Arterial spin-labeled (ASL) multiplexed echo planar imaging (m-epi)
a multiplexed echo and planar imaging technology, applied in the field of magnetic resonance imaging, can solve the problems of limited slice size, epi has not been able to satisfactorily image perfusion in the entire brain, and asl perfusion, so as to reduce the time to scan the brain, reduce the time to sequential echo trains, and improve the interdependence of slice saturation effects on arterial input functions and recorded mr signals.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
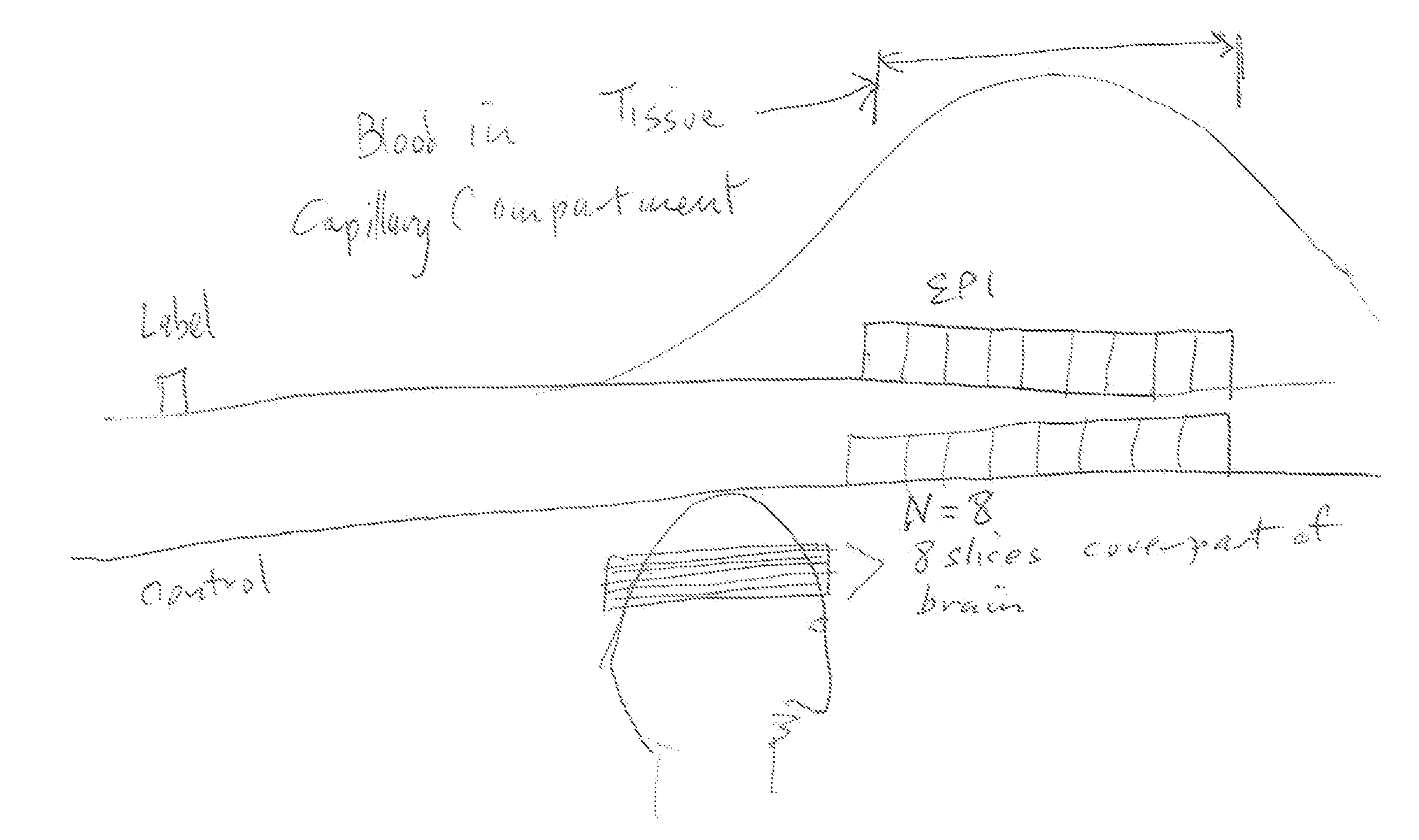
[0014]FIG. 1 illustrates conventional multi-slice 2D EPI in which several slice images are acquired one after the other in time. The different blood inflow times in consecutively acquired slice images limit the accuracy of blood flow quantization. Different vascular compartments are filled at different times, resulting in undesirable coupling to spatial slice position.
[0015]FIGS. 2a and 2b illustrate important differences between ASL multi-slice EPI imaging and ASL multiplexed EPI imaging. The example of FIG. 2a illustrates that MR signals for multiple 2D slice images are obtained in time sequence over a time span that is much longer than that seen in FIG. 2b, where MR signals for the same number of multiple 2D slice images are obtained using M-EPI essentially simultaneously.
[0016]FIG. 3 illustrates some important consequences of differences between ASL using conventional EPI and the new approach of using ASL with M-EPI. With the old approach, the acquisition time of MR signals for ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com