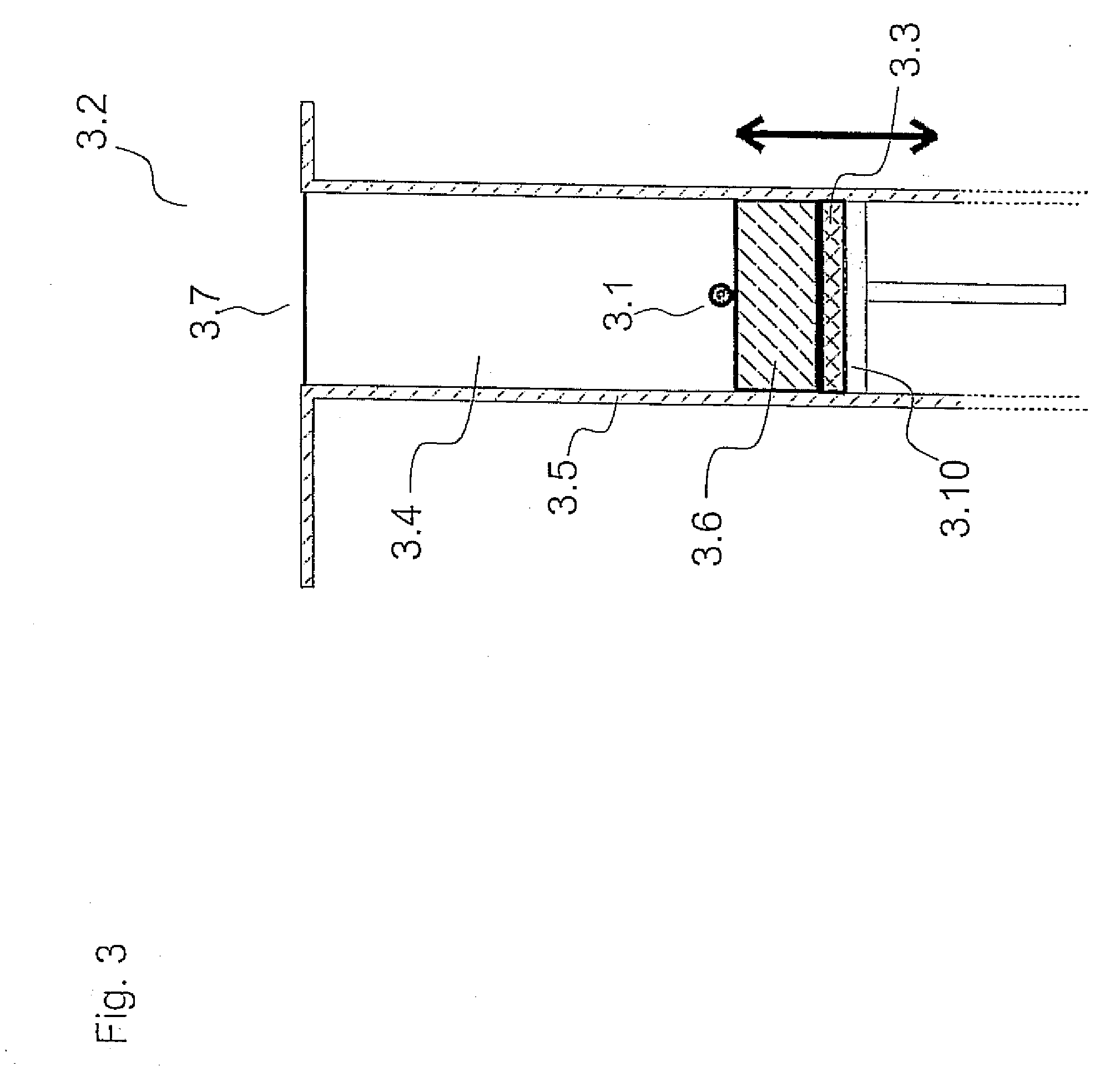
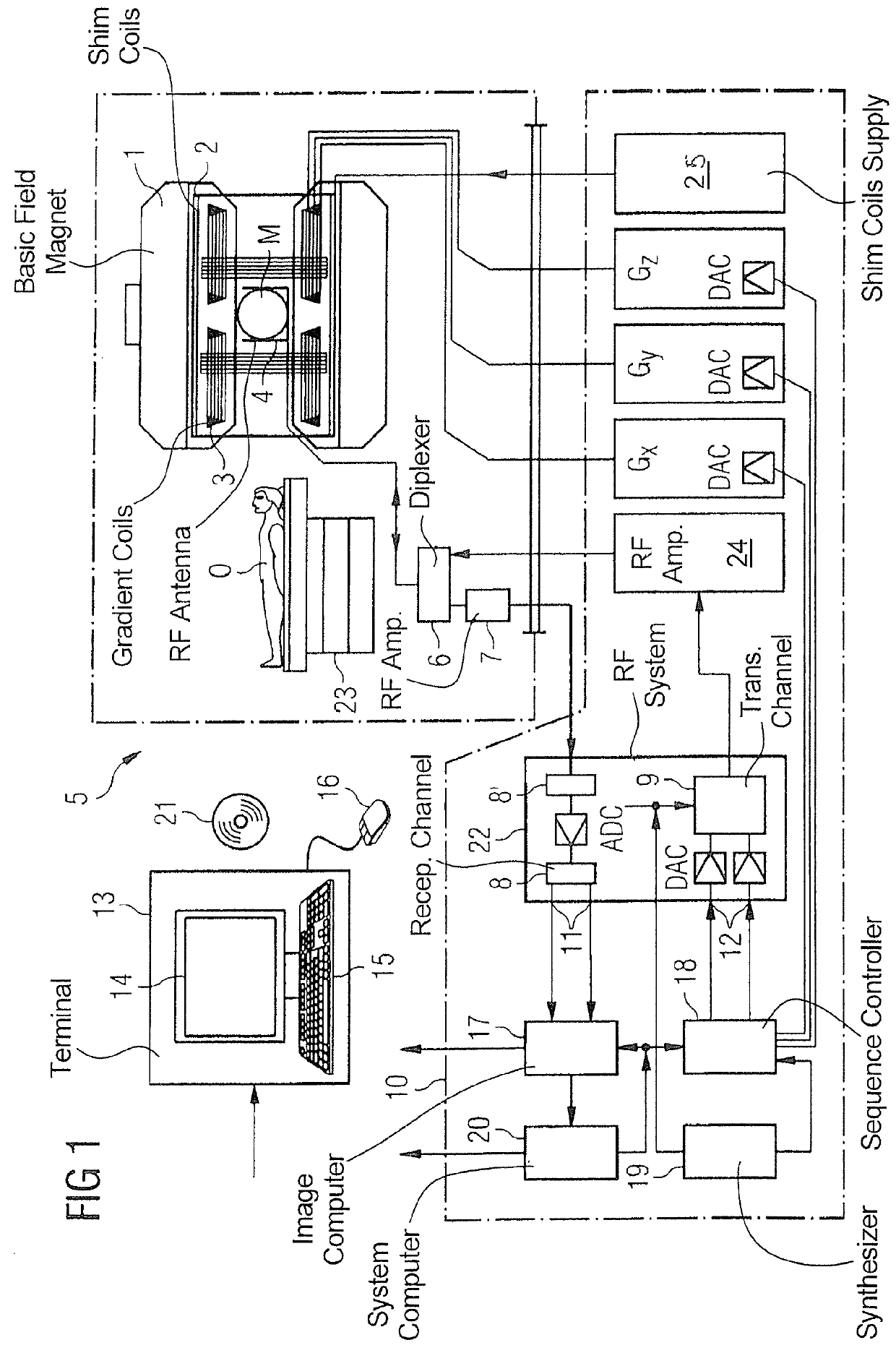
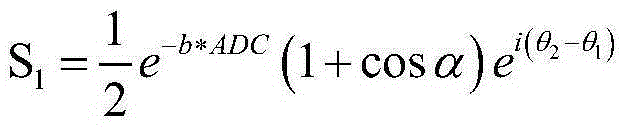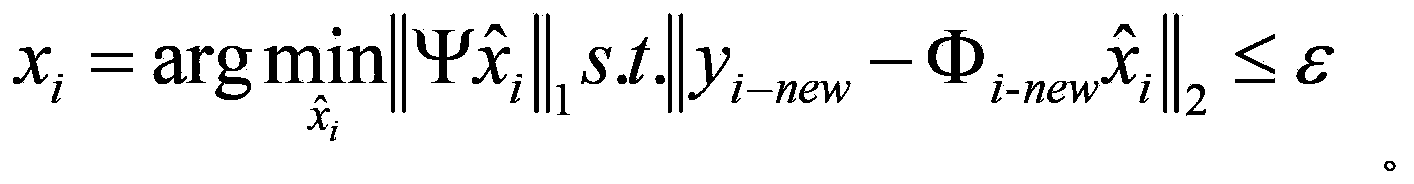Patents
Literature
85 results about "Diffusion gradient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
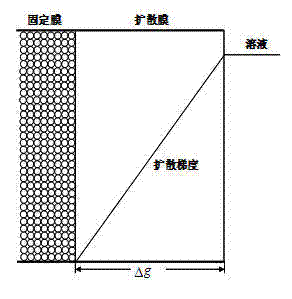
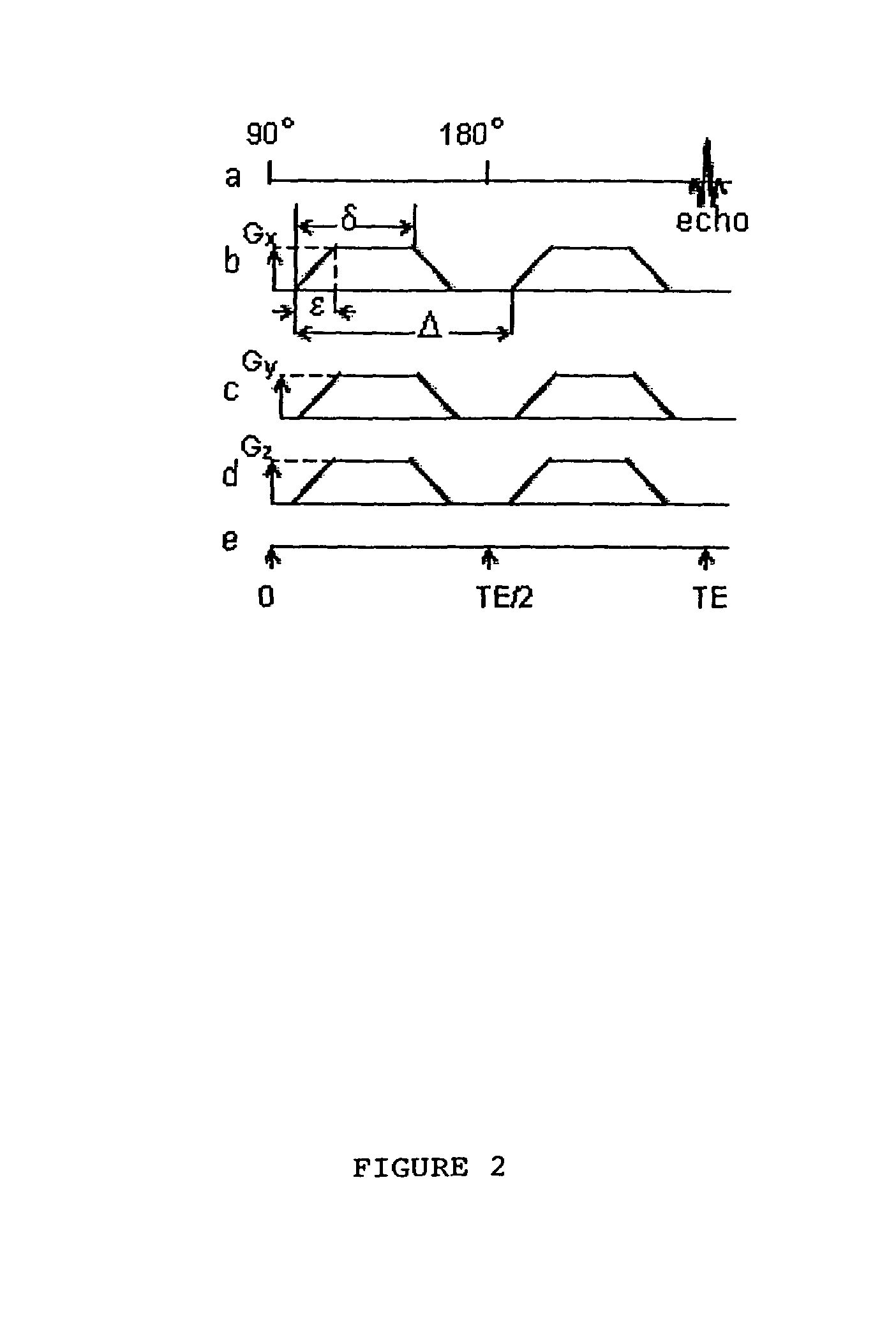
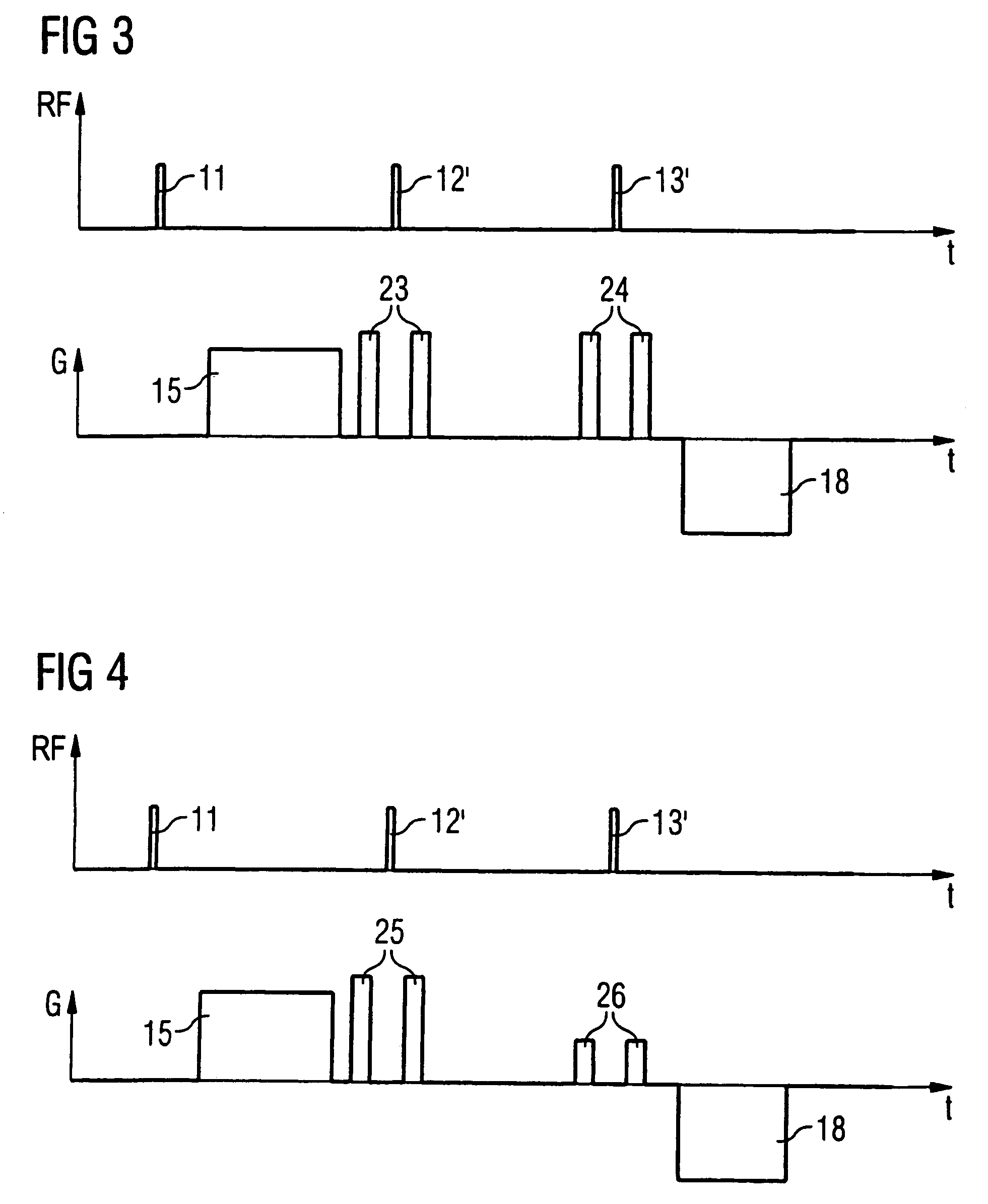
Diffusion gradient. [də′fyü·zhən ‚grād·ē·ənt] (physics) The graphed distance of penetration (diffusion) versus concentration of the material (or effect) diffusing through a second material; applies to heat, liquids, solids, or gases.
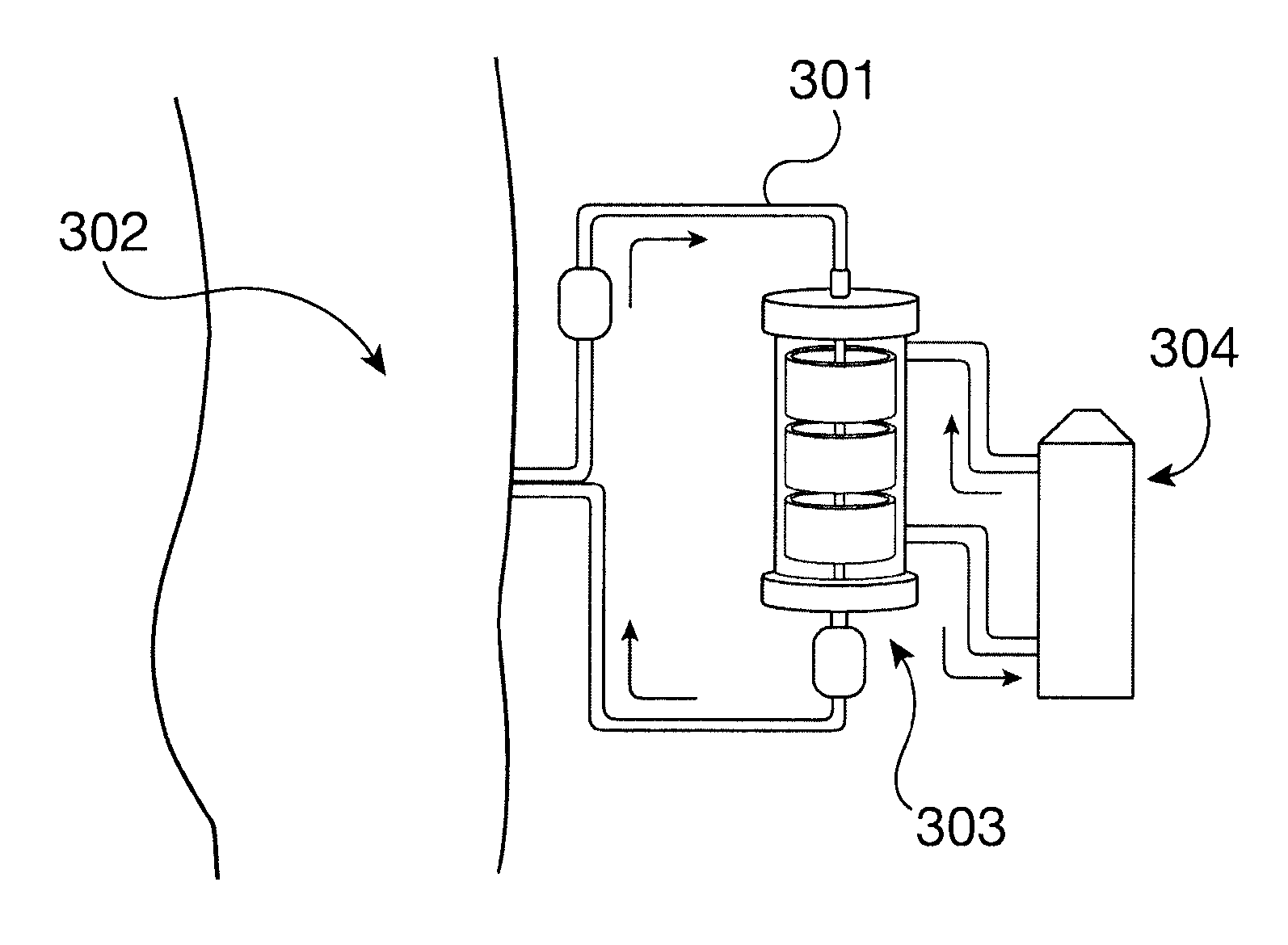
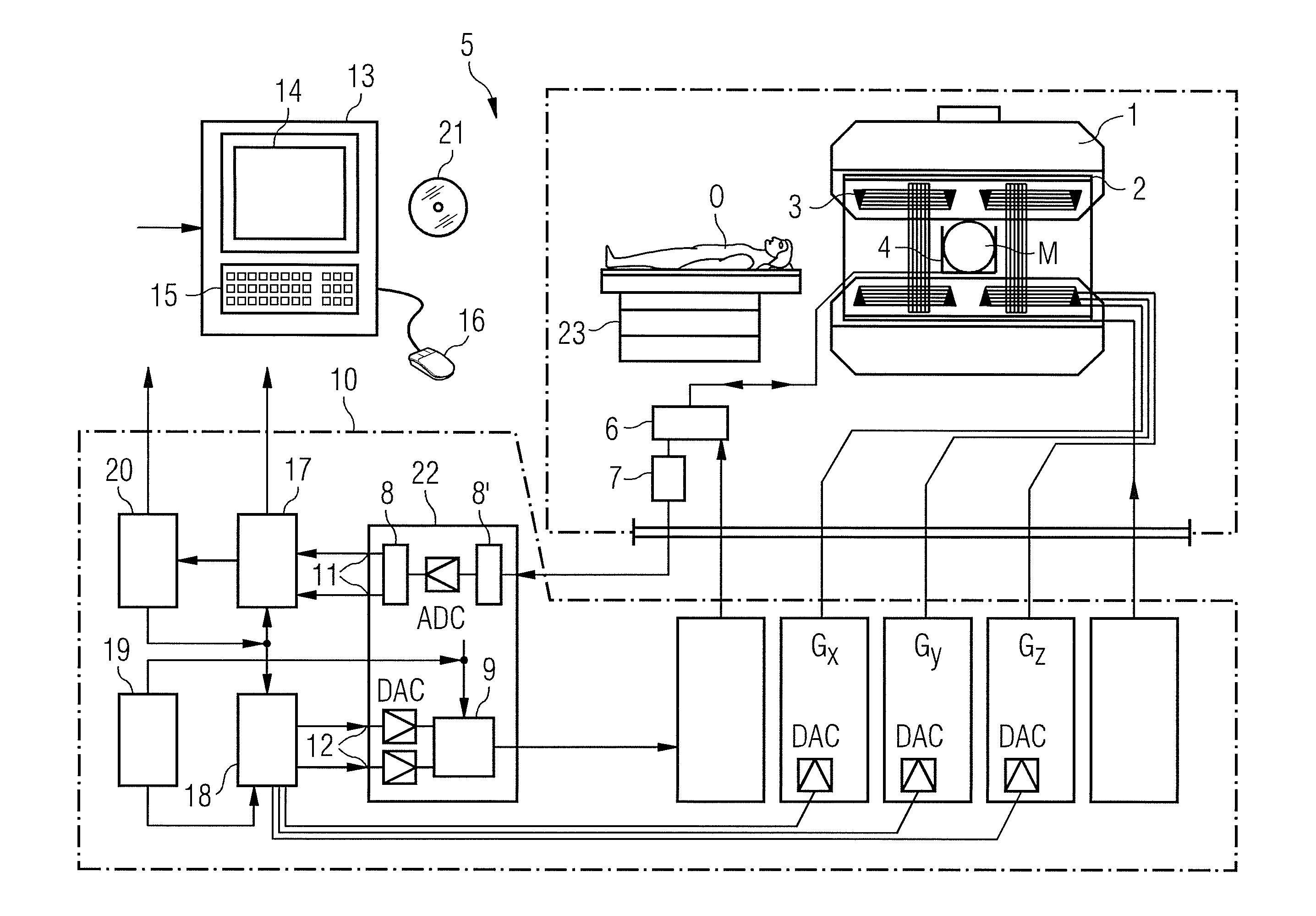
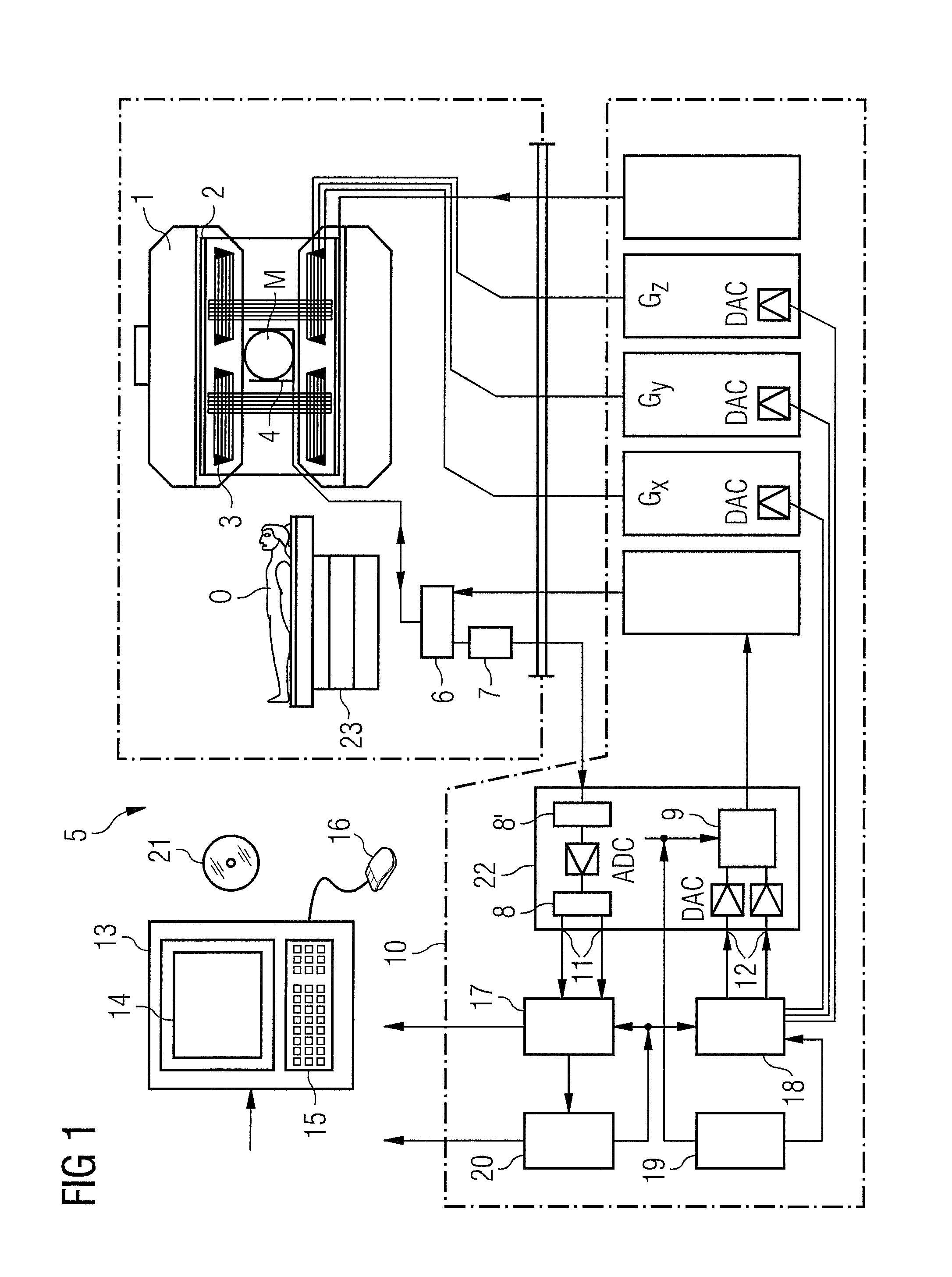
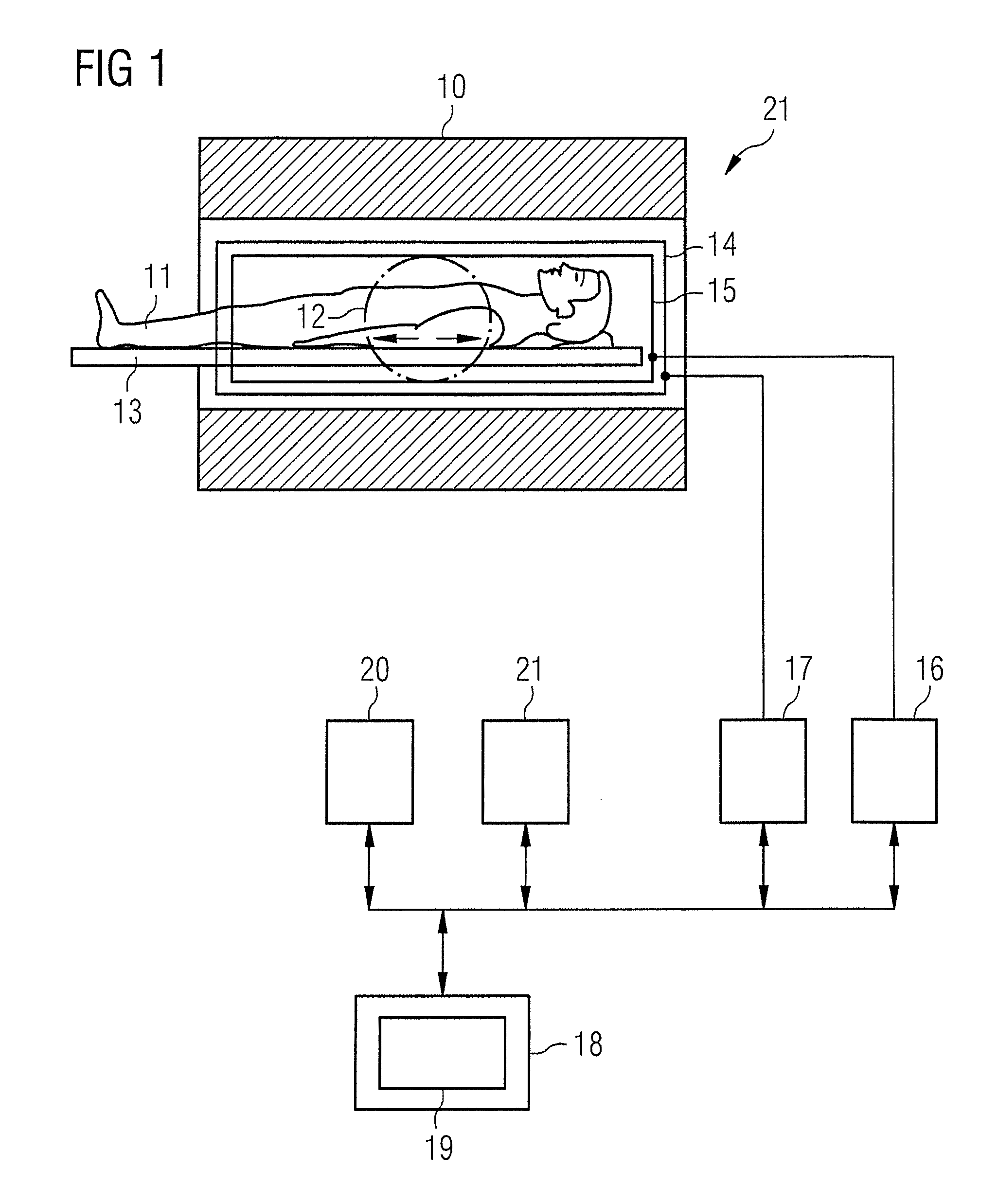
System and Method for Administering Peritoneal Dialysis
Systems and methods are provided for improved techniques associated with administering peritoneal dialysis. Embodiments of the invention relate to the continuous introduction and circulation of dialysate fluid in and through the peritoneal cavity. This constant influx of fresh fluid results in a perpetually high diffusion gradient between the toxin solute concentration of the blood and the dialysate fluid traversing the abdominal cavity, which promotes a much more efficient and rapid transfer of toxic solutes from the blood stream into the abdominal fluid. The fluid is continuously removed from the abdominal cavity and passed through an external filter using a pulsatile pump. The external filter cleanses the toxic solutes from the fluid before returning the fluid to the abdominal cavity. Embodiments of the invention also relate to improvements in catheters used to access the peritoneal cavity.
Owner:MASON ROGER ALAN
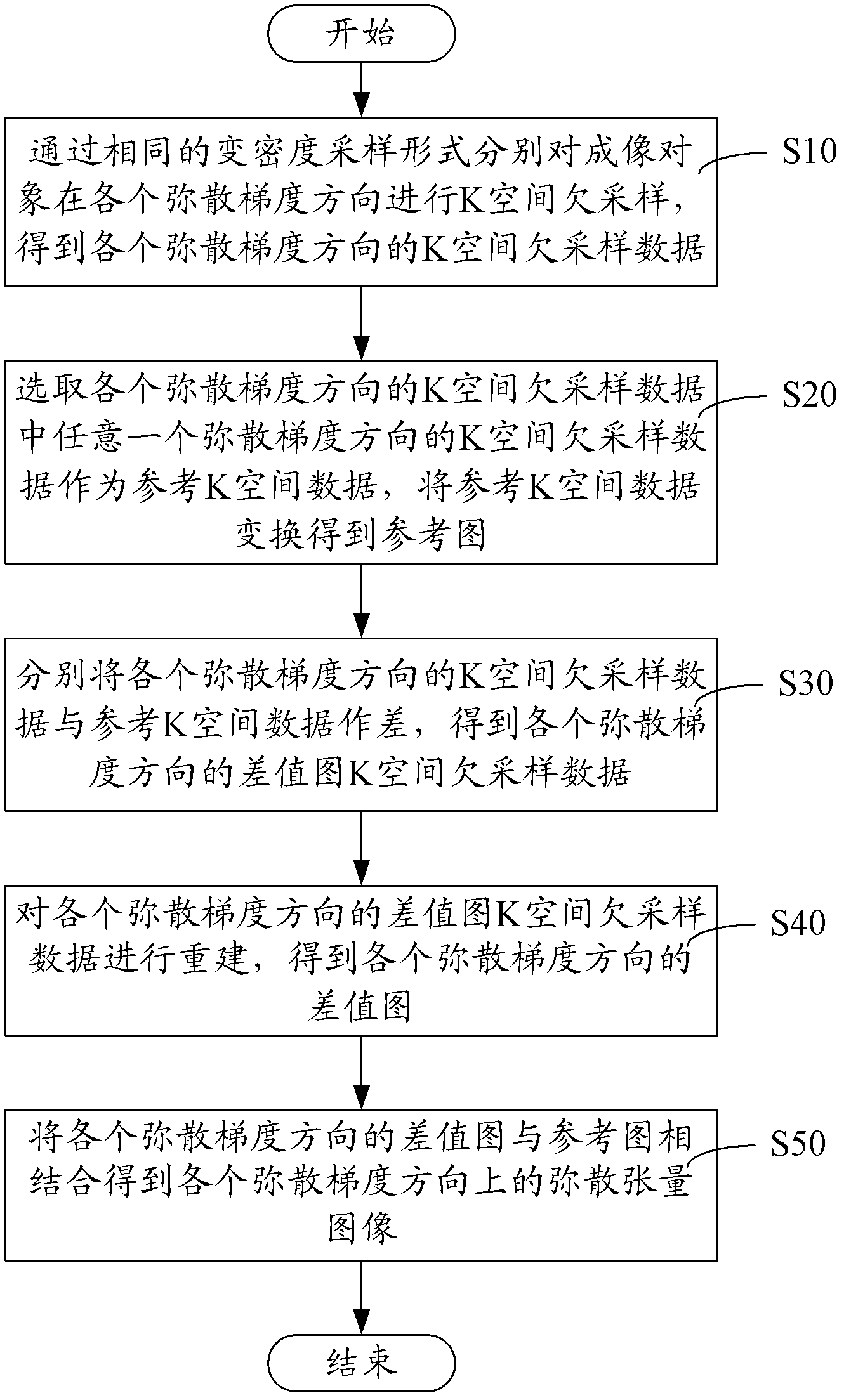
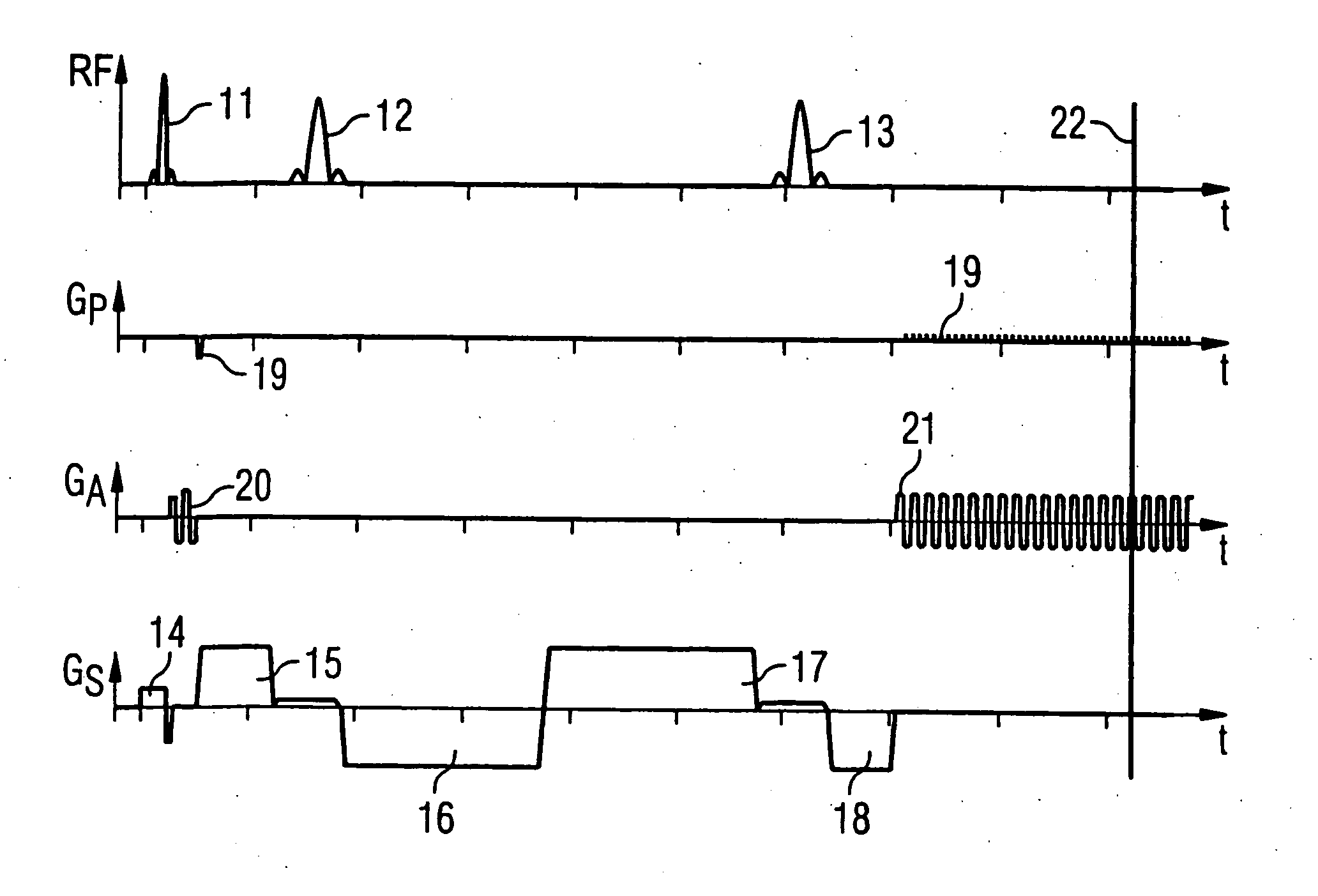
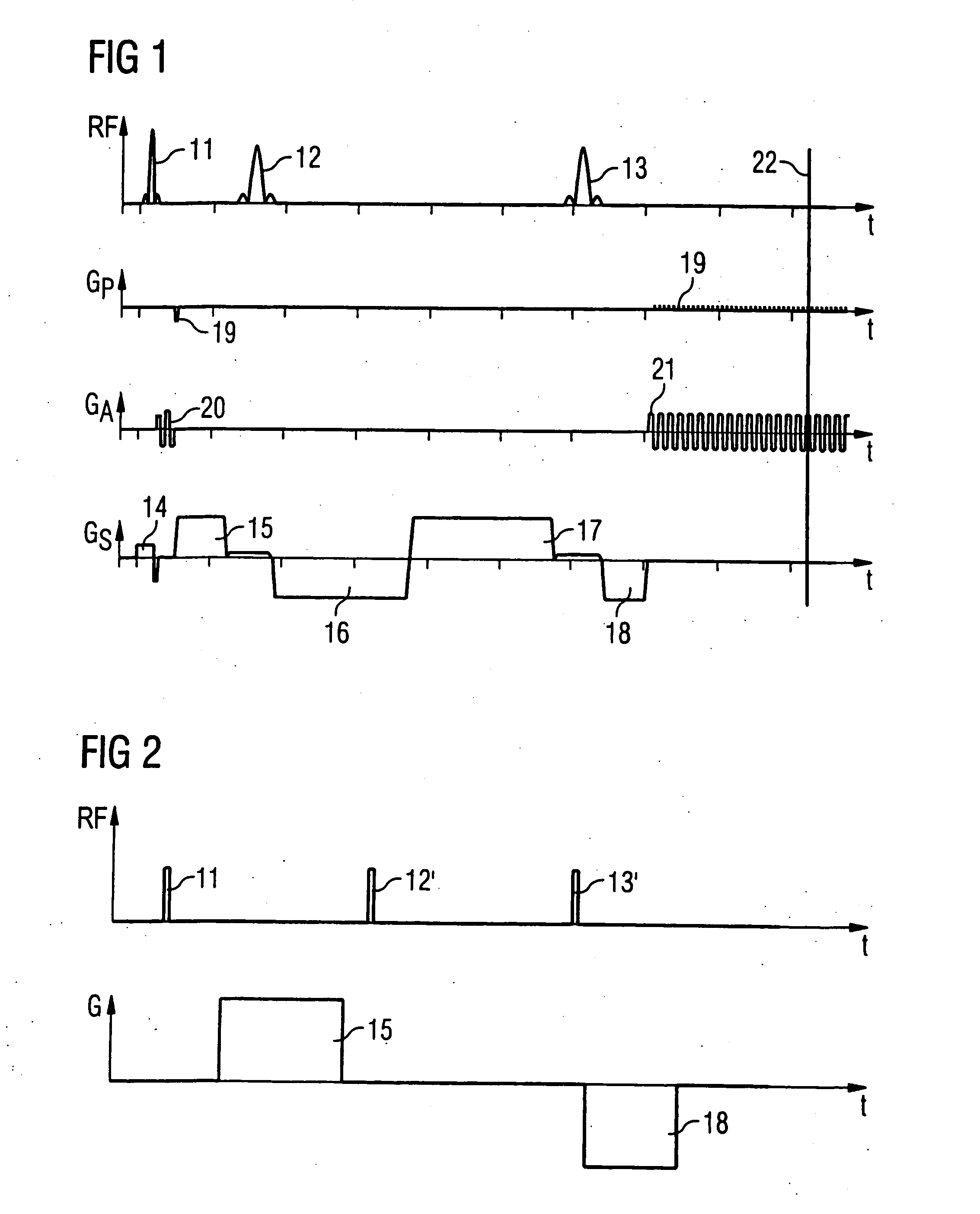
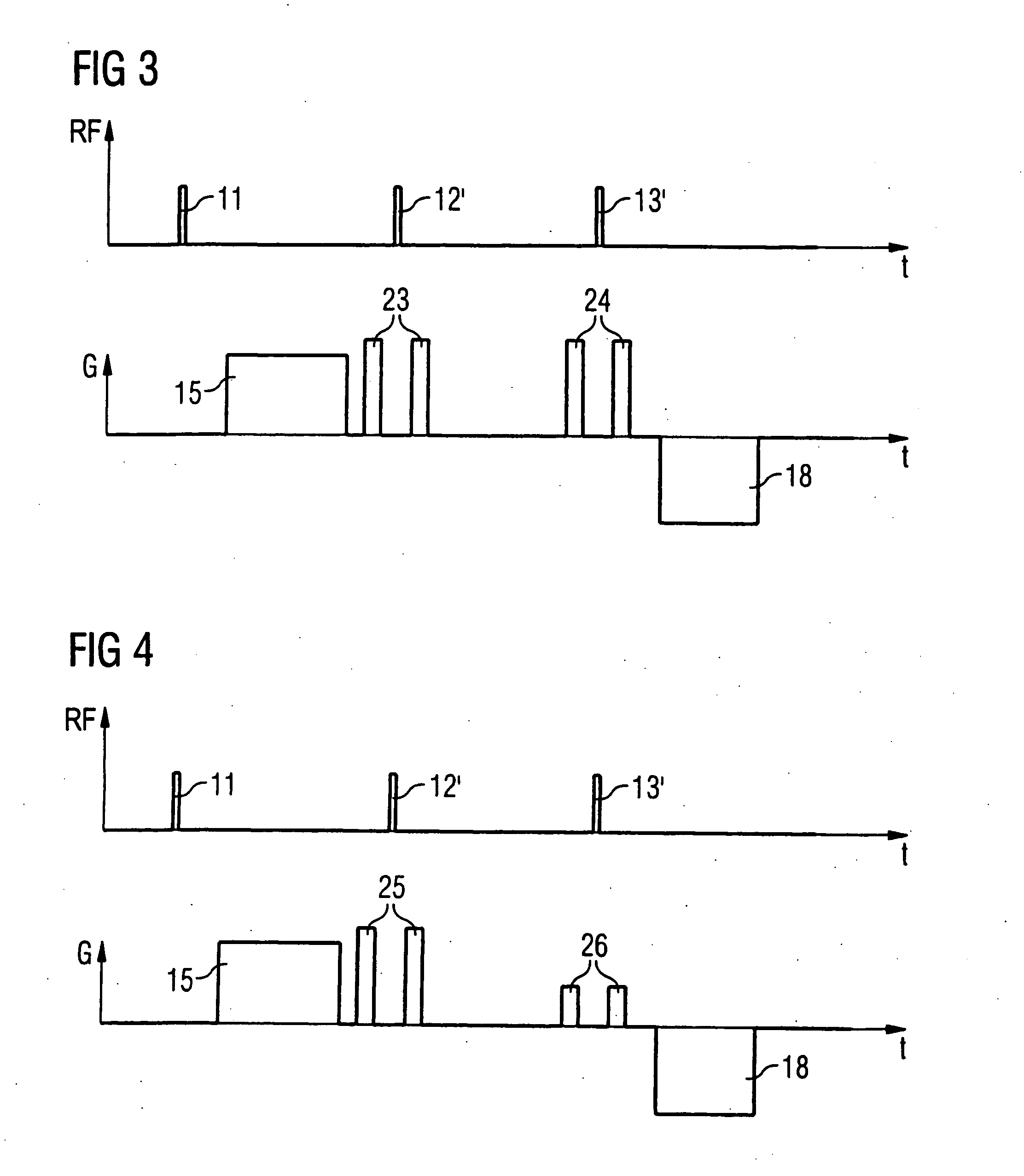
Diffusion-tensor imaging method and system
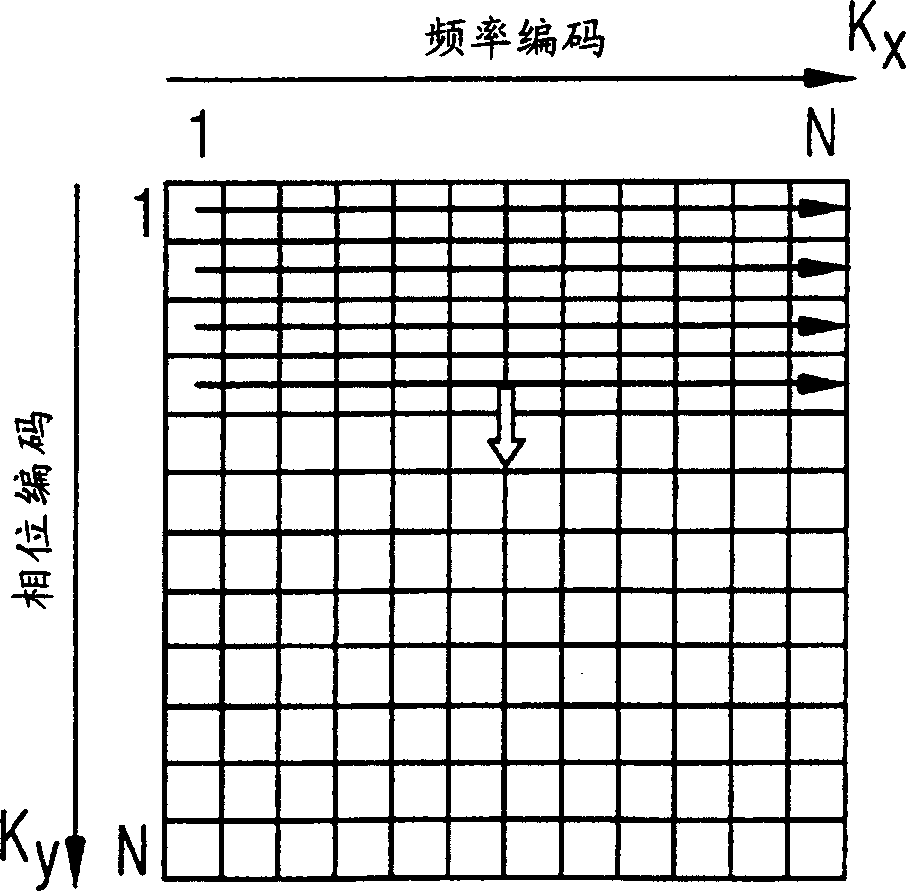
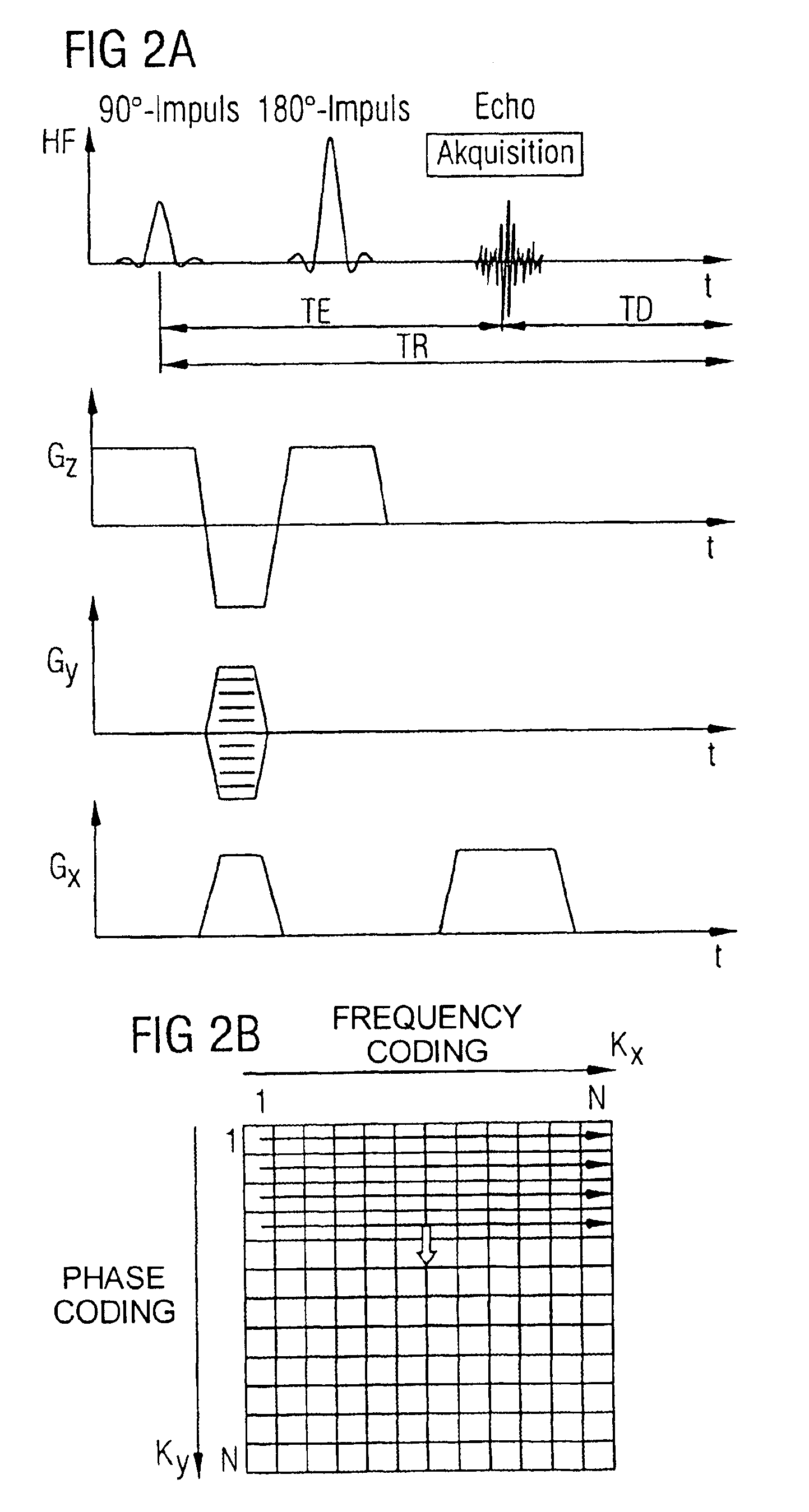
ActiveCN102309328AReduce acquisition timeDiffusion Tensor Imaging FastDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiffusionReference image
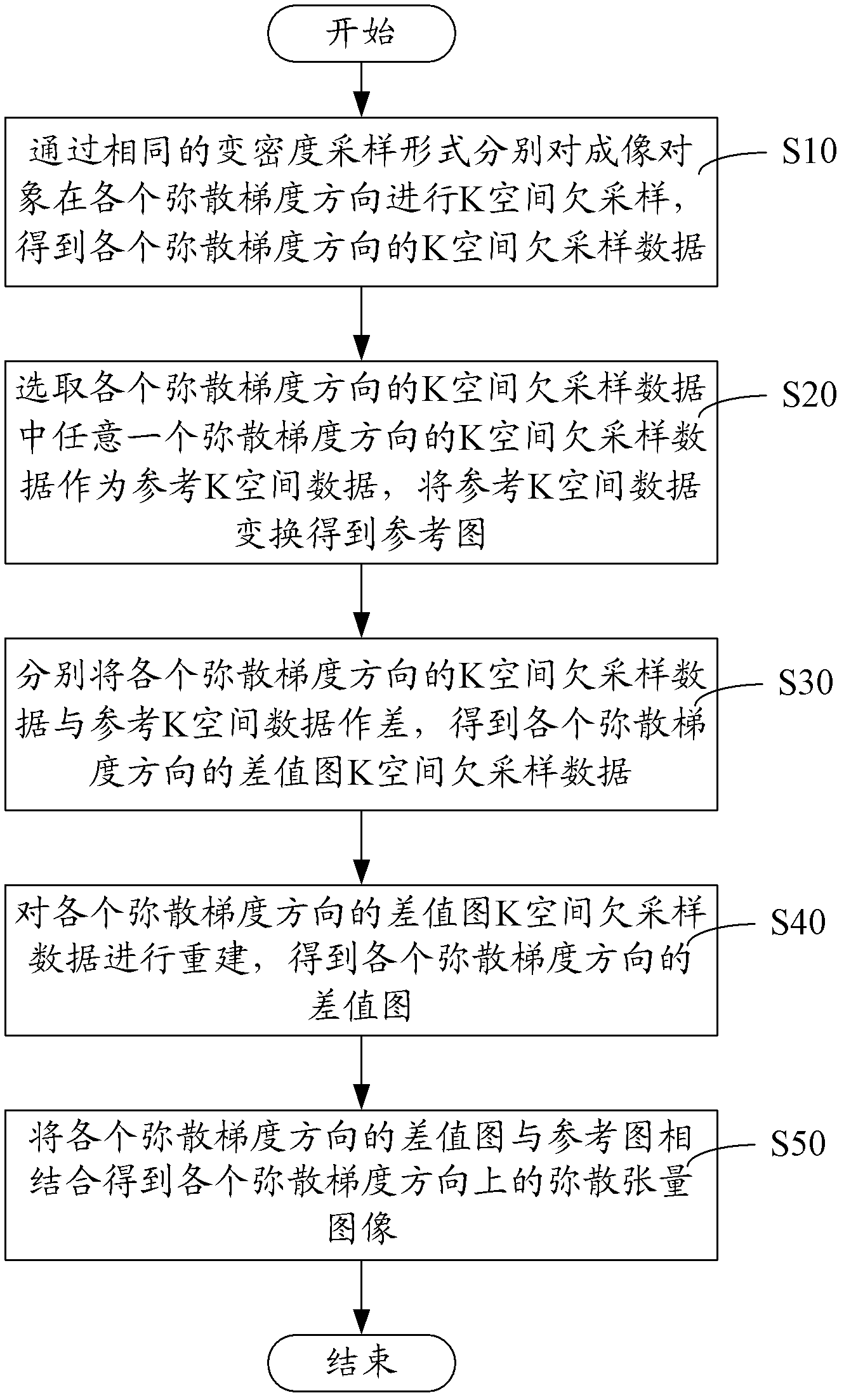
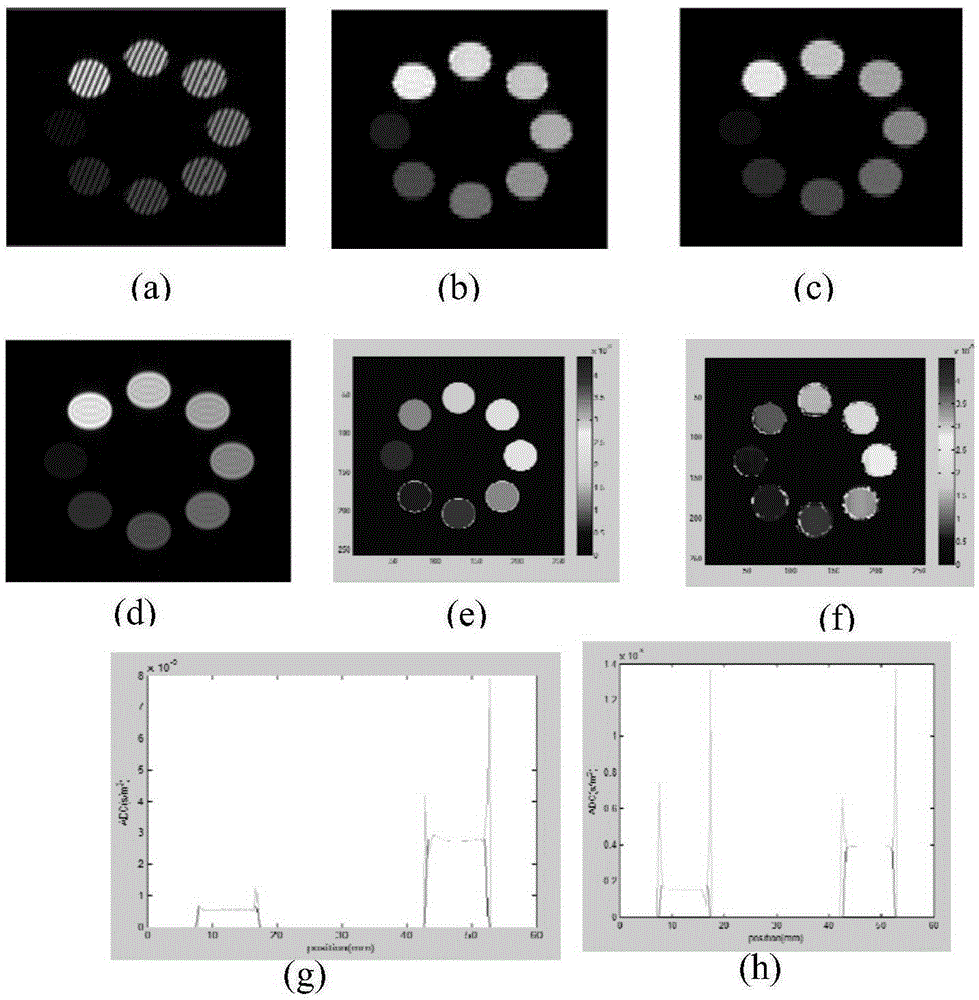
The invention provides a diffusion-tensor imaging method, which comprises the following steps of: respectively performing K space under sampling on an imaged target in each diffusion gradient direction in the same variable density sampling form to acquire K space under sampling data of each diffusion gradient direction; selecting the K space under sampling data of any diffusion gradient direction in the K space under sampling data of each diffusion gradient direction as reference K space data, and converting the reference K space data to acquire a reference image; making a difference between the K space under sampling data of each diffusion gradient direction and the reference K space data to acquire differential chart K space under sampling data of each diffusion gradient direction; rebuilding the differential chart K space under sampling data of each diffusion gradient direction to acquire a differential chart of each diffusion gradient direction; and combining the differential chart of each diffusion gradient direction and the reference image to acquire a diffusion-tensor image in each diffusion gradient direction. The invention also provides a diffusion-tensor imaging system at the same time.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
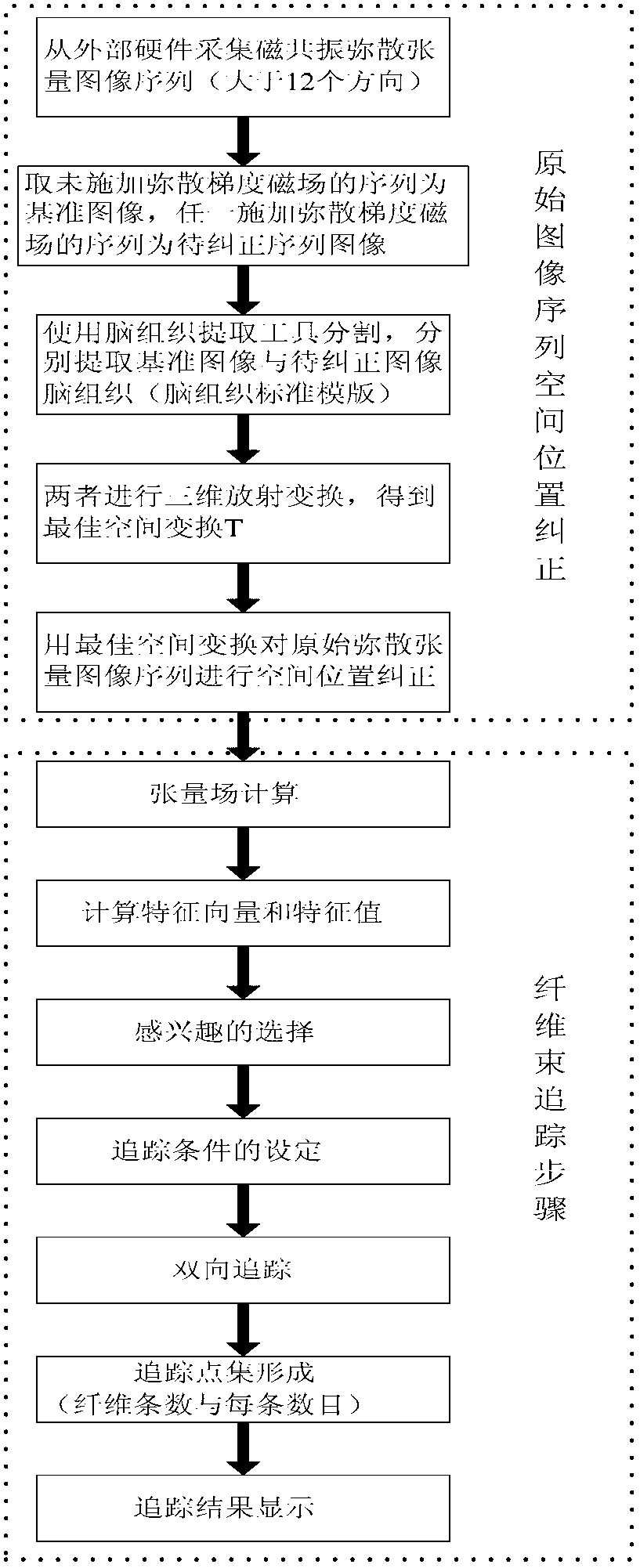
Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging fiber bundle tracking device
InactiveCN103049901AAccurate Tracking AlgorithmAccurate white matter fiber tractsImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringTensor fieldWhite matter
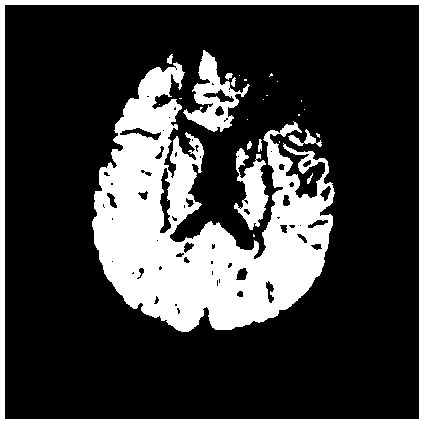
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging fiber bundle tracking device. The process is respectively completed by each component through the following steps of (1) collecting magnetic resonance diffusion tensor images; (2) carrying out brain issue dividing on a sequence without a diffusion gradient magnetic field and any sequence with the diffusion gradient magnetic field, and using the sequence without the diffusion gradient magnetic field as an image reference template of the brain tissues; (3) carrying out three-dimensional affine conversion on the two image sequences of the brain tissues after being extracted, to obtain a space conversion relationship; (4) carrying out space conversion on the remained diffusion tensor images by an optimum conversion relationship; (5) calculating tensor fields and feature vectors; (6) setting the interested areas and tracking conditions; and (7) carrying out the bidirectional tracking and displaying based on a fiber bundle with variable step size, so as to quickly and effectively carry out fiber bundle tracking and displaying on the white matters of human brain. In the diffusion tensor imaging process, the image deviation caused by space positions can be corrected, and the elastic step size is adopted in the tracking process, so as to ensure the reliable fiber bundle tracking.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
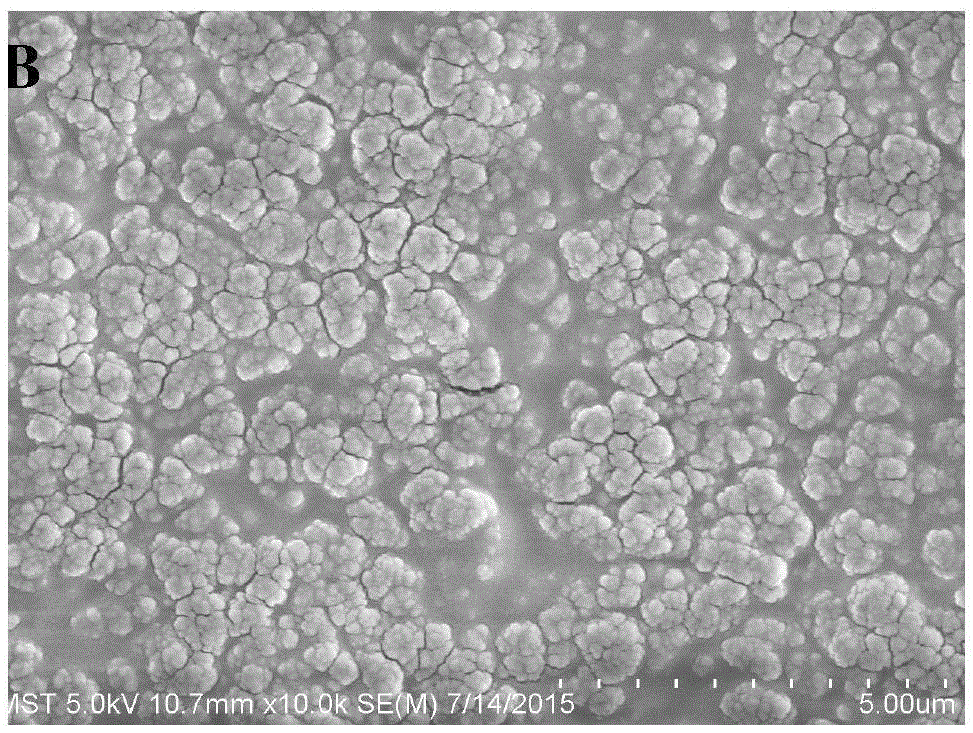
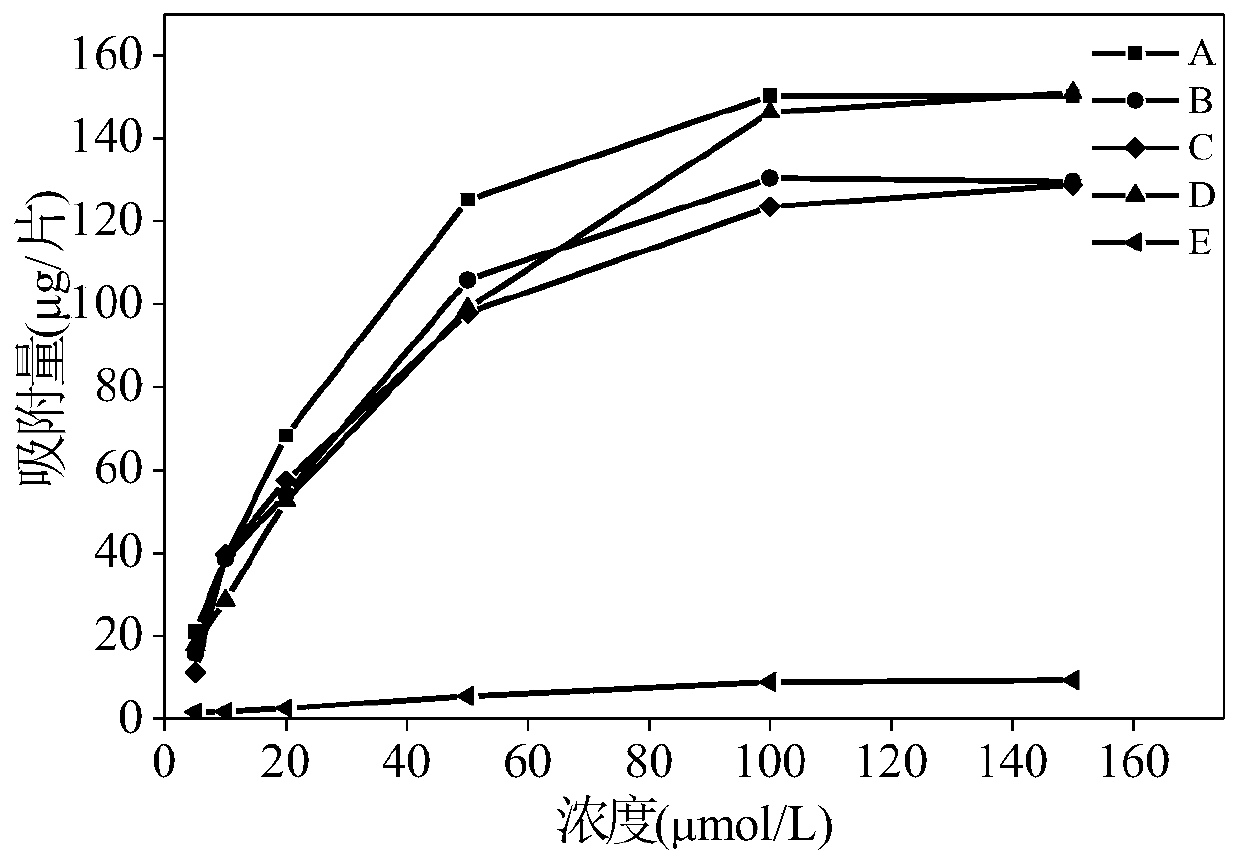
Preparation method of activated carbon adsorption film and method for measuring bisphenol substances in wetland soil or sediment based on thin-film diffusion gradient technique
InactiveCN104492376AStrong toughnessLarge adsorption capacityOther chemical processesComponent separationSorbentBisphenol
The invention discloses a preparation method of an activated carbon adsorption film and a method for measuring bisphenol substances in wetland soil or sediment based on a thin-film diffusion gradient technique, and belongs to the fields of environmental sciences and earth sciences. According to the preparation method of the activated carbon adsorption film, the activated carbon adsorption film is prepared by mixing activated carbon as an adsorbent with agar, and then is overlapped on an agar diffusion film and a PTFE filter film to form a DGT device; after nitrogen introduction pretreatment, the DGT device is put into the wetland soil or the sediment to be tested for 24 hours, and then the activated carbon adsorption film is taken out and eluted by use of an eluent which is the mixed solution of methanol and sodium hydroxide; next, the adsorbing capacity of the bisphenol compounds in the adsorption film is measured and the concentration of the bisphenol substances in the wetland soil or the sediment is calculated according to the Fick's first law of diffusion. The preparation method of the activated carbon adsorption film is simple in process, the adsorbent is even in distribution, the adsorbing capacity is high and the quality guarantee period is long; the DGT technique based on the adsorption film is simple and easy to operate and the testing result is representative, and therefore, the DGT technique is suitable for in-situ detection of the bisphenol substances in the wetland soil or the sediment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method to generate magnetic resonance exposures
ActiveUS20130033262A1Fast wayImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiffusionData set
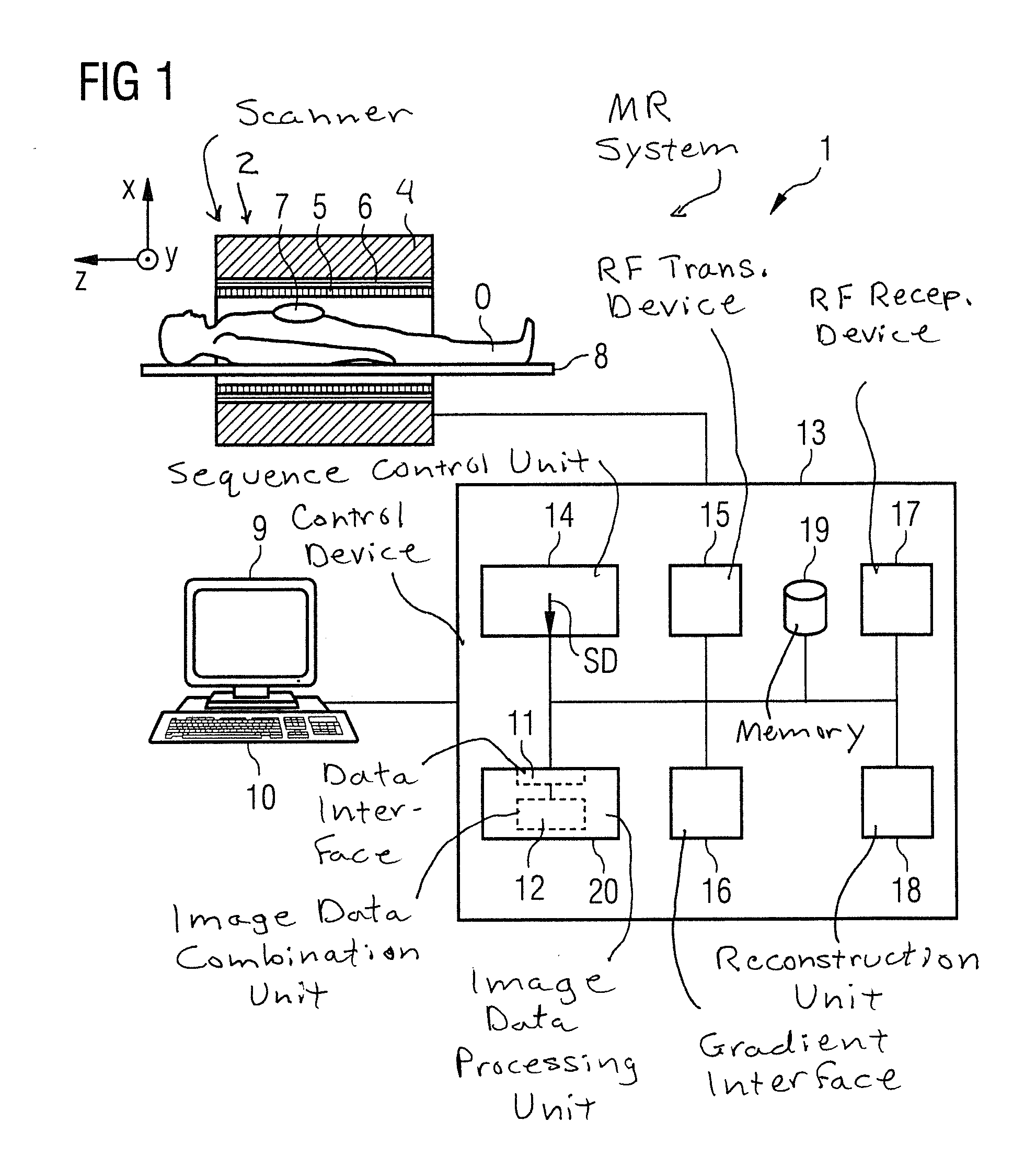
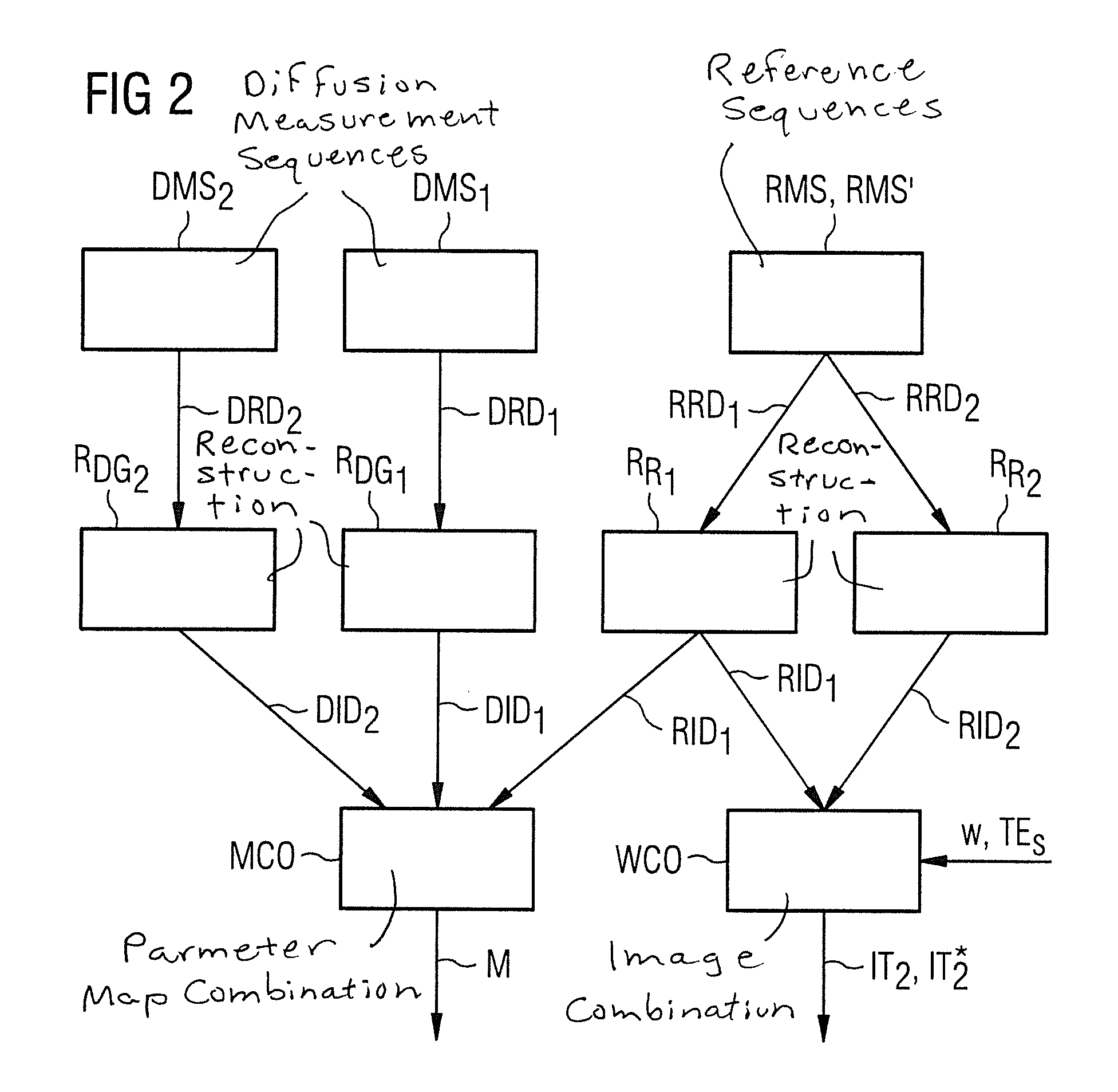
In a method described for generating magnetic resonance exposures in which diffusion-coded raw data are acquired with of a diffusion gradient measurement sequence having a number of partial diffusion gradient sequences, at least one diffusion coding gradient pulse is emitted in each partial data set, and raw data of a k-space region are acquired during a first echo after a defined first echo time the k-space regions in total covering a complete k-space. Raw data of an established navigator k-space region are acquired during a second echo after a second echo time the navigator k-space region being identical for different partial diffusion gradient sequences. Reference raw data are acquired by a reference measurement sequence with multiple partial reference sequences.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
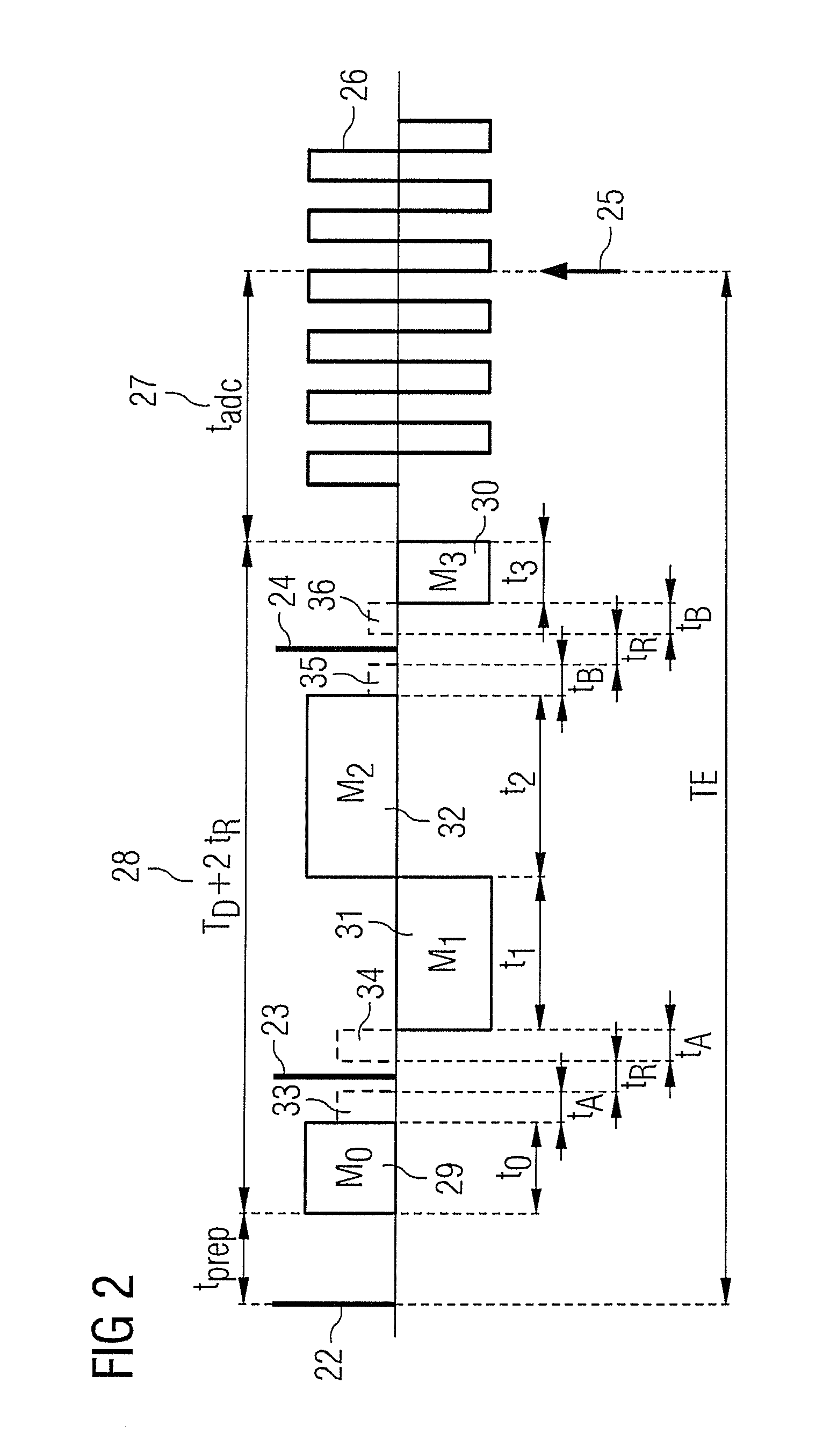
Method of determining ADC coefficient using steady sequency in diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging
In a magnetic resonance apparatus and method to acquire a diffusion-weighted image in diffusion-weighted MRT imaging, a non-diffusion-weighted data set and a diffusion-weighted data set are measured and stored by means of a DESS sequence (Double Echo Steady State Sequence), with two readout gradients being switched successively for the non-diffusion-weighted data set, and a bipolar diffusion gradient pulse sequence being switched between two readout gradients for the diffusion-weighted data set. A diffusion-weighted MRT image is calculated based on the non-diffusion-weighted data set and the diffusion-weighted data set, as well as on the basis of a value characterizing the diffusion-weighted measurement.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method to determine the ADC coefficients in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging given use of steady-state sequences
ActiveUS6891373B2Reduced measurement timeHigh bandwidthMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDiffusionData set
In a magnetic resonance apparatus and method to acquire a diffusion-weighted image in diffusion-weighted MRT imaging, a non-diffusion-weighted data set and a diffusion-weighted data set are measured and stored by means of a DESS sequence (Double Echo Steady State Sequence), with two readout gradients being switched successively for the non-diffusion-weighted data set, and a bipolar diffusion gradient pulse sequence being switched between two readout gradients for the diffusion-weighted data set. A diffusion-weighted MRT image is calculated is calculated based on the non-diffusion-weighted data set and the diffusion-weighted data set, as well as on the basis of a value characterizing the diffusion-weighted measurement.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
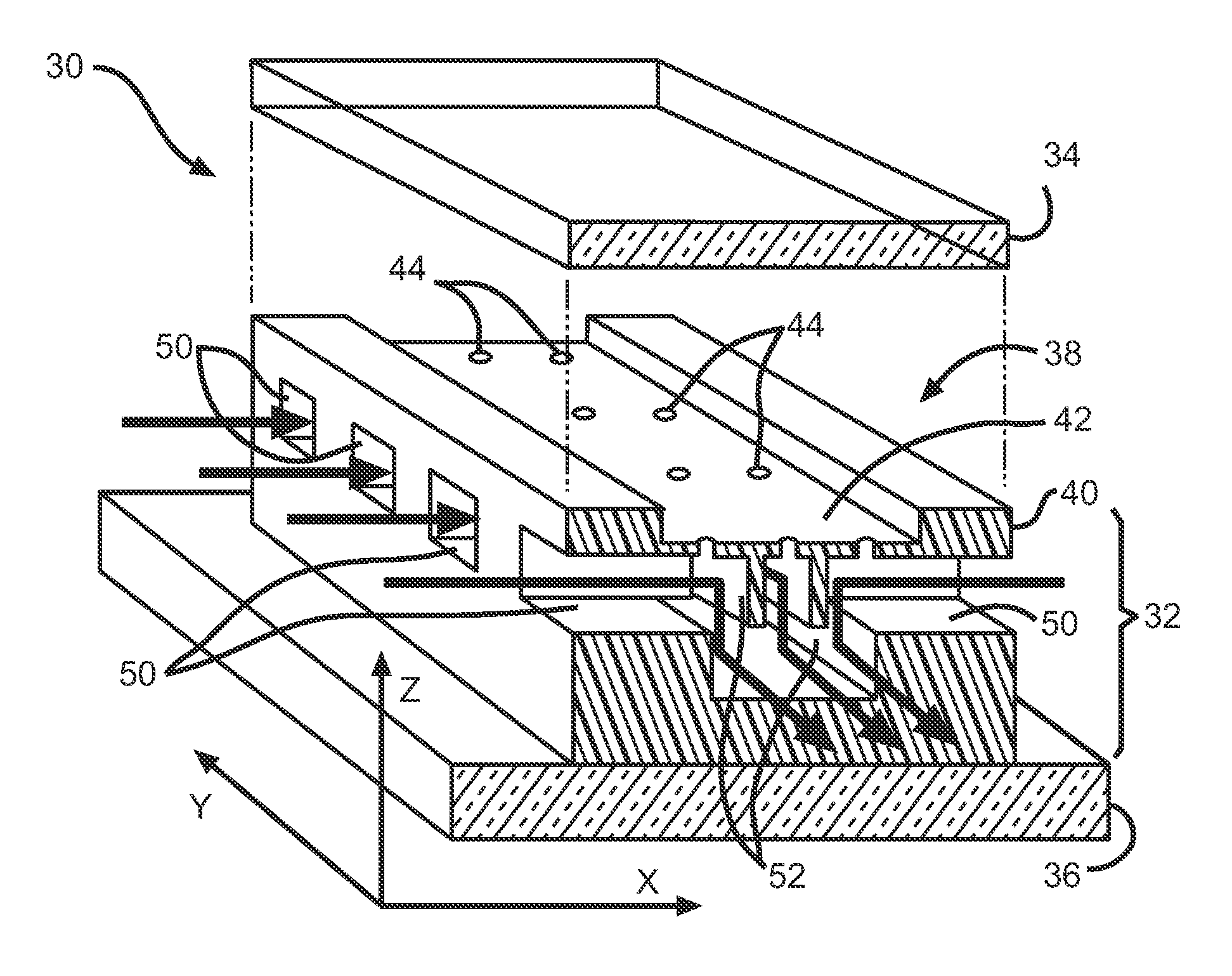
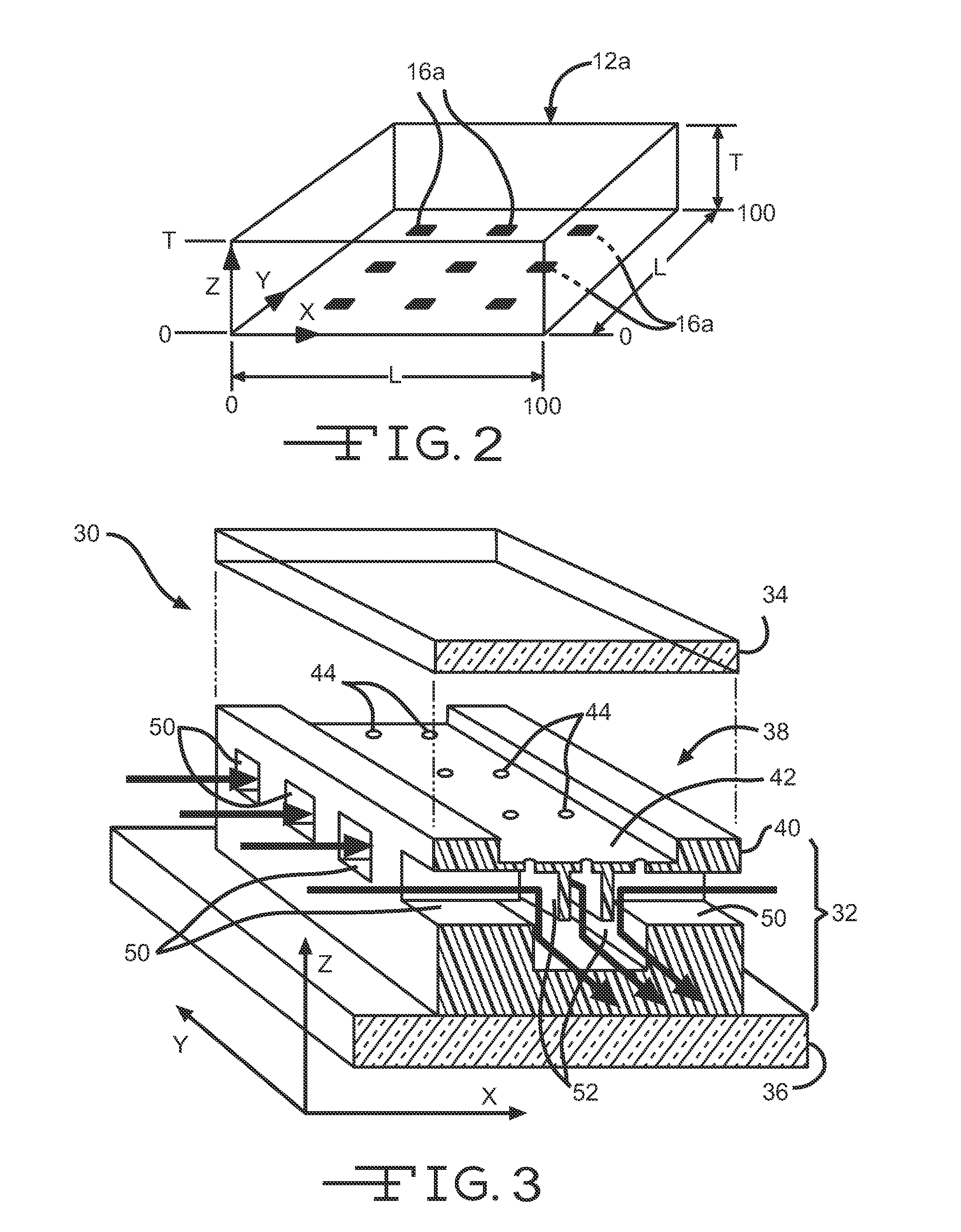
Microfluidic Device and Related Methods
InactiveUS20120135446A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningDiffusionConcentration gradient
A combinatorial microenvironment generator is configured for the generation of arbitrary, user-defined, steady-state, concentration gradients with negligible to no flow through the growth medium to perturb diffusion gradients or cellular growth. More importantly, the absolute concentrations and / or gradients can be dynamically altered upon request both spatially and temporally to impose tailored concentration fields for in-situ stimulus studies. Here, diffusion occurs via an array of ports, each of which can be an independently controlled source / sink. Together, the array of ports establishes a user-defined, 3D concentration profile. Useful methods related to this device are also provided.
Owner:MAINE INST FOR HUMAN GENETICS & HEALTH +1
Single-scanning quantitative magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method based on dual echoes
The invention provides a single-scanning quantitative magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method based on dual echo, and relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method. According to the method, two echoes with the same evolution time are generated through two small-angle excitation pulses with the same turning angle, so that the same transverse relaxation time is achieved; a displacement gradient is added after each excitation pulse to achieve central displacement of the two echo signals in a signal space, and a diffusion gradient is added after the first excitation pulse, so that diffusion reduction only exists in the first echo signal; accordingly, signals under different diffusion factors are obtained. The two echo signals are from one imaging slice, so that the two echo signals can be separated through priori knowledge of the two echo signals by matching sparse conversion with a corresponding separation algorithm. Finally, a quantitative ADC image is obtained by performing apparent diffusion coefficient calculation on two signals obtained through separation. Single-scanning quantitative ADC imaging is obtained through the method, and the quality of the obtained ADC image is good.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Cooling Article of Clothing and Method of Use for Same
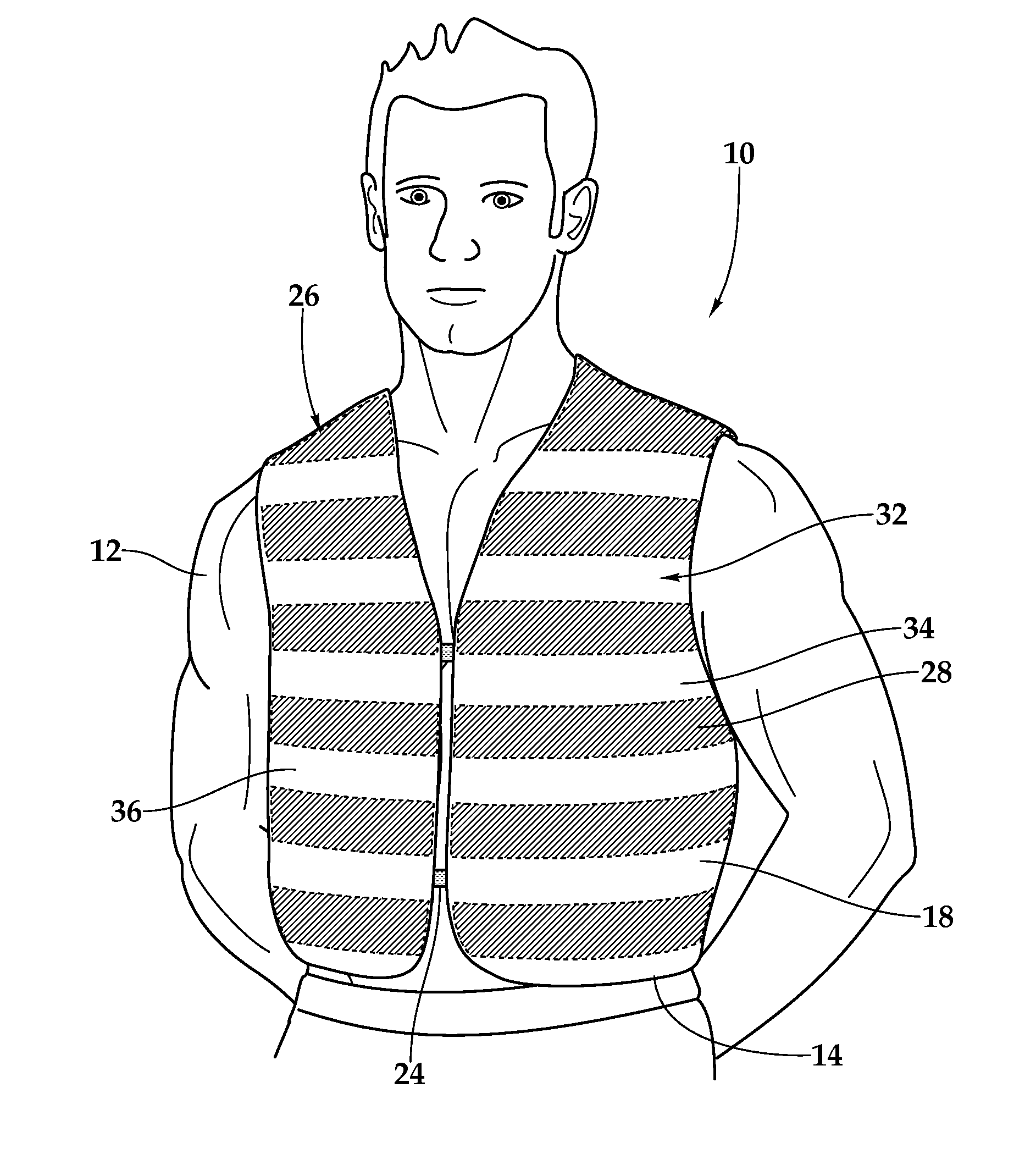
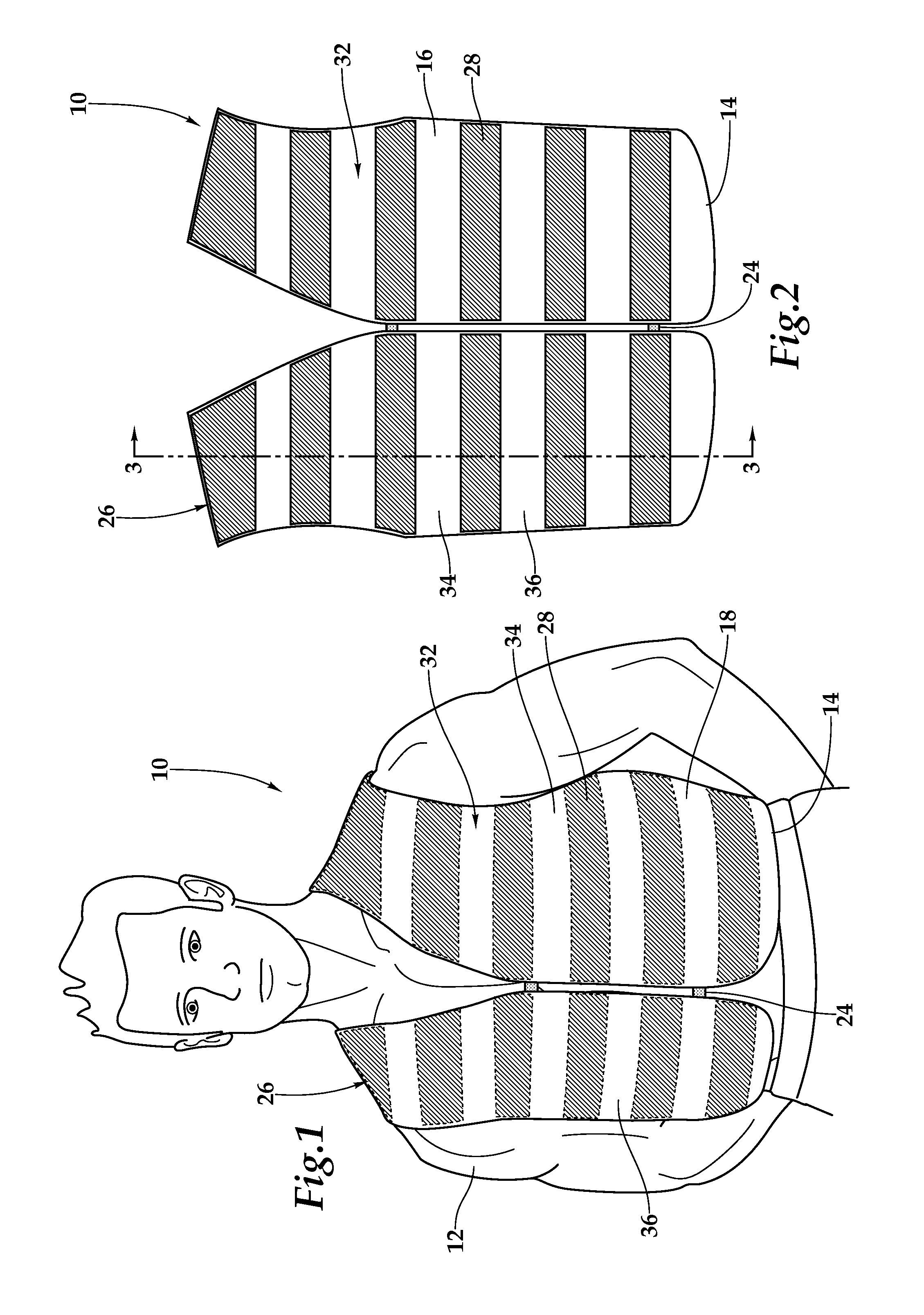
A cooling article of clothing and method for use of the same are disclosed for providing temporary cooling comfort to a human wearer. In one embodiment, sealed elongated envelopes are formed on the inside of a layer of the fabric, which may be fashioned into a vest or shirt. Each of the sealed elongated envelopes defines a volume for containing a pre-determined amount of polyacrylamide material. Offset spacings are interleaved between the sealed elongated envelopes. A diffusion gradient is formed from the polyacrylamide material to the sealed elongated envelopes to the layer of fabric. A diffusion gradient provides for the transfer of water from the polyacrylamide material to the layer of fabric. Water within the layer of fabric is evaporated by way of airflow through the layer of fabric, thereby providing temporary cooling comfort to the human wearer.
Owner:GALLAHER STEVEN H
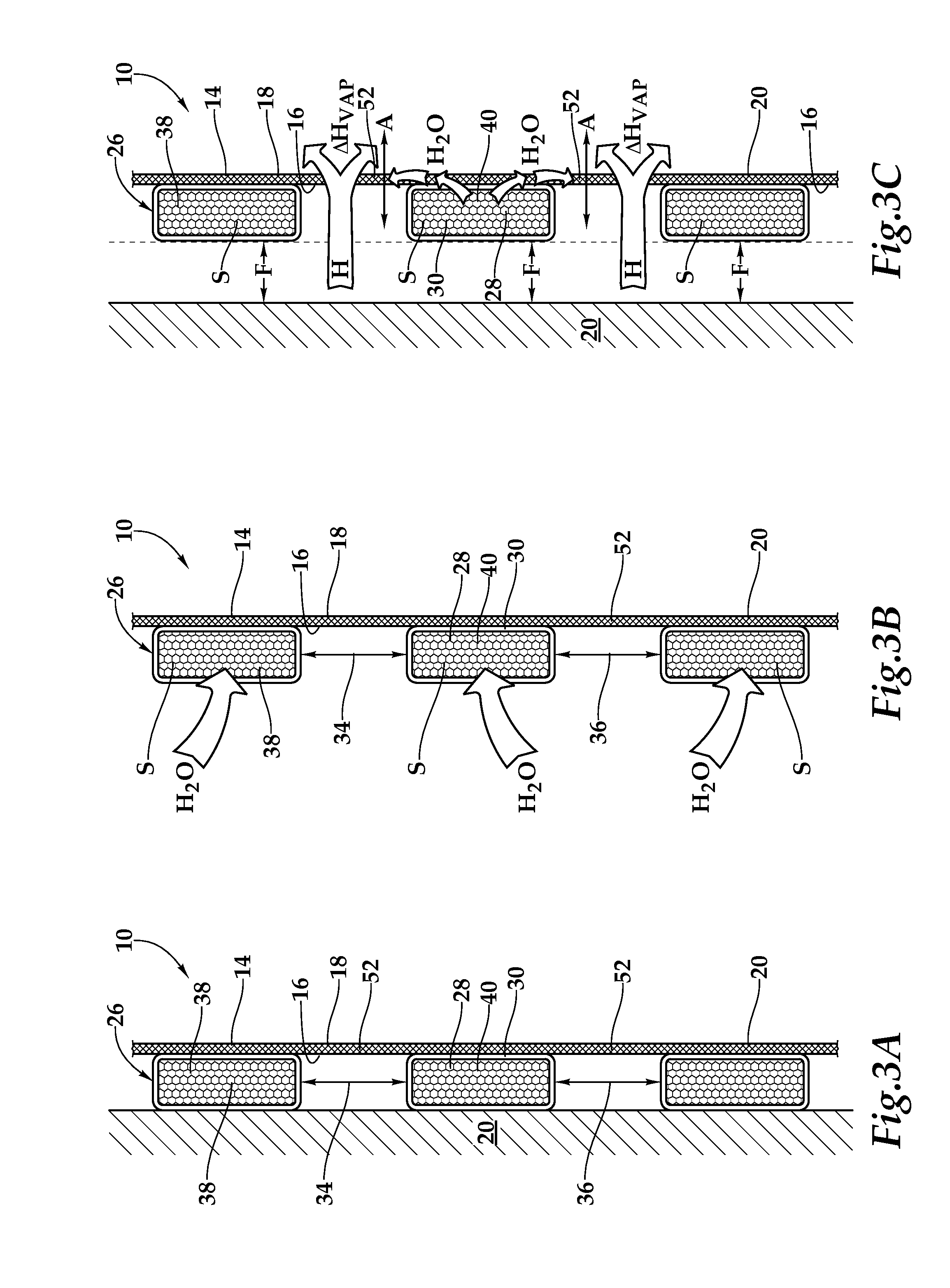
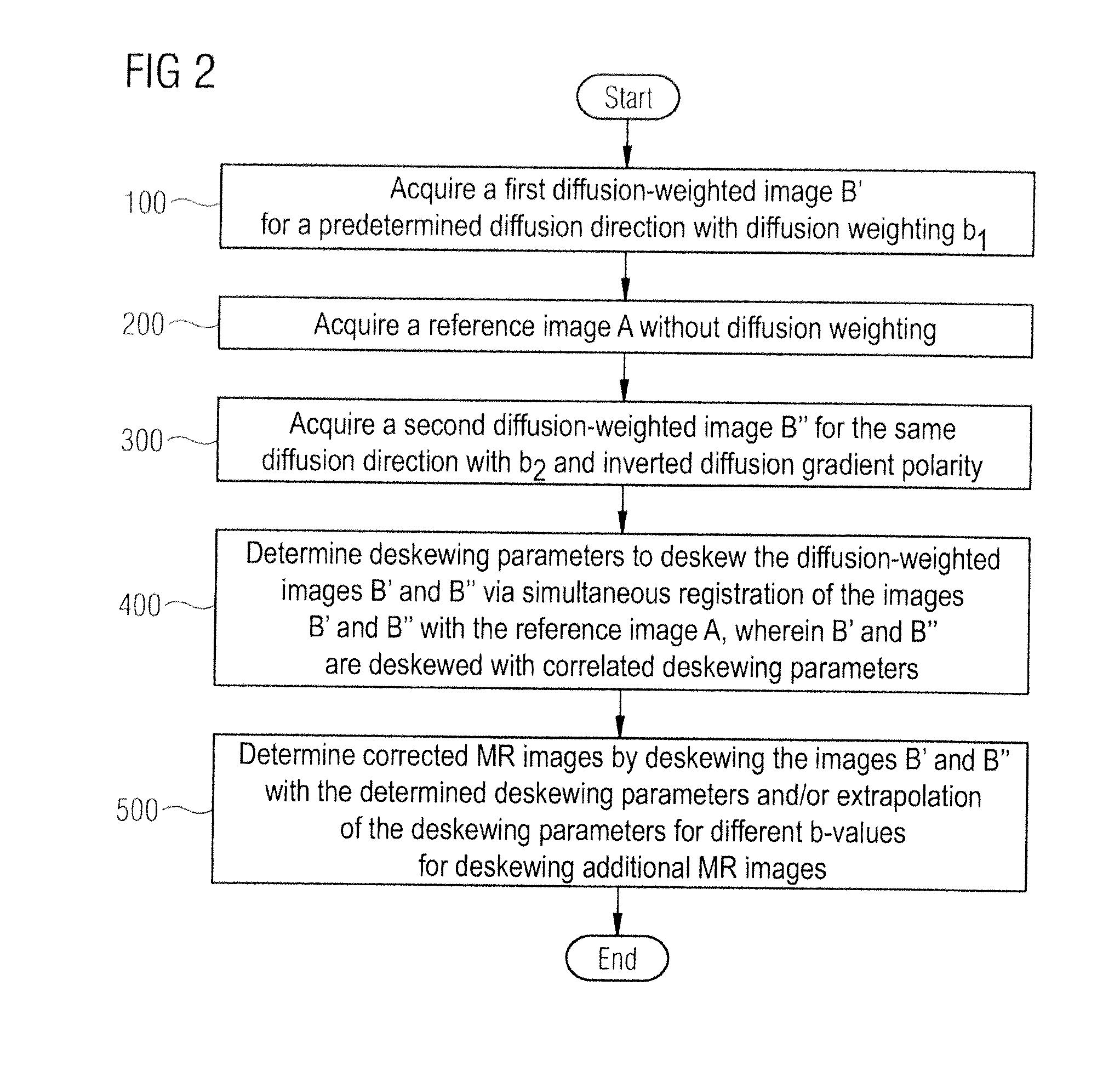
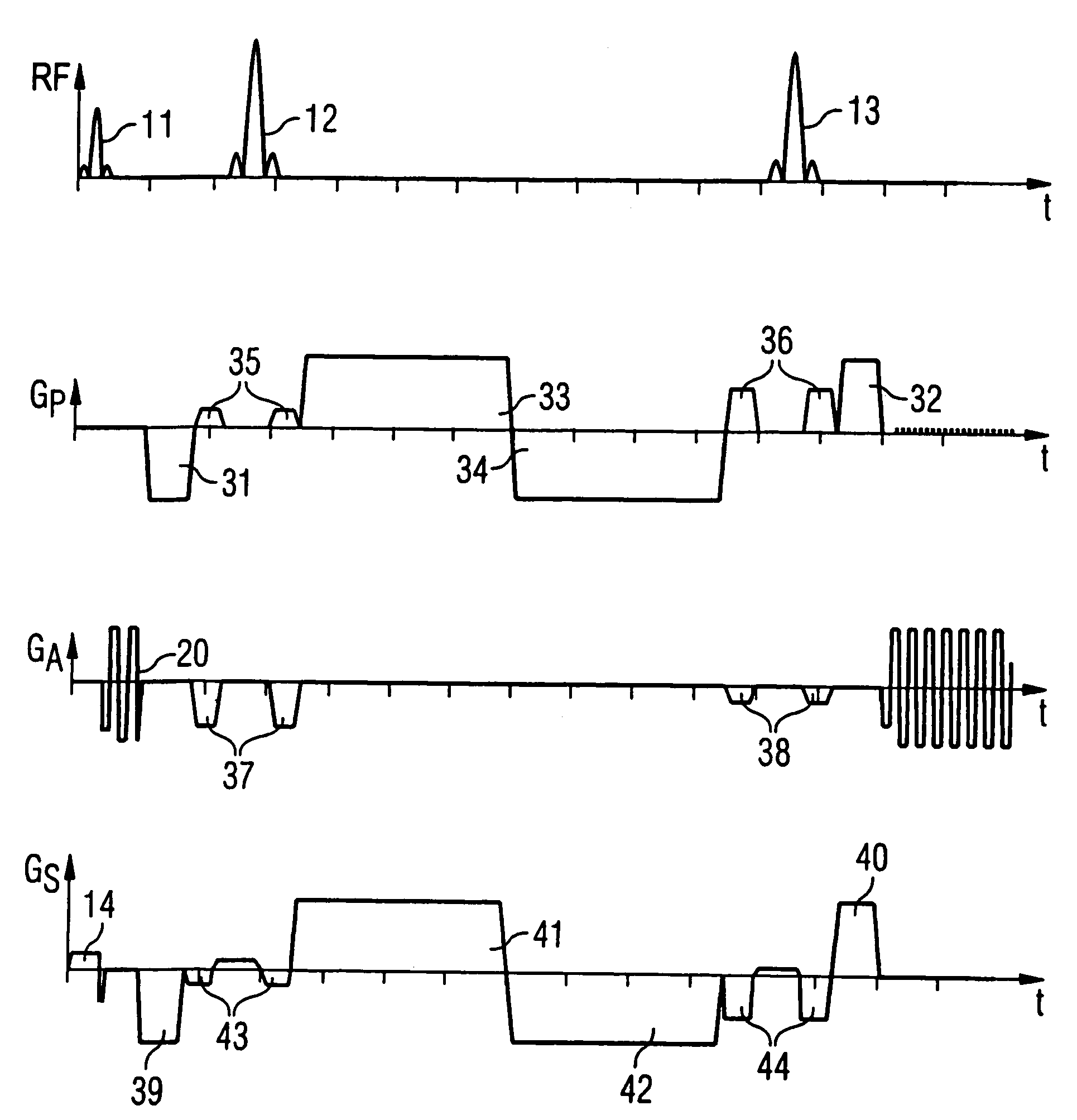
Correction of distortions in diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110085722A1Easy to correctCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceReference image
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus for correction of image distortions that occur in acquisition of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images of an examination subject, a reference image is acquired without diffusion weighting, a first diffusion-weighted image is acquired for a diffusion direction, a second diffusion-weighted image is acquired for the same diffusion direction, with the acquisition of the second diffusion-weighted image taking place at least with a different diffusion weighting or a different diffusion gradient polarity than the acquisition of the first diffusion-weighted image. Distortion parameters for the correction of image distortions in the acquired diffusion-weighted images are acquired, and the first diffusion-weighted image is deskewed with a first set of deskewing parameters, and the second diffusion-weighted image is deskewed with a second set of deskewing parameters. The first set and second set of deskewing parameters are correlated, and the deskewing parameters are determined by simultaneous minimization of differences between the deskewed first image and the reference image and differentiation between the deskewed second image and the reference image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for acquiring two-dimensional distribution of sediment dissolved reactive phosphorus (DRP)
ActiveCN102507471AHigh-resolutionUniform and dense distributionColor/spectral properties measurementsDiffusionSolid content
The invention discloses a method for acquiring two-dimensional distribution of sediment dissolved reactive phosphorus (DRP), which comprises: vertically placing a diffusion gradient in thin-films (DGT) device containing a modified phosphorus immobilizing film in a sediment to extract the DRP in the section of the sediment by using modified ZrO2 polyacrylamide gel thin film, in which the particle size of zirconium dioxide is less than or equal to 5mu m, as a phosphorus immobilizing film based on a DGT principle, and keeping 3 to 5 centimeters of overlying water; marking a sediment-water interface, taking out the immobilizing film, and performing two-dimensional and submillimeter slicing on the part below the interface; and extracting the DRP in the slices by using NaOH, measuring the DRP content in the extract by using microcolorimetry, converting the DRP content into the DRP solid content in the slices, calculating the DRP concentration at the corresponding position in the section of the sediment based on Fick's first law of diffusion, and drawing a two-dimensional distribution map.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
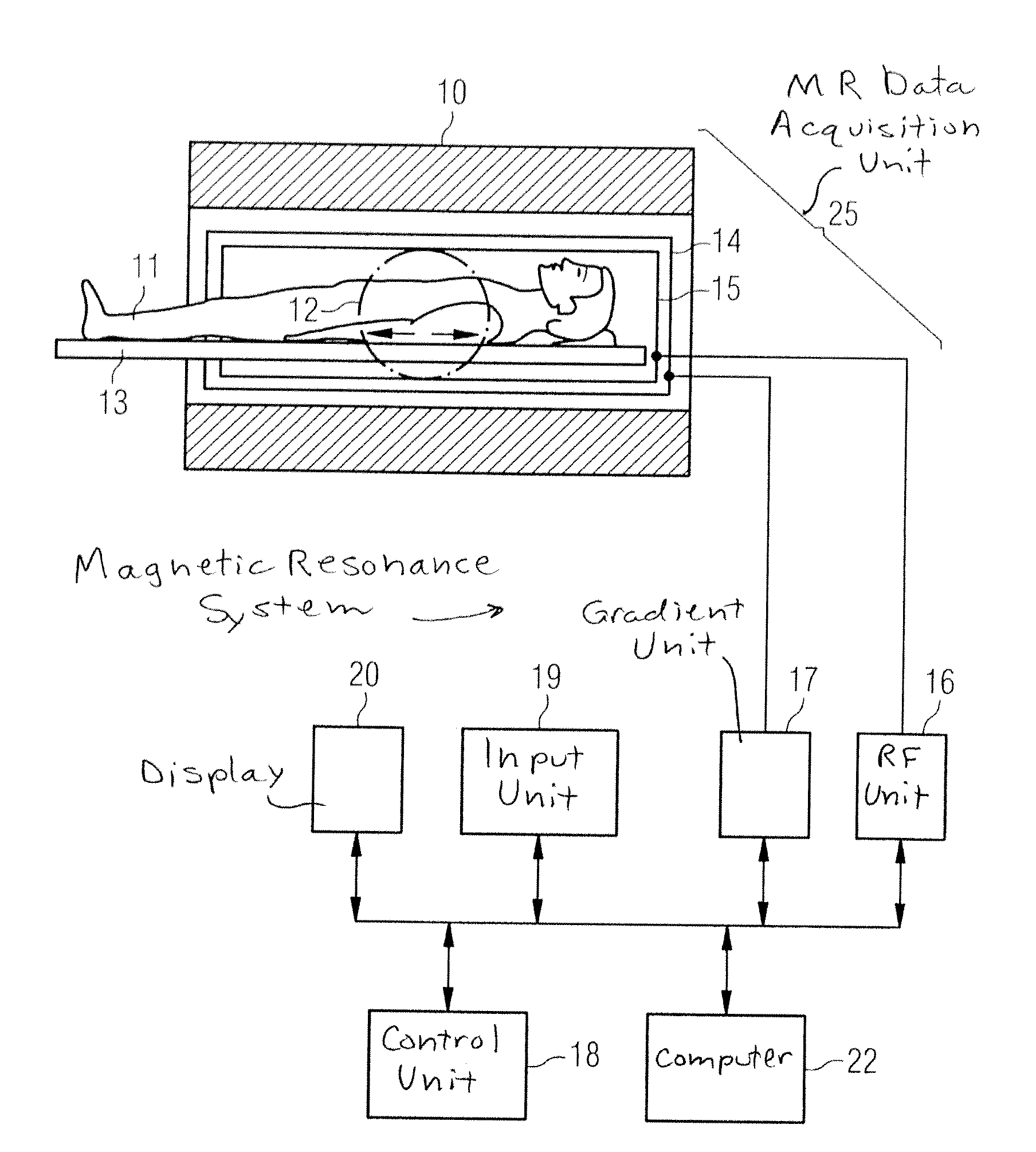
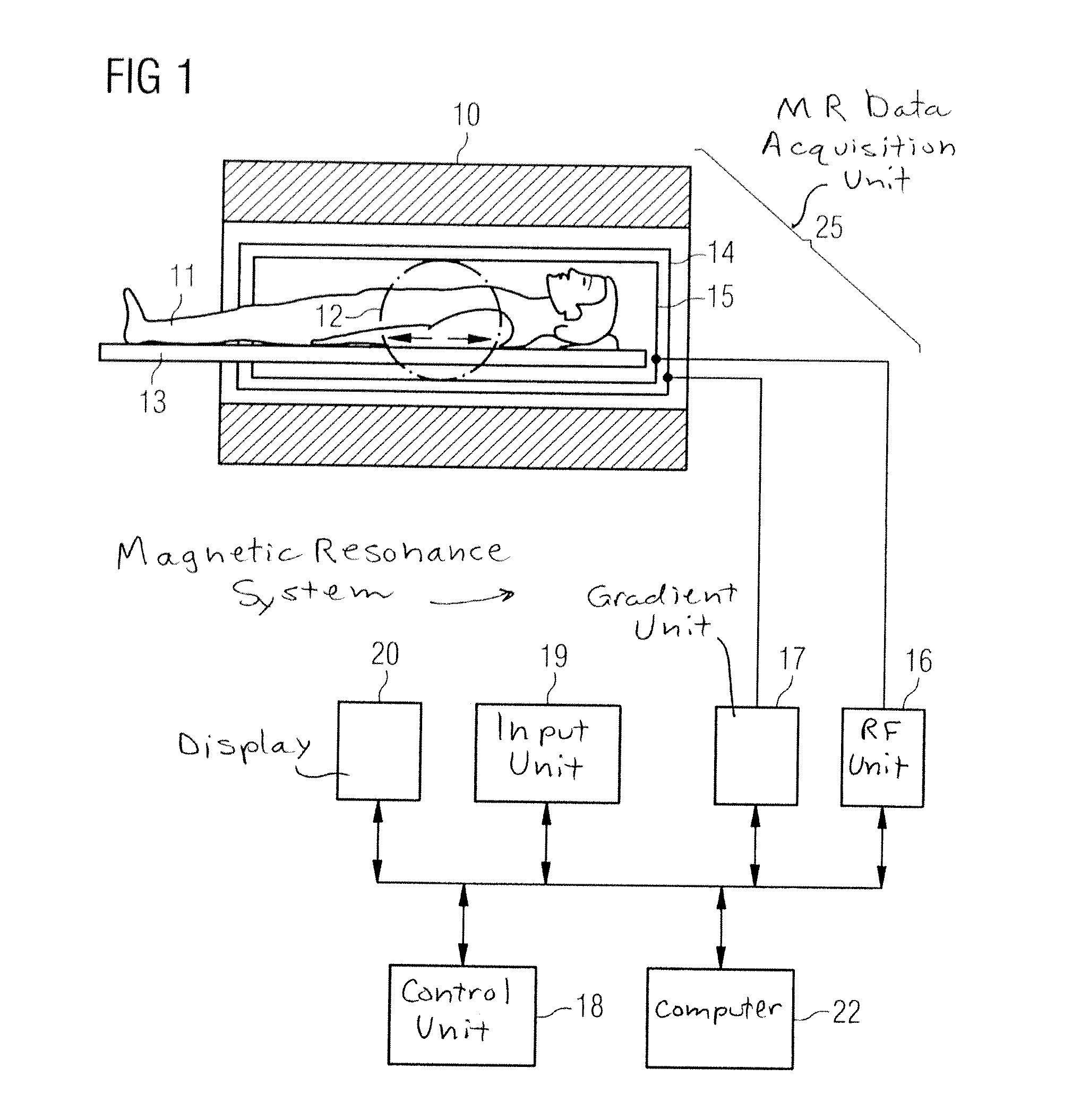
Magnetic resonance system and method to generate diffusion information
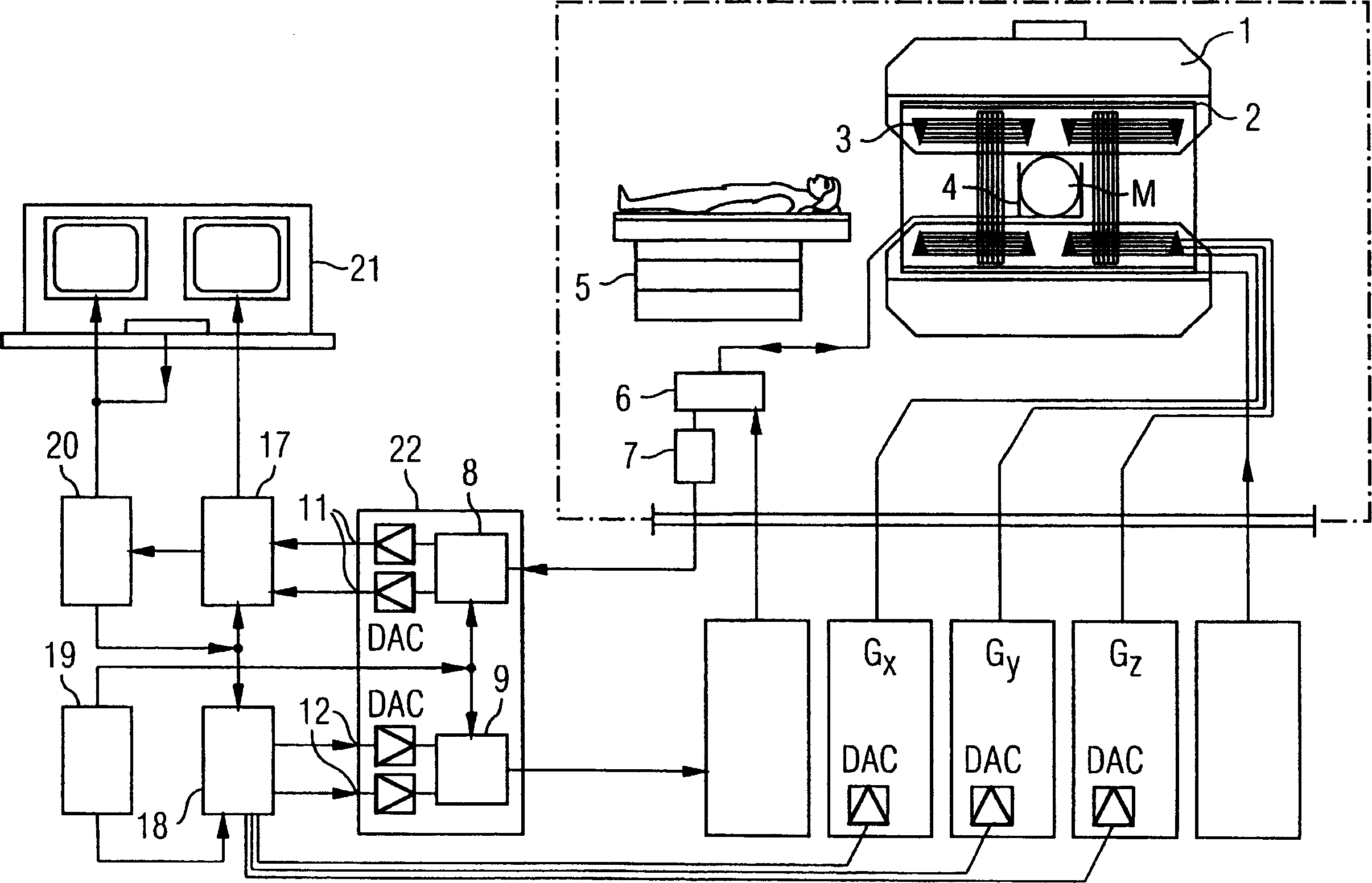
In a magnetic resonance (MR) method and system for the generation of diffusion information, diffusion-weighted MR images of an examination subject are generated, each image being generated using an individual diffusion gradient. The diffusion gradients, and therefore the MR images, are sorted such that, after the sorting, a predefined number of diffusion gradients respectively forms a group. Each diffusion gradient belongs to at least one of these groups, and the diffusion gradients of the respective same group are all as linearly independent of one another as possible. The MR images whose diffusion gradients form a group are assembled into an MR result image. Spatial transformations between the MR result images are determined, and the MR images are modified using these spatial transformations. The diffusion information is formed with the aid of the modified MR images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
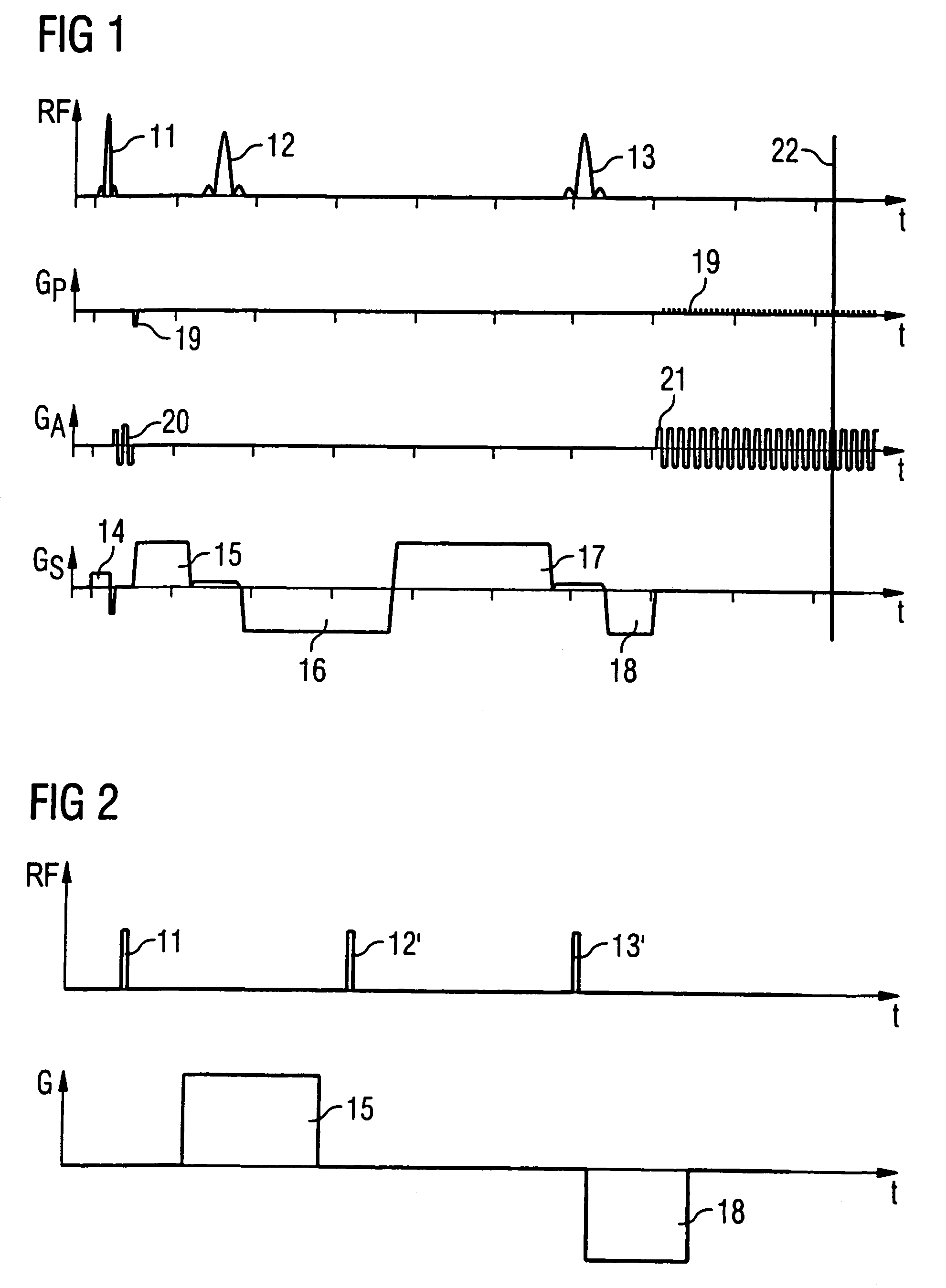
Magnetic resonance system and method for determining a diffusion-weighted image
InactiveUS20070167732A1Avoid artifactsIncreased formationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setResonance
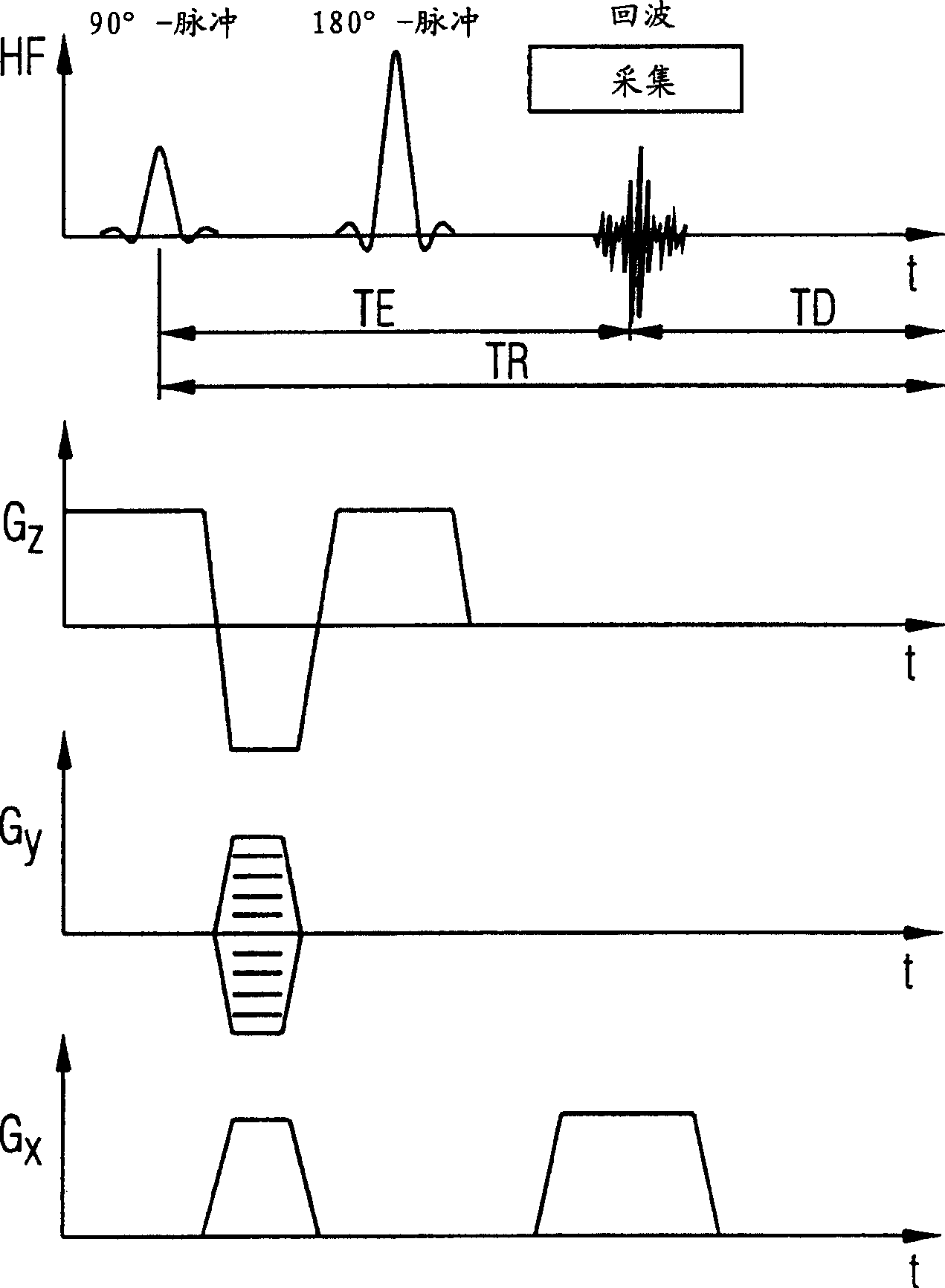
In a method for determination of a diffusion-weighted image of an examination subject in a magnetic resonance system, a diffusion-weighted data set is acquired with magnetic diffusion gradients being activated; a diffusion-weighted image of the examination subject is calculated using this diffusion-weighted data set; dephasing or spoiler gradients are activated in order to reduce artifacts in the diffusion-weighted image due to additional signal echoes and the position and / or amplitude and / or polarity of the dephasing gradients is / are selected dependent on the diffusion gradients.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
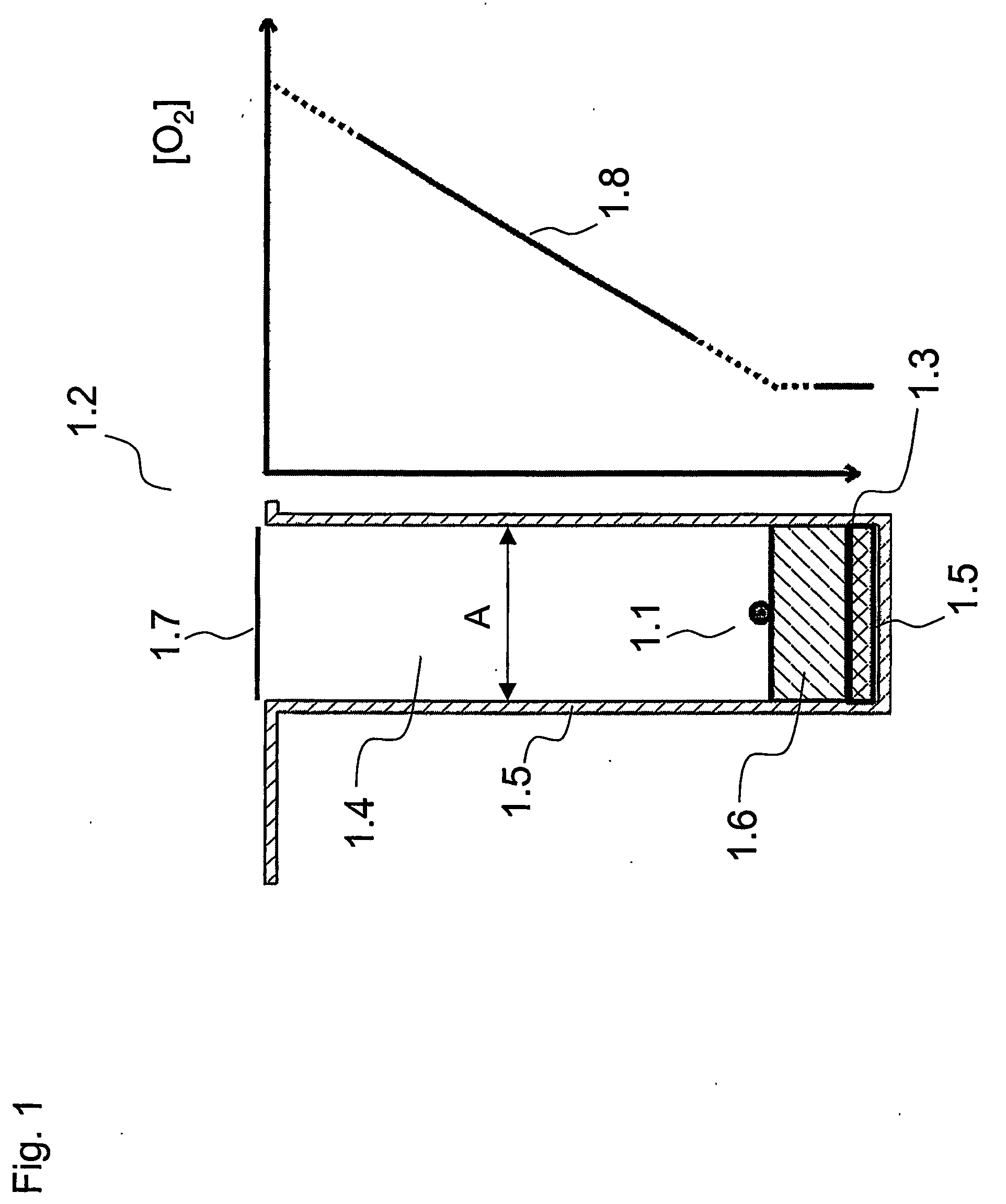
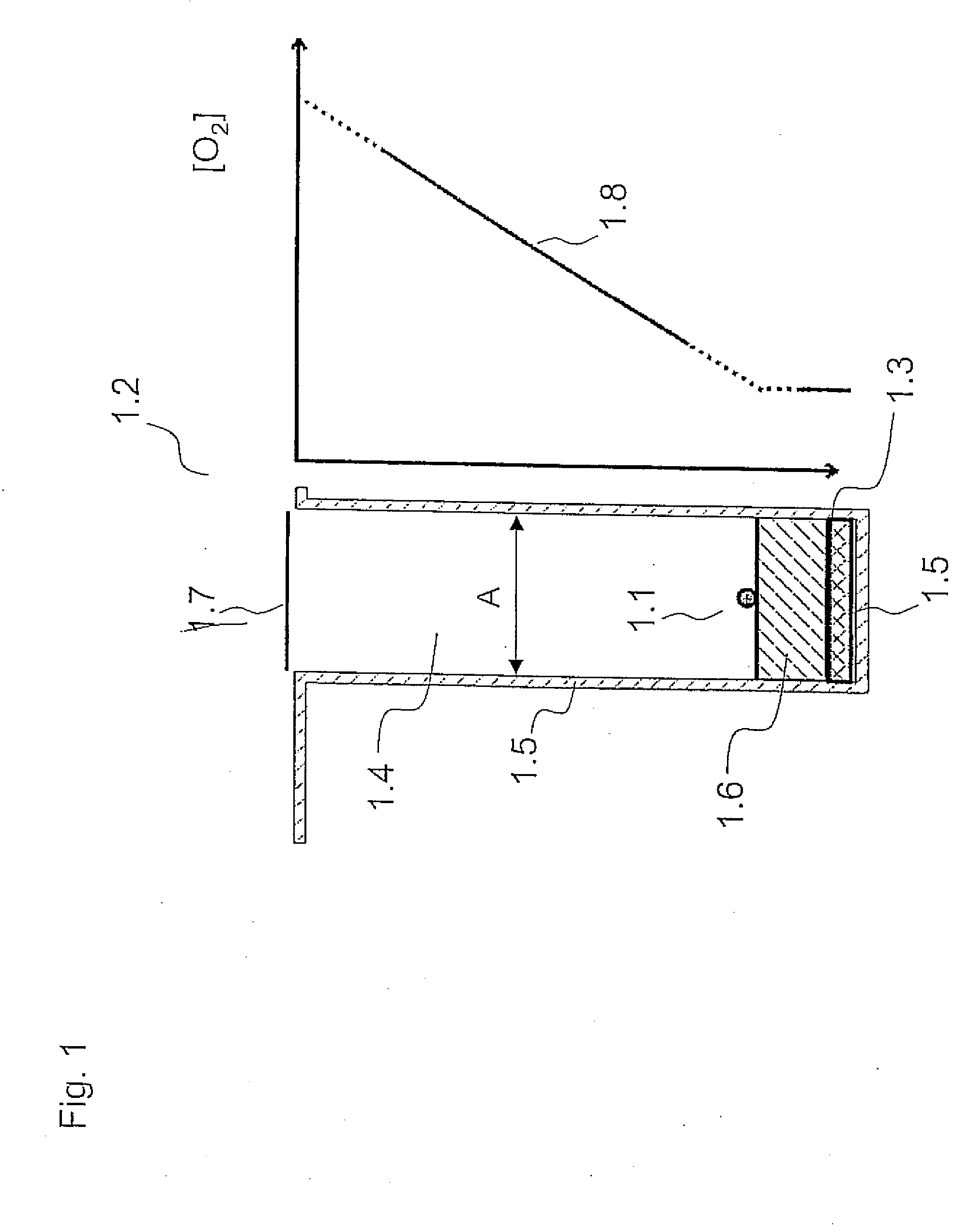
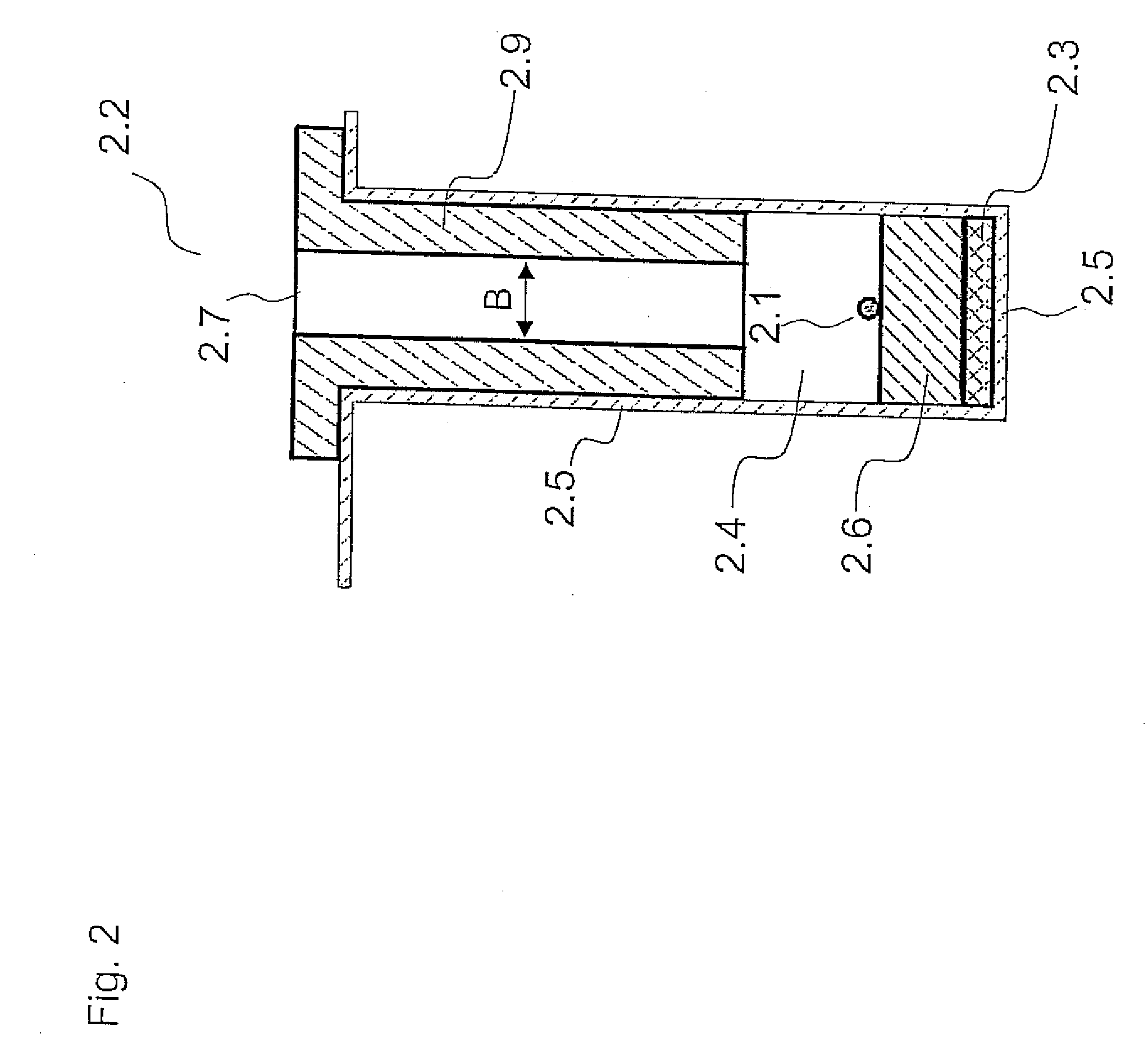
Device and method for non-invasive measurement of the individual metabolic rate of a substantially spherical metabolizing particle
InactiveUS20060099570A1Reduced cross sectionReduce penetrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMetaboliteMetabolic rate
The present invention relates to methods and devices for non-invasive and non-disturbing measurements of metabolizing rates of substantially spherical metabolizing particles, such as an embryo, and to a method and device for controlling oxygen partial pressure at the level of the embryo. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for regulating supply of metabolites to a substantially spherical metabolizing particle, as well as a method for selecting substantially spherical metabolizing particles of a predetermined quality. The invention is carried out in a device capable of establishing a diffusion gradient of metabolites between the substantially spherical metabolizing particle inside a compartment in the device and the environment outside the compartment. The metabolizing rate is determined based on information of the metabolite diffusion gradient.
Owner:UNISENSE FERTILITECH AS
Microfluidic device and related methods
InactiveUS20150111239A1Compound screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDiffusionConcentration gradient
A combinatorial microenvironment generator is configured for the generation of arbitrary, user-defined, steady-state, concentration gradients with negligible to no flow through the growth medium to perturb diffusion gradients or cellular growth. More importantly, the absolute concentrations and / or gradients can be dynamically altered upon request both spatially and temporally to impose tailored concentration fields for in-situ stimulus studies. Here, diffusion occurs via an array of ports, each of which can be an independently controlled source / sink. Together, the array of ports establishes a user-defined, 3D concentration profile. Useful methods related to this device are also provided.
Owner:MAINE INST FOR HUMAN GENETICS & HEALTH +1
Method and system for performing rapid diffusion tensor imaging under compression sensing framework
ActiveCN103356193AQuality improvementReduce sampling pointsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiffusionImaging quality
The invention provides a method and a system for performing rapid diffusion tensor imaging under a compression sensing framework. The rapid diffusion tensor imaging method comprises the following steps: A, initializing a sampling mask1 which corresponds to a first diffusion gradient, and adopting a ray type sampling locus; and B, rotating the sampling mask 1 which corresponds to the first diffusion gradient by a fixed angle to obtain a sampling mask2 which corresponds to a second diffusion gradient, rotating the sampling mask2 which corresponds to the second diffusion gradient by a fixed angle in the same direction to obtain a sampling mask3 which corresponds to a third diffusion gradient, and so on till L sampling masks are obtained in total. The method and the system have the beneficial effects that under the situation of same sampling points, diffusion images of higher quality can be obtained by remodeling. In other words, less sampling points are needed in a novel scheme while the same image quality is obtained, the sampling time is shortened, and the aim of accelerating imaging is fulfilled.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
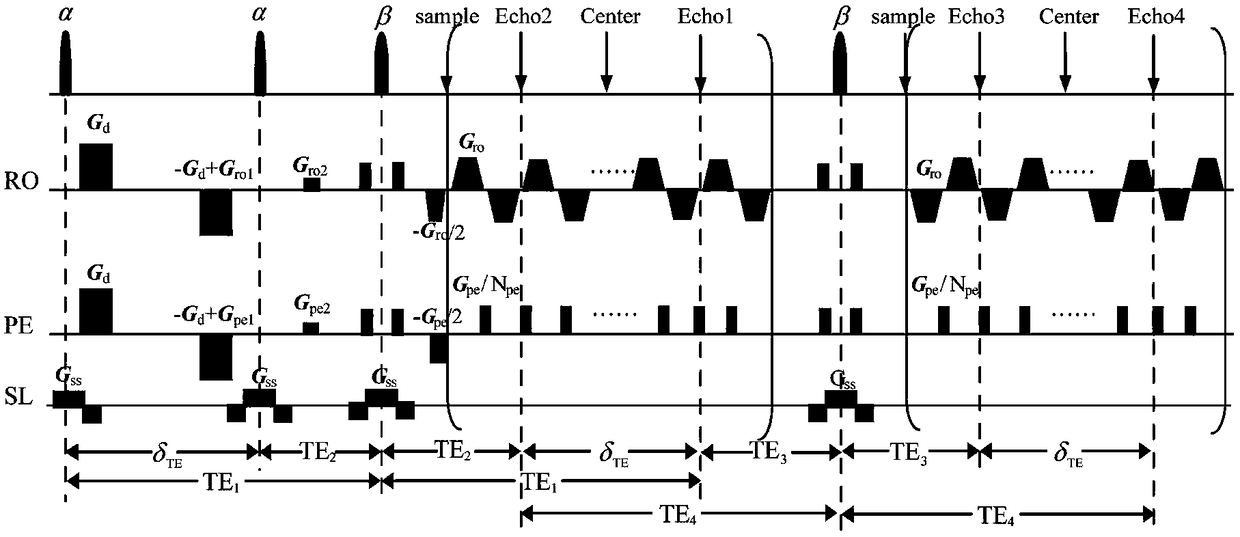
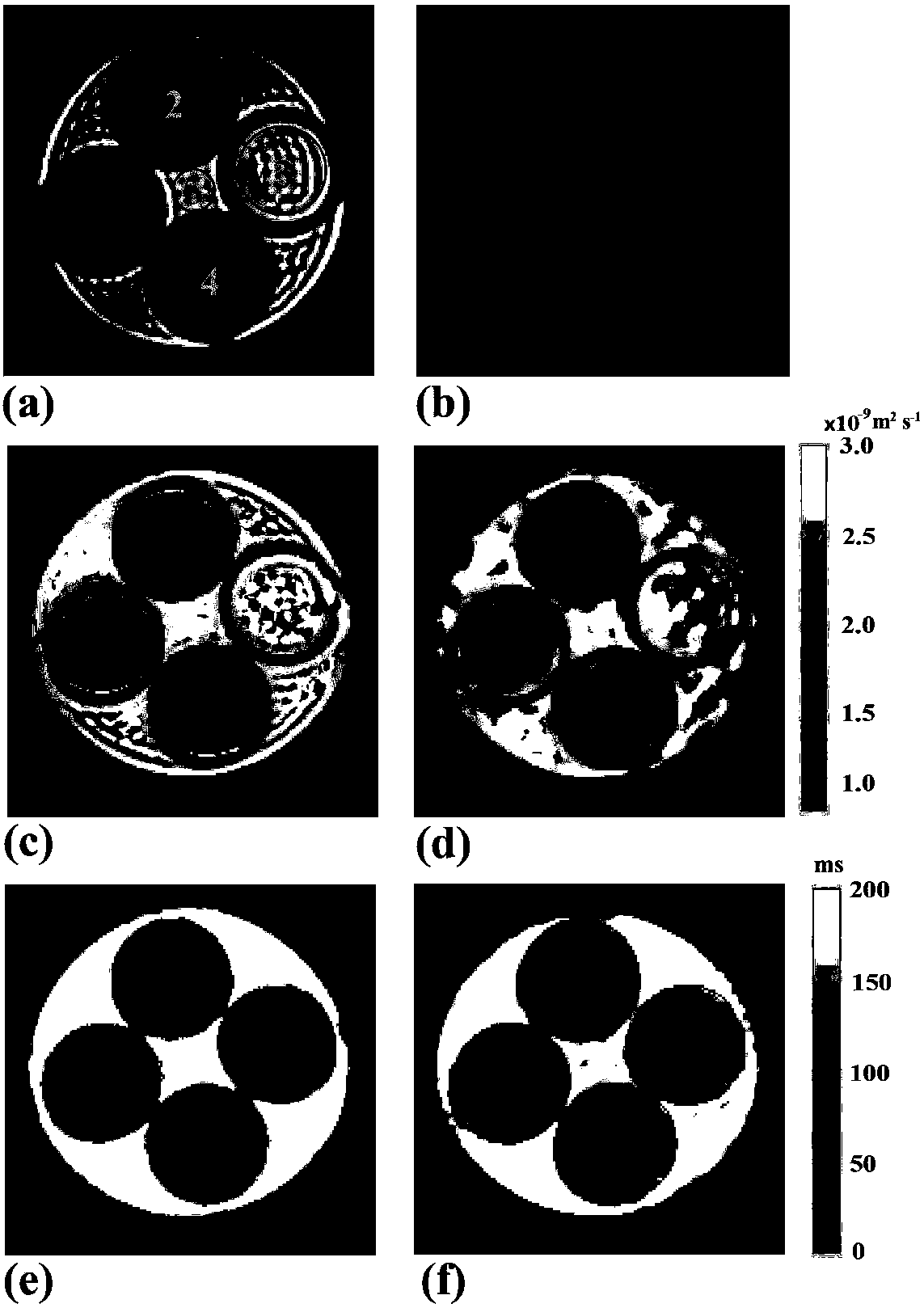
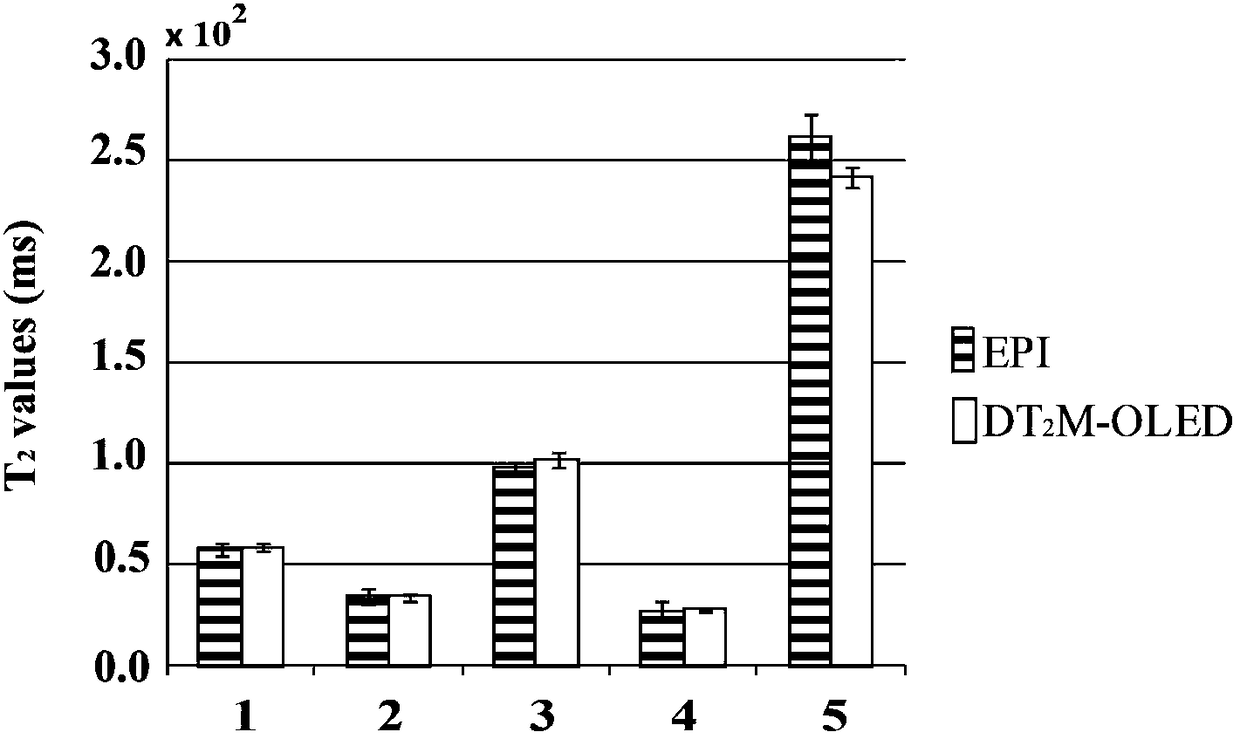
Single-scan synchronous magnetic resonance diffusion and T2 imaging method based on overlapping echoes
A single-scan synchronous magnetic resonance diffusion and T2 imaging method based on overlapping echoes, relates to magnetic resonance imaging. Four echoes are produced by using a small angle excitation pulse and two echo chain samplings with two identical deflection angles, and each echo chain collects two echo signals. There is an evolution time and a pair of diffusion gradients after the firstexcitation pulse, due to which the transverse relaxation times and diffusion weights of the two echo signals in the first sampling are different. A shifting gradient of frequency dimension and phasedimension is added after each excitation pulse so that the signals generated by the different excitation pulses are different in position in the k-space. Two echo signals are re-converged with one refocusing pulse after finishing the first sampling, and then the second sampling is performed, in which two echo signals with the same transverse relaxation time and different diffusion weights can be obtained. The sampled signal is reconstructed using deep learning to obtain quantitative T2 and ADC images, and T2 and ADC images can be obtained in a single-scan.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Device and method for non-invasive measurement of the individual metabolic rate of a substantially spherical metabolizing particle
InactiveUS20110183367A1The process is simple and fastBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMetaboliteMetabolic rate
The present invention relates to methods and devices for non-invasive and non-disturbing measurements of metabolizing rates of substantially spherical metabolizing particles, such as an embryo, and to a method and device for controlling oxygen partial pressure at the level of the embryo. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for regulating supply of metabolites to a substantially spherical metabolizing particle, as well as a method for selecting substantially spherical metabolizing particles of a predetermined quality. The invention is carried out in a device capable of establishing a diffusion gradient of metabolites between the substantially spherical metabolizing particle inside a compartment in the device and the environment outside the compartment. The metabolizing rate is determined based on information of the metabolite diffusion gradient.
Owner:UNISENSE RESPIROMETRY
Method for ceramic treatment of metal surface
InactiveCN1621563ATightly boundAvoid breakingHot-dipping/immersion processesVacuum evaporation coatingAlloyPre treatment
The ceramic treating process for the surface of metal base includes the following steps: coating the pre-treated base with one aluminum layer through hot soaking or vacuum treating; and treating the coated aluminum layer to obtain composite system comprising transitional compound layer and outer ceramic phase layer. The key of the present invention is to form alloy layer with matched thickness as the transition layer between the base and the ceramic layer, and the transition layer has metallurgical diffusion gradient change. The present invention features that there are micro plastic aluminum areas between the alloy layer and the Al2O3 ceramic layer to coordinate the deformation resisting effect between the ceramic layer and the base for tight combination.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite membrane for in-situ simultaneous monitoring of labile phosphorus and dissolved oxygen and preparation method thereof
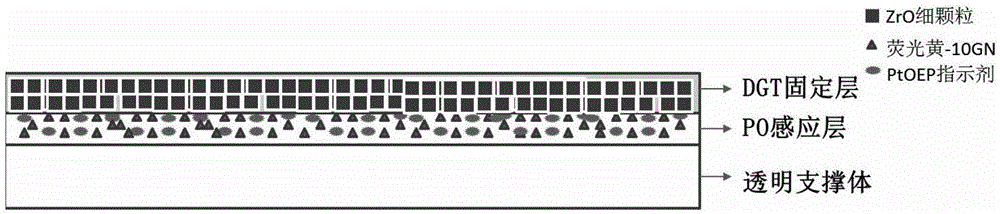
ActiveCN105466899AIncreased sensitivitySmall particle sizeFluorescence/phosphorescencePlatinumFluorescence sensing
The invention discloses a DGT-PO composite membrane for in-situ simultaneous monitoring of labile phosphorus and dissolved oxygen. The composite membrane is characterized by comprising a transparent supporting body, a fluorescence sensing layer and a DGT fixing layer; the fluorescence sensing layer is obtained by uniformly mixing fluorochrome octaethyl porphilin platinum and fluorescein 10-GN, and fixing the two fluorochromes to the surface of a transparent supporting body through chemical embedding; the DGT fixing layer adopts submicron ZrO particles as a fixing agent and adopts polyurethane as a matrix, and the DGT fixing layer is obtained on the fluorescence sensing layer through a coating method. According to the composite membrane, on the basis of a slab photoelectrode and a film diffusion gradient principle, two channels are adopted for obtaining DO and SRP information, and SRP fixation and DO induction in the matrix such as water or sediments or soil or the like can be achieved.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
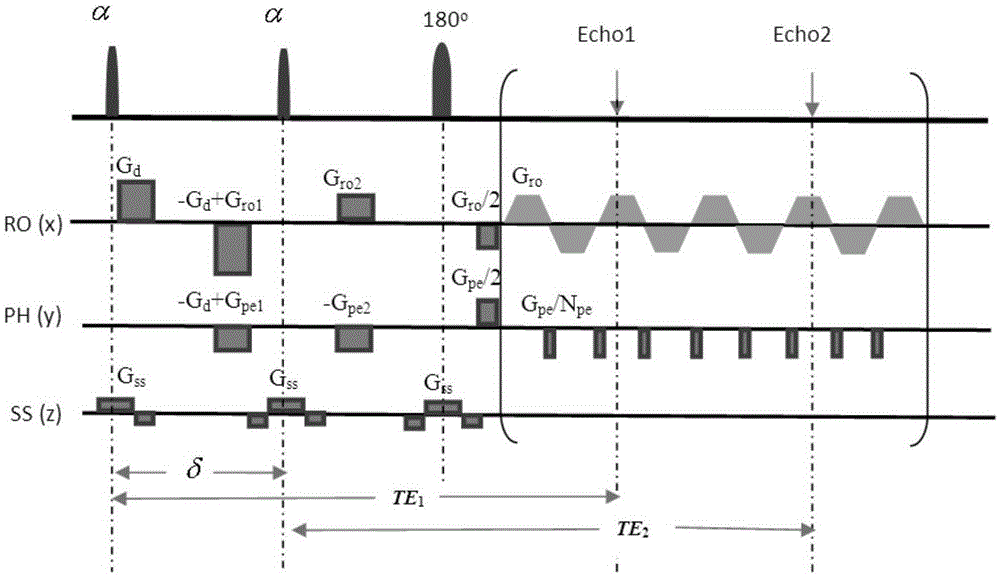
Method for imaging diffusion anisotropy and diffusion gradient simultaneously
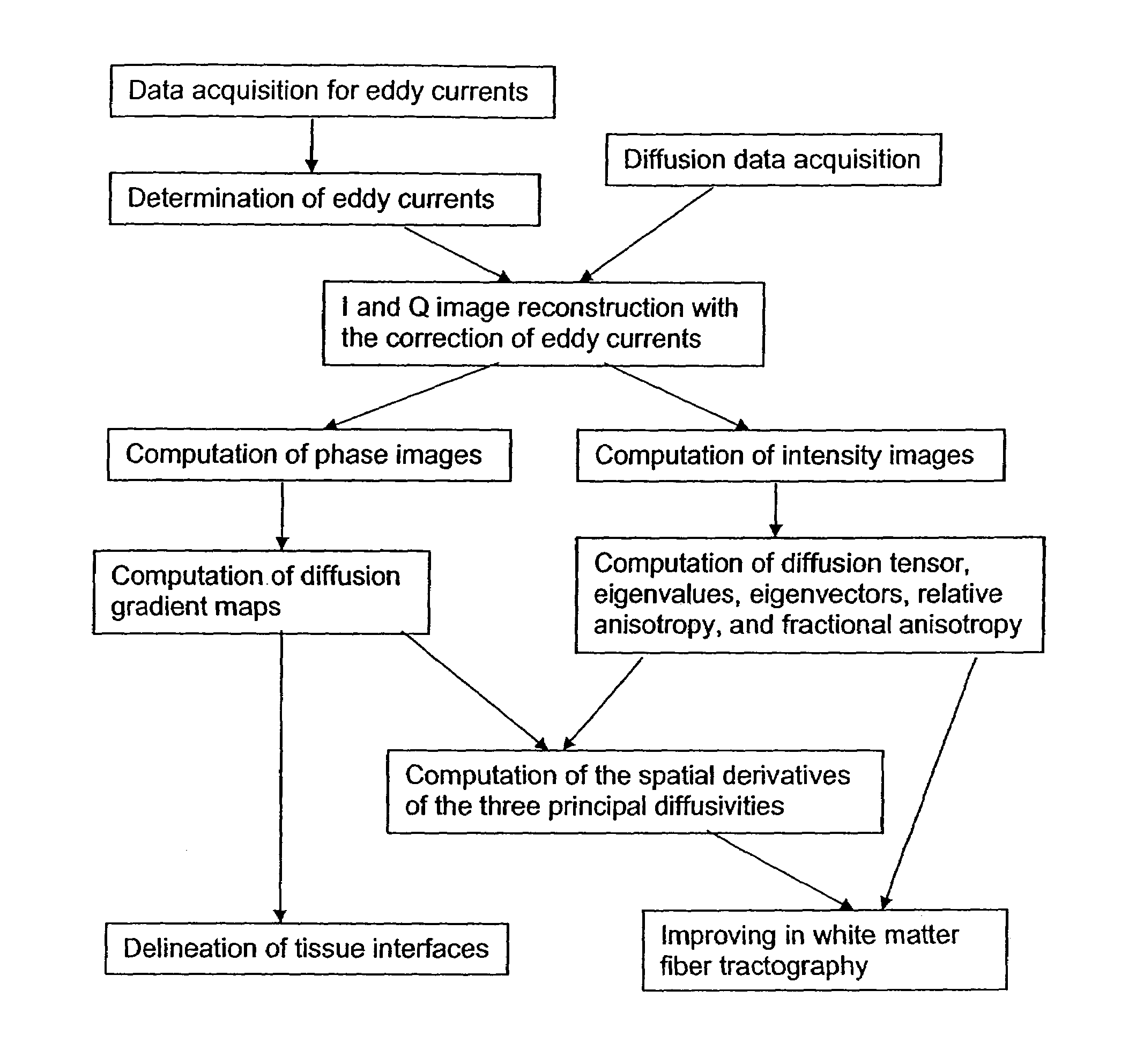
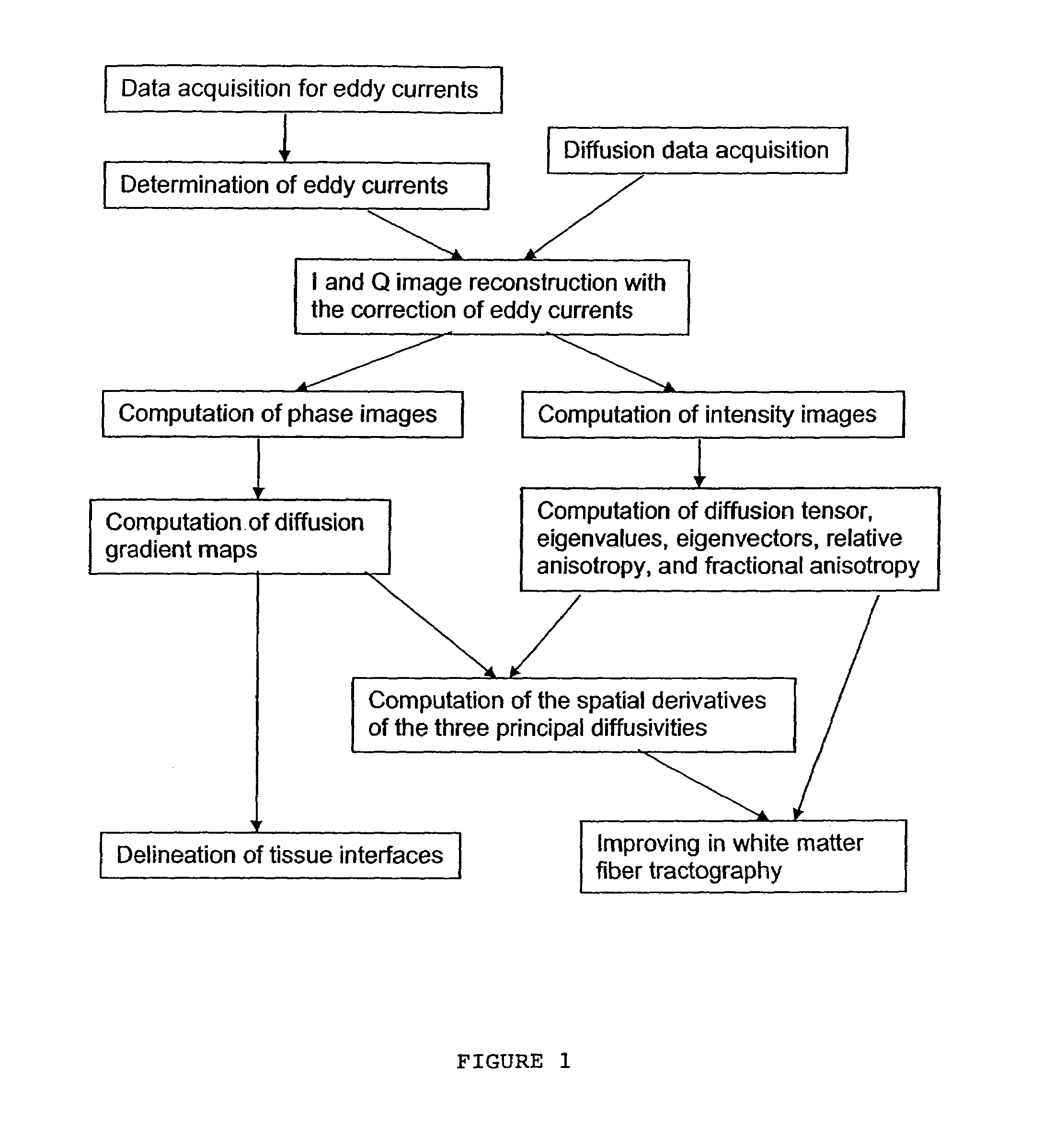
InactiveUS7411394B2Improve white matter fiber tractograpyMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionDiffusion AnisotropyTissue architecture
Inhomogeneous tissue structures cause spatial-varying water molecule diffusion that is characterized by the spatial derivative of diffusivity, i.e., diffusion gradient. In a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system, the effects of diffusion and diffusion gradient are simultaneously encoded in an echo signal using diffusion-encoding magnetic field gradient pulses. A method for imaging the diffusion gradient of water molecules in tissues and for delineating the interface between two tissues having different diffusion properties is disclosed. The method also describes imaging diffusion anisotropy and diffusion gradient simultaneously without any additional scans in comparison with diffusion tensor MRI.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Magnetic resonance system and method to generate diffusion information
In a magnetic resonance (MR) method and system for the generation of diffusion information, diffusion-weighted MR images of an examination subject are generated, each image being generated using an individual diffusion gradient. The diffusion gradients, and therefore the MR images, are sorted such that, after the sorting, a predefined number of diffusion gradients respectively forms a group. Each diffusion gradient belongs to at least one of these groups, and the diffusion gradients of the respective same group are all as linearly independent of one another as possible. The MR images whose diffusion gradients form a group are assembled into an MR result image. Spatial transformations between the MR result images are determined, and the MR images are modified using these spatial transformations. The diffusion information is formed with the aid of the modified MR images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Preparation method and application of antibiotic molecular imprinting adsorption membrane
InactiveCN110327903AAchieving Selective Adsorption RemovalEasy to operateOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMembrane technologyRoom temperature
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of an antibiotic molecular imprinting adsorption membrane, and belongs to the fields of pollutant control and detection. An antibiotic molecularly imprinted membrane is prepared by doping an antibiotic molecularly imprinted material into agarose gel, is capable of selectively adsorbing antibiotic contaminants in a water body, and servesas a binding phase of diffusion gradient membrane technology for antibiotic determination in the water body. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the antibiotic molecularlyimprinted material firstly, then mixing the molecularly imprinted material with an agarose solution in a certain ratio, injecting the mixture into a glass plate with a U-shaped plastic insulation pad, placing at room temperature and immersing into gel to form the antibiotic molecular imprinting adsorption membrane. The method provided by the invention is simple to operate and low in cost; the obtained molecularly imprinted membrane is good in hydrophilicity, high in adsorption capacity on antibiotics in the water body and good in selectivity, can be used for high-efficiency adsorption removalof antibiotics in the water body, and serves as a binding phase of diffusion gradient membrane technology for antibiotic determination in the water body.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
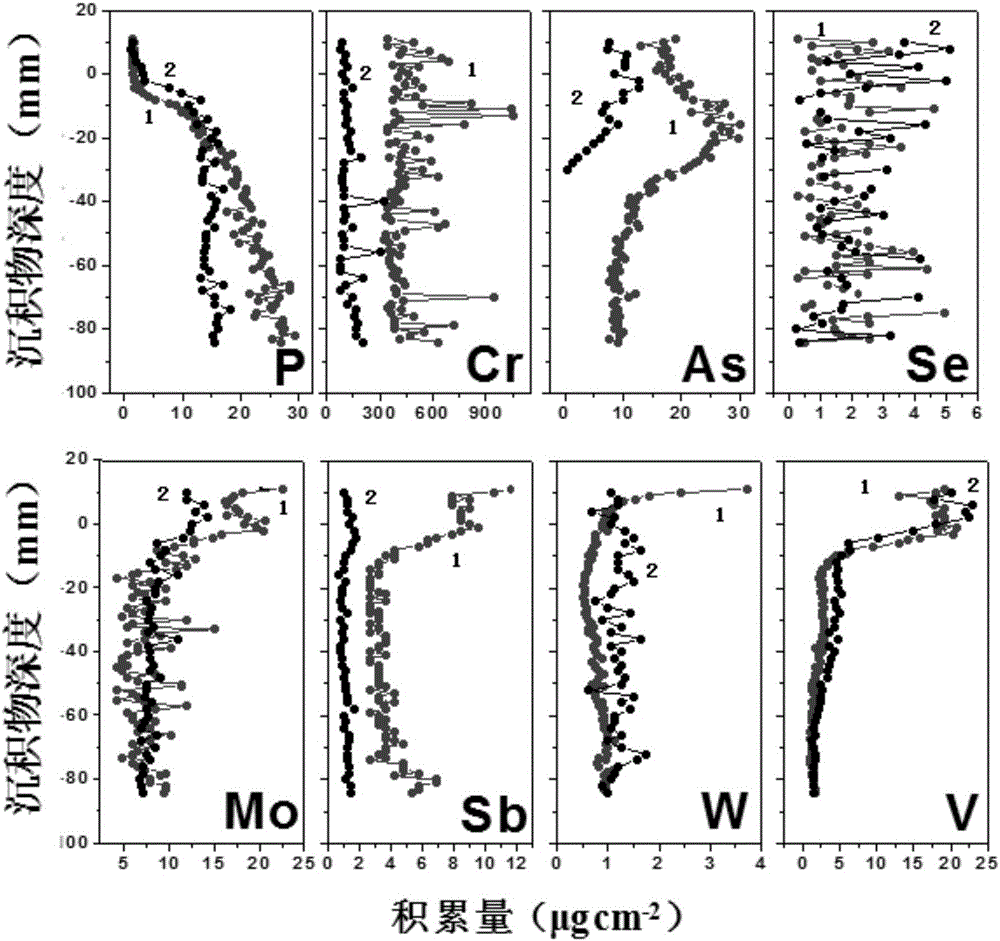
DGT-based method for synchronously measuring eight kinds of oxidized anions
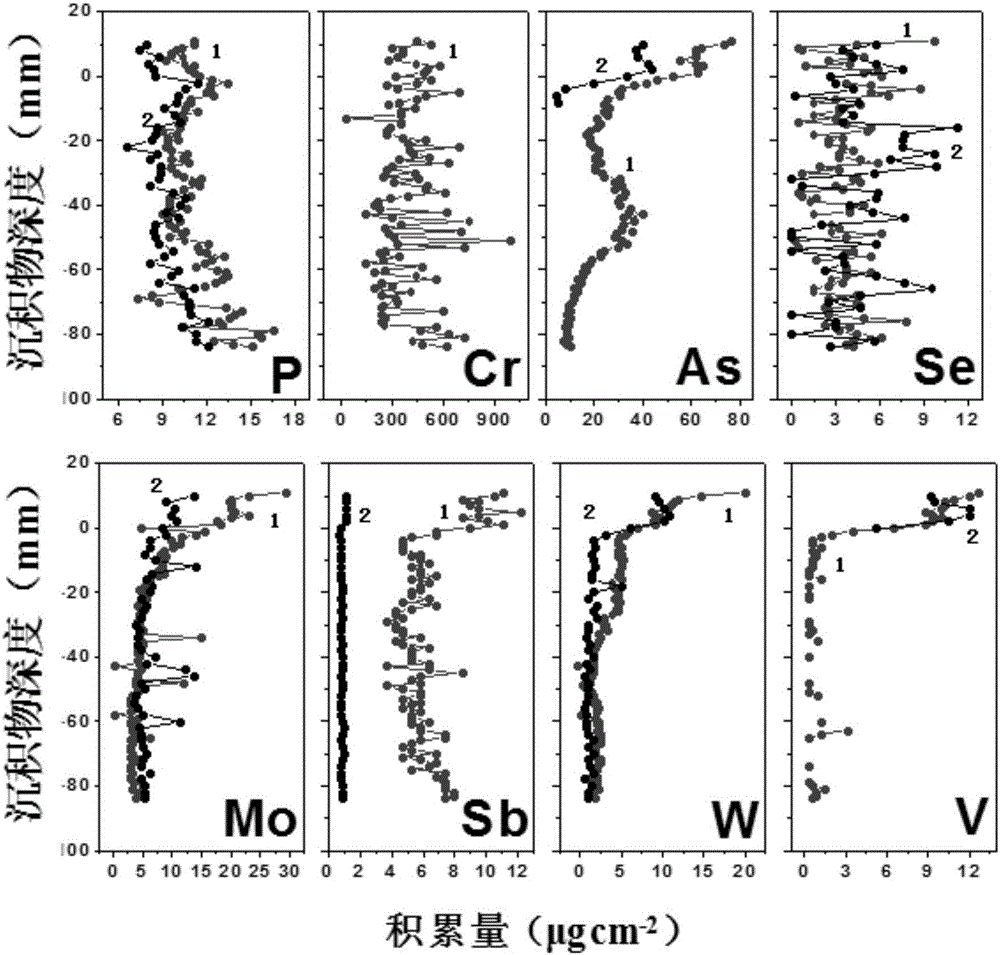
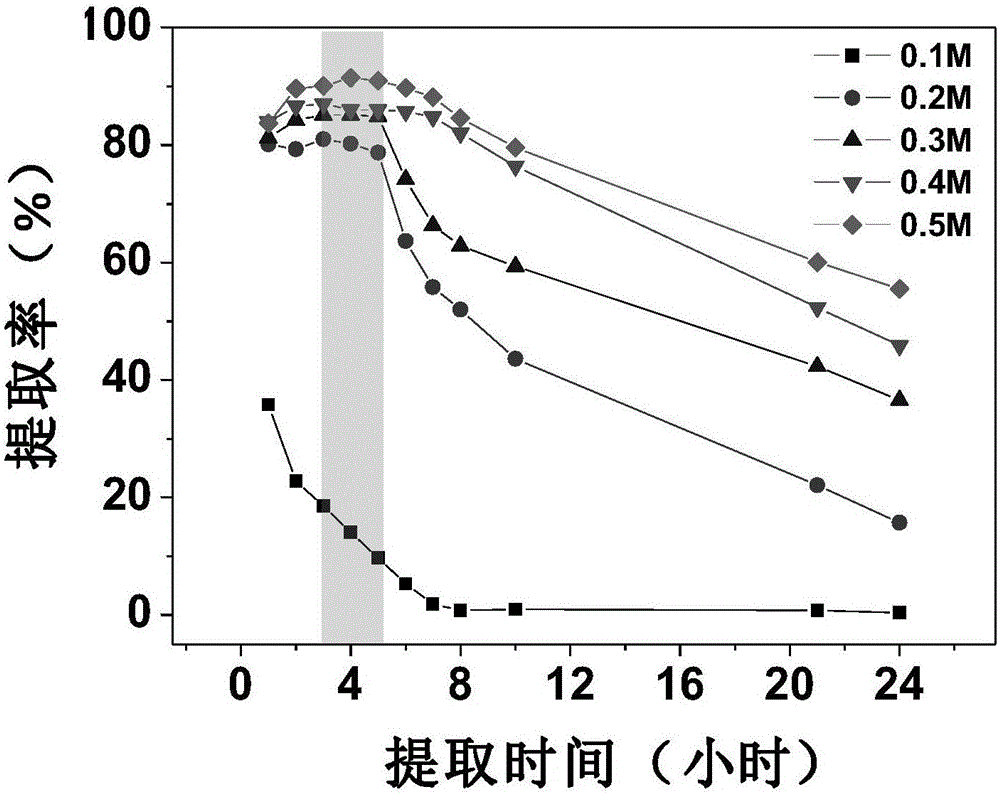
InactiveCN106198319AIncrease capacityImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationZirconium dioxideDiffusion gradient
The invention discloses a DGT-based method for synchronously measuring eight kinds of oxidized anions. The oxidized anions include P (V), As (V), Cr (VI), Mo (VI), Sb (V), Se (VI), V (V) and W (VI). The method includes: on the basis of thin film diffusion gradient principles, adopting a zirconium dioxide polyacrylamide gel thin film (Zr-oxide film) as a fixing film, and assembling the fixing film, a diffusion film and an osmosis film into a DGT device; adopting a mild mixed solution 0.2M NaOH-0.5M H2O2 to further elute the anions accumulated on the fixing film for 3-5h; measuring accumulation amounts of the oxidized anions in the fixing film; calculating according to Fick first diffusion laws to obtain concentration of the oxidized ions. The Zr-oxide film is used for synchronously measuring the oxidized anions and has the characteristics of high DGT capacity and high interference resistance, and type of DGT measuring and number of synchronous measuring are increased; by adopting an extraction method, interference on phosphor measuring caused by too high H2O2 concentration of existing eluents, elution efficiency can be improved remarkably, elution time can be shortened, detection limit of DGT measuring of anions can be lowered, and analysis efficiency and accuracy are improved greatly.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
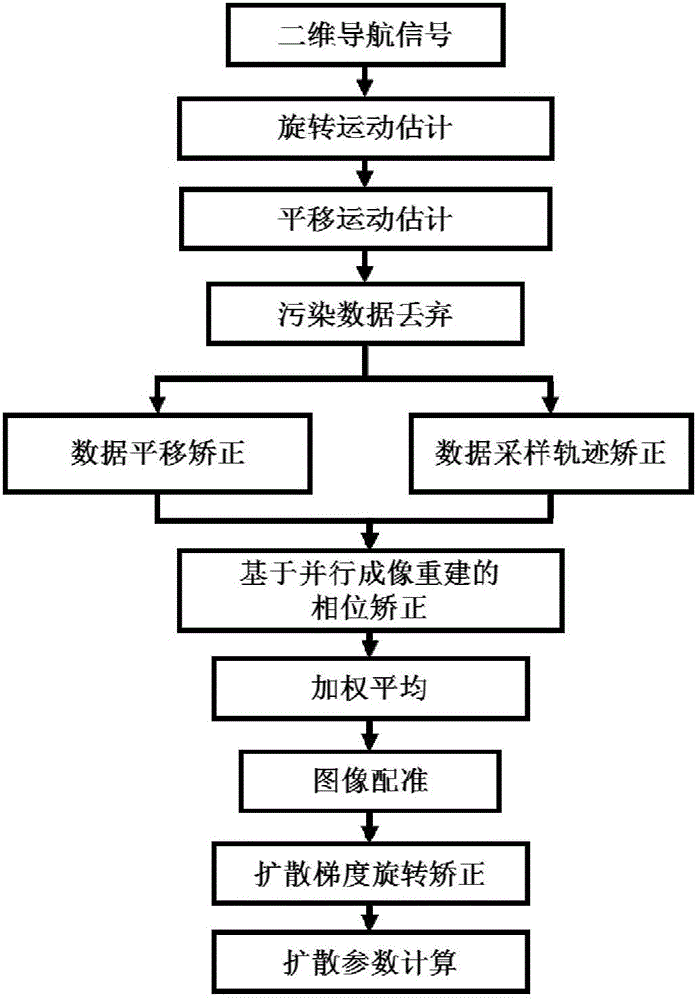
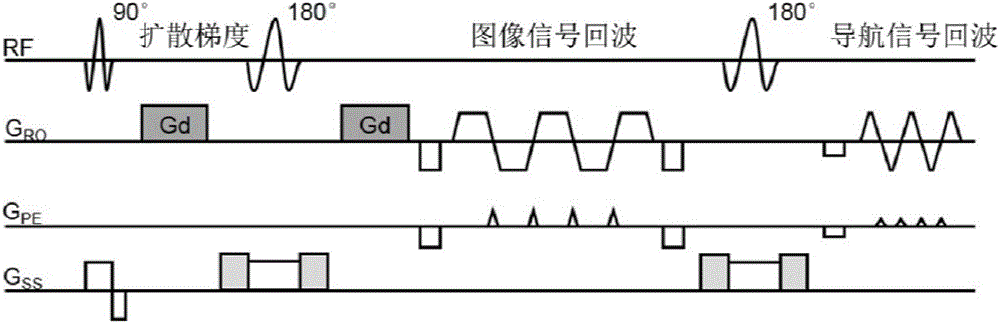
Motion correction method for magnetic resonance multiple excitation diffusion imaging
ActiveCN106780643AHigh resolutionLess geometric distortionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionParallel imagingDiffusion gradient
The invention discloses a motion correction method for magnetic resonance multiple excitation diffusion imaging. The method comprises the steps of collecting a magnetic resonance multiple excitation sequence; obtaining an image echo signal and a two-dimensional navigation signal through a magnetic resonance scanning sequence; estimating motion parameters through the two-dimensional navigation signal; performing rotational and translational correction on the image echo signal and the two-dimensional navigation signal according to the motion parameters, and discarding tainted data, thereby obtaining corrected data; integrating the corrected data collected in multiple excitation to perform parallel imaging reconstruction; estimating rotational motion parameters through an image registration algorithm to perform diffusion gradient correction on a reconstructed image; and performing final calculation by utilizing corrected diffusion image and diffusion gradient to obtain diffusion tensor imaging parameters. According to the method, various motion errors in a magnetic resonance diffusion imaging scanning process can be effectively corrected, so that an artifact-free high-resolution diffusion tensor image is obtained, the errors are effectively reduced, and the accuracy of calculating magnetic resonance diffusion imaging tensor parameters is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
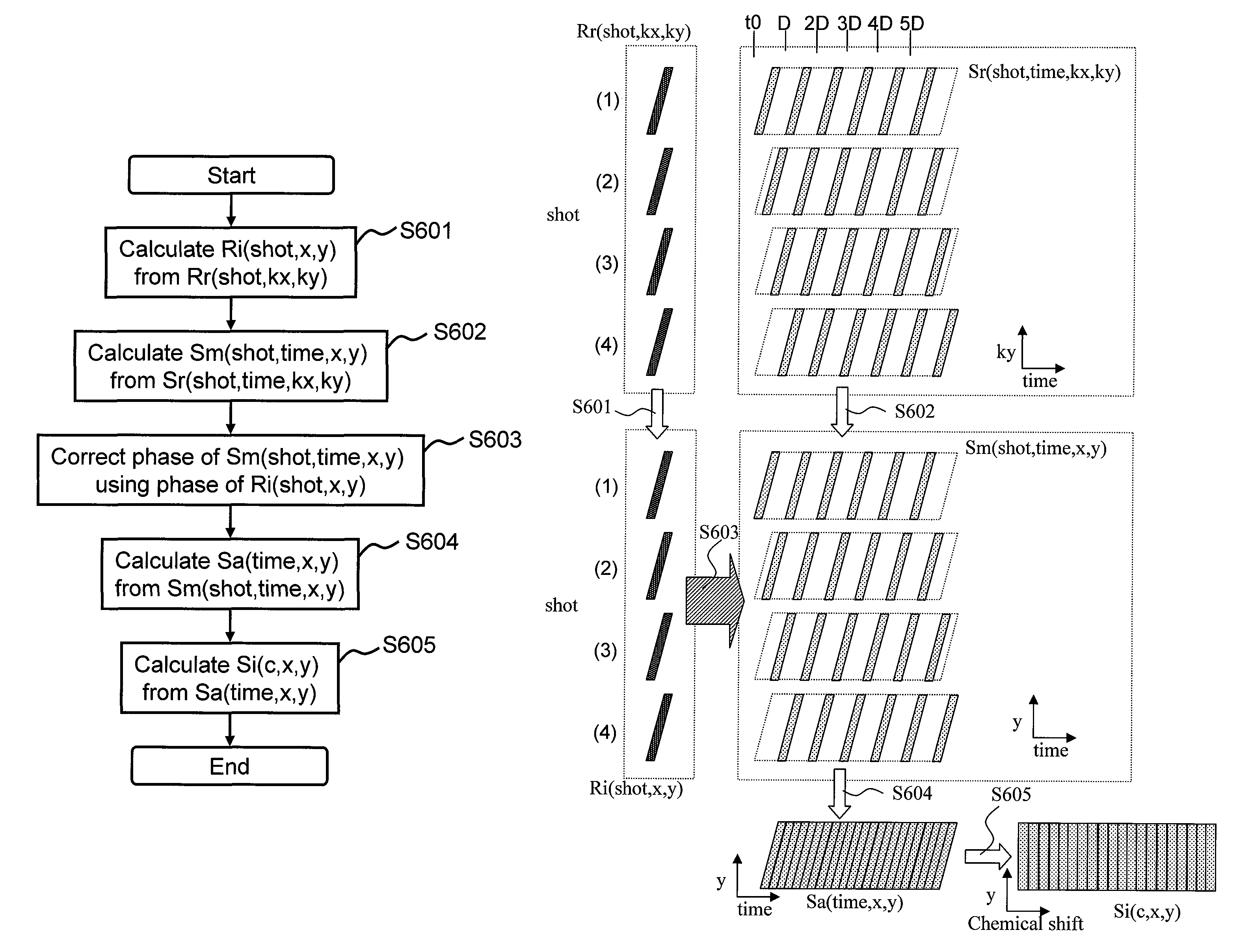
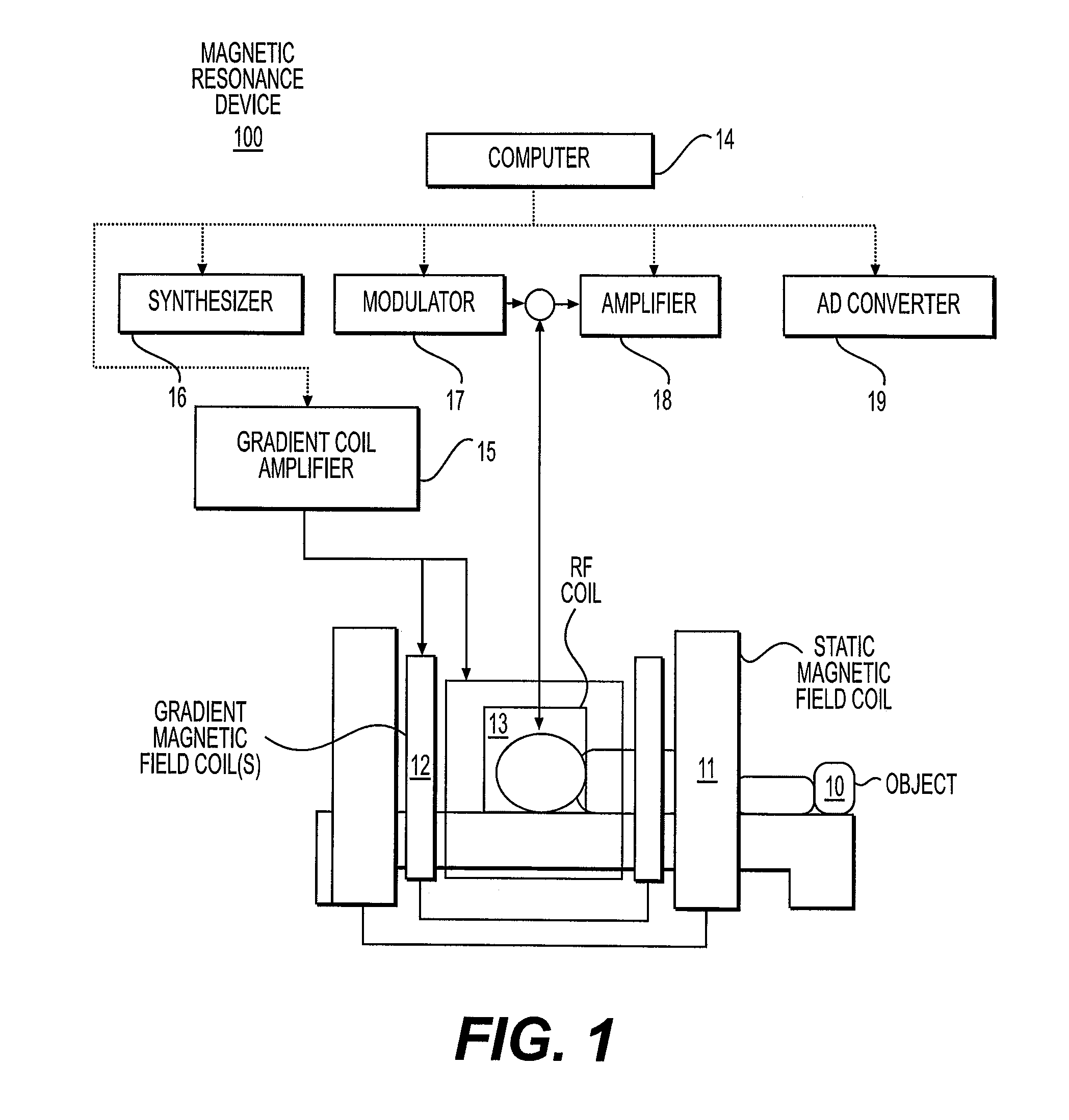
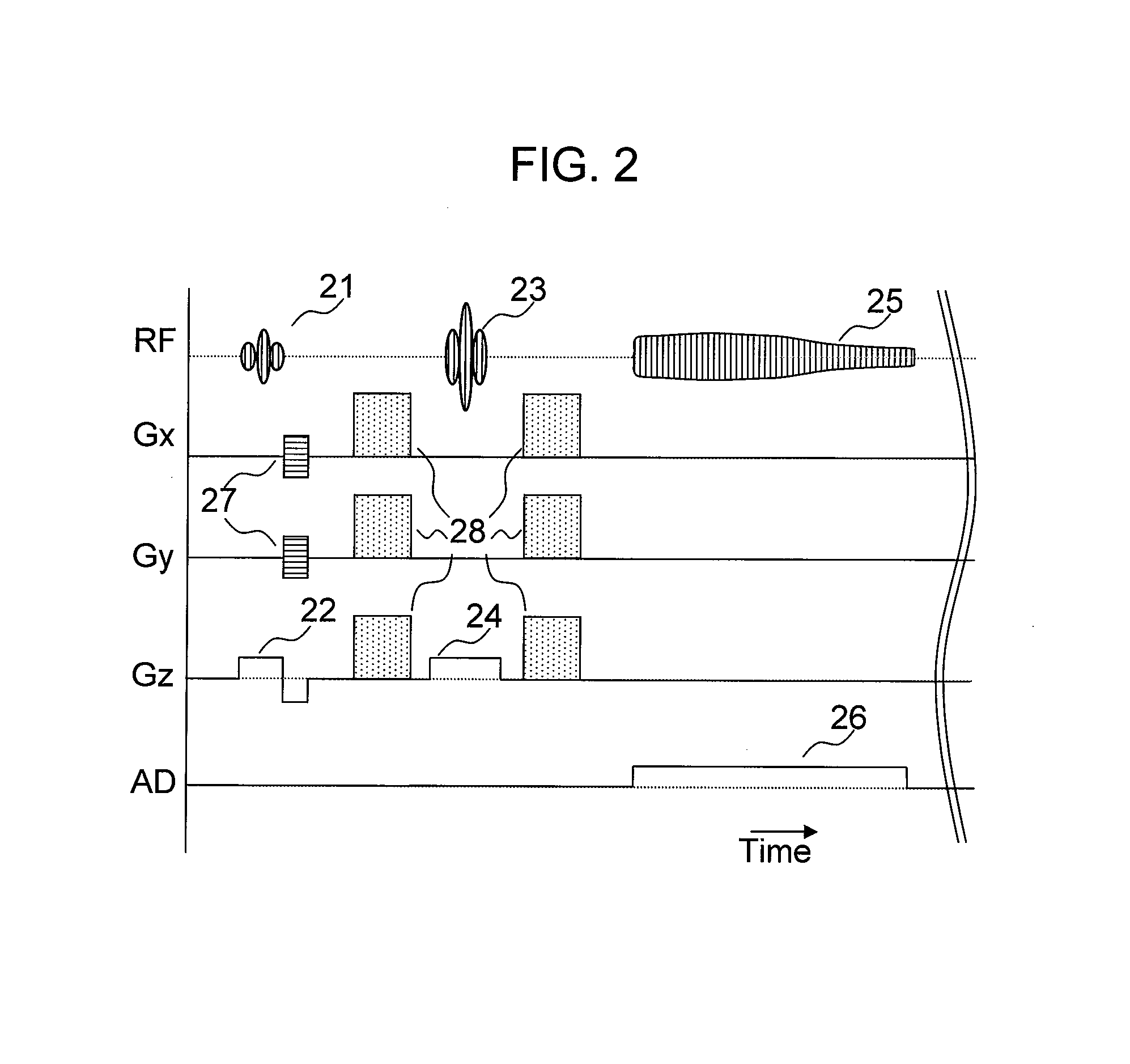
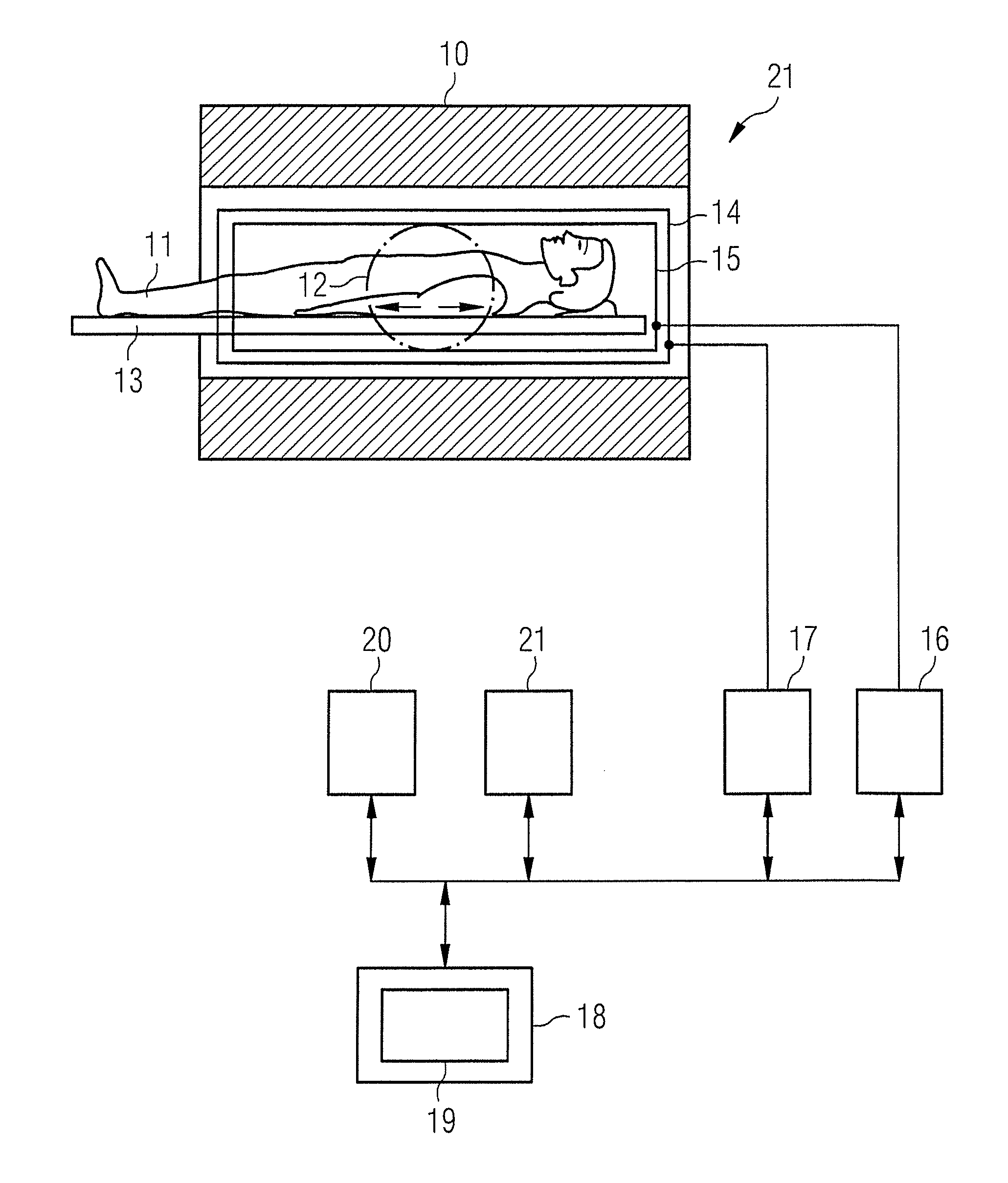
Magnetic resonance device with diffusion gradient phase variation positionally corrected
InactiveUS9097778B2Accurate measurementMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionObject motionSpectral bands
In the diffusion spectroscopic imaging, in which intensity of molecular diffusion is imaged with separating chemical substances, with suppressing artifacts resulting from object motion of an object, spatial resolution, spectral band and SNR are maintained, and measurement accuracy is enhanced. A measurement for acquiring diffusion SI data is repeated a plurality of times with changing acquisition timing, phase variation of each measurement result is corrected, and a diffusion SI image is reconstructed from the corrected measurement results. In addition, the phase variation is calculated for every point in the space from the diffusion SI data acquired by each measurement or navigation data obtained by each measurement. The phase correction is independently performed for every point in the space.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus to reduce artifacts in diffusion-weighted imaging
ActiveUS20130063144A1Reduce eddy current artifactEliminate interference artifactMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDiffusionResonance
In a method and system for diffusion-weighted acquisition of MR signals with an image acquisition sequence that has multiple diffusion coding gradients and readout gradients to read out the MR signals, MR signal portions are generated with a desired signal coherence path and MR signal portions are generated with unwanted signal coherence paths, with predominantly the MR signal portions with the desired signal coherence path being acquired by the readout gradients by activating dephasing gradients that reduce the acquisition of MR signal portions with unwanted coherence paths. The dephasing gradients are determined under consideration of the diffusion gradients that are used and under consideration of the unwanted signal coherence paths, so that each has a dephasing gradient moment for each unwanted signal coherence path that is greater than a threshold.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance system and method for determining a diffusion-weighted image
InactiveUS7633291B2Avoid artifactsIncreased formationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiffusionData set
In a method for determination of a diffusion-weighted image of an examination subject in a magnetic resonance system, a diffusion-weighted data set is acquired with magnetic diffusion gradients being activated; a diffusion-weighted image of the examination subject is calculated using this diffusion-weighted data set; dephasing or spoiler gradients are activated in order to reduce artifacts in the diffusion-weighted image due to additional signal echoes and the position and / or amplitude and / or polarity of the dephasing gradients is / are selected dependent on the diffusion gradients.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for collecting free-state Pb (II) ions in environment quantitatively in situ
ActiveCN103592153AWithdrawing sample devicesColor/spectral properties measurementsDiffusionPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for collecting free-state Pb (II) ions in an environment quantitatively in situ and relates to an environmental monitoring method of metal ions. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1) a diffusion membrane capable of permeating a monitored matter is provided; and (2) a Pb (II) ion imprinted material having the ability of specific binding to the free-state Pb (II) ions is contained on the inner side of the membrane. Within a certain period of time, the diffusion effect of the free-state Pb (II) ions of a to-be-tested system in the diffusion membrane is used for enabling the free-state Pb (II) ions to enter the inner side of the diffusion membrane; and the free-state Pb (II) ions entering the inner side of the diffusion membrane are immediately bound to the Pb (II) ion imprinted material, so that a constant diffusion gradient is formed inside and outside the diffusion membrane, the quantity accumulated by the Pb (II) ion imprinted material on the inner side of the diffusion membrane has a linear relation with the concentration and the collection time of the free-state Pb (II) ions of the to-be-tested system, and the purpose of in-situ and quantitative collection of the free-state Pb (II) ions in the environment system is achieved.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com