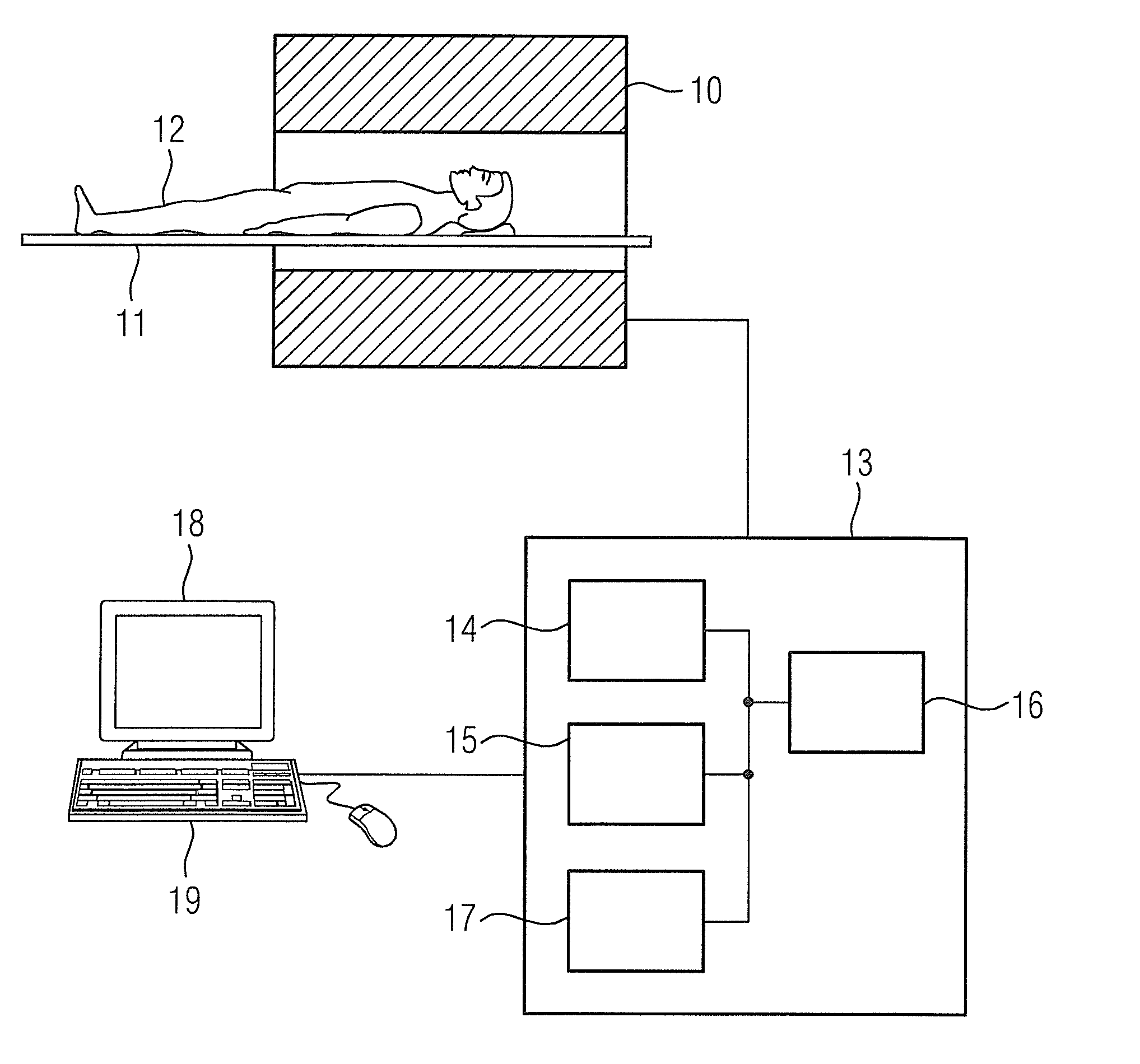
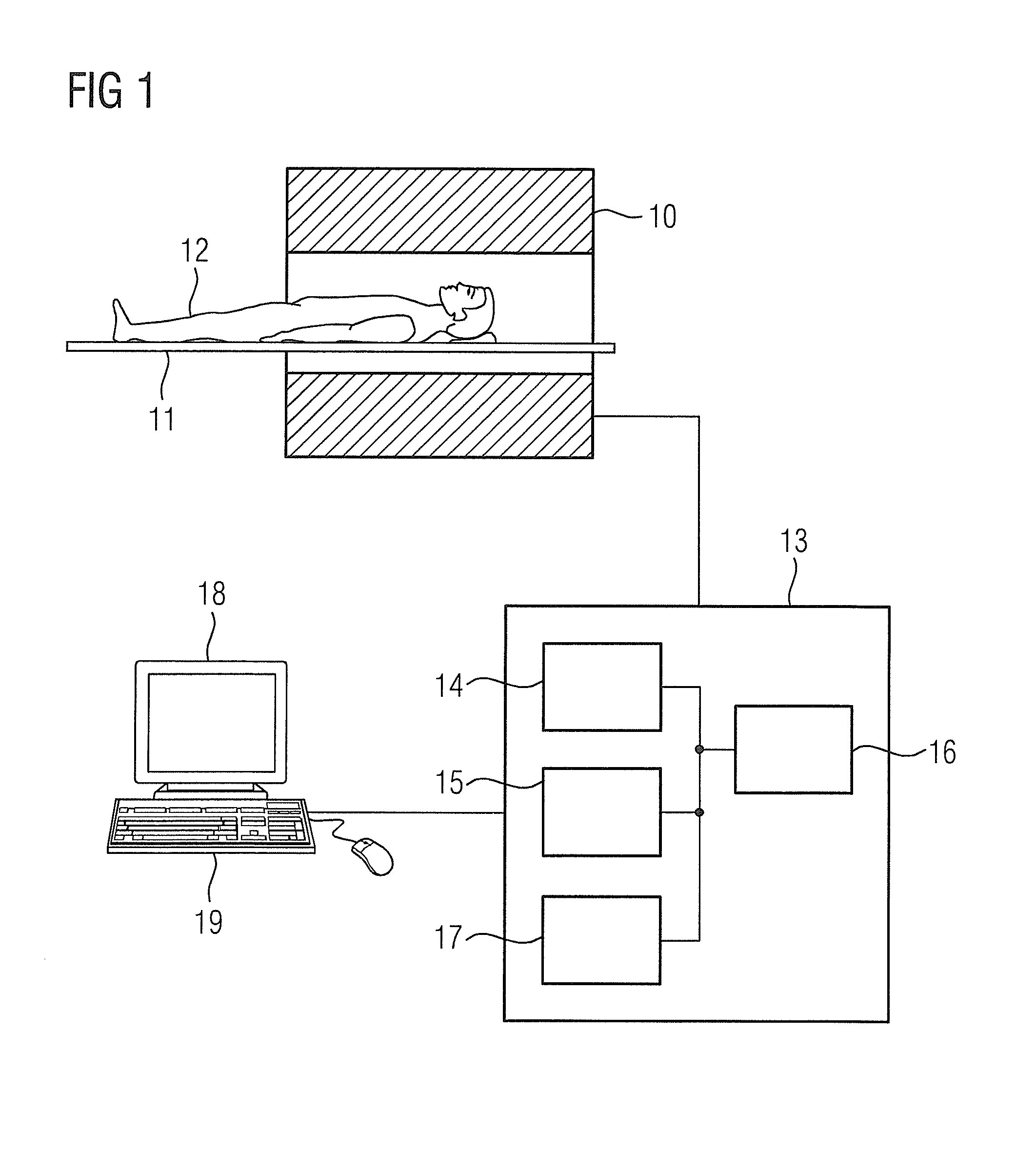
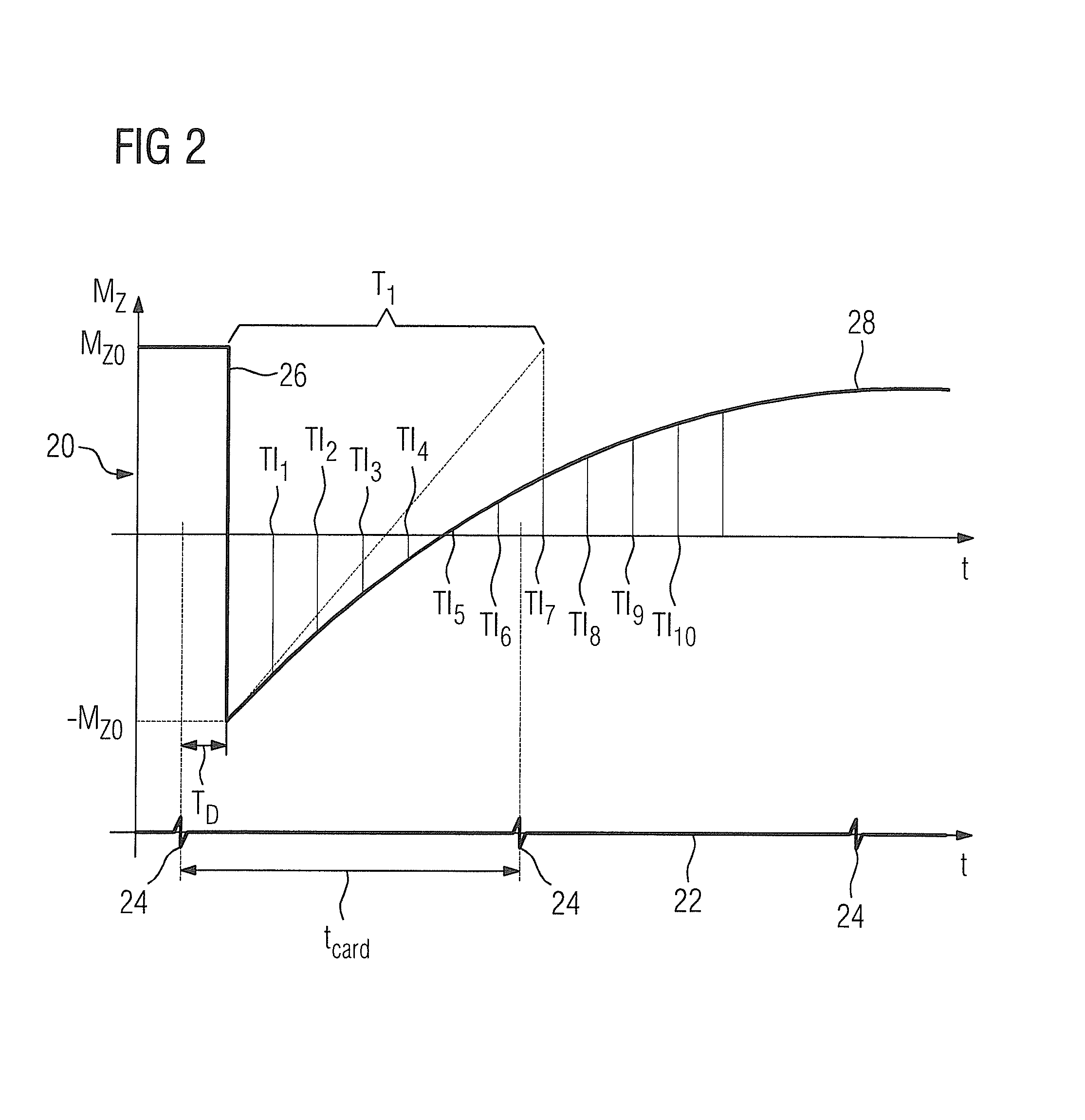
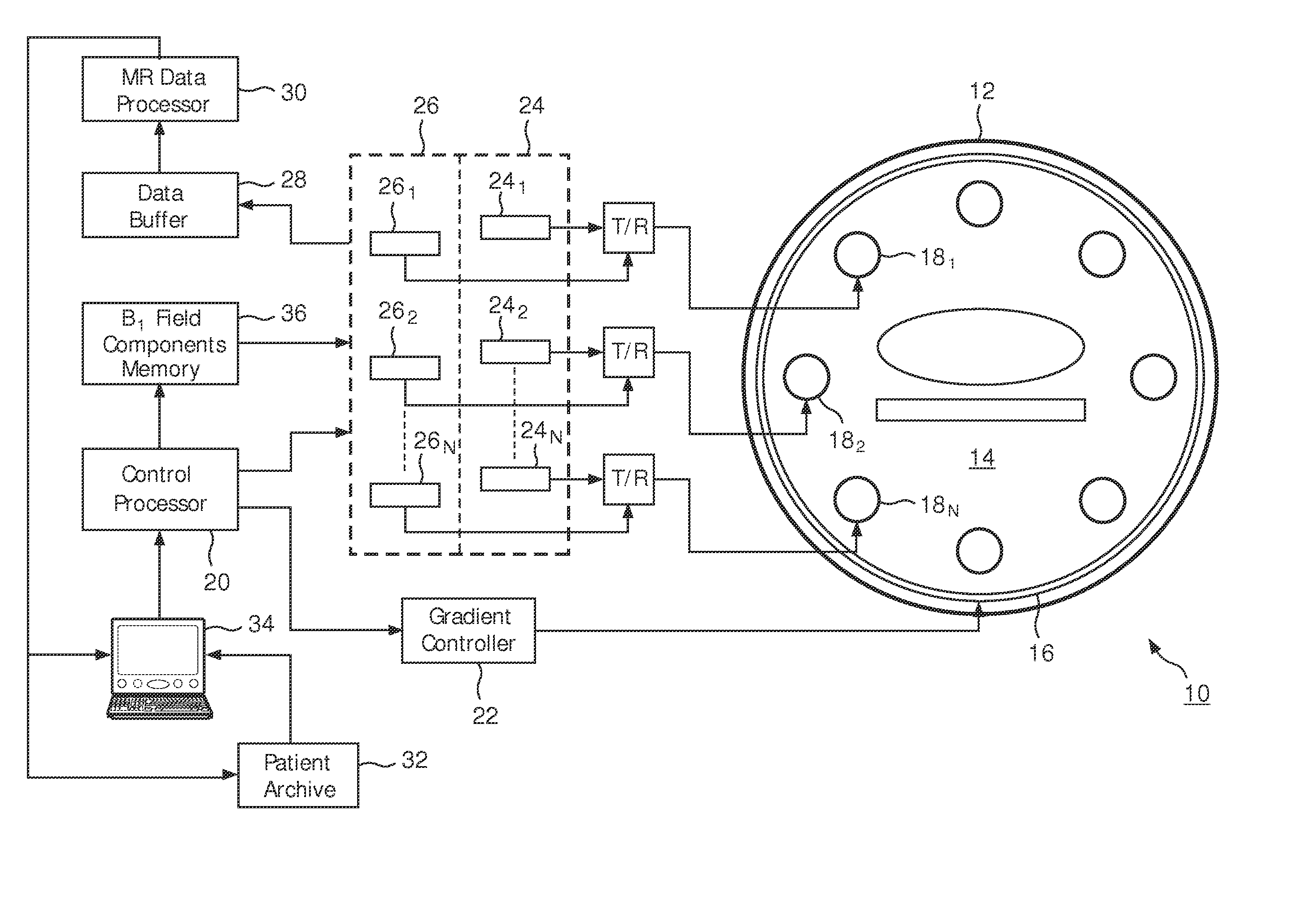
Patents
Literature
93 results about "Magnetic resonance sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
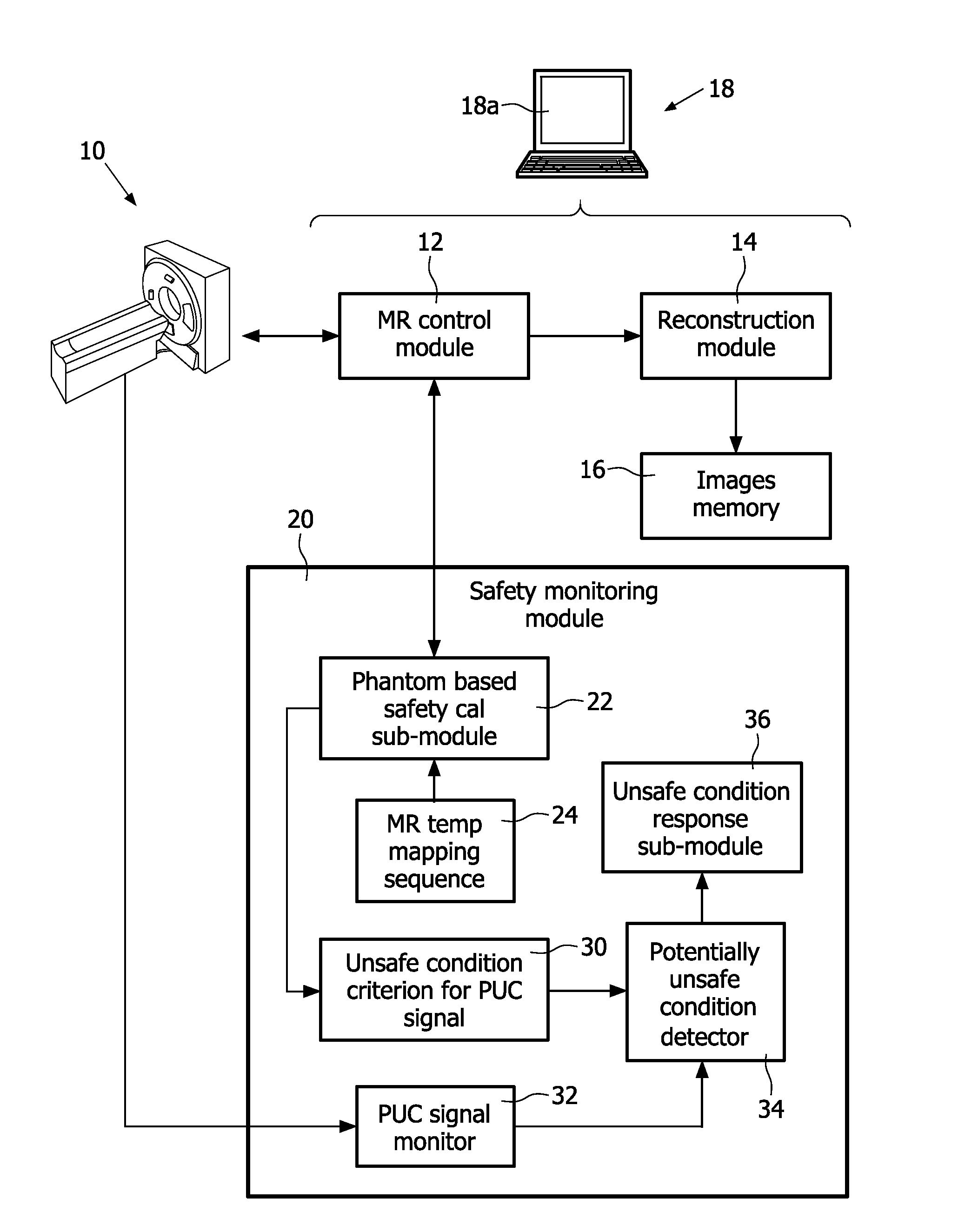
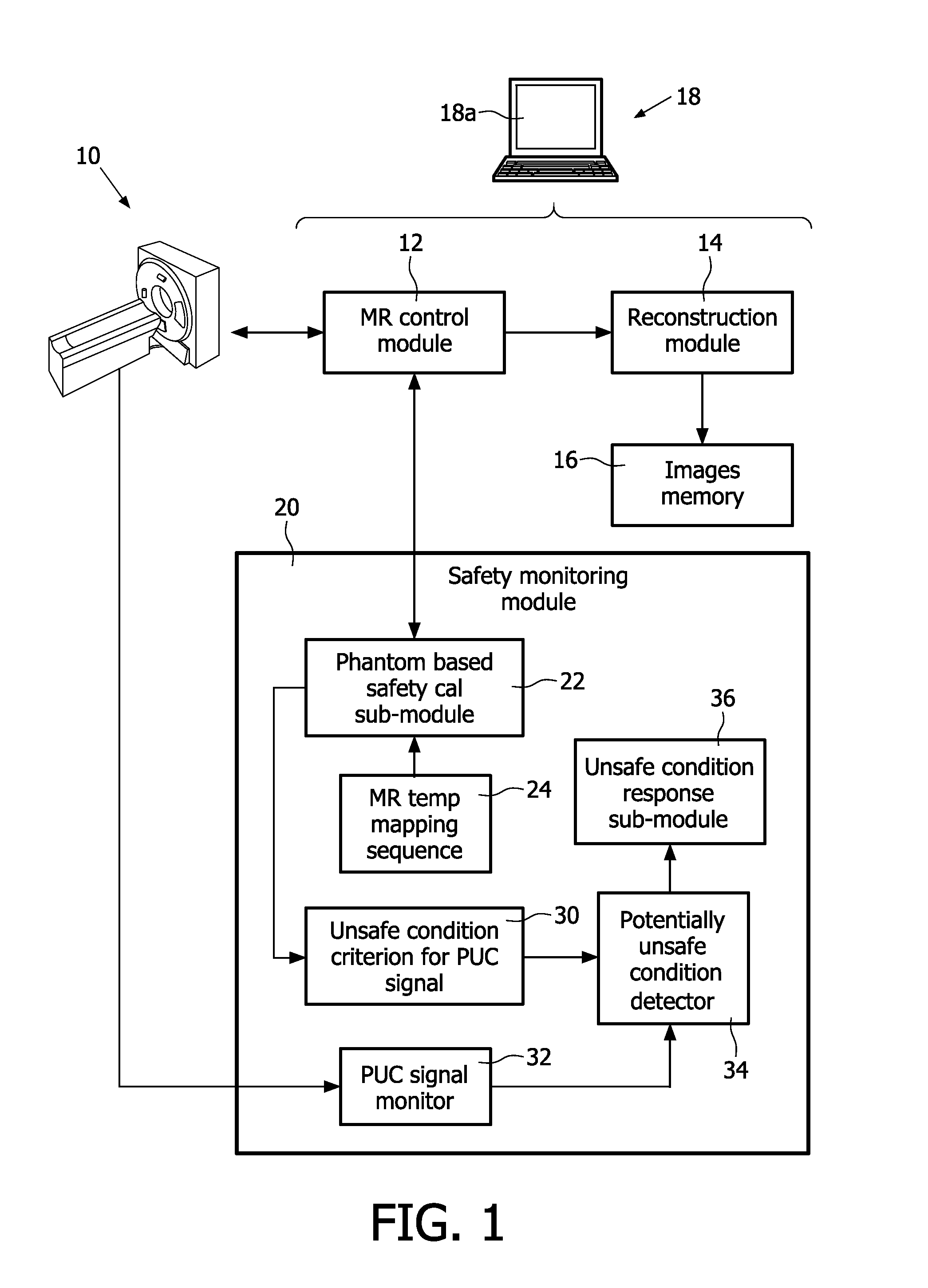
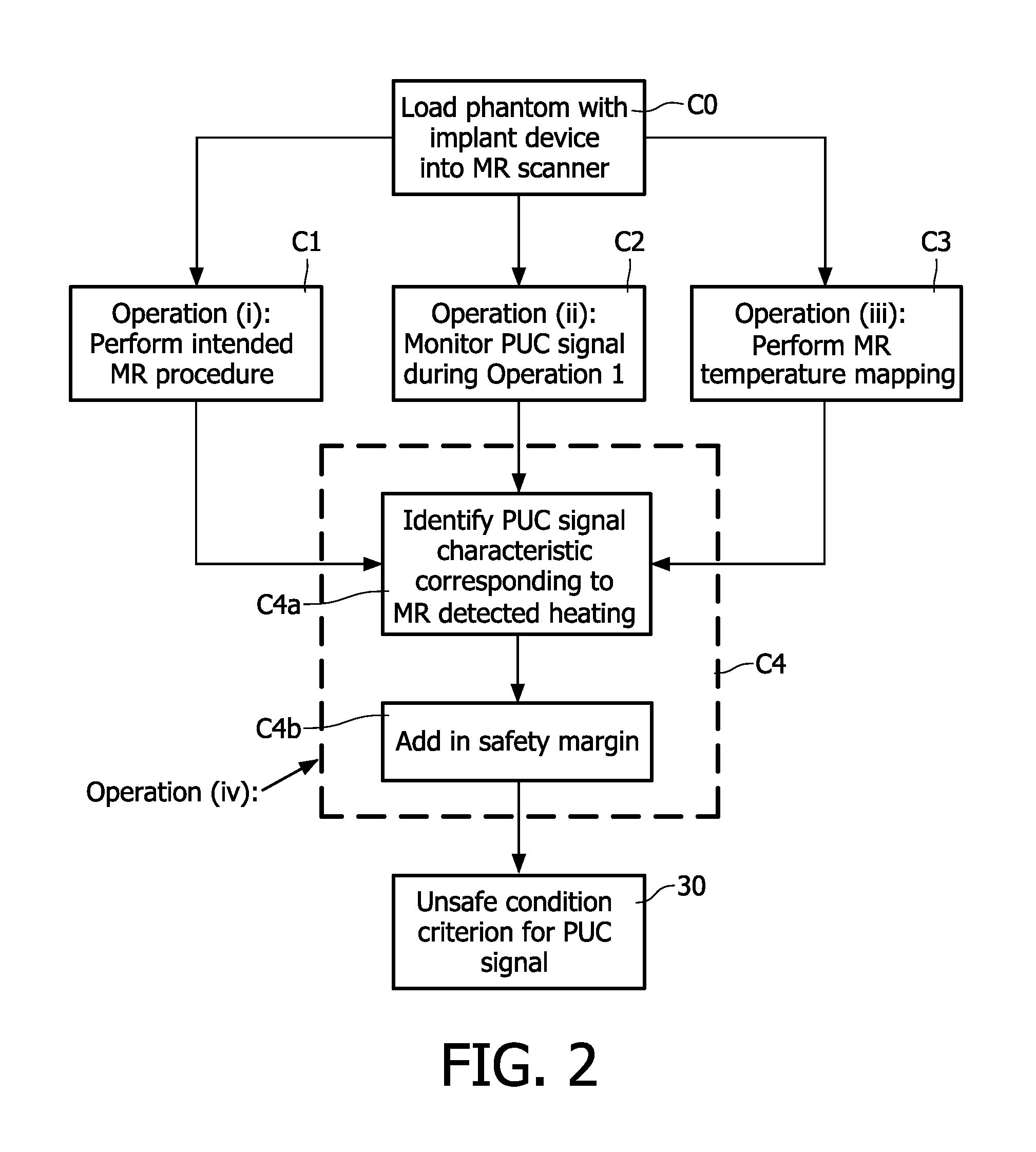
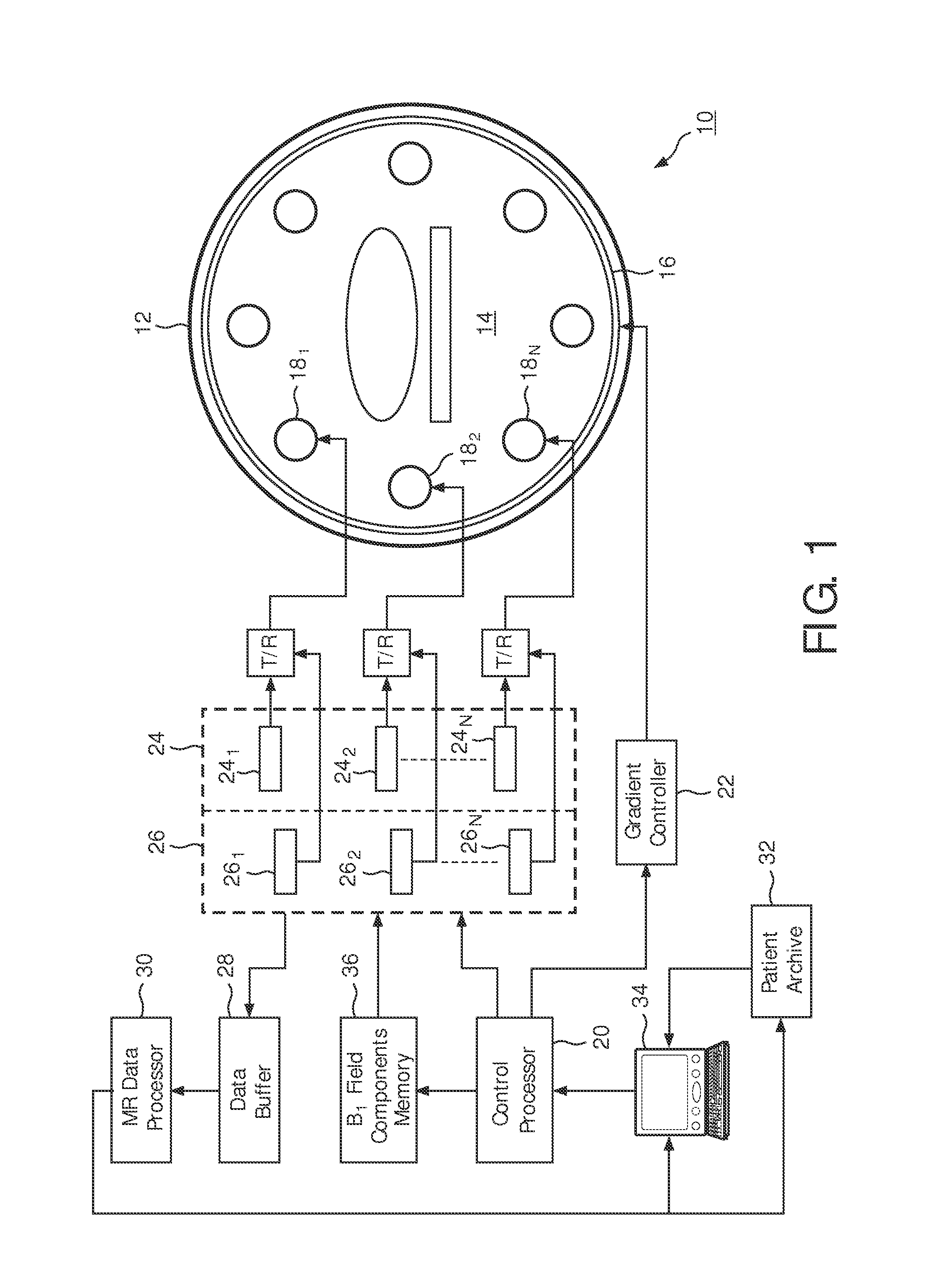
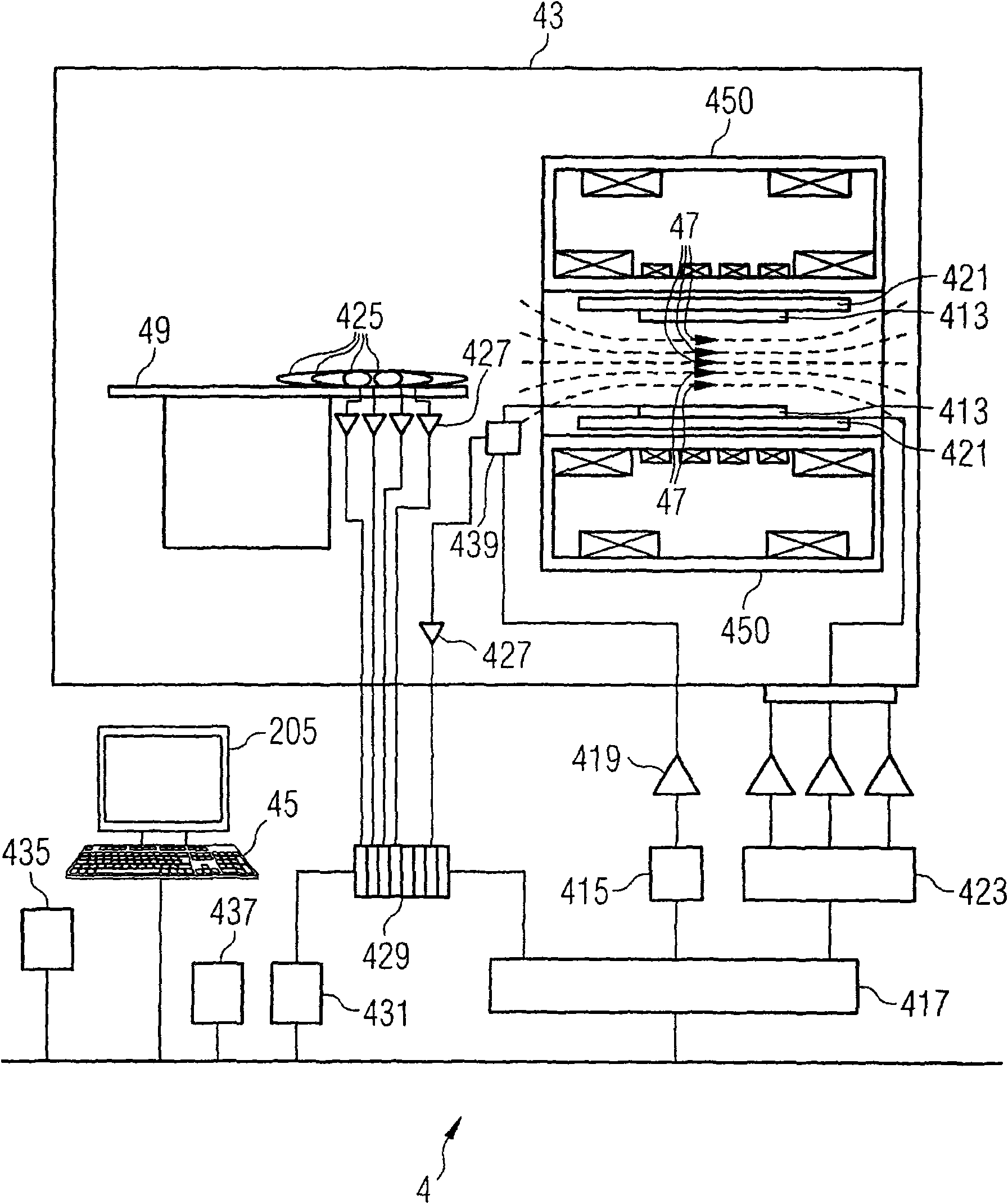
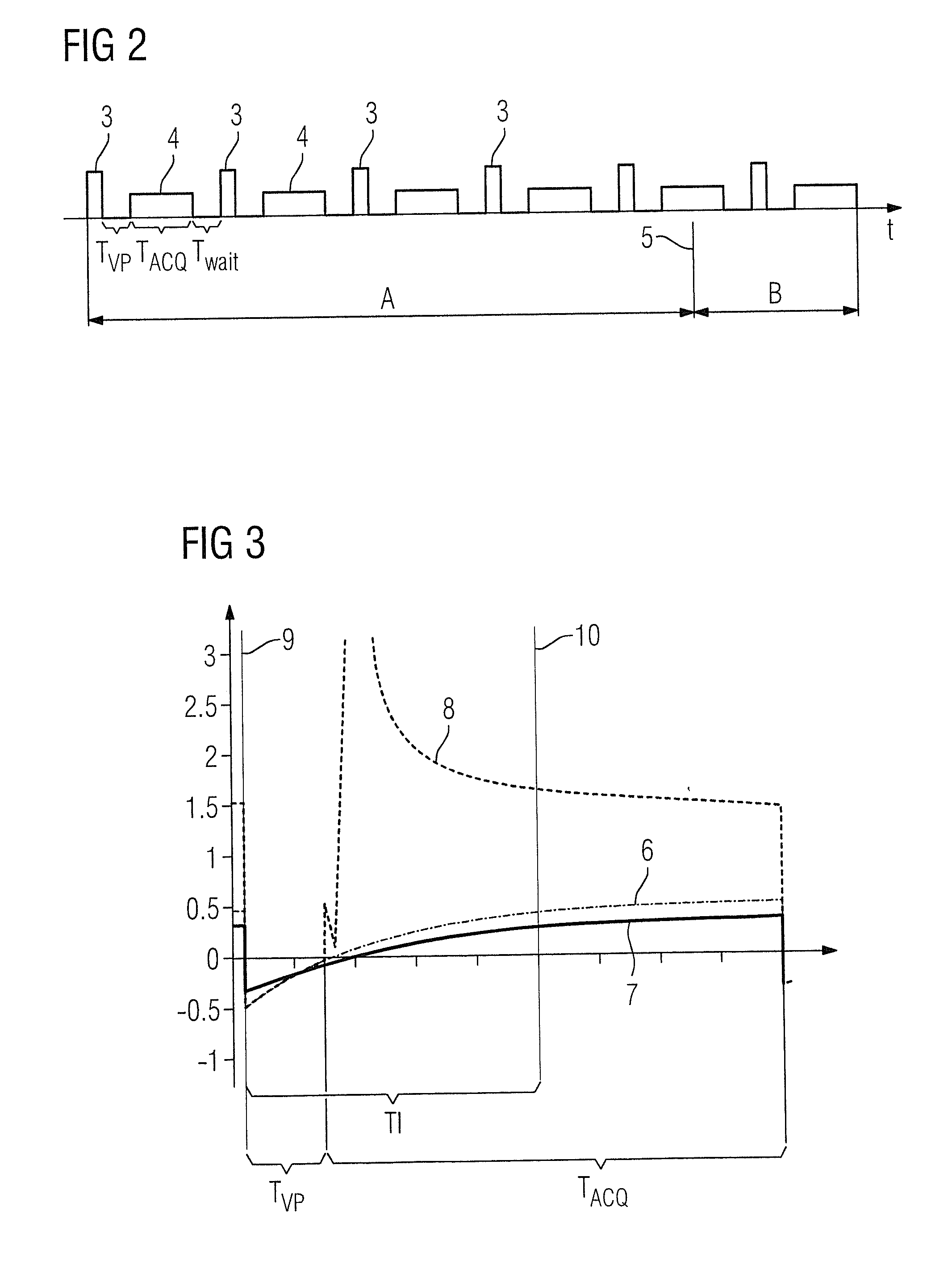
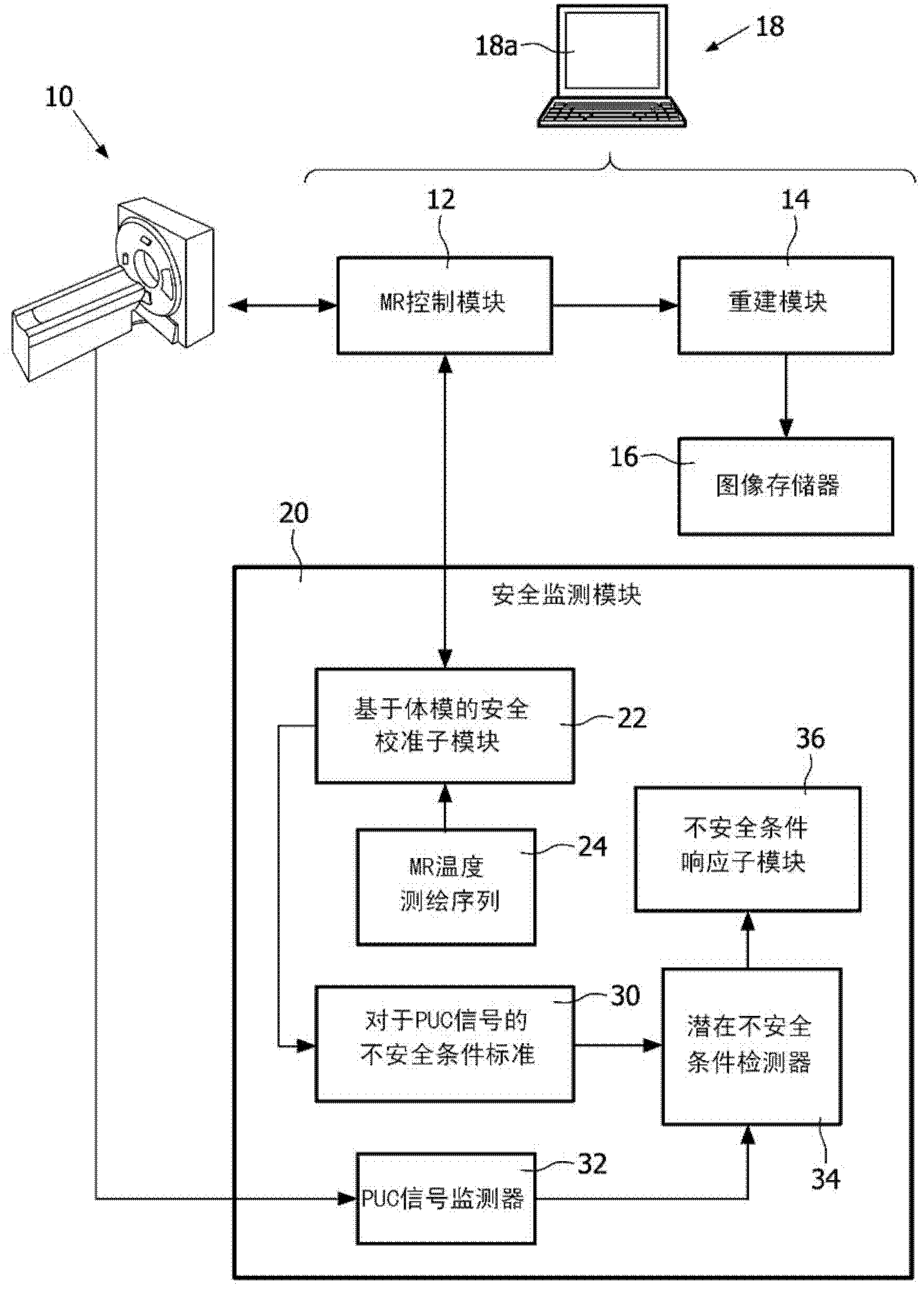
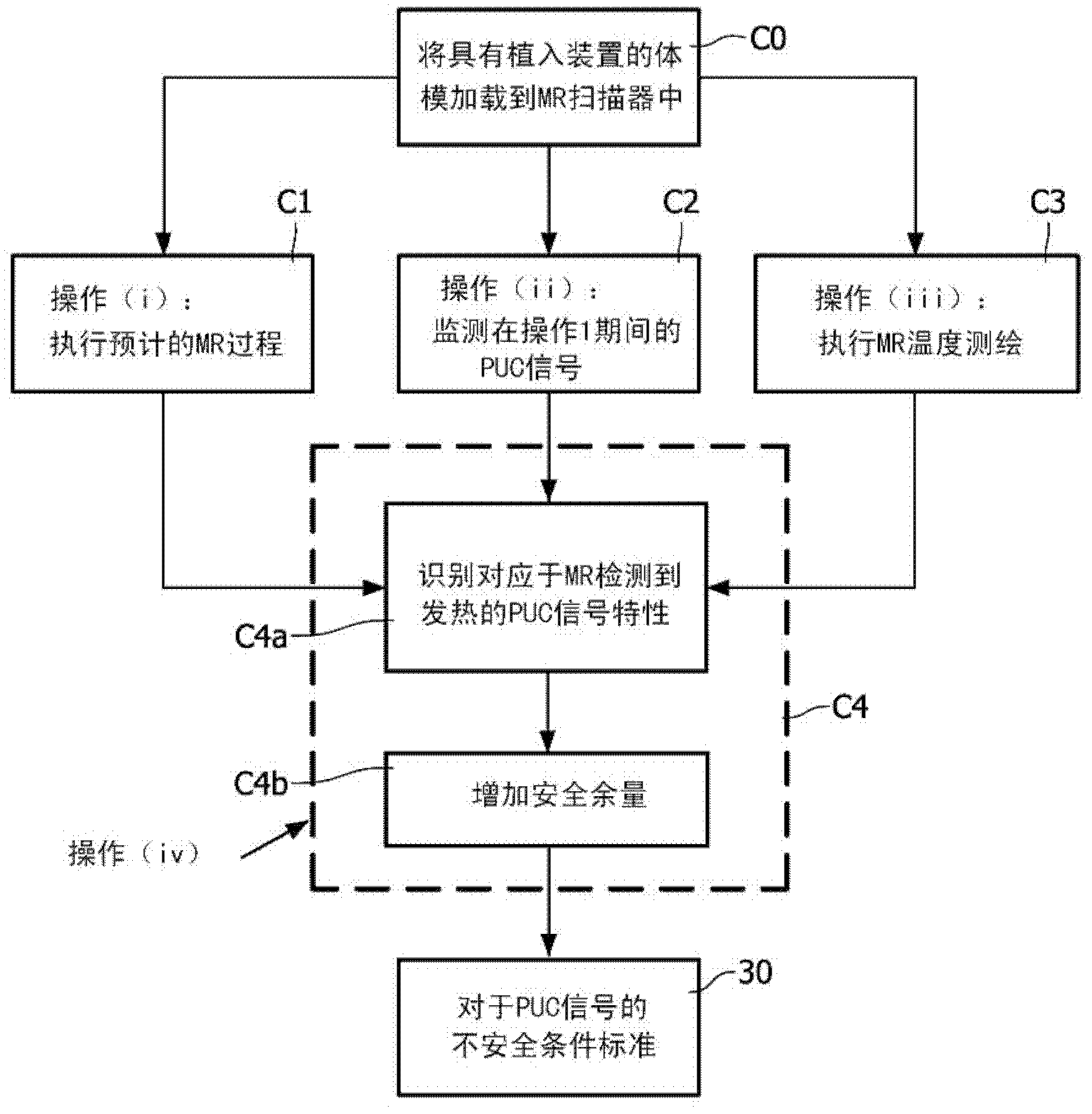
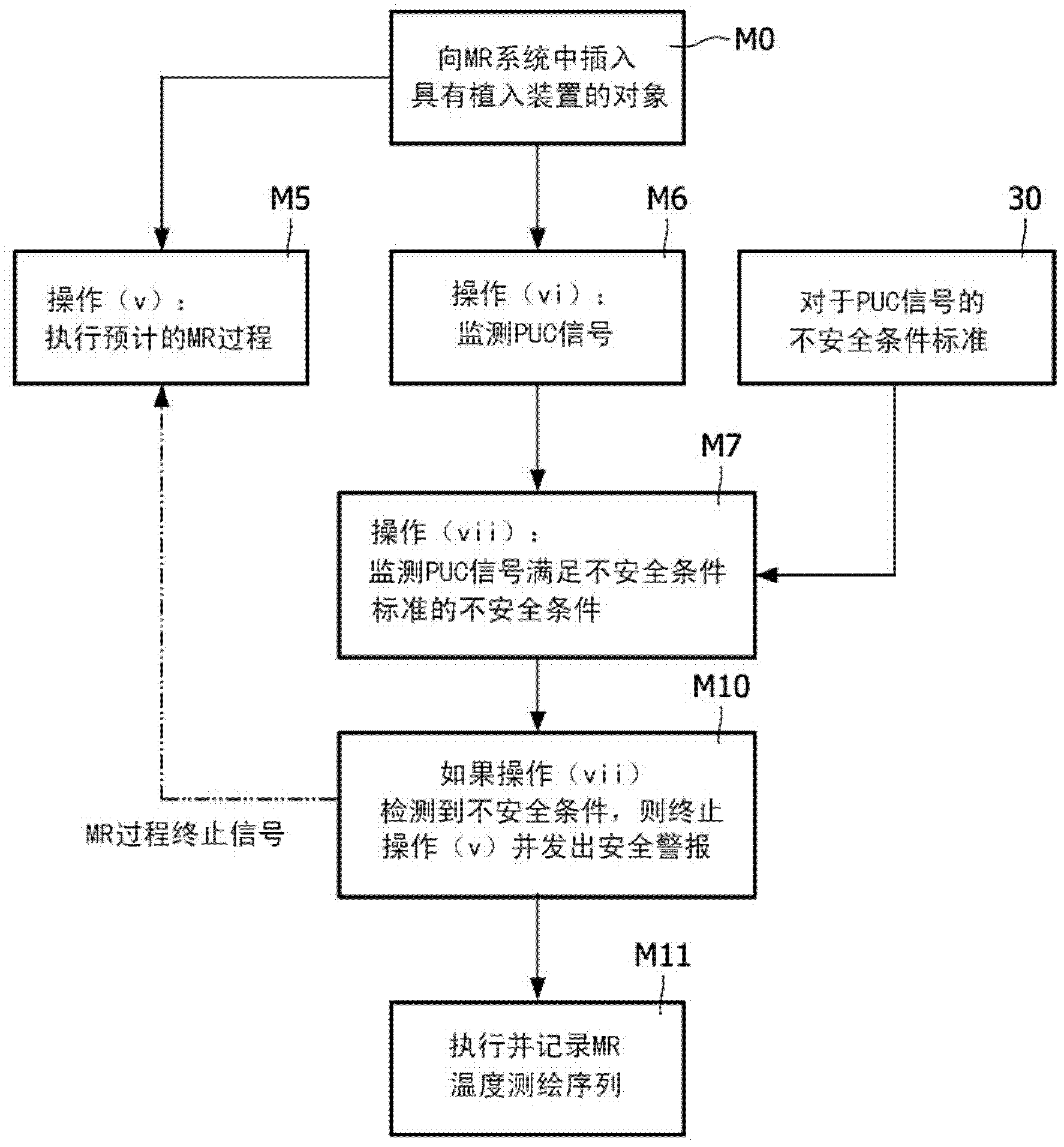
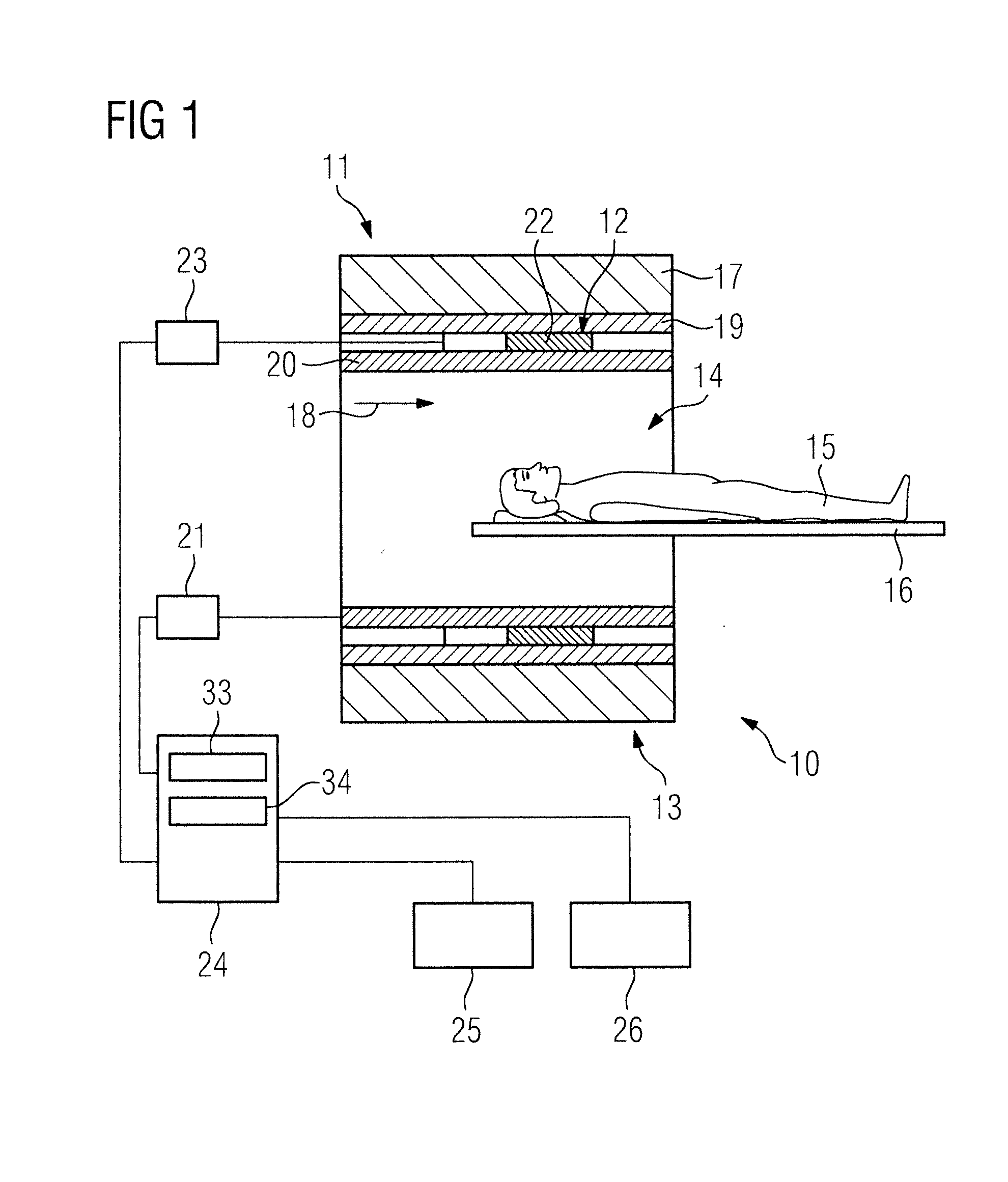
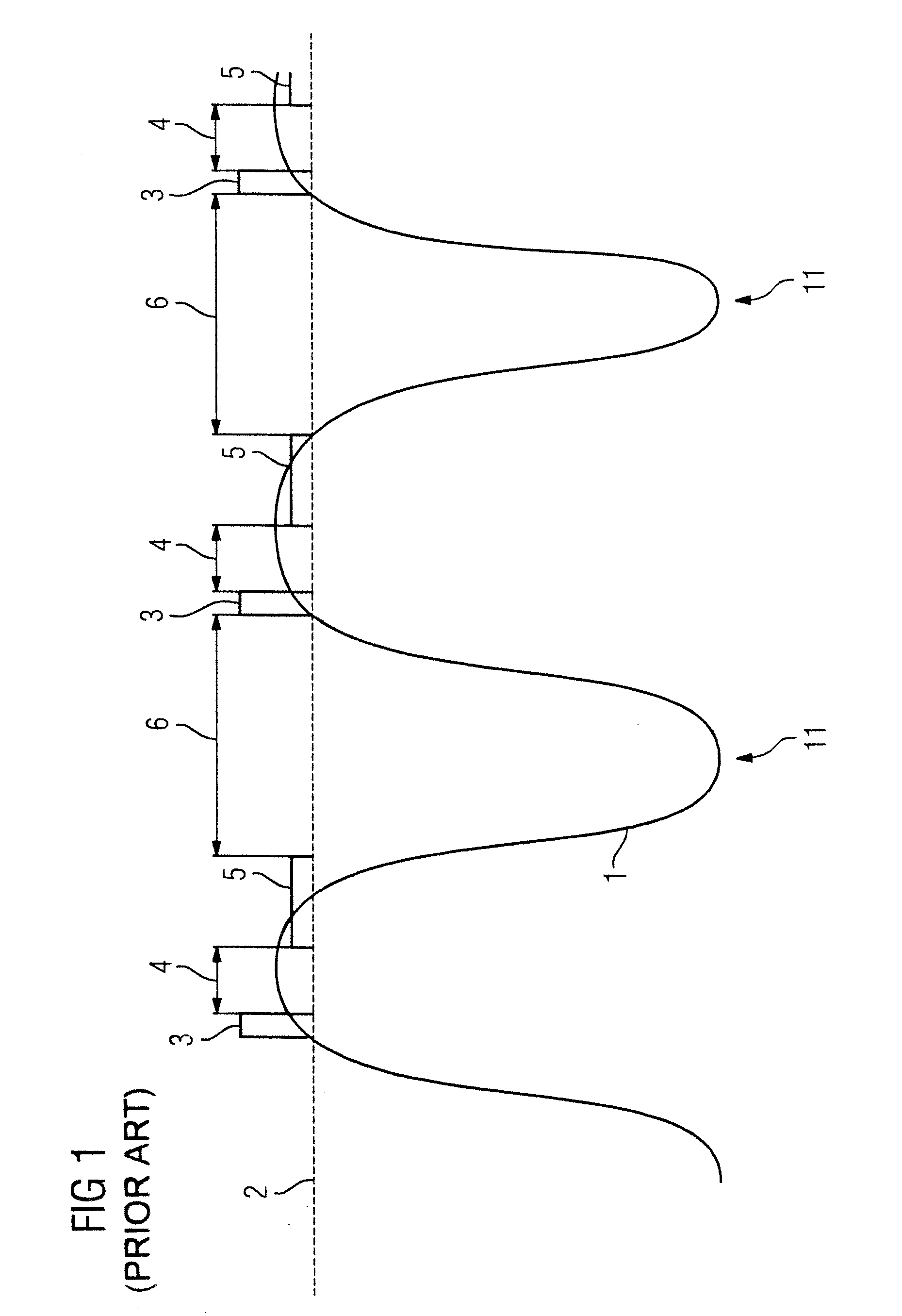
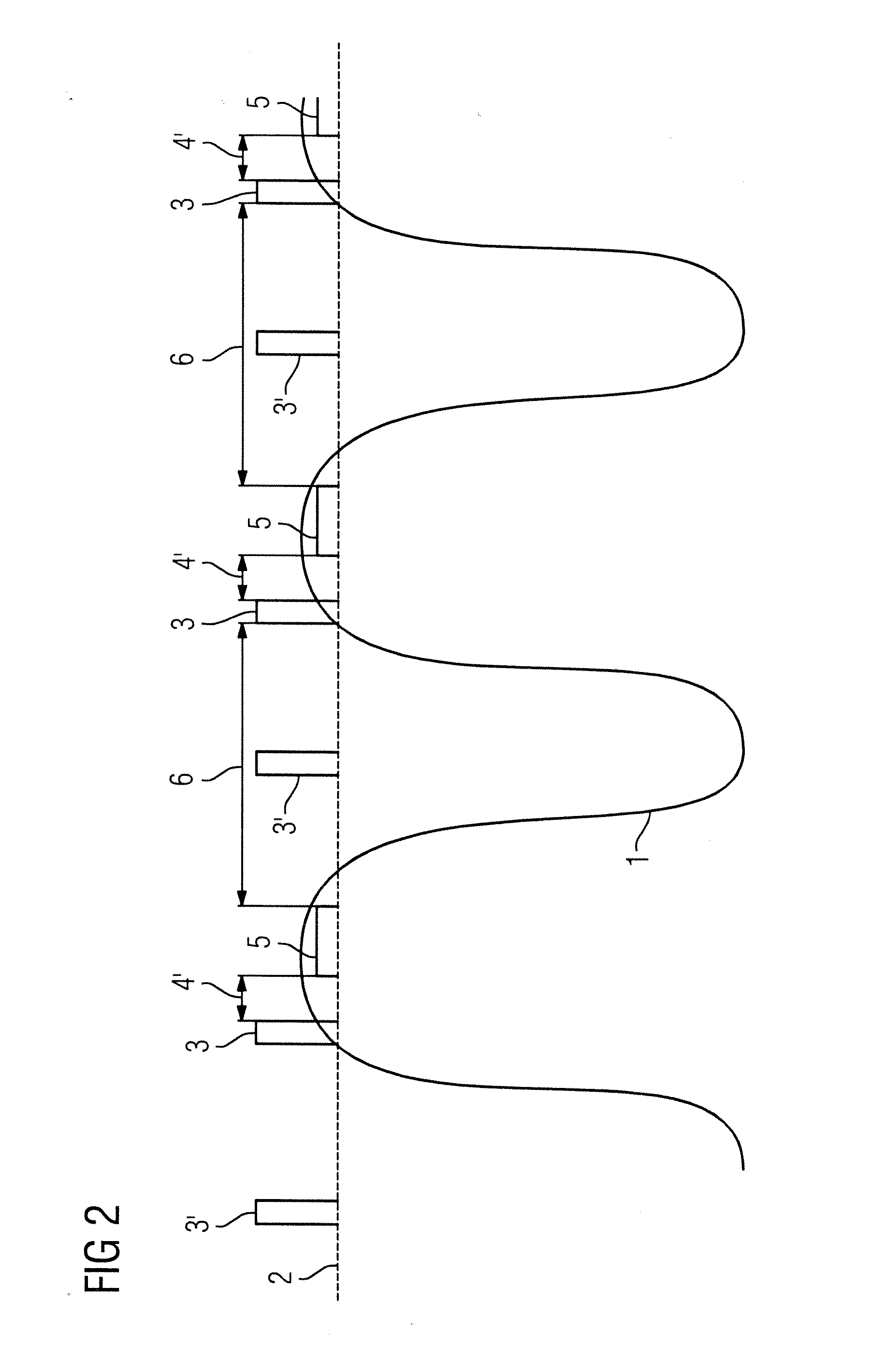
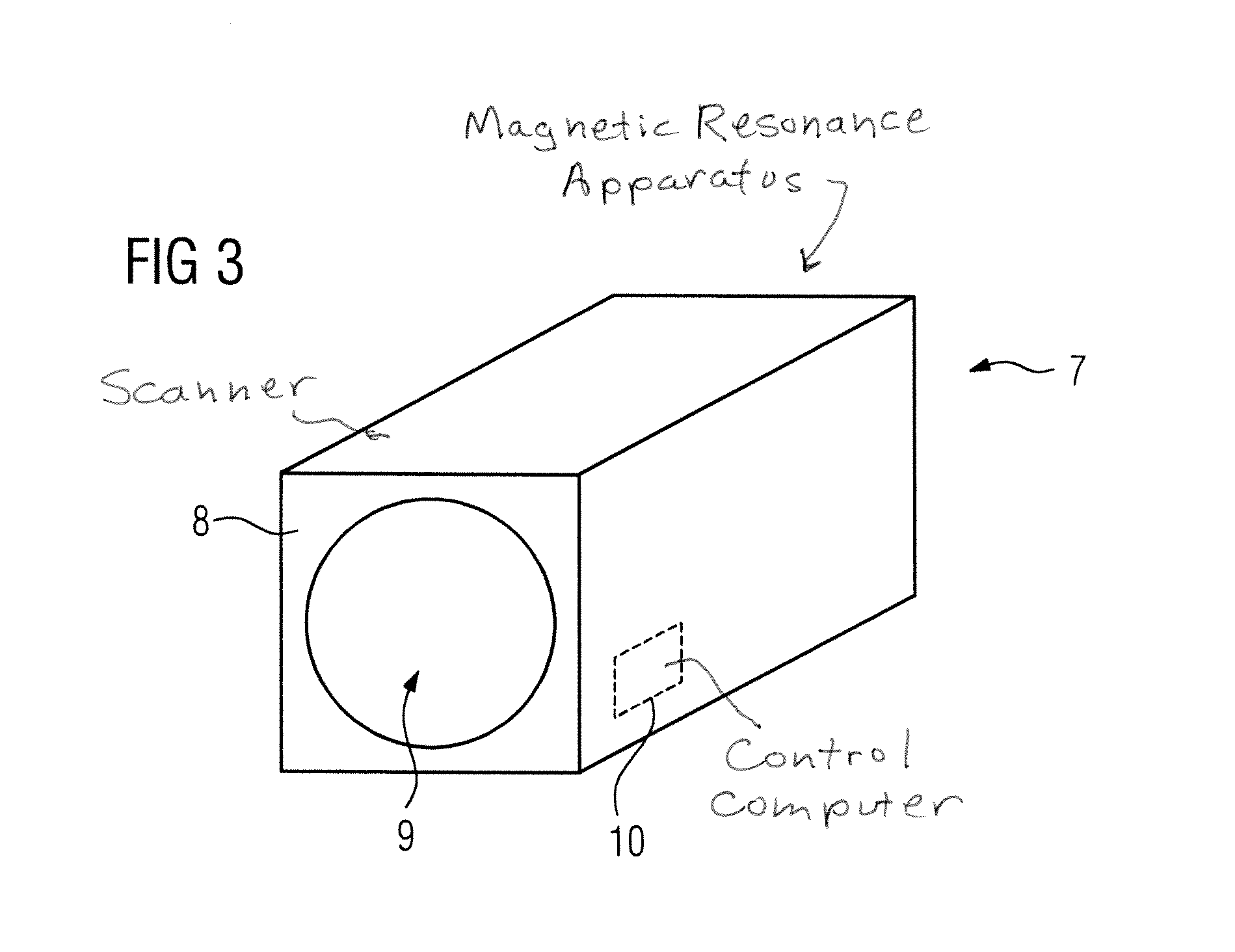
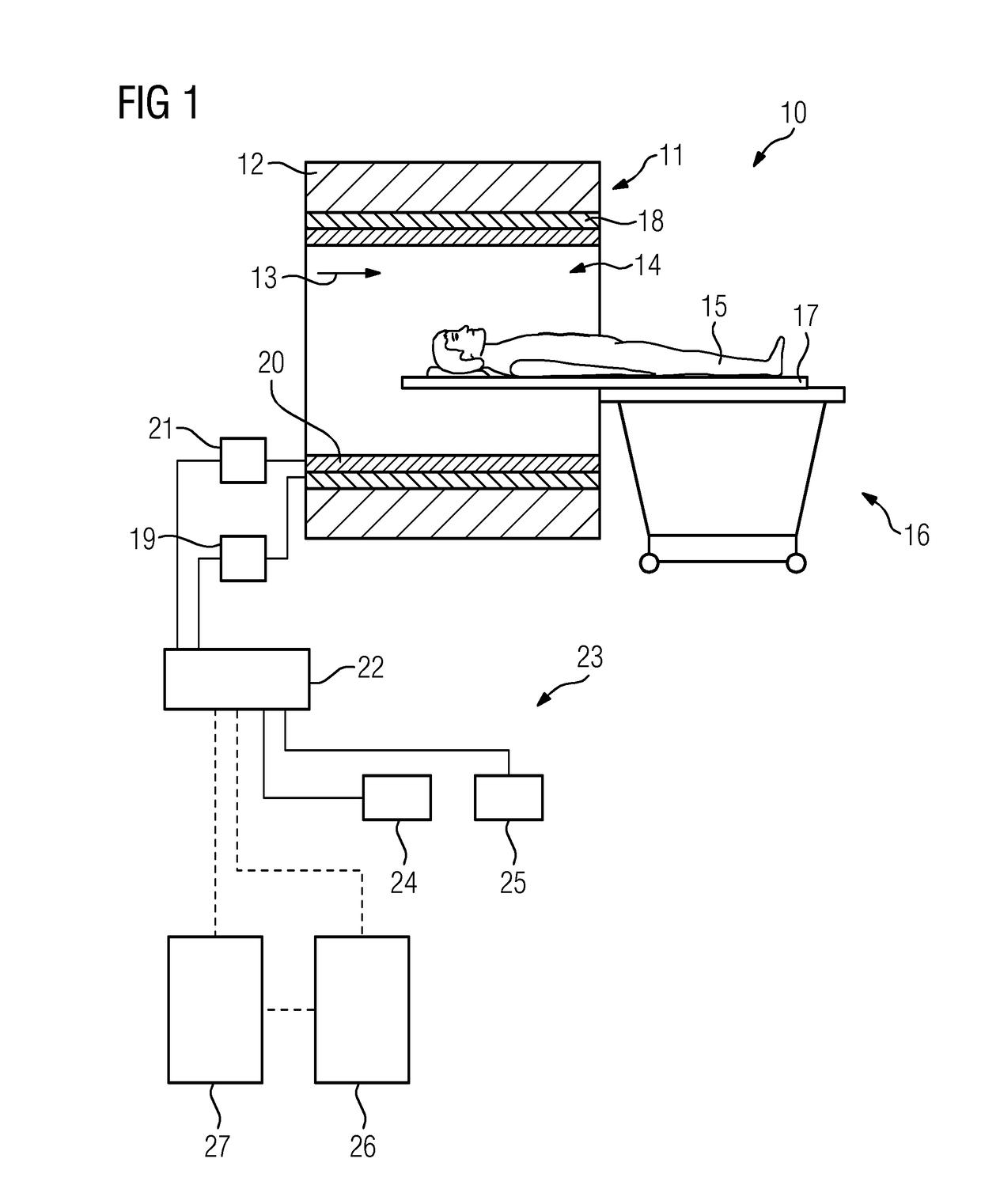
Magnetic resonance system and method for comprehensive implantable device safety tests and patient safety monitoring
InactiveUS20120086449A1Rapid assessmentReduce the possibilityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRStage iibUnsafe condition
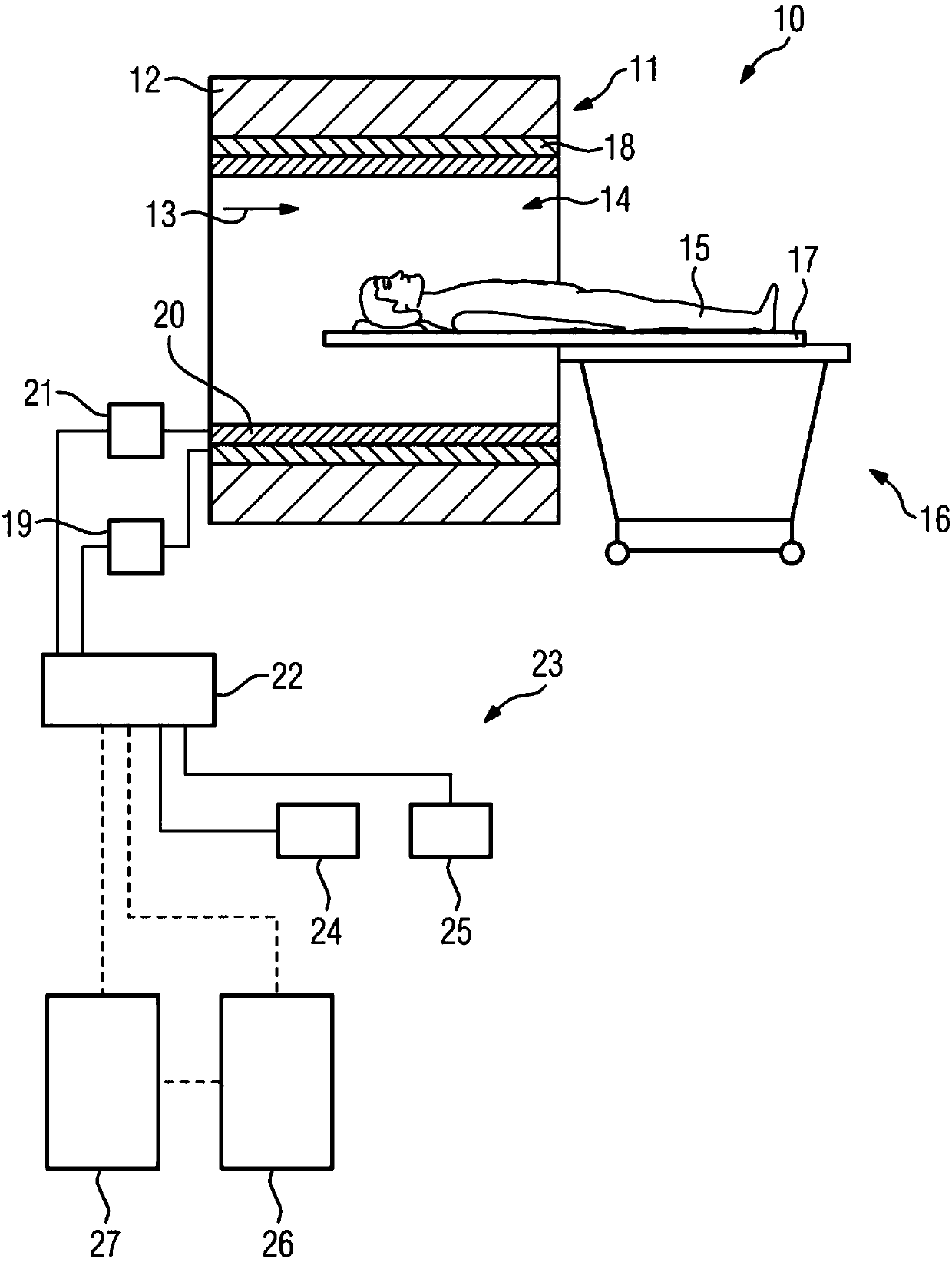
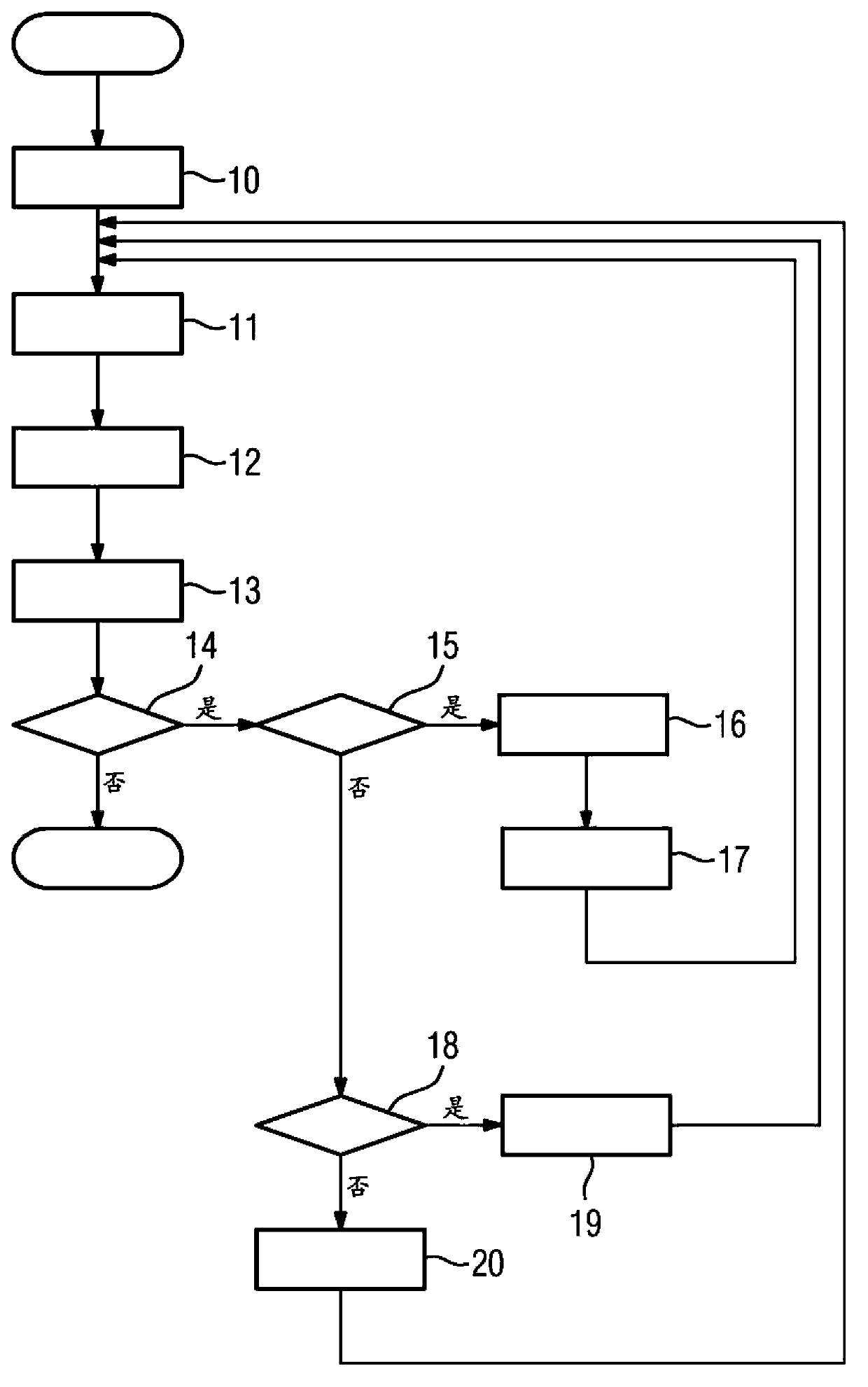
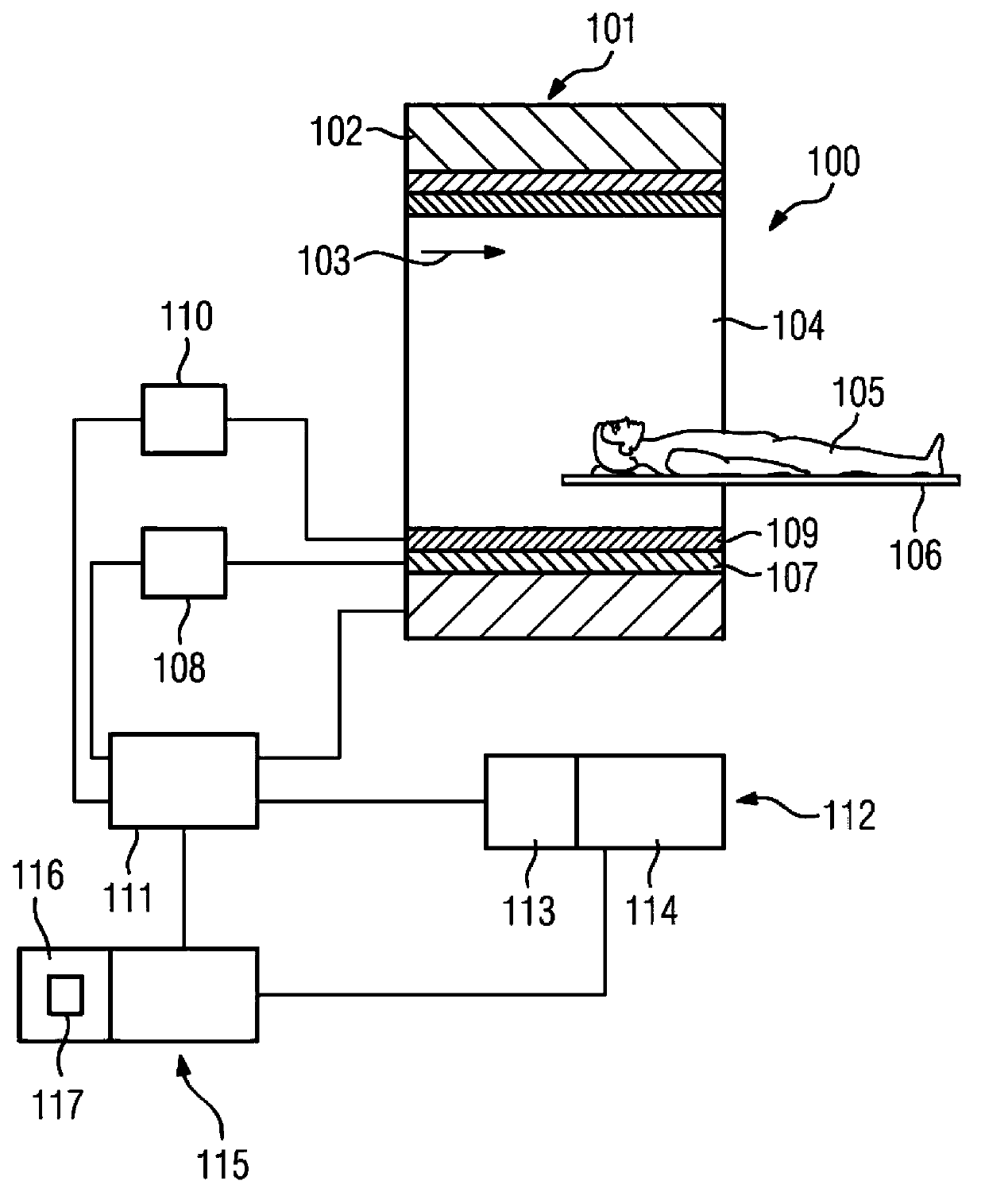
A magnetic resonance method comprises: performing (C1) a magnetic resonance procedure on a calibration subject including an implant device; detecting (C2) a pick-up coil (PUC) signal at least during a radio frequency transmit phase of operation (C1); performing (C3) three dimensional temperature mapping of the calibration subject using a magnetic resonance sequence configured to detect any temperature change induced in any part of the implant device by operation (C1); generating (C4) an unsafe condition criterion (30) for the detected PUC signal based on correlating a PUC signal characteristic detected by operation (C2) with a temperature change detected by operation (C3); performing (M5) the magnetic resonance procedure on a subject containing an implant device; detecting (M6) a PUC signal at least during a radio frequency transmit phase of operation (M5); and monitoring (M7) for an unsafe condition indicated by the PUC signal detected in operation (M6) satisfying the unsafe condition criterion (30).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for establishing body lumbar three-dimensional simulation model through registration and fusion of CT (Computed Tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) signals
ActiveCN108711187AIncrease profitStereoscopic Medical ImagingImage enhancementImage analysisThree dimensional simulationLumbar
The invention relates to a method for establishing a body lumbar three-dimensional simulation model through registration and fusion of CT (Computed Tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) signals. The method comprises the steps of collecting a computed tomography (CT) image; collecting a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image; establishing a computed tomography image three-dimensional model; establishing a magnetic resonance imaging image three-dimensional; and carrying out registration and fusion on the computed tomography image three-dimensional model and the magnetic resonance imaging image three-dimensional, wherein the registration and fusion comprise carrying out simple registration and global computing registration according to a lumbar anatomic structure. According to themethod, existing routine examinations such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are utilized fully, through combination of optimized magnetic resonance scanning sequences, lumbar intervertibral disc, nerve root and ligamentum flavum important soft tissue three-dimensional models capable of mutually verifying accuracy in various magnetic resonance sequences are established, a new lumbar intervertibral disc medical image high-accuracy modeling mode is established, and a utilization rate of medical image examination data is greatly improved.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
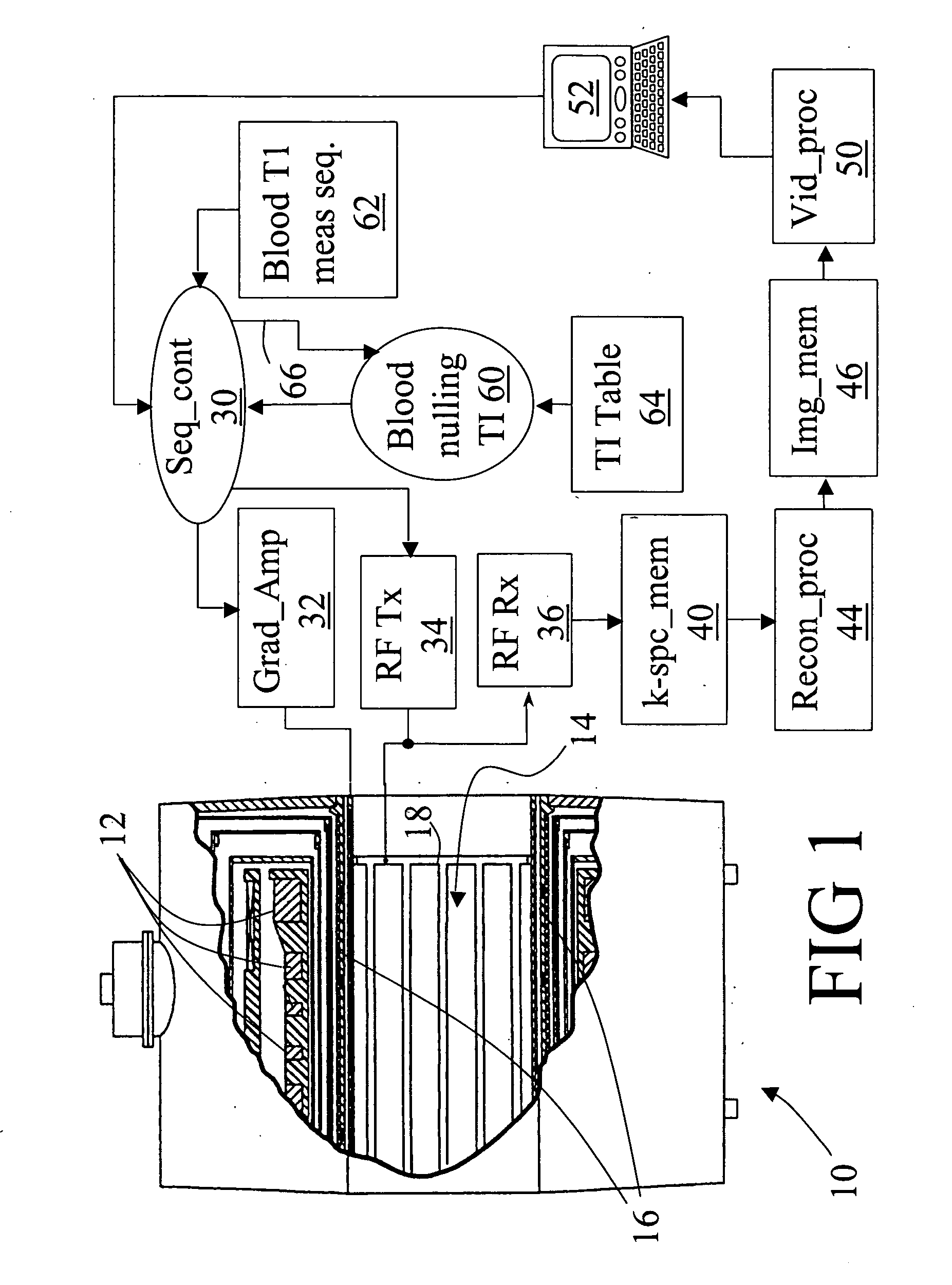
Microvascular blood volume magnetic resonance imaging
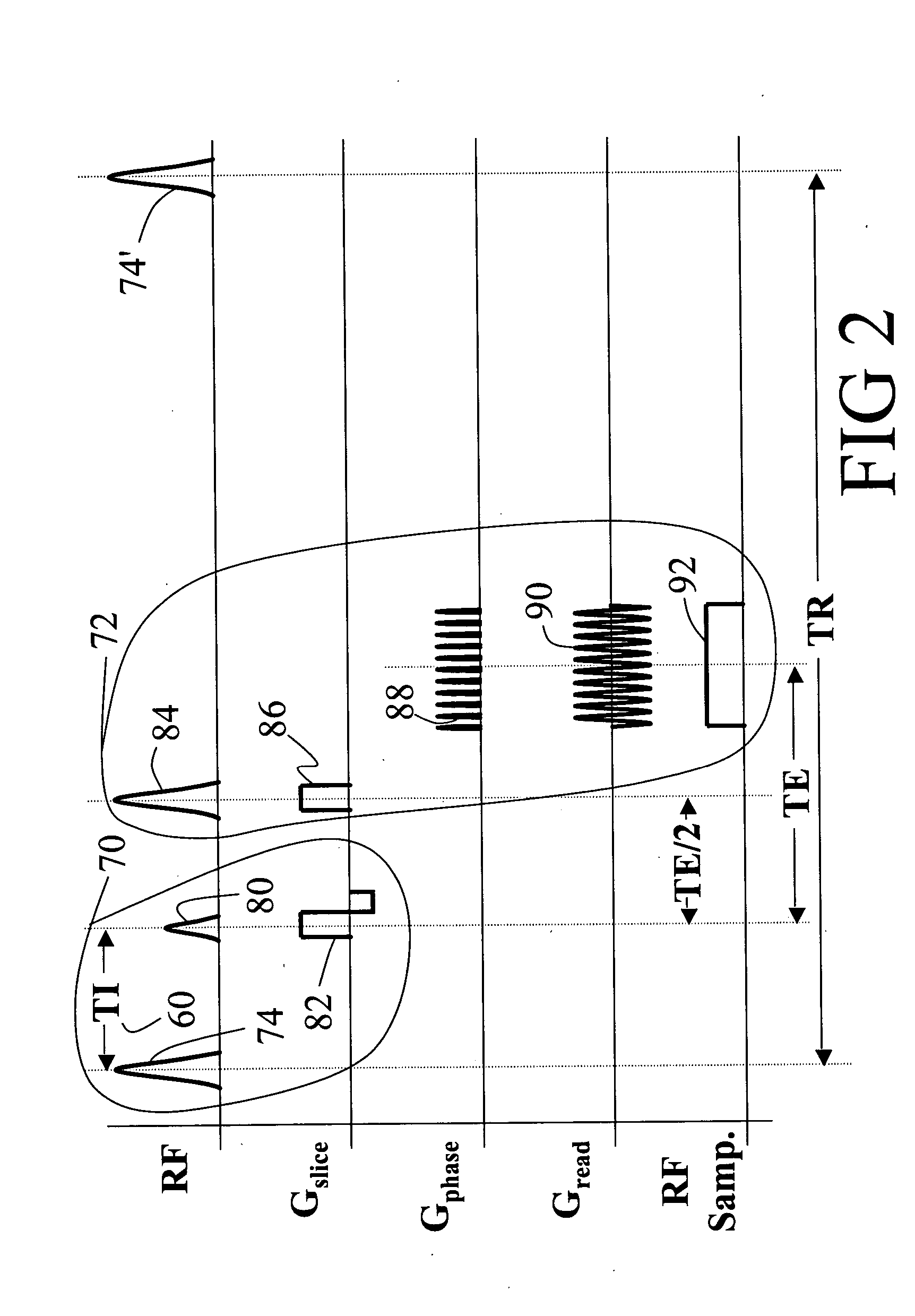
ActiveUS20050215881A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientRed blood cell
A magnetic resonance imaging system includes a magnetic resonance imaging scanner (10) that performs an inversion recovery magnetic resonance excitation sequence (70) having a blood-nulling inversion time (60) determined based on a blood T1 value appropriate for a selected magnetic field and blood hematocrit, whereby magnetic resonance of blood is substantially nulled. The inversion recovery excitation sequence (70) includes an inversion radio frequency pulse (74) applied with a small or zero slice-selective magnetic field gradient pulse to avoid inflow effects, and an excitation radio frequency pulse (80). The inversion pulse (74) and excitation pulse (80) are separated by the inversion time (60). The magnetic resonance imaging scanner (10) subsequently performs a readout magnetic resonance sequence (72) or spectroscopy sequence to acquire a magnetic resonance signal from tissue other than the nulled blood. A reconstruction processor (44) generates a reconstructed image from the acquired magnetic resonance signal.
Owner:KENNEDY KRIEGER INST
Method and magnetic resonance system for acquiring magnetic resonance data
ActiveUS20150084629A1Improve qualitySimple technologyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionImage resolutionResonance
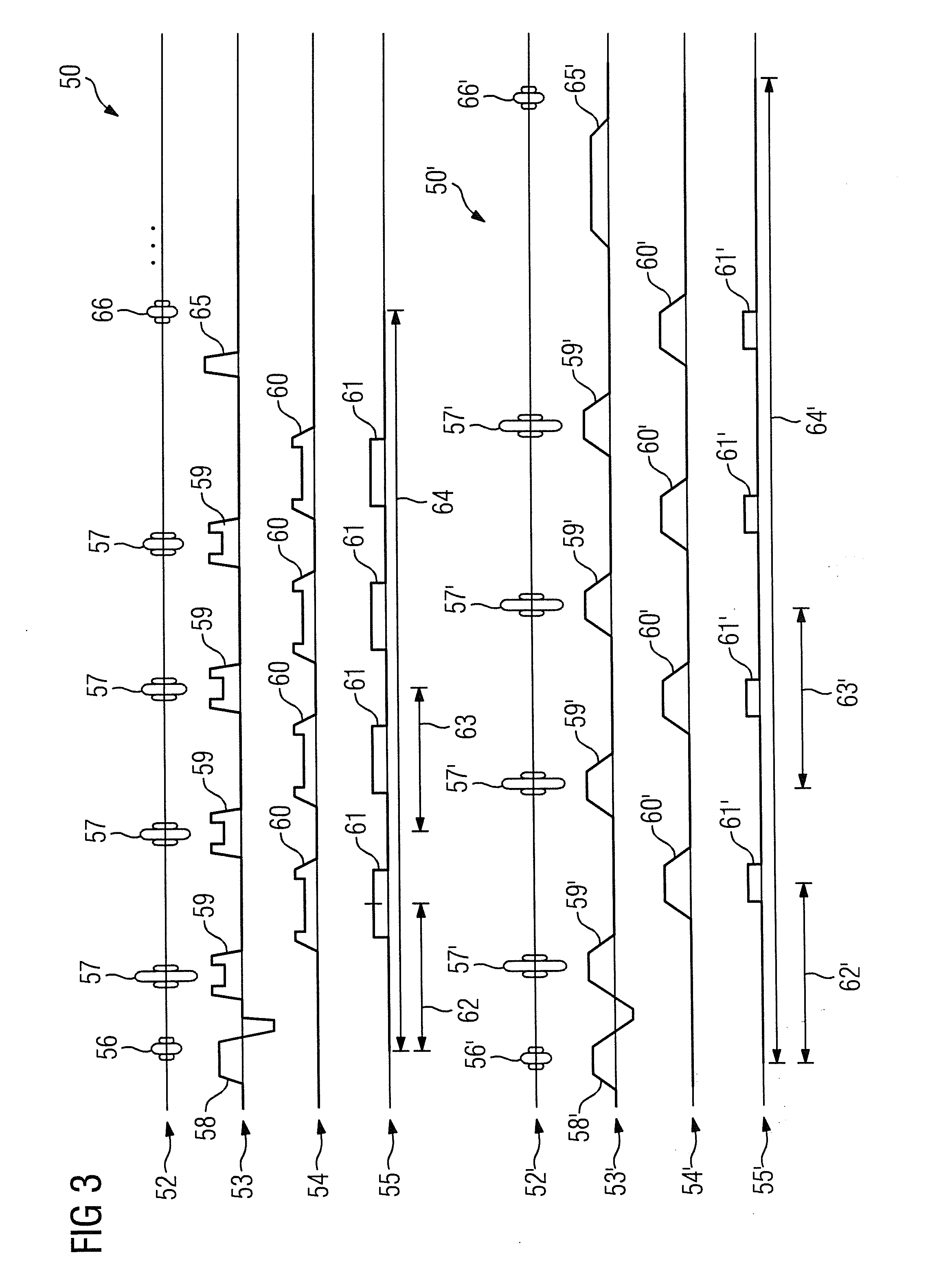
In a method for acquiring magnetic resonance data with a magnetic resonance system using a magnetic resonance sequence, the sequence has a first partial sequence in which magnetic resonance data are acquired for multiple slices that have to be acquired simultaneously, from which image data for the individual slices are calculated by a reconstruction algorithm. The sequence also has a second partial sequence for determining additional data, which are used to evaluate and / or assess the magnetic resonance data, and which have a spatial resolution that is lower than the magnetic resonance data, in which radio-frequency pulses and readout processes take place in a slice-specific manner through a time offset within a single measuring process, in which a single continuous excitation period with the radio-frequency pulses and a single continuous readout period with the readout processes follow one another, so that separate additional data are directly determined for each slice.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
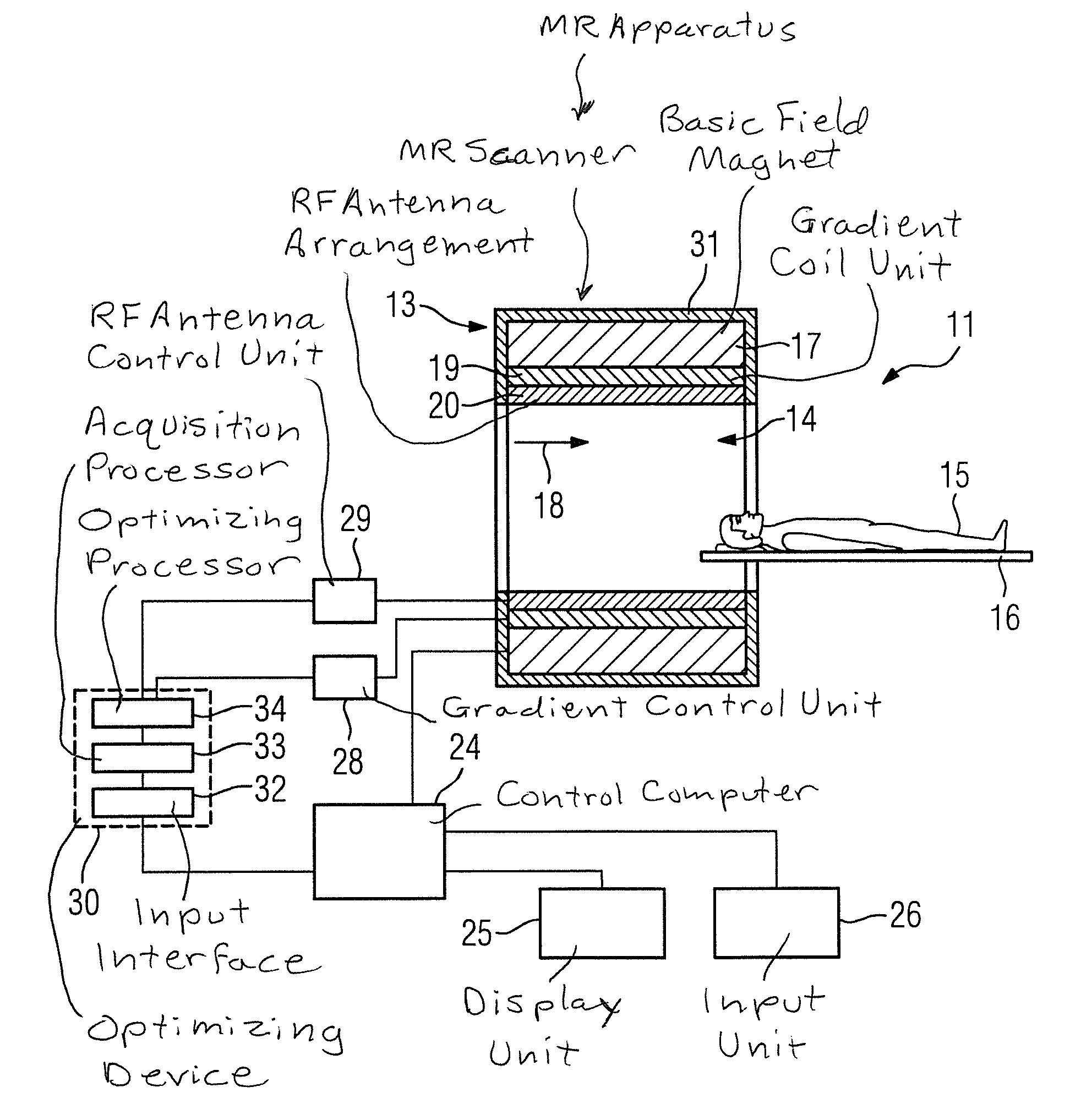
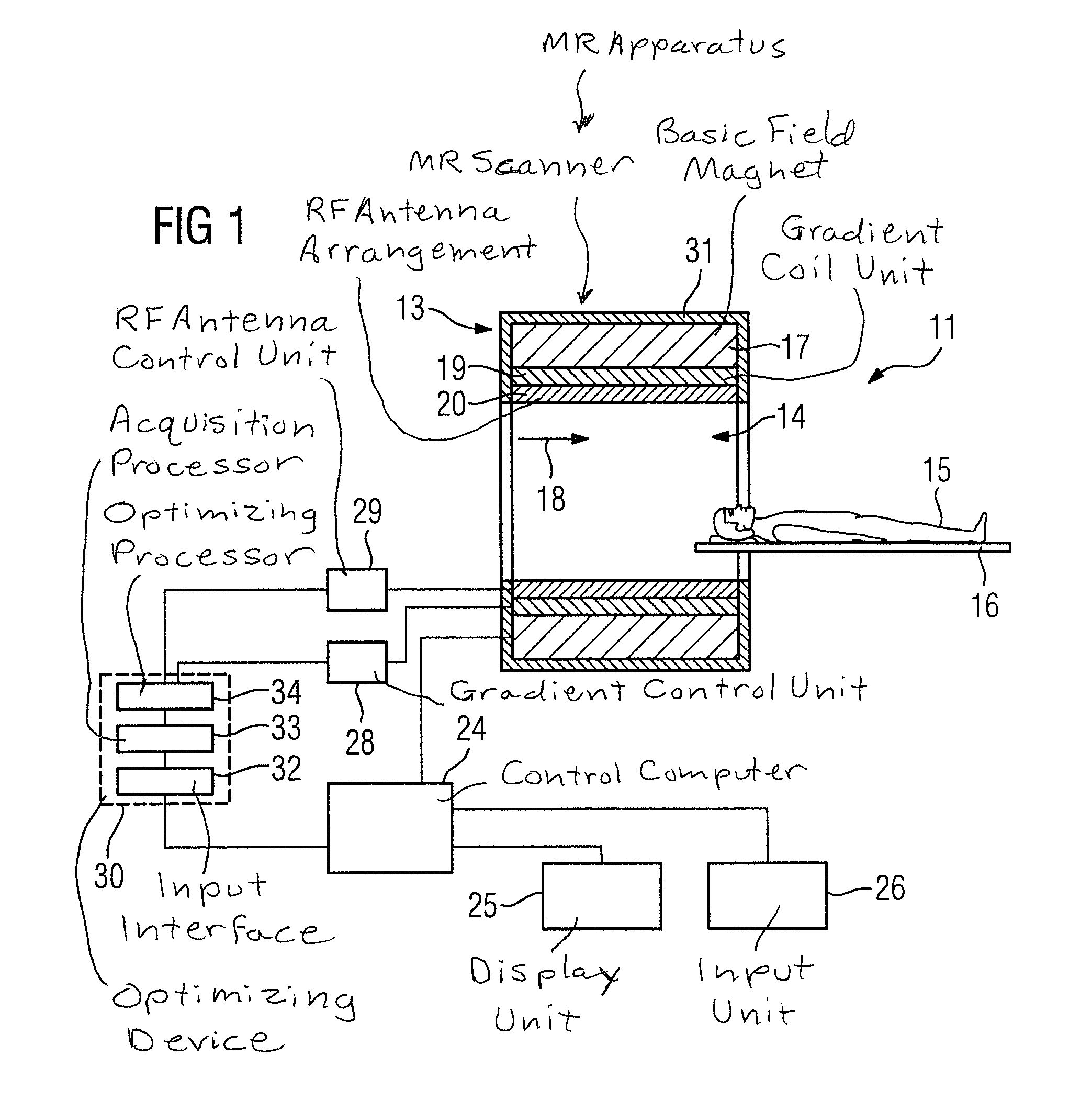
Method and device for automated generation of a formal description of a magnetic resonance system measurement sequence, using a sequence model
InactiveUS8299789B2Easy to controlReduce effortDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceSequence model
A magnetic resonance sequence model that is a formal description of a measurement sequence is used to automate measurement sequence programming. The sequence model allows a system-independent specification of the measurement sequence for execution in a magnetic resonance scanner. The sequence model is as formal as possible; it is limited to the minimum required information for description of a measurement sequence without limiting the flexibility in the sequence programming. A method for formal description of the measurement sequence describes the measurement sequence by a number of parameters to be parameterized. The parameterization of the measurement sequence can ensue automatically from the formalized description of the measurement sequence, except for a set of parameters that are still be determined. For automatic generation of an executable measurement sequence, the method determines the parameters to be determined using a solver, under consideration of boundary conditions, so that a consistent set of parameters is created that completely describes the measurement sequence. This complete description of parameter values of the measurement sequence is then be translated automatically into a programming language that can be directly executed in the magnetic resonance scanner.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20150253408A1QuietAttenuation bandwidthMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceSlew rate
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging, a particularly quiet magnetic resonance sequence, uses echo-planar imaging with at least one gradient switching in a readout direction, wherein the at least one gradient switching in the readout direction has a slew rate that is less than a maximum slew rate defined by system specification parameters of the magnetic resonance apparatus.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
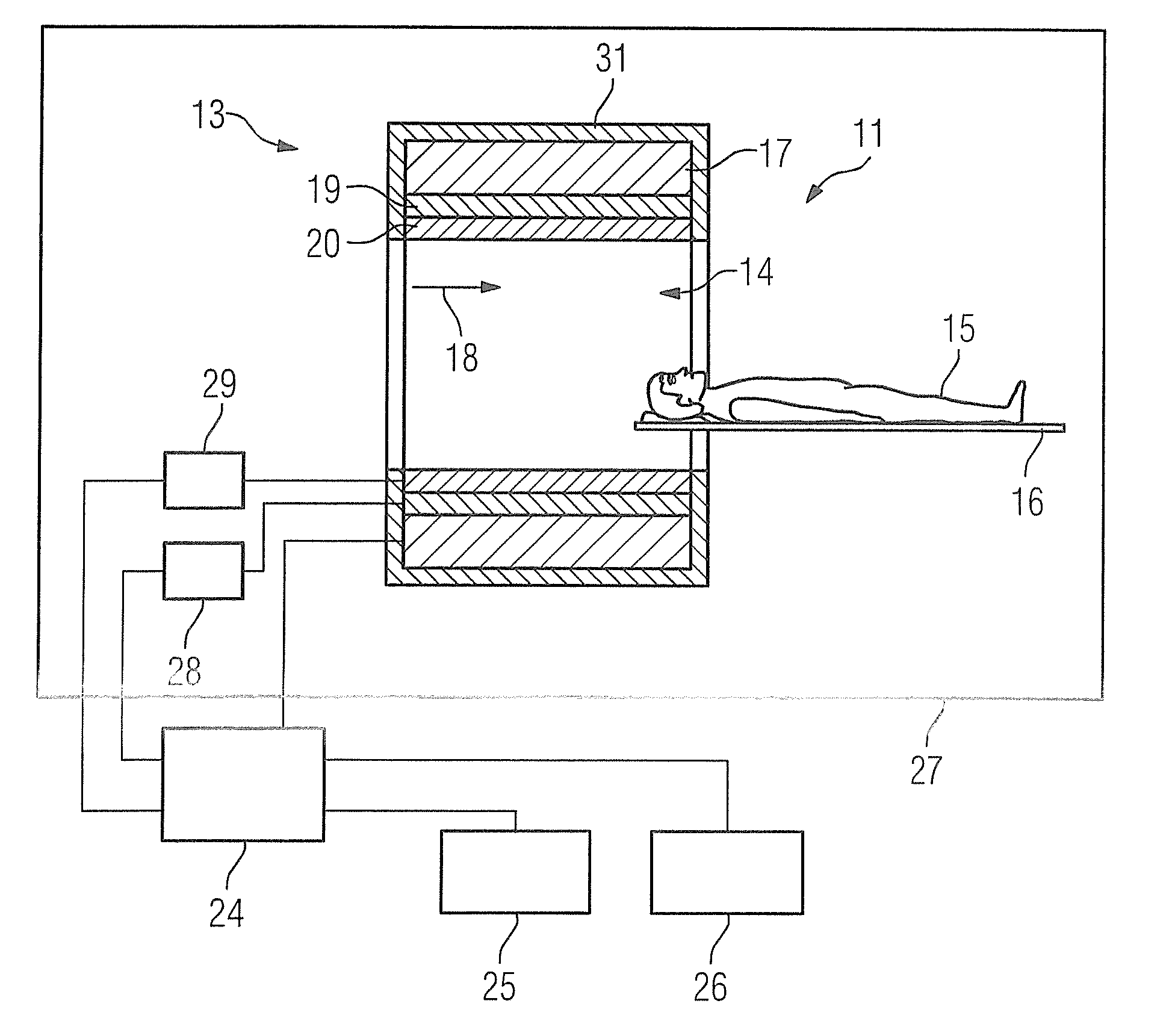
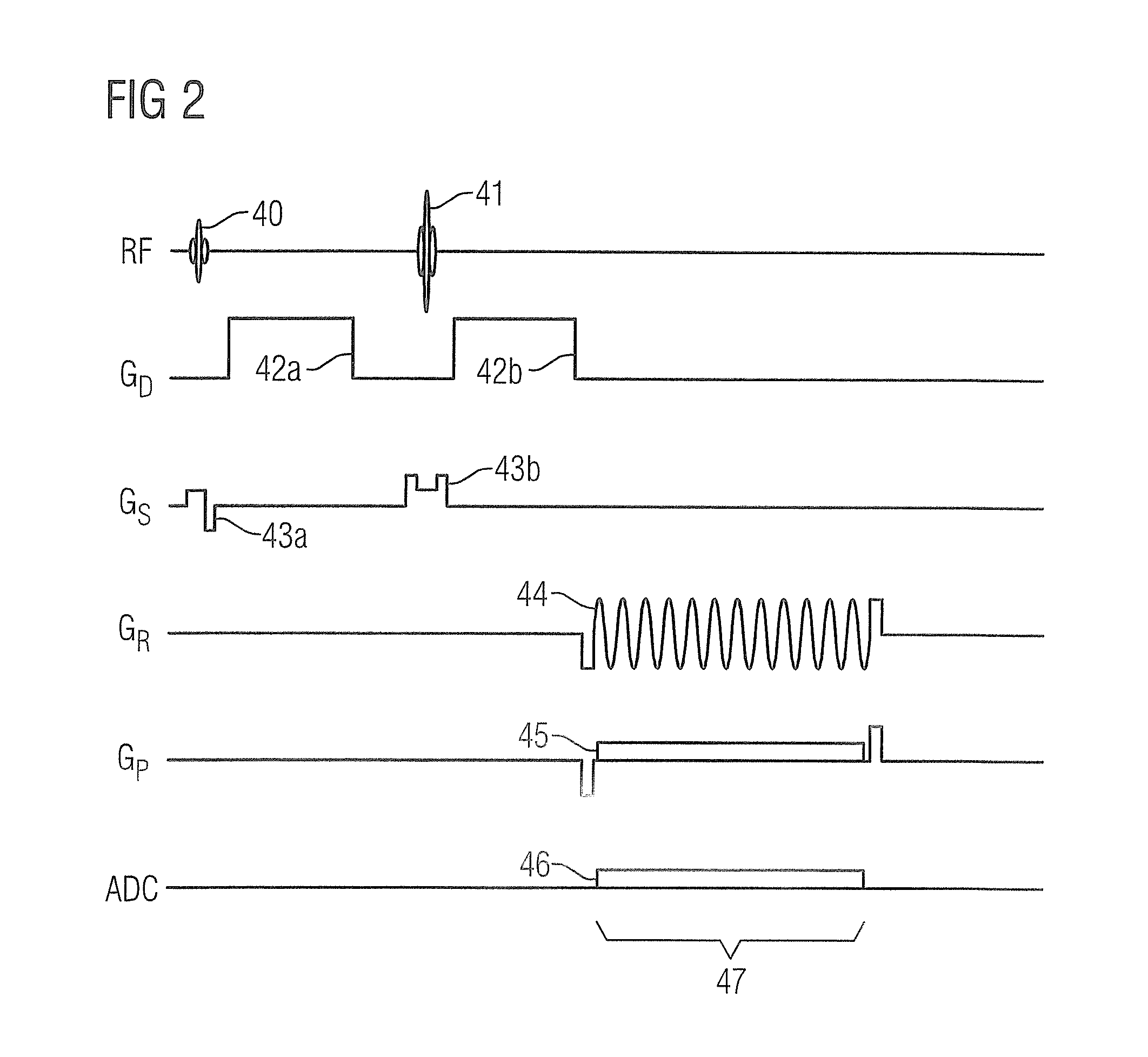
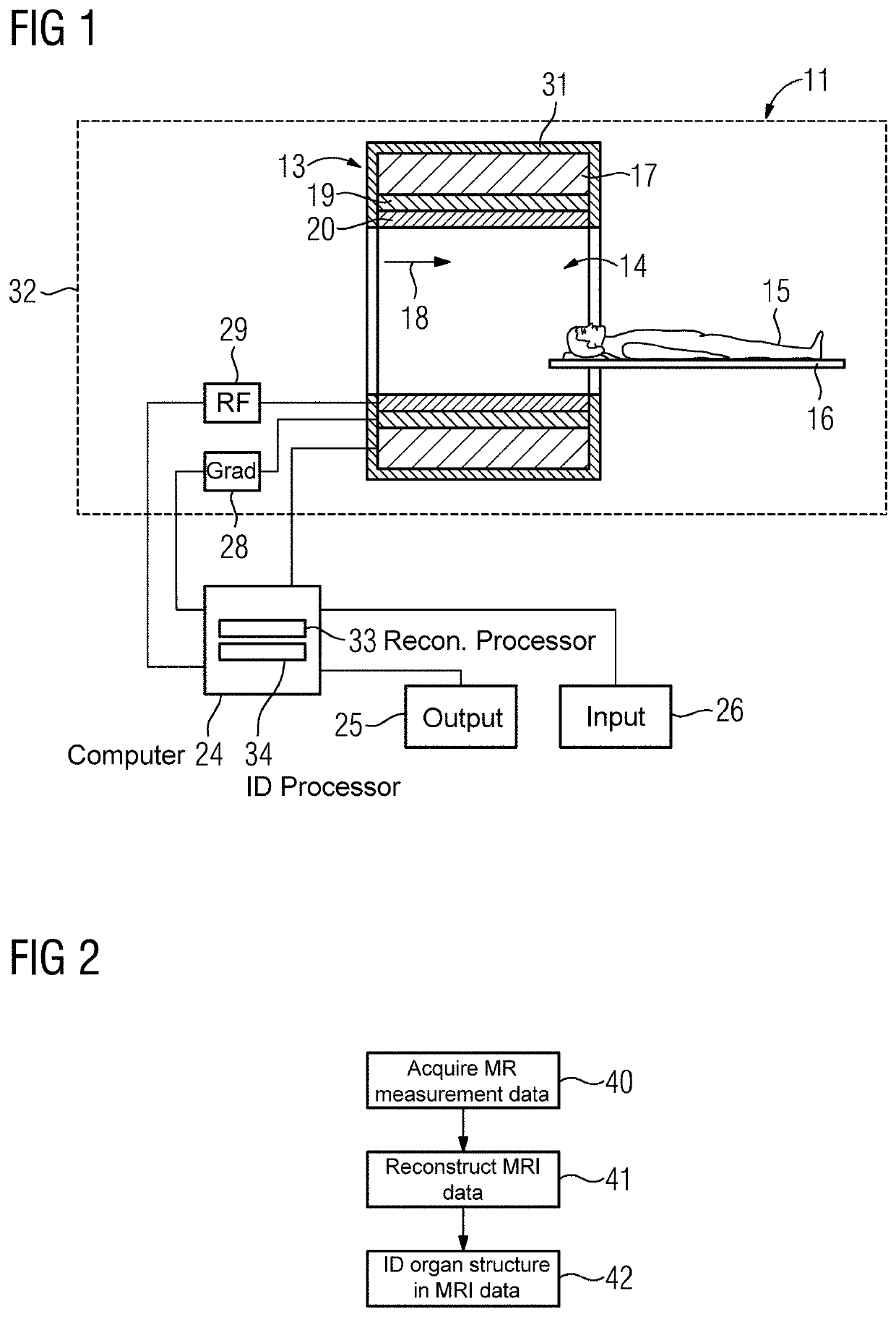
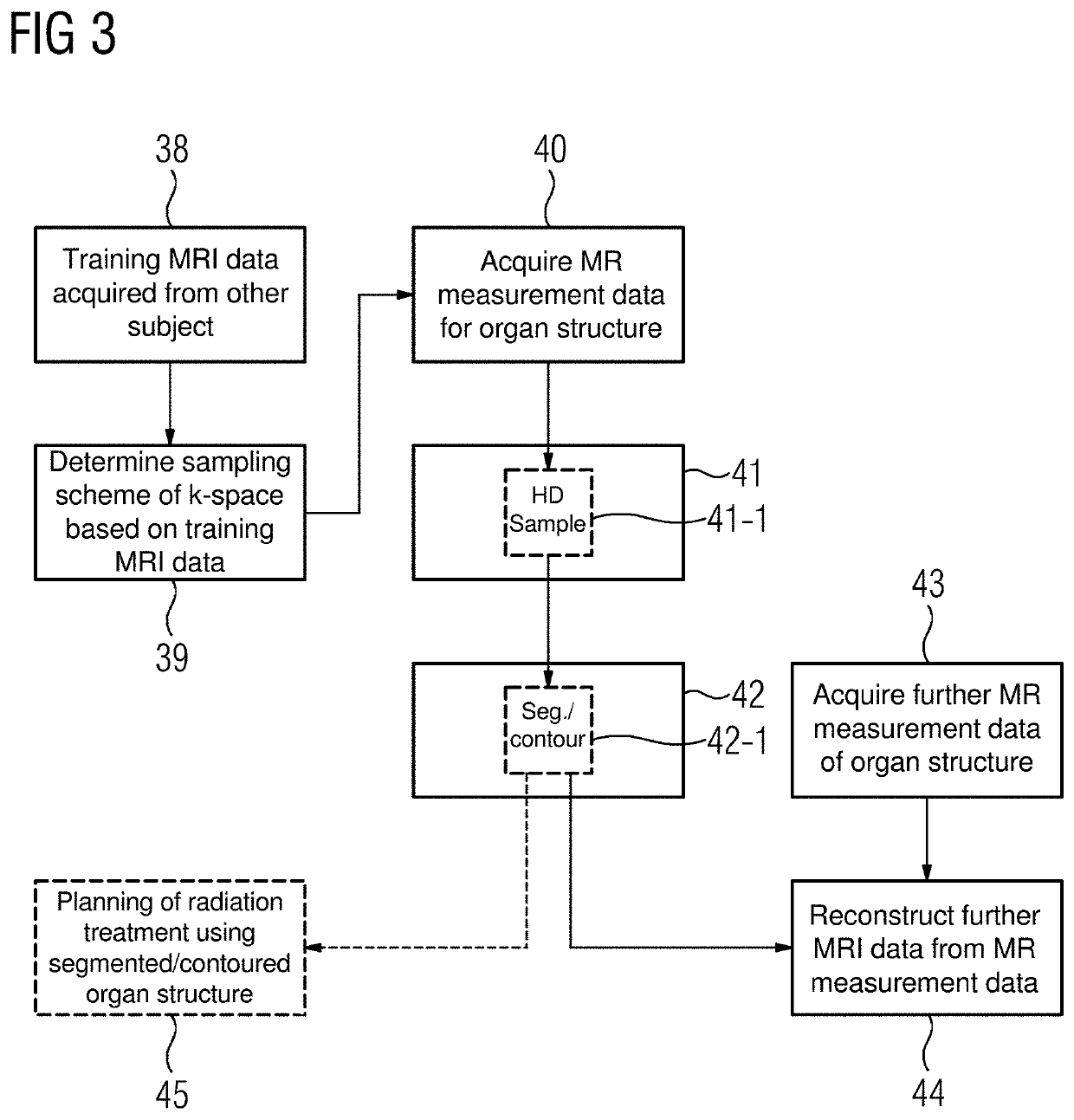
Method and apparatus for identifying an organ structure of an examined object in magnetic resonance image data
ActiveUS10702186B2Quality improvementMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringResonance measurementMri image
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
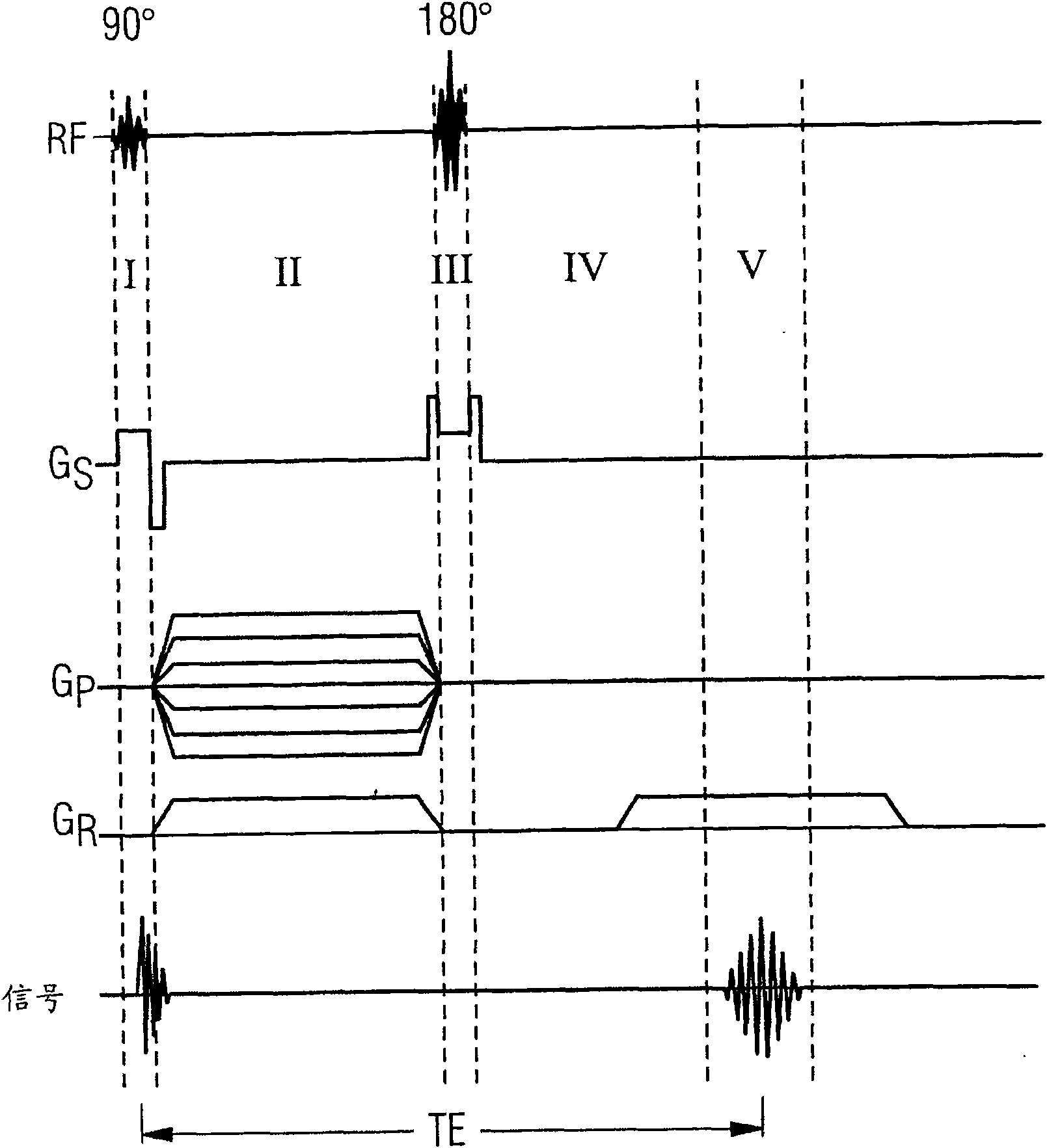
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus to acquire magnetic resonance data with a diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance sequence
ActiveUS20150115960A1Short echo timeImprove image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceMR - Magnetic resonance
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus to acquire magnetic resonance data with a diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance sequence wherein the magnetic resonance apparatus as a gradient coil arrangement with three gradient coils designed to generate a gradient in gradient directions orthogonal to one another, the readout gradient is flipped relative to at least one of the gradient directions such that at least two gradient coils contribute to a possible slew rate of a readout gradient pulse, and such that a phase coding gradient that is constant over the readout time period is selected.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
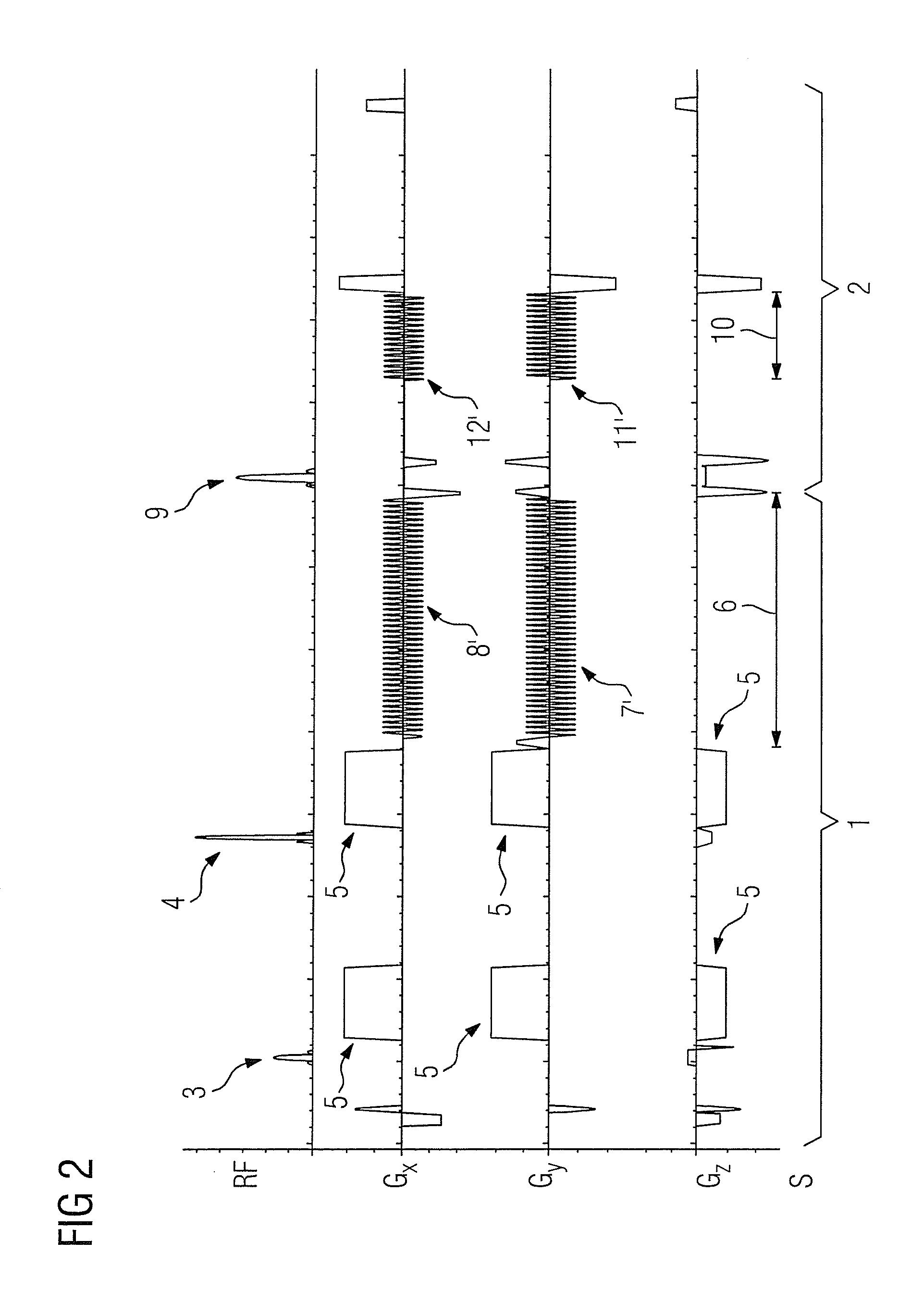
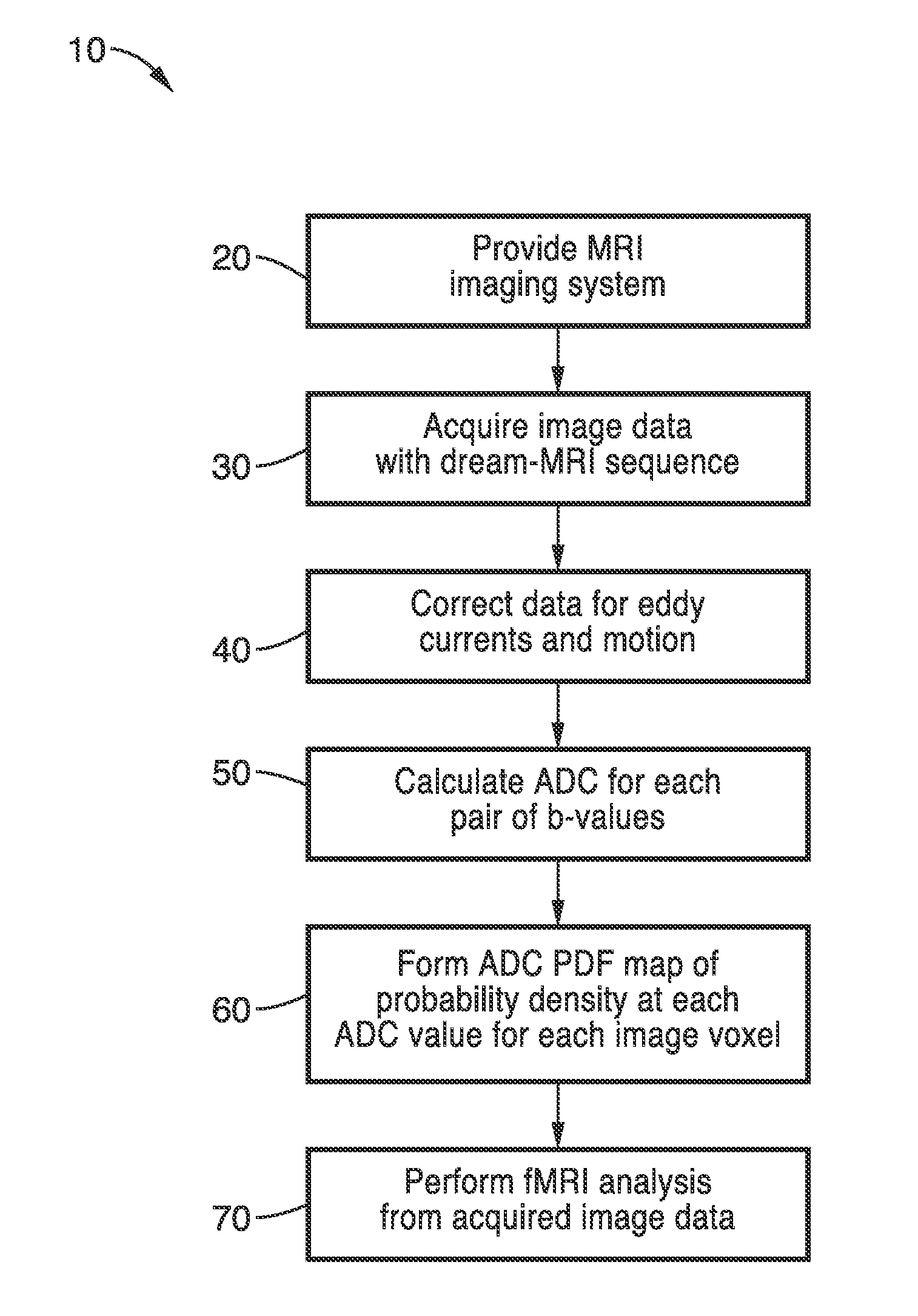
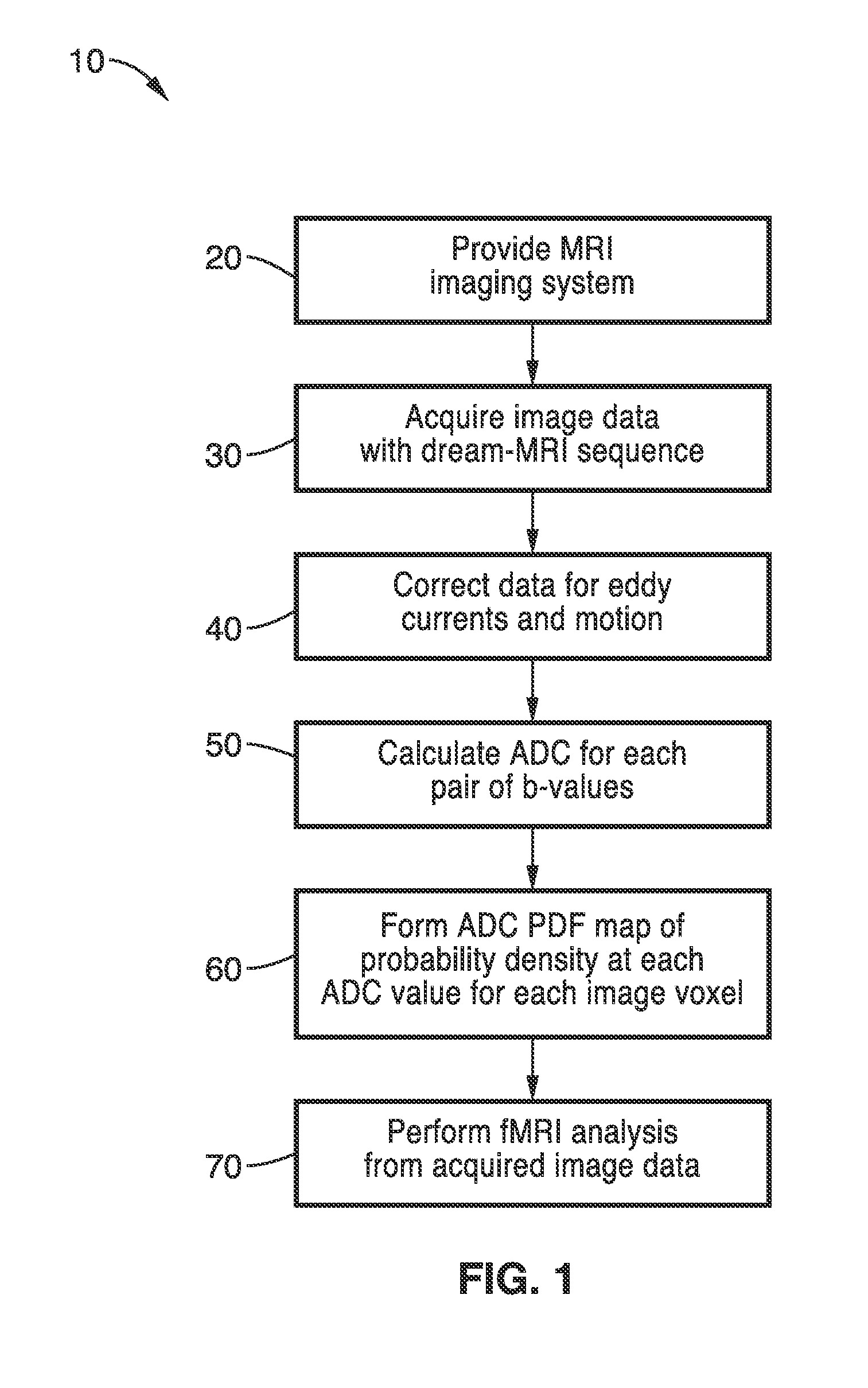
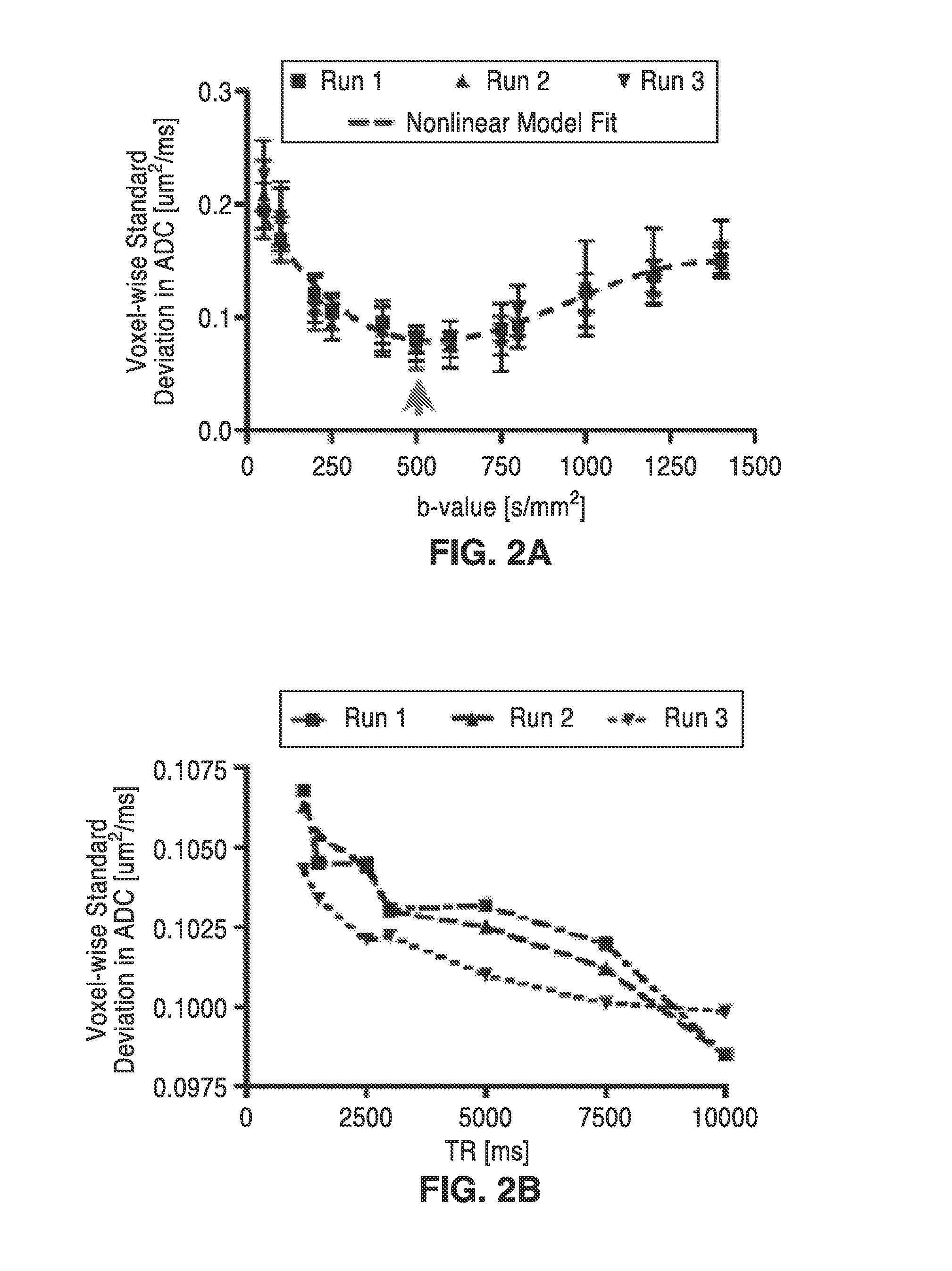
Diffusion reproducibility evaluation and measurement (DREAM)-mri imaging methods
ActiveUS20160157746A1Improving patient careGood estimateMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFunctional connectivityVoxel
Methods for quickly estimating apparent diffusion coefficient probability density functions (ADC PDFs) for each image voxel are provided using a “diffusion reproducibility evaluation and measurement” (DREAM) magnetic resonance sequence. Non-diffusion-weighted (reference) images collected simultaneously have blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) sensitivity that can be used for resting-state fMRI data to measure functional connectivity, an unbiased parameter reflecting neurological integrity. ADC coefficient of variation (ADC CV) measurements can be used to isolate and label regions of non-enhancing tumor and predict future enhancement independent of FLAIR, T2, or average ADC maps. Functional diffusion mapping (fDMs) using voxel-wise changes in ADC PDFs can be used to spatially visualize and statistically quantify response to treatment. Additionally, the temporal (time-resolved) diffusivity information can be used for real-time MR thermometry, which is useful for cancer treatment monitoring, and for microperfusion quantification, and tumor / tissue characterization.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for a rapid determination of spatially resolved magnetic resonance relaxation parameters in an area of examination
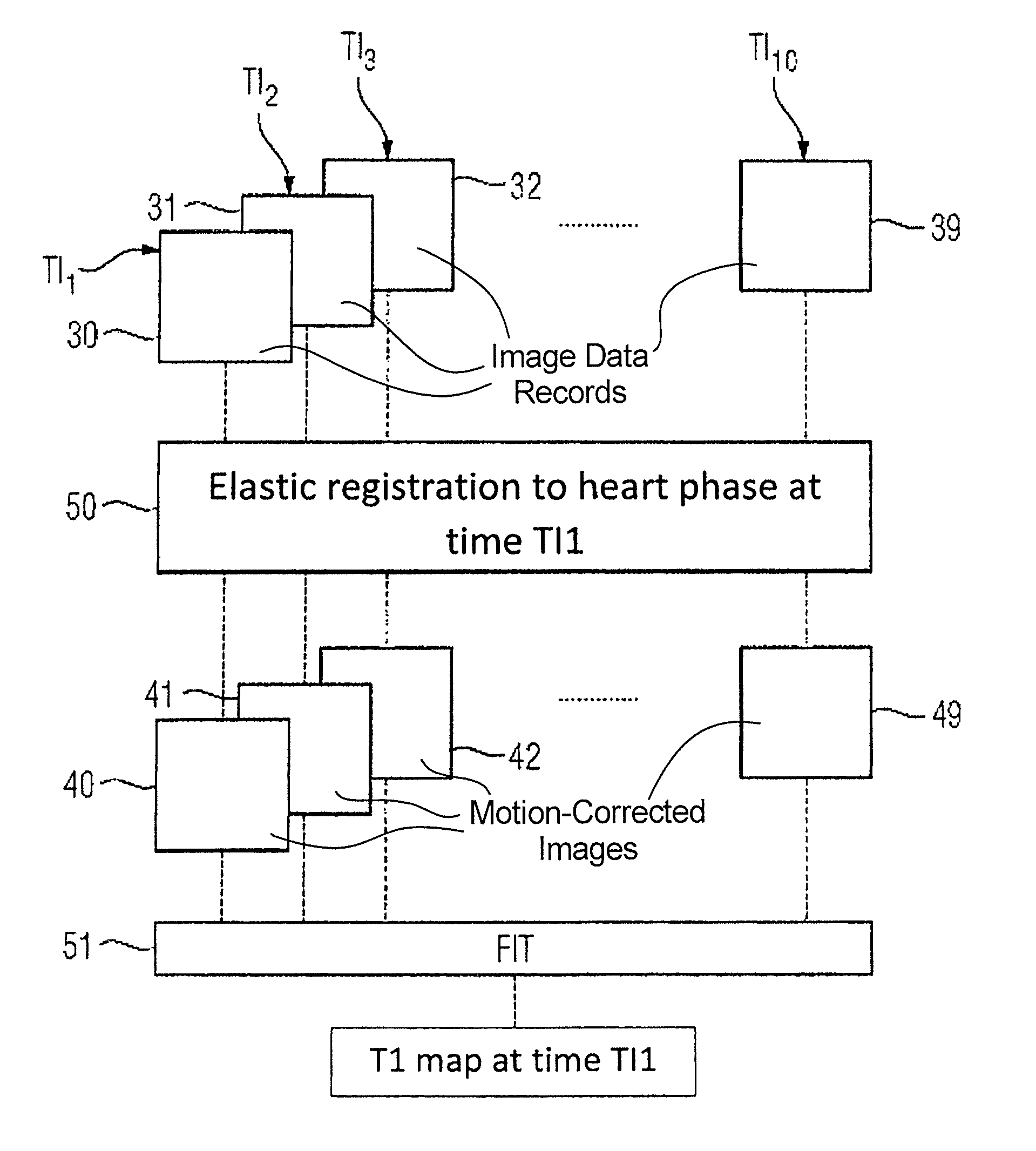
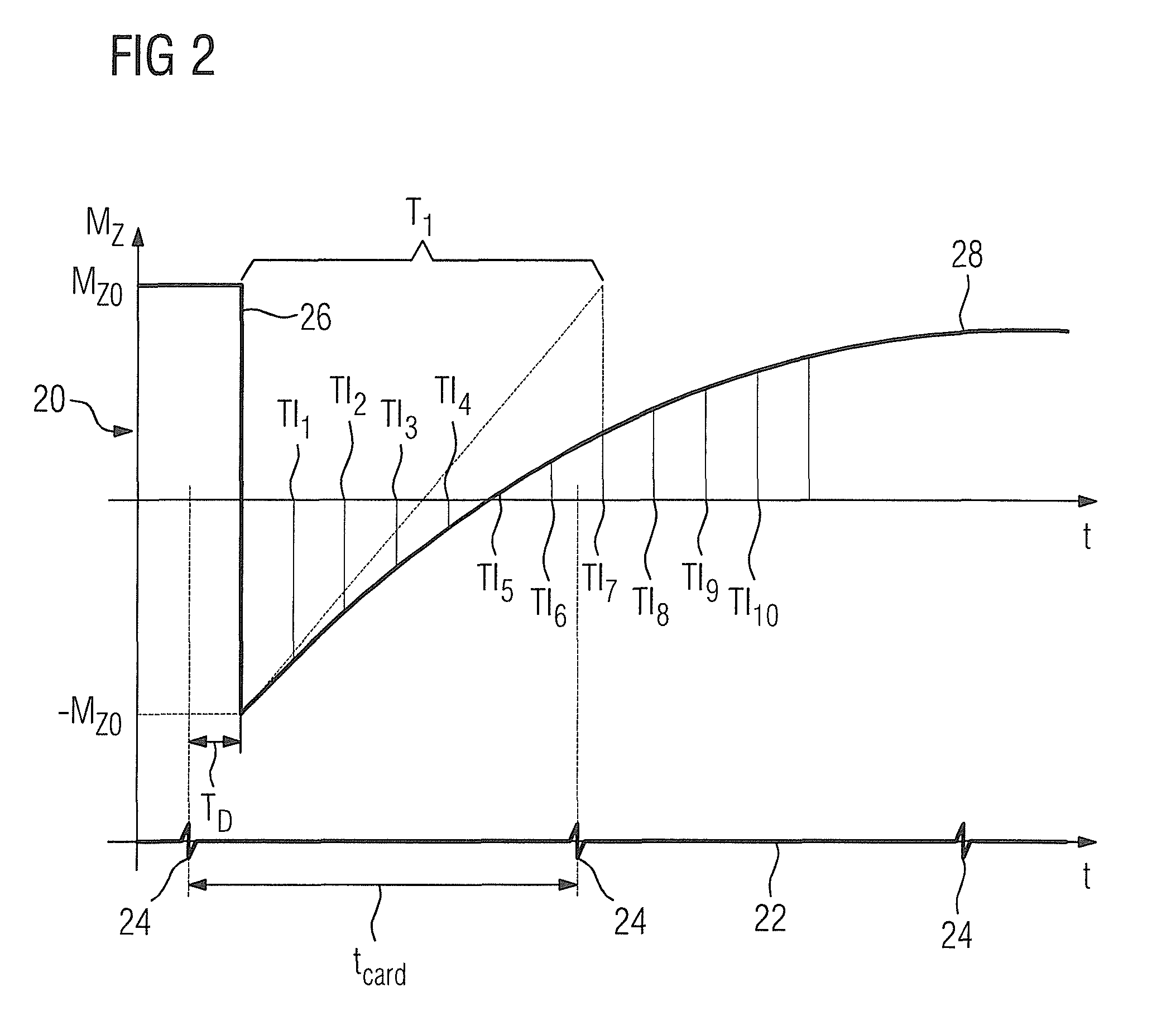
ActiveUS20130278259A1Method is fastAvoid artifactsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSpatially resolvedMagnetization
In a method for a rapid determination of spatially resolved magnetic resonance relaxation parameters in an area of examination, a preparation pulse is radiated into the area of examination. During the relaxation of the longitudinal magnetization, spatially encoded magnetic resonance signals are acquired at a minimum of two different points in time using a fast magnetic resonance sequence. At each inversion time, an image data record is reconstructed from the magnetic resonance signals, which are elastically registered to each other. From the recorded image data records, values of magnetic resonance relaxation parameters are spatially accurately determined.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
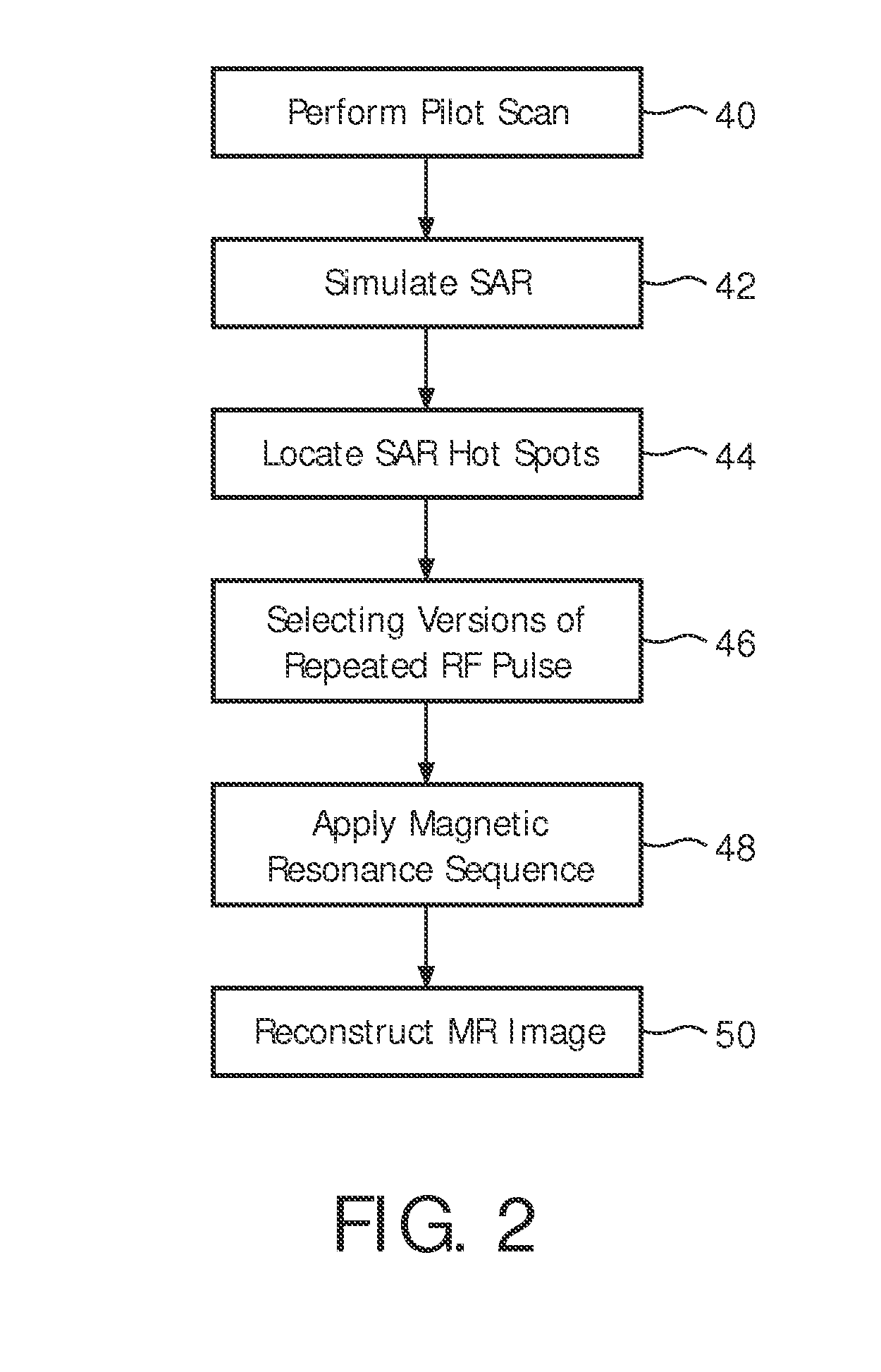
SAR hotspot reduction by temporal averaging in parallel transmission MRI
ActiveUS20120013337A1Increased duty cycleIncreased flip angleElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRPatient modelSpecific absorption rate
A magnetic resonance sequence includes a repetitively applied radiofrequency B1 pulse capable of causing a specific absorption rate (SAR) hot spot. The composition of the repetitive B1 pulse is varied to generate versions of the repetitive B1 pulse such that the SAR hot spot changes locations with subsequent applications of the repetitive B1 pulse. To generate versions of the B1 pulse, a pilot scan is performed to generate a patient model. A simulation of the SAR response to each of the versions of the repetitive B1 pulse is performed to determine the location of SAR hot spot(s). A plurality of versions of the repetitive B1 pulse is selected to be used in the magnetic resonance sequence.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
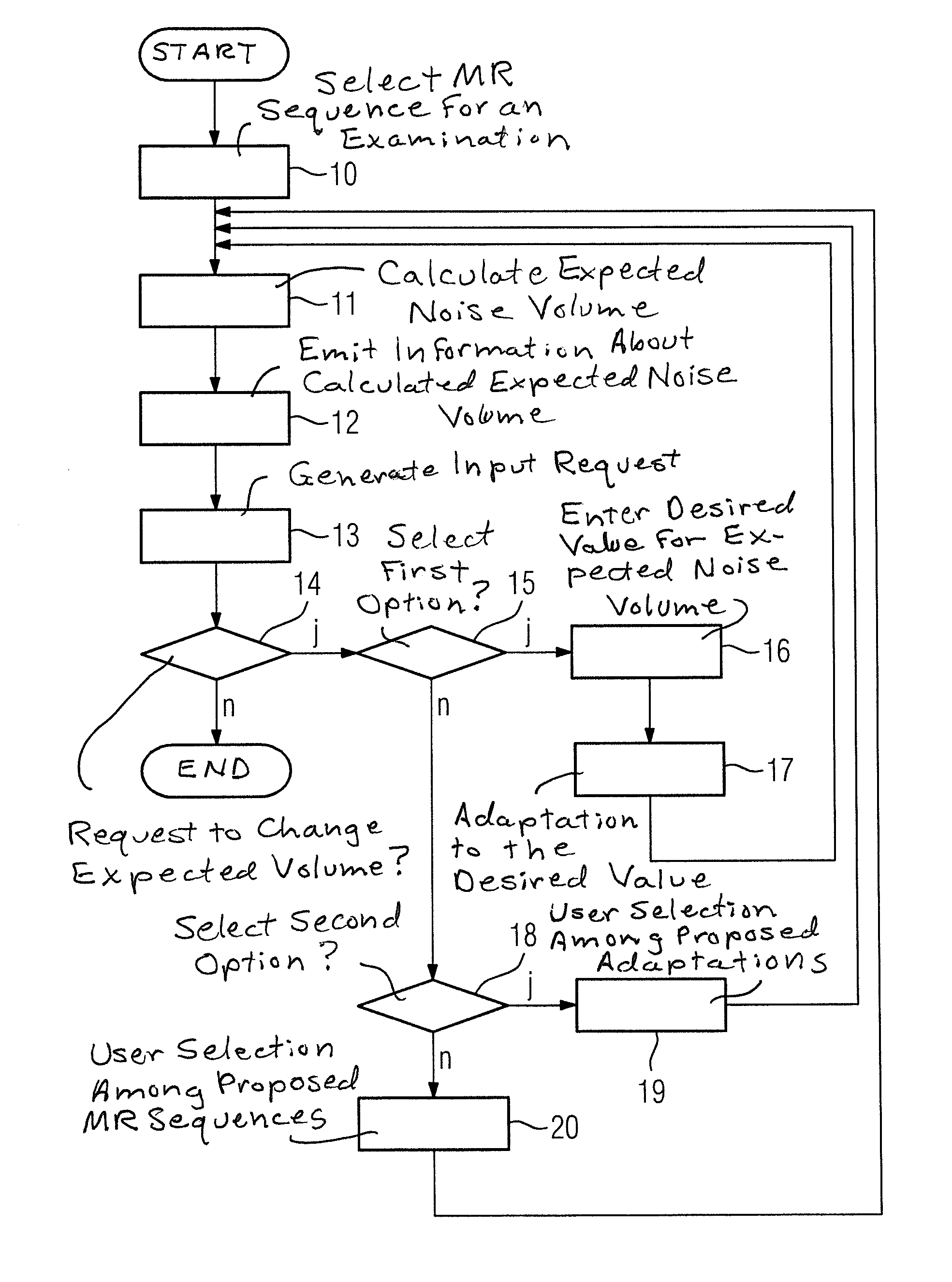
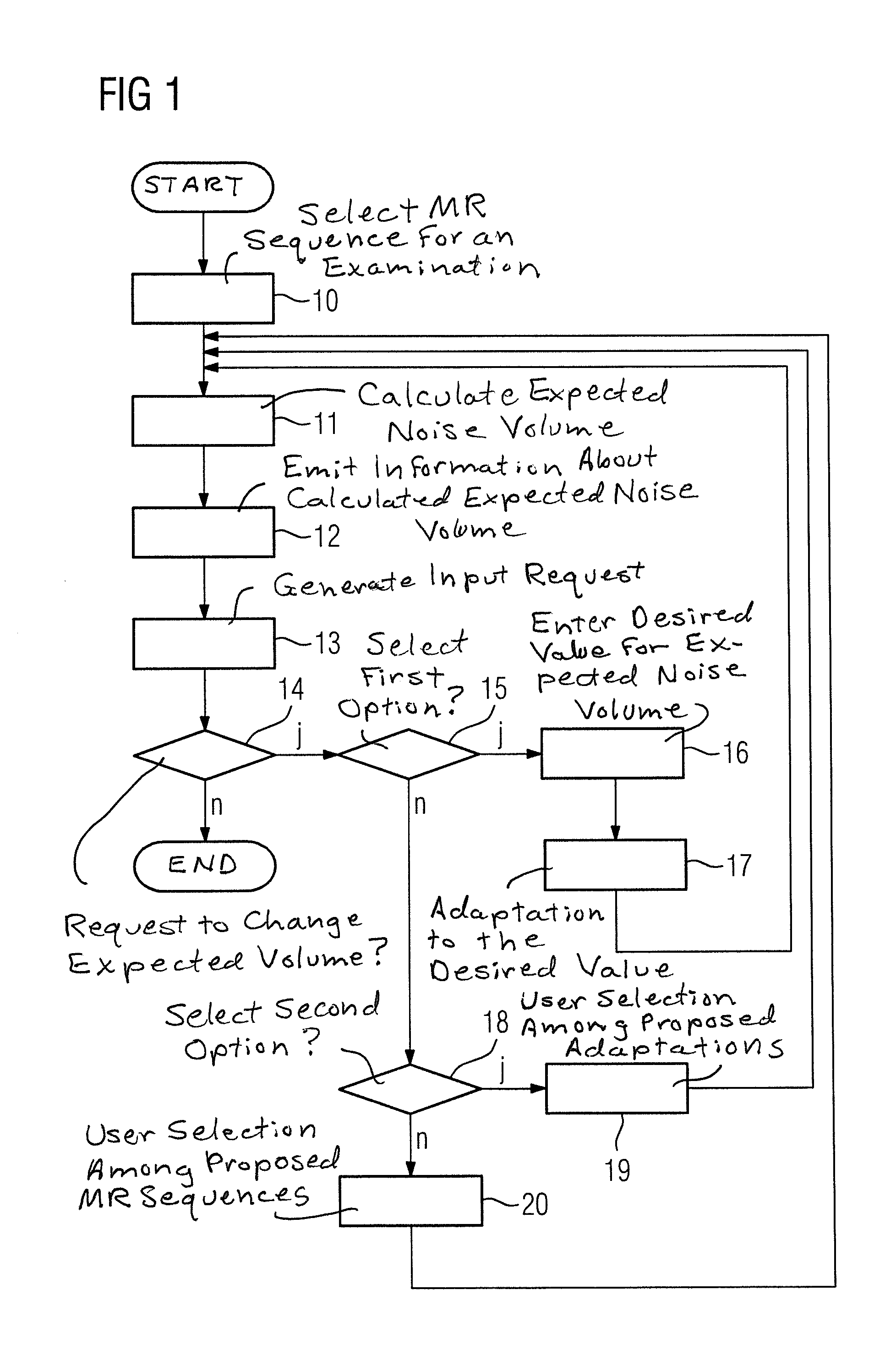
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus to identify a noise volume for a magnetic resonance examination
InactiveUS20130275086A1Effective countermeasureLower the volumeDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringResonanceUser interface
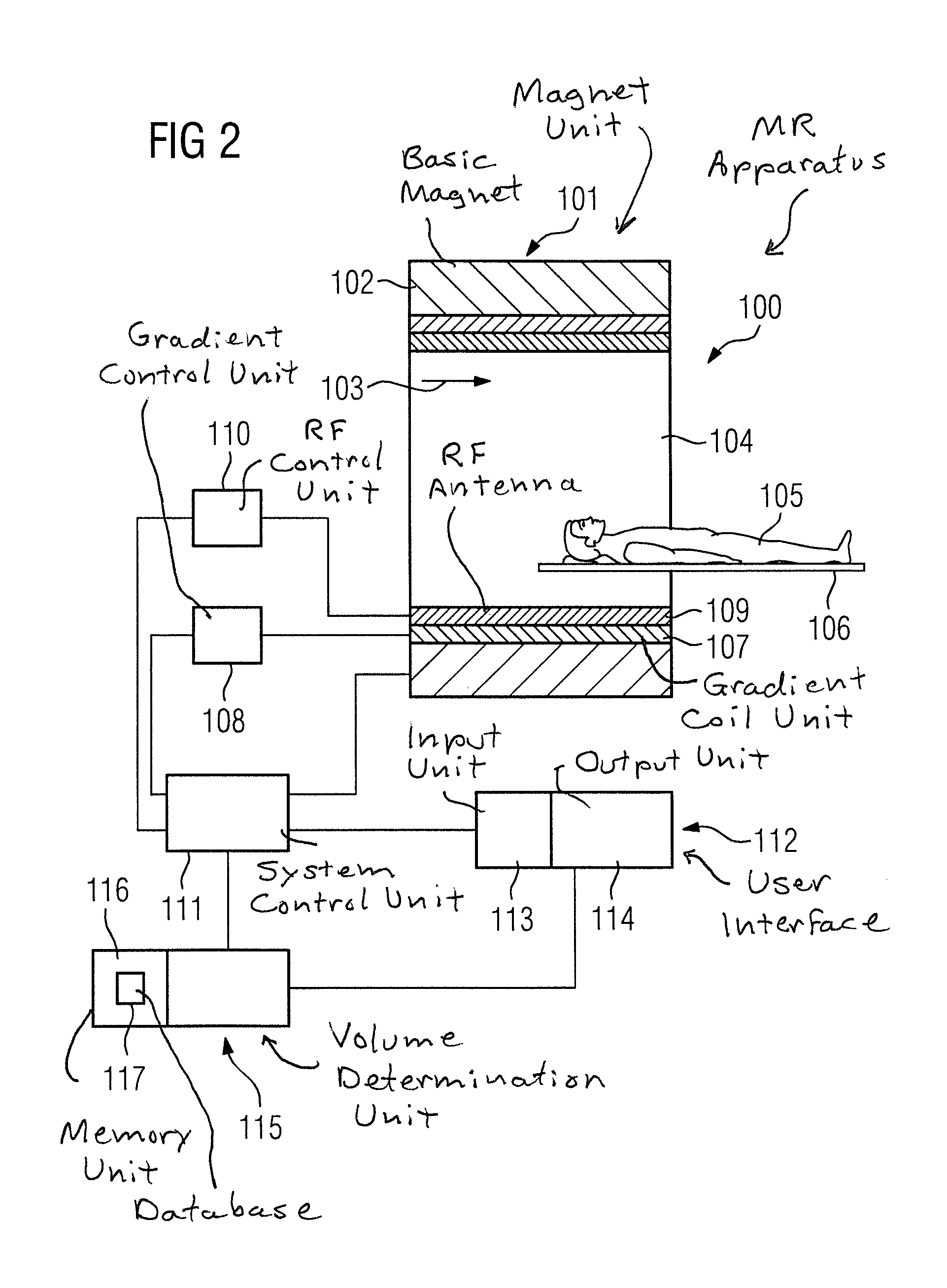
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus to determine and / or adjust a noise volume for a magnetic resonance examination, a selection of a magnetic resonance sequence for the magnetic resonance examination of a subject to be examined hereby is made and an automatic calculation of an expected noise volume for the magnetic resonance examination is made in a volume determination unit using protocol parameters of the selected magnetic resonance sequence. Information about the expected volume is provided to an operator via a user interface.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Wireless local transmit coils and array with controllable load
ActiveCN103703384AControl frequencyControl phaseMeasurements using magnetic resonanceResonanceParallel imaging
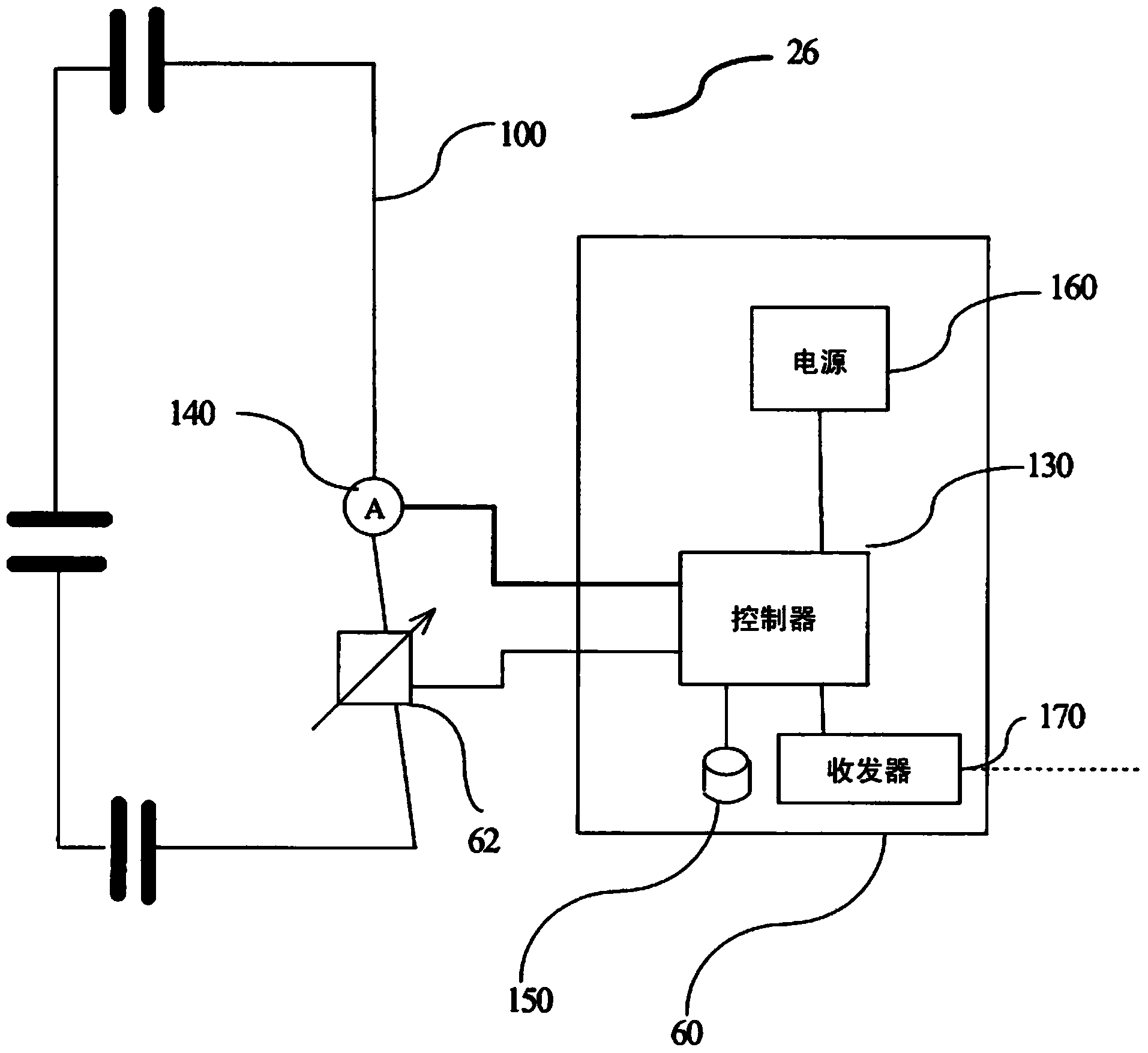
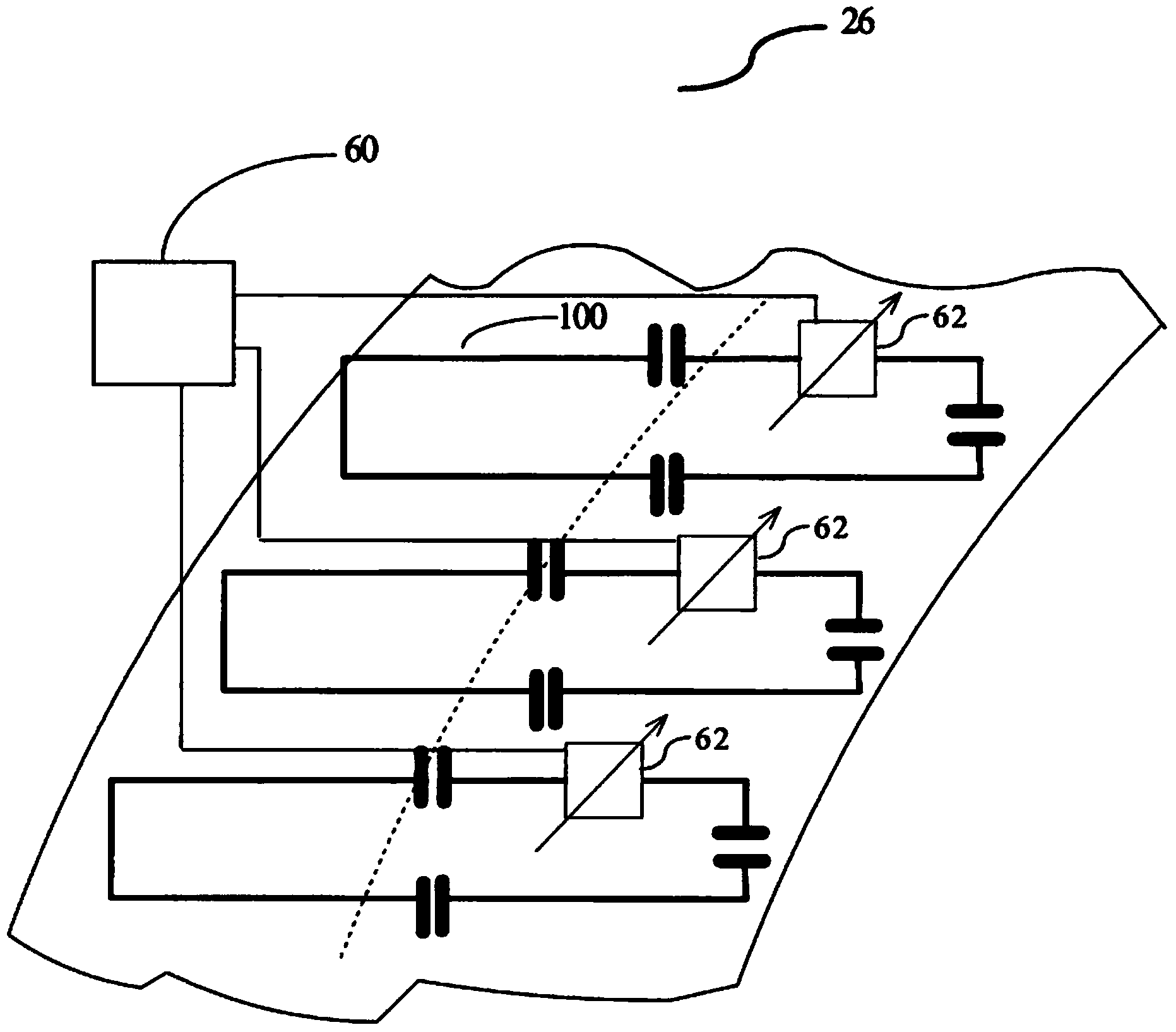
A local radio frequency (RF) transmitting coil (26) of a magnetic resonance imaging system (5) has a plurality of coil elements (100). Each coil element (100) has an adjustable load (62) which is adjusted by a control unit (60) to adjust a transmitted B1field distribution. The load can be adjusted to shim for a uniform B1 field distribution. Non-uniform B1 field distributions can be selected to perform magnetic resonance sequences that use such B1 field distributions, such as parallel imaging. The B1 field distribution can be changed during the magnetic resonance sequence to track a moving region of interest, time division multiplex parallel imaging, and the like.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus to optimize a magnetic resonance data acquisition sequence
ActiveUS20150077109A1Increased user comfortReduce the amount of noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceData acquisition
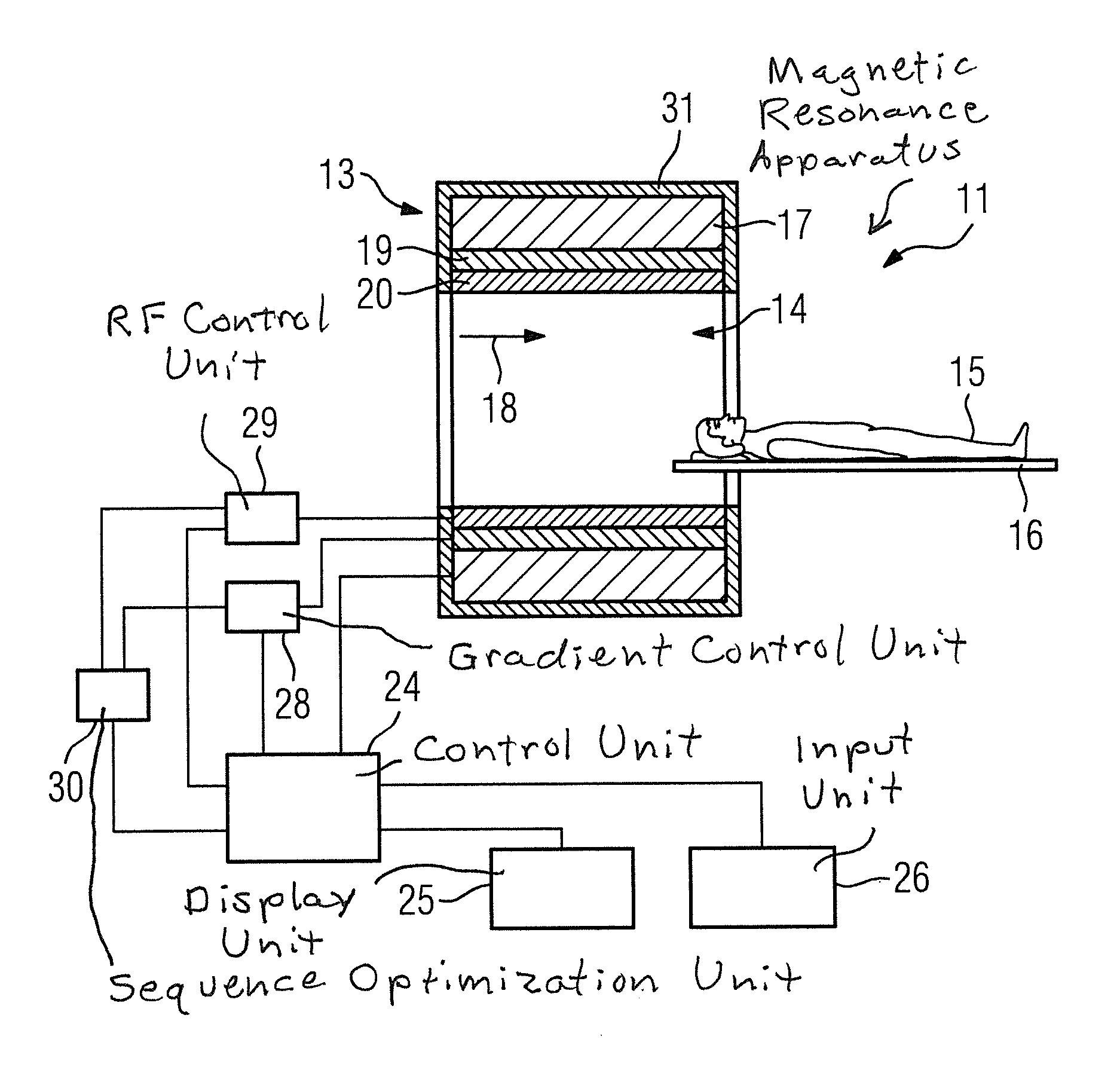
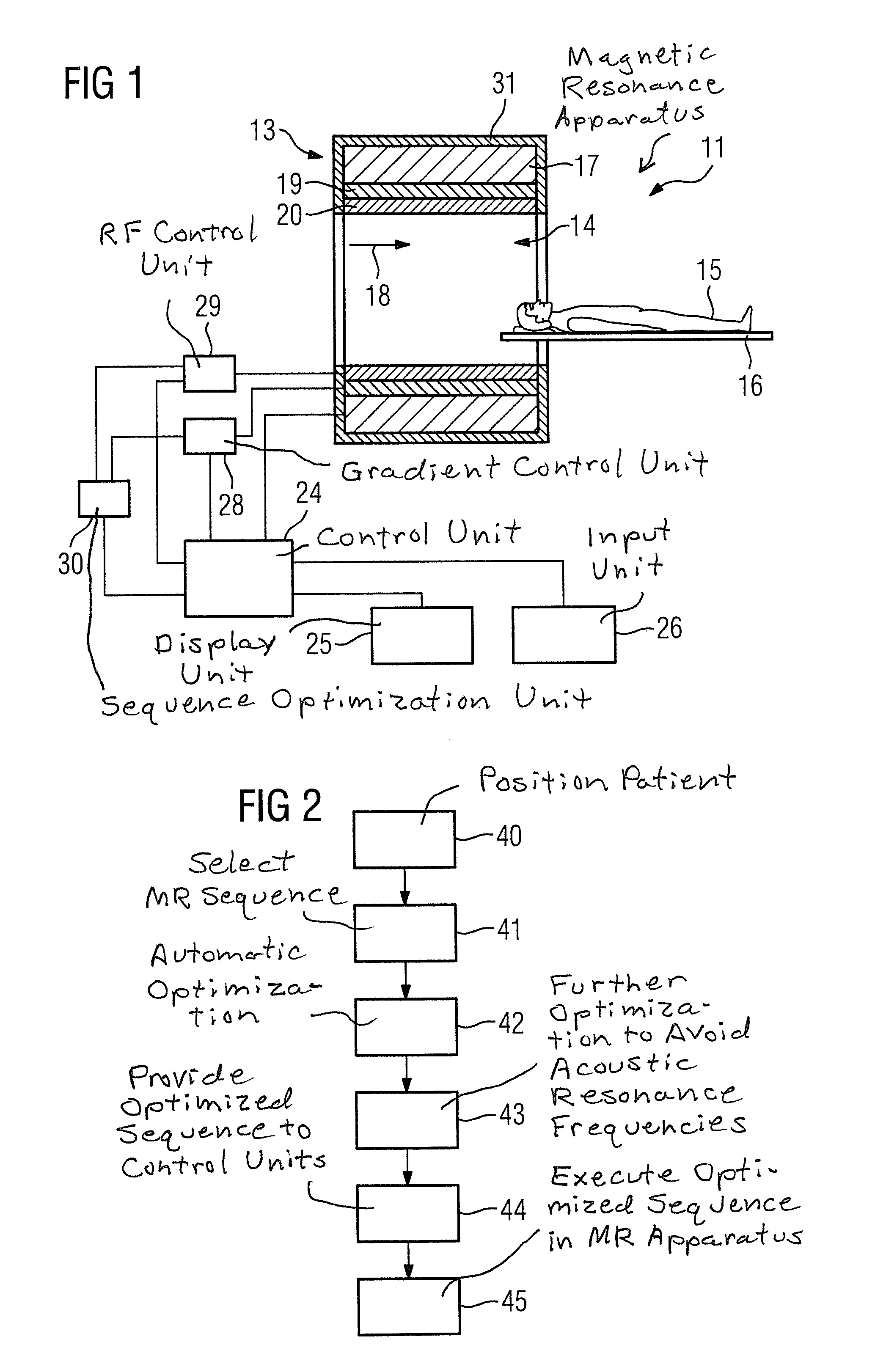
In a method to optimize a magnetic resonance sequence of a magnetic resonance apparatus, the magnetic resonance sequence includes first imaging parameters that, during acquisition of magnetic resonance images by the magnetic resonance sequence, the first imaging parameters produce acoustic noise with a first acoustic noise volume level and magnetic resonance images with image noise at a first signal-to-image noise ratio. An automatic optimization of the imaging parameters is implemented such that during acquisition of magnetic resonance images by the magnetic resonance sequence, the optimized imaging parameters produce acoustic noise with a second acoustic noise volume level and magnetic resonance images with image noise at a second signal-to-image noise ratio. The second acoustic noise volume is reduced by at least 3 dB relative to the first acoustic noise volume and the second signal-to-image noise ratio is reduced by a maximum of 35 percent relative to the first signal-to-image noise ratio.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for adjusting a parameter value of a parameter of a magnetic resonance protocol for a magnetic resonance sequence
The invention relates to a method for adjusting and / or matching a parameter value of at least one parameter of a magnetic resonance protocol for at least one magnetic resonance sequence. The method includes selecting a magnetic resonance protocol; providing a boundary condition for adjusting and / or matching parameter values of at least one parameter of the magnetic resonance protocol; providing anadjustment criterion for the parameter values of the aforementioned at least one parameter for adjusting and / or matching the magnetic resonance protocol; and depending on the provided boundary condition and depending on the provided adjustment criteria, adjusting and / or matching the parameter values of at least one parameter of the magnetic resonance protocol.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and device for optimizing a magnetic resonance sequence
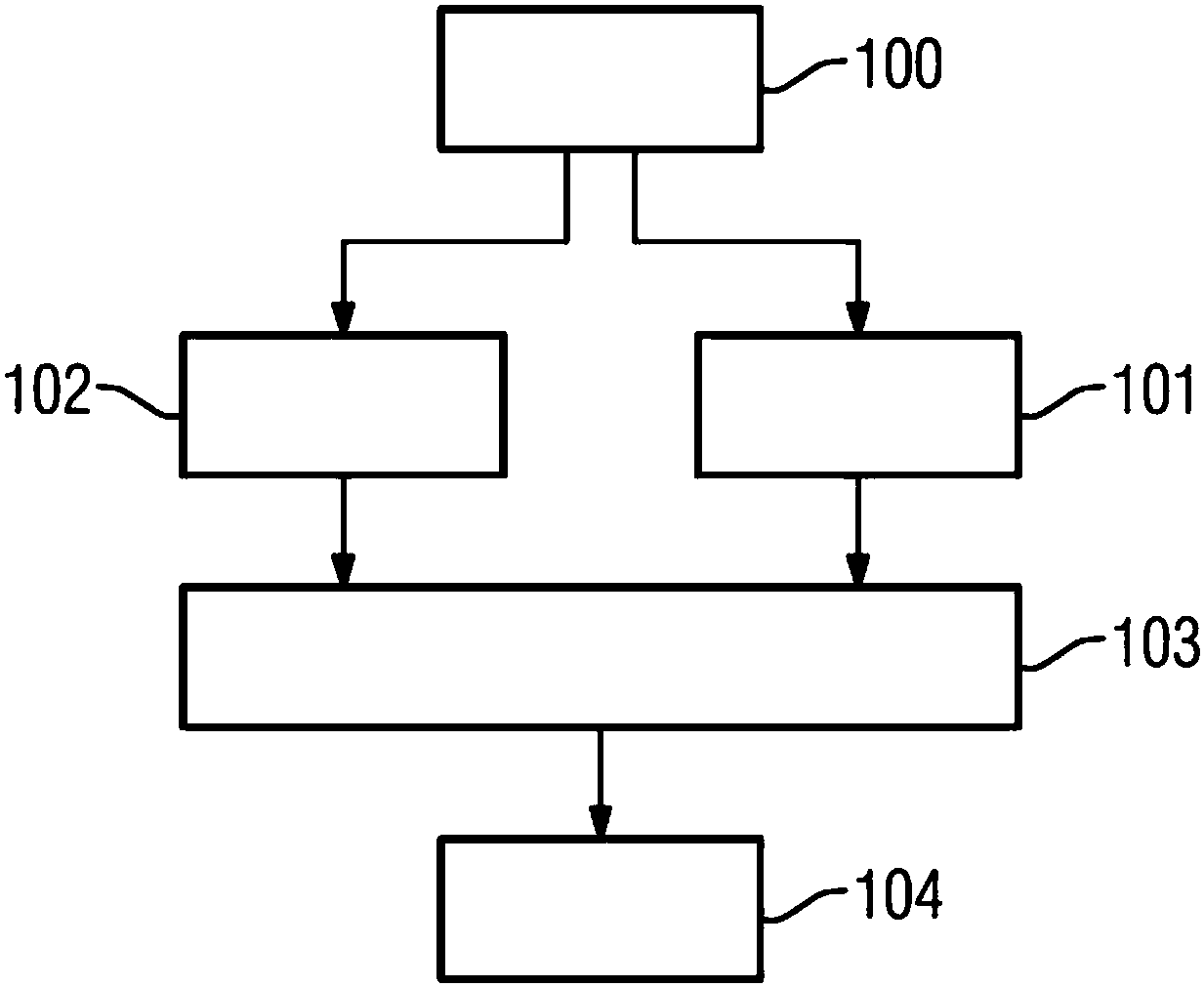
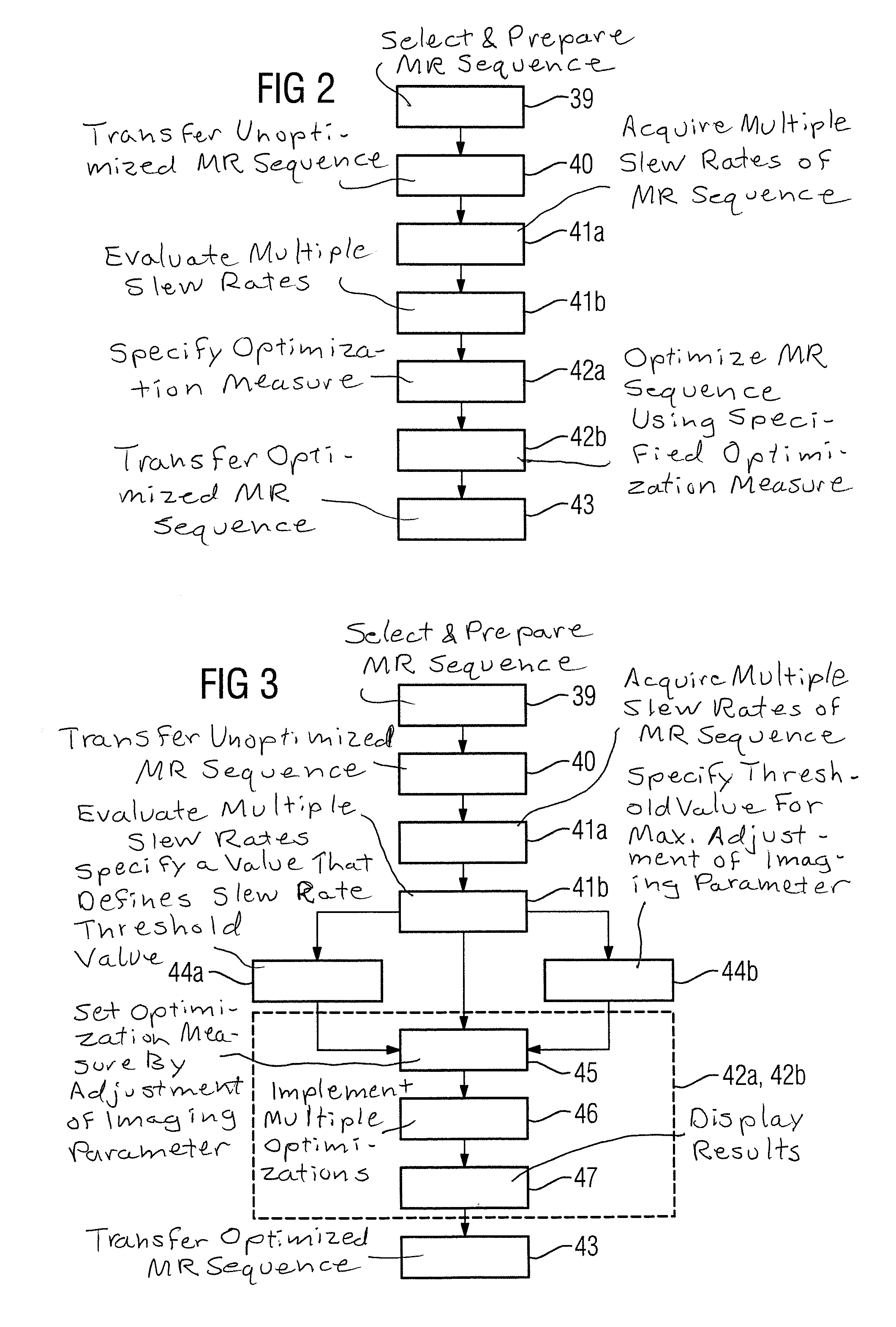
ActiveUS20150293190A1Improve efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceSlew rate
In order to provide an effective optimization of a magnetic resonance sequence, particularly with regard to optimizing the slew rates of gradient switching sequences of the magnetic resonance sequence, in a method for optimizing a magnetic resonance sequence of a magnetic resonance apparatus, wherein the magnetic resonance sequence includes multiple pre-set gradient switching sequences with multiple pre-set slew rates, the multiple pre-set slew rates are provided to a computer wherein the multiple pre-set slew rates are evaluated. At least one optimization measure for the magnetic resonance sequence is defined based on the evaluation of the multiple pre-set slew rates. The magnetic resonance sequence is optimized based on the at least one pre-set optimization measure, wherein the optimized magnetic resonance sequence has multiple optimized gradient switching sequences with multiple optimized slew rates, and the multiple optimized slew rates being optimized in relation to the multiple pre-set slew rates.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and device for automated generation of a formal description of a magnetic resonance system measurement sequence
InactiveCN101661087ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceSequence model
A magnetic resonance sequence model that is a formal description of a measurement sequence is used to automate measurement sequence programming. The sequence model allows a system-independent specification of the measurement sequence for execution in a magnetic resonance scanner. The sequence model is as formal as possible; it is limited to the minimum required information for description of a measurement sequence without limiting the flexibility in the sequence programming. A method for formal description of the measurement sequence describes the measurement sequence by a number of parameters to be parameterized. The parameterization of the measurement sequence can ensue automatically from the formalized description of the measurement sequence, except for a set of parameters that are still be determined. For automatic generation of an executable measurement sequence, the method determines the parameters to be determined using a solver, under consideration of boundary conditions, so that a consistent set of parameters is created that completely describes the measurement sequence. This complete description of parameter values of the measurement sequence is then be translated automatically into a programming language that can be directly executed in the magnetic resonance scanner.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
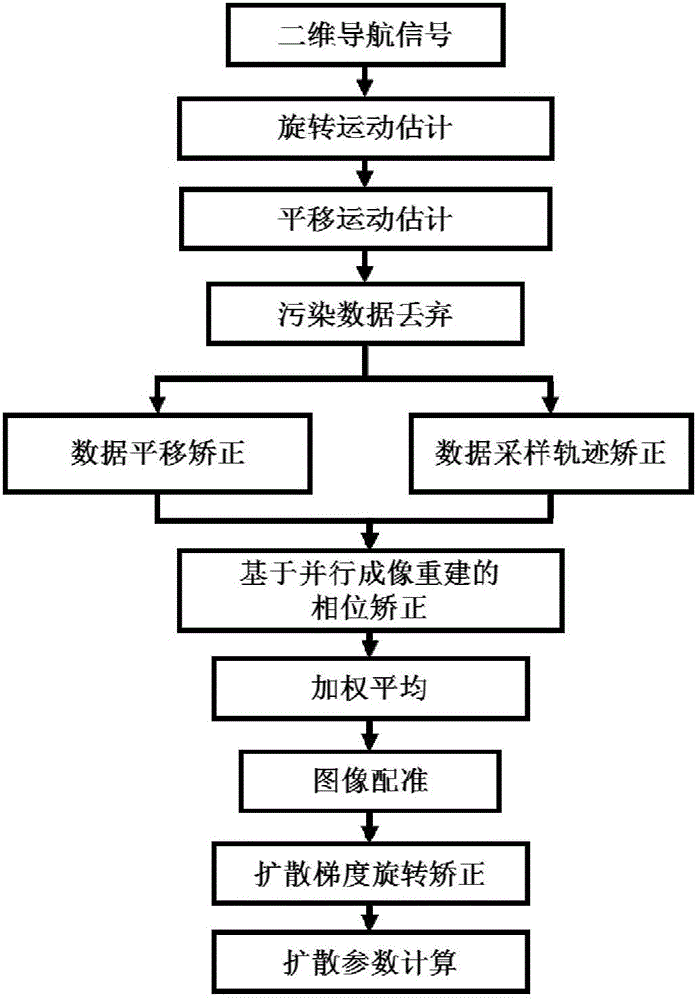
Motion correction method for magnetic resonance multiple excitation diffusion imaging
ActiveCN106780643AHigh resolutionLess geometric distortionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionParallel imagingDiffusion gradient
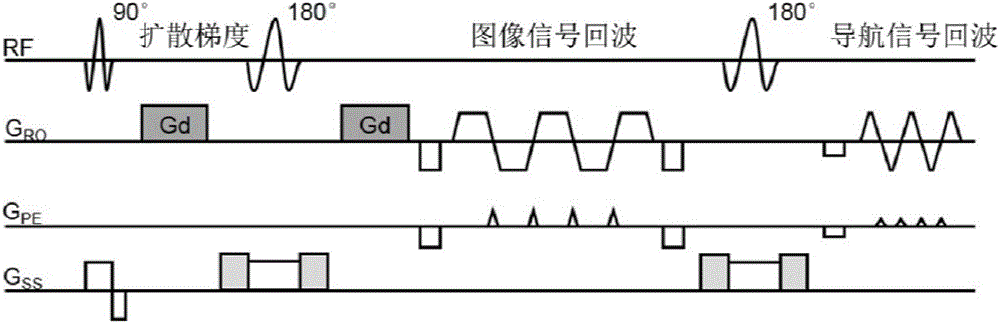
The invention discloses a motion correction method for magnetic resonance multiple excitation diffusion imaging. The method comprises the steps of collecting a magnetic resonance multiple excitation sequence; obtaining an image echo signal and a two-dimensional navigation signal through a magnetic resonance scanning sequence; estimating motion parameters through the two-dimensional navigation signal; performing rotational and translational correction on the image echo signal and the two-dimensional navigation signal according to the motion parameters, and discarding tainted data, thereby obtaining corrected data; integrating the corrected data collected in multiple excitation to perform parallel imaging reconstruction; estimating rotational motion parameters through an image registration algorithm to perform diffusion gradient correction on a reconstructed image; and performing final calculation by utilizing corrected diffusion image and diffusion gradient to obtain diffusion tensor imaging parameters. According to the method, various motion errors in a magnetic resonance diffusion imaging scanning process can be effectively corrected, so that an artifact-free high-resolution diffusion tensor image is obtained, the errors are effectively reduced, and the accuracy of calculating magnetic resonance diffusion imaging tensor parameters is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Magnetic resonance scanning trigger method and device
InactiveCN108186015AAccurately reflect breathing statusSuppresses Motion ArtifactsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAcquisition timeResonance
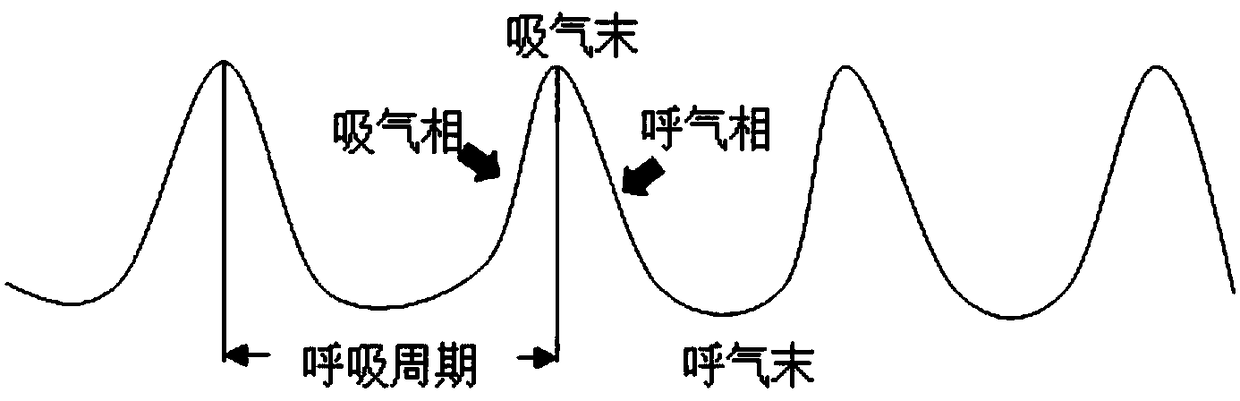
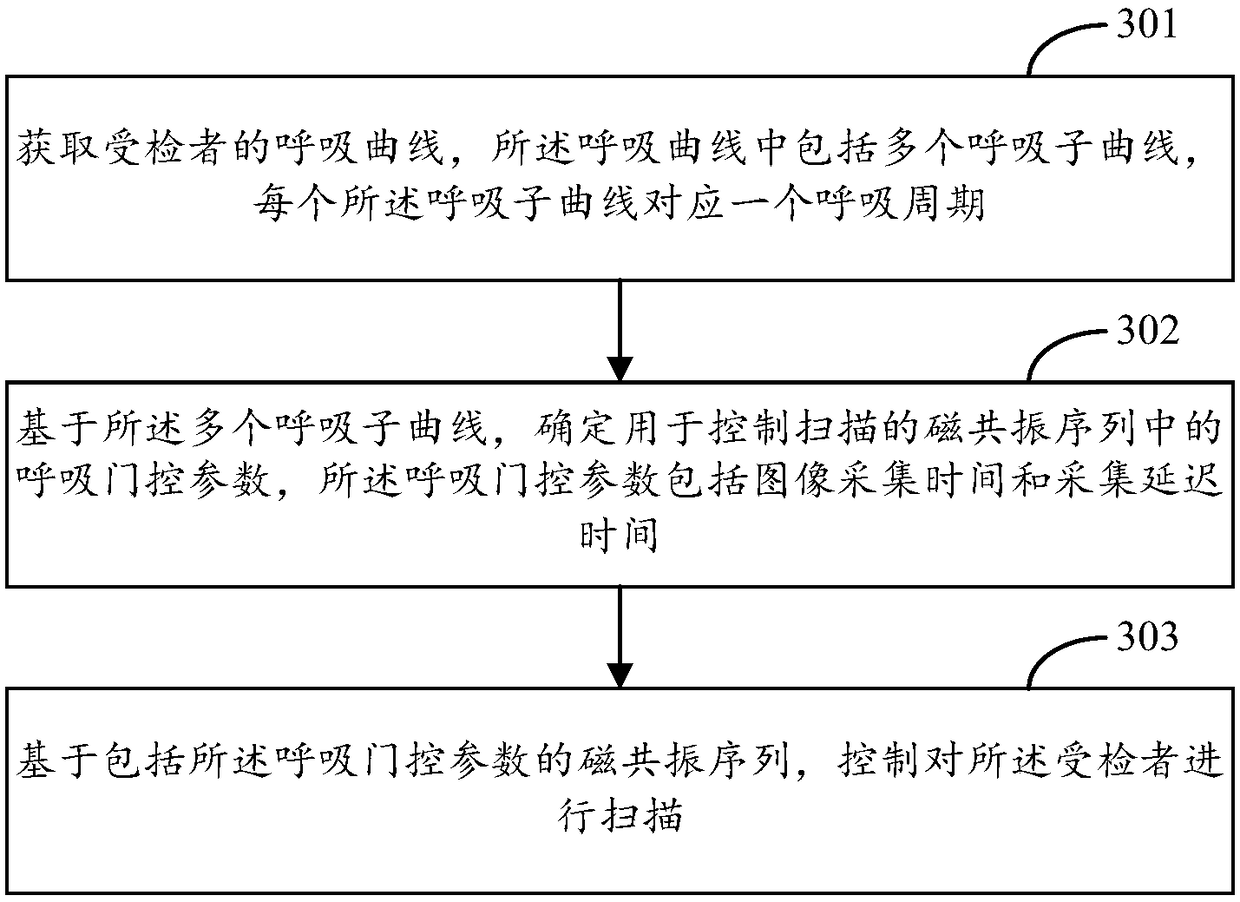
The invention provides a magnetic resonance scanning trigger method and device. The method includes the steps that a respiration curve of a subject is acquired, wherein the respiration curve comprisesmultiple respiration sub-curves, and each respiration sub-curve corresponds to one respiration period; based on the respiration sub-curves, respiration gating parameters in magnetic resonance sequences for controlling scanning are determined, wherein the respiration gating parameters comprise image acquisition time and acquisition delay time; based on the magnetic resonance sequences comprising the respiration gating parameters, the subject is controlled to be scanned. By means of the technical scheme, motion artifacts caused by respiration motion of the subject can be effectively restrained,and high-quality magnetic resonance images are obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEUSOFT MEDICAL TECH LTD
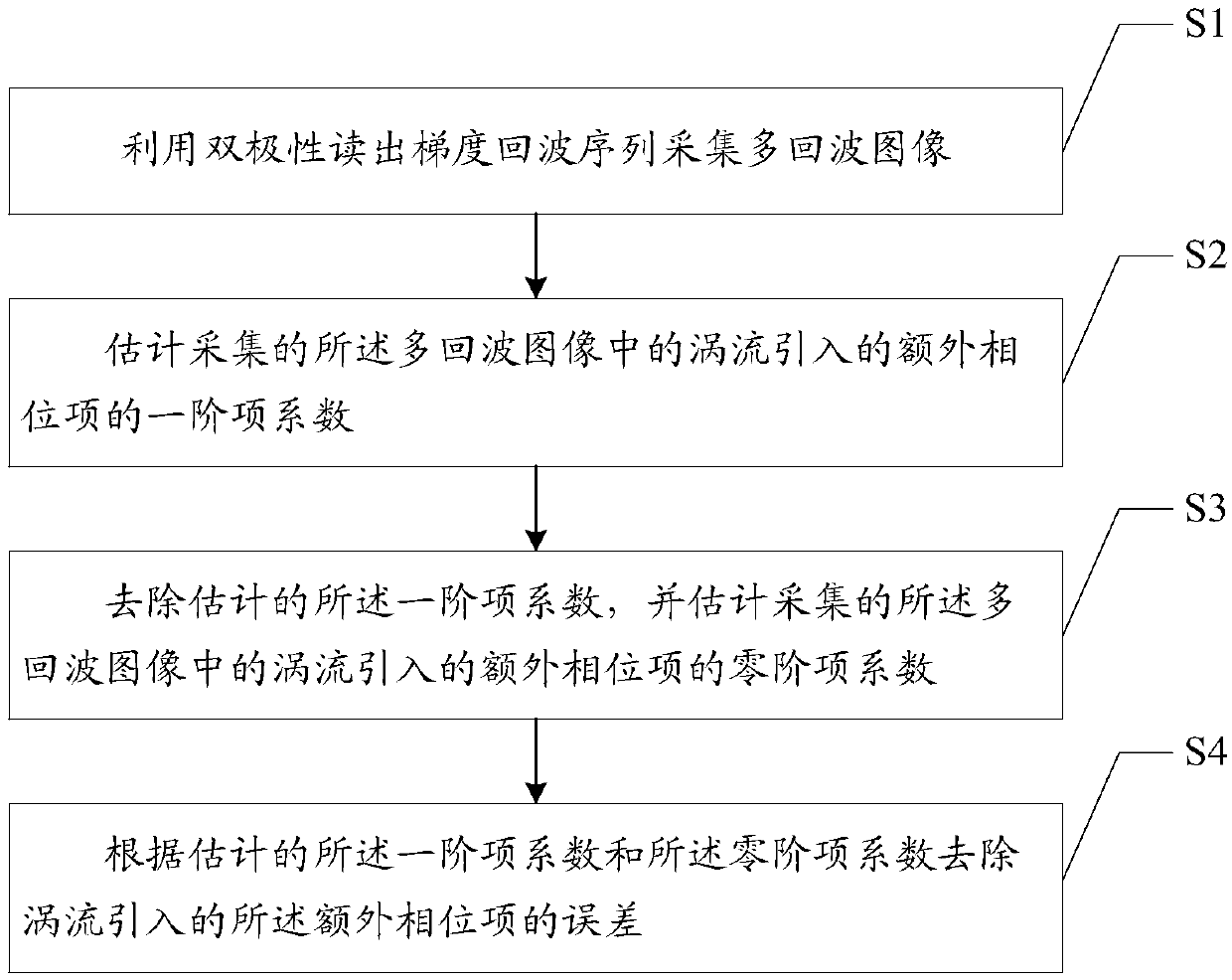
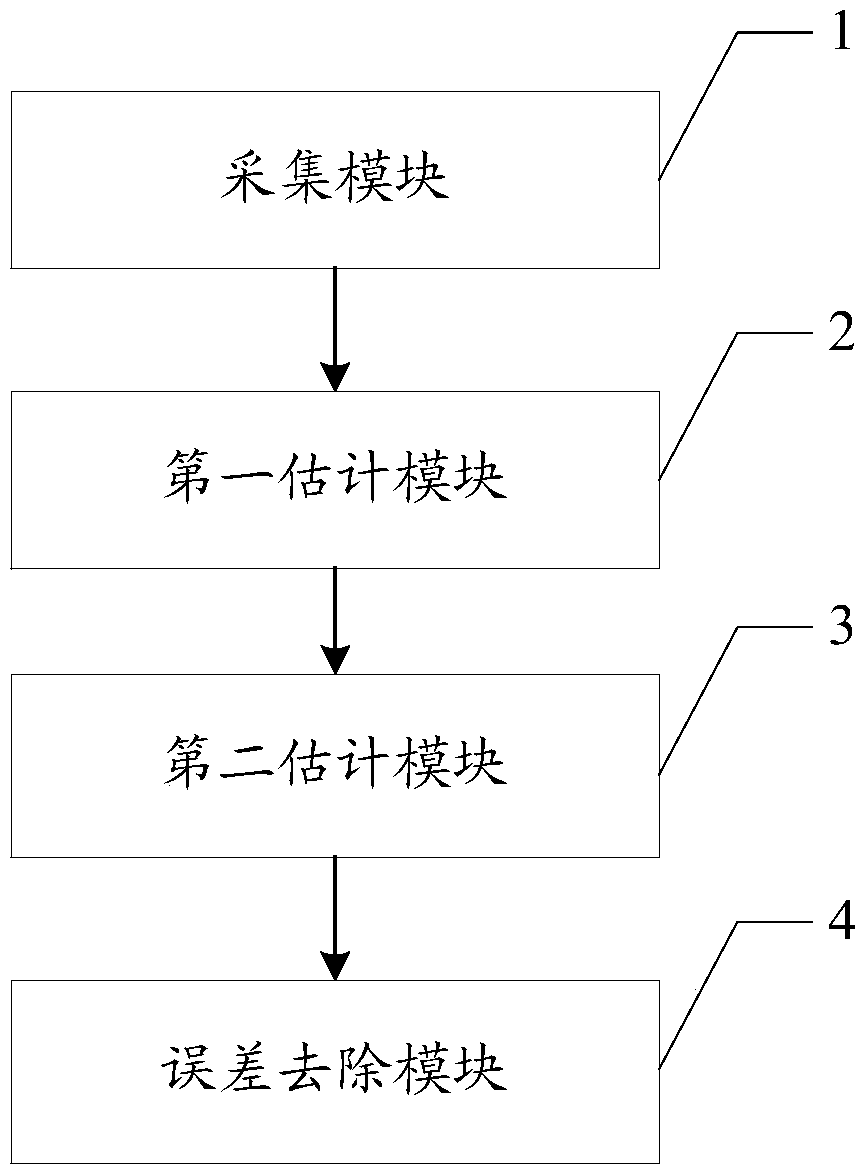
Eddy current correction method and device, mobile terminal and readable storage medium
ActiveCN107907846AThe separation result is accurateMagnetic measurementsComputer terminalEddy current
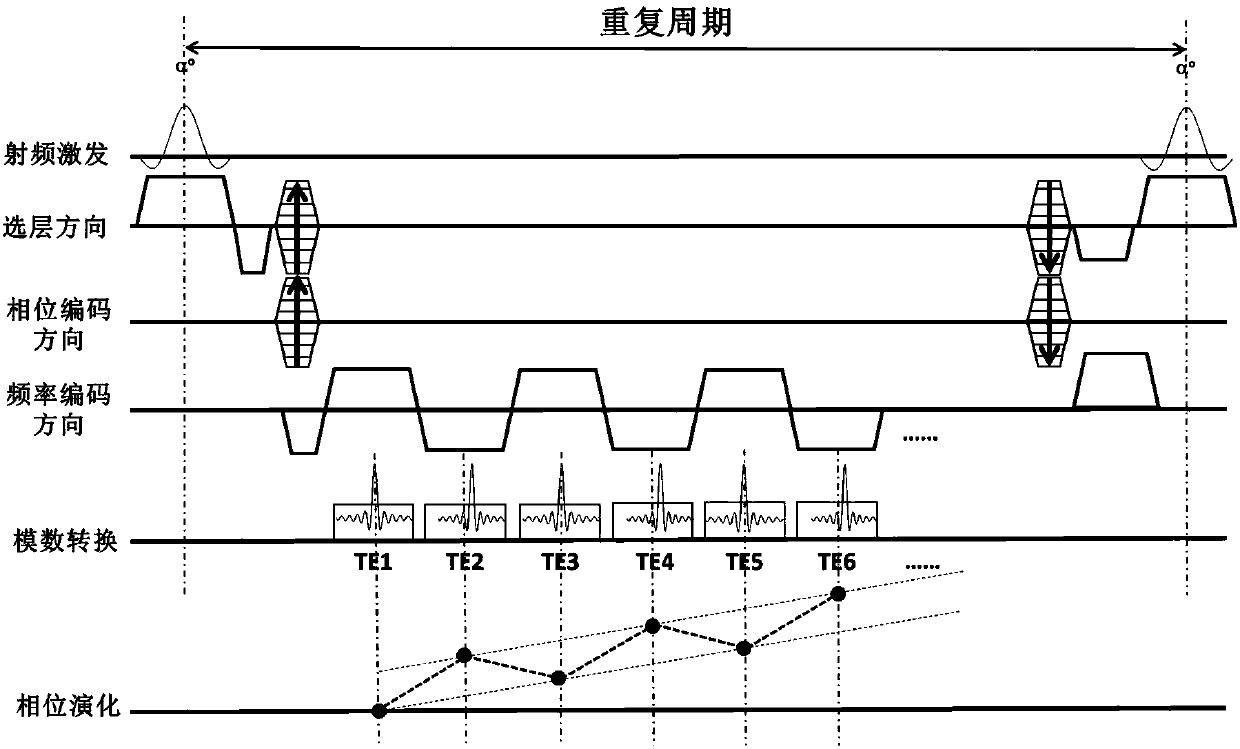
The invention is suitable for and belongs to the field of magnetic resonance sequence design, and provides an eddy current correction method and device, a mobile terminal and a readable storage medium. The method includes the following steps: S1, using a bipolar readout gradient echo sequence to collect a multi-echo image; S2, estimating the first-order phase coefficient of an additional phase term introduced by eddy current in the collected multi-echo image; S3, removing the estimated first-order phase coefficient, and estimating the zero-order phase coefficient of the additional phase term introduced by eddy current in the collected multi-echo image; and S4, removing the error of the additional phase term introduced by eddy current according to the estimated first-order phase coefficientand the estimated zero-order phase coefficient. Through the eddy current correction method provided by the invention, the phase error caused by eddy current in the collected image can be removed, andthe correctness of the result of a subsequent water-fat separation algorithm can be ensured.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus for image acquisition
ActiveUS20140097840A1Improve contrast ratioImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMeasurement pointSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
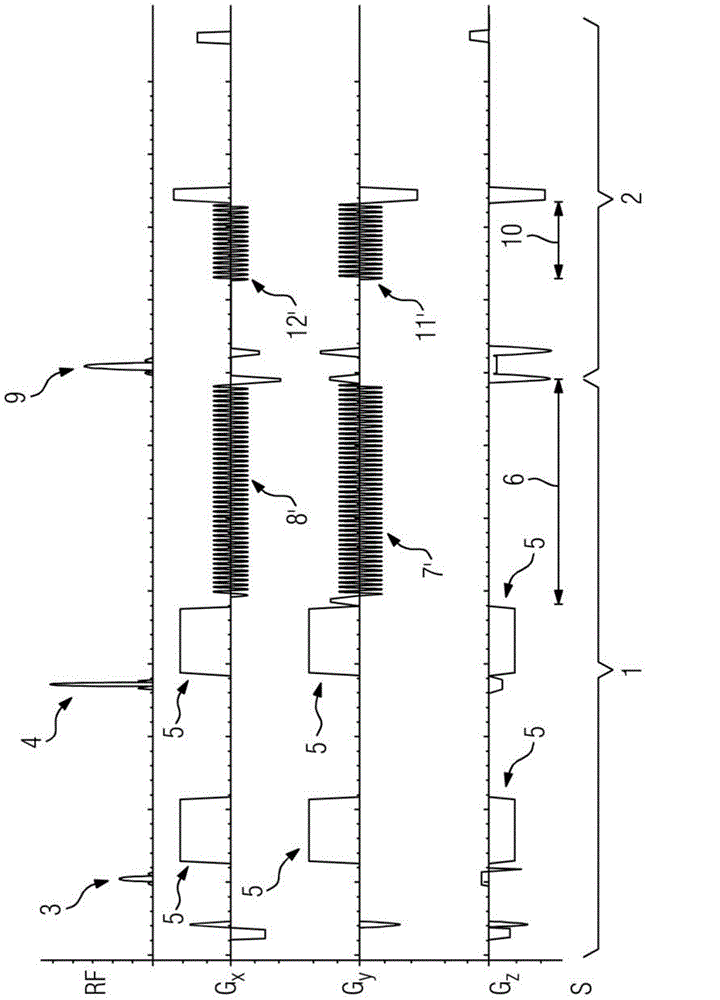
A method and magnetic resonance apparatus for image acquisition using a magnetic resonance sequence (in particular a PETRA sequence) in which k-space corresponding to the imaging area is scanned, with a first region of k-space, which does not include the center of k-space, being scanned radially along a number of spokes emanating from the center of k-space, and with at least two phase coding gradients being completely ramped up before administration of the excitation pulse, and a second central region of k-space, which remains without the first region, is scanned in a Cartesian manner (in particular via single point imaging). For the purpose of a contrast increase a pre-pulse—in particular an inversion pulse to establish a T1 contrast—is provided before a predetermined number of individual measurements. The number of spokes to be measured is selected such that a measurement point located (in a Cartesian manner) nearest to the center of k-space is measured at a predetermined point in time after a pre-pulse, which point in time is optimal with regard to the signal-to-noise ratio and / or the contrast.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance system and method for comprehensive implantable device safety tests and patient safety monitoring
InactiveCN102369450AReal-time security monitoringReduce safety monitoringMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic variable regulationUnsafe conditionResonance
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus to determine and/or adjust a noise volume for a magnetic resonance examination
InactiveCN103376427AMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceUser interface
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus to determine and / or adjust a noise volume for a magnetic resonance examination, a selection of a magnetic resonance sequence for the magnetic resonance examination of a subject to be examined hereby is made and an automatic calculation of an expected noise volume for the magnetic resonance examination is made in a volume determination unit using protocol parameters of the selected magnetic resonance sequence. Information about the expected volume is provided to an operator via a user interface.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus to acquire magnetic resonance data with a diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance sequence
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus to acquire magnetic resonance data with a diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance sequence wherein the magnetic resonance apparatus as a gradient coil arrangement with three gradient coils designed to generate a gradient in gradient directions orthogonal to one another, the readout gradient is flipped relative to at least one of the gradient directions such that at least two gradient coils contribute to a possible slew rate of a readout gradient pulse, and such that a phase coding gradient that is constant over the readout time period is selected.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for a rapid determination of spatially resolved magnetic resonance relaxation parameters in an area of examination
ActiveUS9547059B2Method is fastAvoid artifactsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSpatially resolvedInversion Time
In a method for a rapid determination of spatially resolved magnetic resonance relaxation parameters in an area of examination, a preparation pulse is radiated into the area of examination. During the relaxation of the longitudinal magnetization, spatially encoded magnetic resonance signals are acquired at a minimum of two different points in time using a fast magnetic resonance sequence. At each inversion time, an image data record is reconstructed from the magnetic resonance signals, which are elastically registered to each other. From the recorded image data records, values of magnetic resonance relaxation parameters are spatially accurately determined.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for attenuation correction of emission tomography scan data
ActiveUS20160259024A1High resolutionAccurate informationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
In a method for attenuation correction of emission tomography scan data acquired from an examination object in a combined magnetic resonance emission tomography apparatus, wherein an interference object is situated in the examination region, which causes a magnetic interference field during combined magnetic resonance emission tomography imaging, magnetic resonance scan data of the examination object are acquired by executing a magnetic resonance sequence designed to at least partially compensate inference due to the magnetic interference field. Emission tomography scan data are acquired and an attenuation map is generated using the acquired magnetic resonance scan data. Attenuation correction of the emission tomography scan data is implemented using the generated attenuation map.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
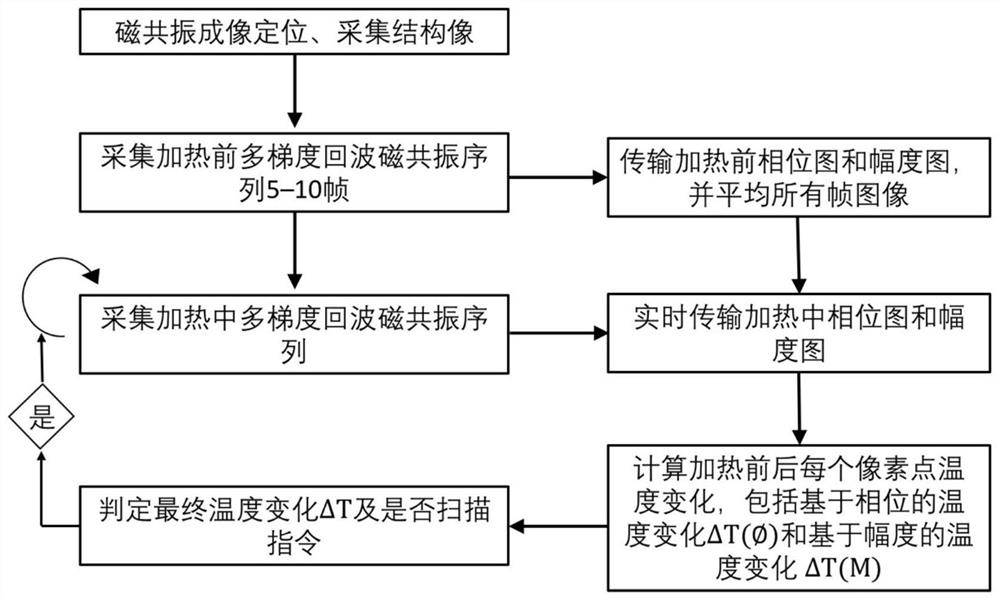
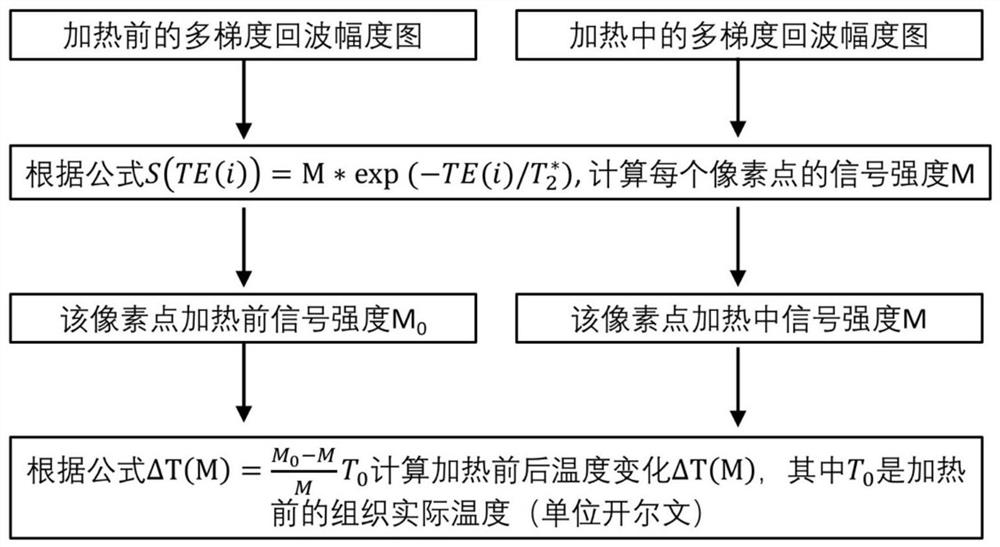
Bimodal magnetic resonance temperature measurement method based on multi-gradient echo sequence
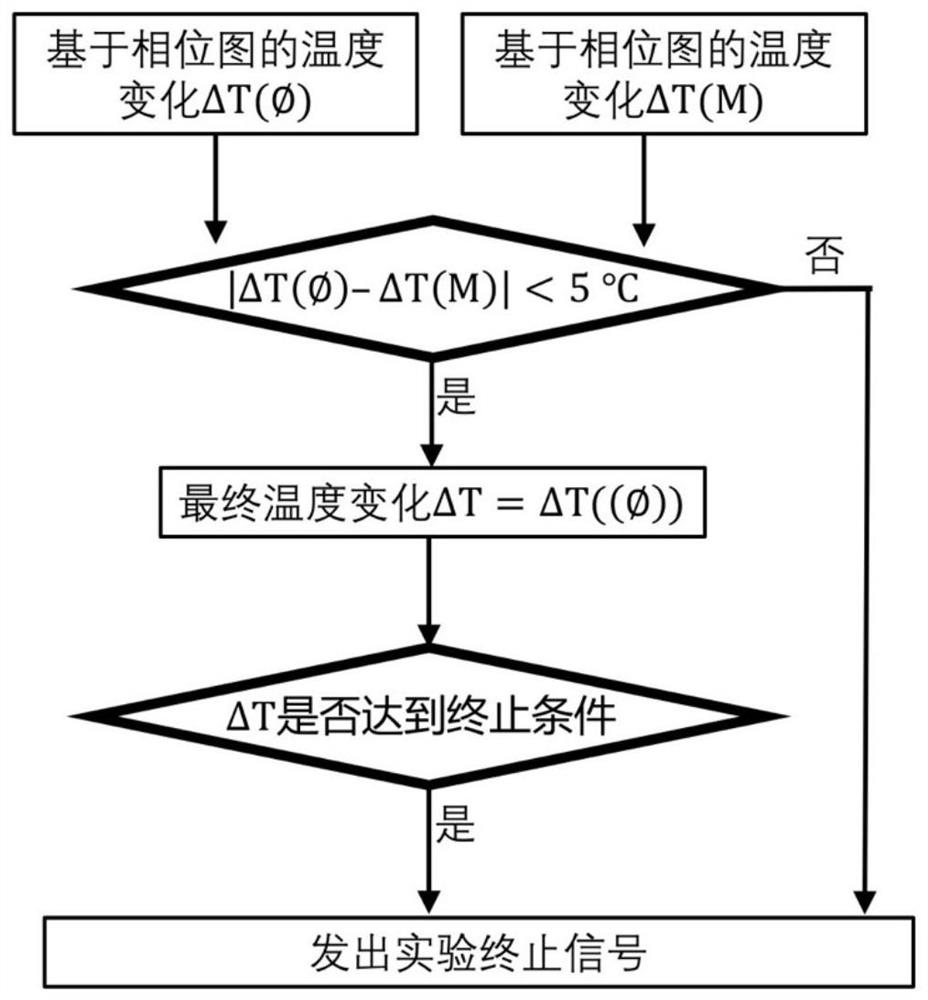
ActiveCN111714097AImprove temperature measurement accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGradient echoMagnetic resonance sequence
The invention discloses a bimodal magnetic resonance temperature measurement method based on a multi-gradient echo sequence. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring magnetic resonance signals before and during heating through the multi-gradient echo magnetic resonance sequence, and meanwhile, reserving a phase diagram and an amplitude diagram of each echo; according to the phase diagrams of different echoes before and during heating, calculating temperature changes of each pixel point on the phase diagrams before and after heating, and according to the amplitude diagrams of different echoes during heating, calculating signal intensity of each pixel point when TE is 0; according to the signal intensity of the amplitude diagrams before heating and the signal intensity of each pixel point when TE is 0, calculating temperature change delta T(M) of each pixel point based on an amplitude value; and according to the sum delta T(M), judging final actual temperature T of each pixelpoint or giving out an error warning. According to the temperature measurement method, by synchronous use of the amplitude diagrams and the phase diagrams in multi-gradient echo magnetic resonance temperature imaging, bimodal temperature imaging is realized, and accuracy of magnetic resonance temperature imaging is further improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU GENLIGHT MEDTECH CO LTD
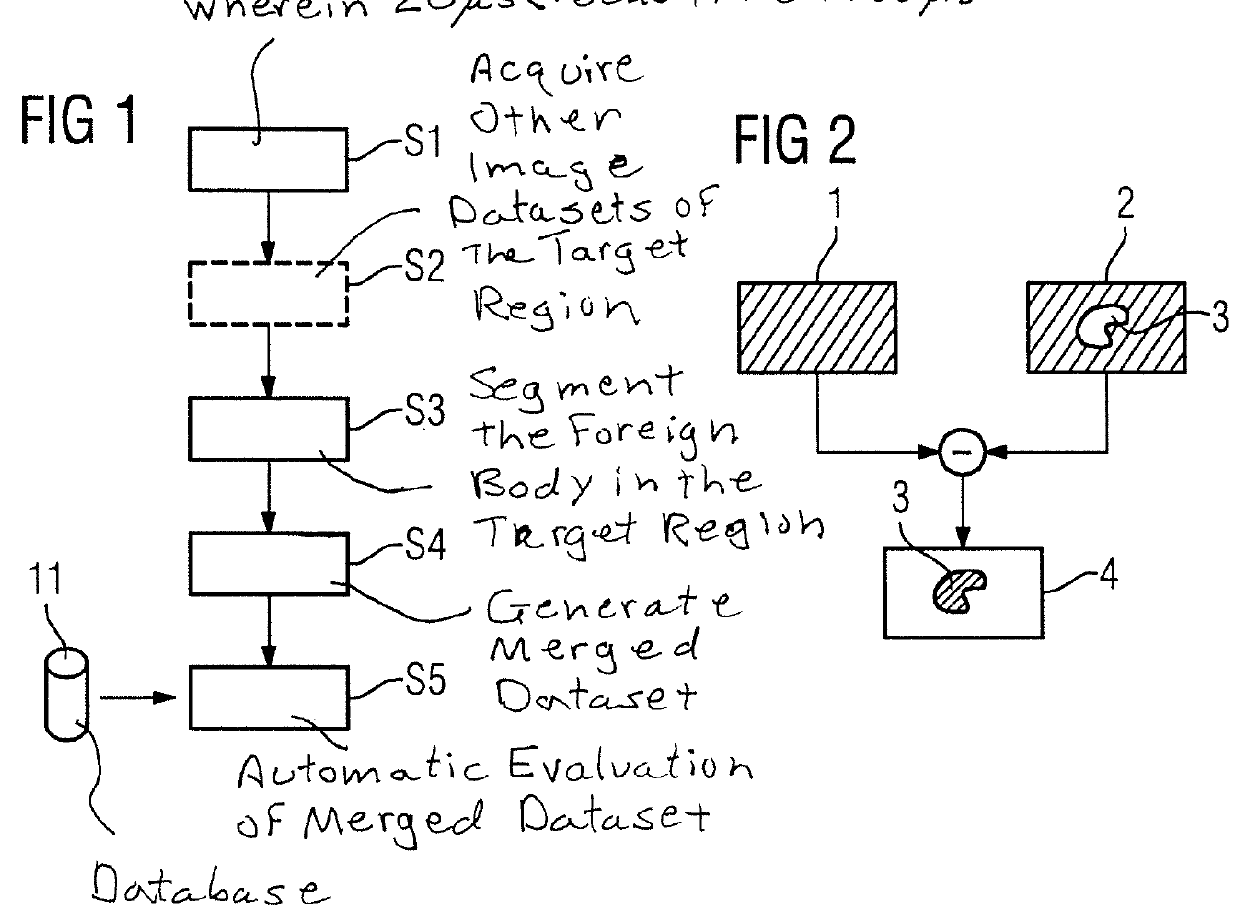
Method and apparatus for recording a magnetic resonance dataset of at least one foreign body in a patient
ActiveUS20160033602A1Rapid signal decaySimplify the segmentation processMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionProton magnetic resonanceResonance
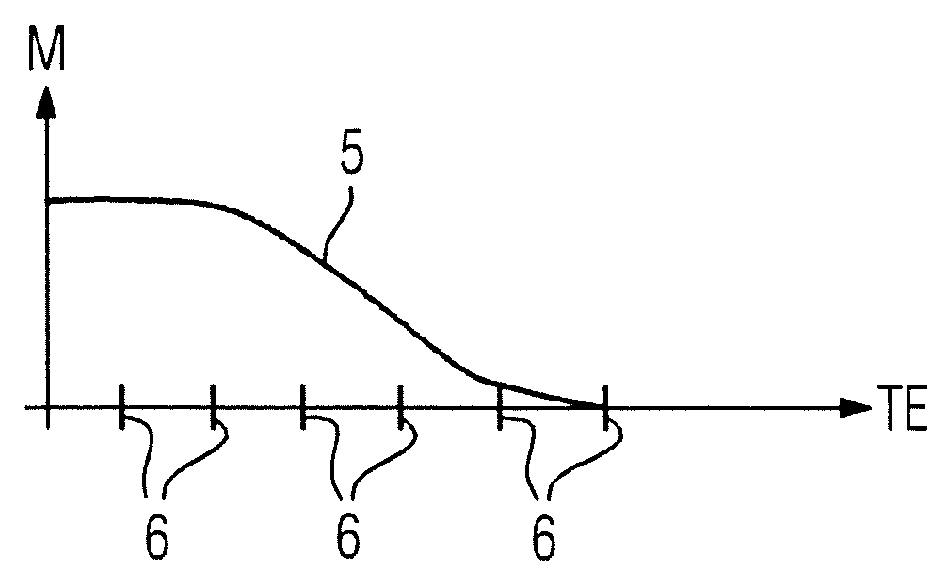
In a method and apparatus for recording a magnetic resonance dataset of at least one foreign body in a target region of a patient, a magnetic resonance sequence having an ultra-short echo time, which is less than 500 μs is used for recording the magnetic resonance data.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method and apparatus for acquiring magnetic resonance data from a target region while the target region moves due to respiration
ActiveUS20160069976A1Reduced conversion timeLarge in inversion timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceInversion Time
In a method for recording magnetic resonance data in a target region of a patient while the target region moves due to respiration a single-shot turbo spin echo sequence is used as a magnetic resonance sequence in a magnetic resonance apparatus. SPAIR fat saturation is used by emitting an inversion pulse at an inversion time before the data recording with the magnetic resonance apparatus. Multiple repetitions of the sequence of an inversion pulse, an inversion time and a data recording using the magnetic resonance sequence are triggered by a respiratory signal describing the respiratory cycle, each repetition occurring upon fulfillment of a recording criterion. At least one further inversion pulse is emitted in a waiting time between the sequences.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for setting and/or adjusting a parameter value of a parameter of a magnetic resonance protocol for a magnetic resonance sequence
InactiveUS20180038930A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceComputer science
In a method and apparatus for setting and / or adjusting a parameter value of at least one parameter of a magnetic resonance protocol for at least one magnetic resonance sequence, a manual entry that selects the magnetic resonance protocol is made into a computer, and a further entry is made that provides boundary conditions for setting and / or adjusting the parameter value of the at least one parameter of the magnetic resonance protocol. The computer provides setting criteria from previous settings and / or adjustments of the parameter value of the at least one parameter of the magnetic resonance protocol. The computer sets and / or adjusts the parameter value of the at least one parameter of the magnetic resonance protocol on the basis of the provided boundary conditions and on the basis of the provided setting criteria.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com