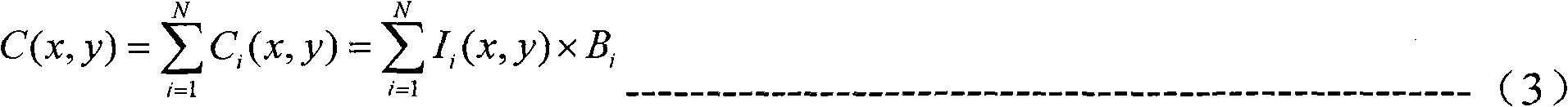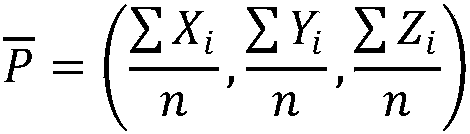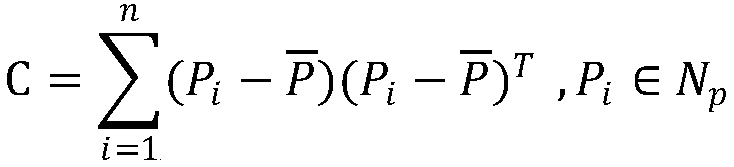Patents
Literature
149 results about "Multiple echo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
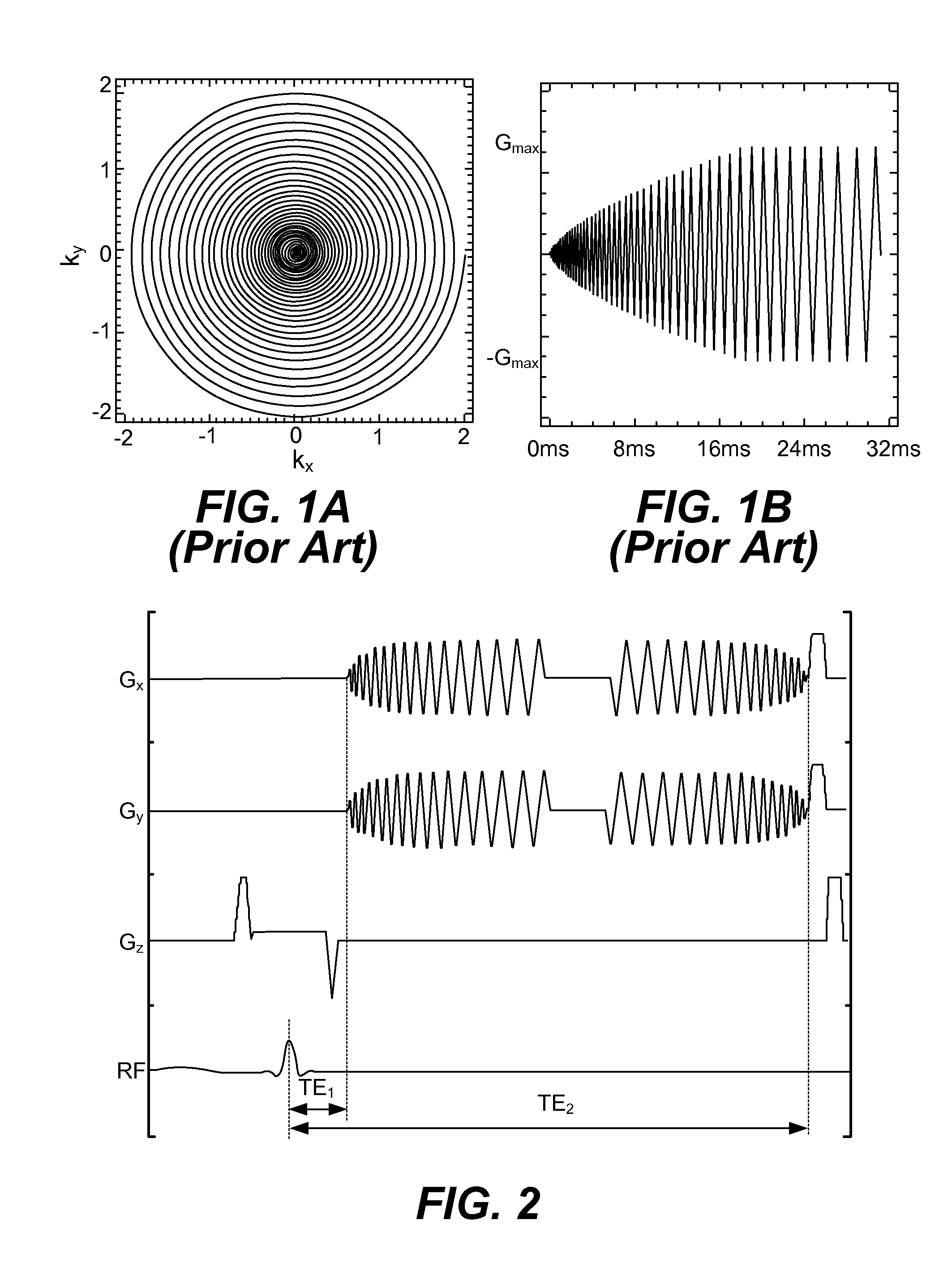
MULTIPLE ECHOES. Radar echoes which may occur when a strong echo is received from another ship at close range. A second or third or more echoes may be observed on the radarscope at double triple, or other multiples of the actual range of the radar target, resulting from the echo’s being reflected by own ship back to the target...
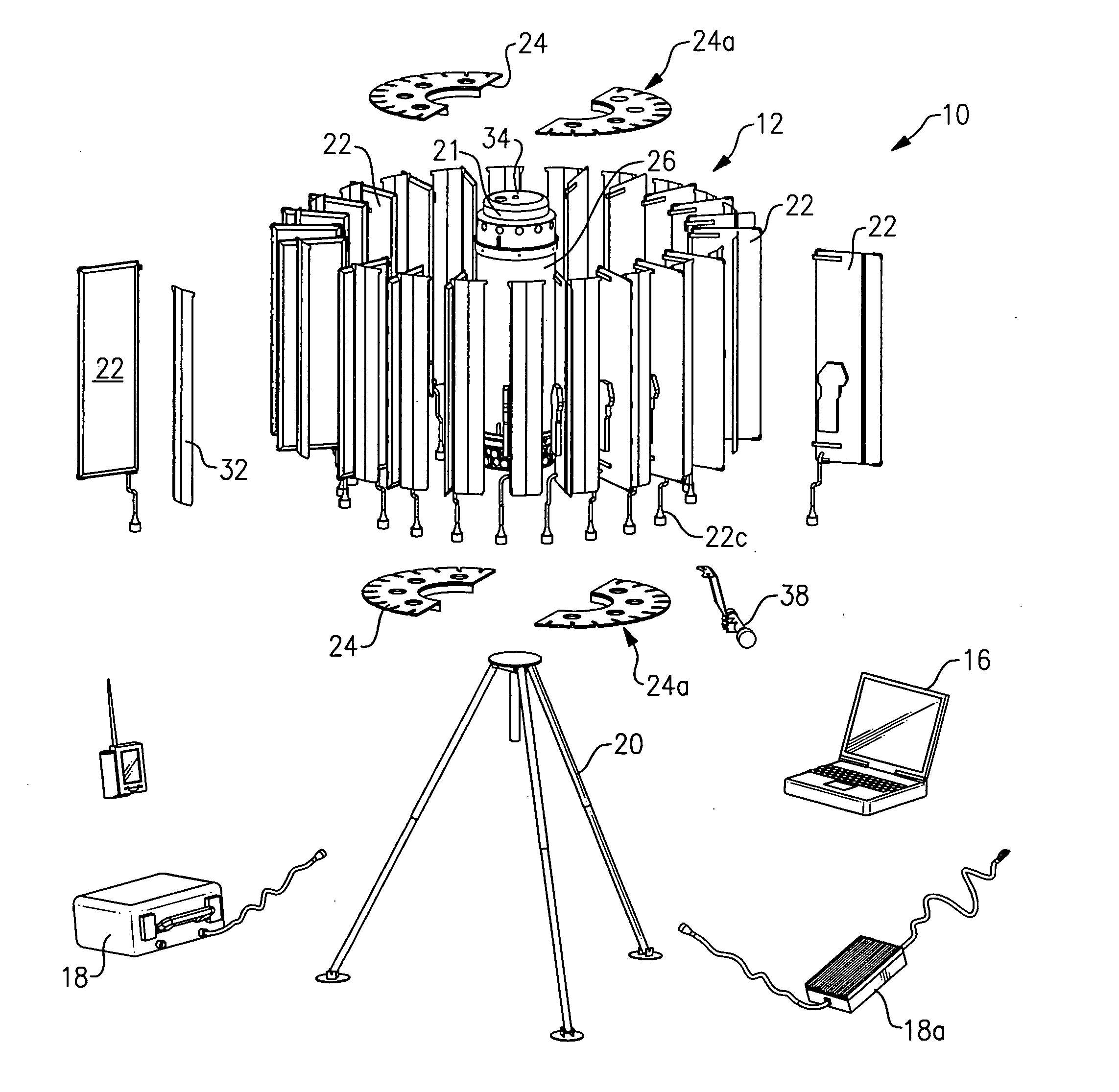
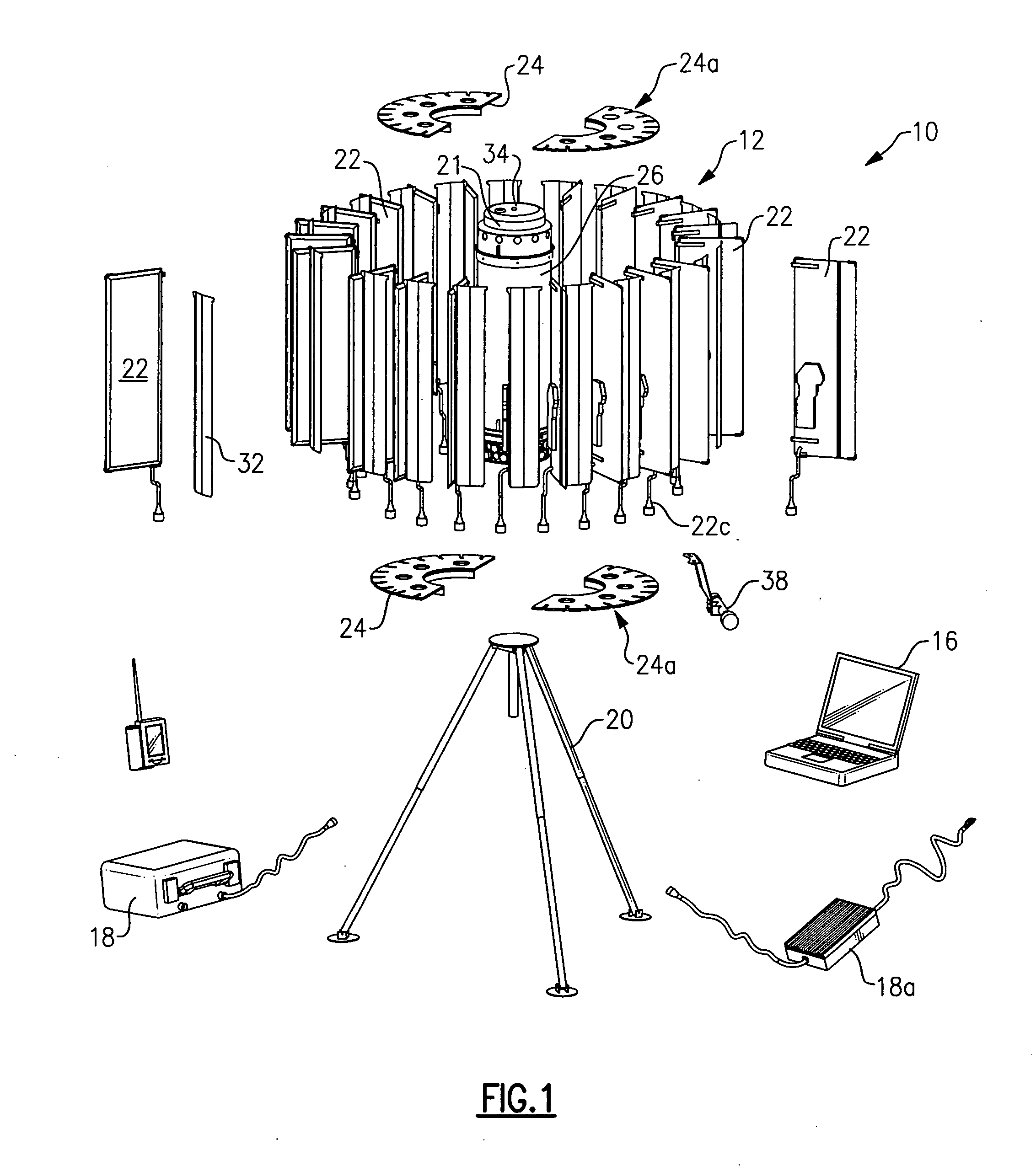
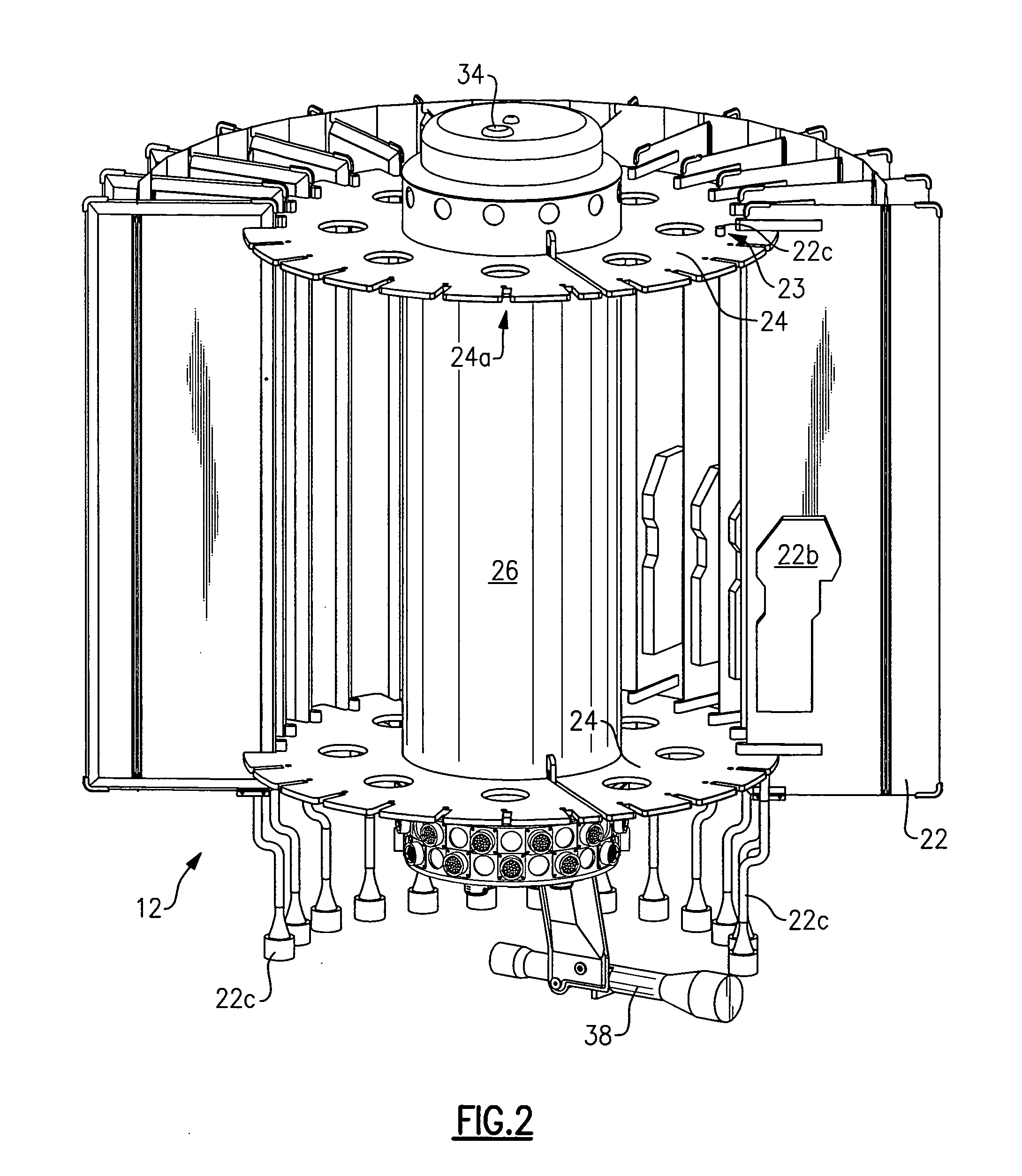
Man-portable counter mortar radar system
ActiveUS20060092075A1Carried and moved with easeCollapsable antennas meansAntenna arraysCountermeasureRadar systems
The present invention is a man-portable counter-mortar radar (MCMR) radar system that detects and tracks enemy mortar projectiles in flight and calculates their point of origin (launch point) to enable and direct countermeasures against the mortar and its personnel. In addition, MCMR may also perform air defense surveillance by detecting and tracking aircraft, helicopters, and ground vehicles. MCMR is a man-portable radar system that can be disassembled for transport, then quickly assembled in the field, and provides 360-degree coverage against an enemy mortar attack. MCMR comprises an antenna for radiating the radar pulses and for receiving the reflected target echoes, a transmitter that produces the radar pulses to be radiated from the antenna, a receiver-processor for performing measurements (range, azimuth and elevation) on the target echoes, associating multiple echoes to create target tracks, classifying the tracks as mortar projectiles, and calculating the probable location of the mortar weapon, and a control and display computer that permits the operation of the radar and the display and interpretation of the processed radar data.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIV RES
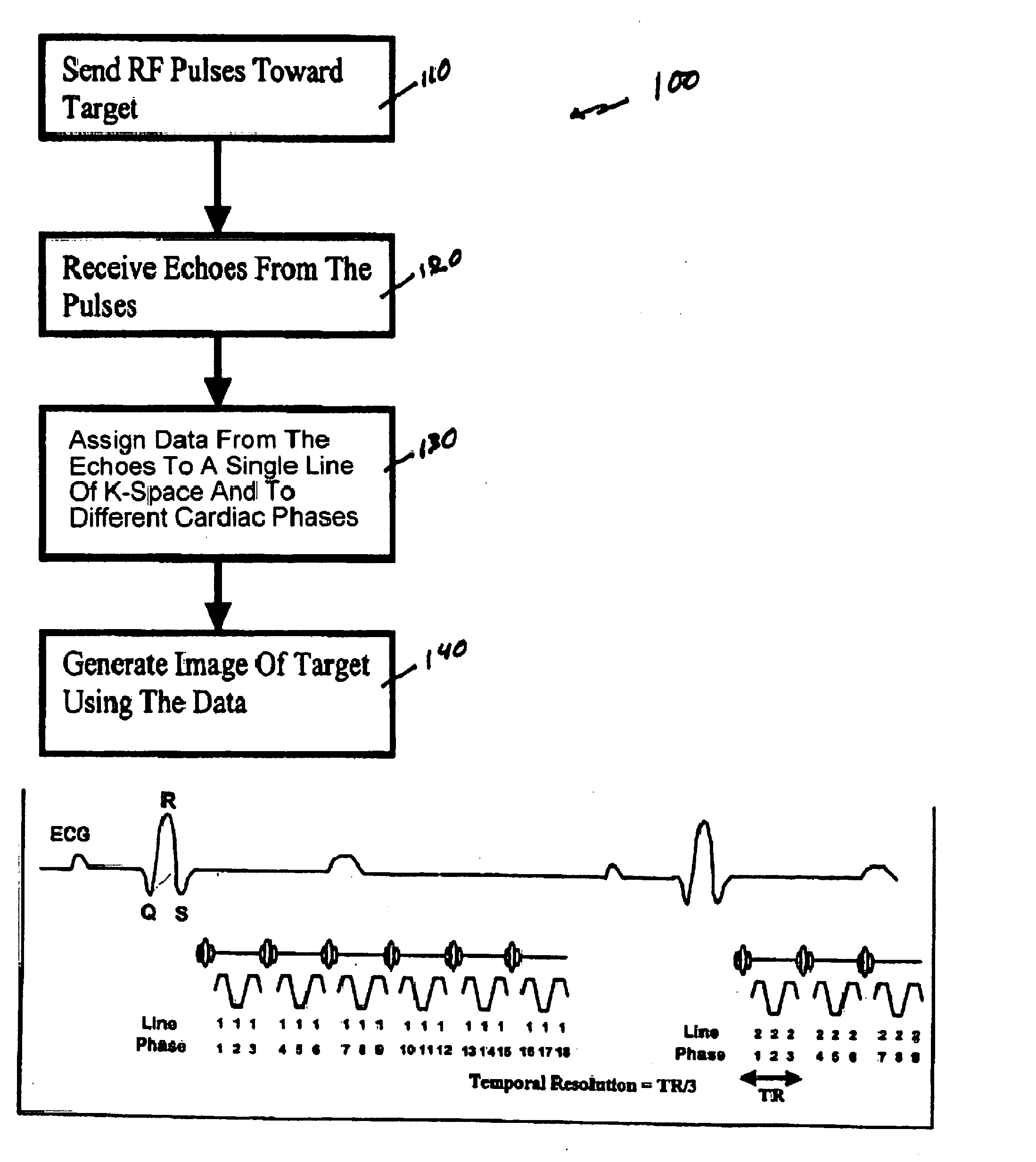
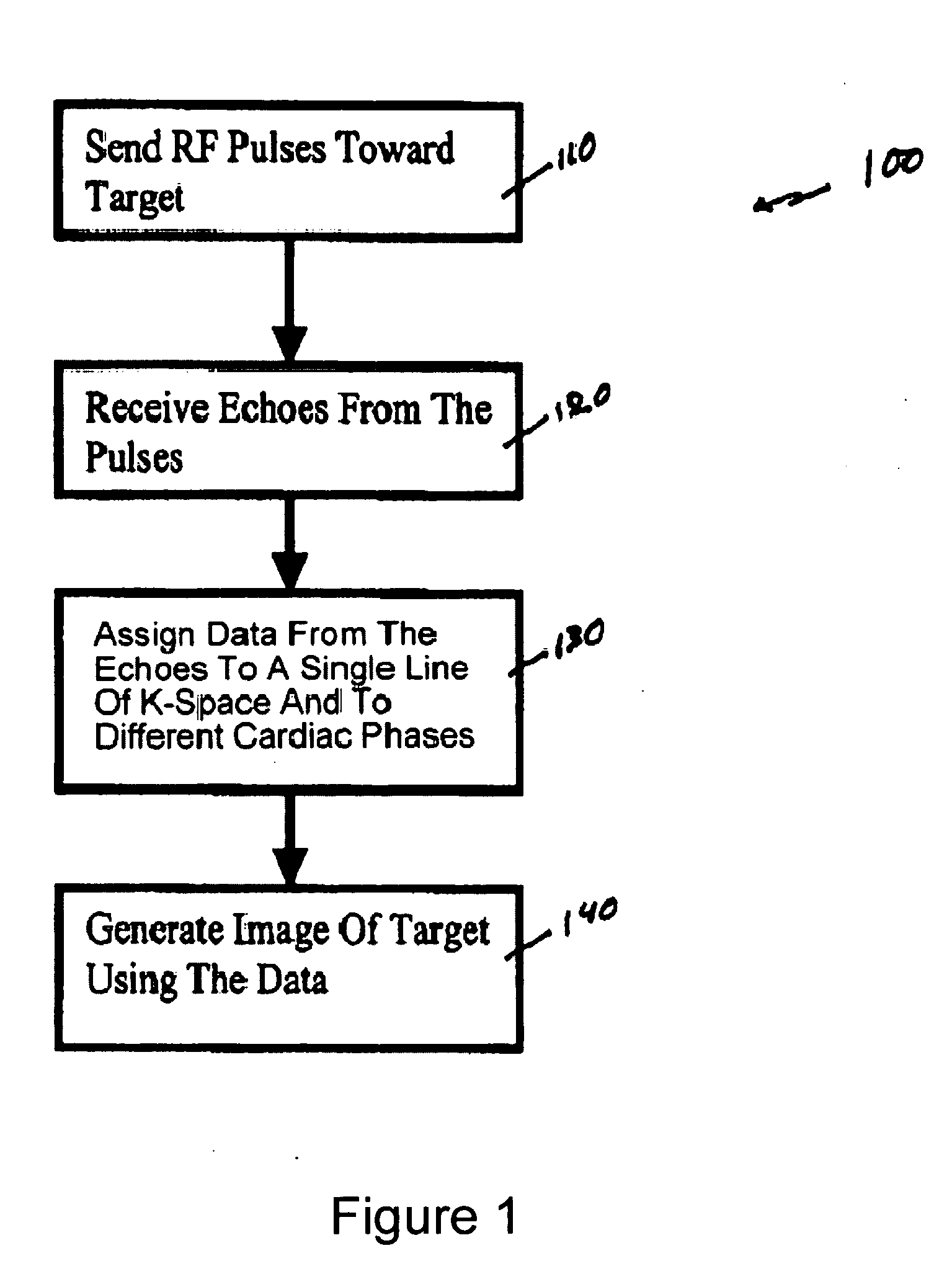
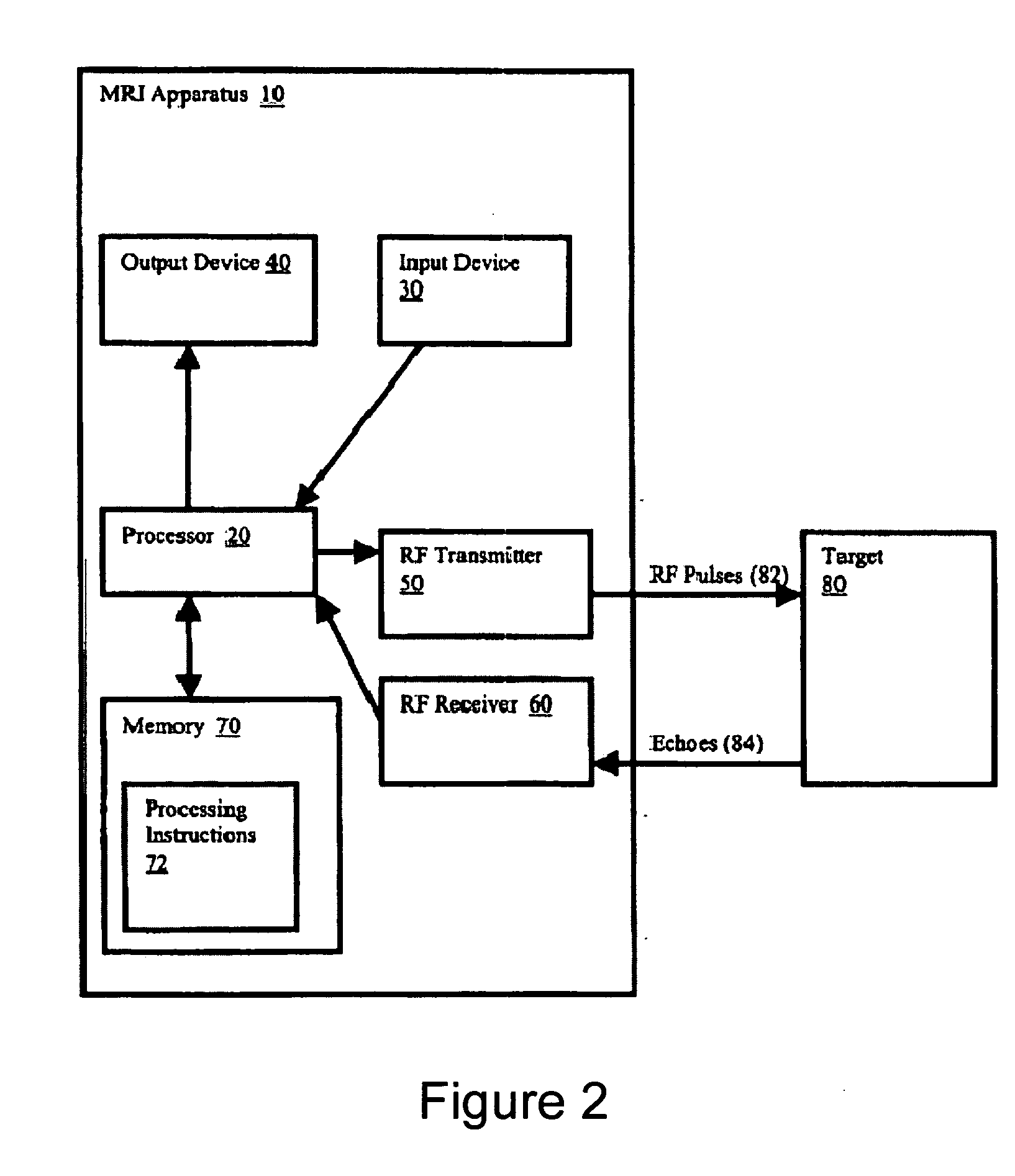
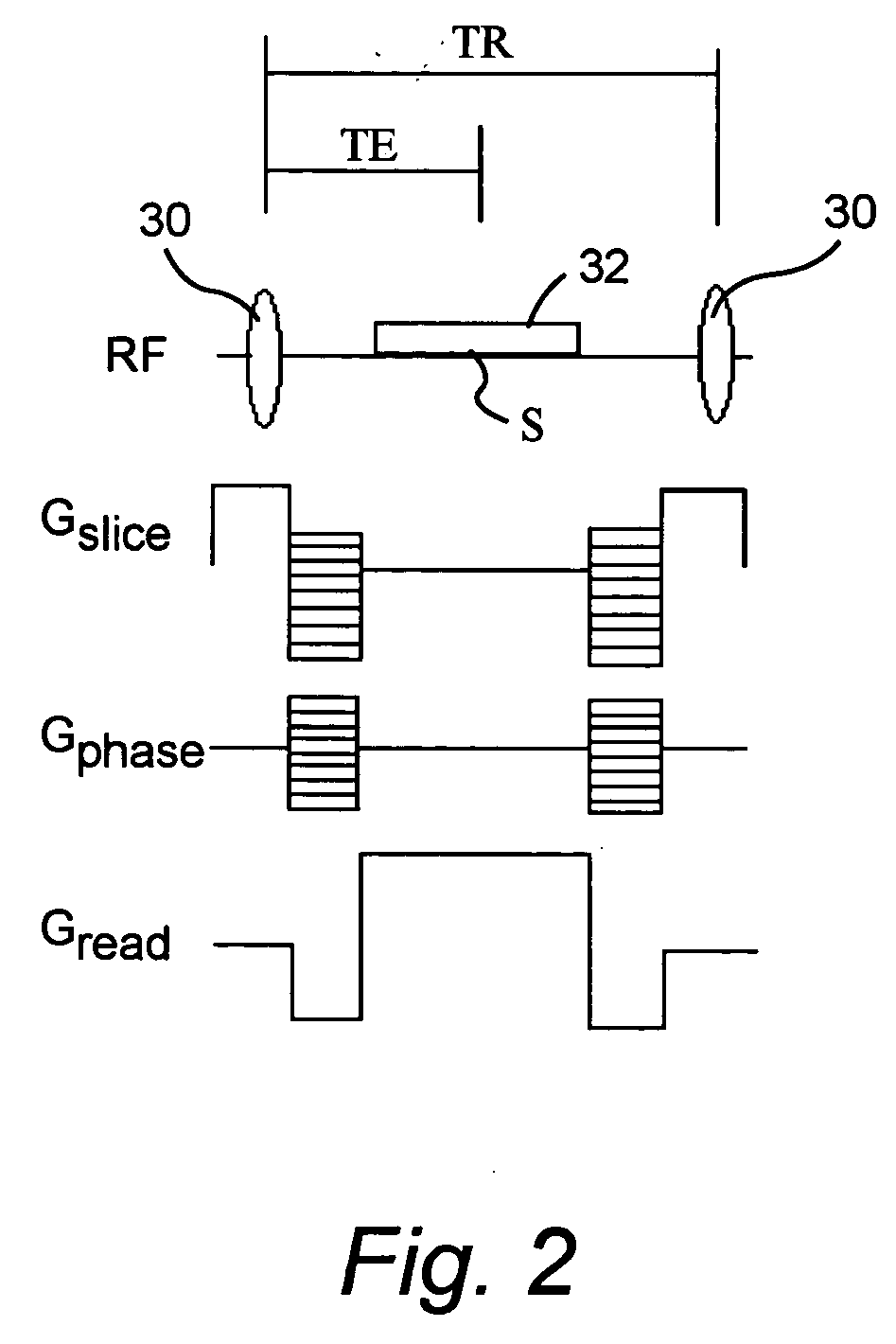
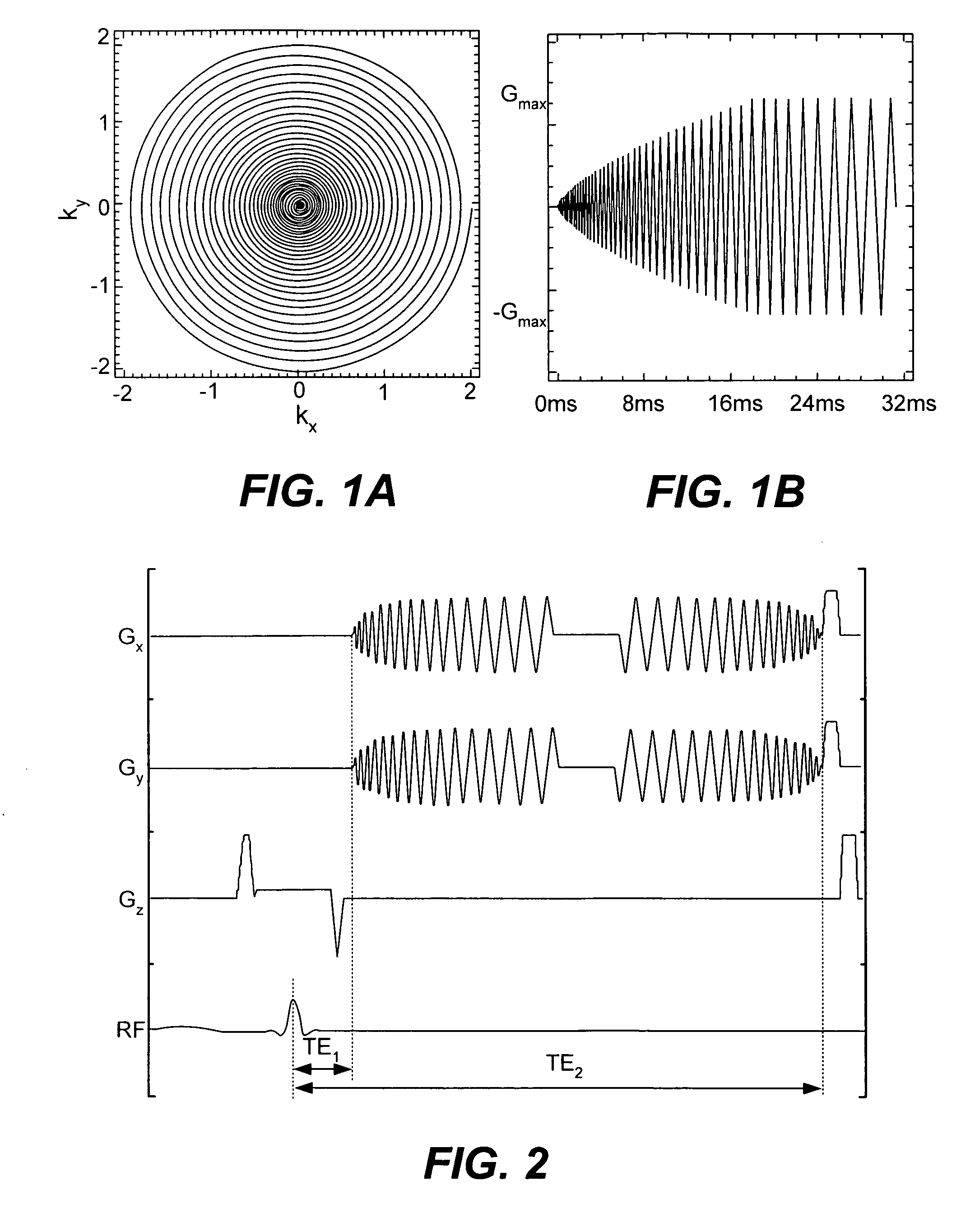
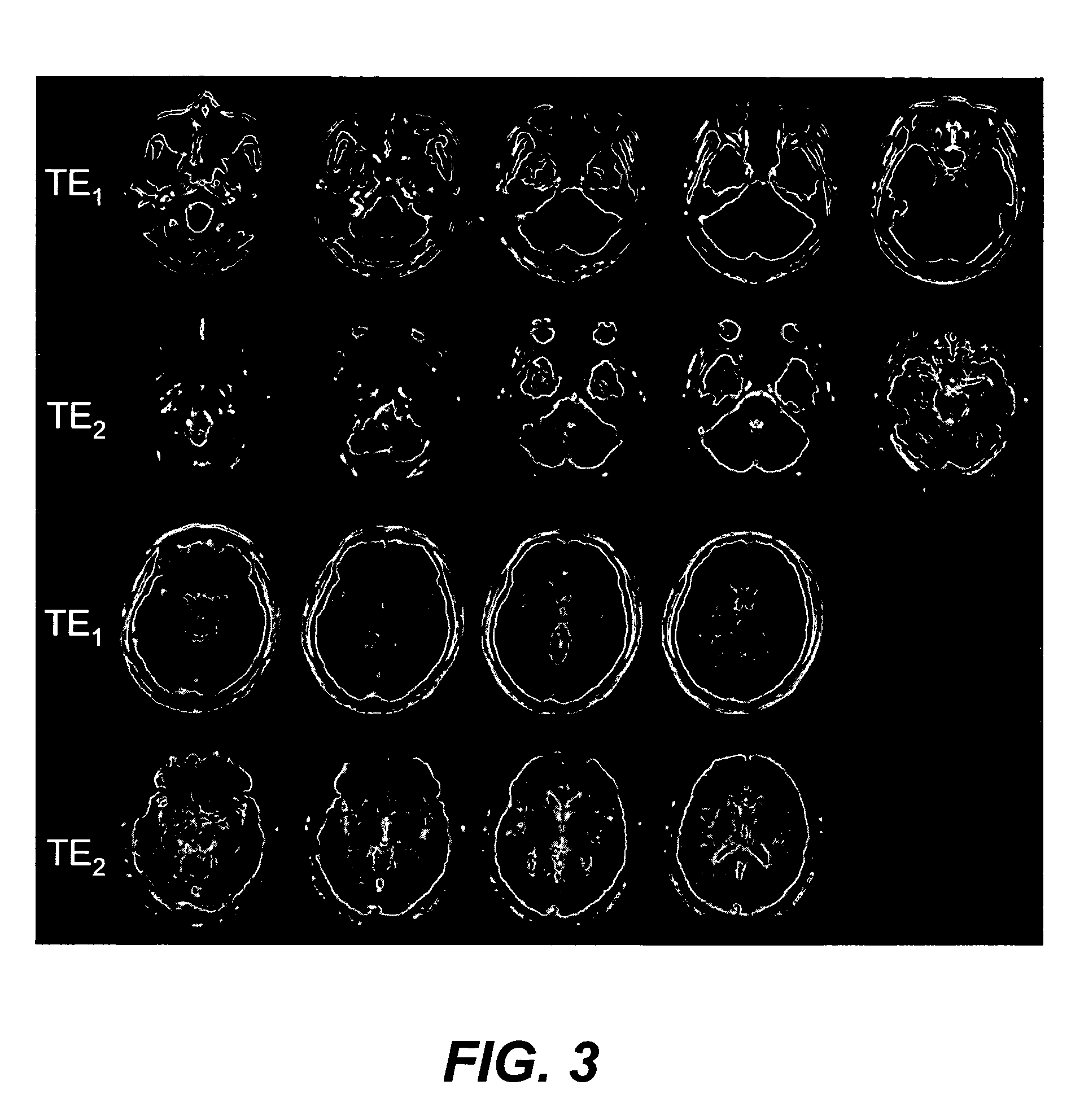
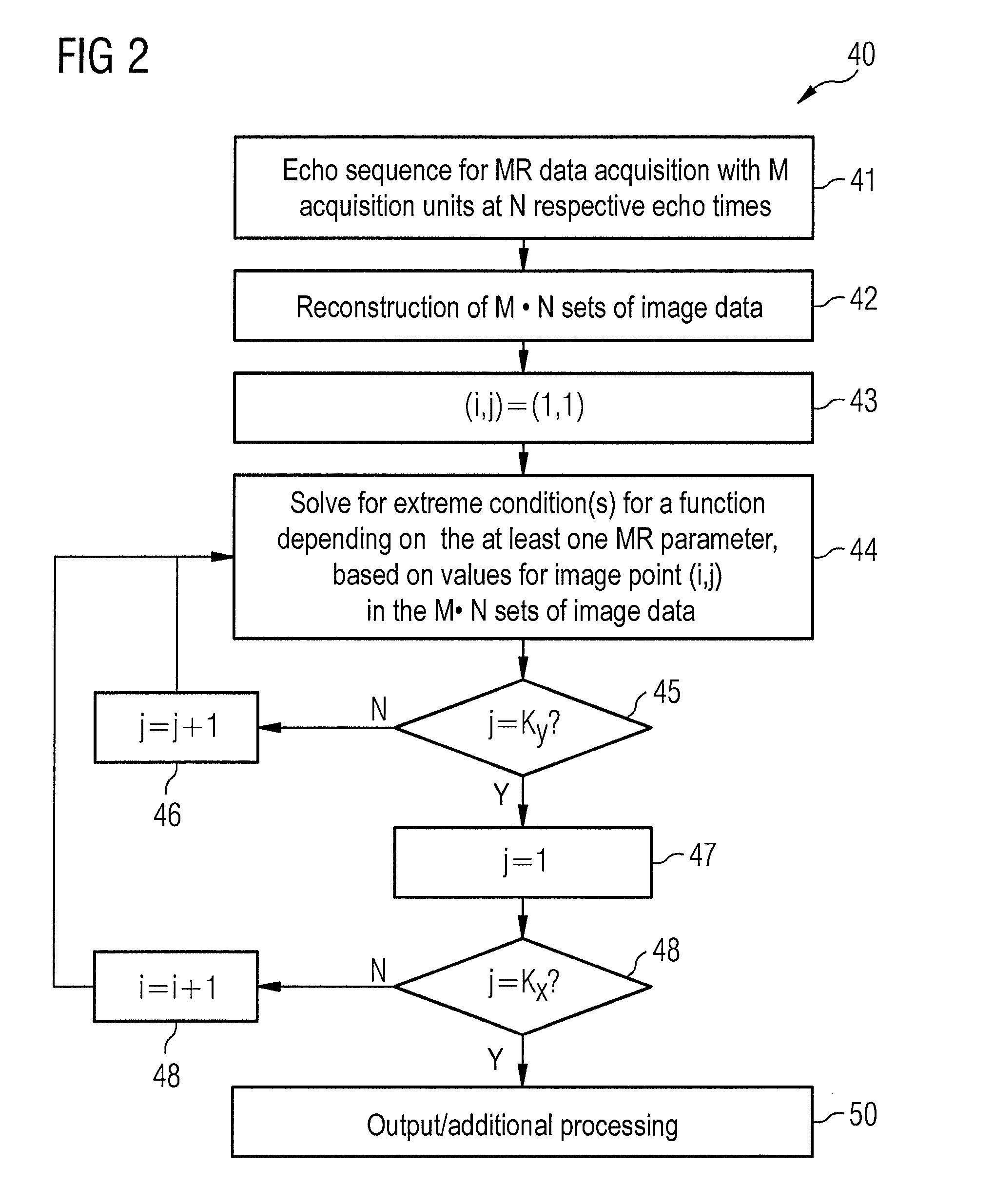
Multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveUS20060161060A1Faster and accurate perfusion mapImprove time resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac phaseRadio frequency
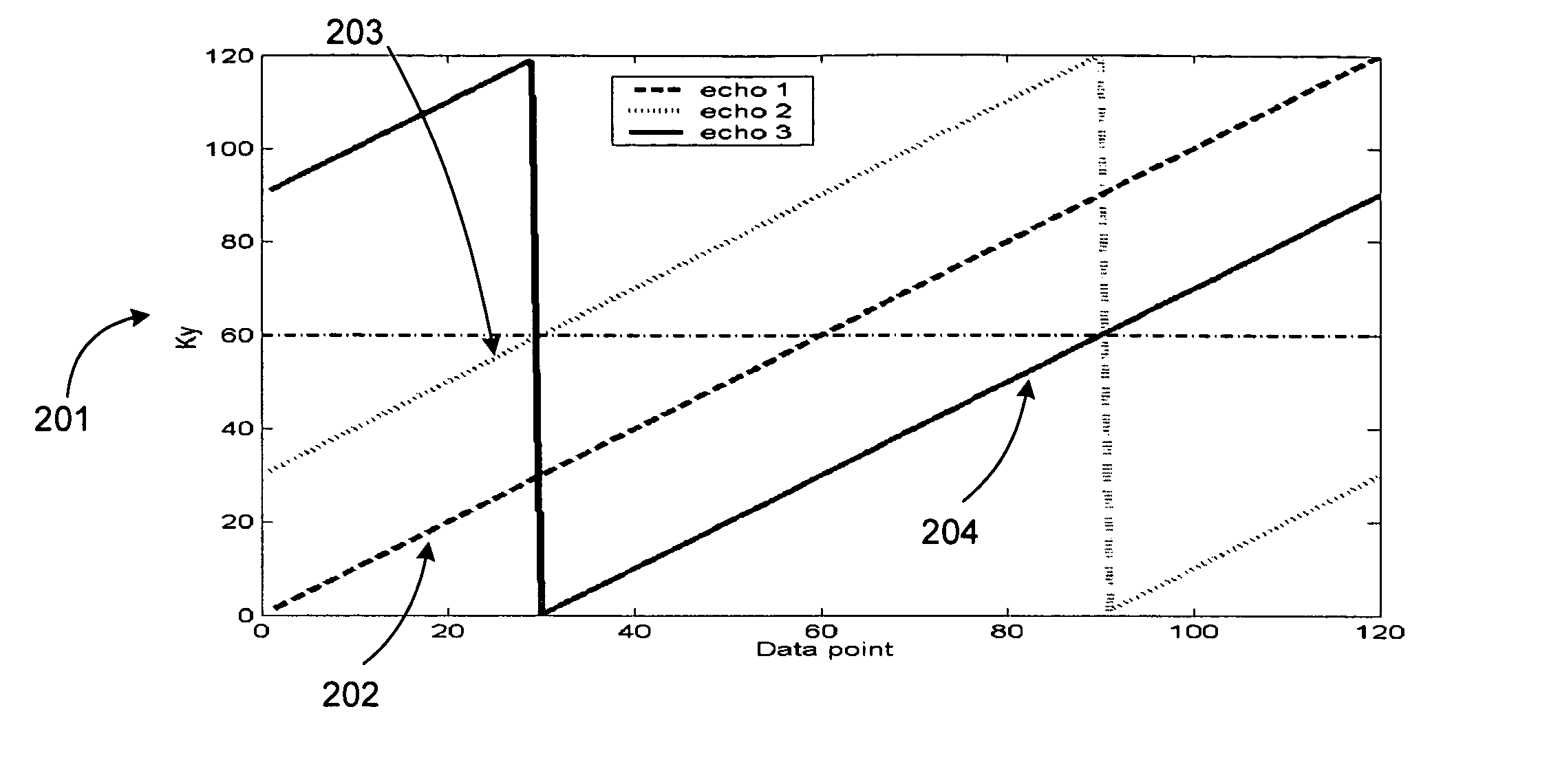
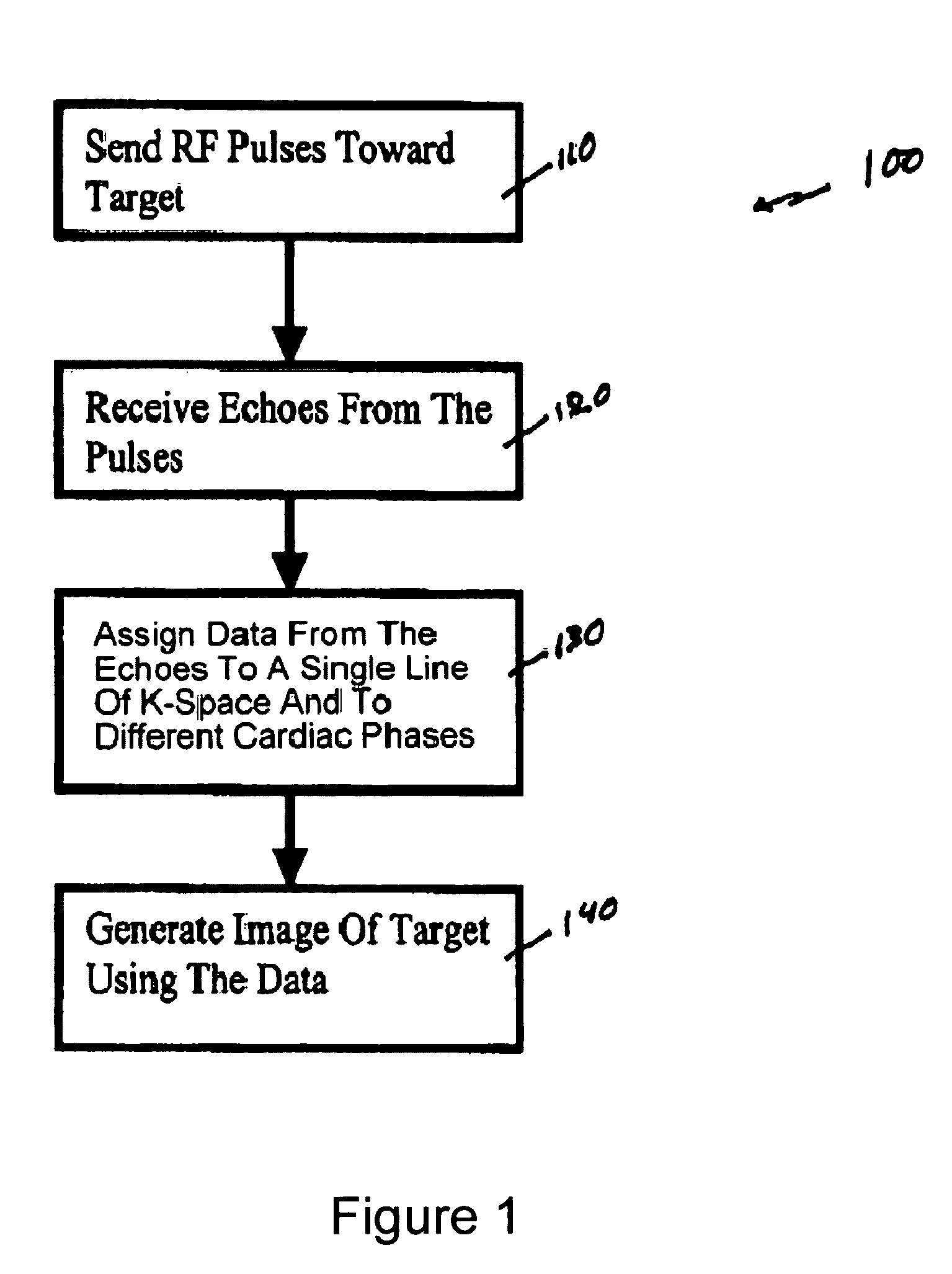
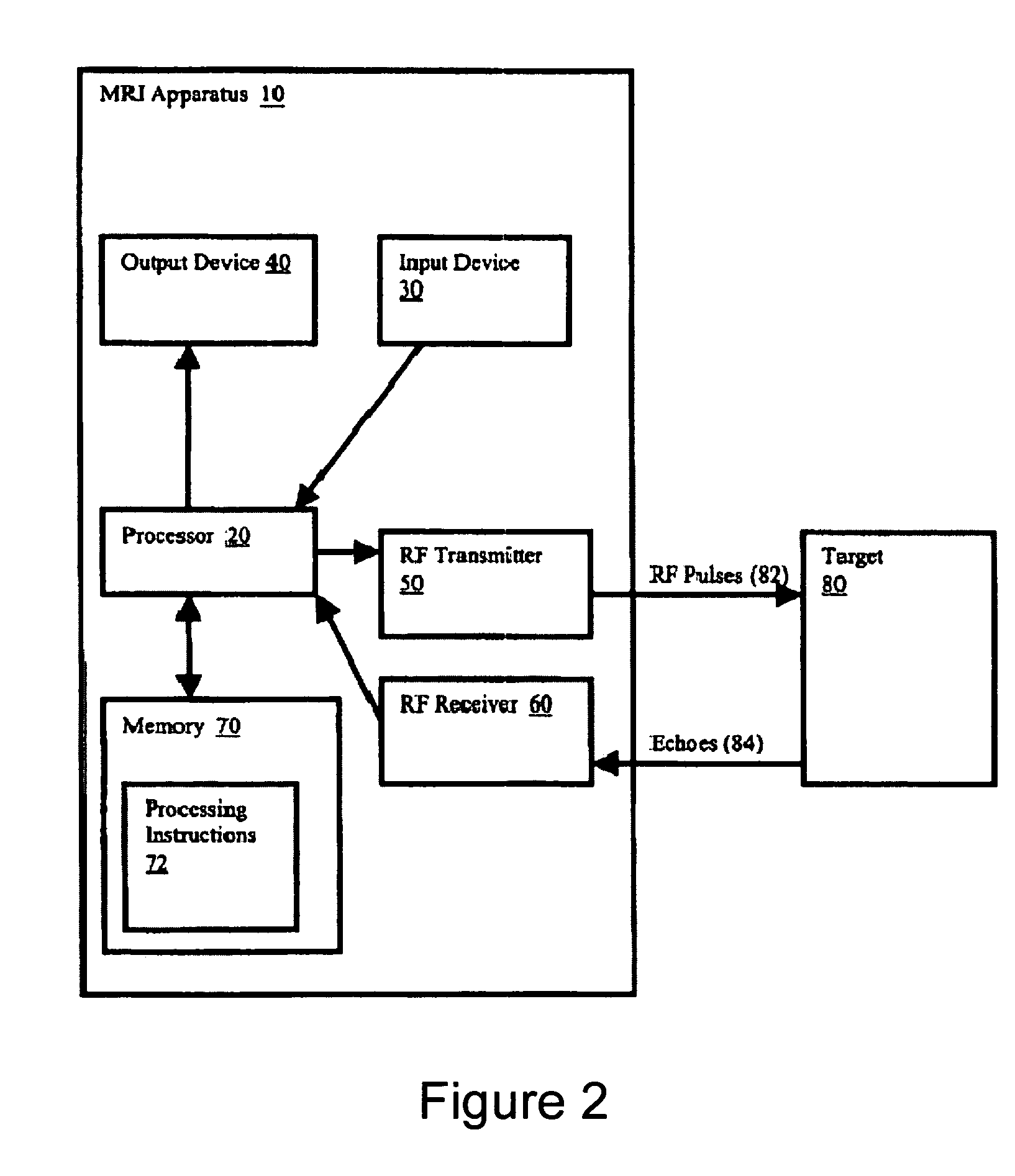
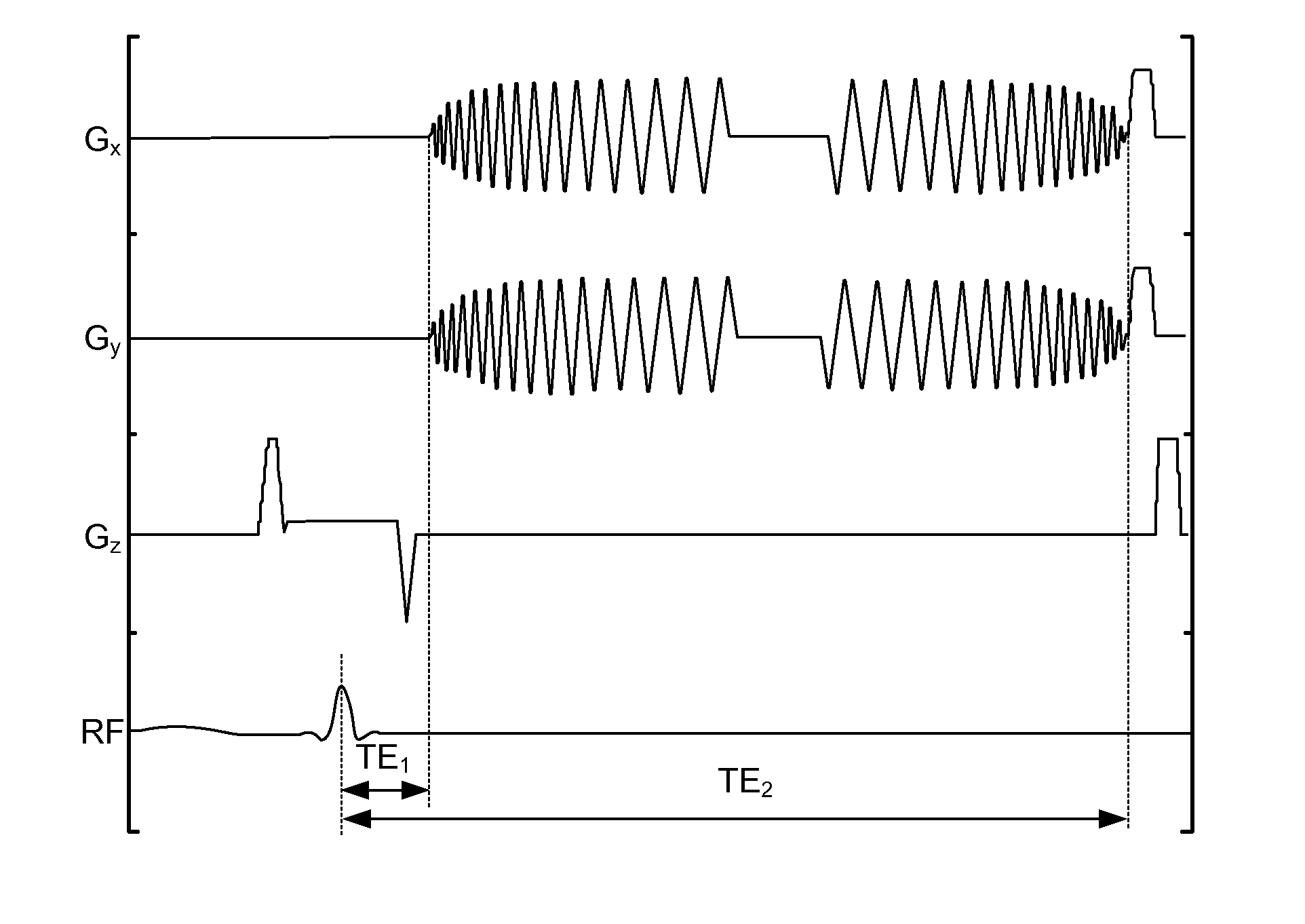
Method, systems and arrangements are provided for creating a high-resolution magnetic resonance image (“MRI”) or obtaining other information of a target, such as a cardiac region of a patient. Radio-frequency (“RF”) pulses can be transmitted toward the target by, e.g., an RF transmitter of an MRI apparatus. In response, multiple echoes corresponding to the plurality of pulses may be received from the target. Data from each of the echoes can be assigned to a single line of k-space, and stored in memory of the apparatus. An image of the target, acceleration data and / or velocity data associated with a target can be generated as a function of the data. In one exemplary embodiment, the data from different echoes may be assigned to the same k-space line, and to different cardiac phases. In one further embodiment, parallel processing may be used to improve the resolution of the image acquired during a single breath-hold duration. In yet another embodiment, utilizing a segmented implementation, multiples lines of k-space are acquired for a given cardiac phase (or time stamp) per trigger signal. The present invention may be utilized for the heart or for any other anatomical organ or region of interest for the evaluation and study of flow dynamics with very high temporal resolution.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
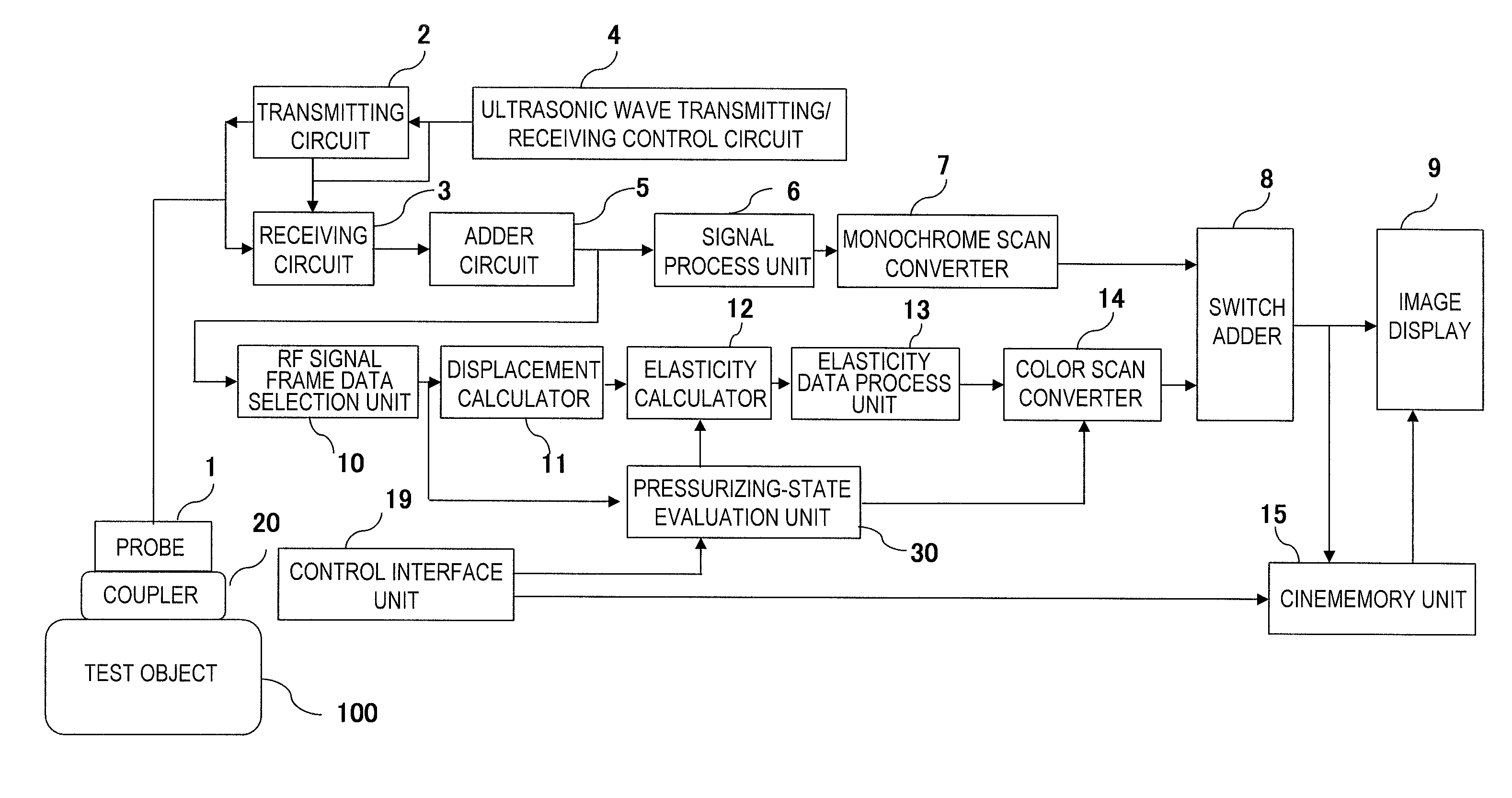
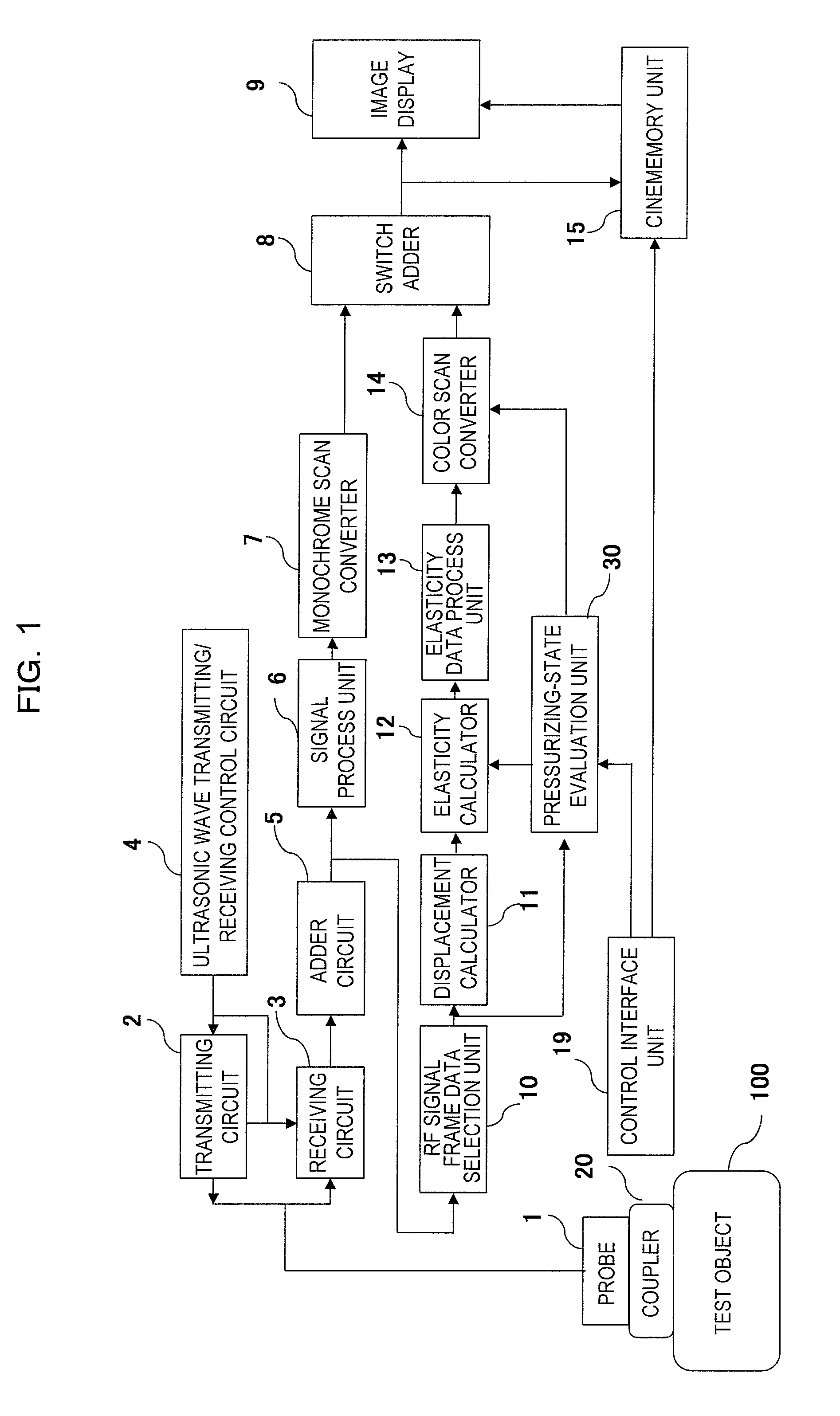
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
InactiveUS20110040187A1Easy to operateImprove usabilityBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringHigh availabilityTest object
The invention was made to simplify the operation relating to the detection of an absolute pressure applied to a test body by an ultrasonic probe and thereby to enhance usability. The fact that an elastic coupler has been attached to the ultrasonic wave transmitter / receiver surface and the fact that the elastic coupler is in an initial state with no pressure are detected (S2, S3), an initial thickness of the elastic coupler in the initial state is obtained (S6), the fact that the elastic coupler is in the pressurized state is detected based on the disappearance of a multiple echo which is included in an RF signal and caused due to the elastic coupler, the thickness of the elastic coupler in the pressurized state is obtained by detecting the boundary between the test body and the elastic coupler in the pressurized state, the thickness change is obtained based on the thickness in the pressurized state and the initial thickness (S7), and the absolute pressure applied to the test object is evaluated based on the thickness change and the pre-set elasticity property of the elastic coupler (S8).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
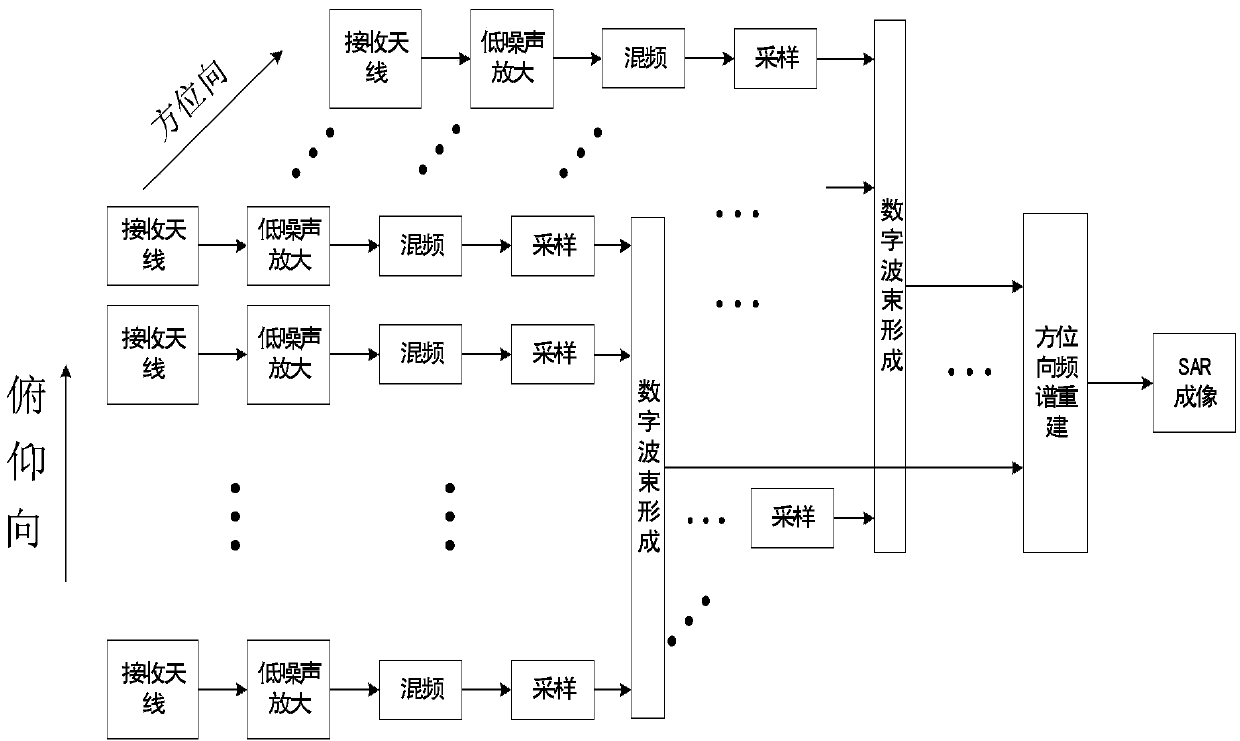
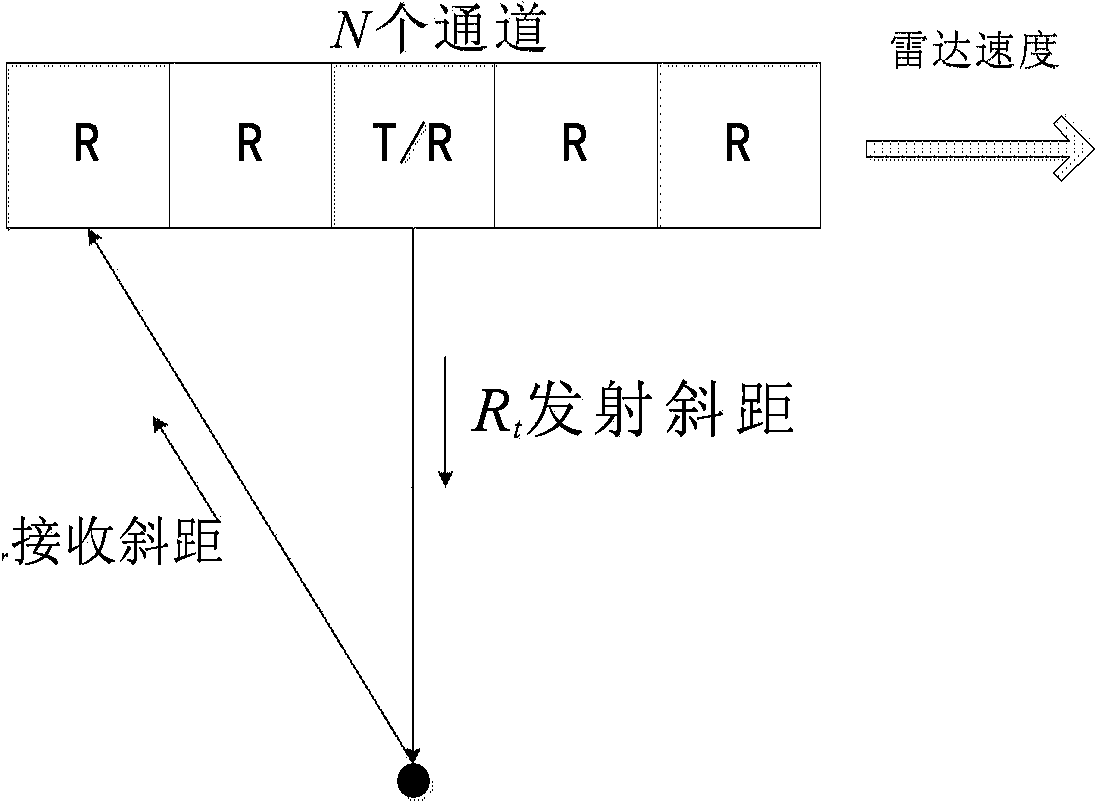
Satellite-borne multi-channel synthetic aperture radar imaging device
ActiveCN103744080AHigh imaging performanceLarge swathRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumSynthetic aperture radar
The invention relates to a satellite-borne multi-channel synthetic aperture radar imaging device, which is characterized in that multiple channels of pitching direction receiving antenna assemblies are arranged in the pitching direction of the radar at equal distance, echoes received by the multiple channels of pitching direction receiving antenna assemblies are formed into a channel of echo signal after passing through pitching direction digital beam forming units, multiple channels of pitching direction receiving antennas corresponding to the channel of echo signal are used as a row of receiving antennas, multiple rows of azimuth receiving antenna assemblies are arranged in the azimuth of the radar, multiple echo signals are formed after the multiple rows of azimuth receiving antenna assemblies pass through respective digital beam forming units, and enter azimuth frequency spectrum reestablishing units to be subjected to azimuth frequency spectrum reestablishing, the azimuth frequency spectrum reestablishing units are respectively connected with the multiple channels of pitching direction digital beam forming units for carrying out azimuth frequency spectrum reestablishing on the multiple channels of echo signals to generate and output a synthetic aperture radar echo signal, and an imaging device is connected with the azimuth frequency spectrum reestablishing units, and is used for receiving and generating the synthetic aperture radar echo signal into a synthetic aperture radar image.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
Ultrasonic elastography with angular compounding
ActiveUS7601122B2Reduce Image ArtifactsReduce image noiseOrgan movement/changes detectionPerson identificationSonificationMultiple echo
Ultrasonic strain measurements, which characterize the structure of tissue, may be obtained by combining multiple echo signals acquired at different compressions and at different angles. Such angular compounding may improve the quality of the elastic signal and provide at one time both an axial and lateral strain measurement.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
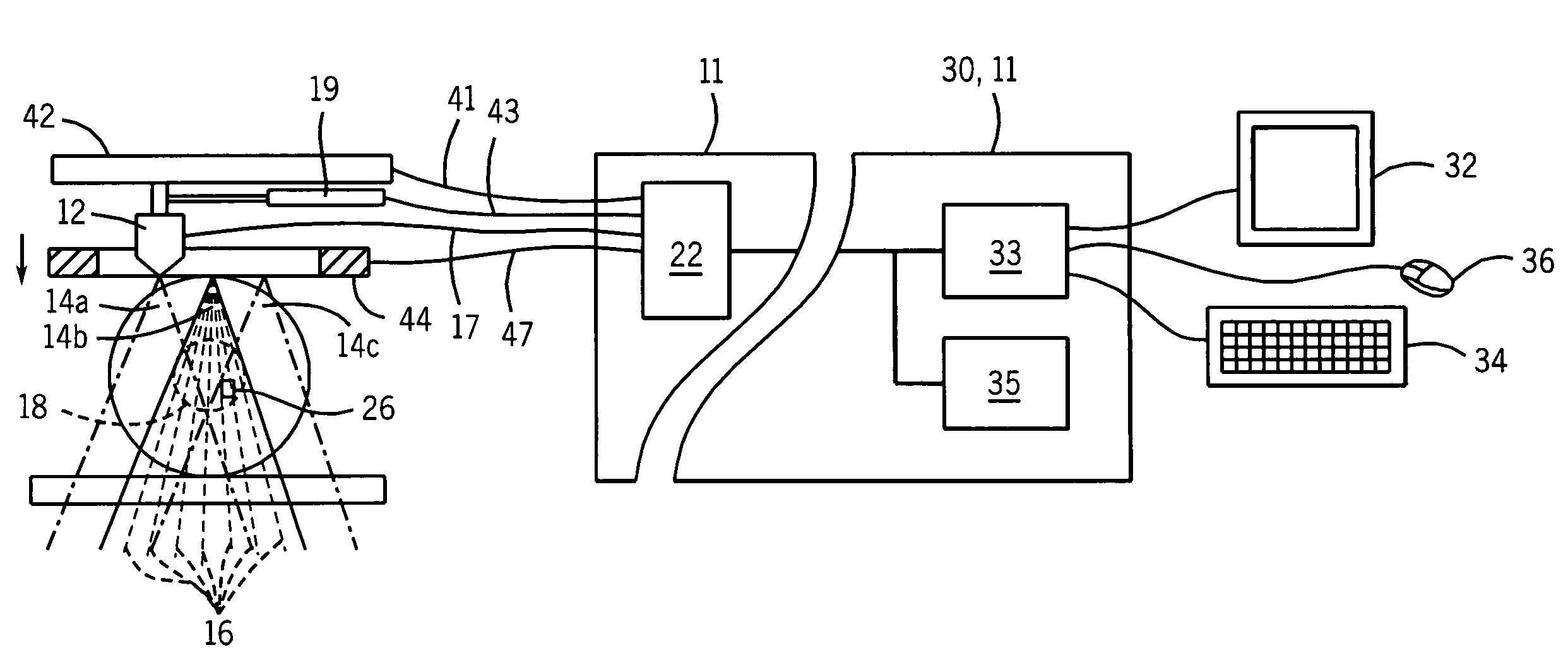
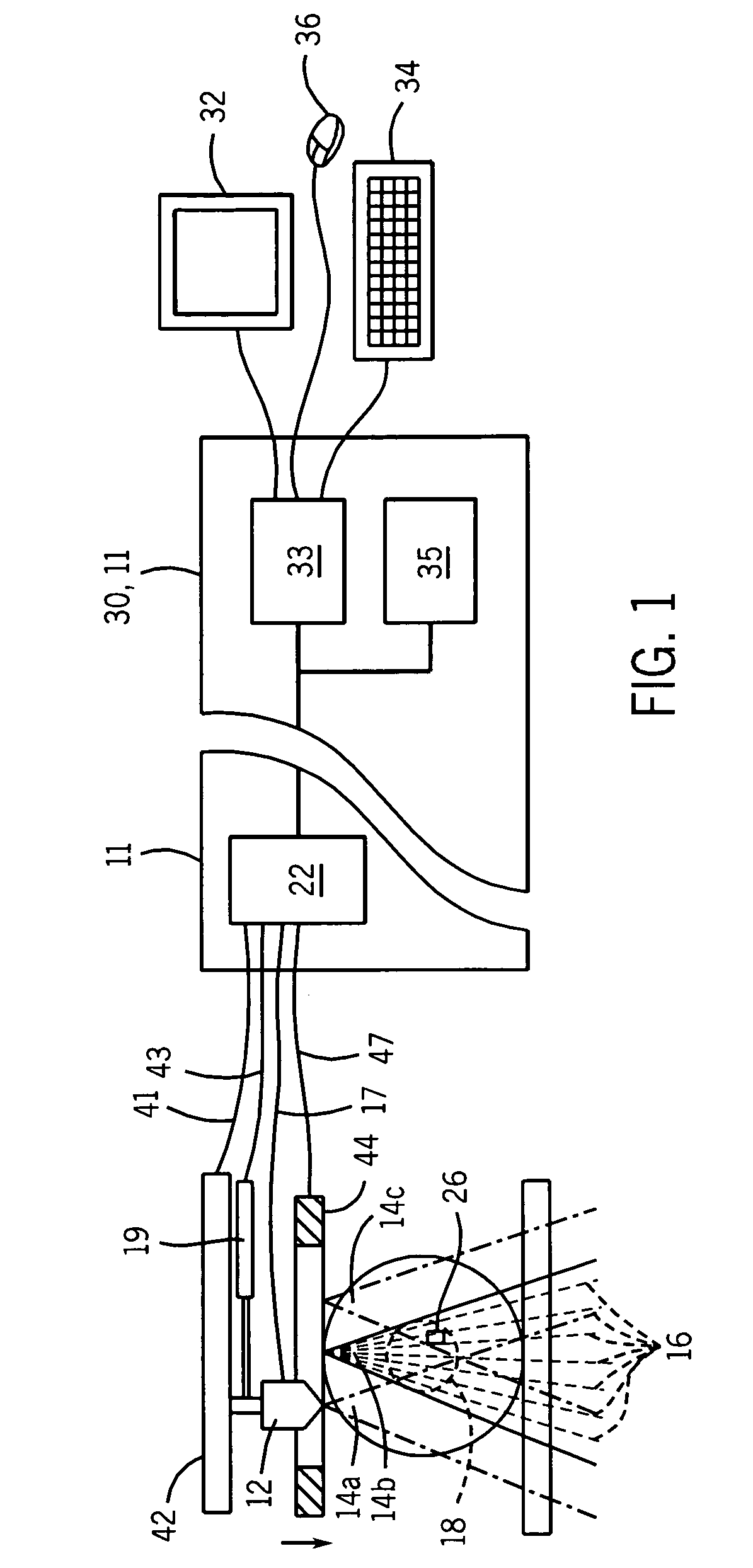
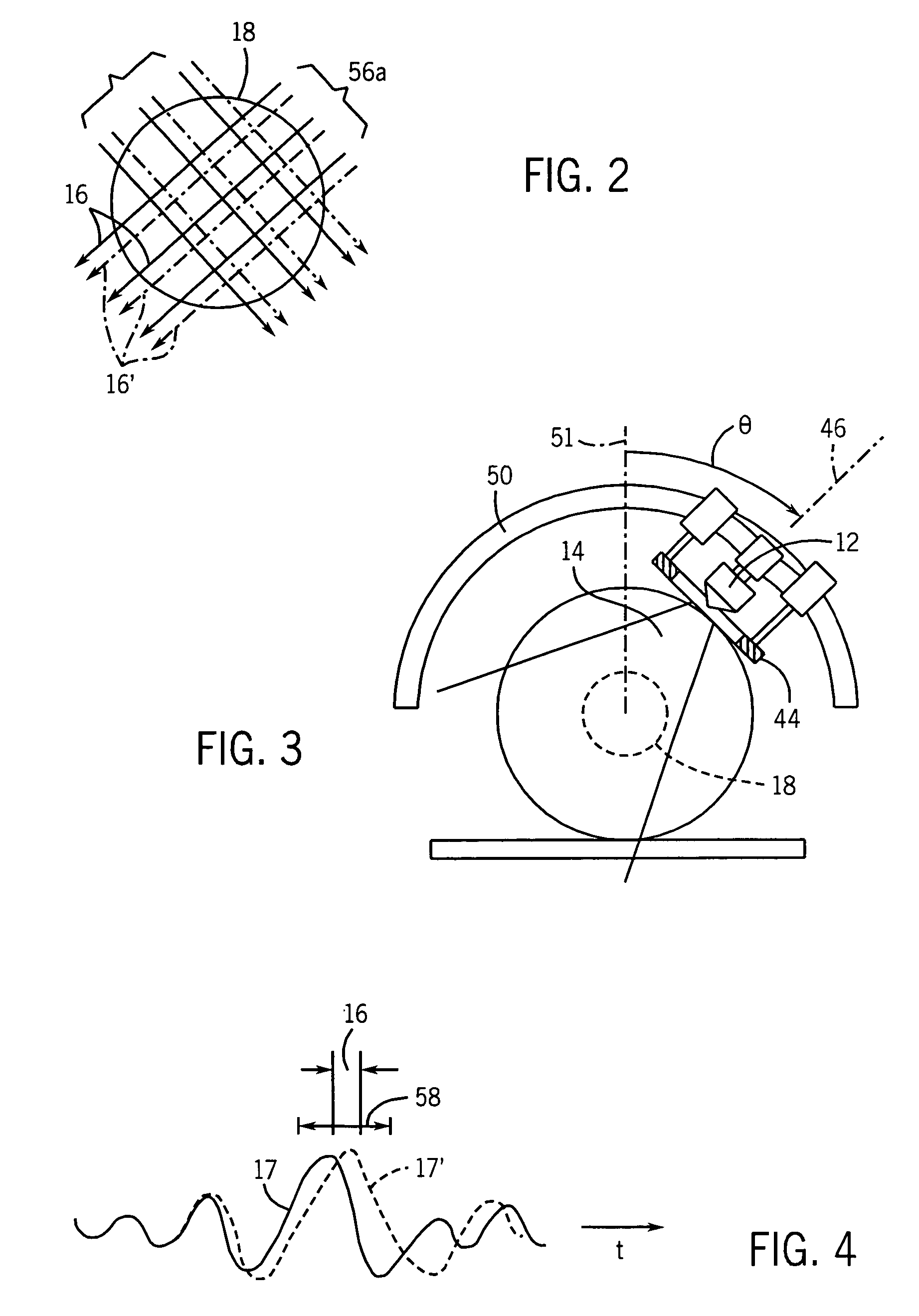
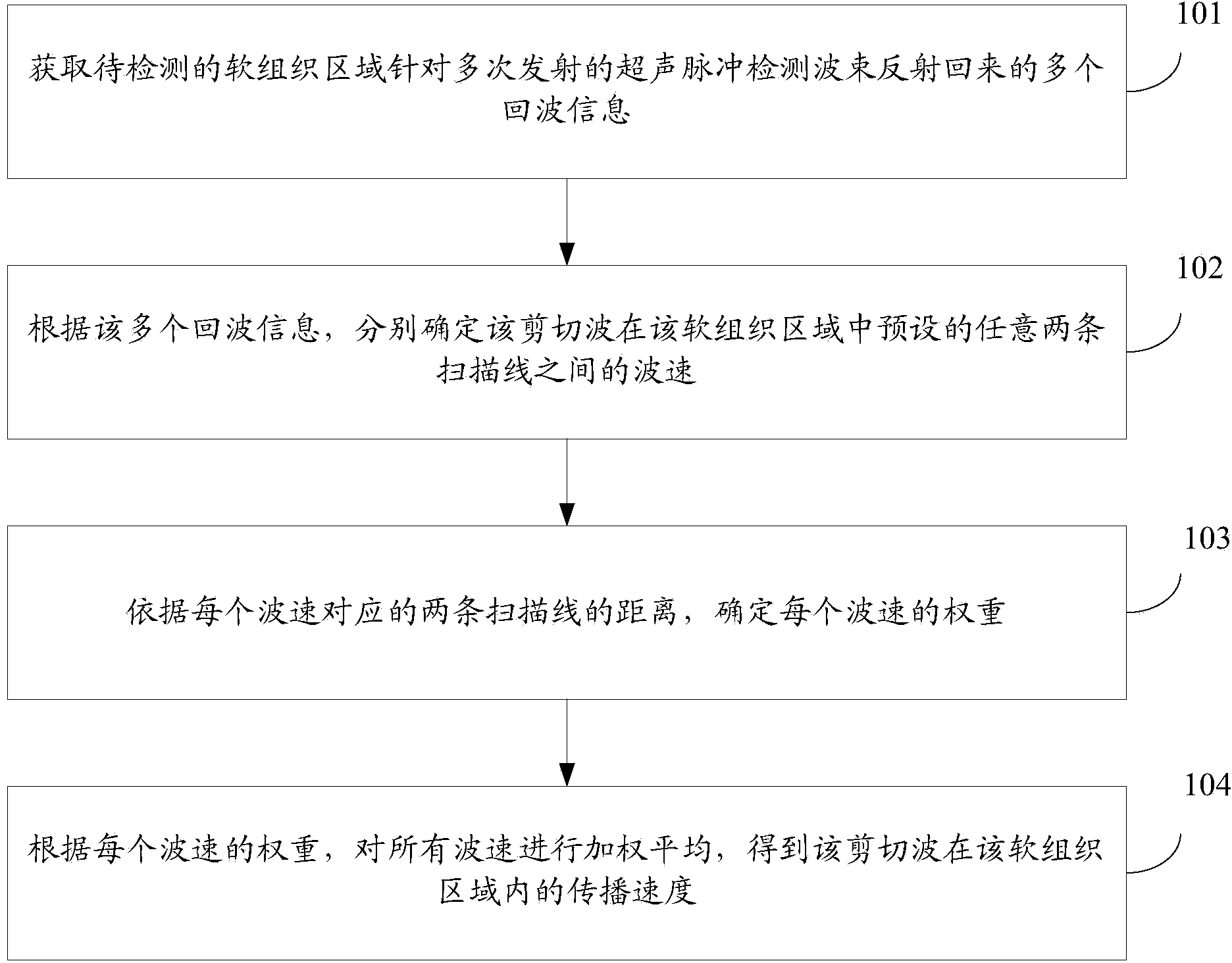
Shear wave speed measurement method, device and system
ActiveCN103462643AImprove accuracyReduce the impactOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsScan lineAcoustics
The invention discloses a shear wave speed measurement method, device and system. The method comprises the steps of obtaining multiple echo information reflected by a to-be-detected soft tissue region aiming at ultrasonic pulse detection wave beams which are transmitted for many times, wherein shear wave propagation exists in the to-be-detected soft tissue region; according to the multiple echo information, respectively determining the wave speeds of shear wave between preset any two scan lines in the soft tissue region, and determining the weight of each wave speed according to the distance of two scan lines corresponding to each wave speed, wherein the longer the distance of two scan lines corresponding to each wave speed is, the larger the weight of the wave speed is; carrying out weighted average on all the wave speed according to the weight of each wave speed, so as to obtain the propagation speed of the shear wave in the soft tissue region. By using the shear wave speed measurement method, the measurement accuracy and reliability of the propagation speed of the shear wave in soft tissue are improved.
Owner:SONOSCAPE MEDICAL CORP
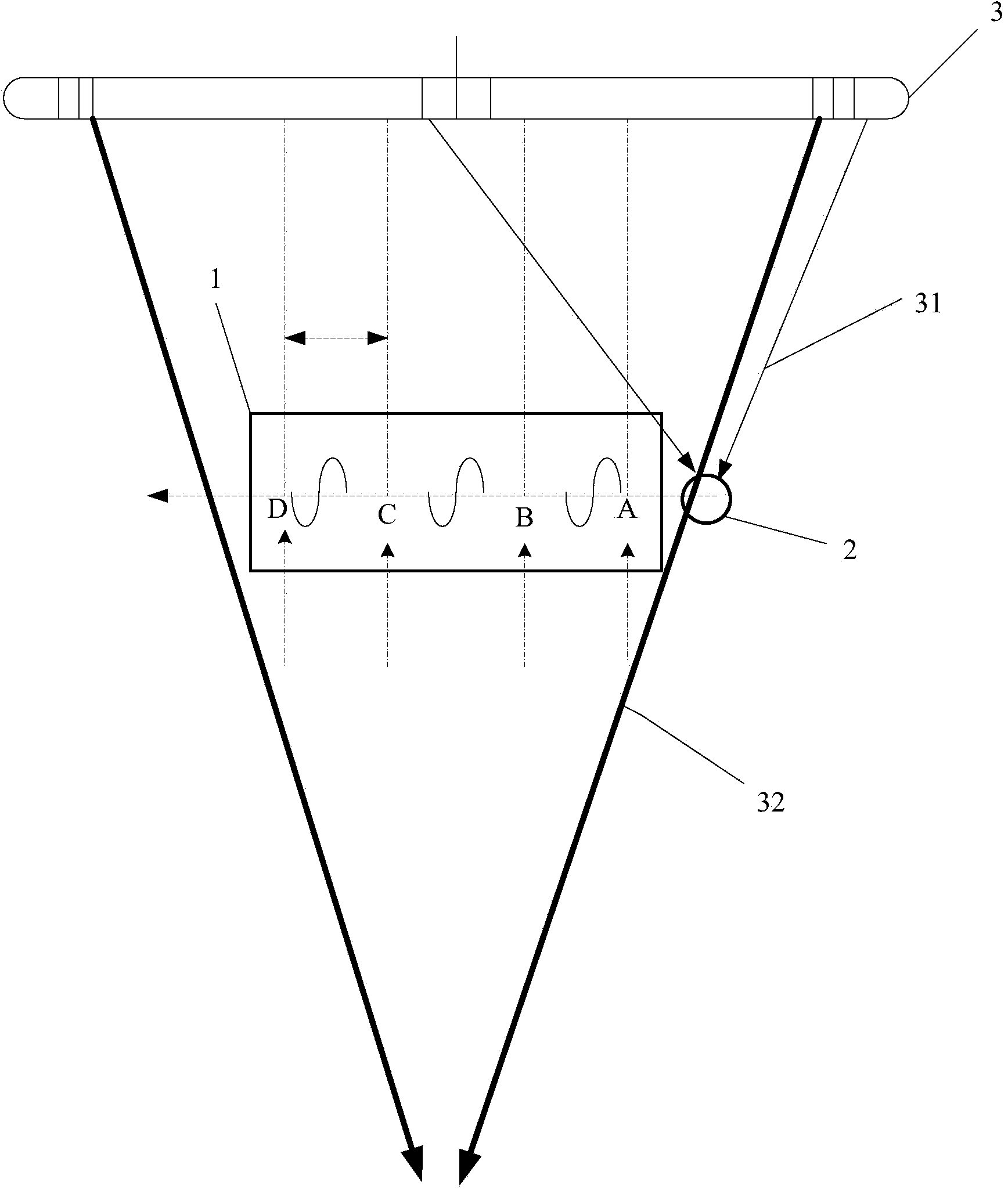
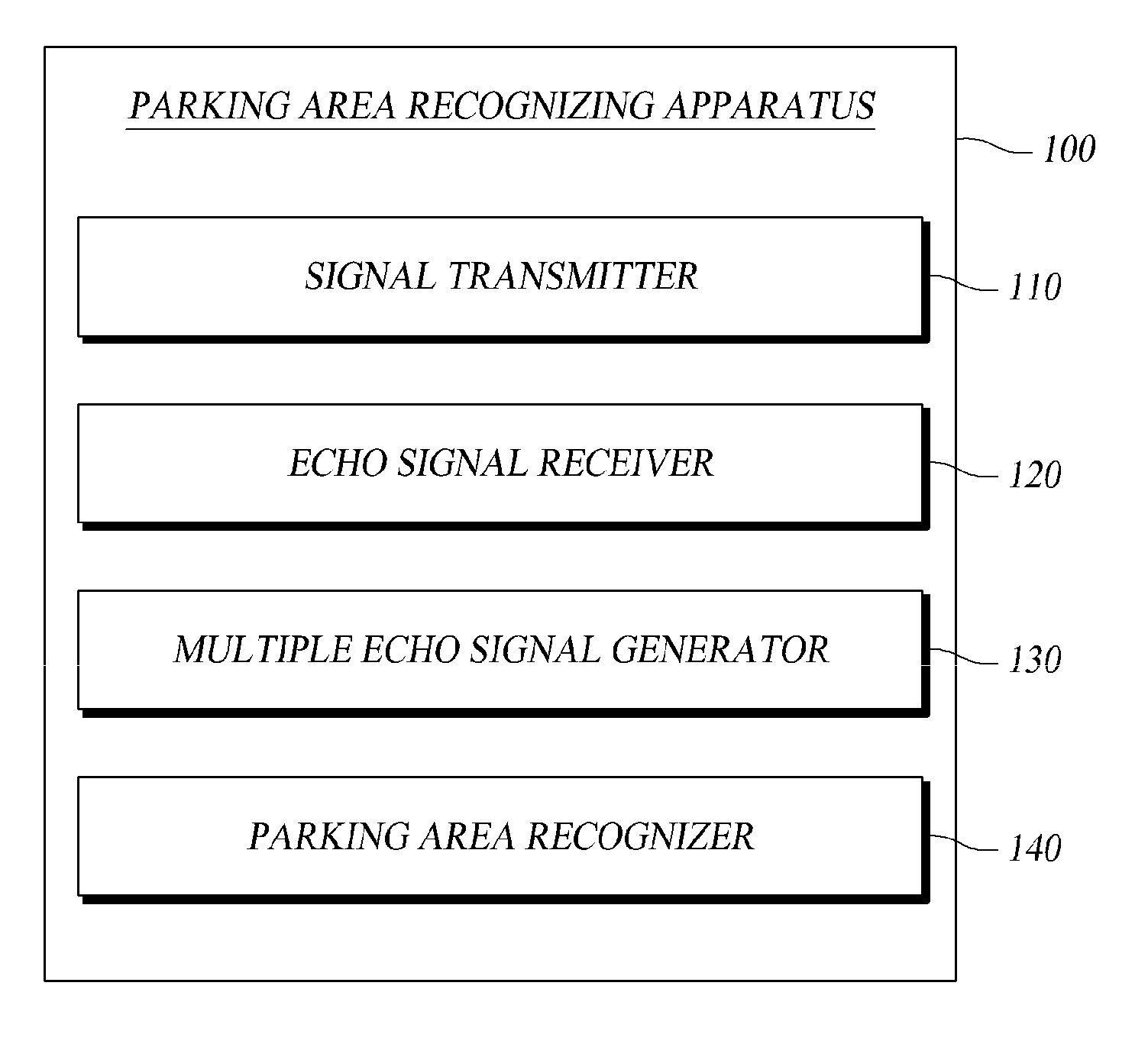
Method and apparatus for recognizing parking area
ActiveUS20100134321A1High precisionReduce measurement errorIndication of parksing free spacesOptical signallingParking areaRadar
A method and an apparatus for recognizing a parking area are disclosed. The parking area recognizing apparatus includes: a signal transmitter transmitting a signal using a sensor; an echo signal receiver receiving an echo signal for the signal; a multiple signal generator generating a multiple echo signal using the echo signal based on first and second preset thresholds; and a parking area recognizer recognizing a parking area by calculating a round trip time and a duration time for the multiple echo signal and selecting an available echo signal based on at least one of the round trip time and the duration time. Accordingly, a precision in recognition of a parking area is enhanced by reducing a measurement error by processing an echo signal received after it is reflected on an object with a multiple echo signal in recognition of the parking area using a sensor such as an ultrasonic sensor or a radar sensor.
Owner:HL KLEMOVE CORP
Three-dimensional imaging method based on single detector correlated imaging theory
InactiveCN102062861AEliminate the effects ofIncrease contrastElectromagnetic wave reradiationSpatial light modulatorTarget signal
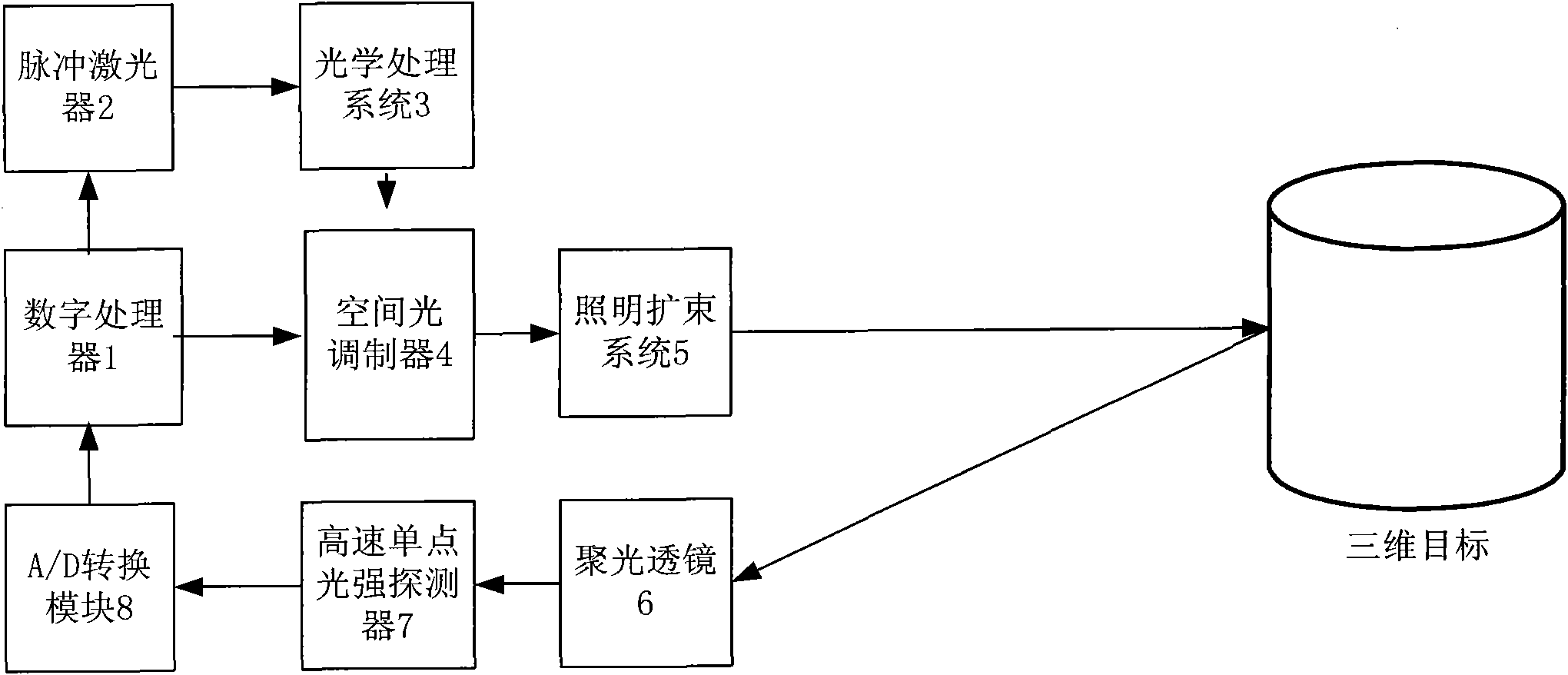
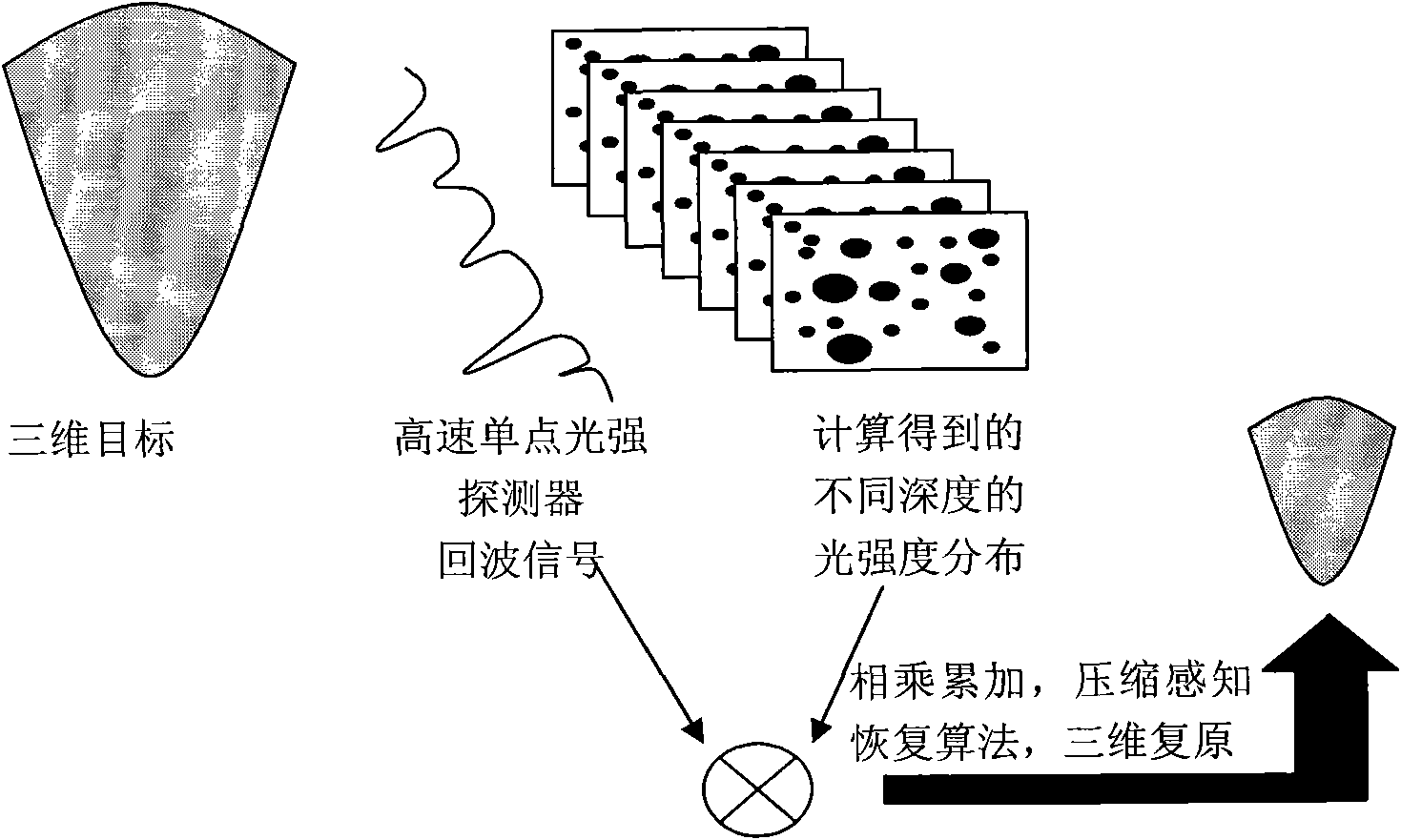
The invention discloses a three-dimensional imaging method based on a single detector correlated imaging theory. In the method, a digital processor controls a pulse laser to emit intense pulsed light, which is optically processed into the intense pulsed light with a known spatial pattern for irradiating to a spatial optical modulator, and the spatial optical modulator generates a pseudorandom additive phase position for the incident intense pulsed light, wherein the distribution of the pseudorandom additive phase position is known and has been stored already for the subsequent processing of the digital processor; the intense pulsed light passes through an illumination beam expansion system after passing through the spatial optical modulator, irradiates to a target and is reflected, and then is condensed to a high-speed single-point light intensity detector by a condenser lens; detector signals are transmitted to the digital processor after A / D (Analog to Digital) conversion; and after a plurality of times of detection, the digital processor processes the collected information and the stored pseudorandom distribution phase positions to finally produce a three-dimensional image. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for acquiring the three-dimensional information of the target at high speed, and has the advantages of capability of acquiring multiple echo target signals, long detection distance and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Water-fat separation magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveCN107997763ARemove periodic fluctuationsShorten Separation Scan TimeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsStable statePrecession
The invention relates to a water-fat separation magnetic resonance imaging method. The method is particularly applicable to a high field and super high field magnetic resonance system. The method comprises the following steps of 1, setting an integrated stable-state free precession imaging sequence capable of adjusting multiple echo times; 2, imaging the same imaging area and acquiring a magneticresonance signal corresponding to each echo time; 3, conducting Fourier image rebuilding on the acquired magnetic resonance signal to obtain a magnetic resonance complex number image corresponding toeach echo time; 4, integrating magnetic resonance complex number image information corresponding to the multiple echo times, wherein the magnetic resonance plural number image information comprises anamplitude and a phase; adopting a water-fat separation algorithm to solve images of separated water and fat. The water-fat separation magnetic resonance imaging method can be widely applied to various magnetic resonance high field imaging systems, particularly a super high field imaging system.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Water fat separated magnetic resonance imaging method and system using steady-state free-precession
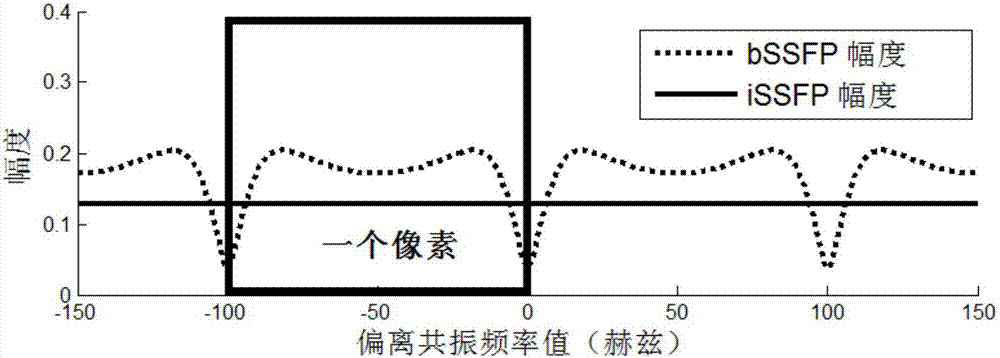
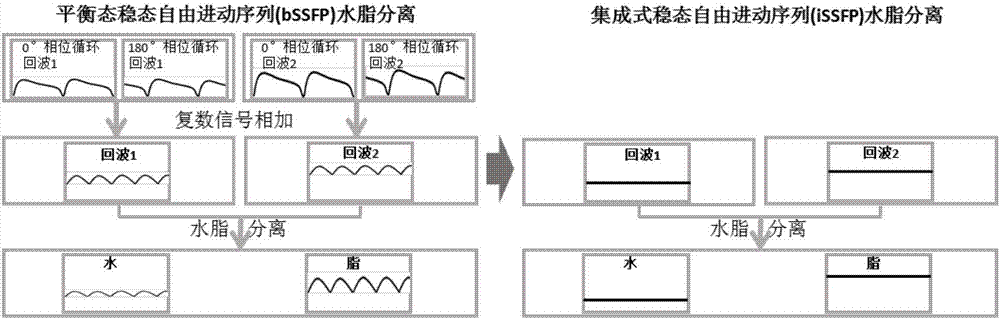
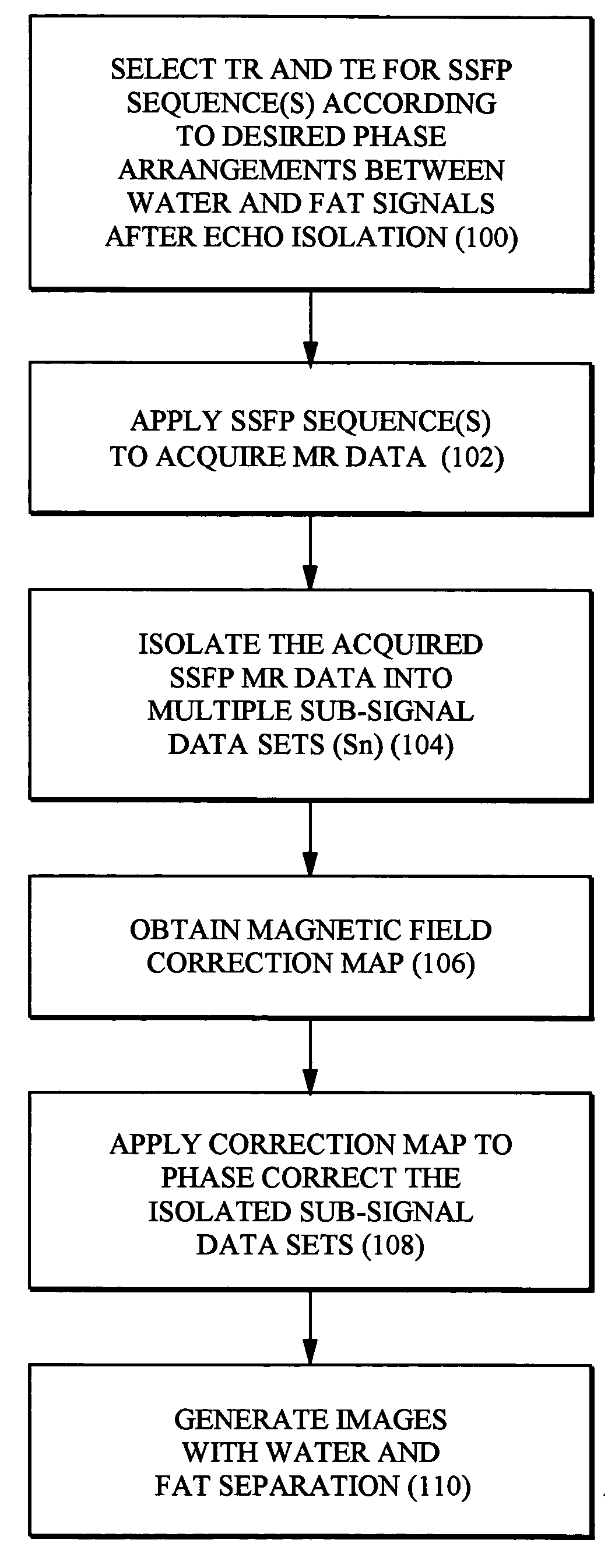
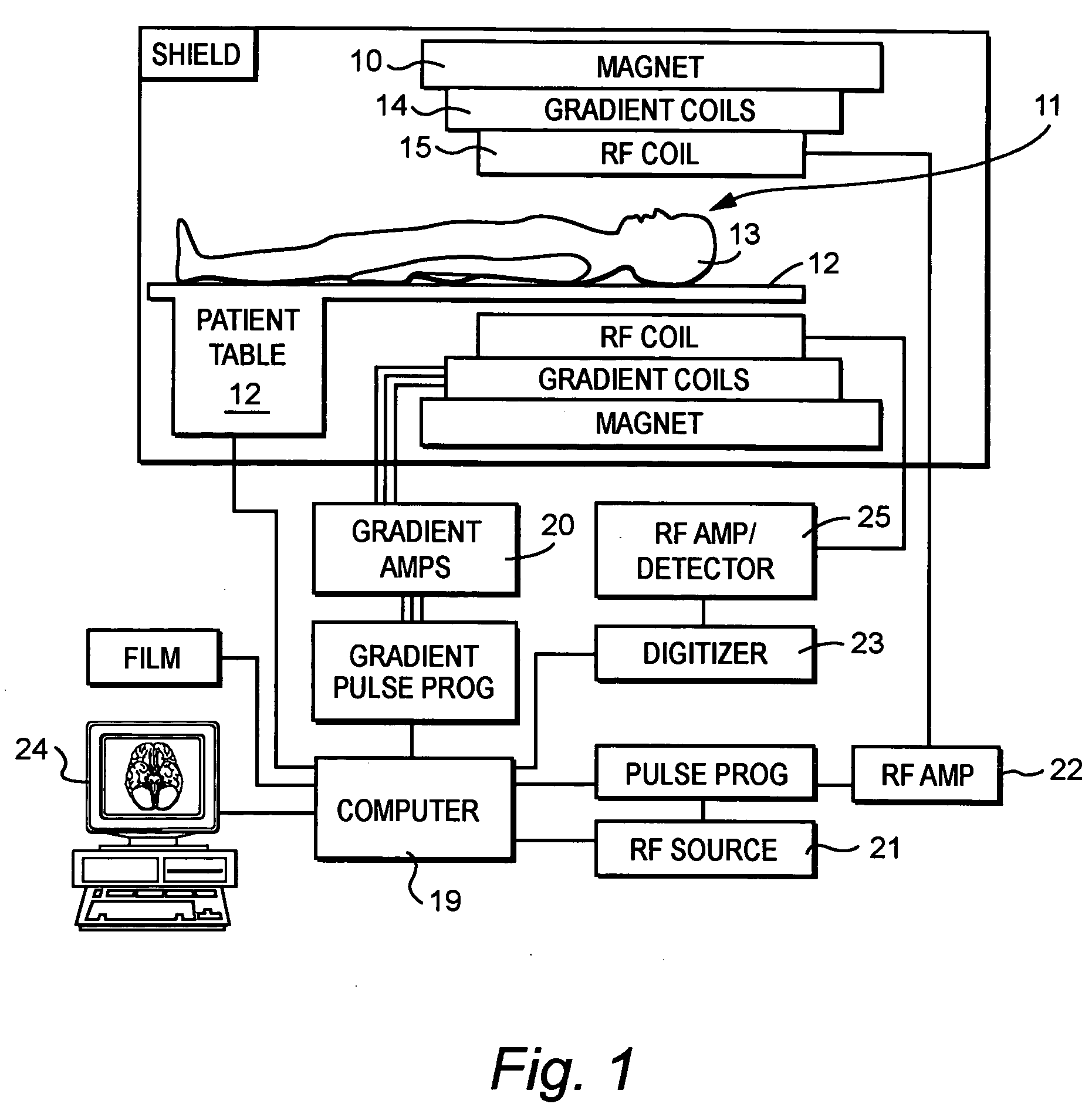
InactiveUS20050171422A1Reduce scan timeGood water-fat separationDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceMultiple echo
Water-fat separated magnetic resonance (MR) images with balanced steady-state free precession (SSFP) are produced. The acquired SSFP signals are isolated into multiple echo components in which the phase arrangements between the water and fat signals are controlled by appropriately selecting the TR and TE values of the SSFP imaging sequence. From the isolated echo components, the effects of the field inhomogeneities are corrected and water and fat images are separated.
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
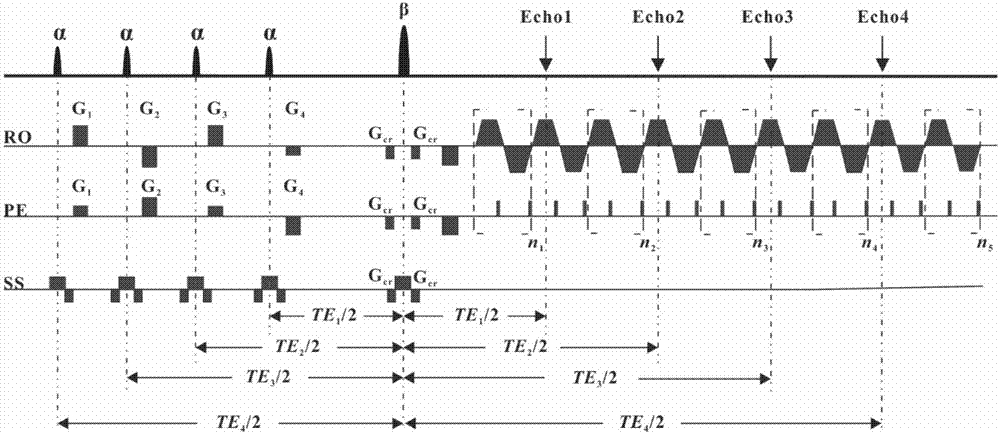
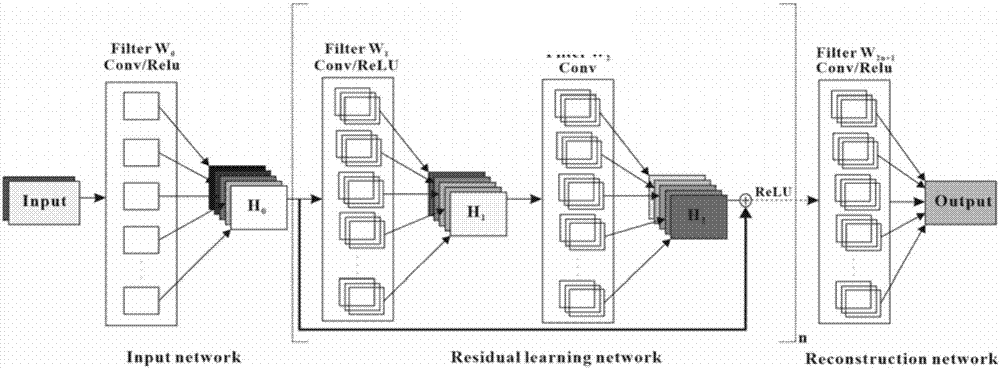
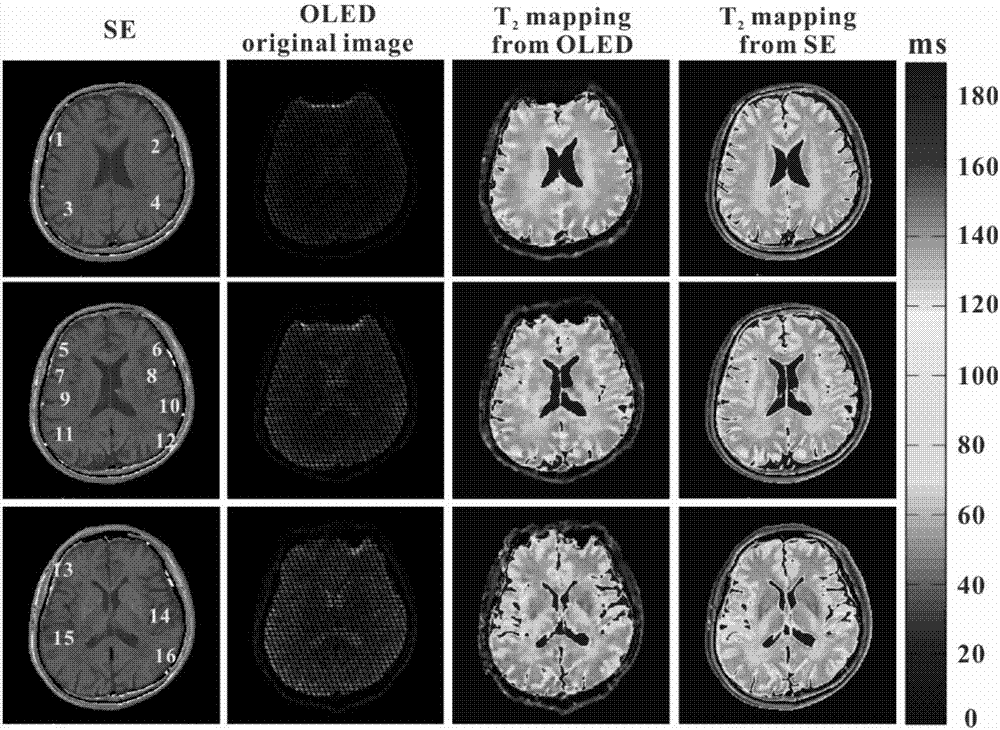
Single-scanning magnetic resonance quantitative T2 imaging reconstruction method based on residual network
ActiveCN108010100ALarge measuring rangeHigh precisionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionReconstruction methodMultiple echo
The invention discloses a single-scanning magnetic resonance quantitative T2 imaging reconstruction method based on a residual network and relates to magnetic resonance imaging methods. According to the method, four small-angle excitation pulses with the same deflection angle are utilized, and a period of evolution time is available after each excitation pulse, so that transverse relaxation time T2 of each echo signal is different; a shift gradient of a frequency coding dimension and a phase coding dimension is added after each excitation pulse, so that the positions of the signals generated by different excitation pulses in a k space are different; multiple echo signals with different transverse relaxation time are obtained in one time of sampling; then the sampling signals are input intothe trained residual network after being subjected to normalization, zero-setting and fast Fourier transformation for reconstruction to obtain a quantitative T2 image; training data of the residual network comes from simulation data; and a template is randomly generated first, then an input image of the network is obtained by simulating experiment environment sampling, the template is used as a tag, and a mapping relation between the input image and an output image is obtained through training.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
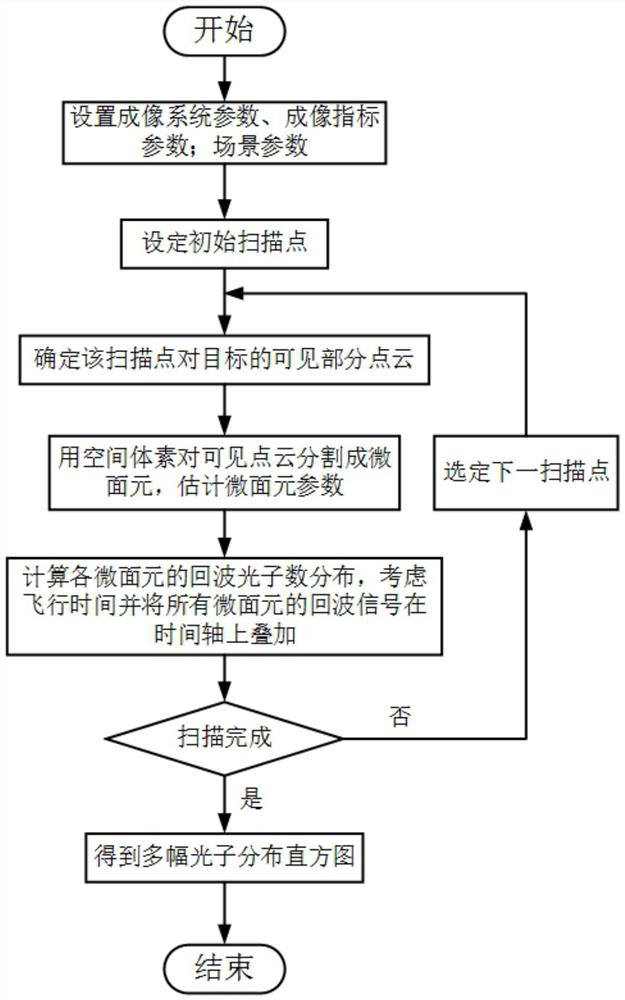
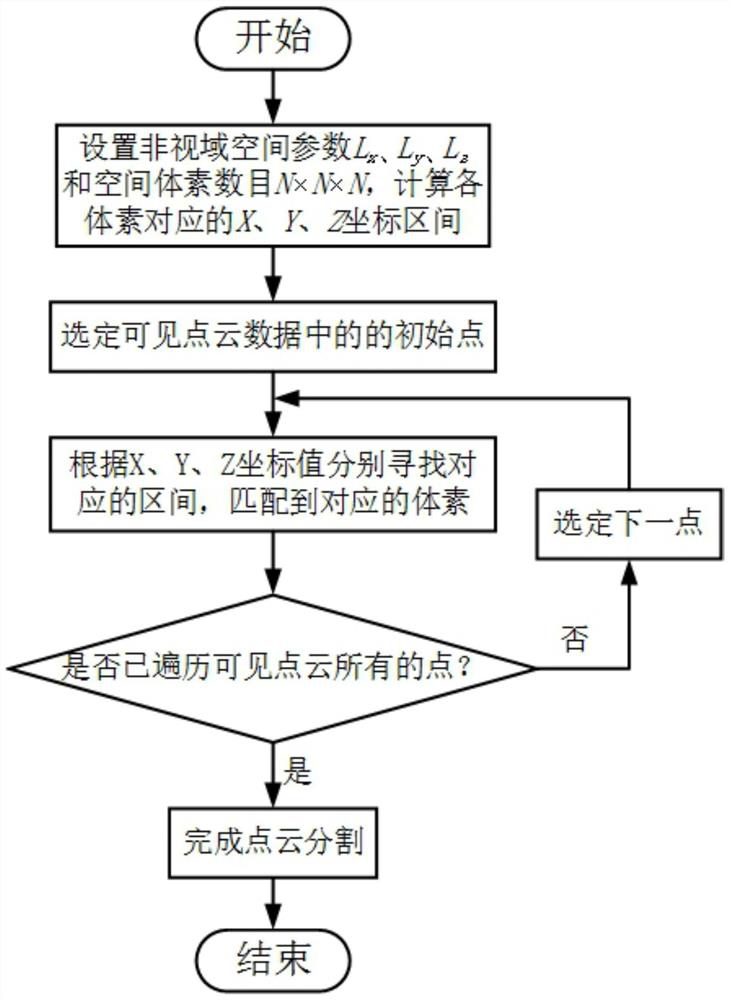
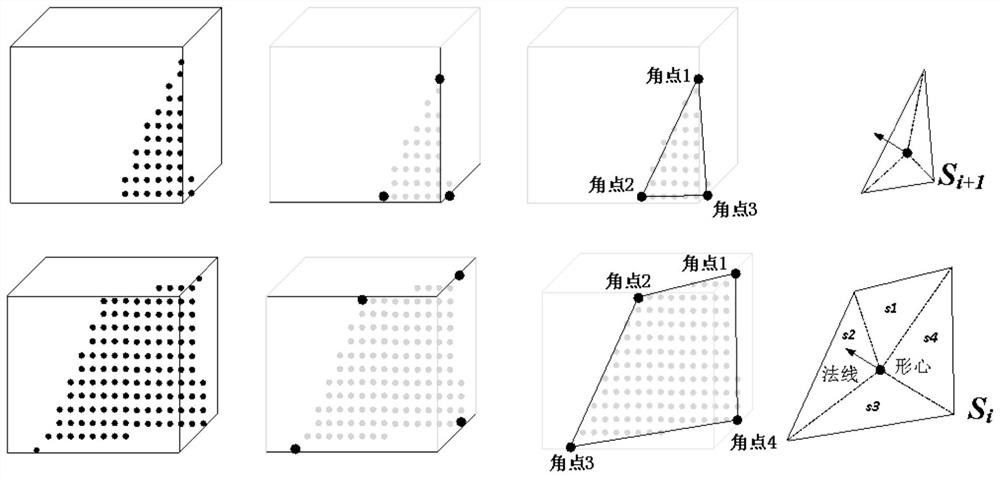
Laser non-visual-field three-dimensional imaging scene modeling method based on point cloud model
The invention discloses a laser non-visual-field three-dimensional imaging scene modeling method based on a point cloud model. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, setting non-visual-field scene space parameters, imaging system parameters and imaging index parameters, and determining a visible region of a specified scanning point-to-point cloud target; secondly, segmenting the visible region point cloud into a plurality of micro-point clouds by utilizing space voxels; detecting angular points to form micro-surface elements, estimating the region, the centroid and the surface normal of each micro-surface element, and establishing an energy transmission model of signals emitted from a laser through three times of diffuse reflection and received by a detector in combination with imaging system parameters to obtain echo energy and echo photon distribution histograms, and finally, setting different scanning points, and repeating the above steps to obtain a photon distribution histogram of multiple echo signals. The modeling method is advantaged in that the process that signals are emitted from a laser, subjected to three times of diffuse reflection of an intermediate surface and a point cloud target with three-dimensional characteristics and finally detected and counted is simulated for the first time.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
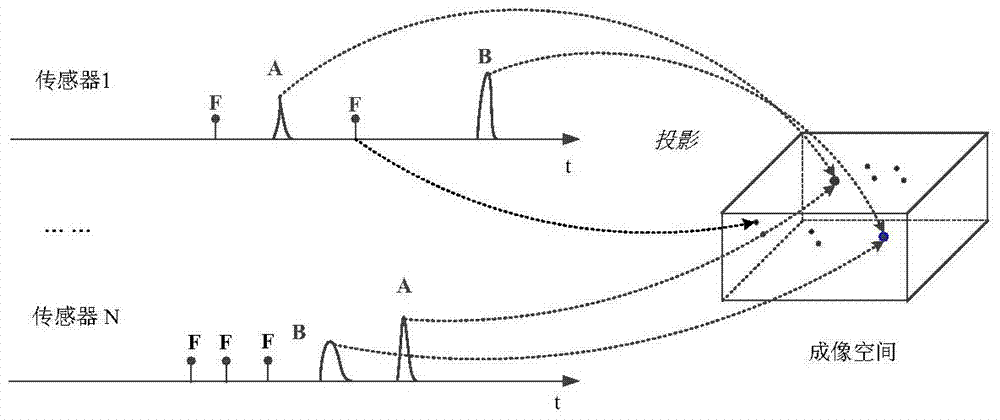
Multi-sensor multi-target location method based on imaging strategies
ActiveCN103576137AImprove signal-to-noise ratioIncrease the probability of multiple target localizationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Greedy algorithm
The invention discloses a multi-sensor multi-target location method based on imaging strategies. According to the method, a sensor network is modeled to form a two-dimensional sparse array, the multi-target location problem based on the sensor network is converted into an imaging problem, and projection strategies like the BP algorithm are adopted to solve complex data association problems; the peak value of a three-dimensional image is searched for through the greedy algorithm, false targets are removed and multiple targets are located through the culling algorithm. Compared with a traditional multi-target location method, the method has the advantages that phase-coherent accumulation is carried out on multiple echoes of the targets from the point of imaging, and therefore the signal-noise ratio of the targets can be further improved, and the multiple targets can be conveniently and accurately calculated; multi-target location is conveniently achieved in an imaging space, and therefore the probability of multi-target location is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Establishment of parameters to adjust a magnetic field shim for a magnetic resonance examination of a patient
ActiveUS20100182007A1Efficiently obtainedShort amount of timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPatients positionExcitation signal
A fast, efficient, qualitatively high-grade shim is enabled in a magnetic resonance apparatus and a method to set shim parameters of a magnetic resonance apparatus, to prepare the implementation of a magnetic resonance examination of a patient with an imaging medical magnetic resonance apparatus having a displaceable patient bed, wherein an examination region of the patient that is to be examined is larger than an imaging region of the magnetic resonance apparatus.Field inhomogeneities are measured while the examination region is moved through the imaging region by a continuous displacement of the patient bed with the patient positioned thereon. Information representing field inhomogeneities (B0 map) is acquired at multiple positions of the patient bed from respective magnetic resonance signals received at these positions. Information representing field inhomogeneities is acquired by excitation of multiple respective slices before the readout of the echo of the first of these slices, with one echo train composed of multiple echoes being generated per excitation signal.Shim parameters of the magnetic resonance apparatus are adjusted dependent on the measured information.A magnetic resonance examination of the examination region is implemented with the apparatus shimmed according to the shim parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Device and method for determining media characteristics and container characteristics
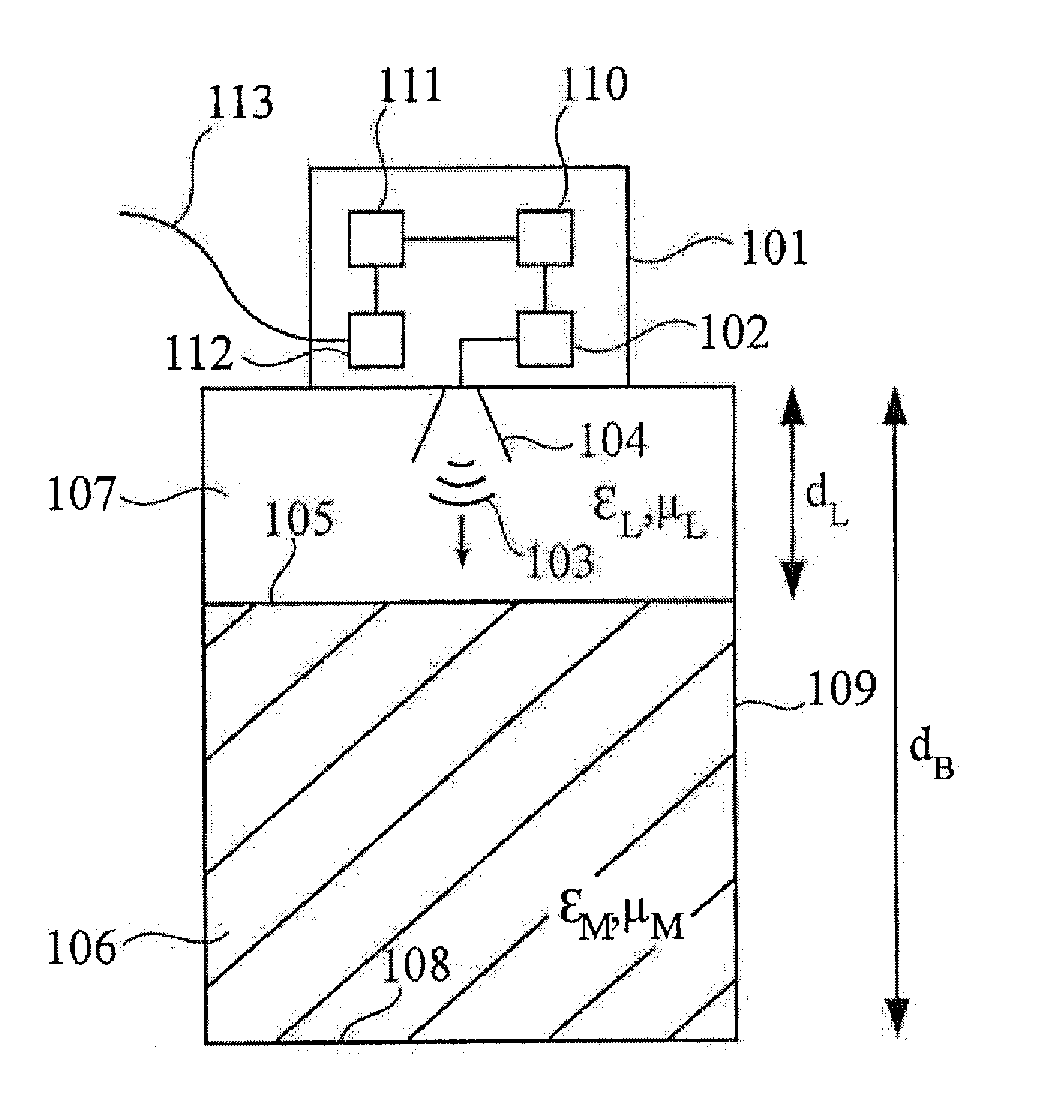
ActiveUS20120299768A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesMachines/enginesEngineeringMultiple echo
A fill-level measuring device includes a self-learn device that is able to automatically determine the length of the dome shaft of the container. To this effect the self-learn device uses a multiple echo classified as such by a multiple-echo detection device. In this manner the result of fill level measuring may be improved.
Owner:VEGA GRIESHABER GMBH & CO
Echo planar imaging method and system
ActiveCN107037386AImprove fitting accuracyFast operationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceMri image
The invention discloses an echo planar imaging method, including: obtaining multiple echo planar imaging data of a scanned part and obtaining several reference echo signals that have not been subject to phase encoding; establishing a fitting model between the actual phase deviation of the reference echo signals and the readout direction position and establishing the Hoff space related to the parameters of the fitting model; based on the actual phase deviation of the reference echo signals and the readout direction position, determining the optimal parameter group in the Hoff space; according to fitting model and the optimal parameter group, correcting the echo planar imaging data; reconstructing the corrected echo planar imaging data and obtaining the magnetic resonance image of the scanned part. The echo planar imaging method of the invention can accurately correct the phases of an imaging signal. In addition, the invention also presents an echo planar imaging system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
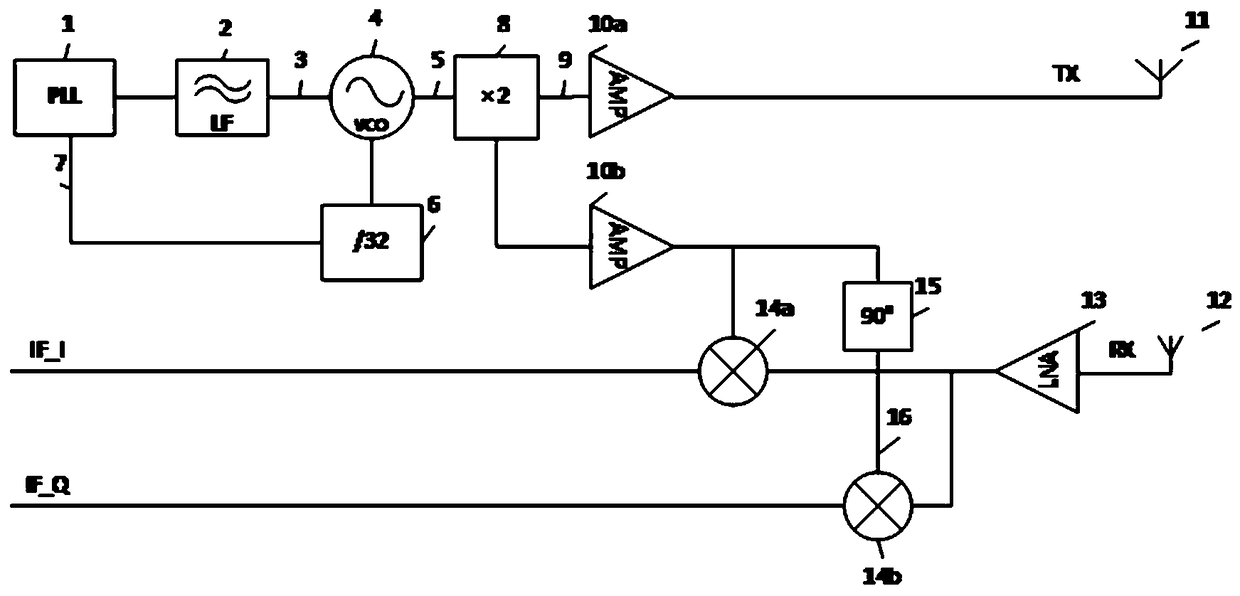
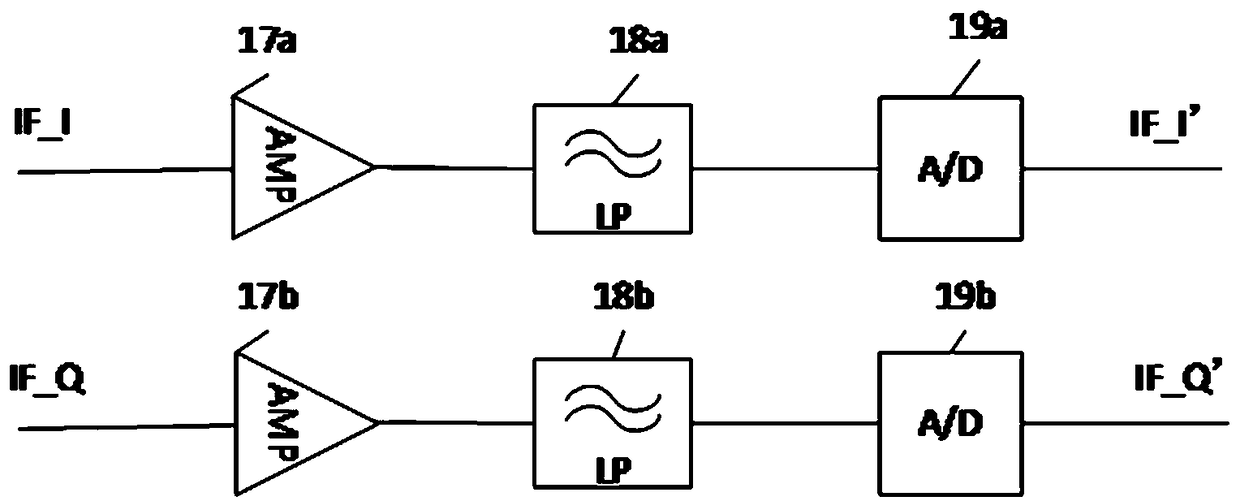
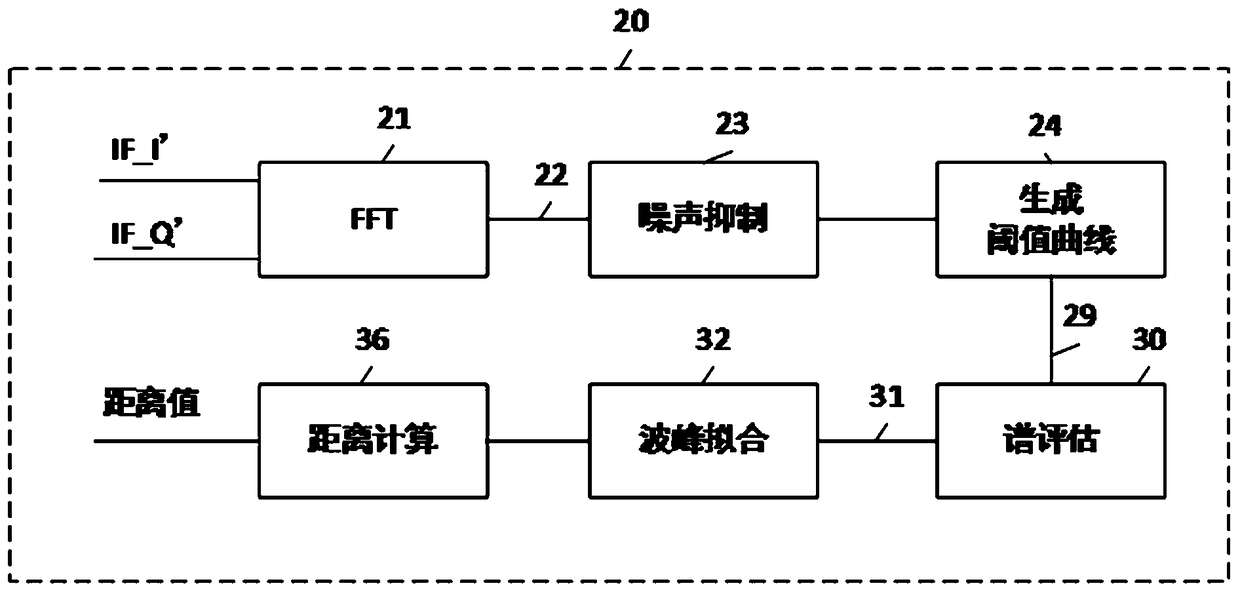
Frequency modulated continuous wave radar level meter of 120 GHz and distance measurement method
The invention discloses a frequency modulated continuous wave radar level meter of 120 GHz and a distance measurement method. The radar level meter comprises a frequency modulating module, an intermediate frequency signal conditioning and sampling module, an echo signal processing module, a threshold value curve generation module and a spectrum estimation module; the frequency modulating module isarranged to be used for generating a difference frequency in-phase signal IF_I and a difference frequency orthogonal signal IF_Q of sending frequency TX and receiving frequency RX; the intermediate frequency signal conditioning and sampling module is arranged to be used for sequentially processing the difference frequency in-phase signal IF_I and the difference frequency orthogonal signal IF_Q togenerate digitalized intermediate frequency orthogonal signals IF_I' and IF_Q'; the echo signal processing module is arranged to be used for converting the intermediate frequency orthogonal signals IF_I' and IF_Q' as time domain signals into a frequency spectrum curve; the threshold value curve generation module is arranged to be used for dynamically generating a threshold value curve according to the generated frequency spectrum curve so that multiple echoes can be obtained. The frequency modulated continuous wave radar level meter of 120 GHz has the advantages that the area of a measurementblind region is small, and precision is high.
Owner:福州盛博电子有限公司
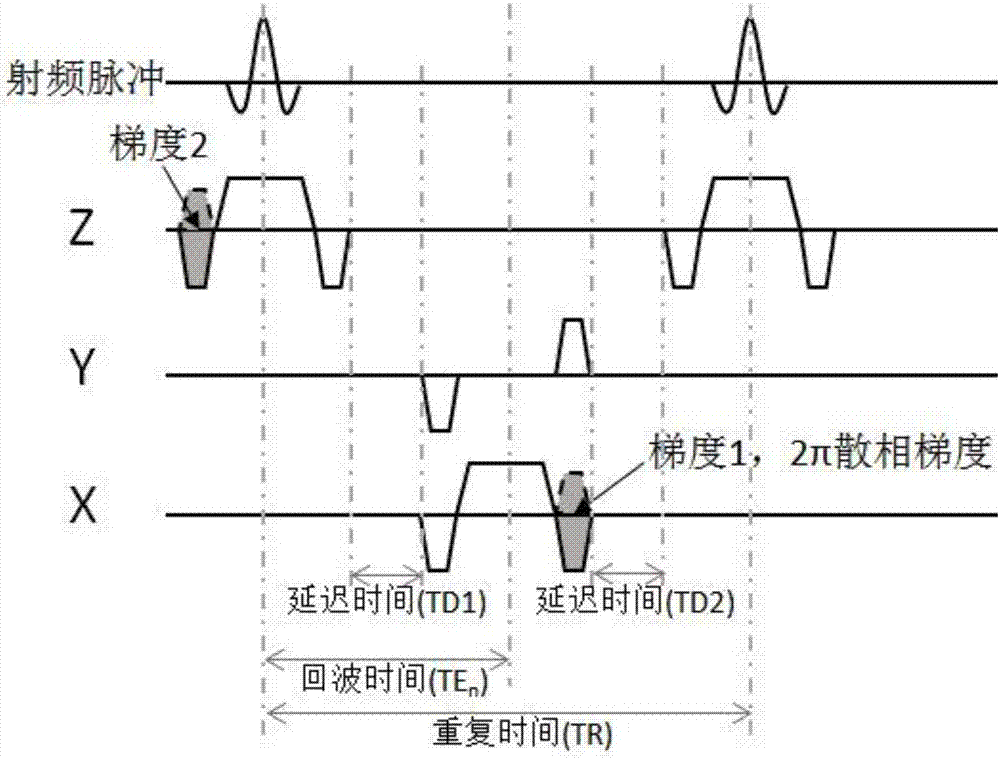
Dual gradient echo pulse sequence using interleaved spiral-out spiral-in k-space trajectories
ActiveUS20060062731A1Avoids saturation effectMore sensitivityMagnetic measurementsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsMagnetic susceptibilityBlood flow
Measurements of functional, hemographic, and blood flow parameters use a multiple echo or spin echo gradient pulse sequence whereby an early echo is acquired near the beginning of the pulse sequence which avoids saturation effects and a later echo near the end of the pulse sequence which can provide information with more sensitivity to a contrast agent for a susceptibility weighted image.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
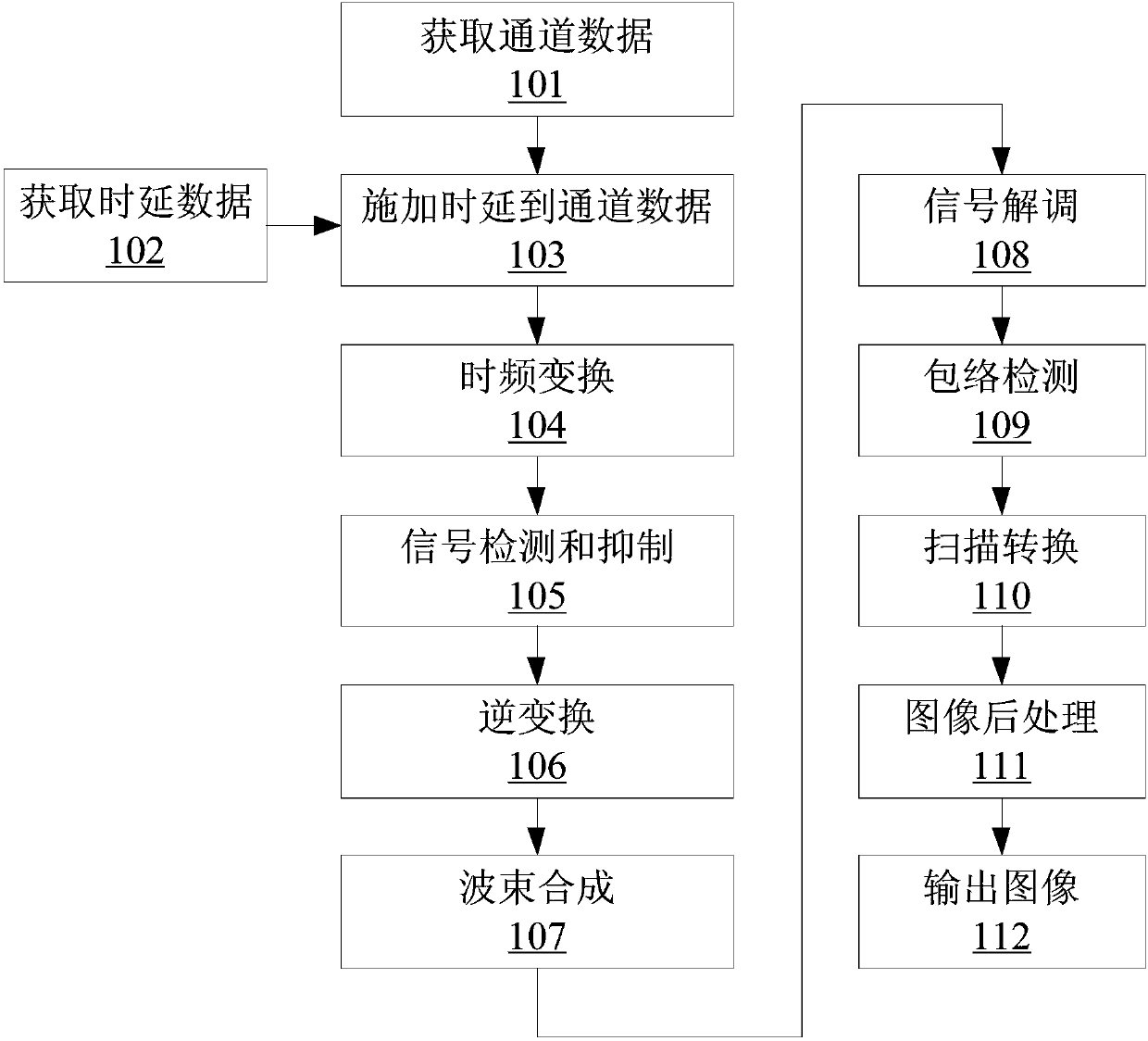
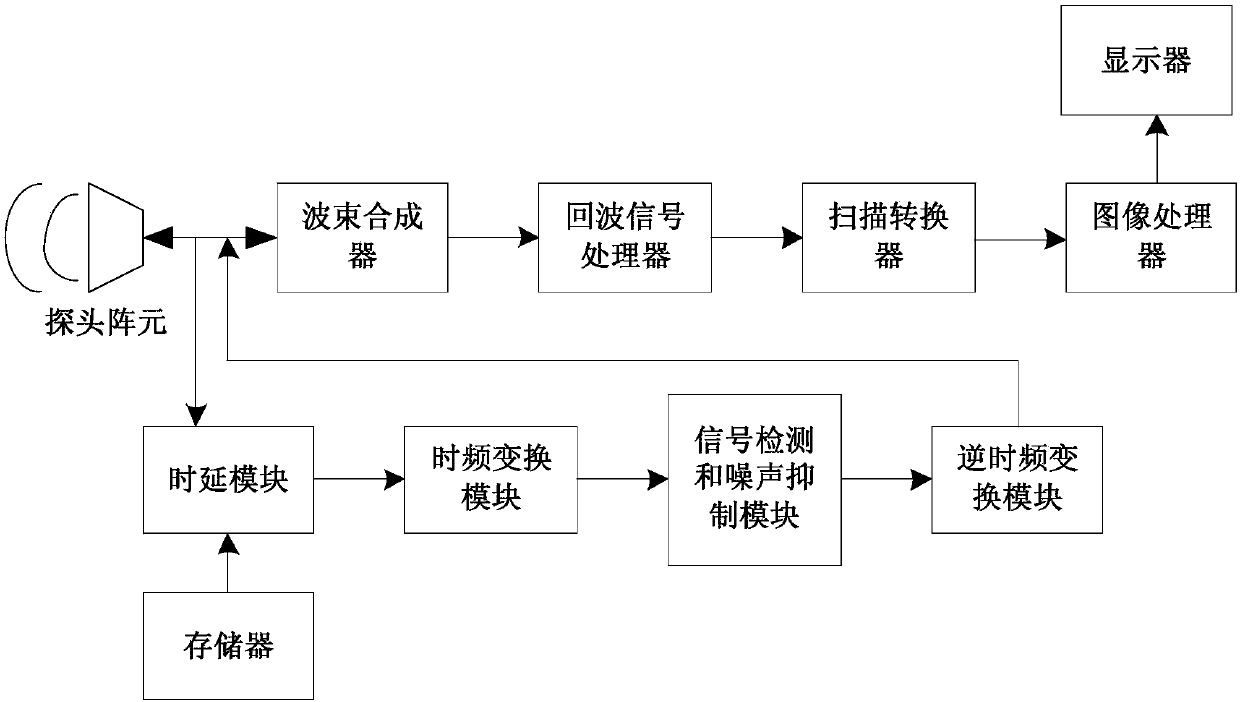
Self-adaption ultrasonic beamforming method and system based on channel data
ActiveCN107789008AIncreased Noise Removal EfficiencyImprove removal efficiencyInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic image/data processingSonificationSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a self-adaption ultrasonic beamforming method and system based on channel data. Unwished sidelobes can be removed, noise generated by the channel data can be stored, and the removing efficiency is high. The method comprises the steps of conducting multiple times of ultrasonic emission, and obtaining first channel data according to corresponding multiple echo signals; obtaining time delay data corresponding to each focus point; regarding each focus point, applying the corresponding time delay to the first channel data to obtain vector data; conducting discrete time-frequency transformation on one or multiple vectors in the vector data to generate frequency domain signals; conducting inverse transformation on each vector in the frequency domain signals which are subjected to noise suppression to obtain second channel data; conducting beamforming on the obtained second channel data; conducting signal demodulation, envelope detection, scanning conversion and image postprocessing on signals which are subjected to beamforming in sequence to generate a frame of image.
Owner:SASET CHENGDU TECH LTD
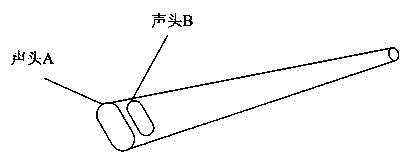
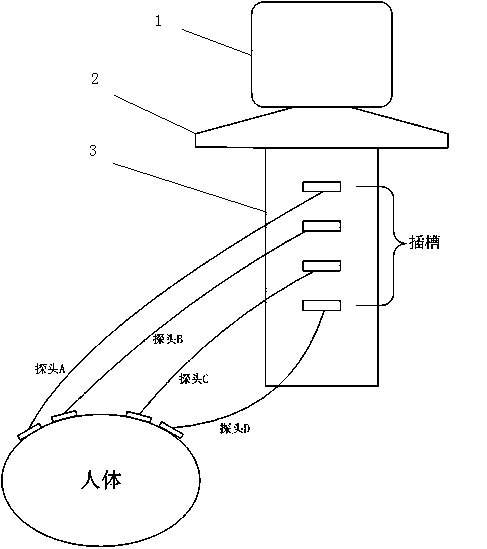
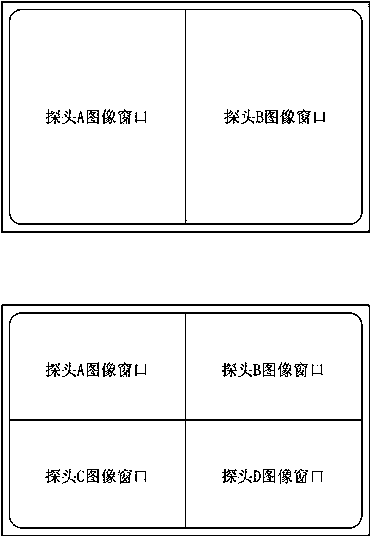
Ultrasonic diagnosis equipment and ultrasonic diagnosis method supporting multi-probe synchronous scanning
InactiveCN104107067AAvoid Sound Power RisksFacilitates ultrasound scan monitoringDiagnostic probe attachmentInfrasonic diagnosticsMedicineDiagnosis methods
An ultrasonic diagnosis device and method that support synchronous scanning by multiple probes. The ultrasonic diagnosis device comprises a display module (1), an imaging system (3), and multiple probes (A, B, C, D). The multiple probes (A, B, C, D) closely contact different portions of the body surface of a diagnosed person, synchronously scan the different portions of the body surface of the diagnosed person in real time, obtain echo signals after the scanning, and then transmit the echo signals to the imaging system (3); the imaging system (3) converts the multiple echo signals transmitted by the multiple probes (A, B, C, D) into multiple ultrasonic images; and the display module (1) is coupled to the imaging system (3), receives the multiple ultrasonic images output by the imaging system (3) after processing, and synchronously displays the images. The multiple probes (A, B, C, D) work independently at the same time, so that the ultrasonic diagnosis device obtains image scanning data of the different probes at the same time, thereby meeting the requirement on diagnosing different body portions at the same time.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and device to process complex image data
InactiveUS20120224757A1Reduce disadvantagesSimplified determinationCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase differenceImage resolution
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
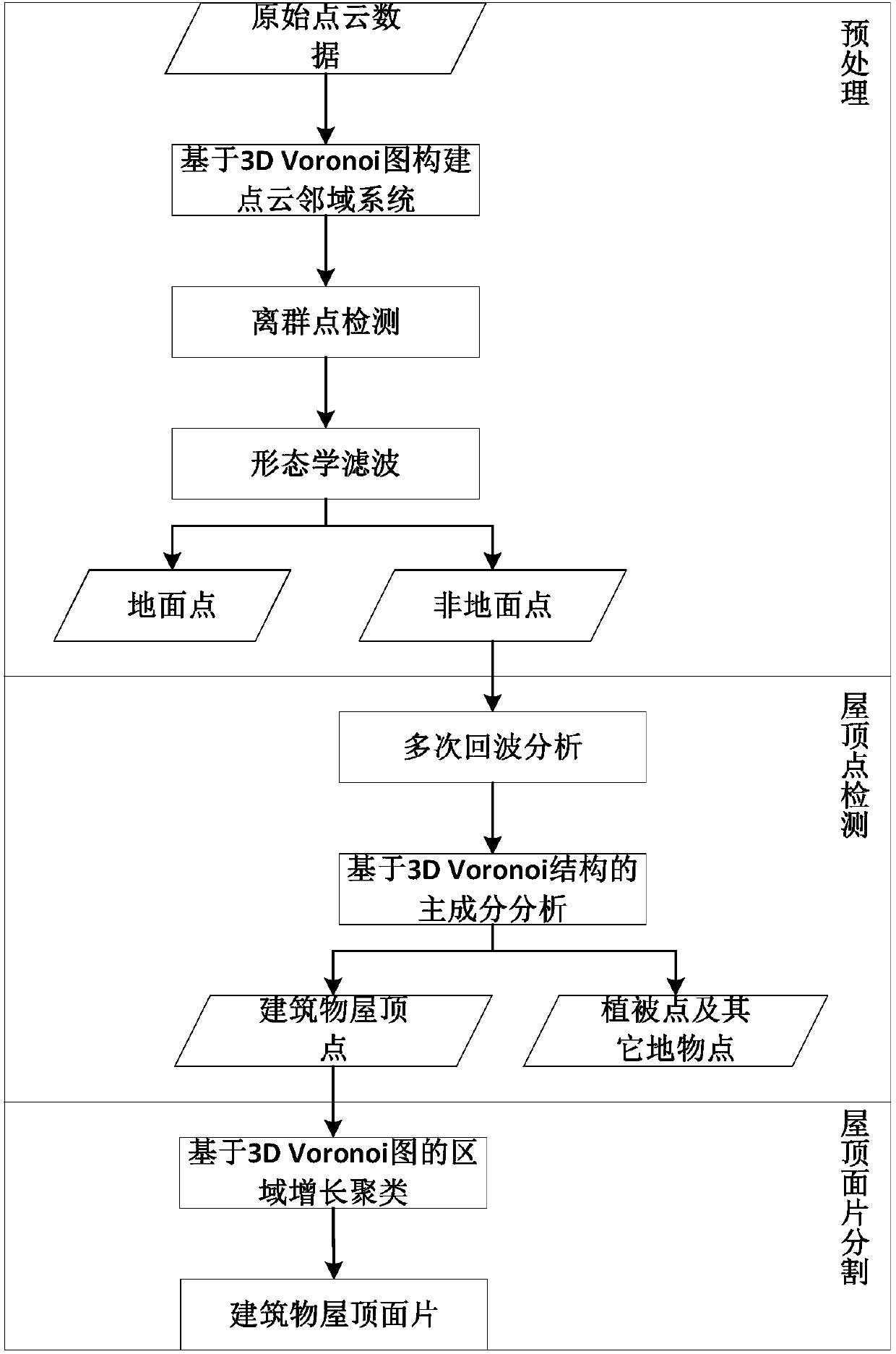
Airborne LiDAR point cloud roof patch segmentation method and system
InactiveCN107644452ADisplay spaceShow Proximity AnalysisElectromagnetic wave reradiation3D-image renderingVegetationPoint cloud
The invention provides an airborne LiDAR point cloud roof patch segmentation method and system. Based on a 3D Voronoi diagram, airborne LiDAR point cloud roof patch segmentation is carried out. The method comprises the steps that a point cloud neighborhood system is built based on the 3D Voronoi diagram for airborne LiDAR point cloud data; outlier detection is carried out, and outliers are deleted; morphological filtering is used to separate ground points and non-ground points in the point cloud data; the difference between a building and vegetation in multiple echo information of the point cloud data is used to initially distinguish building points and vegetation points to acquire initial building point cloud; based on a 3D Voronoi neighborhood, vegetation points and fracture line pointson the ridge of the building are removed from the initial building point cloud; the characteristic that a building wall normal vector is perpendicular to the direction of a plumb line is used to remove the wall points of the building to acquire the roof points of the building; and based on the 3D Voronoi neighborhood connectivity, the final building roof patch is acquired through area growth.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging method and system
InactiveUS8060180B2Improve time resolutionHigh resolutionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceCardiac phase
Exemplary method, systems and arrangements can be provided for creating a high-resolution magnetic resonance image (“MRI”) or obtaining other information of a target. For example, radio-frequency (“RF”) pulses can be transmitted toward the target by a RF transmitter of a MRI apparatus. In response, multiple echoes corresponding to each pulse may be received from the target. Data from each of the echoes can be assigned to a single line of k-space of a distinct image, and stored in memory of the apparatus. An image of the target, velocity data and / or acceleration data associated with a target can be generated as a function of the data. In one exemplary embodiment, the data from different echoes can be assigned to the same k-space line and to different cardiac phases. The exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure can be utilized for the heart or for any other anatomical organ or region of interest.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Dual gradient echo pulse sequence using interleaved spiral-out spiral-in k-space trajectories
ActiveUS7368910B2More sensitivityInhibition effectMagnetic measurementsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsHematological testPulse sequence
Measurements of functional, hemographic, and blood flow parameters use a multiple echo or spin echo gradient pulse sequence whereby an early echo is acquired near the beginning of the pulse sequence which avoids saturation effects and a later echo near the end of the pulse sequence which can provide information with more sensitivity to a contrast agent for a susceptibility weighted image.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
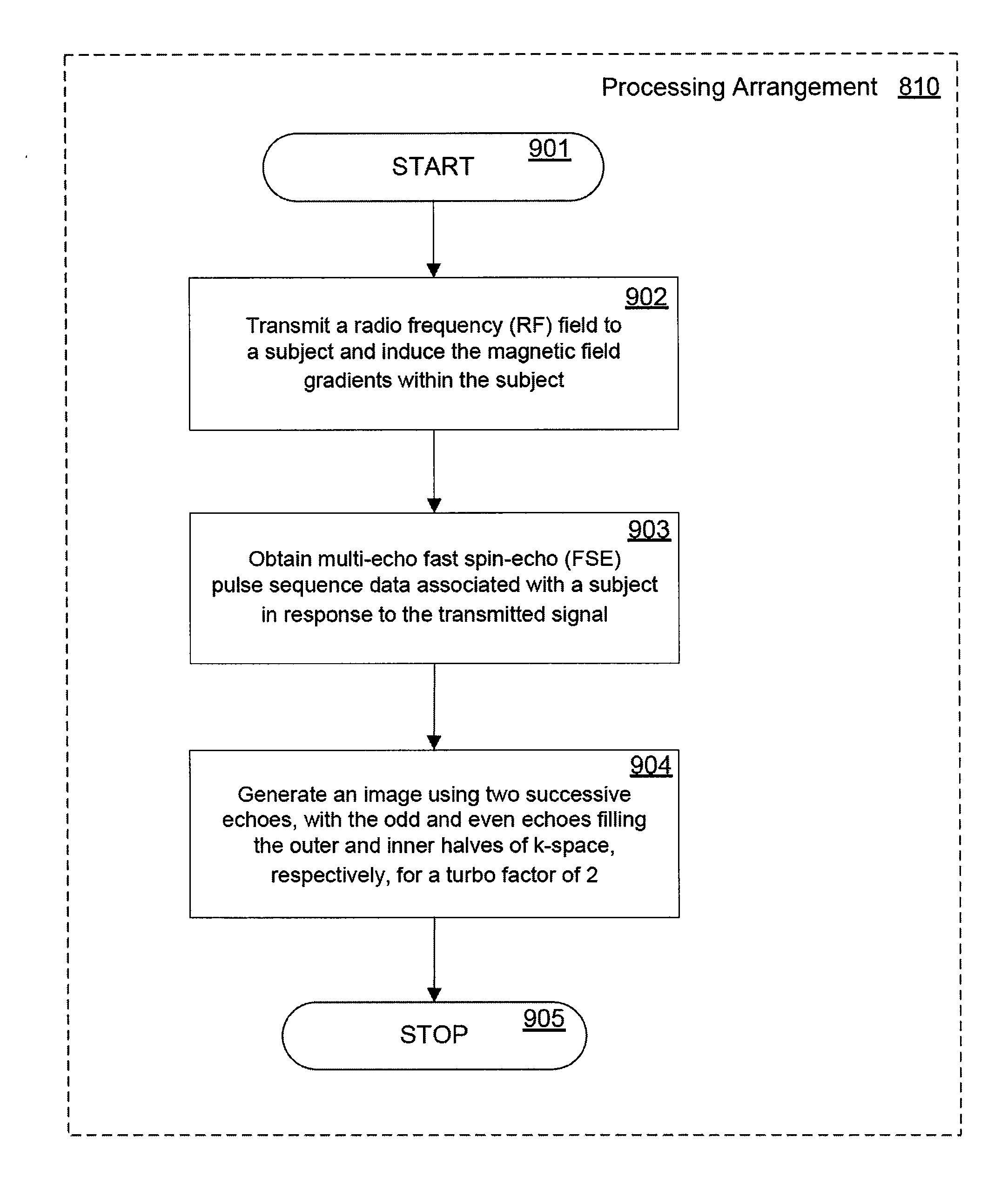
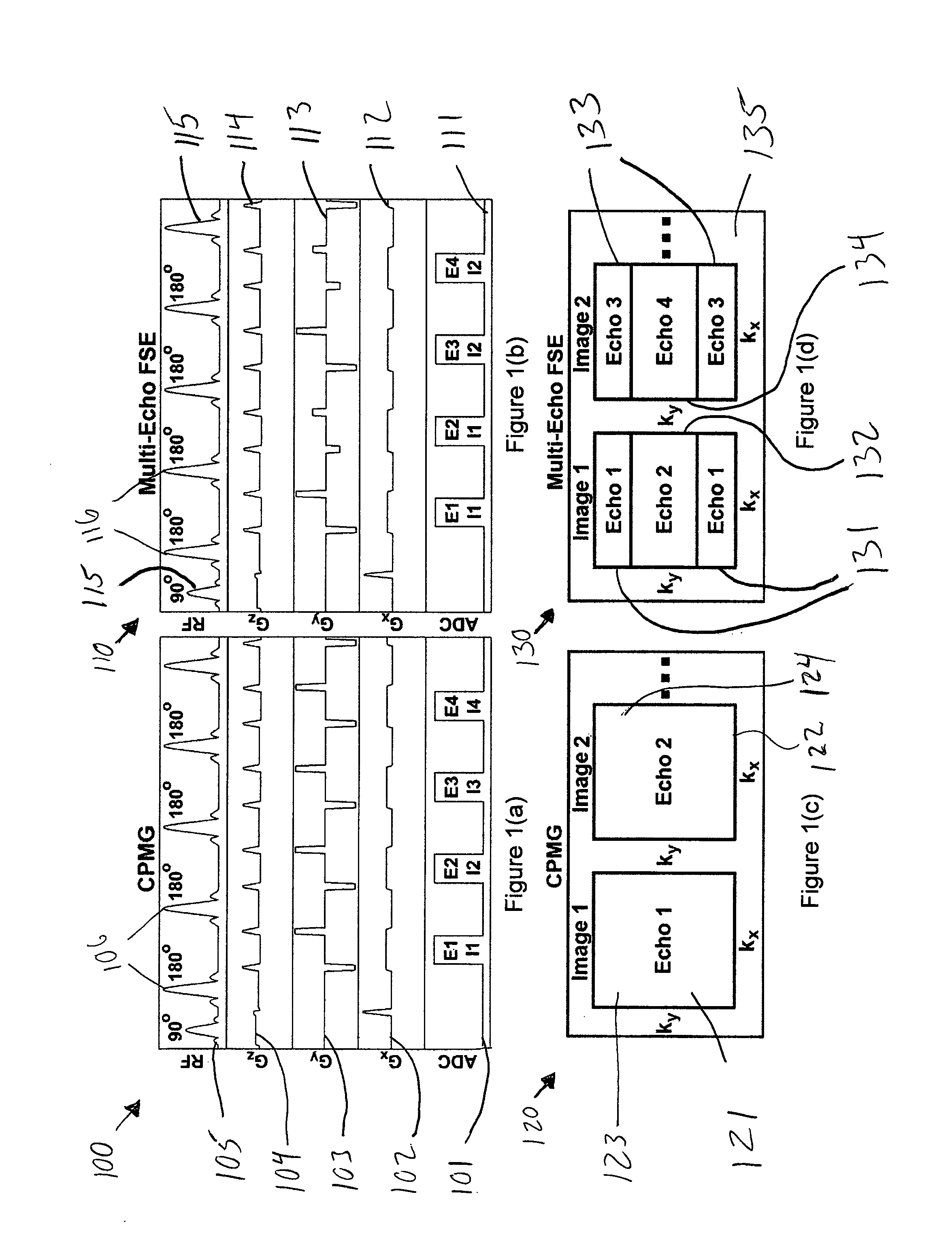
System, method and computer-accessible medium for providing breath-hold multi-echo fast spin-echo pulse sequence for accurate r2 measurement
ActiveUS20100301860A1Accurate measurementMean usedMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionAnatomical structuresFast spin echo
Exemplary embodiments of system, method and computer-accessible medium can be provided in accordance with the present disclosure can be provided for generating a plurality of images associated with at least one anatomical structure using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data. For example, using such exemplary embodiments, it is possible to obtain at least one multi-echo fast spin-echo (FSE) pulse sequence based on the MRI data, which can include, e.g., hardware specifications of the MRI system. Further, it is possible to generate each of the images based on a particular arrangement of multiple echoes produced by the multi-echo FSE pulse sequence(s).
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
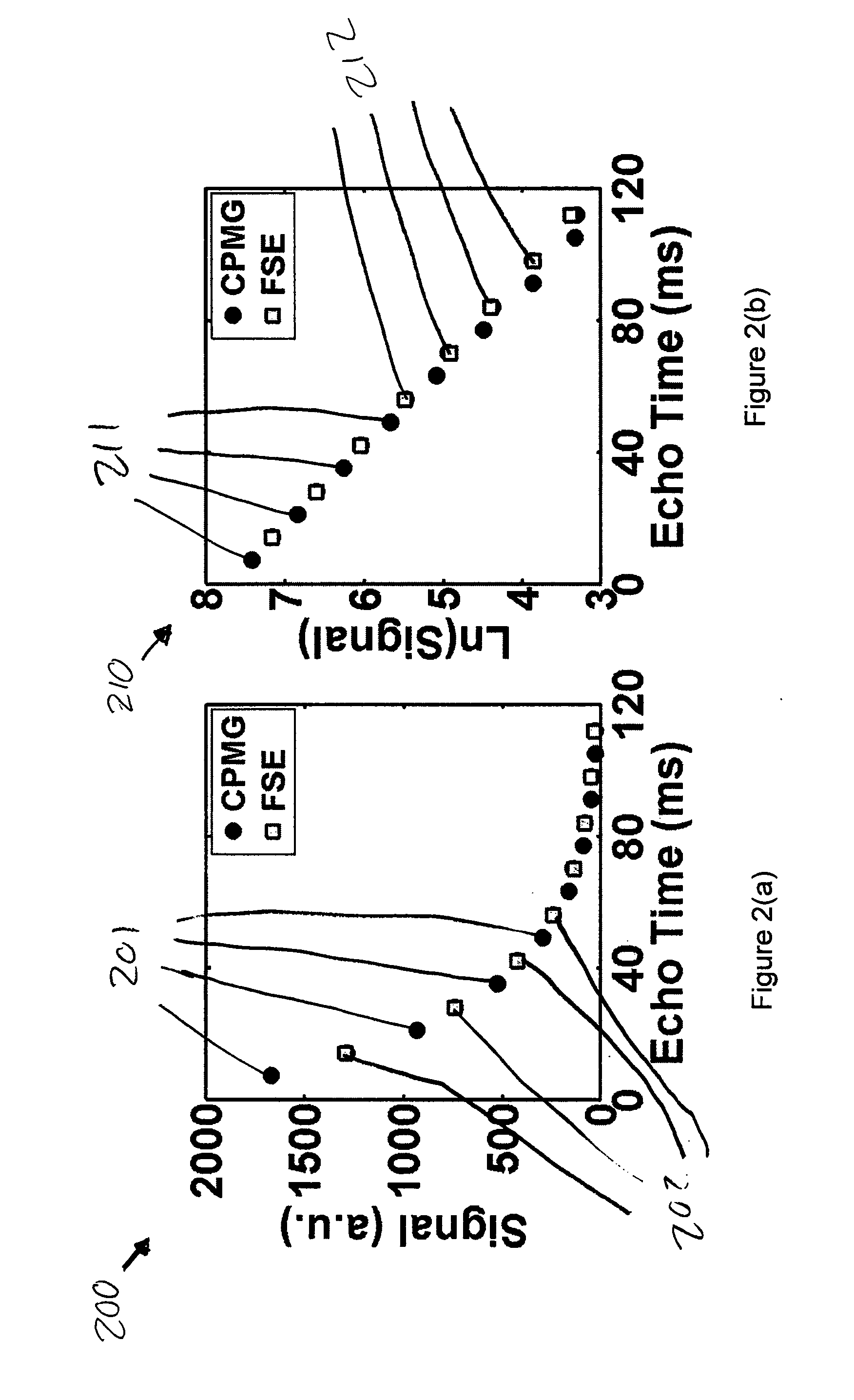
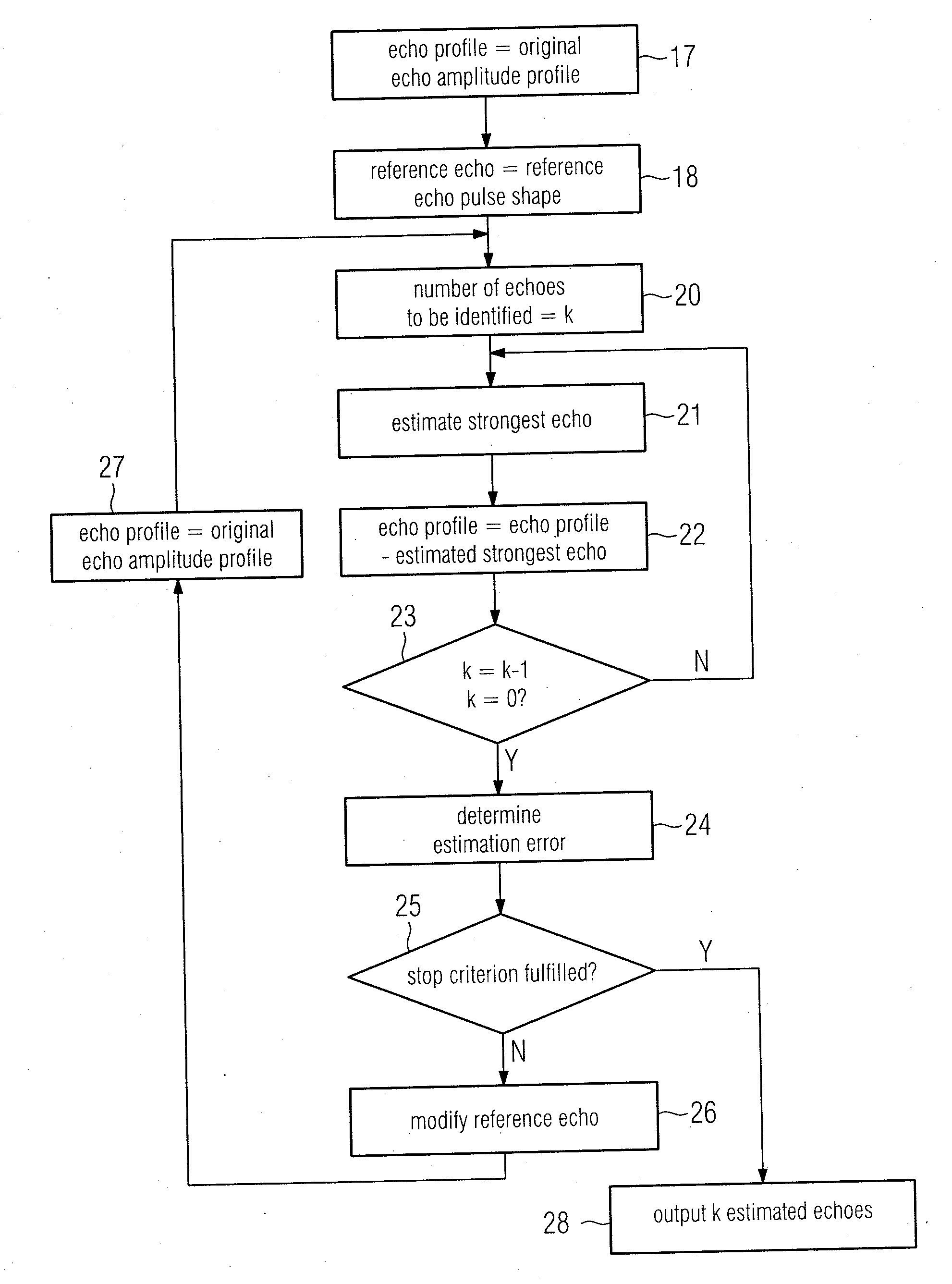
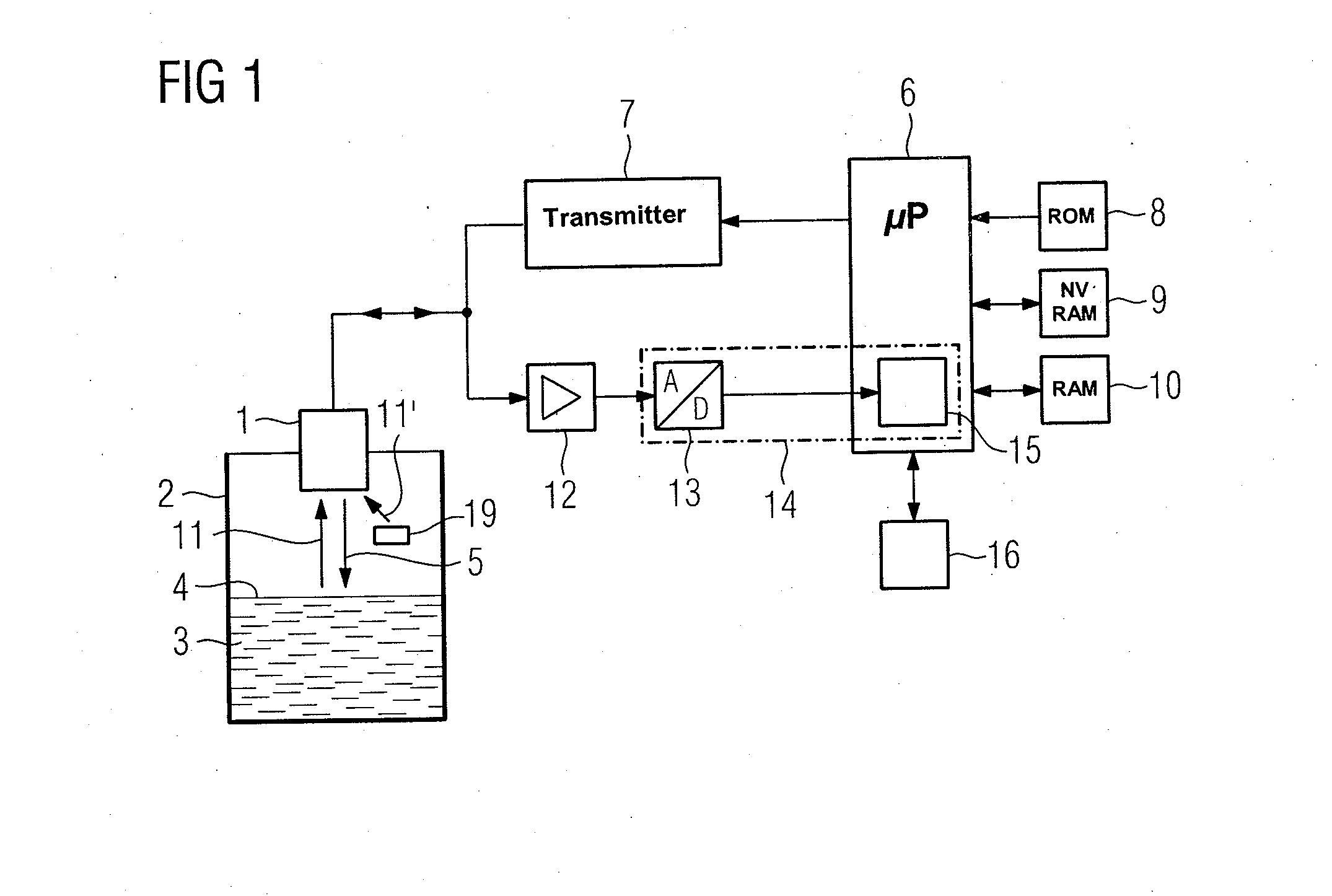
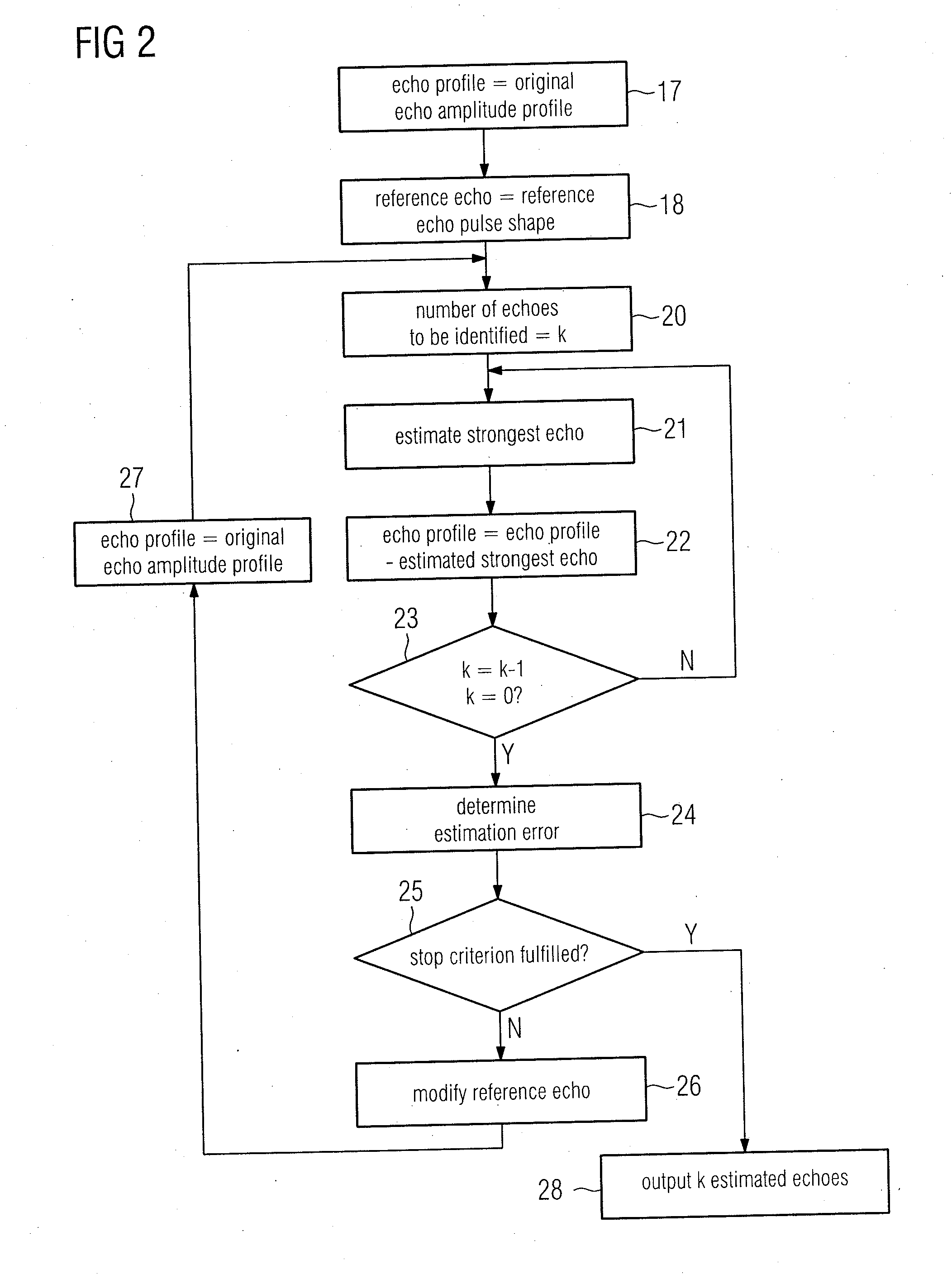
Method for Processing an Echo Amplitude Profile Generated by a Pulse-Echo Ranging System
InactiveUS20120092210A1Effective estimateLevel indicatorsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEcho detectionComputer science
A method for considering an echo amplitude profile as a result of convoluting a single echo with a channel response sequence, wherein for multiple echo detection, an estimation task is broken into three major steps comprising estimating a channel response, recovering a full shape of a single echo, and iteratively updating the channel response and echo shape to increase their accuracy. The estimation of the channel response is treated as a single echo detection problem and includes estimating the strongest echo for its position and amplitude, removing an echo corresponding to this recovered channel from the echo amplitude profile, and repeating the preceding steps for the next strongest echo.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography with chemical shift encoding for fat suppression
ActiveUS20140043022A1Rapid and reliable mannerEfficiently signaledDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFat suppressionData set
The invention relates to a method of performing contrast enhanced first pass magnetic resonance angiography, the method comprising: acquiring (302) magnetic resonance datasets of a region of interest using a single- or multi-echo data acquisition technique, wherein the echo times of the one or multiple echoes are flexible, wherein at the time of the data acquisition the region of interest comprises fat, water and a contrast agent, processing (304) the datasets using a generalized Dixon water-fat separation technique to eliminate the signal originating from the fat from the background for reconstruction of an image data set.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Evaluation device and method for determining a characteristic variable for the position of a boundary surface in a container
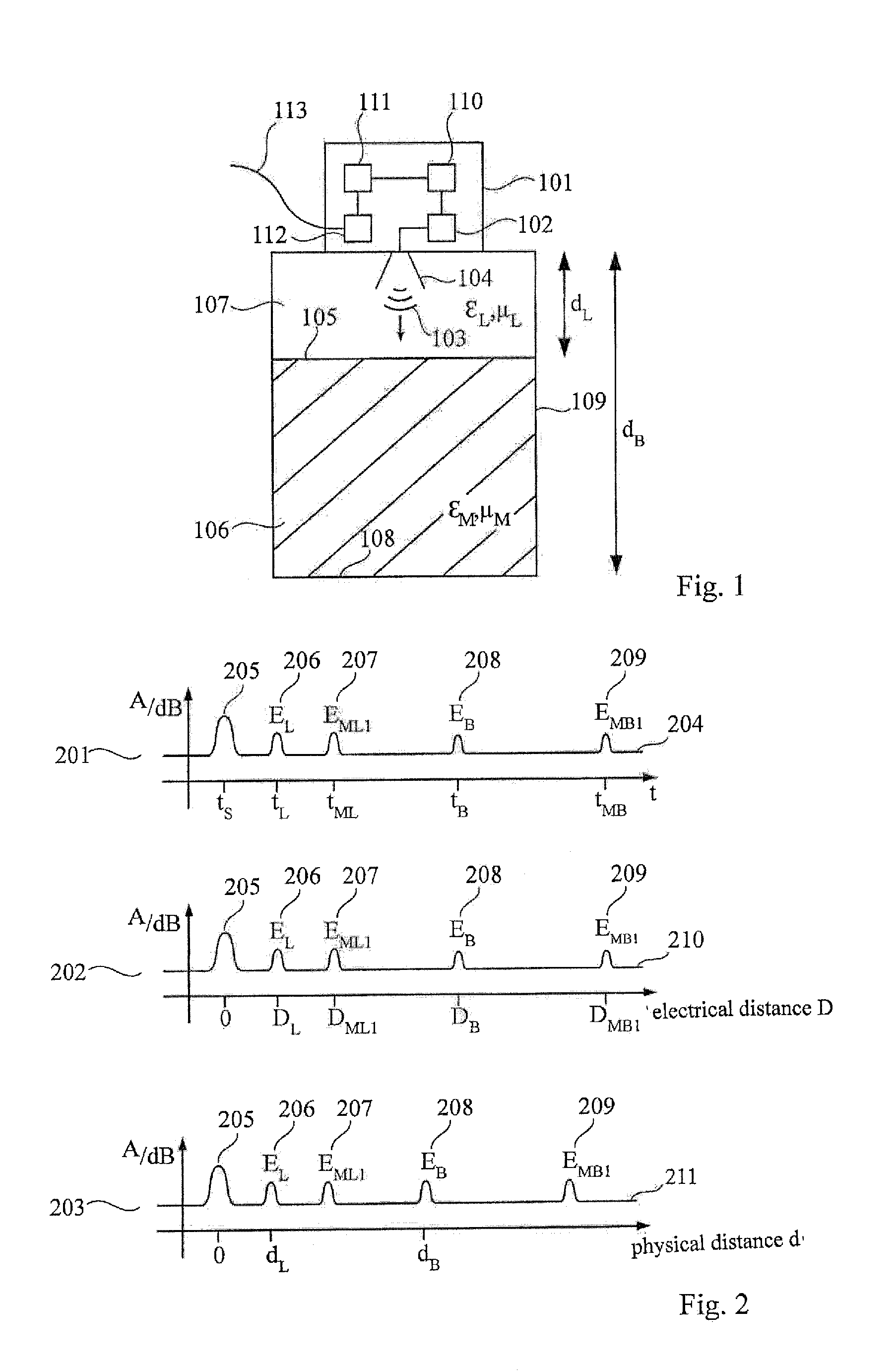
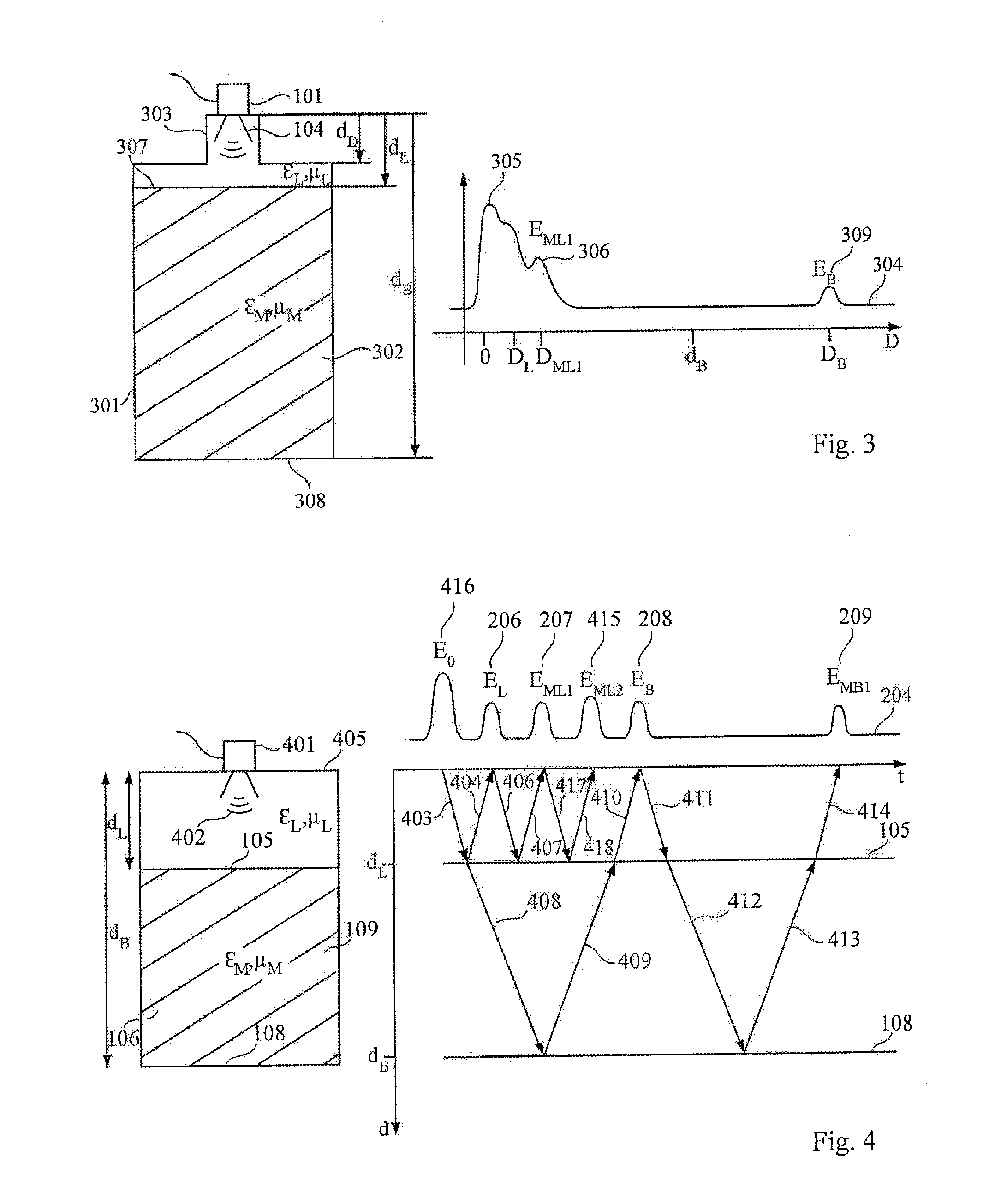
ActiveCN102798434AVolume measurement apparatus/methodsLevel indicators by physical variable measurementMechanical engineeringMultiple echo
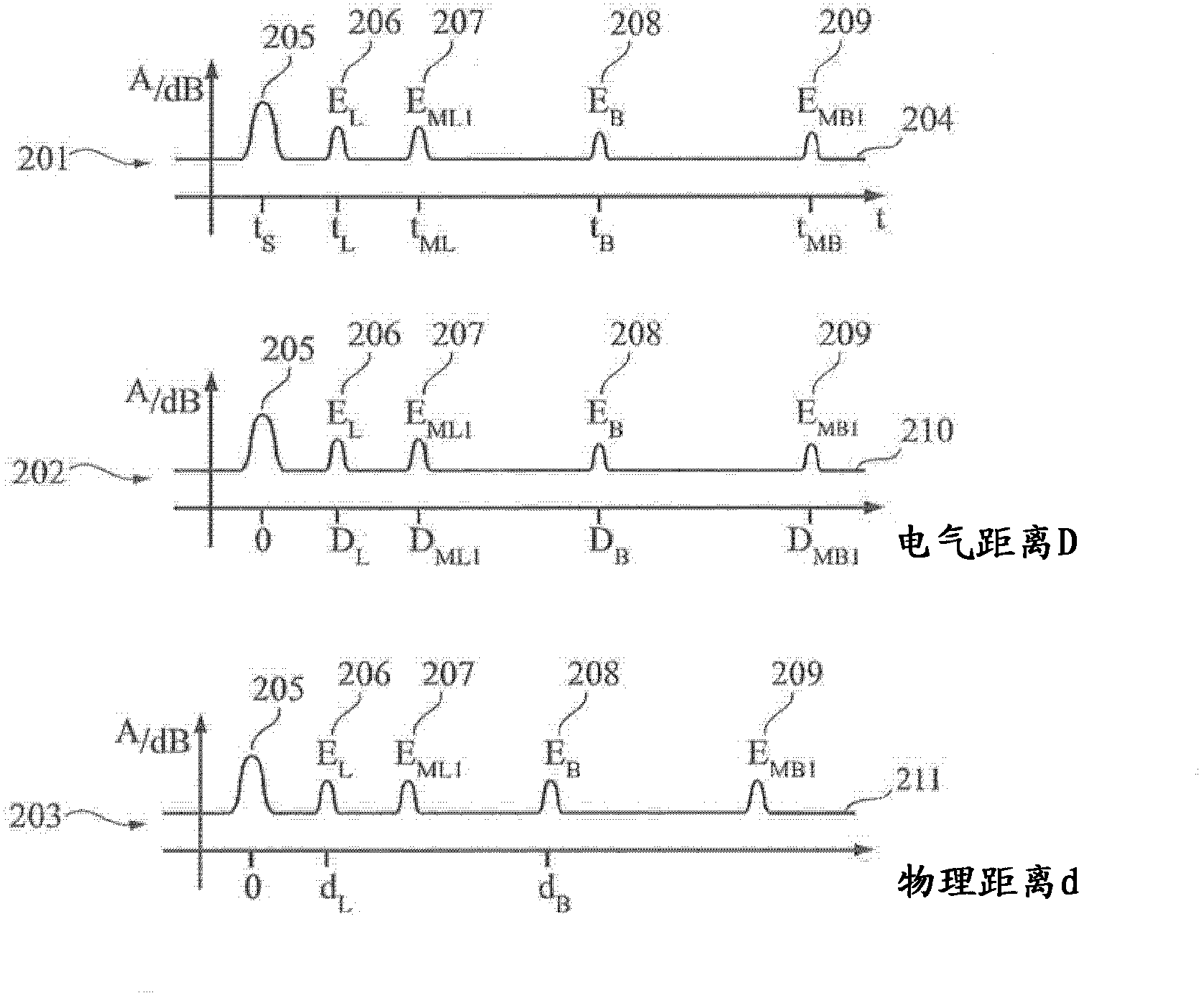
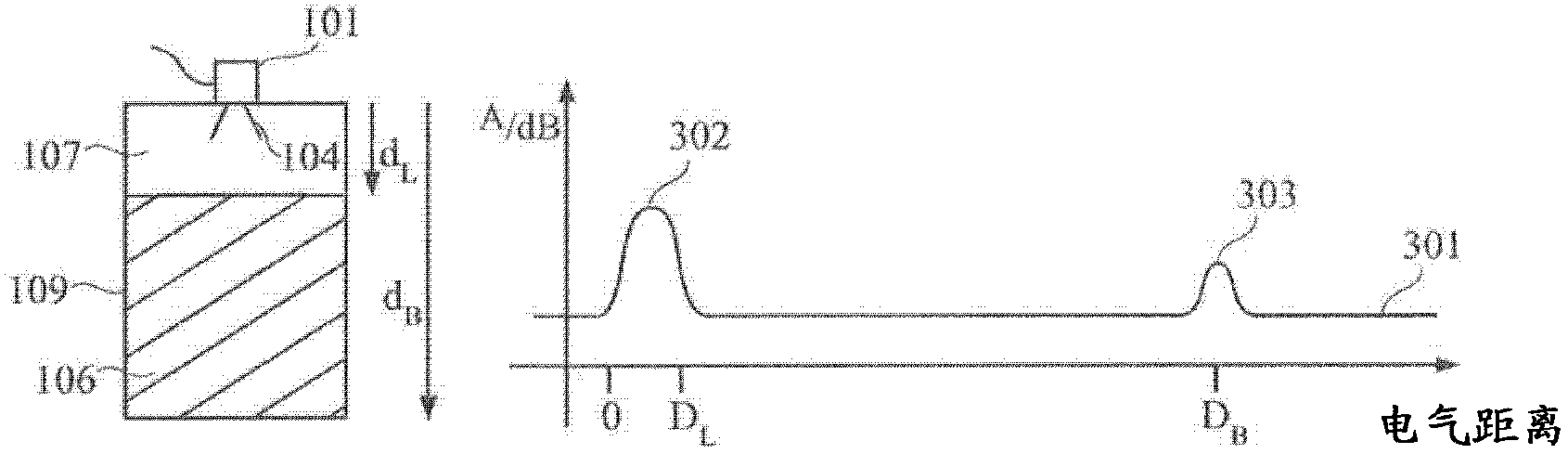
The invention describes an evaluation device (701) and a method for determining a characteristic variable (dL) for the position of a boundary surface (105, 108) in a container (109, 501, 601), wherein multiple echoes (207, 209, 405, 611) including at least one stage (N, N1, N2) is identified in the echo curve (204, 427), wherein the characteristic variable (dL) of the boundary surface in the container is determined based on the positions (DML1, DML2, DMB1) of the multiple echoes and the stages (N, N1, N2)of the multiple echoes.
Owner:VEGA GRIESHABER GMBH & CO
Establishment of parameters to adjust a magnetic field shim for a magnetic resonance examination of a patient
ActiveUS8362771B2Efficiently obtainedShort amount of timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionExcitation signalPatients position
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
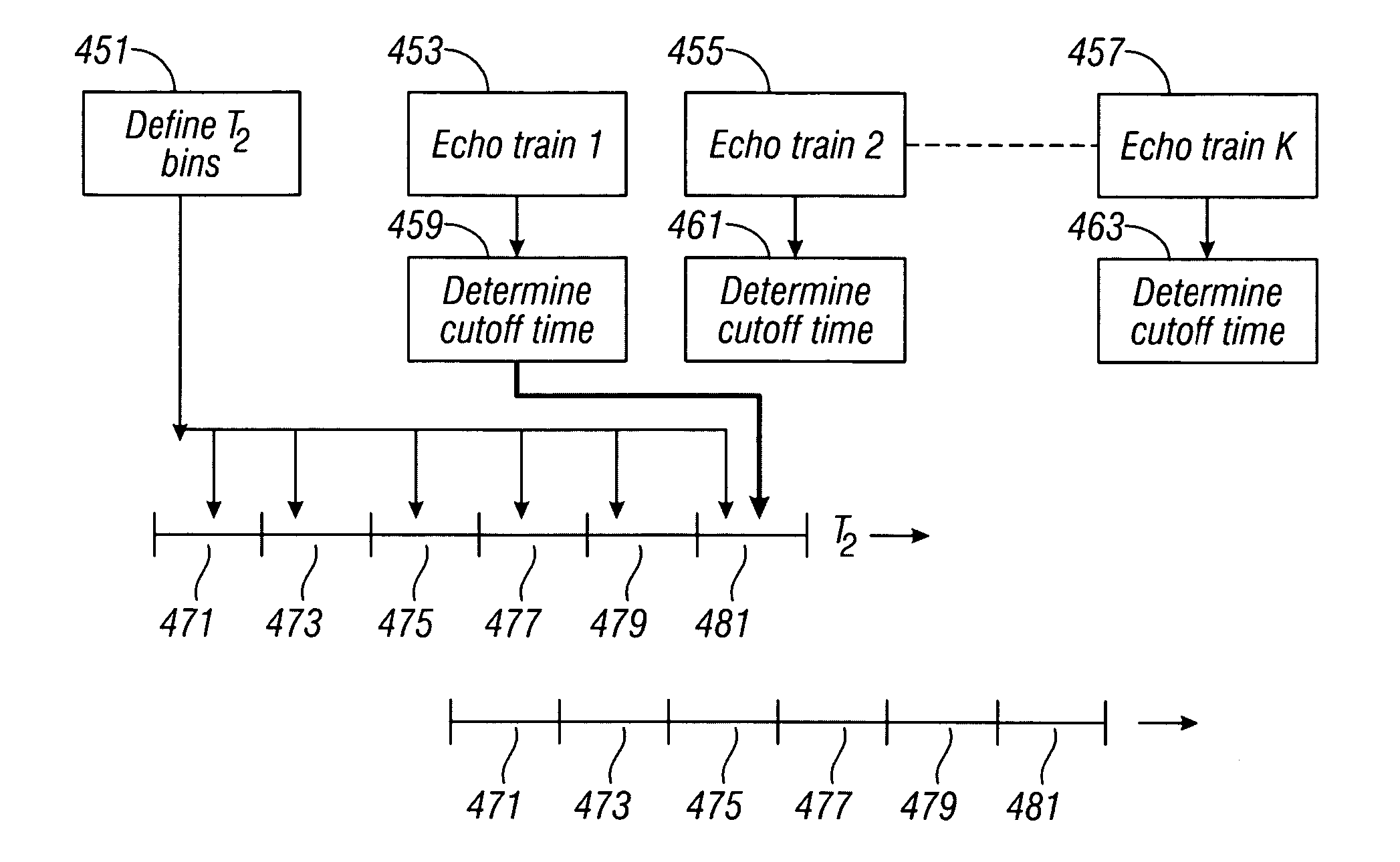
Multiple echo train inversion
InactiveUS20060158184A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMultiple echoWaiting time
A method for inversion of multiple echo trains with different wait times uses a cutoff times for each of the echo trains for full polarization. Simultaneous inversion is carried out for T2 bins where full polarization exists
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com