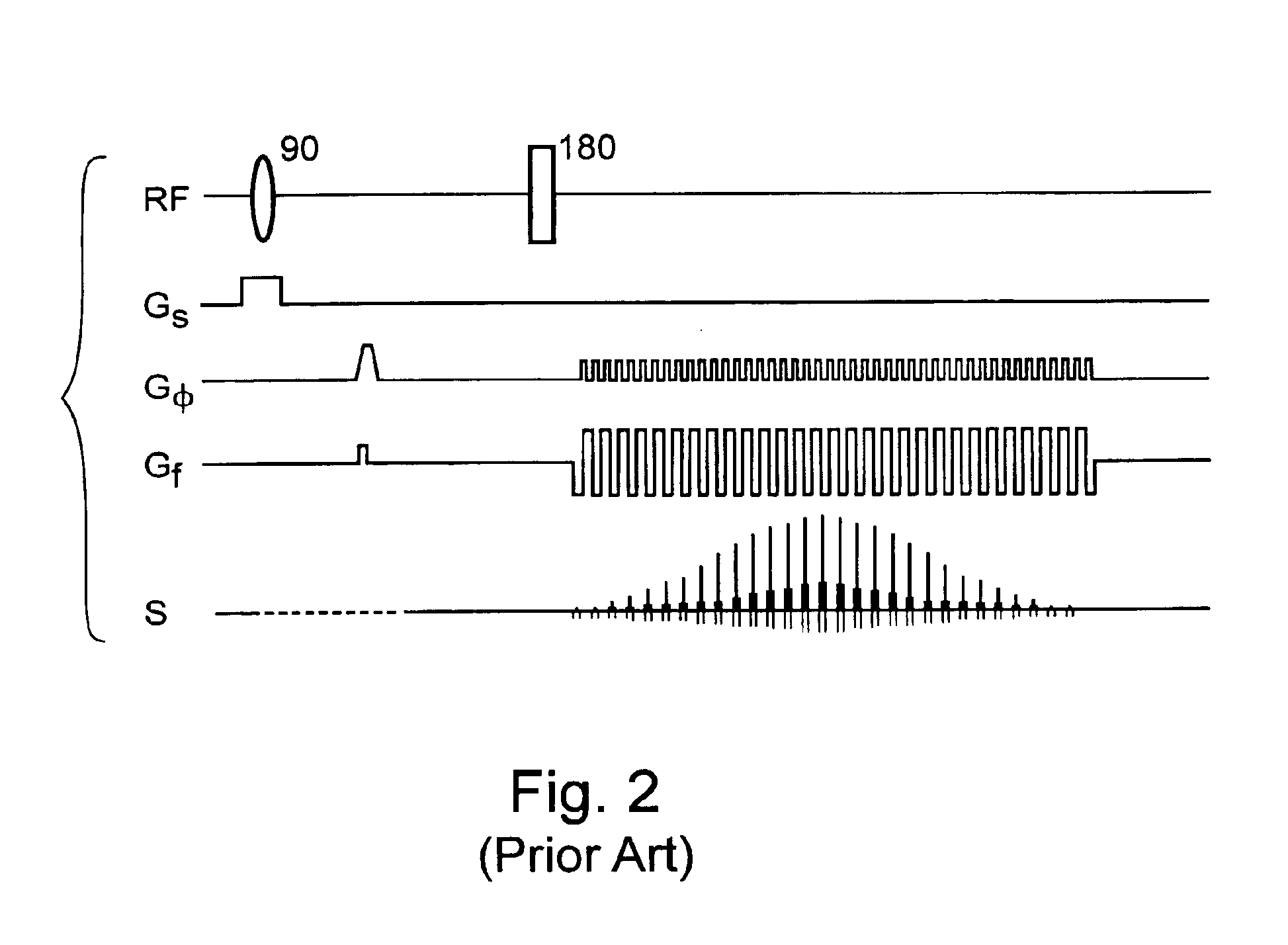
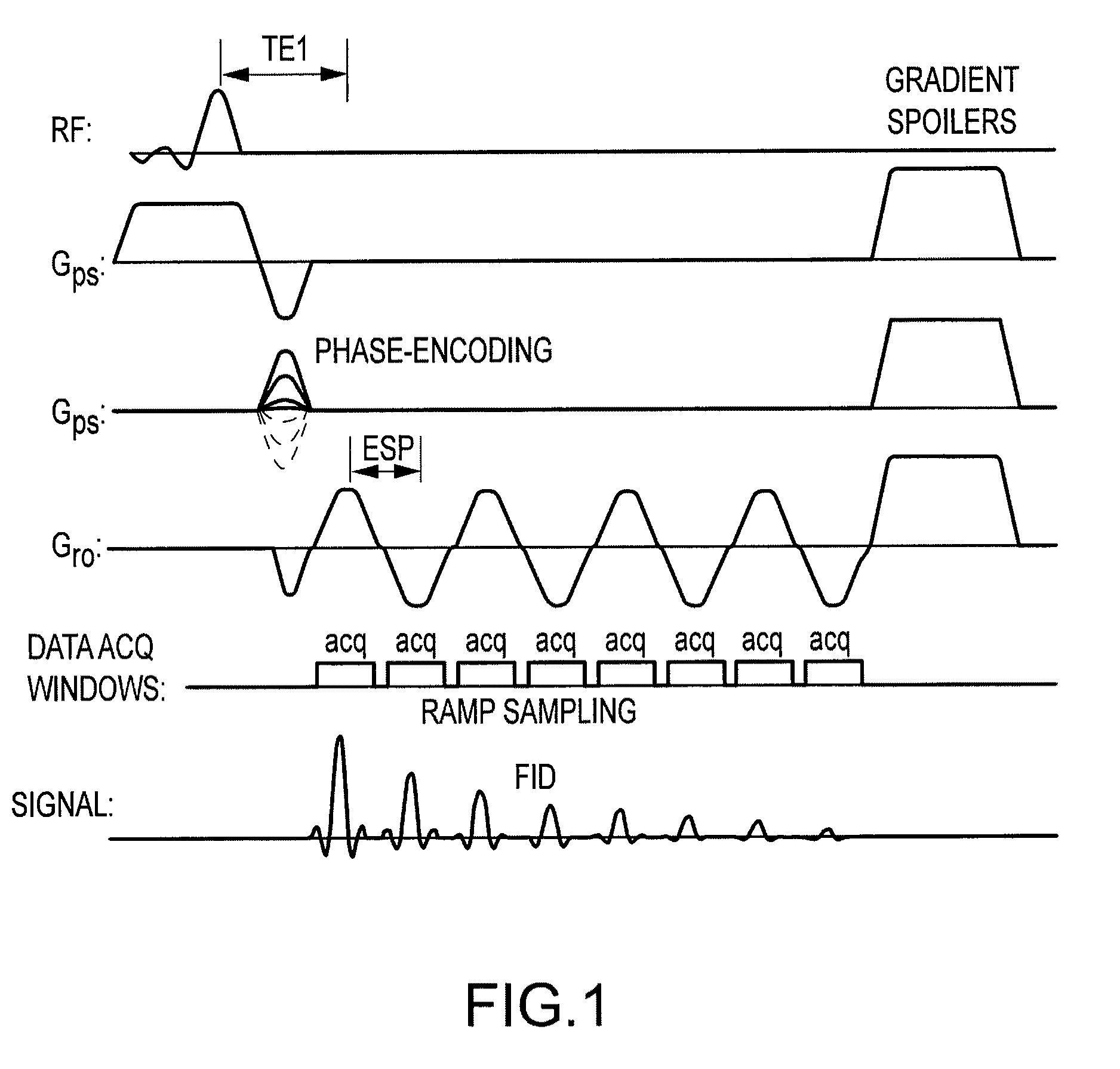
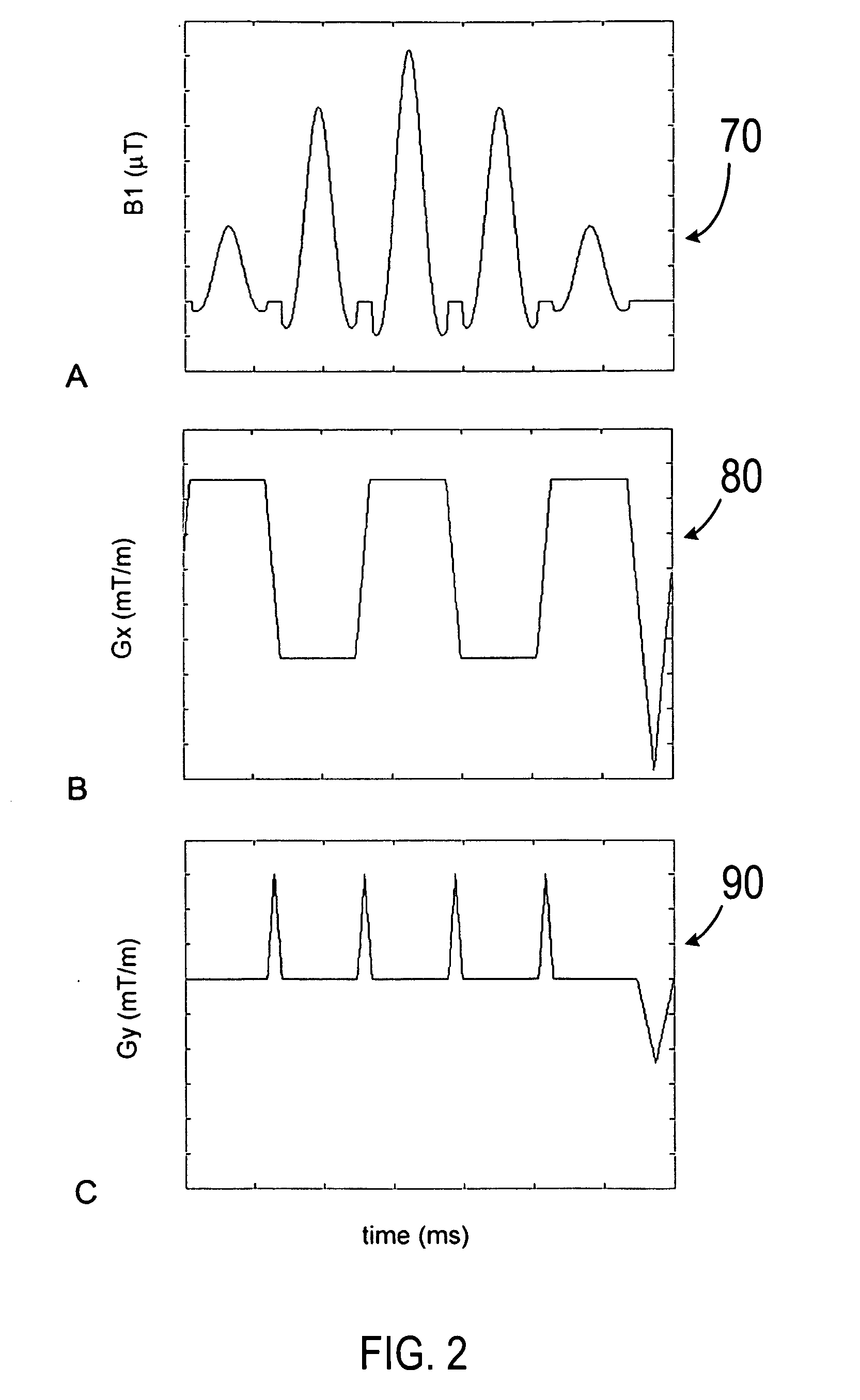
An improved magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) methodology uses an abbreviated initial MRI sequence to generate sequence diagnostic parameters. The sequence diagnostic parameters have a fixed relationship to certain sequence-conditioning parameters, and are used for calculating characteristic values of the sequence-conditioning parameters. The read out gradient pulse sequence is modified in accordance with the calculated characteristic values of the sequence-conditioning parameters. The modified read out gradient pulse sequence is then incorporated into a subsequent MRI pulse sequence used for obtaining a diagnostic image. The methodology has particular application in so called ultra fast MRI process which include echo-planar imaging (EPI) and echo-volume imaging (EVI).
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
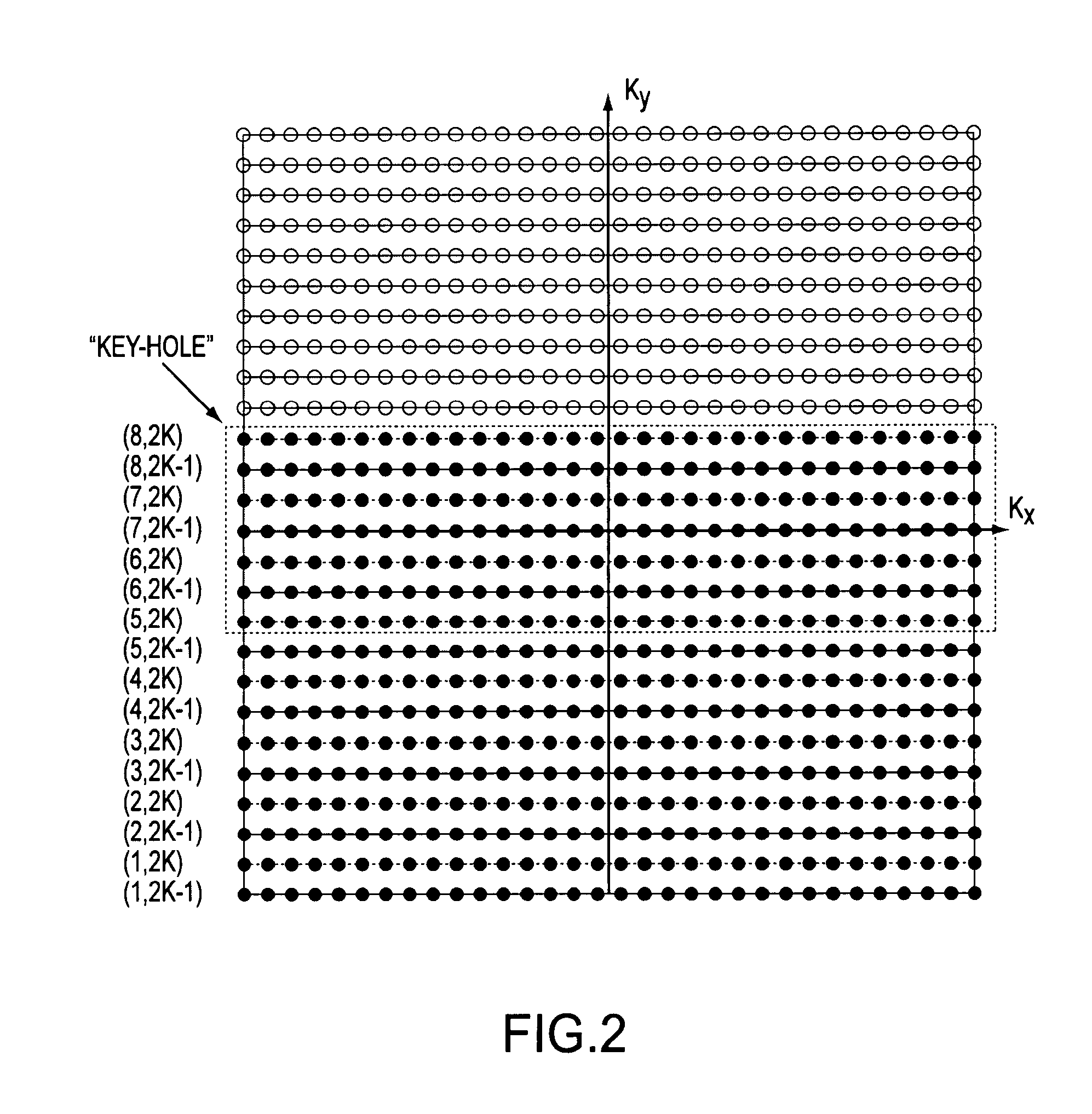
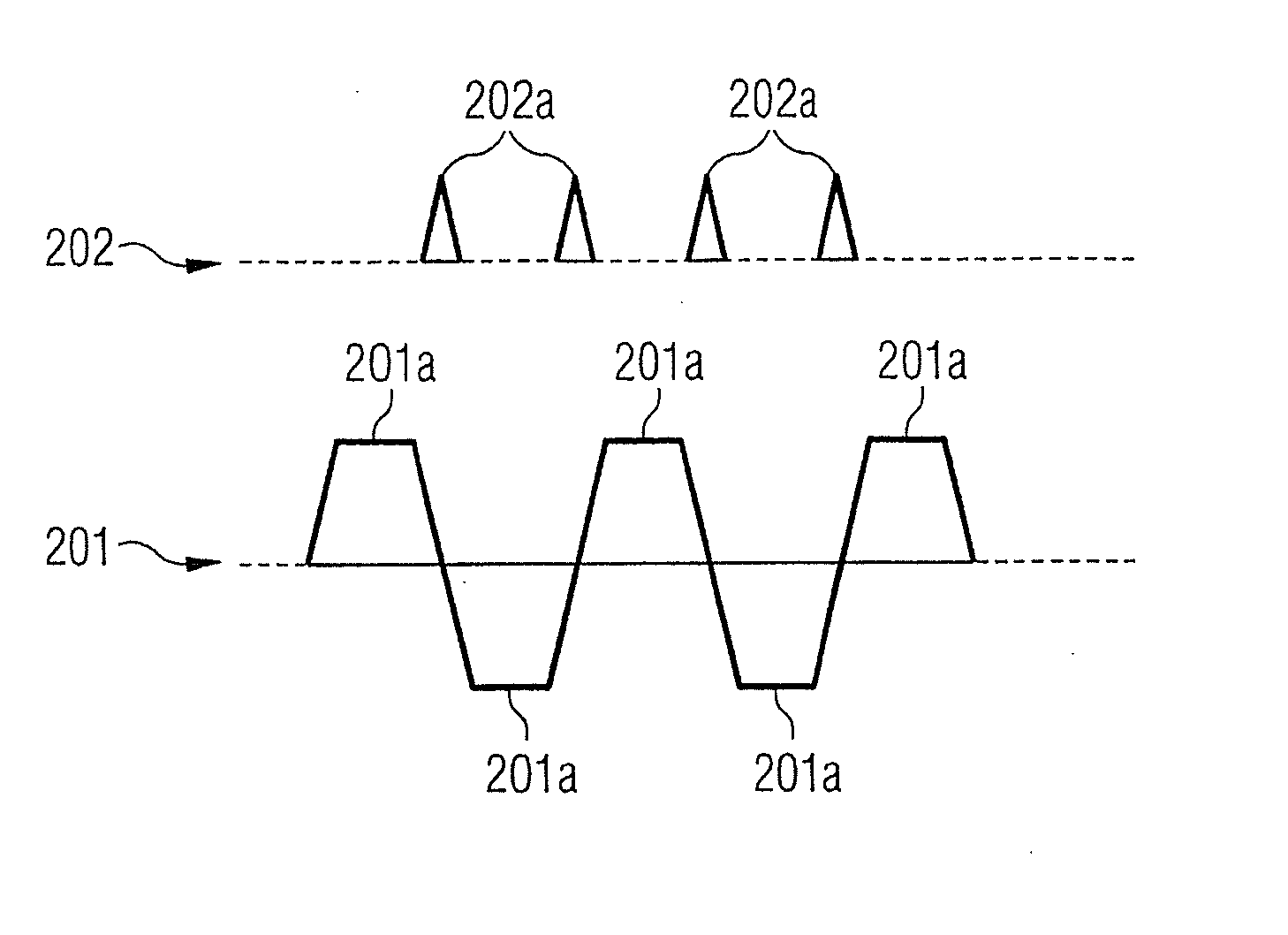
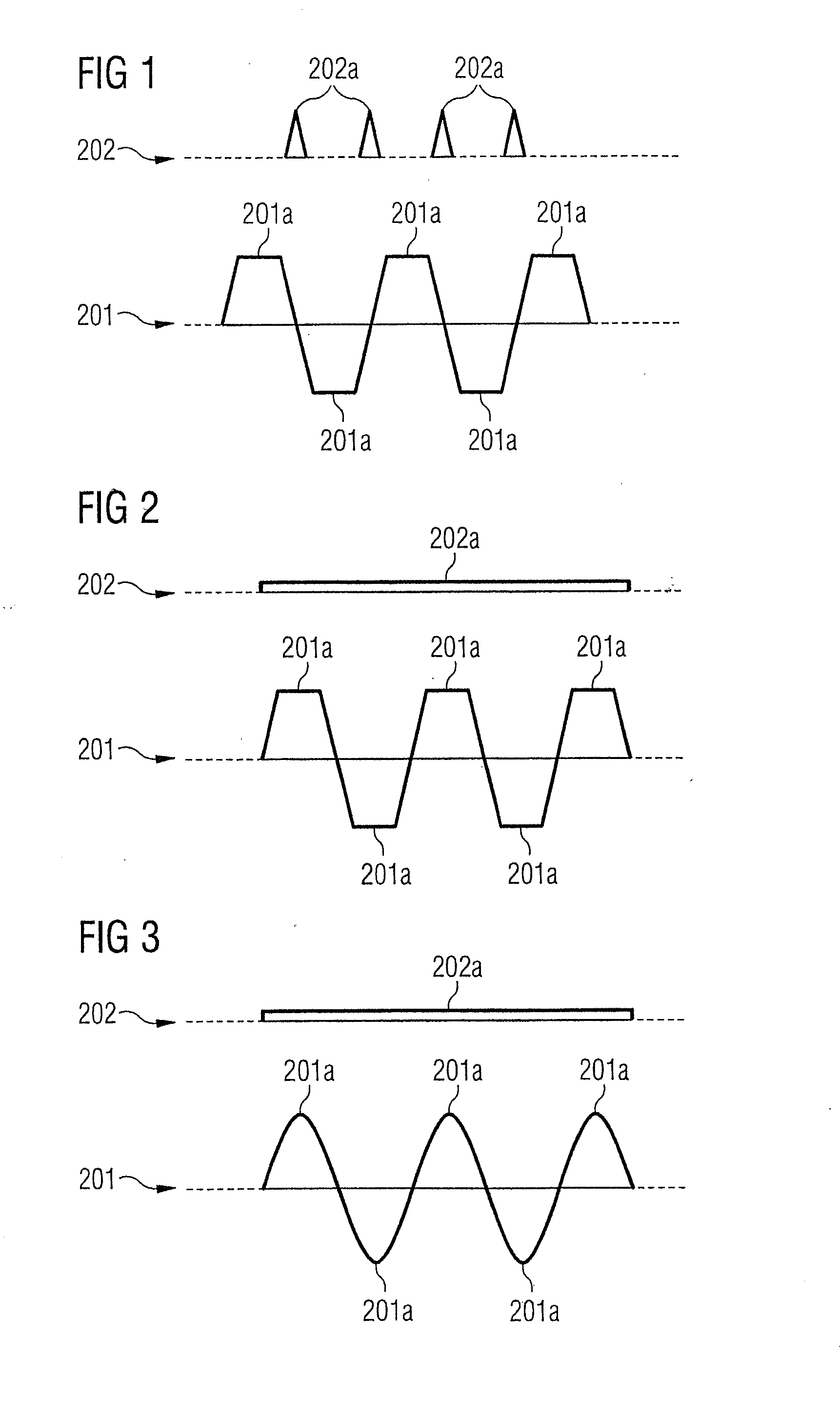
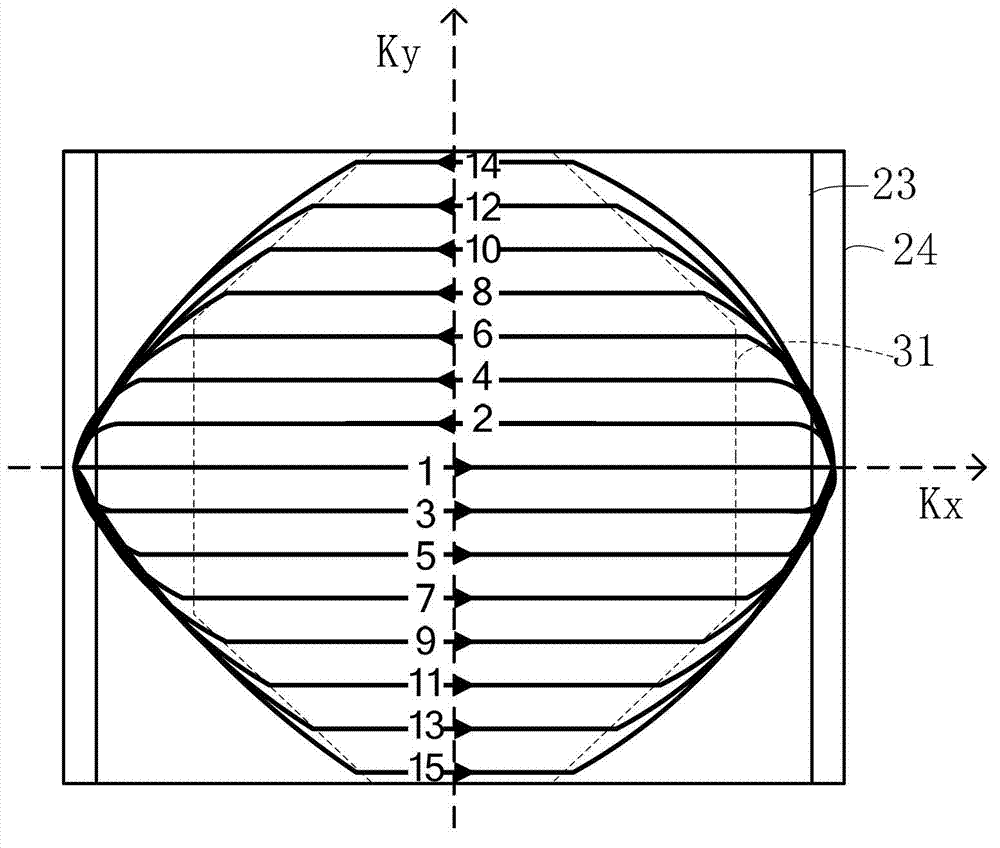
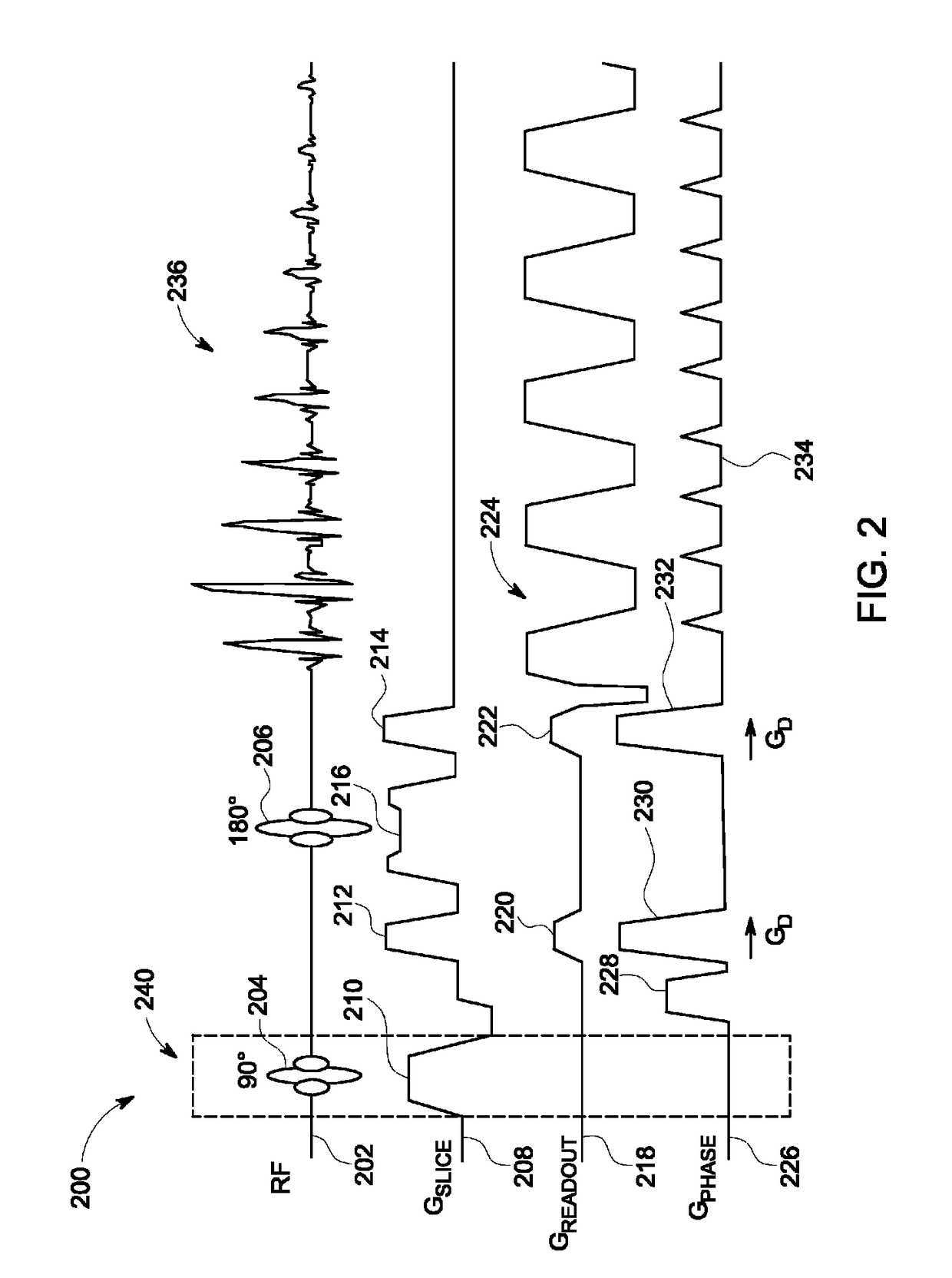
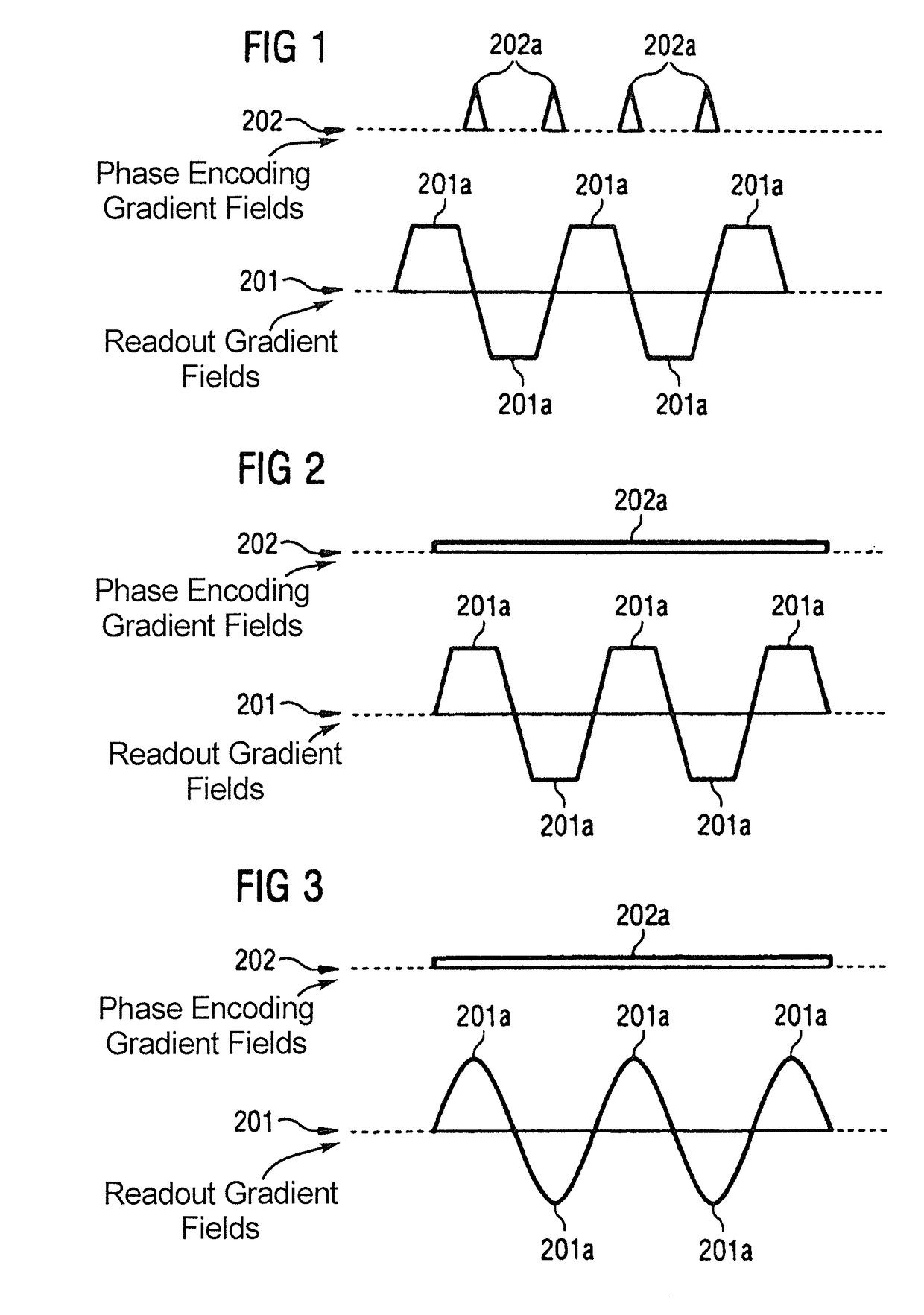
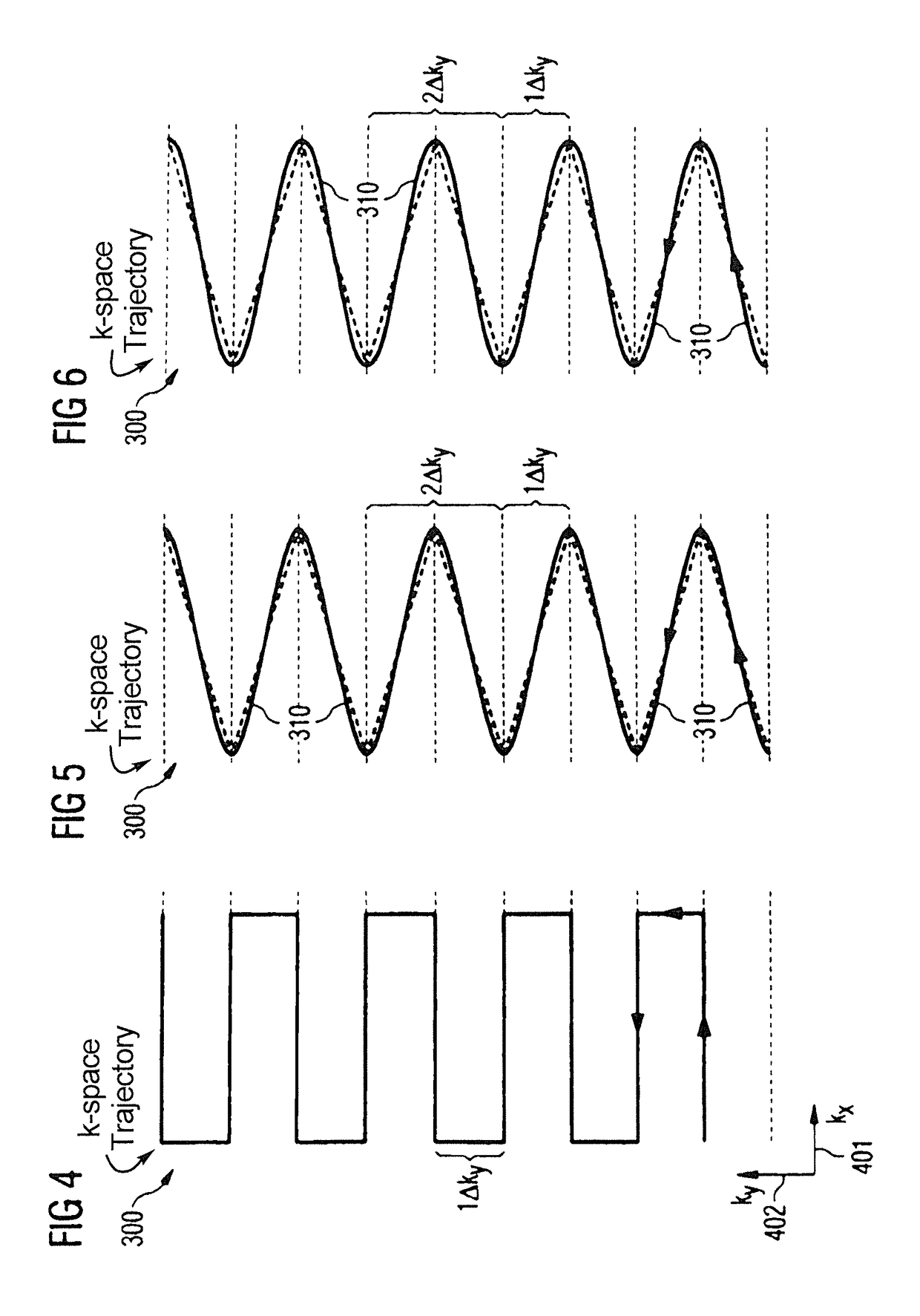
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus for echo planar imaging with data entry into k-space along a zigzag trajectory
ActiveUS20140197834A1Simple methodData augmentationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceImage sequence
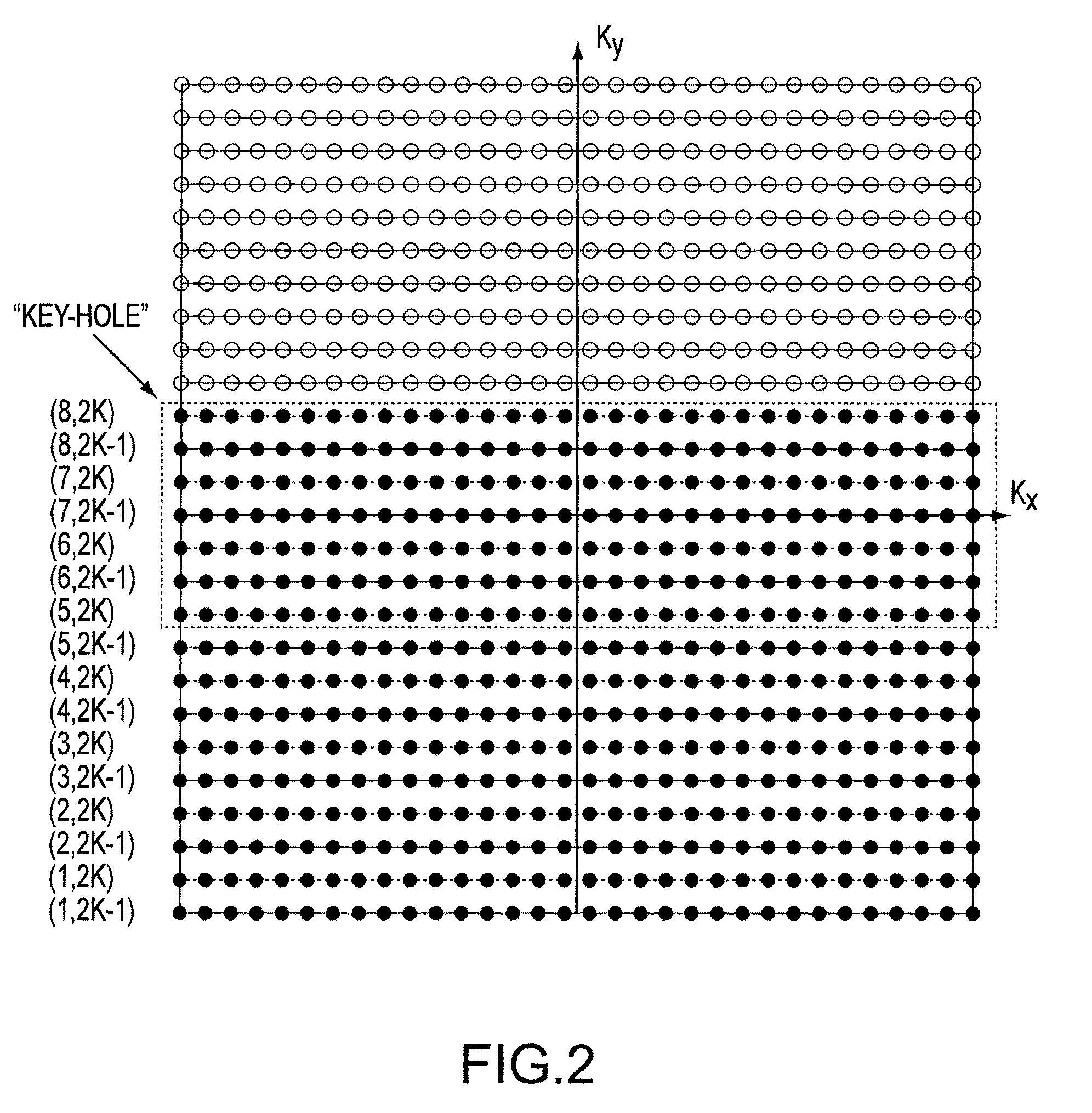
In a method and apparatus for echo planar magnetic resonance (MR) imaging sequence of phase encoding gradient fields and a sequence of readout gradient fields are applied in order to produce a well-defined zigzag-type trajectory for entering raw data into k-space. Zigzag-type trajectories can be achieved that have flanks without curvature, or without significant curvature. Cartesian methods for image reconstruction of parallel MR imaging are applied to echo planar MR imaging with such zigzag-type trajectories.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
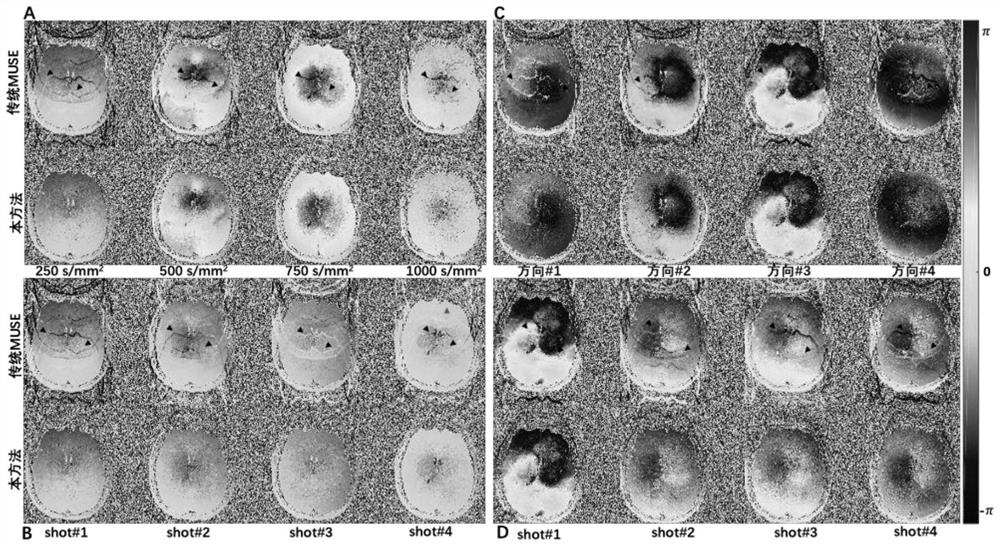
Echo planar imaging method and system
ActiveCN107037386AImprove fitting accuracyFast operationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceMri image
The invention discloses an echo planar imaging method, including: obtaining multiple echo planar imaging data of a scanned part and obtaining several reference echo signals that have not been subject to phase encoding; establishing a fitting model between the actual phase deviation of the reference echo signals and the readout direction position and establishing the Hoff space related to the parameters of the fitting model; based on the actual phase deviation of the reference echo signals and the readout direction position, determining the optimal parameter group in the Hoff space; according to fitting model and the optimal parameter group, correcting the echo planar imaging data; reconstructing the corrected echo planar imaging data and obtaining the magnetic resonance image of the scanned part. The echo planar imaging method of the invention can accurately correct the phases of an imaging signal. In addition, the invention also presents an echo planar imaging system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Plane echo imaging method and system
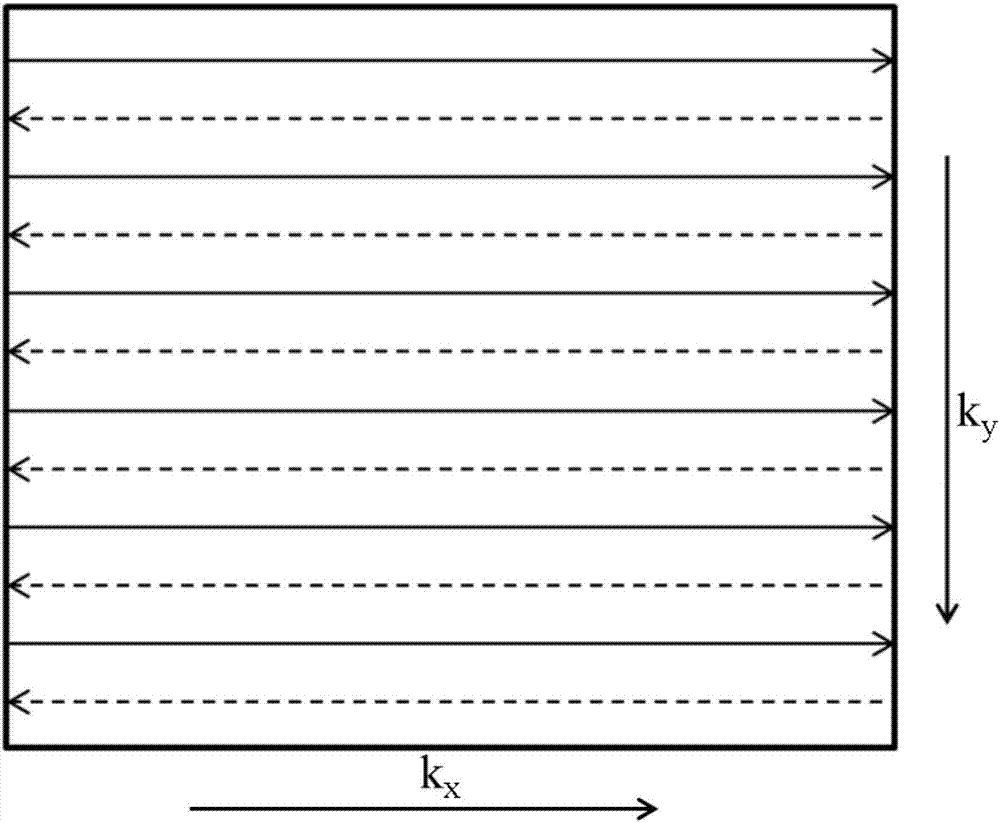
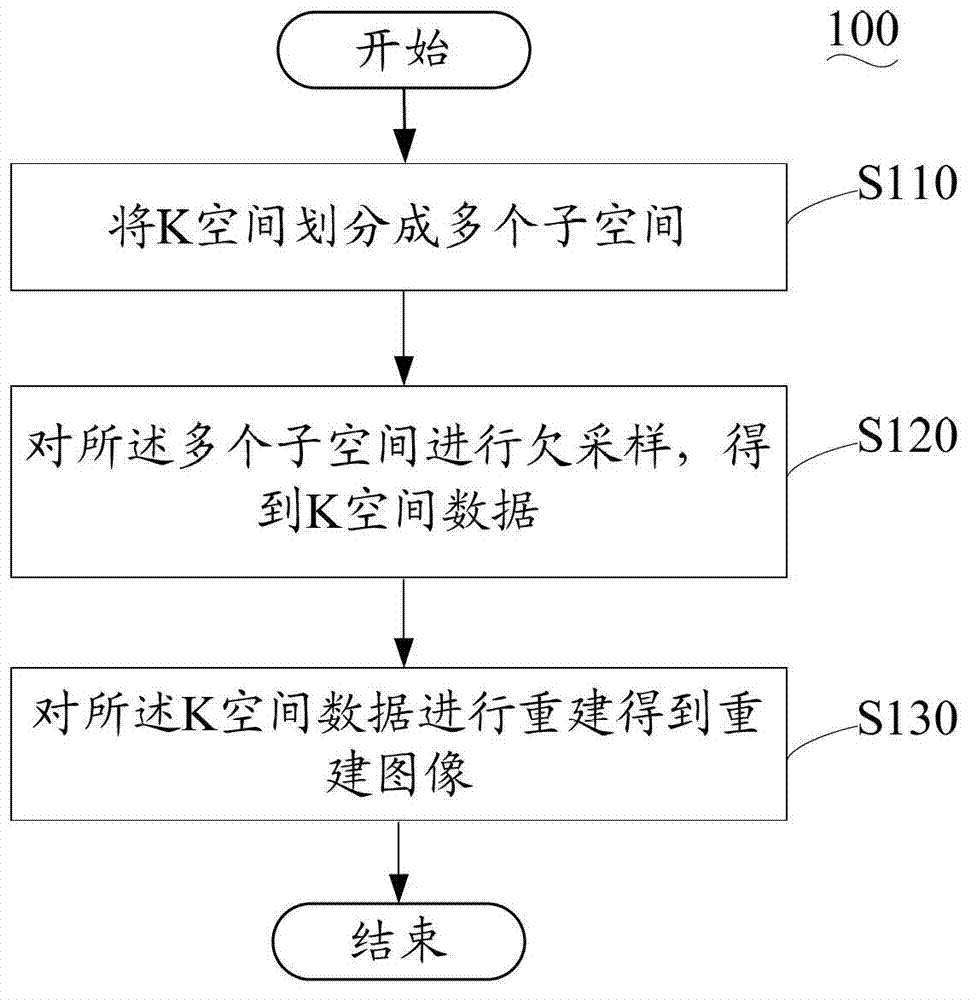
InactiveCN103163496AAvoid artifacts such as distortionThe number of samples is reducedMagnetic measurementsRapid imagingImaging quality
Provided is a plane echo imaging method. The plane echo imaging method includes the follow steps: dividing a K space into a lot of subspaces; carrying out an under-sampling over the multiple subspaces and obtaining a K space data; reconstructing the K space data and obtaining a reconstructed image. The plane echo imaging method divides the K space into a lot of subspaces, and carried out the under-sampling over the multiple subspaces and obtains the K space data and finally reconstructs the K space data to obtain the reconstructed image. Due to the fact that compared with a full sampling, the sampling numbers are dramatically decreased, on the basis of guaranteeing the rapid imaging, the gradient switching rate and climbing gradient are reduced, and the vortex is prevented from influencing the image imaging quality by the distortion and other artifact influences. The plane echo imaging method and the system can reduce the sampling points, so that the plane echo imaging can not only guarantee the improvement of the image quality, but the calculation process and the reconstruction process are simple, convenient and feasible. The invention further provides the imaging system.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Echo planar imaging method and device
ActiveCN104865545AEvenly distributedEliminate or weaken Nyquist GhostMagnetic measurementsVisual field lossPhase difference
An echo planar imaging method comprises the following steps of: applying an echo planar imaging sequence, obtaining pre-scanning K space data after a pre-scanning progress, grouping the pre-scanning K space data to obtain odd number data line and even number data line K spaces, and respectively integrating the odd number data line and even number data line K spaces and carrying out the Fourier transformation to obtain an image domain data Iodd of odd number data lines and an image domain data Ieven of even number data lines; carrying out operation on the image domain data Iodd and Ieven, and obtaining a phase difference change rate [lambda] along a phase encoding direction; obtaining a phase difference scope [phi] of an imaging visual field FOV; obtaining offset data in the phase encoding directions of the K space odd number data lines and even number data lines, and carrying out phase encoding gradient compensation on the echo planar imaging sequence according to the offset data; carrying out formal scanning on the compensated echo planar imaging sequence, and obtaining imaging K space data; and carrying out the Fourier transformation to obtain an image. The invention further discloses a echo planar imaging device.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Inside-out echo-planar imaging method for shortening echo time
InactiveCN102890255AShortened echo timeImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Arterial spin labeling
The invention discloses an inside-out echo-planar imaging method for shortening echo time. The method is characterized in that: a k-space trajectory extends to the outer side of a phase encoding direction from the center, wherein a gradient for generating the trajectory is composed of reading-out gradients which switch between forward and reverse directions and phase encoding gradients which switch between forward and reverse directions and gradually increases from zero. The method further comprises a step that: in order to accommodate the phase encoding gradients of which the area increases gradually without adding an echo spacing, the phase encoding gradient and a data collecting window are permitted to be overlapped. According to the method disclosed by the invention, an effective echo time in a sequence is located in the center of a first echo, the echo time is shortened greatly, and the signal to noise ratio is increased; since the contrast ratio of an image depends on signals of a k-space centre, and data of the k-space center are from an initial echo, T2 or T2* weighing of the obtained image is very small; and in diffusion imaging and arterial spin labeling imaging, the decreasing of the T2 or the T2* weighing is beneficial to improving the quality of the image.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
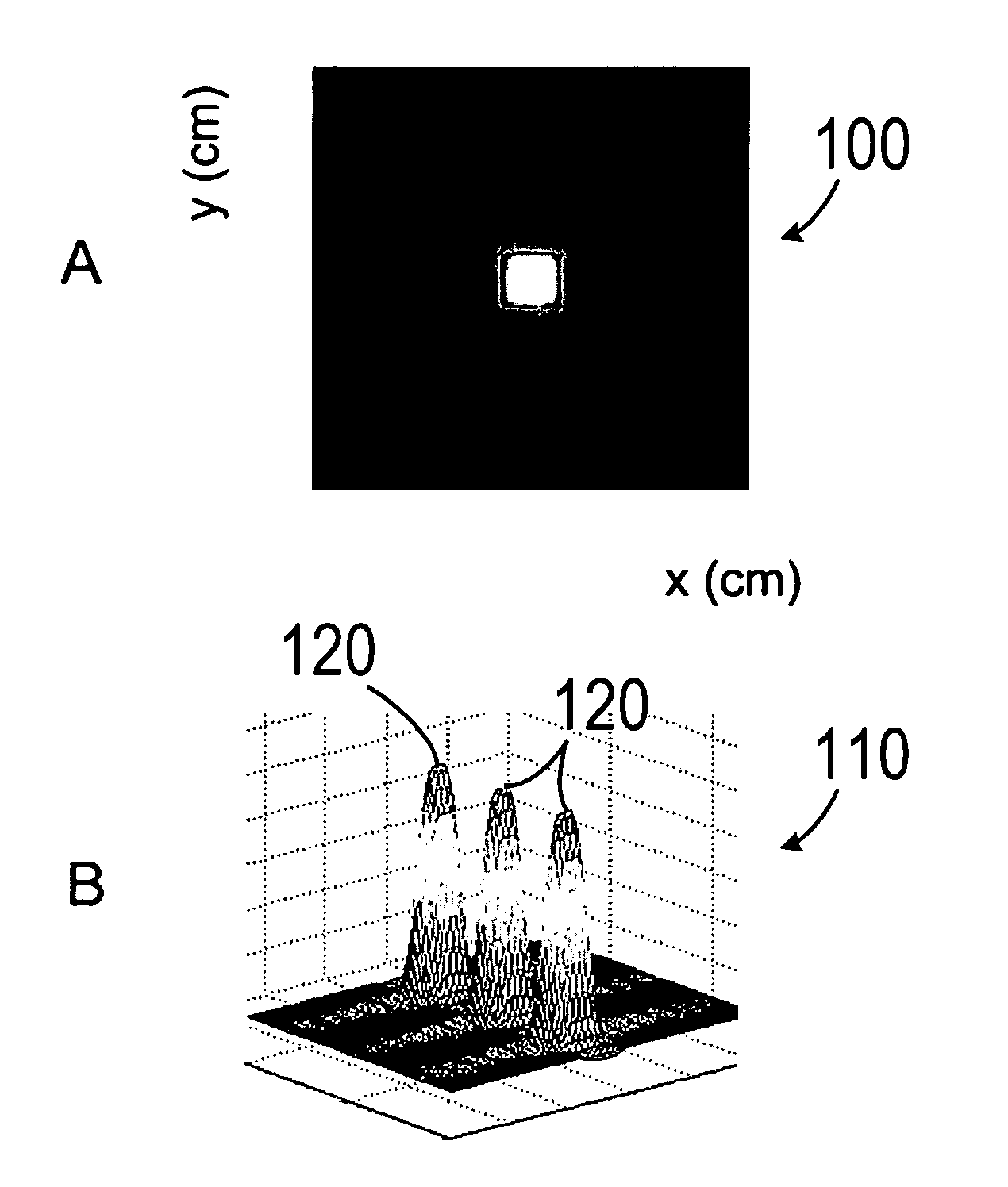
System and method for reduced field of view magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20150301143A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceSide lobe
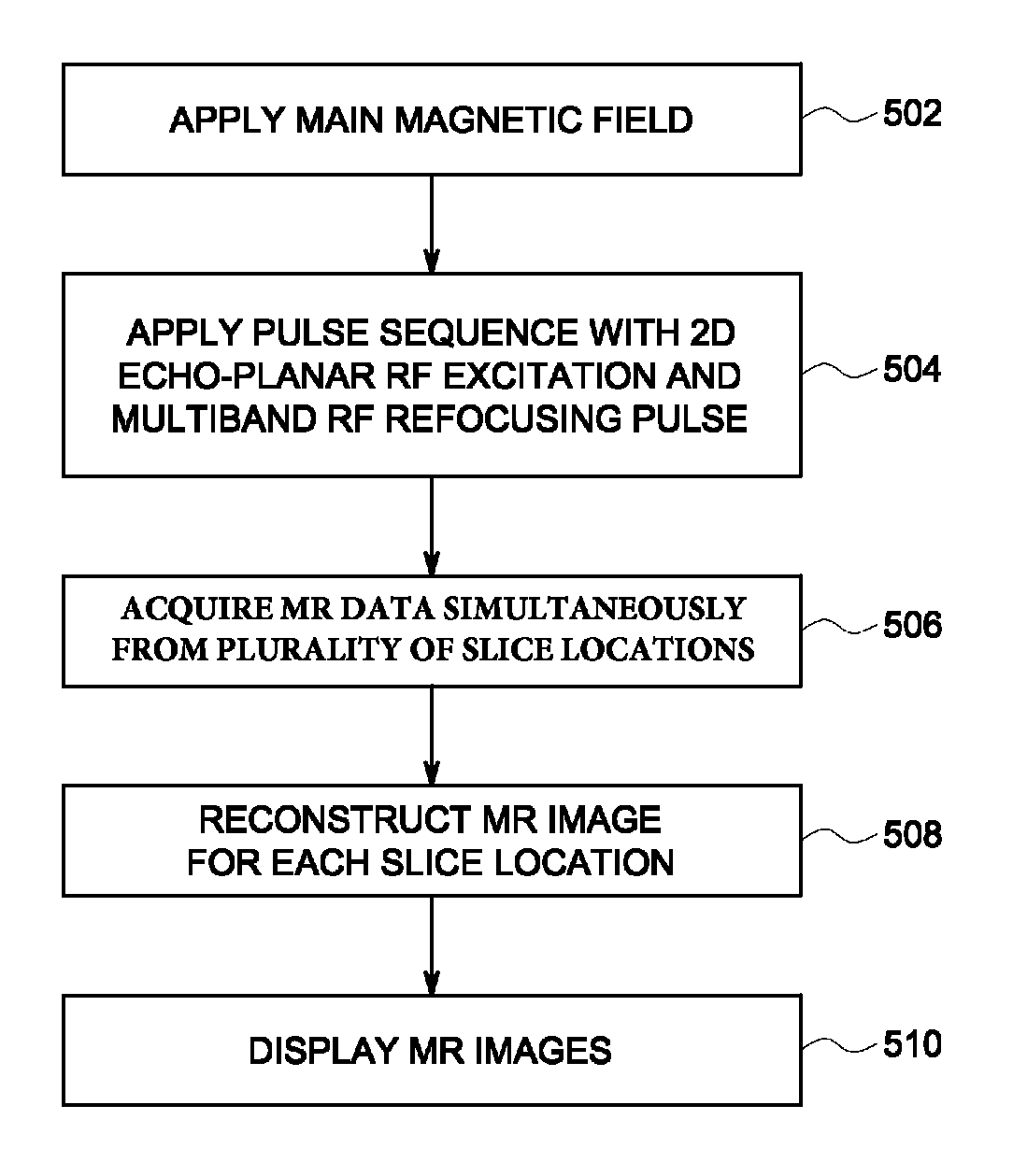
A method for reduced field of view magnetic resonance (MR) imaging includes applying a pulse sequence using a plurality of gradient coils and at least one RF coil of a magnetic resonance imaging system. The pulse sequence includes a two dimensional (2D) echo-planar RF excitation pulse with a plurality of side lobes along a slice select axis and a multiband RF refocusing pulse. MR data is acquired in response to the application of the pulse sequence and at least one MR image is reconstructed based on the MR data. The at least one MR image may then be displayed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
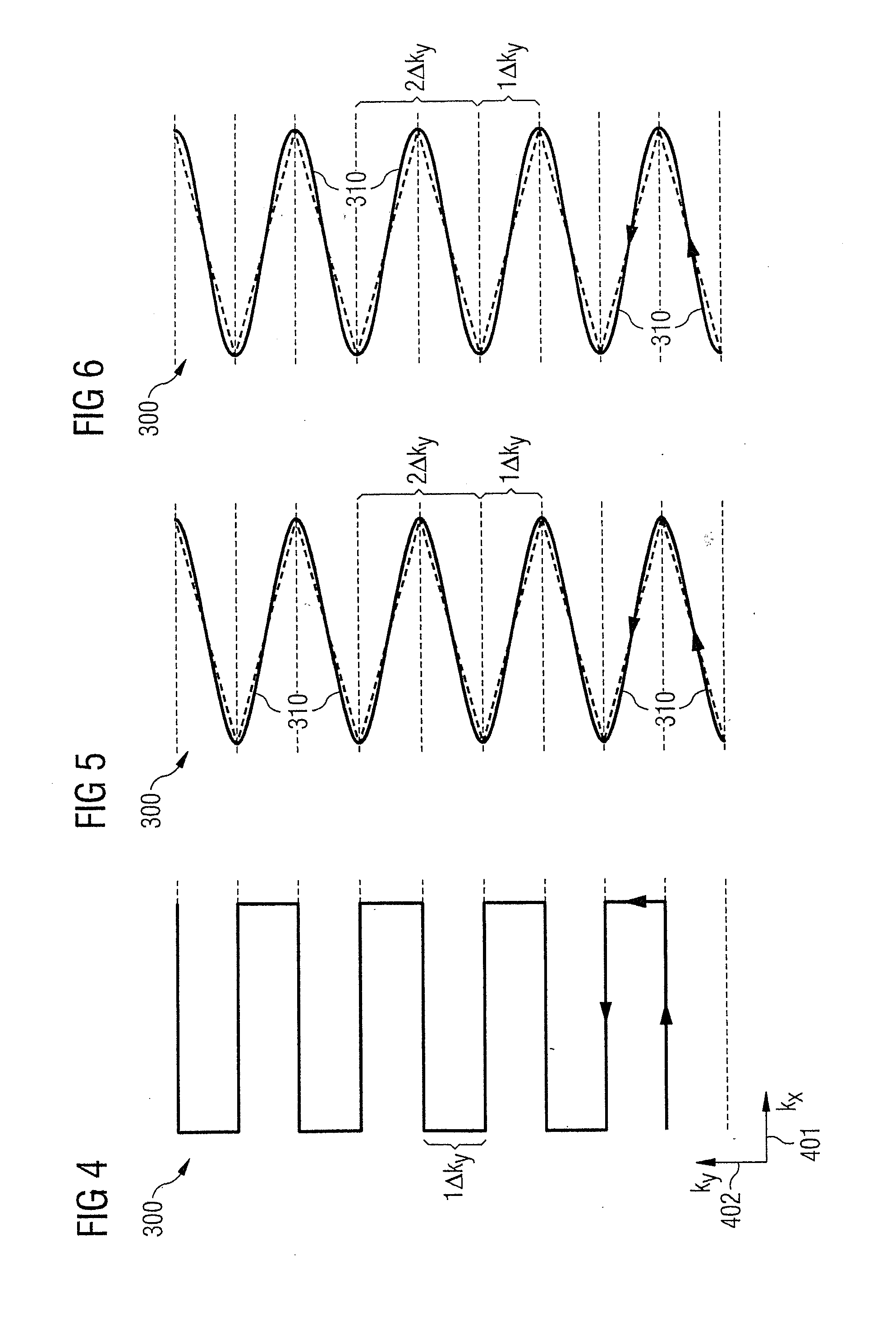
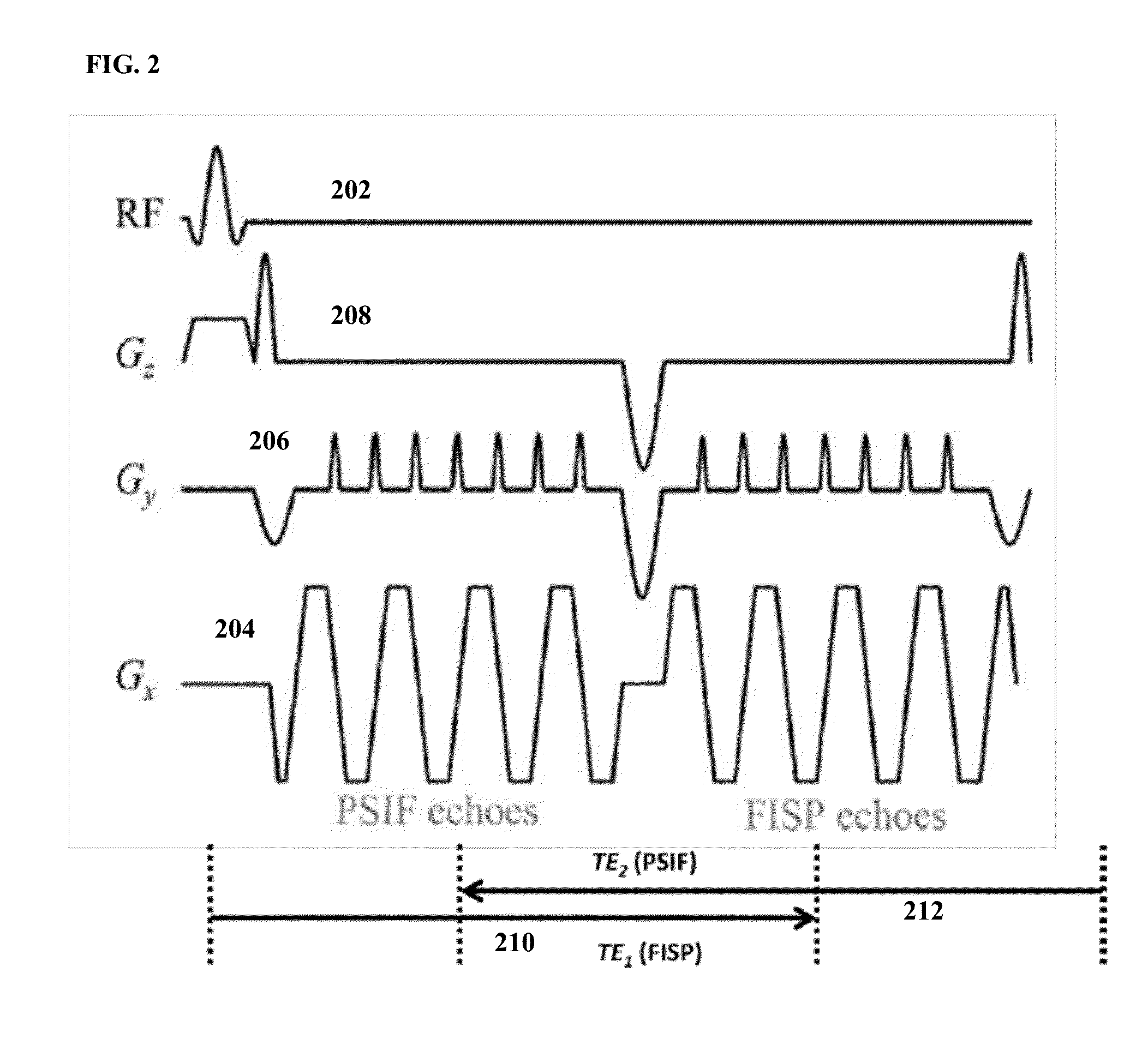
Method for echo planar time-resolved magnetic resonance imaging
Systems and methods for magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”) that address the geometric distortions and blurring common to conventional echo planar imaging (“EPI”) sequences, and that provide new temporal signal evolution information across the EPI readout, are described. Echo planar time-resolved imaging (“EPTI”) schemes are described to implement an accelerated sampling of a hybrid space spanned by the phase encoding dimension and the temporal dimension. In general, each EPTI shot covers a segment of this hybrid space using a zigzag trajectory with an interleaved acceleration in the phase-encoding direction. The hybrid space may be undersampled and a tilted reconstruction kernel used to synthesize additional data samples.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
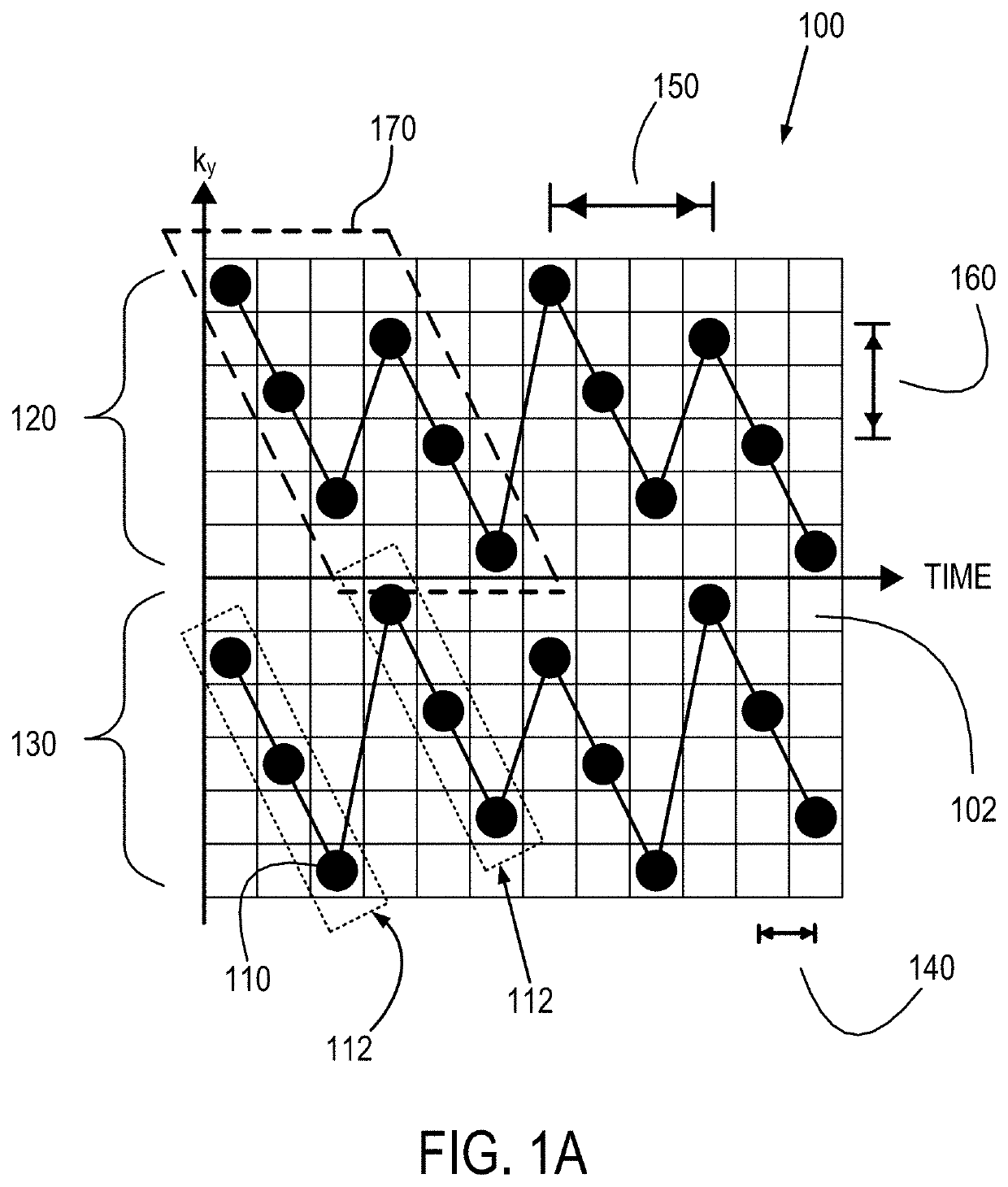
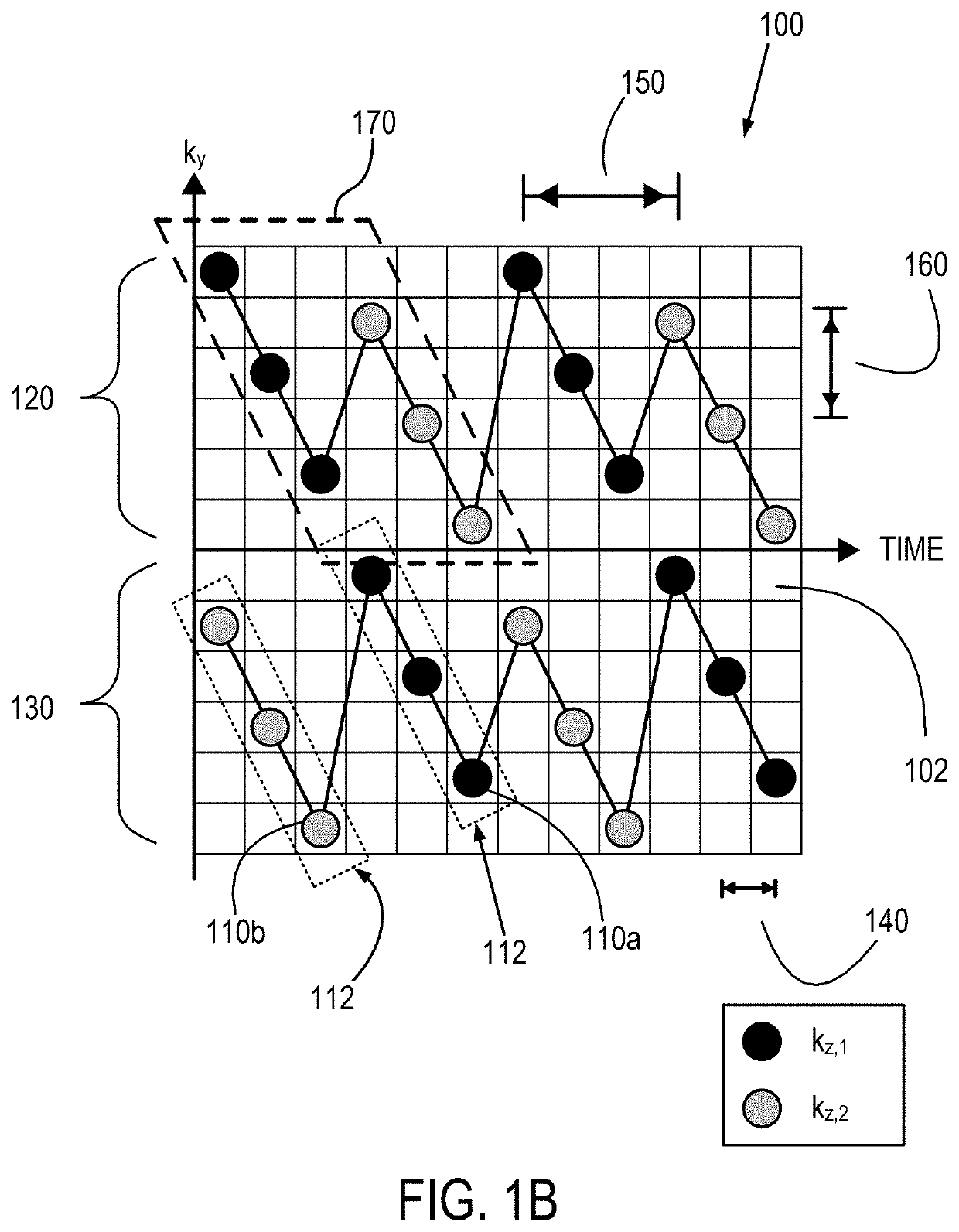
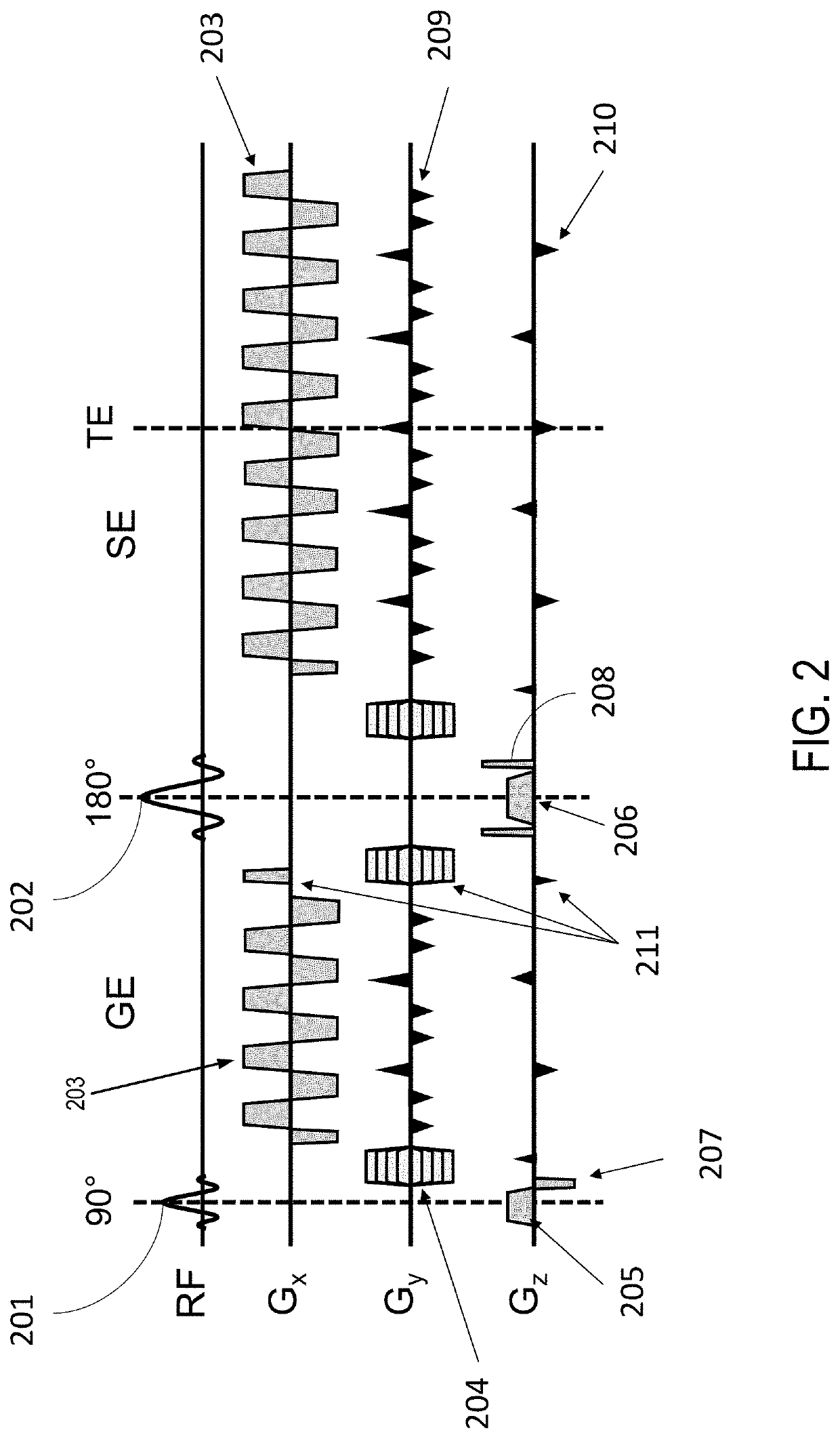
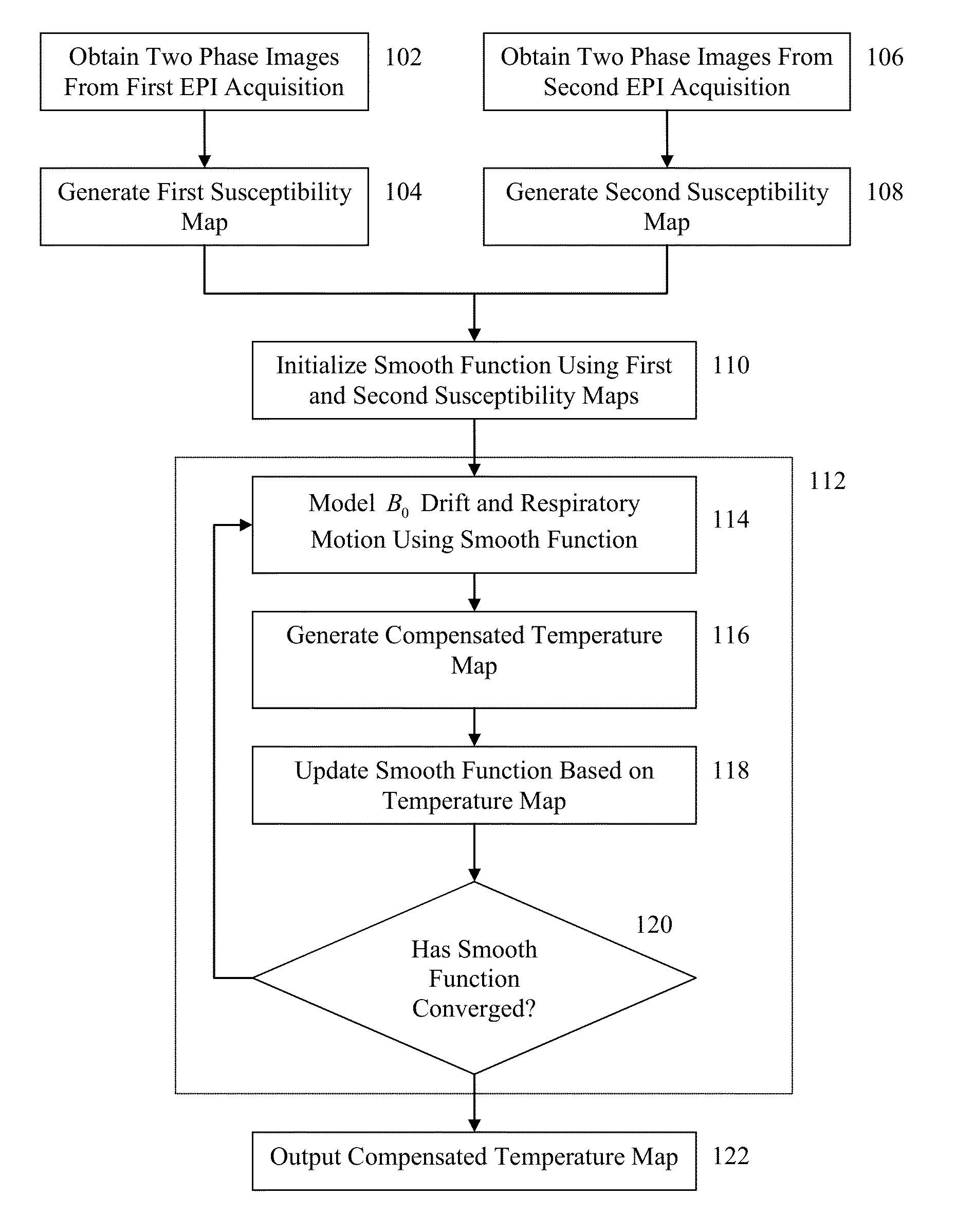
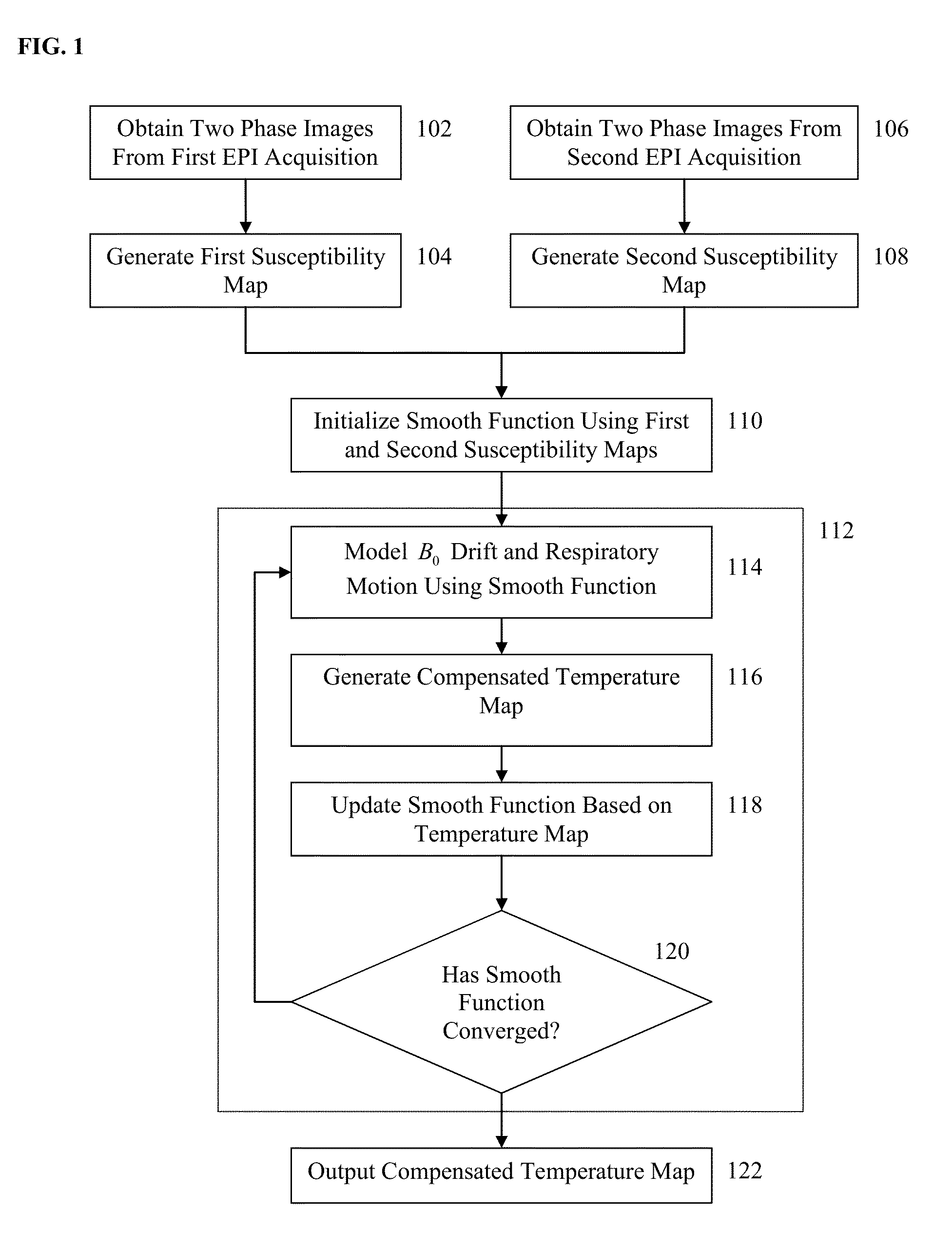
Method and System for B0 Drift and Respiratory Motion Compensation in Echo-Planar Based Magnetic Resonance Imaging
InactiveUS20150160321A1Minimize respiratory motion artifactHigh-temperature-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisResonanceMri image
A method and apparatus for B0 correction in echo-planar (EP) based magnetic resonance image (MRI) is disclosed. Two phase images are obtained from each of a first echo-planar imaging (EPI) acquisition and a second EPI acquisition. A first susceptibility map is generated based on the two phase images obtained from the first EPI acquisition and a second susceptibility map is generated based on the two phase images obtained from the second EPI acquisition. A smooth polynomial function for modeling the B0 drift and respiratory motion between the first EPI acquisition and the second EPI acquisition is initialized based on the first and second susceptibility maps. A compensated temperature map is then iteratively reconstructed based on the smooth polynomial function.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
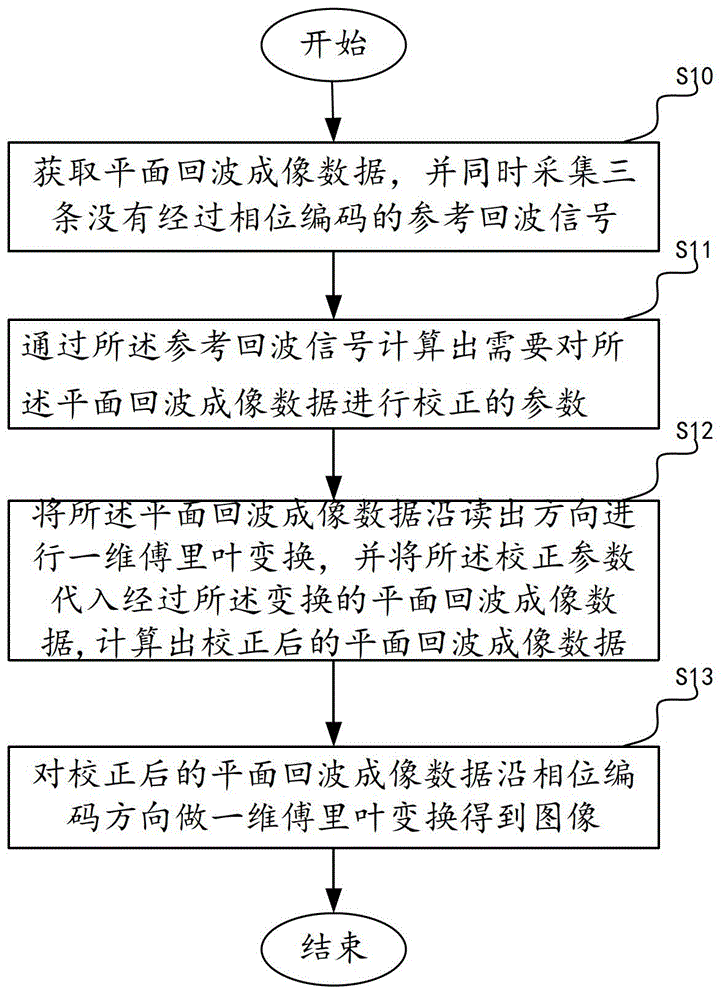
Echo planar imaging sequence image reconstruction method
ActiveCN104035059AEfficient removalOne-dimensional phase correction method is fast and simpleMagnetic measurementsRapid imagingReconstruction method
The invention provides an echo planar imaging sequence image reconstruction method comprising the following steps: acquiring echo planar imaging data Si and simultaneously acquiring three non-phase-encoded reference echo signals R1, R2 and R3; working out a parameter required for correcting the echo planar imaging data according to the reference echo signals; performing one-dimensional Fourier transform on the echo planar imaging data along a readout direction to obtain a transform result FSi, correcting FSi with the use of the correction parameter, and working out corrected echo planar imaging data; and performing one-dimensional Fourier transform on the corrected echo planar imaging data along a phase encoding direction to obtain an image. According to the echo planar imaging sequence image reconstruction method provided by the invention, in the presence of a stray field, the quick imaging advantage of echo planar sequence imaging can be kept, N / 2 artifacts can be effectively removed, and image deformation due to the existence of the stray field can be corrected.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Method and system for correcting image distortion and magnetic resonance imaging device
ActiveCN103376433ACorrect image distortionEffective correctionMagnetic measurementsComputer scienceDistortion
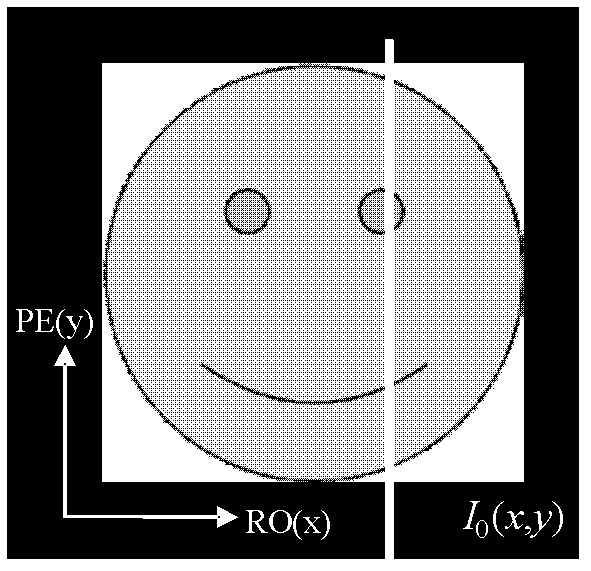
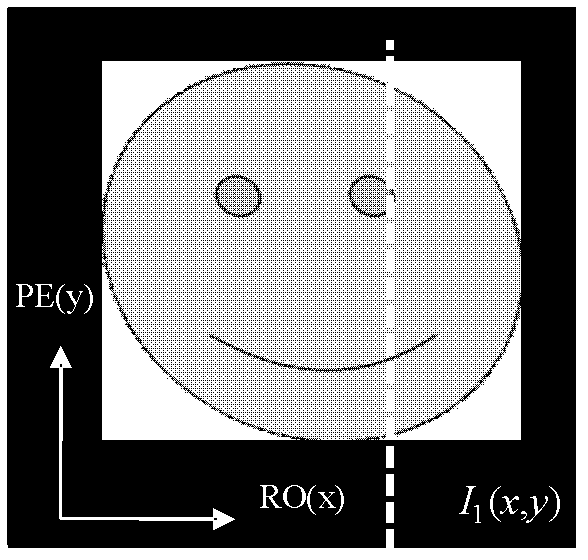
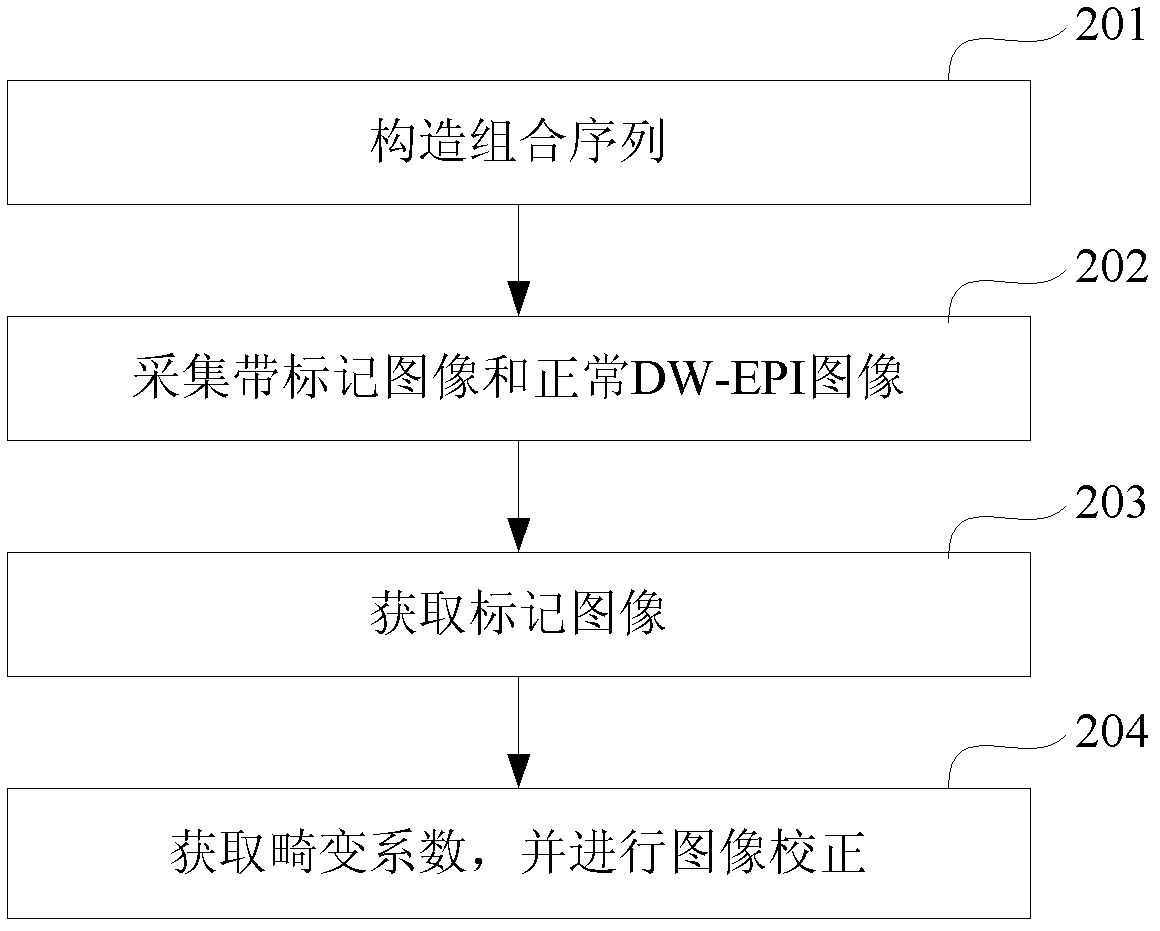
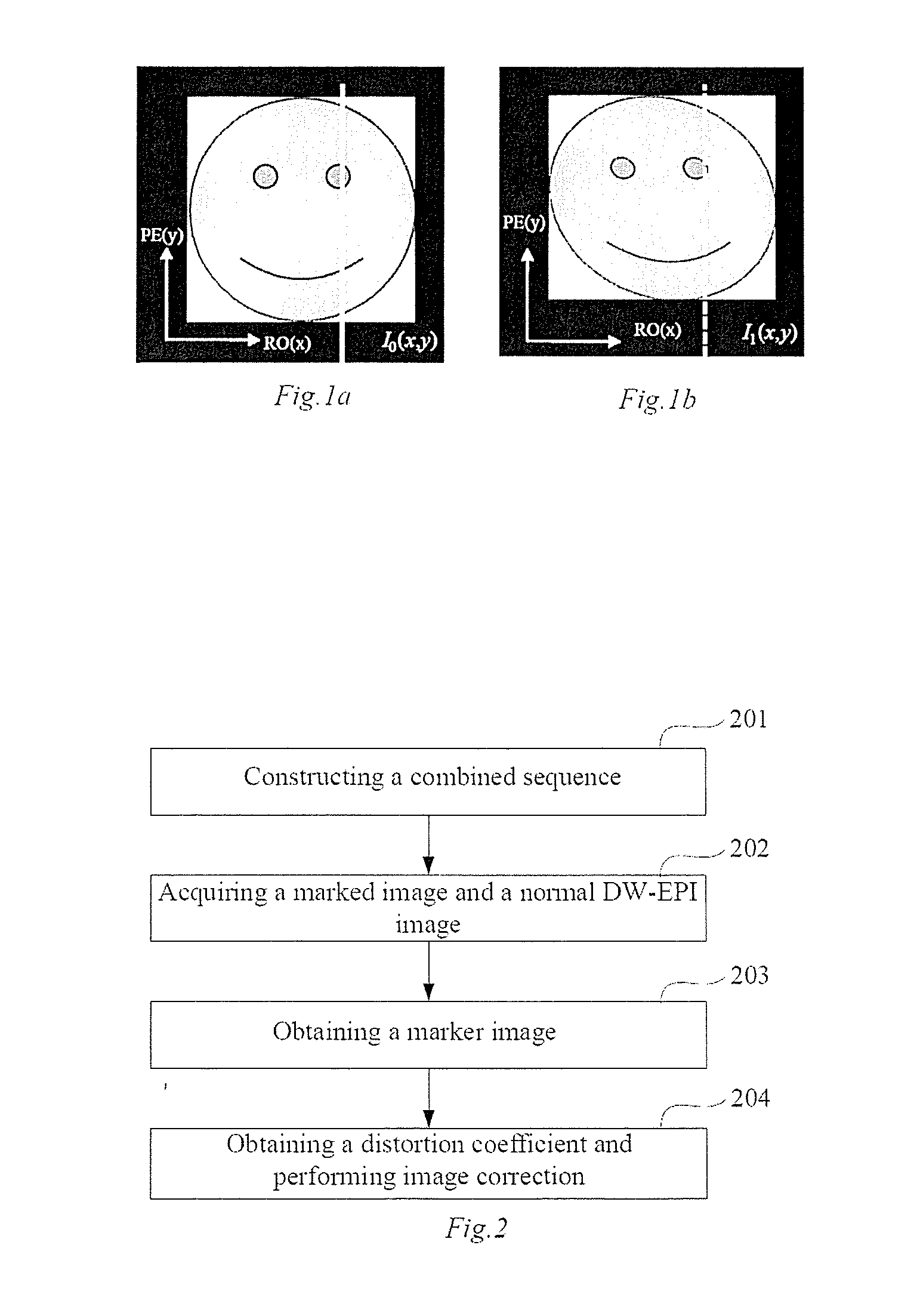
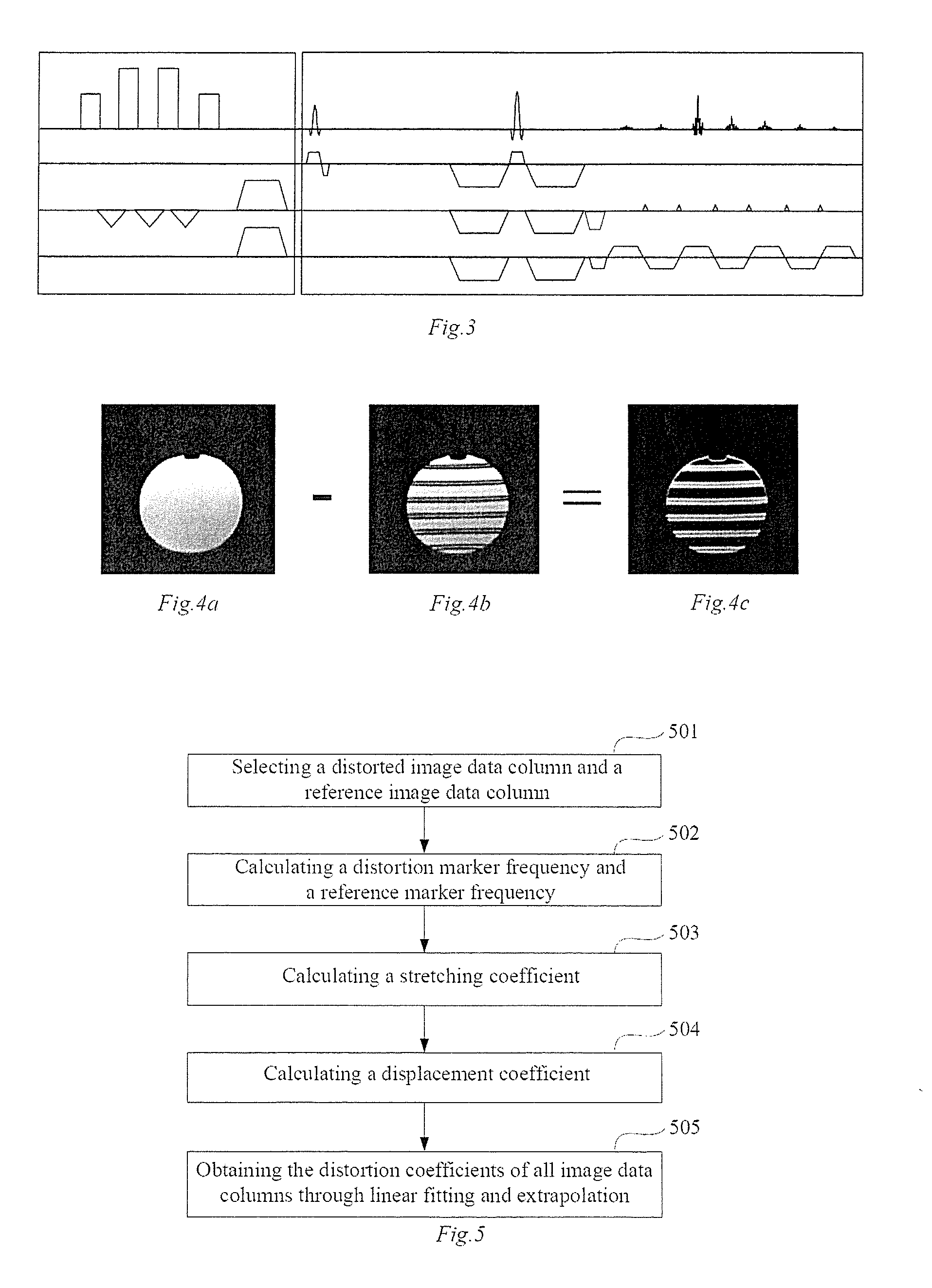
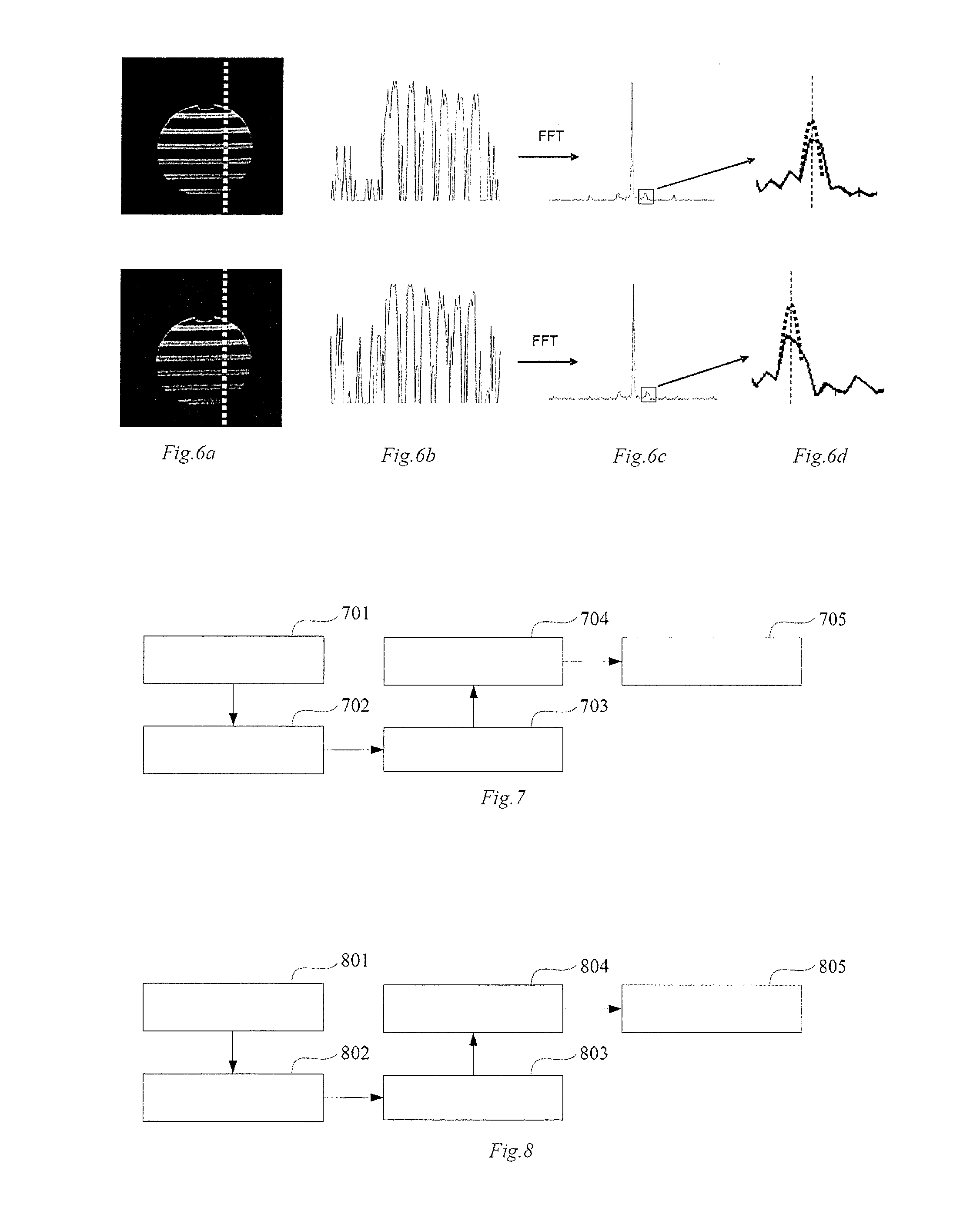
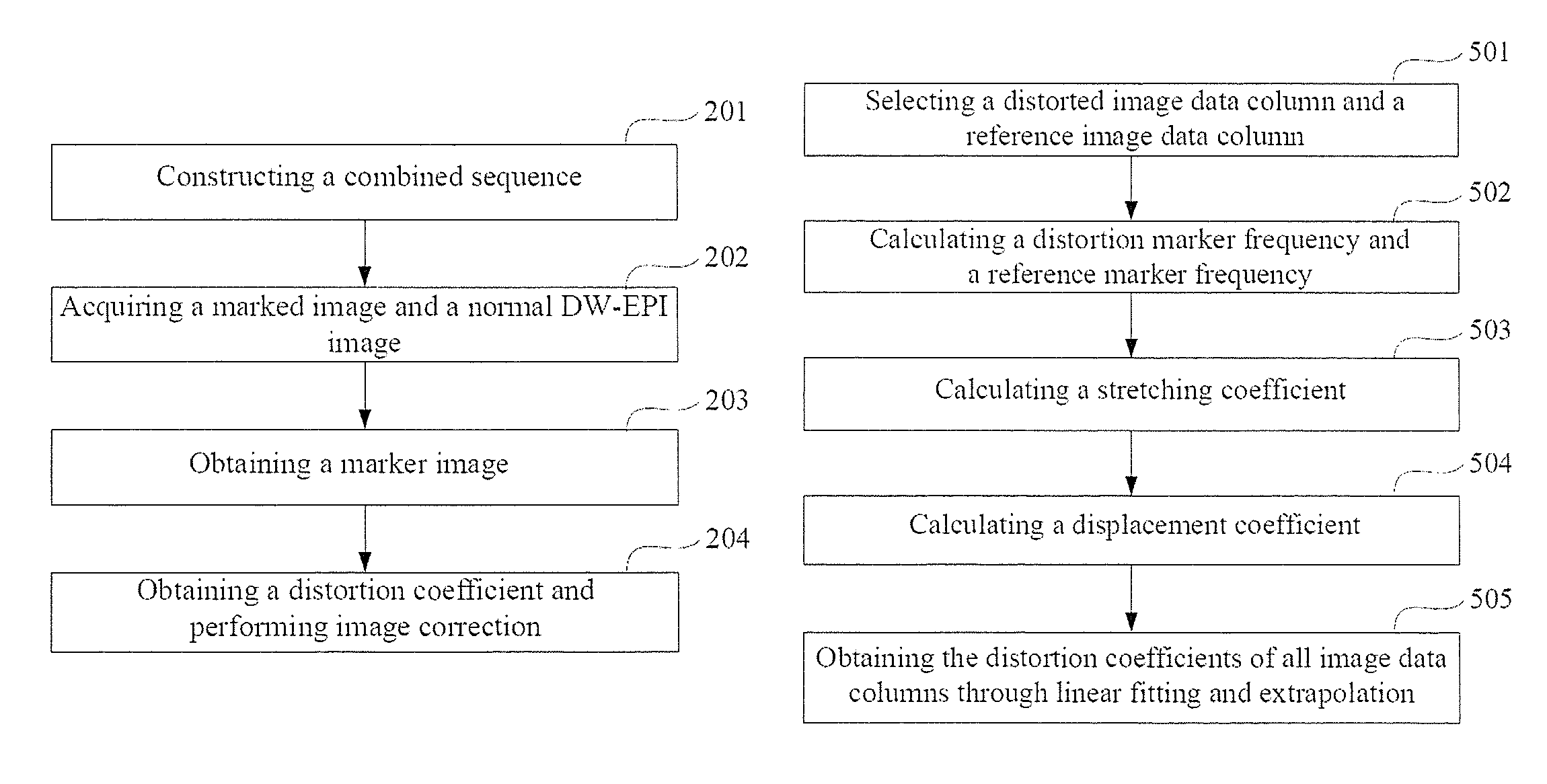
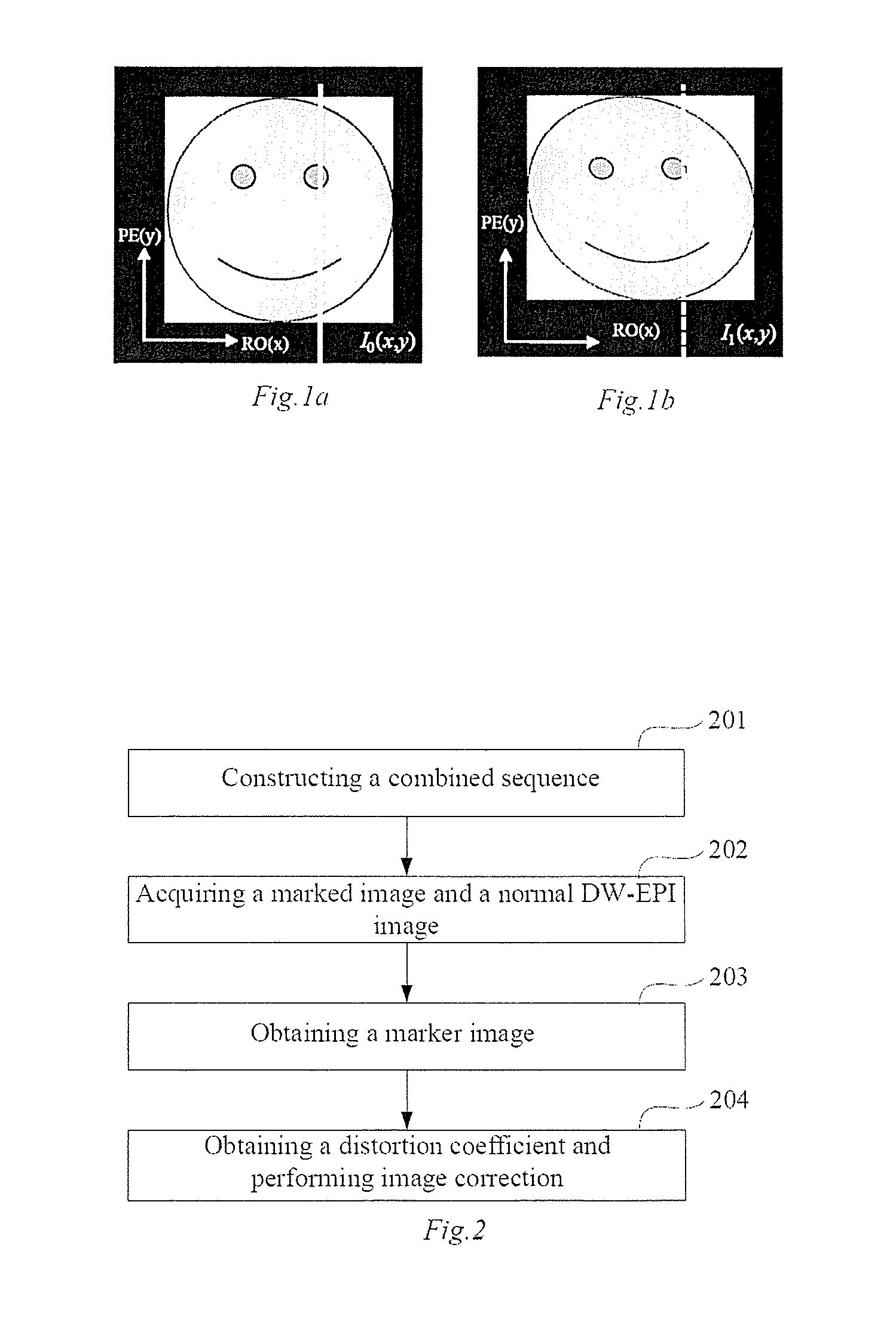
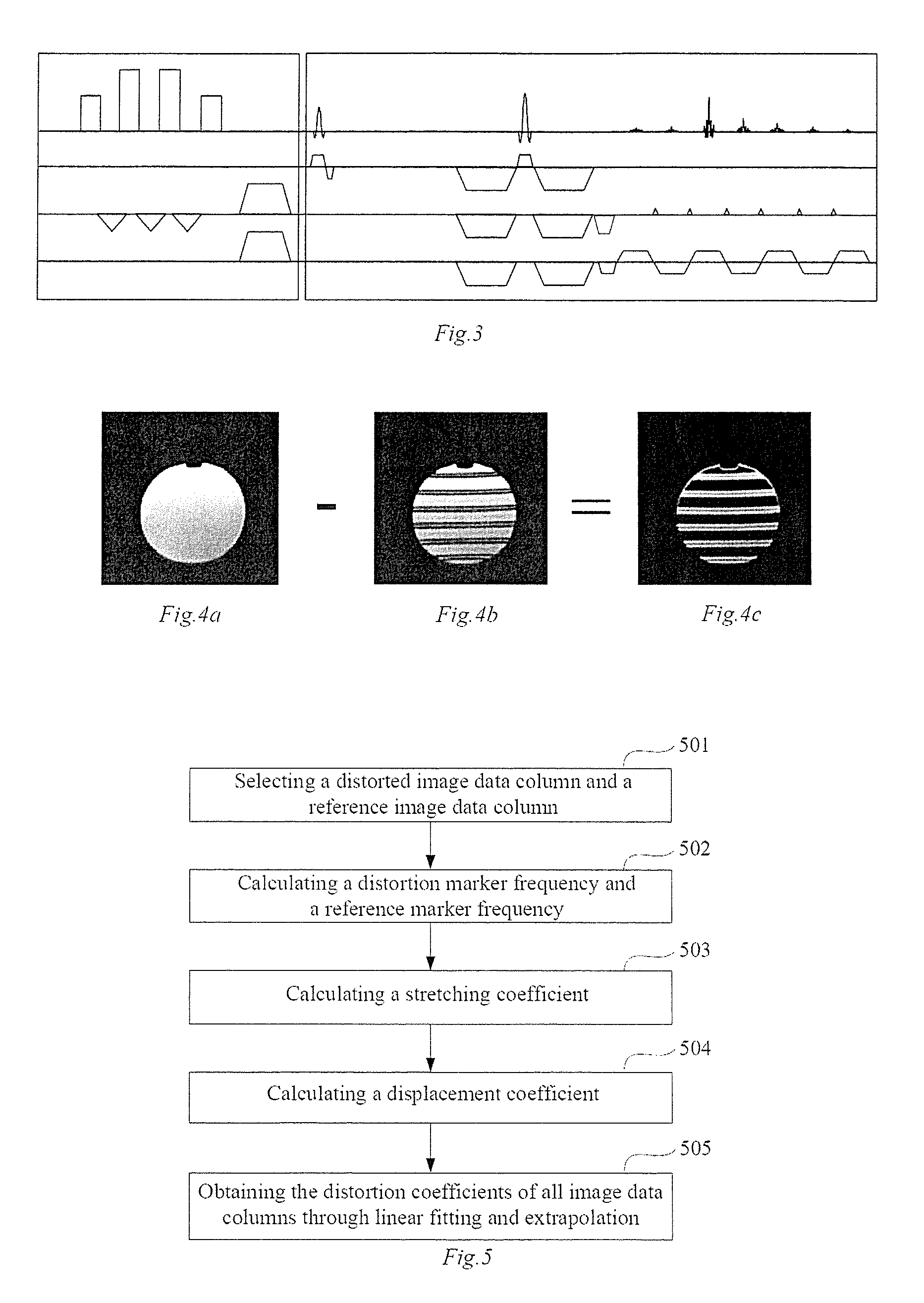
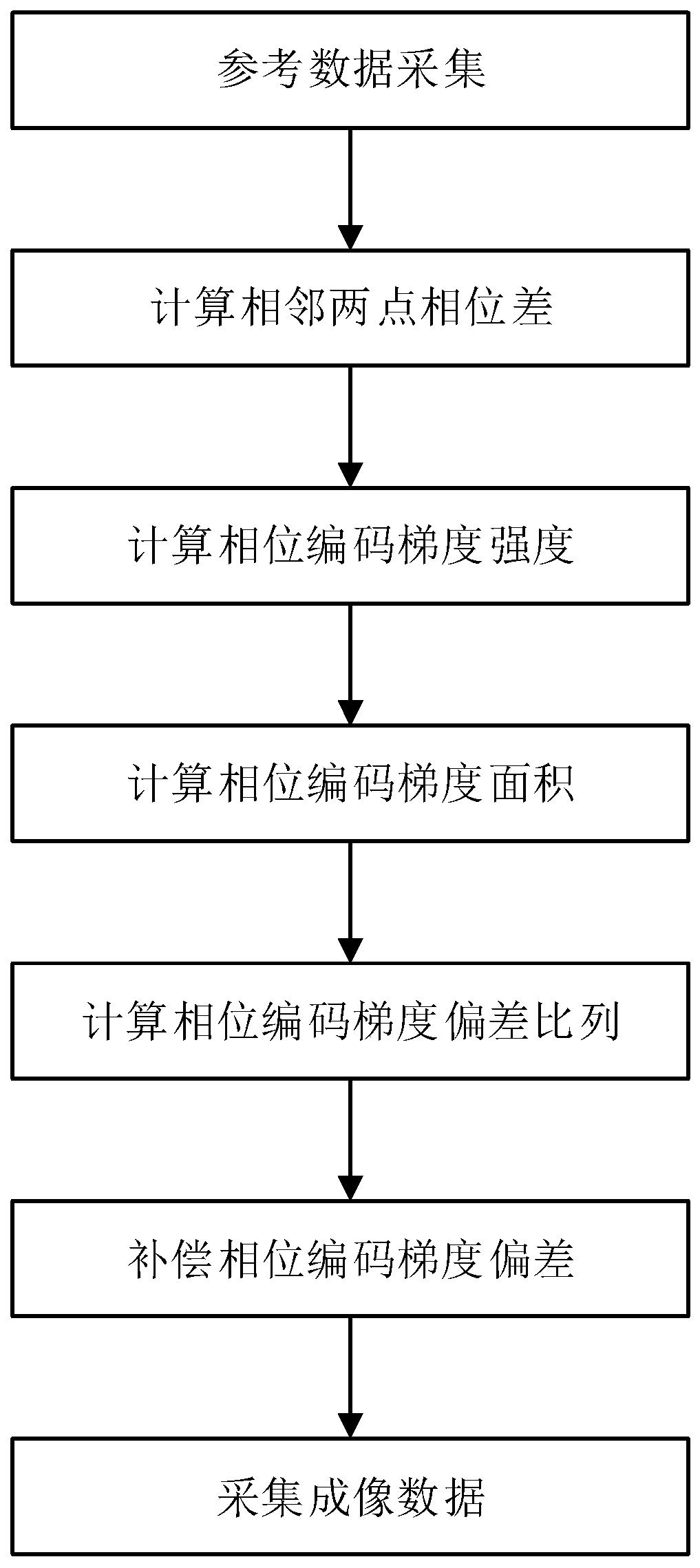
In a method for an apparatus correcting image distortion in diffusion-weighted echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging, a marker sequence is applied before a diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging sequence, to form a combined sequence. The combined sequence is used to obtain marked images with different preset b values and different preset diffusion directions. The diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging sequence is used to obtain diffusion-weighted echo planar images with the same b values and diffusion directions as the marked images. A stretching coefficient and a displacement coefficient are calculated for each image data column of the diffusion-weighted echo planar image. The stretching coefficient and displacement coefficient are used to correct the diffusion-weighted echo planar images.
Owner:SIEMENS SHENZHEN MAGNETIC RESONANCE
Neural network based planar echo imaging method and device
ActiveCN110095742AQuality improvementElimination of chemical shift artifactsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceMri image
The invention provides a neural network based planar echo imaging method and device. The method comprises that according to a selected magnetic resonance parameter, a planar echo imaging sequence is used to scan a detected body, and k-space data is obtained; according to the k-space data, an initial magnetic resonance image of the detected body is obtained; and the initial magnetic resonance imageis input to pre-trained first and second neutral networks to obtain a final magnetic resonance image of the detected body. The first neural network is configured to eliminate a chemical displacementartifact, and the second neural network is configured to correct image deformation. Based on the neural network based planar echo imaging method and device, the chemical displacement artifact can be eliminated effectively while deformation can be corrected, and the quality of the magnetic resonance image obtained by reconstruction is higher.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEUSOFT MEDICAL TECH LTD +1
Chemical shift imaging method and system
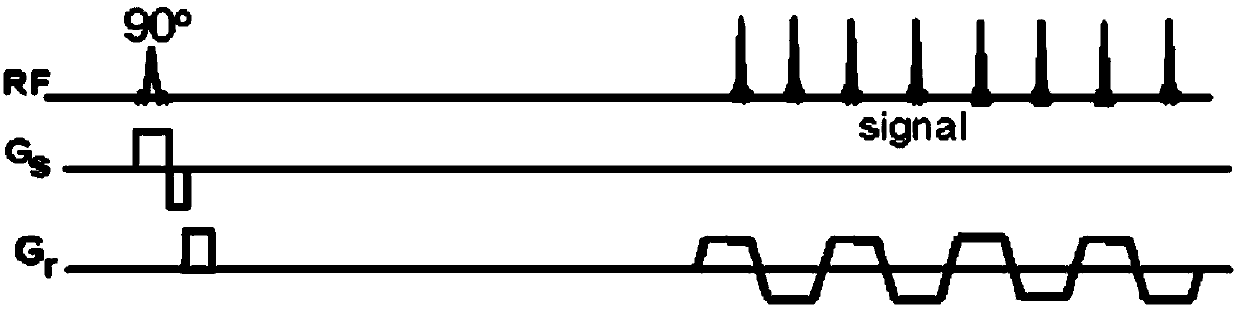
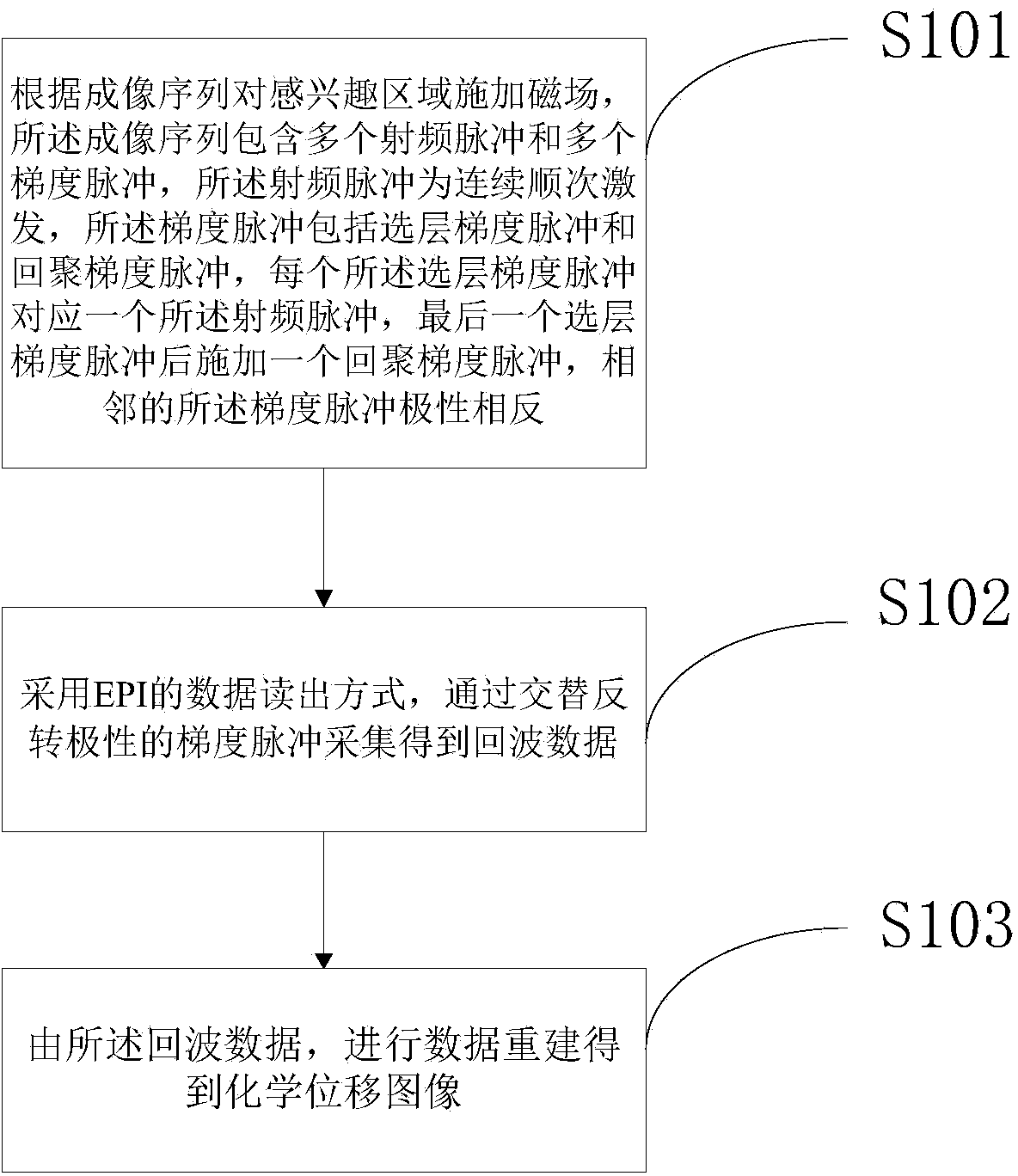
ActiveCN104181482AEasy diagnosisFacilitate Spectrum AcquisitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsChemical shift imagingRadio frequency
The invention discloses a chemical shift imaging method and system. The method comprises the following steps: a) applying a magnetic field to a region of interest according to an imaging sequence, the imaging sequence comprising a plurality of radio-frequency pulses and a plurality of gradient pulses, wherein the radio-frequency pulses are excited continuously in sequence, and the gradient pulses comprise layer-selection gradient pulses and convergence gradient pulses, the last layer-selection gradient pulse being applied with one phase convergence gradient pulse, and the polarities of adjacent gradient pulses being opposite; b) collecting echo data through a series of gradient pulses with alternatively-opposite polarities by adopting a data reading mode of EPI; and c)carrying out data reconstruction to obtain a chemical shift image based on the echo data. Compared with a conventional chemical shift imaging CSI, according to the chemical shift imaging method and system in the technical scheme of the invention, the collection time is reduced to one order of magnitude, thereby helping to finish spectrum collection is a short time; and compared with echo planar spectrum imaging EPSI, 3-4 times of volume elements are collected under the same time and conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
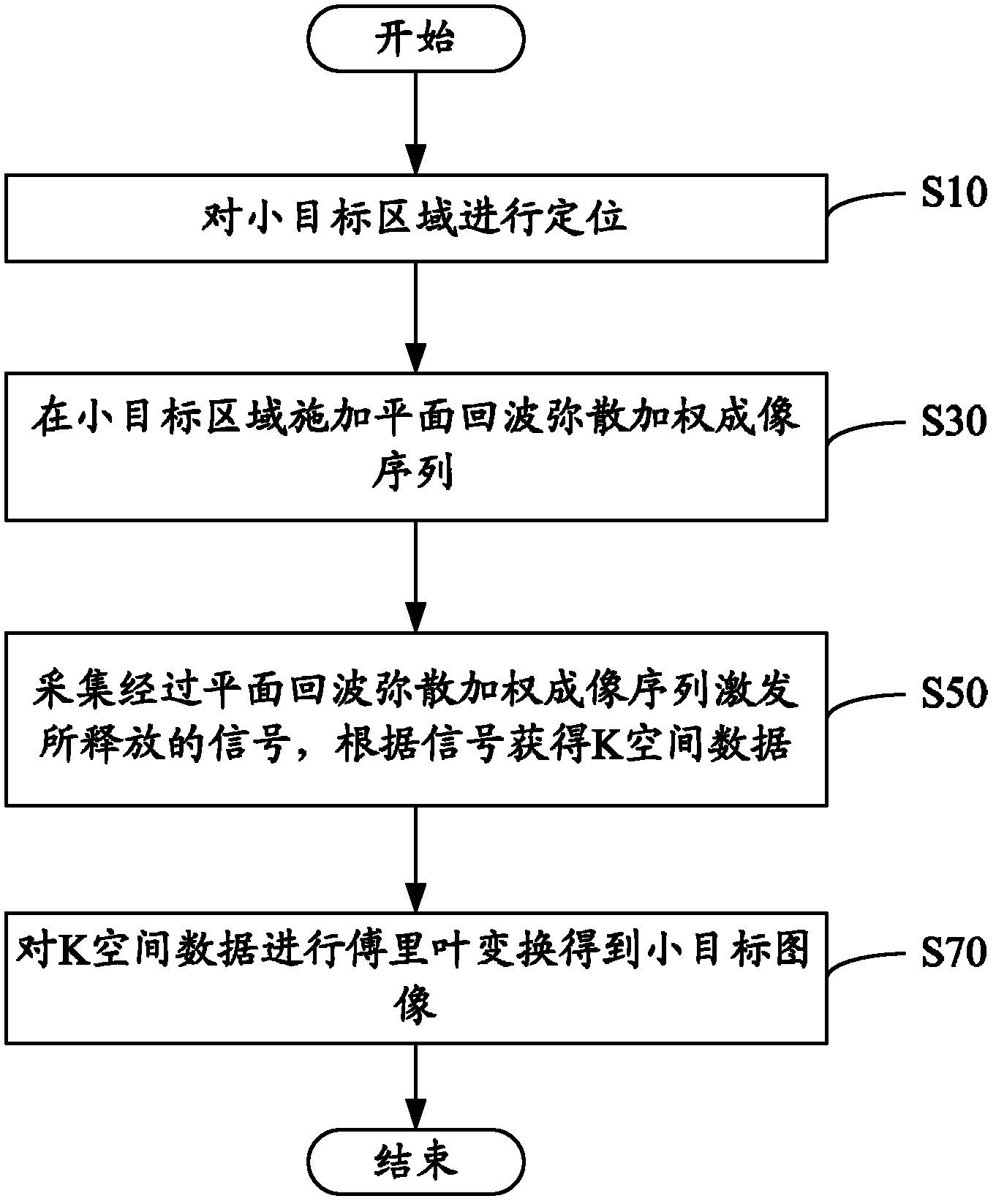
Magnetic resonance imaging method and system aiming at small targets
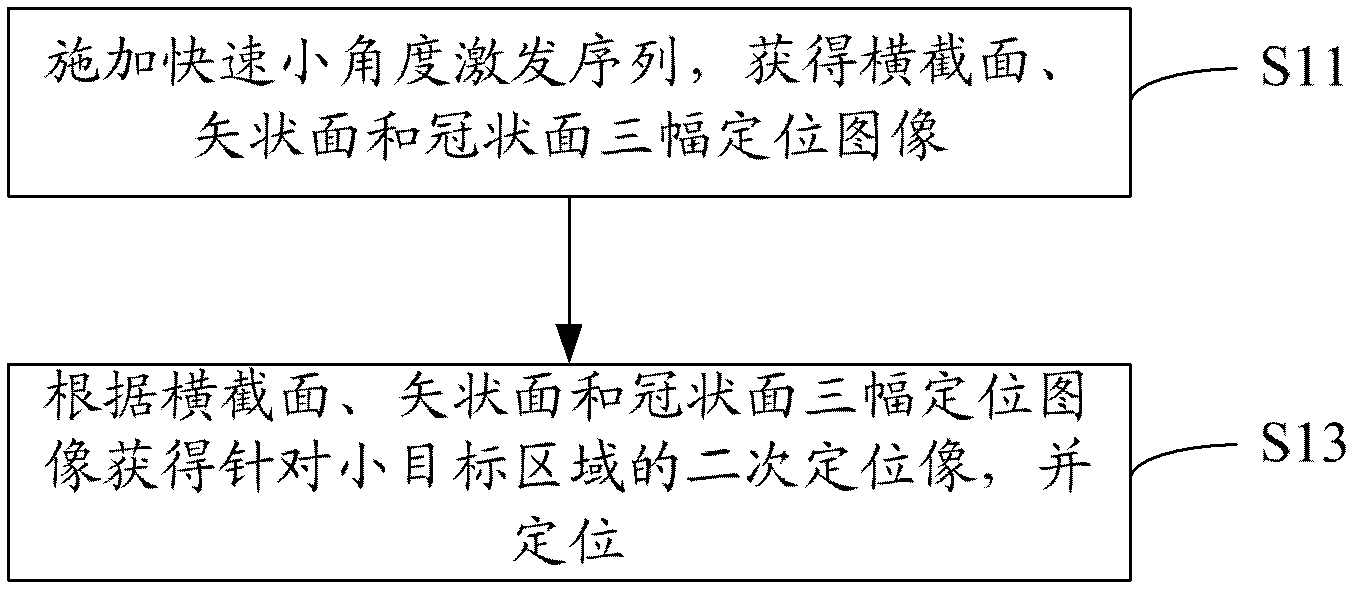
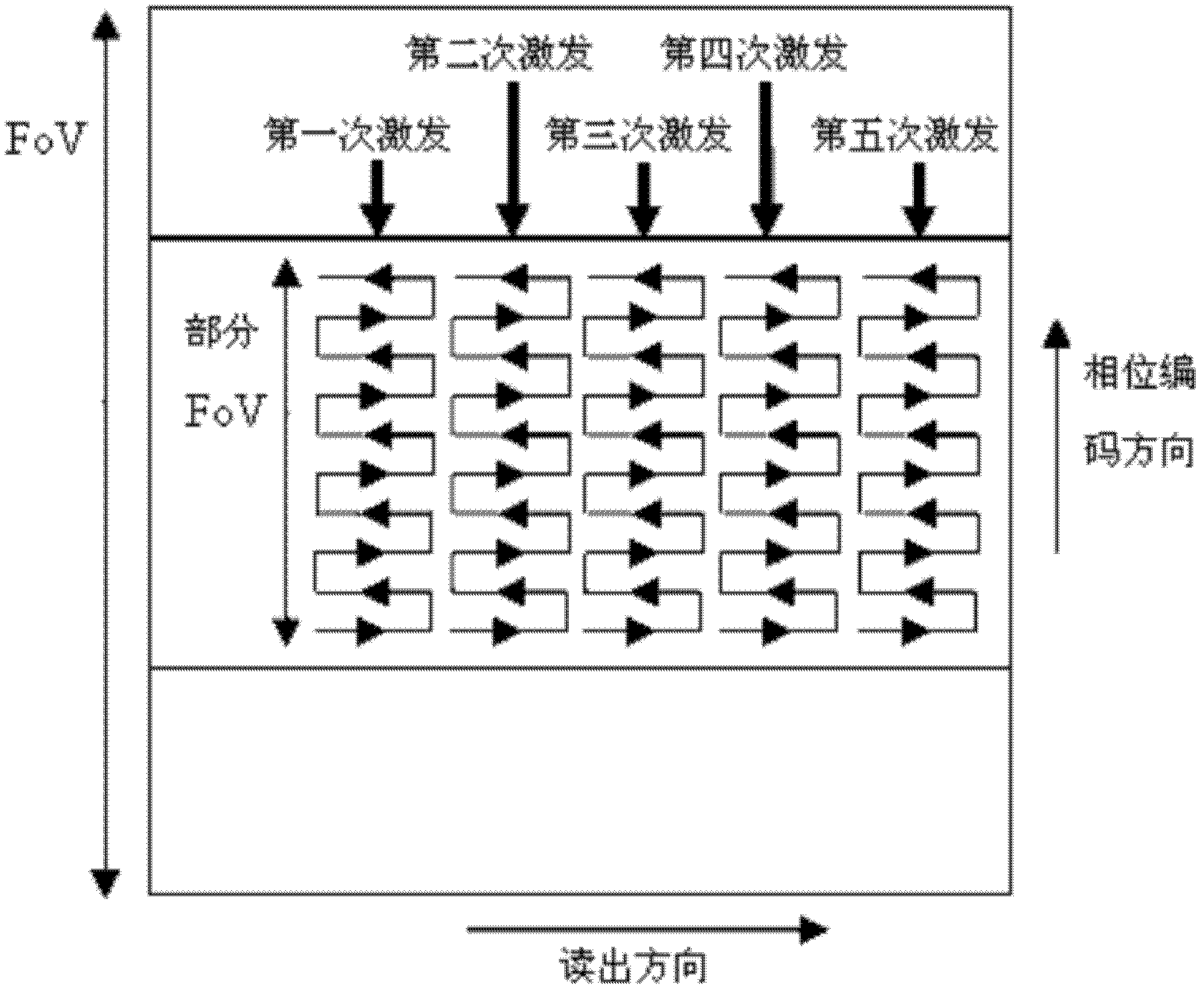
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method and a magnetic resonance imaging system aiming at small targets. The magnetic resonance imaging method comprises the steps of: positioning a small-target region; exerting plane echo dispersion weighted imaging sequences in the small-target region; collecting signals released through the excitation of the plane echo dispersion weighted imaging sequences, and obtaining K space data according to the signals; and carrying out Fourier transform on the K space data to obtain small target images. The small-target region positioning comprises the steps of: exerting fast small-angle excitation sequences, and obtaining three positioning images of the cross section, the sagittal plane and the coronal plane; and obtaining secondary positioning images aiming at the small-target region according to the three positioning images of the cross section, the sagittal plane and the coronal plane, and carrying out positioning. The plane echo dispersion weighted imaging sequence exertion step comprises the process that: the plane echo dispersion weighted imaging sequences formed through the combination of selective excitation of the two-dimensional space is excited for many times. Through positioning the small-target region and exerting the plane echo dispersion weighted imaging sequences on the small-target region, the goal of carrying out magnetic resonance imaging on the small-target region is reached.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Method for fast multi-slice mapping of myelin water fraction
InactiveUS8170644B2Increase the number ofExpand coverageMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionDiseaseMulti slice
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Method for correcting image distortion and system, and magnetic resonance imaging equipment
ActiveUS20130285653A1Correct image distortionSimple calculationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionComputer scienceDistortion
In a method for an apparatus correcting image distortion in diffusion-weighted echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging, a marker sequence is applied before a diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging sequence, to form a combined sequence. The combined sequence is used to obtain marked images with different preset b values and different preset diffusion directions. The diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging sequence is used to obtain diffusion-weighted echo planar images with the same b values and diffusion directions as the marked images. A stretching coefficient and a displacement coefficient are calculated for each image data column of the diffusion-weighted echo planar image. The stretching coefficient and displacement coefficient are used to correct the diffusion-weighted echo planar images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
System and method for reduced field of view magnetic resonance imaging
A method for reduced field of view magnetic resonance (MR) imaging includes applying a pulse sequence using a plurality of gradient coils and at least one RF coil of a magnetic resonance imaging system. The pulse sequence includes a two dimensional (2D) echo-planar RF excitation pulse with a plurality of side lobes along a slice select axis and a multiband RF refocusing pulse. MR data is acquired in response to the application of the pulse sequence and at least one MR image is reconstructed based on the MR data. The at least one MR image may then be displayed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus for echo planar imaging with data entry into k-space along a zigzag trajectory
ActiveUS9739857B2Data augmentationHigh strengthMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceImage sequence
In a method and apparatus for echo planar magnetic resonance (MR) imaging sequence of phase encoding gradient fields and a sequence of readout gradient fields are applied in order to produce a well-defined zigzag-type trajectory for entering raw data into k-space. Zigzag-type trajectories can be achieved that have flanks without curvature, or without significant curvature. Cartesian methods for image reconstruction of parallel MR imaging are applied to echo planar MR imaging with such zigzag-type trajectories.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
3D gradient spin echo imaging method and device for oscillation gradient preparation
ActiveCN111352054AReduce scan timeImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsMultiplexingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
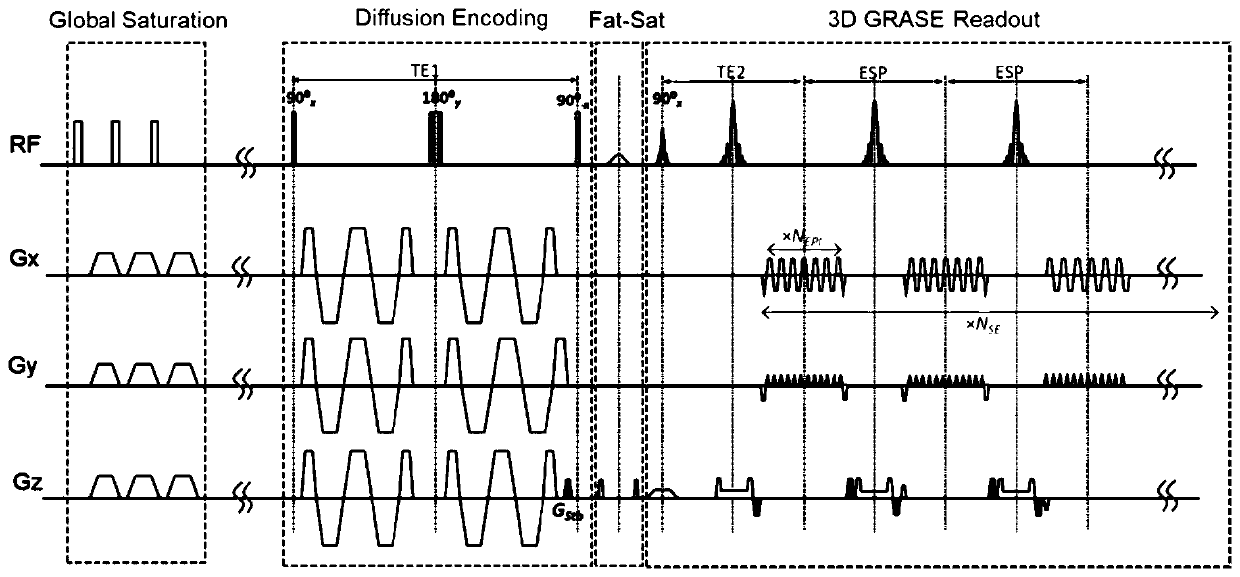
The invention discloses a 3D gradient spin echo imaging method and device for oscillation gradient preparation. The imaging method comprises the following steps: firstly, destroying previous residualtransverse magnetization in a global saturation module; secondly, embedding a pair of trapezoidal cosine oscillation gradients into a 90 degrees <x>- 180 degrees <y>- 90 degrees <-x> radio frequency pulse through a diffusion coding module, and separating diffusion coding from signal acquisition; then, using a fat saturation module\ for inhibiting the fat signal; and finally, acquiring signals in agradient spin echo reading mode, and using multiplexing sensitivity coding for reconstructing and correcting phase errors among multiple excitations. Compared with an oscillation gradient dispersionsequence based on 2D plane echo used on a 3T clinical system, the gradient spin echo sequence prepared by 3D oscillation gradient effectively improves the imaging time and the signal to noise ratio, and is beneficial to clinical conversion of a time-dependent dispersion MRI technology.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
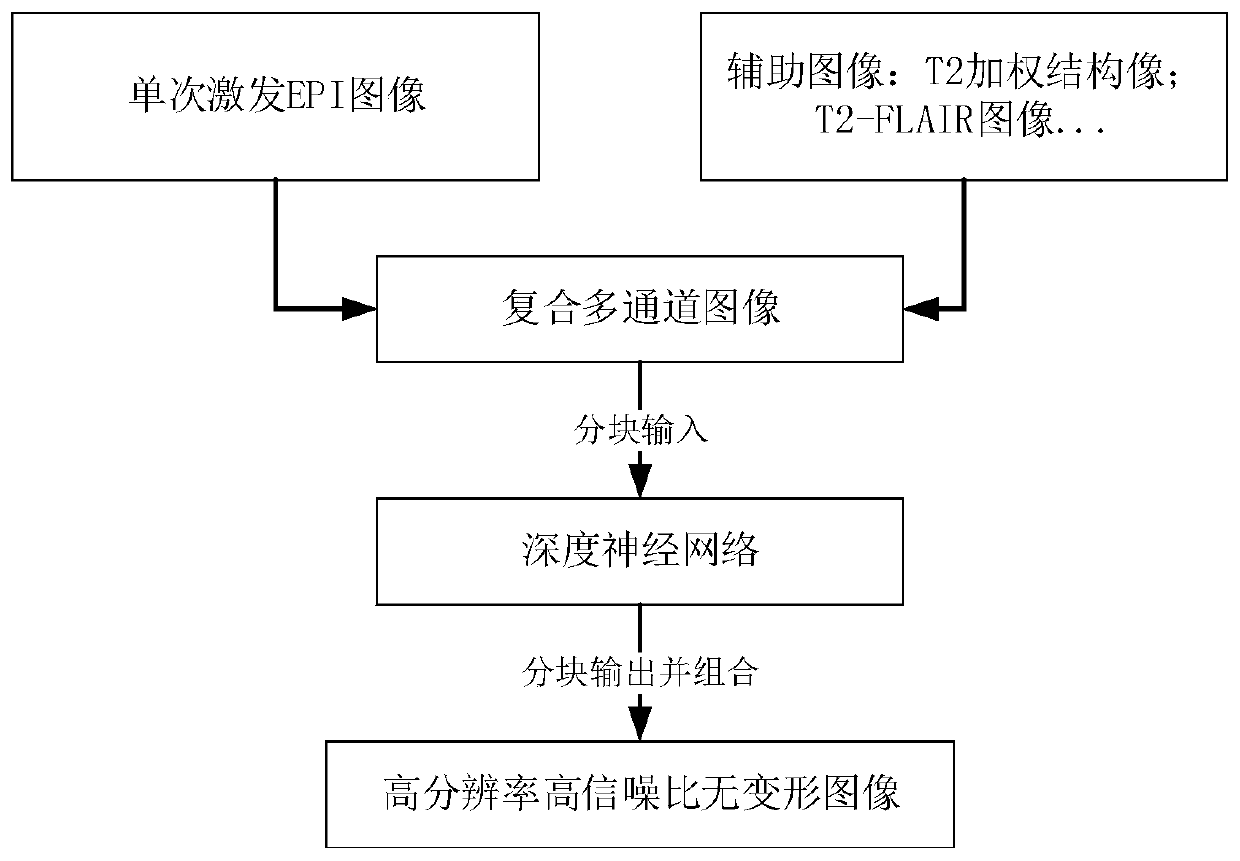
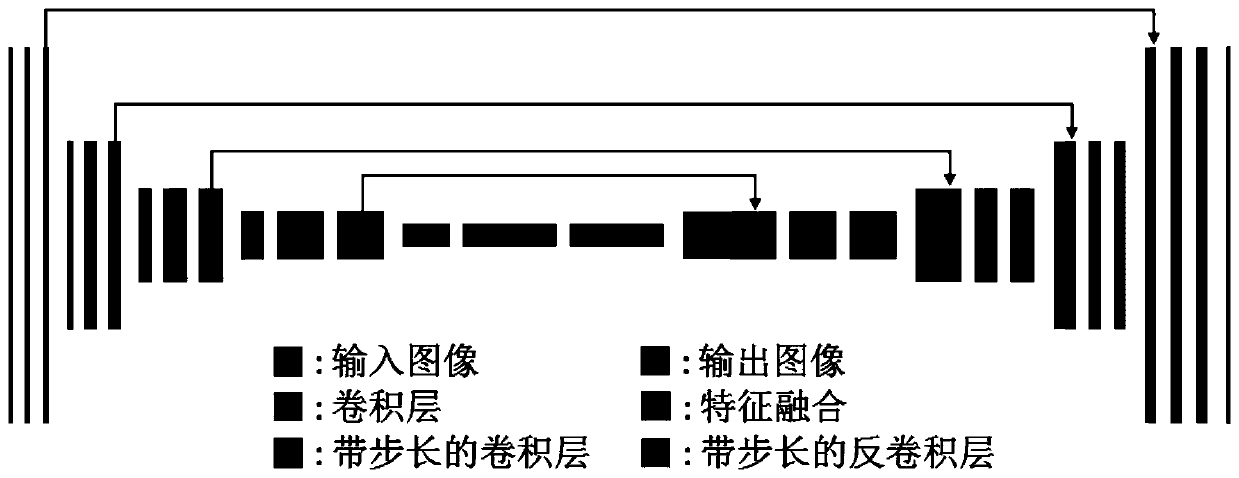
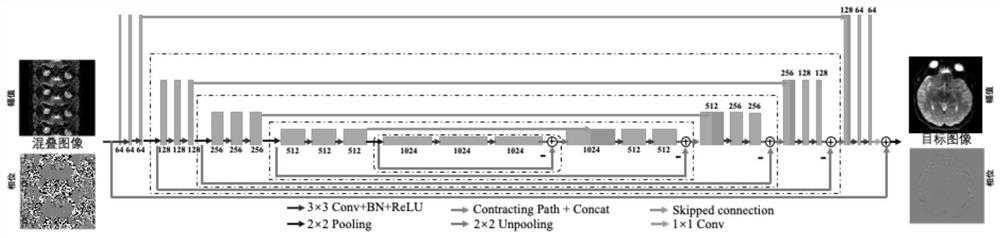
Deformation-free single-excitation plane echo imaging method and device based on deep learning
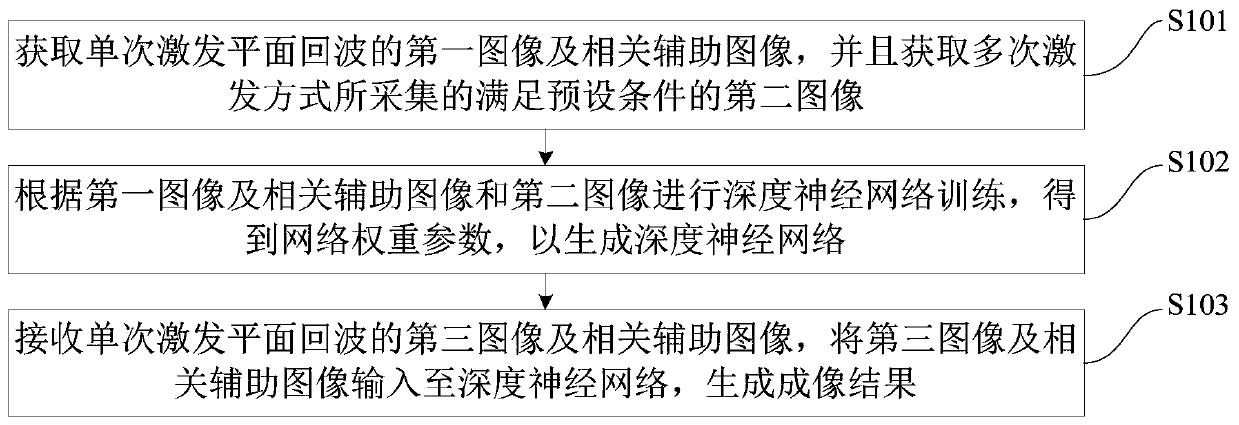
ActiveCN110895320AQuality improvementHigh resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImage resolutionRapid scan
The invention discloses a high-resolution high-signal-to-noise-ratio deformation-free single excitation plane echo imaging method and device based on deep learning, and the method comprises the steps:obtaining a first image and a related auxiliary image of a single excitation plane echo, and obtaining a second image which is collected in a mode of multiple excitation and meets a preset condition;performing deep neural network training according to the first image, the related auxiliary image and the second image to obtain a network weight parameter so as to generate a deep neural network; and receiving a third image and a related auxiliary image of the single excitation plane echo, and inputting the third image and the related auxiliary image into the deep neural network to generate an imaging result. According to the method, the high-resolution and high-signal-to-noise-ratio non-deformation magnetic resonance image can be obtained under rapid scanning of single excitation, and the problems that in an existing single excitation EPI technology, the signal-to-noise ratio and deformation artifacts are serious, and the resolution ratio is low are effectively solved, and the problem that the collection time is too long when a multi-excitation technology is used is effectively solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
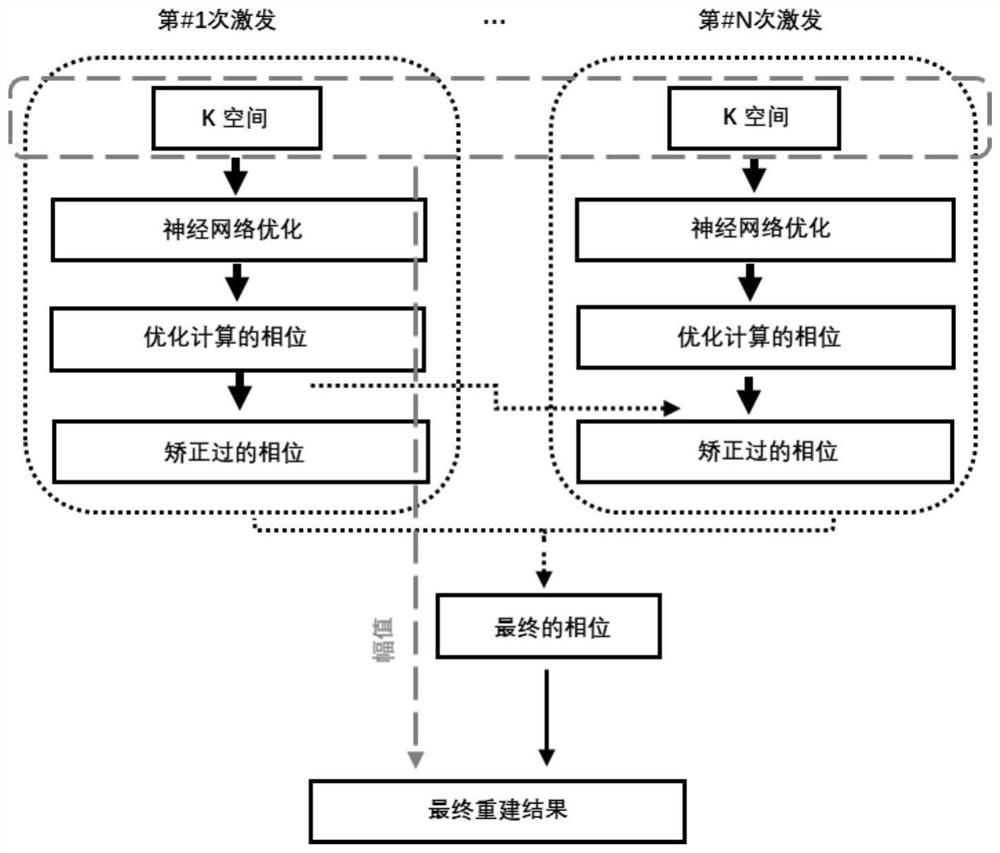
Multiple-shot planar echo magnetic resonance imaging method based on neural network
ActiveCN112763958AAccurate phase estimationRebuild fastMagnetic measurementsSample imageReconstruction algorithm
The invention belongs to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging, and particularly relates to a multiple-shot plane echo magnetic resonance imaging method based on a deep learning neural network. The invention provides a brand-new method for accurate phase correction and rapid image reconstruction for multiple-shot plane echo magnetic resonance imaging. Compared with a traditional under-sampling image reconstruction algorithm based on a model, the deep learning neural network is utilized, deep learning is applied to aliasing correction of multiple shot echo planar imaging (MSH-EPI) images, and an aliasing-free single shot echo planar imaging (SSH-EPI) image is used as a target in the training stage. An aliasing SSH-EPI image having the same under-sampling factor and trajectory as the multiple shot plane echo is sent to the network so as to improve the precision of phase estimation.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
System and method for accelerated MR imaging
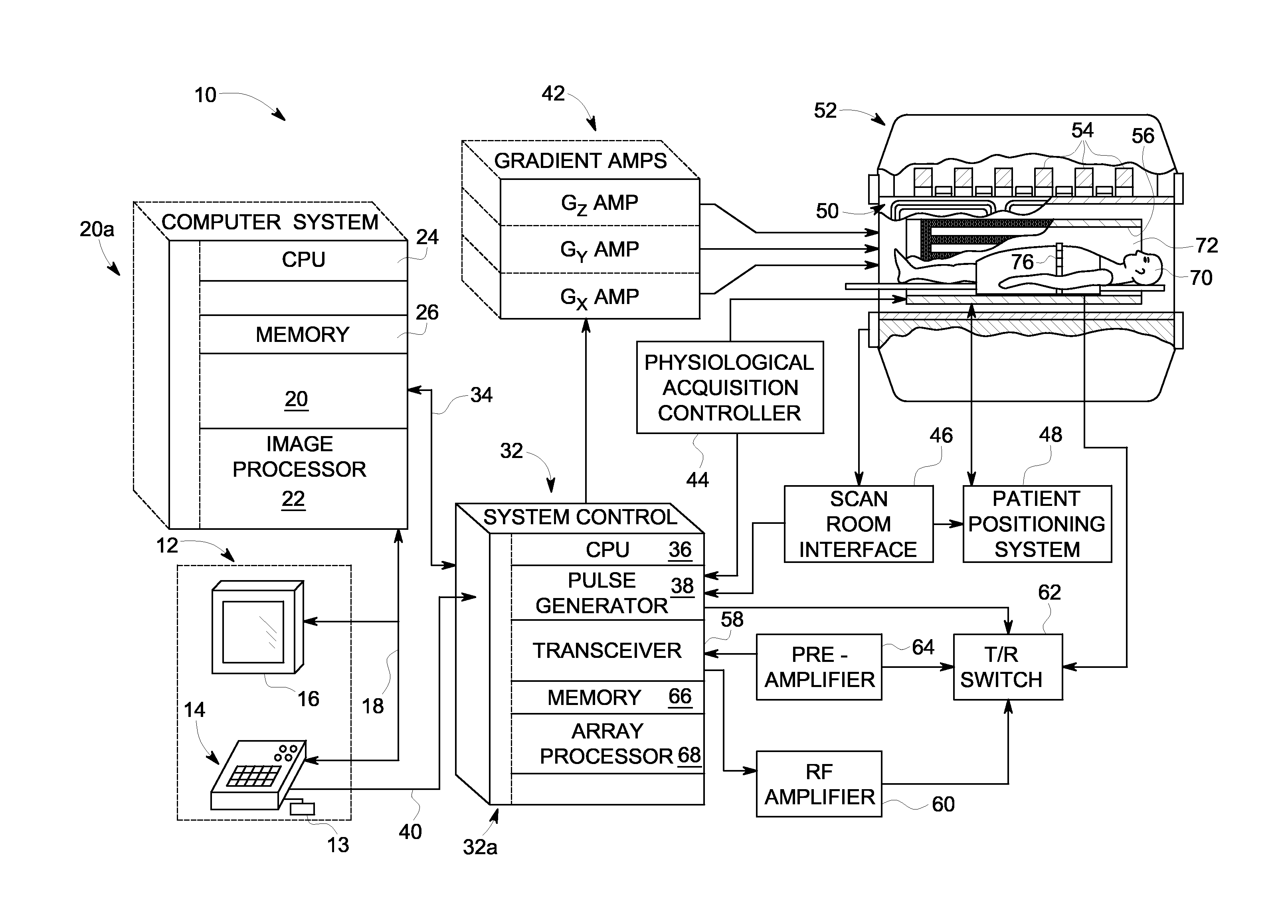
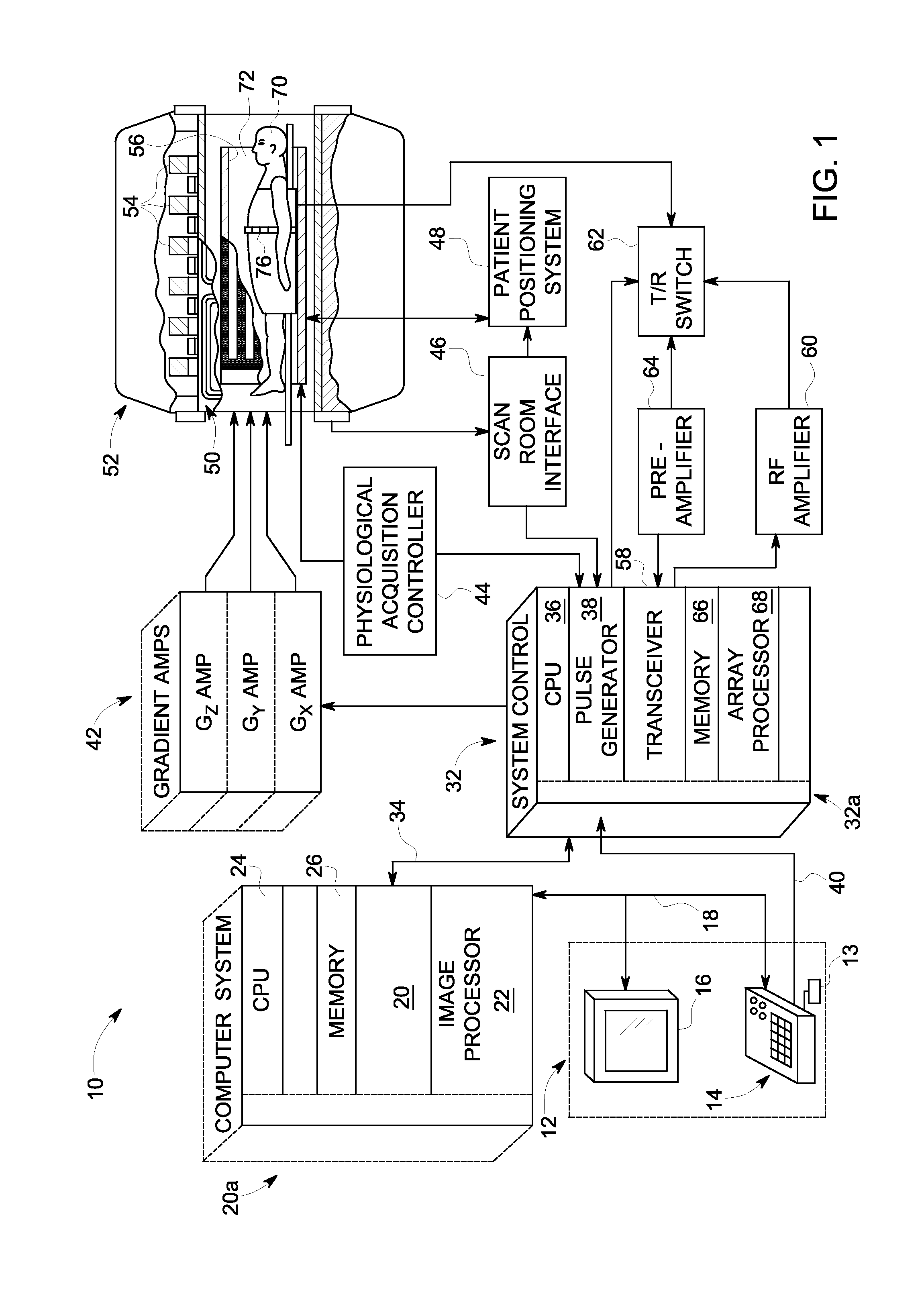
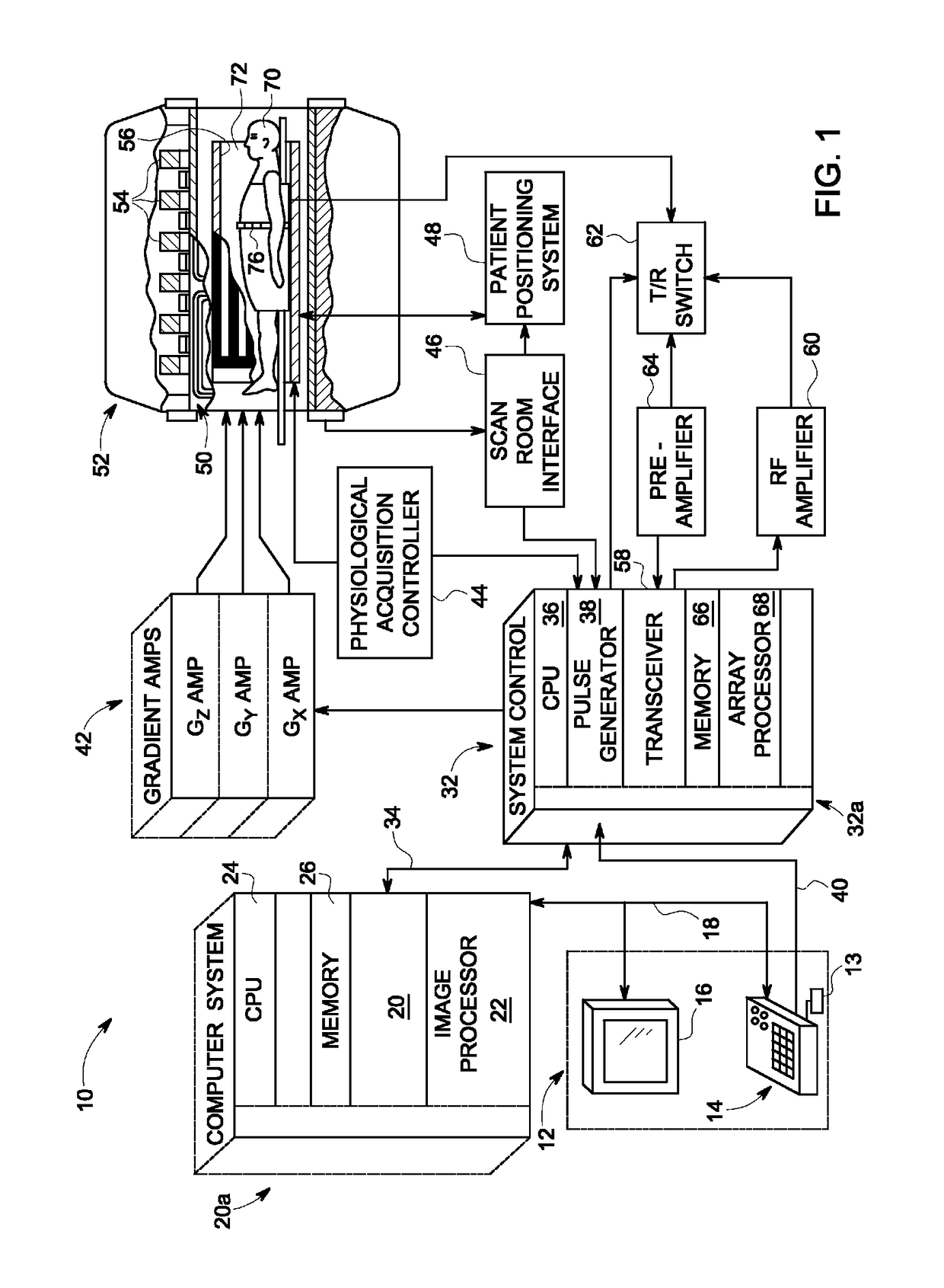
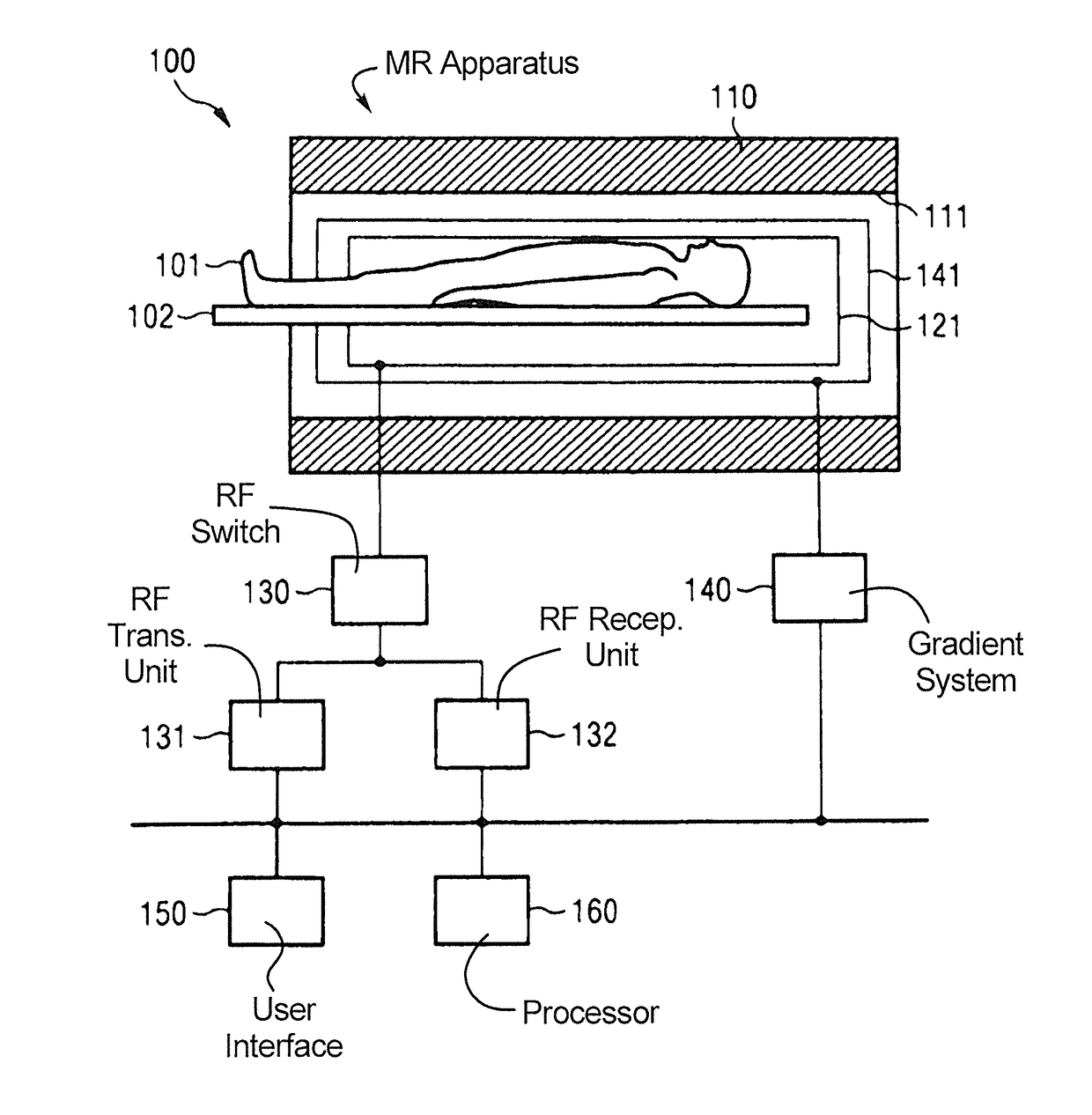
A system and method for accelerated MR imaging includes a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system having a plurality of gradient coils positioned about a bore of a magnet, and an RF transceiver system and an RF switch controlled by a pulse module to transmit RF signals to an RF coil assembly comprising at least one RF transmit coil and comprising multiple coils to acquire MR images. The MRI apparatus also has a computer programmed to excite multiple pencil regions by use of an under-sampled echo-planar excitation trajectory and acquire MR signals simultaneously on multiple channels of the RF coil assembly. The computer is also programmed to separate contributions from the various multiple pencil regions by use of parallel imaging reconstruction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
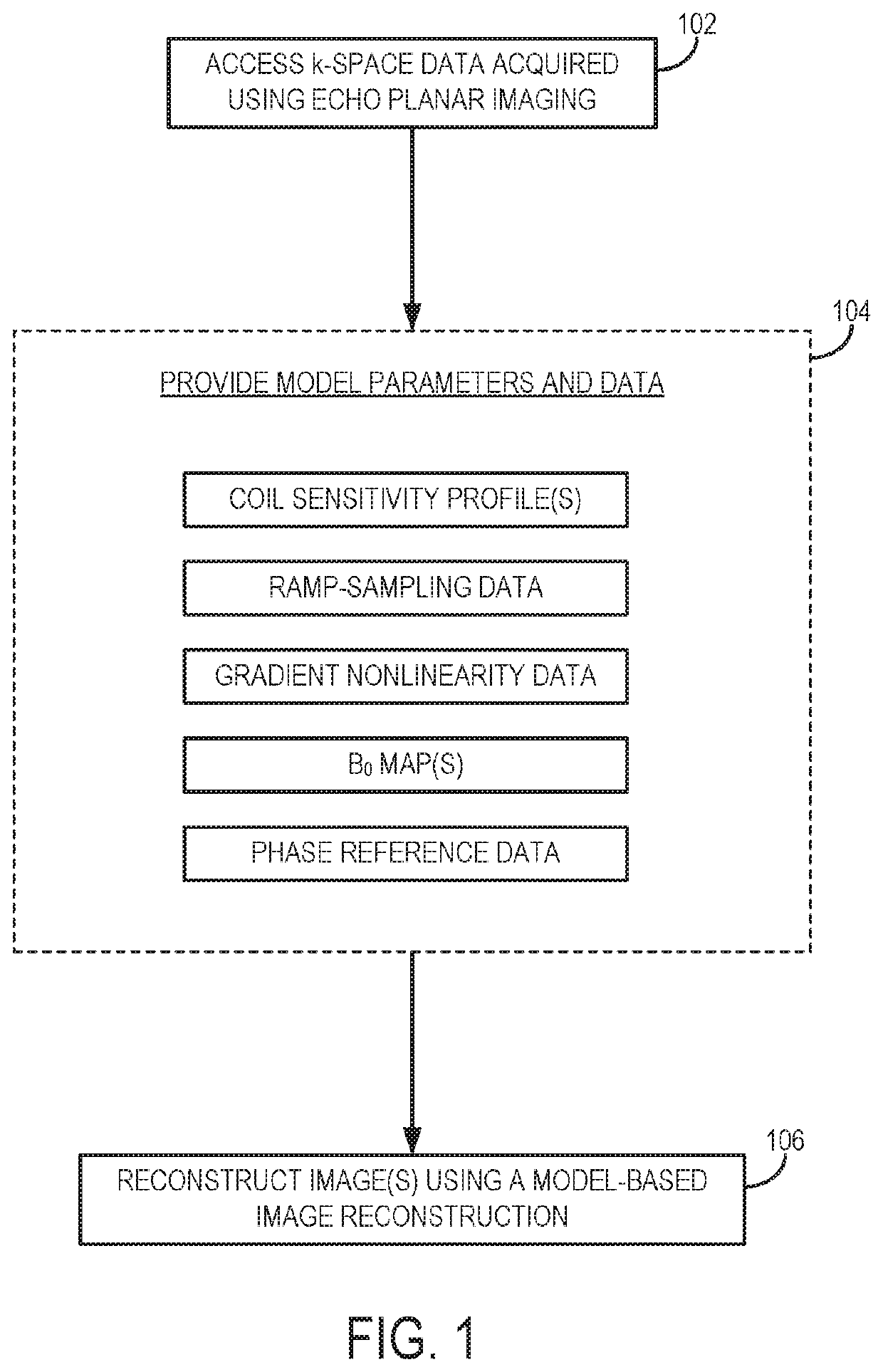
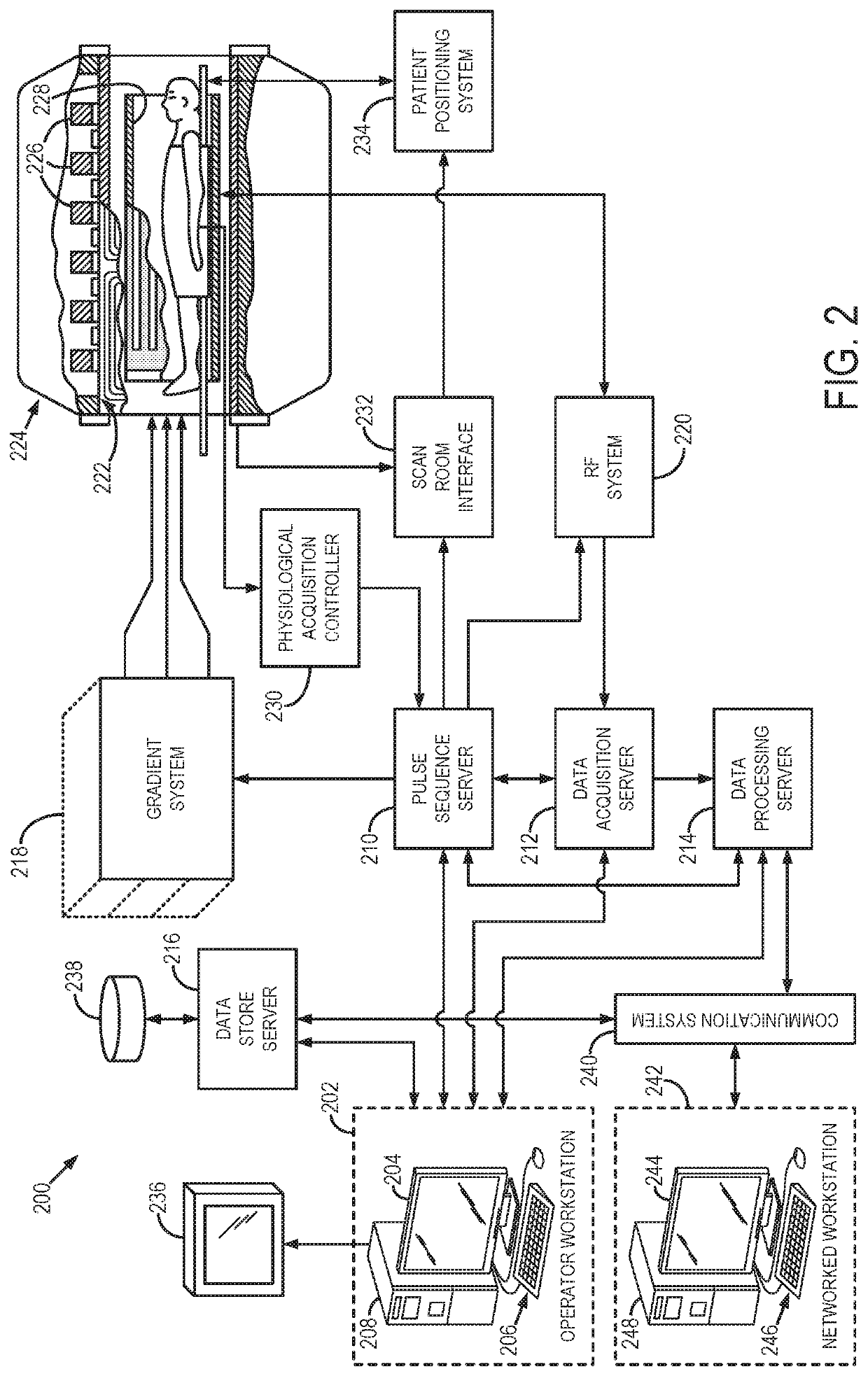
Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction for Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Echo Planar Readout
PendingUS20220236358A1Improve Noise PerformanceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnet resonance imagingMR - Magnetic resonance
Images are reconstructed from k-space data using a model-based image reconstruction that prospectively and simultaneously accounts for multiple non-idealities in accelerated single-shot-EPI acquisitions. In some implementations, nonlinear regularization (e.g., sparsity regularization) is also incorporated to mitigate noise amplification. The reconstructed images have reduced distortions and noise amplification effects relative to those images that are processed using conventional post-reconstruction techniques to correct for non-idealities.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
System and method for accelerated mr imaging
ActiveUS20090267602A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTransceiverParallel imaging
A system and method for accelerated MR imaging includes a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system having a plurality of gradient coils positioned about a bore of a magnet, and an RF transceiver system and an RF switch controlled by a pulse module to transmit RF signals to an RF coil assembly comprising at least one RF transmit coil and comprising multiple coils to acquire MR images. The MRI apparatus also has a computer programmed to excite multiple pencil regions by use of an under-sampled echo-planar excitation trajectory and acquire MR signals simultaneously on multiple channels of the RF coil assembly. The computer is also programmed to separate contributions from the various multiple pencil regions by use of parallel imaging reconstruction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for correcting image distortion and system, and magnetic resonance imaging equipment
ActiveUS9404987B2Improve image qualityCorrect distortionMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionDiffusionComputer science
In a method for an apparatus correcting image distortion in diffusion-weighted echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging, a marker sequence is applied before a diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging sequence, to form a combined sequence. The combined sequence is used to obtain marked images with different preset b values and different preset diffusion directions. The diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging sequence is used to obtain diffusion-weighted echo planar images with the same b values and diffusion directions as the marked images. A stretching coefficient and a displacement coefficient are calculated for each image data column of the diffusion-weighted echo planar image. The stretching coefficient and displacement coefficient are used to correct the diffusion-weighted echo planar images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
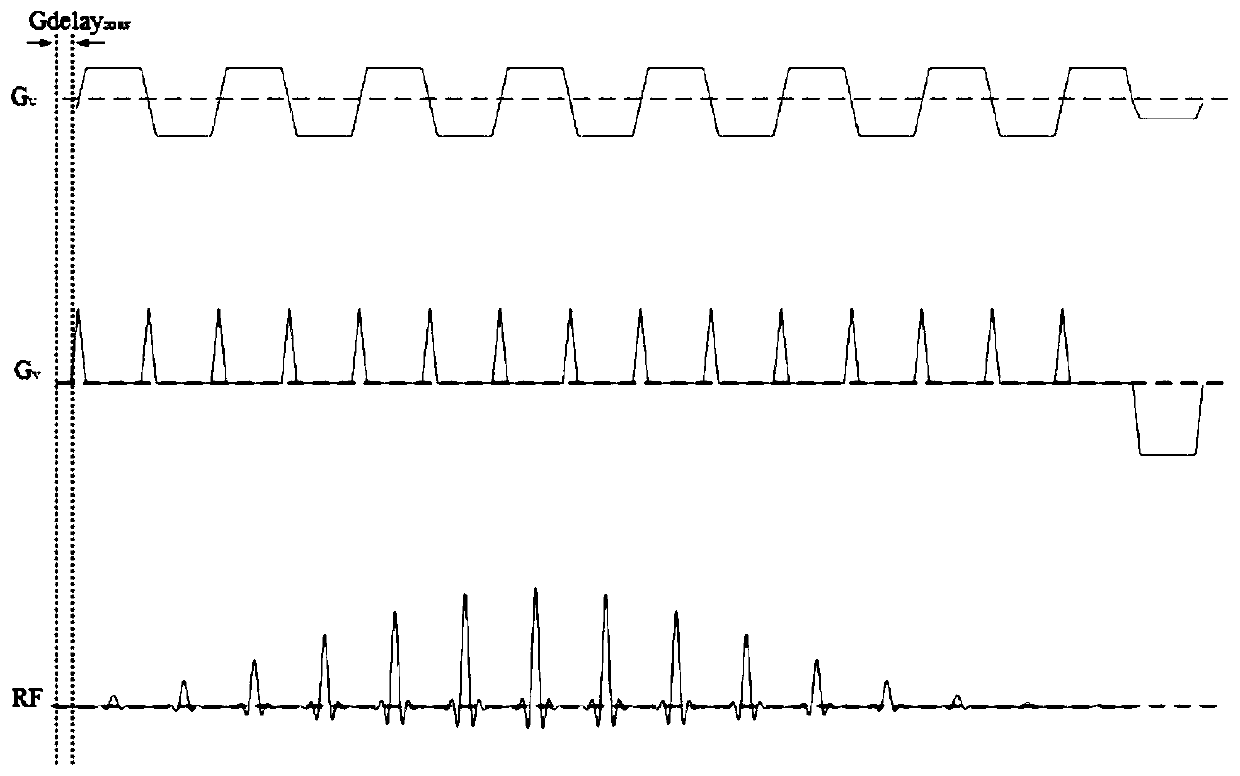
Prospective phase correction plane echo imaging technology
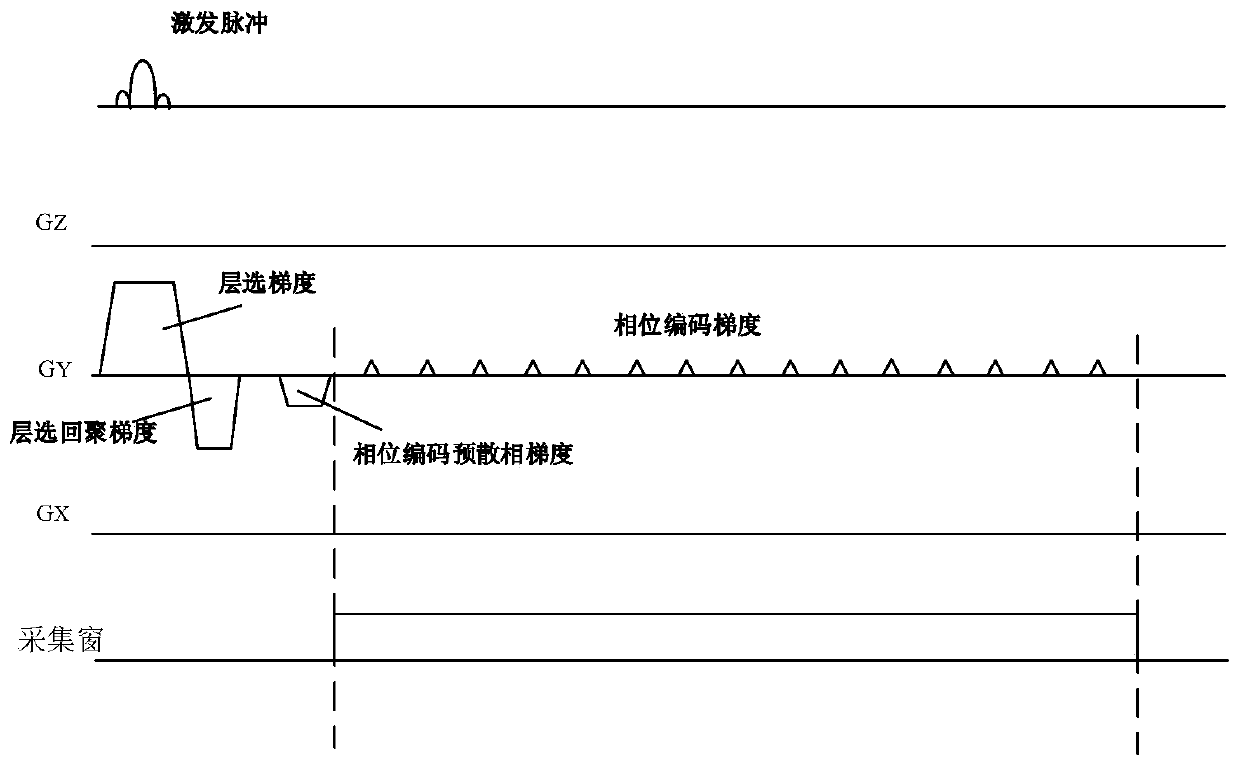
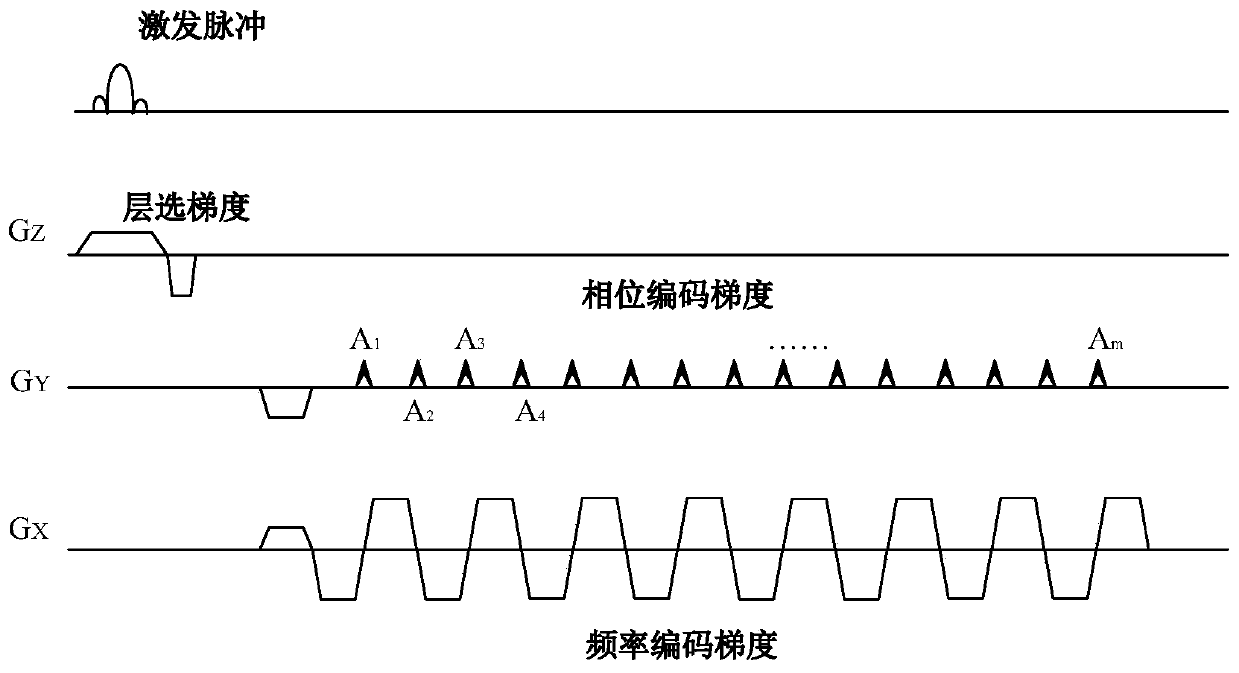
ActiveCN111352055AReduce artifactsImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsPhase correctionNuclear medicine
The invention discloses a prospective phase correction planar echo imaging technology, which comprises a planar echo imaging phase encoding error measurement sequence, a phase encoding error calculation method, a phase encoding error compensation sequence and a phase encoding error compensation method in planar echo imaging. A phase encoding error is measured and calculated through a reference scanning sequence, and then a compensation gradient is added to phase encoding in a scanning sequence of planar echo imaging to compensate the influence of B0 field heterogeneity, an eddy current field,gradient channel asymmetry and the like, so that artifacts can be reduced, and the signal-to-noise ratio can be increased.
Owner:MARVEL STONE HEALTHCARE CO LTD
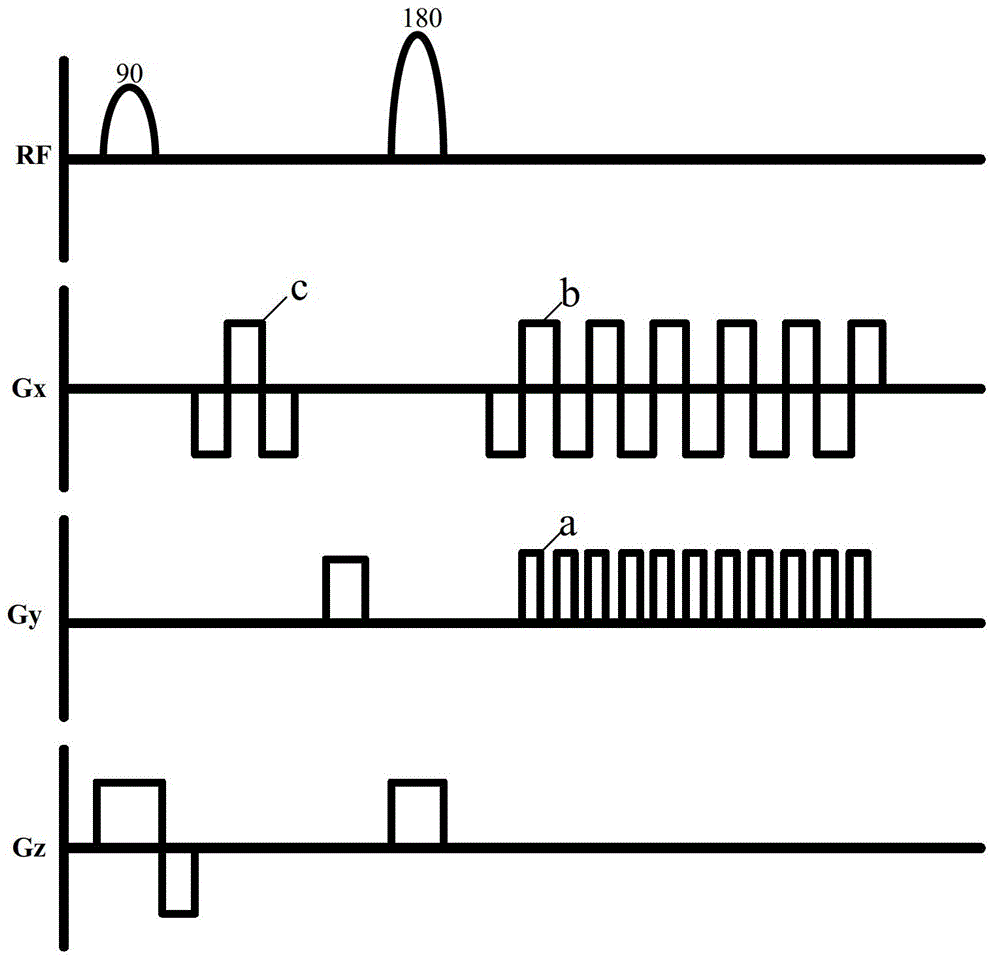
Method for correcting planar echo two-dimensional spatial selective pulses
ActiveCN111142056AImprove image qualityImproved 2D excitation profileMeasurements using magnetic resonanceImaging qualityK-space
The invention discloses a method for correcting planar echo two-dimensional spatial selective pulses. The method comprises the steps of: increasing a delay compensation amount between a gradient channel and a radio frequency channel of a two-dimensional spatial selective excitation pulse, and moving the position of excitation K space, so as to enable the centers of the excitation K spaces in odd and even rows to be aligned. For the two-dimensional spatial selective pulse adopting the planar echo to excite the K space track, the method can ensure that the centers of the K spaces excited by theodd and even sub SINC waveforms are aligned, and can greatly improve the two-dimensional excitation contour, thereby improving the image quality of small-view imaging.
Owner:ALLTECH MEDICAL SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com