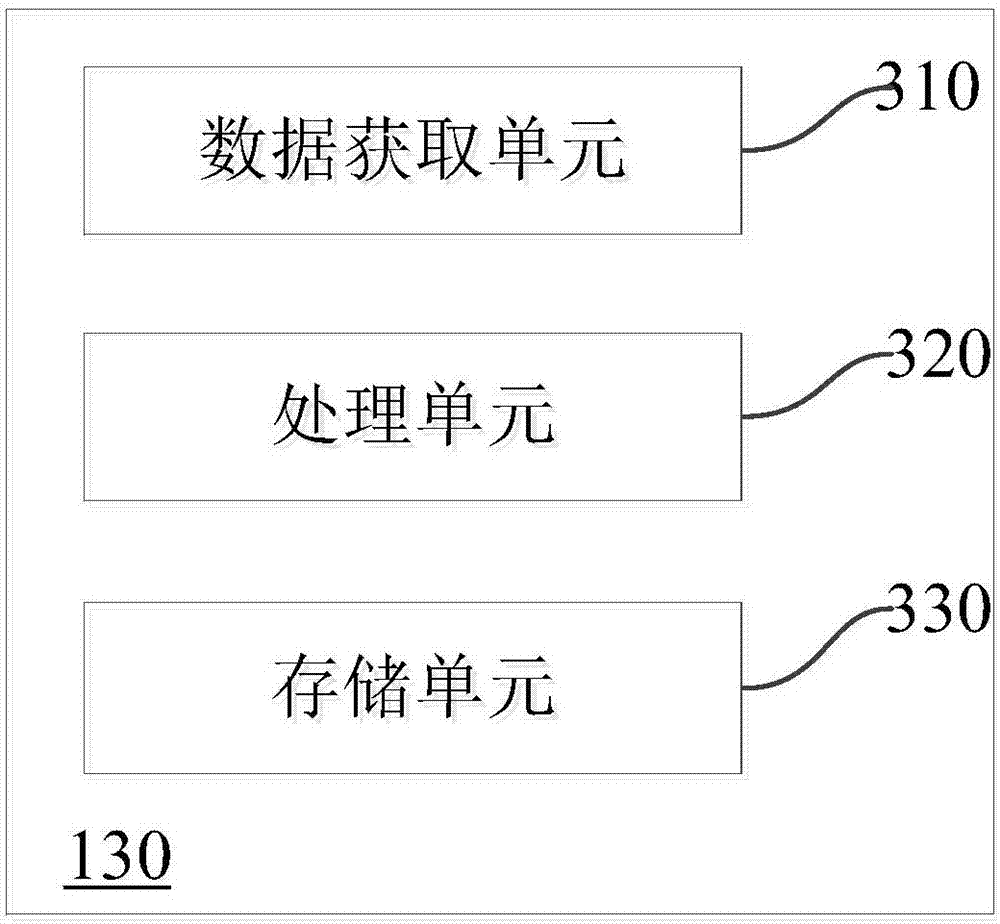
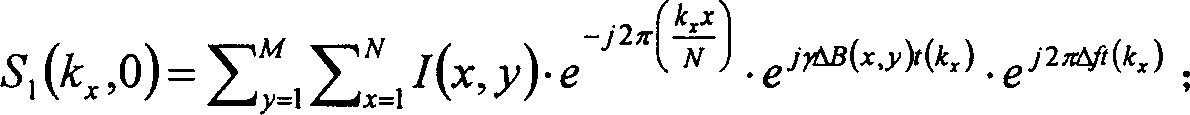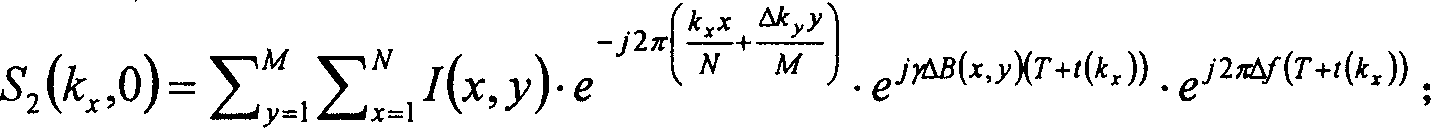Patents
Literature
105 results about "Echo-planar imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
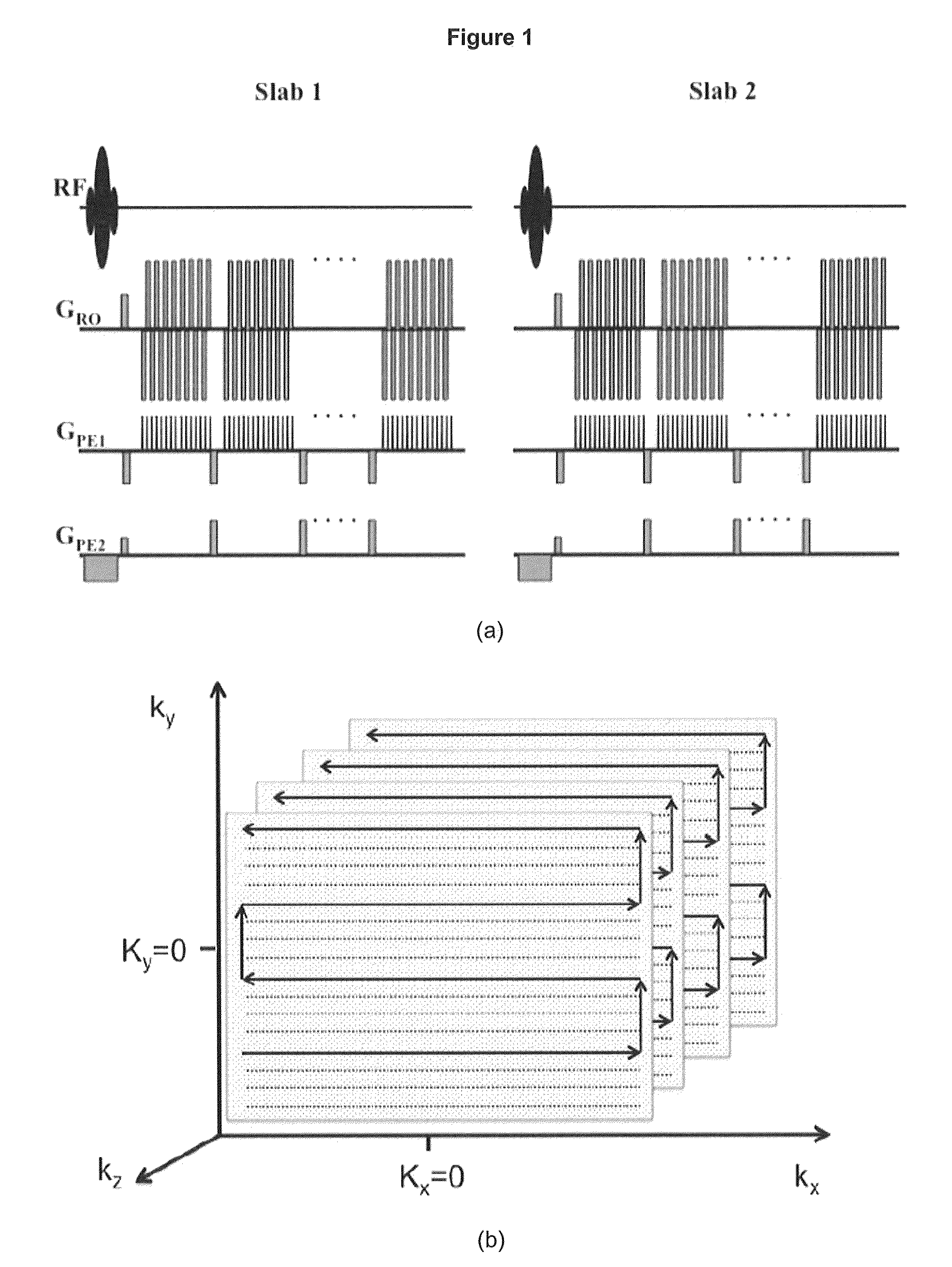
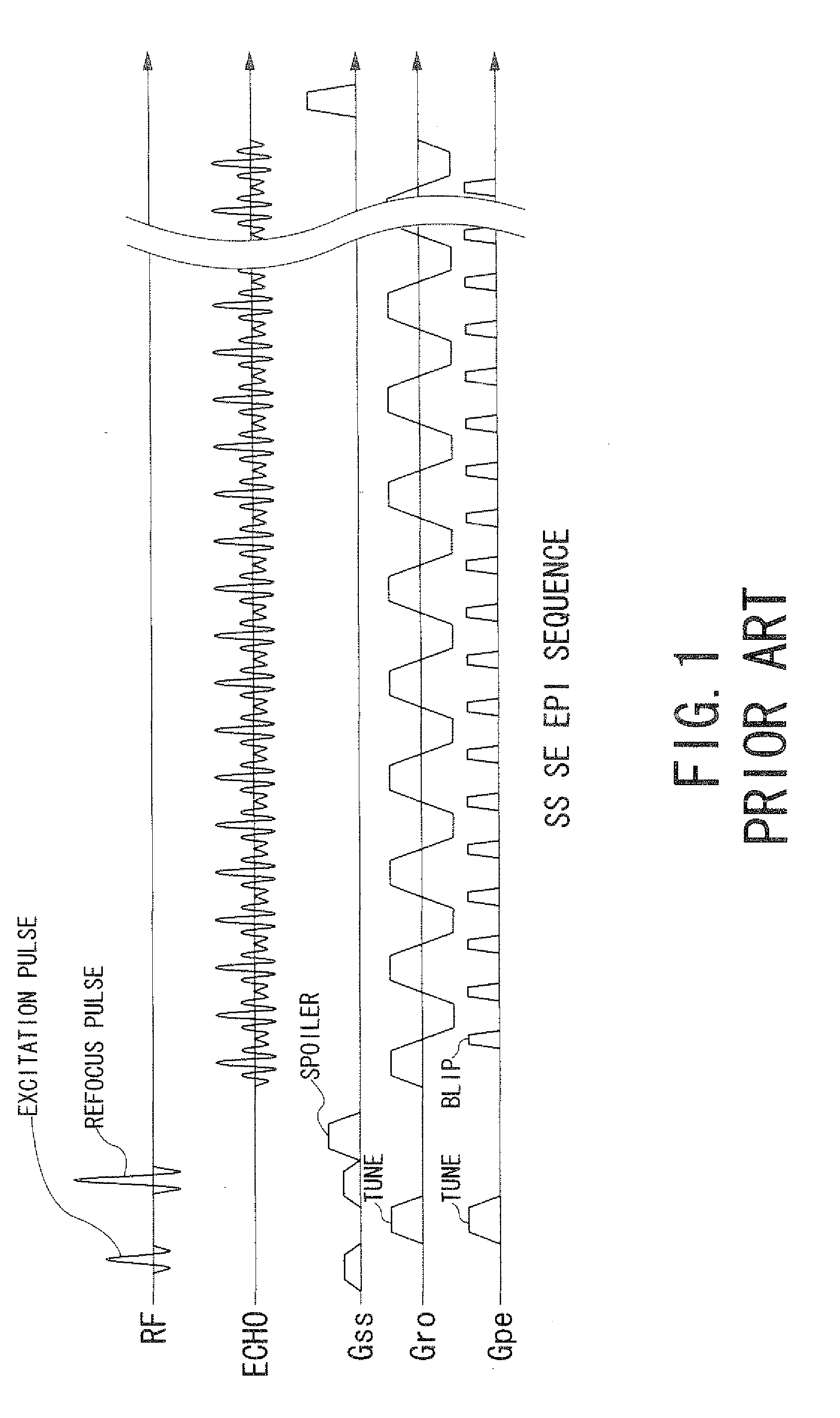
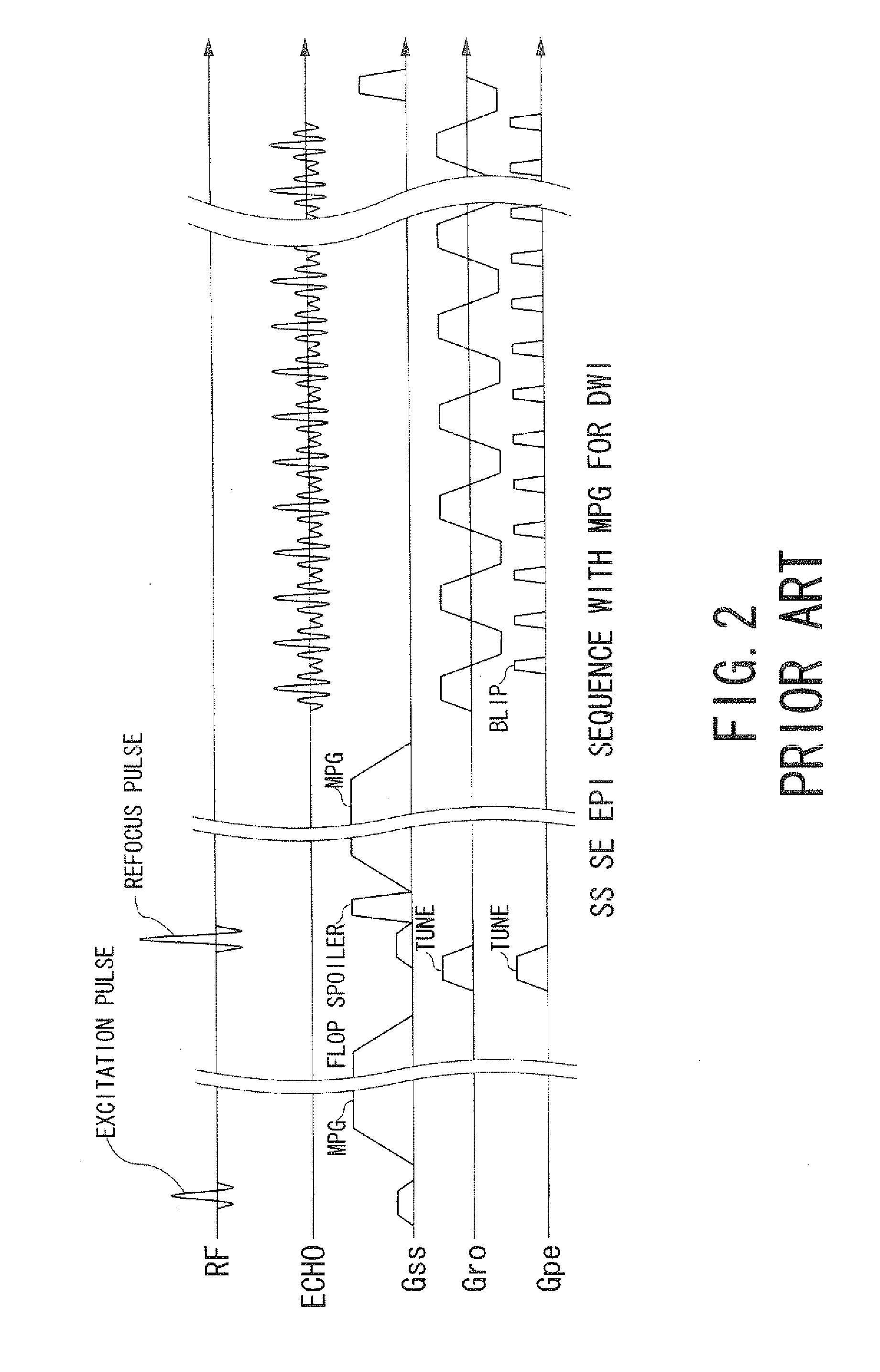
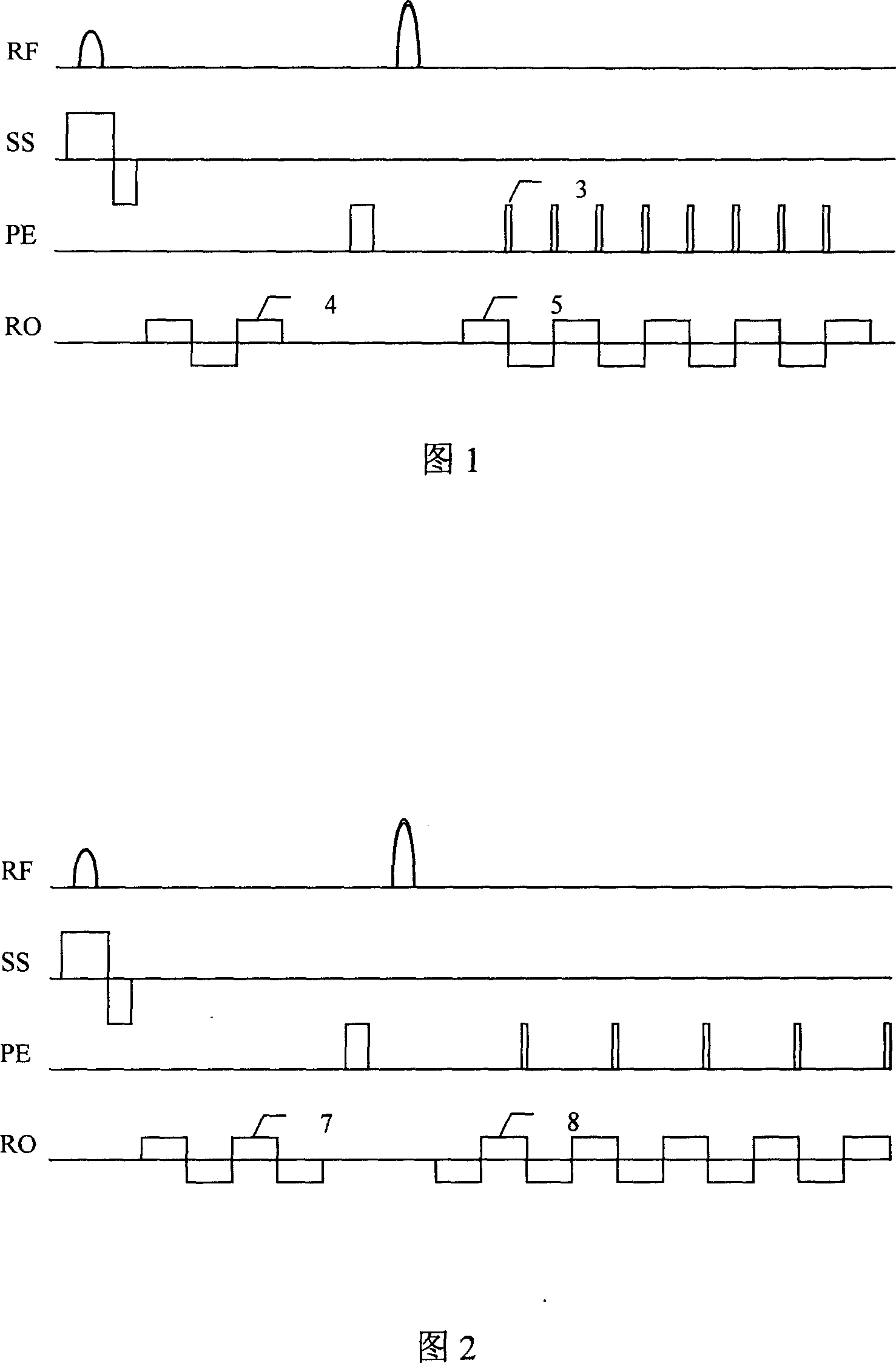
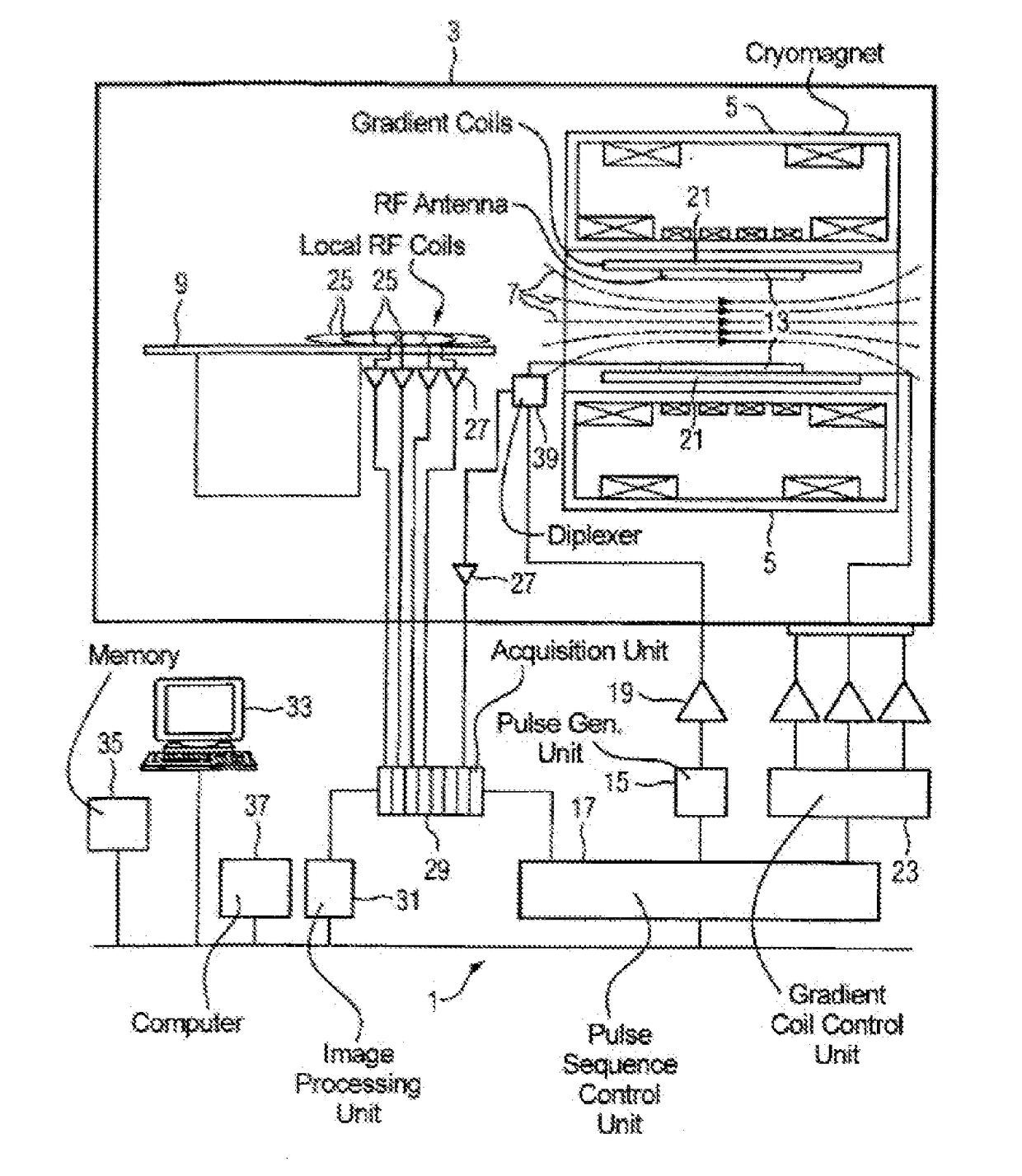
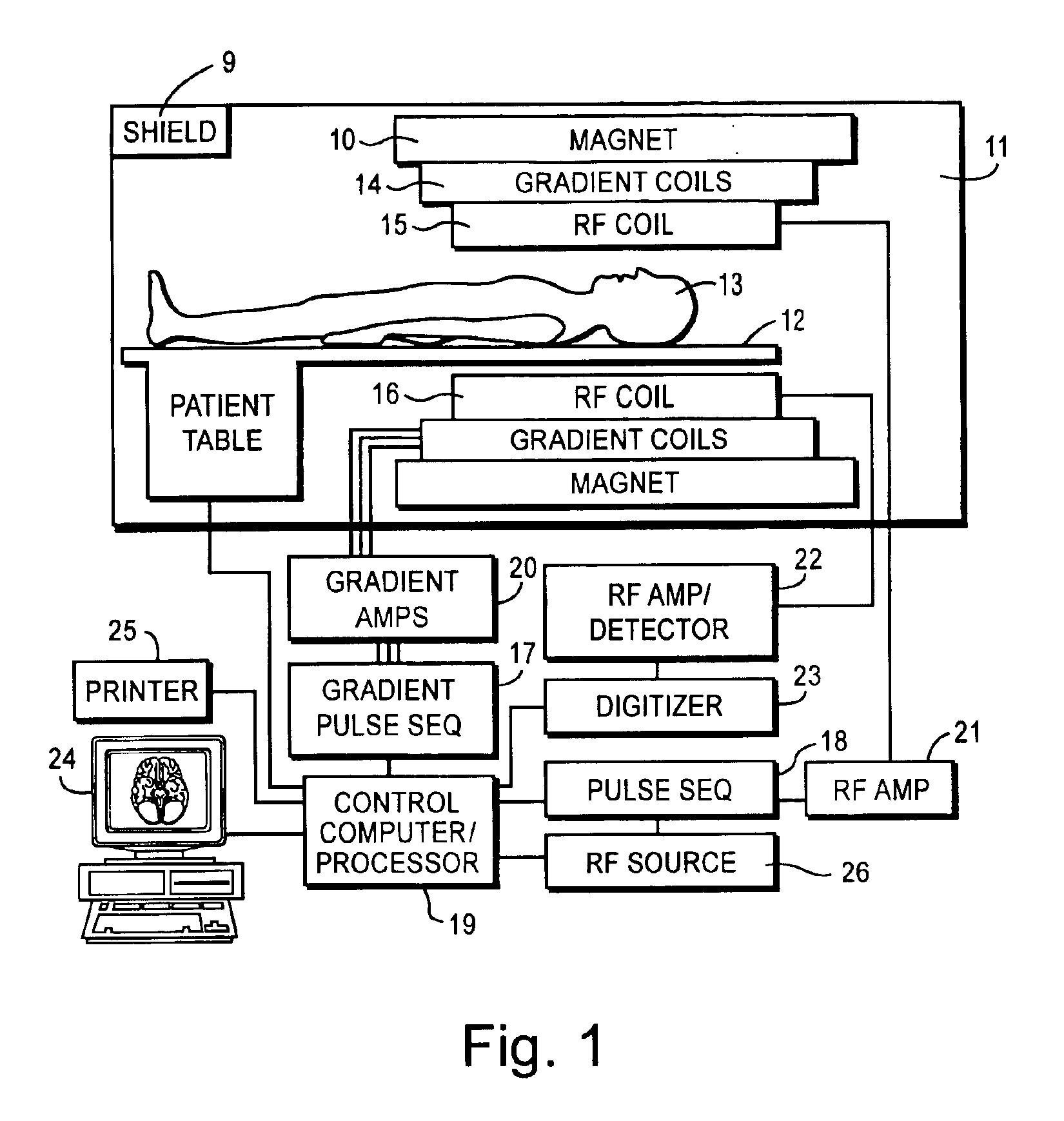
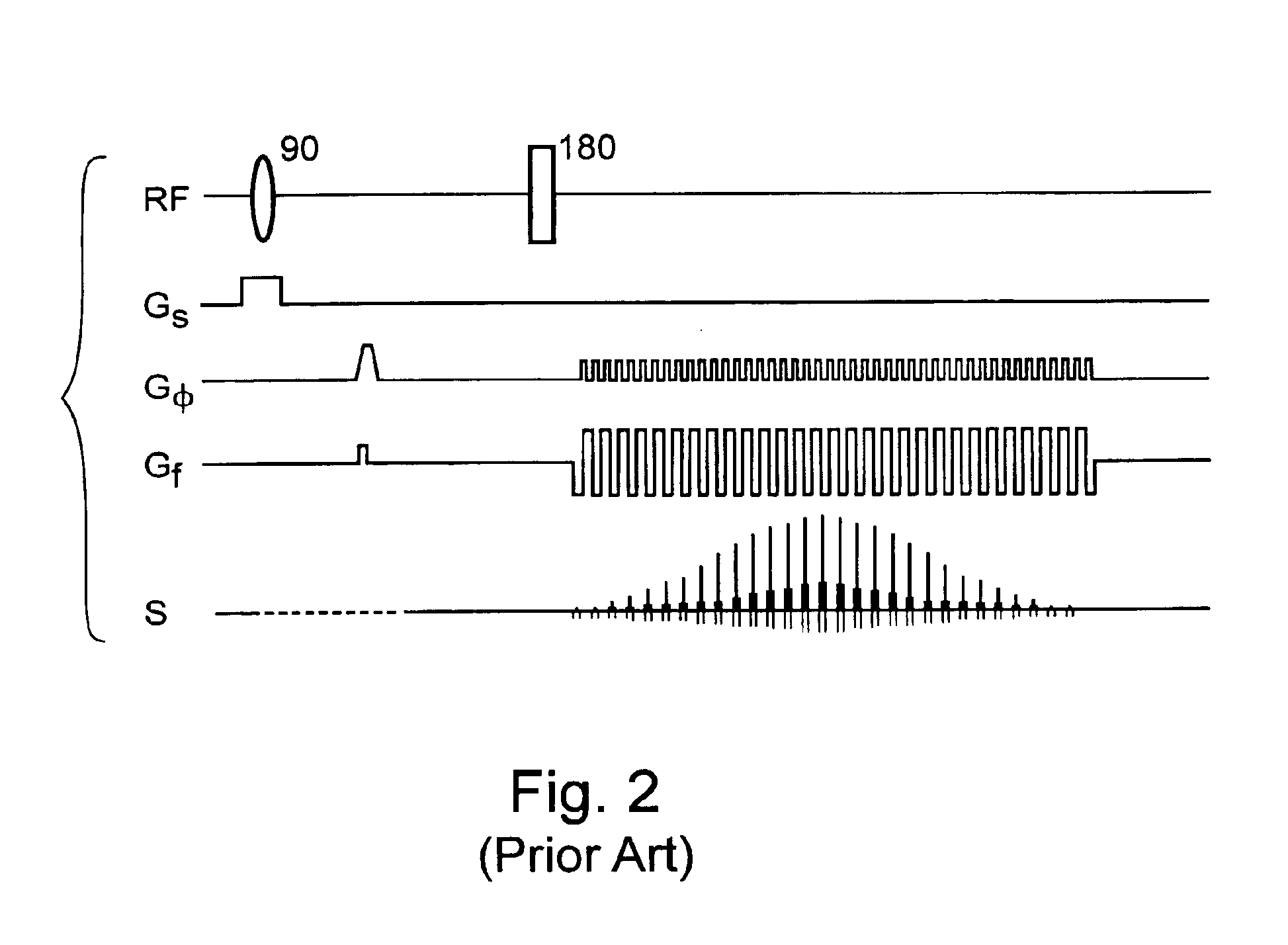
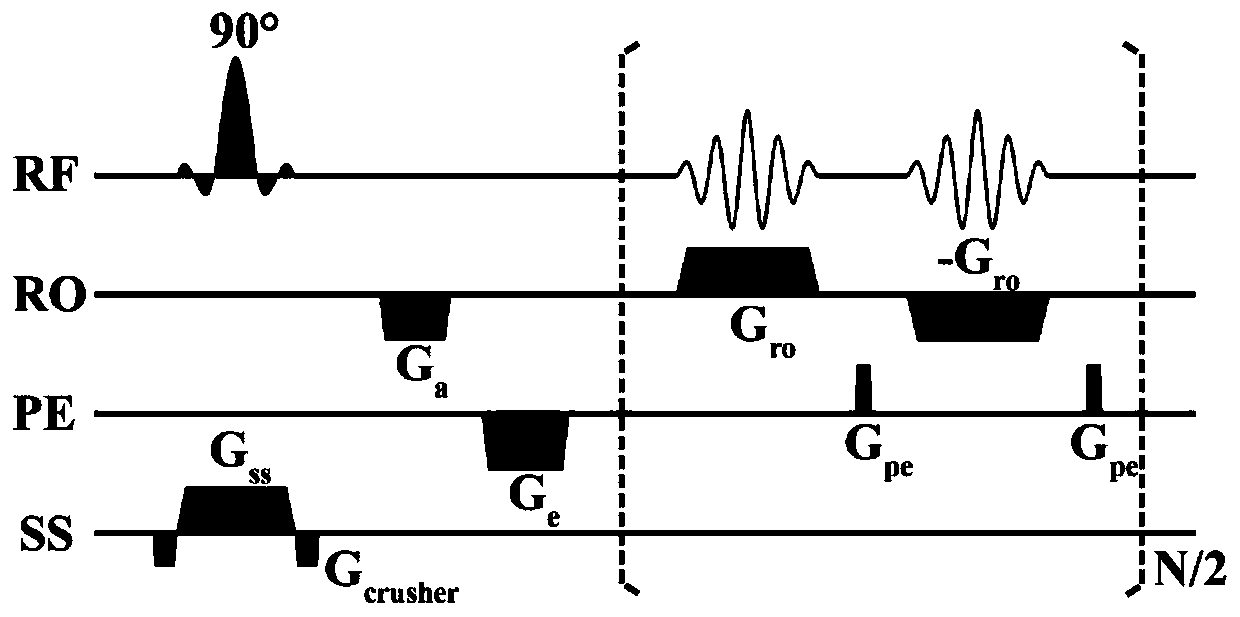
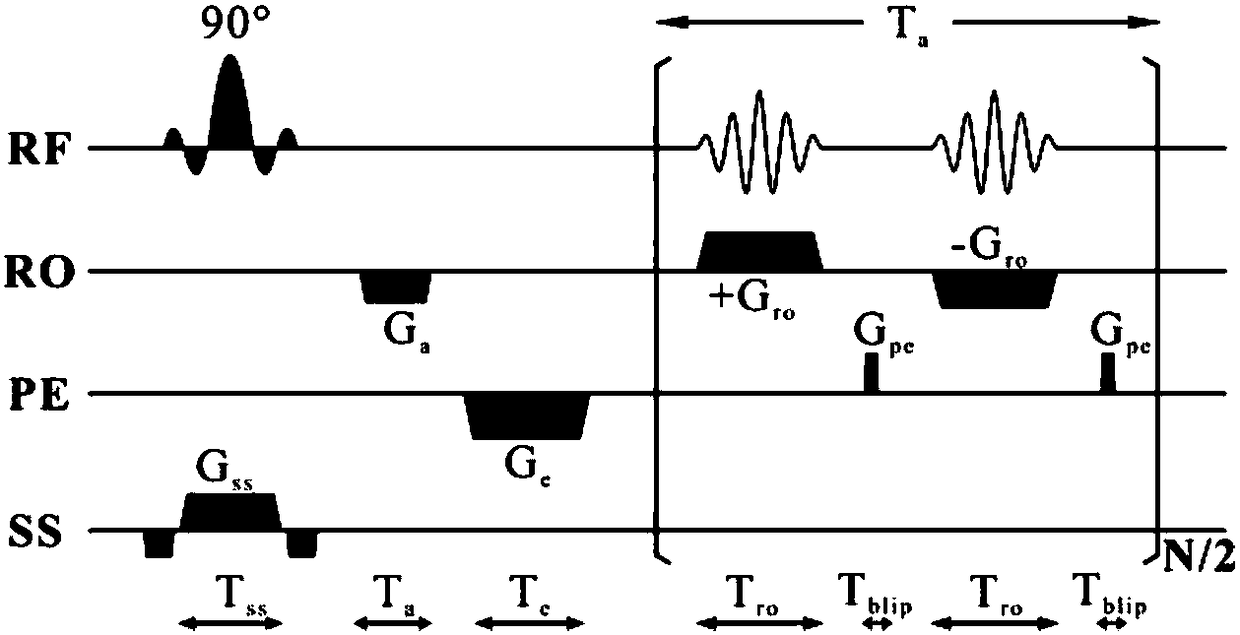
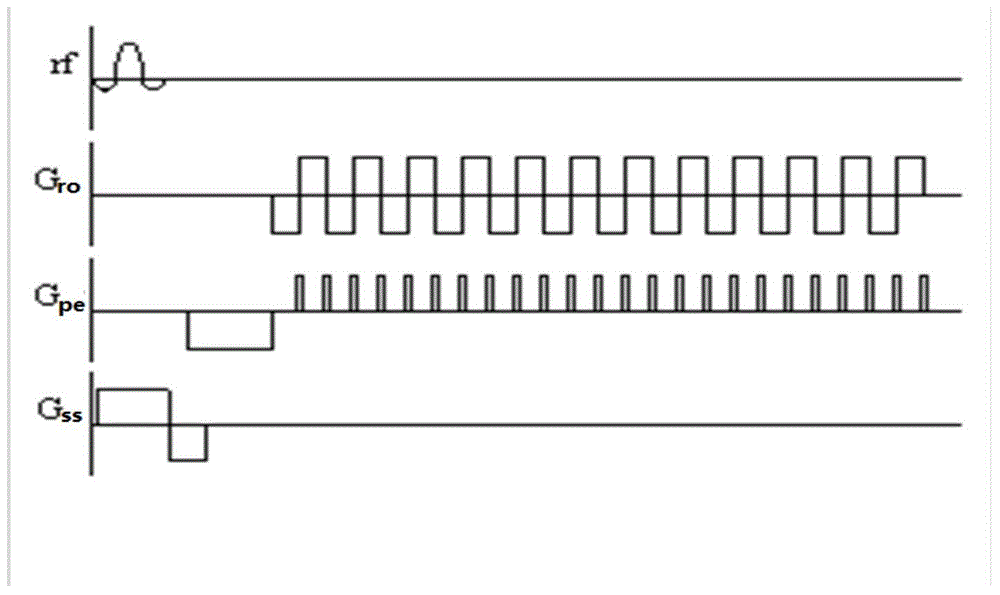
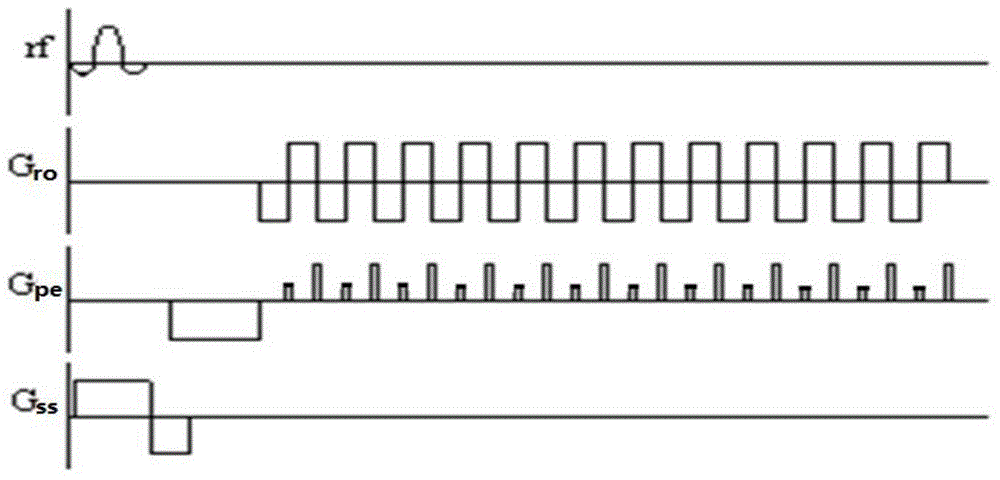
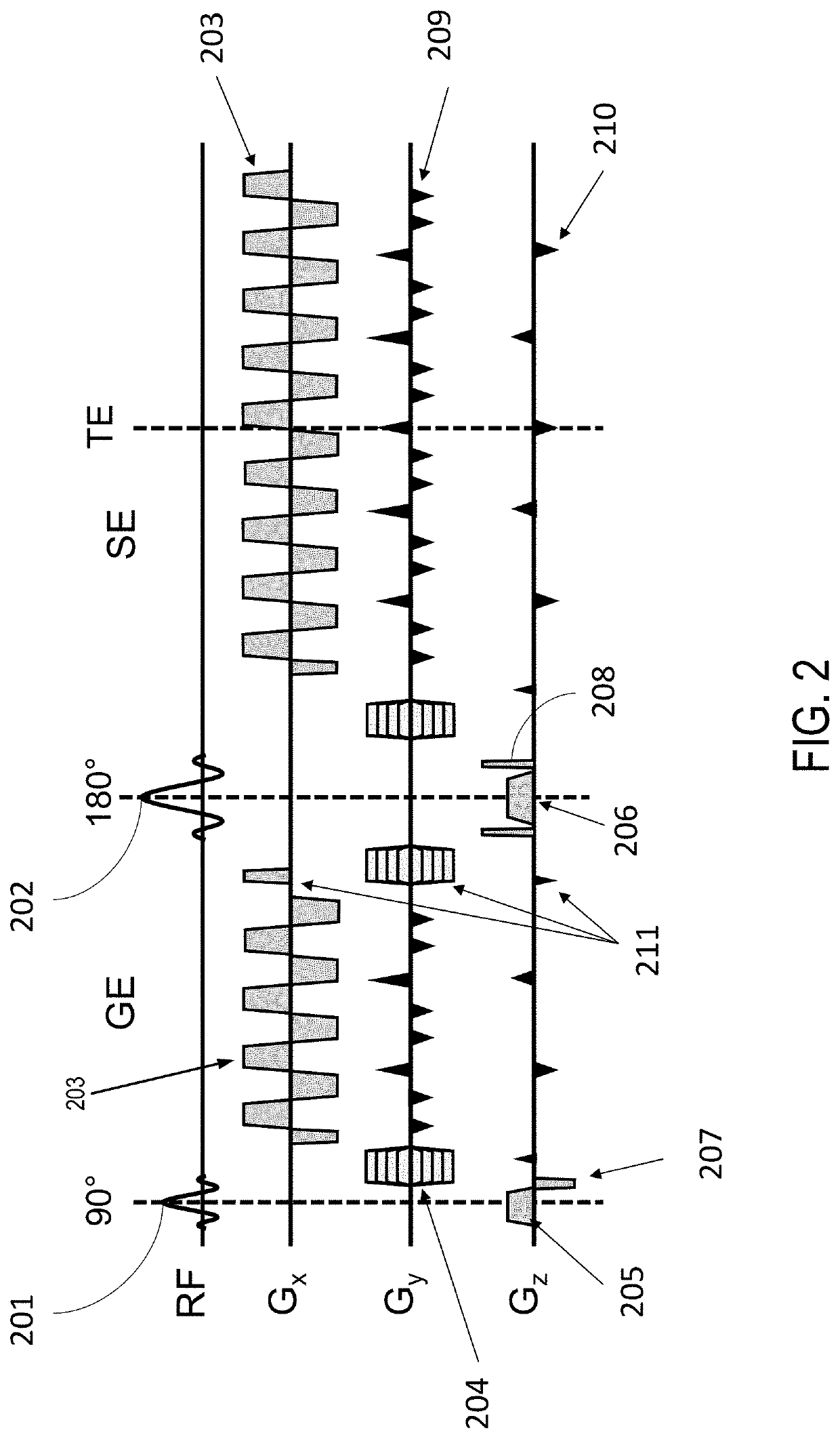
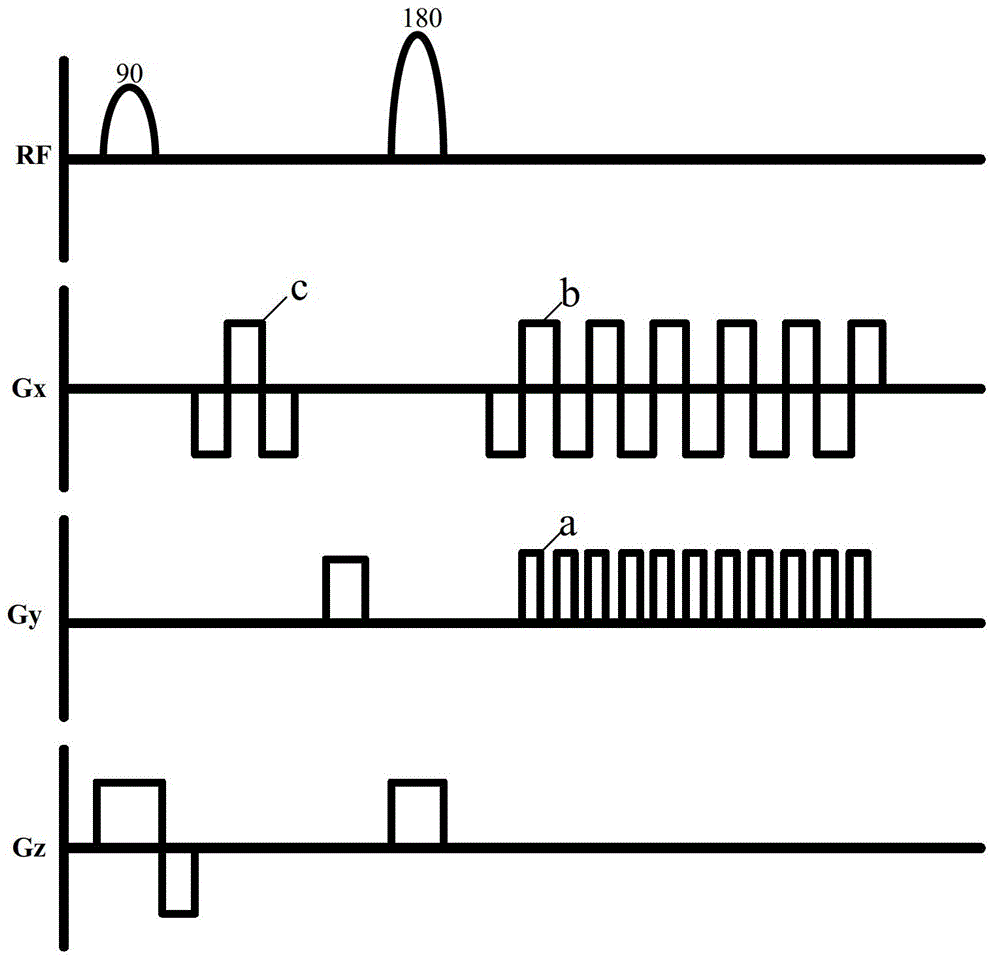
Echo planar imaging is performed using a pulse sequence in which multiple echoes of different phase steps are acquired using rephasing gradients instead of repeated 180o RF pulses following the 90°/180° in a spin echo sequence. This is accomplished by rapidly reversing the readout or frequency- encoding gradient.
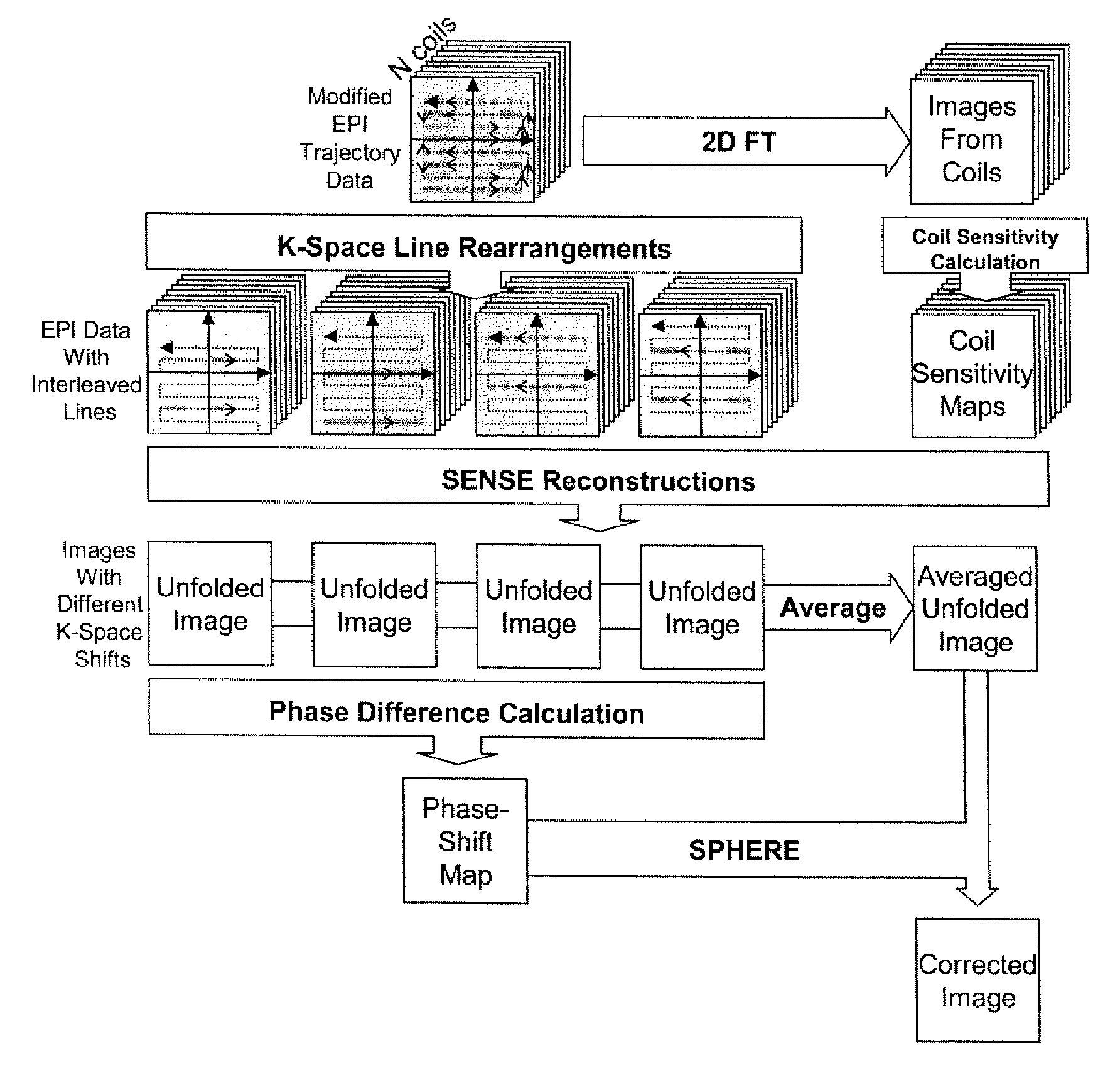
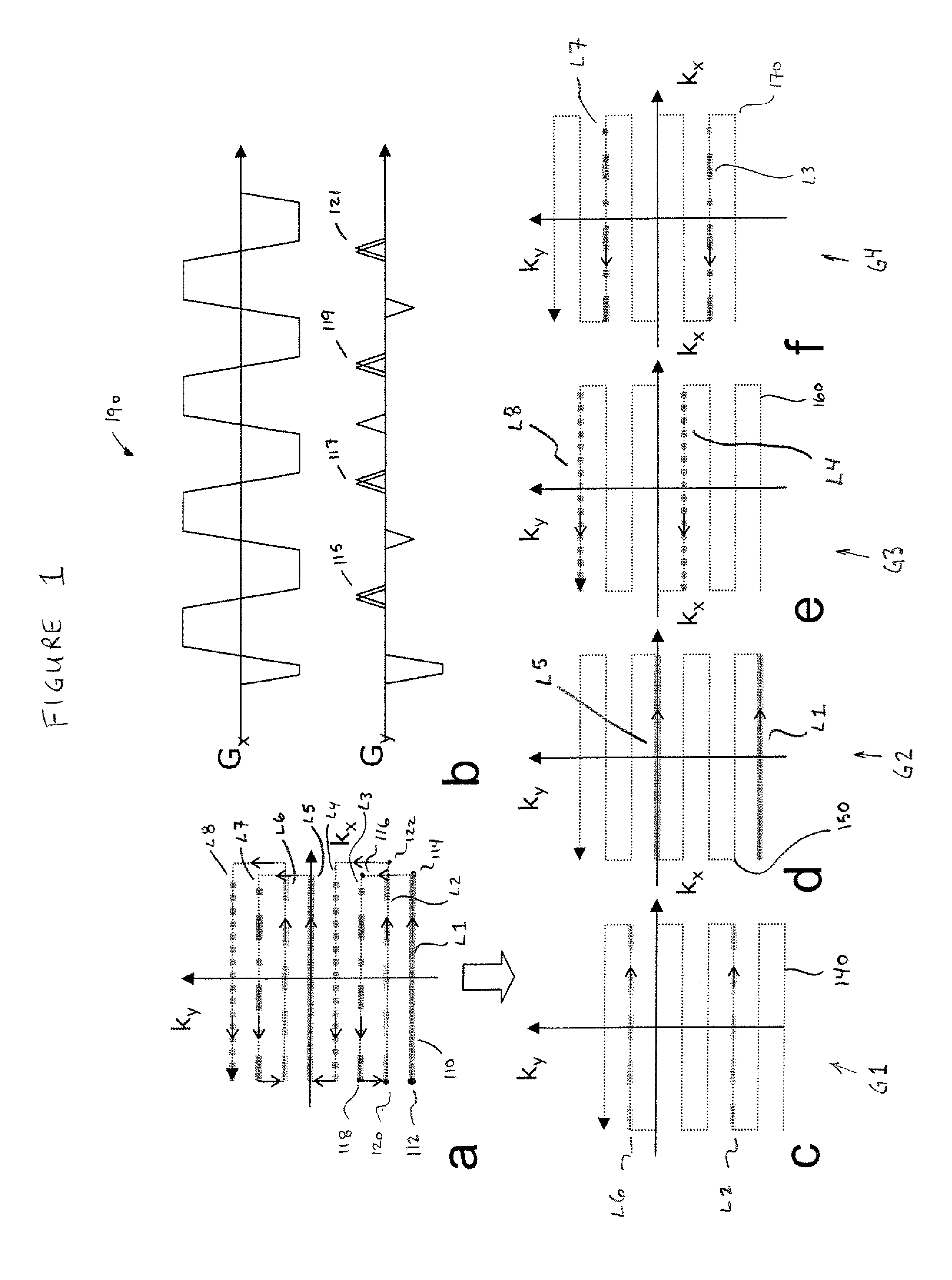
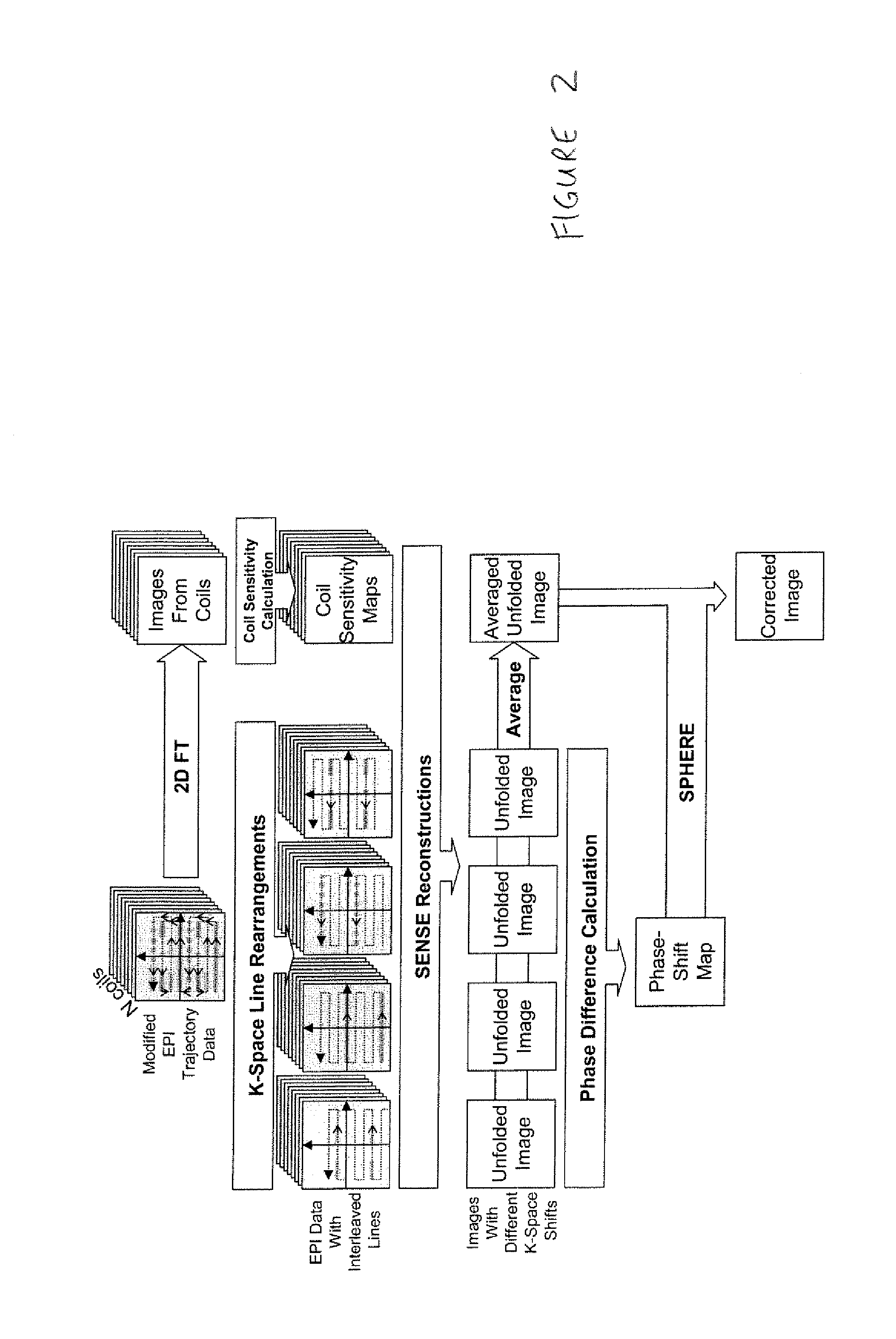
Phase labeling using sensitivity encoding: data acquisition and image reconstruction for geometric distortion correction in epi
InactiveUS20110260726A1Easy to pass to SPHERE calculationReduce artifactsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase shiftedData acquisition
A phase labeling using sensitivity encoding system and method for correcting geometric distortion caused by magnetic field inhomogeneity in echo planar imaging (EPI) uses local phase shifts derived directly from the EPI measurement itself, without the need for extra field map scans or coil sensitivity maps. The system and method employs parallel imaging and k-space trajectory modification to produce multiple images from a single acquisition. The EPI measurement is also used to derive sensitivity maps for parallel imaging reconstruction. The derived phase shifts are retrospectively applied to the EPI measurement for correction of geometric distortion in the measurement itself.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
System and methods for improved real time functional magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS9116219B1Suppress physiological noiseWiden meansMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionBlood oxygenation level dependentParallel imaging
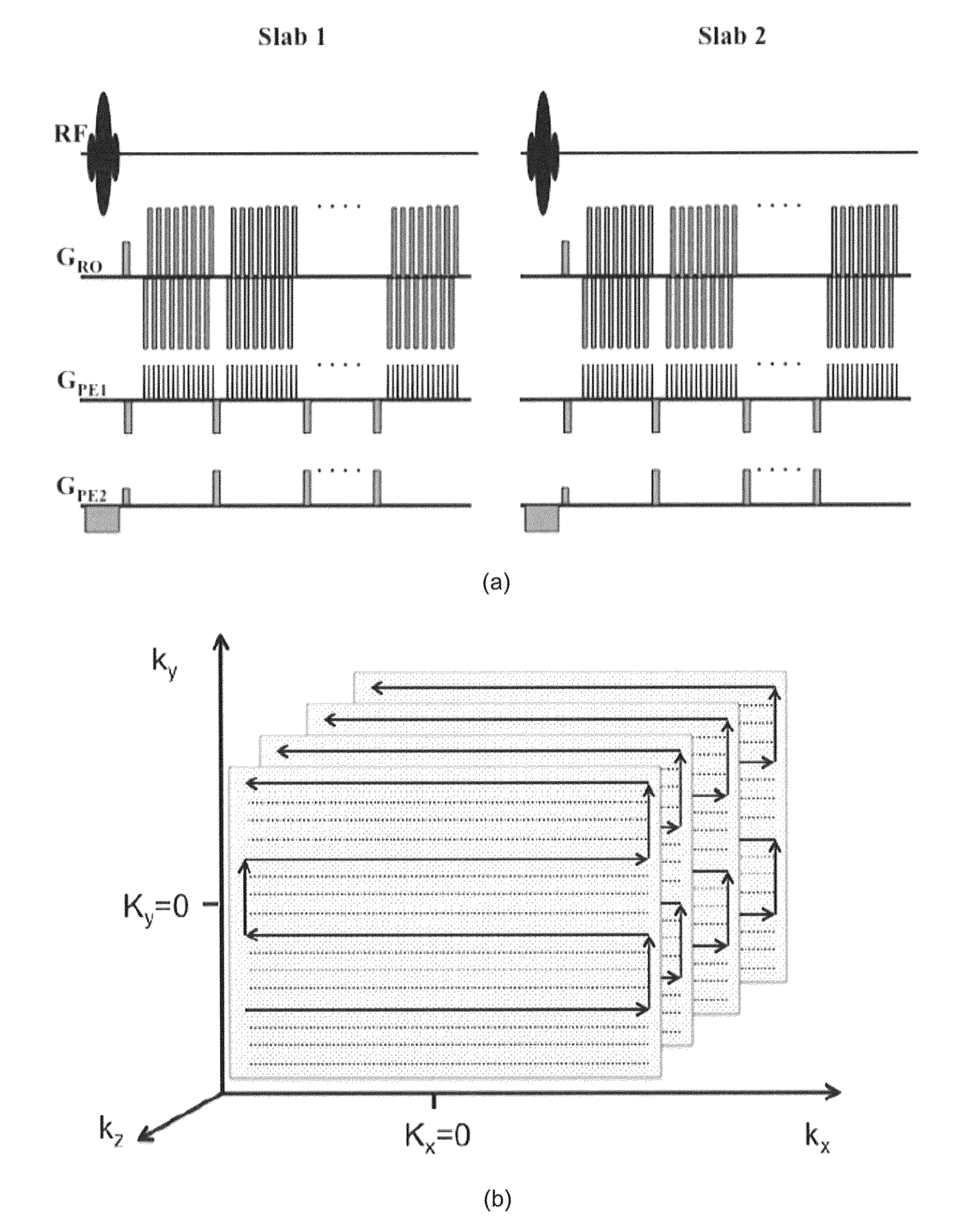
A system and methods for high-speed functional magnetic resonance imaging using multi-slab echo-volumar imaging (EVI), specifically a combination of multi-slab excitation and single-shot 3D encoding with parallel imaging to reduce geometrical image distortion and blurring, and to increase blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) sensitivity compared to conventional echo-planar imaging (EPI).
Owner:STC UNM
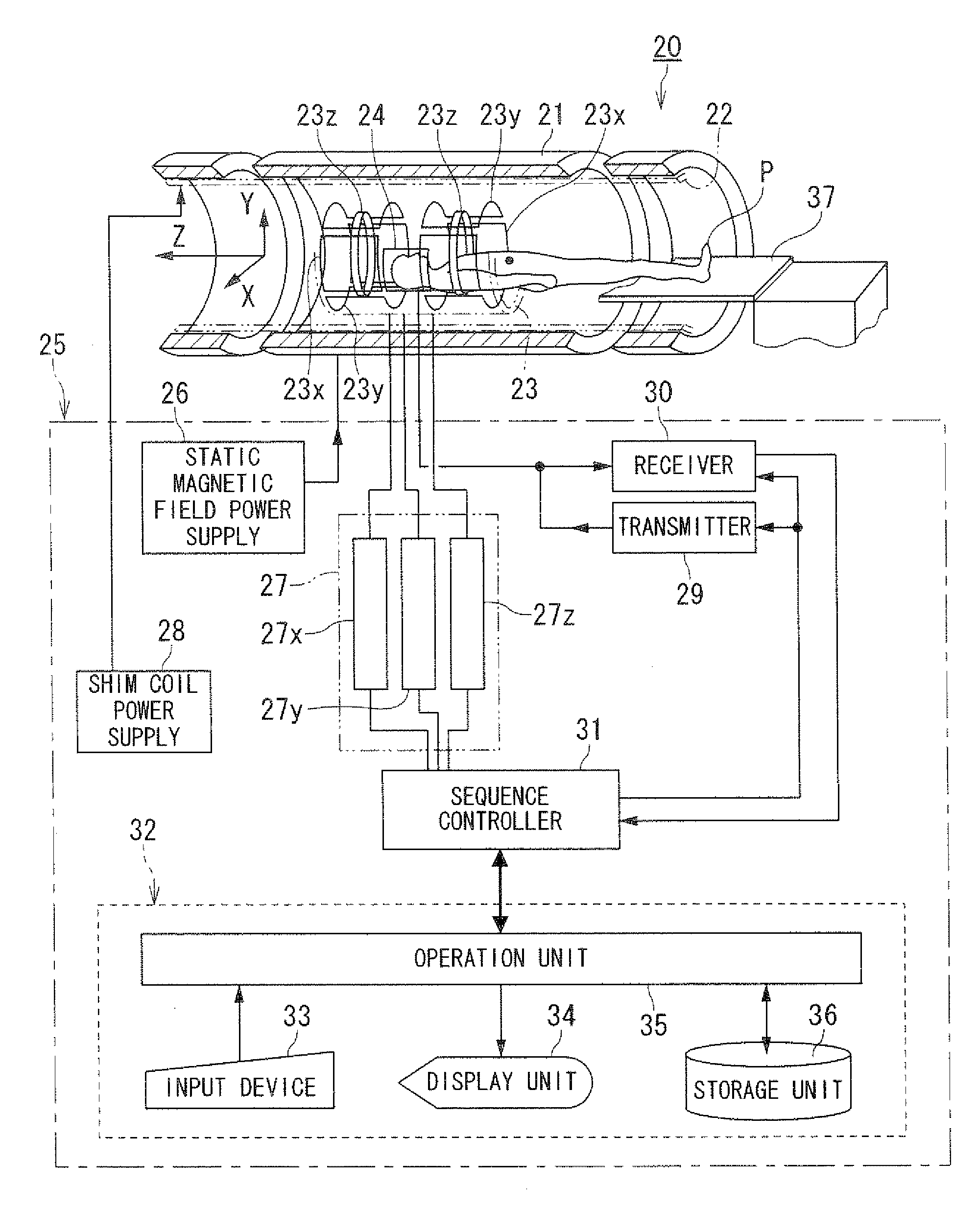
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS20090212772A1Reduce distortion problemsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionENCODEImaging data
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes a data acquisition unit and an image generating unit. The data acquisition unit acquires echo signals by echo planar imaging which generates the echo signals with correcting and applying plural gradient magnetic fields for phase encode and with continuously inverting a gradient magnetic field for readout after one nuclear magnetic excitation. Each of the plural gradient magnetic fields for phase encode has an intensity set so as to compensate an influence of an eddy current distributing spatially adaptively to each of imaging positions. The image generating unit generates image data based on the echo signals.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method for correcting echo wave plane imaging sequence
ActiveCN101109791ACorrect displacementImprove accuracyMagnetic property measurementsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase differenceImaging data
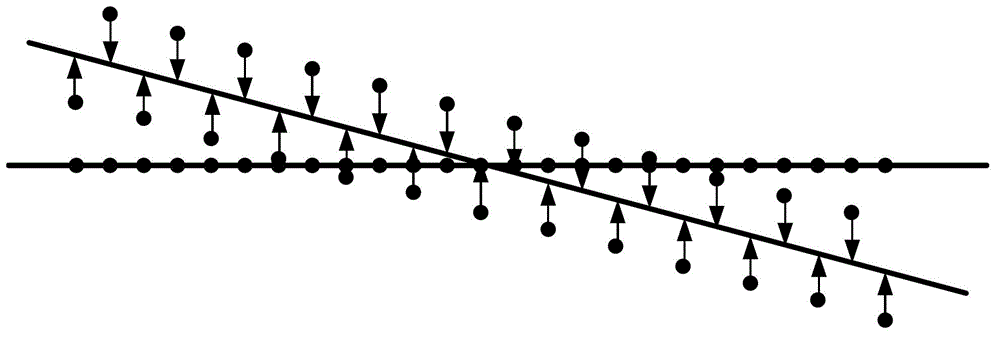
The invention provides a way for correcting the imaging sequence of an echo plane. A plurality of echo signals are collected, the phase difference of the echo signals is calculated to correct the image data. Wherein, the phase difference goes through multi-order fitting, a fitting coefficient reflecting the cross-infection volume and frequency drift is worked out to carry out phase correction for the image data. The invention collects the EPI signals of two echoes to form two images, the info on time difference for collecting the two images is used to calculate the phase diagram reflecting the unevenness in the magnetic field, and the phase diagram is used to carry out deformation correction for the image. The invention takes full consideration of the influence from the uneven field during the calculation, basically corrects the displacement of the image, improves the accuracy for deformation correction in subsequent images without using additional sequence to get phase diagram, and saves scanning time.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS LTD
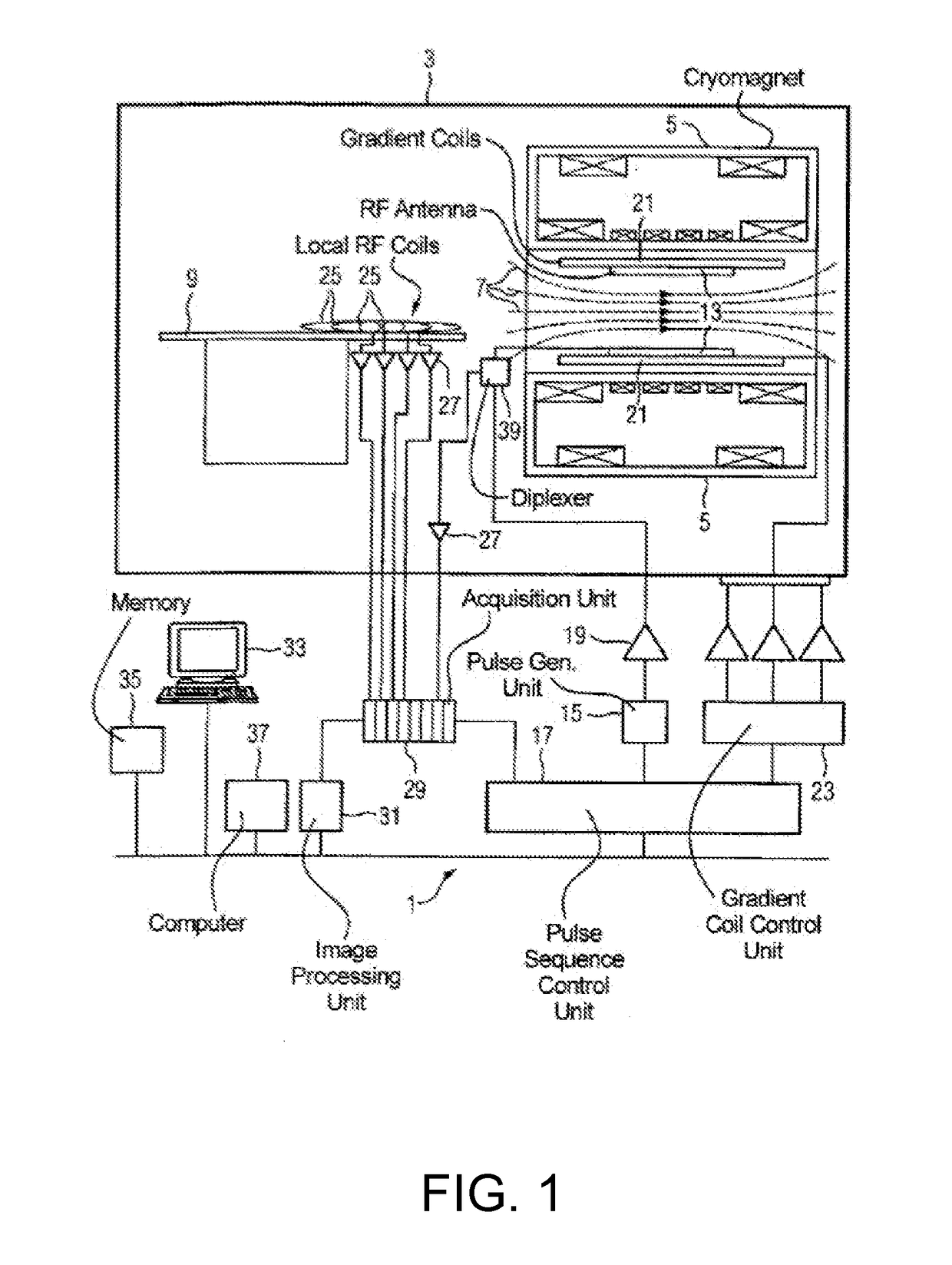
Navigator-Based Data Correction For Simultaneous Multislice MR Imaging
ActiveUS20170089999A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to correctImage enhancementImage analysisData setElectrical polarity
A magnetic resonance method and system are provided for providing improved simultaneous multislice echo planar imaging (EPI) with navigator-based correction of image data for B0 drift and N / 2 ghosting. The correction is based on two types of multi-echo phase-encoded navigator sequences having opposite readout gradient polarities, and optionally also uses a non-phase-encoded navigator sequence. One or more navigator sequences can be generated between each RF excitation pulse and the subsequent EPI readout sequence. A dynamic off-resonance in k-space technique can be used to correct for B0 drift, and a modified slice GRAPPA technique that is based on odd and even kernels can provide slice-specific correction for N / 2 ghosting effects for the EPI MR image data sets. Various patterns of navigator sequences and / or interpolation of navigator data can be used to improve accuracy of the image data corrections.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
K space reconstruction method and device
ActiveCN104181487AFast imagingAchieving Artifact ReductionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
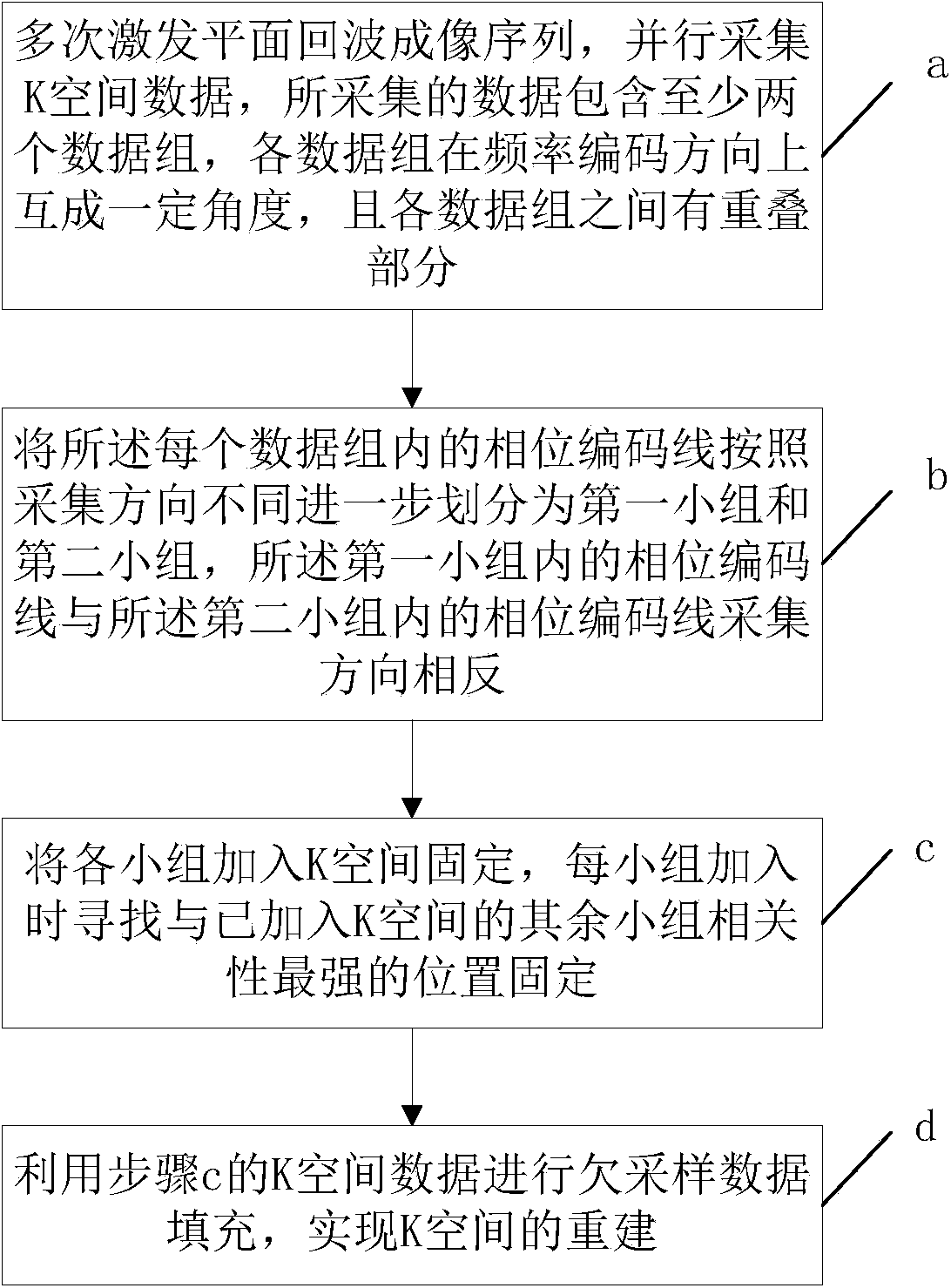
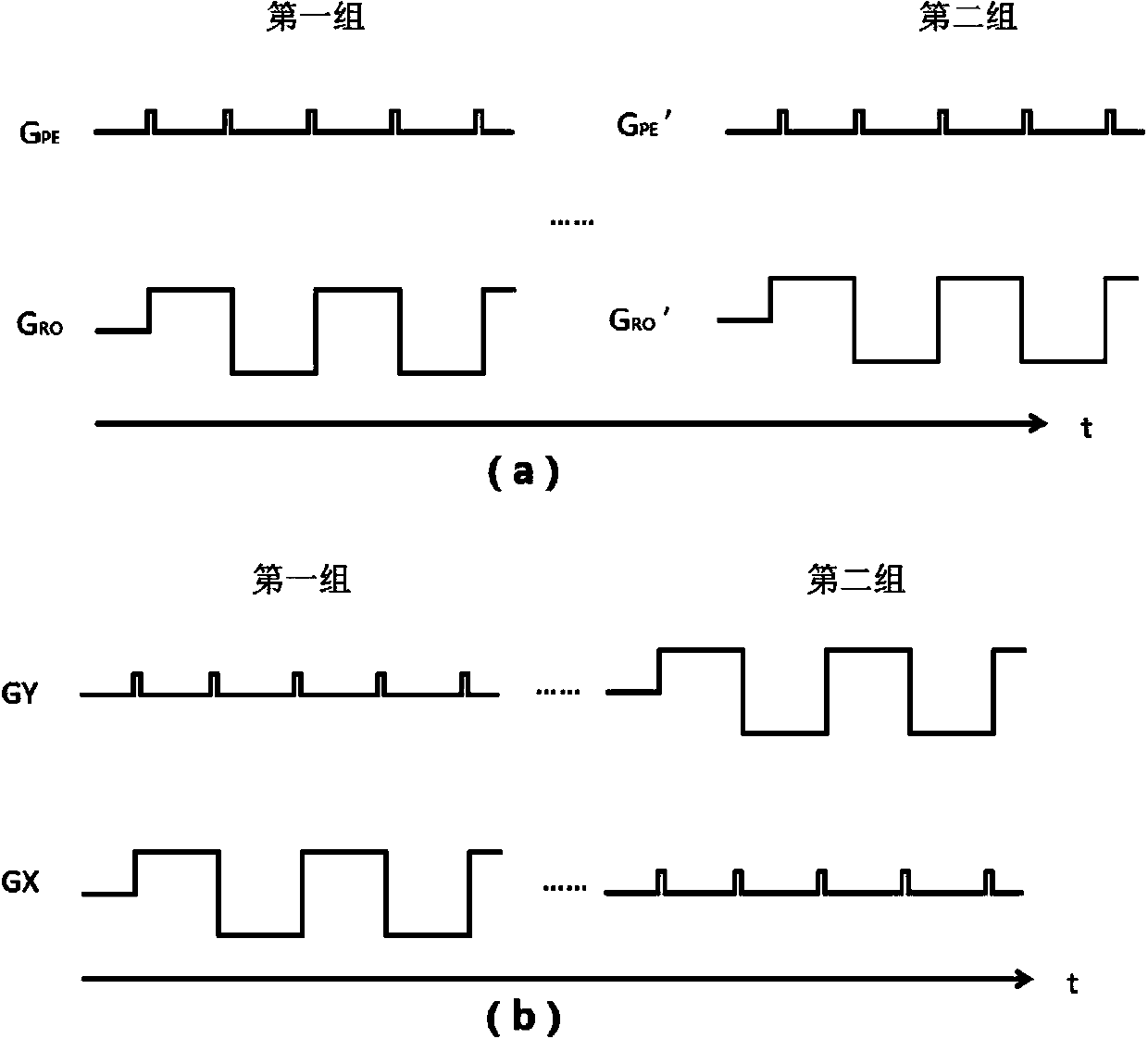
The invention provides a K space reconstruction method comprising exciting echo planar imaging (EPI) sequence for many times and collecting K space data in parallel, wherein the collected data comprises at least two data groups, a certain angle in the frequency encoding direction is formed between every two data groups and overlap portions are formed between data groups; further dividing phase encoding lines in each data group into a first group and a second group according to the difference of collection directions, the phase encoding lines in the first group being opposite to the phase encoding lines in the second group in collection direction; adding each group to the K space for fixing, wherein a position, most associated with other groups already added to the K space, is found for fixing when each group is added; and carrying out undersampled data filling by utilizing optimized K space data to realize K space reconstruction. According to the K space reconstruction method and device, EPI artifact correction can be realized without collecting calibration data additionally, thereby saving collection time and improving imaging speed.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Method and system for image artifact reduction using nearest-neighbor phase correction for echo planar imaging
ActiveUS7102352B2Reduce Image ArtifactsEffectively provide phase unwrappingMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase correctionImaging quality
A nearest neighbor phase correction technique is implemented to reduce image artifacts due to phase errors in data acquired in an EPI scan. Image quality for EPI applications, such as DWI, DTI, and fMRI, is improved.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Sequence preconditioning for ultra-fast magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6933720B2Improve image qualityQuality improvementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVolumetric imagingUltra fast
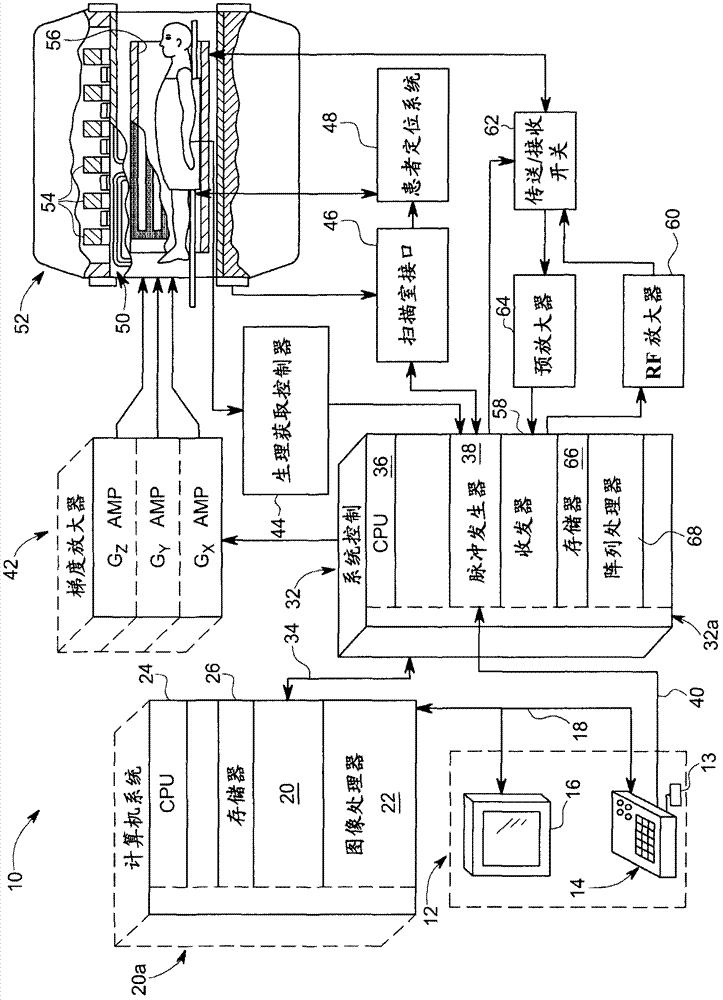
An improved magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) methodology uses an abbreviated initial MRI sequence to generate sequence diagnostic parameters. The sequence diagnostic parameters have a fixed relationship to certain sequence-conditioning parameters, and are used for calculating characteristic values of the sequence-conditioning parameters. The read out gradient pulse sequence is modified in accordance with the calculated characteristic values of the sequence-conditioning parameters. The modified read out gradient pulse sequence is then incorporated into a subsequent MRI pulse sequence used for obtaining a diagnostic image. The methodology has particular application in so called ultra fast MRI process which include echo-planar imaging (EPI) and echo-volume imaging (EVI).
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20150253408A1QuietAttenuation bandwidthMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceSlew rate
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging, a particularly quiet magnetic resonance sequence, uses echo-planar imaging with at least one gradient switching in a readout direction, wherein the at least one gradient switching in the readout direction has a slew rate that is less than a maximum slew rate defined by system specification parameters of the magnetic resonance apparatus.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
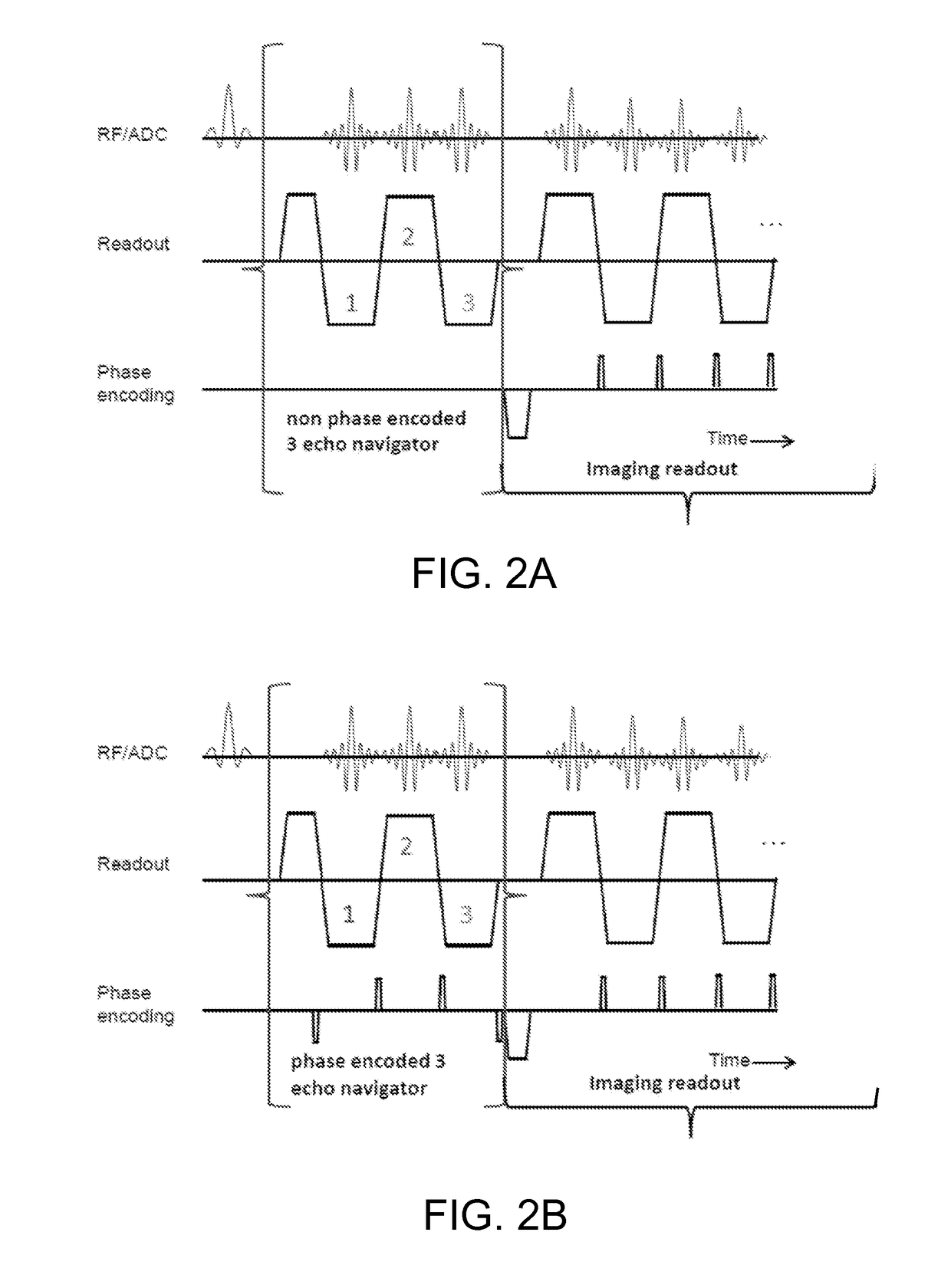
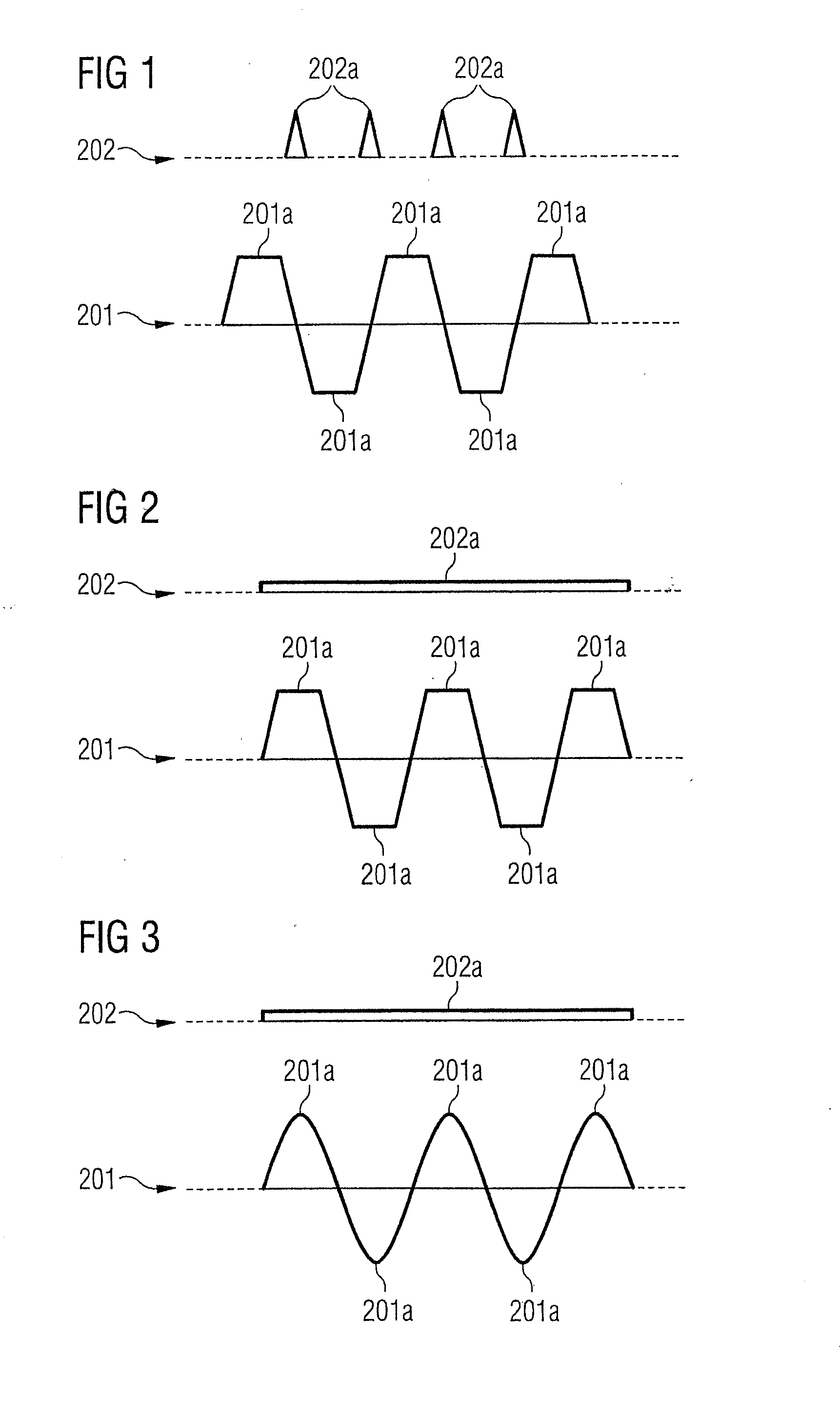
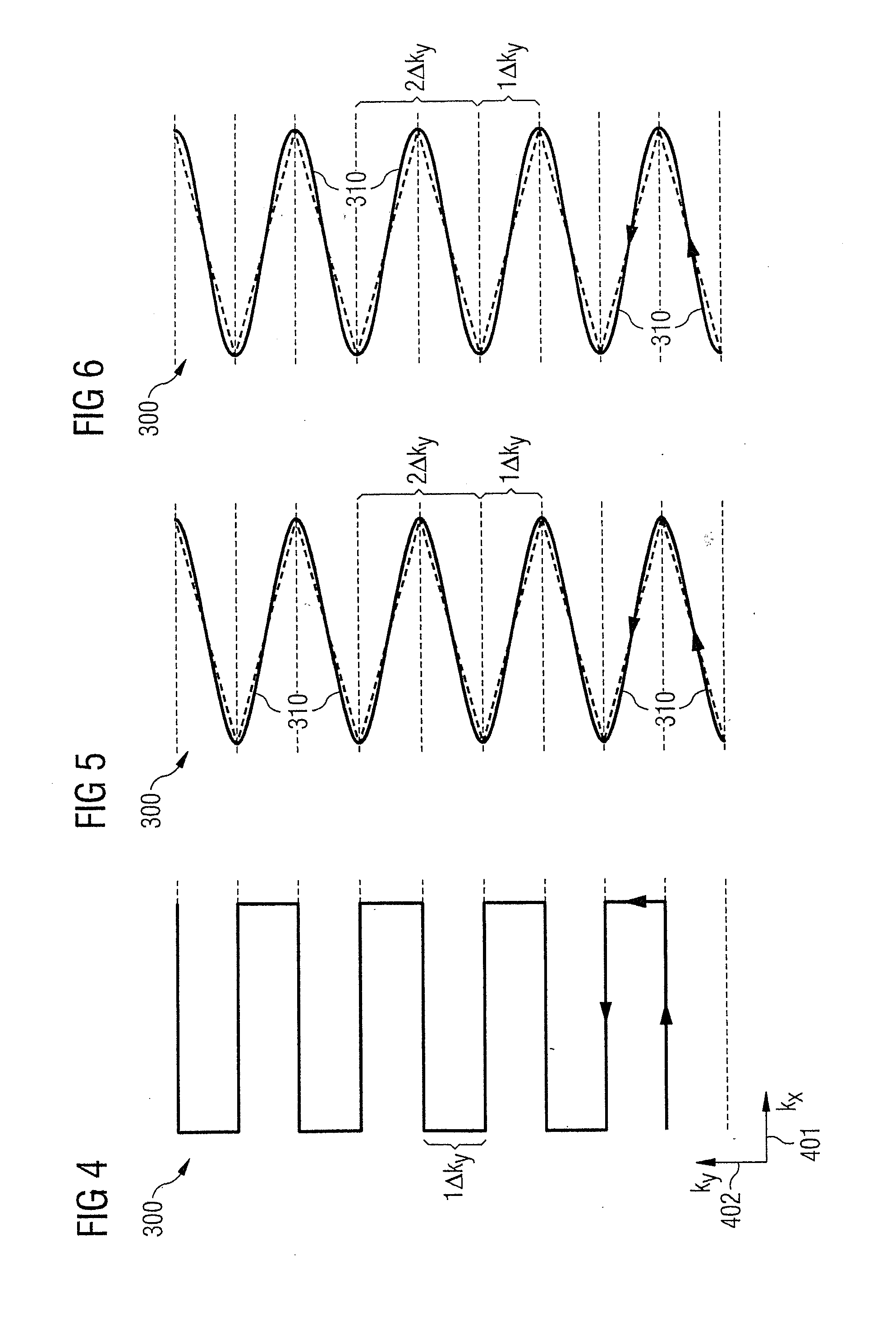
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus for echo planar imaging with data entry into k-space along a zigzag trajectory
ActiveUS20140197834A1Simple methodData augmentationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceImage sequence
In a method and apparatus for echo planar magnetic resonance (MR) imaging sequence of phase encoding gradient fields and a sequence of readout gradient fields are applied in order to produce a well-defined zigzag-type trajectory for entering raw data into k-space. Zigzag-type trajectories can be achieved that have flanks without curvature, or without significant curvature. Cartesian methods for image reconstruction of parallel MR imaging are applied to echo planar MR imaging with such zigzag-type trajectories.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
Artifact correction method based on even marker in plane echo imaging technique
InactiveCN1803092AEffective correctionImprove noise immunityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsIn planePhase difference
The invention discloses a ghost false-shadow method of echo plane imaging technique based on even marking object, which is characterized by the following: placing a magnetic sensitive marker on the left side of imaging view field out of rectangle region; proceeding magnetic resonance imaging of marker and object; transmitting two-dimensional inversed Fuliye operation through placing 0; proceeding time inversing operation of image rebuilding or placing 0 and two-dimensional inversed Fuliye transmission; obtaining two plural images; calculating the even phase difference of each row of pixel in two plural image marking regions; fitting the even phase difference through higher-order polynomial; estimating the even phase difference out of the marker region; correcting the image phase; adding; obtaining the magnetic resonance image of ghost false-shadow. The invention improves the noise-proof property, which is convenient to operate.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Arterial spin-labeled (ASL) multiplexed echo planar imaging (m-epi)
InactiveUS20130085379A1Reduce trainingIncreased complexityMagnetic measurementsSensorsSpin labeledPerfusion
An MRI system and method for imaging perfusion in an arterial spin labeled (ASL) process in which multiplexed echo-planar imaging (M-EPI) is used rather than conventional EPI, to thereby speed up imaging and generate sets of images that show different phases of perfusion and provide additional benefits. A single multiband RF excitation pulse can be used to excite multiple slices for imaging, or a time sequence of multiband pulses can be used to further increase the number of slices.
Owner:FEINBERG DAVID
Method and system for image artifact reduction using nearest-neighbor phase correction for echo planar imaging
ActiveUS20060066307A1Reduce Image ArtifactsCorrection errorMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase correctionImaging quality
A nearest neighbor phase correction technique is implemented to reduce image artifacts due to phase errors in data acquired in an EPI scan. Image quality for EPI applications, such as DWI, DTI, and fMRI, is improved.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
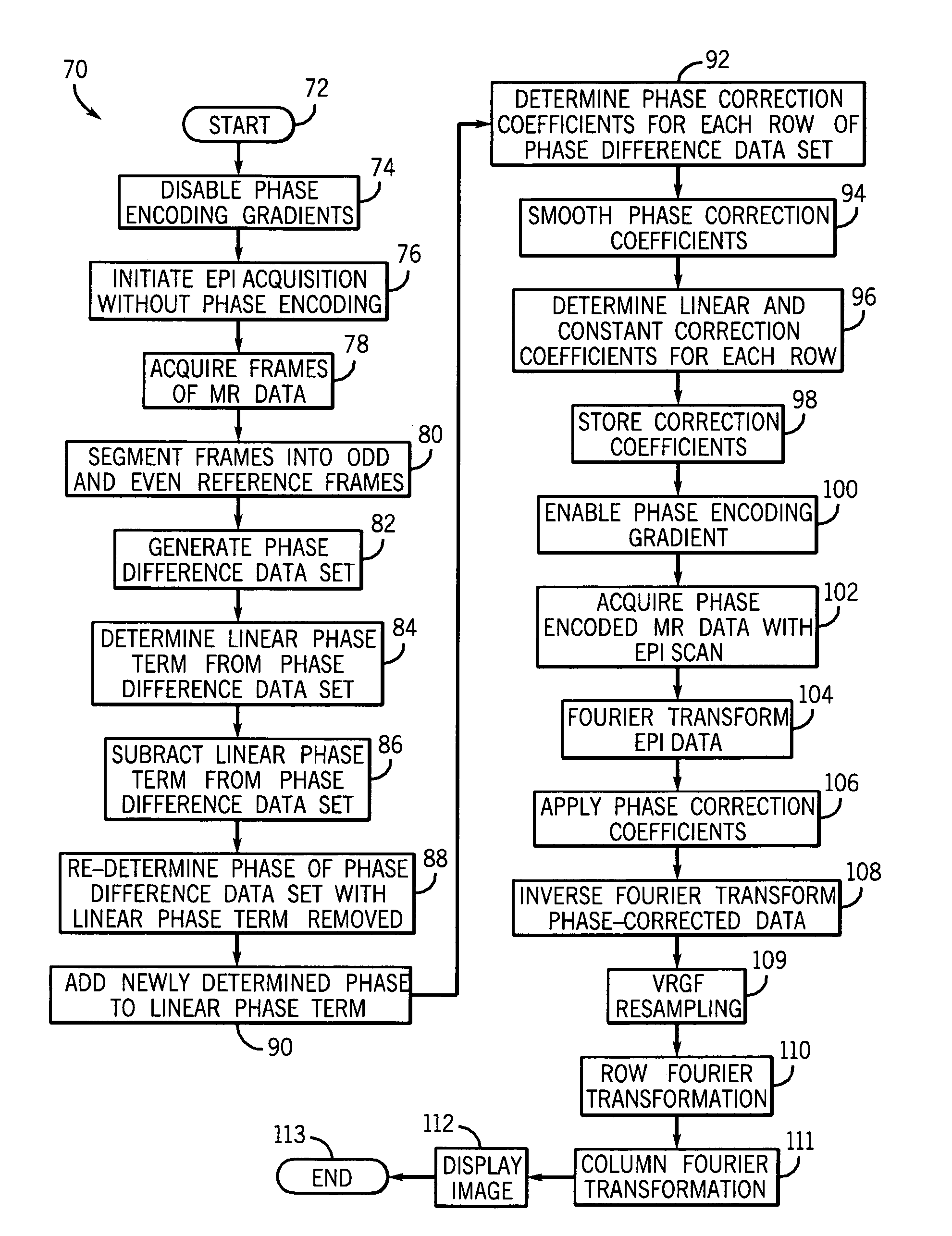
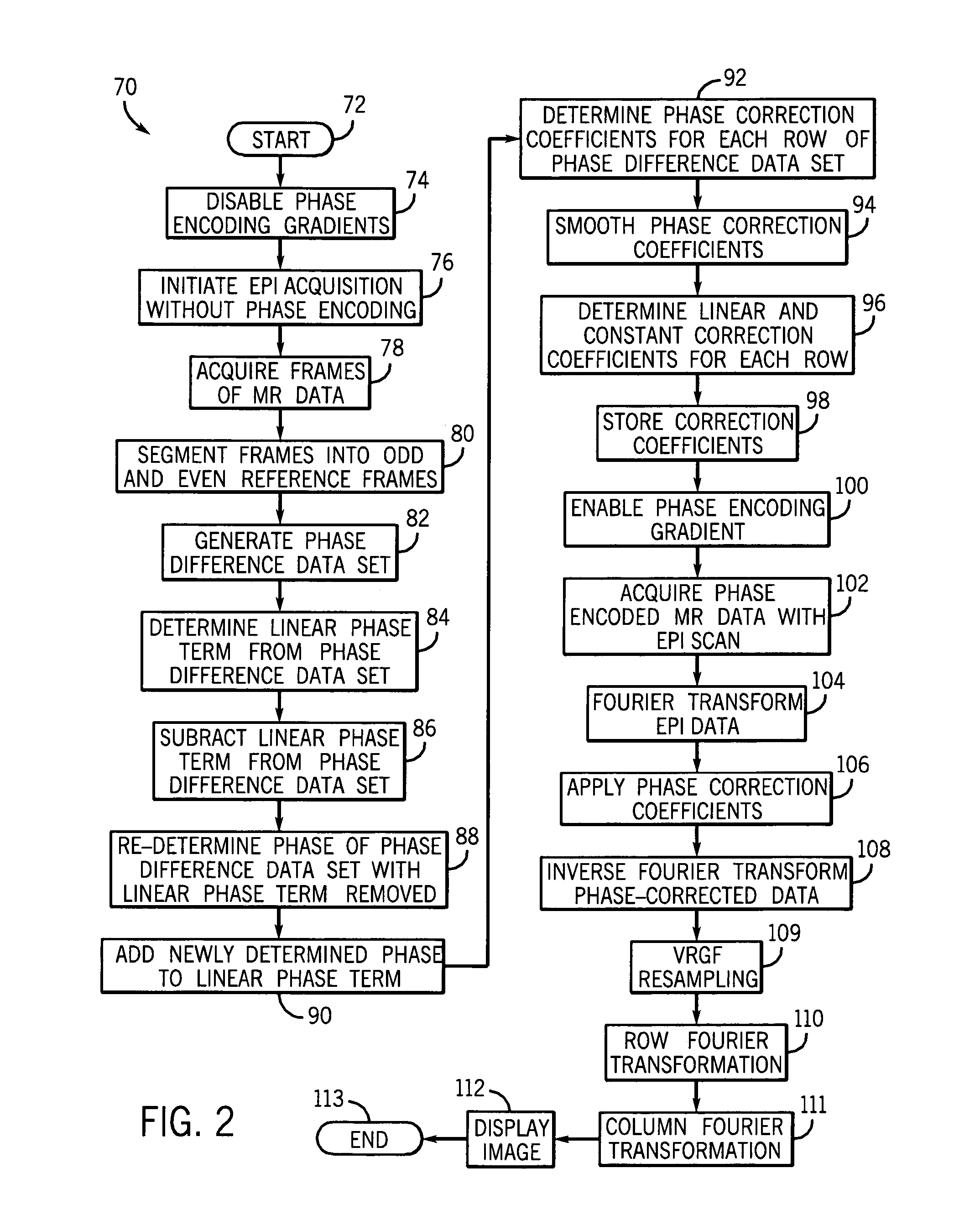
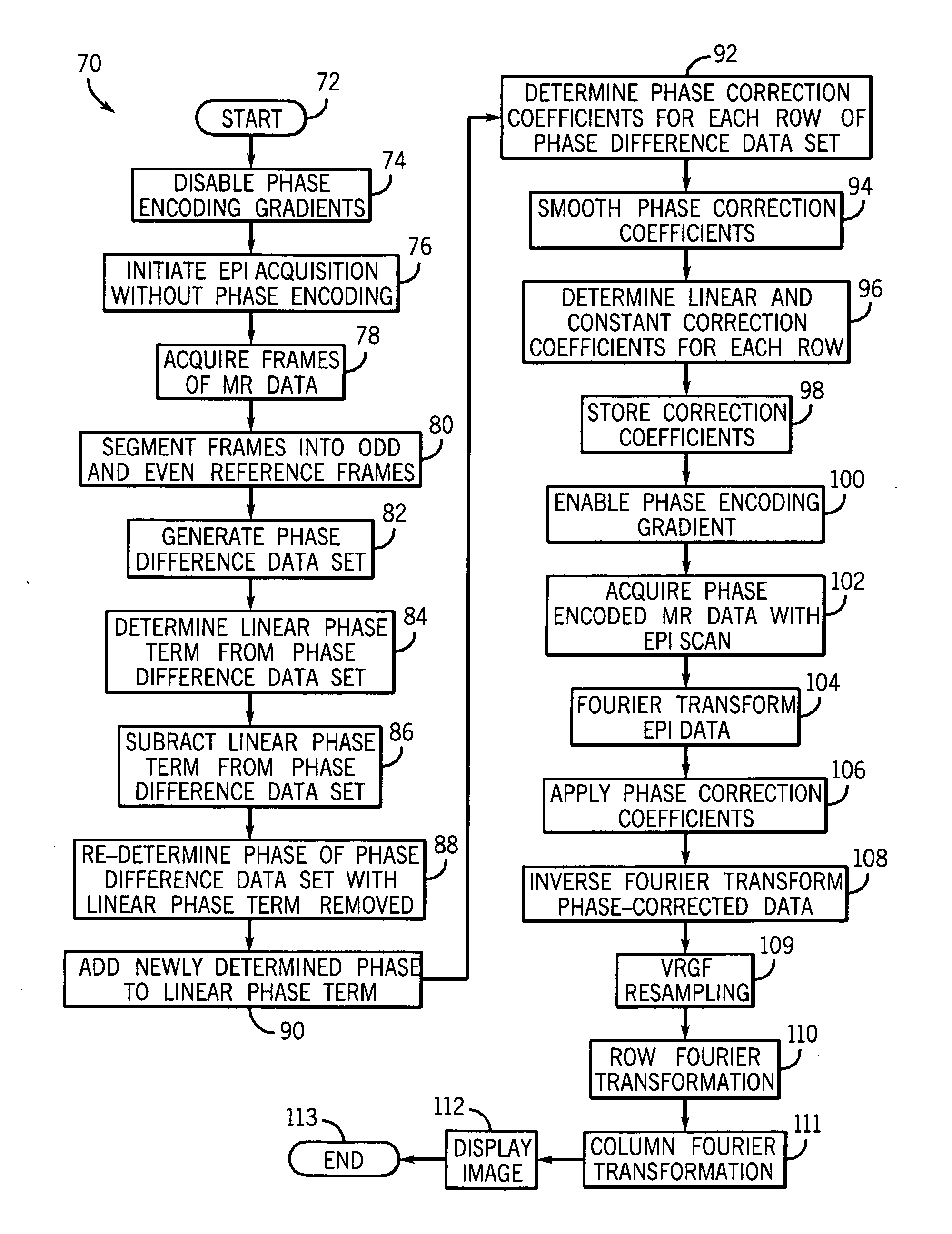
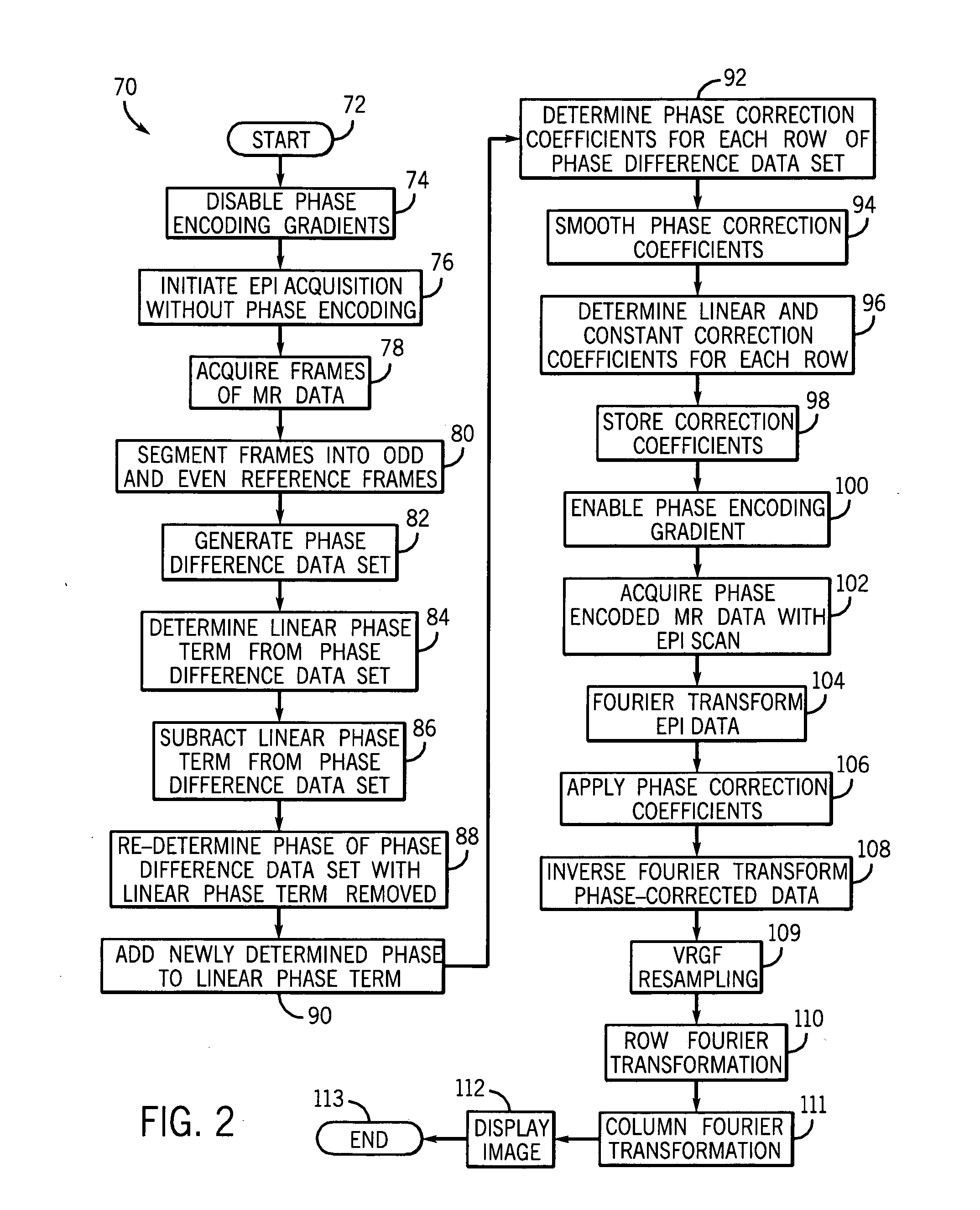
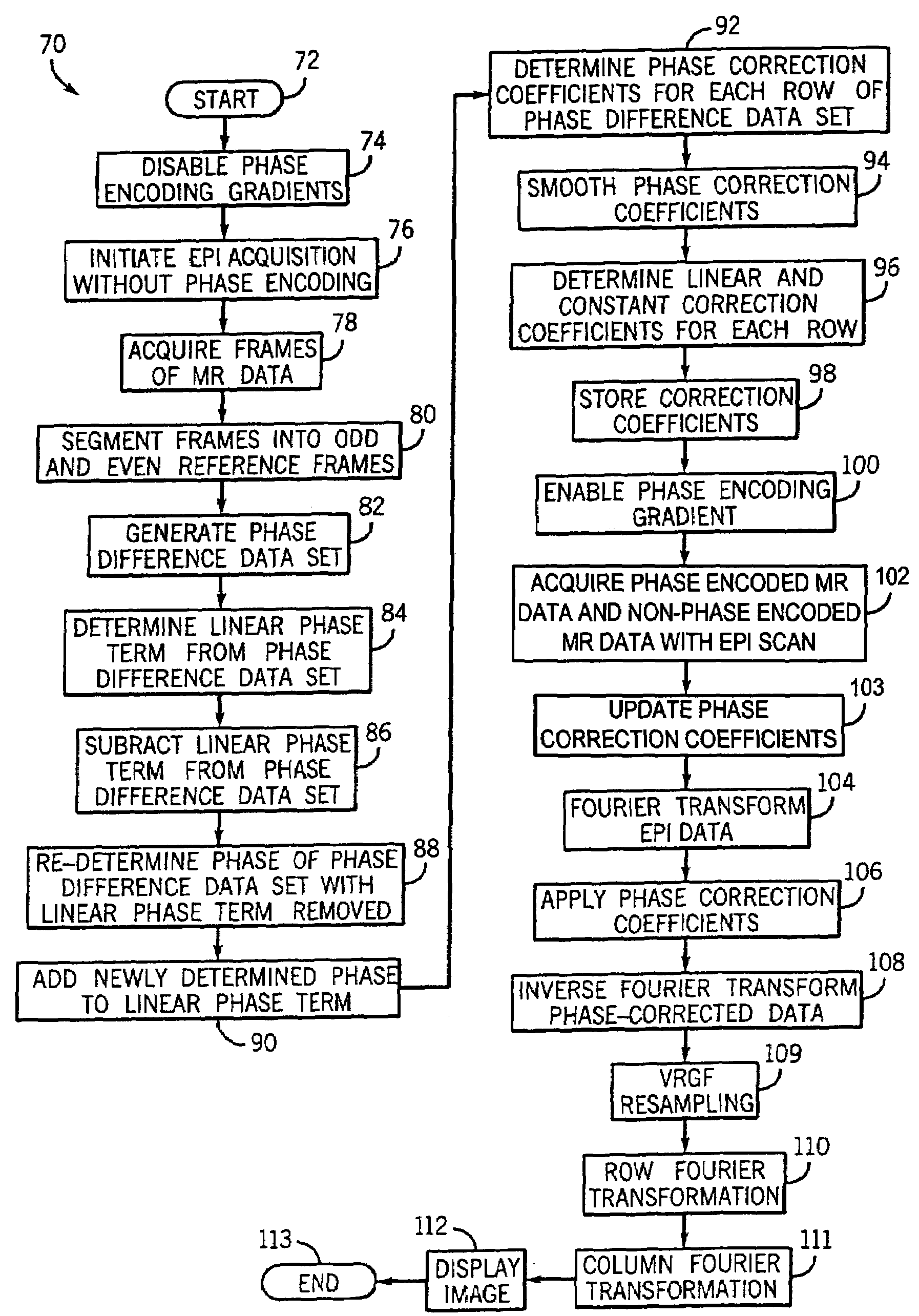
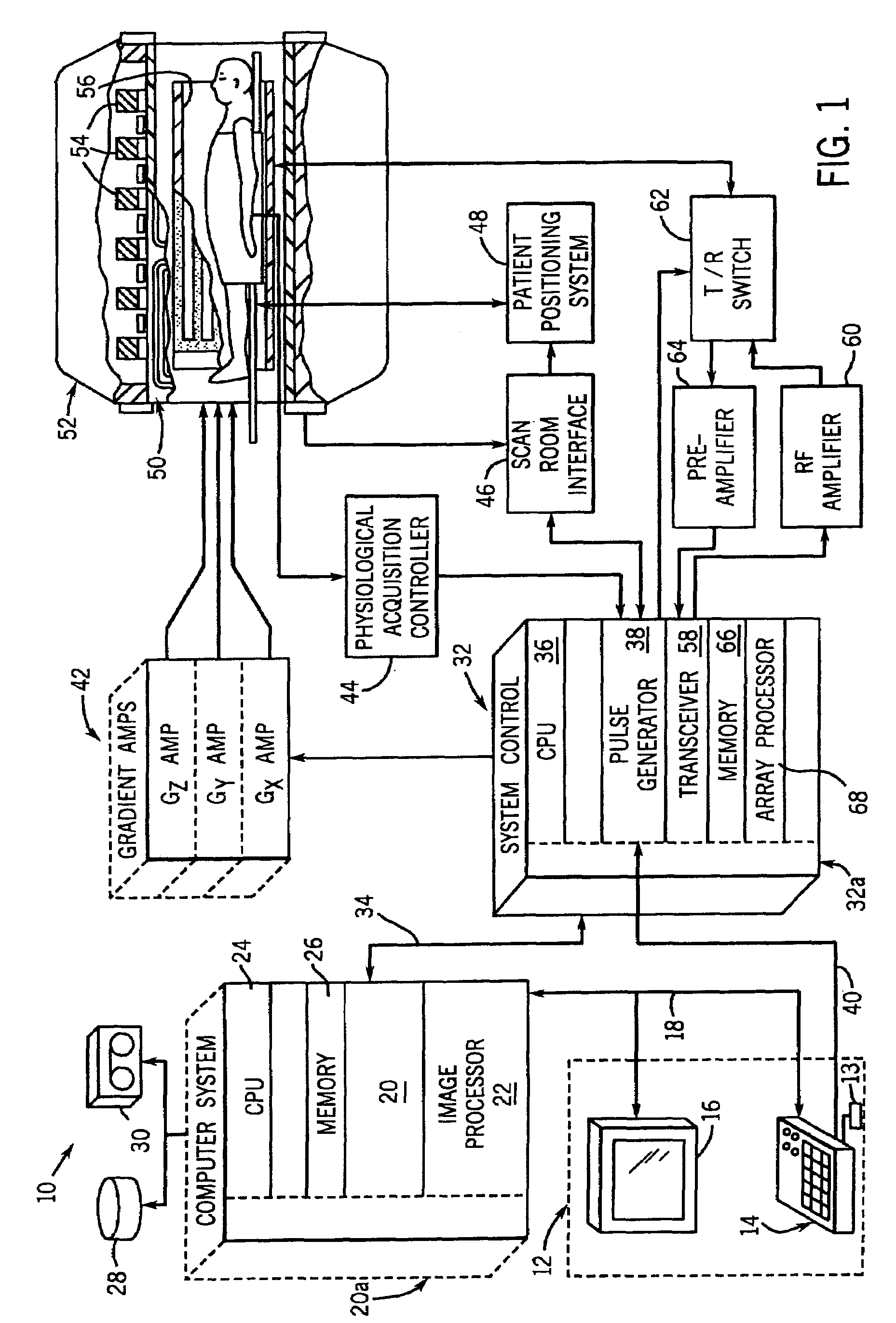
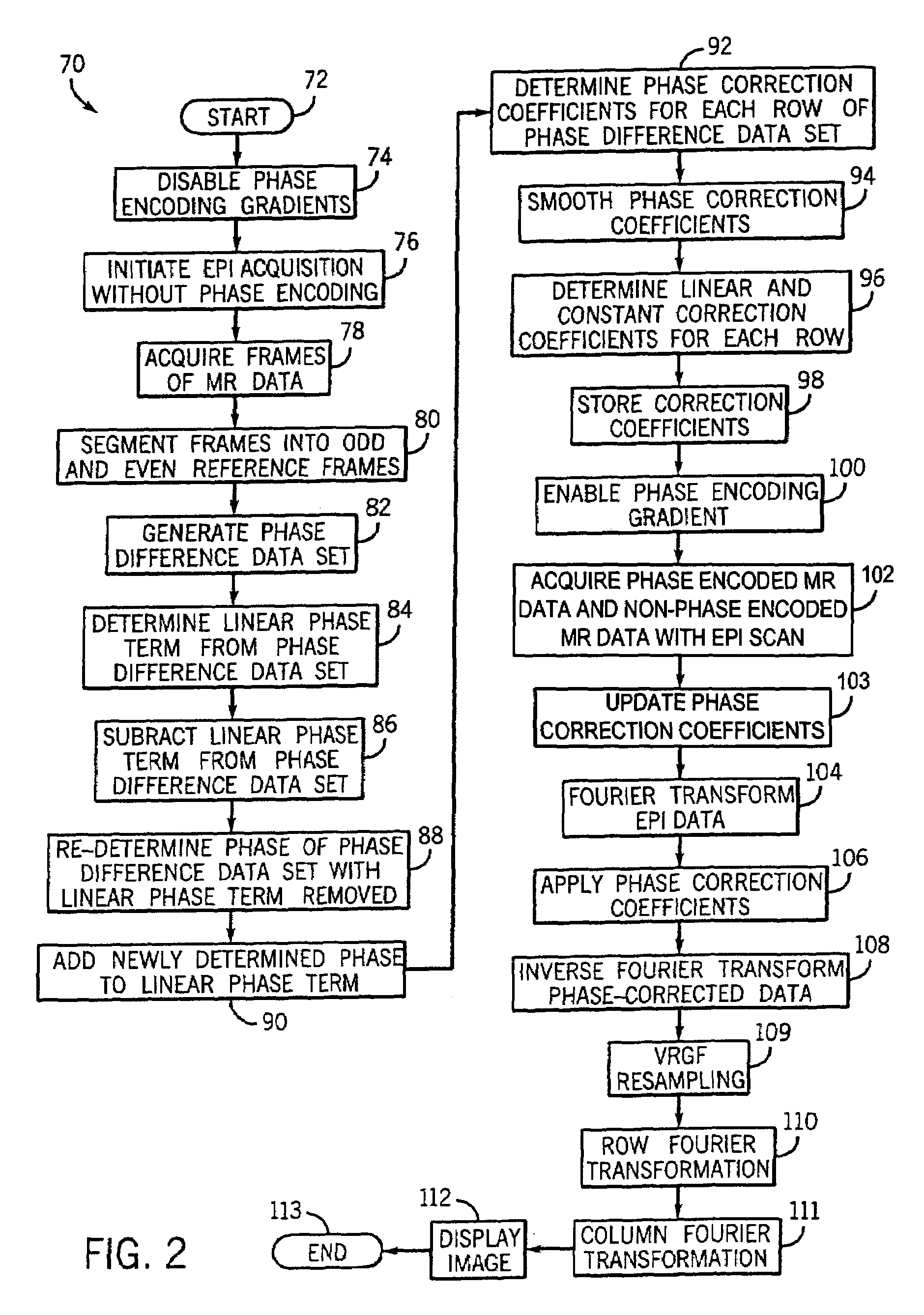
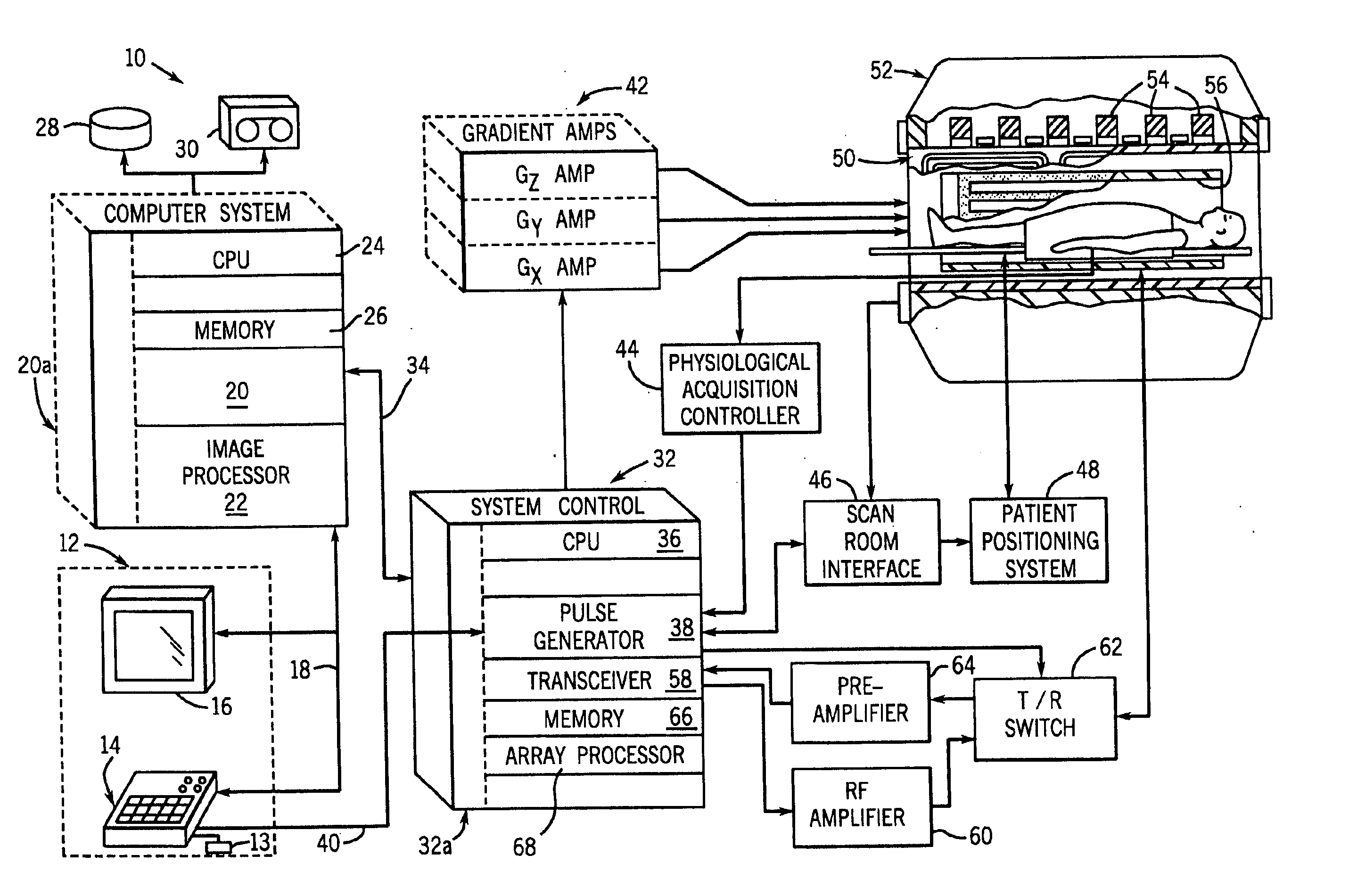
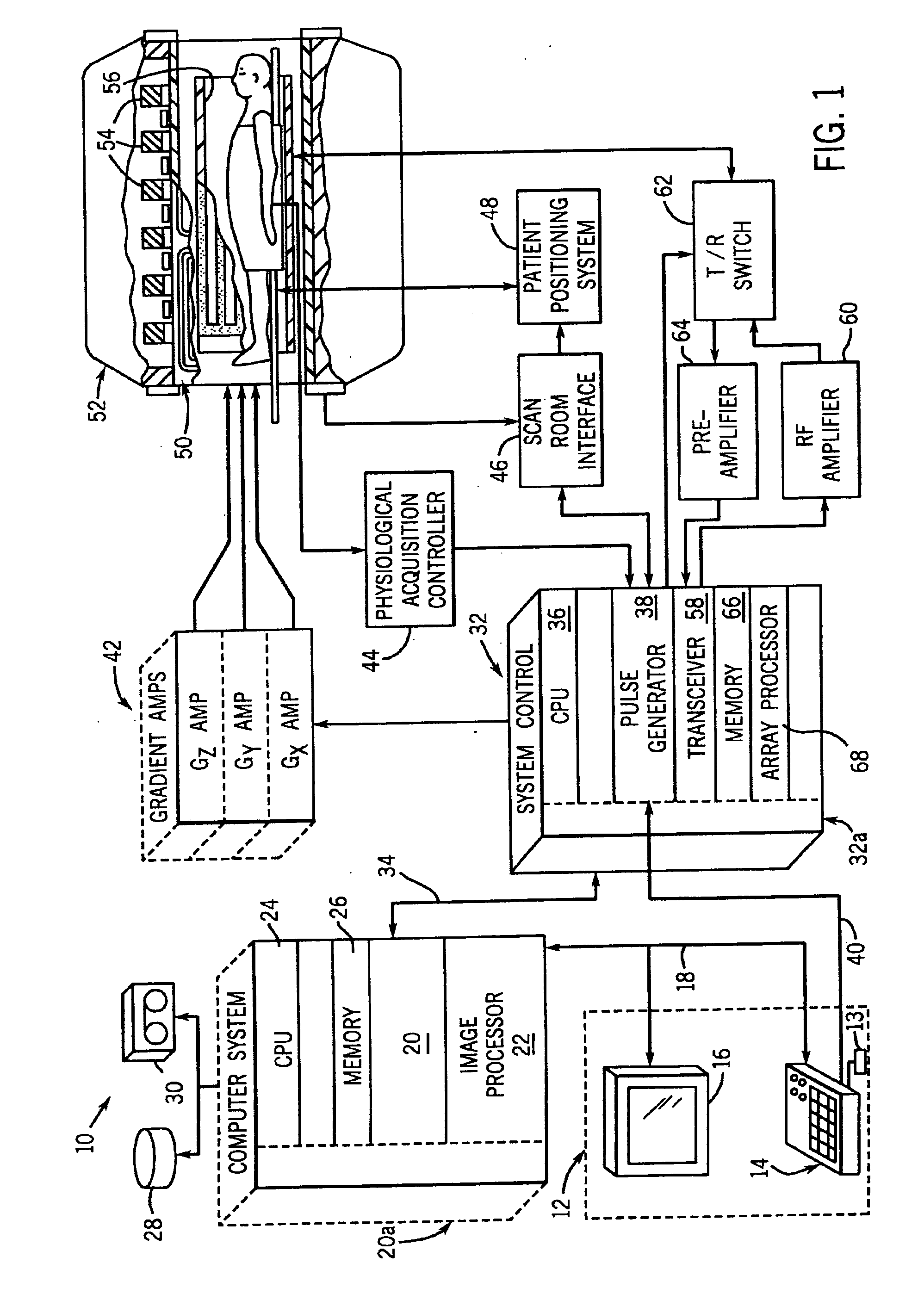
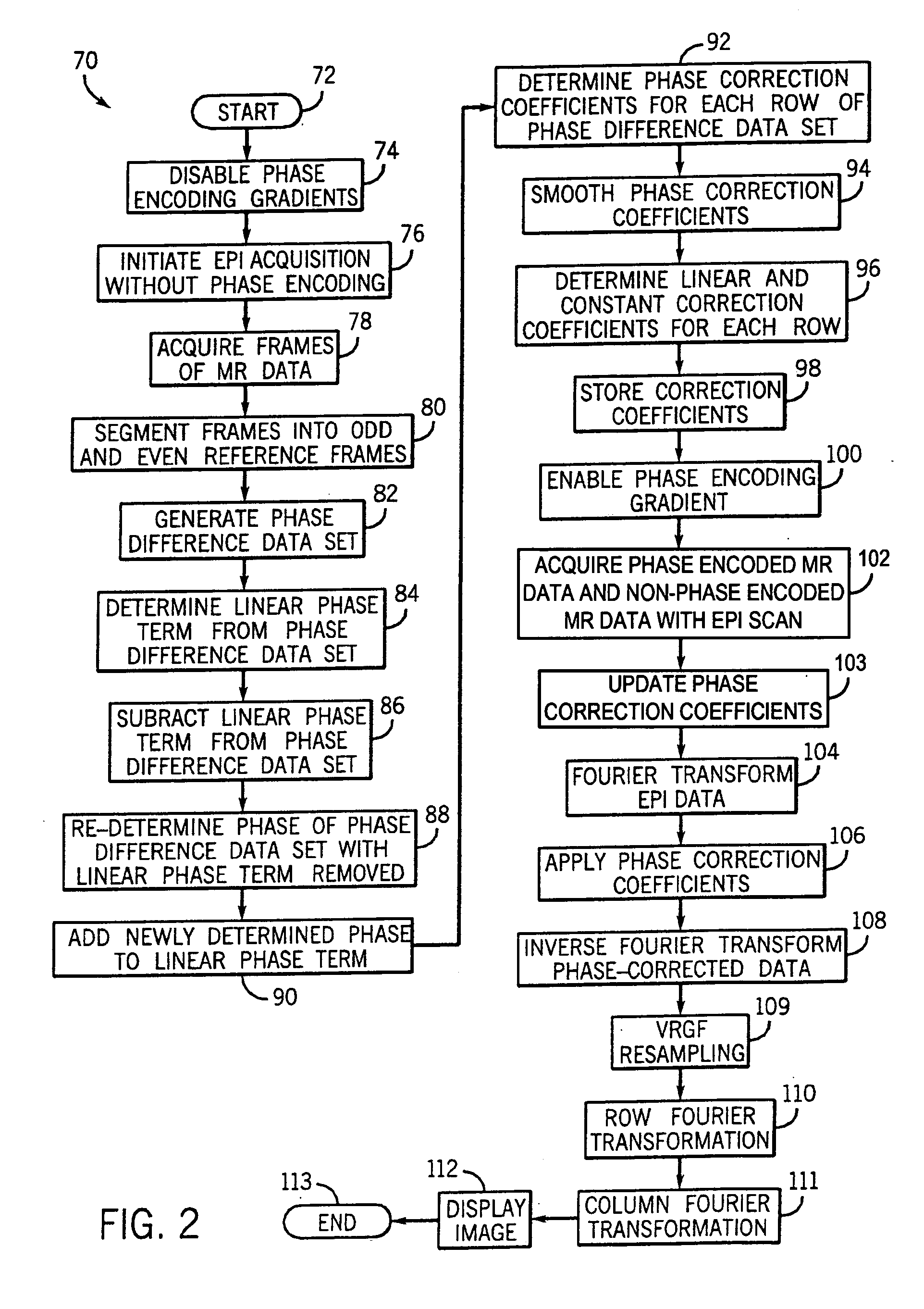
Method and apparatus of echo planar imaging with real-time determination of phase correction coefficients
ActiveUS7259557B2Low variabilityOvercomes drawbackMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase correctionData acquisition
The present invention provides an apparatus and method of phase correction whereby changes in phase characteristics are measured during data acquisition and, accordingly, phase correction parameters that are applied during image reconstruction are updated in real-time. This adaptive and dynamic phase correction reduces variability in image fidelity during the course of long MR scans, such as EPI scans, and provides consistent artifact reduction during the course of an MR scan.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Echo planar imaging method and system
ActiveCN107037386AImprove fitting accuracyFast operationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceMri image
The invention discloses an echo planar imaging method, including: obtaining multiple echo planar imaging data of a scanned part and obtaining several reference echo signals that have not been subject to phase encoding; establishing a fitting model between the actual phase deviation of the reference echo signals and the readout direction position and establishing the Hoff space related to the parameters of the fitting model; based on the actual phase deviation of the reference echo signals and the readout direction position, determining the optimal parameter group in the Hoff space; according to fitting model and the optimal parameter group, correcting the echo planar imaging data; reconstructing the corrected echo planar imaging data and obtaining the magnetic resonance image of the scanned part. The echo planar imaging method of the invention can accurately correct the phases of an imaging signal. In addition, the invention also presents an echo planar imaging system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
No-reference scanning correction method for echo plane imaging eddy current artifacts
InactiveCN109741409AQuality improvementImage enhancement2D-image generationData setEddy current effect
A no-reference scanning correction method for echo plane imaging eddy current artifacts comprises the following steps: firstly, training parameters of a neural network: randomly generating simulationsamples in batches by utilizing simulation software, and then introducing pre-compiled EPI sequences to sample the simulation samples to obtain K space data corresponding to each sample; and accordingto the phase characteristics of the eddy current effect, carrying out phase modification on the collected signal, and carrying out Fourier transform to obtain a simulated EPI image influenced by theeddy current effect, and storing the modified phase information as a label, and training the neural network model by taking the images as a training data set, and storing network parameters when the training error is reduced to be lower than a set threshold value, and after training of the neural network model is completed, inputting the truly acquired EPI image into the neural network model for reconstruction, thereby obtaining the EPI image without the eddy current artifact. According to the method, the EPI image eddy current artifacts are removed under the condition of no reference scanning, and assistance can be provided for clinical application of EPI.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
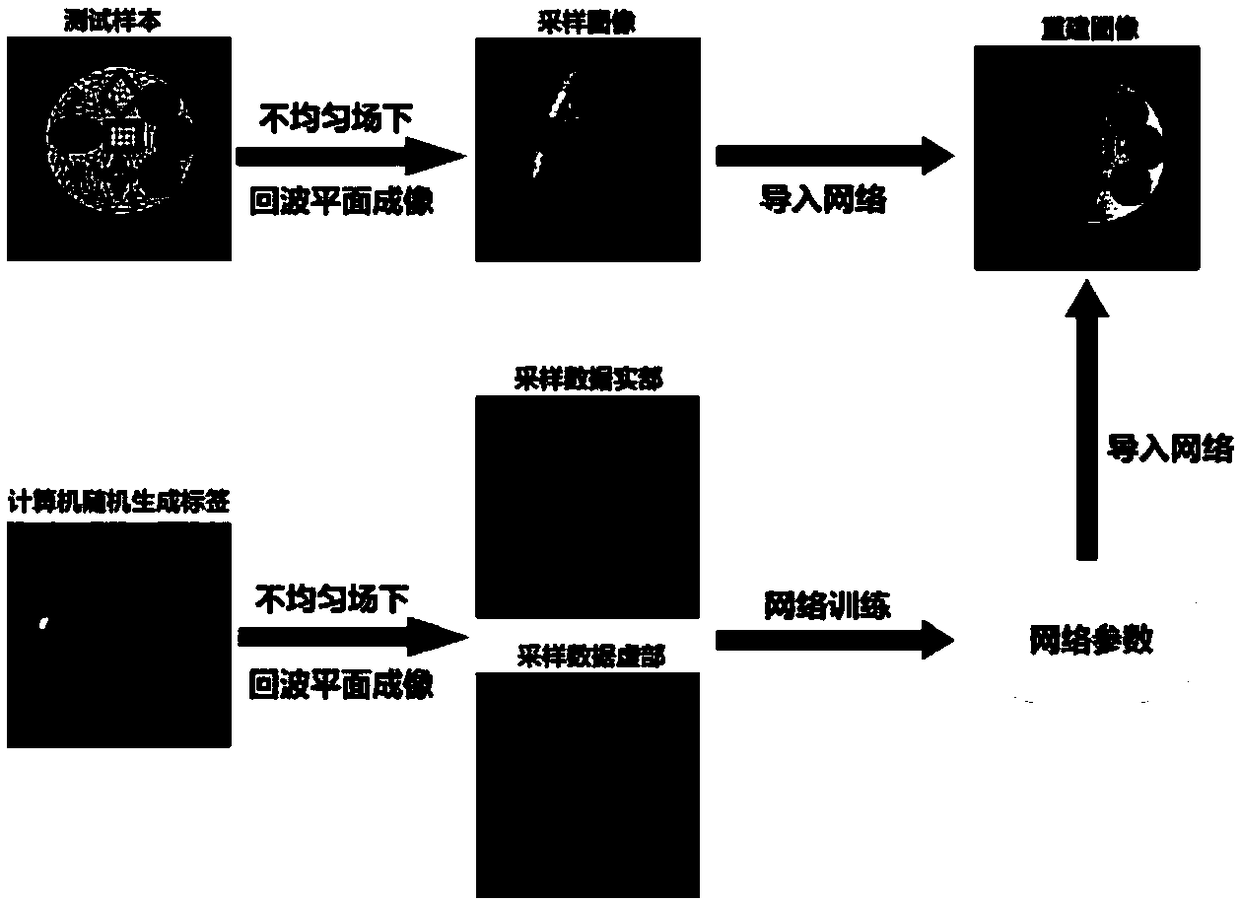
Echo planar imaging no-reference scanned image distortion rectification method under nonuniform magnetic field
ActiveCN108132274AQuality improvementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData setReconstruction method
The invention discloses an echo planar imaging no-reference scanned image distortion rectification method under nonuniform magnetic field, and belongs to the field of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging reconstruction method. According to the method, a single scanning echo planar imaging sequence is adopted for coding and sampling of signals, after one time of 90 DEG pulse excitation, a series of echo gradient sampling are carried out so as to obtain the signals in the whole k space, influences of nonuniform magnetic fields are accumulated in the whole sampling process. Singles obtained via sampling are subjected to two dimensional Fourier transform of image reconstruction, the real part and the imaginary part are taken as inputs of residual network. Neural network training is realized based on simulated data sets. At first random generation of labels is carried out, and then the image of distortion corresponding to the labels is achieved based on sampling conditions; batch generation of a plurality of groups of data is realized, and the obtained data is adopted for network training; network hyper-parameter is adjusted to ensure convergence of training error is realized; and at lastafter network training, network parameters are introduced, and input of actual measurement single scanning echo planar imaging is carried out so as to obtain orthoscopic images.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Echo planar imaging method and device
ActiveCN104865545AEvenly distributedEliminate or weaken Nyquist GhostMagnetic measurementsVisual field lossPhase difference
An echo planar imaging method comprises the following steps of: applying an echo planar imaging sequence, obtaining pre-scanning K space data after a pre-scanning progress, grouping the pre-scanning K space data to obtain odd number data line and even number data line K spaces, and respectively integrating the odd number data line and even number data line K spaces and carrying out the Fourier transformation to obtain an image domain data Iodd of odd number data lines and an image domain data Ieven of even number data lines; carrying out operation on the image domain data Iodd and Ieven, and obtaining a phase difference change rate [lambda] along a phase encoding direction; obtaining a phase difference scope [phi] of an imaging visual field FOV; obtaining offset data in the phase encoding directions of the K space odd number data lines and even number data lines, and carrying out phase encoding gradient compensation on the echo planar imaging sequence according to the offset data; carrying out formal scanning on the compensated echo planar imaging sequence, and obtaining imaging K space data; and carrying out the Fourier transformation to obtain an image. The invention further discloses a echo planar imaging device.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Inside-out echo-planar imaging method for shortening echo time
InactiveCN102890255AShortened echo timeImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Arterial spin labeling
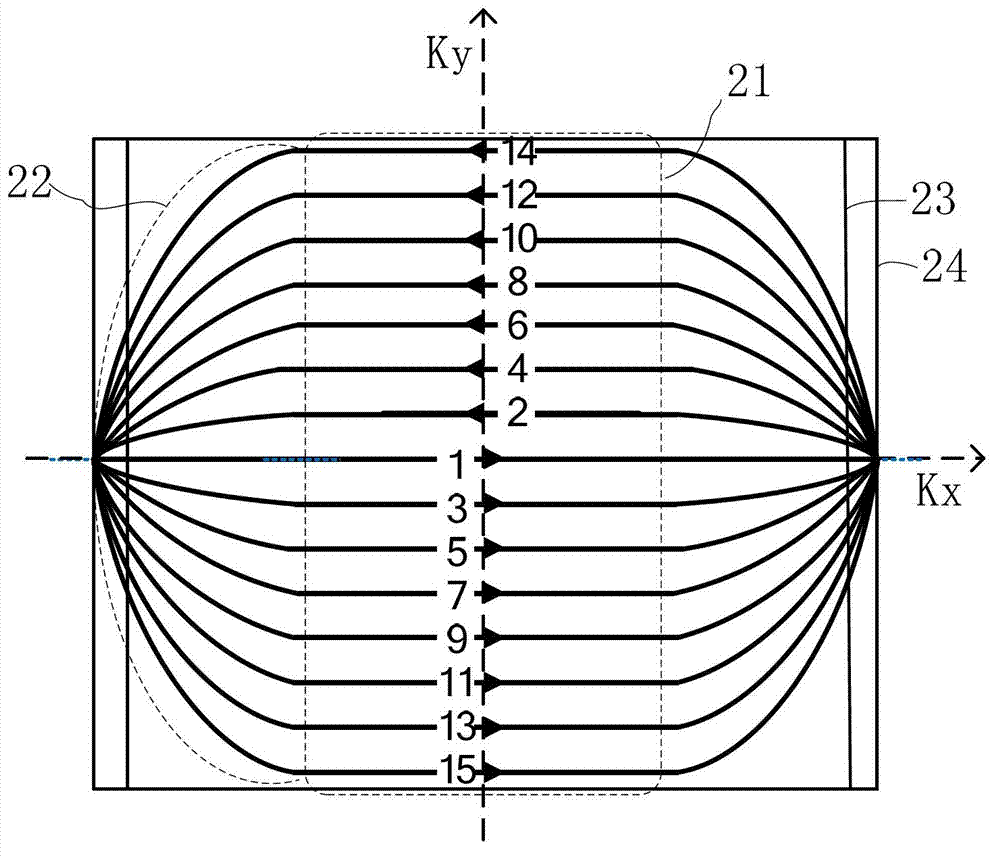
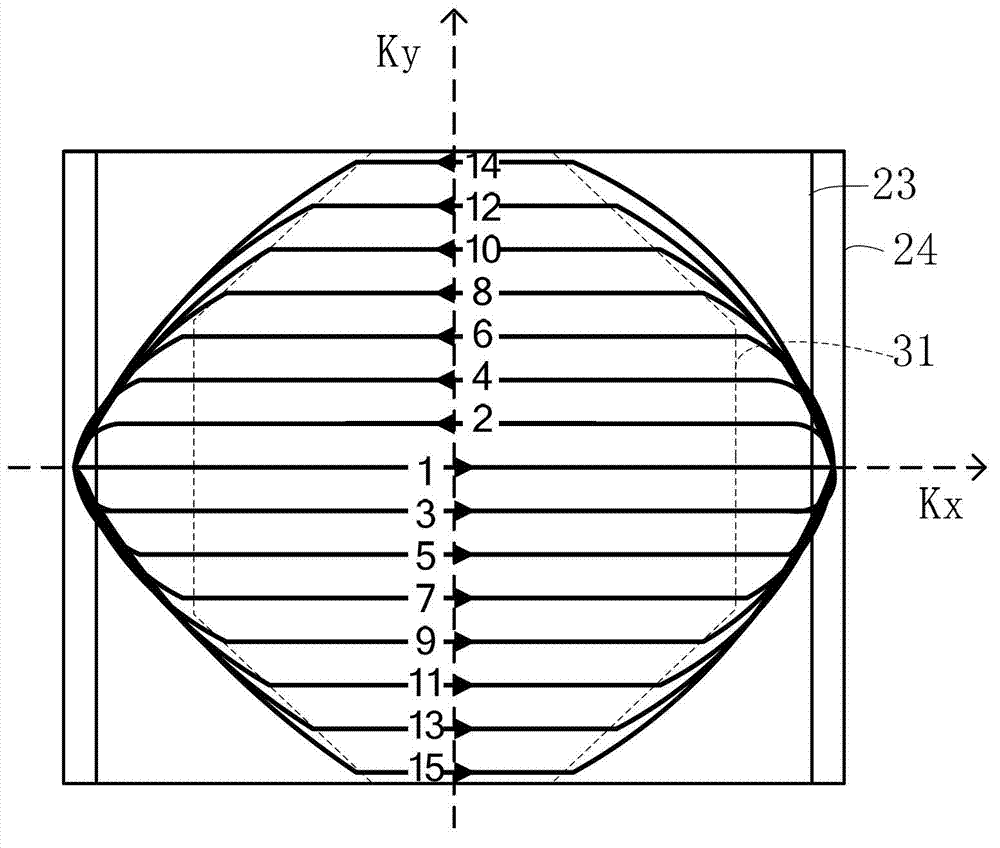
The invention discloses an inside-out echo-planar imaging method for shortening echo time. The method is characterized in that: a k-space trajectory extends to the outer side of a phase encoding direction from the center, wherein a gradient for generating the trajectory is composed of reading-out gradients which switch between forward and reverse directions and phase encoding gradients which switch between forward and reverse directions and gradually increases from zero. The method further comprises a step that: in order to accommodate the phase encoding gradients of which the area increases gradually without adding an echo spacing, the phase encoding gradient and a data collecting window are permitted to be overlapped. According to the method disclosed by the invention, an effective echo time in a sequence is located in the center of a first echo, the echo time is shortened greatly, and the signal to noise ratio is increased; since the contrast ratio of an image depends on signals of a k-space centre, and data of the k-space center are from an initial echo, T2 or T2* weighing of the obtained image is very small; and in diffusion imaging and arterial spin labeling imaging, the decreasing of the T2 or the T2* weighing is beneficial to improving the quality of the image.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus of echo planar imaging with real-time determination of phase correction coefficients
ActiveUS20070085538A1Low variabilityOvercomes drawbackMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase correctionData acquisition
The present invention provides an apparatus and method of phase correction whereby changes in phase characteristics are measured during data acquisition and, accordingly, phase correction parameters that are applied during image reconstruction are updated in real-time. This adaptive and dynamic phase correction reduces variability in image fidelity during the course of long MR scans, such as EPI scans, and provides consistent artifact reduction during the course of an MR scan.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
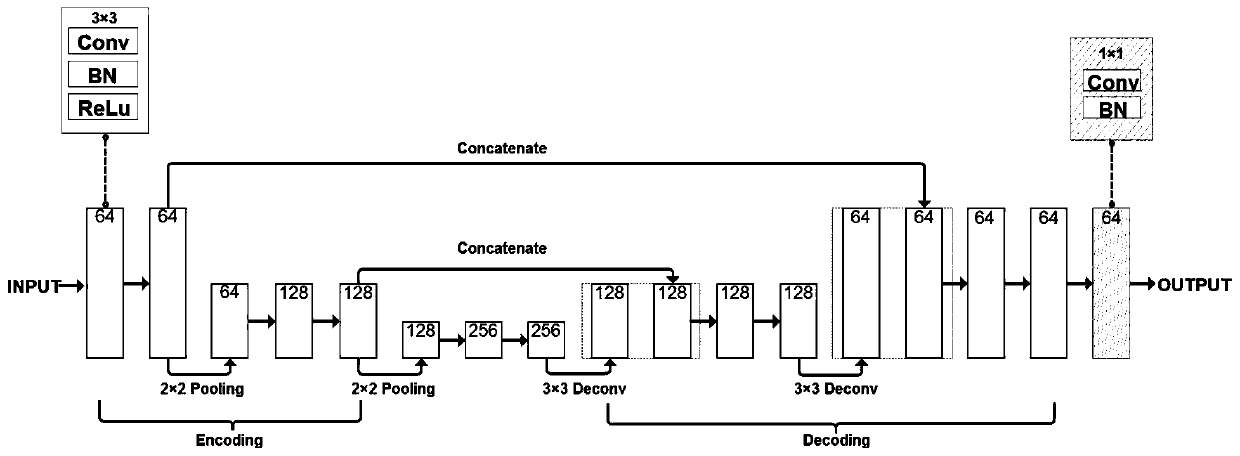
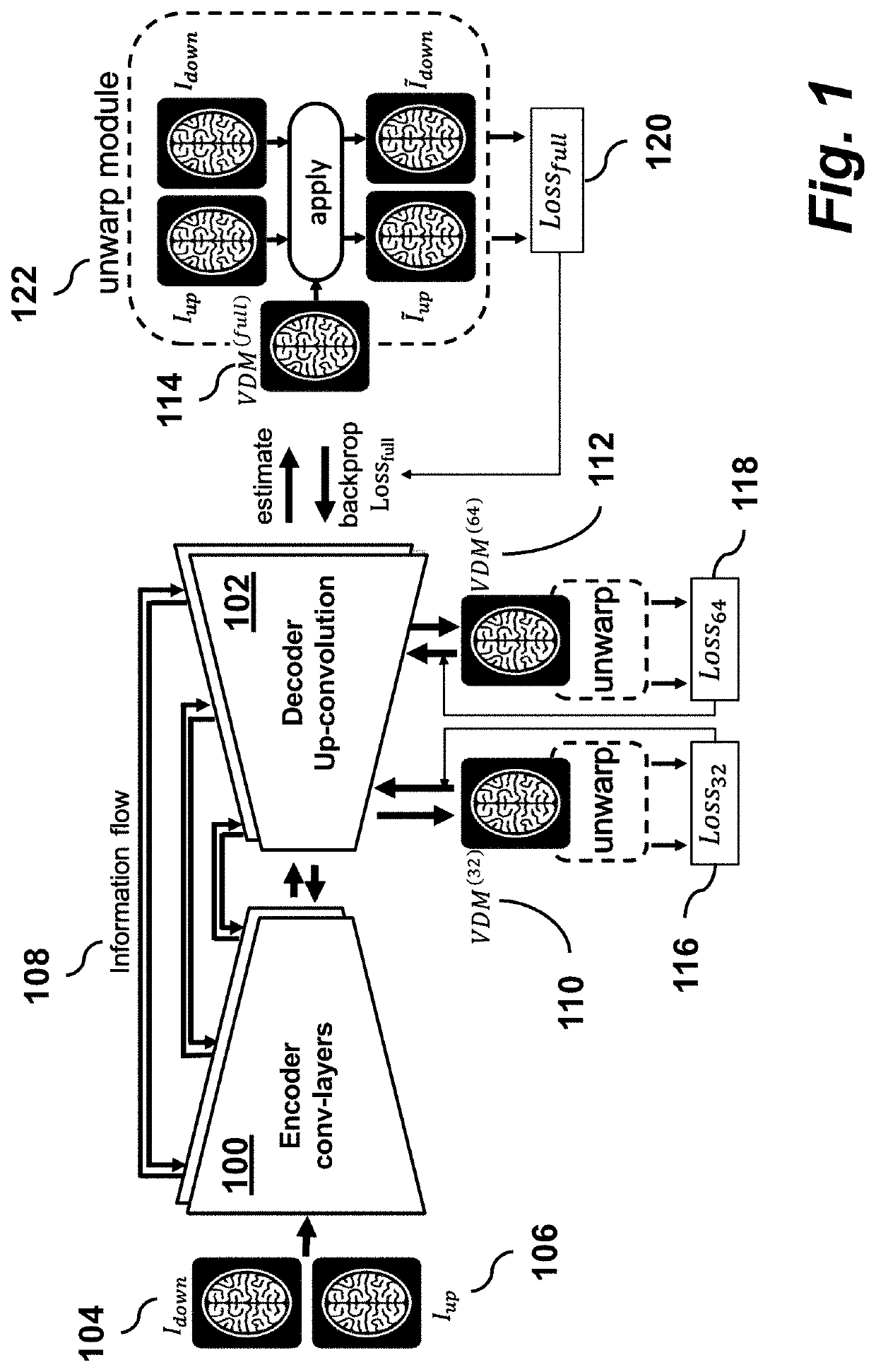
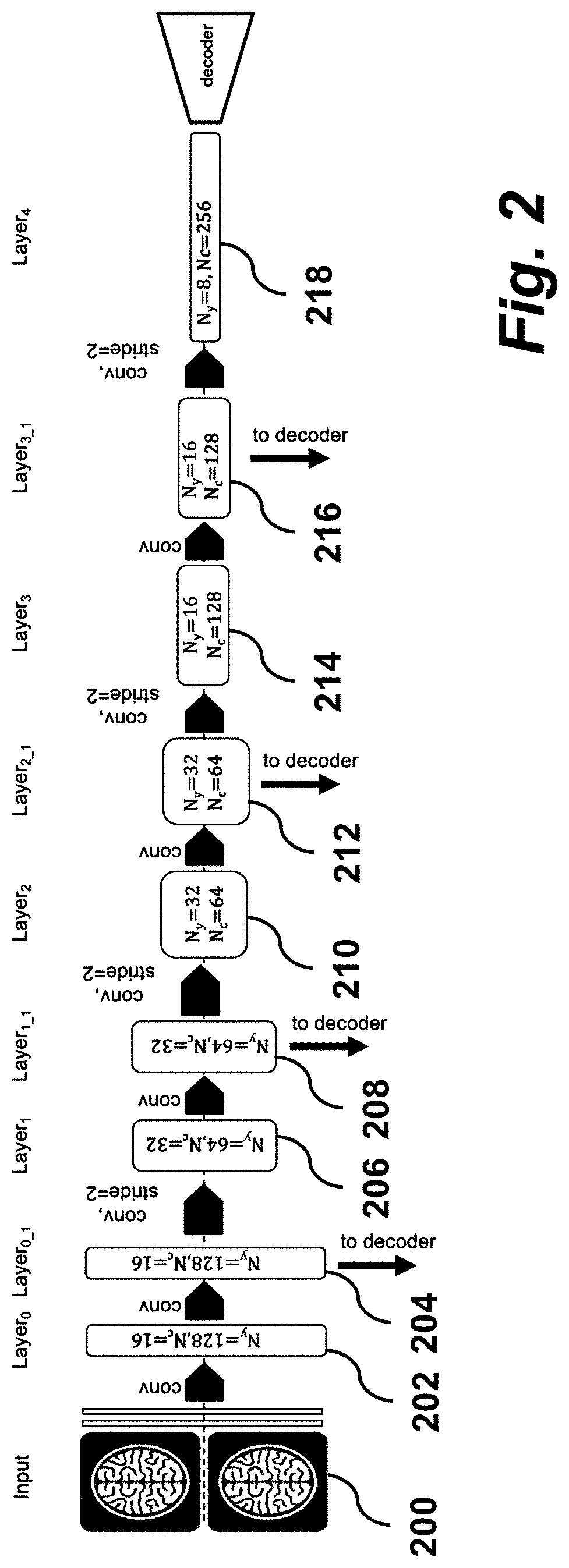
Un-supervised convolutional neural network for distortion map estimation and correction in MRI
ActiveUS20200020082A1Easy to useConvenient and accurateImage enhancementImage analysisMR - Magnetic resonanceNeural network nn
A method for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) includes performing an echo planar imaging acquisition using inverted up / down phase encoding directions and reconstructing acquired images having geometric distortions along the phase encoding directions due to off-resonant spins; feed-forward estimating by a convolutional neural network (CNN) a phase distortion map from the acquired images; where the CNN is trained to minimize a similarity metric between un-warped up / down image pairs; and performing geometric distortion correction of the acquired images using the phase distortion map to unwarp the acquired images.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
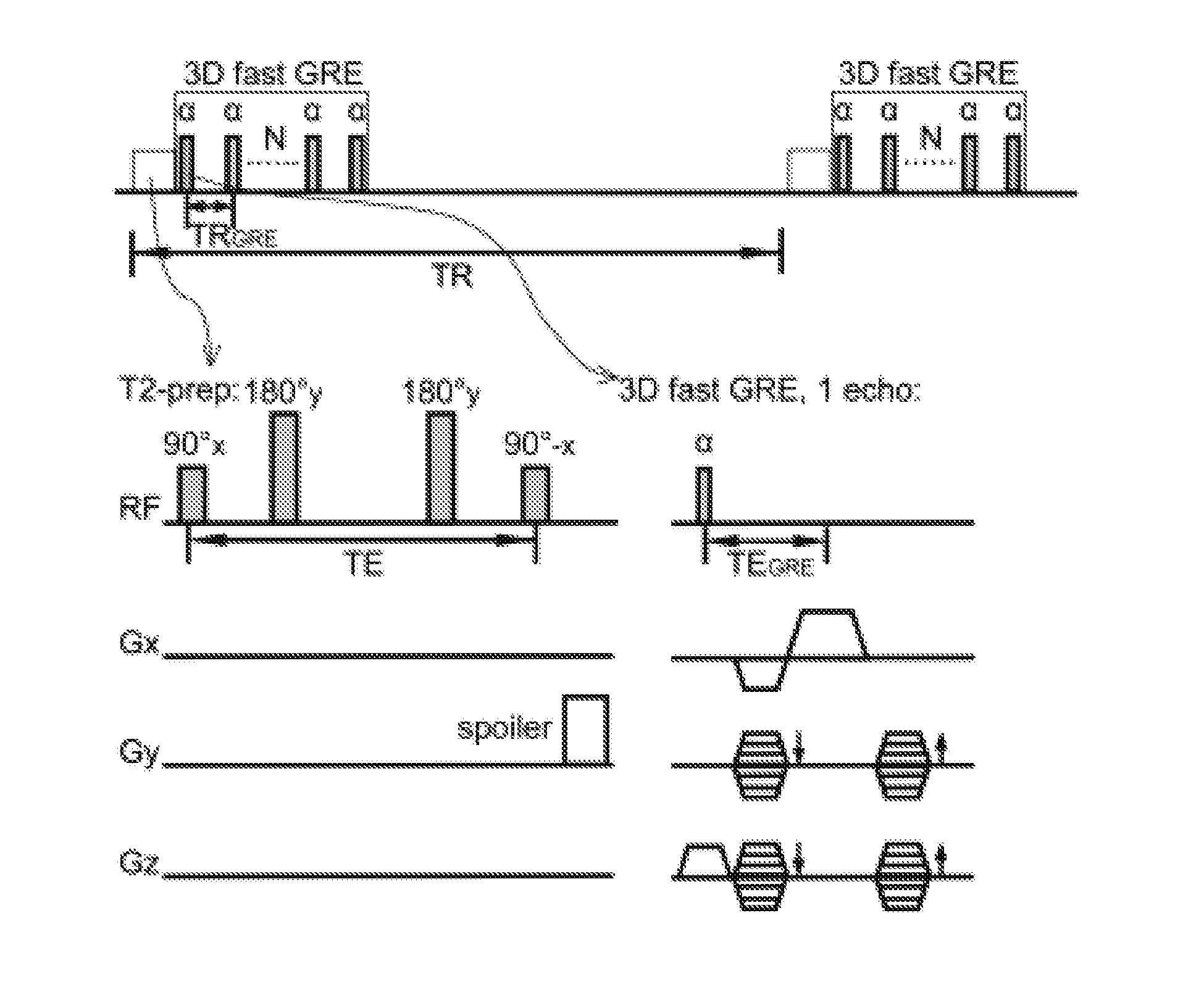
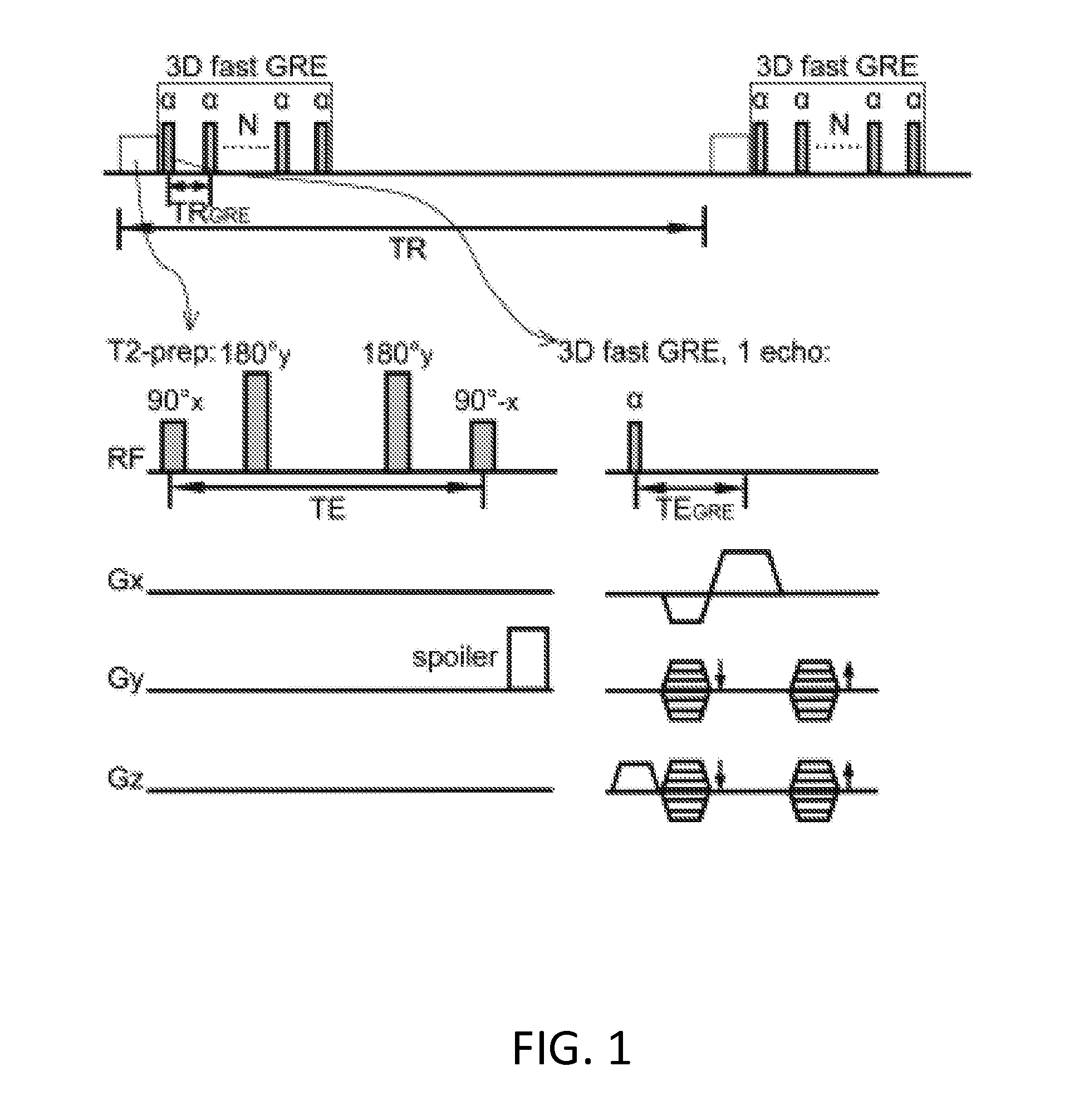
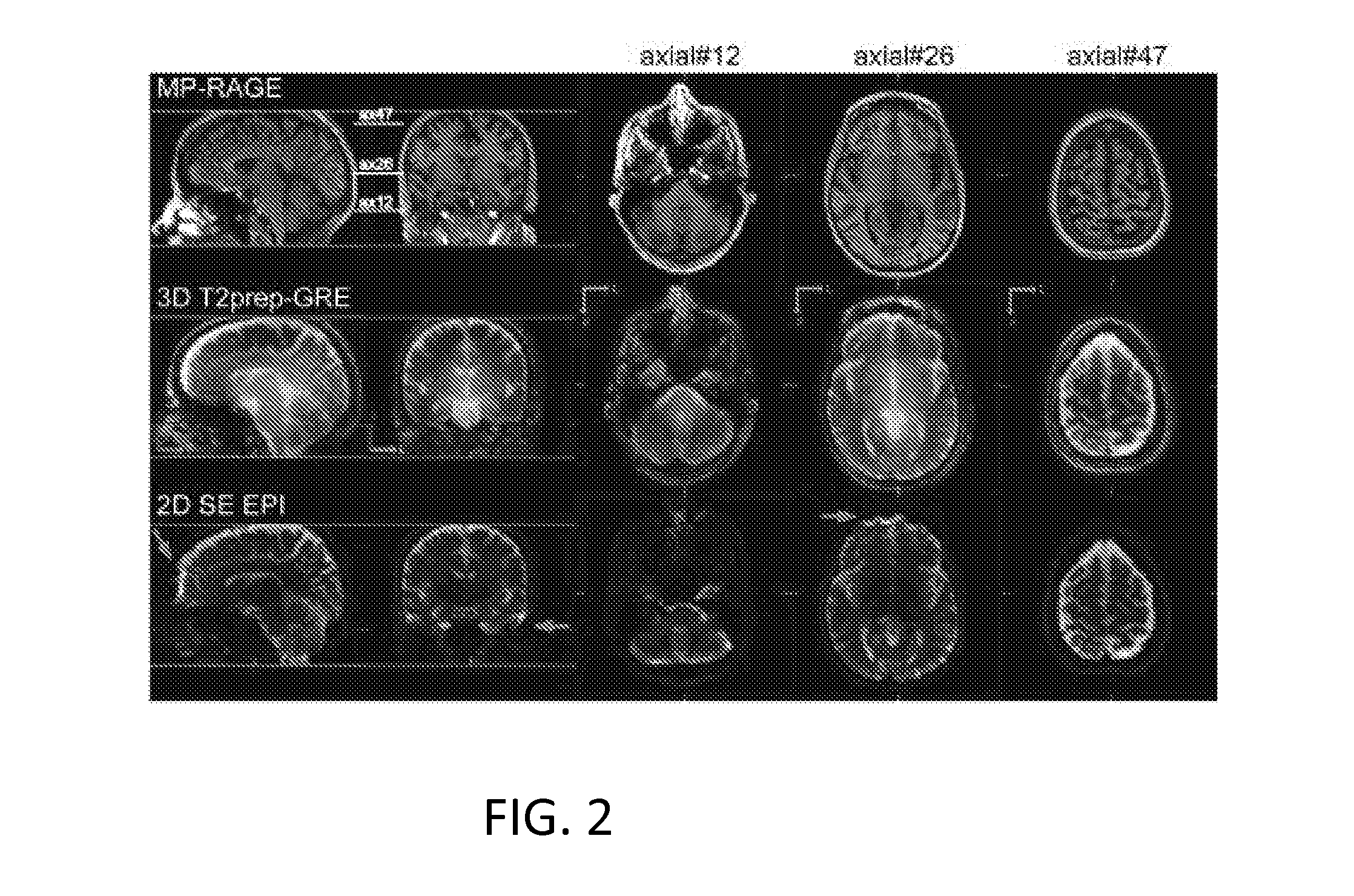
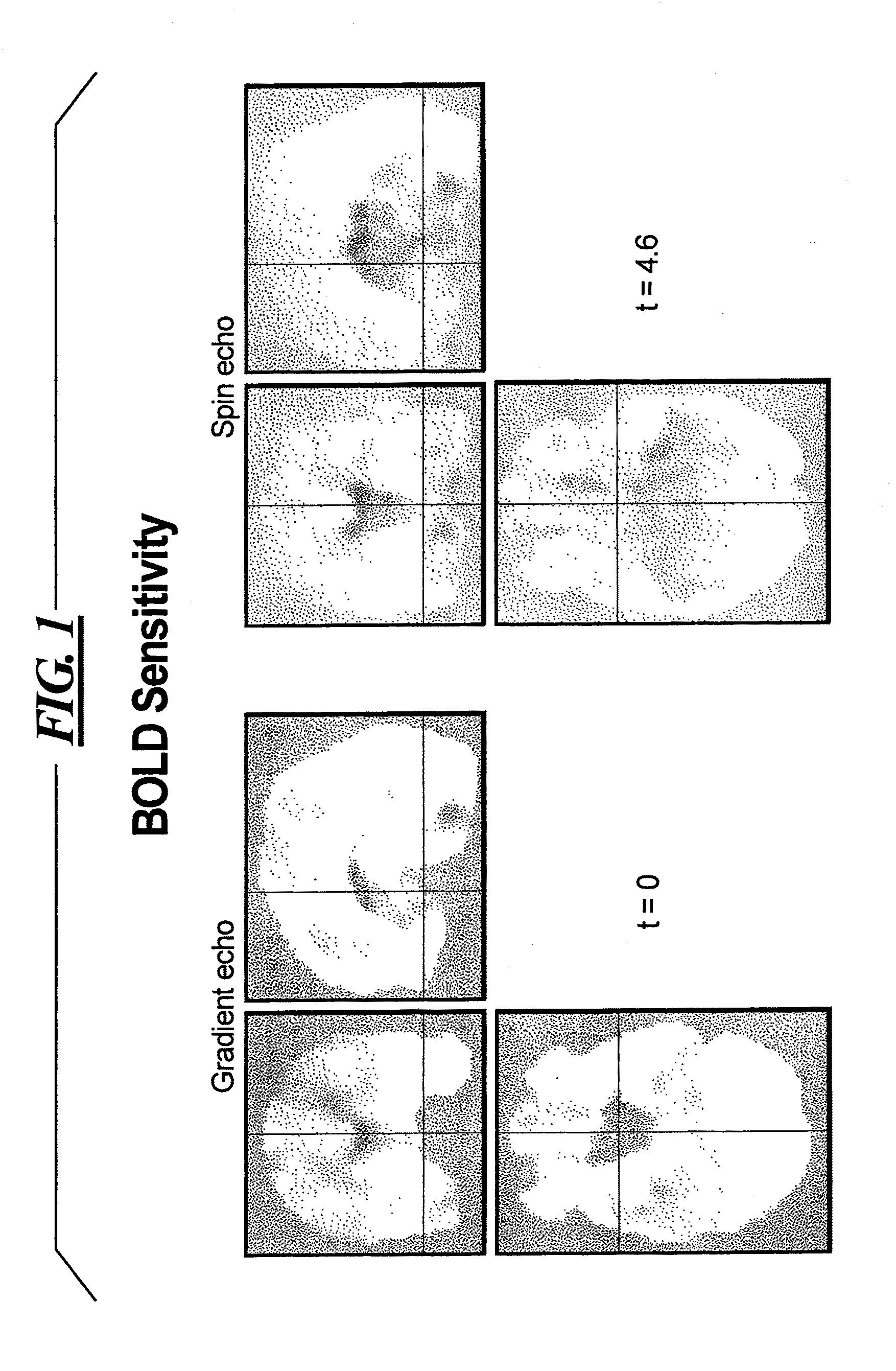
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Methodology Using Transverse Relaxation Preparation and Non-Echo-Planar Imaging (EPI) Pulse Sequences
InactiveUS20160113501A1Short timeEliminate the effects ofMedical imagingMagnetic measurementsDead timePulse sequence
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a new acquisition scheme for T2-weighted BOLD fMRI. It employs a T2 preparation module to induce the BOLD contrast, followed by a single-shot 3D fast gradient echo (GRE) readout with short echo time (TE<2 ms). The separation of BOLD contrast generation from the readout substantially reduces the “dead time” due to long TE required in spin echo (SE) BOLD sequences. This approach termed “3D T2prep-GRE,” can be implemented with any magnetic resonance imaging machine, known to or conceivable by one of skill in the art. This approach is expected to be useful for ultra-high field fMRI studies that require whole brain coverage, or focus on regions near air cavities. The concept of using T2 preparation to generate BOLD contrast can be combined with many other fast imaging sequences at any field strength.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
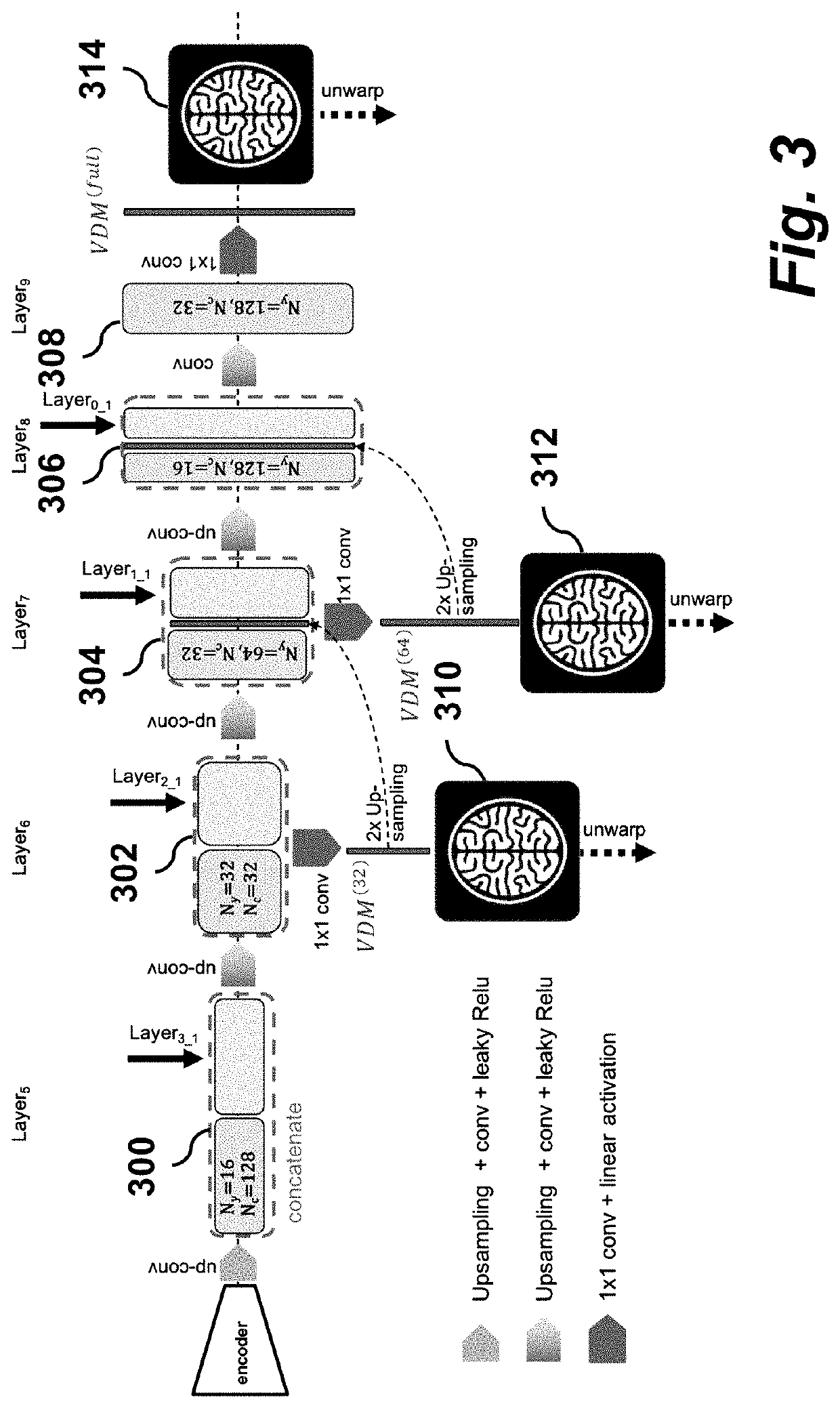
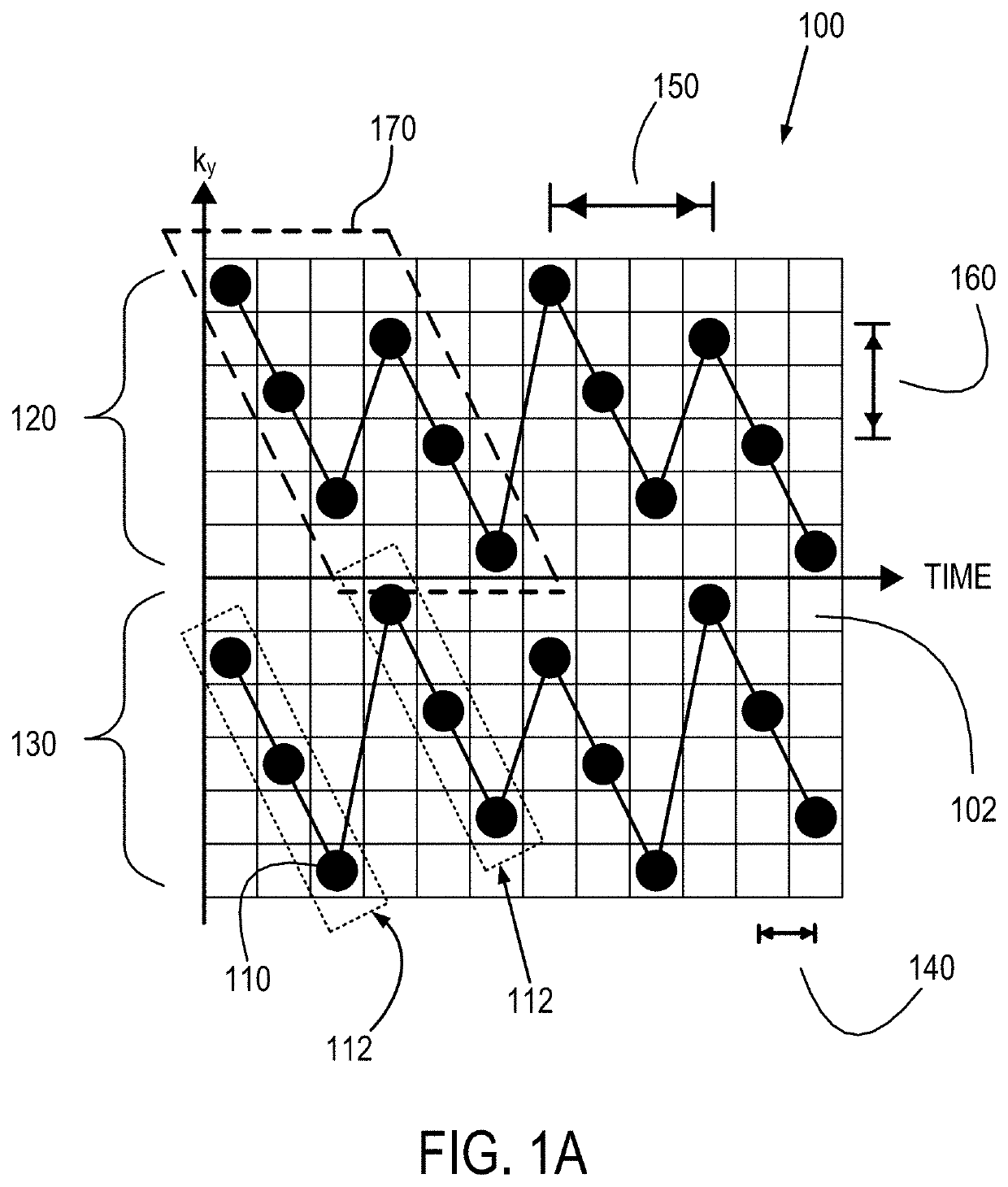
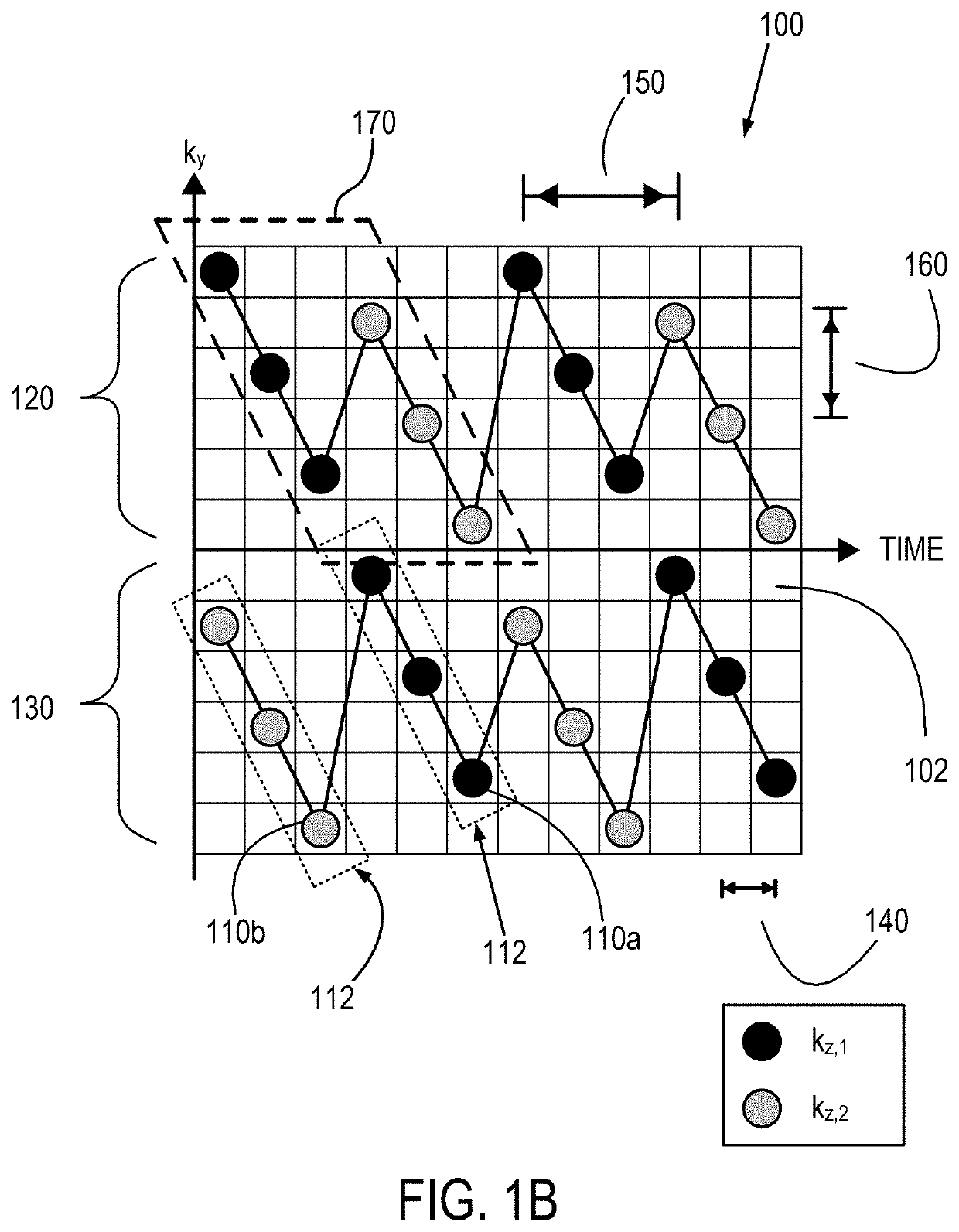
Method for echo planar time-resolved magnetic resonance imaging
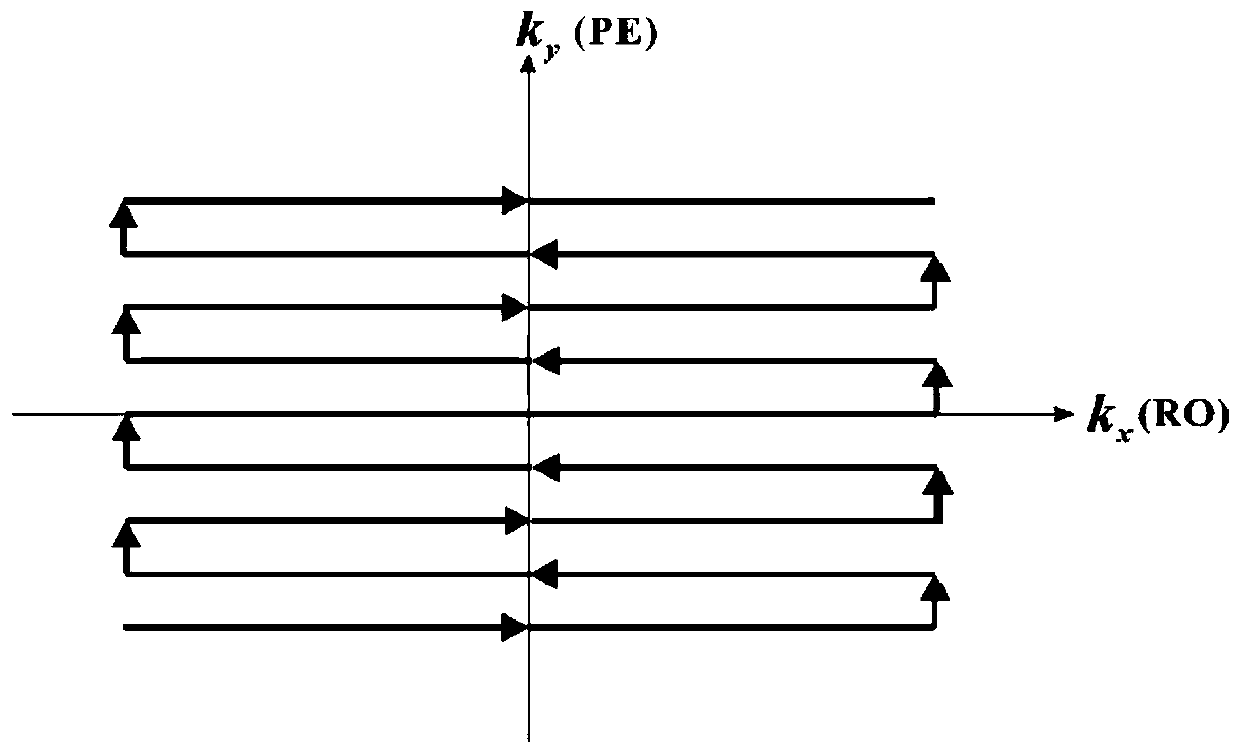
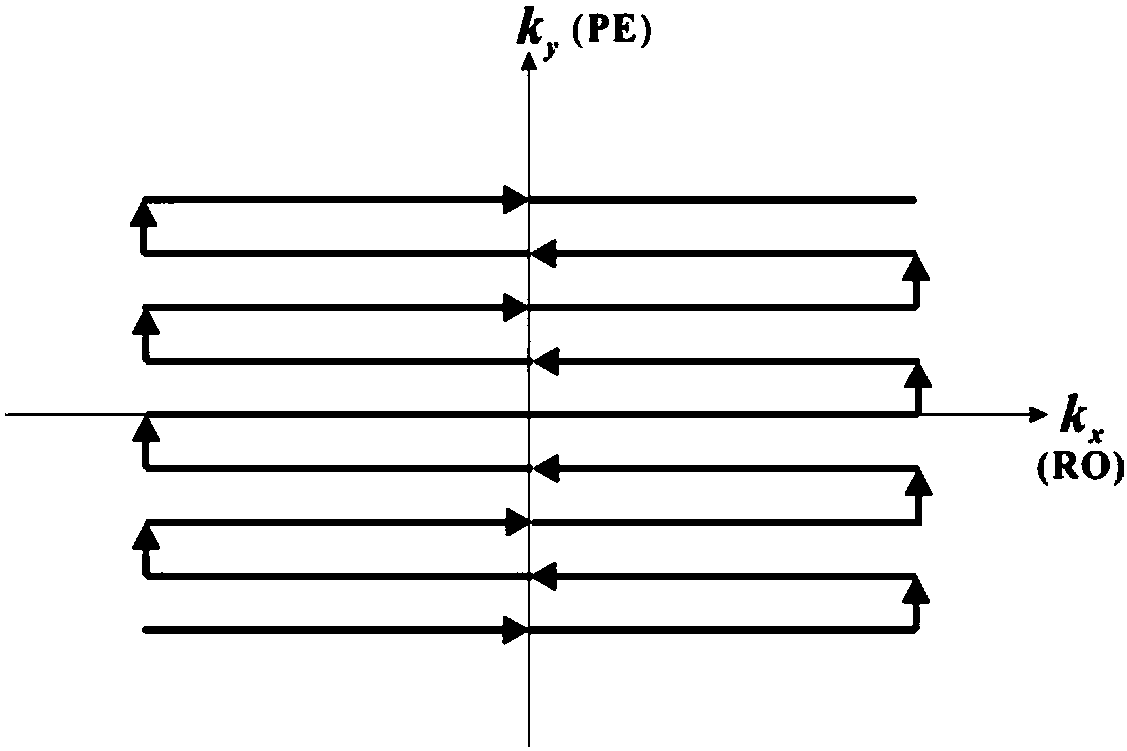
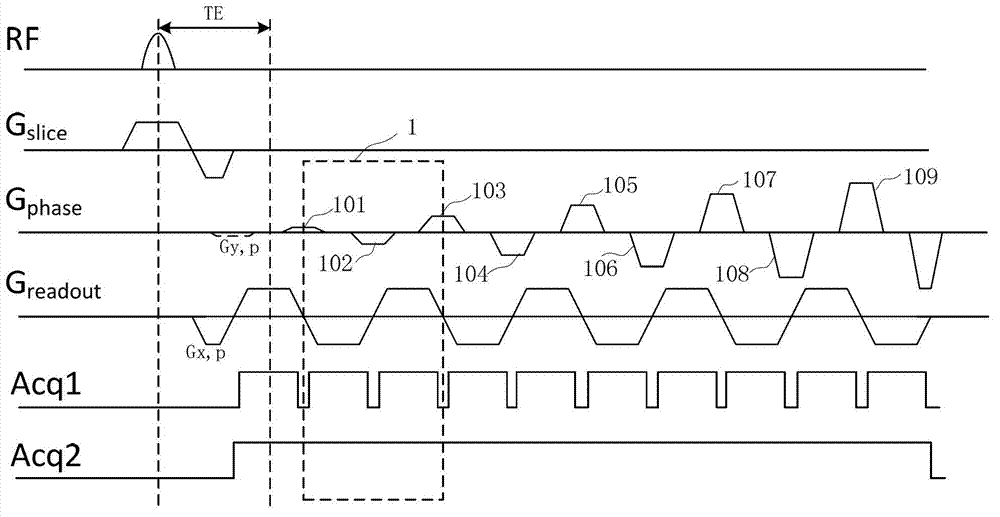
Systems and methods for magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”) that address the geometric distortions and blurring common to conventional echo planar imaging (“EPI”) sequences, and that provide new temporal signal evolution information across the EPI readout, are described. Echo planar time-resolved imaging (“EPTI”) schemes are described to implement an accelerated sampling of a hybrid space spanned by the phase encoding dimension and the temporal dimension. In general, each EPTI shot covers a segment of this hybrid space using a zigzag trajectory with an interleaved acceleration in the phase-encoding direction. The hybrid space may be undersampled and a tilted reconstruction kernel used to synthesize additional data samples.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
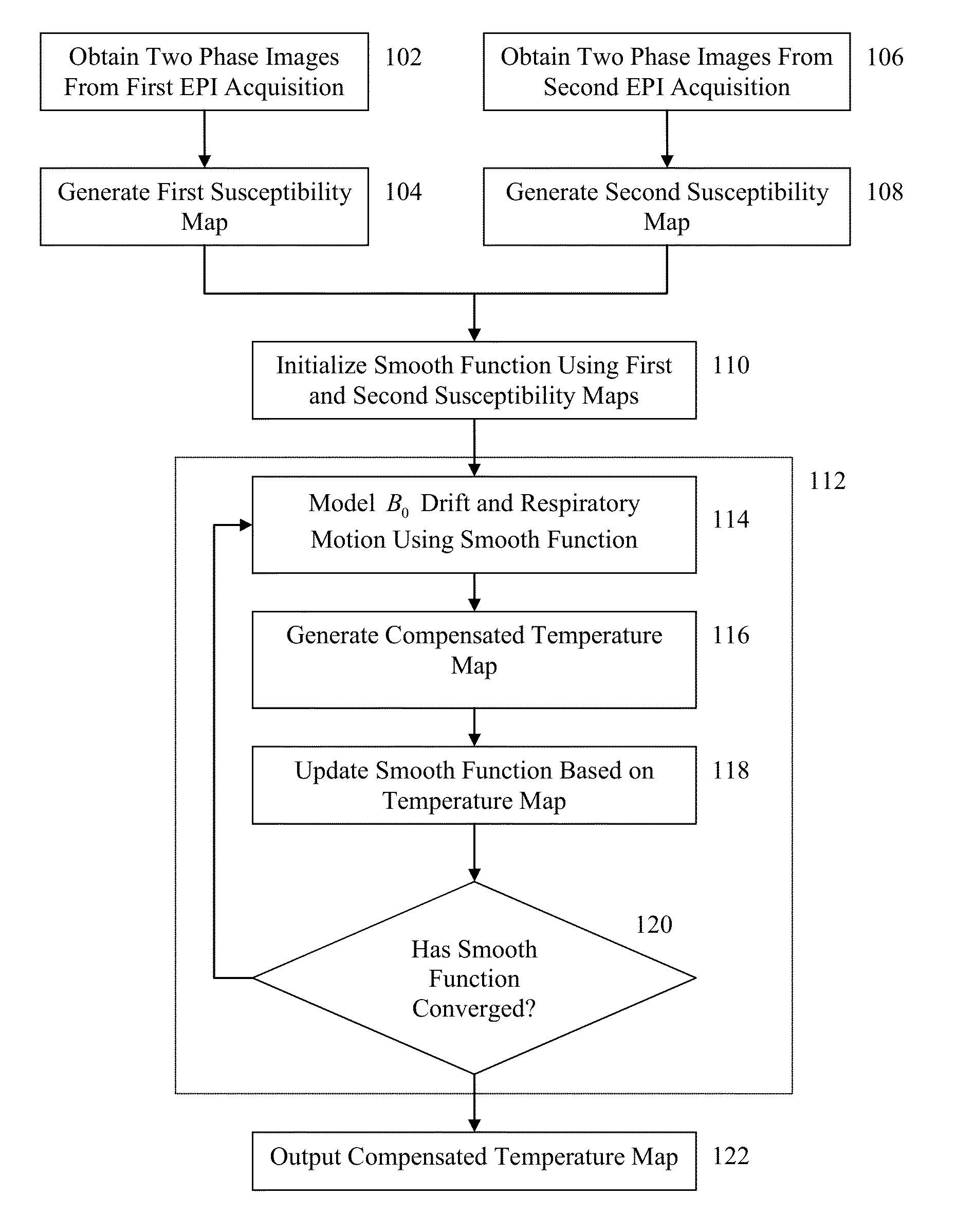
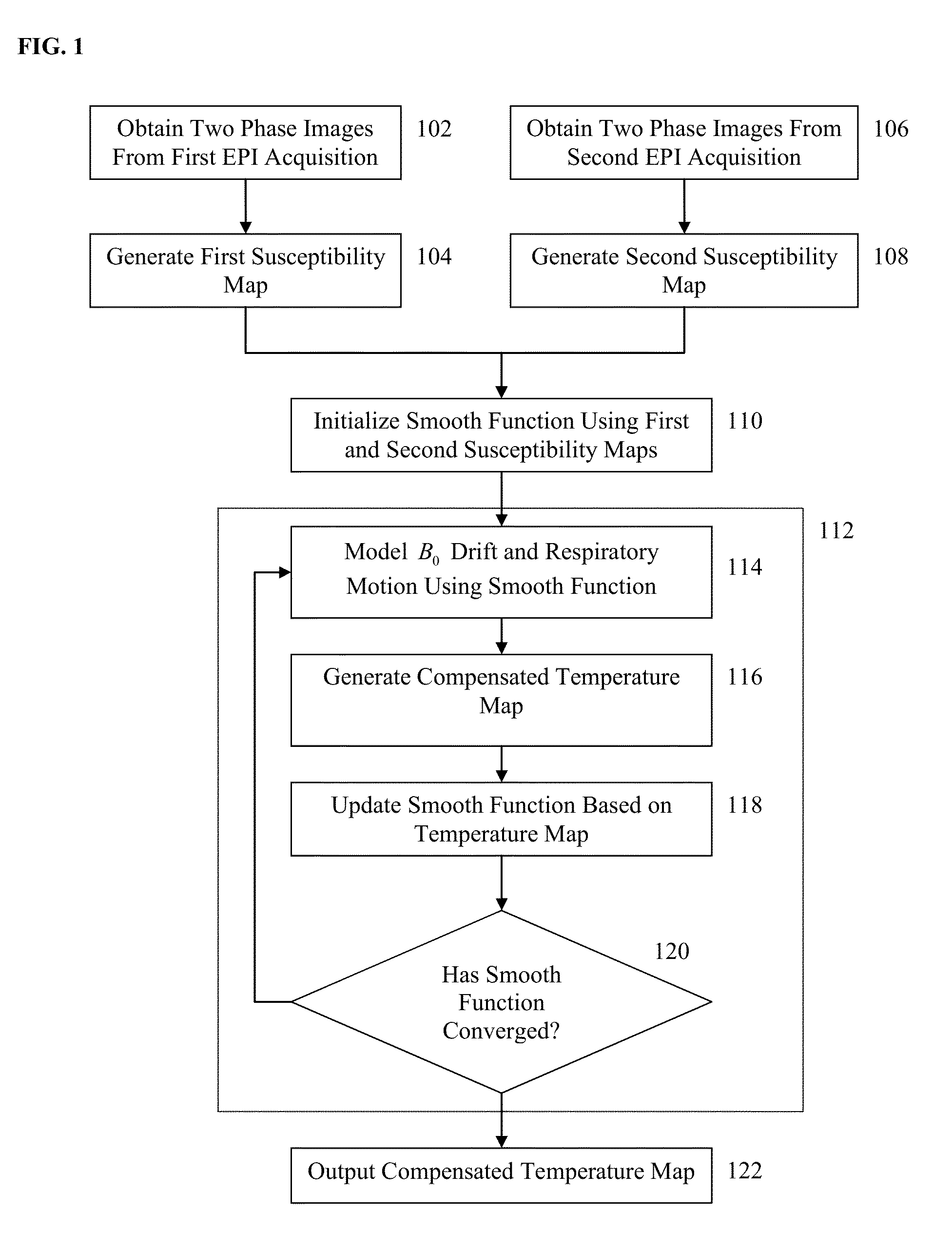
Method and System for B0 Drift and Respiratory Motion Compensation in Echo-Planar Based Magnetic Resonance Imaging
InactiveUS20150160321A1Minimize respiratory motion artifactHigh-temperature-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisResonanceMri image
A method and apparatus for B0 correction in echo-planar (EP) based magnetic resonance image (MRI) is disclosed. Two phase images are obtained from each of a first echo-planar imaging (EPI) acquisition and a second EPI acquisition. A first susceptibility map is generated based on the two phase images obtained from the first EPI acquisition and a second susceptibility map is generated based on the two phase images obtained from the second EPI acquisition. A smooth polynomial function for modeling the B0 drift and respiratory motion between the first EPI acquisition and the second EPI acquisition is initialized based on the first and second susceptibility maps. A compensated temperature map is then iteratively reconstructed based on the smooth polynomial function.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
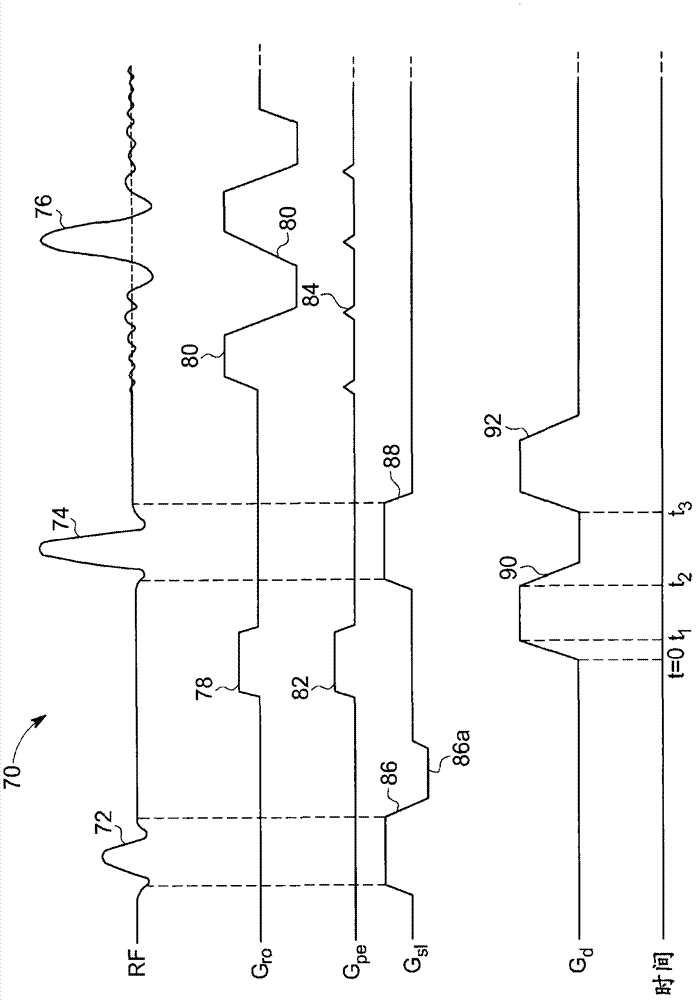
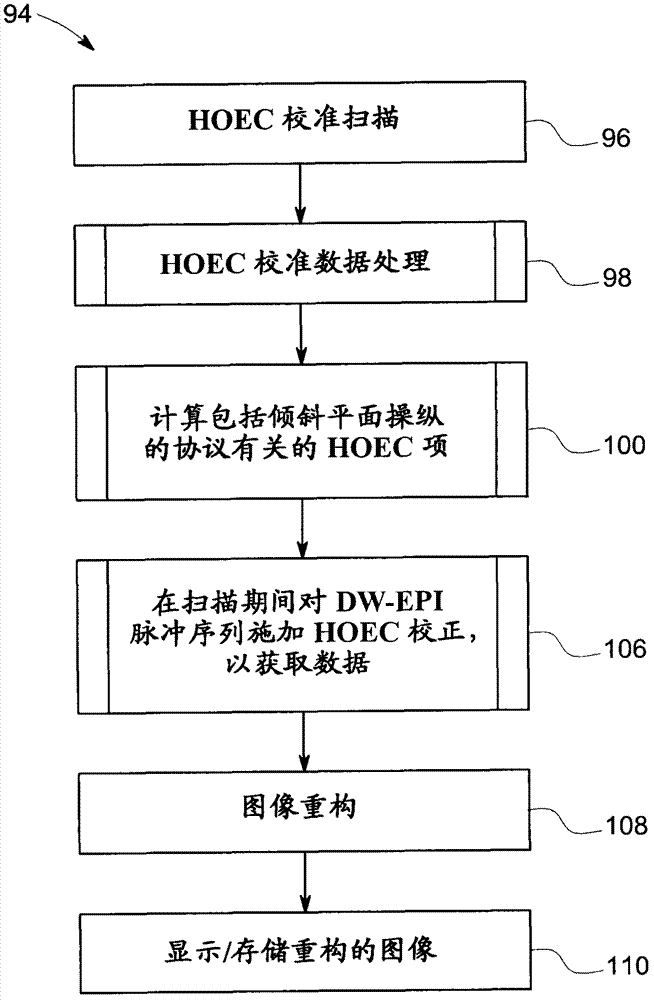
System and method for prospective correction of high order eddy-current-induced distortion in diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging
A computer is programmed to acquire calibration data from a calibration scan, the calibration data configured to characterize high order eddy current (HOEC) generated magnetic field error of an imaging system. The computer is also programmed to process the calibration data to generate a plurality of basis coefficients and a plurality of time constants and to calculate a plurality of basis correction coefficients based on the plurality of basis coefficients, the plurality of time constants, and gradient waveforms in a given pulse sequence. The computer is further programmed to execute a diffusion-weighted imaging scan that comprises application of a DW-EPI pulse sequence to acquire MR data from an imaging subject and reconstruction of an image based on the acquired MR data. The computer is also programmed to apply HOEC-generated magnetic field error correction during application of the DW-EPI pulse sequence configured to reduce HOEC-induced distortion in the reconstructed image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
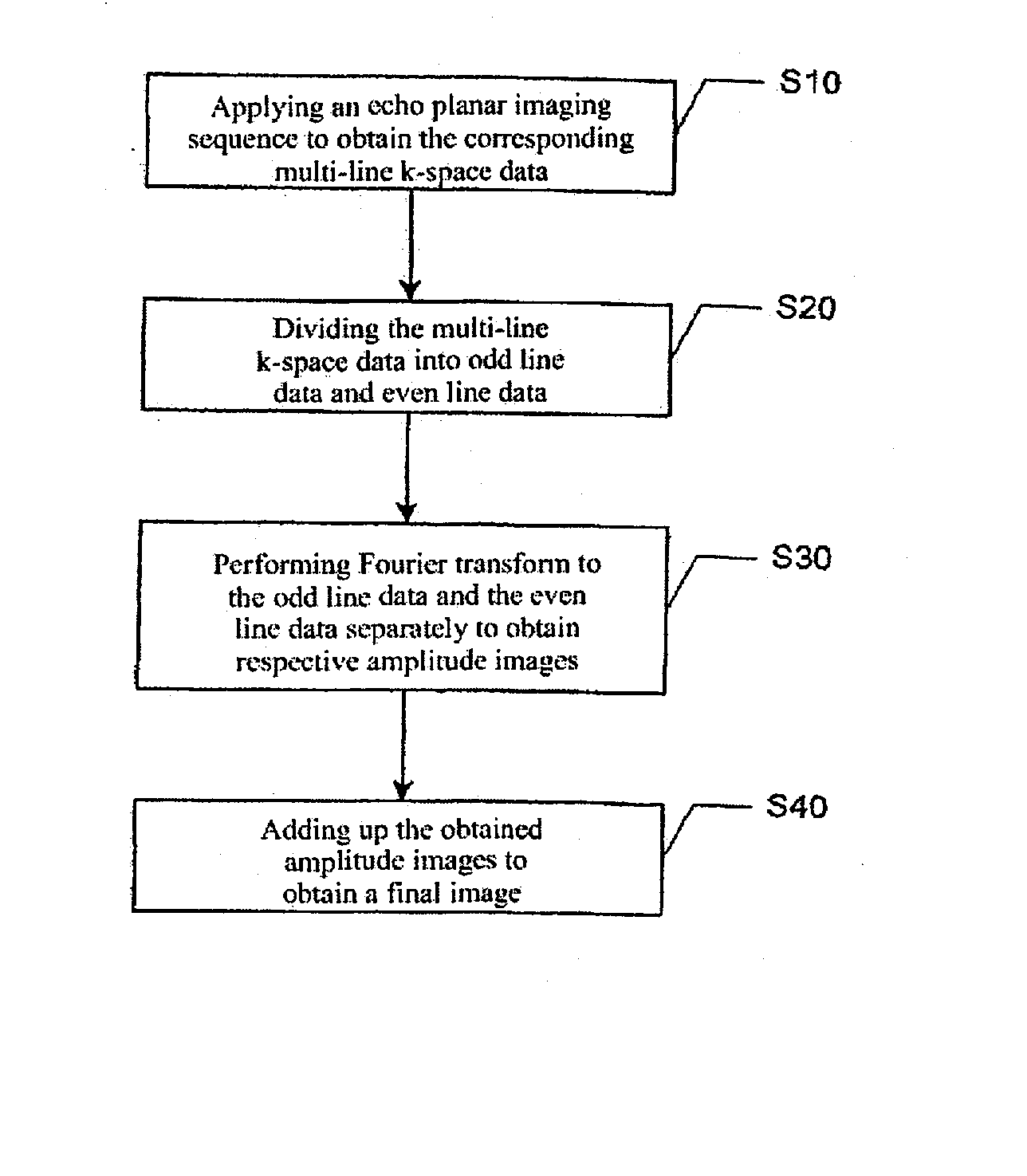
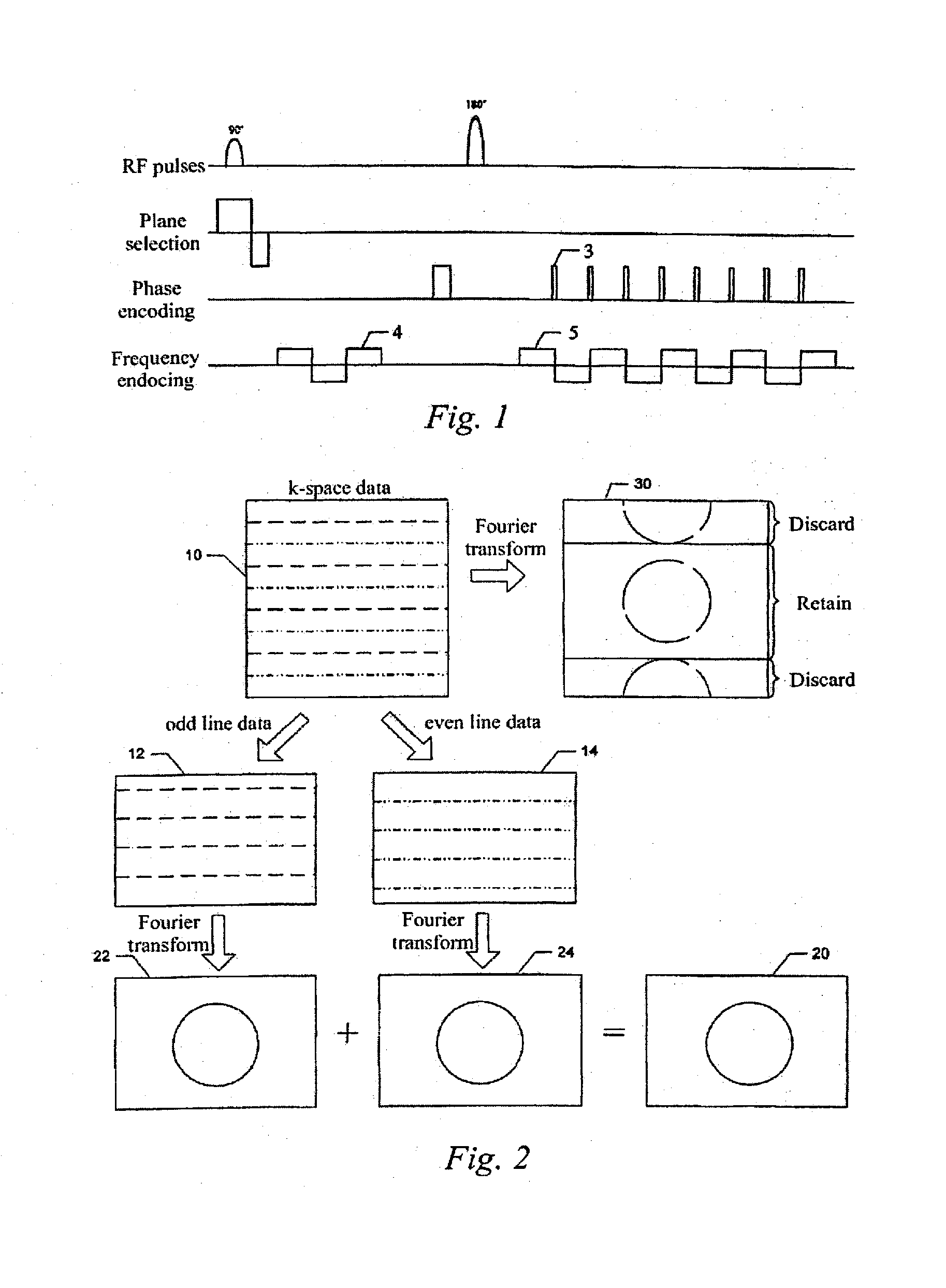
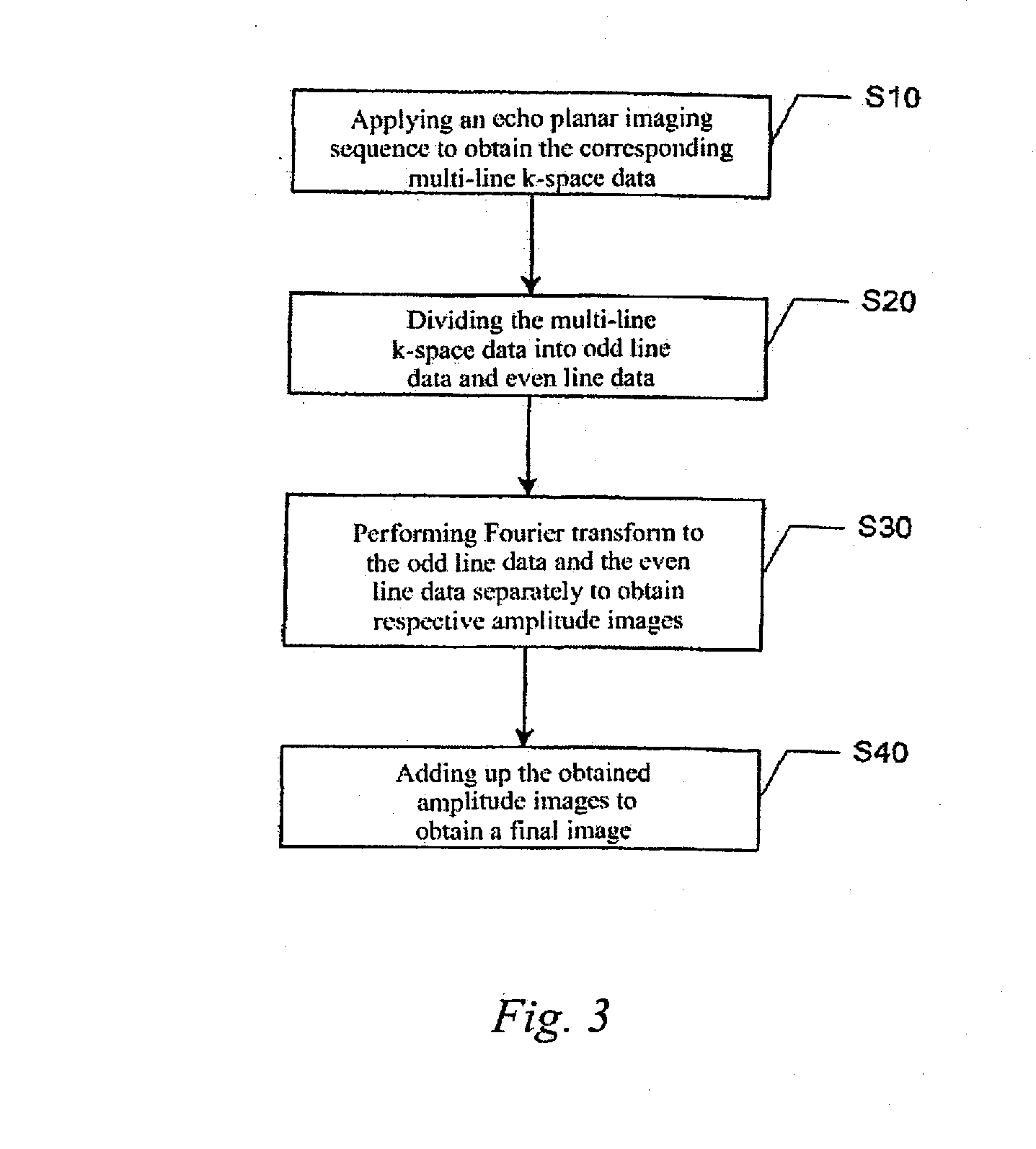
Method for reconstructing image from echo planar imaging sequence
InactiveUS20080089570A1Eliminate artifactsAvoid problemsMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage signalImaging Signal
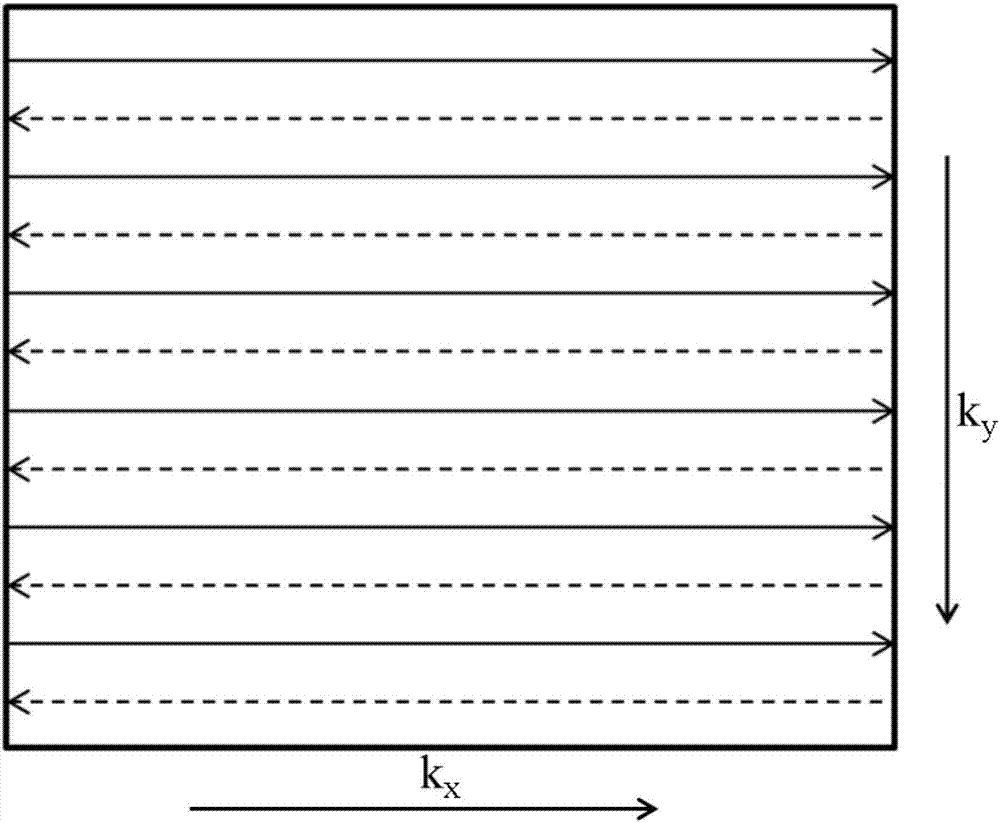
In a method for reconstructing an image from an echo planar imaging sequence, the echo planar imaging sequence is used to obtain multi-line k-space data from a subject and the multi-line k-space data are divided into odd line data and even line data. Fourier transform is performed on the odd line data and on the even line data separately to obtain corresponding amplitude images. The amplitude images obtained is this manner are added to produce the final image. The method effectively eliminates N / 2 artifacts by over-sampling in the phase direction. By image reconstruction being carried out separately on the odd line data and even line data of k-space data and then integrating the images, the method effectively avoids the problem of the image signal loss caused by the mutual cancellation of the odd line data and even line data.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
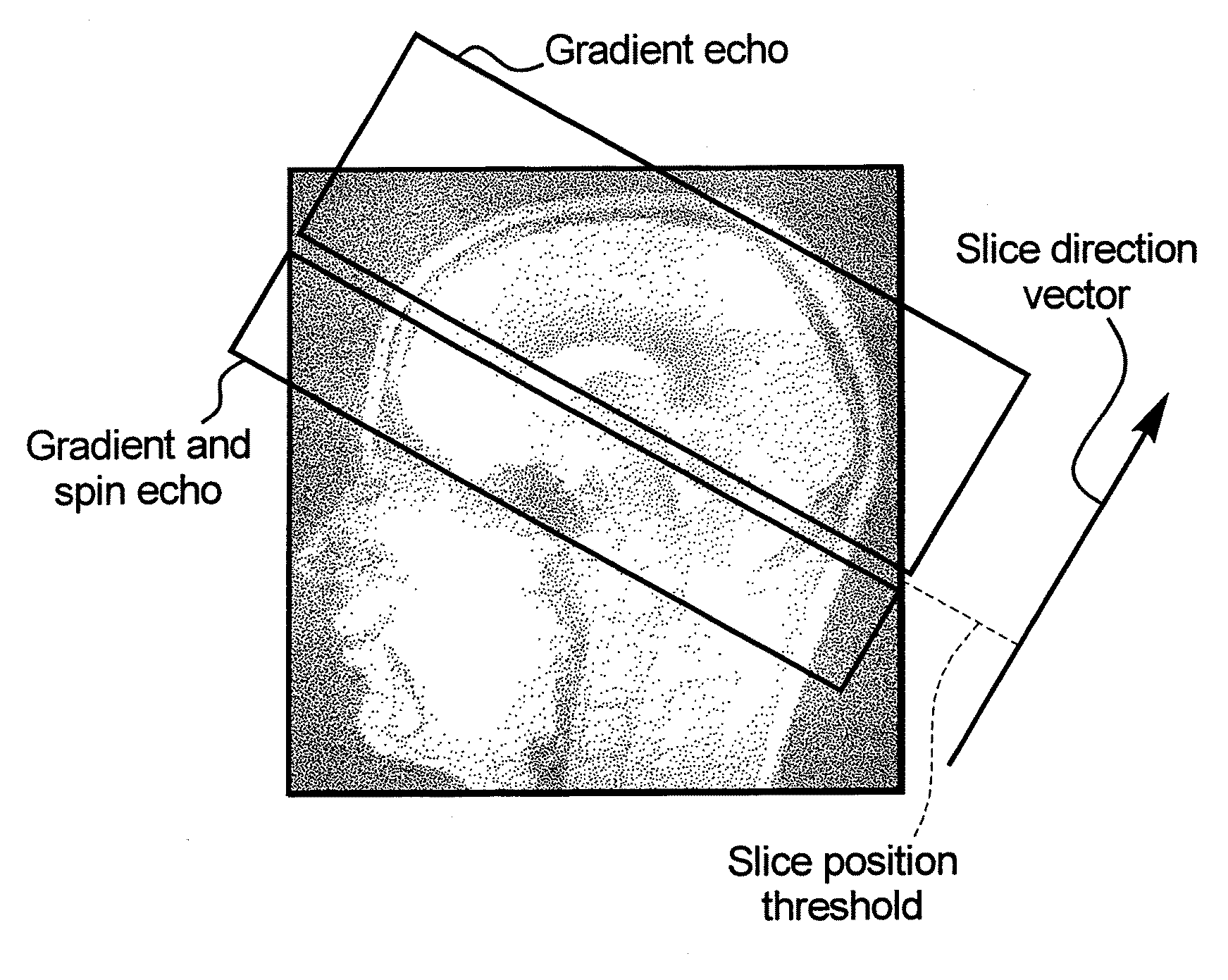
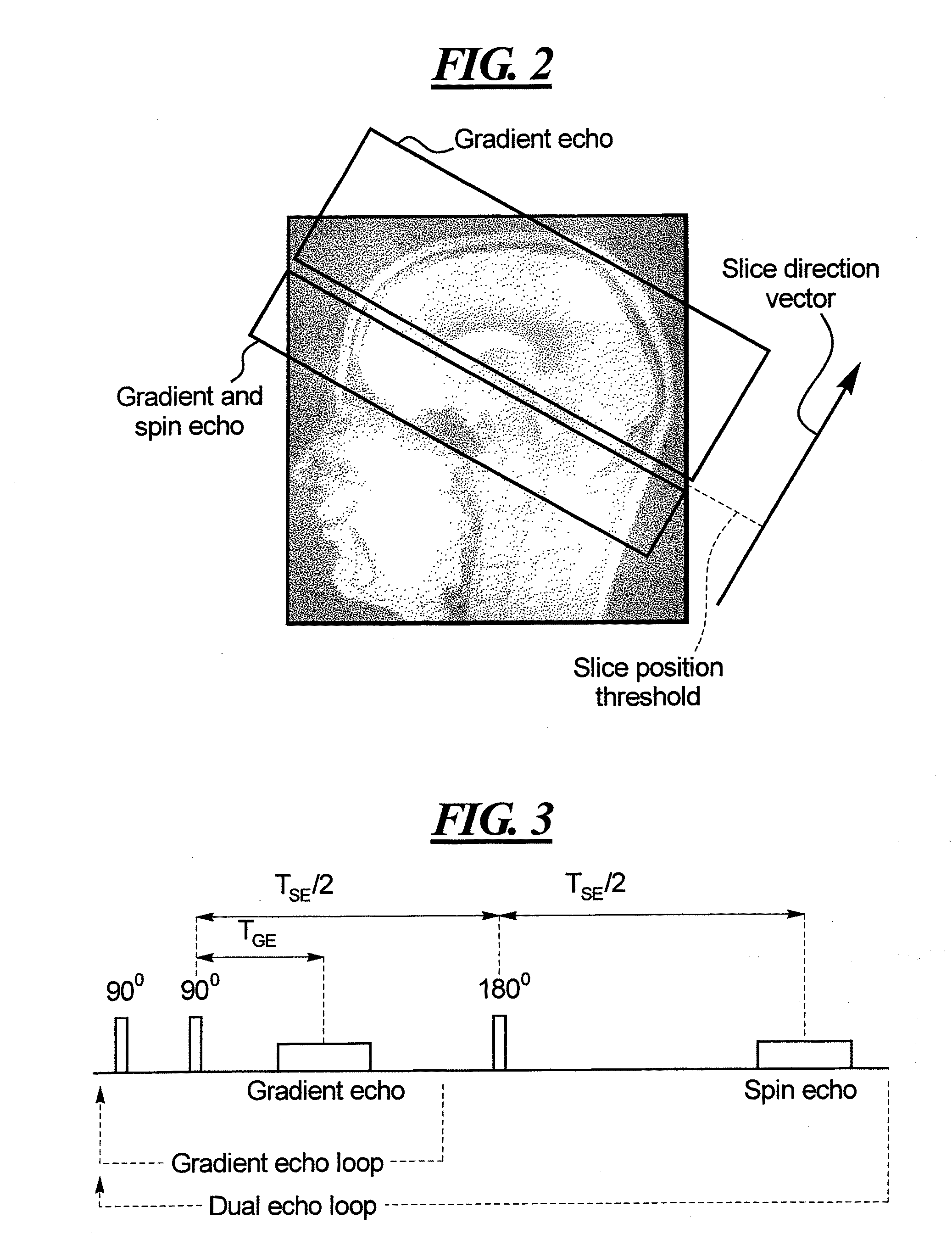
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus using dual echoes for data acquisition
ActiveUS20100268061A1Improve image qualityImproved brain imageMagnetic measurementsSurgical instrument detailsResonanceData acquisition
In a method and system for acquiring magnetic resonance image data from a subject, using a data acquisition unit in which a basic magnetic field is generated, a division is designated in a planar section through the subject that divides the planar section into a first section and a second section, with the homogeneity of the basic magnetic field being better in said first section than in said second section. An echo planar imaging sequence is implemented to acquire the magnetic resonance imaging data, with magnetic resonance data being acquired from the first section only from gradient echo signals in the echo planar imaging sequence, and magnetic resonance data from said the second section being acquired from both gradient echo signals and spin echo signals in the echo planar imaging sequence. The method and apparatus are particularly suited for acquiring functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data from the brain of a subject, in which the first section is an upper portion of the brain and the second section is a lower portion of the brain.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD +1
Echo planar imaging sequence image reconstruction method
ActiveCN104035059AEfficient removalOne-dimensional phase correction method is fast and simpleMagnetic measurementsRapid imagingReconstruction method
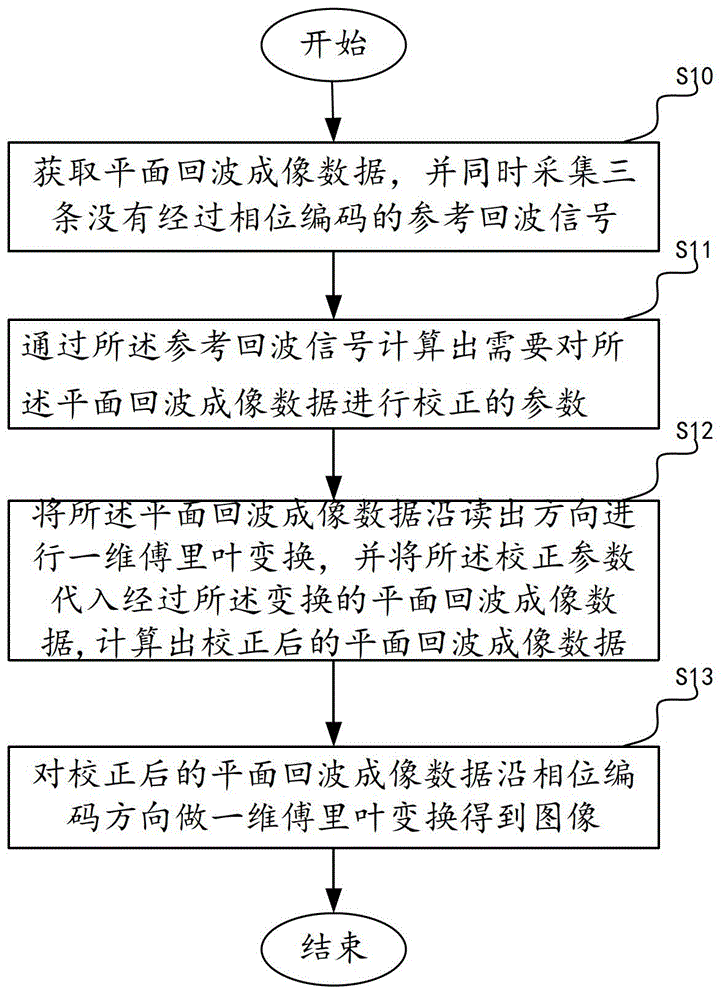
The invention provides an echo planar imaging sequence image reconstruction method comprising the following steps: acquiring echo planar imaging data Si and simultaneously acquiring three non-phase-encoded reference echo signals R1, R2 and R3; working out a parameter required for correcting the echo planar imaging data according to the reference echo signals; performing one-dimensional Fourier transform on the echo planar imaging data along a readout direction to obtain a transform result FSi, correcting FSi with the use of the correction parameter, and working out corrected echo planar imaging data; and performing one-dimensional Fourier transform on the corrected echo planar imaging data along a phase encoding direction to obtain an image. According to the echo planar imaging sequence image reconstruction method provided by the invention, in the presence of a stray field, the quick imaging advantage of echo planar sequence imaging can be kept, N / 2 artifacts can be effectively removed, and image deformation due to the existence of the stray field can be corrected.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
System and method for prospective correction of high order eddy-current-induced distortion in diffusion-weighted echo planar imaging
A computer is programmed to acquire calibration data from a calibration scan, the calibration data configured to characterize high order eddy current (HOEC) generated magnetic field error of an imaging system. The computer is also programmed to process the calibration data to generate a plurality of basis coefficients and a plurality of time constants and to calculate a plurality of basis correction coefficients based on the plurality of basis coefficients, the plurality of time constants, and gradient waveforms in a given pulse sequence. The computer is further programmed to execute a diffusion-weighted imaging scan that comprises application of a DW-EPI pulse sequence to acquire MR data from an imaging subject and reconstruction of an image based on the acquired MR data. The computer is also programmed to apply HOEC-generated magnetic field error correction during image reconstruction configured to reduce HOEC-induced distortion in the reconstructed image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for recording calibration data for a grappa magnetic resonance imaging algorithm
ActiveUS20180017655A1Reduce recording timeShorten the timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceComputer science
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) apparatus for recording calibration data for establishing convolution kernels for GRAPPA algorithms for reconstruction of image data from measurement data recorded using echo planar imaging with simultaneous recording of a number of slices of a slice stack. A slice GRAPPA algorithm is used to reconstruct the image data of the individual slices and an inplane GRAPPA algorithm is used to reconstruct undersampled magnetic resonance data within the slices. In order to record the calibration data to be used for establishing the convolution kernels of the two GRAPPA algorithms, in a predetermined slice order for the slices of the slice stack, for one slice in each case, at least one segment of k-space to be sampled is read out in the readout direction for a completely sampled readout in the phase encoding direction, and at least one such segment extends around the center of k-space in the readout direction, and the segment width is selected so that the phase encoding bandwidth matches that of the recording of the measurement data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com